
Original text

What is a break-even analysis? The break-even point is the point when your business’s total revenues equal its total expenses.
Your business is “breaking even”—not making a profit but not losing money, either.
After the break-even point, any additional sales will generate profits.
To use this break-even analysis template, gather information about your business’s fixed and variable costs, as well as your 12-month sales forecast .
When should you use a break-even analysis.
A break-even analysis is a critical part of the financial projections in the business plan for a new business. Financing sources will want to see when you expect to break even so they know when your business will become profitable.
But even if you’re not seeking outside financing, you should know when your business is going to break even. This will help you plan the amount of startup capital you’ll need and determine how long that capital will need to last.
In general, you should aim to break even in six to 18 months after launching your business. If your break-even analysis shows that it will take longer, you need to revisit your costs and pricing strategy so you can increase your margins and break even in a reasonable amount of time.
Existing businesses can benefit from a break-even analysis, too.
In this situation, a break-even analysis can help you calculate how different scenarios might play out financially. For instance, if you add another employee to the payroll, how many extra sales dollars will be needed to recoup that additional expense? If you borrow money, how much will be needed to cover the monthly principal and interest payments?
A break-even analysis can also be used as a motivational tool. For instance, you can calculate a monthly, weekly, or even daily break-even analysis to give your sales team a goal to aim for.
Do you need help completing your break-even analysis? Connect with a SCORE mentor online or in your community today.
Business Planning & Financial Statements Template Gallery Download SCORE’s templates to help you plan for a new business startup or grow your existing business.
Sales Forecast (12 months) The sales forecast is the key to the whole financial plan, so it is important to use realistic estimates. Download SCORE's Sales Forecast template.
Copyright © 2024 SCORE Association, SCORE.org
Funded, in part, through a Cooperative Agreement with the U.S. Small Business Administration. All opinions, and/or recommendations expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SBA.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Quick Guide to Breakeven Analysis
It’s a simple calculation, but do you know how to use it?
In a world of Excel spreadsheets and online tools, we take a lot of calculations for granted. Take breakeven analysis. You’ve probably heard of it. Maybe even used the term before, or said: “At what point do we break even?” But because you may not entirely understand the math — and because understanding the formula can only deepen your understanding of the concept — here’s a closer look at how the concept works in reality.
- Amy Gallo is a contributing editor at Harvard Business Review, cohost of the Women at Work podcast , and the author of two books: Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People) and the HBR Guide to Dealing with Conflict . She writes and speaks about workplace dynamics. Watch her TEDx talk on conflict and follow her on LinkedIn . amyegallo
Partner Center
What is Break-Even Analysis?
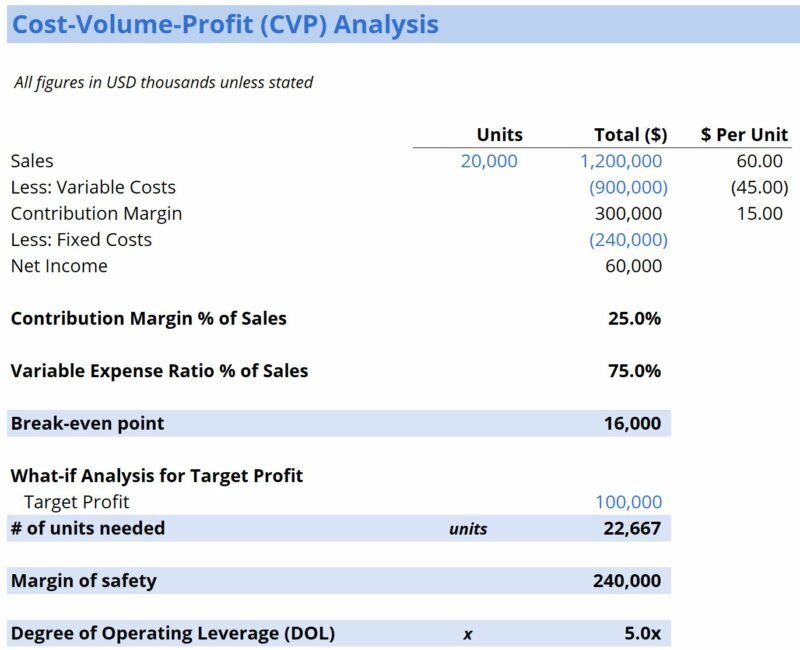
What is the break-even analysis formula, break-even analysis example, graphically representing the break-even point, free cost-volume-profit analysis template, download the free template, interpretation of break-even analysis, sensitivity analysis.
- Factors that Increase a Company’s Break-Even Point
How to reduce the break-even point
Additional resources, break even analysis.
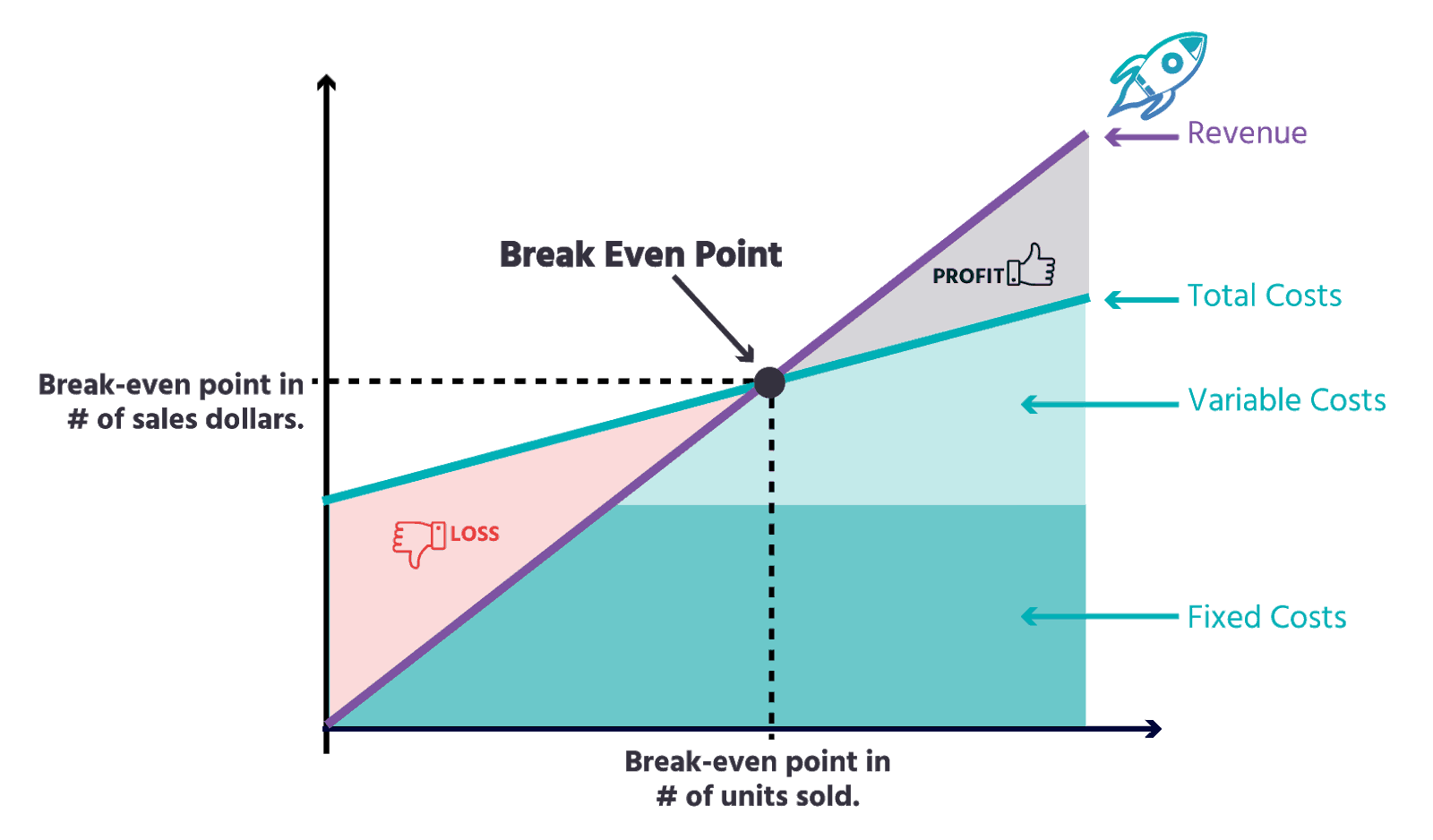
The point in which total cost and total revenue are equal
Break-even analysis in economics, business, and cost accounting refers to the point at which total costs and total revenue are equal. A break-even point analysis is used to determine the number of units or dollars of revenue needed to cover total costs ( fixed and variable costs ).
Key Highlights
- Break-even analysis refers to the point at which total costs and total revenue are equal.
- A break-even point analysis is used to determine the number of units or dollars of revenue needed to cover total costs.
- Break-even analysis is important to business owners and managers in determining how many units (or revenues) are needed to cover fixed and variable expenses of the business.
The formula for break-even analysis is as follows:
Break-Even Quantity = Fixed Costs / (Sales Price per Unit – Variable Cost Per Unit)
- Fixed Costs are costs that do not change with varying output (e.g., salary, rent, building machinery)
- Sales Price per Unit is the selling price per unit
- Variable Cost per Unit is the variable cost incurred to create a unit
It is also helpful to note that the sales price per unit minus variable cost per unit is the contribution margin per unit. For example, if a book’s selling price is $100 and its variable costs are $5 to make the book, $95 is the contribution margin per unit and contributes to offsetting the fixed costs.
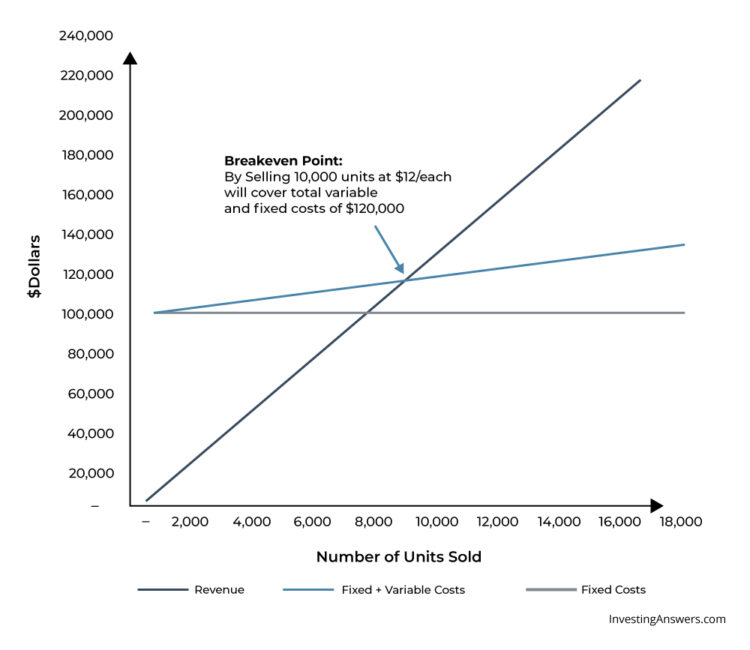
Colin is the managerial accountant in charge of Company A, which sells water bottles. He previously determined that the fixed costs of Company A consist of property taxes, a lease, and executive salaries, which add up to $100,000. The variable cost associated with producing one water bottle is $2 per unit. The water bottle is sold at a premium price of $12. To determine the break-even point of Company A’s premium water bottle:
Break Even Quantity = $100,000 / ($12 – $2) = 10,000
Therefore, given the fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price of the water bottles, Company A would need to sell 10,000 units of water bottles to break even.
For more information about variable costs, check out the following video:
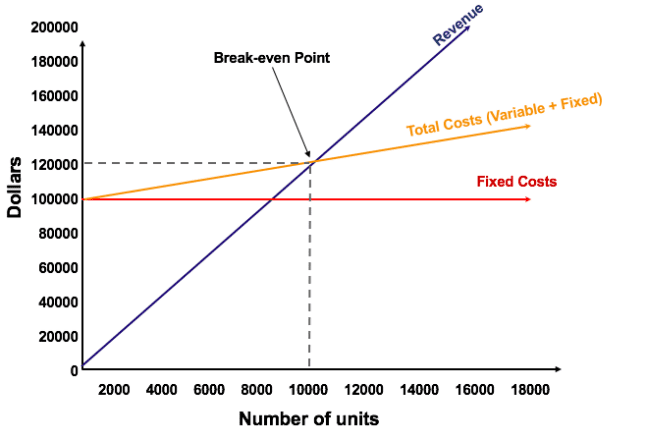
The graphical representation of unit sales and dollar sales needed to break even is referred to as the break-even chart or cost-volume-profit (CVP) graph. Below is the CVP graph of the example above:

Explanation:
- The number of units is on the X-axis (horizontal) and the dollar amount is on the Y-axis (vertical).
- The red line represents the total fixed costs of $100,000.
- The blue line represents revenue per unit sold. For example, selling 10,000 units would generate 10,000 x $12 = $120,000 in revenue.
- The yellow line represents total costs (fixed and variable costs). For example, if the company sells 0 units, then the company would incur $0 in variable costs but $100,000 in fixed costs for total costs of $100,000. If the company sells 10,000 units, the company would incur 10,000 x $2 = $20,000 in variable costs and $100,000 in fixed costs for total costs of $120,000.
- The break even point is at 10,000 units. At this point, revenue would be 10,000 x $12 = $120,000 and costs would be 10,000 x 2 = $20,000 in variable costs and $100,000 in fixed costs.
- When the number of units exceeds 10,000, the company would be making a profit on the units sold. Note that the blue revenue line is greater than the yellow total costs line after 10,000 units are produced. Likewise, if the number of units is below 10,000, the company would be incurring a loss. From 0-9,999 units, the total costs line is above the revenue line.
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now!
As illustrated in the graph above, the point at which total fixed and variable costs are equal to total revenues is known as the break-even point. At the break-even point, a business does not make a profit or loss. Therefore, the break-even point is often referred to as the “no-profit” or “no-loss point.”
The break-even analysis is important to business owners and managers in determining how many units (or revenues) are needed to cover fixed and variable expenses of the business.
Therefore, the concept of break-even point is as follows:
- Profit when Revenue > Total Variable Cost + Total Fixed Cost
- Break-even point when Revenue = Total Variable Cost + Total Fixed Cost
- Loss when Revenue < Total Variable Cost + Total Fixed Cost
Break-even analysis is often a component of sensitivity analysis and scenario analysis performed in financial modeling . Using Goal Seek in Excel, an analyst can backsolve how many units need to be sold, at what price, and at what cost to break even.
Factors that Increase a Company’s Break-Even Point
It is important to calculate a company’s break-even point in order to know the minimum target to cover production expenses. However, there are times when the break-even point increases or decreases, depending on certain of the following factors:
1. Increase in customer sales
When there is an increase in customer sales, it means that there is higher demand. A company then needs to produce more of its products to meet this new demand which, in turn, raises the break-even point in order to cover the extra expenses.
2. Increase in production costs
The hard part of running a business is when customer sales or product demand remains the same while the price of variable costs increases, such as the price of raw materials. When that happens, the break-even point also goes up because of the additional expense. Aside from production costs, other costs that may increase include rent for a warehouse, increases in salaries for employees, or higher utility rates.
3. Equipment repair
In cases where the production line falters, or a part of the assembly line breaks down, the break-even point increases since the target number of units is not produced within the desired time frame. Equipment failures also mean higher operational costs and, therefore, a higher break-even.
In order for a business to generate higher profits, the break-even point must be lowered. Here are common ways of reducing it:
1. Raise product prices
This is something that not all business owners want to do without hesitation, fearful that it may make them lose some customers.
2. Outsourcing
Profitability may be increased when a business opts for outsourcing , which can help reduce manufacturing costs when production volume increases.
Every company is in business to make some type of profit. However, understanding the break-even number of units is critical because it enables a company to determine the number of units it needs to sell to cover all of the expenses it’s accrued during the process of creating and selling goods or services.
Once the break-even number of units is determined, the company then knows what sales target it needs to set in order to generate profit and reach the company’s financial goals.
How the 3 Financial Statements are Linked
Cost Behavior Analysis
Analysis of Financial Statements
Shutdown Point
See all accounting resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- HR & Payroll

Break-Even Analysis Explained - Full Guide With Examples

Did you know that 30% of operating small businesses are losing money? Running your own business is trickier than it sounds. You have to plan ahead carefully to break-even or be profitable in the long run.
Building your own small business is one of the most exciting, challenging, and fun things you can do in this generation.
To start and sustain a small business it is important to know financial terms and metrics like net sales, income statement and most importantly break-even point .
Performing break-even analysis is a crucial activity for making important business decisions and to be profitable in business.
So how do you do it? That is what we will go through in this article. Some of the key takeaways for you when you finish this guide would be:
- Understand what break-even point is
- Know why it is important
- Learn how to calculate break-even point
- Know how to do break-even analysis
- Understand the limitations of break-even analysis
So, if you are tired of your nine-to-five and want to start your own business, or are already living your dream, read on.

What is Break-Even Point?
Small businesses that succeeds are the ones that focus on business planning to cross the break-even point, and turn profitable .
In a small business, a break-even point is a point at which total revenue equals total costs or expenses. At this point, there is no profit or loss — in other words, you 'break-even'.
Break-even as a term is used widely, from stock and options trading to corporate budgeting as a margin of safety measure.
On the other hand, break-even analysis lets you predict, or forecast your break-even point. This allows you to course your chart towards profitability.
Managers typically use break-even analysis to set a price to understand the economic impact of various price and sales volume calculations.
The total profit at the break-even point is zero. It is only possible for a small business to pass the break-even point when the dollar value of sales is greater than the fixed + variable cost per unit.
Every business must develop a break-even point calculation for their company. This will give visibility into the number of units to sell, or the sales revenue they need, to cover their variable and fixed costs.
Importance of Break-Even Analysis for Your Small Business
A business could be bringing in a lot of money; however, it could still be making a loss. Knowing the break-even point helps decide prices, set sales targets, and prepare a business plan.
The break-even point calculation is an essential tool to analyze critical profit drivers of your business, including sales volume, average production costs, and, as mentioned earlier, the average sales price. Using and understanding the break-even point, you can measure
- how profitable is your present product line
- how far sales drop before you start to make a loss
- how many units you need to sell before you make a profit
- how decreasing or increasing price and volume of product will affect profits
- how much of an increase in price or volume of sales you will need to meet the rise in fixed cost
How to Calculate Break-Even Point
There are multiple ways to calculate your break-even point.
Calculate Break-even Point based on Units
One way to calculate the break-even point is to determine the number of units to be produced for transitioning from loss to profit.
For this method, simply use the formula below:
Break-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs ÷ (Revenue per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
Fixed costs are those that do not change no matter how many units are sold. Don't worry, we will explain with examples below. Revenue is the income, or dollars made by selling one unit.
Variable costs include cost of goods sold, or the acquisition cost. This may include the purchase cost and other additional costs like labor and freight costs.
Calculate Break-Even Point by Sales Dollar - Contribution Margin Method
Divide the fixed costs by the contribution margin. The contribution margin is determined by subtracting the variable costs from the price of a product. This amount is then used to cover the fixed costs.
Break-Even Point (sales dollars) = Fixed Costs ÷ Contribution Margin
Contribution Margin = Price of Product – Variable Costs
Let’s take a deeper look at the some common terms we have encountered so far:
- Fixed costs: Fixed costs are not affected by the number of items sold, such as rent paid for storefronts or production facilities, office furniture, computer units, and software. Fixed costs also include payment for services like design, marketing, public relations, and advertising.
- Contribution margin: Is calculated by subtracting the unit variable costs from its selling price. So if you’re selling a unit for $100 and the cost of materials is $30, then the contribution margin is $70. This $70 is then used to cover the fixed costs, and if there is any money left after that, it’s your net profit.
- Contribution margin ratio: is calculated by dividing your fixed costs from your contribution margin. It is expressed as a percentage. Using the contribution margin, you can determine what you need to do to break-even, like cutting fixed costs or raising your prices.
- Profit earned following your break-even: When your sales equal your fixed and variable costs, you have reached the break-even point. At this point, the company will report a net profit or loss of $0. The sales beyond this point contribute to your net profit.
Small Business Example for Calculating Break-even Point
To show how break-even works, let’s take the hypothetical example of a high-end dressmaker. Let's assume she must incur a fixed cost of $45,000 to produce and sell a dress.
These costs might cover the software and materials needed to design the dress and be sure it meets the requirement of the brand, the fee paid to a designer to design the look and feel of the dress, and the development of promotional materials used to advertise the dress.
These costs are fixed as they do not change per the number of dresses sold.
The variable costs would include the materials used to make each dress — embellishment’s for $30, the fabric for the body for $20, inner lining for $10 — and the labor required to assemble the dress, which amounted to one and a half hours for a worker earning $50 per hour.
Thus, the unit variable costs to make a single dress is $110 ($60 in materials and $50 in labor). If she sells the dress for $150, she’ll make a unit margin of $40.
Given the $40 unit margin she’ll receive for each dress sold, she will cover her $45,500 total fixed cost will be covered if she sells:
Break-Even Point (Units) = $45,000 ÷ $40 = 1,125 Units
You can see per the formula , on the right-hand side, that the Break-even is 1,125 dresses or units
In other words, if this dressmaker sells 1,125 units of this particular dress, then she will fully recover the $45,000 in fixed costs she invested in production and selling. If she sells fewer than 1,125 units, she will lose money. And if she sells more than 1,125 units, she will turn a profit. That’s the break-even point.

What if we change the price?
Suppose our dressmaker is worried about the current demand for dresses and has concerns about her firm’s sales and marketing capabilities, calling into question her ability to sell 1,125 units at a price of $150. What would be the effect of increasing the price to $200?
This would increase the unit margin to $90.Then the number of units to be sold would decline to 500 units. With this information, the dressmaker could assess whether she was better off trying to sell 1,125 dresses at $150 or 500 dresses at $200, and priced accordingly.
What if we want to make an investment and increase the fixed costs?
Break-even analysis also can be used to assess how sales volume would need to change to justify other potential investments. For instance, consider the possibility of keeping the price at $150, but having a celebrity endorse the dress (think Madonna!) for a fee of $20,000.
This would be worthwhile if the dressmaker believed that the endorsement would result in total sales of $66,000 (the original fixed cost plus the $20,000 for Ms. Madonna).
With the Fixed Costs at $66,000 we see, it would only be worthwhile if the dressmaker believed that the endorsement would result in total sales of 1,650 units.
In other words, if the endorsement led to incremental sales of 525 dress units, the endorsement would break-even. If it led to incremental sales of greater than 525 dresses, it would increase profits.
What if we change the variable cost of producing a good?
Break-even also can be used to examine the impact of a potential change to the variable cost of producing a good.
Imagine that our dressmaker could switch from using a rather plain $20 fabric for the dress to a higher-end $40 fabric, thereby increasing the variable cost of the dress from $110 to $130 and decreasing the unit margin from $40 to $20. How much would your sales need to increase to compensate for the extra cost?
Suppose the Variable Cost is $130 (and the Fixed Cost is $45,000 – our dressmaker can’t afford to have nice fabric plus get Ms. Madonna). It would make better sense to switch to the nicer fabric if the dressmaker thought it would result in sales of 2,250 units, an additional 1125 dresses, which is double the number of initial sale numbers.
You likely aren’t a dressmaker or able to get a celebrity endorsement from Ms. Madonna, but you can use break-even analysis to understand how the various changes of your product, from revenue, costs, sales, impact your small business’s profitability .
What Are the Benefits of Doing a Break-even Analysis?
Smart Pricing : Finding your break-even point will help you price your products better. A lot of effort and understanding goes into effective pricing, but knowing how it will affect your profitability is just as important. You need to make sure you can pay all your bills.
Cover Fixed Costs : When most people think about pricing, they think about how much their product costs to create. Those are considered variable costs. You will still need to cover your fixed costs like insurance or web development fees. Doing a break-even analysis helps you do that.
Avoid Missing Expenses : When you do a break-even analysis, you have to lay out all your financial commitments to figure out your break-even point. It’s easy to forget about expenses when you’re thinking through a business idea. This will limit the number of surprises down the road.

