What are market trends in a business plan?
Table of Contents

What are market trends?
Why do i need market trends in my business plan, how to keep up with market trends, what market trends to monitor frequently, customer behaviours, technological advances, industry regulations, how to write the market trends in your business plan, using countingup to streamline your business.
Market trends in a business plan are key pieces of information that share where your company sits in the wider picture of your industry. Your business plan should prove why your business is viable, show where you fit in the market and what customers you serve. Examining what the market looks like is a smart business move when starting out.
This article on market trends in a business plan will cover:
- What are market trends
- Why market trends are necessary in my business plan
Market trends are the direction changes of a specific industry and can be influenced by customer behaviours or developing technology.
Take the mobile phone industry for example, as technology has improved over the last twenty years consumers have moved from bulky handsets to slimmer smartphones, that can do everything a computer can and more. Consumers have even gone back to the fashion of flip phones now that technology has allowed a bigger screen that can be folded to save space. This is a good example where both technology and customer demand has influenced the direction of the industry,
Acknowledging these trends when running a business ensures that you stay on the same path as the industry itself, moving with customer needs and adapting your business as the sector and technology evolve. Ignoring market trends in the long term could mean you are left behind by customers, as they may move to businesses that meet their needs more.
Your market trend research should be part of wider market analysis in your business plan. Understanding where you fit in a sector and what separates your company from competitors will help you shape everything from your product to pricing and marketing plans.
It’s important to focus on trends in this process so you can understand what appeals to your target audience. By analysing the market landscape and trends, you will be able to serve your customers better. It will also feed into your marketing messaging and content creation strategy later on.
A market and trend analysis should be both quantitative (using numbers and statistics such as projections and financial forecasts) and qualitative (based on experience or observation). Trends will fit into both categories of research and you should be able to find data and non-numerical information to support your examination of trends when writing your business plan.
It’s important to remember that a business plan is not set in stone. It can be a document that you regularly update to reflect changes in your industry and company.
Keeping pace in a fast-changing market is not easy – after all, you’ve got a business to run. Using social media and subscribing to relevant industry emails make it simpler to get the information you need. Doing this will allow you to stay on top of market trends to include in your initial business plan and for more long-term future planning.
Follow influencers in your industry to see what they talk about and how they create content for the audience that you serve. This will give you an idea of what resonates with your target customers when it comes to content and the form of content the influencer tends to use (video, written blogs, imagery etc.).
Read relevant publications in your sector to find out what is making headlines. Magazines or online blogs that share up-to-date opinions and thought leadership (influential content) will help you stay on the pulse of what is currently important to the industry.
Reading detailed reports and research can be time-consuming but will give you a good overview of the industry’s current state and any new developments. You can then update your business plan to follow the trends that arise from any data you’ve seen.
Some common areas will affect the running of your business, the trends in your business plan and the whole market landscape. Keeping on top of the following aspects and regularly checking in on them will ensure your business develops as the market does.
Your customer can make or break your business. If you don’t cater to their needs and wants, your business will not be on the radar of your target audience.
Let’s take an example – if your target customer is under 45, and you primarily do business online, you will need to ensure your website is optimised for mobile. This is because consumer behaviours have changed in recent years, and most searches are now conducted via mobile . If you don’t pick up on this development, your business risks being left behind when competitors optimise for mobile and you don’t.
Like our previous example, customer behaviour often changes with advances in technology. As mobile phones, and then smartphones, have become more able to operate as a computer, consumers have moved to using their phones out of convenience.
Keep on top of developments that are relevant to your business and make sure you can move with, and not against, the technology changes.
Every now and again, there will be a law change or new regulation that rocks many industries – such as GDPR in 2018. Staying up to date with regulations that could affect the way you run and market your business will save you weighty fines (especially in the case of data protection).
There may be more frequent regulation updates if you operate in an industry that requires you to follow safety guidelines or best practices, such as those that an electrician or builder will have to follow.
Ensuring that you are up to date on precautions and rules, as well as renewing any professional certifications you need to operate, will ensure your business plan reflects the changing face of your industry.
Using your research on your target customers and the sector, use the following steps to write up the market trends section of your business plan:
- Current market overview, including which company has the biggest share or most influence
- Where you fit in that market, what gives your business a competitive edge.
- Current trends that impact your business operation
- Any upcoming trends that may impact your business or the products/services you offer
- Outline any plans on how you will keep up with trends
- Upcoming regulatory changes
You can then follow this with your competitor research in your business plan, to give a full picture of your industry and where you fit in.
Now that you have the answers to questions like ‘what are market trends in a business plan’, you will be able to prepare a thorough market analysis to set up your new venture for success.
Countingup can help your new business by making your business accounting simple, too. Countingup is the business account with built-in accounting software. The app is helping thousands of business owners across the UK save time and money by automating the time consuming parts of accounting. Find out more here and get started today.

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
Business insurance from superscript.
We’re partnered with insurance experts, Superscript to provide you with small business insurance.
How to register a company in the UK
There are over five million companies registered in the UK and 500,000 new
How to set up a TikTok shop (2024)
TikTok can be an excellent platform for growing a business, big or small.
Best Side Hustle Ideas To Make Extra Money In 2024 (UK Edition)
Looking to start a new career? Or maybe you’re looking to embrace your
How to throw a launch party for a new business
So your business is all set up, what next? A launch party can
How to set sales goals
Want to make manageable and achievable sales goals for your business? Find out
10 key tips to starting a business in the UK
10 things you need to know before starting a business in the UK
How to set up your business: Sole trader or limited company
If you’ve just started a business, you’ll likely be faced with the early
How to register as a sole trader
Running a small business and considering whether to register as a sole trader?
How to open a Barclays business account
When starting a new business, one of the first things you need to
6 examples of objectives for a small business plan
Your new company’s business plan is a crucial part of your success, as
How to start a successful business during a recession
Starting a business during a recession may sound like madness, but some big
Analyze your market like a pro with this step-by-step guide + insider tips
Don’t fall into the trap of assuming that you already know enough about your market.
No matter how fantastic your product or service is, your business cannot succeed without sufficient market demand .
You need a clear understanding of who will buy your product or service and why .
You want to know if there is a clear market gap and a market large enough to support the survival and growth of your business.
Industry research and market analysis will help make sure that you are on the right track .
It takes time , but it is time well spent . Thank me later.
WHAT is Market Analysis?
The Market Analysis section of a business plan is also sometimes called:
- Market Demand, Market Trends, Target Market, The Market
- Industry Analysis & Trends, Industry & Market Analysis, Industry and Market Research
WHY Should You Do Market Analysis?
First and foremost, you need to demonstrate beyond any reasonable doubt that there is real need and sufficient demand for your product or service in the market, now and going forward.
- What makes you think that people will buy your products or services?
- Can you prove it?
Your due diligence on the market opportunity and validating the problem and solution described in the Product and Service section of your business plan are crucial for the success of your venture.
Also, no company operates in a vacuum. Every business is part of a larger overall industry, the forces that affect your industry as a whole will inevitably affect your business as well.
Evaluating your industry and market increases your own knowledge of the factors that contribute to your company’s success and shows the readers of your business plan that you understand the external business conditions.
External Support
In fact, if you are seeking outside financing, potential backers will most definitely be interested in industry and market conditions and trends.
You will make a positive impression and have a better chance of getting their support if you show market analysis that strengthens your business case, combining relevant and reliable data with sound judgement.
Let’s break down how to do exactly that, step by step:
HOW To Do Market Analysis: Step-by-Step
So, let’s break up how market analysis is done into three steps:
- Industry: the total market
- Target Market: specific segments of the industry that you will target
- Target Customer: characteristics of the customers that you will focus on
Step 1: Industry Analysis
How do you define an industry.
For example, the fashion industry includes fabric suppliers, designers, companies making finished clothing, distributors, sales representatives, trade publications, retail outlets online and on the high street.
How Do You Analyze an Industry?
Briefly describe your industry, including the following considerations:
1.1. Economic Conditions
Outline the current and projected economic conditions that influence the industry your business operates in, such as:
- Official economic indicators like GDP or inflation
- Labour market statistics
- Foreign trade (e.g., import and export statistics)
1.2. Industry Description
Highlight the distinct characteristic of your industry, including:
- Market leaders , major customer groups and customer loyalty
- Supply chain and distribution channels
- Profitability (e.g., pricing, cost structure, margins), financials
- Key success factors
- Barriers to entry preventing new companies from competing in the industry
1.3. Industry Size and Growth
Estimate the size of your industry and analyze how industry growth affects your company’s prospects:
- Current size (e.g., revenues, units sold, employment)
- Historic and projected industry growth rate (low/medium/high)
- Life-cycle stage /maturity (emerging/expanding/ mature/declining)
1.4. Industry Trends
- Industry Trends: Describe the key industry trends and evaluate the potential impact of PESTEL (political / economic / social / technological / environmental / legal) changes on the industry, including the level of sensitivity to:
- Seasonality
- Economic cycles
- Government regulation (e.g. environment, health and safety, international trade, performance standards, licensing/certification/fair trade/deregulation, product claims) Technological change
- Global Trends: Outline global trends affecting your industry
- Identify global industry concerns and opportunities
- International markets that could help to grow your business
- Strategic Opportunity: Highlight the strategic opportunities that exist in your industry
Step 2: Target Customer Identification
Who is a target customer.
One business can have–and often does have–more than one target customer group.
The success of your business depends on your ability to meet the needs and wants of your customers. So, in a business plan, your aim is to assure readers that:
- Your customers actually exist
- You know exactly who they are and what they want
- They are ready for what you have to offer and are likely to actually buy
How Do You Identify an Ideal Target Customer?
2.1. target customer.
- Identify the customer, remembering that the decision-maker who makes the purchase can be a different person or entity than the end-user.
2.2. Demographics
- For consumers ( demographics ): Age, gender, income, occupation, education, family status, home ownership, lifestyle (e.g., work and leisure activities)
- For businesses ( firmographic ): Industry, sector, years in business, ownership, size (e.g., sales, revenues, budget, employees, branches, sq footage)
2.3. Geographic Location
- Where are your customers based, where do they buy their products/services and where do they actually use them
2.4 Purchasing Patterns
- Identify customer behaviors, i.e., what actions they take
- how frequently
- and how quickly they buy
2.5. Psychographics
- Identify customer attitudes, i.e., how they think or feel
- Urgency, price, quality, reputation, image, convenience, availability, features, brand, customer service, return policy, sustainability, eco-friendliness, supporting local business
- Necessity/luxury, high involvement bit ticket item / low involvement consumable
Step 3: Target Market Analysis
What is a target market.
Target market, or 'target audience', is a group of people that a business has identified as the most likely to purchase its offering, defined by demographic, psychographic, geographic and other characteristics. Target market may be broken down to target customers to customize marketing efforts.
How Do You Analyze a Target Market?
So, how many people are likely to become your customers?
To get an answer to this questions, narrow the industry into your target market with a manageable size, and identify its key characteristics, size and trends:
3.1. Target Market Description
Define your target market by:
- Type: B2C, B2B, government, non-profits
- Geographic reach: Specify the geographic location and reach of your target market
3.2. Market Size and Share
Estimate how large is the market for your product or service (e.g., number of customers, annual purchases in sales units and $ revenues). Explain the logic behind your calculation:
- TAM (Total Available/Addressable/Attainable Market) is the total maximum demand for a product or service that could theoretically be generated by selling to everyone in the world who could possibly buy from you, regardless of competition and any other considerations and restrictions.
- SAM (Serviceable Available Market) is the portion of the TAM that you could potentially address in a specific market. For example, if your product/service is only available in one country or language.
- SOM (Service Obtainable Market / Share of Market) is the share of the SAM that you can realistically carve out for your product or service. This the target market that you will be going after and can reasonably expect to convert into a customer base.
3.3. Market Trends
Illustrate the most important themes, changes and developments happening in your market. Explain the reasons behind these trends and how they will favor your business.
3.4. Demand Growth Opportunity
Estimate future demand for your offering by translating past, current and future market demand trends and drivers into forecasts:
- Historic growth: Check how your target market has grown in the past.
- Drivers past: Identify what has been driving that growth in the past.
- Drivers future: Assess whether there will be any change in influence of these and other drivers in the future.
How Big Should My Target Market Be?
Well, if the market opportunity is small, it will limit how big and successful your business can become. In fact, it may even be too small to support a successful business at all.
On the other hand, many businesses make the mistake of trying to appeal to too many target markets, which also limits their success by distracting their focus.
What If My Stats Look Bad?
Large and growing market suggests promising demand for your offering now and into the future. Nevertheless, your business can still thrive in a smaller or contracting market.
Instead of hiding from unfavorable stats, acknowledge that you are swimming against the tide and devise strategies to cope with whatever lies ahead.
Step 4: Industry and Market Analysis Research
The market analysis section of your business plan should illustrate your own industry and market knowledge as well as the key findings and conclusions from your research.
Back up your findings with external research sources (= secondary research) and results of internal market research and testing (= primary research).
What is Primary and Secondary Market Research?
Yes, there are two main types of market research – primary and secondary – and you should do both to adequately cover the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Primary market research is original data you gather yourself, for example in the form of active fieldwork collecting specific information in your market.
- Secondary market research involves collating information from existing data, which has been researched and shared by reliable outside sources . This is essentially passive desk research of information already published .
Unless you are working for a corporation, this exercise is not about your ability to do professional-level market research.
Instead, you just need to demonstrate fundamental understanding of your business environment and where you fit in within the market and broader industry.
Why Do You Need To Do Primary & Secondary Market Research?
There are countless ways you could go collecting industry and market research data, depending on the type of your business, what your business plan is for, and what your needs, resources and circumstances are.
For tried and tested tips on how to properly conduct your market research, read the next section of this guide that is dedicated to primary and secondary market research methods.
In any case, tell the reader how you carried out your market research. Prove what the facts are and where you got your data. Be as specific as possible. Provide statistics, numbers, and sources.
When doing secondary research, always make sure that all stats, facts and figures are from reputable sources and properly referenced in both the main text and the Appendix of your business plan. This gives more credibility to your business case as the reader has more confidence in the information provided.
Go to the Primary and Secondary Market Research post for my best tips on industry, market and competitor research.
7 TOP TIPS For Writing Market Analysis
1. realistic projections.
Above all, make sure that you are realistic in your projections about how your product or service is going to be accepted in the market, otherwise you are going to seriously undermine the credibility of your entire business case.
2. Laser Focus
Discuss only characteristic of your target market and customers that are observable, factual and meaningful, i.e. directly relate to your customers’ decision to purchase.
Always relate the data back to your business. Market statistics are meaningless until you explain where and how your company fits in.
For example, as you write about the market gap and the needs of your target customers, highlight how you are uniquely positioned to fill them.
In other words, your goal is to:
- Present your data
- Analyze the data
- Tie the data back to how your business can thrive within your target market
3. Target Audience
On a similar note, tailor the market analysis to your target audience and the specific purpose at hand.
For example, if your business plan is for internal use, you may not have to go into as much detail about the market as you would have for external financiers, since your team is likely already very familiar with the business environment your company operates in.
4. Story Time
Make sure that there is a compelling storyline and logical flow to the market information presented.
The saying “a picture is worth a thousand words” certainly applies here. Industry and market statistics are easier to understand and more impactful if presented as a chart or graph.
6. Information Overload
Keep your market analysis concise by only including pertinent information. No fluff, no repetition, no drowning the reader in a sea of redundant facts.
While you should not assume that the reader knows anything about your market, do not elaborate on unnecessary basic facts either.
Do not overload the reader in the main body of the business plan. Move everything that is not essential to telling the story into the Appendix. For example, summarize the results of market testing survey in the main body of the business plan document, but move the list of the actual survey questions into the appendix.
7. Marketing Plan
Note that market analysis and marketing plan are two different things, with two distinct chapters in a business plan.
As the name suggests, market analysis examines where you fit in within your desired industry and market. As you work thorugh this section, jot down your ideas for the marketing and strategy section of your business plan.
Final Thoughts
Remember that the very act of doing the research and analysis is a great opportunity to learn things that affect your business that you did not know before, so take your time doing the work.
Related Questions
What is the purpose of industry & market research and analysis.
The purpose of industry and market research and analysis is to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the environment of a business and to confirm that the market opportunity is sufficient for sustainable success of that business.
Why are Industry & Market Research and Analysis IMPORTANT?
Industry and market research and analysis are important because they allow you to gain knowledge of the industry, the target market you are planning to sell to, and your competition, so you can make informed strategic decisions on how to make your business succeed.
How Can Industry & Market Research and Analysis BENEFIT a Business?
Industry and market research and analysis benefit a business by uncovering opportunities and threats within its environment, including attainable market size, ideal target customers, competition and any potential difficulties on the company’s journey to success.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
What Is an Industry Analysis and Trends Business Plan?
An industry analysis and trends business plan is a component of a business plan that provides a comprehensive insight into industry conditions and trends. 3 min read updated on September 19, 2022
An industry analysis and trends business plan is a component of a business plan that provides a comprehensive insight into industry conditions and trends that can impact a company's success and growth. A thorough analysis of your industry and its trends can give you and other people a clearer idea of the feasibility and relevance of your business idea or goals.
Elements of a Business Plan
There are many different types of business plans. When you are creating your business plan, the information you choose to include will depend on your audience and personal preferences, as well as the questions you wish to answer and problems you seek to solve. While business plans may vary greatly, most of them contain the following elements:
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Analysis of business environment analysis
- Industry analysis
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Marketing plan
- Management plan
- Operations plan
- Financial projections
- What Is an Industry Analysis?
An industry analysis enables you to gain a better understanding of the industry and market in which you will be conducting business. By conducting an industry analysis before you start writing your business plan , you will be able to:
- Identify industry trends, such as potentially problematic aspects of the industry
- Identify trends and opportunities in products and services
- Calculate capital requirements
- Determine business risks and find ways to reduce them
An industry analysis must be specific to the industry in which you are conducting or are planning to conduct business. With the information you obtain from the analysis, you can devise a long-term strategy to mitigate risks and take full advantage of growth opportunities.
It is important not to confuse an industry analysis with a competitor or market analysis. An industry analysis seeks to describe the products or services offered in a specific industry and the boundaries of the marketplace in relation to economic, political, and regulatory issues. In other words, it defines the scope of the marketplace. A market analysis , on the other hand, helps you determine whether or not a market within your industry will be profitable for your products or services.
Conducting an Industry Analysis
The most widely used method for evaluating any industry was devised by Michael E. Porter from Harvard University. This method can help you create an effective strategy for competing in your industry. According to Porter, all industries and markets are influenced by five forces, which include:
- Ease of entry — Companies that are already operating in an industry will enjoy a competitive advantage over newcomers. However, their profits will be reduced unless they find a way to slow down or block the new entries. As for new businesses, they will face a variety of barriers, including government regulations, patents and copyrights, and customer loyalty.
- Suppliers' power — Suppliers of materials, products, or services can have a significant impact on a business' ability to compete. In the event that there are few suppliers offering the products or materials or few alternative products, the suppliers have the power to dictate quantities, prices, and delivery times for companies that have no choice but to buy from them.
- Buyers' power — In an industry where buyers can choose from many competing products, consumers will have strong bargaining power. This can affect the ability of a company to price its products or services without being afraid of losing customers.
- Availability of alternative products — In the situation where two businesses with similar products are competing within an industry, both of them will benefit as their marketing efforts will generally increase demand for their products. However, their market share will be reduced if there is another company selling a different kind of products that can serve as a substitute for theirs.
- Competitive rivalry — Competitive rivalry takes into account the number of competitors present in a particular industry, as well as their relative strength. In an industry where many companies are selling similar products, there is little opportunity for one company to control consumers' or suppliers' tendency to go elsewhere.
There are many free industry analysis tools and resources available to business owners who are preparing to create a business plan, such as:
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- U.S. Census Bureau
- Hoover's Online
- Thomas Register
- Library of Congress Legislative Information
- Websites of trade associations and companies
If you need help creating an industry analysis and trends business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Plan Outline: Everything You Need To Know
- How to Make a Business Plan Format
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- Business Description Outline
- Market Analysis: Everything You Need To Know
- Service Business Plan
- IT Company Business Plan
- Clothing Boutique Business Plan Outline
- Business Plan for Existing Company
How to Conduct an Industry Analysis? Steps, Template, Examples
Appinio Research · 16.11.2023 · 41min read

