sapGyan.com
Sap q&a.
- SAP User Guide

SAP Q&A : What is Account Assignment Category in SAP?
- are not subject to inventory management at the store location,
- are not managed at value basis in Inventory management
- material which procured with/without maintaining the material master record
- Stationery Items,
- Computer operating systems,
- Company promotion item
- Consumable material master creating using Following Material type
- UNBW: Non Valuated materials
- NLAG: Non stock material
- you have to Create the PO using T Code- ME21N
- select the material if you created under material type UNBW / NLAG or Directly write description in material description field without selecting any number in item code
- when you press enter , system will ask you to select the item code or maintain the account assignment Category
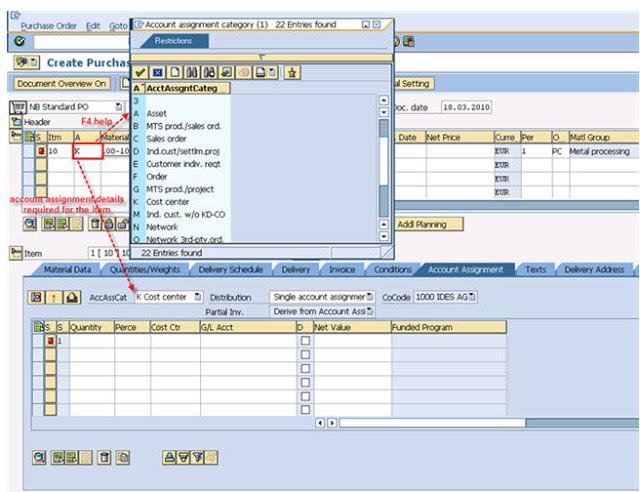
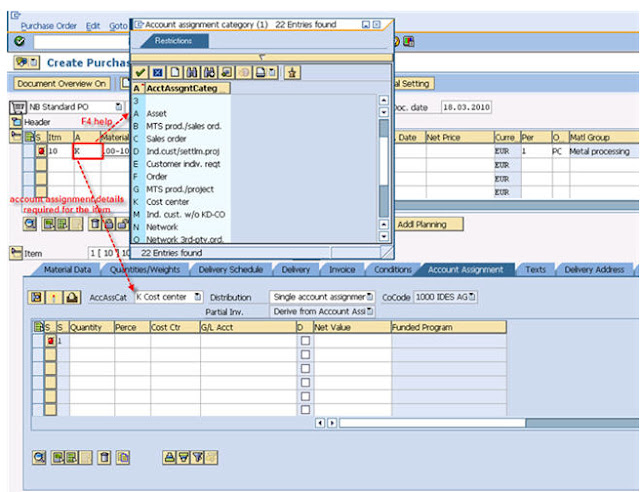
- when you Create the materiel in SAP, you maintain the material valuation in material master , but in case Consumable item you don't maintain the valuation .
- but in Finance prospective, you must maintain the material valuation & here come the account assignment Category in picture
- When you want to procure the Consumable items you must specify the account assignment Category
- account assignment Category determine
- the account assignment object category that is to be charged ( (cost center, sales order, and so on))
- which account assignment data you must provide
- which account are debited when goods receipt or Invoice is posted
About Admin
Related posts, 12 comments:.
You can even have your sim find a job so they'll have money to take others out on virtual dates. Projectsdeal UK Review
I have read your blog and I gathered some needful information from your blog. Keep update your blog. Awaiting for your next update. Purchase Order
Our assignment specialists are proficient essayists who are sufficiently able to give account assignment-help and they likewise ensure that they present the assignment before the cutoff time so customers can edit the record prior to submitting it. narrative essay outline
A portion of your clients have key importance to your business. financial life coach
In this case you will begin it is important, it again produces a web site a strong significant internet site: tourism assignment help
Client belief of the organization is essential towards the improvement as well as ultimate achievement associated with any kind of company effort API platform , consequently it is crucial every single child determine the right support dependent someone to greatest match the actual person's requirements.
I understand this column. I realize You put a many of struggle to found this story. I admire your process. STATA expert help
We have an expansive group that covers a wide scope of subjects. We have the top Need Assignment composing assist specialists on staff, every one of them with holding a Ph.D. Assignment Help UK
I should say only that its awesome! The blog is informational and always produce amazing things. CIPD assignment help
Your blog provided us with valuable information to work with. Each & every tips of your post are awesome. Thanks a lot for sharing. Keep blogging.. 加拿大代写
Students often have different misconceptions about assignment writing services online. Thus, they are barred from taking to help from a professional. The articles discuss some of such thoughts and the reality of it. Assignment Help London
This is very interesting, but it is necessary to click on this link: Assignment Help London
SAPMMFRIENDS.BLOGSPOT.COM
Tuesday, february 26, 2013, account assignment category in sap mm.
- Which accounts are to be charged when the incoming invoice or goods receipt is posted
- Which account assignment data you must provide
- When entering an item on the item overview screen, specify the account assignment category for the item.
- Choose Item ® Account assignments.
- Enter the account assignment data that is dependent on the account assignment category.
- If additional information is available on a specific account assignment, the More field is displayed.
- If you wish to enter further items with the same account assignment data, choose Acct. assgt. on . The account assignment data will then automatically be adopted in the next item.
- Branch to the item overview and repeat the process if necessary.
- Save the purchase order.
- How the net value of a PO item to be distributed is (apportioned) among the individual account assignment items?
- How are the costs to be apportioned if only a part of the ordered quantity has been delivered and invoiced?
- When entering an item, specify the account assignment category for the desired item on the item overview screen.
- To do so, choose Item ® Account assignments.
- Enter the account assignment data for the first account assignment item.
- In the item fields (upper part of this screen) enter the relevant data:
- For each account assignment item, enter either the quantity or the percentage of the total value to be charged to the relevant account assignment item.
- Repeat as necessary for other items.
4 comments:
Good article
Amazing blog thanks for sharing Wonderful information
Thanks for sharing this blog. finance guest post
Thank you for your post. This is excellent information. It is amazing and wonderful to visit your site. And I would like to share some information about virtue solutions. www.virtuesolutionsonline.com
Post a Comment
Pros and Cons of API vs IDOC in SAP

- SAP MM Interview Questions & Answers for Freshers Source: http://www.atoziq.com 1 . Introduction to SAP MM 1. What is SAP? How is it used in industries? ...
- Free SAP MM tutorial with screenshots Currently this Post Changes in Progress
- Corporate Training
- Become an Instructor
Valuation and Account Assignment In SAP MM