Setting Revenue Targets : After completing a break-even analysis, you know exactly how much you need to sell to be profitable. This will help you set better sales goals for you and your team.
Decision Making : Usually, business decisions are based on emotion. How you feel is important, but it’s not enough. Successful entrepreneurs make their decisions based on facts. It will be a lot easier to decide when you’ve put in the work and have useful data in front of you.
Manage Financial Strain : Doing a break-even analysis will help you avoid failures and limit the financial toll that bad decisions can have on your business. Instead, you can be realistic about the potential outcomes by being aware of the risks and knowing when to avoid a business idea.
Business Funding : For any funding or investment, a break-even analysis is a key component of any business plan. You have to prove your plan is viable. It’s usually a requirement if you want to take on investors or other debt to fund your business.
When to Use Break-even Analysis
Starting a new business.
If you’re thinking about a small online business or e-commerce, a break-even analysis is a must. Not only does it help you decide if your business idea is viable, but it makes you research and be realistic about costs, as well as think through your pricing strategy.
Creating a new product
Especially for a small business, you should still do a break-even analysis before starting or adding on a new product in case that product is going to add to your expenses. There will be a need to work out the variable costs related to your new product and set prices before you start selling.
Adding a new sales channel
If you add a new sales channel, your costs will change. Let's say you have been selling online, and you’re thinking about opening an offline store; you’ll want to make sure you at least break-even with the brick and mortar costs added in. Adding additional marketing channels or expanding social media spends usually increases daily expenses. These costs need to be part of your break-even analysis.
Changing the business model
Let's say you are thinking about changing your business model; for example, switching from buying inventory to doing drop shipping or vice-versa, you should do a break-even analysis. Your costs might vary significantly, and this will help you figure out if your prices need to change too.
Limitations of Break-even Analysis
- The Break-even analysis focuses mostly on the supply-side (i.e., costs only) analysis. It doesn't tell us what sales are actually likely to be for the product at various prices.
- It assumes that fixed costs are constant. However, an increase in the scale of production is likely to lead to an increase in fixed costs.
- It assumes average variable costs are constant per unit of output, per the range of the number of sales
- It assumes that the number of goods produced is equal to the number of goods sold. It believes that there is no change in the number of goods held in inventory at the beginning of the period and the number of goods held in inventory at the end of the period
- In multi-product companies, the relative proportions of each product sold and produced are fixed or constant.
So that's a wrap. Hope you found this article interesting and informative. Feel free to subscribe to our blog to get updates on awesome new content we publish for small business owners.
Key Takeaways
Break-even analysis is infinitely valuable as it sets the framework for pricing structures, operations, hiring employees, and obtaining future financial support.
- You can identify how much, or how many, you have to sell to be profitable.
- Identify costs inside your business that should be alleviated or eliminated.
Remember, any break-even analysis is only as strong as its underlying assumptions.
Like many forecasting metrics, break-even point is subject to it's limitations; however it can be a powerful and simple tool to provide a small business owner with an idea of what their sales need to be in order to start being profitable as quickly as possible.
Lastly, please understand that break-even analysis is not a predictor of demand .
If you go to market with the wrong product or the wrong price, it may be tough to ever hit the break-even point. To avoid this, make sure you have done the groundwork before setting up your business.
Head over to our small business guide on setting up a new business if you want to know more.
Want to calculate break even point quickly? Use our handy break-even point calculator.
Hey! Try Deskera Now!
Everything to Run Your Business
Get Accounting, CRM & Payroll in one integrated package with Deskera All-in-One .
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Break-Even Analysis?
- How It Works
Calculating Contribution Margin and BEPs
Who calculates beps, why break-even analysis matters.
- Break-Even Analysis FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Investing Basics
Break-Even Analysis: Formula and Calculation
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Break-even analysis compares income from sales to the fixed costs of doing business. The five components of break-even analysis are fixed costs, variable costs, revenue, contribution margin, and break-even point (BEP).
When companies calculate the BEP, they identify the amount of sales required to cover all fixed costs before profit generation can begin. The break-even point formula can determine the BEP in product units or sales dollars.
Key Takeaways:
- Using the break-even point formula, businesses can determine how many units or dollars of sales cover the fixed and variable production costs.
- The break-even point (BEP) is considered a measure of the margin of safety.
- Break-even analysis is used for different reasons, from stock and options trading to corporate budgeting for various projects.
- Once a company meets the break-even point, subsequent sales will exceed expenses and profits can be generated.
Investopedia / Paige McLaughlin
Understanding Break-Even Analysis
Break-even analysis looks at fixed costs relative to the profit earned by each additional unit produced and sold.
A firm with lower fixed costs will have a lower break-even point of sale and $0 of fixed costs will automatically have broken even with the sale of the first product, assuming variable costs do not exceed sales revenue.
Fixed costs remain the same regardless of how many units are sold. Examples of fixed and variable costs include:
| Rent | Raw materials |
| Taxes | Production supplies |
| Insurance | Utilities |
| Wages or salaries | Packaging |
Break-Even Point Formula
Break-even analysis involves a calculation of the break-even point (BEP) . The break-even point formula divides the total fixed production costs by the price per individual unit less the variable cost per unit.
BEP = Total Fixed Costs / (Price Per Unit - Variable Cost Per Unit)
Contribution Margin
A product's contribution margin is the difference between the selling price of the product and its variable costs. So, relative to the BEP formula above, you could also say that the BEP = Total Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin.
Contribution Margin = Item Price - Variable Cost Per Unit
For example, if an item sells for $100, with fixed costs of $25 per unit, and variable costs of $60 per unit, the contribution margin is:
$40 = ($100 - $60)
This $40 reflects the revenue collected to cover the remaining fixed costs, which are excluded when figuring the contribution margin.
Break-Even Point in Units
To find the total units required to break even, divide the total fixed costs by the unit contribution margin.
BEP (Units) = Total Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin
Assume total fixed costs are $20,000. With a contribution margin of $40 (shown above), the break-even point is:
500 units = $20,000 divided by $40.
Upon selling 500 units, the payment of all fixed costs is complete, and the company will report a net profit or loss of $0.
Break-Even Point in Dollars
To calculate the break-even point in sales dollars, you'll need to divide the total fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio. So, first, you must determine the ratio:
Contribution Margin Ratio = Contribution Margin Per Unit / Item Price
Continuing with the example above, the contribution margin ratio is:
40% = ($40 / $100) x 100 to convert to a percentage
Now, as noted just above, to calculate the BEP in dollars, divide total fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio.
BEP (Sales Dollars) = Total Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin Ratio
$50,000 = $20,000 / 40%
In accounting, the margin of safety is the difference between actual sales and break-even sales. Managers utilize the margin of safety to know how much sales can decrease before the company or project becomes unprofitable.
- Entrepreneurs
- Financial Analysts
- Stock and Option Traders
- Government Agencies
Although investors may not be interested in an individual company's break-even analysis of production, they may use the calculation to determine at what price they will break even on a trade or investment. The calculation is useful when trading in or creating a strategy to buy options or a fixed-income security product.
- Pricing : With a clear understanding of their cost structure and a break-even numbers, companies can set prices for their products that cover their fixed and variable costs and provide a reasonable profit margin.
- Decision-Making : When it comes to new products and services, operational expansion, or increased production, businesses can chart their profit to sales volume and use break-even analysis to help them make informed decisions about those activities.
- Cost Reduction : Break-even analysis helps businesses to pinpoint areas where they can reduce costs to increase profitability.
- Performance Metric: Break-even analysis is a financial performance tool that helps businesses ascertain where they stand in achieving their goals.
What Are Some Limitations of Break-Even Analysis?
Break-even analysis assumes that the fixed and variable costs remain constant over time. However, costs may change due to factors such as inflation, changes in technology, and changes in market conditions. It also assumes that there is a linear relationship between costs and production. Break-even analysis ignores external factors such as competition, market demand, and changes in consumer preferences.
What Are the Components of Break-Even Analysis?
There are five components of break-even analysis: fixed costs, variable costs, revenue, contribution margin, and the break-even point (BEP).
Why Is the Contribution Margin Important in Break-Even Analysis?
The contribution margin represents the revenue required to cover a business' fixed costs and contribute to its profit. With the contribution margin calculation, a business can determine the break-even point and where it can begin earning a profit.
How Do Businesses Use the Break-Even Point in Break-Even Analysis?
The break-even point (BEP) helps businesses with pricing decisions, sales forecasting, cost management, and growth strategies. A business would not use break-even analysis to measure its repayment of debt or how long that repayment will take.
Break-even analysis, or the comparison of sales to fixed costs, is a tool used by businesses and stock and option traders. It is essential in determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even. Beyond the break-even point, it's all profit. That is, sales will exceed expenses.
