Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


Author Affiliations in Research Papers: Answering Your Top 3 Queries
Author affiliation in research papers is an important element because it offers readers useful information about where the research was conducted. However, the time from research to manuscript creation and then publication is so long that by the time the research paper is published authors may have moved to a different institution or location.
In such cases, researchers may have questions about how these affiliation changes could be handled because it’s important for readers to know both old and new author affiliations in research papers. This article aims to answer a few common questions researchers may have regarding this process.
Table of Contents
1. Do I need an affiliation for journal publication ? Can I list multiple author affiliations in research papers ? 1
In academic publishing, an affiliation is the university or institution to which an author belongs or where authors have conducted a major part of the research that is discussed in their paper. Author affiliation in research papers is usually listed after the author names and provide credibility to the research and give readers confidence that the research is backed by an institution or university. The name of the institution clarifies who oversees the research integrity because these institutes usually have review boards that approve the research conducted at their institute. Because of the increase in the number of international collaborations among authors, an individual author may have multiple affiliations, all of which must be listed in the paper to ensure transparency. However, while some manuals or journal style guides may restrict the number of affiliations per author (e.g., APA manual, 7 th ed, no more than 2 affiliations per author; AMA style manual, no more than 1 or 2 affiliations per author in some types of manuscripts like viewpoints or research letters), other journals may have no such restrictions. 2

2. What should my author affiliation in research papers be if my workplace changes after manuscript submission? Can/should I mention both old and new author affiliations in research papers ? 3
Usually, it is acceptable to mention both current and previous author affiliations in research papers. In general, if your research was primarily conducted at your previous institution using its resources, then this institute should definitely be included in the author affiliations. This same institution should also be mentioned in the Materials and Methods section of your paper and as the sponsor of your work. However, the name of your current institute should also be mentioned so that readers could contact you if required. Different journals or publishers may have different rules for listing old and new author affiliations in research papers, so it is always advisable to consult the specific journal’s instructions for authors.
Here are a few examples of how different publishers or journals address pre- and post-submission changes in author affiliations in research papers :
- The American Medical Association’s style manual (11 th edition): As per the American Medical Association’s style manual’s rules for author affiliation in research papers, if the author has moved after submitting a manuscript, the current affiliation should still be provided to the journal so that it could be added to the list of affiliations.
- Cambridge University Press : As per the Cambridge University Press’s rules for author affiliation in research papers, if an author has moved before manuscript submission, the current affiliation could be included under Acknowledgments.
- Sage journals : As per Sage journals ’ rules for author affiliation in research papers, an author must include new affiliations after submission as a note at the end of the manuscript.
- American Chemical Society Publications, Wiley : As per American Chemical Society Publication’s rules for author affiliation in research papers, if the current address of the author is different from the one where the research was conducted, then this current address should be included in a footnote on the title page.

3. Is it possible to change author affiliation in research papers after the manuscript is accepted/has already been published?
Most journals accept requests for changes in author affiliation in research papers after acceptance , although there are a few exceptions. However, once an article has been published, changes may not necessarily be accepted or may require special permission and approval from the journal editor.
Listed below are a few examples of how different publishers address post-acceptance or post-publication requests for changes in author affiliation in research papers :
- Cambridge University Press : 4 May accept an affiliation change request after submission in the event of a genuine reason. If the article has been published, a change in author affiliation in research papers would require the publishing of a linked correction notice.
- Taylor and Francis : 5 If the authors have changed affiliations since completing their research, then the new affiliation can be acknowledged in a note; however, they don’t usually make changes to affiliations after accepting a manuscript for publication.
- Springer : 6 Do not update or change affiliations once an article has been published.
Author affiliations in research papers constitute an important part of the author information and should be mentioned accurately and clearly for all authors. Always refer to the journal or publisher’s instructions for authors for up-to-date information on the format for writing author affiliations in research papers . We hope this article has elaborated the importance of affiliations for journal publication and helped clarify any questions about handling changes in them.
Other Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does author affiliation in research paper mean?
Author affiliation in research papers refers to the academic, research, or professional institutions to which the paper’s authors are affiliated. Usually mentioned below the author’s name, author affiliation in research papers are important as they provide important information about the author’s background and the context in which the research was conducted. Author affiliations help identify experts in specific fields or disciplines. They establish the credibility and trustworthiness of the research, and affiliations with top institutions add weight to the author’s work and indicate a higher level of expertise and academic rigor. This information also allows readers to identify potential conflicts of interest or connections, which fosters collaborations that further scientific progress.
Q: What is the first author’s affiliation?
The first author affiliation in a research paper refers to the institution or organization to which the lead author is primarily affiliated. The first author is the individual who makes the most substantial contribution to the research work, hence their affiliation is significant. This detail serves as an indicator of the research environment and resources available for the research project, which can bolster the credibility, reach, and impact of the research paper.
Q: Can an author have two affiliations?
Yes, it is possible for an author to have two or more affiliations. Authors may have joint appointments or collaborations between different institutions, allowing them to be affiliated with multiple organizations simultaneously. In such cases, authors often indicate their affiliations using superscript numbers or symbols to denote different institutions. This information helps readers understand the diverse institutional connections and collaborations of the authors.
References
- E. Bik. False affiliations and fake authors. Science Integrity Digest. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://scienceintegritydigest.com/2019/06/04/false-affiliations-and-fake-authors/
- American Medical Association style manual. 11 TH edition, Section 2.3.3
- Q&A Forum. Editage Insights. Accessed December 16, 2022. https://www.editage.com/insights/what-should-my-affiliation-be-if-i-changed-my-workplace-during-a-manuscript-submission
- Author affiliations. Cambridge University Press. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/authors/journals/author-affiliations#1a
- Defining authorship in your research paper. Author services: Taylor & Francis. https://authorservices.taylorandfrancis.com/editorial-policies/defining-authorship-research-paper/
- Authorship principles. Springer. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.springer.com/gp/editorial-policies/authorship-principles
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What are the Best Research Funding Sources

Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach
- Interlibrary Loan and Scan & Deliver
- Course Reserves
- Purchase Request
- Collection Development & Maintenance
- Current Negotiations
- Ask a Librarian
- Instructor Support
- Library How-To
- Research Guides
- Research Support
- Study Rooms
- Research Rooms
- Partner Spaces
- Loanable Equipment
- Print, Scan, Copy
- 3D Printers
- Poster Printing
- OSULP Leadership
- Strategic Plan
Scholarly Articles: How can I tell?
- Journal Information
- Literature Review
Author and affiliation
Learn more about the author.
- Introduction
- Specialized Vocabulary
- Methodology
- Research sponsors
- Peer-review
If you can't find an author affiliation or want to learn more about the authors and their credentials, here are some ways to do so:
- Search for the author on Google. Sometimes you can find a personal page about an individual. Many of the faculty members at OSU have a website that lists their credentials (education) and research.
- Do a search in one of the online databases to see what else the author has written. Is this person someone who published a lot in this field? For example, a search in the Academic Search Complete database for the author Sandra Hofferth shows the articles she has co-authored on a range of children's issues .
- Look up the institution. What kind of institution is it? Is the author still affiliated with the institution?
One of the first things to look for is the author or authors. In a research article, the authors will list their affiliation, usually with a university or research institution. In this example, the author's affiliation is clearly shown on the first page of the article. In a research article, you will never have an anonymous author or need to look for the author's name or affiliation.
- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Abstract >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 3:26 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.oregonstate.edu/ScholarlyArticle
Contact Info
121 The Valley Library Corvallis OR 97331–4501
Phone: 541-737-3331
Services for Persons with Disabilities
In the Valley Library
- Oregon State University Press
- Special Collections and Archives Research Center
- Undergrad Research & Writing Studio
- Graduate Student Commons
- Tutoring Services
- Northwest Art Collection
Digital Projects
- Oregon Explorer
- Oregon Digital
- ScholarsArchive@OSU
- Digital Publishing Initiatives
- Atlas of the Pacific Northwest
- Marilyn Potts Guin Library
- Cascades Campus Library
- McDowell Library of Vet Medicine
- Translation
Understanding Author Affiliation and accurately mentioning it in different scenarios
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 16 April, 2022
In academic publishing, the affiliation of an author is the place (institution) at which the author conducted the research that they have reported / written about . However, given the frequent mobility of academics, that place may not necessarily be the place the author happens to be based at the time of submitting the paper . This article explains the significance of affiliation and illustrates how to accurately mention your affiliation in different scenarios.
The importance of affiliation
In some cases, affiliation is linked to authenticity . Imagine a research paper on field pollination of rice by an author whose affiliation is that of an institute in the polar region. It is not that this work cannot be done, but it would seem incongruous and may raise doubts.
In many cases, it is a matter of prestige . Science may be democratic, but not all research institutions and laboratories are considered equal.
Some may be better equipped than others. Some may have more luminaries on their staff – people who have outstanding work (or even prizes) to their credit. Some may have enviable collections of records or research material.
Therefore, by proxy, work carried out at those institutions is regarded more highly, at least initially, than that carried out at lesser-known institutions.
A study by Peters and Ceci (1982) found that when 12 already published papers were resubmitted after doctoring the affiliations to replace the original high-status institutions with fictitious ones with no status in the field, eight of those papers were rejected.
Mentioning your affiliation in a paper
In nearly all published papers, affiliations of their authors are given after their names but before the abstract. The typical sequence is:
- Title of the paper
- Names of authors
- Affiliations
- Abstract and keywords

Paper with title, author names, affiliation, abstract and keywords
Mentioning affiliation and address
Authors of research papers must keep an important distinction in mind: that an affiliation is not the same thing as a mailing address . The former names the institution at which the work in question was carried out whereas the latter simply supplies the current contact details of the author.
For example…
A PhD candidate submitting a paper based on their doctoral work should name, as their affiliation, the university/institution that is granting them the doctorate. However, that author may have since moved to another institution for a post-doctoral job. This is not considered their affiliation, but just provides their current contact details.
Therefore, you may have to name two institutions in your manuscript:
- Under Affiliation : Name the institution where the work (that forms the subject of the present study) was undertaken.
- Under Current address : Name the institution at which you happen to be working at the time of submission or even your home address if you have retired.
Note : The ‘current address’ serves as the means of contact and can change; the affiliation cannot.
Mentioning affiliation when you change your institute
It may also happen that when you submitted the paper, you were stationed at Institute A and accordingly gave that as your contact address, and subsequently, you moved to Institute B. In such cases, so long as your paper is yet to be published, you should inform the journal of your new current address at Institute B. The paper is based on the work you carried out while you were based at institute A, which constitutes the affiliation and remains unchanged.
Mentioning affiliations for multi-author papers
Most research papers have multiple authors and not all of them may have the same affiliation. To match their names to their affiliations, journals may use the method used for indicating footnotes . The names of authors are followed by superscript letters, numerals or other symbols, and the same symbols precede the respective affiliations.
We recommend : Note the journal’s preferred method (letters, numerals or other symbols) and be sure to follow the journal guidelines when preparing your manuscripts for submission .

Numerals indicating authors (above) and their affiliations (below) in a paper
Dealing with affiliations during peer review
To avoid the kind of bias mentioned earlier, affiliation information is removed in manuscripts sent out for review: in a blind review , the reviewers do not know who wrote the paper under review, nor their institutional affiliation. To make this easier, many journals ask that such identifying information be separated from the body of the paper . Authors are advised to attend to the journal’s instructions in this regard, which typically involve a separate title page explicitly showing the names and affiliations. This page is usually removed before sending the paper to reviewers.
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Share with your colleagues
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- APA Title Page (7th edition) | Template for Students & Professionals
APA Title Page (7th edition) | Template for Students & Professionals
Published on November 6, 2020 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on January 17, 2024.
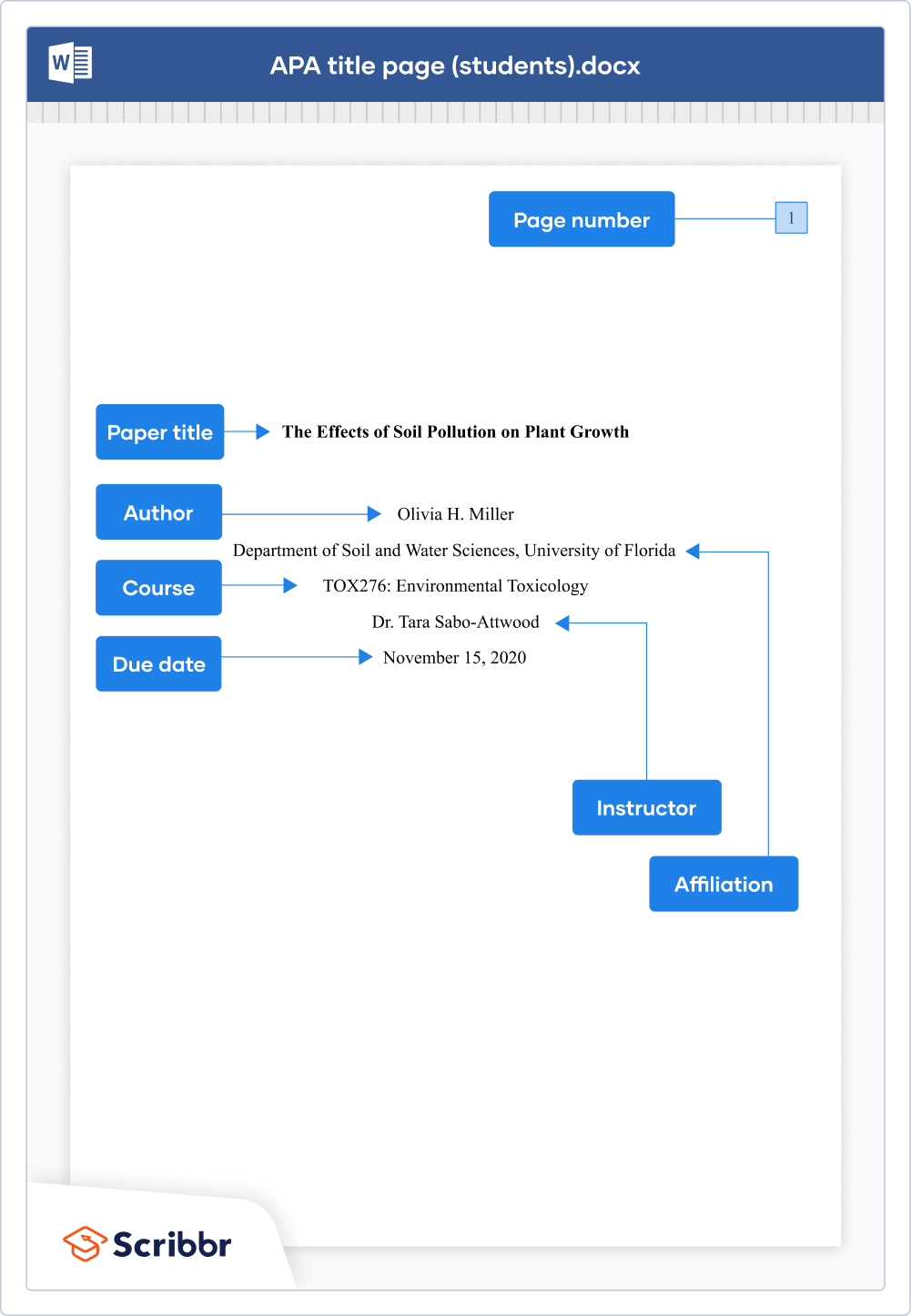
APA provides different guidelines for student and professional papers. The student version of the APA title page should include the following information (double spaced and centered):
Paper title
- Author name
- Department and university name
- Course number and name
- Instructor name
- Due date of the assignment
The professional title page also includes an author note (flushed left), but not a course name, instructor name, or due date.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Title page example (student and professional version), institutional affiliation, course information, author note, page header, including an image on the title page.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Write an informative, striking title that summarizes the topic of your paper. Try to keep the title focused and use relevant keywords.
Place the title three or four lines down from the top of the paper. Center align and bold it. Don’t forget to use title case capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each word, except small words such as articles and short prepositions).
Write the author’s name under the paper title (leave a blank line in between). Give their full names (first name, middle initial(s) and last name), but don’t include titles (Dr., Prof.) or degrees (Ph.D., MSc).
Multiple authors on the title page
List the authors in order of their contribution. If there are two authors, separate their names with the word “and”, like this:
If there are more than two authors, separate their names with a comma. Only write “and” before the last author, like this:
Write the author’s affiliation on the next line under the author names. Students should specify the department and institution where they’re attending school. Professional researchers should specify the department and institution where they conducted their research.
Multiple authors with different affiliations
Use superscript numbers on the author line to indicate which institution they’re affiliated with. Don’t use superscript numbers if all authors are affiliated with the same institution (and department).
On a student title page, provide information about the course. List the following information on separate (double spaced) lines under the author’s affiliation:
- Instructor(s)
- Assignment’s due date
For professional papers, you may include an author note. This note may contain the author’s ORCID iD, affiliation changes, disclosures of conflicts of interest, brief acknowledgments, and contact information (in that specific order). Present this information in separate paragraphs.
Place the author note on the bottom half of the page. Center the label “Author note” and apply bold styling. The paragraphs in the author note are left-aligned. The first line of each new paragraph is indented.
For more information about formatting the author note, see section 2.7 of the APA Publication Manual.
For a student title page, the page header consists of just a page number in the top-right corner. There is no need for a running head (as was the case in APA 6th edition).
A professional title page does have a running head. The running head is an abbreviated version of the paper title in all capital letters. The maximum length is 50 characters (counting spaces).
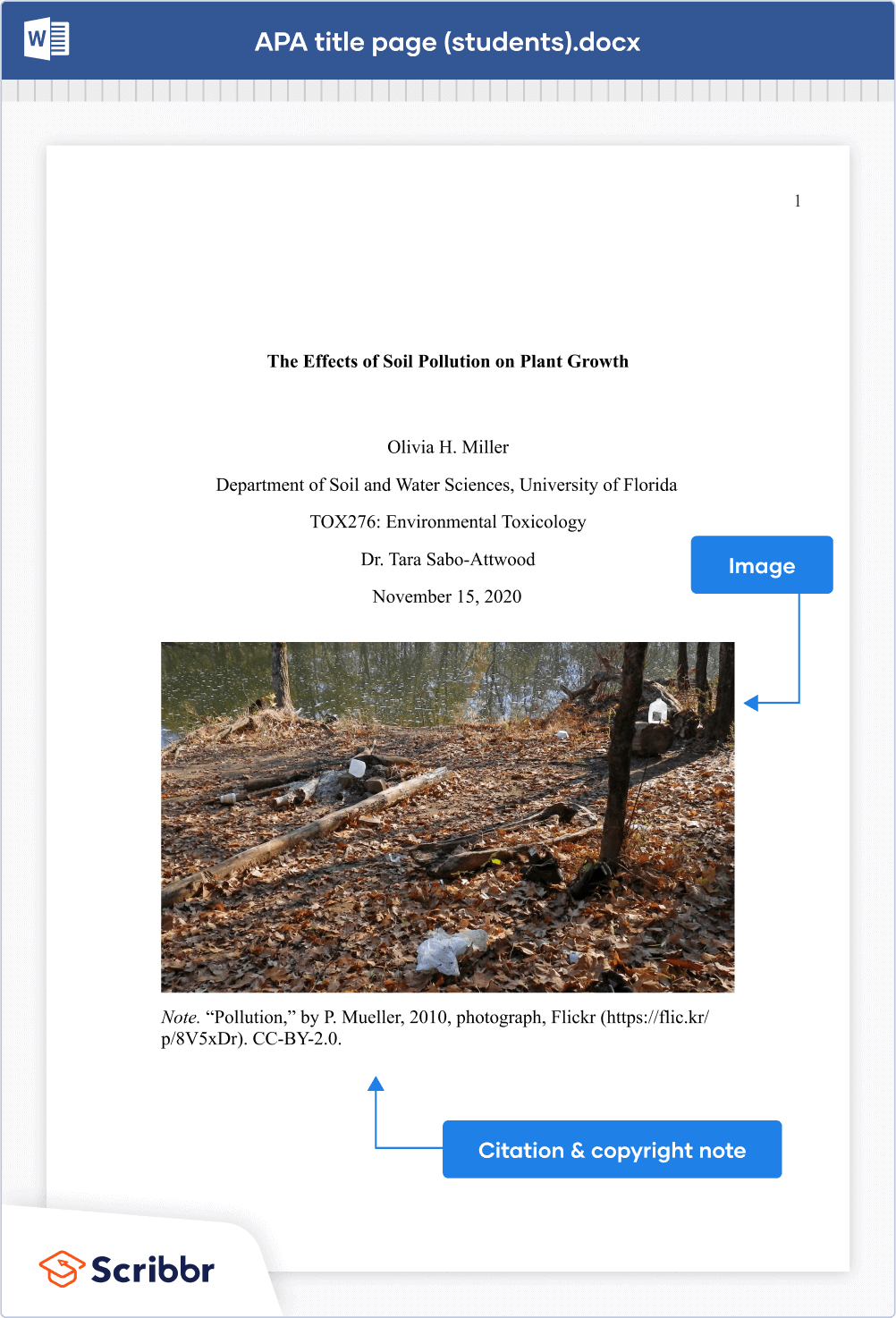
Images are not usually included on an APA title page, and APA does not provide any guidelines for doing so. It’s usually viewed as unprofessional to include an image, since the title page is there to provide information, not for decoration.
If you do decide to include an image on your title page, make sure to check whether you need permission from the creator of the image. Include a note directly underneath the image acknowledging where it comes from, beginning with the word “ Note .” (italicized and followed by a period):
- If you found the image online or in another source, include a citation and copyright attribution .
- If it’s an image you created yourself (e.g., a photograph you took, an infographic you designed), explain this (e.g., “Photograph taken by the author.”).
Don’t give the image a label, title, or number. Only images within the text itself are labeled as figures .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, January 17). APA Title Page (7th edition) | Template for Students & Professionals. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/apa-title-page/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, apa headings and subheadings, forging good titles in academic writing, apa running head, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!
- Insights blog
Defining authorship in your research paper
Co-authors, corresponding authors, and affiliations, why does authorship matter.
Authorship gives credit and implies accountability for published work, so there are academic, social and financial implications.
It is very important to make sure people who have contributed to a paper, are given credit as authors. And also that people who are recognized as authors, understand their responsibility and accountability for what is being published.
There are a couple of types of authorship to be aware of.
Co-author Any person who has made a significant contribution to a journal article. They also share responsibility and accountability for the results of the published research.
Corresponding author If more than one author writes an article, you’ll choose one person to be the corresponding author. This person will handle all correspondence about the article and sign the publishing agreement on behalf of all the authors. They are responsible for ensuring that all the authors’ contact details are correct, and agree on the order that their names will appear in the article. The authors also will need to make sure that affiliations are correct, as explained in more detail below.
Open access publishing
There is increasing pressure on researchers to show the societal impact of their research.
Open access can help your work reach new readers, beyond those with easy access to a research library.
How common is co-authorship and what are the challenges collaborating authors face? Our white paper Co-authorship in the Humanities and Social Sciences: A global view explores the experiences of 894 researchers from 62 countries.
If you are a named co-author, this means that you:
Made a significant contribution to the work reported. That could be in the conception, study design, execution, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation, or in all these areas.
Have drafted or written, substantially revised or critically reviewed the article.
Have agreed on the journal to which the article will be submitted.
Reviewed and agreed on all versions of the article before submission, during revision, the final version accepted for publication, and any significant changes introduced at the proofing stage.
Agree to take responsibility and be accountable for the contents of the article. Share responsibility to resolve any questions raised about the accuracy or integrity of the published work.