SAP MM valuation and Account Assignment
This is completely integrated with FI(Financial Accounting). material Valuation: stock value= stock Qty x Price. The material valuation will update the G/L accounts in Financial Accounting.
SAP MM valuation:
The procurement process begins with generating a purchase order plus ends with invoice verification. Within the entire process, one of the relevant parts is material Valuation. While developing purchase orders, material price is a necessary field plus it is automatically determined. It arises because material valuation is attested within the SAP system in the material master. Material valuation describes integration among MM & FI (Financial Accounting) modules as it updates the general ledger accounts within financial accounting. The important points to note regarding material Valuation are −
Material valuation assists in managing the price of the material.
Stock obtained from one vendor is valuated at a different price than the stock, which is obtained from the other vendor.
We can evaluate the material based on various types of Procurement which are called Split Valuation.
Split Valuation:
Split valuation assists in evaluating the stocks of materials within the same valuation area differently. Some of the examples where we use split valuations are:
A stock that is procured externally from a vendor has a distinct valuation price than the stock of in-house production.
Stock acquired from one vendor is valuated at a distinct price than the stock obtained from another vendor.
The same material possessing a different batch may maintain distinct valuation prices.
Split Valuation requires to be activated before setting any other configuration.
| This course will help you to master SAP MM |
Valuation and Account Assignment :
- This is fully integrated with FI. Material Valuation: Stock value = Stock Qty X Price
- The material valuation will update the G/L accounts in Financial Accounting.
Material Valuation features:
- It allows you to evaluate the materials
- You can evaluate the materials differently based on sub stocks.
- It allows you to evaluate the balance sheet.
Material Valuation control:
This valuation is controllable by
- System settings (where valuation has to be done)
- Material master records (As a rule for each material has to be evaluated under a material type). If this material type is evaluated or not
For every material, you are assigning a valuation class.
- You are grouping a material type under the valuation class.
- All materials of a material type can have one material valuation class.
- Under a material type, you can have different valuation class for different materials
Materials under different material types can have the same valuation class.
Valuation structure:
Data over material is evaluated using the following structure
- Valuation area
- Valuation class
- Valuation category
- Valuation type
- Material type
- Movement type
Valuation area:
The valuation area is an Organizational level at which material valuation is done; the valuation area is defined as
Valuation area= company code
Complete stocks of that particular material in the company code are evaluated together
Valuation area= one plant
Valuation class:
We can group the different materials with the same properties into the valuation calls so that there is no need to control a separate stock account for each material.
All the materials with the same type are assigned to one valuation class.
Various materials with the same material type are assigned to different valuation classes.
Valuation category:
The criterion, according to which split Valuation is carried out:
Procurement: You can evaluate a material uniquely depending on whether it is made in-house or procured externally.
Origin: You can evaluate a material uniquely depending on where it comes from (such as home or else from abroad).
Status: You can evaluate a material uniquely depending on its status (such as new, used, or repaired).
Valuation Type:
The valuation type defines the unique character of the valuation category, like internal or external, within the case of Procurement. In the valuation category Origin, you can determine the different countries as the valuation types. You determine valuation types within Customizing. You first define all the correct valuation types for a valuation category.
You specify within this material master record that valuation types are permitted for a different material. For every material subject to split valuation, you must enter all the valuation types permitted within the material master record.
Material Type:
We can assign every material to a material type when we create it. Examples of material types in the standard system incorporate operating supplies, raw materials, and finished products.
Movement Type:
For every material movement, there is a movement type within the SAP System. The movement type manages the properties of the movement, for instance, which entries you have to make when entering a material movement, and which updates are taken out when the movement is posted.
Customization
SPRO -> Material Management -> Valuation and Account Assignment -> Define Price Control for Material Types
SPRO -> Material Management -> Valuation and Account Assignment -> Account Determination -> Account Determination Without Wizard
- Define Valuation Control (OMWM)
- Group Together Valuation Areas
- Define Valuation Classes
- Define Account Grouping for Movement Types (OMWN)
- Configure Automatic Postings
Define Valuation Control (OMWM):
Choosing the valuation level is one of the first steps we will perform while customizing the system.
If using the PP Production module, the valuation area must be set at the plant level. For account determination, you can group valuation areas by activating the valuation grouping code. This makes the configuration of automatic postings much easier.
Group Together Valuation Areas:
Valuation areas are grouped with the objective of simplifying the management of the standard accounts table by minimizing the number of entries.
Along with other factors, the valuation grouping code determines the G/L Accounts, to which a goods movement is posted (Automatic Account Determination).
The valuation grouping code makes it easier to set the automatic account determination.
Within the chart of accounts, we assigned the same valuation grouping code to the valuation areas.
Since we want to assign to the same G/L account, we assigned the same valuation grouping code to the valuation areas.
Define Valuation Classes:
The Valuation class is a group of material with the same G/L account.
When you create a material master record, you must assign the material to a valuation class. The valuation class is assigned to a material at the plant level. However, if using the split valuation, the valuation class will be assigned at the valuation type level.
The choices for valuation class are dependent on the material type. In general, several valuation classes can be allowed for one material type. Also, the same valuation class could be allowed for different material types.
The link between the valuation class and the material type is the account category reference. The account category reference is assigned to a material type.
The G/L account determined for the material is carried out according to the settings for its valuation class.
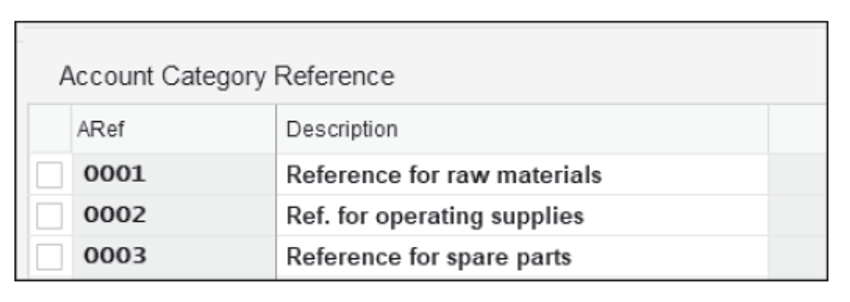
Step1: Account Category Reference: Account Category Reference (4 Char): Group of valuation classes that’s the system uses to check whether the valuation class you have entered is allowed when you maintain accounting data in a material master record.
Step2: Valuation Class: Here The Valuation Class is defined and an Account Category Reference is attached to a Valuation Class. Example: 3000 (Raw Materials) -> 0001 (Reference for Raw Materials)
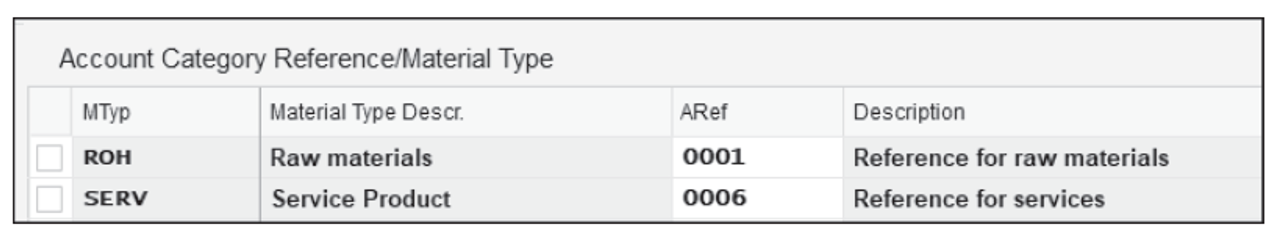
Step3: Material Type / Account Category Reference: Here the Material Type can be assigned to an Account Category Reference. Example: ROH (Raw Materials) -> 0001 (Reference For Raw Materials)
Define Account Grouping for Movement Types: Movement type - Special stock indicator - Value updating - Quantity updating - Movement Indicator - Consumption posting - Posting string for values - Counter - Transaction/event key - Account modification - Check
The following diagram shows the relation between Chart of account, Transaction, account modifiers, accounts posting keys.
TRANSACTION / EVENT KEYS IN SAP
AUM: Stock transfers are there between plants and from one movement type to another with split valuation. The difference between the price at the delivery plant and the receiving point is booked at the latter.
Account to be opened: Loss – Stock Transfer Gain – Stock Transfer A/c
BO1: Check up Subsequent settlement of Provisions (e.g.: volume-based rebate)
BO2: Check up Subsequent settlement of revenues -conditions in inv. Verification
BO3: Check up Provision Differences
BSV: The Company sends materials for subcontract work, this transaction is considered, Accounts to be opened, Materials Consumed/Trading Goods w/o cost element, for ROH Inventory Change, Cost of Goods sold w/o Cost element, for FERT s
BSX: All stock postings to Stock Accounts due to Goods receipts & goods issues in Inventory Management. B/s Inventory A/c s 11101 to 11111
DIF: Small Differences that may arise during invoice verification in the invoice amount not exceeding tolerance.
Accounts to be opened: Loss—Inventory Differences A/c, Gain---Inventory Differences A/c
FRX: These are used for posting delivery costs when goods and invoices are received for purchase orders
FR1: Freight Clearing 69002 Separate A/c s is required
FR2: Provisions for freight Charges 69002
FR3: Customs Clearing 69002
FR4: Provisions for Customs Clearing
FRL: Services are performed for the company externally. Account to be opened: Purchased Services A/c
FRN: Services are performed for the company externally and hence delivery costs
Account to be opened: External Procurement Costs A/c
GBB: Offsetting Entries for Inventory Postings AUA For Order settlement 68005 (Factory output for Production)
AUF: For GRs for orders (w/o account assignment) 68005
BSA: For initial entry of stock balances 11199
INV: Expenditure/Income from Inventory differences 68004 – Raw Material Consumption A/c
VAX: For goods issues for sales orders with no assignment object The account will not be a cost element 68002 –Raw Material Indigenous 72001 – Stores & Spares
VAY: For goods issues for sales orders with assignment object The account is a cost element
VBO: Consumption from stock provided to vendor 68002 –Raw Material Indigenous
VBR: For internal goods issues (e.g.: to a cost center) 68005—Factory output for Production 72001 – Stores & Spares
VKA: For consumption in Sales Order without SD (Mvt. Type 231) 68005—Factory output for Production
VNG: For Scrapping & destruction 68004 – Raw Material Consumption – Others
VQY: For sampling with account assignment
ZOB: For goods issues with no Purchase order reference (Mvt 501)
ZOF: For goods issues with no production order reference (Mvt 521)
KBS: Account - assigned Purchase Order ie. account assignment taken from PO Account need not be assigned in OBYC
KDR: Exchange rate rounding differences in case of foreign currency invoices 80029 -- Exchange Rate Difference - Valuation 1
KDM: Exchange rate rounding differences for open items (invoice posting with a Different exch. rate than the GR/due to Std price difference/insufficient stock coverage) 80028 --Exchange Rate Difference - foreign currency to local
KDV: Material ledger from low levels E/R diff.
KON: Consignment payables
KTR: Offsetting entry for price differences in cost object hierarchies 68005—Factory output for Production
LKW: Accruals and deference. acct (material ledger)
PRD: Price Differences, Loss/Gain Inventory Differences (Two A/cs to be opened & assigned) 68004 – Raw Material Consumption – Others A/c is assigned
PRK: Price Differences in cost object hierarchies Loss/Gain Inventory Differences (Two A/cs to be opened & assigned)
RKA: Inv. reductions from logistic invoice verification
UMB: Gain/loss from revaluation Checkup- 68004 is found attached (Raw Material Consumption – Others A/c )
UPF: Unplanned delivery costs
VST: Input Tax
WGI: Goods issue inflation revaluation
WGR: Goods receipt inflation revaluation
WRX: GR/IR clearing account 40051 – GR/IR Clearing A/c
WRY: GR/IR clearing acct (mat. ledger) (old)
[Check Out: SAP MM Tutorial ]
Account assignment in SAP MM:
Account Assignment category is a very relevant field available and utilized in the purchasing documents. It has various control functions and assists in managing the objects (e.g. sales order, cost center, project) that are charged within the case of a purchase order for material that is meant for direct usage or consumption.
Use of account assignment:
You define which account assignment object is to be charged through the account assignment category such as (sales order, cost center, etc.,) Which accounts are to be charged. At the same time, the incoming invoice or else goods receipt is posted, and which account assignment data you have to give. The account assignment category is utilized at the time of the creation of a purchase order. For regular PO, no account assignment category is used.
Account assignment category:
The account assignment category defines:
The quality of the account assignment (sales order, cost center, and so on)
Which accounts are to be charged while the incoming invoice or goods receipt is posted.
Which account assignment data you have to provide.
Account assignment categories:
|
|
|
| Asset (A) | Main asset number and sub-number |
| Order ( F) | Order and G/L account number |
| Production order | Production order number |
| Cost center(K) | Cost center and G/L account number |
| Sales order (C) | Sales order and G/L account number |
| Individual customer requirement(E) | Sales order and G/L account number |
| Project | Project and G/L account number |
| Unknown | None |
Conclusion :
A valuation modifier is used to let the system find the predefined posting rules discover how the accounts of the financial accounting system are to be posted and update the stock fields within the material master data. Whereas by using the account assignment, we can specify which object is to be charged through the account assignment.
You liked the article?
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium
Recommended Articles
Recommended courses, about author.
TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.
- SAP MM Tutorial
- SAP MM Interview Questions
- Enterprise Structure in SAP MM
- Material Master Data in SAP MM
- Vendor Master In SAP MM
- Procurement Cycle In SAP MM
Understanding Account Categories in SAP MM