Break-even analysis helps businesses choose pricing strategies, and manage costs and operations. In stock and options trading, break-even analysis helps determine the minimum price movements required to cover trading costs and make a profit. Traders can use break-even analysis to set realistic profit targets, manage risk, and make informed trading decisions.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Break-Even Point ."
Professor Rosemary Nurre, College of San Mateo. " Accounting 131: Chapter 6, Cost-Volume-Profit Relationships ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/BreakevenPoint-b6ed6dc69b2742358a937e280a3fc103.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
The Superfast Guide to Break-Even Analysis [PPT Templates Included] [Free PDF Attached]
Lakshya Khurana
In a business, the first major breakthrough is breaking-even. This means that you will make enough money to cover the capital you have invested. This, however, is not a matter of chance. Every business needs to plan its finances to reach the break-even point as it will ultimately lead to profits. Break-even analysis is used to conduct this planning.
If you're looking to do this analysis, this guide is for you. We'll cover everything you need to know, including what break-even analysis is, how it's used, and what factors are to be considered when conducting your own analysis. In addition, we've included a few break-even analysis templates to help you get started. Let’s begin by learning more about this tool.
What is Break-Even Analysis?
Break-even analysis is a tool used to calculate the point at which a company's revenues equal its expenses. This point is known as the Break-Even Point (BEP) . It is used to assess whether a business is likely to be profitable.
There are two main types of break-even analysis: Graphical and chart.
Graphical break-even analysis is a visual way to calculate the break-even point. This method uses a graph, which plots total revenue and total cost. The BEP is the point at which total revenue and total cost intersect.
The break-even chart, however, is a table that shows the break-even point in terms of units sold and currency. This method is more precise than graphical break-even analysis, but it can be more difficult to understand.
Taking note of the graphical method, let us understand the steps you need to take to conduct your own break-even analysis through PowerPoint.
How to Conduct Break-Even Analysis?
There are a number of factors you should consider when conducting a break-even analysis. These are:
- Sale price: The price at which a product or service is sold.
- Unit cost: The cost of producing one unit of a product or service.
- Fixed costs: The costs that remain constant regardless of the level of activity or sales. Examples include rent, insurance, and salaries.
- Variable costs : The costs that vary in relation to the level of activity or sales. Examples include raw materials and commission.
- Break-even point: The point at which revenue equals costs.
With these parameters in mind, let us look at the steps that will help you conduct a graphical analysis.
Step 1: Insert Line Chart into the Slide
The graph will be made of a line chart. You can select it using
Insert > Chart > Line Chart > OK.
You will find an Excel sheet dialog box that has appeared on top of the graph.
Step 2: Add the Values of the Variables in the Excel Sheet
Add the values of the fixed cost, variable cost, and revenue into the Excel sheet.
Step 3: Check the Results and Customize the Graph
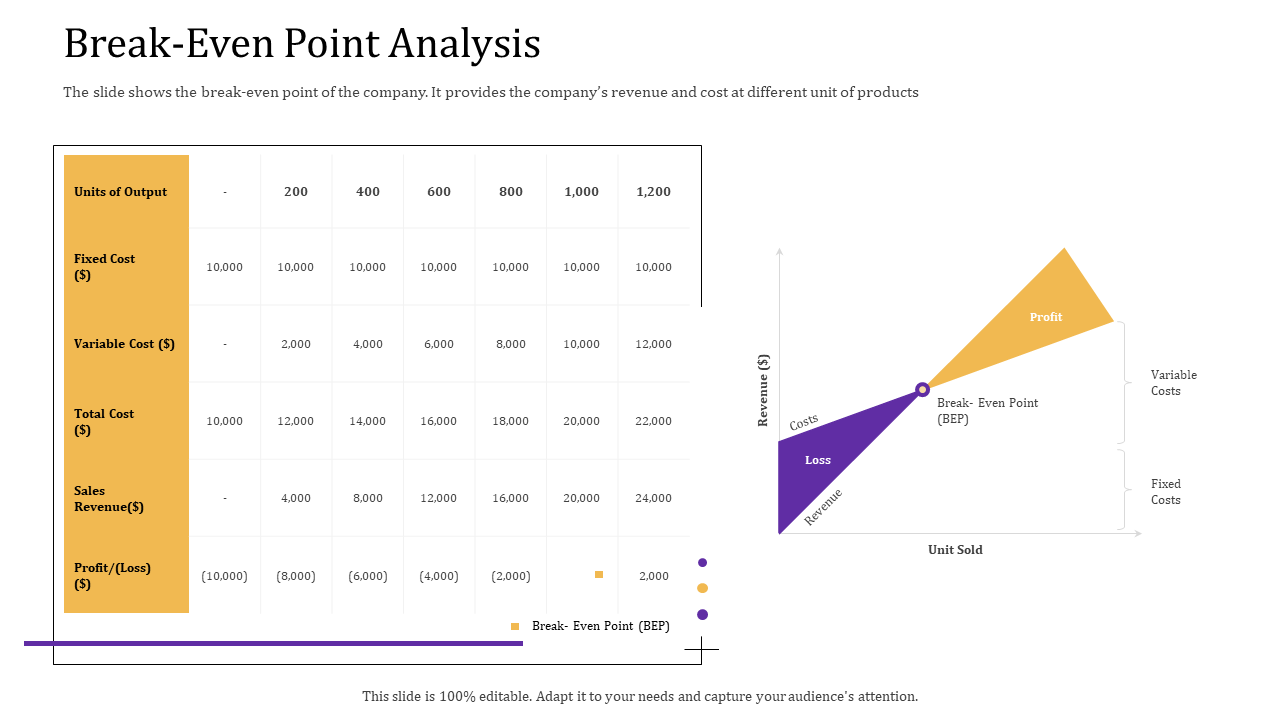
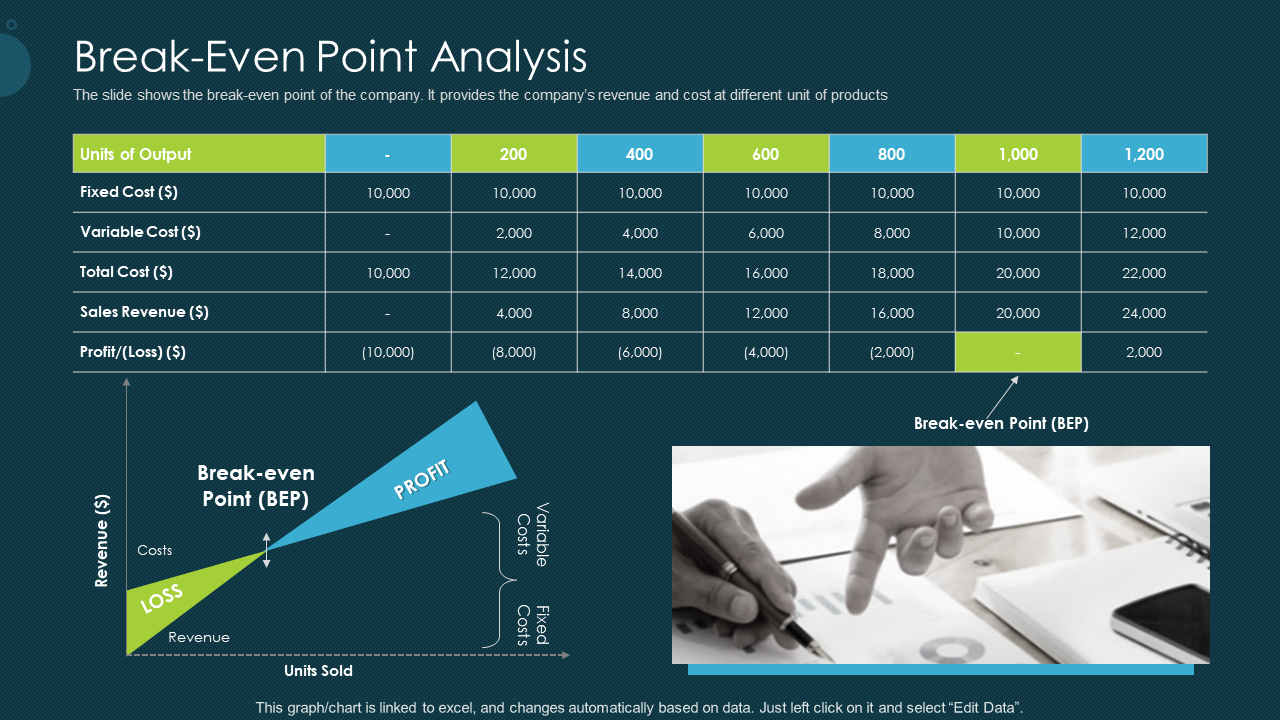
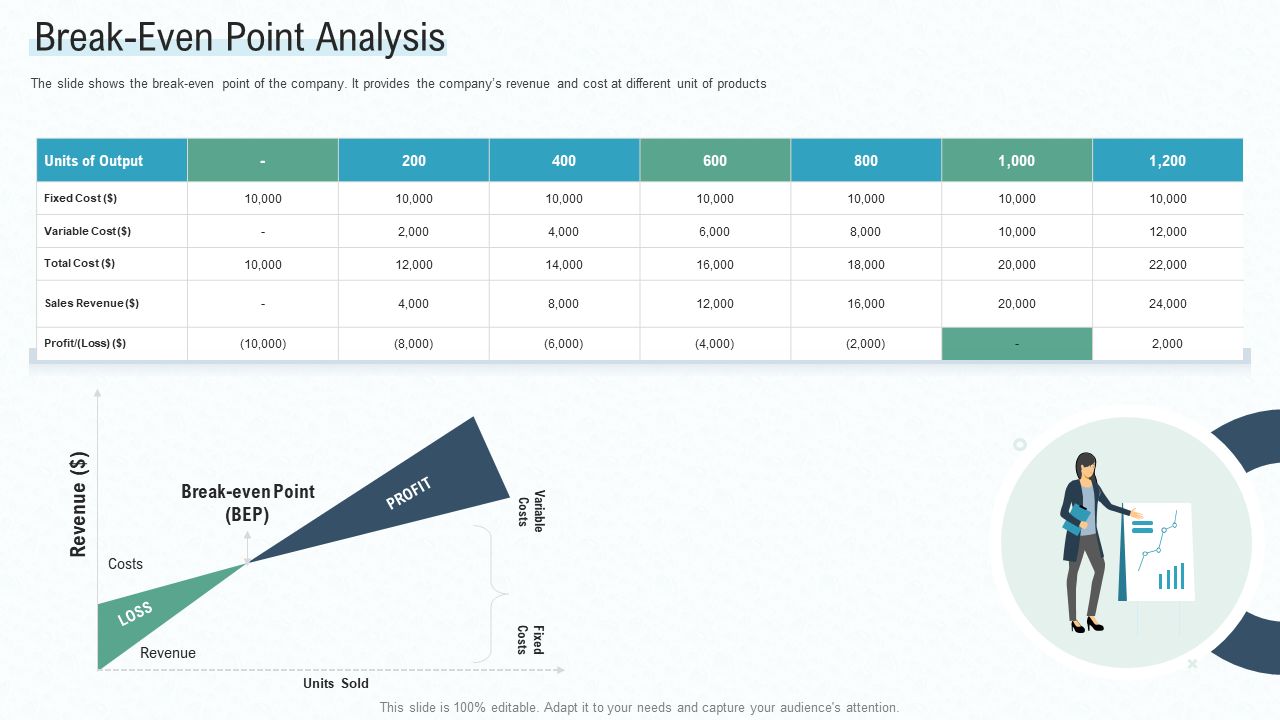
You will see that the intersection of total cost and revenue is the break-even point. The final result should look like this:
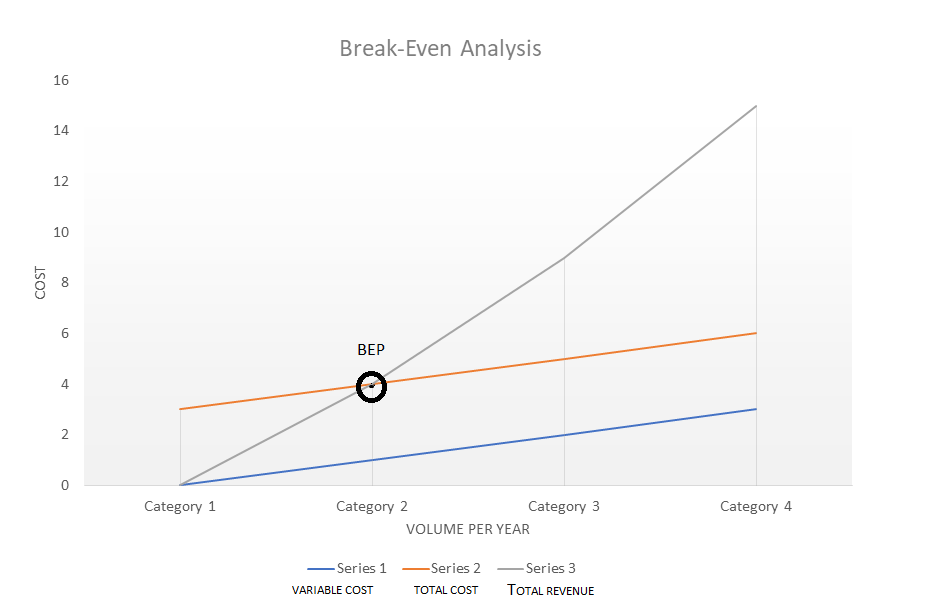
To go even deeper into the process, we present a full-fledged break-even analysis graph with notations:
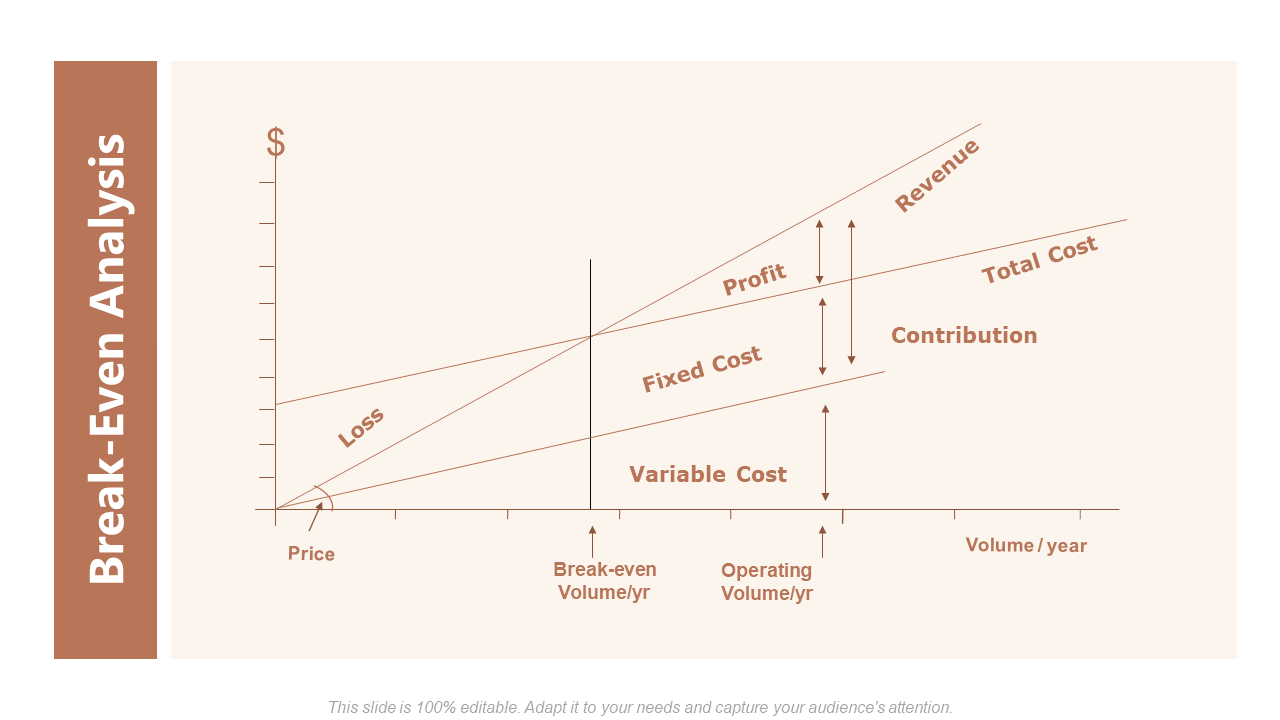
Download this template
With these easy steps and a simple line chart, you can create a graph based on your own data. In this format, the data is quite useful.
Applications of Break-Even Analysis
There are numerous applications of break-even analysis. This is done by estimating the fixed and variable costs associated with the business and then calculating the break-even point. Some common applications include:
- Determining the desired sales volume needed to break even
- Determining the price of a product or service
- Predicting the financial impact of changes in variable costs, fixed costs, and selling price
- Assessing the financial viability of a business idea
- Understanding how changes in costs or prices will impact profitability
Break-even analysis can ensure that the company’s profitability heads North.
Advantages of Break-Even Analysis
There are several advantages of break-even analysis:
First, it can help owners and managers understand the relationship between revenue and costs. This information can be used to make decisions about pricing, production levels, and other factors that affect the bottom line.
Second, break-even analysis can help owners and managers predict how changes in costs will affect the break-even point. This information can be used to make decisions about how to respond to changes in the business environment.
Third, break-even analysis can help owners and managers compare the financial performance of different businesses. This insight can be used to make decisions about which business to invest in or expand.
Finally, break-even analysis can help owners and managers monitor the financial performance of their business over time.
Despite its many advantages, break-even analysis is not without its cons.
Disadvantages of Break-Even Analysis
One of the main disadvantages of break-even analysis is that it can be quite difficult to estimate all costs. Hence, the break-even point could be overestimated or underestimated, leading to losses or missed opportunities.
Another downside of break-even analysis is that it only looks at the financials of a product or project. Factors like customer demand or satisfaction are not accounted for. This can create a false sense of security among decision-makers who may think that a product is more successful than it actually is.
Finally, break-even analysis can be quite simplistic and does not always provide the most accurate picture of a business's financial health. This tool is only one part of the decision-making process and can never be used as the sole criteria to value a business.
With such complete knowledge of break-even analysis, let us learn how to best communicate the analysis and its results across the rank and file of your business.
Editable Break-Even Analysis Templates to Make Better Financial Decisions
Without the worry of choosing the design, font, or size, selecting one of our pre-designed break-even analysis templates can be the best gift for this analysis. Raw data from such a financial study can be difficult to understand, so it is essential that we use either a graph or a chart to present it.
Let’s take a look at the ten break-even analysis templates we have curated.
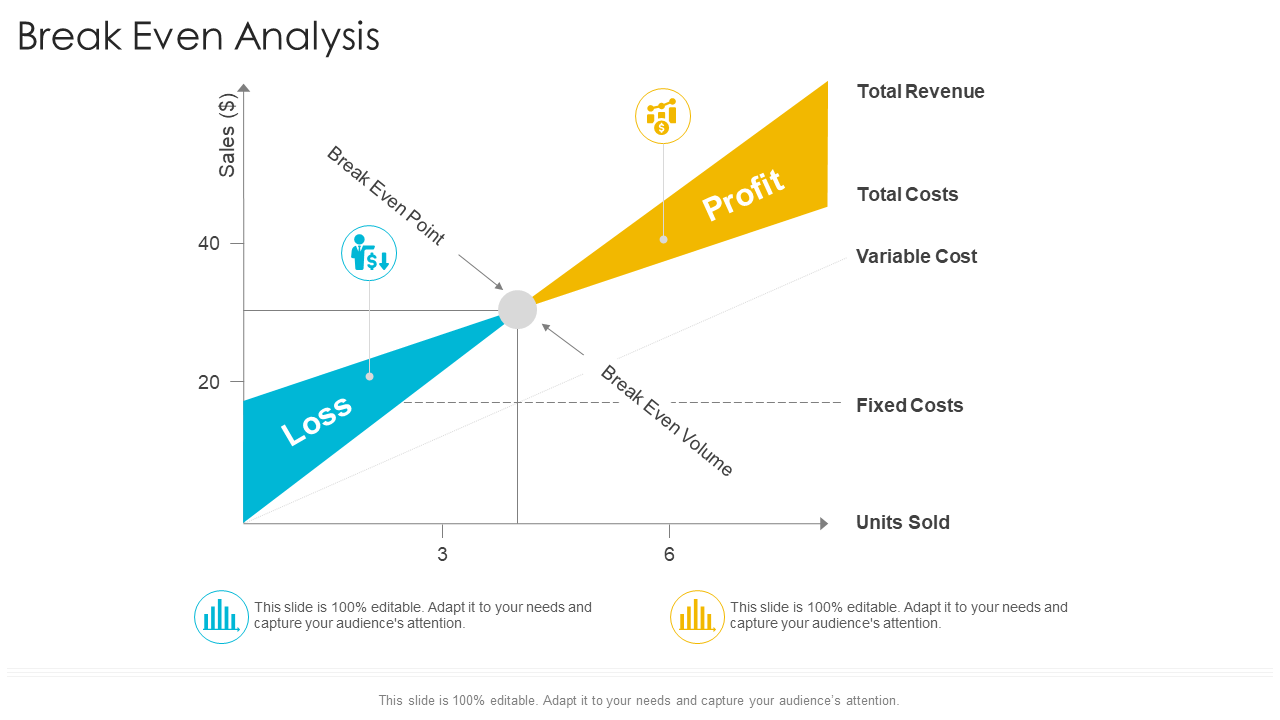
Template 1: Break-Even Analysis PowerPoint Presentation
This PPT layout showcases a graph to represent the terms necessary to understand break-even analysis. It presents costs, revenue, profit and loss, contribution, etc. Use this PowerPoint slide to present and explain your company’s financial data and its significance. Download it now.
Download this template
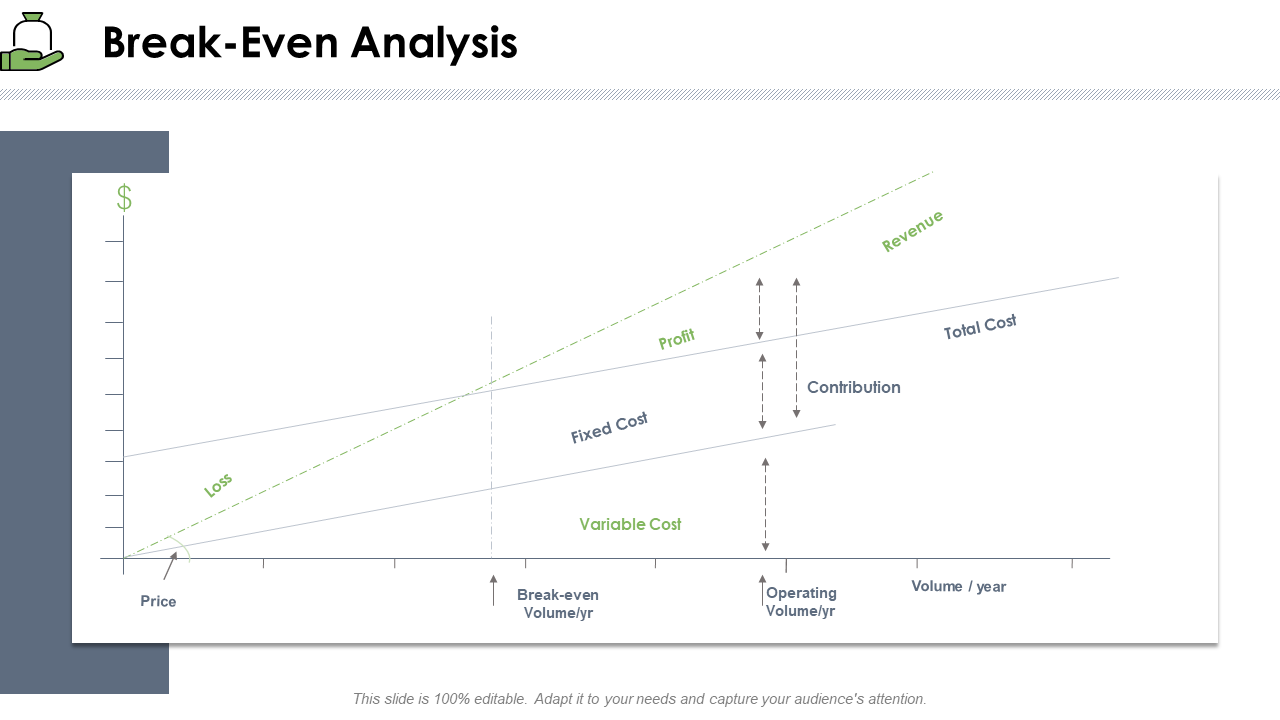
Template 2: Break-Even Analysis Startup Company Strategy PPT
This PowerPoint theme focuses on the profit and loss areas that surround the BEP. It allows your company to focus on the sales volume needed to not only break even but start earning profits. Incorporate it now.
Grab this template
Template 3: Break-Even Analysis New Service Initiation Plan PPT
This PPT preset presents your sales data in a way to inspire the employees to meet your goals. The color scheme allows the company to visualize its short and long terms goals, in terms of profitability. Use it right away!
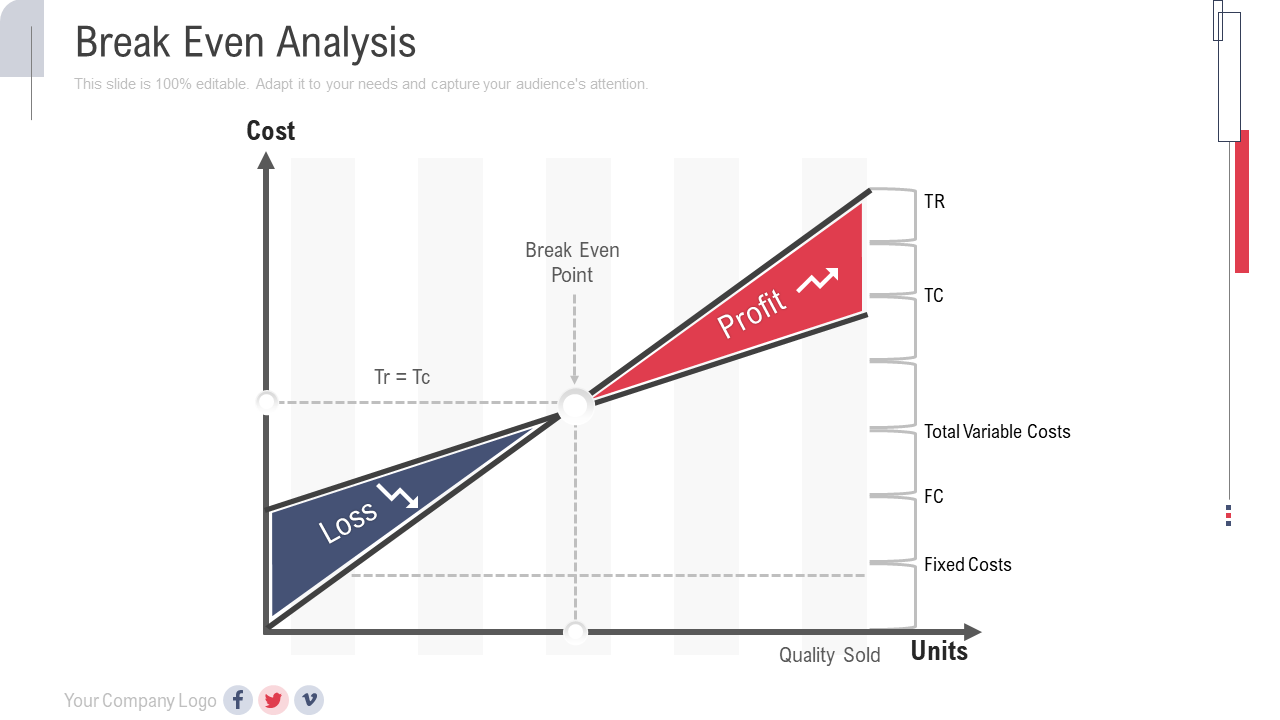
Template 4: Break-Even Analysis PowerPoint Slide
This PowerPoint slide presents a ballpark view of the sales goal of the company. It provides an emphasis on the BEP, hence, it is suitable for a start-up. The Tr and Tc represent the total revenue and total cost. Assimilate it now.
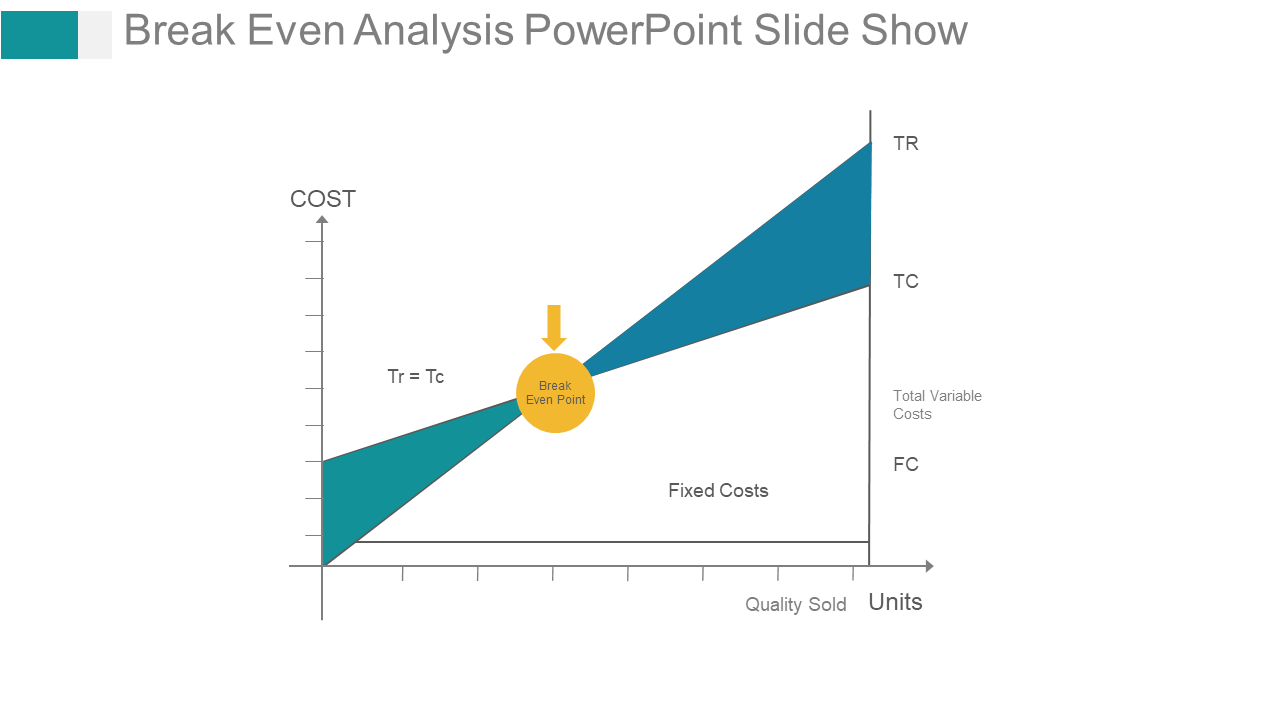
Template 5: Break-Even Point Chart
With the help of this PPT set, you can graphically present the logistics of your operations. It also allows extra space to note down any significant conclusions made from the graph. Incorporate it now.
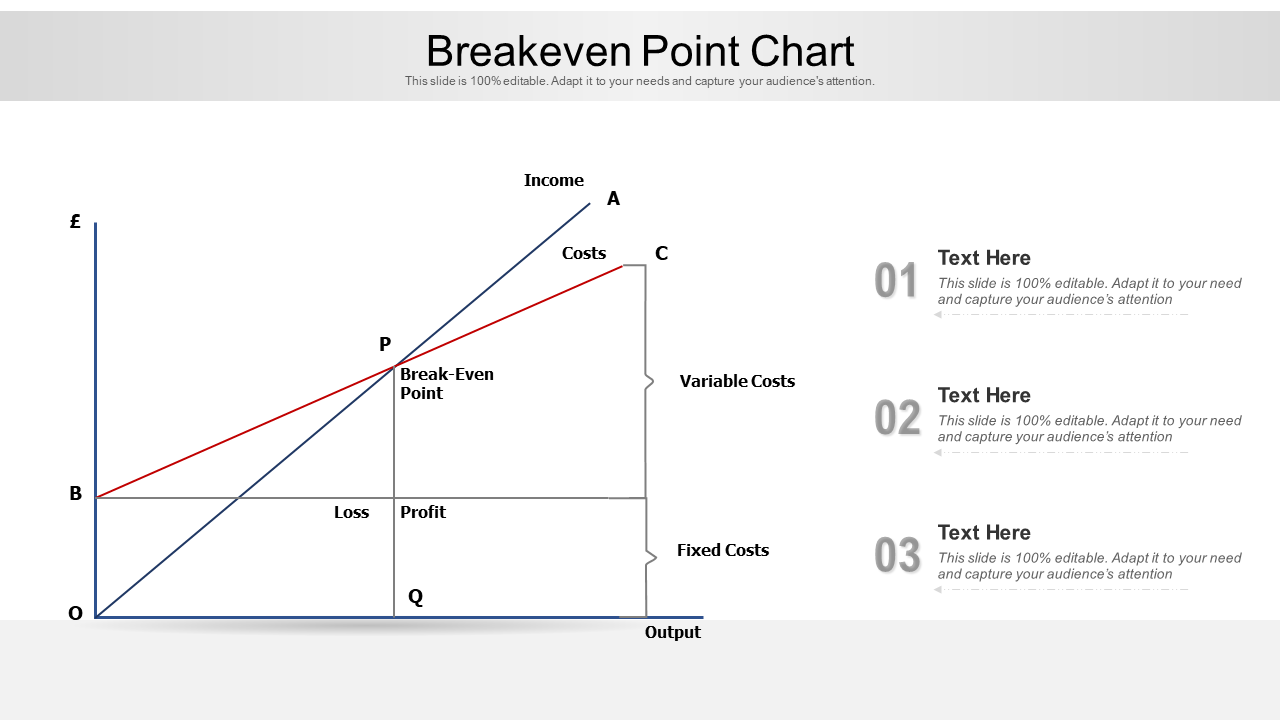
Template 6: Break-Even Analysis With Fixed and Variable Cost
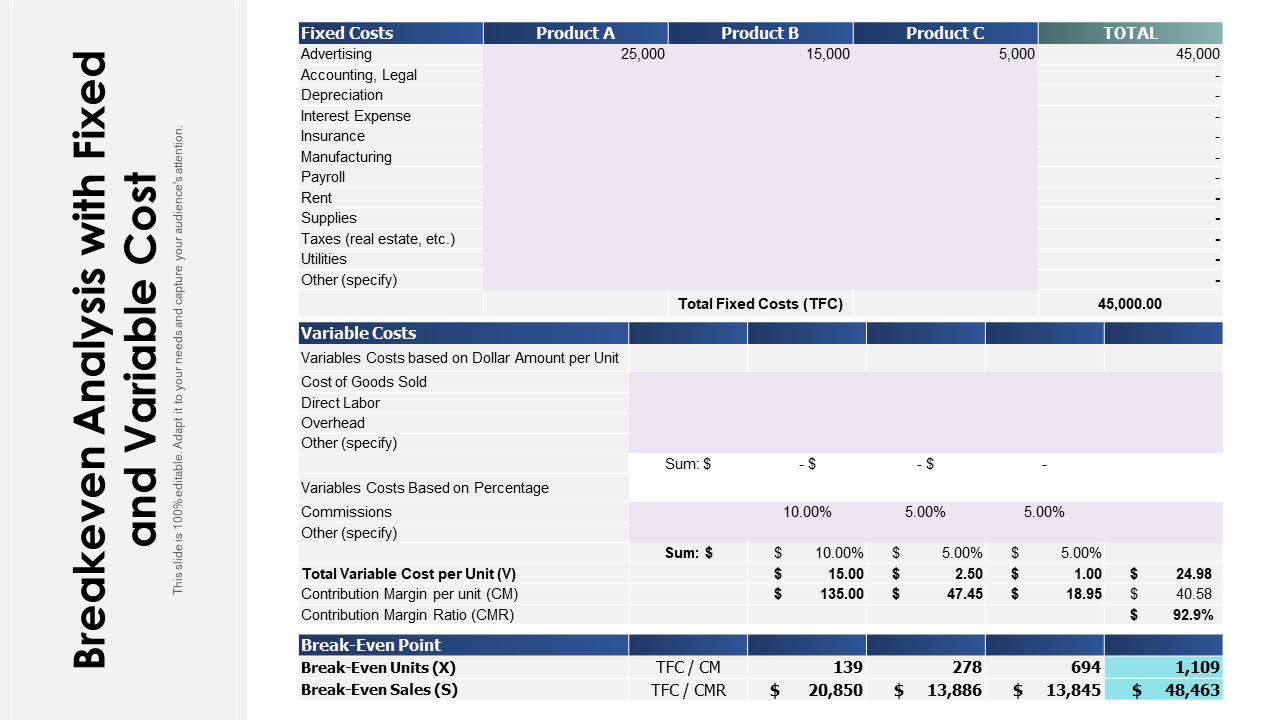
This PowerPoint bundle presents the second form of the break-even analysis, the chart. It allows for a more detailed understanding of the cost and revenue of the operations by splitting up the variables into individual categories. This includes advertising, rent, payroll, etc. Download it now.
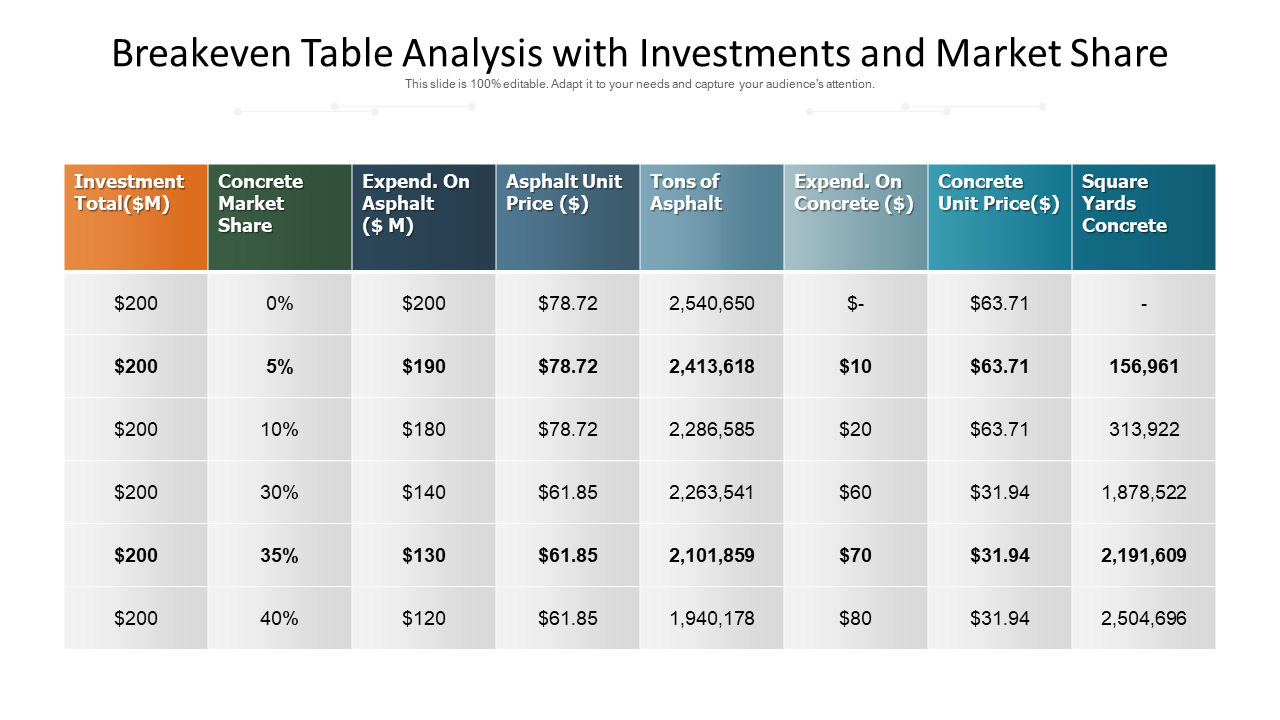
Template 7: Break-Even Table Analysis With Investments and Market Share
This PPT layout presents a tabular analysis. The table showcases variables such as investment total, concrete market share, expense, and market share. The columns are color-coded and the significant values are given in BOLD to allow better comprehension of data. Get it now.
Template 8: Break-Even Point Analysis Loan Stock Financing PPT
Utilize this PowerPoint bundle to help finance your firm. With both the chart as well as the graph, you will be able to make a detailed yet easy-to-understand pitch to your investors. Incorporate it now.
Template 9: Funding Pre-Seed Capital Break-Even Point Analysis PPT
Use this PPT theme to attract capital for your start-up. It allows angel investors to understand the cost details and sales goals of your firm. Download it now and present a clear view of the horizons of your business.
Template 10: Break-Even Point Analysis Early Stage Funding PPT
With the help of this PowerPoint deck, you can pitch your corporation’s financial plans to gain early-stage investment. Utilize this slide to break down the costs and expected sales forecast for your operation. Leave nothing to chance and get this PPT template now.
Use our break-even analysis templates to conduct your own analysis. Simply input your sales price, unit cost, and fixed costs, and the break-even point calculator will do the rest!
P.S: Handling the finances of the business means maintaining a proper budget. Check out this guide to help your company’s employees keep finances in order. All the best templates are included!
Download the free Break-Even Analysis Templates PDF .
Related posts:
- Best Financial Asset Management Templates To Help You Manage Your Finances Precisely!
- 25 Best PowerPoint Slides for the Financial Services Industry to Win Clients
- 25 Best Banking and Finance PowerPoint Templates For Financial Experts
- An All-Encompassing Guide to Business Management (Best Templates Included)
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