Every submission to our medical and health science journals should comply with the International Committee on Medical Journal Ethics’ definition of authorship .
Please include any other form of specific personal contribution in the acknowledgments section of your paper.
Affiliations: get it right
Your affiliation in the manuscript should be the institution where you conducted the research. You should also include details of any funding received from that institution.
If you have changed affiliation since completing the research, your new affiliation can be acknowledged in a note. We can’t normally make changes to affiliation after the journal accepts your article.

Changes to authorship
Authorship changes post-submission should only be made in exceptional circumstances, and any requests for authors to be removed or added must be in line with our authorship criteria.
If you need to make an authorship change, you will need to contact the Journal Editorial Office or Editorial team in the first instance. You will be asked to complete our Authorship Change request form ; all authors (including those you are adding or removing) must sign this form. This will be reviewed by the Editor (and in some instances, the publisher).
Please note any authorship change is at the Editor’s discretion; they have the right to refuse any authorship change they do not believe conforms with our authorship policies.
Some T&F journals do not allow any authorship changes post-submission; where this is applicable, this will be clearly indicated on the journal homepage or on the ‘instructions for authors’ page.
If the corresponding author changes before the article is published (for example, if a co-author becomes the corresponding author), you will need to write to the editor of the journal and the production editor. You will need to confirm to them that both authors have agreed the change.
Requested changes to the co-authors or corresponding authors following publication of the article may be considered, in line with the authorship guidelines issued by COPE , the Committee on Publication Ethics. Please see our corrections policy for more details. Any requests for changes must be made by submitting the completed Authorship Change Request form .
Authorship Change Request form
Important: agree on your corresponding author and the order of co-authors, and check all affiliations and contact details before submitting.
Taylor & Francis Editorial Policies on Authorship
The following instructions (part of our Editorial Policies ) apply to all Taylor & Francis Group journals.
Corresponding author
Co-authors must agree on who will take on the role of corresponding author. It is then the responsibility of the corresponding author to reach consensus with all co-authors regarding all aspects of the article, prior to submission. This includes the authorship list and order, and list of correct affiliations.
The corresponding author is also responsible for liaising with co-authors regarding any editorial queries. And, they act on behalf of all co-authors in any communication about the article throughout: submission, peer review, production, and after publication. The corresponding author signs the publishing agreement on behalf of all the listed authors.
AI-based tools and technologies for content generation
Authors must be aware that using AI-based tools and technologies for article content generation, e.g. large language models (LLMs), generative AI, and chatbots (e.g. ChatGPT), is not in line with our authorship criteria.
All authors are wholly responsible for the originality, validity and integrity of the content of their submissions. Therefore, LLMs and other similar types of tools do not meet the criteria for authorship.
Where AI tools are used in content generation, they must be acknowledged and documented appropriately in the authored work.
Changes in authorship
Any changes in authorship prior to or after publication must be agreed upon by all authors – including those authors being added or removed. It is the responsibility of the corresponding author to obtain confirmation from all co-authors and to provide a completed Authorship Change Request form to the editorial office.
If a change in authorship is necessary after publication, this will be amended via a post-publication notice. Any changes in authorship must comply with our criteria for authorship. And requests for significant changes to the authorship list, after the article has been accepted, may be rejected if clear reasons and evidence of author contributions cannot be provided.
Assistance from scientific, medical, technical writers or translators
Contributions made by professional scientific, medical or technical writers, translators or anyone who has assisted with the manuscript content, must be acknowledged. Their source of funding must also be declared.
They should be included in an ‘Acknowledgments’ section with an explanation of their role, or they should be included in the author list if appropriate.
Authors are advised to consult the joint position statement from American Medical Writers Association (AMWA), European Medical Writers Association (EMWA), and International Society of Medical Publication Professionals (ISMPP).
Assistance with experiments and data analysis
Any significant contribution to the research reported, should be appropriately credited according to our authorship criteria.
If any parts of the research were outsourced to professional laboratories or to data analysts, this should be clearly stated within the manuscript, alongside an explanation of their role. Or, they should be included in the author list if appropriate.
Authors are responsible for retaining all of the original data related to their work, and should be prepared to share it with the journal editorial office if requested.
Acknowledgments
Any individuals who have contributed to the article (for example, technical assistance, formatting-related writing assistance, translators, scholarly discussions which significantly contributed to developing the article), but who do not meet the criteria for authorship, should be listed by name and affiliation in an ‘Acknowledgments’ section.
It is the responsibility of the authors to notify and obtain permission from those they wish to identify in this section. The process of obtaining permission should include sharing the article, so that those being identified can verify the context in which their contribution is being acknowledged.
Any assistance from AI tools for content generation (e.g. large language models) and other similar types of technical tools which generate article content, must be clearly acknowledged within the article. It is the responsibility of authors to ensure the validity, originality and integrity of their article content. Authors are expected to use these types of tools responsibly and in accordance with our editorial policies on authorship and principles of publishing ethics.
Biographical note
Please supply a short biographical note for each author. This could be adapted from your departmental website or academic networking profile and should be relatively brief (e.g. no more than 200 words).Authors are responsible for retaining all of the original data related to their work, and should be prepared to share it with the journal editorial office if requested.

Author name changes on published articles
There are many reasons why an author may change their name in the course of their career. And they may wish to update their published articles to reflect this change, without publicly announcing this through a correction notice. Taylor & Francis will update journal articles where an author makes a request for their own name change, full or partial, without the requirement for an accompanying correction notice. Any pronouns in accompanying author bios and declaration statements will also be updated as part of the name change, if required.
When an author requests a name change, Taylor & Francis will:
Change the metadata associated with the article on our Taylor & Francis Online platform.
Update the HTML and PDF version of the article.
Resupply the new metadata and article content to any abstracting and indexing services that have agreements with the journal. Note: such services may have their own bibliographic policies regarding author name changes. Taylor \u0026amp; Francis cannot be held responsible for controlling updates to articles on third party sites and services once an article has been disseminated.
If an author wishes for a correction notice to be published alongside their name change, Taylor & Francis will accommodate this on request. But, it is not required for an author name change to be made.
To request a name change, please contact your Journal’s Production Editor or contact us.
Taylor & Francis consider it a breach of publication ethics to request a name change for an individual without their explicit consent.
Additional resources
Co-authorship in the Humanities and Social Sciences – our white paper based on a global survey of researchers’ experiences of collaboration.
Discussion Document: Authorship – produced by COPE (Committee on Publication Ethics), this updated guide includes practical advice on addressing the most common ethical issues in this area
Taylor & Francis Editorial Policies
Ethics for authors – guidelines, support, and your checklist.

Publishing Strategies: Author Affiliations
- Author Affiliations
- Where to Publish
- Finding Collaborators

Affiliations in academic papers refer to places (institutions) where authors belong when they are conducting the published research. Given the mobility of faculty, the affiliated institutions may not always be the ones that authors based at the time of paper submission. Publishing with accurate affiliation(s) facilitates not only authorship identification, but also citation tracking for both authors themselves and their affiliated organisations, which prevents scattered citation counts in split profiles. Note that publishers seldom allow changes on affiliations once the paper is accepted, and it takes time and effort for both authors and publishers to communicate and rectify the wrong data. Authors are therefore advised to check and display correct affiliation data in their publications to minimise problems with authorship misattribution, paper disappearance, citation loss, etc.
What are publishers saying about affiliations?
- Taylor & Francis: https://authorservices.taylorandfrancis.com/editorial-policies/defining-authorship-research-paper/#affiliations
- Springer: https://www.springer.com/us/editorial-policies/authorship-principles#toc-49266
- Elsevier: https://service.elsevier.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/34306/supporthub/publishing/
- Cambridge University Press: https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/authors/journals/author-affiliations
| of organisations and departments. Check the name information from official sources and avoid using abbreviations |
: Department of Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China : Department of Advanced Design and Systems Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China : Department of Neuroscience, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China |
| Observe the . List and separate each structural element of an affiliation with proper punctuation marks. |
: Department of Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China : Department of Biomedical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China : Department of English, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China |
| , write down each affiliation clearly and separate them with proper labels or punctuation. Primary affiliation should go first. |
: Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China; Mechanical Behavior Division of Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. |
| helps others to find your publications by city, country, or organisation's profile. |
: Department of Chemistry, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China |
- Next: Where to Publish >>
- Last Updated: Dec 7, 2023 8:31 AM
- URL: https://libguides.library.cityu.edu.hk/publishing_strategies
© City University of Hong Kong | Copyright | Disclaimer
Library Research Guides - University of Wisconsin Ebling Library
Uw-madison libraries research guides.
- Course Guides
- Subject Guides
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Research Guides
- Publication Tracking
- Searching for an Affiliation in Google Scholar
Publication Tracking : Searching for an Affiliation in Google Scholar
- Getting Started
- Searching for an Individual Author in PubMed
- Searching for a Group of Authors in PubMed
- Searching for an Institution or Department in PubMed
- Searching for an Individual Author in Scopus
- Searching for a Group of Authors in Scopus
- Searching for an Affiliation in Scopus
- Searching for an Individual Author in Google Scholar
- Searching for a Group of Authors in Google Scholar
- Exporting Search Results
This page gives tips on how to search for an affiliation in Google Scholar. Click here to access this information as a downloadable PDF.
Click here to access a PDF containing search templates and examples of searching for an affiliation in Google Scholar.
Constructing Your Search
1. construct a search using affiliation keywords.
Unfortunately Google Scholar does not have a field tag for affiliations. In consequence, you will need to construct your search using affiliation keywords, and combine them with the Boolean OR (or the “|” symbol in Google Scholar), like so:
wisconsin|Madison|UW|wi|wisc
“|” works the same as a Boolean OR would, in that it will be retrieving publications that mention wisconsin, Madison, UW, wi, or wisc, or all of the terms in them.
2. Increase Specificity by Using Quotation Marks
If any of your affiliation keywords are comprised of more than one word, you can use quotation marks to search for the keyword as a phrase. So, for example, searching "young adult" is going to search for that intact phrase, whereas searching young adult, without quotation marks, will look for articles that have young and adult anywhere in the article, regardless of how apart those two words might be in the article (e.g., it could retrieve an article that says, "The young polar bear was now an adult").
So if you wanted to narrow your search to only publications that mention some variation of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, and not just Wisconsin, your search could look something like this:
“University of Wisconsin Madison”|”University of Wisconsin-Madison”|”UW Madison”
This search will only retrieve publications that mention the University of Wisconsin Madison, the University of Wisconsin-Madison, UW Madison, or all of these terms.
3. Limit by Date
You can limit by date by using the date filters on the left-hand side of the page. If you would like to search by a specific date range, you can click “Custom Range.”

Google Scholar has a character limit!
Important : Note that Google Scholar has a limit of only 256 characters for searches
How Do I Interpret These Searches?
Boolean Operators (AND and OR, represented by a space and | in Google Scholar)
OR ("|" in Google Scholar) is used to combine synonyms together. For example, a search of parent|guardian is going to retrieve publications that have the word parent, the word guardian, or both the words parent and guardian in them.
AND (a space in Google Scholar " ") is used to combine concepts together. For example, a search of parent guardian is going to retrieve publications that have BOTH the words parent and guardian in them. If a publication has the word parent, and not the word guardian, your search will not retrieve that publication.