Account Category Reference in SAP MM is a crucial aspect of managing financial transactions within the Materials Management module. This article provides valuable insights into understanding and utilizing account category reference in SAP MM effectively. By comprehending the significance of account categories and their role in various business processes, users can streamline accounting procedures, ensure accurate reporting, and maintain financial transparency. With this knowledge, businesses can optimize their operations and enhance overall efficiency within the SAP MM system.
- 1.1 Activating Valuation Grouping Code in SAP MM
- 2.1 Defining Valuation Area and Valuation Grouping Code in SAP MM
- 3 What is the purpose of account assignment category in SAP MM?
- 4.1 Account Reference and Valuation Class Definition Path in SAP MM
- 5 Can we use one valuation class for multiple account category references?
- 6.1 Automatic Posting Configuration Path in SAP MM
- 7 Account grouping code in SAP MM: An Explanation
- 8 Understanding Account Determination in SAP MM
- 9 The significance of account category reference in SAP
- 10 Configuring account category reference in SAP
- 11 Creating account category reference and valuation class in SAP
- 12 Distinguishing account assignment category from item category
Define Valuation Control
Valuation areas can be grouped together and can be assigned to one grouping code, if they belong to the same G/L account. For example, different plants under one company code can be assigned the same valuation grouping code and vice versa. Before this, valuation grouping code must be activated and this can be done by following the steps given below.
Activating Valuation Grouping Code in SAP MM
To access the Account Determination settings in SAP MM, go to IMG and navigate through Materials Management, Valuation and Account Assignment, Account Determination, and then select Account Determination without Wizard. From there, you can define the Valuation Control according to your requirements.
To begin, go to the Display IMG screen and navigate to Define Valuation Control using the path mentioned above.
Proceed to Step 2 by choosing the Valuation grouping code and then save it. This will activate the Valuation grouping code.
Valuation Area Grouping in SAP MM
To assign valuation area and valuation grouping code to the company code in SAP MM, you can follow the steps outlined below.
Defining Valuation Area and Valuation Grouping Code in SAP MM
Navigate to the IMG (Implementation Guide) and go to Materials Management. From there, access Valuation and Account Assignment followed by Account Determination. Next, choose Account Determination without Wizard and then proceed to Group Together Valuation Areas.
To begin, navigate to the Display IMG screen and choose the option to group valuation areas together. This can be done by following the path mentioned above.
In the second step, you have the option to create a valuation area and assign it to a company code by using a grouping code. Once saved, the valuation area and grouping code will be established for that specific company code.
What is the purpose of account assignment category in SAP MM?
The account assignment category in SAP MM is a way to describe how the material that is being purchased will be used. For example, it can specify whether the material will be used for a cost center or a sales order. This helps in keeping track of how different materials are being utilized within an organization.
In addition to describing the usage of materials, the account assignment category also determines how accounting entries are made when goods receipts (GR) or invoice receipts (IR) documents are posted. When these documents are created, they need to be recorded in the accounting system accurately and assigned to appropriate accounts based on their purpose.
For instance, if a material is procured for a cost center, the accounting entry needs to reflect this by debiting the cost center account and crediting the relevant inventory or expense account. On the other hand, if it is procured for a sales order, then different accounts need to be debited and credited accordingly.
Account Category Reference in SAP MM
The G/L account in SAP MM is categorized based on the material type using a valuation class. This means that different types of materials, such as raw materials and finished products, will have different G/L accounts due to their varying costs. Along with the valuation class, an account reference is also maintained. To define the account reference and valuation class in SAP MM, you can follow the steps provided below.
Account Reference and Valuation Class Definition Path in SAP MM
Navigate to the IMG menu and go to Materials Management. From there, select Valuation and Account Assignment followed by Account Determination. Choose Account Determination without Wizard and then proceed to Define Valuation Classes.
To begin, go to the Display IMG screen and choose Define Valuation Classes using the path mentioned above.
Proceed to the next step by selecting the button labeled “Account Category Reference.
Step 4 – Enter the name and description of the ARef (Account reference).
Proceed to the same screen and select Valuation Class.
Step 7 involves entering the valuation class name, account reference (ARef), and a brief description for the valuation class.
Step 8 – Next, navigate to the same screen and select Material Type/Account Category Reference.
Step 9 – In this step, you can establish a connection between material types and account references (ARef). Remember to save the changes. This will enable posting of general ledger accounts for various material types.
Can we use one valuation class for multiple account category references?
To ensure accurate accounting, it is important to assign the same account category reference to both material types. This helps in organizing and categorizing materials effectively. Additionally, an Account Category Reference allows for the assignment of multiple valuation classes. These classes help determine the value of materials based on various factors such as cost or market price.
Furthermore, an Account Category Reference also allows for the assignment of multiple Material Types. This means that different categories of materials can be grouped together under one reference for better organization and analysis purposes.
Continuing with our previous example, apart from wood and metal, there might be other material types like fabric or plastic used in furniture production. By assigning all these material types to a single account category reference specifically created for furniture manufacturing, it becomes easier to analyze costs associated with each type of material used.
Automatic Posting Configuration in SAP MM
The determination of the G/L account is automated for every transaction in SAP. This occurs through the configuration of automatic postings within the SAP system. The steps to configure automatic posting are as follows…
Automatic Posting Configuration Path in SAP MM
Navigate to IMG, then go to Materials Management. From there, select Valuation and Account Assignment followed by Account Determination. Next, choose Account Determination without Wizard and proceed to Configure Automatic Postings.
To begin, navigate to the Display IMG screen and access the Configure Automatic Postings option by following the path mentioned earlier.
Step 3 – In this step, you can set up the transaction that requires automatic account determination. Simply click on the Save button to save your configuration. Now, the system is ready for automatically posting transactions.
Account grouping code in SAP MM: An Explanation
In order to effectively manage inventory and track material movements within an organization, SAP MM provides a comprehensive system that assigns specific accounts based on different types of transactions. The account grouping code or account modifier plays a crucial role in this process by allowing users to break down account determination according to various movement types.
To delve deeper into configuring and customizing these settings for proper account determination using SAP MM functionalities like assigning appropriate general ledger (GL) accounts or defining specific rules for each combination of valuation class and G/L accounts associated with different movements types – consult relevant documentation provided by SAP India or reach out for expert guidance if needed.
Understanding Account Determination in SAP MM
In SAP MM, account determination is determined based on a combination of valuation grouping code, general modifier/account modifier, and valuation class. This is defined for a specific transaction event key, which in turn is defined for each movement type in SAP MM.
1. Account determination is based on the combination of valuation grouping code, general modifier/account modifier, and valuation class.
2. This determination is done for a particular transaction event key.
3. The transaction event key is defined for each movement type in SAP MM.
The significance of account category reference in SAP
In practical terms, the ACR acts as an artificial code that facilitates the association between different components within SAP MM. By assigning specific ACRs to material types, organizations can effectively manage their inventory and accounting processes. The ACR serves as a crucial reference point for determining how materials are valued and accounted for.
Overall, understanding and correctly implementing account category references play a vital role in optimizing inventory management processes within SAP MM. By leveraging this functionality effectively, organizations can enhance their financial reporting accuracy while streamlining overall business operations
Configuring account category reference in SAP
– Each material type has one assigned account category reference.
– In standard SAP, there is an association between an account category reference and each material.
Creating account category reference and valuation class in SAP
To define the account reference and valuation class in SAP MM, follow these steps. First, go to the Display IMG screen and select Define Valuation Classes. Next, click on the Account Category Reference button. Then, click on New Entries to add a new account reference. In this step, you need to provide a name for the account reference (ARef) along with its description.
Defining valuation classes is an important task in SAP MM as it helps in determining how materials are valued within the system. By assigning an account category reference to a valuation class, you can ensure that appropriate accounts are used for recording financial transactions related to material movements.
When defining a new account category reference, it is essential to give it a meaningful name and provide a clear description so that users can easily understand its purpose and usage.
Distinguishing account assignment category from item category
1. Cost center: The item is charged directly to a specific cost center.
3. Project: The item is associated with a project and its costs are allocated accordingly.
4. Asset: The item represents an asset acquisition or capital expenditure.
5. Order: The item relates to an internal order for tracking expenses.
Related Posts
A comprehensive guide to implementing sap transportation management step by step, list of sap transaction codes for accounts payable in pdf format, list of sap t codes for finance.
Defining Default Account Assignments
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Introduce posting controls .
- Describe the account assignment settings .
- Create a default account assignment .
- Analyze the impact of the assignment during journal entry .
Posting Controls
Meet Chris, an experienced management accounting employee at Bike Company SE. He's skilled at using SAP S/4HANA, having extensive knowledge of his department's processes and a comprehensive understanding of the company's operations. Apart from maintaining crucial applications that streamline work for others, Chris also acts as an administrator and business process configuration expert. He is the contact person for establishing and managing Overhead Cost Accounting processes within the company.
Chris loves discovering and utilizing new features and helping other users. Recently, Sarah, a colleague from the financial accounting department, sought his expertise for support and assistance. This is what they talked about:
Let’s now take a closer look at the tools that help streamline accounting data.
You'll learn how to define default values for cost assignment. In the next lessons, you will also delve into more sophisticated features like validation and substitution rules that can identify inconsistencies in account assignment objects and ensure precise postings.
We'll start with an in-depth exploration of the default account assignment.
Default Account Assignment
Application area.
The default account assignment is a tool that automatically proposes specific cost assignment objects, such as cost centers or profit centers during journal entry. You can determine which management accounting object is defaulted for each line item based on the combination of primary cost and revenue G/L account and company code.
As an example, consider recurring utility expenses, which should be charged to the Utilities cost center. For this purpose, a default account assignment can be established as shown in the figure below.