What Is the BCG Matrix and Why Do You Need It (Best Templates Included)?

Top 10 Pricing Strategy PPT Templates to Make Sure the Price Is Right
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

--> Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

--> Sales funnel results presentation layouts
--> 3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

--> Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Future plan powerpoint template slide

--> Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

--> Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

--> Agenda powerpoint slide show

--> Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

--> Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

--> Meet our team representing in circular format

Break-Even Analysis

What Is Break Even Analysis?
Break even analysis is a calculation of the quantity sold which generates enough revenues to equal expenses. In securities trading, the meaning of break even analysis is the point at which gains are equal to losses.
Another definition of break even analysis is the examination and calculation of the margin of safety that’s based on a company’s revenue – as well as the related costs of running the organization.
How Is Break Even Analysis Used?
A break-even analysis helps business owners determine when they'll begin to turn a profit, which can help them better price their products. Usually, management uses this metric to help guide strategic decisions to grow/maintain the business.
Break-Even Analysis vs. Break-Even Point
Break-even analysis uses a calculation called the break even point (BEP) which provides a dynamic overview of the relationships among revenues, costs, and profits. More specifically, it looks at a company’s fixed costs in relation to profits that are earned from each unit sold.
Break Even Analysis Varies Among Industries
Typical variable and fixed costs differ widely among industries. This is why comparison of break-even points is generally most meaningful among companies within the same industry. The definition of a 'high' or 'low' break-even point should be made within this context.
Break Even Analysis Formula

Fixed Costs
Fixed costs do not change with the quantity of output. In other words, they’re not affected by sales. Examples include rent and insurance premiums, as well as fees paid for marketing or loan payments.
Variable Costs
Variable costs change depending on the amount of output. Examples include raw materials and labor that are directly involved in a company's manufacturing process.
Contribution Margin
The contribution margin is the amount remaining (i.e. the excess) after total variable costs are deducted from a product’s selling price.
Say that an item sells for $5,000 and your total variable costs are $3,000 per unit. Your contribution margin would be $2,000 (after subtracting $3,000 from $5,000). This is the revenue that’ll be used to cover your fixed costs – which isn’t considered when calculating the contribution margin.
Earned Profit
Earned profit is the amount a business earns after taking into account all expenses. You can calculate this number by subtracting the costs that go into your company’s operations from your sales.
Example of Break Even Analysis
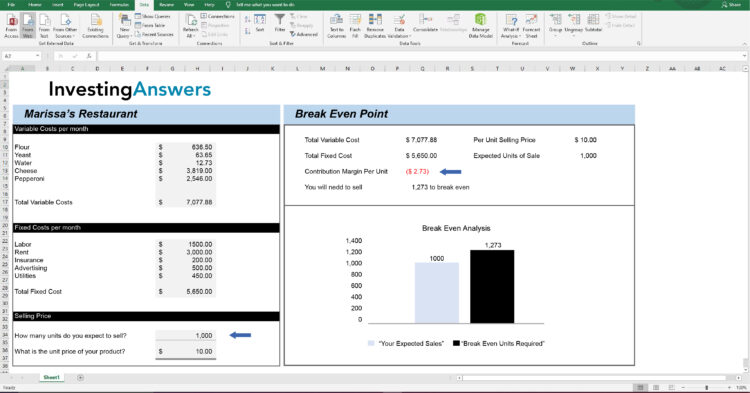
In this break even analysis sample, Restaurant ABC only sells pepperoni pizza. Its variable expenses for each pizza include:
Flour: $0.50
Yeast: $0.05
Water: $0.01
Cheese: $3.00
Pepperoni: $2.00
Adding all of these costs together, we determine that it has $5.56 in variable costs per pizza. Based on the total variable expenses per pizza, Restaurant ABC must price its pizzas at $5.56 or higher to cover those costs.
The fixed expenses per month include:
Labor: $1,500
Rent: $3,000
Insurance: $200
Advertising: $500
Utilities: $450
In total, Restaurant ABC's fixed costs are $5,650.
Let’s say that each pizza is sold for $10.00. Therefore the contribution margin is $4.44 ($10.00 - $5.56).
To determine the number of pizzas (or units) Restaurant ABC needs to sell, take its fixed costs and divide them by the contribution margin:
$5,650 ÷ $4.44 = 1,272.5
This means the restaurant needs to sell at least 1,272.53 pizzas (rounded up to 1,273 whole pizzas), to cover its monthly fixed costs. Or, the restaurant needs to have at least $12,730 in sales (1,272.5 x $10) to reach the break-even point.
Note: If your product must be sold as whole units, you should always round up to find the break-even point.
Remember: Fixed Costs Can Increase
Some fixed costs increase after a certain level of revenue is reached. For example, if Restaurant ABC begins selling 5,000 pizzas per month – rather than 2,000 – it might need to hire a second manager, thus increasing labor costs.
Break-Even Analysis Benefits
Break-even analysis is a great way to determine a business’ profitability. It can show business owners and management how many units need to be sold in order to cover both fixed and variable expenses. It also provides a specific benchmark or goal so businesses not only survive but also remain profitable.
Calculating Break Even Analysis in Excel
Excel users can utilize Goal Seek (a tool that’s built into the program) to calculate a break-even rate. To do this, you’ll need to have an Excel break-even calculator set up:
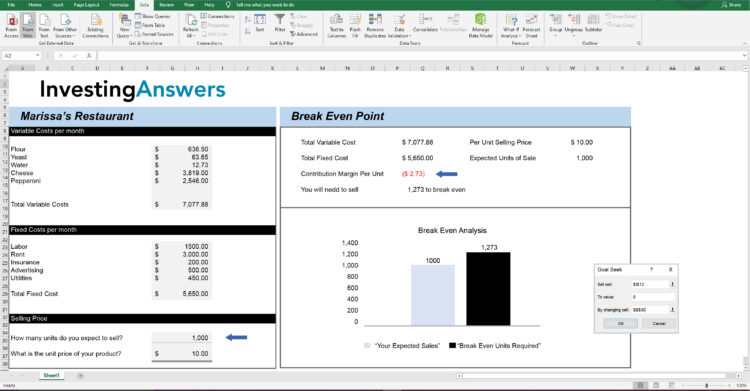
Step 1: Find Goal Seek
Step 2: Enter Your Numbers Into the Break Even Point
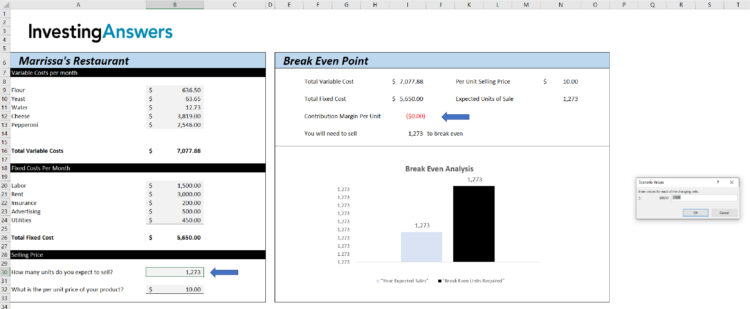
In the inputs, enter:
Set Cell = Contribution Margin Per Unit($I$12);
To Value = 0;
By Changing Sells = $B$30 i.e. How many units do you want to sell (see blue arrows).
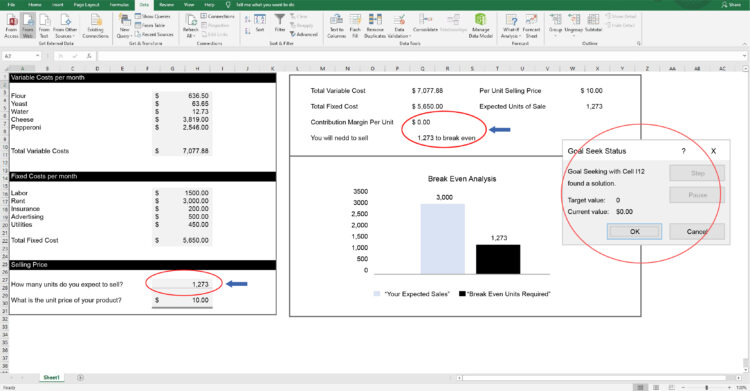
Step 3: Review the Number of Units Required to Break Even
Excel will automatically populate the required number of units to ensure that Contribution Margin is $0.
Optional: Create A Scenario Simulator for Multiple Units of Sale
If you want to see profitability based on many sales figures, then a scenario simulator may be helpful.
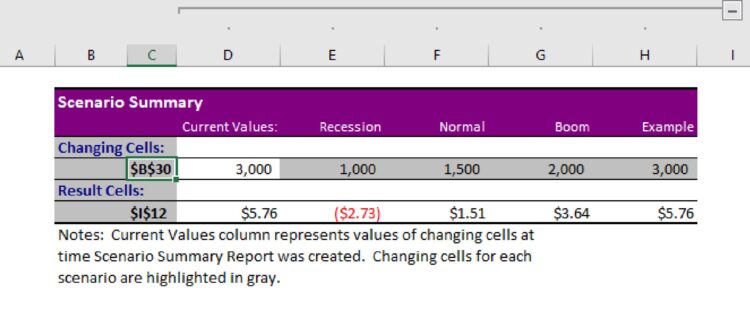
To do this, In Excel, go to: DATA → What-if Scenario → Scenario Manager. Here, you can input multiple scenarios with different sales units.
IA has recreated 3 scenarios as a starting point(Recession = 1000 Units; Normal = 1500 Units; Boom= 2000 Units)
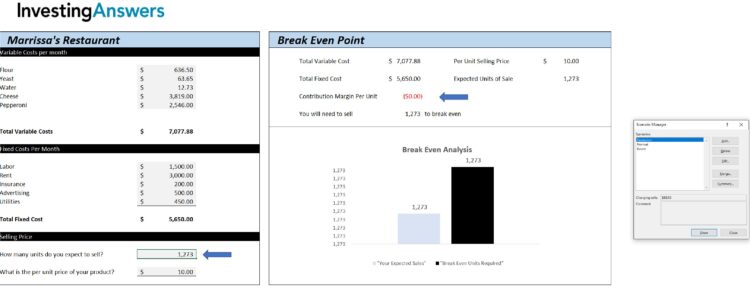
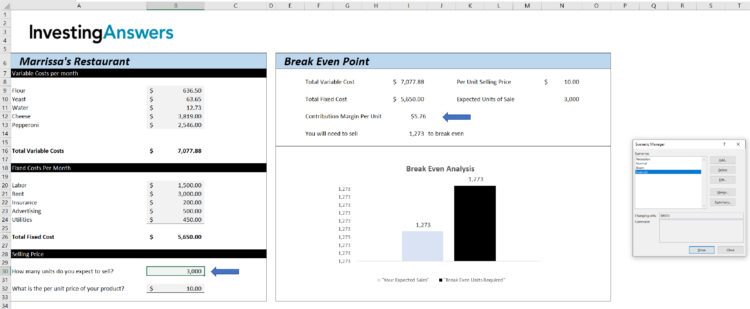
Excel will then ask you to enter how many units you want this scenario to contain. In this instance, it is 3000 units. Click “Ok.”
If you click on a scenario and click “SHOW,” Excel will automatically update the expected sales figure and calculate the contribution margin. In the following screenshot, the chosen Example scenario has 3000 units:
To view all your scenarios simultaneously, click on “Summary.” Excel will ask you which resulting cell you want to see. In order to see “Contribution Margin Per Unit,” our example set that to cell $I$12 and Excel inserted a new tab which shows the scenarios ($B$30 is our units of expected sale) plus the associated Contribution Margin Per Unit ($I1$12).
Related Articles

How Did Warren Buffett Get Rich? 4 Key Stocks to Follow
5 Money Moves That Made Warren Buffett Rich Warren Buffett is perhaps the most famous investor in the world, amassing a fortune of over $80 billion during his lifetime. His ...

How Sean Quinn Went from Billionaire to Bankruptcy
Sean Quinn was once the richest man in Ireland. In 2008, Forbes estimated Quinn's riches reached $6 billion. Today, however, he owes Anglo Irish Bank $2.7 billion and in ...

After A Huge Sell-Off, Here's Where The Market's Heading
A nearly 2% pullback for the S&P 500 shouldn’t be of much concern. The fact that index had risen for five straight months prior to the pullback suggests a bit of ...
- How to Profit from Real Estate Without Becoming a Landlord
- Robo Advisors - Here's Why 15+ Million People Have Already Opened Up Accounts
- Personal Capital - Our #1 Choice for Free Financial Planning Tools
- Fundrise - 23% Returns Last Year from Real Estate - Get Started with Just $10
- CrowdStreet - 18.5% Average IRR from Real Estate (Accredited Investors Only)
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
Business.com aims to help business owners make informed decisions to support and grow their companies. We research and recommend products and services suitable for various business types, investing thousands of hours each year in this process.
As a business, we need to generate revenue to sustain our content. We have financial relationships with some companies we cover, earning commissions when readers purchase from our partners or share information about their needs. These relationships do not dictate our advice and recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates and recommends products and services based on their research and expertise. Learn more about our process and partners here .
In Pursuit of Profit: Applications and Uses of a Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis is an essential element of financial planning. Here’s how to apply it to your business.

Table of Contents
Every entrepreneur should use a break-even analysis in their financial planning. It helps you understand your business’s revenue, expenses and cash flow so you can keep your doors open and your business profitable.
Read on to learn more about a break-even analysis and how this essential form of financial planning helps business owners make informed decisions.
What is a break-even analysis?
A break-even analysis is a financial tool that helps determine when your company, service or product will be profitable. This calculation determines the number of products or services a company must sell to cover its expenses, especially fixed costs.
Here’s an example of the elements that go into a break-even analysis:
- Fixed costs: Fixed costs, also called overhead costs , are the expenses that stay the same no matter how much the business sells. They include utilities, bills, salaries and wages, rent and insurance.
- Variable costs: Variable costs are based on a business’s sales. They can include additional labor from independent contractors, materials and payment processing fees.
- Average price: This is the average amount you charge for your products and services.
Editor’s note: Looking for a small business loan? Fill out the questionnaire below to have our vendor partners contact you about your needs.
What is the break-even-point formula?
Taken together, these elements create a formula known as the break-even-point formula. This relatively simple calculation is essential for planning for profitability.
Fixed Costs / (Average Price – Variable Cost) = Break-Even Point
The term “break-even” refers to a situation in which you are neither making nor losing money but all of your costs have been covered. With a break-even analysis, you can determine when your company will generate enough revenue to cover its expenses and earn a profit. The same holds true for a particular product or service. This data is often used for financial projections.
Examples of break-even analysis
Here are two examples of the break-even-point formula.
The price of one of your products is $100. Your fixed costs are $10,000 per month, and the variable cost is $50 per product. The formula to calculate how many products you must sell to break even would look like this:
$10,000 / ($100 – $50) = 200
Based on the formula, you must sell 200 products to cover your costs, effectively breaking even. To be profitable, you would have to sell at least 201 products.
If a company has $20,000 in fixed costs and a gross margin of 35 percent, the business would need to make $57,143 to break even.
$20,000 / 0.35 = $57,143
If revenue greater than $57,143 is achieved, the company can pay for its fixed and variable costs and make a profit.
Why is a break-even analysis important?
A break-even analysis informs you of the bare minimum performance your business must meet to avoid losing money. It also helps you understand at which point you’ll generate profits so you can set production goals accordingly.
You can use this information when your business is in the planning stages to determine whether your idea is feasible. Then, once your business is established, you can use a break-even analysis to develop direct cost structures and to identify opportunities for promotions and discounts.
Although there are many reasons to conduct a break-even analysis, let’s focus on the three most common uses.
It helps you identify the point of profitability.
A business that doesn’t turn a profit could take a turn for the worse at any time. This is why every company needs to focus on its point of profitability. Ask yourself these questions:
- How much revenue do I need to generate to cover all of my expenses?
- Which products or services generate a profit?
- Which products or services are sold at a loss?
A company’s goal is to become profitable as soon as possible. To ensure you’re on the right track, you need to focus on your numbers upfront. If you don’t calculate the break-even points for your products or services, you risk not generating a profit (or generating a smaller one than you expected).
It ensures that you price products and services correctly.
When most people think about pricing, they primarily consider how much their product costs to create, and they fail to take into account overhead costs. This leads businesses to underprice their products. Finding your break-even point will help you price your products correctly. You will know where to set your margins to generate the right revenue to break even and begin turning a profit.
Determining your break-even point is simple if you offer only a couple of products or services. It becomes more challenging as your service offerings and production increase.

Image via Business Tool Pro
As you determine your break-even point for a product or service, ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the total cost?
- What are the fixed costs?
- What are the variable costs?
- What is the total variable cost?
- What are the costs of any raw materials?
- What is the cost of labor?
It gives you the information you need to implement the best strategy.
Using your break-even analysis, you can create a strategy for the future. Suppose your business’s profitability is determined by the success of one or more products. In that case, the break-even point for each product provides a timeline for the company, which can help you implement a better overall financial strategy that fits the projected costs and profits.
This analysis can also help you determine ways to reach your company’s break-even point sooner, such as reducing your overall fixed costs, lowering the variable costs per unit, improving the sales mix by selling more of the products that have larger contribution margins, and increasing the prices (as long as it doesn’t cause the number of units sold to decline significantly).
When should I use a break-even analysis?
There are many situations where a break-even analysis comes in handy. According to Rick Vazza, owner of Driven Franchising, you should use a break-even analysis to answer the following questions about your business:
- How much of my product or service do I need to sell per month?
- How much volume do I expect to sell?
- What price makes those figures match my break-even calculation?
- What price allows me to generate a reasonable profit?
Your goal is to get an accurate look at your profit, net cash flow and finances.
“It’s much easier for people to decide whether they can beat that minimum than guessing how many sales they may make,” said Rob Stephens, founder of CFO Perspective.
Here are three times you should consider performing a break-even analysis.
You are expanding your business.
Stephens suggested using a break-even analysis to assess how long it will take for any planned investments or changes in your business to become profitable.
“These investments might be a new product or location,” Stephens said. “I’ve done break-even calculations many times for modeling the minimum sales needed to cover the costs of a new location.”
You need to lower your pricing.
This analysis is also helpful when you’re lowering your prices to beat a competitor . “You can also use break-even analysis to determine how many more units you need to sell to offset a price decrease,” Stephens said. “The most common use of break-even analysis in my career has been modeling price changes.”
You want to narrow down your options.
When making changes to your business, you may be bombarded with various scenarios and possibilities, which can be overwhelming when you’re trying to make a decision. Stephens suggested using a break-even analysis to narrow down your choices to scenarios with straightforward yes-or-no questions. For example, “Can we do better than the minimum needed for success?”
What are the limitations of a break-even analysis?
Although a break-even analysis is a classic tool for predicting business sustainability, it does have some limitations. You should always use multiple tools when analyzing business processes and profitability.
It assumes market conditions are consistent.
Once you open your business, it will quickly become apparent that every day, month and year can be completely different. You might have an increased customer demand, multiple competitors or a change in consumer spending.
It’s not sufficient for long-term planning.
A break-even analysis is most useful for short-term planning. For example, the analysis can accurately predict how many units must be sold for you to be profitable this month, but it cannot help you analyze business conditions over time, especially if you have busy and slow periods.