Are you ready to unlock the secrets of Industry Analysis, equipping yourself with the knowledge to navigate markets and make informed strategic decisions? Dive into this guide, where we unravel the significance, objectives, and methods of Industry Analysis.
Whether you're an entrepreneur seeking growth opportunities or a seasoned executive navigating industry shifts, this guide will be your compass in understanding the ever-evolving business terrain.
What is Industry Analysis?
Industry analysis is the process of examining and evaluating the dynamics, trends, and competitive forces within a specific industry or market sector. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the factors that impact the performance and prospects of businesses operating within that industry. Industry analysis serves as a vital tool for businesses and decision-makers to gain a deep understanding of the environment in which they operate.
Key components of industry analysis include:
- Market Size and Growth: Determining the overall size of the market, including factors such as revenue, sales volume, and customer base. Analyzing historical and projected growth rates provides insights into market trends and opportunities.
- Competitive Landscape: Identifying and analyzing competitors within the industry. This includes assessing their market share , strengths, weaknesses, and strategies. Understanding the competitive landscape helps businesses position themselves effectively.
- Customer Behavior and Preferences: Examining consumer behavior , preferences, and purchasing patterns within the industry. This information aids in tailoring products or services to meet customer needs.
- Regulatory and Legal Environment: Assessing the impact of government regulations, policies, and legal requirements on industry operations. Compliance and adaptation to these factors are crucial for business success.
- Technological Trends: Exploring technological advancements and innovations that affect the industry. Staying up-to-date with technology trends can be essential for competitiveness and growth.
- Economic Factors: Considering economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and economic cycles, that influence the industry's performance.
- Social and Cultural Trends: Examining societal and cultural shifts, including changing consumer values and lifestyle trends that can impact demand and preferences.
- Environmental and Sustainability Factors: Evaluating environmental concerns and sustainability issues that affect the industry. Industries are increasingly required to address environmental responsibility.
- Supplier and Distribution Networks: Analyzing the availability of suppliers, distribution channels, and supply chain complexities within the industry.
- Risk Factors: Identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could affect industry stability and profitability.
Objectives of Industry Analysis
Industry analysis serves several critical objectives for businesses and decision-makers:
- Understanding Market Dynamics: The primary objective is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the industry's dynamics, including its size, growth prospects, and competitive landscape. This knowledge forms the basis for strategic planning.
- Identifying Growth Opportunities: Industry analysis helps identify growth opportunities within the market. This includes recognizing emerging trends, niche markets, and underserved customer segments.
- Assessing Competitor Strategies: By examining competitors' strengths, weaknesses, and strategies, businesses can formulate effective competitive strategies. This involves positioning the company to capitalize on its strengths and exploit competitors' weaknesses.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities specific to the industry allows businesses to develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of adverse events.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Industry analysis provides the data and insights necessary for informed strategic decision-making. It guides decisions related to market entry, product development, pricing strategies, and resource allocation.
- Resource Allocation: By understanding industry dynamics, businesses can allocate resources efficiently. This includes optimizing marketing budgets, supply chain investments, and talent recruitment efforts.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Staying updated on technological trends and shifts in customer preferences enables businesses to innovate and adapt their offerings effectively.
Importance of Industry Analysis in Business
Industry analysis holds immense importance in the business world for several reasons:
- Strategic Planning: It forms the foundation for strategic planning by providing a comprehensive view of the industry's landscape. Businesses can align their goals, objectives, and strategies with industry trends and opportunities.
- Risk Management: Identifying and assessing industry-specific risks allows businesses to manage and mitigate potential threats proactively. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected disruptions.
- Competitive Advantage: In-depth industry analysis helps businesses identify opportunities for gaining a competitive advantage. This could involve product differentiation, cost leadership, or niche market targeting .
- Resource Optimization: Efficient allocation of resources, both financial and human, is possible when businesses have a clear understanding of industry dynamics. It prevents wastage and enhances resource utilization.
- Informed Investment: Industry analysis assists investors in making informed decisions about allocating capital. It provides insights into the growth potential and risk profiles of specific industry sectors.
- Adaptation to Change: As industries evolve, businesses must adapt to changing market conditions. Industry analysis facilitates timely adaptation to new technologies, market shifts, and consumer preferences .
- Market Entry and Expansion: For businesses looking to enter new markets or expand existing operations, industry analysis guides decision-making by evaluating the feasibility and opportunities in target markets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding the regulatory environment is critical for compliance and risk avoidance. Industry analysis helps businesses stay compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
In summary, industry analysis is a fundamental process that empowers businesses to make informed decisions, stay competitive, and navigate the complexities of their respective markets. It is an invaluable tool for strategic planning and long-term success.
How to Prepare for Industry Analysis?
Let's start by going through the crucial preparatory steps for conducting a comprehensive industry analysis.
1. Data Collection and Research
- Primary Research: When embarking on an industry analysis, consider conducting primary research . This involves gathering data directly from industry sources, stakeholders, and potential customers. Methods may include surveys , interviews, focus groups , and observations. Primary research provides firsthand insights and can help validate secondary research findings.
- Secondary Research: Secondary research involves analyzing existing literature, reports, and publications related to your industry. Sources may include academic journals, industry-specific magazines, government publications, and market research reports. Secondary research provides a foundation of knowledge and can help identify gaps in information that require further investigation.
- Data Sources: Explore various data sources to collect valuable industry information. These sources may include industry-specific associations, government agencies, trade publications, and reputable market research firms. Make sure to cross-reference data from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
2. Identifying Relevant Industry Metrics
Understanding and identifying the right industry metrics is essential for meaningful analysis. Here, we'll discuss key metrics that can provide valuable insights:
- Market Size: Determining the market's size, whether in terms of revenue, units sold, or customer base, is a fundamental metric. It offers a snapshot of the industry's scale and potential.
- Market Growth Rate: Assessing historical and projected growth rates is crucial for identifying trends and opportunities. Understanding how the market has evolved over time can guide strategic decisions.
- Market Share Analysis: Analyzing market share among industry players can help you identify dominant competitors and their respective positions. This metric also assists in gauging your own company's market presence.
- Market Segmentation : Segmenting the market based on demographics, geography, behavior, or other criteria can provide deeper insights. Understanding the specific needs and preferences of various market segments can inform targeted strategies.
3. Gathering Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence is the cornerstone of effective industry analysis. To gather and utilize information about your competitors:
- Competitor Identification: Begin by creating a comprehensive list of your primary and potential competitors. Consider businesses that offer similar products or services within your target market. It's essential to cast a wide net to capture all relevant competitors.
- SWOT Analysis : Conduct a thorough SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis for each competitor. This analysis helps you identify their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats they face.
- Market Share Analysis: Determine the market share held by each competitor and how it has evolved over time. Analyzing changes in market share can reveal shifts in competitive dynamics.
- Product and Pricing Analysis: Evaluate your competitors' product offerings and pricing strategies . Identify any unique features or innovations they offer and consider how your own products or services compare.
- Marketing and Branding Strategies: Examine the marketing and branding strategies employed by competitors. This includes their messaging, advertising channels, and customer engagement tactics. Assess how your marketing efforts stack up.
Industry Analysis Frameworks and Models
Now, let's explore essential frameworks and models commonly used in industry analysis, providing you with practical insights and examples to help you effectively apply these tools.
Porter's Five Forces Model
Porter's Five Forces is a powerful framework developed by Michael Porter to assess the competitive forces within an industry. This model helps you understand the industry's attractiveness and competitive dynamics.
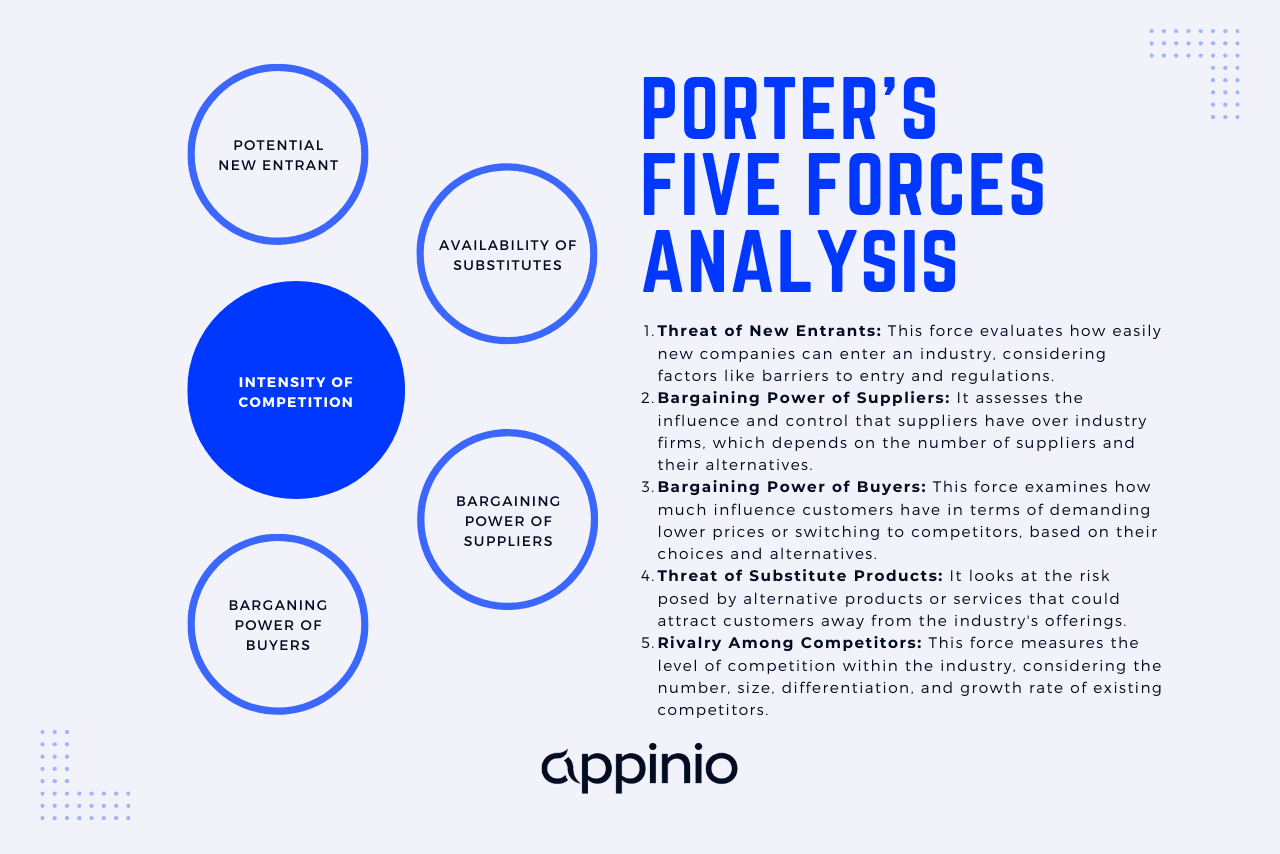
It consists of five key forces:
- Threat of New Entrants: This force evaluates how easy or difficult it is for new companies to enter the industry. Factors that increase barriers to entry include high capital requirements, strong brand loyalty among existing players, and complex regulatory hurdles. For example, the airline industry has significant barriers to entry due to the need for large capital investments in aircraft, airport facilities, and regulatory approvals.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force examines the influence suppliers have on the industry's profitability. Powerful suppliers can demand higher prices or impose unfavorable terms. For instance, in the automotive industry, suppliers of critical components like microchips can wield significant bargaining power if they are few in number or if their products are highly specialized.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers assesses how much influence customers have in negotiating prices and terms. In industries where buyers have many alternatives, such as the smartphone market, they can demand lower prices and better features, putting pressure on manufacturers to innovate and compete.
- Threat of Substitutes: This force considers the availability of substitute products or services that could potentially replace what the industry offers. For example, the rise of electric vehicles represents a significant threat to the traditional gasoline-powered automotive industry as consumers seek eco-friendly alternatives.
- Competitive Rivalry: Competitive rivalry assesses the intensity of competition among existing firms in the industry. A highly competitive industry, such as the smartphone market, often leads to price wars and aggressive marketing strategies as companies vie for market share.
Example: Let's consider the coffee shop industry . New entrants face relatively low barriers, as they can set up a small shop with limited capital. However, the bargaining power of suppliers, such as coffee bean producers, can vary depending on the region and the coffee's rarity. Bargaining power with buyers is moderate, as customers often have several coffee shops to choose from. Threats of substitutes may include energy drinks or homemade coffee, while competitive rivalry is high, with numerous coffee chains and independent cafes competing for customers.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a versatile tool used to assess an organization's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. By conducting a SWOT analysis, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your industry and formulate effective strategies.
- Strengths: These are the internal attributes and capabilities that give your business a competitive advantage. For instance, if you're a tech company, having a talented and innovative team can be considered a strength.
- Weaknesses: Weaknesses are internal factors that hinder your business's performance. For example, a lack of financial resources or outdated technology can be weaknesses that need to be addressed.
- Opportunities: Opportunities are external factors that your business can capitalize on. This could be a growing market segment, emerging technologies, or changing consumer trends.
- Threats: Threats are external factors that can potentially harm your business. Examples of threats might include aggressive competition, economic downturns, or regulatory changes.
Example: Let's say you're analyzing the fast-food industry. Strengths could include a well-established brand, a wide menu variety, and efficient supply chain management. Weaknesses may involve a limited focus on healthy options and potential labor issues. Opportunities could include the growing trend toward healthier eating, while threats might encompass health-conscious consumer preferences and increased competition from delivery apps.
PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL Analysis examines the external macro-environmental factors that can impact your industry. The acronym stands for:
- Political: Political factors encompass government policies, stability, and regulations. For example, changes in tax laws or trade agreements can affect industries like international manufacturing.
- Economic: Economic factors include economic growth, inflation rates, and exchange rates. A fluctuating currency exchange rate can influence export-oriented industries like tourism.
- Social: Social factors encompass demographics, cultural trends, and social attitudes. An aging population can lead to increased demand for healthcare services and products.
- Technological: Technological factors involve advancements and innovations. Industries like telecommunications are highly influenced by technological developments, such as the rollout of 5G networks.
- Environmental: Environmental factors cover sustainability, climate change, and ecological concerns. Industries such as renewable energy are directly impacted by environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
- Legal: Legal factors encompass laws, regulations, and compliance requirements. The pharmaceutical industry, for instance, faces stringent regulatory oversight and patent protection laws.
Example: Consider the automobile manufacturing industry. Political factors may include government incentives for electric vehicles. Economic factors can involve fluctuations in fuel prices affecting consumer preferences for fuel-efficient cars. Social factors might encompass the growing interest in eco-friendly transportation options. Technological factors could relate to advancements in autonomous driving technology. Environmental factors may involve emissions regulations, while legal factors could pertain to safety standards and recalls.
Industry Life Cycle Analysis
Industry Life Cycle Analysis categorizes industries into various stages based on their growth and maturity. Understanding where your industry stands in its life cycle can help shape your strategies.
- Introduction: In the introduction stage, the industry is characterized by slow growth, limited competition, and a focus on product development. New players enter the market, and consumers become aware of the product or service. For instance, electric scooters were introduced as a new mode of transportation in recent years.
- Growth: The growth stage is marked by rapid market expansion, increased competition, and rising demand. Companies focus on gaining market share, and innovation is vital. The ride-sharing industry, exemplified by companies like Uber and Lyft, experienced significant growth in this stage.
- Maturity: In the maturity stage, the market stabilizes, and competition intensifies. Companies strive to maintain market share and differentiate themselves through branding and customer loyalty programs. The smartphone industry reached maturity with multiple established players.
- Decline: In the decline stage, the market saturates, and demand decreases. Companies must adapt or diversify to survive. The decline of traditional print media is a well-known example.
Example: Let's analyze the video streaming industry . The introduction stage saw the emergence of streaming services like Netflix. In the growth stage, more players entered the market, and the industry saw rapid expansion. The industry is currently in the maturity stage, with established platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ competing for market share. However, with continued innovation and changing consumer preferences, the decline stage may eventually follow.
Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain Analysis dissects a company's activities into primary and support activities to identify areas of competitive advantage. Primary activities directly contribute to creating and delivering a product or service, while support activities facilitate primary activities.
- Primary Activities: These activities include inbound logistics (receiving and storing materials), operations (manufacturing or service delivery), outbound logistics (distribution), marketing and sales, and customer service.
- Support Activities: Support activities include procurement (acquiring materials and resources), technology development (R&D and innovation), human resource management (recruitment and training), and infrastructure (administrative and support functions).
Example: Let's take the example of a smartphone manufacturer. Inbound logistics involve sourcing components, such as processors and displays. Operations include assembly and quality control. Outbound logistics cover shipping and distribution. Marketing and sales involve advertising and retail partnerships. Customer service handles warranty and support.
Procurement ensures a stable supply chain for components. Technology development focuses on research and development of new features. Human resource management includes hiring and training skilled engineers. Infrastructure supports the company's administrative functions.
By applying these frameworks and models effectively, you can better understand your industry, identify strategic opportunities and threats, and develop a solid foundation for informed decision-making.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
Once you have your data, it's time to start interpreting and analyzing the data you've collected during your industry analysis.
You can unlock the full potential of your data with Appinio 's comprehensive research platform. Beyond aiding in data collection, Appinio simplifies the intricate process of data interpretation and analysis. Our intuitive tools empower you to effortlessly transform raw data into actionable insights, giving you a competitive edge in understanding your industry.
Whether it's assessing market trends, evaluating the competitive landscape, or understanding customer behavior, Appinio offers a holistic solution to uncover valuable findings. With our platform, you can make informed decisions, strategize effectively, and stay ahead of industry shifts.
Experience the ease of data collection and interpretation with Appinio – book a demo today!
Get a free demo and see the Appinio platform in action!
1. Analyze Market Size and Growth
Analyzing the market's size and growth is essential for understanding its dynamics and potential. Here's how to conduct a robust analysis:
- Market Size Calculation: Determine the total market size in terms of revenue, units sold, or the number of customers. This figure serves as a baseline for evaluating the industry's scale.
- Historical Growth Analysis: Examine historical data to identify growth trends. This includes looking at past year-over-year growth rates and understanding the factors that influenced them.
- Projected Growth Assessment: Explore industry forecasts and projections to gain insights into the expected future growth of the market. Consider factors such as emerging technologies, changing consumer preferences, and economic conditions.
- Segmentation Analysis: If applicable, analyze market segmentation data to identify growth opportunities in specific market segments. Understand which segments are experiencing the most significant growth and why.
2. Assess Market Trends
Stay ahead of the curve by closely monitoring and assessing market trends. Here's how to effectively evaluate trends within your industry.
- Consumer Behavior Analysis: Dive into consumer behavior data to uncover shifts in preferences, buying patterns, and shopping habits. Understand how technological advancements and cultural changes influence consumer choices.
- Technological Advancements: Keep a keen eye on technological developments that impact your industry. Assess how innovations such as AI, IoT, blockchain, or automation are changing the competitive landscape.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay informed about regulatory shifts and their potential consequences for your industry. Regulations can significantly affect product development, manufacturing processes, and market entry strategies.
- Sustainability and Environmental Trends: Consider the growing importance of sustainability and environmental concerns. Evaluate how your industry is adapting to eco-friendly practices and how these trends affect consumer choices.
3. Evaluate Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive landscape is critical for positioning your business effectively. To perform a comprehensive evaluation:
- Competitive Positioning: Determine where your company stands in comparison to competitors. Identify your unique selling propositions and areas where you excel.
- Market Share Analysis: Continuously monitor market share among industry players. Identify trends in market share shifts and assess the strategies that lead to such changes.
- Competitive Advantages and Weaknesses: Analyze your competitors' strengths and weaknesses. Identify areas where you can capitalize on their weaknesses and where you need to fortify your own strengths.
4. Identify Key Success Factors
Recognizing and prioritizing key success factors is crucial for developing effective strategies. To identify and leverage these factors:
- Customer Satisfaction: Prioritize customer satisfaction as a critical success factor. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal advocates and contribute to long-term success.
- Quality and Innovation: Focus on product or service quality and continuous innovation. Meeting and exceeding customer expectations can set your business apart from competitors.
- Cost Efficiency: Strive for cost efficiency in your operations. Identifying cost-saving opportunities can lead to improved profitability.
- Marketing and Branding Excellence: Invest in effective marketing and branding strategies to create a strong market presence. Building a recognizable brand can drive customer loyalty and growth.
5. Analyze Customer Behavior and Preferences
Understanding your target audience is central to success. Here's how to analyze customer behavior and preferences:
- Market Segmentation: Use market segmentation to categorize customers based on demographics, psychographics , and behavior. This allows for more personalized marketing and product/service offerings.
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Gather customer feedback through surveys and feedback mechanisms. Understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations to tailor your offerings.
- Consumer Journey Mapping: Map the customer journey to identify touchpoints where you can improve engagement and satisfaction. Optimize the customer experience to build brand loyalty.
By delving deep into data interpretation and analysis, you can gain valuable insights into your industry, uncover growth opportunities, and refine your strategic approach.
How to Conduct Competitor Analysis?
Competitor analysis is a critical component of industry analysis as it provides valuable insights into your rivals, helping you identify opportunities, threats, and areas for improvement.
1. Identify Competitors
Identifying your competitors is the first step in conducting a thorough competitor analysis. Competitors can be classified into several categories:
- Direct Competitors: These are companies that offer similar products or services to the same target audience. They are your most immediate competitors and often compete directly with you for market share.
- Indirect Competitors: Indirect competitors offer products or services that are related but not identical to yours. They may target a slightly different customer segment or provide an alternative solution to the same problem.
- Potential Competitors: These companies could enter your market in the future. Identifying potential competitors early allows you to anticipate and prepare for new entrants.
- Substitute Products or Services: While not traditional competitors, substitute products or services can fulfill the same customer needs or desires. Understanding these alternatives is crucial to your competitive strategy.
2. Analyze Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Once you've identified your competitors, you need to analyze their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis helps you understand how to position your business effectively and identify areas where you can gain a competitive edge.
- Strengths: Consider what your competitors excel at. This could include factors such as brand recognition, innovative products, a large customer base, efficient operations, or strong financial resources.
- Weaknesses: Identify areas where your competitors may be lacking. Weaknesses could involve limited product offerings, poor customer service, outdated technology, or financial instability.
3. Competitive Positioning
Competitive positioning involves defining how you want your business to be perceived relative to your competitors. It's about finding a unique position in the market that sets you apart. Consider the following strategies:
- Cost Leadership: Strive to be the low-cost provider in your industry. This positioning appeals to price-conscious consumers.
- Differentiation: Focus on offering unique features or attributes that make your products or services stand out. This can justify premium pricing.
- Niche Market: Target a specific niche or segment of the market that may be underserved by larger competitors. Tailor your offerings to meet their unique needs.
- Innovation and Technology: Emphasize innovation and technology to position your business as a leader in product or service quality.
- Customer-Centric: Prioritize exceptional customer service and customer experience to build loyalty and a positive reputation.
4. Benchmarking and Gap Analysis
Benchmarking involves comparing your business's performance and practices with those of your competitors or industry leaders. Gap analysis helps identify areas where your business falls short and where improvements are needed.
- Performance Benchmarking: Compare key performance metrics, such as revenue, profitability, market share, and customer satisfaction, with those of your competitors. Identify areas where your performance lags behind or exceeds industry standards.
- Operational Benchmarking: Analyze your operational processes, supply chain, and cost structures compared to your competitors. Look for opportunities to streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Product or Service Benchmarking: Evaluate the features, quality, and pricing of your products or services relative to competitors. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Marketing and Sales Benchmarking: Assess your marketing strategies, customer acquisition costs, and sales effectiveness compared to competitors. Determine whether your marketing efforts are performing at a competitive level.
Market Entry and Expansion Strategies
Market entry and expansion strategies are crucial for businesses looking to enter new markets or expand their presence within existing ones. These strategies can help you effectively target and penetrate your chosen markets.
Market Segmentation and Targeting
- Market Segmentation: Begin by segmenting your target market into distinct groups based on demographics , psychographics, behavior, or other relevant criteria. This helps you understand the diverse needs and preferences of different customer segments.
- Targeting: Once you've segmented the market, select specific target segments that align with your business goals and capabilities. Tailor your marketing and product/service offerings to appeal to these chosen segments.
Market Entry Modes
Selecting the proper market entry mode is crucial for a successful expansion strategy. Entry modes include:
- Exporting: Sell your products or services in international markets through exporting. This is a low-risk approach, but it may limit your market reach.
- Licensing and Franchising: License your brand, technology, or intellectual property to local partners or franchisees. This allows for rapid expansion while sharing the risk and control.
- Joint Ventures and Alliances: Partner with local companies through joint ventures or strategic alliances. This approach leverages local expertise and resources.
- Direct Investment: Establish a physical presence in the target market through subsidiaries, branches, or wholly-owned operations. This offers full control but comes with higher risk and investment.
Competitive Strategy Formulation
Your competitive strategy defines how you will compete effectively in the target market.
- Cost Leadership: Strive to offer products or services at lower prices than competitors while maintaining quality. This strategy appeals to price-sensitive consumers.
- Product Differentiation: Focus on offering unique and innovative products or services that stand out in the market. This strategy justifies premium pricing.
- Market Niche: Target a specific niche or segment within the market that is underserved or has particular needs. Tailor your offerings to meet the unique demands of this niche.
- Market Expansion : Expand your product or service offerings to capture a broader share of the market. This strategy involves diversifying your offerings to appeal to a broader audience.
- Global Expansion: Consider expanding internationally to tap into new markets and diversify your customer base. This strategy involves thorough market research and adaptation to local cultures and regulations.
International Expansion Considerations
If your expansion strategy involves international markets, there are several additional considerations to keep in mind.
- Market Research: Conduct in-depth market research to understand the target country's cultural, economic, and legal differences.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with international trade regulations, customs, and import/export laws.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Adapt your marketing and business practices to align with the cultural norms and preferences of the target market.
- Localization: Consider adapting your products, services, and marketing materials to cater to local tastes and languages.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the political, economic, and legal risks associated with operating in the target country. Develop risk mitigation strategies.
By carefully analyzing your competitors and crafting effective market entry and expansion strategies, you can position your business for success in both domestic and international markets.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk assessment and mitigation are crucial aspects of industry analysis and strategic planning. Identifying potential risks, assessing vulnerabilities, and implementing effective risk management strategies are essential for business continuity and success.
1. Identify Industry Risks
- Market Risks: These risks pertain to factors such as changes in market demand, economic downturns, shifts in consumer preferences, and fluctuations in market prices. For example, the hospitality industry faced significant market risks during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in decreased travel and tourism .
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Regulatory changes, compliance requirements, and government policies can pose risks to businesses. Industries like healthcare are particularly susceptible to regulatory changes that impact operations and reimbursement.
- Technological Risks: Rapid technological advancements can disrupt industries and render existing products or services obsolete. Companies that fail to adapt to technological shifts may face obsolescence.
- Operational Risks: These risks encompass internal factors that can disrupt operations, such as supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, or cybersecurity breaches.
- Financial Risks: Financial risks include factors like liquidity issues, credit risk , and market volatility. Industries with high capital requirements, such as real estate development, are particularly vulnerable to financial risks.
- Competitive Risks: Intense competition and market saturation can pose challenges to businesses. Failing to respond to competitive threats can result in loss of market share.
- Global Risks: Industries with a worldwide presence face geopolitical risks, currency fluctuations, and international trade uncertainties. For instance, the automotive industry is susceptible to trade disputes affecting the supply chain.
2. Assess Business Vulnerabilities
- SWOT Analysis: Revisit your SWOT analysis to identify internal weaknesses and threats. Assess how these weaknesses may exacerbate industry risks.
- Financial Health: Evaluate your company's financial stability, debt levels, and cash flow. Identify vulnerabilities related to financial health that could hinder your ability to withstand industry-specific challenges.
- Operational Resilience: Assess the robustness of your operational processes and supply chain. Identify areas where disruptions could occur and develop mitigation strategies.
- Market Positioning: Analyze your competitive positioning and market share. Recognize vulnerabilities in your market position that could be exploited by competitors.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Ensure that your business complies with relevant regulations and standards. Identify vulnerabilities related to non-compliance or regulatory changes.
3. Risk Management Strategies
- Risk Avoidance: In some cases, the best strategy is to avoid high-risk ventures or markets altogether. This may involve refraining from entering certain markets or discontinuing products or services with excessive risk.
- Risk Reduction: Implement measures to reduce identified risks. For example, diversifying your product offerings or customer base can reduce dependence on a single revenue source.
- Risk Transfer: Transfer some risks through methods such as insurance or outsourcing. For instance, businesses can mitigate cybersecurity risks by purchasing cyber insurance.
- Risk Acceptance: In cases where risks cannot be entirely mitigated, it may be necessary to accept a certain level of risk and have contingency plans in place to address potential issues.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish a system for continuous risk monitoring. Regularly assess the changing landscape and adjust risk management strategies accordingly.
4. Contingency Planning
Contingency planning involves developing strategies and action plans to respond effectively to unforeseen events or crises. It ensures that your business can maintain operations and minimize disruptions in the face of adverse circumstances. Key elements of contingency planning include:
- Risk Scenarios: Identify potential risk scenarios specific to your industry and business. These scenarios should encompass a range of possibilities, from minor disruptions to major crises.
- Response Teams: Establish response teams with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Ensure that team members are trained and ready to act in the event of a crisis.
- Communication Plans: Develop communication plans that outline how you will communicate with employees, customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders during a crisis. Transparency and timely communication are critical.
- Resource Allocation: Determine how resources, including personnel, finances, and equipment, will be allocated in response to various scenarios.
- Testing and Simulation: Regularly conduct tests and simulations of your contingency plans to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement. Ensure your response teams are well-practiced and ready to execute the plans effectively.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive documentation of contingency plans, response procedures, and communication protocols. This documentation should be easily accessible to relevant personnel.
- Review and Update: Continuously review and update your contingency plans to reflect changing industry dynamics and evolving risks. Regularly seek feedback from response teams to make improvements.
By identifying industry risks, assessing vulnerabilities, implementing risk management strategies, and developing robust contingency plans, your business can navigate the complexities of the industry landscape with greater resilience and preparedness.
Industry Analysis Template
When embarking on the journey of Industry Analysis, having a well-structured template is akin to having a reliable map for your exploration. It provides a systematic framework to ensure you cover all essential aspects of the analysis. Here's a breakdown of an industry analysis template with insights into each section.
Industry Overview
- Objective: Provide a broad perspective of the industry.
- Market Definition: Define the scope and boundaries of the industry, including its products, services, and target audience.
- Market Size and Growth: Present current market size, historical growth trends, and future projections.
- Key Players: Identify major competitors and their market share.
- Market Trends: Highlight significant trends impacting the industry.
Competitive Analysis
- Objective: Understand the competitive landscape within the industry.
- Competitor Identification: List direct and indirect competitors.
- Competitor Profiles: Provide detailed profiles of major competitors, including their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning.
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis for each major competitor.
- Market Share Analysis: Analyze market share distribution among competitors.
Market Analysis
- Objective: Explore the characteristics and dynamics of the market.
- Customer Segmentation: Define customer segments and their demographics, behavior, and preferences.
- Demand Analysis: Examine factors driving demand and customer buying behavior.
- Supply Chain Analysis: Map out the supply chain, identifying key suppliers and distribution channels.
- Regulatory Environment: Discuss relevant regulations, policies, and compliance requirements.
Technological Analysis
- Objective: Evaluate the technological landscape impacting the industry.
- Technological Trends: Identify emerging technologies and innovations relevant to the industry.
- Digital Transformation: Assess the level of digitalization within the industry and its impact on operations and customer engagement.
- Innovation Opportunities: Explore opportunities for leveraging technology to gain a competitive edge.
Financial Analysis
- Objective: Analyze the financial health of the industry and key players.
- Revenue and Profitability: Review industry-wide revenue trends and profitability ratios.
- Financial Stability: Assess financial stability by examining debt levels and cash flow.
- Investment Patterns: Analyze capital expenditure and investment trends within the industry.
Consumer Insights
- Objective: Understand consumer behavior and preferences.
- Consumer Surveys: Conduct surveys or gather data on consumer preferences, buying habits , and satisfaction levels.
- Market Perception: Gauge consumer perception of brands and products in the industry.
- Consumer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback and reviews.
SWOT Analysis for Your Business
- Objective: Assess your own business within the industry context.
- Strengths: Identify internal strengths that give your business a competitive advantage.
- Weaknesses: Recognize internal weaknesses that may hinder your performance.
- Opportunities: Explore external opportunities that your business can capitalize on.
- Threats: Recognize external threats that may impact your business.
Conclusion and Recommendations
- Objective: Summarize key findings and provide actionable recommendations.
- Summary: Recap the most critical insights from the analysis.
- Recommendations: Offer strategic recommendations for your business based on the analysis.
- Future Outlook: Discuss potential future developments in the industry.
While this template provides a structured approach, adapt it to the specific needs and objectives of your Industry Analysis. It serves as your guide, helping you navigate through the complex landscape of your chosen industry, uncovering opportunities, and mitigating risks along the way.
Remember that the depth and complexity of your industry analysis may vary depending on your specific goals and the industry you are assessing. You can adapt this template to focus on the most relevant aspects and conduct thorough research to gather accurate data and insights. Additionally, consider using industry-specific data sources, reports, and expert opinions to enhance the quality of your analysis.
Industry Analysis Examples
To grasp the practical application of industry analysis, let's delve into a few diverse examples across different sectors. These real-world scenarios demonstrate how industry analysis can guide strategic decision-making.
Tech Industry - Smartphone Segment
Scenario: Imagine you are a product manager at a tech company planning to enter the smartphone market. Industry analysis reveals that the market is highly competitive, dominated by established players like Apple and Samsung.
Use of Industry Analysis:
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, identifying areas where they excel (e.g., Apple's brand loyalty ) and where they might have vulnerabilities (e.g., consumer demand for more affordable options).
- Market Trends: Identify trends like the growing demand for sustainable technology and 5G connectivity, guiding product development and marketing strategies.
- Regulatory Factors: Consider regulatory factors related to intellectual property rights, patents, and international trade agreements that can impact market entry and operations.
- Outcome: Armed with insights from industry analysis, you decide to focus on innovation, emphasizing features like eco-friendliness and affordability. This niche approach helps your company gain a foothold in the competitive market.
Healthcare Industry - Telehealth Services
Scenario: You are a healthcare entrepreneur exploring opportunities in the telehealth sector, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Industry analysis is critical due to rapid market changes.
- Market Size and Growth: Evaluate the growing demand for telehealth services, driven by the need for remote healthcare during the pandemic and convenience factors.
- Regulatory Environment: Understand the evolving regulatory landscape, including changes in telemedicine reimbursement policies and licensing requirements.
- Technological Trends: Explore emerging technologies such as AI-powered diagnosis and remote monitoring that can enhance service offerings.
- Outcome: Industry analysis underscores the potential for telehealth growth. You adapt your business model to align with regulatory changes, invest in cutting-edge technology, and focus on patient-centric care, positioning your telehealth service for success.
Food Industry - Plant-Based Foods
Scenario: As a food industry entrepreneur , you are considering entering the plant-based foods market, driven by increasing consumer interest in health and sustainability.
- Market Trends: Analyze the trend toward plant-based diets and sustainability, reflecting changing consumer preferences.
- Competitive Landscape: Assess the competitive landscape, understanding that established companies and startups are vying for market share.
- Consumer Behavior: Study consumer behavior, recognizing that health-conscious consumers seek plant-based alternatives.
- Outcome: Informed by industry analysis, you launch a line of plant-based products emphasizing both health benefits and sustainability. Effective marketing and product quality gain traction among health-conscious consumers, making your brand a success in the plant-based food industry.
These examples illustrate how industry analysis can guide strategic decisions, whether entering competitive tech markets, navigating dynamic healthcare regulations, or capitalizing on shifting consumer preferences in the food industry. By applying industry analysis effectively, businesses can adapt, innovate, and thrive in their respective sectors.
Conclusion for Industry Analysis
Industry Analysis is the compass that helps businesses chart their course in the vast sea of markets. By understanding the industry's dynamics, risks, and opportunities, you gain a strategic advantage that can steer your business towards success. From identifying competitors to mitigating risks and formulating competitive strategies, this guide has equipped you with the tools and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the business world.
Remember, Industry Analysis is not a one-time task; it's an ongoing journey. Keep monitoring market trends, adapting to changes, and staying ahead of the curve. With a solid foundation in industry analysis, you're well-prepared to tackle challenges, seize opportunities, and make well-informed decisions that drive your business toward prosperity. So, set sail with confidence and let industry analysis be your guiding star on the path to success.
How to Conduct Industry Analysis in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the real-time market research platform that transforms how you conduct Industry Analysis. Imagine getting real-time consumer insights in minutes, putting the power of data-driven decision-making at your fingertips. With Appinio, you can:
- Gain insights swiftly: Say goodbye to lengthy research processes. Appinio delivers answers fast, ensuring you stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
- No research degree required: Our intuitive platform is designed for everyone. You don't need a PhD in research to harness its capabilities.
- Global reach, local insights: Define your target group precisely from over 1200 characteristics and access consumer data in over 90 countries.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