First, the cost element for Utilities for the relevant Company Code is connected to the respective cost center in the default account assignment configuration.
Now whenever you enter a utility expense in Financial Accounting, the system automatically proposes the Utilities cost center. You still have the option to manually overwrite the cost center if necessary.
This leads to a more efficient accounting workflow, as the account assignment object is entered automatically during the posting process, minimizing the need for manual input.
Default account assignments are especially useful when line items are automatically posted, such as when posting exchange rate differences and discounts in Financial Accounting, or price differences in Material Management.
In addition to cost centers, you can also indicate profit centers or profitability segments for allocating costs and revenues to.
In summary, the default account assignment establishes a default value for the controlling objects when posting costs or revenues, ensuring that these are automatically charged to the right entities.
Configuration
To configure a default account assignment, you perform the following steps:

- For each cost assignment, enter the company code and the cost element that should be included in the account assignment.
- Enter the corresponding account assignment object (cost center or profit center). If you want the system to determine a profitability segment instead, you can use the PrfSeg checkbox. This is used when transferring data, such as price differences, to Margin Analysis.
- You have the option to specify detailed account assignments, which can be differentiated by valuation area or profit center. To do this, enter the following values in the "Acct assignmt detail" column: 1 for valuation area or 3 for profit center. Then select the corresponding entry in the Dialog structure on the left and enter the relevant cost assignment.
Define a Default Account Assignment
Overall benefits.
The default account assignment feature suggests default values for specific accounts, improving the accuracy of financial data and streamlining the process through automatic assignment. This reduces the likelihood of errors in manual data entry and saves a considerable amount of time that would otherwise be spent repeatedly assigning these costs.
Log in to track your progress & complete quizzes
- Programming
- Admin & EIM
- BI & BW
- FICO & BPC
- CRM & Sales
- Introductions
- SAP PRESS Subscription
Account Determination in SAP S/4HANA Materials Management