The analysis can quickly become obsolete.
Due to the short-term nature of a break-even analysis, it needs to be constantly updated to be accurate. If you fall behind on importing new data, the analysis can quickly become obsolete, leading to uninformed business decisions.
It’s not detailed enough.
If you have only one price point, a break-even analysis can be beneficial. However, most businesses have multiple price levels to encourage and engage a wide variety of consumers.
With multiple product tiers, your costs can fluctuate from supplies, inventory demand and shipping. With all of these factors to consider, you’ll need to use additional tools beyond a break-even analysis to accurately portray the financial health of your business.
It doesn’t account for competition.
Because there is no formula for a fluctuating marketplace, a break-even analysis can’t account for competition. You will need to monitor your competitors separately so you can accurately account for supply and demand, product price changes and promotional offers.
Julie Thompson and Julianna Lopez contributed to this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
- TemplateLab
Break Even Analysis Templates
41 free break even analysis templates & excel spreadsheets.
In business, you perform a break-even analysis for a specific purpose. You can use it to determine if your revenue will be able to cover all your expenses within a specific time period. Generally, businesses use a month as the time period in this analysis process.
If the revenue is more than the break-even point, then your company stands to gain profits. But if it doesn’t reach the point, your business may suffer losses. When performing such an analysis, you may need to create a break-even analysis in Excel.
Table of Contents
- 1 Break Even Analysis Templates
- 2 Common terminologies used in break-even analysis
- 3 Break Even Spreadsheet
- 4 Creating your own break-even analysis template in Microsoft Excel
- 5 Break Even Analysis Excel
- 6 Break Even Spreadsheet Templates
- 7 Completing the break-even analysis template
You can create the template yourself or download one from here. Some companies need to plan carefully in order to avoid any losses. You have to make accurate calculations.
To do this, you enter the data in a break-even spreadsheet and use that for your analysis. In different types of businesses, there are different things to consider. That is if you want to gain profit rather than suffer losses .
Some startup businesses use such an analysis to calculate financial viability. Through it, they can determine whether it’s feasible to pursue a new venture or release a new product . This process is a tool that’s usually part of a strong business plan.
Calculating the break-even point is fairly simple. What’s challenging is coming up with the other variables. These include the sale price, projected sales, fixed, and variable costs. The business owner still needs to come up with all these in order to complete the template.
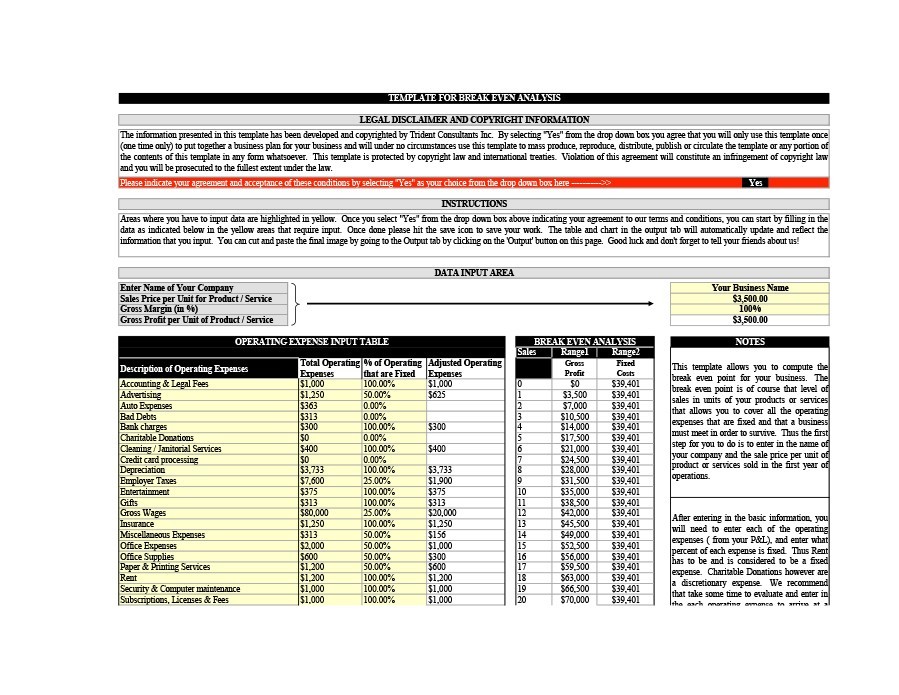
Common terminologies used in break-even analysis
You may have a plan to make a break-even analysis template. Before that, you need to know the different terminologies to use. These basic terminologies are important if you want to make accurate calculations. You need to understand what they mean and why they are part of the analysis.
- Fixed costs This refers to costs which remain constant throughout the payback period. They don’t depend on how many units you produced within that period. These include insurance, advertising, rent, taxes, supplies, and more. There are a lot of fixed costs involved in a business. They may also include the wages and payroll taxes you give to non-direct labor.
- Payback period This is how long it would take your investment to reach the break-even point. When you’re making an analysis, you need to calculate that point. Before you can do that, you need to define your payback period already. This period may be a few years or just a matter of months. It would depend on the change rate in your market. If you’re starting your business , you’ll definitely need this information. Banks or financial institutions may ask for evidence. They’ll want to prove that you’ll start making a profit after a certain amount of time.
- Sales price This refers to the price you’re selling your products for. Whether it be goods or services, you need to establish the sales price. Usually, this value remains constant when you’re making an analysis. Then you can compute your total revenue by multiplying this value by the number of products sold.
- Variable costs There are a lot of factors which you can consider as variable costs. These include direct labor, production, materials, and other costs. The costs usually depend on how many products you’ve made and how many you’ve sold. Some variable costs may be currency-based while some are percentage-based.
These are the most basic terminologies. You need to understand them if you’re planning to make a break-even analysis. When you perform this, you need a break-even spreadsheet. In it, you’ll input all the relevant information.
You can download a template here or create one on your own. To help you out, we’ll discuss some helpful steps next.
Break Even Spreadsheet
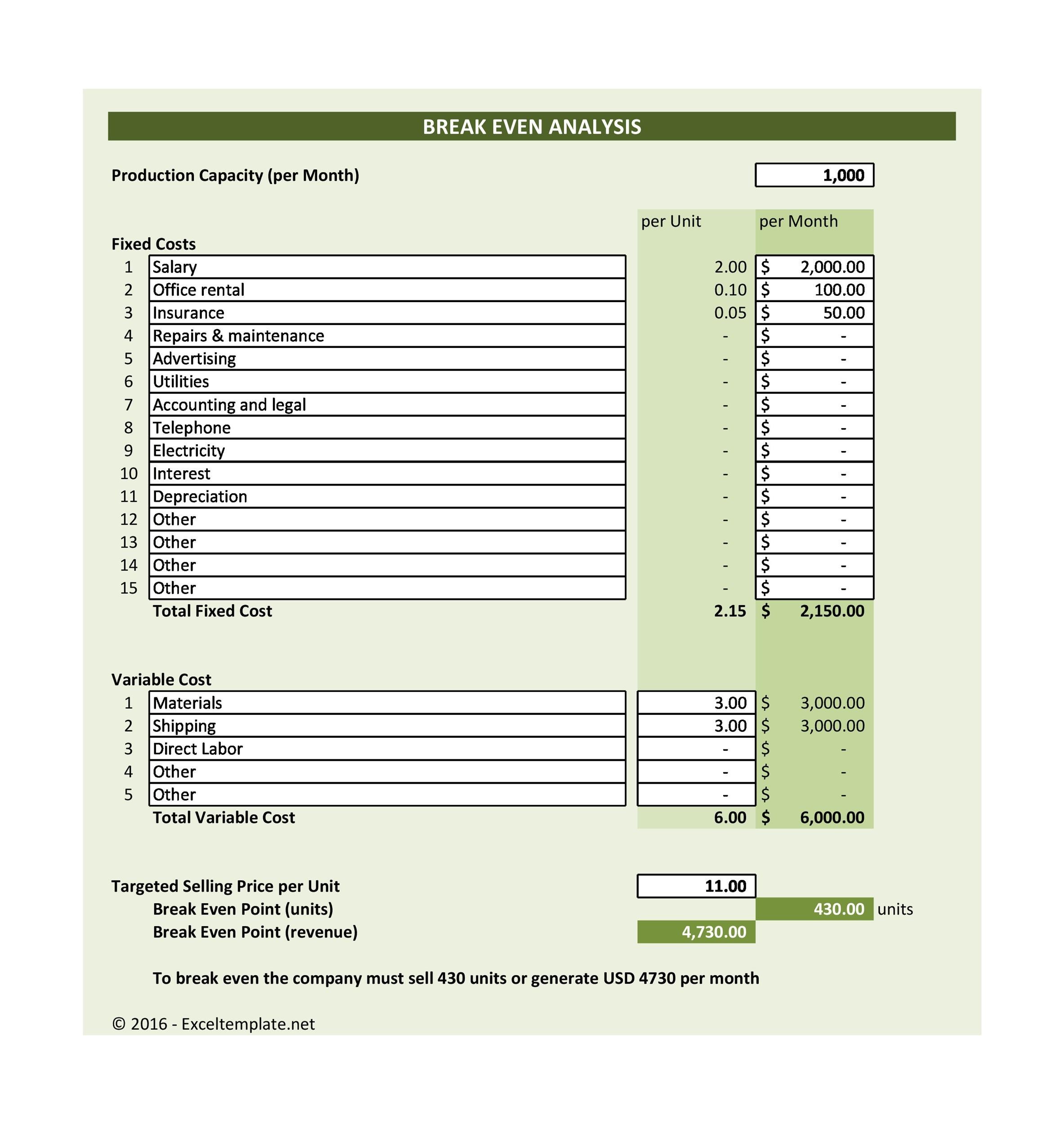
Creating your own break-even analysis template in Microsoft Excel
It’s important for businesses to perform a break-even analysis. You need to know the appropriate price you should charge for your goods or services. This information can make or break your business.
Part of making the decision would depend on the analysis process. The break-even point or BEP is the point where your costs will be equal to your sales (revenue). When you reach this point, it means your product is making a profit but you’re still covering your costs.
So if the value goes beyond the BEP, it means you’re making a profit. But if the value falls below the BEP, you’re suffering a loss. Before you make your analysis, you need to come up with some variables. There are:
- Price of each unit
- Cost of each unit
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
When you’re trying to establish your BEP, remember that it isn’t a standard value. It’s more of an estimate which will provide insight into how profits and losses will change. These changes happen as your sales rise and fall.
If you want to perform your analysis well, you need a break-even analysis template. You’ll input all your information on it in order to come up with accurate calculations. You can easily create a break-even analysis in Excel.
Break Even Analysis Excel
Here are some general steps and tips to guide you:
- First, you need to create some tables. You need these to record all the costs.
- Remember that there are 2 kinds of costs – fixed and variable. Use the table feature of Excel to record all this data. This will make customization easier for you. In the program, you don’t have to make updates to the cell references.
- Create tables in 2 different sheets. One for the fixed costs and one for the variable costs. Format the table to fit the needs of your business.
- To start off, input the labels. Then make a table on the sheet. To do this, select a cell then click the “Insert” tab. Click on the “Table” found in the Tables group, tick the “My Table Has Headers” option then click on “OK.” You can use the tables you create to record the costs.
- Create a sheet for your BEP analysis and give the sheet its own name. You can use the color fill option to indicate input cells. This will make it easier for you but it’s not required. Make use of this sheet to input different values. These include the costs per unit and the number of units sold. These will help you come up with the BEP.
- The next thing for you to do is to create the range names. When you’ve placed your labels, come up with the range names. You’ll use these for your formulas. To do this, select the cells you need then click on the “Formulas” tab. Click on the “Create From Selection” option found in the Defined Names group and click on “OK.” Keep on doing this for all the cells where you want to add formulas. When you do this, Excel embeds underscore characters automatically. These characters are in between the words in the range names.
- Once that’s done, it’s time to input your BEP formulas. You need to enter these formulas so you can generate your BEP value.
- When you’ve finished the last step, it’s time to enter the cost values. Go back to the tables you’ve made for costs. Input the corresponding values for the product you’re planning to launch. You can modify the tables to fit your needs.
- As you enter the values, keep in mind that the template won’t consider the period costs. So you have to make sure that the values you enter represent a single period consistently. You may enter monthly or annual costs into your tables.
- After inputting these values, the next step is to input your BEP variables. Before you can do this, you need to evaluate the costs. Then you can input your best-estimated unit price and unit sold values. These values will help you generate your BEP.
- You can also input the labels for a sales analysis. By this time, you may think you’re done with the template. You can stop here but you can also continue to enhance your analysis. In doing this, you’ll give a bigger picture for your report.
- Finally, you can finish your template. Do this when you’re sure that all the formulas are in place and are working correctly. Before you save your file, you may want to protect your formulas. You can do this by enabling protection.
- Select the cells which contain the formulas. Right-click your selection and click “Format Cells.” Click on the “Protection” tab, tick “Locked,” and click on “OK.”
- You can also protect the whole sheet. To do this, click on the Home tab. Select the Format drop-down menu in the Cells group and choose “Protect Sheet.” In the dialogue box, uncheck the “Select Locked Cells” option. In doing this, the protection will guide you to input the cells. Click on “OK” and you can even add a password for the file if you prefer.
- If you’ve made a sales analysis sheet, you can also protect it. Do so by repeating all the steps for enabling protection.
The values and formulas that you input in your sheet are very important. You need to make sure they’re all correct. Do this so you’ll be able to get an accurate result for your analysis.
Aside from tables, you can also use a grid to analyze the information. Plot the values in the grid and interpret it accordingly. You’ll be able to see if your BEP is high or low. Then, you can determine whether you need to increase or decrease the prices of your products.
If you increase your prices, it will reduce your BEP. But if you decrease your prices, it will raise your BEP. Analyzing the data in a graph will also provide you with insight for you to make good decisions.
When you’re done with all the templates, make sure to save your work. You can save a blank template which contains all the formulas already. Then you can use that template to record all your data. Once you’re done, save the file with a different file name.
If you want to generate a new BEP, modify any of the values you’ve entered. If you want to keep the modification, save the file with a different file name again. Otherwise, just exit the program without saving the changes.
Break Even Spreadsheet Templates

Completing the break-even analysis template
A break-even spreadsheet can help you out with your business . You can use it to establish the scenarios your company must do in order to become profitable. One of the most important uses of such an analysis is to be able to see different scenarios.
For example, if you want to hire another person for the business. How much would more sales you need to cover the employee’s salary? You may also plan to borrow money to increase your principal.
How much more money will you need to make to cover the monthly amortization payments ? A lot of business owners perform break-even analyses when they’re planning something new.
It will give you an idea of what you need to reach to keep your business going.
If you’ve made a template for your analysis, then you should know how to complete it correctly. Here are some tips for you:
- Input all your estimated fixed and variable costs. You can get these figures from your projection of profits and losses.
- Remember, fixed costs are those that remain constant. They stay the same regardless of the volume of your sales. They’re usually expressed in currency units. On the other hand, variable costs are the ones which will change as your sales volume changes too. They’re usually expressed in percentages.
- When you’re entering variable costs in your table, always use whole numbers. Do this instead of decimal numbers.
These are helpful tips and reminders for you to follow when filling up your template. When you’re entering the labels of your template, make sure they reflect your own business.
A break-even analysis is a tool which helps you see the “big picture.” So knowing how to fill up the report is very helpful.
More Templates

After Action Report Templates
Project Summary Templates

Payroll Report Templates

Annual Report Templates
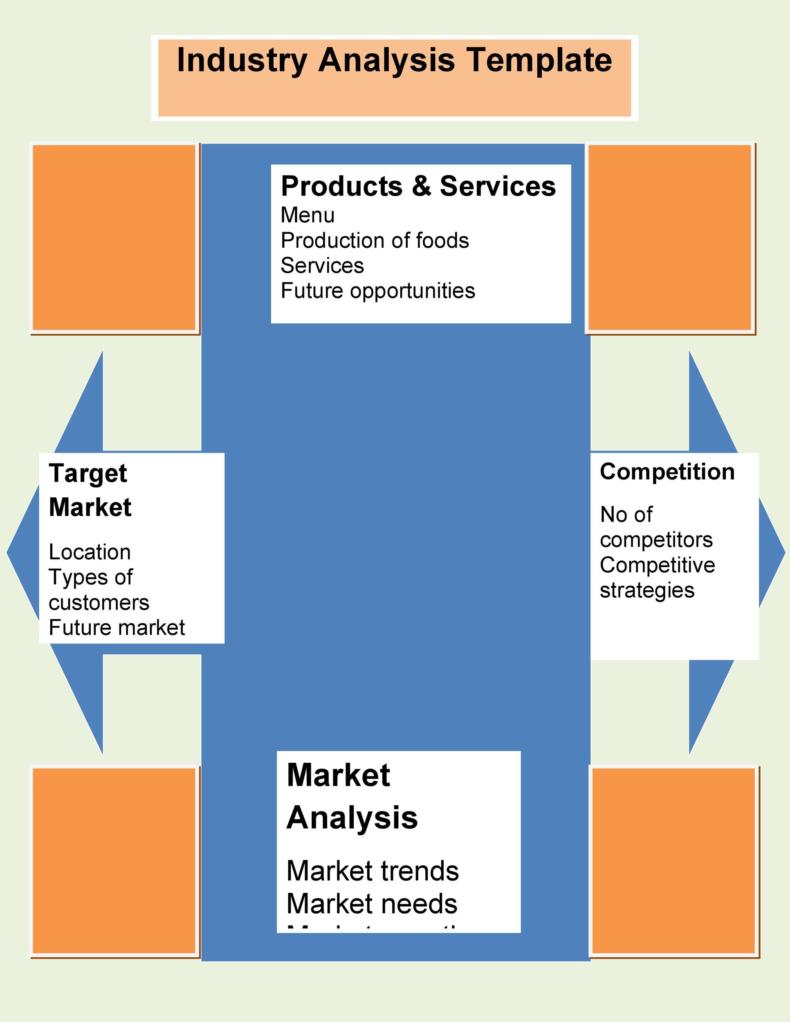
Industry Analysis Examples
Technical Report Examples
Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan
By Andy Marker | July 29, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up expert-tested financial templates for your business plan, all of which are free to download in Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find the essential financial statement templates, including income statement templates , cash flow statement templates , and balance sheet templates . Plus, we cover the key elements of the financial section of a business plan .
Financial Plan Templates
Download and prepare these financial plan templates to include in your business plan. Use historical data and future projections to produce an overview of the financial health of your organization to support your business plan and gain buy-in from stakeholders
Business Financial Plan Template
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Download Financial Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Financial Plan Projections Template for Startups
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business.
Download Startup Financial Projections Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Income Statement Templates for Business Plan
Also called profit and loss statements , these income statement templates will empower you to make critical business decisions by providing insight into your company, as well as illustrating the projected profitability associated with business activities. The numbers prepared in your income statement directly influence the cash flow and balance sheet forecasts.
Pro Forma Income Statement/Profit and Loss Sample
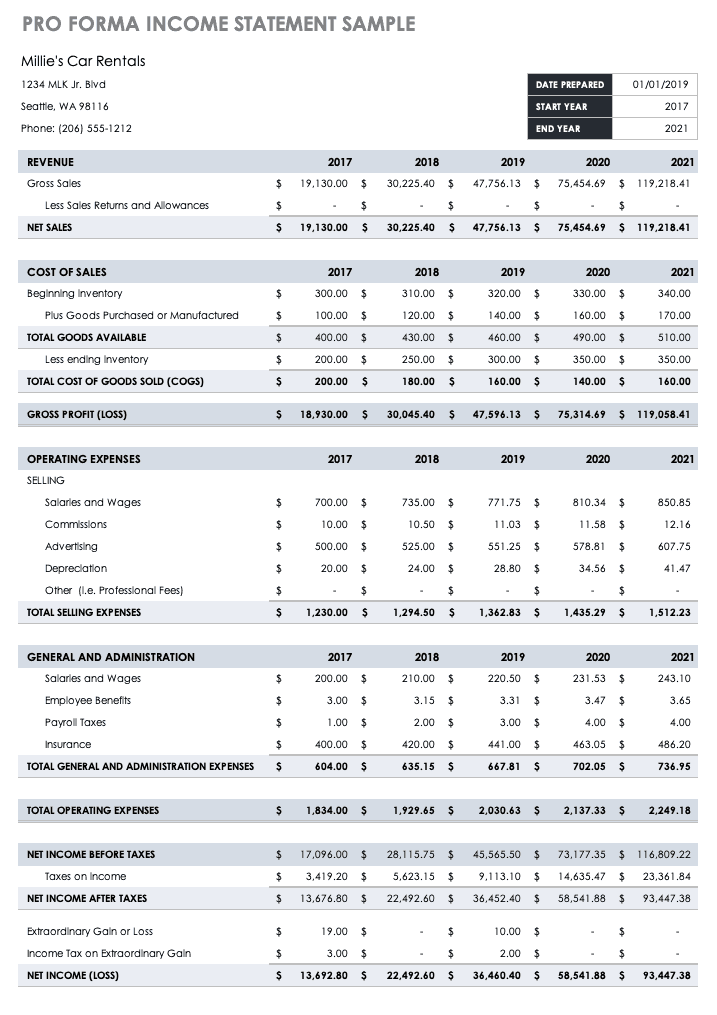
Use this pro forma income statement template to project income and expenses over a three-year time period. Pro forma income statements consider historical or market analysis data to calculate the estimated sales, cost of sales, profits, and more.
Download Pro Forma Income Statement Sample - Excel
Small Business Profit and Loss Statement
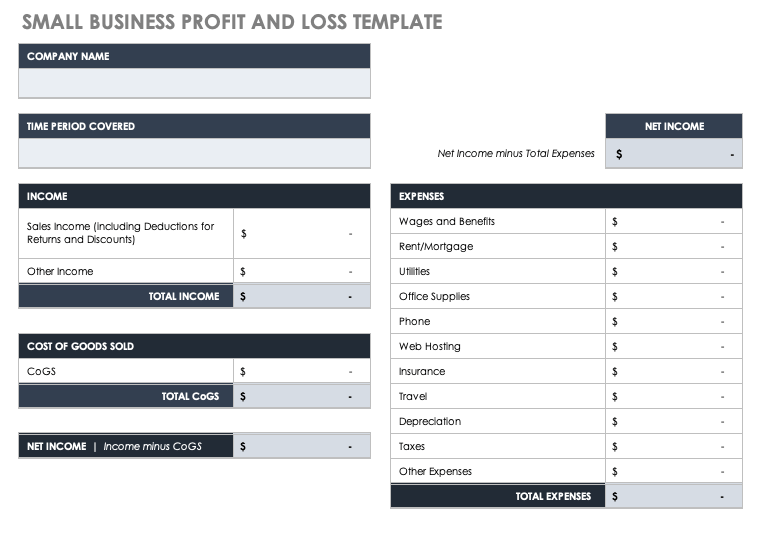
Small businesses can use this simple profit and loss statement template to project income and expenses for a specific time period. Enter expected income, cost of goods sold, and business expenses, and the built-in formulas will automatically calculate the net income.
Download Small Business Profit and Loss Template - Excel
3-Year Income Statement Template
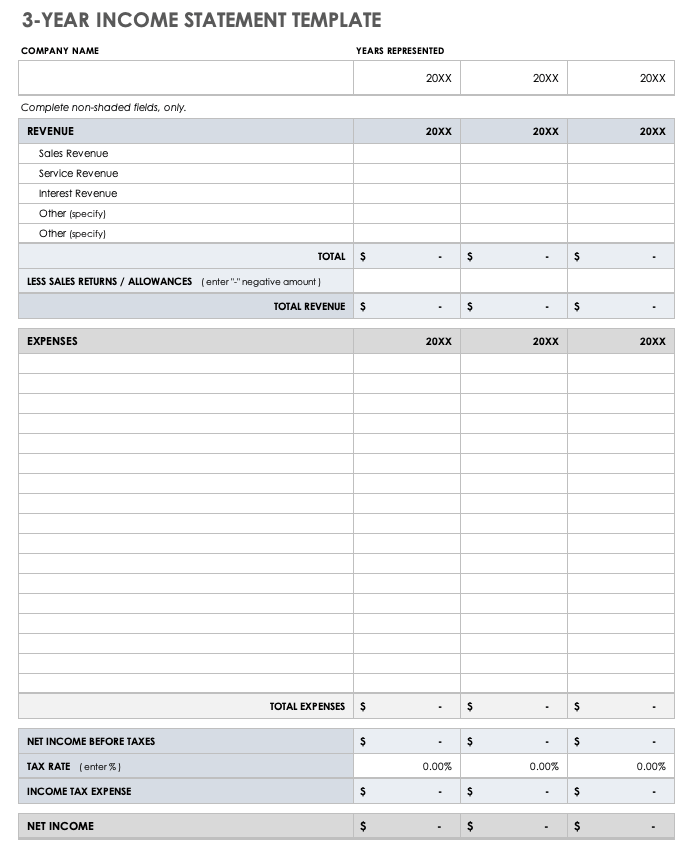
Use this income statement template to calculate and assess the profit and loss generated by your business over three years. This template provides room to enter revenue and expenses associated with operating your business and allows you to track performance over time.
Download 3-Year Income Statement Template
For additional resources, including how to use profit and loss statements, visit “ Download Free Profit and Loss Templates .”
Cash Flow Statement Templates for Business Plan
Use these free cash flow statement templates to convey how efficiently your company manages the inflow and outflow of money. Use a cash flow statement to analyze the availability of liquid assets and your company’s ability to grow and sustain itself long term.
Simple Cash Flow Template