Quotation Marks " "
These tell Google Scholar to search for two or more words as an intact phrase. So, for example, search ing "young adult" is going to search for that intact phrase, whereas search ing young adult, without quotation marks, will look for articles that have young and adult anywhere in the article, regardless of how apart those two words might be in the article (e.g., it could retrieve an article that says, "The young polar bear was now an adult ").
- << Previous: Searching for a Group of Authors in Google Scholar
- Next: Exporting Search Results >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2024 11:48 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.wisc.edu/publication-tracking
Instructions for Authors
Contact Monica Mungle for help if edits are needed to the top section.
Original Investigation
Caring for the critically ill patient, brief report, research letter, systematic review (without meta-analysis), narrative review, special communication, clinical challenge, diagnostic test interpretation, a piece of my mind, letter to the editor, letter in reply.
- Randomized Clinical Trial
- Parallel-Design Double-blind Trial
- Crossover Trial
- Equivalence and Noninferiority Trial
- Cluster Trial
- Nonrandomized Clinical Trial
Meta-analysis
- Cohort Study
- Case-Control Study
- Cross-sectional Study
- Case Series
- Economic Evaluation
- Decision Analytical Model
- Comparative Effectiveness Research
- Genetic Association Study
- Diagnostic/Prognostic Study
- Quality Improvement Study
- Survey Study
- Qualitative Study
Manuscript Submission
Copies of previous editorial and reviewer comments, cover letter, manuscript style, manuscript components, recommended file sizes, manuscript file formats, abbreviations, units of measure, names of drugs, devices, and other products, gene names, symbols, and accession numbers, reproduced and re-created material, online-only supplements and multimedia.
What to Expect
Editorial and Peer Review
The jama network advantage.
- JAMA-Express
Authorship Form and Publishing Agreement
Publication.
- Postpublication Online Commenting
Reprints/e-Prints
Corrections, previous publication, related manuscripts and reports, and preprints, previous or planned meeting presentation or release of information, embargo policy, research article public access, depositing in repositories, and discoverability.
Editorial Policies for Authors
Authorship and Disclosures
Authorship criteria and contributions, role of the corresponding author, changes in authorship, name change policy, group authorship, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, funding/support and role of funder/sponsor, data access, responsibility, and analysis, acknowledgment section, equator reporting guidelines, use of causal language, timeliness of data, statistical methods and data presentation, reporting demographic information for study participants, ethical approval of studies and informed consent, patient identification, use of ai in publication and research, personal communications and unpublished data, manuscripts that pose security risks.
Journal Policies, Forms, Resources
Decisions and Management of Editorial Conflicts of Interest
Publishing agreement, unauthorized use.
- Patient Permission Form
- AMA Manual of Style
- EQUATOR Network
- About This Journal
Contact Information
JAMA , Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, PhD, MD, MAS, Editor in Chief, 330 N Wabash Ave, Chicago, IL 60611-5885; telephone: (312) 464-4444; fax: (312) 464-5824; email: [email protected] . Manuscripts should be submitted online at http://manuscripts.jama.com .
Determine My Article Type
Categories of articles.
Original Investigation full info
Clinical trial Meta-analysis Intervention study Cohort study Case-control study Epidemiologic assessment Survey with high response rate Cost-effectiveness analysis Decision analysis Study of screening and diagnostic tests Other observational study
- ≤5 tables and/or figures
- Structured abstract
Data Sharing Statement
Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines
Caring for the Critically Ill Patient full info
Original research reports, preferably clinical trials or systematic reviews that address virtually any aspect of critical illness, from prevention and triage, through resuscitation and acute treatment, to rehabilitation and palliative care.
- See also requirements for Clinical Trial , Meta-analysis , and Systematic Review
Brief Report full info
Short reports of original studies or evaluations or unique, first-time reports of clinical case series.
It is very rare for this journal to publish case reports.
- 15 references
- ≤3 tables and/or figures
Research Letter full info
Concise, focused reports of original research. Can include any of the study types listed under Original Investigation.
- ≤6 references
- ≤2 small tables and/or figures
- No Abstract or Key Points
Back to top
Clinical Review and Education
Systematic Review (without meta-analysis) full info
This article type requires a presubmission inquiry. See the "full info" below for requirements and contact information.
Critical assessments of the literature and data sources pertaining to clinical topics, emphasizing factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention.
Systematic Reviews without meta-analysis are published as Reviews; those with meta-analysis are published as Original Investigations (see Meta-analysis ).
- 50-75 references
- A PRISMA-style flow diagram should be included as an online supplement
- Include a table with ratings of the quality of the studies/evidence
- Subtitle should be "A Systematic Review"
Narrative Review full info
Up-to-date review for clinicians on a topic of general common interest from the perspective of internationally recognized experts in these disciplines.
The focus should be an update on current understanding of the physiology of the disease or condition, diagnostic consideration, and treatment.
These reviews should address a specific question or issue that is relevant for clinical practice.
- 2000-3500 words
- 3-part structured abstract
- No Key Points
- Subtitle should be "A Review"
Special Communication full info
This journal publishes very few of these types of articles.
These manuscripts describe an important issue in clinical medicine, public health, health policy, or medical research in a scholarly, thorough, well-referenced, systematic, and evidence-based manner.
- 50 references
- ≤4 tables and/or figures
- Requires a presubmission inquiry
Clinical Challenge full info
Presents an actual patient case with a specific disease or condition with an accompanying clinical image.
- "What Would You Do Next?" with 4 single-phrase plausible treatment options describing possible courses of action with 1 being preferred
- Case presentation: 250 words
- Discussion: 500-600 words
- ≤10 references
- 1-2 small figures
- Patient permission required
Diagnostic Test Interpretation full info
This article requires a presubmission inquiry.
Presentation of the results of a diagnostic test from a single patient with exploration of the clinical application of the test result; intended to help clinicians understand the underlying rationale in ordering tests, interpreting test results, and acting on the diagnostic test findings.
- How Do You Interpret These Test Results? (or What Would You Do Next?) with 4 plausible responses
- Case presentation: 200 words
- Discussion: 650 words
Viewpoint full info
May address virtually any important topic in medicine, public health, research, discovery, prevention, ethics, health policy, or health law and generally are not linked to a specific article.
- 1200 words (or 1000 words with 1 small table or figure)
- ≤7 references at submission
- ≤3 authors, with no more than 2 affiliations per author
A Piece of My Mind full info
Personal vignettes (eg, exploring the dynamics of the patient-physician relationship) taken from wide-ranging experiences in medicine; occasional pieces express views and opinions on the myriad issues that affect the profession.
- ≤1600 words
- Patient permission may be needed
Poetry full info
Original poems related to the medical experience, whether from the point of view of a health care worker or patient, or simply an observer.
- No longer than 44 lines
Correspondence
Letter to the Editor full info
Letters discussing a recent article in this journal should be submitted within 4 weeks of the article's publication in print.
- ≤5 references (1 of which should be to the recent article)
Letter in Reply full info
Replies by authors of original articles to letters from readers.
Determine My Study Type
Randomized Clinical Trial full info
A trial that prospectively assigns participants to intervention or comparison groups to study the cause-and-effect relationship between an intervention and a health outcome. Interventions include but are not limited to drugs, surgical procedures, devices, behavioral treatments, educational programs, dietary interventions, quality improvement interventions, process-of-care changes, and the like.
- ≤5 tables and/or figures, including CONSORT flow diagram
- Subtitle should be "A Randomized Clinical Trial"
- Trial registration and ID
- Trial protocol
- CONSORT checklist
- Follow CONSORT Reporting Guidelines
Parallel-Design Double-blind Trial full info
A randomized trial that prospectively assigns participants to 2 or more groups to receive different interventions. Participants and those administering the interventions are unaware of which intervention individual participants are receiving.
Crossover Trial full info
A trial in which participants receive more than 1 of the treatments under investigation, usually in a randomly determined sequence, and with a prespecified amount of time (washout period) between sequential treatments.
Equivalence and Noninferiority Trial full info
A trial designed to assess whether the treatment or intervention under study (eg, a new intervention) is no worse than an existing alternative (eg, an active control). In these trials, authors must prespecify a margin of noninferiority that is consistent with all relevant studies and within which the new intervention can be assumed to be no worse than the active control.
Cluster Trial full info
A trial that includes random assignment of groups rather than individuals to intervention and control groups.
Nonrandomized Clinical Trial full info
A trial that prospectively assigns groups or populations to study the efficacy or effectiveness of an intervention but in which the assignment to the intervention occurs through self-selection or administrator selection rather than through randomization. Control groups can be historic, concurrent, or both. This design is sometimes called a quasi-experimental design.
- ≤5 tables and/or figures, including a trial flow diagram
- Subtitle should be "A Nonrandomized Clinical Trial"
- TREND checklist
Meta-analysis full info
A systematic review that includes a statistical technique for quantitatively combining the results of multiple studies that measure the same outcome into a single pooled or summary estimate.
- Subtitle should include "A Meta-analysis"
- Follow PRISMA Reporting Guidelines or MOOSE Reporting Guidelines
Cohort Study full info
An observational study that follows a group (cohort) of individuals who are initially free of the outcome of interest. Individuals in the cohort may share some underlying characteristic, such as age, sex, diagnosis, exposure to a risk factor, or treatment.
- Follow STROBE Reporting Guidelines
Case-Control Study full info
An observational study designed to determine the association between an exposure and outcome in which study participants are selected by outcome. Those with the outcome (cases) are compared with those without the outcome (controls) with respect to an exposure or event. Cases and controls may be matched according to specific characteristics (eg, age, sex, or duration of disease).
Cross-sectional Study full info
An observational study of a defined population at a single point in time or during a specific interval, in which exposure and outcome are ascertained simultaneously.
Case Series full info
An observational study that describes a selected group of participants with similar exposure or treatment and without a control group. A case series may also involve observation of larger units such as groups of hospitals or municipalities, as well as smaller units such as laboratory samples.
- Follow Reporting Guidelines
Economic Evaluation full info
A study using formal, quantitative methods to compare 2 or more treatments, programs, or strategies with respect to their resource use and expected outcomes. This includes cost-effectiveness, cost-benefit, and cost-minimization analyses.
- Follow CHEERS Reporting Guidelines
Decision Analytical Model full info
A mathematical modeling study that compares consequences of decision options by synthesizing information from multiple sources and applying mathematical simulation techniques, usually with specific software. Reporting should address the relevant non-cost aspects of the CHEERS guideline.
Comparative Effectiveness Research full info
A study that compares different interventions or strategies to prevent, diagnose, treat, and monitor health conditions to determine which work best for which patients, under what circumstances, and are associated with the greatest benefits and harms.
- Follow ISPOR Reporting Guidelines
Genetic Association Study full info
A study that attempts to identify and characterize genomic variants that may be associated with susceptibility to multifactorial disease.
- Follow STREGA Reporting Guidelines
Diagnostic/Prognostic Study full info
A prospective study designed to develop, validate, or update the diagnostic or prognostic accuracy of a test or model.
- Follow STARD Reporting Guidelines or TRIPOD Reporting Guidelines
Quality Improvement Study full info
A study that uses data to define, measure, and evaluate a health care practice or service to maintain or improve the appropriateness, quality, safety, or value of that practice or service.
- Follow SQUIRE Reporting Guidelines
Survey Study full info
A survey study includes a representative sample of individuals who are asked to describe their opinions, attitudes, or behaviors. Survey studies should have sufficient response rates (generally ≥60%) and appropriate characterization of nonresponders to ensure that nonresponse bias does not threaten the validity of the findings.
- Follow AAPOR Best Practices for Survey Research
- Optional: Survey instrument as supplemental file
Qualitative Study full info
A study based on observation and interview with individuals that uses inductive reasoning and a theoretical sampling model and that focuses on social and interpreted, rather than quantifiable, phenomena and aims to discover, interpret, and describe rather than to test and evaluate. This includes mixed-methods studies that combine quantitative and qualitative designs in a sequential or concurrent manner.
- Follow SRQR Reporting Guidelines or COREQ Reporting Guidelines
These reports typically include randomized trials (see Clinical Trial ), intervention studies, cohort studies, case-control studies, epidemiologic assessments, other observational studies, surveys with high response rates (see Reports of Survey Research ), cost-effectiveness analyses and decision analyses (see Reports of Cost-effectiveness Analyses and Decision Analyses ), and studies of screening and diagnostic tests (see also Reports of Diagnostic Tests ). Each manuscript should clearly state an objective or hypothesis; the design and methods (including the study setting and dates, patients or participants with inclusion and exclusion criteria and/or participation or response rates, or data sources, and how these were selected for the study); the essential features of any interventions; the main outcome measures; the main results of the study; a discussion section placing the results in context with the published literature and addressing study limitations; and the conclusions and relevant implications for clinical practice or health policy. Data included in research reports must be original and should be as timely and current as possible (see Timeliness of Data ). Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines .
A structured abstract is required; for more information, see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Reports of Original Data . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and online-only material) with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures.
These manuscripts are original research reports, preferably clinical trials, or systematic reviews (see above classifications for manuscript submission requirements by category of article) that address virtually any aspect of critical illness, from prevention and triage, through resuscitation and acute treatment, to rehabilitation and palliative care. Manuscripts that provide new insights into the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of critically ill patients, as well as those that explore pathophysiological, technological, ethical, or other related aspects of critical care medicine, are welcome. Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines . For reports of original data and systematic reviews, a structured abstract is required; see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Reports of Original Data or Abstracts for Reviews . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and online-only material) with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures.
These manuscripts are short reports of original studies or evaluations or unique, first-time reports of clinical case series. Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines . A structured abstract is required; for more information, see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Reports of Original Data . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Recommended length: 1200 words (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and online-only material) with no more than a total of 3 tables and/or figures and no more than 15 references. Note: It is very rare for this journal to publish case reports.
Research Letters are concise, focused reports of original research. These should not exceed 600 words of text and 6 references and may include up to 2 tables or figures. Online supplementary material is only allowed for brief additional and absolutely necessary methods but not for any additional results or discussion. The text should include the full name, academic degrees, and institutional affiliation for each author and the email address for the corresponding author. Other persons who have contributed to the study may be indicated in an Acknowledgment, with their permission, including their academic degrees, affiliation, contribution to the study, and an indication if compensation was received for their role. Letters must not duplicate other material published or submitted for publication. In general, Research Letters should be divided into the following sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. They should not include an abstract or key points, but otherwise should follow all of the guidelines in Manuscript Preparation and Submission Requirements . Letters not meeting these specifications are generally not considered.
This article type requires a presubmission inquiry to [email protected] .
The journal will consider 2 types of review articles:
Systematic Reviews
These types of Review articles differ by the scope and level of analysis of the literature searches and the titles used. Systematic Reviews require a complete systematic search of the literature using multiple databases, covering many years, and grading of the quality of the cited evidence. Narrative Reviews do not require a rigorous literature search but should rely on evidence and should be written by established experts in the field. See below for more detail on each type of Review.
Titles for these Reviews should include a concise description of the main topic. Use specific and not overly broad wording for the title; the type of review should be indicated in the subtitle. For example:
Behavioral Treatment of Obesity: A Systematic Review
Behavioral Treatment of Obesity: A Review (note: the word "narrative" is not included in the subtitle)
Systematic Reviews are critical assessments of the literature and data sources pertaining to clinical topics, emphasizing factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention. Systematic Reviews without meta-analysis are published as Reviews; those with meta-analysis are published as Original Investigations (see Meta-analysis ). Systematic Reviews should address a specific question or issue that is relevant for clinical practice and provide an evidence-based, balanced, patient-oriented review on a focused topic. Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines .
The basic structure of manuscripts reporting Systematic Reviews should include the following: Abstract (structured abstract of no more than 350 words); Introduction (150-250 words); Methods (150-250 words); Results (1000-1250 words, with the following subsections, if appropriate, depending on the specific question or issue addressed: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, Assessment and Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis); Discussion (1000 words); and Conclusions (2-3 sentences).
Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and online-only material), with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures and no more than 50-75 references. For an example of a published Systematic Review, see JAMA . 2014;312(6):631-640 and below for the general structure of a Systematic Review article.
Prospective authors interested in submitting a review manuscript should prepare a detailed outline of the proposed article. There should also be a brief summary of the extent and quality of the literature supporting the proposed review. Alternatively, if a draft of the manuscript has been completed, this can be sent. Prospective authors should also summarize their publication record in the field. Send this information to the editorial office via email to Mary McDermott, MD, at [email protected] .
Specific Components of a Systematic Review
Key Points (75-100 words)
This feature provides a quick structured synopsis of the Review, following 3 key points: Question, Findings, and Meaning. Limit to no more than 100 words. This is different from the Abstract.
Question: What are the most effective medical treatments for adult chronic sinusitis? Findings: In this systematic review, symptoms of chronic sinusitis were improved with saline irrigation and topical corticosteroid therapy compared to no therapy. Compared with placebo, 3-week courses of systemic corticosteroids or oral doxycycline were associated with reduced polyp size, and a 3-month course of macrolide antibiotic was associated with improved symptoms in patients without polyps. Meaning: First-line therapy for chronic sinusitis should begin with daily topical intranasal corticosteroid in conjunction with saline irrigation; subsequent therapies should be based on the patient's polyp status and severity of symptoms.
Abstract (350 words)
A structured abstract is required; Systematic Review articles should include a structured abstract of no more than 350 words using the headings listed below.
Importance: Include 1 or 2 sentences describing the clinical question or issue and its importance in clinical practice or public health. Objective: State the precise primary objective of the review. Indicate whether the review emphasizes factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention and include information about the specific population, intervention, exposure, and tests or outcomes that are being reviewed. Evidence Review: Describe the information sources used, including the search strategies, years searched, and other sources of material, such as subsequent reference searches of retrieved articles. Methods used for inclusion of identified articles and quality assessment should be explained. Findings: Include a brief summary of the number of articles included, numbers of various types of studies (eg, clinical trials, cohort studies), and numbers of patients/participants represented by these studies. Summarize the major findings of the review of the clinical issue or topic in an evidence-based, objective, and balanced fashion, with the highest-quality evidence available receiving the greatest emphasis. Provide quantitative data. Conclusions and Relevance: The conclusions should clearly answer the questions posed if applicable, be based on available evidence, and emphasize how clinicians should apply current knowledge. Conclusions should be based only on results described in the abstract Findings subsection.
Introduction (150-250 words)
The first 2 to 3 sentences of the Introduction should draw in readers such that they want to continue reading the article and should establish the importance of the Review. Reviews should include the clinical question or issue and its importance for general medical practice, specialty practice, or public health. The first paragraph should provide a general summary of the clinical problem (eg, obesity). The next paragraph should focus on the specific aspect of the clinical problem the article will explore (eg, treatments for obesity). The epidemiology of the disease or condition should be briefly summarized and generally should include disease prevalence and incidence. The third paragraph should discuss exactly what material will be covered in the Review (eg, obesity treatments reported in trials with a minimum follow-up of 2 years including 80% of the original cohort).
Methods/Literature Search (150-250 words)
The literature search should be as current as possible, ideally with end dates within a month or two before manuscript submission. A search of the primary literature should be conducted, including multiple bibliographic databases (eg, PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO). This can be facilitated by collaborating with a medical librarian to help with the search.
Briefly describe characteristics of the literature searched and included in the review, following the PRISMA reporting guidelines , including the bibliographic databases and other sources searched, search terms used, dates included in the search, date the literature search was conducted, screening process, language limitations, and inclusion and exclusion criteria. The rating system used to evaluate the quality of the evidence should be specified (see table below) and the methods used to evaluate quality should be described, including number of quality raters, how agreement on quality ratings was assessed, and how disagreements on quality ratings were resolved.
The highest-quality evidence (eg, randomized clinical trials, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and high-quality prospective cohort studies) should receive the greatest emphasis. Clinical practice guidelines ordinarily should not be used as a primary component of the evidence base for the systematic review, although relevant guidelines should be addressed in the Discussion section of the article.
The search methods should be described in sufficient detail so the search can be reproduced based on the information provided in the manuscript. A summary of the methods of the literature search including this information should be included in the main article; details can be included in an online-only supplement. A PRISMA-style flow diagram showing this information should also be included as an online-only supplement. In addition, a completed PRISMA checklist should be submitted for the items completed that apply to systematic reviews (the checklist items that apply to meta-analyses do not need to be completed for systematic reviews without meta-analysis). The checklist will be used during review but will not be published.
Results (1000-1250 words)
First, briefly report the results of the literature search, including the number of articles reviewed and included, numbers of various types of studies (eg, clinical trials, cohort studies) included, and the aggregate numbers of patients included in the reviewed studies. Also provide a brief summary of the quality of the evidence. Details of this information can be included in a PRISMA-style flow diagram and table(s).
Next, the subsections listed below should generally appear in the Results sections of most Reviews although all of these subsections may not be necessary for some topics, depending on the specific question or issue addressed. The word counts following each subsection are suggested to assist with keeping the overall Results section limited to 1000-1250 words.
Pathophysiology (150-250 words). Provide a brief overview of the pathophysiology of the disease. The intent is to provide readers with sufficient background information about the underpinnings of a disease to provide context for the rest of the article. Clinical Presentation (150-250 words). Briefly describe the clinical characteristics that result in a patient seeking medical care for the condition or what features of the disease should lead a clinician to evaluate or treat it. Assessment and Diagnosis (250-300 words). Describe the clinical examination for evaluation of the disease and explain the most salient physical examination findings. If laboratory or imaging studies are necessary, provide the sensitivity and specificity and diagnostic accuracy of these tests and consider providing positive and negative likelihood ratios. Sequences of diagnostic tests are best presented as algorithms or in tables. Treatment (250-500 words). Treatments should be based on the most recently available and highest level of evidence. Treatment options should be summarized in the text and presented in detail in tables along with an indication of the strength of evidence supporting the individual treatments. In general, treatment recommendations should be supported by a systematic review of the literature, either performed by the author of the Review or published in the form of a high-quality review or guideline. If possible, the costs for various treatments should be provided. Prognosis (100-150 words). A section outlining the overall prognosis for the condition, once treated, should be included. Discussion (Approximately 1000 words)