Various transactions in materials management (MM) are relevant for accounting, such as goods receipts, goods issues, and invoice receipts.
In such cases, the system always creates an accounting document and posts the amount in the appropriate general ledger accounts.
General ledger accounts are automatically determined with the help of automatic account determination settings. Consider, for example, a manufacturing enterprise that stores stock materials purchased from vendors. Whenever a material is received in a storage location with reference to a PO, the company wants its system to automatically determine and update the stock general ledger account. Similarly, whenever an invoice is posted, the system should automatically determine the vendor general ledger account and post the liability.
The SAP S/4HANA system provides automatic general ledger account posting via the automatic account determination process. When posting a goods receipt against a PO, the system creates an accounting document (along with the material document), and general ledger account postings are made. The system determines which general ledger accounts should be debited and credited based on configuration settings you’ve maintained for automatic account determination.
Essential Terms
Before discussing these configuration settings, let’s define a few essential terms:
Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts provides a framework for recording values to ensure an orderly rendering of accounting data. The general ledger accounts it contains are used by one or more company codes. For each general ledger account, the chart of accounts contains the account number, the account name, and technical information.
Valuation Class
A valuation class is used to determine the general ledger account for the materials stock account. In automatic account determination, valuation classes must be created and then assigned to material types. While creating material master records, selecting the appropriate valuation class under the Accounting 1 tab is required. The valuation class list in the material master record will depend on the material type. For example, in a standard SAP system, material type ROH (raw material) has three valuation classes: 3000, 3001, and 3002.
Transaction Key
Transaction keys are used to determine accounts or posting keys for line items that are automatically created by the system. They’re defined in the system and can’t be changed.
Now that you have an understanding of the key terms in automatic account determination and understand how it can work in your business, we’ll move on to describe the configuration steps and business processes involved.
Configuration with the Automatic Account Determination Wizard
Automatic account determination can be configured either with or without the automatic account determination wizard, a tool provided by SAP to help you manage the automatic account determination functionality. To configure automatic account determination using the wizard, follow the configuration menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination Wizard .
The wizard will ask you a number of questions and, based on your answers, finds the correct settings and saves them in the corresponding SAP tables. Except for a few restrictions (as documented in the wizard), the wizard will perform the following steps:
- Defines valuation control
- Groups valuation areas
- Defines valuation classes
- Defines account grouping for movement types
- Manages purchase accounts
- Configures automatic postings
We’ll explain how to set up automatic account determination without the wizard because this manual and step-by-step approach to account determination will help you understand how to work with the wizard. Further, using account determination without the wizard enables the creation of more complex configurations. Once you’ve gained the concepts and the fundamentals behind account determination, you can use the automatic account determination’s wizard tool to quickly setup account determination processes in SAP systems.
Configuration without the Automatic Account Determination Wizard
We’ll now follow a step-by-step approach to setting up account determination in an SAP system. We’ll cover the necessary configuration steps involved, followed by steps for assigning the configured objects in the master data. Business processes involving account determination and that use the master data are covered next. We’ll also cover the accounting entries that occur as the result of a stock posting.
Let’s walk through the required steps next:
Define a Valuation Control
In account determination, you can group together valuation areas by activating the valuation grouping code (also known as the valuation modifier ), which makes configuring automatic postings much easier. A valuation grouping code can be made active or inactive by choosing the respective radio button.
To define a valuation control, follow the configuration menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination without Wizard > Define Valuation Control .
By default, the valuation grouping code is active in the standard SAP system.
Assign Valuation Grouping Codes to Valuation Areas
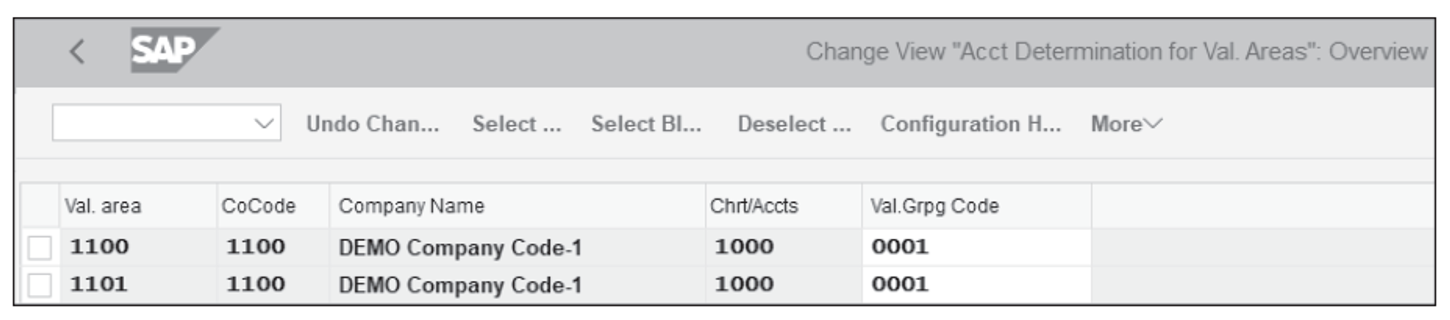
The valuation grouping code makes setting up automatic account determination easier. Within the chart of accounts, assign the same valuation grouping codes to the valuation areas you want assigned to that account. As shown in the figure below, valuation grouping code 0001 has been assigned to valuation area 1100 and company code 1100. If another valuation area also uses the same set of general ledger accounts as valuation area 0001, then assign valuation grouping code 0001 to that valuation area.
To assign valuation grouping codes to valuation areas, follow the configuration menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination without Wizard > Group Together Valuation Areas .
Define Valuation Classes
In this step, you’ll define the valuation classes allowed for each material type. Then, you’ll assign the account category reference to the material type. As shown in the second figure below, account category references 0001 and 0002 have been defined, and for each account category reference, one or more valuation classes can be assigned. Account category reference 0001 has been assigned to material type ROH, and valuation classes 3000, 3001, and 3002 have been assigned to account category reference 0001. Consequently, valuation classes 3000, 3001, and 3002 have been assigned to material type ROH. While creating the material master record for material type ROH, select any of these valuation classes. Similarly, for material type HALB, select valuation classes 7900 or 7901.
In this section, through an example, we’ll create the new valuation class 3004 and cover all the associated configuration settings required to ensure a working end-to-end business process.
To define which valuation classes are allowed for a material type, use Transaction OMSK or follow the configuration menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination without Wizard > Define Valuation Classes . On the screen that appears, you’ll see three options: Account Category Reference , Valuation Class , and Material Type/Account Category Reference . Follow these steps:
- Click on Account Category Reference and, if needed, create an account category reference, as shown here:
- Click on Valuation Class , shown below, and then click on the New Entries Create a new valuation class ( ValCl ) 3004 (with Description Raw Materials- Steel ) and assign the valuation class to account category reference ( ARef ) 0001 . 2
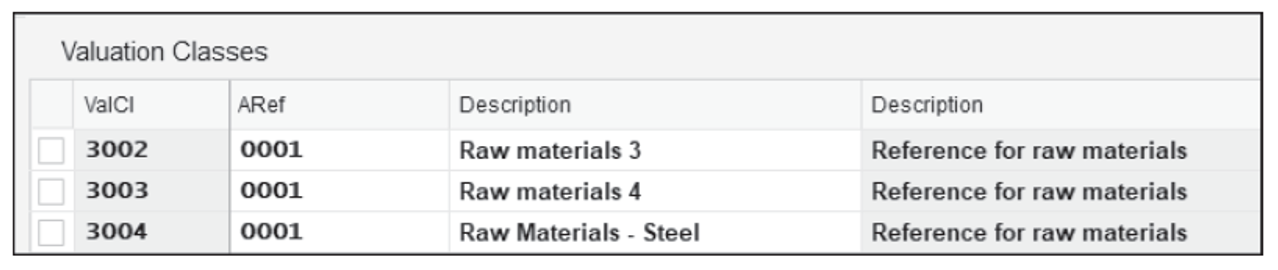
- Click on Account Category Reference and maintain a mapping between the material types and account references. For material type ( MType ) ROH , assign the account reference ( ARef ) 0001 , as shown here:
Define an Account Grouping for Movement Types
Now, assign an account grouping to movement types. The account grouping is a finer subdivision of the transaction/event keys for account determination. For example, during a goods movement, the offsetting entry for the inventory posting (Transaction GBB) can be made to different accounts, depending on the movement type. The account grouping is provided for the following transactions:
- Transaction GBB (Offsetting Entry for Inventory Posting)
- Transaction PRD (Price Differences)
- Transaction KON (Consignment Liabilities)
The account grouping in the standard system is only active for Transaction GBB. To define account groupings for movement types, follow the configuration menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination without Wizard > Define Account Grouping for Movement Types . Define the account grouping code, the movement type, and the transaction/event key combination, as shown in the next figure.
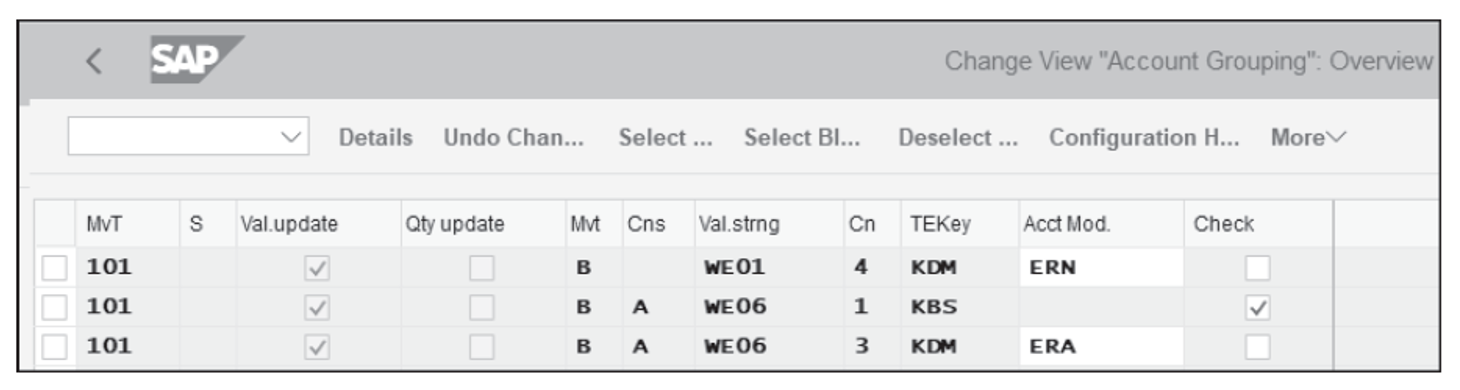
Note: Value strings group together the various transactions used in account determination. For example, the value string WE01 can be seen by following the configuration menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination Without Wizard > Define Account Grouping for Movement Types . On this screen, if you double-click on any entries that contain WE01, a list of transactions along with their descriptions will appear. The transactions that appear in the value string are hard coded in the system, so you should never try to change them.
Configure Automatic Postings
In this step, enter the system settings for inventory management and invoice verification transactions that result in automatic posting to general ledger accounts. A transaction/event key is a key to differentiate account determination by business transaction. For example, we must differentiate general ledger account posted by goods receipt transaction and posted by invoice receipt transaction.
You don’t need to define these transaction keys; they are determined automatically from the transaction of the movement type (inventory management) or from the transaction of invoice verification. All you need to do is assign the relevant general ledger account to each posting transaction.
To assign general ledger accounts to transaction/event keys, use Transaction OMWB or follow the menu path SAP IMG > Materials Management > Valuation and Account Assignment > Account Determination > Account Determination without Wizard > Configure Automatic Posting . Click on Cancel , as shown below.
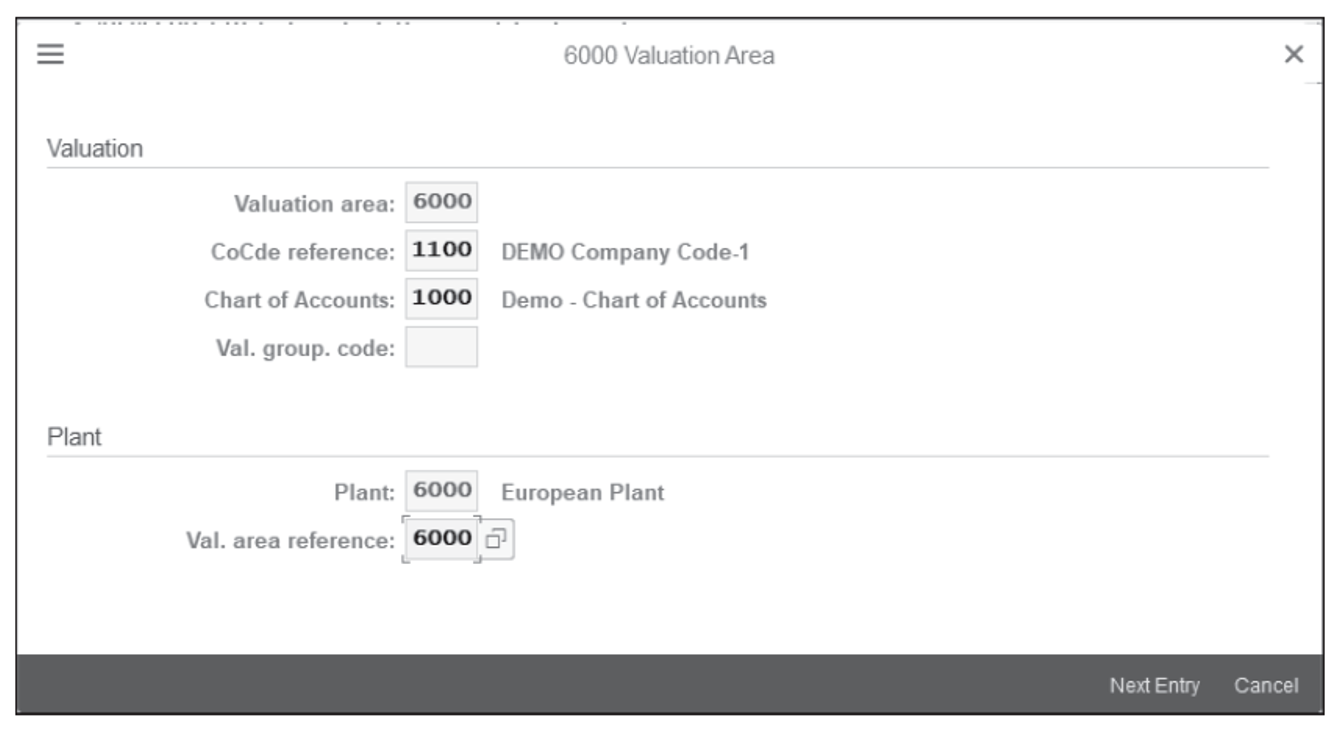
To assign a general ledger account, on the screen shown above, click on Account Assignment (not shown). A list of transaction keys will appear; double click on the key for which setting the general ledger accounts is required. Next, define the valuation grouping code (also known as the valuation modifier ), valuation class, and general ledger account, as shown below. Then, check the settings function by using the simulation function.
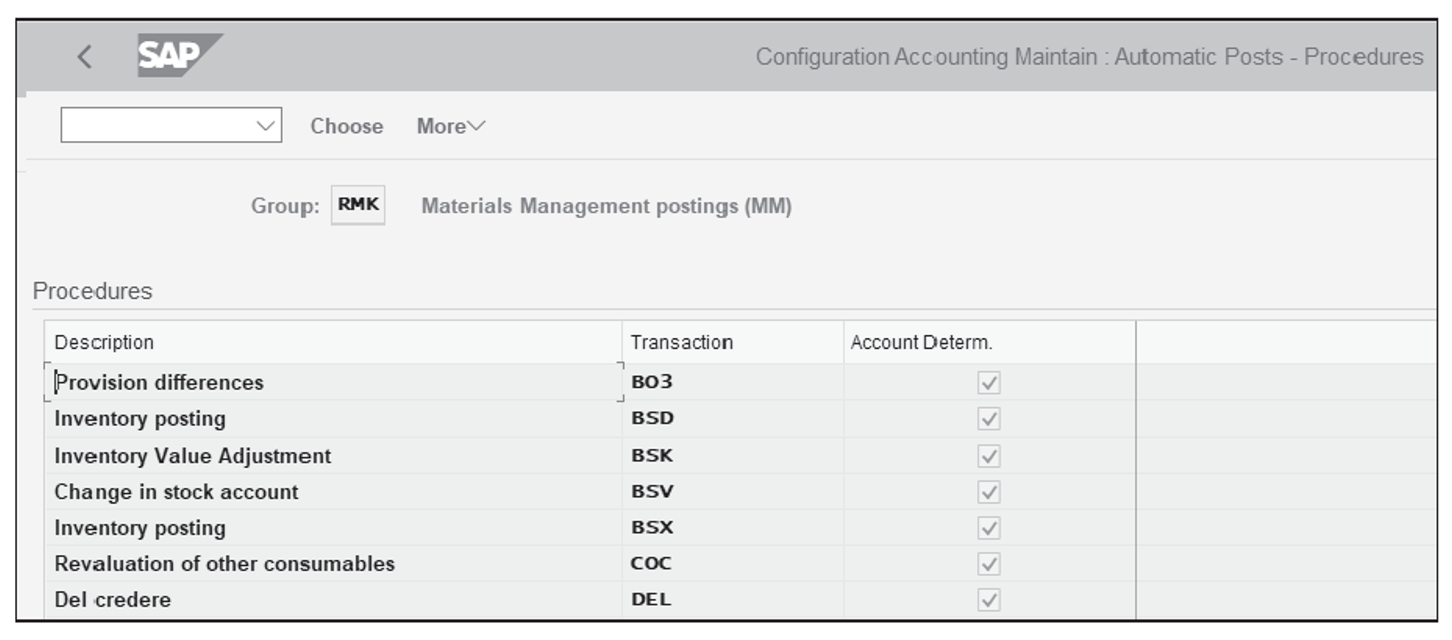
Use Transaction BSX for inventory posting and for assigning general ledgers. In the popup window that appears, enter the Chart of Accounts 1100 , and the screen shown below will appear.
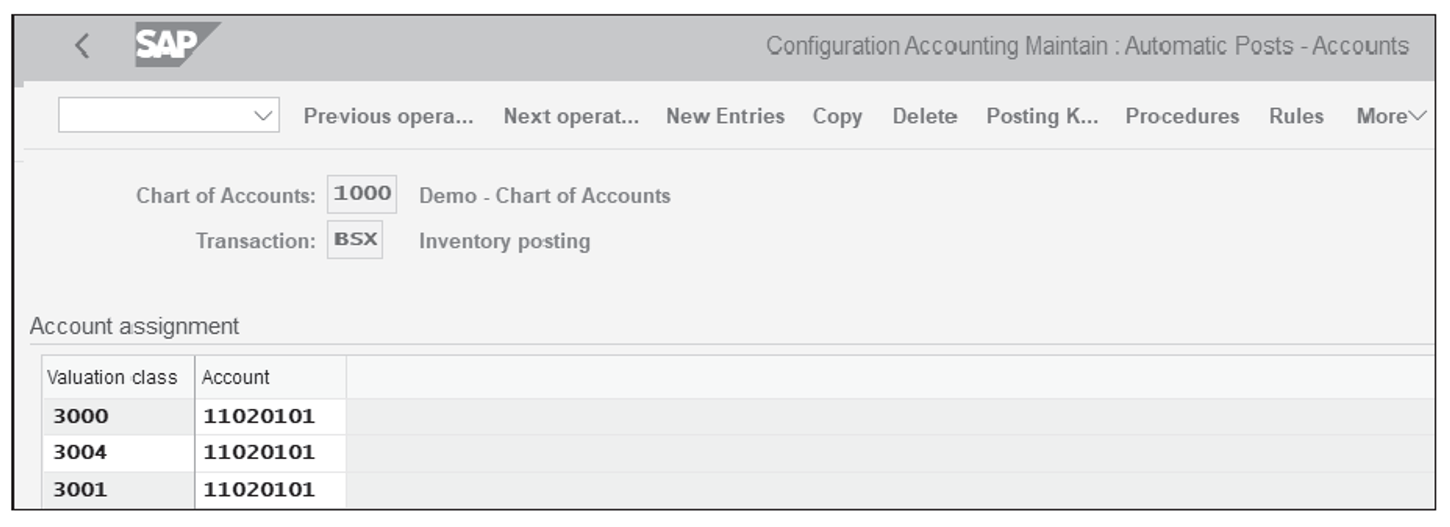
This figure shows the Transaction BSX screen for posting inventory. Click New Entries and enter the newly created Valuation Class 3004 and assign the Account 11020101 .
Go back to the screen shown when utilizing Transaction OMWB, and this time, use Transaction WRX (for the goods receipt/invoice receipt [GR/IR] clearing account) and maintain the general ledger account of the newly created Valuation class 3004 . Similarly, repeat the same steps for Transaction PRD (for price difference account).
Let’s now look at the business processes and the associated master data setup and transactions, not only to check that the newly created valuation class 3004 works correctly, but also that the associated general ledger accounts are correct.