08.08.2024 | 30min read
Environmental Analysis: Definition, Steps, Tools, Examples
06.08.2024 | 32min read
Marketing Mix: The 4 Ps of Marketing & How to Use Them?

01.08.2024 | 27min read
Multistage Sampling: Definition, Guide, Examples
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
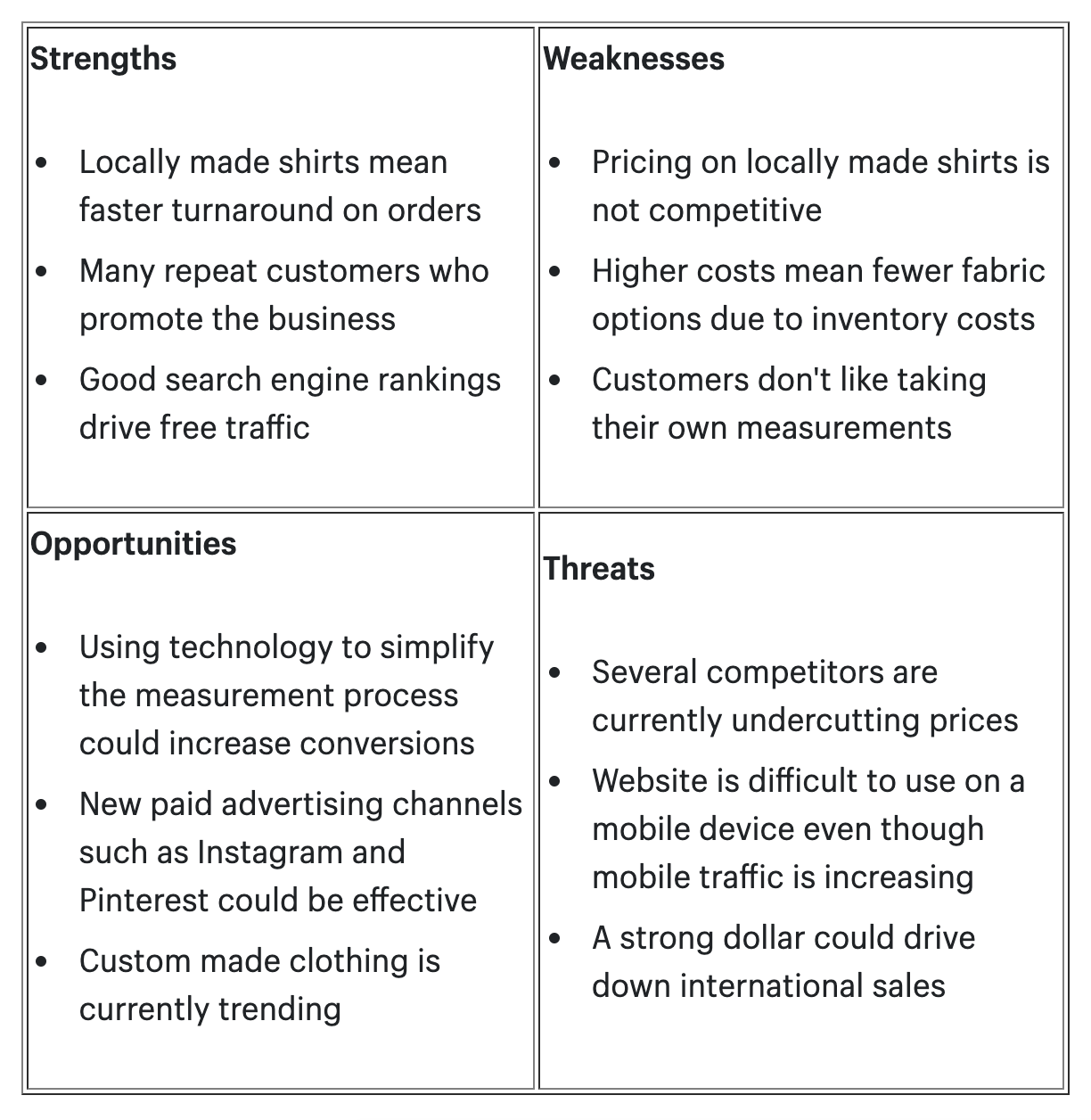
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 12, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.

How to Conduct an Industry Analysis
- March 21, 2024
- Business Plan , How to Write

An industry analysis is a fundamental component of any business plan, offering insights into the market dynamics, competitive landscape , and future market trends . This analysis helps businesses understand their industry’s environment, make informed strategic decisions, and identify potential opportunities and threats.
This guide will walk you through the steps of conducting a thorough industry analysis, using examples to illustrate key points.
Identify Your Industry
Before diving into the analysis, it’s crucial to clearly identify and define your industry. This involves outlining the scope in terms of products, services, and geographic reach.
Understanding the industry’s value chain and how your business fits within this ecosystem is essential. Consider the broader market forces at play, the typical customer base, and the regulatory landscape that shapes your industry’s boundaries.
- Example for a Hair Salon : If you’re opening a hair salon, your industry encompasses beauty and personal care services focused on hair treatment and styling.
Gather Information
The foundation of a solid industry analysis is robust data collection.
Utilize a variety of sources to gather information about your industry, including industry reports online, government publications, academic journals, and news articles. Attend industry conferences or trade shows and engage with other professionals on social media or industry forums to gain firsthand insights.
- Example for a Hair Salon : For a hair salon, look into beauty industry trends, salon service pricing strategies , and consumer spending habits in personal care services.
Analyze Market Trends
Identifying and understanding current market trends that affect your industry is vital.
Look for patterns in technological advancements, consumer behavior changes, regulatory developments, and economic factors. Projecting these trends into the future can help predict shifts in the industry landscape, allowing your business to adapt and innovate proactively.
- Example for a Hair Salon : An increasing preference for organic and eco-friendly hair care products is a significant trend in the hair salon industry.
Assess the Competitive Landscape
Analyze who your direct and indirect competitors are, what strategies they employ, their strengths and weaknesses, and their market positioning.
Tools like SWOT analyses analysis can help assess the competitive intensity and the profitability potential within the industry. This analysis also identifies potential barriers to entry and the threat of substitute products or services.
- Example for a Hair Salon : Examine other salons in your area, noting services offered, pricing levels, customer reviews, and marketing tactics.
Determine Market Entry Barriers
Barriers to entry can vary significantly across industries and affect your strategy for market entry and growth.
[link to Market Entry Barriers]
High capital requirements, strict regulatory standards, established brand loyalty, and access to distribution channels are common barriers. Identifying these early on helps in formulating strategies to overcome them, whether through innovation, strategic partnerships, or niche targeting.
- Example for a Hair Salon : For a hair salon, barriers might include the cost of acquiring a prime location, compliance with health and safety regulations, and establishing a brand in a competitive market.
Predict Future Industry Changes
Leveraging the information gathered, anticipate potential changes in the industry. This could involve innovations that disrupt traditional business models, regulatory changes, or shifts in consumer preferences. Understanding these potential changes allows businesses to be agile and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Example for a Hair Salon : Anticipate how the growing use of online booking platforms and social media marketing could transform customer engagement strategies in the hair salon industry.
Identify Opportunities and Threats
Synthesize your findings to pinpoint opportunities for your business to exploit and threats you may need to mitigate. This SWOT analysis will be crucial for your strategic planning.
[link to SWOT]
- Example for a Hair Salon : Opportunities might include a gap in the market for salons specializing in sustainable practices. A threat could be the rising cost of eco-friendly products.
Related Posts

Pro One Janitorial Franchise Costs $9K – $76K (2024 Fees & Profits)
- July 5, 2024

Dance Studio Business Plan PDF Example
- June 17, 2024
- Business Plan

Carpet and Upholstery Cleaning Business Plan PDF Example
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
Market Trend Analysis: A Simple Step-by-Step Guide

Market trend analysis helps executives and investors spot the next big trends before they peak.
However, the quality of your market trend analysis process directly impacts the quality of the insights you'll generate.
For example, the data quality you use, the metrics you select for analysis, and how you draw conclusions from that data significantly impact the insights you'll generate from market trend analysis.
So in this guide we'll walk you through an effective market trend analysis process that outlines:
- Specific data points to identify
- Quality resources to find data
- How to use the insights you discover to inform your business strategy
What is Market Trend Analysis?
Market trend analysis is a process that executives, investors, entrepreneurs, and other business professionals use to identify and assess market patterns based to make informed strategic decisions.
For business leaders, market trend analysis provides insights they need to make sound strategic decisions about new features, product lines, and marketing campaigns to launch (or pivot).
For investors and entrepreneurs, market trend analysis provides insights that guide them toward the most profitable markets and businesses to invest in.
For example, if you’re in the health food market, market trend analysis would help you realize that investing in prebiotic soda is an emerging category.
Why is Market Trend Analysis Important?
Here are the four main ways market trend analysis helps business executives, entrepreneurs, and investors make better strategic decisions.
Identify Emerging Trends Early
An effective market trend analysis process helps you identify emerging trends before they mature.
Spotting trends early is useful for investors as early investments often yield a higher ROI. This data is also useful for business leaders and entrepreneurs as it allows them to create new products and services to meet future demand before their competitors.
Reduce Investment Risk
Market trend analysis provides insight into market volatility and lets you gauge whether demand increases, decreases, or remains consistent.
This can help you identify the lowest risk opportunities or at least be aware of the risk associated with each investment decision.
Improve Forecasting Accuracy
Launching a new product, service, or marketing campaign requires an accurate estimate of future demand.
Market trend analysis assists your demand calculation by providing an overview of historical consumer interest, which you can use to forecast future demand.
Maintain a Competitive Advantage
Market trend analysis helps businesses maintain a competitive advantage by:
- Uncovering up-and-coming competitors
- Providing insights into why consumers like the new competitors’ products/services
- Providing data on how consumers feel underserved by competitors
For example, Meta has been losing significant market share to TikTok over the last few years. This is mainly because Meta failed to keep up with consumer demand trends.
If Facebook had identified these market trends earlier and pivoted to implement the aspects of TikTok that users love (short, funny videos), it might have retained this market share.
How to Conduct Market Trend Analysis
Whether you’re researching market trends to launch a new business or invest in a startup, here’s a step-by-step process to analyze market trends and inform your business strategy.
Step 1: Identify Emerging Competitors, Products, and Industry Terms
Identifying which trends to analyze is arguably the most important task in this process.
That’s because a great analysis of a mediocre market trend can still lead to a dead end.
Most people approach the trend discovery process by reading industry publications, following industry influencers on social media, and browsing free market trend reports .
While this process can work, it's time-consuming. Plus, there's always a chance that you'll overlook the next emerging trend.
To help you predictably identify under-the-radar trends in seconds, we built Exploding Topics.
The flagship feature is the Trends Database, a curated selection of 1 million data-backed trends our team manually vetted.
To identify emerging competitors, industry terms, and products, simply sort the Trends Database by one of the 35+ categories (fashion, pets, finance, marketing, CPG etc.) and then trend status ("exploding," "regular," and "peaked").
After discovering an interesting trend, click "Track Topic" and save it to a custom Project for more in-depth analysis.
So how do you know that the trends in Exploding Topics are reliable?
We have a thorough trend identification and qualification process to ensure:
- We consistently identify under-the-radar trends and don't miss the next big trend.
- Each trend has long-term growth potential.
- Trends are backed by reliable data – not randomly selected by a single person.
You can use the free Exploding Topics database now to complete this step, or try Exploding Topics Pro to access our premium trends and other market analysis features.
Step 2: Analyze Quantitative Data For Each Trend
It's easy to scan market reports and get lost in endless data without learning anything meaningful about that trend.
So instead of collecting random data, here are the most important quantitative metrics to assess market trends:
- Market size
- Competitor traffic
- Industry funding
- Industry hiring
Below, we'll show you how to collect and use this data to gauge a market's potential.
Market Size
If you Google the trend's keyword combined with the words "market report," you can usually find a market report from Globe Newswire or Grand View Research that shows its market size and growth trend data. This data can help you analyze a market's maturity and estimate its future growth trend.
If a market has a strong compounding annual growth rate (CAGR), it will likely continue to grow.
Traffic Trends
If you used Exploding Topics to identify market trends, you already have search volume trend data. Otherwise, search the trend in Google Trends or Trends Analysis (an Exploding Topics Pro feature) and view its search volume trend.
If you see steady growth, there's a good chance it's a sustainable, long-term trend, whereas spikes and dips indicate that it's either a fad that will die out or a seasonal trend with volatile revenue.
Funding Trends
Another good sign that a market is promising is if venture capitalists are pouring money into that market. While venture capitalists aren't always correct in their predictions, they dedicate all their resources to identifying industry trends, so it's still a good benchmark.
A quick Google search of the industry will usually pull up data on VC investment history for that particular trend. For example, a quick search for "VC funding in sustainable beauty" pulled up this data from a Pitchbook blog post :
Databases like Pitchbook and CB Insights are excellent resources for providing funding data.
Hiring Trends
Hiring trends also help you gauge the market's general health. If most of the top players in a market are all hiring, there's a good chance that the market is growing.
You can find hiring data by looking at the LinkedIn profiles of the top competitors in the space:
You can also check the specific jobs they’re hiring for by looking at their LinkedIn Jobs and Indeed profiles.
Step 3: Gather Qualitative Secondary Data Around Each Trend
Quantitative data provides a good general overview of trend potential. However, qualitative data can help you understand why a trend is becoming popular and the pain points it's solving.
This information helps you understand how to find gaps in the market and provide a solution to unmet consumer demand.
Here are three ways you can collect qualitative data for various trends.
Reading Customer Reviews
Customer reviews help you understand more about the specific pain points that a particular trend solves and general customer enthusiasm for the new product or service.
The trend will likely continue to thrive if it is highly effective at solving a pain point and customers are enthusiastic about it.
You'll also learn more about your target demographic and the ideal customer persona by reading reviews.
To find reviews, you can use Amazon to research D2C products or Capterra or G2 to read B2B reviews.
Once you have a few hundred reviews to analyze, here are a few key things to look for:
- What specific pain points does the product/service solve?
- How did consumers solve the pain point before this product/service existed, and what alternatives did they use?
- What are common customer complaints with the current products/services available?
- The general sentiment around this trend – what kind of tone do they use when reviewing the product?
For example, if you're researching "bamboo baby clothes," you'll see that customers like the product because the fabric is much softer and more flexible.