Key findings should be summarized in the first paragraph of the Discussion section. All statements made should be supported by evidence. It is very important to not simply list findings from the studies reviewed. This information is best presented in tables. The Discussion should provide a critical synthesis of data and information based on the results of the review, an assessment of the quality of studies summarized, and a description of how studies can be interpreted and used to guide clinical practice. The limitations of the evidence and of the review should be discussed, and gaps in evidence should be addressed. A discussion of controversial or unresolved issues and topics in need of future research also should be included.
Clinical Practice Guidelines: In the Discussion section, describe current clinical practice guidelines, relevant to the topic of the review, if available, and whether the conclusions of this review agree with, or disagree with, the current clinical practice guidelines. If this is done and there is more than 1 guideline, a table should be prepared comparing the major features that differ between the guidelines. Guideline quality should be discussed using the standards outlined for the JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis .
Conclusions
Include a 2- to 3-sentence summary of the major conclusions of the review.
Construct tables that summarize the search results. Tables summarizing treatments should have information organized by category of treatment and then by individual treatments. Columns should include the name of the treatment, strength of evidence supporting the treatment, the treatment's effect (preferably shown as the treatment's effect as compared to control on the measured outcome together with 95% confidence intervals), adverse effects, and very brief comments, if necessary. Lengthy text-based tables should be avoided. Additional or lengthy tables may be published online only, if justified.
Ratings of the quality of the evidence. Tables summarizing evidence should include ratings of the quality of the evidence. Use the rating scheme listed below with ratings of 1-5 for Reviews that include individual studies (modified from the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine for ratings of individual studies).
| Quality Rating Scheme for Studies and Other Evidence | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Properly powered and conducted randomized clinical trial; systematic review with meta-analysis |
| 2 | Well-designed controlled trial without randomization; prospective comparative cohort trial |
| 3 | Case-control studies; retrospective cohort study |
| 4 | Case series with or without intervention; cross-sectional study |
| 5 | Opinion of respected authorities; case reports |
There are several other preferred systems for rating the quality of evidence in Review articles. For Reviews that synthesize findings from numerous studies into a single summary recommendation, use the rating scale shown above or the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine's Levels of Evidence and Grades of Recommendation or the recommendations in the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . For reviews that include diagnostic studies, use The Rational Clinical Examination Levels of Evidence table .
Follow additional instructions for preparation and submission of Tables .
A PRISMA-style flow diagram should be included as an online supplement that summarizes the results of the literature search and the numbers of articles/records/studies and patients/participants represented in the studies identified, screened, eligible, and included in the final review.
Additional figures that illustrate pathophysiology or clinical presentation may be considered. Note: All figures will be re-created. For each proposed illustration, the authors should provide a list of the elements to be included in the illustration; 3-4 relevant recent references; example illustrations, if available; a working figure title and legend; and an explanation of how this new illustration would add to the published literature. We encourage videos, if appropriate, to illustrate a point made or process described in the Review.
Follow additional instructions for preparation and submission of Figures and Video .
Narrative Reviews on clinical topics provide an up-to-date review for clinicians on a topic of general common interest from the perspective of internationally recognized experts in these disciplines. The focus of Narrative Reviews will be an update on current understanding of the physiology of the disease or condition, diagnostic consideration, and treatment. These reviews should address a specific question or issue that is relevant for clinical practice. Narrative Reviews do not require (but may include) a systematic review of the literature search. Recommendations should be supported with evidence and should rely on recent systematic reviews and guidelines, if available, emphasizing factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention.
The basic structure of manuscripts reporting Narrative Reviews should include the following: Abstract (structured abstract of no more than 300 words); Introduction (150-250 words); Methods, if included (150-250 words); Discussion/Observations (1000-1250 words, with the following subsections, if appropriate: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, Assessment and Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis); and Conclusions (2-3 sentences).
Typical length: 2000-3500 words (maximum), with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures, and no more than 50-75 references. For an example of this type of article, see JAMA . 2015;314(23):2544-2554 .
Specific Components of a Narrative Review
Abstract (300 words)
Narrative Review articles should include a 3-part structured abstract of no more than 300 words using the headings listed below:
Importance: An overview of the topic and discussion of the main objective or reason for this review. Observations: The principal observations and findings of the review. Conclusions and Relevance: The conclusions of the review that are supported by the information, along with clinical applications. How the findings are clinically relevant should be specifically stated.
The first 2 to 3 sentences of the Introduction should draw in readers in such that they want to continue reading the article and should establish the importance of the Review. Reviews should include the clinical question or issue and its importance for general medical practice, specialty practice, or public health. The first paragraph should provide a general summary of the clinical problem (eg, obesity). The next paragraph should focus on the specific aspect of the clinical problem the article will explore (eg, treatments for obesity). Briefly summarize the epidemiology of the disease. This information should include disease prevalence and incidence and perhaps discussion of the presence and frequency of any relevant subpopulations and any geographic or seasonal variations of the disease if these are relevant. The third paragraph should discuss exactly what material will be covered in the Review (eg, obesity treatments).
Methods (150-250 words)
A Methods section is not required for Narrative Reviews, but may be included to summarize a literature search that was conducted for this Review. If included, briefly describe the characteristics of the literature searched and included in the review, including the bibliographic databases and other sources searched, search terms used, dates included in the search, date the literature search was conducted, and any process used to evaluate the literature.
Discussion/Observations (1000-1250 words)
The principal observations of the Narrative Review generally should include the subsections listed below, although each section may not be necessary for some topics. The word counts following each subsection are suggested to assist with keeping the overall Observations section limited to 1000-1250 words.
Pathophysiology (150-250 words). Provide a brief overview of the pathophysiology of the disease. The intent is to provide readers with sufficient background information about the underpinnings of a disease to provide context for the rest of the article. Clinical Presentation (150-250 words). Briefly describe the clinical characteristics that result in a patient seeking medical care for the condition or what features of the disease should lead a physician to evaluate or treat it. Assessment and Diagnosis (250-300 words). Describe the clinical examination for evaluation of the disease and explain the most salient physical examination findings. If laboratory or imaging studies are necessary, provide the sensitivity and specificity and diagnostic accuracy of these tests and consider providing positive and negative likelihood ratios. Sequences of diagnostic tests are best presented as algorithms or in tables. Treatment (250-500 words). Treatments should be based on the most recently available and highest level of evidence. Treatment options should be summarized in the text and presented in detail in tables along with an indication of the strength of evidence supporting the individual treatments. In general, treatment recommendations should be supported by a systematic review or a high-quality guideline. If possible, the costs for various treatments should be provided. Prognosis (100-150 words). A section outlining the overall prognosis for the condition, once treated, should be included.
For most Narrative Reviews, tables should be included that summarize the epidemiology, diagnostic tools, and therapies available for the disease. In some cases, these 3 topics may not all be relevant to the review topic and tables may be appropriately modified to fit the review. Include a fourth table that compares the findings of the review and current clinical practice recommendations or diagnostic and therapeutic uncertainty or controversies.
Table 1: Major epidemiologic and burden of disease facts Table 2: Major diagnostic tools available Table 3: Major therapies available Table 4: Current clinical practice recommendations and/or diagnostic and therapeutic uncertainty, and controversies
Tables summarizing treatments should have information organized by category of treatment and then by individual treatments. Columns may include the treatment, strength of evidence supporting the treatment, the effect of the treatment (preferably shown as the treatment's effect as compared to control on the measured outcome together with 95% confidence intervals), adverse effects, and very brief explanatory comments, if necessary. Lengthy text-based tables should be avoided. Additional or lengthy tables may be published online only, if justified.
Figures that illustrate pathophysiology or clinical presentation may be included. Note: All figures will be re-created. For each proposed illustration, the authors should provide a list of the elements to be included in the illustration; 3-4 relevant recent references; example illustrations, if available; a working figure title and legend; and an explanation of how this new illustration would add to the published literature. We encourage videos, if appropriate, to illustrate a point made or process described in the Review.
Note: This journal publishes very few of these types of articles. These manuscripts describe an important issue in clinical medicine, public health, health policy, or medical research in a scholarly, thorough, well-referenced, systematic, and evidence-based manner.
A structured abstract is required. Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including tables, figures, or references) with no more than a total of 4 tables and/or figures and no more than 50 references. For a recently published example, see JAMA . 2019;322(20):1996-2016 .
Clinical Challenge presents an actual patient scenario about a specific disease or condition with an accompanying clinical image.
Authors should provide 4 single-phrase plausible treatment options describing possible courses of action with one of these being the most correct response for the question "What Would You Do Next?" Manuscripts should include a brief discussion of the relevant clinical issues and provide well-supported (evidence-based) explanations discussing the 4 potential courses of action. For a recently published example, see JAMA . 2022;327(24):2448-2449. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.8384 .
All diagnostic and treatment recommendations should be supported by referencing recent authoritative texts or journal articles. Preferably, these recommendations should be supported by governmental or multisociety guidelines, clinical trials, meta-analyses, or systematic reviews. The text should have a maximum length of 850 words, consisting of no more than 250 words for the case presentation, question, and 4 one-sentence answers, followed by no more than 600 words that include the diagnosis and a brief discussion. There should be no more than 3 authors. At least 1 of the authors, ideally the corresponding author, should have sufficient expertise and experience with the topic. There should be no more than 10 references, and no more than 2 small figures totaling 3 image components (Figure 1, with no more than 2 components, for the case presentation; and Figure 2, with no more than 1 component, for the diagnosis and discussion).
Provide a short title that briefly describes the disease entity or case presentation and does not include the diagnosis. Do not include the patient's race, ethnicity, or country of origin in the title or the first line of the article. If this information is clinically relevant and necessary, it can be included in the case description.
In addition, the JAMA Network Patient Permission form must be completed and signed by the patient (or a family member if the patient has died, is a minor, or is an adult without decisional capacity) and included at the time of manuscript submission. Please read Patient Identification before submitting your manuscript.
The image and case presentation should be from the same patient and must not have been published previously. In some cases, additional figures may be included to accompany the answer explanations (see description of additional figure(s) above). All images submitted should be high-quality .jpg or .tif files. Submit the original version of all image files at the highest resolution possible without labels. In general, the original image file should have a minimum resolution of 350 dpi at a width of about 5 inches. Do not increase the original resolution, resize, or crop the image; where applicable, we will crop to maintain patient confidentiality. If any labels, arrowheads, or A/B panel indicators are desired, provide a separate labeled version of the figure(s) for reference. All labels will be reformatted to journal style.
For more information on how to submit figures, see Figures.
We would like to receive common problems presenting uncommonly, rather than unusual or rare conditions (ie, "zebras"). These cases should be of interest to clinicians; they should be problems that clinicians are likely to encounter and have an outstanding image that illustrates the disorder and contributes to the diagnostic challenge.
Manuscripts not meeting these guidelines will not be considered.
Diagnostic Test Interpretation presents the results of a diagnostic test from a single patient and explores the clinical application of the test result. The Diagnostic Test Interpretation is intended to help clinicians understand the underlying rationale in ordering tests, interpreting test results, and acting on the diagnostic test findings.
The diagnostic test result must be obtained from the care of an actual patient and must include that patient's written permission. The JAMA Network Patient Permission form should be read and completed and signed by the patient (or a family member if the patient has died, is a minor, or is an adult without decisional capacity) and included at the time of manuscript submission. The results of laboratory, pathologic, or radiographic tests are appropriate but clinical images are not. Results of the diagnostic test of interest (and related tests) and the range of reference values should be included after the case. Authors of manuscripts based on clinical images should consult the instructions for Clinical Challenge .
Provide a short title that briefly describes the disease entity or case presentation and does not include the diagnosis. Do not include the patient's race, ethnicity, or country of origin in the title or first line of the article. If this information is clinically relevant and necessary, it can be included in the case description.
Manuscripts for Diagnostic Test Interpretation should have the following sections:
Case presentation. The case presentation should be brief and focus on the diagnostic test in question. At the end of the case presentation the pertinent diagnostic test results and reference ranges should be provided (200 words). Include: JAMA Exclude: Specialty Journals, JNO Comments: How do you interpret these test results? How do you interpret these test results? (or What would you do next?) Four plausible responses should be provided. While most Diagnostic Test Interpretation articles will pose the question "How do you interpret these results?" a subset may more appropriately focus on the next best step regarding workup of the abnormal test result. In these cases, the question "How do you interpret these test results?" can be replaced with "What would you do next?" Either question should be presented in the format of a multiple choice question with a single correct (or best) answer. The answers may be brief phrases or short sentences, should be similar in length, and should be arranged alphabetically by first word in the answer. Response options should not describe treatments (about 50 words). Include: CAR,ONC Exclude: JAMA, DER, IMD, NEU, OPH, PED, OTO, PSY, SUR, JNO Comments: How do you interpret these test results? Test characteristics. A brief review of the diagnostic test should be provided (approximately 200 words). For biomarkers, this should include a brief description of the related physiology. Test accuracy should be reported using sensitivity and specificity or likelihood ratios, and predictive values should be provided for common clinical scenarios. Please use likelihood ratios whenever possible, since they do not depend on disease prevalence. The prevalence of the disease should be stated so that the pretest probability may be estimated. For example, "For patients with a typical disease prevalence of 10%, the predictive values of positive and negative test results are approximately 50% and 1%, respectively." Discussion of the application and utility of the diagnostic test should be based on a high-quality systematic review or authoritative practice guideline. If a more recent, original study supersedes or adds meaningfully to the prior synthesis of research, that article also should be cited. The approximate fee for the test should be provided. For example, some fees for laboratory tests can be obtained from the Medicare fee schedules . Radiology procedure fees can be found at the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule website . Application of test result to this patient. A brief discussion of how the diagnostic test result will facilitate the next steps in a patient's management should be presented. Please also address the correct answer to the question about test interpretation in this section (200 words). What Are Alternative Diagnostic Testing Approaches? If there are different testing strategies that can be used to evaluate patients to establish a diagnosis, please discuss them (100 words). Patient Outcome. Long-term follow-up (most recent as possible) regarding the patient's condition and outcome of treatment is necessary (100 words). Clinical Bottom Line. Please provide a bulleted list of 3-5 items that reflect the most important message readers should obtain from this article.
The overall text of the manuscript should have a maximum of 850 words, no more than 10 references, and no more than 3 authors. At least 1 of the authors, ideally the corresponding author, should have sufficient expertise and experience with the topic. The case presentation must not have been previously published.
For an example of this article type, see JAMA . 2022;327(13):1284-1285. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.2037 .
If there are questions about patient identifiability, please contact the editorial office. Authors interested in submitting a manuscript for Diagnostic Test Interpretation should contact the editorial office prior to manuscript preparation and submission by sending an email to Kristin Walter at [email protected] .
Viewpoints may address virtually any important topic in medicine, public health, research, discovery, prevention, ethics, health policy, or health law and generally are not linked to a specific article. Viewpoints should be well focused, scholarly, and clearly presented but should not include the findings of new research or data that have not been previously published.
Viewpoints must have no more than 3 authors. Editors encourage diversity of gender, race, ethnicity, geographic location, and discipline for Viewpoint authors, and the first author should have sufficient expertise and experience with the topic to provide an authoritative opinion. The text should include the full name, academic degrees, and no more than 2 institutional affiliations for each author. Maximum length: up to 1200 words of text—or 1000 words of text with 1 small table or figure—and no more than 7 references, which should be as current as possible. Viewpoints not meeting these guidelines will not be considered.
Most essays published in A Piece of My Mind are personal vignettes (eg, exploring the dynamics of the patient-physician relationship) taken from wide-ranging experiences in medicine; occasional pieces express views and opinions on the myriad issues that affect the profession. If the patient(s) described in these manuscripts is identifiable, a Patient Permission form , which provides consent for publication, must be completed and signed by the patient(s) or family member(s) and submitted with the manuscript. Manuscripts that describe identifiable patients that do not have a signed form will not be reviewed. Omitting data or making data less specific to deidentify patients is acceptable, but changing any such data is not acceptable. Fictional or composite accounts are not permitted.
Manuscripts are not published anonymously or pseudonymously and must have no more than 3 authors. All manuscripts must be submitted formally via the journal's manuscript submission system; we do not review drafts or unfinished manuscripts prior to submission. Length limit: 1600 words.
Poems related to the medical experience, whether from the point of view of a health care worker or patient, or simply an observer, will be considered. Poems should be original, not previously published or under consideration elsewhere, no longer than 44 lines, and with individual lines no longer than 55 characters (including spaces). Authors should submit each poem separately (ie, one poem per submission record, and only one author per poem). Submissions containing multiple poems will be returned with instructions to split into individual files. Do not submit artwork, music/audio, or other accompanying materials, which are not considered. All poems must be submitted online via the online manuscript submission and review system . Authors of poems that are accepted for publication are required to complete Authorship Forms and transfer copyright to the publisher as part of a publishing agreement. An email with links to the Authorship Form will be sent to authors for completion before final acceptance. Author requests to republish poems are generally granted by our permissions department following a formal request.
Questions about submitting poems (but not submissions) may be sent to [email protected] .
Letters discussing a recent article in this journal should be submitted within 4 weeks of publication of the article in print. 3 Letters received after 4 weeks will rarely be considered. Letters should not exceed 400 words of text and 5 references, 1 of which should be to the recent article. Letters may have no more than 3 authors. The text should include the full name, academic degrees, and a single institutional affiliation for each author and the email address for the corresponding author. Letters must not duplicate other material published or submitted for publication and should not include unpublished data. Letters not meeting these specifications are generally not considered. Letters being considered for publication ordinarily will be sent to the authors of the original article, who will be given the opportunity to reply. Letters will be published at the discretion of the editors and are subject to abridgement and editing for style and content. To read more about Letters, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Replies by authors should not exceed 500 words of text and 6 references. They should have no more than 3 authors.
Clinical Trial
These manuscripts include reports of Randomized Clinical Trials, Parallel-Design Double-blind Trials, Crossover Trials, Equivalence and Noninferiority Trials, Cluster Trials, and Nonrandomized Clinical Trials.
The ICMJE defines a clinical trial as any research project that prospectively assigns human participants to intervention or comparison groups to study the cause-and-effect relationship between an intervention and a health outcome. 4 Interventions include but are not limited to drugs, surgical procedures, devices, behavioral treatments, educational programs, dietary interventions, quality improvement interventions, process-of-care changes, and the like. All manuscripts reporting clinical trials, including those limited to secondary exploratory or post hoc analysis of trial outcomes, must include the following:
- Copy of the original trial protocol, including the complete statistical analysis plan and any amendments. The journal recommends using the SPIRIT reporting guidelines when preparing original protocols (see Protocols ).
- CONSORT flow diagram (see Figure ).
- Completed trial checklist (see Checklist ).
- Registry at an appropriate online public clinical trial registry (see Trial Registration requirements).
- A Data Sharing Statement to indicate if data will be shared or not. Specific questions regarding the sharing of data are included in the manuscript submission system.
For additional guidance on reporting Randomized Clinical Trial, Parallel-Design Double-blind Trial, Crossover Trial, Equivalence and Noninferiority Trial, Cluster Trial, and Nonrandomized Clinical Trial, see Study Types .
Each manuscript should clearly state an objective or hypothesis; the design and methods (including the study setting and dates, patients or participants with inclusion and exclusion criteria, or data sources, and how these were selected for the study); the essential features of any interventions; the primary and secondary outcome measures (consistent with those reported in the trial protocol); the main results of the study; a discussion section placing the results in context with the published literature and addressing study limitations; and the conclusions.
A structured abstract is required, and trial registration information (registry name, trial ID, and URL) must be listed at the end of the abstract; for more information, see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Reports of Original Data . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and supplemental material) with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures and no more than 50-75 references. The subtitle should include the phrase "A Randomized Clinical Trial" or, for Nonrandomized Clinical Trials, "A Nonrandomized Clinical Trial." To read more about clinical trials, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Trial Registration:
In concert with the ICMJE, JAMA Network requires, as a condition of consideration for publication, registration of all trials in a public trials registry that is acceptable to the ICMJE (ie, the registry must be owned by a not-for-profit entity, be publicly accessible, and require the minimum registration data set as described by ICMJE). 4 , 8 , 9
Acceptable trial registries include the following and others listed at http://www.icmje.org :
- anzctr.org.au
- clinicaltrials.gov
- trialregister.nl
- umin.ac.jp/ctr
All clinical trials, regardless of when they were completed, and secondary analyses of original clinical trials must be registered before submission of a manuscript based on the trial. Secondary data analyses of primary (parent) clinical trials should not be registered as separate clinical trials, but instead should reference the trial registration number of the primary trial. Please note: for clinical trials starting patient enrollment after July 2005, trials must have been registered before onset of patient enrollment. For trials that began before July 2005 but that were not registered before September 13, 2005, trials must have been registered before journal submission. Trial registry name, registration identification number, and the URL for the registry should be included at the end of the abstract and also in the space provided on the online manuscript submission form.
Authors of manuscripts reporting clinical trials must submit trial protocols (including the complete statistical analysis plan) along with their manuscripts. Protocols in non-English languages should be translated into English. This should include the original approved protocol and statistical analysis plan, and all subsequent amendments to either document. Do not submit a summary version that was published as an article in another journal. If the manuscript is accepted, the protocol and statistical analysis plan will be published as a supplement.
CONSORT Flow Diagram and Checklist:
Manuscripts reporting the results of randomized trials must include the CONSORT flow diagram showing the progress of patients throughout the trial. The CONSORT checklist also should be completed and submitted with the manuscript. 10
Figure. Profile of a Randomized Clinical Trial