Master Data Setup
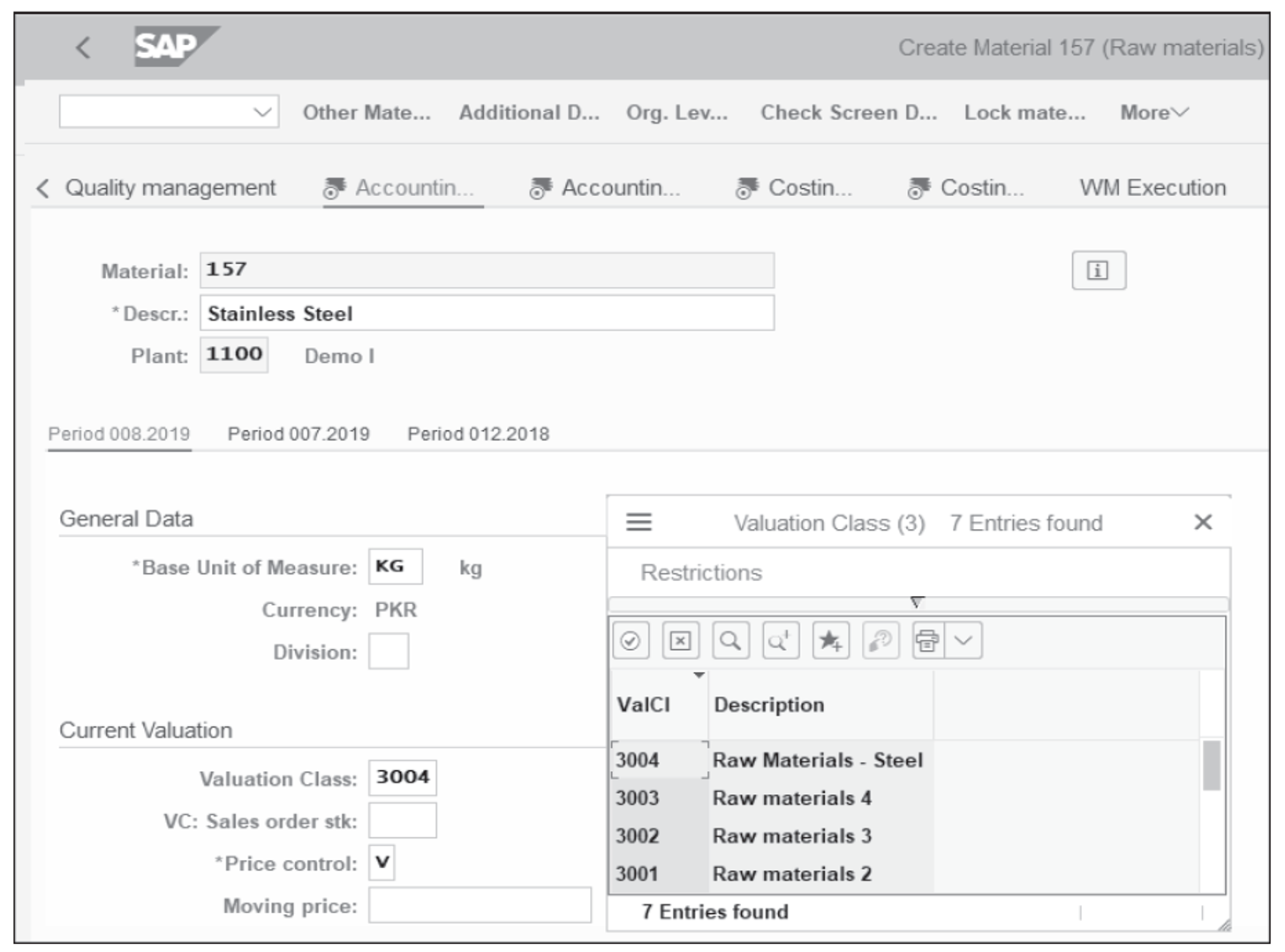
Access the screen shown below via Transaction MM01. Under the Accounting 1 tab of the material master 157 , assign the newly created Valuation Class 3004 .
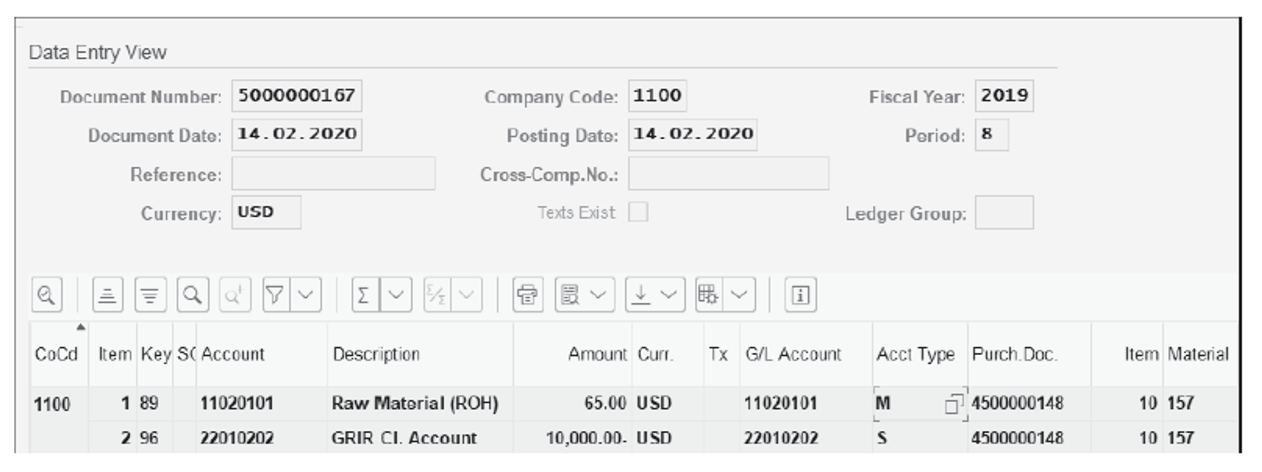
Now, let’s discuss the account determination for the general ledger as it relates to goods receipt and goods issue postings. Post a good receipt of the material 157 with reference to a PO via Transaction MIGO. Then, display the goods receipt document and go to the Doc. info tab. Click on the FI Documents button, which will display a list of financial documents created for the goods receipt document. Select Accounting document to see the details of that accounting document.
As shown below, you’ll see the general ledger account postings, which are determined based on the automatic account determination configuration. General ledger account 11020201 (inventory raw material stock account) is debited, and GR/IR account 22010202 is credited.
In this blog post, we covered the account determination process that is useful to those running materials management with SAP .
Editor’s note : This post has been adapted from a section of the book Materials Management with SAP S/4HANA: Business Processes and Configuration by Jawad Akhtar and Martin Murray.
Recommendation