Other reviewers claimed they purchased bamboo baby clothes to help with their eczema symptoms.
These reviews help you understand why bamboo baby clothes are popular, which is another positive sign that this trend has long-term growth potential.
You can also extract valuable customer demographic insights from reviews like:
- B2C customer persona (age, gender, knowledge level of the pain point, etc.)
- B2B customer persona (position, company size, budget, etc.)
- Parallel interests
- Goals/ambitions
- How they enjoy spending time
- Activities they don't enjoy
All of this information will be useful in informing future marketing efforts, like how to position products and where to advertise online.
Read Industry Forums
Similar to reviews, industry forums and platforms like Quora and Reddit can provide more detailed discussions on customer pain points around niche trends.
For example, there are several subreddits dedicated to new parents.
Many of which have active discussions about baby clothes:
This subreddit alone is everything you need to track the current market for baby clothes (including clothes made from bamboo fabric), as it discusses what people like and dislike about the major brands in the space.
You can also join these discussions and get members' feedback on new product ideas.
If you're struggling to find industry forums, you can use a tool like SparkToro to help you. Just type in the trend keyword, and it will show you the websites people searching that keyword frequently visit:

Social Listening
You can also gather plenty of qualitative data and competitive insights by simply listening to what customers say on social media.
For example, you can use a social listening tool like Brand24 or Awario to track competitor brand mentions on social media. Most social listening tools also offer sentiment analysis, which can help you understand how potential customers feel about a particular trend.
Here’s the sentiment analysis trend from Awario of Starbucks:
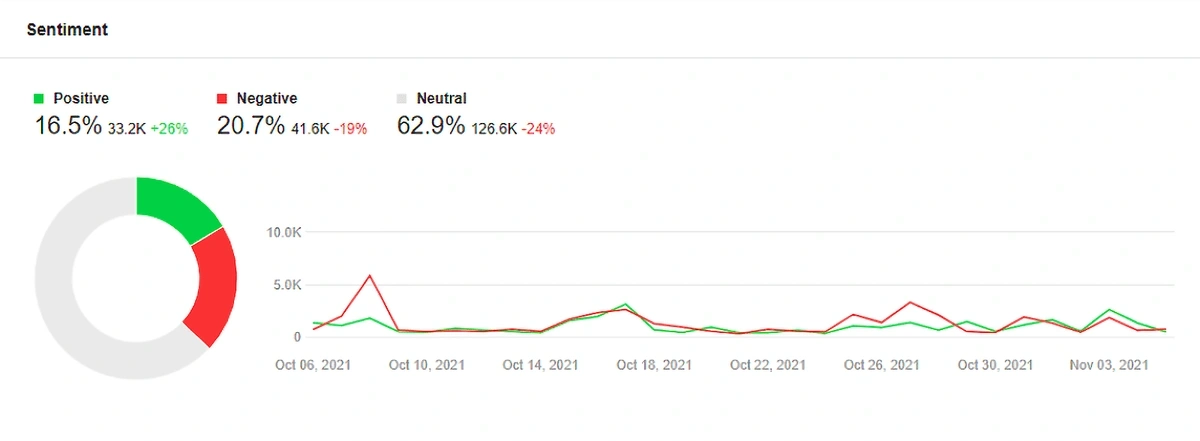
If you notice that most people have a negative outlook on most of the top brands in the space, that's a negative sign that the trend you're tracking might not be short-term and on its way out.
However, it could also mean that there is unmet demand that you can capitalize on.
Step 4: Conduct Primary Research and Talk to Your Target Market
The secondary market research we did above is great for narrowing down the market trends you're considering, but it's important to also do primary research and talk to your customers before launching a product or service to understand where the gaps in the market exist.
There are two popular methods to execute primary research:
- Survey potential customer
- Interview potential customers
Surveying Potential Customers
If you already have an audience, you can survey your existing email list to gauge their feelings about a particular trend.
However, if you don't have an audience in the market you're analyzing, there are plenty of survey tools like SurveyMonkey and Pollfish that allow you to run a survey to a specific audience.
For example, if you're analyzing the bamboo baby clothing market, you could use one of those survey tools to run a survey to an audience of parents with children under four years old. To get even more specific, you could add a screening question like "Have you ever bought bamboo baby clothing?"
Pricing is usually about $1 per response, making it relatively cost-effective.
Interviewing Customers
Perhaps the best way to assess market demand and learn what customers want is to talk to them one-on-one. Live conversations usually reveal golden insights often missed with other market research methods, as you can ask follow-up questions to get to the root of any pain point.
For example, if you're marketing bamboo baby clothing, you might discover on customer research calls that most users received it as a gift from friends or parents.
That insight means that you should probably adjust your marketing messaging from targeting just new parents to also targeting friends and grandparents who provide more detailed insights.
To conduct customer interviews, you can use a tool like Discuss.io , which records the customer research calls, creates auto-generated clips based on keywords (like "gifts"), and even provides sentiment analysis.
If you're doing B2B customer research, you can find people to interview through a service like Respondent .
Step 5: Create a Beta Offer Around That Trend
By now, you've thoroughly analyzed the market trend from a data perspective. Still, the only way to assess whether or not this trend is worth investing in is to see if customers will buy it.
So create a beta offer and see if people buy it.
Most companies make the mistake of developing a product or service before selling it, only to discover that it's not quite the solution their target demographic actually wants.
To prevent you from making this costly error, create a landing page advertising the offer and see if you can get people to pay real money for the product.
For example, Carry is a platform designed to help freelancers create solo 401ks. Before launching, they created a landing page to see if enough business owners would sign up for it:

The founder only started building the product after enough people joined.
Even if you're planning to launch an ecommerce product, you can still create a landing page and offer pre-orders before building the product.
If people purchase the product, you can create it and send it to that initial beta group.
If your target audience doesn't buy, you just saved yourself from spending thousands, if not millions, on a market trend that doesn't resonate with your audie
Start The Market Trend Analysis Process Today
A key difference between unicorn companies and legacy companies overtaken by unicorns is their ability to accurately identify, analyze, and swiftly take action on the right market trends.
However, many companies fail to identify the right trends early enough.
So to help you solve this problem, we built Exploding Topics.
It executes the trend discovery process for you by analyzing billions of webpages and extracting the most promising trends. Then, a human analyst manually vets each topic for relevancy before adding it to the Trends Database.
By using the Trends Database, you can find relevant emerging trends in a matter of seconds rather than spending hours reading industry publications, scrolling X, and combing other data sources for potential trends. Which can really help with the trend analysis process.
Find Thousands of Trending Topics With Our Platform
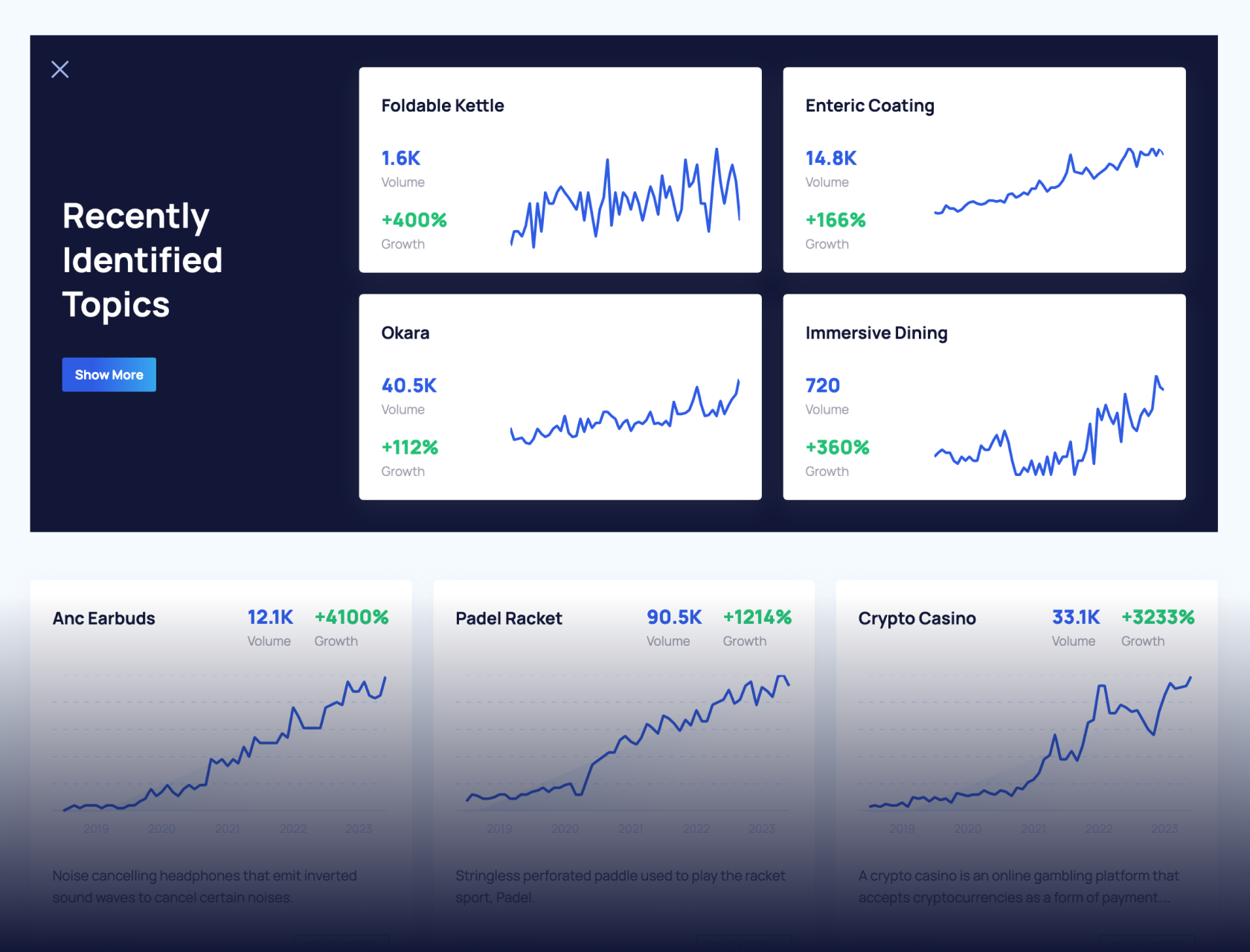
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Executive summary.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
Company Description
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market
Market analysis.
The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
Competitive Analysis
Organization and management team.
Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
Logistics and Operations Plan
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Income Statement
Cash flow statement.
A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Brief overview of the business plan | Overview of EcoTech and its mission |
| Overview & Objectives | Outline of company's goals and strategies | Market leadership in sustainable technology |
| Company Description | Detailed explanation of the company and its unique selling proposition | EcoTech's history, mission, and vision |
| Target Market | Description of ideal customers and their needs | Environmentally conscious consumers and businesses |
| Market Analysis | Examination of industry trends, customer needs, and competitors | Trends in eco-friendly technology market |
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluation of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats | Strengths and weaknesses of EcoTech |
| Competitive Analysis | In-depth analysis of competitors and their strategies | Analysis of GreenTech and EarthSolutions |
| Organization & Management | Overview of the company's structure and management team | Key roles and team members at EcoTech |
| Products & Services | Description of offerings and their unique features | Energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers |
| Marketing & Sales | Outline of marketing channels and sales strategies | Digital advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships |
| Logistics & Operations | Details about daily operations, supply chain, inventory, and quality control | Partnerships with manufacturers, quality control |
| Financial Projections | Forecast of revenue, expenses, and profit for the next 3-5 years | Projected growth in revenue and net profit |
| Income Statement | Summary of company's revenues and expenses over a specified period | Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Net Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Overview of cash inflows and outflows within the business | Net Cash from Operating Activities, Investing Activities, Financing Activities |
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
What is a Business Plan?
Why you should write a business plan.
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
| Type of Business Plan | Purpose | Key Components | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Business Plan | Outlines the company's mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. | Mission Statement, Company Description, Market Analysis, Competitive Analysis, Organizational Structure, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Internal Business Plan | Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. | Strategies, Milestones, Deadlines, Resource Allocation. | Internal Team Members |
| Strategic Business Plan | Outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them. | SWOT Analysis, Market Research, Competitive Analysis, Long-Term Goals. | Executives, Managers, Investors |
| Feasibility Business Plan | Assesses the viability of a business idea. | Market Demand, Competition, Financial Projections, Potential Obstacles. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Growth Business Plan | Focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. | Market Analysis, New Product/Service Offerings, Financial Projections. | Business Owners, Investors |
| Operational Business Plan | Outlines the company's day-to-day operations. | Processes, Procedures, Organizational Structure. | Managers, Employees |
| Lean Business Plan | A simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements. | Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Revenue Streams, Cost Structure. | Entrepreneurs, Startups |
| One-Page Business Plan | A concise summary of your company's key objectives, strategies, and milestones. | Key Objectives, Strategies, Milestones. | Entrepreneurs, Investors, Partners |
| Nonprofit Business Plan | Outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation for nonprofit organizations. | Mission Statement, Goals, Target Audience, Fundraising Strategies, Budget. | Nonprofit Leaders, Board Members, Donors |
| Franchise Business Plan | Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. | Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. | Franchisors, Franchisees, Investors |
Using Business Plan Software
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
| Software | Key Features | User Interface | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LivePlan | Over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking against KPIs | User-friendly, visually appealing | Allows creation of professional-looking business plans |
| Upmetrics | Customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, collaboration capabilities | Simple and intuitive | Provides a resource library for business planning |
| Bizplan | Drag-and-drop builder, modular sections, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking | Simple, visually engaging | Designed to simplify the business planning process |
| Enloop | Industry-specific templates, financial forecasting tools, automatic business plan generation, unique performance score | Robust, user-friendly | Offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget |
| Tarkenton GoSmallBiz | Guided business plan builder, customizable templates, financial projection tools | User-friendly | Offers CRM tools, legal document templates, and additional resources for small businesses |
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
Can i write a business plan by myself, is it possible to create a one-page business plan.
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
What is a business plan outline, what are the 5 most common business plan mistakes, what questions should be asked in a business plan.
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
How is business planning for a nonprofit different.

- Content Marketing
- Content Strategy
- Pillar-Based Marketing
- SEO Keyword Research
- SEO Pillars
- SEO Strategy
- Website Content
- DJ For Agencies
- Customer Stories
- Documentation
- Press Releases

Types of Market Trends: An Industry Trends Analysis
November 4, 2020 • DJ Team

A market trend is anything that alters the market your company operates in. This could be something as far-reaching as artificial intelligence technology, as fickle as consumer preferences, or as industry-specific as new regulations. In fact, it’s almost certain there are multiple market trends affecting your business at the same time, right now.
Why is it important to keep up to date with industry trends and developments? Well, because that’s how you grow and stay ahead of your competition. As author and motivational speaker John Maxwell once said, “Change is inevitable, but growth is optional.” While you can’t stop the momentum of change like technology or regulations, you can take steps to grow in tandem with those changes.
This trend-tracking doesn’t have to add up to hours of research every week. By understanding the types of market trends , you can distinguish what makes sense for your business. This focused analysis helps you adapt and stay competitive in any rapidly changing business environment.
What is an Example of a Market Trend?
If you try a simple Google search for “market trends,” you’re likely to get a lot of information about stocks, financials, and investing. Today this term applies to many industries, but it does have its roots in finance. And though your industry of operation might be B2B services, retail, energy, technology, healthcare, or many other sectors of the economy, you can still learn from the three ways financial professionals think about a market trend.
1. Short-Term Market Trends
Short-term trends occur over a few hours or days. In marketing or business positioning, this would include news and current events, social media trends, or sales events like Amazon Prime Day and Black Friday. For example, if a news story breaks that is relevant to your business, you need to create content about that quickly to capture interest before it ebbs away.
2. Intermediate Market Trends
Intermediate trends last anywhere from two to eight weeks. In finance, these are rallies and turnarounds that can mystify analysts. In business, causes of intermediate trends can be easier to pinpoint, but not always. Events like the holiday season, elections, tax time, or industry-specific compliance deadlines represent some factors that can drive intermediate market trends. Maybe your competitors do something every year to mark some of these occasions, or your customers are looking for unique products or services for a few months. Other times, social media influencers or emerging research drives these trends in interest.
3. Long-Term Market Trends
Long-term trends last years and even decades. These are big societal changes that affect your business, like mobile devices and artificial intelligence, gaps or deficiencies in the talent pipeline, the COVID-19 pandemic, and culture shifts like the #metoo movement or demands for racial equity and justice . While you might need to adapt to the new environment as these long-term trends manifest, responses should be more thoughtful than reactionary. For instance, just because you know consumers want a mobile-friendly experience doesn’t mean you should implement one without strategy.

What Are Some Important Trends in Marketing?
Let’s explore two real-world recent trends in marketing with examples to further illustrate the point.
- Short and Sweet Video Marketing: While video watching hit an all-time high in 2020, forecasts estimate that adults will spend approximately 80 minutes per day watching digital videos on mobile devices by 2023. One of the best ways to get them to watch and engage with your videos is by keeping them short. Reddit took this to an extreme during the 2021 Super Bowl, buying a five-second commercial slot as a part of a brand awareness campaign. It worked, and the Tweet linked to the video has racked up over 464,000 views.
- Pillar-Based Marketing: Content still remains one of the most effective ways to get your audience’s attention. Pillar-based marketing is a strategy that builds authority, pushing your content further up the rankings on search engine results pages. Sharing our own win with pillar-based marketing, we published six pieces of content per week for three weeks around the topic of SEO Keyword Research. The results? We went from 10 to 59 first page rankings.
How to Determine Market Trends You Should Focus On
There are lots of trends that matter to different consumers at different times. But if your business tries to be everything to everyone, your message won’t speak to your ideal customer over all the others. Focusing on short-term market trends might be one way to make customers aware of you through social media or Google results, but it’s how you speak to long-term trends and show your value that will take them from casual reader to dedicated customer.
There are a few ways you can find out about the market trends affecting your business. As you explore these trends, it’s also important to be asking critical questions about how your values and service offerings align, fit in, or even run counter to the trends.
Follow Types of Recent Trends in Marketing
One way to hone in on market trends unique to your industry is to read the publications that are reporting on the current issues. For example, if you’re looking to stay up to date with recent trends in content marketing, you might follow Search Engine Journal or Search Engine Land . If possible, sign up for newsletters to receive articles and insights right to your inbox. If podcasts are more your thing, our own Page One or Bust talks SEO strategy with business leaders and SEO experts alike.
Use Industry Trends Analytics
Digital analytics tools, like those we offer at DemandJump, for consumer behavior insights can help you get the bigger picture on your market, your audience, what they are searching for, and how it relates to the greater economy.
Observe Your Competitors
If all your competitors are doing something, does that mean you should do it? Maybe yes, or maybe no. But observing their marketing is a way to make more educated decisions.
But don’t forget, it’s not just about what your brand considers important. The whole reason for focusing on trends to begin with is to appeal better to your customers. Your trends analysis should also be paired with market research to inform your messaging strategy and content creation plan. With DemandJump, customers can dive into the exact keywords and phrases their competitors are ranking for—giving them the knowledge they need to take over the market share.
What are the 3 Main Types of Market Research?
Following along with trends just because they exist is never a great idea. To make sure your choices will result in more business and more customer loyalty, you can’t skip market research. This process will help you understand the problems customers are facing, and refine the way you present your solutions.
There are three main types of market research:
- Exploratory Research: This approach is used to better-define a problem and your organization's opportunity to solve it. This research is usually conducted through in-depth customer interviews or discussions.
- Descriptive Research: This approach is used to determine if a product or service is a good fit for the market, or to judge the general attitudes of customers toward a service or product. In addition to interviews, surveys may also be used.
- Causal Research: This market research is used to test scenarios or determine cause-and-effect. This might be conducted through focus groups or A-B testing to see if changing one aspect of the pitch or marketing strategy changes the outcome with customers.
These market research tactics will help you understand what customers are looking for and what elements motivate them toward a buying decision. How do their questions change along with their needs? What solutions are they seeking? With these answers, you will be able to put current market trends in the context of your business and your market.
What Are the Advantages of Trend Analysis?
There are several advantages of conducting market trend analysis, including establishing better relationships with customers and driving your business’s sales. Let’s dive into each of these as well as some of the other benefits.
- Building Better Relationships With Customers: When you know who your customers are and what they are searching for, you can create a marketing plan that will better attract them and keep them once they are customers.
- Creating Competition: You want to keep up with the competition, and analyzing marketing trends allows you to do so. What is your competition doing well? What could they be doing better? Look at those areas and determine what your business can do to remain competitive.
- Supporting Business Growth: When you look at marketing trends, you can determine where your business can develop new products and services to attract new customers.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement: What could your business do better? Look at marketing trends to determine what those areas might be and improve upon them.
- Avoiding Crises: The unexpected happens all the time. When you look at marketing trends, you can start to predict what might cause problems for your business before you actually face those problems.
- Driving Sales: Ultimately, all of these points lead to one big benefit for your business: an increase in sales. Once you figure out what your customers want and how to give it to them, then hopefully you can improve the financial well-being of your business via increased sales.
Get On-Demand Industry Trends Analysis With DemandJump
We created DemandJump to help marketers get insights and drive outcomes faster and more efficiently. DemandJump doesn’t just track search trends and consumer behavior in real-time, but also draws in insights from competitors to help you see how they are reacting to trends.
With the insights provided by DemandJump, market trends will already be put in the context of your target customer’s experience, so you can skip many of these steps and get focused on the work of improving your business. Get started today!