Trial Protocol
These manuscripts are documents that describe the organization and plan for a randomized clinical trial, including the trial's objective(s), design, methodology, all outcomes to be measured, and statistical analysis plan. All trial protocol manuscripts must include a copy of the trial protocol including the complete statistical analysis plan (see Protocols ). All clinical trials that have begun randomization must be registered at an appropriate online public registry (see Trial Registration requirements). Follow SPIRIT Reporting Guidelines .
A structured abstract is required, and trial registration information (registry name, trial ID, and URL) must be listed at the end of the abstract; for more information, see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Trial Protocols . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and supplemental material) with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures and no more than 50-75 references. The subtitle should include the phrase "A Trial Protocol."
These manuscripts are systematic, critical assessments of literature and data sources pertaining to clinical topics, emphasizing factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention, and that includes a statistical technique for quantitatively combining the results of multiple studies that measure the same outcome into a single pooled or summary estimate. All articles or data sources should be searched for and selected systematically for inclusion and critically evaluated, and the search and selection process should be described in the manuscript. The specific type of study or analysis, population, intervention, exposure, and tests or outcomes should be described for each article or data source. The data sources should be as current as possible, ideally with the search having been conducted within several months of manuscript submission. Authors of reports of meta-analyses of clinical trials should submit the PRISMA flow diagram and checklist . Authors of meta-analyses of observational studies should submit the MOOSE checklist . Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines .
A structured abstract is required; for more information, see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Meta-analysis . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and online-only material), with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures and no more than 50-75 references. The subtitle should include the phrase "A Meta-analysis." To read more about meta-analyses, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Other Observational Studies
These manuscripts include Cohort Study, Case-Control Study, Cross-sectional Study, Case Series, Economic Evaluation, Decision Analytical Model, Comparative Effectiveness Research, Genetic Association Study, Diagnostic/Prognostic Study, Quality Improvement Study, Survey Study, and Qualitative Study. Each manuscript should clearly state an objective or hypothesis; the design and methods (including the study setting and dates, patients or participants with inclusion and exclusion criteria and/or participation or response rates, or data sources, and how these were selected for the study); the essential features of any interventions or exposures; the main outcome measures; the main results of the study; a discussion section placing the results in context with the published literature and addressing study limitations; and the conclusions and relevant implications for clinical practice or health policy. Data included in research reports must be original and should be as timely and current as possible (see Timeliness of Data ). Follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines .
A structured abstract is required; for more information, see instructions for preparing Abstracts for Reports of Original Data . A list of 3 Key Points is required (see guidance on preparing Key Points ). Maximum length: 3000 words of text (not including abstract, tables, figures, acknowledgments, references, and supplemental material) with no more than a total of 5 tables and/or figures and no more than 50-75 references.
Format My Manuscript
Manuscript preparation and submission requirements.
All manuscripts must be submitted online via the online manuscript submission and review system .
At the time of submission, complete contact information (affiliation, postal/mail address, email address, and telephone numbers) for the corresponding author is required. First and last names, email addresses, and institutional affiliations of all coauthors are also required. After the manuscript is submitted, the corresponding author will receive an acknowledgment confirming receipt and a manuscript number. Authors will be able to track the status of their manuscripts via the online system. After manuscript submission, all authors of papers under consideration for publication will be sent a link to the Authorship Form to complete and submit. See other details in these instructions for additional requirements. 2 , 4
As recommended by the ICMJE, "if the manuscript has been submitted previously to another journal, it is helpful to include the previous editors' and reviewers' comments with the submitted manuscript, along with the authors' responses to those comments." 4 It is not uncommon for manuscripts to have been submitted to and peer reviewed by other journals and sharing this information will not bias an editor's decision for this journal. Thus, authors are encouraged to submit these previous comments in their entirety and indicate how they have revised the manuscript in response to these comments, which may expedite the review process. In the submission system, there is a file type for Previous Peer Review and Editorial Comments.
Include a cover letter and complete contact information for the corresponding author (affiliation, postal/mail address, email address, and telephone number) and whether the authors have published, posted, or submitted any related papers from the same study (see Previous Publication, Related Manuscripts and Reports, and Preprints ).
Manuscripts should be prepared in accordance with the AMA Manual of Style , 11th edition, 2 and/or the ICMJE Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals . 4
Include in the manuscript file a title page, abstract, text, references, and as appropriate, figure legends and tables. Start each of these sections on a new page, numbered consecutively, beginning with the title page. Figures should be submitted as separate files (1 file per figure) and not included in the manuscript text.
We recommend individual file sizes of no more than 500 kB and not exceeding 1 MB, with the total size for all files not exceeding 5 MB (not including any video files).
For submission and review, please submit the manuscript as a Word document. Do not submit your manuscript in PDF format.
Use 10-, 11-, or 12-point font size, double-space text, and leave right margins unjustified (ragged).
The title page should be the first page of your manuscript file. It should include a manuscript title; the full names, highest academic degrees, and affiliations of all authors (if an author's affiliation has changed since the work was done, the new affiliation also should be listed); name and complete contact information for corresponding author; and manuscript word count (not including title, abstract, acknowledgment, references, tables, and figure legends).
Titles should be concise, specific, and informative. 2(p8) Please limit the length of titles to 100 characters (including spaces) for reports of research and other major articles and 60 characters for shorter article types such as opinion articles and Letters as well as for subtitles to major articles. For scientific manuscripts, do not use overly general titles, declarative titles, titles that include the direction of study results, or questions as titles. For reports of clinical trials, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews, include the type of study as a subtitle (eg, A Randomized Clinical Trial, A Meta-analysis, A Systematic Review). For reports of other types of research, do not include study type or design in the title or subtitle. Depending on the context, avoid inclusion of specific locations (eg, state, province, or country) and specific years. To read more about titles, see the AMA Manual of Style .
In the manuscript, include a separate section called "Key Points" before the Abstract.
This feature provides a quick structured synopsis of the findings of your manuscript (required only for research and review manuscripts), following 3 key points: Question, Findings, and Meaning. Limit this section to 75-100 words or less.
Question: Focused question based on the study hypothesis or goal/purpose. Limit to 1 sentence. Findings: Results of the study/review. Include the design (eg, clinical trial, cohort study, case-control study, meta-analysis). Focus on primary outcome(s) and finding(s). Do not emphasize secondary outcomes. Report basic numbers only but state if results are statistically significant or not significant; do not include results of statistical tests or measures of variance (see example below). Can include 1 to 2 sentences. Meaning: Key conclusion and implication based on the primary finding(s). Limit to 1 sentence. Example of Research Article Question: What is the immunogenicity of an inactivated influenza A vaccine with and without adjuvant? Findings: In this randomized clinical trial that included 980 adults, the proportion achieving an effective antibody response was 84% with adjuvant vs 2% without adjuvant, a significant difference. Meaning: In an influenza pandemic the use of an adjuvant with inactivated influenza A vaccine may be warranted. Include: All Journals except JNO and JHF Exclude: JNO and JHF Comments: Example of Review Article Example of Review Article Question: What are the most effective medical treatments for adult chronic sinusitis? Findings: In this systematic review, symptoms of chronic sinusitis were improved with saline irrigation and topical corticosteroid therapy compared to no therapy. Compared with placebo, 3-week courses of systemic corticosteroids or oral doxycycline were associated with reduced polyp size, and a 3-month course of macrolide antibiotic was associated with improved symptoms in patients without polyps. Meaning: First-line therapy for chronic sinusitis should begin with daily topical intranasal corticosteroid in conjunction with saline irrigation; subsequent therapies should be based on the patient's polyp status and severity of symptoms.
Include a structured abstract for reports of original data, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews. Abstracts should be prepared in JAMA Network style—see instructions for preparing abstracts below. Abstracts are not required for Editorials, Viewpoints, and special features. No information should be reported in the abstract that does not appear in the text of the manuscript. To read more about abstracts, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Abstracts for Reports of Original Data:
Reports of original data should include an abstract of no more than 350 words using the headings listed below. For brevity, parts of the abstract may be written as phrases rather than complete sentences. Each section should include the following content:
Importance: The abstract should begin with a sentence or 2 explaining the clinical (or other) importance of the study question. Objective: State the precise objective or study question addressed in the report (eg, "To determine whether..."). If more than 1 objective is addressed, the main objective should be indicated and only key secondary objectives stated. If an a priori hypothesis was tested, it should be stated. Design: Describe the basic design of the study and include the specific study type (eg, randomized clinical trial, cohort, cross-sectional, case-control, case series, survey, meta-analysis, bibliometric analysis). State the years of the study and the duration of follow-up. For older studies (eg, those completed >3 years ago), add the date of the analysis being reported. If applicable, include the name of the study (eg, the Framingham Heart Study). As relevant, indicate whether observers were blinded to patient groupings, particularly for subjective measurements. Setting: Describe the study setting to assist readers to determine the applicability of the report to other circumstances, for example, multicenter, population-based, primary care or referral center(s), etc. Participants: State the clinical disorders, important eligibility criteria, and key sociodemographic features of patients (or other study participants). The numbers of eligible participants and how they were selected should be provided, including the number approached but who refused or were excluded. For selection procedures, these terms should be used, if appropriate: random sample (where random refers to a formal, randomized selection in which all eligible individuals have a fixed and usually equal chance of selection); population-based sample; referred sample; consecutive sample; volunteer sample; convenience sample. If matching is used for comparison groups, characteristics that are matched should be specified. In follow-up studies, the proportion of participants who completed the study must be indicated.
Note: The preceding 3 sections are usually combined for accepted papers during the editing process as "Design, Setting, and Participants," but for manuscript submission these sections should be kept separate.
Intervention(s) (for clinical trials) or Exposure(s) (for observational studies): The essential features of any interventions, or exposures, should be described, including their method and duration. The intervention, or exposure, should be named by its most common clinical name, and nonproprietary drug names should be used. Main Outcome(s) and Measure(s): Indicate the primary study outcome measurement(s) as planned before data collection began. If the manuscript does not report the main planned outcomes of a study, this fact should be stated and the reason indicated. State clearly if the hypothesis being tested was formulated during or after data collection. Explain outcomes or measurements unfamiliar to a general medical readership. Results: Summary demographic information (eg, characteristics such as sex and age) and the number of study participants should be reported in the first sentence of the Results paragraph. The main outcomes of the study should be reported and quantified, including final included/analyzed sample. When possible, present numerical results (eg, absolute numbers and/or rates) with appropriate indicators of uncertainty, such as confidence intervals. Include absolute numbers and/or rates with any ratio measures and avoid redundant reporting of relative data (eg, % increase or decrease). Use means and standard deviations (SDs) for normally distributed data and medians and ranges or interquartile ranges (IQRs) for data that are not normally distributed. Avoid solely reporting the results of statistical hypothesis testing, such as P values, which fail to convey important quantitative information. For most studies, P values should follow the reporting of comparisons of absolute numbers or rates and measures of uncertainty (eg, 0.8%, 95% CI −0.2% to 1.8%; P =.13). P values should never be presented alone without the data that are being compared. See also Reporting Standards and Data Presentation . Measures of relative risk also may be reported (eg, relative risk, hazard ratios) and should include confidence intervals. Studies of screening and diagnostic tests should report sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratio. If predictive value or accuracy is reported, prevalence or pretest likelihood should be given as well. All randomized clinical trials should include the results of intention-to-treat analysis as well. In intervention studies, the number of patients withdrawn because of adverse effects should be given. Approaches such as number needed to treat to achieve a unit of benefit may be included when appropriate. All surveys should include response/participation rates. Conclusions and Relevance: Provide only conclusions of the study that are directly supported by the results. Give equal emphasis to positive and negative findings of equal scientific merit. Also, provide a statement of relevance indicating implications for clinical practice or health policy, avoiding speculation and overgeneralization. The relevance statement may also indicate whether additional study is required before the information should be used in clinical settings. Trial Registration: For clinical trials only (not nontrial observational studies), the name of the trial registry, registration number, and URL of the registry must be included. See Trial Registration .
Abstracts for Meta-analysis:
Manuscripts reporting the results of meta-analyses should include an abstract of no more than 350 words using the headings listed below. The text of the manuscript should also include a section describing the methods used for data sources, study selection, data extraction, and data synthesis. Each heading should be followed by a brief description:
Importance: A sentence or 2 explaining the importance of the systematic review question that is used to justify the meta-analysis. Objective: State the precise primary objective of the meta-analysis. Indicate whether the systematic review for the meta-analysis emphasizes factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention and include information about the specific population, intervention, exposure, and tests or outcomes that are being analyzed. Data Sources: Succinctly summarize data sources, including years searched. The search should include the most current information possible, ideally with the search being conducted within several months before the date of manuscript submission. Potential sources include computerized databases and published indexes, registries, meeting abstracts, conference proceedings, references identified from bibliographies of pertinent articles and books, experts or research institutions active in the field, and companies or manufacturers of tests or agents being reviewed. If a bibliographic database is used, state the exact indexing terms used for article retrieval, including any constraints (for example, English language or human study participants). If abstract space does not permit this level of detail, summarize sources in the abstract including databases and years searched, and place the remainder of the information in the Methods section. Study Selection: Describe inclusion and exclusion criteria used to select studies for detailed review from among studies identified as relevant to the topic. Details of selection should include particular populations, interventions, outcomes, or methodological designs. The method used to apply these criteria should be specified (for example, blinded review, consensus, multiple reviewers). State the proportion of initially identified studies that met selection criteria. Data Extraction and Synthesis: Describe guidelines (eg, PRISMA , MOOSE ) used for abstracting data and assessing data quality and validity. The method by which the guidelines were applied should be stated (for example, independent extraction by multiple observers). Indicate whether data were pooled using a fixed-effect or random-effects model. Main Outcome(s) and Measure(s): Indicate the primary study outcome(s) and measurement(s) as planned before data collection began. If the manuscript does not report the main planned outcomes of a study, this fact should be stated and the reason indicated. State clearly if the hypothesis being tested was formulated during or after data collection. Explain outcomes or measurement unfamiliar to a general medical readership. Results: Provide the number of studies and patients/participants in the analysis and state the main quantitative results of the review. When possible, present numerical results (eg, absolute numbers and/or rates) with appropriate indicators of uncertainty, such as confidence intervals. Include absolute numbers and/or rates with any ratio measures and avoid redundant reporting of relative data (eg, % increase or decrease). Use means and standard deviations (SDs) for normally distributed data and medians and ranges or interquartile ranges (IQRs) for data that are not normally distributed. Avoid solely reporting the results of statistical hypothesis testing, such as P values, which fail to convey important quantitative information. For most studies, P values should follow the reporting of comparisons of absolute numbers or rates and measures of uncertainty (eg, 0.8%, 95% CI −0.2% to 1.8%; P = .13). P values should never be presented alone without the data that are being compared. See also Reporting Standards and Data Presentation . Meta-analyses should state the major outcomes that were pooled and include odds ratios or effect sizes and, if possible, sensitivity analyses. Evaluations of screening and diagnostic tests should include sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios, receiver operating characteristic curves, and predictive values. Assessments of prognosis should summarize survival characteristics and related variables. Major identified sources of variation between studies should be stated, including differences in treatment protocols, co-interventions, confounders, outcome measures, length of follow-up, and dropout rates. Conclusions and Relevance: The conclusions and their applications (clinical or otherwise) should be clearly stated, limiting interpretation to the domain of the review.
Abstracts for Systematic Reviews or Special Communications:
Systematic Review articles should include a structured abstract of no more than 350 words using the headings listed below.
Importance: Include 1 or 2 sentences describing the clinical question or issue and its importance in clinical practice or public health. Objective: State the precise primary objective of the review. Indicate whether the review emphasizes factors such as cause, diagnosis, prognosis, therapy, or prevention and include information about the specific population, intervention, exposure, and tests or outcomes that are being reviewed. Evidence Review: Describe the information sources used, including the search strategies, years searched, and other sources of material, such as subsequent reference searches of retrieved articles. Methods used for inclusion of identified articles and quality assessment should be explained. Findings: Include a brief summary of the number of articles included, numbers of various types of studies (eg, clinical trials, cohort studies), and numbers of patients/participants represented by these studies. Summarize the major findings of the review of the clinical issue or topic in an evidence-based, objective, and balanced fashion, with the highest-quality evidence available receiving the greatest emphasis. Provide quantitative data. Conclusions and Relevance: The conclusions should clearly answer the questions posed if applicable, be based on available evidence, and emphasize how clinicians should apply current knowledge. Conclusions should be based only on results described in the abstract Findings subsection.
Abstracts for Narrative Reviews or Special Communications:
Importance: An overview of the topic and discussion of the main objective or reason for this review. Observations: The principal observations and findings of the review. Conclusions and Relevance: The conclusions of the review that are supported by the information, along with clinical applications. How the findings are clinically relevant should be specifically stated.
Ratings of the quality of the evidence
Tables summarizing evidence should include ratings of the quality of the evidence. Use the rating scheme listed below with ratings of 1-5 for Reviews that include individual studies (modified from the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine for ratings of individual studies).
Do not use abbreviations in the title or abstract and limit their use in the text. Expand all abbreviations at first mention in the text. To read more about abbreviation use, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Laboratory values are expressed using conventional units of measure, with relevant Système International (SI) conversion factors expressed secondarily (in parentheses) only at first mention. Articles that contain numerous conversion factors may list them together in a paragraph at the end of the Methods section. In tables and figures, a conversion factor to SI should be presented in the footnote or legend. The metric system is preferred for the expression of length, area, mass, and volume. For more details, see the Units of Measure conversion table on the website for the AMA Manual of Style . 2
To read more about units of measure, click here .
Use nonproprietary names of drugs, devices, and other products and services, unless the specific trade name of a drug is essential to the discussion. 2(pp567-569) In such cases, use the trade name once and the generic or descriptive name thereafter. Do not include trademark symbols. To read more about names of drugs, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Authors describing genes or related structures in a manuscript should include the names and official symbols provided by the US National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) or the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee . Before submission of a research manuscript reporting on large genomic data sets (eg, protein or DNA sequences), the data sets should be deposited in a publicly available database, such as NCBI's GenBank , and a complete accession number (and version number if appropriate) must be provided in the Methods section or Acknowledgment of the manuscript. To read more about gene nomenclature, see the AMA Manual of Style .
JAMA does not republish text, tables, figures, or other material from other publishers, except under rare circumstances. Please delete any such material and replace with originals.
The submission and publication of content created by artificial intelligence, language models, machine learning, or similar technologies is discouraged, unless part of formal research design or methods, and is not permitted without clear description of the content that was created and the name of the model or tool, version and extension numbers, and manufacturer. Authors must take responsibility for the integrity of the content generated by these models and tools. See also Use of AI in Publication and Research .
Authors are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of their references and for correct text citation. Number references in the order they appear in the text; do not alphabetize. In text, tables, and legends, identify references with superscript arabic numerals. When listing references, follow AMA style and abbreviate names of journals according to the journals list in PubMed . List all authors and/or editors up to 6; if more than 6, list the first 3 followed by "et al." Note: Journal references should include the issue number in parentheses after the volume number.
Examples of reference style:
Youngster I, Russell GH, Pindar C, Ziv-Baran T, Sauk J, Hohmann EL. Oral, capsulized, frozen fecal microbiota transplantation for relapsing Clostridium difficileinfection. JAMA . 2014;312(17):1772-1778. Murray CJL. Maximizing antiretroviral therapy in developing countries: the dual challenge of efficiency and quality [published online December 1, 2014]. JAMA . doi:10.1001/jama.2014.16376 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. CMS proposals to implement certain disclosure provisions of the Affordable Care Act. http://www.cms.gov/apps/media/press/factsheet.asp?Counter=4221 . Accessed January 30, 2012. McPhee SJ, Winker MA, Rabow MW, Pantilat SZ, Markowitz AJ, eds. Care at the Close of Life: Evidence and Experience . New York, NY: McGraw Hill Medical; 2011.
For more examples of electronic references, click here .
Tables and Figures
Restrict tables and figures to those needed to explain and support the argument of the article and to report all outcomes identified in the Methods section. Number each table and figure and provide a descriptive title for each. Every table and figure should have an in-text citation. Verify that data are consistently reported across text, tables, figures, and supplementary material.
See also Tables and Figures .
Frequency data should be reported as "No. (%)," not as percentages alone (exception, sample sizes exceeding ~10,000). Whenever possible, proportions and percentages should be accompanied by the actual numerator and denominator from which they were derived. This is particularly important when the sample size is less than 100. Do not use decimal places (ie, xx%, not xx.xx%) if the sample size is less than 100. Tables that include results from multivariable regression models should focus on the primary results. Provide the unadjusted and adjusted results for the primary exposure(s) or comparison(s) of interest. If a more detailed description of the model is required, consider providing the additional unadjusted and adjusted results in supplementary tables.
Tables have a minimum of 2 columns. Comparisons must read across the table columns.
Do not duplicate data in figures and tables. For all primary outcomes noted in the Methods section, exact values with measures of uncertainty should be reported in the text or in a table and in the Abstract, and not only represented graphically in figures.
Pie charts and 3-D graphs should not be used and should be revised to alternative graph types.
Bar graphs should be used to present frequency data only (ie, numbers and rates). Avoid stacked bar charts and consider alternative formats (eg, tables or splitting bar segments into side-by-side bars) except for comparisons of distributions of ordinal data.
Summary data (eg, means, odds ratios) should be reported using data markers for point estimates, not bars, and should include error bars indicating measures of uncertainty (eg, SDs, 95% CIs). Actual values (not log-transformed values) of relative data (for example, odds ratios, hazard ratios) should be plotted on log scales.
For survival plots, include the number at risk for each group included in the analysis at intervals along the x-axis scale. For any figures in which color is used, be sure that colors are distinguishable.
All symbols, indicators, line styles, and colors in statistical graphs should be defined in a key or in the figure legend. Axes in statistical graphs must have labels. Units of measure must be provided for continuous data.
Note: All figures are re-created by journal graphics experts according to reporting standards using the JAMA Network style guide and color palette.
- Number all tables in the order of their citation in the text.
- Include a brief title for each table (a descriptive phrase, preferably no longer than 10 to 15 words).
- Include all tables at the end of the manuscript file.
- Refer to Categories of Articles for limits on the number of tables.
- NOTE: Do not embed tables as images in the manuscript file or upload tables in image formats, and do not upload tables as separate files.
Table Creation
Use the table menu in the software program used to prepare the text. Tables can be built de novo using Insert→Table or copied into the text file from another document (eg, Word, Excel, or a statistical spreadsheet).
Avoid using tabs, spaces, and hard returns to set up the table; such tables will have to be retyped, creating delays and opportunities for error.
Tables should be single-spaced and in a 10- or 12-point font (do not shrink the point size to fit the table onto the page). Do not draw extra lines or rules—the table grid will display the outlines of each cell.
Missing data and blank space in the table field (ie, an empty cell) may create ambiguity and should be avoided; use abbreviations such as NA for not applicable or not available. Each piece of data needs to be contained in its own cell. Do not try to align cells with hard returns or tabs; alignment will be imposed in the production system if the manuscript is accepted. To show an indent, add 2 spaces.
When presenting percentages, include numbers (numerator and denominator).
Include statistical variability where applicable (eg, mean [SD], median [IQR]). For additional detail on requirements for data presentation in tables, see Statistical Methods and Data Presentation .
Place each row of data in a separate row of cells, and note that No. (%) and measures of variability are presented in the same cell as in the example Table 1 below:
Table 1. Baseline Values in the Editors' Health Study