Ready to streamline your SAP S/4HANA Finance system? Learn how to determine accounts for your core business areas via the SAP GUI, including materials management, sales and distribution, accounts receivable and payable, cash and banking, and fixed assets. Follow step-by-step instructions to configure automatic account determination for each process in your system. Your journey to simplified accounting starts here!
SAP PRESS is the world's leading SAP publisher, with books on ABAP, SAP S/4HANA, SAP CX, intelligent technologies, SAP Business Technology Platform, and more!
Latest Blog Posts

3 Steps to Pre-Planning Repetitive Manufacturing and MRP with SAP S/4HANA
How to Delete Business Partners in SAP S/4HANA Sales
The official sap press blog.
As the world’s leading SAP publisher, SAP PRESS’ goal is to create resources that will help you accelerate your SAP journey. The SAP PRESS Blog is designed to provide helpful, actionable information on a variety of SAP topics, from SAP ERP to SAP S/4HANA. Explore ABAP, FICO, SAP HANA, and more!
SAP Blog Topics
- Administration
- Business Intelligence
- Human Resources
Blog curated by
- Legal Notes
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Guest Posting
Account Assignment Categories and Document Types for PR in SAP
How to assign categories and document types for purchase requisition.
The following training tutorials guide how to assign account categories and document types for PR. You can assign categories and document types for PR by using one of the following navigation methods.
- SAP IMG Path : – Project system >> material >> procurement >> Account Assignment Categories and Document Types for Purchase Requisitions
- Transaction code: – OPS8
Refer below step by step procedure to assign account assignment categories to document types for purchase requisition in SAP.
Step 1: – Enter transaction code “OPS8” in the SAP command field and press enter key.
Step 2: – On material flow in the network overview screen, click on new entries to assign categories and document types
Step 3: – On new entries of the Account assignment screen, update the following fields.
- Procurement: – Update the three digits alpha-numeric id that identifies the procurement indicator and updates the descriptive text.
- Priorities: – Priorities control various stock types, for example, you can set priority project to 1, priority plant to 2, and priority sales to 3.
- Control data: – Control data control the purchase requisition network, third-party material is delivered to customers, and preliminary purchase requisitions.
- Default item category: – Update the default item category for the item category MRP (Material Requirement Planning)
After maintaining the required details Account Assignment Categories and Document Types for PR Click on the save button to save the configured data.
Continue to read SAP PS Tutorial with real-time scenarios.

- ERPCorp FI/CO Books
- Access SAP Modules
- SAP Webinars
- Client Roster
- BECOME A MEMBER

ERPCorp SAP FICO Blog
Display sap mm-fi automatic account assignment.

by John Jordan

Table of Contents
Introduction, display obyc accounts with se16n, more information.
You use configuration Transaction OBYC to assign SAP General Ledger (GL) accounts in Financial Accounting (FI) to movement types in Materials Management (MM), also known as SAP MM-FI Automatic Account Determination or Assignment.
End users do not typically have the authorization to run configuration Transaction OBYC.
You can easily display automatic account assignments as follows:
View table T030, which stores OBYC configuration settings, with Transaction SE16N.
Type in Table T030 and press Enter to display the selection screen shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 : Table T030 Selection Screen To Display SAP MM-FI Configuration Settings
You restrict the table entries displayed on the subsequent results screen by making entries in the Selection Criteria section. To display G/L accounts posted during goods issues (GI) to production orders, make the following entries:
- Chart of Accounts : Restrict your selection by your chart of accounts, INT in this example
- Transaction : You display inventory movements with Transaction GBB
- Valuation Grouping Code : A group of company codes (set up with transaction OMWD)
- Account modifier : VBR for GI to production orders
- Valuation Class : You assign a valuation class in the Costing 2 view
Click the execute icon to display the screen shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 : Table T030 Entries Display SAP MM-FI Configuration Settings
This screen displays the G/L Accounts posted during goods issues to production orders.
For more information on entries in table T030, follow IMG menu path:
Materials Management • Valuation and Account Assignment • Account Determination • Account Determination Without Wizard • Configure Automatic Postings
Figure 3 displays the menu path.

Figure 3 : Configure Automatic Postings Menu Path
Click the paper and glasses icon to the left of Configure Automatic Postings at the bottom to display standard SAP documentation on setting up automatic postings.
Activity Type
An activity type identifies activities provided by a cost center to manufacturing orders. The secondary cost element associated with an activity type identifies the activity costs on cost center and detailed reports
Alternative Hierarchy
While there can only be one cost center standard hierarchy, you can create as many alternative hierarchies as you like. You create an alternative hierarchy by creating cost center groups
Automatic Account Assignment
Automatic account assignment allows you to enter a default cost center per cost element within a plant with Transaction OKB9.
Condition Type
A condition type is a key that identifies a condition. The condition type indicates, for example, whether the system applies a price, a discount, a surcharge, or some other pricing, such as freight costs and sales taxes.
Cost Center Accounting
A cost center is a function within an organization that does not directly add to profit but still costs money to operate, such as the accounting, HR, or IT departments. The main use of a cost center is to track actual expenses for comparison to the budget.
Cost Estimate
A cost estimate calculates the plan cost to manufacture a product or purchase a component. It determines material costs by multiplying BOM quantities by the standard price, labor costs by multiplying operation standard quantities by plan activity price, and overhead values by costing sheet configuration.
Cost Object
An SAP Cost object such as a cost center or internal order describes where the cost occurs. A cost element or account describes what the cost is.
Costing Lot Size
The costing lot size in the Costing 1 view determines the quantity cost estimate calculations are based on. The costing lot size should be set as close as possible to actual purchase and production quantities to reduce lot size variance.
Goods Issue
A goods issue is the movement (removal) of goods or materials from inventory to manufacturing or to a customer. When goods are issued, it reduces the number of stock in the warehouse.
Goods Receipt
It is a goods movement that is used to post goods received from external vendors or from in-plant production. All goods receipts result in an increase of stock in the warehouse.
Internal Order
An internal order monitors costs and revenue of an organization for short- to medium-term jobs. You can carry out planning at a cost element and detailed level, and you can carry out budgeting at an overall level with availability control.
Production Variance
Production variance is a type of variance calculation based on the difference between net actual costs debited to the order and target costs based on the preliminary cost estimate and quantity delivered to inventory. You calculate production variance with target cost version 1.
Profit Center
A profit center receives postings made in parallel to cost centers and other master data such as orders. Profit Center Accounting (PCA) is a separate ledger that enables reporting from a profit center point of view. You normally create profit centers based on areas in a company that generate revenue and have a responsible manager assigned.
If PCA is active, you will receive a warning message if you do not specify a profit center, and all unassigned postings are made to a dummy profit center. You activate profit center accounting with configuration Transaction OKKP, which maintains the controlling area.
Purchasing Info Record
A purchasing info record stores all of the information relevant to the procurement of a material from a vendor. It contains the Purchase Price field, which the standard cost estimate searches for when determining the purchase price.
Scheduling Agreement
A scheduling agreement is a longer-term purchase arrangement with a vendor covering the supply of materials according to predetermined conditions. These apply for a predefined period and a total purchase quantity.
Standard Hierarchy
A standard hierarchy represents your company structure. A standard hierarchy is guaranteed to contain all cost centers or profit centers because a mandatory field in cost and profit center master data is a standard hierarchy node.
To learn more about MM-FI, and SAP S/4HANA FICO topics become a member Click here now :