Use this basic cash flow template to compare your business cash flows against different time periods. Enter the beginning balance of cash on hand, and then detail itemized cash receipts, payments, costs of goods sold, and expenses. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate total cash payments, net cash change, and the month ending cash position.
Download Simple Cash Flow Template
12-Month Cash Flow Forecast Template
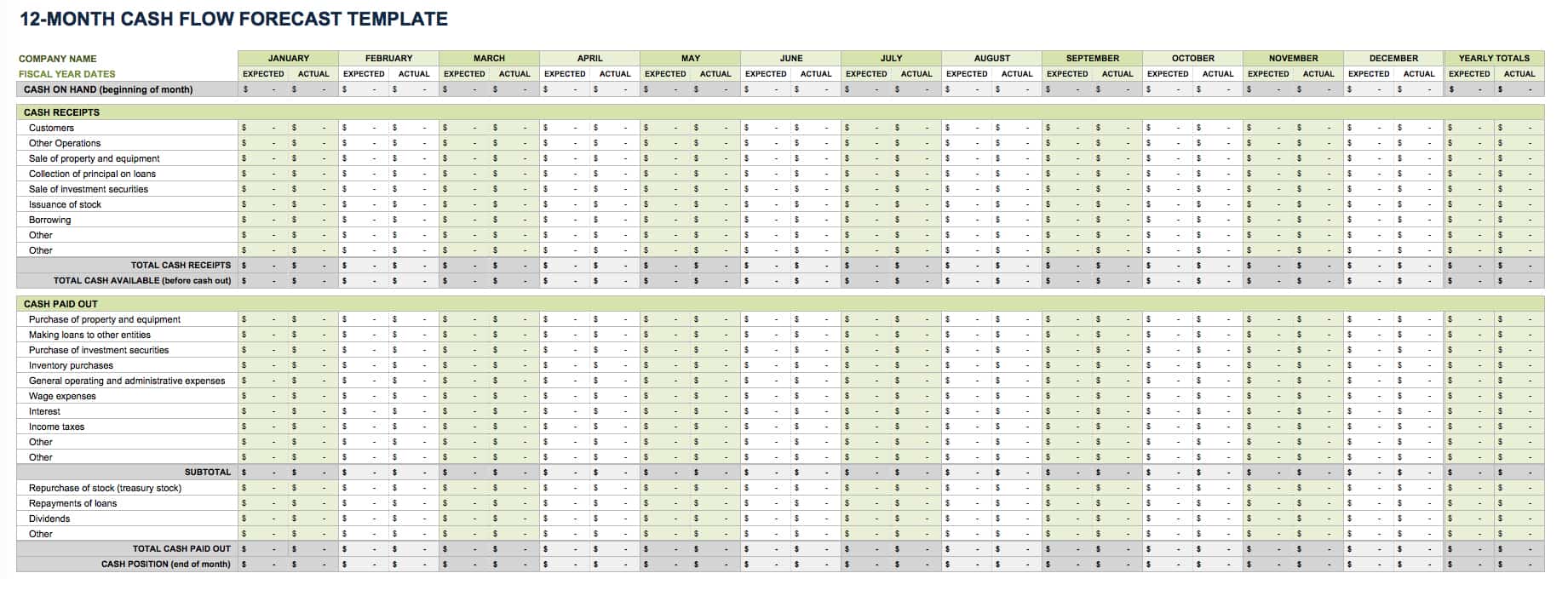
Use this cash flow forecast template, also called a pro forma cash flow template, to track and compare expected and actual cash flow outcomes on a monthly and yearly basis. Enter the cash on hand at the beginning of each month, and then add the cash receipts (from customers, issuance of stock, and other operations). Finally, add the cash paid out (purchases made, wage expenses, and other cash outflow). Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate your cash position for each month with.
Download 12-Month Cash Flow Forecast
3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template Set
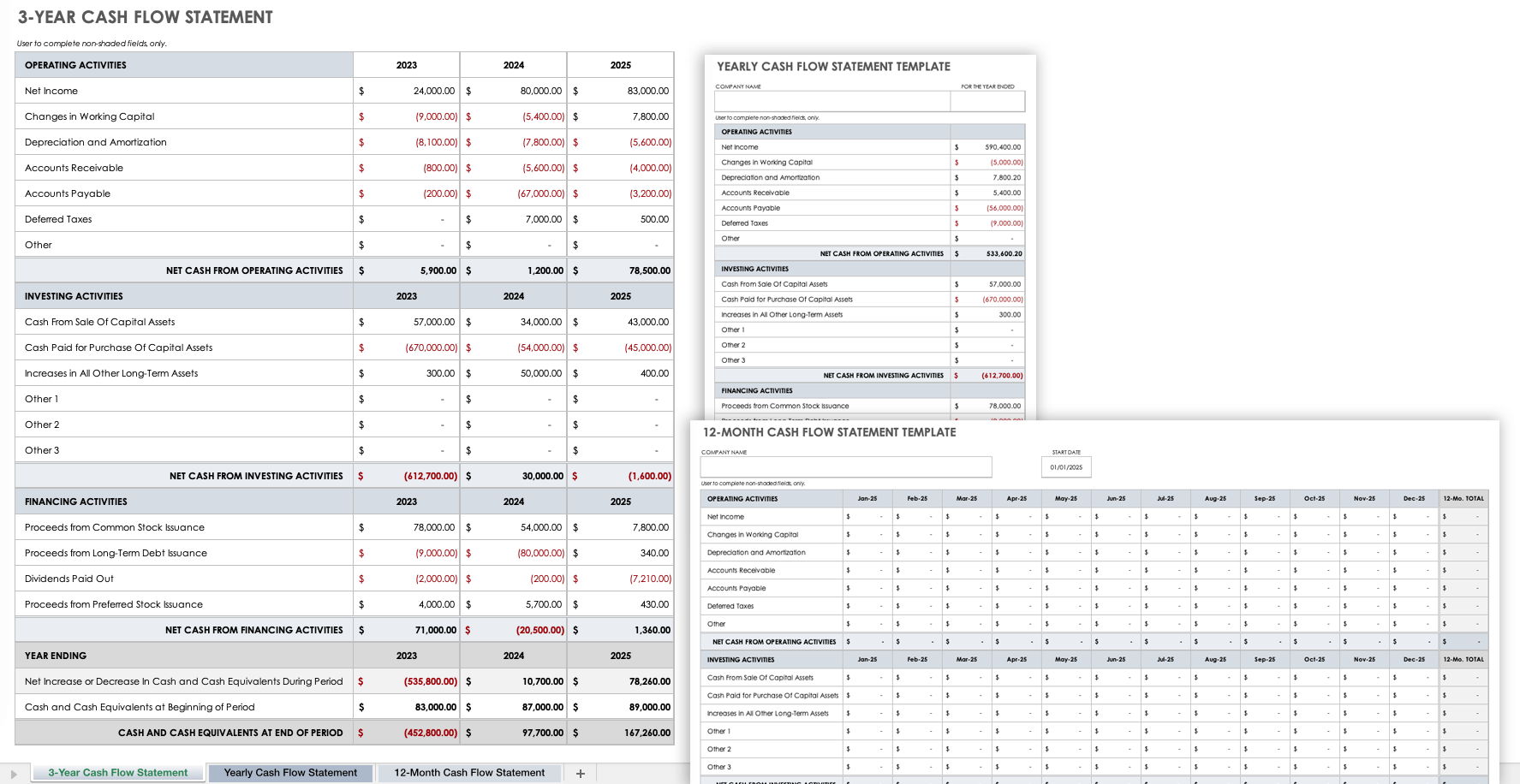
Use this cash flow statement template set to analyze the amount of cash your company has compared to its expenses and liabilities. This template set contains a tab to create a monthly cash flow statement, a yearly cash flow statement, and a three-year cash flow statement to track cash flow for the operating, investing, and financing activities of your business.
Download 3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template
For additional information on managing your cash flow, including how to create a cash flow forecast, visit “ Free Cash Flow Statement Templates .”
Balance Sheet Templates for a Business Plan
Use these free balance sheet templates to convey the financial position of your business during a specific time period to potential investors and stakeholders.
Small Business Pro Forma Balance Sheet
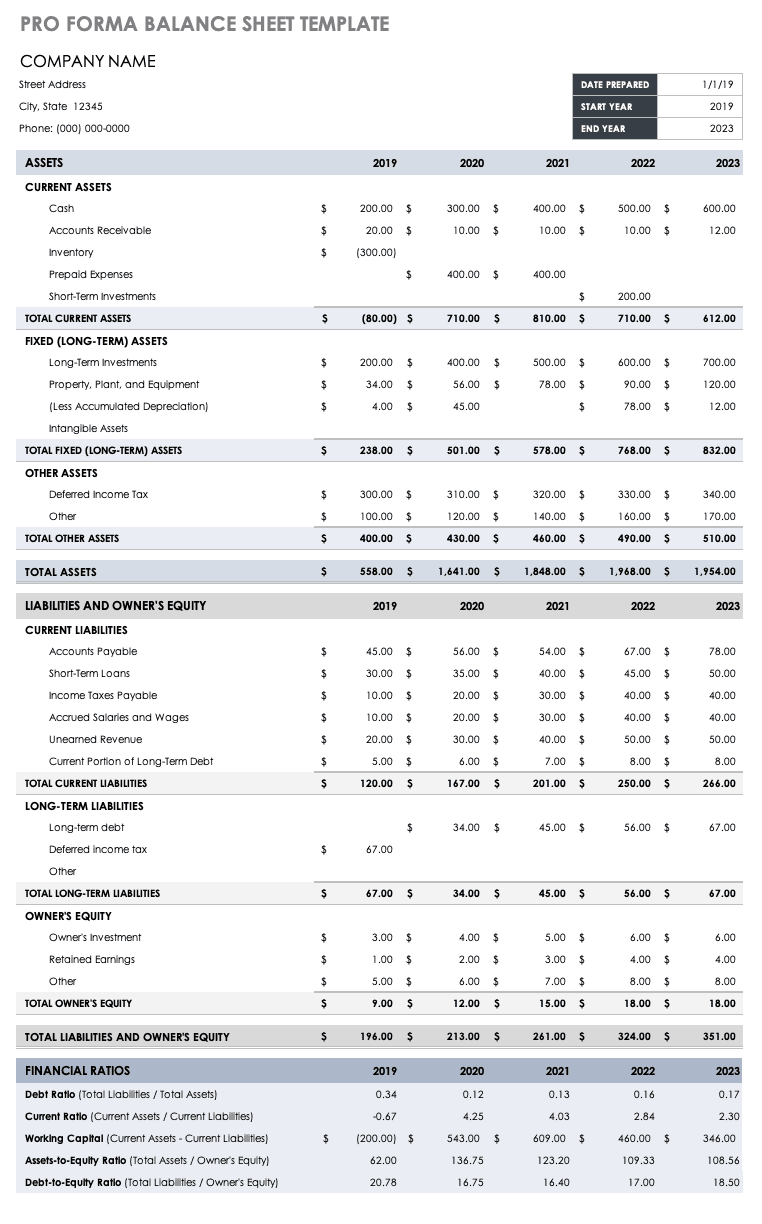
Small businesses can use this pro forma balance sheet template to project account balances for assets, liabilities, and equity for a designated period. Established businesses can use this template (and its built-in formulas) to calculate key financial ratios, including working capital.
Download Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template
Monthly and Quarterly Balance Sheet Template
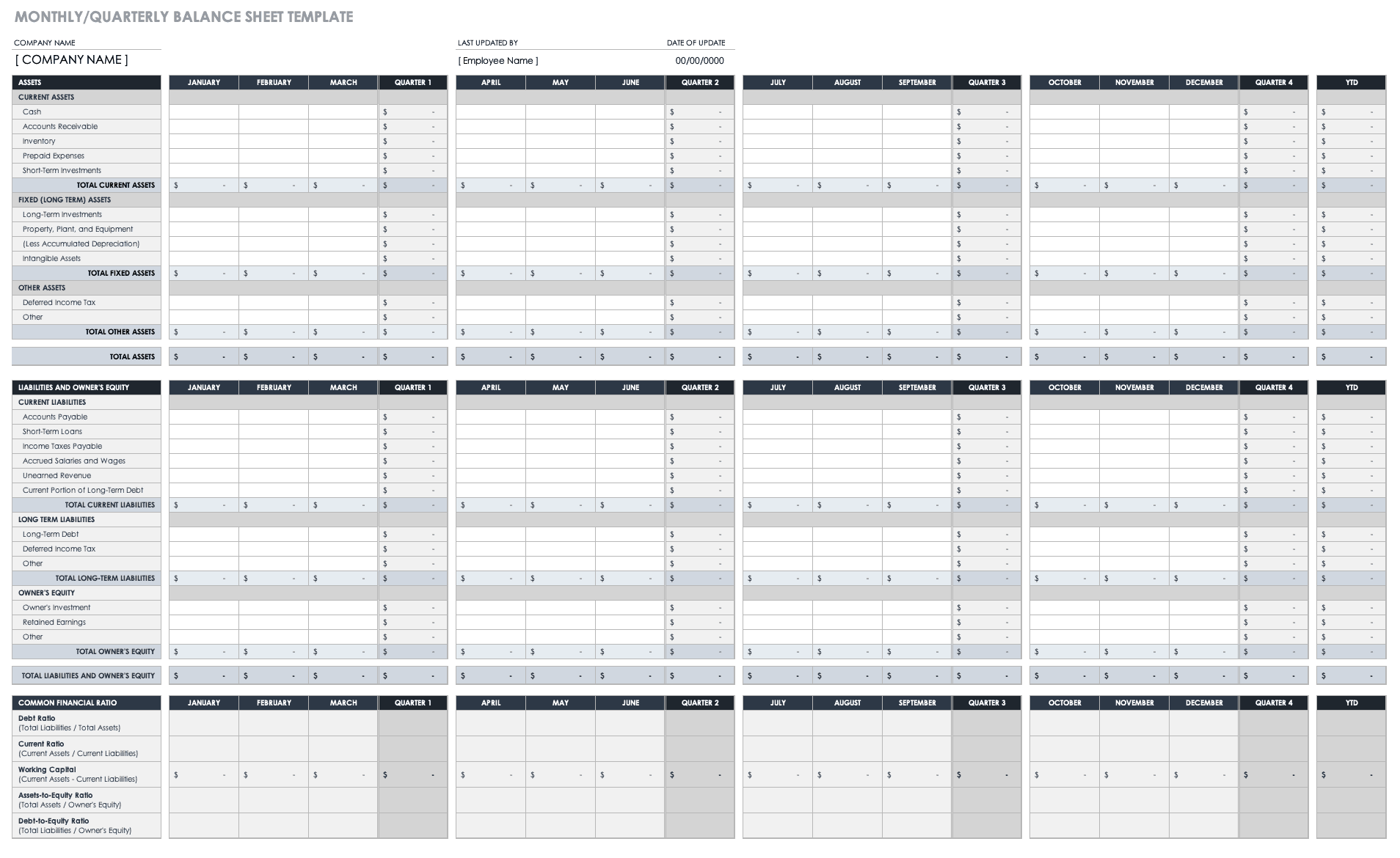
Use this balance sheet template to evaluate your company’s financial health on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can also use this template to project your financial position for a specified time in the future. Once you complete the balance sheet, you can compare and analyze your assets, liabilities, and equity on a quarter-over-quarter or year-over-year basis.
Download Monthly/Quarterly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
Yearly Balance Sheet Template
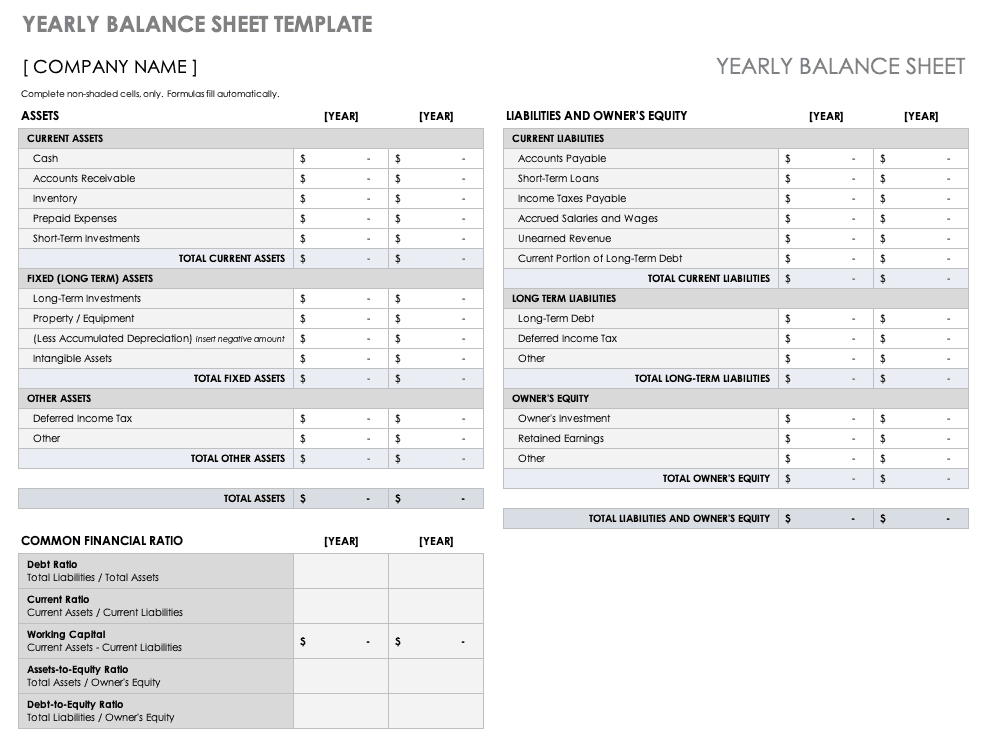
Use this balance sheet template to compare your company’s short and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity year-over-year. This template also provides calculations for common financial ratios with built-in formulas, so you can use it to evaluate account balances annually.
Download Yearly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
For more downloadable resources for a wide range of organizations, visit “ Free Balance Sheet Templates .”
Sales Forecast Templates for Business Plan
Sales projections are a fundamental part of a business plan, and should support all other components of your plan, including your market analysis, product offerings, and marketing plan . Use these sales forecast templates to estimate future sales, and ensure the numbers align with the sales numbers provided in your income statement.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
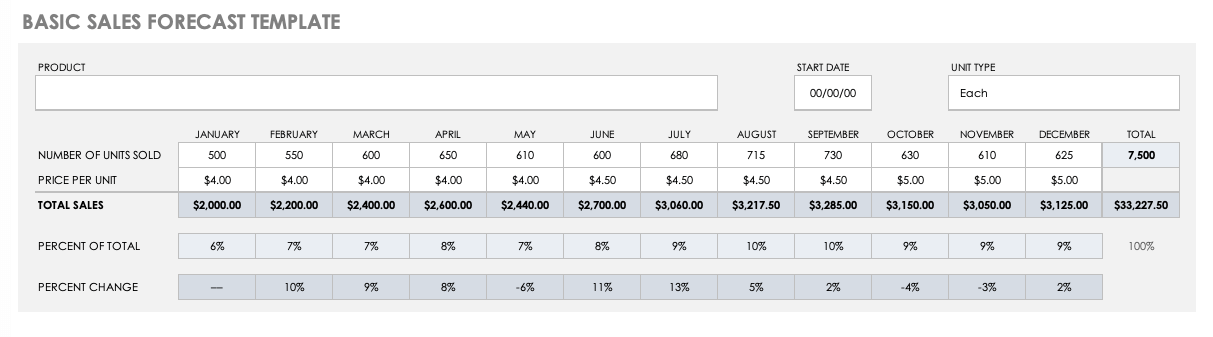
Use this basic forecast template to project the sales of a specific product. Gather historical and industry sales data to generate monthly and yearly estimates of the number of units sold and the price per unit. Then, the pre-built formulas will calculate percentages automatically. You’ll also find details about which months provide the highest sales percentage, and the percentage change in sales month-over-month.
Download Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
12-Month Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
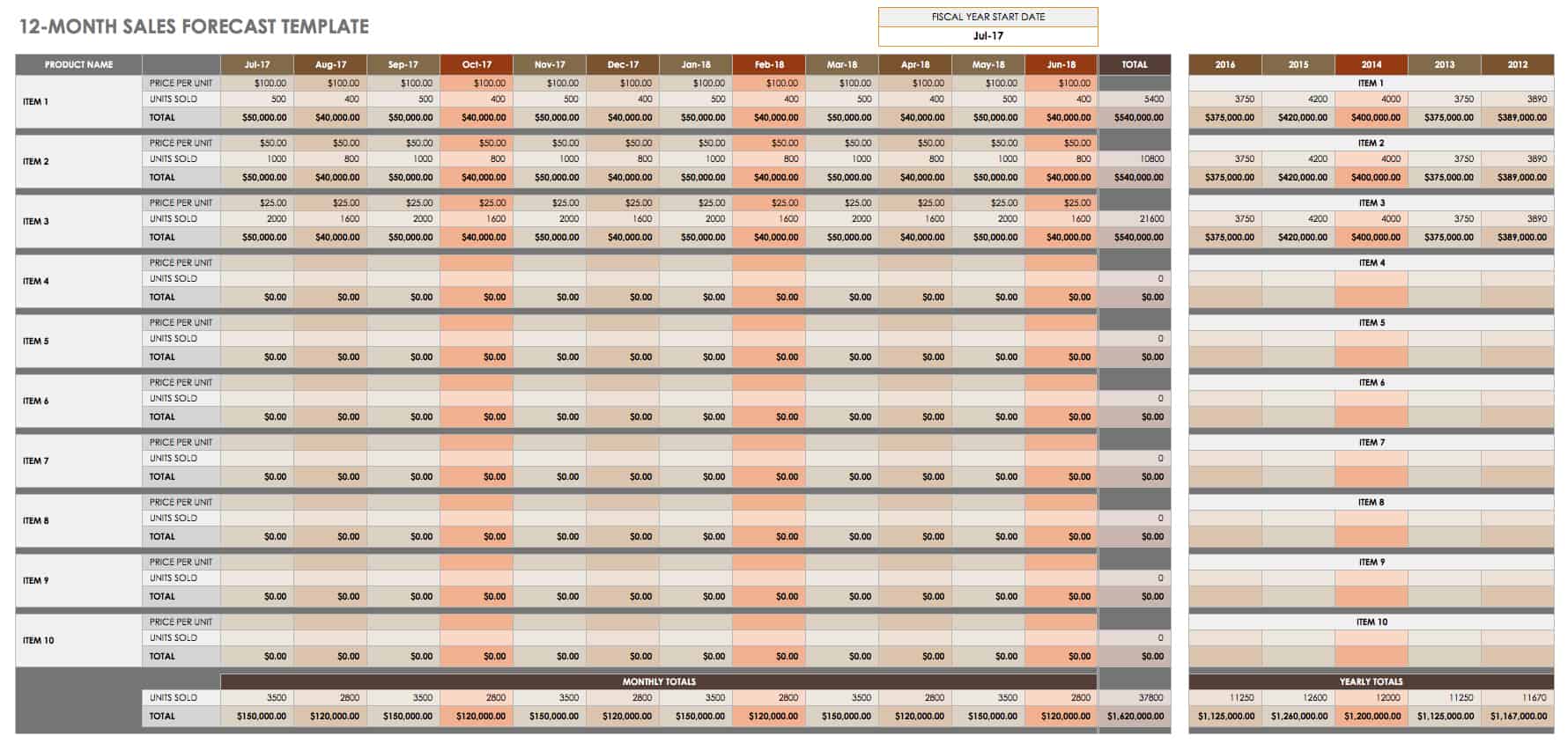
Use this sales forecast template to project the future sales of a business across multiple products or services over the course of a year. Enter your estimated monthly sales, and the built-in formulas will calculate annual totals. There is also space to record and track year-over-year sales, so you can pinpoint sales trends.
Download 12-Month Sales Forecasting Template for Multiple Products
3-Year Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
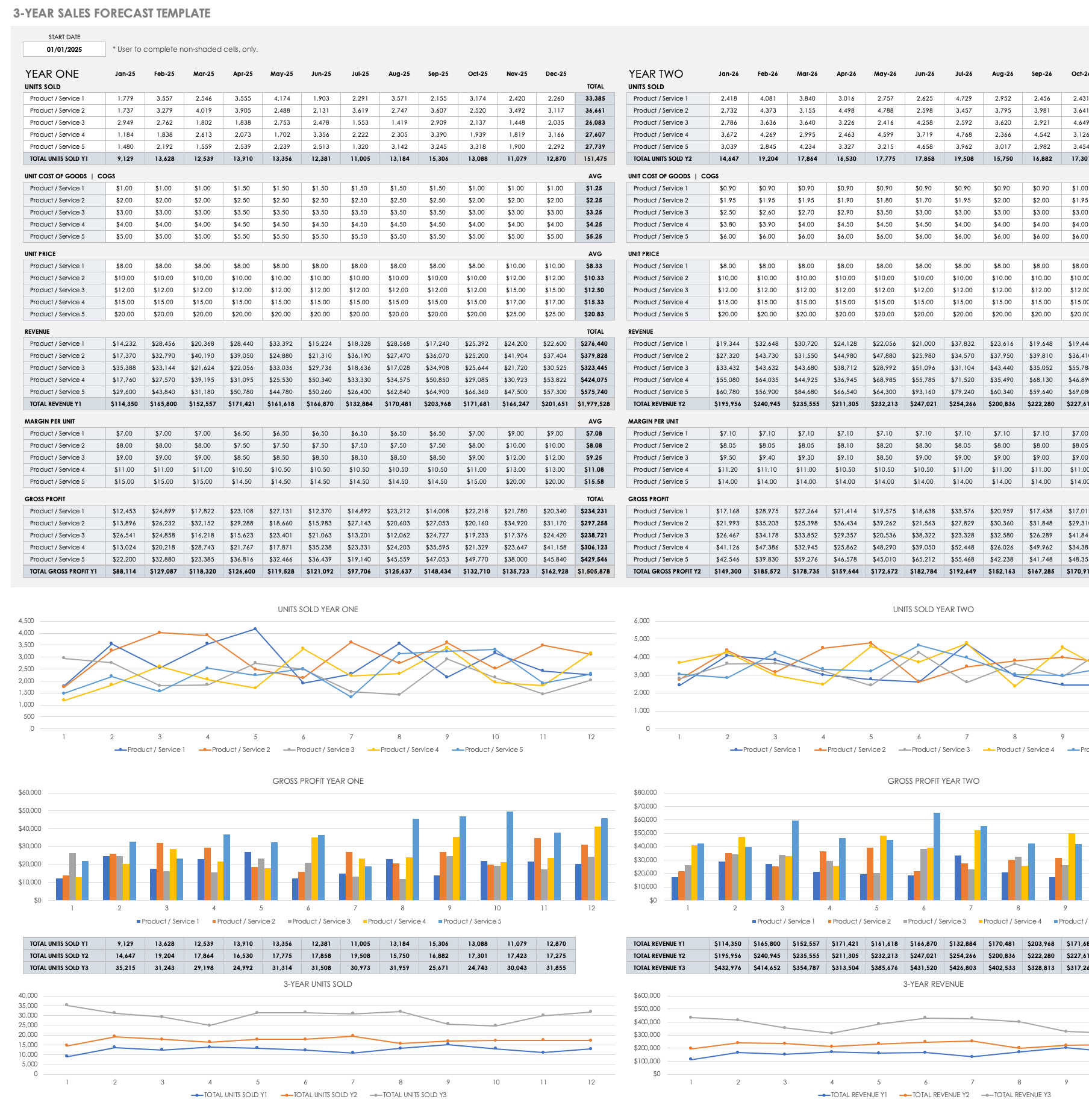
Use this sales forecast template to estimate the monthly and yearly sales for multiple products over a three-year period. Enter the monthly units sold, unit costs, and unit price. Once you enter those values, built-in formulas will automatically calculate revenue, margin per unit, and gross profit. This template also provides bar charts and line graphs to visually display sales and gross profit year over year.
Download 3-Year Sales Forecast Template - Excel
For a wider selection of resources to project your sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Break-Even Analysis Template for Business Plan
A break-even analysis will help you ascertain the point at which a business, product, or service will become profitable. This analysis uses a calculation to pinpoint the number of service or unit sales you need to make to cover costs and make a profit.
Break-Even Analysis Template
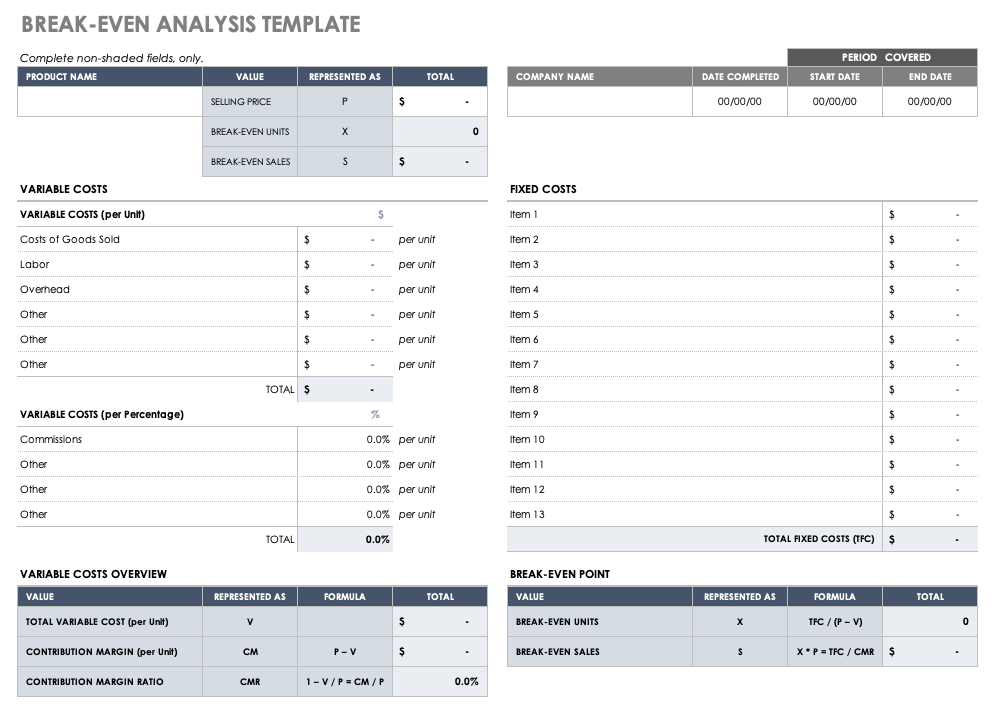
Use this break-even analysis template to calculate the number of sales needed to become profitable. Enter the product's selling price at the top of the template, and then add the fixed and variable costs. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate the total variable cost, the contribution margin, and break-even units and sales values.
Download Break-Even Analysis Template
For additional resources, visit, “ Free Financial Planning Templates .”
Business Budget Templates for Business Plan
These business budget templates will help you track costs (e.g., fixed and variable) and expenses (e.g., one-time and recurring) associated with starting and running a business. Having a detailed budget enables you to make sound strategic decisions, and should align with the expense values listed on your income statement.
Startup Budget Template
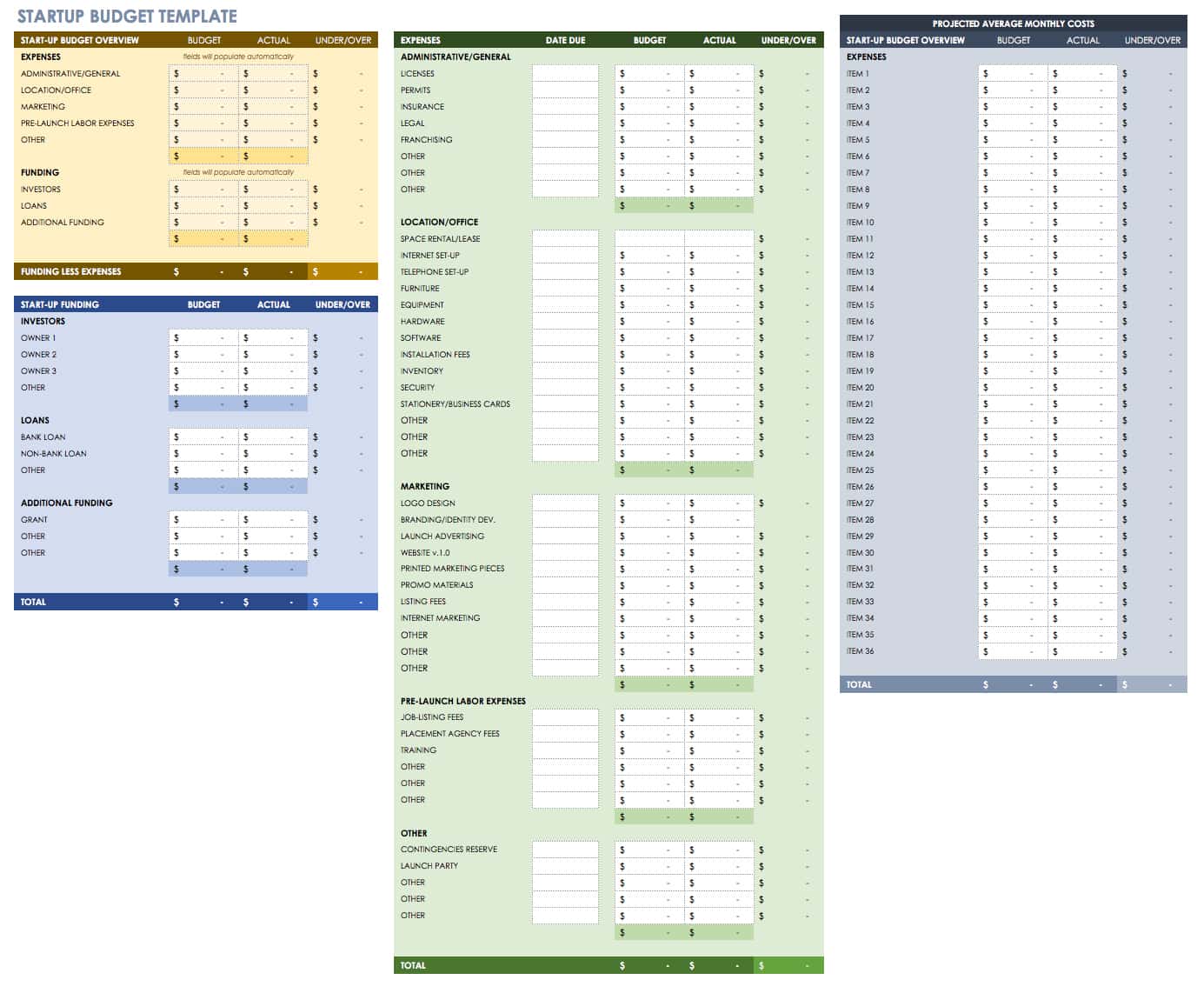
Use this startup budget template to track estimated and actual costs and expenses for various business categories, including administrative, marketing, labor, and other office costs. There is also room to provide funding estimates from investors, banks, and other sources to get a detailed view of the resources you need to start and operate your business.
Download Startup Budget Template
Small Business Budget Template
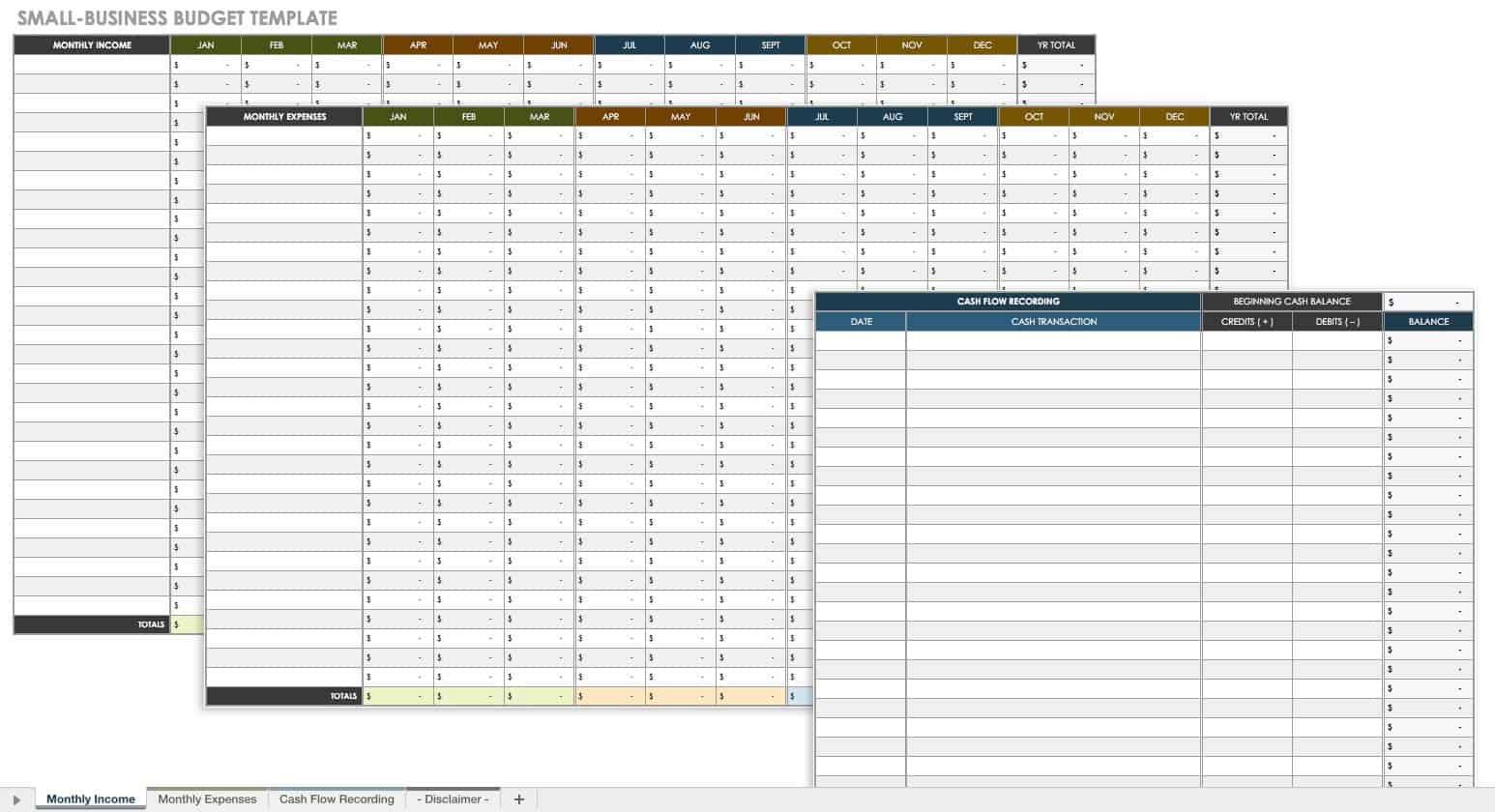
This business budget template is ideal for small businesses that want to record estimated revenue and expenditures on a monthly and yearly basis. This customizable template comes with a tab to list income, expenses, and a cash flow recording to track cash transactions and balances.
Download Small Business Budget Template
Professional Business Budget Template