SI conversion factors: To convert cholesterol to mmol/L, multiply values by 0.0259.
Note that JAMA Network journals report laboratory values in conventional units. In a table, provide a footnote with the conversion factor to SI units. For a calculator of SI and conventional units, see the AMA Manual of Style . 2
To present data that span more than 1 row, merge the cells vertically. For example, in Table 2 the final column presents the P value for overall age comparisons.
Table 2. Blood Pressure Values Stratified by Age

The table should be constructed such that the primary comparison reads horizontally. For example, see Table 3 (incorrect) and Table 4 (correct).
Table 3. Patient Data by Study Group

Table 4. Patient Data by Study Group

If a table must be continued, repeat the title and column headings on the second page, followed by "(continued)."
Table Footnotes
Footnotes to tables may apply to the entire table, portions (eg, a column), or an individual entry.
The order of the footnotes is determined by the placement in the table of the item to which the footnote refers.
When both a footnote letter and reference number follow data in a table, set the superscript reference number first followed by a comma and the superscript letter.
Use superscript letters (a, b, c) to mark each footnote and be sure each footnote in the table has a corresponding note (and vice versa).
List abbreviations in the footnote section and explain any empty cells.
If relevant, add a footnote to explain why numbers may not sum to group totals or percentages do not add to 100%.
For more detail on the components and recommended structure of tables, see the AMA Manual of Style . 2
Number all figures (graphs, charts, photographs, and illustrations) in the order of their citation in the text. The number of figures should be limited. Avoid complex composite or multipart figures unless justified. See Categories of Articles for limits on the number of figures and/or tables according to article type.
For initial manuscript submissions, figures must be of sufficient quality and may be embedded at the end of the file for editorial assessment and peer review. If a revision is requested and before a manuscript is accepted, authors will be asked to provide figures that meet the requirements described in Figure File Requirements for Publication .
Graphs, charts, some illustrations, titles, legends, keys, and other elements related to figures in accepted manuscripts will be re-created and edited according to JAMA Network style and standards prior to publication. Online-only figures will not be edited or re-created (see Online-Only Supplements and Multimedia ).
Image Integrity
Preparation of scientific images (clinical images, radiographic images, micrographs, gels, etc) for publication must preserve the integrity of the image data. Digital adjustments of brightness, contrast, or color applied uniformly to an entire image are permissible as long as these adjustments do not selectively highlight, misrepresent, obscure, or eliminate specific elements in the original figure, including the background. Selective adjustments applied to individual elements in an image are not permissible. Individual elements may not be moved within an image field, deleted, or inserted from another image. Cropping may be used for efficient image display or to deidentify patients but must not misrepresent or alter interpretation of the image by selectively eliminating relevant visual information. Juxtaposition of elements from different parts of a single image or from different images, as in a composite, must be clearly indicated by the addition of dividing lines, borders, and/or panel labels.
The submission and publication of images created by artificial intelligence, machine learning tools, or similar technologies is discouraged, unless part of formal research design or methods, and is not permitted without clear description of the content that was created and the name of the model or tool, version and extension numbers, and manufacturer. Authors must take responsibility for the integrity of the content generated by these models and tools. See also Use of AI in Publication and Research .
When inappropriate images or image adjustments are detected by the journal staff, authors will be asked for an explanation and will be requested to submit the image as originally captured prior to any adjustment, cropping, or labeling. Authors may be asked to resubmit the image prepared in accordance with the above standards.
Acceptable Figure Files for Initial Submission and Review
Each figure for the main article may be uploaded as a separate file or appended to the end of the manuscript with the figure titles and legends. Online-only figures must be combined into the PDF of the online-only supplement (see Online-Only Supplements and Multimedia ). Note: If a revision is requested and before acceptance, authors must upload each figure for the main article as a separate file and follow the instructions in Figure File Requirements for Publication .
See the Table of Figure Requirements for additional guidance for specific types of figures for suggested resolution and file formats. In general each figure should be no larger than 1 MB.
Figure File Requirements for Publication
Each figure for the main article must be uploaded as a separate file. Online-only figures must be combined into the PDF of the online-only supplement (see Online-Only Supplements and Multimedia ).
See the Table of Figure Requirements for additional guidance and file formats for specific types of figures.
Files created by vector programs are best for accurately plotting and maintaining data points. JAMA Network journals are unable to use file formats native to statistical software applications to prepare figures for publication; most statistical software programs allow users to save or export files in digital vector formats.
Images created digitally (by digital camera or electronically created illustrations) must meet the minimum resolution requirements at the time of creation. Electronically increasing the resolution of an image after creation causes a breakdown of detail and will result in an unacceptable poor-quality image. Each component of a composite image must be uploaded separately at submission and individually meet the minimum resolution requirement.
Color photographs should be submitted in RGB mode using profiles such as Adobe RGB or sRGB. Digital cameras capture images in RGB. Do not change any color settings once the file is on the computer. Black-and-white photographs (eg, radiographs, ultrasound images, CT and MRI scans, and electron micrographs) can be submitted in either RGB or grayscale modes.
Figure Titles and Legends (Captions)
At the end of the manuscript, include a title for each figure. The figure title should be a brief descriptive phrase, preferably no longer than 10 to 15 words. A figure legend (caption) can be used for a brief explanation of the figure or markers if needed and expansion of abbreviations. For photomicrographs, include the type of specimen, original magnification or a scale bar, and stain in the legend. For gross pathology specimens, label any rulers with unit of measure. Digitally enhanced images must be clearly identified in the figure legends as enhanced or manipulated, eg, computed tomographic scans, magnetic resonance images, photographs, photomicrographs, x-ray films.
Figures With Labels, Arrows, or Other Markers
Photographs, clinical images, photomicrographs, gel electrophoresis, and other types that include labels, arrows, or other markers must be submitted in 2 versions: one version with the markers and one without. Provide an explanation for all labels, arrows, or other markers in the figure legend. The Figure field in the File Description tab of the manuscript submission system allows for uploading of 2 versions of the same figure.
Number of Figures
Refer to Categories of Articles because there may be a limit on the number of figures by article type.
General Figure Guidelines
- Primary outcome data should not be presented in figures alone. Exact values with measure of variability should be reported in the text or table as well as in the abstract.
- All symbols, indicators (including error bars), line styles, colors, and abbreviations should be defined in a legend.
- Each axis on a statistical graph must have a label and units of measure should be labeled.
- Do not use pie charts, 3-D graphs, and stacked bar charts as these are not appropriate for accurate statistical presentation of data and should be revised to another figure type or converted to a table.
- Error bars should be included in both directions, unless only 1-sided variability was calculated.
- Values for ratio data—odds ratios, relative risks, hazard ratios—should be plotted on a log scale. Values for ratio data should not be log transformed.
- For footnotes, use letters (a, b, c, etc) not symbols.
- Do not submit figures with more than 4 panels unless otherwise justified.
- See the AMA Manual of Style for more guidance on figure types and components.
For images featuring patients or other identifiable persons, it is not acceptable to use black bars across the eyes in an attempt to deidentify. Cropping may be acceptable as long as the condition under discussion is clearly visible and necessary anatomic landmarks display. If the person in the image is possibly identifiable (not only by others but also by her/himself), permission for publication is required (see Patient Identification ).
Table of Figure Requirements

To present frequency data (numbers or percentages). Each bar represents a category.
Bar graphs are typically vertical but when categories have long titles or there are many of them, they may run horizontally.
The scale on the frequency axis should begin at 0, and the axis should not be broken.
If the data plotted are a percentage or rate, error bars may be used to show statistical variability.
Acceptable File Formats for Initial Submission: .ai, .bmp, .docx, .emf, .eps, .jpg, .pdf, .ppt, .psd, .tif, .wmf, .xls
Acceptable File Formats for Revision and Publication: .ai, .emf, .eps, .pdf, .wmf, .xls

To demonstrate the relationship between 2 or more quantitative variables, such as changes over time.
The dependent variable appears on the vertical axis (y) and the independent variable on the horizontal axis (x); the axes should be continuous, not broken.
Flow diagram

To show participant recruitment and follow-up or inclusions and exclusions (such as in a systematic review).
Acceptable File Formats for Initial Submission: .ai, .docx, .emf, .eps, .jpg, .pdf, .ppt
Acceptable File Formats for Revision and Publication: .ai, .docx, .emf, .eps, .pdf
Survival plot

To display the proportion or percentage of individuals (represented on the y-axis) remaining free of or experiencing a specific outcome over time (represented on the x-axis).
The curve should be drawn as a step function (not smoothed).
The number of individuals followed up for each time interval (number at risk) should be shown underneath the x-axis.
Box-and-whisker plot (box plot)

To show data distribution from 1 or more groups, particularly aggregate/summary data.
Each element should be described (the ends of the boxes, the middle line, and the whiskers). Data points that fall beyond the whiskers are typically shown as circles.
Forest plot

To illustrate summary data, particularly in meta-analyses and systematic reviews.
The data are presented both tabularly and graphically.
The sources (with years and citations, when relevant) should comprise the first column.
Provide indicators of both directions of results at the top of the plot on either side of the vertical line (eg, favors intervention).
Typically, proportionally sized boxes represent the weight of each study and a diamond shows the overall effect at the bottom of the plot.

To display quantitative data other than counts or frequencies on a single scaled axis according to categories on a baseline (horizontal or vertical). Point estimates are represented by discrete data markers, preferably with error bars (in both directions) to designate variability.
Scatterplot

To show individual data points plotted according to coordinate values with continuous, quantitative x- and y-axis scales.
A curve that is generated mathematically may be fitted to the data to summarize the relationship among the variables.
Illustration

To explain physiological mechanisms, describe clinical maneuvers and surgical techniques, or provide orientation to medical imaging.
Required minimum resolution for publication: ≥350 ppi
Acceptable File Formats for Initial Submission: .ai, .docx, .eps, .jpg, .pdf, .ppt, .psd., tif
Acceptable File Formats for Revision and Publication: .ai, .eps, .jpg, .pdf, .psd, .tif
Photographs and other clinical images

To display clinical findings, experimental results, or clinical procedures, including medical imaging, photomicrographs, clinical photographs, and photographs of biopsy specimens.
Legends for photomicrographs should include details about the type of stain used and magnification.
Acceptable File Formats for Initial Submission: .eps, .jpg, .pdf, .ppt, .psd, .tif
Acceptable File Formats for Revision and Publication: .eps, .jpg, .psd, .tif
Line drawings

To illustrate anatomy or procedures.
Line drawings are almost always black and white.
Required minimum resolution for publication: ≥600 ppi
Acceptable File Formats for Initial Submission: .docx, .jpg, .pdf, .ppt, .psd, .tif
Acceptable File Formats for Revision and Publication: .jpg, .psd, .tif
Authors may submit supporting material to accompany their article for online-only publication when there is insufficient space to include the material in the print article. This material should be important to the understanding and interpretation of the report and should not repeat material in the print article. The amount of online-only material should be limited and justified. Online-only material should be original and not previously published.
Online-only material will undergo editorial and peer review with the main manuscript. If the manuscript is accepted for publication and if the online-only material is deemed appropriate for publication by the editors, it will be posted online at the time of publication of the article as additional material provided by the authors. This material will not be edited or formatted; thus, authors are responsible for the accuracy and presentation of all such material.
Online-only material should be submitted in a single Word document with pages numbered consecutively. Each element included in the online-only material should be cited in the text of the main manuscript (eg, eTable in the Supplement) and numbered in order of citation in the text (eg, eTable 1, eTable 2, eFigure 1, eFigure 2, eMethods). The first page of the online-only document should list the number and title of each element included in the document.
Online-Only Text
Online-only text should be set in Times New Roman font, 10 point in size, and single-spaced. The main heading of the online-only text should be in 12 point and boldface; subheadings should be in 10 point and boldface.
Online-Only References
All references cited within the online-only document must be included in a separate reference section, including those that also were cited in the main manuscript. They should be formatted just as in the main manuscript and numbered and cited consecutively in the online-only material.
Online-Only Tables
Online-only tables should be inserted in the document and numbered consecutively according to the order of citation as eTable 1, eTable 2, etc. All online-only tables should be cited in the relevant text of the main manuscript. The text and data in online tables should be Arial font, 10 point in size, and single-spaced. The table title should be set in Arial font, 12 point, and bold. Headings within tables should be set in 10 point and bold. Table footnotes should be set in 8 point and single-spaced. See also instructions for Tables above. If a table runs on to subsequent pages, repeat the column headers at the top of each page. Wide tables may be presented using a landscape orientation.
If data are better displayed in a separate Excel file, this can be submitted, provided that the Excel file is cited as an eTable and is numbered in the order cited in the text. If multiple Excel files of data are submitted, these should be placed in a single Excel file, with multiple tabs (sheets) at the bottom of the file. The first tab (sheet) should include a table of contents with eTable numbers and titles, and the subsequent tabs (sheets) should be labeled as eTable 1, eTable 2, etc. Please note: the journal is not a data repository; large data sets should be deposited into publicly accessible data repositories, and a link should be provided in the Methods or Results section and the Data Sharing Statement .
Online-Only Figures
Online-only figures should be inserted in the document and numbered consecutively according to the order of citation as eFigure 1, eFigure 2, etc. All online-only figures should be cited in the relevant text of the main manuscript. Figure titles should be set in Arial font, 12 point, bold, and single-spaced. Text within figures should be set as Arial font, 10 point. Figure legends should be set in 8 point and single-spaced. Graphs and diagrams should be exported directly out of the software application used to create them in a vector file format, such as .wmf, and then inserted into the Word document. Image file formats such as .jpg, .tif, and .gif are generally not suitable for graphs. Photographs, including all radiological images, should be prepared as .jpg (highest option) or .tif (uncompressed) files at a resolution of 300 dpi and width of 3-5 inches, but the resolution of photographic files with an original resolution <300 dpi should not be increased digitally to achieve a 300-dpi resolution. Photographs should be inserted in the document with the "Link to File" button turned off. Wide figures may be presented using a landscape orientation.
For editorial and review of an initial submission, submit videos according to the following specifications:
- Acceptable file formats: .mov, .wmv, .mpg, .mpeg, .mp4, or .avi
- Maximum file size: ≤25 MB
- Preferred dimensions: 1920x1080 (HD) or greater (4k UHD footage is acceptable)
- Minimum dimensions: 640 pixels wide by 360 pixels deep
- Recommended frame rate: 24 fps (or 23.976 fps), 25 and 30 fps (or 29.97 fps)
- Maximum length: ≤5 minutes
- Desired aspect ratio: 4:3 (standard) or 16:9 (widescreen)
- If compression is required to reduce file size for uploading, please use a minimum bit rate of 10,000 kbit/s – 20,000 kbit/s
- When filming, please use a landscape orientation, not a portrait orientation. This is especially important when filming video or taking photographs with a smartphone or a mobile device.
Verify that the videos are viewable in QuickTime or Windows Media Player before uploading.
For each video, provide an in-text citation (eg, Video 1). At the end of the manuscript file, include a title (a brief phrase, preferably no longer than 10 to 15 words) and a caption that includes the file format and a brief explanation for each video. The same title and caption must be entered in the designated fields in the manuscript submission system when uploading each video. If multiple video files are submitted, number them in the order in which they should be viewed.
If patient(s) are identifiable in the video, authors must submit a Patient Permission form completed and signed by each patient. See also Patient Identification .
If the author does not hold copyright to the video, the author must obtain permission for the video to be published in the journal. This permission must be for unrestricted use in all print, online, and licensed versions of the journal.
NOTE: If your manuscript and accompanying videos are accepted for publication, the video files will be placed into a journal video frame and will be edited by JAMA Network video production staff according to journal style. In addition, a JAMA Network staff person may contact you to resubmit your videos to meet our production specifications. For example, a larger size may be needed, and if your videos were submitted with embedded text such as titles, annotations, labels, or captions, we will ask you to remove the text at this stage and resubmit the video without text, and JAMA Network video production will re-create all text using our house style.
Guidelines for Optimal Video Quality
- Use plenty of diffuse light; avoid shadows.
- Use the appropriate white-balance based on your lighting conditions. Different cameras have different settings, but most have presets for incandescent (yellow) light, fluorescent light, daylight, and tungsten light. Please make sure to select the correct one so that the color of your footage renders accurately.
- Do not overexpose the image; a bit underexposed is preferable.
- Use a tripod. This is especially important in close-ups.
- Avoid excessive zooming. Use the optical zoom only; do not use a digital zoom.
- Turn off all camera special effects.
- Avoid using autofocus. Manual focus is more accurate. Keep the camera at a fixed distance from the subject.
- Instruct people on camera to speak clearly and face the camera when speaking. Try to avoid large movements while speaking or immediately after speaking. Allow pauses before and after speaking for easier editing.
- If the situation permits, ensure that individuals being filmed are not wearing white clothing or clothing with busy patterns or stripes, especially shirts, jackets, and ties. Subdued medium blue, brown, tan, beige, and green colors all work well for shirt and clothing choices.
- Do not include an introduction by the physician as a "talking head" explaining a procedure. All footage should be of the procedure or relevant subject matter only.
- Record a few extra seconds before and after each cut or after changing the camera's position. This allows for easier editing.
Additional Considerations for Filming Surgical Procedures
- Coordinate with the surgical staff to establish a vantage point for the camera that has a clear view of the surgical field.
- Before the procedure, if the situation permits, identify the surgical staff's positions for access into and out of the surgical field to ensure there is no immediate obstruction of the camera.
- During the procedure, avoid typical obstructions of the camera's main view such as arms reaching across the field or soiled surgical sponges. Where possible, keep the heads, hands, and any instruments away from the immediate sightline of the camera. This will ensure that all moments of the procedure are captured in full view and focus.
- If the situation permits a choice of glove type, use brown or tan. White gloves reflect bright light; vividly colored surgical gloves can distract the viewer from the teaching point of the video.
- If the situation permits, avoid rapid movements for procedural steps that should be noticed and understood. To demonstrate a key moment or use of an instrument, movement that is deliberate and steady will allow a standard camera to focus properly.
For editorial and review of an initial submission, submit audio files according to the following minimum requirements:
- Acceptable file formats: .mp3, .wav, or .aiff
- Maximum file size: 25 MB
- To achieve the best quality, use a setting of 256 kbps or higher for stereo or 128 kbps or higher for mono.
- Sampling rate should be either 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz.
- Bit rate should be either 16 or 24 bit.
- To avoid audible clipping noise, please make sure that audio levels do not exceed 0 dBFS.
For each audio file, provide an in-text citation. At the end of the manuscript, include a title (a brief phrase, preferably no longer than 10-15 words) and a caption that includes the file format and a brief explanation for each audio.
NOTE: If your manuscript is accepted for publication, JAMA Network video production staff may contact you to request an original uncompressed audio file in .wav or .aiff format. There is no maximum file size requirement for publication at this stage.
After Submission
Authors will be sent notifications of the receipt of manuscripts and editorial decisions by email. During the review process, authors can check the status of their submitted manuscript via the online manuscript submission and review system . Authors should not disclose the fact that their manuscript has been submitted to anyone, except coauthors and contributors, without permission of the editor.
All submitted manuscripts are reviewed initially by one of the editors. Manuscripts are evaluated according to the following criteria: material is original and timely, writing is clear, study methods are appropriate, data are valid, conclusions are reasonable and supported by the data, information is important, and topic has general interest to readers of this journal. From these basic criteria, the editors assess a paper's eligibility for publication. Manuscripts with insufficient priority for publication are rejected promptly. Other manuscripts are sent to expert consultants for peer review. The journal uses a single-anonymized peer review process: peer reviewer identities are kept confidential (unless reviewers choose to reveal their names in their formal reviews); author identities are made known to reviewers. The existence of a manuscript under review is not revealed to anyone other than peer reviewers and editorial staff. Peer reviewers are required to maintain confidentiality about the manuscripts they review and must not divulge any information about a specific manuscript or its content to any third party without prior permission from the journal editors. Reviewers are instructed to not submit confidential manuscripts, abstracts, or other text into a chatbot, language model, or similar tool. At submission, authors may choose to have manuscripts that are not accepted by the journal referred to one of the JAMA Network specialty journals and/or JAMA Network Open along with reviewers' comments (if available). Information from submitted manuscripts may be systematically collected and analyzed as part of research to improve the quality of the editorial or peer review process. Identifying information remains confidential. Final decisions regarding manuscript publication are made by an editor who does not have any relevant conflicts of interest.
At the time of manuscript submission, authors may preselect the option to have their manuscript and reviewers' comments automatically referred to one of the JAMA Network specialty journals if the manuscript is not accepted by JAMA .