Please Share:
Consumer Insights • Organic Search • Marketing Management • Content Marketing
Featured Articles
- Attribution Tracking (13)
- Channel Optimization (11)
- Consumer Insights (68)
- Content Marketing (251)
- Data Science (8)
- Digital Marketing (6)
- Digital Transformation (26)
- Enterprise (10)
- Lead Generation (14)
- Market Intelligence (8)
- Marketing Analytics (39)
- Marketing Attribution (57)
- Marketing Management (153)
- Marketing Operations (86)
- Organic Search (222)
- Paid Search (52)
- Pillar-Based Marketing (63)
- Programmatic Advertising (9)
- SaaS Content (14)
- SaaS Marketing (29)
- Search Marketing (111)
- SEO Keyword Research (28)
- SEO Pillar (18)
- SEO Strategy (46)
- Website Content (12)
Get Your Free Pillar Strategy Report
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.

Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plans
How to Write a Business Plan Industry Analysis
How do you conduct industry analysis for a business plan? Do you need help conducting market research and industry analysis for your business plan? Then I advice you read on. So you have a great business idea, you have refined and fine-tuned it, and you are ready to launch. You are going to offer a product or service with a clearly defined customer base, and you are confident that you will be successful in the long term.
Well, if the above applies perfectly to you, then you have not completed your assignment. What happens when you enter an examination hall without having studied for the exam at all? You’d spend all your time in the hall blaming yourself for being silly, right? Now, starting a business is even much more important because there’s a lot more at stake than passing or failing a grade. So, you must not leave out any aspect of research undone.
In this section of your business plan, you will demonstrate that the industry’s market size is worth going after, who your main competitors will be if you decide to take a plunge, and how you will be able to carve out a niche for yourself and give your competitors a run for their money. Planning a business goes beyond analyzing the potential of your offer. You must analyze the following three factors as well:
- The strengths and weaknesses of your business
- The competition
- Who your customers are, what they want, and how they want it
These are the major components of a business plan’s market or industrial analysis and it is also known as a SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis. This section of your business plan reveals the chances of your business to achieve success with its offers. And that’s why the industry analysis is a very important section of your business plan, which must be carefully conducted and documented.
So in this article, we will be looking at how to conduct industry analysis for a business plan. If you are a budding entrepreneur, or you are planning to start a new business; then below are the exact steps to follow when conducting an industry analysis for a new business:
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan
1. analyze the competition.
Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors. If you are planning to start a new restaurant in an area, your direct competitors are other restaurants within that locality, while your indirect competitors are those that are slightly remote but still around.
Now, you are not just counting the number of rivals you have. You are trying to see how you can push ahead of them by filling a loophole they never noticed all these while. Some people find it hard to leave their workplace for the restaurant at lunchtime, but it’s either they do it or go hungry. You can disrupt the market’s status quo by offering to deliver lunch to people right in their workplaces. Filling loopholes like this one should be your goal.
If you don’t device strategies for pushing ahead of the competition, you will just enter the industry and join the survival race that you may never win. So, you need to introduce an innovation that will threaten your rivals. Remember, it’s either you differentiate or you fizzle out fast!
2. Assess the industry / market size
After analyzing your direct and indirect competitors, you will need to analyze your chances of standing firm even in the face of stiffer competition. Your first step in market research is to get an idea of how big the opportunity is and why it’s worth going after.
This means finding out how many customers you are catering to and much revenue you are likely to make. This is a convincing first step to lure in whoever is reading your business plan to become intrigued and dig further into your findings. Here are some factors you should consider:
- The individual strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
- The rate at which new competitors enter the market or the rate at which old competitors are leaving the market.
- The products or services that fetch most revenue for your competitors.
- How you will overcome the threat of substitute goods.
You can get lots of helpful information about your market from government sources, trade associations, financial services firms, online data providers, and free resources on the web.
3. Analyze industry forces and trends
You will need to outline what’s happening in the industry from many perspectives that would help the reader get the full gist on whether the market is lucrative or not. A great general-purpose tool for doing just that is the PEST Analysis. Here’s what it stands for and what you should consider:
- P – Political factors ( the role government plays in your industry )
- E – Economic factors ( the state of the economy on both local and national level )
- S – Social factors ( relevant changes in matters like lifestyle trends, demographics, consumer attitudes, buying patterns and opinions )
- T – Technological factors ( the impact of changing technological trends on your industry )
4. Develop your marketing plan
Developing your marketing plan entails answering the following questions:
- What products or services are you offering?
- How much will you charge for your offers?
- Where will you sell your product, and who are your target customers?
- What special incentives would you use to encourage customers to buy your product?
In short, this section of your industry analysis outlines how you will deliver your product to the customers and how you will win customers to your side.
5. Craft your growth plan
While some entrepreneurs are of the opinion that this step should come only after you have established your business, crafting your market development plan helps you envision your company growing in a few years. Your growth plan should address the following questions:
- According to recent data, is the market for your product growing or dwindling?
- Do you plan to introduce new products or line extensions in the next few years?
- If you plan to introduce new offers, would they be closely related to your current offers or within another niche entirely?
- Are there strategies for giving your business the competitive advantage in the industry?
- Are there plans to handle increasing demand?
6. Fine-tune your analysis
After the steps discussed above, cross check your analyses to ensure that your findings are factual and your figures are accurate. Another handy tool to have in your arsenal when conducting industry research is the almighty Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis . ( Don’t worry if you’ve never attended a business strategy class in your life, it’s actually quite straightforward ). Here’s the breakdown:
Threat of new entrants
How difficult ( or easy ) is it for someone to enter your specific vertical? If it’s very easy then most likely the space will be crowded with competitors fighting for margins. Conversely, if it’s very difficult, that that in itself can become a competitive advantage.
Threat of substitute products or services
How likely is it that another product or service could decrease demand or displace you and potentially the entire industry all together?
Bargaining power of customers
When it comes to pricing and terms, how much power does your customer have? Are they organized enough to exercise their purchase power, or is there so much competition that they have their pick resulting in pricing wars amongst providers?
Bargaining power of suppliers
This refers to how dependent you are on a given supplier to operate your business. If it’s difficult or near impossible for you to switch, that means they have the upper hand, whereas, if the switching costs are low, you can negotiate better terms for yourself.
Competitive rivalry of the market
Factoring in the first four forces, you can arrive at a good understanding of the playing field and whether it’s in your favor if you enter it, how long you’ll be able to last, through what means you’ll carve a space for yourself, and what you’re up against.
As a final note, you must never forget that the industry analysis is a vital part of your business plan and it will probably be the most extensive portion of it. So, take your time to conduct extensive research on your competitors and market trends over the recent years.
- Go to Chapter 9 Part B: Writing a Business Plan Competitive Market Analysis
- Go Back to Chapter 8: Writing your Company’s Profile
- Go Back to Introduction and Table of Content
More on Business Plans

- Entrepreneurship
- Starting a Business
- My #1 Online Biz
- Business Planning
- Advertising
- Content Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Public Relations
- Business Model
- Financial Forecasting
- Market Research
- Risk Management
- Business Plan
- Conferences
- Online Communities
- Professional Associations
- Social Media
- Human Resource
- Productivity
- Legal Requirements
- Business Structure
- Mission Statement
- Financial Plan
- Market Analysis
- Operational Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Target Market
- Competitor Analysis
- Customer Profiling
- Market Trends
- Pricing Strategies
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Cooperative
- Corporation
- Limited Liability
A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Industry Trends
by Mike Vestil
This article provides an in-depth look at the importance of understanding and staying ahead of industry trends for business success. Readers will learn the definition and different types of trends, including technology, consumer demand, regulatory, and more.
Further, the article explores various methods to identify and analyze trends, such as data analysis, competitor insights, and expert reports. It also discusses impactful tools for monitoring trends, the effect of trends on business strategy, and how to capitalize on industry trends. Finally, through case studies, readers will gain insights into companies that have successfully adapted to trends and those that have faced challenges due to lagging behind.
Understanding Industry Trends
Definition of industry trends.
Industry trends refer to the general direction that a specific industry or market is moving towards, influenced by various factors like technology, consumer demand, economic factors, and more. They are a collective pattern observed in the responses, behaviors, and performance of the players within a particular industry. These trends can be short-term or long-term and can dictate how businesses within the industry strategize their operations, product development, and marketing efforts.
Importance of Identifying and Analyzing Trends
Identifying and analyzing industry trends is crucial for any business to stay ahead in a constantly changing and evolving market landscape. By understanding the trends, businesses can make sound decisions on various aspects such as R&D, production, sales, marketing, and overall business strategy. A good understanding of industry trends can help businesses:

- Keep up with competitors
- Identify potential markets and customers
- Predict and prepare for changes in consumer demand
- Discover new business opportunities
- Stay compliant with regulations
- Gain insights for innovation and product development
Different Types of Industry Trends
Industry trends can be broadly classified into the following categories:
1. Technology
Technology-based trends are innovations that drive changes in the industry. These could include the integration of artificial intelligence, automation, IoT, or the adoption of new software platforms. As technology advances, so do the expectations and demands of consumers and businesses in terms of product offerings and processes.
2. Consumer Demand
Consumer demand trends are driven by the changing preferences and needs of the customers. This could range from the desire for environmentally-friendly products to the preference of online services over traditional offerings. Businesses must stay in tune with these shifts to deliver relevant products and services to their audience.
3. Regulatory and Legal
Regulatory and legal trends involve changes in laws, rules, and regulations governing a specific industry. Compliance with these changes is necessary to avoid legal repercussions and maintain a positive brand reputation.
4. Economic Factors
Economic trends are driven by changes in the overall economic climate, such as currency fluctuations, interest rates, employment, and inflation. These factors can impact consumer spending, investment opportunities, and overall business performance.
5. Globalization and Geopolitics
Trends in globalization and geopolitics can greatly affect businesses as they involve political, social, and economic forces that impact an industry in a specific region or globally.
6. Demographics and Social Lifestyle
Demographic trends refer to changes in the composition and attitudes of the population, such as aging, urbanization, and growing cultural diversity. Social lifestyle trends involve changes in behavior, values, and cultural norms that influence consumer preferences.
Methods to Identify Industry Trends
Data analysis and market research.
Analyzing data and conducting market research help businesses to identify trends by providing insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and competitor strategies. This can be done through data mining, collecting data from various sources and understanding customer segments, buying patterns, market size, and growth rates.
Competitor Insights
It is important to keep track of competitor activities and strategies as their advancements may impact your business as well. Monitoring press releases, financial reports, product launches, and other company news can provide valuable insights into the industry trends.
Customer Feedback and Surveys
Understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points can help businesses identify trends early. Conducting surveys and gathering customer feedback through various channels can provide valuable insights into rising expectations and preferences.
Expert Insights, Reports, and Publications
Another method of identifying trends is by following industry experts, news sources, and publications relevant to your industry. Analyst reports, government resources, trade publications, and white papers are excellent sources of information that can provide reliable and detailed insights on the latest trends.
Industry Events and Conferences
Attending industry events, trade shows, and conferences can provide valuable opportunities to network with experts, get insights into new trends, and observe emerging technologies and products firsthand.
Tools for Analyzing and Monitoring Trends
Industry and market reports.
Many organizations, such as research firms or consultancies, produce detailed reports on specific industries and markets. These reports are a valuable resource for understanding market dynamics, trends, and growth opportunities, as well as competitor analysis.
Data Analytics Tools
Data analytics tools can help businesses sort and analyze large volumes of data from various sources to identify trends and patterns. Examples of these tools include data visualization software, data mining tools, and business intelligence solutions.
News Aggregators and Alerts
Staying up-to-date with industry news can help businesses recognize trends as they arise. News aggregators and alerts, such as Google Alerts or Feedly, can be customized for your specific industry to find and deliver relevant news to your inbox or app.
Competitor Tracking Tools
Competitor tracking tools, like Owler or SEMRush, can give valuable insights into your competitors’ activities, such as news, funding, and product launches, helping you stay aware of their strategies and detect trends early on.
Social Media Listening Tools
Lastly, social media listening tools, such as Mention or Hootsuite, can help businesses track what customers and industry influencers are saying, providing insights into customer opinions, pain points, and preferences, as well as high-level industry trends.
Impact of Industry Trends on Businesses
Industry trends not only reflect the evolution of markets, customer needs, and technologies, but also help shape the business landscape. Organizations that can identify and successfully adapt to these trends often lead to improved market share, profitability, and long-term stability. However, businesses that struggle to embrace industry trends may face stagnant growth, reduced relevance, and an accelerated risk of failure. In this discussion, we will explore the impact of industry trends on various aspects of businesses, including strategy, innovation, competitive advantage, and revenue growth.
Effect on Business Strategy
The emergence of new industry trends can have a profound effect on business strategy. These trends often force businesses to re-evaluate and evolve their current approach, to ensure they remain competitive and are aligned with market changes. For instance, the rapid adoption of digital technologies and e-commerce has compelled traditional brick-and-mortar retailers to invest in online presence or partnerships with online platforms.
Aligning business strategies with constantly shifting industry trends requires ongoing assessment of the competitive landscape, recognising evolving customer needs, and anticipating future market changes. Additionally, businesses must be agile in identifying ways to capitalize on these trends, which could involve restructuring internal resources or pursuing mergers and acquisitions to quickly access new capabilities. Do check out our glossary section as well.
Innovation and Adaptability
Innovation is essential for businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors, capture customer interest, and excel in dynamic markets. Industry trends often serve as a catalyst for innovation, as companies must evolve to align with new market paradigms. Adaptability and innovation can be seen in various sectors, such as the rise of streaming services in the entertainment industry, electric vehicles in the automobile sector, and artificial intelligence in most industries.
Organizations that adopt innovative processes, practices, or technologies often stand out from competitors and are better positioned to capitalize on new growth opportunities. Moreover, a culture of innovation and adaptability enables businesses to be more resilient in dealing with unforeseen challenges or changes in market conditions.
Competitive Advantage
Recognizing and leveraging emerging industry trends can provide businesses with a significant competitive advantage. Companies that are ahead of the curve in understanding and seizing opportunities presented by industry trends often establish themselves as market leaders, while late adopters may struggle to catch up or face obsolescence.
A proactive approach to identifying and capitalizing on industry trends can provide businesses opportunities to create a defensible market position, build and strengthen brand differentiation, and develop new revenue streams. Furthermore, keeping abreast of industry trends helps organizations identify potential threats to their business and allows them to take appropriate mitigating actions.
Revenue Growth and Market Share
Successful implementation of strategies based on industry trends often leads to increased revenue growth and market share. As businesses innovate and diversify their product offerings, they can attract a wider customer base and open up new markets, creating additional sources of revenue.
The rapid growth of alternative sources of sustainable energy is an excellent example of how companies that invest in new technologies based on industry trends can increase their market share and revenue. Companies that fail to acknowledge these trends risk being left behind as competitors seize opportunities and customers ultimately shift their allegiance.
Risks and Challenges
Despite the potential benefits of aligning with industry trends, there are inherent risks and challenges that businesses need to be aware of. Identifying and acting on false or short-lived trends can lead to wasted resources and potential damage to brand reputation. Additionally, adapting to new industry trends may require significant investments in resources, infrastructure, and research, without any guarantee of success.
To mitigate these risks, businesses can invest in market research , customer foresight, and employ trend-watching tools to ensure they make informed decisions. Furthermore, by pursuing a flexible and adaptable approach, businesses can pivot their strategy as new trends emerge or fail, ensuring they stay relevant and competitive in their industry.
Capitalizing on Industry Trends
Capitalizing on industry trends is about recognizing and leveraging emerging opportunities in the market. In today’s fast-moving world where technology and innovation are key drivers of change, businesses need to be agile and adaptive to stay ahead of the competition. In this section, we will discuss the process of identifying, understanding and taking advantage of industry trends to maximize profits and growth.
Identifying Opportunities
The first step in capitalizing on industry trends is to identify opportunities that exist within the market. This requires staying informed about the industry, closely monitoring the activities of competitors, understanding customer preferences, and conducting comprehensive research about the latest innovations and technological advancements.
Some useful strategies for identifying opportunities include attending industry conferences and events, subscribing to industry publications, and engaging with thought leaders through social media networks and online forums. Businesses should also consider investing in market research and competitive intelligence tools to gather accurate and up-to-date information about industry trends and opportunities.
Once a business has identified a potential opportunity, it should validate its viability by conducting feasibility studies, market research, and by seeking opinions from experienced professionals and target customers.
Implementing Changes and New Offerings
Upon identifying a viable opportunity, businesses need to strategize and plan for implementing necessary changes within their organization. This could involve developing new products or services, altering existing processes, investing in new technologies, or repositioning marketing strategies to capitalize on the emerging trend.
Implementing changes also involves the allocation of resources, management of risks, and evaluation of the potential impact on business performance. Businesses should maintain open lines of communication across departments and ensure that employees are kept informed and involved in the process of change to encourage a smooth transition.
Collaborations and Partnerships
Forming strategic partnerships and collaborations can expedite entry into new markets and help businesses capitalize on industry trends more effectively. By collaborating with other organizations, a business not only shares the risk and reward of entering a new market but also gains access to new resources and specialized skills.
Strategic partnerships can take various forms, ranging from joint ventures and licensing agreements to co-development and co-marketing arrangements. In such instances, businesses should thoroughly evaluate potential partners for compatibility and reliability, and ensure that the terms of the partnership align with their long-term strategic goals.
Mergers and Acquisitions
In some cases, capturing the value of industry trends may necessitate the acquisition of other companies or mergers with competitors. Mergers and acquisitions can provide numerous benefits, including gaining market share, acquiring new technologies, and improving economies of scale.
However, businesses should carefully evaluate the risks associated with these transactions, including cultural and managerial differences, legal and regulatory concerns, and the possibility of overpaying for assets. A thorough due diligence process can help mitigate such risks and maximize potential benefits.
Case Studies: Success and Failure in Industry Trends
To better understand the importance of capitalizing on trends, it is essential to look at real-world examples. This section highlights successful and unsuccessful adaptations to industry trends.
Successful Trend Adaption: Companies that Flourished
Several companies have managed to capitalize on industry trends and emerged as leaders within their respective markets. For instance, Netflix was initially a DVD rental service but quickly pivoted to streaming content when consumer preferences shifted from physical media to online streaming. This adaptation allowed Netflix to become the dominant player in the global video streaming market.
Similarly, Apple foresaw the trend towards smartphones, and its innovative iPhone disrupted the entire mobile phone industry. Apple’s consistent efforts to introduce new products and services, such as the iPad, Apple Watch, and Apple Music, have helped the company to maintain a leading position in various industries.
In both these cases, the success of these companies can largely be attributed to their ability to understand the shifting trends in their industries and swiftly adapt their business models to accommodate these changes.
Failed Trend Adaption: Lessons Learned
On the other hand, several businesses have suffered due to their inability or reluctance to adapt to evolving industry trends. Kodak, once a pioneer in the photography industry, failed to adapt its product offerings when digital camera technology emerged, leading to its eventual bankruptcy. Similarly, Blockbuster, a once-dominant video rental chain, failed to recognize the trend towards streaming services, ultimately leading to its decline and subsequent liquidation.
These two examples serve as cautionary tales for businesses to recognize and embrace early signs of trend shifts in their industries, and their failure offers valuable lessons in the need for timely adaptation and innovation.
To summarize, capitalizing on industry trends requires businesses to monitor their environments, identify opportunities, evaluate risks and benefits, and adapt strategies when necessary. Companies should be open to change and embrace innovation to remain competitive and position themselves for long-term success. Studying the successes and failures of other businesses can offer valuable lessons for navigating industry trends and staying ahead of the curve.
Industry Trends — FAQ
1. what prominent industry trends have emerged recently due to technological advancements.
Some notable industry trends emerging from technological advancements include artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), cybersecurity, 3D printing, and sustainable energy innovations. Companies utilize these technologies to create more efficient processes, reduce environmental impacts, and maintain a competitive edge.
2. How do industry trends impact the job market and career opportunities?
Industry trends can rapidly change the job market landscape, creating demand for new skill sets and career opportunities. For instance, the growing importance of data analysis, cybersecurity, and sustainable technologies have created high demand for skilled professionals in these areas while decreasing demand for traditional roles in some industries.
3. What are some successful strategies for staying current on industry trends?
To stay current on industry trends, businesses should consider attending conferences, reading industry-specific publications, following experts on social media, and subscribing to relevant newsletters. Additionally, networking with professionals in the industry can provide valuable insights into the latest developments and trends.
4. How can businesses adapt and respond to emerging industry trends?
Businesses can adapt and respond to emerging industry trends by embracing technology, investing in employee training, and adopting a flexible management approach. By partnering with technology innovators, seeking external consultation or collaboration, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can keep up with industry changes.
5. In which industries is the impact of technology trends most pronounced?
The impact of technology trends is particularly pronounced in industries such as manufacturing, finance, healthcare, transportation, and entertainment. These sectors are experiencing significant transformations due to AI, automation, data analysis, and other technology-related advancements.
6. How do industry trends influence customer expectations and demands?
Industry trends shape customer expectations and demands by setting new benchmarks for quality, accessibility, and user experience. For example, innovations in mobile technology and IoT have led consumers to expect faster, more personalized service. Staying current with these trends is essential to maintain customer satisfaction in a competitive market.