Established organizations will appreciate this customizable business budget template, which contains a separate tab to track projected business expenses, actual business expenses, variances, and an expense analysis. Once you enter projected and actual expenses, the built-in formulas will automatically calculate expense variances and populate the included visual charts.
Download Professional Business Budget Template
For additional resources to plan and track your business costs and expenses, visit “ Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company .”
Other Financial Templates for Business Plan
In this section, you’ll find additional financial templates that you may want to include as part of your larger business plan.
Startup Funding Requirements Template
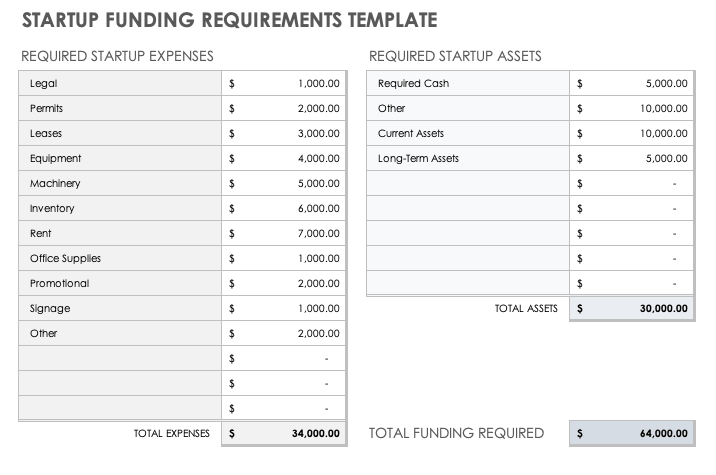
This simple startup funding requirements template is useful for startups and small businesses that require funding to get business off the ground. The numbers generated in this template should align with those in your financial projections, and should detail the allocation of acquired capital to various startup expenses.
Download Startup Funding Requirements Template - Excel
Personnel Plan Template
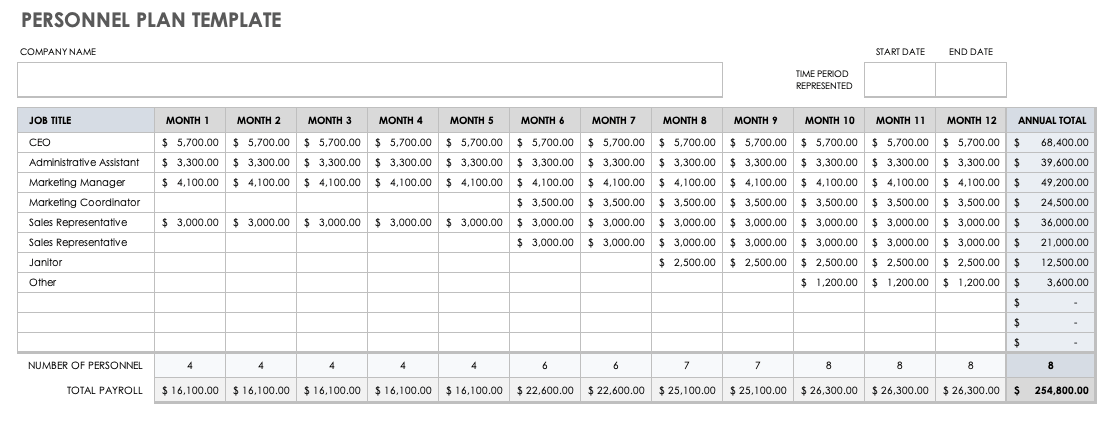
Use this customizable personnel plan template to map out the current and future staff needed to get — and keep — the business running. This information belongs in the personnel section of a business plan, and details the job title, amount of pay, and hiring timeline for each position. This template calculates the monthly and yearly expenses associated with each role using built-in formulas. Additionally, you can add an organizational chart to provide a visual overview of the company’s structure.
Download Personnel Plan Template - Excel
Elements of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Whether your organization is a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, the financial plan is the cornerstone of any business plan. The financial section should demonstrate the feasibility and profitability of your idea and should support all other aspects of the business plan.
Below, you’ll find a quick overview of the components of a solid financial plan.
- Financial Overview: This section provides a brief summary of the financial section, and includes key takeaways of the financial statements. If you prefer, you can also add a brief description of each statement in the respective statement’s section.
- Key Assumptions: This component details the basis for your financial projections, including tax and interest rates, economic climate, and other critical, underlying factors.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculation helps establish the selling price of a product or service, and determines when a product or service should become profitable.
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement, this section details the sales, cost of sales, profitability, and other vital financial information to stakeholders.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: This area outlines the projected cash inflows and outflows the business expects to generate from operating, financing, and investing activities during a specific timeframe.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: This document conveys how your business plans to manage assets, including receivables and inventory.
- Key Financial Indicators and Ratios: In this section, highlight key financial indicators and ratios extracted from financial statements that bankers, analysts, and investors can use to evaluate the financial health and position of your business.
Need help putting together the rest of your business plan? Check out our free simple business plan templates to get started. You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy. If you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering startup business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Plan Financials and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
52+ SAMPLE Break Even Analysis in PDF | MS Word | Excel
Break even analysis | ms word | excel, 52+ sample break even analysis, break-even analysis: what is it, why is break-even analysis important, components of break-even analysis, how to run a break-even analysis, what are the three main assumptions of break-even analysis, what is contribution analysis, what is the formula for profit, who invented break-even analysis.