JAMA -EXPRESS
JAMA -EXPRESS provides rapid peer review and publication of major clinical trials and other original research studies that have immediate or public health importance. Authors who wish to have manuscripts considered for JAMA -EXPRESS should send the manuscript file and a request letter to [email protected] or call (312) 464-4444. Authors will be notified promptly whether the manuscript is approved for rapid peer review. Authors of those manuscripts determined not to qualify for rapid review may be invited to submit the manuscript for further consideration under the standard review process.
Authors may appeal decisions. All appeals are reviewed by the editor in chief, on a case-by-case basis, or a designated editor if the editor in chief is recused from the review.
After Revision/Acceptance
All authors are required to complete an Authorship Form and Publishing Agreement. See Authorship Criteria and Contributions .
Accepted manuscripts are edited in accordance with the AMA Manual of Style , 2 and returned to the corresponding author (or her/his designee) for approval. Authors are responsible for all statements made in their work, including changes made during editing and production that are authorized by the corresponding author.
Authors should not disclose the fact that their manuscript has been accepted to anyone, except coauthors and contributors, until it is published without permission of the editor or as described in the guidance on Previous or Planned Meeting Presentaton or Release of Information and Embargo Policy .
If accepted for publication, all articles are published quickly in one of JAMA 's weekly print/online issues; selected articles are published Online First.
After Publication
Postpublication correspondence.
For accepted manuscripts, the corresponding author will be asked to respond to letters to the editor.
Reprints and e-prints may be ordered online when the edited manuscript is sent for approval to the corresponding author.
Requests to publish corrections should be sent to the editorial office. Errors and requests for corrections are reviewed by editors and authors, and, if warranted, a Correction notice summarizing the errors and corrections is published promptly and linked online to the original article, and the original article is corrected online with the date of correction. 15
First and last authors of peer-reviewed articles are eligible to receive CME credit. See CME From the JAMA Network .
About Previous Release of Information, Embargo, and Access
Manuscripts are considered with the understanding that they have not been published previously and are not under consideration by another publication.
Copies of all related or similar manuscripts and reports by the same authors (ie, those containing substantially similar content or using the same, similar, or a subset of data) that have been previously published or posted electronically or are under consideration elsewhere must be provided at the time of manuscript submission. All related previously published articles should be cited as references and described in the submitted manuscript along with explanation of how the submitted manuscript differs from the related previously published article(s).
Manuscripts that have been previously posted on a preprint server may be submitted for consideration for publication. When the manuscript is submitted, authors must provide information about the preprint, including a link to it and a description of whether the submitted manuscript has been revised or differs from the preprint.
See also Previous or Planned Meeting Presentation or Release of Information and Research Article Public Access, Depositing in Repositories, and Discoverability.
Meeting presentation: A complete manuscript submitted to the journal following or prior to presentation at a scientific meeting or publication of preliminary findings elsewhere (ie, as an abstract) is eligible for consideration for publication. Authors considering presenting or planning to present the work at an upcoming scientific meeting should indicate the name and date of the meeting on the manuscript submission form. For accepted papers, the editors may be able to coordinate publication with the meeting presentation. Authors of submitted papers, including those accepted but not yet published, should not disclose the status of such papers during such meeting presentations that occur before the work is published. Authors who present information contained in a manuscript that is under consideration by this journal during scientific or clinical meetings should not distribute complete reports (ie, copies of manuscripts) or full data presented as tables and figures to conference attendees or journalists. Publication of abstracts in print and online conference proceedings, as well as posting of slides or videos from the scientific presentation on the meeting website, is acceptable. However, for manuscripts under consideration by this journal, publication of full reports in meeting proceedings or online, issuing detailed news releases reporting the results of the study that go beyond the meeting abstract, or participation in formal news conferences will ordinarily jeopardize chances for publication of the submitted manuscript in this journal. 5 Media coverage of presentations at scientific meetings will not jeopardize consideration, but direct release of information through press releases or news media briefings may preclude consideration of the manuscript by this journal. 5 Rare instances of papers reporting public health emergencies should be discussed with the editor. Authors submitting manuscripts or letters to the editor regarding adverse drug or medical device reactions, reportable diseases, etc, should also report this information to the relevant government agency.
Authors should not release information about accepted manuscripts via social media until publication.
See also Previous Publication, Related Manuscripts and Reports, and Preprints . For more information, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Authors should not disclose the fact that their manuscript has been accepted to anyone, except coauthors and contributors, without permission of the editor until it is published. All information regarding the content and publication date of accepted manuscripts is strictly confidential. Unauthorized prepublication release of accepted manuscripts and information about planned publication date may result in rescinding the acceptance and rejecting the paper. This policy applies to all categories of articles, including research, review, opinion, correspondence, etc. Information contained in or about accepted articles cannot appear in print, audio, video, or digital form or be released by the news media until the specified embargo release date. 2 , 5 See also Previous or Planned Meeting Presentation or Release of Information .
The journal makes all JAMA research articles free public access 6 months after publication on the journal website.
Authors of research articles may deposit the accepted version (ie, the peer-reviewed manuscript that you submitted on which this decision is based) of the manuscript in a repository of your choice on or after the date of publication provided that it links to the final published version on the journal website. You may not deposit the published article (version of record), which is the final copyedited, formatted, and proofed version published by the journal. The journal will deposit a copy of the published research article into PubMed Central (PMC) at the time of publication, where it will be publicly available 6 months after publication. A few weeks after publication, you may obtain your PMCID on the PMC site at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/pmctopmid/ . These options apply only to research articles. Non-research articles may not be deposited into repositories.
In addition, the journal will add metadata to all articles to ensure web-based search engine discoverability and will provide publicly discoverable information about your article to PubMed/Medline and numerous other bibliographic databases on the day of publication.
Author Responsibilities
Most of the JAMA Network journals' editorial policies for authors are summarized in these instructions. Citations and links to the AMA Manual of Style: A Guide for Authors and Editors 2 and other publications with additional information are also provided.
Each author should have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content. 2 One or more authors should take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, from inception to published article. According to the guidelines of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE), 4 authorship credit should be based on the following 4 criteria:
- substantial contributions to conception or design of the work, or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; and
- drafting of the work or reviewing it critically for important intellectual content; and
- final approval of the version to be published; and
- agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Each author should be accountable for the parts of the work he or she has done. In addition, each author should be able to identify which coauthors are responsible for specific other parts of the work and should have confidence in the integrity of the contributions of any coauthors.
All those designated as authors should meet all 4 criteria for authorship, and all who meet the 4 criteria should be identified as authors. Those who do not meet all 4 criteria should be acknowledged (see Acknowledgment Section ).
All authors (ie, the corresponding author and each coauthor) must read, complete, and submit an electronic Authorship Form with required statements on Authorship Responsibility, Criteria, and Contributions; Confirmation of Reporting Conflicts of Interest and Funding; and Publishing Agreement. 2(pp128-133) In addition, authors are required to identify their specific contributions to the work described in the manuscript. Requests by authors to designate equal contributions or shared authorship positions (eg, co-first authorship) may be considered if justified and within reason. 6 An email with links to the Authorship Form will be sent to authors for completion after manuscripts have been submitted.
For reports of original data, authors' specific contributions will be published in the Acknowledgment section (see Manuscript Preparation and Submission Requirements , Acknowledgment section ). 2 All other persons who have made substantial contributions to the work reported in this manuscript (eg, data collection, analysis, or writing or editing assistance) but who do not fulfill the authorship criteria should be named with their specific contributions and affiliations in an Acknowledgment in the manuscript. Written permission to include the names of individuals in the Acknowledgment section must be obtained.
Nonhuman artificial intelligence, language models, machine learning, or similar technologies do not qualify for authorship. If these models or tools are used to create content or assist with writing or manuscript preparation, authors must take responsibility for the integrity of the content generated by these tools. Authors should report the use of artificial intelligence, language models, machine learning, or similar technologies to create content or assist with writing or editing of manuscripts in the Acknowledgment section or Methods section if this is part of formal research design or methods. See also Use of AI in Publication and Research , Reproduced and Re-created Material , and Image Integrity .
The authors also must certify that the manuscript represents valid work and that neither this manuscript nor one with substantially similar content under their authorship has been published or is being considered for publication elsewhere (see also About Previous Release of Information, Embargo, and Access ). 2 Authors of manuscripts reporting original data or systematic reviews must provide an access to data statement from 1 or 2 named authors, often the corresponding author (see also Data Access, Responsibility, and Analysis ). If requested, authors should be prepared to provide the data and must cooperate fully in obtaining and providing the data on which the manuscript is based for examination by the editors or their assignees.
A single corresponding author (or coauthor designee in the event that the corresponding author is unavailable) will serve on behalf of all coauthors as the primary correspondent with the editorial office during the submission and review process. If the manuscript is accepted, the corresponding author will review an edited manuscript and proof, make decisions regarding release of information in the manuscript to the news media or federal agencies, handle all postpublication communications and inquiries, and will be identified as the corresponding author in the published article.
The corresponding author also is responsible for ensuring that the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript is complete (see Acknowledgment Section ) and that the conflict of interest disclosures reported in the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript are accurate, up-to-date, and consistent with the information provided in each author's potential conflicts of interest section in the Authorship Form (see Conflicts of Interest and Financial Disclosures ).
The corresponding author also must complete the Acknowledgment statement part of the Authorship Form confirming that all persons who have contributed substantially but who are not authors are identified in the Acknowledgment section and that written permission from each person acknowledged has been obtained (see Acknowledgment Section ).
Requests for co-corresponding authors will be considered on a very limited basis if justified, but no more than 2 co-corresponding authors will be permitted. In such cases, a primary corresponding author must be designated as the point of contact responsible for all communication about the manuscript and article, manage the tasks described above, and will be listed first in the corresponding author section. 6 To read more about the role and responsibilities of corresponding authors, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Authors should determine the order of authorship among themselves and should settle any disagreements before submitting their manuscript. Changes in authorship (ie, order, addition, and deletion of authors) should be discussed and approved by all authors. Any requests for such changes in authorship after initial manuscript submission and before publication should be explained in writing to the editor in a letter or email from all authors. 2(pp128-133)
The JAMA Network recognizes that authors may change their names for personal reasons, and the editors respect authors' rights to autonomy and privacy in this regard. Authors who request confidential name changes after publication because of changes in identity, marital status, religion, or other reasons may have their names changed in articles without indication of the reason for the change and without a formal correction notice. If an author prefers this change to be public, a formal Correction notice can be issued, with or without the reason per author preference. The journal will not request the approval of coauthors, but the requesting author may wish to notify coauthors if this change will affect subsequent citations to the article. The requester may be asked to notify the corresponding author about this change to the published article; alternatively, the journal may inform the corresponding author of this change (without explaining the reason for the change). The journal will make this change to the online and PDF versions of the published article and will notify postpublication indexes and databases as a standard process but cannot guarantee when or if the change will be reflected in these indexes and databases.
If authorship is attributed to a group (either solely or in addition to 1 or more individual authors), all members of the group must meet the full criteria and requirements for authorship as described above, and all group member authors must complete Authorship Forms. 6 If all members of a group do not meet all authorship criteria, a group must designate 1 or more individuals as authors or members of a writing group who meet full authorship criteria and requirements and who will take responsibility for the group. 2 , 6 Group names should appear at the end of the byline and should not be interspersed within the list of individually named authors. Group authors may not be included for article types with limited numbers of authors (eg, opinion articles).
For articles with a large number of authors (eg, >50), a long list of authors will not fit in the byline of a print/PDF version of the article. In such cases, a group byline will be recommended with the individual names of each author listed at the end of the article. All author names would still be individually indexed, displayed, and easily searchable in bibliographic records such as PubMed. 6
Nonauthor Collaborators: Other group members who do not meet the criteria for authorship (eg, investigators, advisors, assistants) may be identified. For group author manuscripts, a Nonauthor Collaborator Template (with names, academic degrees, institution, location, role/contribution, and subgroup) must be completed during revision. The template will be available to authors with the request for revision. The collaborators will be published in an online Supplement based on this template and will be deposited to PubMed.
To read more about authorship, click here .
A conflict of interest may exist when an author (or the author's institution or employer) has financial or personal relationships or affiliations that could influence (or bias) the author's decisions, work, or manuscript. All authors are required to report potential conflicts of interest including specific financial interests relevant to the subject of their manuscript in the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript 2 and in the Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest section of the Authorship Form. Note: These forms will be requested after a manuscript has been submitted, but authors should also include conflict of interest disclosures in the Acknowledgment section of the submitted manuscript.
Definitions and Terms of Conflicts of Interest Disclosures:
Authors are expected to provide detailed information about all relevant financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations (other than those affiliations listed in the title page of the manuscript) including, but not limited to, employment, affiliation, funding and grants received or pending, consultancies, honoraria or payment, speakers' bureaus, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, royalties, donation of medical equipment, or patents planned, pending, or issued.
Following the guidelines of the ICMJE, 4 the definitions and terms of such disclosures include
Any potential conflicts of interest "involving the work under consideration for publication" (during the time involving the work, from initial conception and planning to present), Any "relevant financial activities outside the submitted work" (over the 3 years prior to submission), and Any "other relationships or activities that readers could perceive to have influenced, or that give the appearance of potentially influencing" what is written in the submitted work (based on all relationships that were present during the 3 years prior to submission).
Authors without conflicts of interest, including relevant financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations, should indicate such in their disclosures and include a statement of no such interests in the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript. Failure to include this information in the manuscript may delay evaluation and review of the manuscript. Authors should err on the side of full disclosure and should contact the editorial office if they have questions or concerns.
Although many universities and other institutions and organizations have established policies and thresholds for reporting financial interests and other conflicts of interest, the JAMA Network requires complete disclosure of all relevant financial relationships and potential financial conflicts of interest, regardless of amount or value. For example, authors of a manuscript about hypertension should report all financial relationships they have with all manufacturers and owners of products, devices, tests, and services used in the management of hypertension, not only those relationships with entities whose specific products, devices, tests, and services are mentioned in the manuscript. If authors are uncertain about what constitutes a relevant financial interest or relationship, they should contact the editorial office.
For all accepted manuscripts, the corresponding author will have been asked to confirm that each coauthor's disclosures of conflicts of interest and relevant financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations and declarations of no such interests are accurate, up-to-date, and consistent with the disclosures reported in the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript because this information will be published in the Acknowledgment section of the article. Decisions about whether such information provided by authors should be published, and thereby disclosed to readers, are usually straightforward. Although editors are willing to discuss disclosure of specific conflicts of interest with authors, JAMA Network policy is one of complete disclosure of all potential conflicts of interest, including relevant financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations (other than those affiliations listed in the title page of the manuscript). The policy requiring disclosure of conflicts of interest applies for all manuscript submissions, including letters to the editor. If an author's disclosure of potential conflicts of interest is determined to be inaccurate or incomplete after publication, a correction will be published to rectify the original published disclosure statement, and additional action may be taken as necessary.
All authors must also complete the Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest section of the Authorship Form. 7
All financial and material support for the research and the work should be clearly and completely identified in an Acknowledgment section of the manuscript. At the time of submission, information on the funding source (including grant identification) must also be completed via the online manuscript submission and review system. The specific role of the funding organization or sponsor in each of the following should be specified: "design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication." 7 To read more about reporting funding and other support, see the AMA Manual of Style .
For all reports (regardless of funding source) containing original data, at least 1 named author (eg, the principal investigator), and no more than 2 authors, must indicate that she or he "had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis." 7 This exact statement should be included in the Acknowledgment section at the end of the manuscript. Modified statements or generic statements indicating that all authors had such access are not acceptable. In addition, for all reports containing original data, the names and affiliations of all authors (or other individuals) who conducted and are responsible for the data analysis must be indicated in the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript. If the individual who conducted the analysis is not named as an author, a detailed explanation of his/her contributions and reasons for his/her involvement with the data analysis should be included.
For all reports of research, authors are required to provide a Data Sharing Statement to indicate if data will or will not be shared. Specific questions regarding the sharing of data are included in the manuscript submission system. If authors choose to share or not share data, this information will be published in a Data Sharing Statement in an online supplement linked to the published article. Authors will be asked to identify the data, including individual patient data, a data dictionary that defines each field in the data set, and supporting documentation (eg, statistical/analytic code), that will be made available to others; when, where, and how the data will be available (eg, a link to a data repository); types of analyses that are permitted; and if there will be any restrictions on the use of the data. Authors also have the option to explain why data may not be shared. A list of generalist public repositories that authors may consider using is available from the National Library of Medicine .
The Acknowledgment section is the general term for the list of contributions, disclosures, credits, and other information included at the end of the text of a manuscript but before the references. The Acknowledgment section includes authors' contributions; information on author access to data; disclosure of potential conflicts of interest, including financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations; sources of funding and support; an explanation of the role of funder(s)/sponsor(s); names, degrees, and affiliations of participants in a large study or other group (ie, collaborators); any important disclaimers; information on previous presentation of the information reported in the manuscript; and the contributions, names, degrees, affiliations, and indication if compensation has been received for all persons who have made substantial contributions to the work but who are not authors. 2
All other persons who have made substantial contributions to the work reported in the manuscript (eg, data collection, analysis, and writing or editing assistance) but who do not fulfill the authorship criteria should be named with their specific contributions in an Acknowledgment in the manuscript.
Authors must obtain written permission to include the names of all individuals included in the Acknowledgment section, and the corresponding author must confirm that such permission has been obtained in the Authorship Form.
Authors should report the use of artificial intelligence, language models, machine learning, or similar technologies to create content or assist with writing or editing of manuscripts in the Acknowledgment section or the Methods section if this is part of formal research design or methods. This should include a description of the content that was created or edited and the name of the language model or tool, version and extension numbers, manufacturer, date(s) of use, and confirmation that the authors take responsibility for the integrity of the content generated. (Note: this does not include basic tools for checking grammar, spelling, references, etc.) See also Use of AI in Publication and Research and Statistical Analysis Subsection .
Requirements for Reporting
Authors of research articles should follow the EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines . See specific Study Types for detailed guidance on reporting.
Causal language (including use of terms such as effect and efficacy) should be used only for randomized clinical trials. For all other study designs (including meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials), methods and results should be described in terms of association or correlation and should avoid cause-and-effect wording. To read more about use of causal language, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Research reports should be timely and current and should be based on data collected as recently as possible. Manuscripts based on data from randomized clinical trials should be reported as soon as possible after the trial has ended, ideally within 1 year after follow-up has been completed.
For cohort studies, the date of final follow-up should be no more than 5 years before manuscript submission. Likewise, data used in case-control or cross-sectional studies should have been collected as recently as possible, but no more than 5 years before manuscript submission. Manuscripts in which the most recent data have been collected more than 5 years ago ordinarily will receive lower priority for publication; thus, authors of such manuscripts should provide a detailed explanation of the relevance of the information in light of current knowledge and medical practice as well as the most recent date(s) of analysis of the study.
General Considerations
Authors are encouraged to consult "Reporting Statistical Information in Medical Journal Articles." 1 In the Methods section, describe statistical methods with enough detail to enable a knowledgeable reader with access to the original data to reproduce the reported results. Such description should include appropriate references to the original literature, particularly for uncommon statistical methods. For more advanced or novel methods, provide a brief explanation of the methods and appropriate use in the text and consider providing a detailed description in an online supplement.
In the reporting of results, when possible, quantify findings and present them with appropriate indicators of measurement error or uncertainty, such as confidence intervals (see Reporting Standards and Data Presentation ). Avoid relying solely on statistical hypothesis testing, such as the use of P values, which fails to convey important quantitative information. For observational studies, provide the numbers of observations. For randomized trials, provide the numbers randomized. Report losses to observation or follow up (see Missing Data ). For multivariable models, report all variables included in models, and report model diagnostics and overall fit of the model when available (see Statistical Procedures ).
Define statistical terms, abbreviations, and symbols, if included. Avoid nontechnical uses of technical terms in statistics, such as correlation, normal, predictor, random, sample, significant, trend. Do not use inappropriate hedge terms such as marginal significance or trend toward significance for results that are not statistically significant. Causal language (including use of terms such as effect and efficacy) should be used only for randomized clinical trials. For all other study designs (including meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials), methods and results should be described in terms of association or correlation and should avoid cause-and-effect wording.
Sample Size Calculations
For randomized trials, a statement of the power or sample size calculation is required (see the EQUATOR Network CONSORT Guidelines ). For observational studies that use an established population, a power calculation is not generally required when the sample size is fixed. However, if the sample size was determined by the researchers, through any type of sampling or matching, then there should be some justification for the number sampled. In any case, describe power and sample size calculations at the beginning of the Statistical Methods section, following the general description of the study population.
Descriptive Statistics
It is generally not necessary to provide a detailed description of the methods used to generate summary statistics, but the tests should be briefly noted in the Methods section (eg, ANOVA or Fisher exact test).
Statistical Procedures
Identify regression models with more than 1 independent variable as multivariable and regression models with more than 1 dependent variable as multivariate. Report all variables included in models, as well as any mathematical transformations of those variables. Provide the scientific rationale (clinical, statistical, or otherwise) for including variables in regression models.
For regression models fit to dependent data (eg, clustered or longitudinal data), the models should account for the correlations that arise from clustering and/or repeated measures. Failure to account for such correlation will result in incorrect estimates of uncertainty (eg, confidence intervals). Describe how the model accounted for correlation. For example, for an analysis based on generalized estimating equations, identify the assumed correlation structure and whether robust (or, sandwich) variance estimators were used. Or, for an analysis based on mixed-effects models, identify the assumed structure for the random effects, such as the level of random intercepts and whether any random slopes were included. Fixed-effects estimation should be described as conditional likelihood. Avoid the term fixed effects for describing covariates.
Missing Data
Report losses to observation, such as dropouts from a clinical trial or those lost to follow-up or unavailable in an observational study. If some participants are excluded from analyses because of missing or incomplete data, provide a supplementary table that compares the observed characteristics between participants with complete and incomplete data. Consider multiple imputation methods to impute missing data and include an assessment of whether data were missing at random. Approaches based on "last observation carried forward" should not be used.
Primary Outcomes, Multiple Comparisons, and Post Hoc Comparisons
Both randomized and observational studies should identify the primary outcome(s) before the study began, as well as any prespecified secondary, subgroup, and/or sensitivity analyses. Comparisons arrived at during the course of the analysis or after the study was completed should be identified as post hoc. For analyses of more than 1 primary outcome, corrections for multiple testing should generally be used. For secondary outcomes, address multiple comparisons or consider such analyses as exploratory and interpret them as hypothesis-generating. The reporting of all outcomes should match that included in study protocols. For randomized clinical trials, protocols with complete statistical analysis plans should be cited in the Methods section and submitted as online supplementary content. Randomized clinical trials should be primarily analyzed according to the intention-to-treat approach. Deviations from strict intention-to-treat analysis should be described as "modified intention-to-treat," with the modifications clearly described.
Statistical Analysis Subsection
At the end of the Methods section, briefly describe the statistical tests used for the analysis. State any a priori levels of significance and whether hypothesis tests were 1- or 2-sided. Also include the statistical software used to perform the analysis, including the version and manufacturer, along with any extension packages (eg, the svy suite of commands in Stata or the survival package in R). Do not describe software commands (eg, SAS proc mixed was used to fit a linear mixed-effects model). If analysis code is included, it should be placed in the online supplementary content.
Reporting Standards and Data Presentation
Analyses should follow EQUATOR Reporting Guidelines and be consistent with the protocol and statistical analysis plan, or described as post hoc.
When possible, present numerical results (eg, absolute numbers and/or rates) with appropriate indicators of uncertainty, such as confidence intervals. Include absolute numbers and/or rates with any ratio measures and avoid redundant reporting of relative data (eg, % increase or decrease). Use means and standard deviations (SDs) for normally distributed data and medians and ranges or interquartile ranges (IQRs) for data that are not normally distributed. Avoid solely reporting the results of statistical hypothesis testing, such as P values, which fail to convey important quantitative information. For most studies, P values should follow the reporting of comparisons of absolute numbers or rates and measures of uncertainty (eg, 0.8%, 95% CI −0.2% to 1.8%; P = .13). P values should never be presented alone without the data that are being compared. If P values are reported, follow standard conventions for decimal places: for P values less than .001, report as " P <.001"; for P values between .001 and .01, report the value to the nearest thousandth; for P values greater than or equal to .01, report the value to the nearest hundredth; and for P values greater than .99, report as " P >.99." For studies with exponentially small P values (eg, genetic association studies), P values may be reported with exponents (eg, P = 1×10 −5 ). In general, there is no need to present the values of test statistics (eg, F statistics or χ² results) and degrees of freedom when reporting results.
For secondary and subgroup analyses, there should be a description of how the potential for type I error due to multiple comparisons was handled, for example, by adjustment of the significance threshold. In the absence of some approach, these analyses should generally be described and interpreted as exploratory, as should all post hoc analyses.
For randomized trials using parallel-group design, there is no validity in conducting hypothesis tests regarding the distribution of baseline covariates between groups; by definition, these differences are due to chance. Because of this, tables of baseline participant characteristics should not include P values or statements of statistical comparisons among randomized groups. Instead, report clinically meaningful imbalances between groups, along with potential adjustments for those imbalances in multivariable models. To read more about statistical tests and data presentation, see the AMA Manual of Style .
Researchers are encouraged to report studies that include diverse and representative participants and to indicate participant inclusion and exclusion criteria and how the findings generalize to the population(s) that are the focus of or are compatible with the research question. Aggregate, deidentified demographic information (eg, age, sex, race and ethnicity, and socioeconomic indicators) should be reported for all research reports along all prespecified outcomes. Demographic variables collected for a specific study should be reported in the Methods section. Demographic information assessed should be reported in the Results section, either in the main article or in an online supplement or both. If any demographic characteristics that were collected are not reported, the reason should be stated. Summary demographic information (eg, baseline characteristics of study participants) should be reported in the first line of the Results section of Abstracts.
Reporting Age
Study inclusion or exclusion criteria by age or age group should be defined in the Methods section. Stratification by age groups should be based on relevance to disease, condition, or population (eg, <5 or >65 years). The ages for study participants should be reported in aggregate (ie, mean and SD or median and IQR or range) in the Results section.
Reporting Sex and Gender
The term sex should be used when reporting biological factors and gender should be used when reporting gender identity or psychosocial/cultural factors. The methods used to obtain information on sex, gender, or both (eg, self-reported, investigator observed or classified, or laboratory test) should be explained in the Methods section. 12 The distribution of study participants or samples should be reported in the Results section, including for studies of humans, tissues, cells, or animals. All participants should be reported, not just the category that represents the majority of the sample. Studies that address pregnancy should follow these recommendations, and if the gender identity of participants was not assessed, use the terms pregnant participants , pregnant individuals , pregnant patients , etc, as appropriate.
In research articles, follow recommendations to include all representative populations in study design, data analyses, results, and interpretation of findings. Report sex or gender of study participants, including how sex or gender was defined and assessed. Whenever possible, all main outcomes should be reported by sex or gender (or both if appropriate). In nonresearch reports, choose gender-neutral and sex-neutral terms that avoid bias, suit the material under discussion, and are not confusing to readers. See the Sex and Gender Equity in Research (SAGER) guidelines for additional guidance.
Reporting Race and Ethnicity
The Methods section should include an explanation of who identified participant race and ethnicity and the source of the classifications used (eg, self-report or selection, investigator observed, database, electronic health record, survey instrument).
If race and ethnicity categories were collected for a study, the reasons that these were assessed also should be described in the Methods section. If collection of data on race and ethnicity was required by the funding agency, that should be noted.
Specific racial and ethnic categories are preferred over collective terms, when possible. Authors should report the specific categories used in their studies and recognize that these categories will differ based on the databases or surveys used, the requirements of funders, and the geographic location of data collection or study participants. Categories included in groups labeled as "other" should be defined.
Categories should be listed in alphabetical order in text and tables.
Race and ethnicity of the study population should be reported in the Results section.
For additional information, see " Updated Guidance on Reporting Race and Ethnicity in Medical and Science Journals " and the Summary Guide for Preferred Terms When Reporting Race and Ethnicity .
For all manuscripts reporting data from studies involving human participants or animals, formal review and approval, or formal review and waiver, by an appropriate institutional review board or ethics committee is required and should be described in the Methods section. 2(p226) For those investigators who do not have formal ethics review committees, the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki should be followed. 13 For investigations of humans, state in the Methods section the manner in which informed consent was obtained from the study participants (ie, oral or written) and whether participants received a stipend. Authors of research studies involving humans should not make independent determinations of exemption or exclusion of IRB or ethical review; they should cite the institutional or regulatory policy for that determination and indicate if the data are deidentified and publicly available or protected by prior consent or privacy safeguards. Editors may request that authors provide documentation of the formal review and recommendation from the institutional review board or ethics committee responsible for oversight of the study.
A signed statement of informed consent to publish patient descriptions, photographs, video, and pedigrees should be obtained from all persons (parents or legal guardians for minors) who can be identified (including by the patients themselves) i/n such written descriptions, photographs, or pedigrees and should be submitted with the manuscript and indicated in the Acknowledgment section of the manuscript. Such persons should be offered the opportunity to see the manuscript before its submission. 2(pp229-232)
Omitting data or making data less specific to deidentify patients is acceptable, but changing any such data is not acceptable. Only those details essential for understanding and interpreting a specific case report or case series should be provided. Although the degree of specificity needed will depend on the context of what is being reported, specific ages, race/ethnicity, and other sociodemographic details should be presented only if clinically or scientifically relevant and important. 2 Cropping of photographs to remove identifiable personal features that are not essential to the clinical message may be permitted as long as the photographs are not otherwise altered. Please do not submit masked photographs of patients. Patients' initials or other personal identifiers must not appear in an image.
Patient Permission Form:
The Patient Permission form for publication of identifying material is available here . Translated versions in Arabic, Chinese, French, German, Hindi, Italian, Japanese, Portuguese, and Spanish are available on request.
AI Used in Manuscript Preparation
When traditional and generative AI technologies are used to create, review, revise, or edit any of the content in a manuscript, authors should report in the Acknowledgment section the following:
- Name of the AI software platform, program, or tool
- Version and extension numbers
- Manufacturer
- Date(s) of use
- A brief description of how the AI was used and on what portions of the manuscript or content
- Confirmation that the author(s) take responsibility for the integrity of the content generated
Note this guidance does not apply to basic tools for checking grammar, spelling, references, and similar.
AI Used in Research
When AI (eg, large language model [LLM] or natural language processing [NLP], supervised or unsupervised machine learning [ML] for predictive/prescriptive or clustering tasks, chatbots, or similar other technologies) is used as part of a scientific study, authors should:
- Follow relevant reporting guidelines for specific study designs when they exist and report each recommended guideline element with sufficient detail to enable reproducibility.
- Avoid inclusion of identifiable patient information in text, tables, and figures.
- Be aware of copyright and intellectual property concerns.
- If content protected by copyright was entered into the AI model by authors, include a copy of the permission or license from the copyright owner and describe this permission/license in the Methods section.
- If content (text, images, multimedia) generated by AI is included in a submitted manuscript or supplemental material, indicate rights or permissions to publish that content as determined by the AI service or owner in the Methods section or in the legend(s) of any AI-generated figures or multimedia.
Also address the following:
Methods Section
- Include the study design and, if a relevant reporting guideline exists, indicate how it was followed, with sufficient detail to enable reproducibility.
- Describe how AI was used for specific aspects of the study (eg, to generate or refine study hypotheses, assist in the generation of a list of adjustment variables, create graphs to show visual relationships).
- For studies using LLMs, provide the name of the platform or program, tool, version, and manufacturer; specify dates and prompt(s) used and their sequence and any revisions to prompts in response to initial outputs.
- For studies reporting ML and algorithm development, include details about data sets used for development, training, and validation. Clearly state if algorithms were trained and tested only on previously collected or existing data sets or if the study includes prospective deployment. Include the ML model and describe the variables and outcome(s) and selection of the fine-tuning parameters. Describe any assumptions involved (eg, log linearity, proportionality) and how these assumptions were tested.
- Indicate the metric used to evaluate the performance of the algorithms, including bias, discrimination, calibration, reclassification, and others as appropriate.
- Indicate the methods used to address missing data.
- Indicate institutional review board/ethics review, approval, waiver, or exemption.
- Describe methods or analyses included to address and manage AI-related methodologic bias and inaccuracy of AI-generated content.
- Indicate, when appropriate, if sensitivity analyses were performed to explore the performance of the AI model in vulnerable or underrepresented subgroups.
- Provide a data sharing statement, including if code will be shared.
Results Section
- When reporting comparisons, provide performance assessments (eg, against standard of care), include effect sizes and measures of uncertainty (eg, 95% CIs) and other measurements such as likelihood ratios, and include information about performance errors, inaccurate or missing data, and sufficient detail for others to reproduce the findings.
- Report the results of analyses to address methodologic bias and population representation.
- If examples of generated text or content are included in tables or figures, be sure to indicate the source and licensing information, as noted above.
Discussion Section
- Discuss the potential for AI-related bias and what was done to identify and mitigate such bias.
- Discuss the potential for inaccuracy of AI-generated content and what was done to identify and manage this.
- Discuss generalizability of findings across populations and results of analyses performed to explore the performance of the AI model in vulnerable or underrepresented subgroups.
A signed statement of permission should be included from each individual identified as a source of information in a personal communication or as a source for unpublished data, and the date of communication and whether the communication was written or oral should be specified. 2(p199) Personal communications should not be included in the list of references but added to the text parenthetically.
Authors and reviewers are expected to notify editors if a manuscript could be considered to report dual use research of concern (ie, research that could be misused by others to pose a threat to public health and safety, agriculture, plants, animals, the environment, or material). 14 The editor in chief will evaluate manuscripts that report potential dual use research of concern and, if necessary, consult additional reviewers.
Journal Policies
Final decisions regarding manuscript publication are made by the editor in chief or a designated editor who does not have any relevant conflicts of interest. The journal has a formal recusal process in place to help manage potential conflicts of interest of editors. In the event that an editor has a conflict of interest with a submitted manuscript or with the authors, the manuscript, review, and editorial decisions are managed by another designated editor without a conflict of interest related to the manuscript.
All authors are required to complete and submit a Publishing Agreement that is part of the journal's electronic Authorship Form. In this agreement, authors will transfer copyright or a publication license; or indicate that they are employed by a federal government; or indicate that they are an employee of an institution that considers the work in the manuscript a work for hire, in which case an authorized representative of that institution will assign copyright or a publication license on the author's behalf.
Published articles become the permanent property of the American Medical Association (AMA) and may not be published elsewhere without written permission. Unauthorized use of the journal's name, logo, or any content for commercial purposes or to promote commercial goods and services (in any format, including print, video, audio, and digital) is not permitted by the JAMA Network or the AMA.
1. Cummings P, Rivara FP. Reporting statistical information in medical journal articles. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med . 2003;157(4):321-324. doi:10.1001/archpedi.157.4.321
2. Iverson C, Christiansen S, Flanagin A, et al. AMA Manual of Style: A Guide for Authors and Editors . 11th ed. Oxford University Press; 2020. http://www.amamanualofstyle.com
3. Golub RM. Correspondence course: tips for getting a letter published in JAMA . JAMA . 2008;300(1):98-99. doi:10.1001/jama.300.1.98
4. International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Recommendations for the conduct, reporting, editing, and publication of scholarly work in medical journals. Updated May 2023. Accessed May 18, 2023. http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/
5. Fontanarosa PB, Flanagin A, DeAngelis CD. Update on JAMA 's policy on release of information to the public. JAMA . 2008;300(13):1585-1587. doi:10.1001/jama.300.13.1585
6. Fontanarosa P, Bauchner H, Flanagin A. Authorship and team science. JAMA . 2017;318(24):2433-2437. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.19341
7. Fontanarosa PB, Flanagin A, DeAngelis CD. Reporting conflicts of interest, financial aspects of research, and role of sponsors in funded studies. JAMA . 2005;294(1):110-111. doi:10.1001/jama.294.1.110
8. DeAngelis CD, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, et al; International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Clinical trial registration: a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. JAMA . 2004;292(11):1363-1364. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.6933
9. DeAngelis CD, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, et al; International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Is this clinical trial fully registered? a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. JAMA . 2005;293(23):2927-2929. doi:10.1001/jama.293.23.jed50037
10. The CONSORT Group. The CONSORT statement. Updated 2014. Accessed September 23, 2016. http://www.consort-statement.org/consort-2010
11. American Association for Public Opinion Research. Best practices for survey research. Accessed March 23, 2023. https://aapor.org/standards-and-ethics/best-practices/
12. Clayton JA, Tannenbaum C. Reporting sex, gender, or both in clinical research? JAMA . 2016;316(18):1863-1864. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.16405
13. World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA . 2013;310(20):2191-2194. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.281053
14. Journal Editors and Authors Group. Statement on scientific publication and security. Science . 2003;299(5610):1149. doi:10.1126/science.299.5610.1149 . Published correction appears in Science . 2003;299(5614):1845.
15. Christiansen S, Flanagin A. Correcting the medical literature: "to err is human, to correct divine." JAMA . 2017;318(9):804-805. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.11833
Last Updated: August 14, 2024
Quick Links
- Why Publish in JAMA
- Submit and Track Your Manuscript
- Author Reprints
- Permissions Requests
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
7 Essential Steps for Changing Author Affiliation in Research Paper