Standard Price
The standard price in the Costing 2 view determines the inventory valuation price if price control is set at standard (S). The standard price is updated when a standard cost estimate is released. You normally value manufactured goods at the standard price.
You can apply surcharges to material prices and activity prices in order to take into account increases or decreases in item prices over time when calculating the lifecycle costs for a project.
Target Costs
Target costs are plan costs adjusted by the delivered quantity. For example, if the quantity delivered to inventory is 50% of the plan quantity, target costs are calculated as 50% of the plan costs.
Material Master
A material master contains all of the information required to manage a material. Information is stored in views, and each view corresponds to a department or area of business responsibility. Views conveniently group information together for users in different departments, for example, sales and purchasing.
Origin Group
An origin group separately identifies materials assigned to the same cost element, allowing them to be assigned to separate cost components. The origin group can also determine the calculation base for overhead in costing sheets.
Price Control
The Price control field in the Costing 2 view determines whether inventory is valuated at standard or moving average price.
The price unit is the number of units to which the price refers. You can increase the accuracy of the price by increasing the price unit. To determine the unit price, divide the price by the price unit.
Process Order
Process orders are used for the production of materials or provide services in a certain quantity and on a certain date. They allow resource planning, process order management control, and account assignment and order settlement rules to be specified.
Procurement Alternative
A procurement alternative represents one of a number of different ways of procuring a material. You can control the level of detail in which the procurement alternatives are represented through the controlling level. Depending on the processing category, there are single-level and multilevel procurement alternatives. For example, a purchase order is single-level procurement, while production is multilevel procurement.
Production Order
A production order is used for discrete manufacturing. A BOM and routing are copied from master data to the order. A sequence of operations is supplied by the routing, which describes how to carry out work-steps. An operation can refer to a work center at which it is to be performed. An operation contains planned activities required to carry out the operation. Costs are based on the material components and activity price multiplied by a standard value.
Product Drilldown Reports
Product drilldown reports allow you to slice and dice data based on characteristics such as product group, material, plant, cost component, and period. Product drilldown reports are based on predefined summarization levels and are relatively simple to setup and run.
Production variance is a type of variance calculation based on the difference between net actual costs debited to the order and target costs based on the preliminary cost estimate and quantity delivered to inventory. You calculate production variance with target cost version 1. Production variances are for information only and are not relevant for settlement.
Production Version
A production version determines which alternative BOM is used together with which task list/master recipe to produce a material or create a master production schedule. For one material, you can have several production versions for various validity periods and lot-size ranges.
Purchase Price Variance
When raw materials are valued at the standard price, a purchase price variance will post during goods receipt if the goods receipt or invoice price is different from the material standard price.
Profitability Analysis
Costing-based profitability analysis enables you to evaluate market segments, which can be classified according to products, customers, orders (or any combination of these), or strategic business units, such as sales organizations or business areas concerning your company’s profit or contribution margin.
SAP Profit Center is a management-oriented organizational unit used for internal controlling purposes. Segmenting a company into profit centers allows us to analyze and delegate responsibility to decentralized units.
A purchasing info record stores all the information relevant to the procurement of a material from a vendor. It contains the Purchase Price field, which the standard cost estimate searches for when determining the purchase price.
Raw Materials
Raw materials are always procured externally and then processed. A material master record of this type contains purchasing data but not sales.
A routing is a list of tasks containing standard activity times required to perform operations to build an assembly. Routings, together with planned activity prices, provide cost estimates with the information necessary to calculate labor and activity costs of products.
Sales and Operations Planning
Sales and operations planning (SOP) allows you to enter a sales plan, convert it to a production plan, and transfer the plan to long-term planning.
S&OP is slowly being replaced by SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP), which supports all S&OP features. S&OP is intended as a bridge or interim solution, which allows you a smooth transition from SAP ERP to on-premise SAP S/4HANA and SAP IBP. See SAP Note 2268064 for details.
SAP Fiori is a web-based interface that can be used in place of the SAP GUI. SAP Fiori apps access the Universal Journal directly, taking advantage of additional fields like the work center and operation for improved variance reporting.
Work in process (WIP) and variances are transferred to Financial Accounting, Profit Center Accounting (PCA), and Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) during settlement. Variance categories can also be transferred to value fields in CO-PA.
Settlement Profile
A settlement profile contains the parameters necessary to create a settlement rule for manufacturing orders and product cost collectors and is contained in the order type.
Settlement Rule
A settlement rule determines which portions of a sender’s costs are allocated to which receivers. A settlement rule is contained in a manufacturing order or product cost collector header data.
You need setup time to prepare equipment and machinery for the production of assemblies, and that preparation is generally the same regardless of the quantity produced. Setup time spread over a smaller production quantity increases the unit cost.
Simultaneous Costing
The process of recording actual costs for cost objects, such as manufacturing orders and product cost collectors in cost object controlling, is called simultaneous costing. Costs typically include goods issues, receipts to and from an order, activity confirmations, and external service costs.
Source Cost Element
Source cost elements identify costs that debit objects, such as manufacturing orders and product cost collectors.
Source List
A source list is a list of available sources of supply for a material, which indicates the periods during which procurement is possible. Usually, a source list is a list of quotations for a material from different vendors.
You can specify a preferred vendor by selecting a fixed source of supply indicator. If you do not select this indicator for any source, a cost estimate will choose the lowest cost source as the cost of the component. You can also indicate which sources are relevant to MRP.
The standard price in the Costing 2 view determines the inventory valuation price when price control is set at standard (S). The standard price is updated when a standard cost estimate is released. You normally value manufactured goods at the standard price.
Subcontracting
You supply component parts to an external vendor who manufactures the complete assembly. The vendor has previously supplied a quotation, which is entered in a purchasing info record with a category of subcontracting.
Tracing Factor
Tracing factors determine the cost portions received by each receiver from senders during periodic allocations, such as assessments and distributions.
Universal Journal
The efficiency and speed of the SAP HANA in-memory database allowed the introduction of the Universal Journal single line-item tables ACDOCA (actual) and ACDOCP (plan). The Universal Journal allows all postings from the previous financial and controlling components to be combined in single items. The many benefits include the development of real-time accounting. In this book, we discuss both period-end and event-based processing.
Valuation Class
The valuation class in the Costing 2 view determines which general ledger accounts are updated as a result of inventory movement or settlement.
Valuation Date
The valuation date determines which material and activity prices are selected when you create a cost estimate. Purchasing info records can contain different vendor-quoted prices for different dates. Different plan activity rates can be entered per fiscal period.
Valuation Grouping Code
The valuation grouping code allows you to assign the same general ledger account assignments across several plants with Transaction OMWD to minimize your work. The grouping code can represent one or a group of plants.
Valuation Type
You use valuation types in the split valuation process, which enables the same material in a plant to have different valuations based on criteria such as batch. You assign valuation types to each valuation category, which specify the individual characteristics that exist for that valuation category. For example, you can valuate stocks of a material produced in-house separately from stocks of the same material purchased externally from vendors. You then select procurement type as the valuation category and internal and external as the valuation types.
Valuation Variant
The valuation variant is a costing variant component that allows different search strategies for materials, activity types, subcontracting, and external processing. For example, the search strategy for purchased and raw materials typically searches first for a price from the purchasing info record.
Valuation Variant for Scrap and WIP
This valuation variant allows a choice of cost estimates to valuate scrap and WIP in a WIP at target scenario. If the structure of a routing is changed after a costing run, WIP can still be valued with the valuation variant for scrap and WIP resulting in a more accurate WIP valuation.
Valuation View
In the context of multiple valuation and transfer prices, you can define the following views: – Legal valuation view – Group valuation view – Profit center valuation view
Work Center
Operations are carried out at work centers representing; for example, machines, production lines, or employees. Work center master data contains a mandatory cost center field. A work center can only be linked to one cost center, while a cost center can be linked to many work centers.
Work in Process
Work in process (WIP) represents production costs of incomplete assemblies. For balance sheet accounts to accurately reflect company assets at period end, WIP costs are moved temporarily to WIP balance sheet and profit and loss accounts. WIP is canceled during period-end processing following delivery of assemblies to inventory.
Meet John Jordan, Kent Bettisworth, Gerald Steele and other SAP expert speakers in person at SAP Controlling Financials 2024 Conference in San Diego, CA
Use exclusive coupon code: jj100 for $100 off click here.
For the latest updates
About the author
John Jordan

Author's recent posts
Captcha Image

IMAGES
COMMENTS
the account assignment object category that is to be charged ((cost center, sales order, and so on)) which account assignment data you must provide. which account are debited when goods receipt or Invoice is posted. Account Assignment Categories. Description. Required account assignment data. Asset (A)
Use. The account assignment category determines the account assignment element (for example, cost center or WBS element) to be supplied. Technical data. Available from Release. 2.0B (SAP B2B Procurement) Data element. ACC_CAT. Reference characteristic. External hierarchy.
Here are the definitions by Application Component or Module. Controlling (CO) : A statement of settlement receivers. Examples of account assignment categories include: Asset Cost center Cost object G/L account. Purchasing (MM-PUR) : A key indicating whether an item is to be assigned to an auxiliary account (such as a cost center).
Item Category . Purchase Order - Single-Screen Transaction (ME21N, ME22N, and ME23N) ... Specifying Multiple Account Assignment . Units of Measure in Purchase Orders . Incoterms and Shipping/Delivery Instructions . Goods-Receipt-Based Invoice Verification . Materials Subject to Split Valuation . Goods Receipt Without Reference to Purchase ...
Completion Status of Reservation. Account Assignment Category. Reservation Document Data Extraction. CDS Views for Serial Number Management. CDS Views for Public Sector Management. CDS Views for Industries. CDS Views for Enterprise Technology. CDS Views for Product Master. CDS Views for Master Data Governance.
Account Assignment category is one of the very important fields available and used in the purchasing documents. It has many control functions and helps in determining the objects (e.g. cost center, sales order, project) that are charged in the case of a purchase order for a material that is intended for direct usage or consumption.
Account Assignment category is a very relevant field available and utilized in the purchasing documents. It has various control functions and assists in managing the objects (e.g. sales order, cost center, project) that are charged within the case of a purchase order for material that is meant for direct usage or consumption. ... Description ...
When defining a new account category reference, it is essential to give it a meaningful name and provide a clear description so that users can easily understand its purpose and usage. Distinguishing account assignment category from item category. 1. Cost center: The item is charged directly to a specific cost center. 3.
To procure material for a project and a cost center, Paula must use the account assignment categories P for the account assignment object project and K for the account assignment object cost center. Here are some examples of account assignment categories defined in the SAP S/4HANA system: K for cost center. P for project. C for sales order
You use this DataSource to extract the texts for the account assignment categories that you have defined during Customizing in your Enterprise Buyer system. ... Description of Field in the Extract Structure. Table of Origin. Field in Table of Origin. ACCCAT_D . Description of the account assignment category in Enterprise Buyer . BBP_C_ACCD ...
Application Area. The default account assignment is a tool that automatically proposes specific cost assignment objects, such as cost centers or profit centers during journal entry. You can determine which management accounting object is defaulted for each line item based on the combination of primary cost and revenue G/L account and company ...
Click on Account Category Reference and, if needed, create an account category reference, as shown here: Click on Valuation Class, shown below, and then click on the New Entries Create a new valuation class (ValCl) 3004 (with Description Raw Materials- Steel) and assign the valuation class to account category reference (ARef) 0001. 2
Step 1: - Enter transaction code "OPS8" in the SAP command field and press enter key. Step 2: - On material flow in the network overview screen, click on new entries to assign categories and document types. Step 3: - On new entries of the Account assignment screen, update the following fields. Procurement: - Update the three digits ...
SAP ERP. Purchasing (MM-PUR) Purchase Orders (MM-PUR-PO) Account Assignment. Purchasing (MM-PUR) 6.0 EHP8 Latest. * This product version is out of mainstream maintenance. The documentation is no longer regularly updated. English.
Account assignment objects can be objects such as cost centers, internal orders, projects, or business processes. Project System (PS) : The CO object to which postings can be made. In interest calculation, this is a CO object bearing costs and payments. Account assignment objects include WBS elements, network activities, and orders.
Type in Table T030 and press Enter to display the selection screen shown in Figure 1. Figure 1: Table T030 Selection Screen To Display SAP MM-FI Configuration Settings. You restrict the table entries displayed on the subsequent results screen by making entries in the Selection Criteria section. To display G/L accounts posted during goods issues ...
To mark this page as a favorite, you need to log in with your SAP ID. If you do not have an SAP ID, you can create one for free from the login page.