Break Even Point Analysis
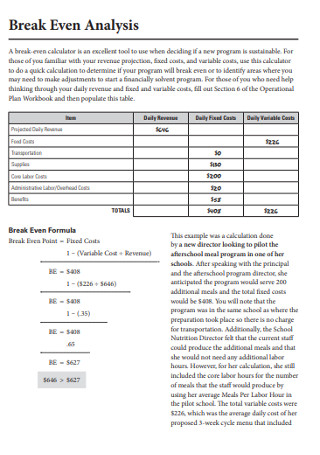
Sample Break Even Analysis

Revenue Costs and Break-Even Analysis
Project Break Even Analysis

Break Even Profit Analysis

Engineering Economic Break Even Analysis
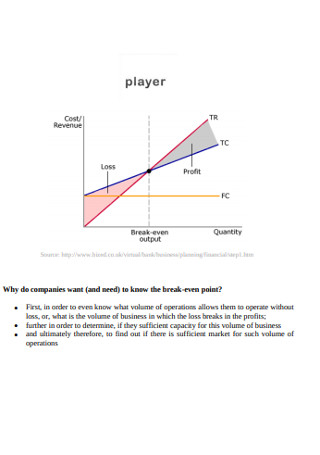
Example of Break-even Analysis Diagram

Basic Break-Even Analysis

Business Break Even Analysis
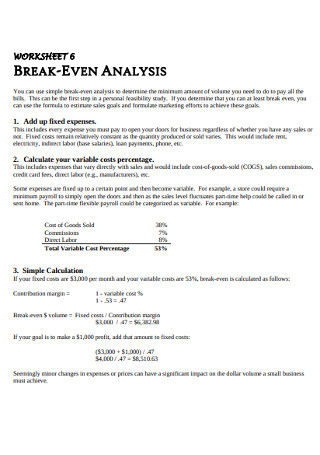
Break Even Analysis Worksheet
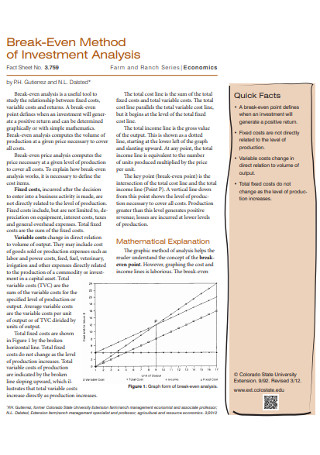
Break Even Method of Investment Analysis

Basic Break Even Analysis

Application of Break-Even Point Analysis
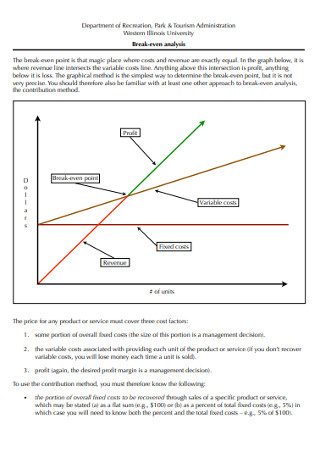
Tourism Administration Break Even Analysis

Municipal Pool Break Even Analysis

Projects Break-Even Analysis

Simple Break Even Analysis

Break Even Analysis for Small Business
Break-Even Analysis in a Retail Store

Break Even Point and Incremental Analysis

Mini Lesson Break-Even Analysis
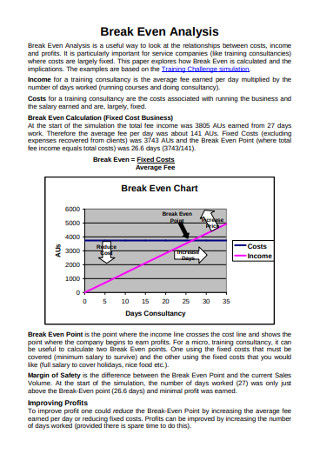
Sample Break Even Analysis Chart

Break-even Analysis in Engineering Projects

Case Study Re-look at Break-Even Analysis

Break Even Business Analysis

Business Textbook Break Even Analysis

Business Studies Break Even Analysis

Rationality of Stochastic Breakeven Analysis

Break Even Analysis as a Decision Tool Template

Standard Break Even Analysis
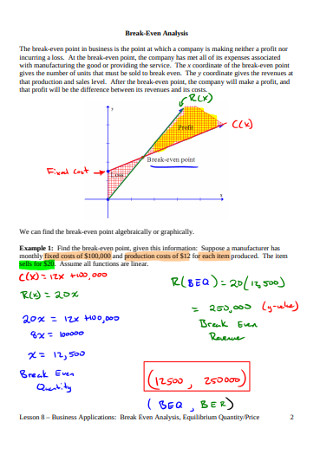
Break-Even Price Analysis

Break-Even Analysis and Market Equilibrium

Fromal Break Even Analysis

Study of Profitability and Break-Even Analysis

Break Even Marketing Analysis

Agricultural Development Break-Even Analysis

Managerial Economics Break Even Analysis

Break Even Budget Analysis
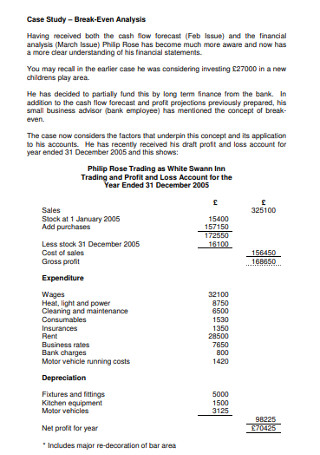
Break Even Case Study Analysis

Break Even Analysis Format

Calculating Breakeven Analysis

Company Break Even Analysis

Break-Even Analysis Worksheet
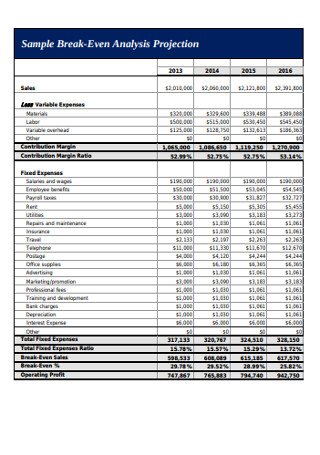
Sample Break-Even Analysis Projection
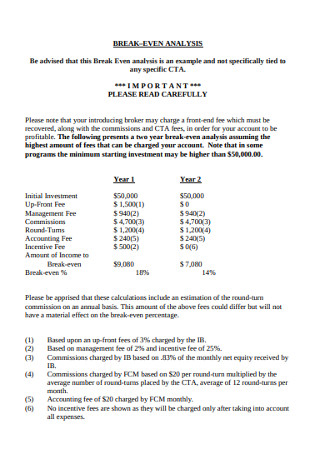
Break Even Analysis in Example
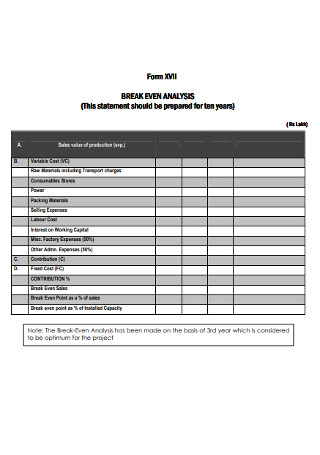
Break Even Analysis Statement Template
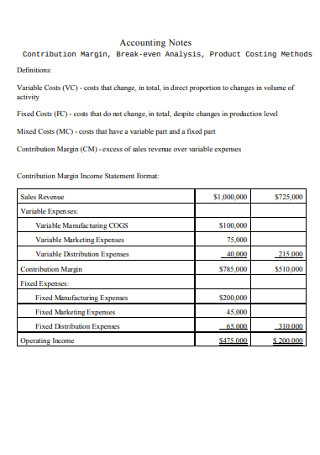
Break Even Accounting Analysis
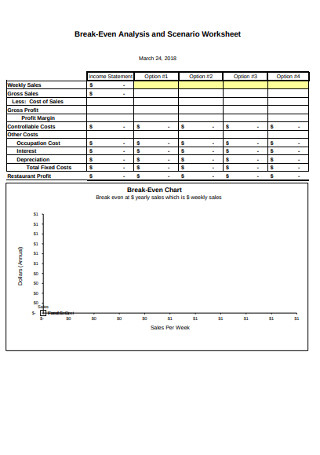
Break-Even Analysis and Scenario Worksheet

Breakeven Construction Analysis
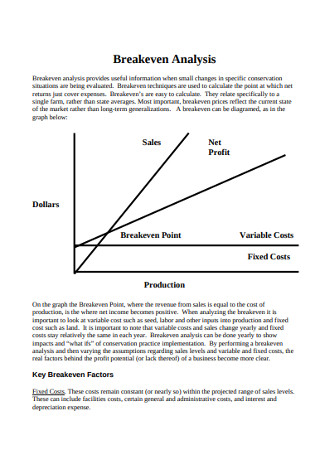
Factors Breakeven Analysis
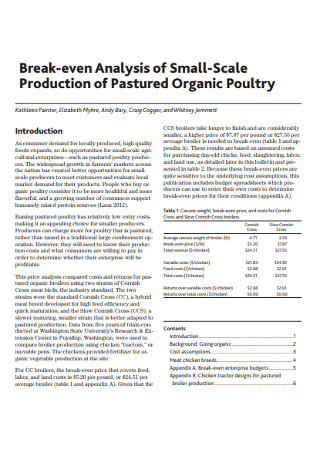
Small Scale Production of Break Even Analysis

Break Even Analysis and Profit Planning Template
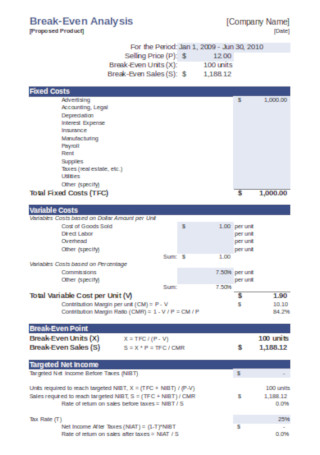
Company Break Even Analysis Template
Covers all types of costs, sets a practical and timely financial projection, benefits different businesses, works as a motivational conduit, step 1: determine the different costs in your business, step 2: choose a sample break-even analysis template, step 3: use the appropriate bep formula, step 4: observe an easy-to-follow structure, step 5: make the right move, share this post on your network, you may also like these articles, 25+ sample business impact analysis templates in pdf | ms word.
As the COVID-19 continues and has already affected many lives of people worldwide, there is also big economic damage that negatively affected the global economy. According to Statista's estimate,…
53+ SAMPLE Analysis Report Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Are you familiar with those complex statistical graphs, detailed organizational charts, or tables presented in business? Such visual representations are useful to give information, define relationships, and show patterns of…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions

Break Even Analysis
Ai generator.
Every single business company’s main goal is to be profitable in order to expand and widen the scope of the business. Given that you have your marketing, operational, and strategies for your planning and preparation, how then will you specifically assess and analyze if your company is being profitable? How will you know how much is your margin before you incur a loss? In these cases, you need to have a break-even analysis. It helps you in a lot of ways including budgeting, setting targets, monitoring, creating strategies, and a lot more. Hence, you must know and understand the break-even computation and analysis. Through this article, we will provide you the necessary knowledge that you need in order to have a clear understanding of the break-even analysis. You may also see case analysis examples
- Product Cost Analysis Examples
- Customer Profitability Analysis Examples
In the next section, provided are several break-even analysis examples that can help you and guide you to know more about break-even analysis. You may also check out here quantitative analysis examples
Basic Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 336.6 KB
Break-Even Analysis Template Example

Size: 46.8 KB
What Is Break-Even Point?
In simple terms, break-even point is where there is neither profit nor loss in a company’s operation. This is the result when the expenses incurred by the entity is equal to the sales. The total costs equals the total revenue. The company has simply net zero. In break-even point, it is assumed that all the costs have been paid off including the opportunity costs and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. You may also see job analysis examples
In order for the company to pass the break-even point, the dollar value of sales is higher than the variable cost per unit. Simply stated, the selling price of an item must be higher than what the company has paid for it or its components and more than enough to cover the initial price they paid.
Break-Even and Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis Example

Size: 259.7 KB
Comprehensive Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 120.6 KB
Concise Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 265 KB
Calculation of Break-Even Point
There are certain formulas relating to the calculation of break-even point. The formulas below may be somewhat confusing at first, but when you start to understand the whole concept, you will find yourself amazed of how you can calculate fast and accurately in terms of break-even point. You may also see hazard vulnerability analysis examples
To start, you must understand that sales (S) less costs or expenses (C) equals profit (P). Note that C can be broken down into fixed costs (FC) and variable costs (VC). In order to break even, your profit must be equal to 0. Hence, S?FC?VC=0.
This is the very basic thing that you need to keep in mind regarding break-even point. Moreover, below are some fundamental formulas that you must also understand. You may also see dust hazard analysis examples
Break-Even Point in Units
In order to calculate for the break-even point (BEP) in units (u), you must divide the total fixed costs of production by the sales price (S) per unit less the variable costs to produce the product.
BEPu=FC/(Su?VCu)
Note that when you thoroughly examine the equation, this is just the same as the basic computation displayed above only that the parts have been rearranged. Furthermore, you must know that Su?VCu is the contribution margin (CM) per unit. So, to simplify the equation, You may also see earned value analysis examples
BEPu=FC/CMu
Break-Even Point in Dollars
In the above section, it presents the calculation of the break-even point in units. On the other hand, if you want to calculate for the break-even point in dollars (d), simply multiply the sales price (SP) per unit by the BEPu.
BEPd=SPu×BEPu
Break-Even Analysis
After knowing the above equation, let us take a step further and compute for the number of units to be sold to achieve a certain level of profitability. To compute, we must divide the goal amount of profit (G) in dollars by the contribution margin per unit. Then, add back the BEPu.
No. of Units to Produce G=(Gd/CMu)+BEPu
Detailed Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 843.7 KB
Discussion on Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 96.3 kb
Where to Start
In order to start your break-even point analysis, especially if you have never conducted a break-even point analysis before, you must assess the entity’s commonly sold goods. Additionally, you must also gather several important information such as the total fixed costs that are incurred in making each product, the variable costs for each product, the sales price of the product, as well as the net profit derived from selling it. These are the first things and amount that you must secure in order complete your equation. You may also see functional behavioral analysis examples
Applying these basic information that you gathered to the formulas presented above, it is now a lot more easy for you to start your break-even point analysis.
Importance and Significance of Break-Even Analysis
As stated above, the break-even point is where your total costs equal your total revenue; hence, you incur neither profit nor loss. This concept is not only limited to economic use but also used by a lot of professionals relating to business and finance such as the entrepreneurs, accountants, financial planners, manager, and marketers, helping them in the decision-making process as well as to calculate the costs and sales in order to be profitable. You may also see force field analysis examples
Until today, break-even analysis is still widely used because of the benefit it has provided to the business people. Speaking of the importance of break-even analysis, below are several key importance and significance of break-even analysis. You may also see data analysis examples
Helps in Determining the Number of Units to be Sold
As we can see from formulas above, through the computation of break-even point, we can determine the number of units needed to be sold in order to compensate all the costs that are incurred in making the product or bringing the product to its current salable condition. Through determining the selling price for each product as well as the variable and fixed costs, you will have a full understanding of the break-even analysis. You may also see cash flow analysis examples
Aids in Budgeting and Setting Targets
We have also observed from the formulas how to reach a break-even point in your product. Accordingly, when you know at which point and how much you are going to sell in order to break even, you can easily set budgets, which is important in making desired profits. Moreover, break-even analysis can also be used in setting realistic targets for the business because you know at which point you become profitable; hence, you can use this knowledge to set benchmarks or targets for your entity. You may also see business systems analysis examples
Helps in the Calculation of the Margin of Safety
Your break-even analysis is also of great help in the calculation of your margin of safety, which is the difference between actual or budgeted sales and the level of break-even sales. It can be calculated by subtracting the current level of sales less the break-even point and then dividing it by the selling price per unit. In instances when there is a recession or an economic downturn, the sales of your company may tend to decline. Hence, with the help of the break-even analysis, it is easy for you to determine the minimum level of sales required so you can still make profits. You may also see vendor analysis examples
Helps in Cost Control and Monitoring
Since it is clearly presented in the equation the fixed and variable costs, business owner can now monitor and assess the changes to these costs with the help of break-even analysis. This also helps in determining the extent of changes in costs which affects the profitability as well as the break-even point. You may also see training needs analysis examples
Aids in Devising a Pricing Strategy
Now that we have understood how the break-even point is computed, we can easily devise a pricing strategy for your products because you already know that a certain change in the selling price can affect the break-even point, thus affecting your income. In general, break-even analysis helps people dealing with businesses to make the right decisions toward creating a pricing strategy that would work given the information from their break-even analysis. You may also see business case analysis examples
Lengthy Explanation on Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 745.3 KB
Managerial Economics Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 890.8 KB
Well-Discussed Break-Even Analysis Example

Size: 44 KB
Break-Even Analysis Assumptions and Limitations
Break-even analysis has proven to be useful by many people in different industries in different ways. More and more people are adopting this concept as this can greatly help them improve their business just as presented in the previous section.
However, just like any other concepts, the break-even analysis has some assumptions and limitations, which is equally its strengths and weakness. Although break-even analysis is beneficial mainly in determining how to increase the profit as well as the specific quantity needed to get pass the break-even point, certain assumptions and limitation may prove that there are other factors that may affect the operation in the real world. You may also see job task analysis examples
On a positive note, break-even analysis are still recommended and used by professionals because although it has limitations, it can still be a functional and practical approach.
Below are the basic assumptions as well as the limitations in the use of break-even analysis.
Assumptions
- The first assumption is that all costs can be categorized as fixed or variable costs.
- Total fixed costs remain the same for all output levels.
- Total variable costs vary proportionately with output level. Hence, the variable cost per unit will not change.
- Sale price per unit remains the same for each output level.
- Costs and revenue act in a linear manner within a relevant range.
- Other than sales volume, no other factor can affect costs and sales revenue.
- It is also assumed that the analysis relates to businesses producing one product only or a constant product mix.
- The technology, production methods, and efficiency remain the same, consistently working in a good condition and producing same quality output.
- Inventory levels are also expected to remain constant.
- Lastly, it has also to be assumed that there are no inventories at beginning or at end of the accounting period.
Limitations
- Because only the variable and fixed costs are considered, semi-variable costs, which is also a kind of cost that usually exists in every business, are ignored and are taken into account.
- Fixed costs may vary if output increases or decreases substantially.
- There might be changes in per unit variable costs when you consider various reasons such as bulk buying discounts, overtime, among others. These costs are being ignored when computing for the break-even point.
- It might also be possible that the sales price may have to be reduced to have more sales or may be increased to cover increased costs.
- Selling prices and variable costs per unit may differ at different output levels.
- This computation does not also consider various inflation rate and other external factors in economic state that may also affect sales volume.
- There might be changes in the practice for the technology or even the production methods.
- When there are changes in technology or production method, there might also be the possibility of any increase in inventory levels, when production volume exceeds sales volume, or de-stocking, when sales volume exceeds the production levels.
Since all business companies need to be profitable to make the business grow, calculating your break-even point is important in order for you to make a target sales and to determine how much you must sell so you won’t incur a loss. Simply, break-even point is the point where there is no profit or loss, where the expenses you incur are in the same amount as the revenue you have earned. You may also see failure analysis examples
Finally, break-even analysis is important especially in determining the number of units to be sold, in budgeting and setting targets, in the calculation of the margin of safety, in cost control and monitoring, and in devising a pricing strategy. You may also see situation analysis examples
Never miss this opportunity to check out the examples of break-even analysis as presented in the above section.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A break-even analysis is a critical part of the financial projections in the business plan for a new business. Financing sources will want to see when you expect to break even so they know when your business will become profitable. But even if you're not seeking outside financing, you should know when your business is going to break even.
Single Project. The analysis is based on the relationship: Profit = revenue - total cost. = R - TC At breakeven, there is no profit or loss, hence, revenue = total cost or, R = TC Note: It is to be noted that +ve sign is used for both the revenue and the costs. If we are to use.
Business owners can use a breakeven calculation (also called breakeven analysis) to determine how many product or service units they need to sell at a given price point to break even. Once you know the fixed and variable costs for the product or service your business produces or a good approximation of them, you can use that information to
It's a simple calculation, but do you know how to use it? In a world of Excel spreadsheets and online tools, we take a lot of calculations for granted. Take breakeven analysis. You've probably ...
business financial plan 1. financial overview 2. assumptions. page 2 3. key financial indicators and ratios . page 3 4. break-even analysis . page 4 5. financial statements 5.1 pro forma profit and loss statement . page 5 5.2 pro forma cash flow statement . page 6 5.3 pro forma balance sheet .
The break-even analysis is important to business owners and managers in determining how many units (or revenues) are needed to cover fixed and variable expenses of the business. Therefore, the concept of break-even point is as follows: Profit when Revenue > Total Variable Cost + Total Fixed Cost. Break-even point when Revenue = Total Variable ...
Importance of Break-Even Analysis for Your Small Business. A business could be bringing in a lot of money; however, it could still be making a loss. ... and prepare a business plan. The break-even point calculation is an essential tool to analyze critical profit drivers of your business, including sales volume, average production costs, and, as ...
Break-even analysis entails the calculation and examination of the margin of safety for an entity based on the revenues collected and associated costs. Analyzing different price levels relating to ...
7.3 BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS Insert chart and or graph depicting your breakeven point below: 7.4 PROJECTED INCOME STATEMENT Insert Projected Income Statement Below: CONFIDENTIAL Page 12 7.5 PROJECTED CASH FLOW STATEMENT ... BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE DISCLAIMER Any articles, templates, or information provided by Smartsheet on the website are for ...
Break-even analysis is a tool used to calculate the point at which a company's revenues equal its expenses. This point is known as the Break-Even Point (BEP). It is used to assess whether a business is likely to be profitable. There are two main types of break-even analysis: Graphical and chart.
with the sale of product - it is also called break-even point. In other words profit = 0. Break-even analysis is accounting tool to help plan and control the business operations. Break-even point represents the volume of business, where company's total revenues (money coming into a business) are equal to its total expenses (total costs).
Break even analysis is a calculation of the quantity sold which generates enough revenues to equal expenses. In securities trading, the meaning of break even analysis is the point at which gains are equal to losses. Another definition of break even analysis is the examination and calculation of the margin of safety that's based on a company ...
The price of one of your products is $100. Your fixed costs are $10,000 per month, and the variable cost is $50 per product. The formula to calculate how many products you must sell to break even would look like this: $10,000 / ($100 - $50) = 200. Based on the formula, you must sell 200 products to cover your costs, effectively breaking even.
Breakeven Analysis: The Definitive Guide to Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis - Free download as PDF File (.pdf) or read online for free. This book is a comprehensive collection of cost-volume-profit applications. Business professionals, entrepreneurs, business professors, and undergraduate and graduate business students will benefit from this one-stop how-to book of formulas, explanations, and ...
To do this, click on the Home tab. Select the Format drop-down menu in the Cells group and choose "Protect Sheet.". In the dialogue box, uncheck the "Select Locked Cells" option. In doing this, the protection will guide you to input the cells. Click on "OK" and you can even add a password for the file if you prefer.
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
After a full introduction of the break-even analysis's definition, importance, and components, you are more than ready to conduct the break-even analysis itself. In fact, you only need to mind these five steps to run an effective break-even analysis: Step 1: Determine the Different Costs in Your Business. Every business is different.
Break-even analysis, as part of a business plan, can be helpful in gaining finance. Target setting made easier. Can identify the margin of safety − aids planning Limitations: Often regarded as too simplistic as some assumptions are unrealistic. It assumes all output is sold, which is often not the case. Assumes that conditions remain unchanged
Break-Even Analysis. After knowing the above equation, let us take a step further and compute for the number of units to be sold to achieve a certain level of profitability. To compute, we must divide the goal amount of profit (G) in dollars by the contribution margin per unit. Then, add back the BEPu.
The break-even point is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal, meaning there is no loss or gain for your small business.In other words, you've reached the level of production at which the costs of production equals the revenues for a product. For any new business, this is an important calculation in your business plan.Potential investors in a business not only want to know ...
le to:Understand the various concepts of Break-Even Analysis.Use the concept of Break-Even Analysis in taking make or buy decisions, s. iness, output, pricing and costing decisions.1.0 IntroductionTradi. ionally the basic objective of the firm is to maximise profits. Economic profit of the production of a commodity is the difference be.
running a business, focusing on break-even point analysis. Students will be able to: 00 Understand the vocabulary associated with revenue and expenses 00 Understand the relationship among revenue, expenses and profit 00 Analyze break-even data in a variety of situations 00 Calculate price, sales units, and revenue values for different situations.
Business Plans. Sue Nugus, in Financial Planning Using Excel (Second Edition), 2009. Break-even analysis. The break-even analysis model is a deterministic plan that calculates the volume at which the total costs are equal to the total revenue. The model is on the CD accompanying this book under the name breakeven.This level of volume is defined as the break-even point.