Want to make your first $10k/month online?
I've tried everything Amazon FBA, Dropshipping, Affiliate Marketing, Network Marketing, Social Media Marketing. I made the most money consistently with the Remote Sales Business, generating sales for small businesses by reading simple scripts and working closely with awesome mentors. Click below to find out more.
About the author
Mike Vestil
Mike Vestil is the author of the Lazy Man's Guide To Living The Good Life. He also has a YouTube channel with over 700,000 subscribers where he talks about personal development and personal finance.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
First Steps: Writing the Industry Section of Your Business Plan This quick guide offers tips that will help you create the industry section for your business plan.
By Teresa Ciulla Jan 4, 2015
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
In their book Write Your Business Plan , the staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any business plan, what's appropriate for your venture, and what it takes to ensure success. In this edited excerpt, the authors outline what type of details you should include in the industry section of your business plan.
It isn't enough to just work hard. If you're in the wrong industry at the wrong time, making your business grow is going to be difficult. The investment community tends to believe that any business can be buoyed by an industry on the rise and that the opposite is true in an industry whose tide is ebbing. This means it's important for you to include an industry analysis in your business plan.
Readers of your business plan may want to see an industry on a fast-growth track with few established competitors and great potential. Or they may be more interested in a big, if somewhat slower-growing, market with competitors who have lost touch with the market, leaving the door open for rivals.
Whatever the facts are, you'll need to support them with a snapshot analysis of the state of your industry and any trends taking place. This can't be mere off-the-cuff thinking. You need to support your opinions with market research that identifies specific competitors and outlines their weaknesses and strengths and any barriers to entry into the market. You need to describe why your industry is valuable and how it will continue to be important. Finally, and perhaps most important, you'll have to convincingly describe what makes you better and destined to succeed.
When preparing the state of the industry section, instead of looking at your business as a self-contained system, you'll describe the whole industry in which you operate and point to your position in that universe. You then zero in on your country, your state and your local community, deepening on how far your business stretches.
This part of your plan may take a little more legwork than other sections because you'll be drawing together information from a number of outside sources. You may also be reporting on or even conducting your own original research into industry affairs.
To start preparing your industry analysis and outlook, dig up the following facts about your field:
1. What is your total industry-wide sales volume? In dollars? In units?
2. What are the trends in sales volumes within your industry?
3. Who are the major players and your key competitors? What are they like?
4. What does it take to compete? What are the barriers to entry?
5. What technological trends affect your industry?
6. What are the main modes of marketing?
7. How does government regulation affect the industry?
8. In what ways are changing consumer tastes affecting your industry?
9. Identify recent demographic trends affecting the industry.
10. How sensitive is the industry to seasons and economic cycles?
11. What are key financial measures in your industry (average profit margins, sales commissions, etc.)?
If your business addresses a trend before it's been widely recognized, you need to include this information in your business plan. Providing some statistics in the trends section of your plan can make it more convincing.
Barriers to Entry
If you want to become a semiconductor manufacturer, you'll need a billion-dollar factory or two. If you want to have a TV network, you'll need programming and cable carriage in the major markets. These problems are called barriers to entry, and they exist to some extent in all industries. The barriers may be monetary, technological, distribution or market-related, or they may simply be a matter of ownership of prime real estate.
An important part of analyzing your market is determining what the barriers to entry are and how high they stretch. If the barriers are high, as is the case with automobile manufacturing, you can be assured new competitors are likely to be slow in springing up. If the barriers are low, such as opening a nail salon, which doesn't have a huge overhead, you have more opportunity to get into the game.
Be alert for innovative competitors when writing the section of your plan in which you analyze barriers to entry. Clearly some markets are also more saturated than others, and today some are dominated by the McDonald's of their industry. For example, it's hard to open a bookstore today with Amazon changing the way people buy books. In that industry, you need to be creative and explore entry into specialty books, mystery books or another niche within the larger market. Exploring entry points in the marketplace carefully will save you from a disastrous error and will certainly demonstrate to investors that you've thought your plan through and aren't jumping to conclusions.
Identifying Competitors
You're not alone, even if you have a one-person business. You also have your competition to worry about, and your backers will worry about competition, too. Even if you're truly in the rare position of addressing a brand-new market where no competition exists, most experienced people reading your plan will have questions about companies they suspect may be competitors. For these reasons, you should devote a special section of your plan to identifying competitors.
If you had to name two competitors in the athletic shoe market, you'd quickly come up with Nike and Reebok. But these by far aren't the only competitors in the sneaker business. They're just two of the main ones, and depending on the business you're in, the other ones may be more important. If you sell soccer shoes, for instance, Adidas is a bigger player than either of the two American firms. And smaller firms such as Etonic, New Balance and Saucony also have niches where they are comparatively powerful.
You can develop a list of competitors by talking to customers and suppliers, checking with industry groups, and reading trade journals. But it's not enough to simply name your competitors. You need to know their manner of operation, how they compete.
Does a competitor stress a selective, low-volume, high-margin business, or does she emphasize sales growth at any cost, taking every job that comes along, whether or not it fits any coherent scheme or offers an attractive profit? Knowing this kind of information about competitors can help you identify their weaknesses as well as their names.
Freelance Editor
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Exclusive: Kevin O'Leary Is Launching a New Agency With the Founder of Shazam — Here's Why He Says It's a Game Changer
- Lock Younger Generations Want to Retire By 60. Their Strategy Is a Win-Win for Everyone.
- These Are the AI Skills You Should Learn Right Now, According to the World's Youngest Self-Made Billionaire
- Lock I Worked at Google for 14 Years — Here's What I Had to Unlearn When I Started My Own Company
- Lock New Research Reveals How Much Money Most Side Hustles Make in 1 Month — and the Number Might Surprise You
- Celebrities Are Collaborating on Iconic Meals With Popular Fast-Food Chains — Did Your Favorite Make the Cut?
Most Popular Red Arrow
Cash app will pay $15 million to settle a class action lawsuit — here's how to claim up to $2500.
Eligible users have until November 18 to claim a part of the cash.
This Fast Casual Deli Franchise Averages Nearly 2MM in Net Sales!
McAlister's Deli® offers guests more than hearty sandwiches piled high and sides worth sharing. Through genuine Southern hospitality and friendly conversation, McAlister's Deli aims to make every guest feel special.
Disney's Latest Innovation Is a HoloTile Floor That Seems to Have a Mind of Its Own
Disney demoed the floor this weekend.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Silicon Valley Pioneer and Former YouTube CEO Susan Wojcicki Dies at 56 — Here's How She Transformed the Tech Industry
Wojcicki was Google's 16th employee.
This 32-Year-Old Started a Side Hustle With $3,000 — Now It Makes Over $100,000 a Month: 'I Can't Get Enough'
Sean Hall needed a solution for his health struggles — so he came up with his own.
Successfully copied link

Market Sizing & Trends Analysis
Written by Dave Lavinsky

In this article you’ll learn about market sizing and trends and how to identify them for your business.
Why You Need to Know Your Market Sizing & Trends
When you’re developing a simple business plan template to start or grow your company, you need to understand the size of your market and trends affecting it.
The market size confirms the market is big enough to warrant an investment of your time, and potentially investor/lender funding, into pursuing the opportunity. If the market is too small, you nor investors will not be able to get a reasonable return on your investment (which will dissuade angel investors and/or VC funding ).
Likewise trends tell you if the market is increasing or decreasing, and how the market is changing. This can help you improve your strategy. For example, if you were starting a fitness center and you learned that there was a trend towards personal training services, it would be important for your strategy and plan to offer such options.
Market Sizing & Trend Analysis Questions to Answer
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis component of your business plan :
- How big is the business (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key manufacturers and/or suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your company. The relevant market size equals a company’s sales if it were to capture 100% of its specific niche of the market. It is calculated by multiplying the number of prospective customers by the amount they could realistically spend on your product/service each year.
Need Help with Market Research?
With Growthink’s Expert Market Research service, you will get solid market research to give lenders and investors confidence in your market opportunity, your competitive advantage, and your financial projections.
Click here to have our team craft your market research to help ensure your success.
How to Conduct Market Sizing & Trend Analysis
We like to determine market sizes using both a top-down (what percent of the market can we reasonably expect to penetrate) and bottom-up (e.g., how many units can we expect to sell at what price) methodology.
As many assumptions are required when sizing a new or emerging market, we tend to rely heavily on case studies of thousands of other companies and clients who have penetrated new markets. We also access paid industry reports from other companies who have done deep dive research into the relevant industries.
In assessing markets, looks at the current market size and what the market size might be in the short, mid and long-term. Specifically, answer the folowing key questions such as the following:
- How has the relevant market size changed over the past one to five years?
- What is the projected growth of the relevant market?
- What factors will affect this growth? Economic factors? Changing regulatory conditions? Changing consumer needs?
Need Help Understanding Your Market Size & Trends?
Would you like Growthink to provide an assessment of your market size and for you? If so, please contact us below.
What Our Clients Say

A Comprehensive Guide to Conducting an Industry Analysis
Understanding the industry you operate in is crucial for any business. An industry analysis helps you see the bigger picture of your market, recognize the forces at play, and identify opportunities and threats. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to grow an existing one, conducting an industry analysis can provide valuable insights. In this guide, we will walk you through the steps to conduct a comprehensive industry analysis.
What is an Industry Analysis
An industry analysis is a comprehensive process that helps you understand the market in which your business operates. It involves examining a range of factors that can influence your industry, such as market size, growth rate, key competitors, and overall trends. This analysis considers the economic, social, technological, political, and environmental aspects that shape the industry’s landscape. By delving into these elements, you can identify the strengths and weaknesses of your business, as well as the opportunities and threats present in the market.
Additionally, industry analysis can uncover customer needs and preferences, helping you tailor your products or services to better meet market demand. Ultimately, conducting an industry analysis provides you with a clear and detailed picture of the environment in which your business competes, enabling you to make informed strategic decisions, anticipate changes, and stay ahead of your competitors.
Key elements of an industry analysis,
- Market size and growth : Assess the current market size and its growth trajectory.
- Key players : Identify major companies and competitors in the industry.
- Trends and changes : Analyze current trends and anticipate future shifts in the industry.
- Competitive landscape : Evaluate the intensity of competition and strategic approaches used by competitors.
- Opportunities and threats : Identify potential growth opportunities and risks that could affect business operations.
Understanding these elements enables businesses to position themselves strategically, seize opportunities, and navigate challenges within their industry effectively. An industry analysis provides the foundation for making strategic decisions that can lead to growth and success.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

How to Do an Industry Analysis
Follow these steps to gain a thorough understanding of your industry’s dynamics and make informed decisions to drive your business forward effectively.
Step 1: Define your industry
Start by clearly defining the industry or market sector you want to analyze. Specify what products or services are included and whether your focus is local, national, or global.
Step 2: Gather information
Collect data from reliable sources such as industry reports, market research firms, government publications, and trade associations. Look for details on market size, growth trends, key players, and regulatory influences to get a comprehensive view.
Step 3: Identify market trends
Analyze current trends impacting the industry, such as technological advancements, changes in consumer preferences, economic conditions, and shifts in regulations. Understanding these trends helps anticipate future developments.
Step 4: Assess competitive landscape
Study the competitive environment by identifying major companies, their market shares, competitive strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. This analysis helps you understand where your business stands relative to others.
Learn how to do a competitive analysis effectively.
Step 5: Use frameworks for analysis
Apply tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) or Porter’s Five Forces (threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitutes, industry rivalry) to evaluate competitive forces and strategic positioning.
Step 6: Evaluate opportunities and threats
Identify potential growth opportunities, such as emerging markets or gaps in the market, as well as threats like new competitors or changes in regulations. Assessing these factors helps in planning strategic responses.
Learn more about the Porter’s Five Forces Model .
Step 7: Forecast future trends
Anticipate future developments in the industry based on current trends and market dynamics. Consider technological advancements, shifts in consumer behavior, and regulatory changes that could impact your business.
Step 8: Draw conclusions and make recommendations
Summarize your findings and insights from the analysis. Based on these insights, develop strategic recommendations for your business to capitalize on opportunities and address potential risks within the industry.
Industry Analysis Methods
The following industry analysis methods provide businesses with comprehensive insights into their competitive landscape, market dynamics, and strategic opportunities, enabling informed decision-making and effective planning for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
1. Porter’s five forces
Developed by Michael Porter, this framework analyzes competitive forces within an industry that shape its attractiveness and profitability. Porter’s Five Forces helps businesses understand the competitive landscape, assess industry profitability, develop competitive strategies, and anticipate changes in competitive dynamics.
How to use it :
- Threat of new entrants : Evaluate barriers to entry such as high capital requirements, economies of scale, and regulatory barriers that deter new competitors.
- Bargaining power of suppliers : Assess how much influence suppliers have over input prices, quality, and availability.
- Bargaining power of buyers : Analyze the power buyers have to negotiate prices, demand better quality, or switch to alternatives.
- Threat of substitutes : Identify alternative products or services that could potentially replace yours and impact demand.
- Industry rivalry : Evaluate competitive intensity among existing firms based on factors like price competition, differentiation strategies, and market concentration.
2. PESTLE analysis
PESTLE stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. It’s a framework that evaluates external macro-environmental factors affecting businesses. PESTLE analysis helps businesses identify external factors impacting their industry, anticipate future trends, assess risks and opportunities, and align strategies with prevailing market conditions.
Learn how to conduct an effective macro environmental analysis .
- Political factors : Analyze government stability, policies, regulations, and political influences impacting business operations.
- Economic factors : Assess economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and consumer spending affecting market demand.
- Social factors : Evaluate demographic trends, cultural shifts, lifestyle changes, and consumer behaviors influencing product demand and market trends.
- Technological factors : Study technological advancements, innovations, research and development trends, and digital transformation impacting industry operations.
- Legal factors : Consider laws, regulations, compliance requirements, and litigation trends affecting industry practices and business operations.
- Environmental factors : Analyze environmental regulations, sustainability practices, climate change impacts, and consumer attitudes towards eco-friendly products.
3. SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It’s a strategic planning tool that helps businesses identify internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats in the market. Use SWOT analysis to align strengths with opportunities to pursue, address weaknesses that could threaten success, capitalize on identified opportunities, and prepare contingency plans for potential threats.
- Strengths : Identify and leverage your company’s strengths such as unique capabilities, strong brand reputation, or talented workforce.
- Weaknesses : Assess areas needing improvement like high costs, limited market presence, or outdated technology.
- Opportunities : Explore external factors that could benefit your business such as new market trends, emerging technologies, or favorable regulatory changes.
- Threats : Evaluate external challenges like new competitors, economic downturns, changing consumer preferences, or regulatory hurdles.
4. Competitive benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking compares a company’s performance metrics, strategies, and practices against industry competitors to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. Competitive benchmarking helps businesses understand their competitive position, identify best practices, uncover areas for improvement, and develop strategies to enhance competitiveness and market share.
- Performance metrics : Compare key indicators such as market share, profitability, sales growth, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
- Strategic analysis : Assess competitors' strategies, product offerings, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and marketing tactics.
- Customer insights : Gain insights into competitors' customer segments, buying behaviors, brand perceptions, and loyalty programs.
- Operational efficiency : Evaluate competitors' supply chain management, production processes, cost structures, and technological investments.
5. Trend analysis
Trend analysis examines historical and current market trends, consumer behaviors, technological advancements, and regulatory changes to forecast future developments. Trend analysis helps businesses anticipate market changes, innovate proactively, identify growth opportunities, mitigate risks, and align strategic initiatives with future market trends.
- Historical trends : Study past industry performance, market cycles, and economic trends to identify patterns and drivers of growth or decline.
- Current trends : Analyze current market dynamics, consumer preferences, innovation trends, and regulatory shifts impacting the industry.
- Forecasting : Use trend analysis to predict future market conditions, emerging opportunities, potential threats, and industry disruptions.
- Risk assessment : Identify risks associated with emerging trends, technological disruptions, or changing consumer preferences that could impact business operations.
6. Broad factor analysis
Broad factor analysis considers overarching economic, social, technological, environmental, political, and legal factors influencing the industry at a macro level. Broad factor analysis provides businesses with a holistic view of external influences shaping the industry, helping them understand market dynamics, anticipate changes, and develop strategies to navigate external challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
- Economic factors : Evaluate economic indicators such as GDP growth, interest rates, inflation, and employment trends impacting industry demand and investment.
- Social factors : Analyze demographic shifts, cultural trends, lifestyle changes, and societal values influencing consumer behavior and market preferences.
- Technological factors : Assess technological advancements, research and development trends, digital transformation, and adoption of new technologies driving industry evolution.
- Environmental factors : Consider environmental regulations, sustainability initiatives, climate change impacts, and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
- Political factors : Evaluate geopolitical stability, government policies, trade agreements, and regulatory frameworks impacting industry operations and market dynamics.
- Legal factors : Analyze industry-specific regulations, compliance requirements, intellectual property laws, and legal challenges affecting business practices.
7. BCG matrix (Boston Consulting Group)
The BCG Matrix categorizes products or business units based on their market growth rate and relative market share to guide investment decisions. The BCG matrix helps businesses allocate resources effectively across their portfolio, prioritize investments, and manage product or business unit lifecycle strategies.
- Stars : High-growth products or units with a high market share, requiring heavy investment to sustain growth.
- Cash cows : Low-growth products or units with a high market share, generating stable cash flow that can be reinvested in other areas.
- Question marks : High-growth products or units with a low market share, requiring strategic decisions to either invest for growth or divest.
- Dogs : Low-growth products or units with a low market share, typically requiring divestment or restructuring efforts.
8. Perceptual mapping
Perceptual mapping visually represents consumer perceptions of brands or products based on key attributes or dimensions. Perceptual mapping helps businesses understand competitive positioning, identify market segments, and develop targeted marketing strategies to enhance brand perception and market share.
Learn how to use perceptual maps to understand consumer perception .
- Identify Attributes : Determine relevant product attributes or characteristics important to consumers (e.g., price, quality, convenience).
- Collect Data : Gather consumer feedback or survey data to assess how brands or products are perceived relative to these attributes.
- Plot Data Points : Map brands or products on a graph based on consumer perceptions, positioning them relative to competitors.
- Analyze Positioning : Interpret the map to identify competitive positioning, market gaps, or opportunities for differentiation.
9. Strategic group analysis
Strategic group analysis identifies groups of firms within an industry that pursue similar strategies or compete on similar dimensions. Strategic group analysis helps businesses understand competitive rivalry, identify strategic groups, and develop differentiated strategies to gain competitive advantage and improve market position.
- Define strategic dimensions : Identify key strategic dimensions such as pricing strategy, product quality, distribution channels, or target market segments.
- Group firms : Cluster firms based on similarities in their strategic choices and market positioning.
- Compare performance : Assess the performance of firms within each strategic group, identifying leaders, followers, and niche players.
- Strategic insights : Gain insights into competitive dynamics, competitive advantages, and strategic options for positioning within the industry.
Explore more industry analysis templates .
Why is an Industry Analysis Important
An industry analysis is crucial for businesses because it helps them understand the environment they operate in and make smart decisions. Here’s why it matters:
- Understand your competition : it lets you see who else is in the market, what they’re doing, and how you can stand out.
- Spot opportunities and risks : by studying trends and changes, you can find new chances to grow and avoid potential problems.
- Plan better strategies : with a clear view of the industry’s landscape, you can plan how to compete effectively and grow your business.
- Stay updated : it keeps you informed about what’s happening in your industry, so you can adapt to changes and stay competitive.
- Make informed decisions : armed with insights, you can make decisions based on facts rather than guesses, which increases your chances of success.
In conclusion, industry analysis is vital for businesses to deeply understand their market. Using tools like SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, PESTLE analysis, competitive benchmarking, trend analysis, and broad factor analysis helps businesses make smarter decisions.
These methods identify what a company does well (strengths) and areas needing improvement (weaknesses). They also highlight market opportunities and potential threats. By analyzing these factors, businesses can plan strategies that maximize strengths and opportunities while preparing for challenges.
Industry analysis isn’t just about today—it’s about predicting tomorrow. By staying ahead of trends and understanding their industry’s dynamics, businesses can stay competitive and grow wisely. This knowledge empowers businesses to adapt, innovate, and succeed in a constantly changing business world.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
More From Forbes
The 10 Biggest Business Trends For 2024 Everyone Must Be Ready For Now
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
It is time once again to look into the crystal ball and predict the direction that business and industry will take in the coming year.
With the general global economic downturn predicted to get worse before it gets better, companies are likely to remain cautious when it comes to spending and investing in radical new ideas in 2024. However, there are a number of technological and societal trends that are simply too big to ignore or put off until better days. These are the areas where we can expect to see continued innovation and investment, and I'll highlight the most prominent in this article.
As has been the case for the past few years, there's some overlap between these and my other predictions, which focus primarily on technology. Simply put, this is because business trends today are largely driven by technology. However, as we develop a better understanding of a technology - artificial intelligence (AI) being the obvious example - we also understand what it isn't. In 2024, this will lead to new perspectives on what makes us human - a theme I believe is reflected in this year's predictions.
Generative AI Everywhere
The Boston Consulting Group asserts that “to be an industry leader in five years, you need a clear and compelling generative AI strategy today.” AI and machine learning have been making waves for more than a decade, and are thoroughly integrated into many of the products and services we buy from major companies. Now, generative AI puts the power to create and intelligently automate the customer experience - as well as internal operations - in the hands of nearly every organization.
Soft Skills And The Human Touch
As it becomes increasingly feasible to automate technical aspects of work - coding, research, or data management, for example - the ability to leverage soft skills for tasks that still require a human touch becomes critical. For this reason, in 2024, we will see organizations increasing their investment in developing and nurturing skills and attributes such as emotional intelligence, communication, interpersonal problem solving, high-level strategy, and thought leadership.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
The Skills Solution
We’ve been hearing about the skills shortage for several years now. Changes in hiring practices that emphasize selecting candidates with the specific experiences and skills needed for a role, rather than qualities such as educational attainment or age, are a part of the industry's response and will continue to be a strong trend. We will also continue to see increased investment in training and upskilling, particularly around disruptive technologies such as generative AI and skills that will be in demand in an AI-driven economy.
Sustainable Business
One driver is clearly customer demand, as research continues to show that consumers increasingly prefer companies with a solid commitment to reducing their environmental footprint. On the other hand, as the green economy grows, we're learning that green solutions often lead to bottom-line growth. For example, Walmart WMT dramatically reduced its spending on fuel and vehicle maintenance by transitioning to an EV delivery fleet. We'll also get better at spotting greenwashing, where companies pay lip service to environmentalism in an attempt to divert attention from environmentally unfriendly practices.
Personalization-at-Scale
One driver is clearly customer demand, as research continues to show that consumers increasingly prefer companies with a solid commitment to reducing their environmental footprint. On the other hand, as the green economy grows, we're learning that green solutions often lead to bottom-line growth. For example, L’Oréal has developed personalized cosmetics to match customers' skin types, and Nike NKE and other manufacturers offer custom shoes in thousands of combinations of styles and colors. This will lead to companies of all sizes offering customized solutions to build stronger relationships with customers.
The Data Economy
Data is an increasingly valuable business asset. By 2024, more companies will have streamlined their operations and improved their customer offerings by taking a strategic approach to their data. As a result, they will be ready to take the next step - monetizing data itself to drive new business opportunities. Leading the way are companies like John Deere, which has pioneered the model of selling data from its sensor-laden farm equipment back to farmers as insights to improve productivity. As access to large-scale data collection and AI-driven analytics becomes increasingly democratized, we'll see this trend adopted by smaller companies in niche and diversified sectors.
The Customer Experience Revolution
Imagine a line on a graph that rates your customers' sentiment at every touchpoint where they interact with your company, goods, or services. This illustrates the concept of customer experience. While traditionally a company might build a business model around superior quality or value, in 2024 the impetus is to ensure that every single interaction and experience makes the customer smile. This means personalized marketing that delivers what they need at the right time, on-time delivery, frictionless setup and installation, and efficient problem resolution. It's becoming increasingly common for companies and brands to appoint a Chief Experience Officer to ensure these principles are fully integrated into all business strategies.
Remote and distributed work
It's no longer about companies surviving the pandemic, it's about offering flexible arrangements, valuing employees' time and harnessing the potential of a global workforce. Yes, workers returning to the office has been a theme of the past 12 months. But employers are also ensuring that they retain the ability to work with geographically dispersed teams and attract talent from anywhere in the world. For these reasons, we'll see the number of job postings with "remote" or "hybrid" locations remain well above pre-Covid levels throughout 2024.
Diversity and Inclusivity
Talent comes in all ages, shapes, sizes and colors. Unconscious racist, sexist or ageist bias can easily seep into systems around hiring, training, performance management or development, resulting in talent being marginalized, mismanaged or overlooked. There has always been a business case for ensuring diverse and inclusive workforces, but in the age of AI, as we increasingly rely on machines to make decisions that impact humans, it's more important than ever.
Resilience.
Ensuring an organization is protected from whatever threat is around the corner. That could mean cyber attacks, economic downturns, environmental events, war, global pandemics, or the emergence of a disruptive new competitor. It's about taking what we've learned from companies that have survived and even thrived in turbulent times and using it to plan and prepare for what might happen tomorrow. Despite my crystal ball, the future is never certain, and building resilience to any threats that might emerge will be a key business trend in 2024.
You can read more about these topics in my book , The Future Internet: How the Metaverse, Web 3.0, and Blockchain Will Transform Business and Society and ‘ Business Trends in Practice , which won the 2022 Business Book of the Year award. And don’t forget to subscribe to my newsletter and follow me on X (Twitter ), LinkedIn , and YouTube for more on the future trends in business and technology.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Business Plan Example: The Industry Overview
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Wondering how to approach the industry overview section of your business plan? Having an example might help. Let's look at the industry overview for Pet Grandma, a fictional pet-based business invented for this business plan sample.
The Pet Industry
According to the American Pet Products Association, pet expenditures in the U.S. totaled slightly over $72.5 billion in 2018, up from $48 billion in 2010, an increase of 51% in eight years. This includes:
- Food: $30.32 billion
- Supplies/OTC Medicine: $16.01 billion
- Vet Care: $18.11 billion
- Live animal purchases: $2.01 billion
- Pet Services: grooming & boarding: $6.11 billion
These figures reflect the increasing humanization of pets, a trend that is showing no signs of waning. More and more people consider their pets to be people too and treat them accordingly. Karen McCullough, then director of marketing (2000-2010) for Winnipeg-based Petland Canada, which operates both company-owned and franchise stores across the country, says, "People are looking for more these days—absolutely. We see a lot now in higher-end products, people are demanding more for their pets, from treats to grooming supplies to brand-name toys and even clothing."
And, because people want the best for their pets, there is also an increasing demand for pet-care services. Across North America, the pet care business has seen an explosion of growth over the last ten years.
Our Position in the Industry
West Vancouver is an affluent area with a high pet density, an ideal market for a pet-sitting business such as Pet Grandma. People in this area not only have pets but can afford to spend money on them and are willing to do so.
Our market research has shown that nine out of 10 pet owners polled in West Vancouver would prefer to have their pets cared for in their own homes when they travel rather than be kenneled, and six out of 10 would consider having a pet sitter provide company for their dog when they were at work.
The Competition
While there are currently eight businesses offering pet sitting in West Vancouver, only three of these offer on-site pet care and none offers pet visit services for working pet owners.
Currently, there is no single company dominating the market. This may be because all of the pet-sitting businesses are relatively new; the oldest, Paula's Pet Sitting, has only been in business five years. However, half of the existing pet-sitting businesses control the majority of the market—Paula's Pet Sitting, Doggie Care Services Inc., Pet Petters, and Pet Sitters on Demand together make up 65% of the market.
Save your full competitive analysis for section four of your business plan , but briefly share competitor insights here as it relates to your industry and your unique position in it.
What Makes Pet Grandma Unique
Pet Grandma's marketing strategy is to emphasize the quality of pet care we provide. As our slogan, "A Grandma for your pet!" says, we treat people's pets as family members and strive to give them the same loving, personal care that their owners would give. In our marketing , we will be emphasizing the quality and personalized service we provide.
We will also offer some services that are currently unique, such as our pet visit services, where one of our trained staff will go to a person's home while they're at work and feed, exercise, and play with their pet, allowing dog owners who work to come home to happy, friendly companions rather than demanding, whiny animals.
Your Business Plan
That's a basic example of an industry overview for your business plan. It provides an look at your business's industry and highlights your place within it. Your plan should present well-researched information to display that you understand the industry well.
Once you have yours written, you can move on to the next section of the business plan, the market analysis .
American Pet Products Association. " Pet Industry Market Size & Ownership Statistics ." Accessed Jan. 8, 2020.
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
Medicare Advantage in 2024: Enrollment Update and Key Trends
Meredith Freed , Jeannie Fuglesten Biniek , Anthony Damico, and Tricia Neuman Published: Aug 08, 2024
Medicare Advantage enrollment has been on a steady climb for the past two decades following changes in policy designed to encourage a robust role for private plan options in Medicare. After a period of some instability in terms of plan participation and enrollment, The Medicare Modernization Act of 2003 created stronger financial incentives for plans to participate in the program throughout the country and renamed private Medicare plans Medicare Advantage. In 2024, 32.8 million people are enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan, accounting for more than half, or 54 percent, of the eligible Medicare population, and $462 billion (or 54%) of total federal Medicare spending (net of offsetting receipts, such as premiums). Medicare Advantage enrolls a disproportionate share of people of color in Medicare as well as an increasing number of dual eligible beneficiaries. The average Medicare beneficiary in 2024 has access to 43 Medicare Advantage plans , the same as in 2023, but more than double the number of plans offered in 2018.
The growth in Medicare Advantage enrollment is due to a number of factors, including the availability of plans that charge no premium (other than the Part B premium), and extra benefits offered by most Medicare Advantage plans. Nearly all Medicare Advantage plans offer some benefits not included in traditional Medicare, such as coverage of dental, vision, or hearing services, often for no additional premium. Medicare beneficiaries are also drawn to the financial protection that comes with an out-of-pocket limit, which Medicare Advantage plans are required to provide, while traditional Medicare has no out-of-pocket cap on spending. On the other hand, Medicare Advantage plans have limited provider networks and apply cost management tools such as prior authorization , which traditional Medicare does not.
Generally, research shows that Medicare pays more to private Medicare Advantage plans for enrollees than their costs would be in traditional Medicare. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) reports that plans receive payments from CMS that are 122% of spending for similar beneficiaries in traditional Medicare, on average, translating to an estimated $83 billion in higher spending in 2024 . As Medicare Advantage takes on a more dominant presence in the Medicare program, and with current payments to plans higher for Medicare Advantage than for traditional Medicare for similar beneficiaries, policymakers have become increasingly focused on how well Medicare’s current payment methodology for Medicare Advantage is working to enhance efficiency and hold down beneficiary costs and Medicare spending.
To better understand trends in the growth of the program, this brief provides current information about Medicare Advantage enrollment, by plan type and firm, and shows how enrollment varies by state and county. A second, companion analysis describes Medicare Advantage premiums, out-of-pocket limits, supplemental benefits offered, and prior authorization requirements in 2024. This analysis does not provide detailed information by enrollee characteristics, such as race/ethnicity, income, or dual status, because that information is not available.
Highlights for 2024:
- More than half (54%) of eligible Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage in 2024. The share of Medicare beneficiaries in Medicare Advantage plans varies across states, ranging from 2% to 63%. In 7 states, AL, CT, MI, HI, ME, FL, RI (and Puerto Rico), 60% or more of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans, an increase from 3 states in 2023.
- More than one-third (37%) of Medicare beneficiaries live in a county where at least 60 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans. Three counties (excluding those in Puerto Rico) enroll 80% or more of Medicare beneficiaries in Medicare Advantage plans: Monroe County, NY (Rochester; 82%), Starr, Texas (81%), and Miami-Dade County, Florida (80%). At the same time, 8 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries nationwide live in a county with relatively low enrollment, where less than one third of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans. The wide variation in county enrollment rates reflect several factors, such as differences in firm strategy, urbanicity of the county, Medicare payment rates, number of Medicare beneficiaries, health care use patterns, and historical Medicare Advantage market penetration.
- Medicare Advantage enrollment is highly concentrated among a small number of firms, with UnitedHealthcare and Humana accounting for nearly half (47%) of all Medicare Advantage enrollees nationwide . In more than a quarter of all U.S. counties (29%; or 931 counties), these two firms account for at least 75 percent of Medicare Advantage enrollment. Since 2017, the market share for UnitedHealthcare and CVS Health has increased (25% to 29% and 8% to 12%, respectively), Humana (18%) and Cigna (2%) have held steady, while other firms’ share of total enrollment has slightly decreased (Blue Cross Blue Shield (BCBS) affiliates, Kaiser Permanente, and Centene). Small firms (which each account for less than 2% of enrollment) have a smaller share of the market in 2024 than in 2017 (19% to 16%).
More than half of eligible Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage in 2024
In 2024, more than half (54%) of eligible Medicare beneficiaries – 32.8 million people out of 61.2 million Medicare beneficiaries with both Medicare Parts A and B – are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans. Medicare Advantage enrollment as a share of the eligible Medicare population has jumped from 19% in 2007 to 54% in 2024 (Figure 1).
Between 2023 and 2024, total Medicare Advantage enrollment grew by about 2.1 million beneficiaries, or 7 percent – a similar growth rate as the prior year (8%). The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects that the share of all Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans will rise to 64% by 2034 (Figure 2).
In 2024, nearly two-thirds of Medicare Advantage enrollees are in individual plans that are open for general enrollment.
More than 6 in 10 Medicare Advantage enrollees (62%), or 20.5 million people, are in plans generally available to all beneficiaries for individual enrollment (Figure 3). That is an increase of 0.9 million enrollees compared to 2023. Individual plans have declined as a share of total Medicare Advantage enrollment since 2010 (71%).
More than 6.6 million Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in special needs plans in 2024, more than double the enrollment in 2019.
More than 6.6 million Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in special needs plans (SNPs). SNPs restrict enrollment to specific types of beneficiaries with significant or relatively specialized care needs, or who qualify because they are eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid. Enrollment in SNPs increased by 16 percent between 2023 and 2024, and accounts for 20 percent of total Medicare Advantage enrollment in 2024, an increase from 12 percent in 2010. Since 2019, SNP enrollment has more than doubled from 2.92 million to 6.64 million (Figure 4). This increase is due in part to the increasing number of SNP plans available on average and more dual eligible individuals having access to these plans .
Most SNP enrollees (88%) are in plans for beneficiaries dually enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid (D-SNPs). Another 10 percent of SNP enrollees are in plans for people with severe chronic or disabling conditions (C-SNPs) and 2 percent are in plans for beneficiaries requiring a nursing home or institutional level of care (I-SNPs).
While D-SNPs are designed specifically for dually-eligible individuals , 1.2 million Medicare beneficiaries with full Medicaid benefits were enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans generally available to all beneficiaries (not designed specifically for this population) in 2021, while 2.3 million full dual eligible individuals were in D-SNPs. D-SNPs have increasingly become the main source of Medicare Advantage coverage for dual eligible individuals.
SNP enrollment varies across states. In the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico, SNP enrollees comprise about half of all Medicare Advantage enrollees (49% in DC and 51% in PR). In nine states, SNP enrollment accounts for at least a quarter of Medicare Advantage enrollment: 46% in MS, 34% in AR, 33% in LA and NY, 28% in FL and GA, and 25% in CT, SC and AL.
C-SNP enrollment in 2024 (about 675,000 people) is 45% higher than it was in 2023 – an increase of about 210,000 enrollees. Nearly all (97%) C-SNP enrollees are in plans for people with diabetes or cardiovascular conditions in 2024. Enrollment in I-SNPs has been increasing slightly, with approximately 115,000 enrollees in 2024, up from about 103,000 in 2023.
Slightly less than one in five (17% or about 5.7 million) Medicare Advantage enrollees are in a group plan offered to retirees by an employer or union.
Group enrollment as a share of total Medicare Advantage enrollment has fluctuated between 17% to 20% since 2010, but the actual number has increased from 1.8 million in 2010 to 5.7 million in 2024 (Figure 5). With a group plan, an employer or union contracts with an insurer and Medicare pays the insurer a fixed amount per enrollee to provide benefits covered by Medicare. For example, 13 states provide health insurance benefits to their Medicare-eligible retirees exclusively through Medicare Advantage plans.
As with other Medicare Advantage plans, employer and union group plans may provide additional benefits and/or lower cost sharing than traditional Medicare and are eligible for bonus payments if they obtain required quality scores. The employer or union (and sometimes the retiree) may also pay an additional premium for these supplemental benefits. Group enrollees comprise a quarter or more of Medicare Advantage enrollees in nine states: Alaska (100%), Michigan (38%), New Jersey (33%), West Virginia (31%), Maryland (30%), Illinois (29%), Vermont (27%), Kentucky (26%), and Connecticut (25%).
The share of Medicare beneficiaries in Medicare Advantage plans varies by state and county
The share of Medicare beneficiaries in Medicare Advantage plans varies across states, ranging from 2% to 63%.
In 30 states, Medicare Advantage enrollees account for more than half of all Medicare beneficiaries, including in 7 states, AL, CT, MI, HI, ME, FL, RI (and Puerto Rico) where 60% or more of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans (Figure 6). In contrast, Medicare Advantage enrollment is relatively low (less than 40%) in 13 states, including five states with less than 30% of beneficiaries enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan – AK, MD, ND, SD, and WY – all of which (beside MD) are mostly rural. Overall, Puerto Rico has the highest Medicare Advantage penetration, with 95 percent of Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan. A decade ago, the share of Medicare beneficiaries in Medicare Advantage plans did not exceed 50 percent in any state (other than Puerto Rico).
The share of Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage varies widely across counties.
For example, in Florida, 60% of all Medicare beneficiaries in the state are enrolled in Medicare Advantage, ranging from 21% in Monroe County (Key West) to 80% in Miami-Dade County (Figure 7). In Ohio, 57% of all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage, with the share ranging from 32% in Mercer County (Celina) to 69% in Stark County (Canton).
In 2024, more than a third (37%) of Medicare beneficiaries live in a county where at least 60 percent of all Medicare beneficiaries in that county are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans (618 counties). That is substantially more than in 2010 when just 3 percent of the Medicare population lived in a county where 60 percent or more of Medicare beneficiaries were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan (83 counties). Many counties with high Medicare Advantage penetration are centered around relatively large, urban areas, such as Monroe County, NY (82%), which includes Rochester, and Allegheny County, PA (74%), which includes Pittsburgh. In contrast, 8 percent of Medicare beneficiaries live in a county where less than one third of all Medicare beneficiaries in that county are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans (849 counties). Counties with relatively low enrollment tend to be less populated rural areas. However, others, such Montgomery County, MD (27%) and Suffolk, NY (31%), which includes much of Long Island, are in more populous areas. (This county-level analysis excludes Medicare Advantage enrollment in Connecticut. See methods for more details.)
Variation in the share of eligible Medicare beneficiaries who are enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan is explained by a combination of factors, including firm-level strategies to target particular geographic areas, the urbanicity of the county and state, variation in Medicare payment rates, the number and characteristics of people eligible for Medicare, health care use patterns, and the historical Medicare Advantage market penetration.
Medicare Advantage enrollment is highly concentrated among a small number of firms
The average Medicare beneficiary is able to choose from Medicare Advantage plans offered by 8 firms in 2024 , one fewer than in 2023 and 2022, and one-third of beneficiaries (33%) can choose among Medicare Advantage plans offered by 10 or more firms.
UnitedHealthcare and Humana account for nearly half of all Medicare Advantage enrollees nationwide in 2024.
Despite most beneficiaries having access to plans operated by several different firms, Medicare Advantage enrollment is highly concentrated among a small number of firms. UnitedHealthcare, alone, accounts for 29% of all Medicare Advantage enrollment in 2024, or 9.4 million enrollees. Together, UnitedHealthcare and Humana (18%) account for nearly half (47%) of all Medicare Advantage enrollees nationwide, the same as in 2023. In more than a quarter of counties (29%; or 931 counties), these two firms account for at least 75% of Medicare Advantage enrollment. These counties include East Baton Rouge (Baton Rouge), LA (81%), Clark County (Las Vegas), NV (79%), Travis County (Austin), FL (78%), and El Paso County (Colorado Springs), CO (76%). (Again, this county-level analysis does not include Connecticut.)
BCBS affiliates (including Anthem BCBS plans) account for 14% of enrollment, and four firms (CVS Health, Kaiser Permanente, Centene, and Cigna) account for another 23% of enrollment in 2024.
UnitedHealthcare and Humana have consistently accounted for a relatively large share of Medicare Advantage enrollment.
UnitedHealthcare has had the largest share of Medicare Advantage enrollment and largest growth in enrollment since 2010, increasing from 20 percent of all Medicare Advantage enrollment in 2010 to 29 percent in 2024. Humana has also had a high share of Medicare Advantage enrollment, though its share of enrollment has grown more slowly, from 16 percent in 2010 to 18 percent in 2024. BCBS plans share of enrollment has been more constant over time but has declined moderately since 2014.
CVS Health, which purchased Aetna in 2018, has seen its share of enrollment double from 6 percent in 2010 to 12 percent in 2024. Kaiser Permanente now accounts for 6 percent of total enrollment, a moderate decline as a share of total Medicare Advantage enrollment since 2010 (9%), mainly due to the growth of enrollment in plans offered by other insurers and only a modest increase in enrollment growth for Kaiser Permanente over that time. However, for those insurers that have seen declines in their overall share of enrollment, the actual number of enrollees for each insurer is larger than it was in 2010.
By absolute numbers, CVS Health had the largest growth in plan year enrollment, increasing by 758,000 beneficiaries between March 2023 and March 2024. Humana had the second largest growth in plan year enrollment, with an increase of about 472,000 beneficiaries between March 2023 and March 2024. UnitedHealthcare plans had the third highest growth in plan year enrollment, increasing by 456,000 beneficiaries – the first time in 8 years it did not have the largest plan growth among all firms. BCBS plans had the fourth largest growth in plan enrollment with an increase of about 283,000, followed by Kaiser Permanente, increasing by about 45,000 beneficiaries between March 2023 and March 2024. However, Centene had fewer enrollees, with enrollment declining by about 202,000 between March 2023 and March 2024.
Meredith Freed, Jeannie Fuglesten Biniek, and Tricia Neuman are with KFF. Anthony Damico is an independent consultant.
| This analysis uses data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Medicare Advantage Enrollment, Benefit and Landscape files for the respective year. KFF uses the Medicare Enrollment Dashboard for enrollment data for March 2023 and 2024, and the CMS Chronic Conditions Data Warehouse Master Beneficiary Summary File (MBSF) for March for earlier years. Trend analysis begins in 2007 because that was the earliest year of data that was based on March enrollment. Enrollment data is only provided for plan-county combinations that have at least 11 beneficiaries; thus, this analysis excludes approximately 400,000 individuals who reside in a county where county-wide plan enrollment does not meet this threshold. Connecticut is excluded from the analysis of Medicare Advantage penetration at the county level due to a change in FIPS codes that are in the Medicare Enrollment Dashboard data but are not yet reflected in the Medicare Advantage enrollment data. KFF calculates the share of Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage, meaning they must have both Part A and B coverage. The share of enrollees in Medicare Advantage would be somewhat smaller if based on the total Medicare population that includes 5.9 million beneficiaries with Part A only or Part B only (in 2024) who are not generally eligible to enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan. In previous years, KFF calculated the share of Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage by including Medicare beneficiaries with either Part A and/or B coverage. We modified our approach in 2022 to estimate the share enrolled among beneficiaries eligible for Medicare Advantage who have both Medicare Part A and Medicare B. In the past, the number of beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage was smaller and therefore the difference between the share enrolled with Part A and/or B vs Part A and B was also smaller. For example, in 2010, 24% of all Medicare enrollees were enrolled in Medicare Advantage versus 25% with just Parts A and B. However, these shares have diverged over time: in 2024, 49% of all Medicare beneficiaries were enrolled in Medicare Advantage versus 54% with just Parts A and B. These changes are reflected in all data displayed trending back to 2007. Additionally, in previous years, KFF had used the term Medicare Advantage to refer to Medicare Advantage plans as well as other types of private plans, including cost plans, PACE plans, and HCPPs. However, cost plans, PACE plans, and HCPPs are now excluded from this analysis in addition to MMPs. In this analysis, KFF excludes these other plans as some may have different enrollment requirements than Medicare Advantage plans (e.g., may be available to beneficiaries with only Part B coverage) and in some cases, may be paid differently than Medicare Advantage plans. These exclusions are reflected in all data displayed trending back to 2007. Medicare projections for 2025-2033 are from the June Congressional Budget Office (CBO) Medicare Baseline for 2024. Using the CBO baseline, Medicare enrollment is based on individuals who are enrolled in Part B, which is designed to include only individuals who are eligible for Medicare Advantage and exclude those who only have Part A only (~5 million people in 2025) and cannot enroll in Medicare Advantage. However, it may include some individuals who have Part B only and also are not eligible for Medicare Advantage. Enrollment counts in publications by firms operating in the Medicare Advantage market, such as company financial statements, might differ from KFF estimates due to inclusion or exclusion of certain plan types, such as SNPs or employer group health plans. |
- Medicare Advantage
Also of Interest
- Medicare Advantage in 2024: Premiums, Out-of-Pocket Limits, Supplemental Benefits, and Prior Authorization
- Medicare Advantage 2024 Spotlight: First Look
- Use of Prior Authorization in Medicare Advantage Exceeded 46 Million Requests in 2022
- Asia Briefing
- China Briefing
- ASEAN Briefing
- India Briefing
- Vietnam Briefing
- Silk Road Briefing
- Russia Briefing
- Middle East Briefing
China’s Economic and Sports Industry Gains from Paris 2024 Olympics
The Paris 2024 Olympics offer China a prime opportunity to enhance its global image, boost trade, and expand its market presence through sports-related exports and e-commerce. Additionally, the Games fuel China’s sports industry growth, supported by government policies and increasing public interest in fitness and sports.
The Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games are one of the premier global events, showcasing athletic excellence and cultural exchange on an international stage. Now underway amidst widespread anticipation, the Games represent not only a celebration of sport but also a pivotal moment for participating nations to enhance their global presence. Renowned for transcending borders and uniting nations under the banner of sportsmanship and competition, the Olympics also serve as a beacon of diplomacy, cultural exchange, and economic opportunity. As such, the Paris 2024 Olympics offer countries a unique platform to showcase their strengths and capabilities to a global audience.
For China, a key player in the global economy, the Olympics present a strategic opportunity to bolster its international image and influence. Participation in this prestigious event allows China to highlight its advancements in technology, infrastructure, and cultural diplomacy. Additionally, the Games serve as a catalyst for expanding trade relations and fostering business partnerships on a global scale.
The Paris 2024 Olympics provide numerous opportunities for Chinese businesses to engage in international trade and commerce. From sponsorship deals and product placements to export opportunities and investment ventures, Chinese enterprises can leverage the global attention surrounding the Games to strengthen their market presence abroad. Sectors such as technology, consumer goods, and sports equipment are particularly poised to benefit from increased visibility and consumer interest generated by the Olympics.
In this article, we explore how the Paris 2024 Olympics influence China’s economic prospects. By examining the strategic implications of the Games on China’s global brand enhancement, trade relations, and economic opportunities, we aim to provide insights into the broader impact of international sporting events on global economies.
Leveraging major sports events for global branding
In the world of marketing, major sports events provide unparalleled reach and engagement, with the Olympics standing as the pinnacle. This global stage allows brands to connect with audiences in meaningful ways.
Coca-Cola, a long-time Olympic sponsor, has used the Games to emphasize unity and togetherness since 1928, while Nike has aligned itself with sports excellence through athlete endorsements and themed apparel. The FIFA World Cup similarly offers branding opportunities, with Adidas showcasing sportswear and Budweiser crafting engaging campaigns. At the Super Bowl, Pepsi and Anheuser-Busch invest heavily in creative ads, with Pepsi’s halftime show becoming a notable cultural event that amplifies the brand’s reach.
The recent UEFA Euro 2024 championship highlighted the growing role of sports events in branding, especially showcasing the increasing influence of Chinese companies. Five of the 13 official global sponsors were Chinese: Hisense, AliExpress, Ant Group (owner of Alipay), Vivo, and BYD. This significant presence underscores Chinese brands’ strategic push for international visibility.
Hisense, continuing its Euros sponsorship from previous years, showcased its products through pitchside ads and provided screens for video assistant referees (VAR). AliExpress partnered with English footballer David Beckham for its ‘Score More with AliExpress’ campaign and engaged fans with app-based prize giveaways. Vivo and BYD also used their sponsorships to strengthen their global presence.
These efforts reflect a broader trend where Chinese companies use sports sponsorships to enhance their international footprint. According to data collected by the China-Britain Business Council, for example, Hisense experienced an 83 percent increase in overseas revenue following its previous Euro sponsorships. Similarly, Alibaba boosted its weekly active users on AliExpress–the e-commerce’s international division–by up to 70 percent through its Euros-related marketing, demonstrating how effectively sports events can drive e-commerce growth and global engagement.
Similarly, the visibility of Chinese brands is further amplified by their roles as official partners and sponsors of the 2024 Olympics. Major Chinese companies, including Alibaba and Mengniu, are top-tier sponsors of the Games. Mengniu, notably, is the sole Chinese consumer goods company among the global Olympic partners, enhancing its brand visibility on an international stage. These partnerships not only boost brand recognition but also create avenues for increased consumer engagement and market penetration.
Economic opportunities arising from the Paris 2024 Olympics
Surge in export demand of sports equipment and olympics-related goods.
The run-up to the Paris Olympics has seen a substantial boost in demand for Chinese-made goods, driven by both the Olympics’ scale and China’s robust manufacturing capabilities. Data from various sources highlight a sharp increase in the export of Chinese sports goods and event-related products.
For instance, from January to April 2024, exports of sports equipment from Guangzhou exceeded RMB 15.9 billion (US$2.22 billion). In Zhejiang, a major manufacturing hub, sports goods exports surpassed RMB 10 billion (US$1.39 billion), during the same period, marking a 24.8 percent year-on-year increase. Notably, Yiwu, a key player in global small commodity trade, reported a remarkable 45.6 percent increase in sports equipment exports.
This surge is partly attributed to the significant role of Chinese manufacturers in producing Olympic merchandise. The Paris Organizing Committee has confirmed that 80 percent of the Olympic mascots are made in China, with a substantial portion produced in Yiwu. This dominance underscores China’s strategic advantage in the global supply chain for the Paris 2024 Olympics event-related products.
Peak in cross border e-commerce activity
The excitement of the 2024 Paris Olympics has significantly impacted the digital marketplace, with Chinese e-commerce platforms like Temu, SHEIN, and AliExpress capitalizing on the event. These platforms have leveraged the Olympic buzz to boost their visibility in Europe, offering everything from budget accessories to high-end sports gear. The competition among these sellers mirrors the intensity of the sports events, featuring aggressive pricing and strategic promotions. This surge in e-commerce is conductive in helping Chinese sellers address challenges in building brand recognition and breaking into mainstream European markets.
Tourism and travel surge for the Paris 2024 Olympics
The Paris 2024 Olympics have significantly impacted tourism and travel between China and France , highlighting the event’s potential to boost international connections and economic activity. A remarkable surge in flight bookings and travel-related activities has been observed covering the period of the Games–from July 24 to August 11, 2024–despite the aviation sector still grappling with the aftermath of the pandemic.
During the Paris 2024 Olympics period, flight bookings from China to France have more than doubled compared to the same period in 2023. Data from Umetrip revealed that bookings surged by 114 percent, and travel to Paris saw a 194 percent increase in hotel reservations year-on-year. This sharp rise reflects the Olympics’ ability to attract a substantial influx of tourists, eager to experience the Games firsthand.
The frequency of flights between China and France also saw a significant uptick. There were over 100 weekly passenger flights between the two countries, marking a 60 percent increase from the previous year. However, this increase still falls short of pre-pandemic levels. Flight Master data indicated that during the Olympics, there were 284 flights scheduled on the China-France route, up 70 percent from 2023 but still well below the 461 flights in the same period of 2019.
Despite these gains, the aviation industry faces challenges in fully restoring pre-pandemic flight volumes. The only foreign carrier on the China-France route, Air France-KLM Group, has yet to restore its pre-pandemic flight levels. For the 2024 summer season, the airline scheduled seven weekly flights each to Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong, down from the 14 weekly flights to Beijing and 10 to Shanghai before the pandemic.
Yet, the surge in travel and tourism associated with the Olympics presents significant economic opportunities for both China and France. The increased visitor numbers are likely to drive spending in local economies, from hospitality to retail sectors. For Chinese travelers, the Paris Olympics offer a unique chance to engage with global events, while boosting international tourism ties.
The “Olympics Effect”: China’s developing sports industry trends
Winning medals and showcasing national athletic prowess are important, but the broader significance of the Olympics lies in sparking public interest in the sports industry , enhancing physical fitness, and improving overall health.
Government support to China’s sports and fitness industry
In recent years , China has implemented several policies to promote comprehensive fitness and the construction of a strong sports nation .
Following the successful hosting of the Beijing Olympics in 2008, China designated August 8 as National Fitness Day each year and elevated national fitness to a strategic priority in 2014. The 19th National Congress of the Communist Party outlined the goal to “widely promote national fitness activities and accelerate the development of a sports powerhouse.” To achieve this goal, in 2019 the State Council released the Outline for Building a Leading Sports Nation , a plan which aims to develop the country of 1.4 billion people into a “modern sports power” by 2050.
Similarly, the 14th Five-Year Plan further specifies the goal of establishing China as a sports powerhouse by 2035, highlighting the nation’s significant focus on sports development.
To advance the level of national fitness and address existing gaps, in 2021 the State Council also issued the National Fitness Plan (2021–2025) . This plan outlines four specific goals and eight major tasks for fitness initiatives during the 14th Five-Year Plan period: by 2025, the proportion of people regularly participating in physical exercise is expected to reach 38.5 percent; public fitness facilities at the county, town, and village levels will achieve full coverage; and there will be 2.16 social sports instructors per thousand people.
The table below includes more policy examples:
| October, 2021 | “14th Five-Year Plan for Sports Development” | General Administration of Sport of China | Comprehensive deployment of national sports development during the “14th Five-Year Plan” period, aiming to better promote the sports industry as a pillar of the national economy. |
| October, 2021 | Guidance on Promoting the Construction of Sports Parks | National Development and Reform Commission, General Administration of Sport of China, and 5 other departments | By 2025, approximately 1,000 new or expanded sports parks will be built nationwide, gradually forming a diversified, distinctive, and universally accessible system of sports parks, serving as a new platform for national fitness. |
| December, 2021 | Notice on Issuing the “Basic Public Service Standards for National Fitness (2021 Edition)” | General Administration of Sport of China and 5 other departments | Support for advancing a higher-level public service system for national fitness, aiming to better meet the basic sports and fitness needs of the people. |
| March, 2022 | Notice on Printing and Issuing the “2022 Mass Sports Work Points” | General Administration of Sport of China | Promoting the establishment of a new pattern for a higher-level public service system for national fitness in 2022: consolidating and expanding the achievements of “driving 300 million people to participate in ice and snow sports”; enhancing the supply of public fitness facilities and the openness of public sports venues; constructing and improving the national mass sports event system. |
| March, 2022 | Opinion on Building a Higher-level Public Service System for National Fitness | State Council (People’s Republic of China) | By 2025, establish a higher-level public service system for national fitness, with per capita sports venue area reaching 2.6 square meters and the proportion of people regularly participating in physical exercise reaching 38.5%. Support the development of mass characteristic sports events, and encourage grassroots fitness organizations to organize activities such as square dancing, brisk walking, and chess. |
| May, 2022 | “14th Five-Year National Health Plan” | National Development and Reform Commission | Strengthen health promotion and education, promote healthy lifestyles, carry out national fitness activities, hold demonstrations of national fitness themes, promote the opening and sharing of public sports venues and school sports venues, and expand coverage of convenient fitness places such as fitness trails. |
| July, 2022 | Notice on Improving the After-school Service Level of School Physical Education and Promoting the Healthy Growth of Primary and Middle School Students | General Administration of Sport of China and 6 other departments | Guide and support professional forces such as sports schools and sports clubs to enter campuses and conduct after-school sports services, promote policies to ensure sincerity and practicality, and promote the healthy growth of youth through concerted efforts. |
| August, 2022 | Notice on Carrying Out the Popularization Work of Scientific Fitness Guidance for National Youth in 2022 | General Administration of Sport of China | Through the establishment of scientific fitness lectures or integration with health education classes in schools, fully utilize venues such as sports halls, libraries, museums, and science education bases. |
| May, 2023 | Action Plan for Enhancing National Fitness Venues and Facilities (2023-2025) | Several departments | Aims to address the challenge of “where to exercise” faced by the public by improving the public service level of national fitness facilities and meeting the people’s needs for a better life. |
| June, 2024 | Implementation Plan for “Weight Management Year” | National Health Commission | Focus on establishing supportive environments, enhancing public awareness and skills, and promoting healthy lifestyles. It aims to integrate scientific guidance on weight management into community settings, encourage social participation, and improve weight management services. |
With economic growth and policy support driving the progress, public fitness services in China have already significantly improved, and sports activities are becoming a part of daily life. As of the end of 2023, the total number of sports venues nationwide reached 4.59 million, with an average per capita sports venue area of 2.89 square meters, and the proportion of people regularly participating in physical exercise reached 37.2 percent. This widespread participation creates a substantial market for the sports industry, setting the stage for rapid development.
Sports industry scale expected to reach over US$500 billion by 2025
China’s sports industry has shown remarkable growth, with total output rising from RMB 1.7 trillion in 2015 to nearly RMB 3 trillion (US$419.71 billion) in 2019. Despite disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020, the sector rebounded in the latter half of the year as the situation improved and public interest in sports surged. By 2022, the industry’s total output had reached RMB 3.3 trillion (U$461.68 billion), up 5.9 percent year-on-year, according to a report by the General Administration of Sport of China and the National Bureau of Statistics.
The added value of the sports sector, which represents the net economic contribution of the industry, rose to RMB 1.3 trillion (U$181.87 billion) in 2022, marking a 6.9 percent year-on-year increase. The sports service industry played a major role in this, contributing RMB 918 billion (U$128.43 billion), or 70.1 percent, to the added value. The manufacturing of sports equipment and related products also performed robustly, contributing RMB 368.6 billion (U$51.56 billion), accounting for 28.2 percent of the sector’s added value.
Looking ahead, the Chinese government aims to grow the sports industry to RMB 5 trillion (U$699.52 billion) by 2025, indicating a promising future for the sector. Internationally, as economies develop and incomes rise, sports industries typically experience accelerated growth and become more integral to national economies. China’s trajectory aligns with this global trend, highlighting the sector’s increasing importance to the national economy.
Rapid growth of sports services and emerging “sports+” business models
The sports industry encompasses various sectors, including sports services, equipment manufacturing, and facility construction. Historically, sports equipment has been the largest segment of China’s sports industry. However, with growing fitness awareness and increased sports consumption, sports services—such as event management, venue operations, and training—have experienced significant growth.
Current per capita sports spending in China is around RMB 3,000 (US$419.72). According to a recent report , the structure of sports consumption is evolving with three notable trends:
- Shift to service-oriented spending : There is a movement from purchasing physical products like sportswear and equipment to spending on services such as event tickets and fitness training.
- Increased demand for new outdoor sports: Outdoor sports activities like cycling, water sports, ice and snow activities , climbing, fishing, marathons, and equestrian sports are becoming more popular.
- Integration of sports with other industries: This trend is leading to new “sports+” business models. For instance, the ice and snow tourism market, driven by the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics , saw significant activity with 230 million visits and over RMB 390 billion (US$54.56 billion) in revenue during the 2020-2021 season.
The “sports+” business model, in particular, refers to the integration of sports with various other industries to create diversified and innovative business opportunities. This approach leverages the popularity and broad appeal of sports to enhance and expand different sectors. Examples include:
- Sports + tourism: Combining sports events and activities with tourism to attract visitors, such as hosting international sports events and developing sports-themed resorts.
- Sports + retail: Integrating sports with the retail sector to boost sales of sports-related products, such as exclusive merchandise collaborations and e-commerce platforms for sports equipment.
- Sports + entertainment: Combining sports with entertainment to enhance the fan experience, including concerts at sports venues and integrating gaming with traditional sports events.
Although China’s sports-related products still lag behind those of other developed economies—where sports-related leisure products account for about 50 percent of the market—the growth of sports media and entertainment is expanding consumer potential and contributing to the sector’s development.
Capital investment shifts towards home fitness and e-sports
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted China’s sports industry severely, with numerous events delayed or canceled, causing a significant decrease in investment. In 2020, the number of investments in sports-related companies dropped to 53, with 40 disclosing a total of RMB 3.03 billion (US$424.47 million), marking the lowest levels since 2015. However, as the pandemic situation improved, investment in the sports sector began to recover.
In the first half of 2021, there were already 50 investments totaling RMB 7.36 billion (US$1.02 billion), surpassing both the previous year and the first half of 2019.
In terms of investment distribution, the fitness/yoga sector led with the highest number of investments and amounts, followed by footwear/apparel manufacturing and e-sports. The e-sports sector saw significant investment, totaling RMB 857 million (US$119.89 million).
The increase in home fitness demand, driven by extended home stays and a heightened focus on health, has led to more investments in fitness-related brands, sports gear, and home exercise content.
These trends have continued into the post-pandemic period as more people have consciously incorporated fitness-related habits into their daily lifestyles and routines.
China Briefing is one of five regional Asia Briefing publications, supported by Dezan Shira & Associates . For a complimentary subscription to China Briefing’s content products, please click here .
Dezan Shira & Associates assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing , Tianjin , Dalian , Qingdao , Shanghai , Hangzhou , Ningbo , Suzhou , Guangzhou , Dongguan , Haikou , Zhongshan , Shenzhen , and Hong Kong . We also have offices in Vietnam , Indonesia , Singapore , United States , Germany , Italy , India , and Dubai (UAE) and partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines , Malaysia , Thailand , Bangladesh , and Australia . For assistance in China, please contact the firm at [email protected] or visit our website at www.dezshira.com .
- Previous Article New 144-Hour Visa-Free Policy for Foreign Tour Groups from Hong Kong and Macao Entering Hainan
- Next Article
Our free webinars are packed full of useful information for doing business in China.

DEZAN SHIRA & ASSOCIATES
Meet the firm behind our content. Visit their website to see how their services can help your business succeed.
Want the Latest Sent to Your Inbox?
Subscribing grants you this, plus free access to our articles and magazines.
Get free access to our subscriptions and publications
Subscribe to receive weekly China Briefing news updates, our latest doing business publications, and access to our Asia archives.

Your trusted source for China business, regulatory and economy news, since 1999.

Subscribe now to receive our weekly China Edition newsletter. Its free with no strings attached.
Not convinced? Click here to see our last week's issue.
Search our guides, media and news archives
Type keyword to begin searching...

COMMENTS
Starting a business. Market trends in a business plan are key pieces of information that share where your company sits in the wider picture of your industry. Your business plan should prove why your business is viable, show where you fit in the market and what customers you serve. Examining what the market looks like is a smart business move ...
Example for a Coffee Shop: If you're planning to open a coffee shop, your analysis might focus on trends in the coffee industry within your city or region, including consumer preferences for coffee types (e.g., organic, fair trade), the popularity of coffee shop formats (e.g., drive-thru, co-working spaces), and the impact of mobile ordering ...
Let the reader know if the market is growing or declining (and at what rate), and what key industry trends are facing your market. Use third-party market research as much as possible to validate the discussion of your industry. ... Business Plan Market Analysis Example #3 - American Insurance Company (AIC), a chain of insurance agencies in ...
Industry Trends: Describe the key industry trends and evaluate the potential impact of PESTEL (political / economic / social / technological / environmental / legal) changes on the industry, including the level of sensitivity to: ... For example, if your business plan is for internal use, you may not have to go into as much detail about the ...
An industry analysis enables you to gain a better understanding of the industry and market in which you will be conducting business. By conducting an industry analysis before you start writing your business plan, you will be able to: Identify industry trends, such as potentially problematic aspects of the industry.
Here's how to conduct a robust analysis: Market Size Calculation: Determine the total market size in terms of revenue, units sold, or the number of customers. This figure serves as a baseline for evaluating the industry's scale. Historical Growth Analysis: Examine historical data to identify growth trends.
Here's the best way to track industry movements. Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own. This is part 5 / 9 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 4: Marketing Your Business ...
The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
An industry analysis is a fundamental component of any business plan, offering insights into the market dynamics, competitive landscape, and future market trends.This analysis helps businesses understand their industry's environment, make informed strategic decisions, and identify potential opportunities and threats.
Whether you're researching market trends to launch a new business or invest in a startup, here's a step-by-step process to analyze market trends and inform your business strategy. Step 1: Identify Emerging Competitors, Products, and Industry Terms. Identifying which trends to analyze is arguably the most important task in this process.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
For example, if a news story breaks that is relevant to your business, you need to create content about that quickly to capture interest before it ebbs away. 2. Intermediate Market Trends. Intermediate trends last anywhere from two to eight weeks. In finance, these are rallies and turnarounds that can mystify analysts.
Writing a Business Plan: Section 2. When writing a business plan, the Industry section is best organized as two parts: an overview of the industry and a summary of your business's position within the overall industry. Before writing this section of the business plan, use these questions to focus your research: What is the size of your industry ...
An example of the industry analysis in a business plan of an Indian soap company: Market overview: The market is estimated to be at INR 195 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at 7% annually ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan. 1. Analyze the competition. Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors.
Industry trends can be broadly classified into the following categories: 1. Technology. Technology-based trends are innovations that drive changes in the industry. These could include the integration of artificial intelligence, automation, IoT, or the adoption of new software platforms.
Whatever the facts are, you'll need to support them with a snapshot analysis of the state of your industry and any trends taking place. This can't be mere off-the-cuff thinking.
3. Retail Media Networks. In the world of digital marketing and adtech, retail media networks (RMNs) will explode. It is forecasted to be a lucrative industry in the next three years, so you will ...
When you're developing a simple business plan template to start or grow your company, you need to understand the size of your market and trends affecting it. The market size confirms the market is big enough to warrant an investment of your time, and potentially investor/lender funding, into pursuing the opportunity.
Industry Analysis Template How to Do an Industry Analysis. Follow these steps to gain a thorough understanding of your industry's dynamics and make informed decisions to drive your business forward effectively. Step 1: Define your industry. Start by clearly defining the industry or market sector you want to analyze.
It is time once again to look into the crystal ball and predict the direction that business and industry will take in the coming year. The 10 Biggest Business Trends For 2024 Everyone Must Be ...
Let's look at the industry overview for Pet Grandma, a fictional pet-based business invented for this business plan sample. The Pet Industry According to the American Pet Products Association, pet expenditures in the U.S. totaled slightly over $72.5 billion in 2018, up from $48 billion in 2010, an increase of 51% in eight years.
Here's where Walz stands on some of the big issues driving the national policy conversation: Labor. Walz has been championing progressive labor policy since Democrats took unified control of the ...
For example, in Florida, 60% of all Medicare beneficiaries in the state are enrolled in Medicare Advantage, ranging from 21% in Monroe County (Key West) to 80% in Miami-Dade County (Figure 7).
This plan outlines four specific goals and eight major tasks for fitness initiatives during the 14th Five-Year Plan period: by 2025, the proportion of people regularly participating in physical exercise is expected to reach 38.5 percent; public fitness facilities at the county, town, and village levels will achieve full coverage; and there will ...