As researchers traverse their academic journey, their affiliations may undergo changes due to new opportunities, collaborations, or career advancements. While the process of publishing research papers often involves meticulous attention to detail, unforeseen circumstances can occasionally lead to inaccuracies in affiliations associated with a published paper.
As a researcher, you might have encountered situations where you needed to update your affiliation on an already published research paper. Whether it’s joining a new institution, relocating to a different country, or transitioning to a different research group, it’s essential to ensure that your affiliations accurately reflect your current standing in the academic community. In this blog post, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide on how to navigate the process of changing affiliations in already published research papers.
Emphasizing the importance of adhering to publication policies and maintaining accuracy in scientific literature, this guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of correcting affiliations. We’ll explore how to initiate the correction process, gather the necessary documentation, and interact with journal publishers in a professional manner. Furthermore, we’ll touch upon considerations for more substantial changes and address the significance of updating personal profiles and notifying indexing services.
By sharing insights and best practices, we hope to empower researchers to navigate the affiliation change process smoothly and responsibly. Ultimately, this blog post aims to contribute to the integrity and reliability of scientific literature, ensuring that affiliations accurately represent the journeys and contributions of researchers in the ever-evolving realm of academia.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of updating affiliations in published research papers, and equip ourselves with the knowledge to make necessary corrections with confidence and efficiency.
Introduction
Importance of understanding publication guidelines:, tips on where to find publication guidelines:, types of documentation for affiliation change:, advice on contacting the journal or publisher:, process of submitting a correction or erratum:.
- Journal's Role in Reviewing the Correction or Erratum:
Emphasizing the Need for Accuracy and Validity:
Importance of notifying indexing services:, informing indexing services:, advice on updating personal profiles:, request letter for affiliation change in published paper.
Research papers are the currency of knowledge dissemination, and the affiliations listed on these papers carry significant weight. Affiliations serve as a vital identifier, linking researchers to their respective institutions or organizations, and they play a crucial role in establishing credibility, recognizing contributions, and fostering collaborations within the scientific community.
When a research paper is published, the affiliations of the authors are essentially imprinted in time, forever associated with the findings and insights presented in the work. However, the journey of a researcher is dynamic, and circumstances can change over time. Researchers may find themselves faced with situations where their affiliations need to be updated in already published papers. These situations can arise due to a variety of reasons, such as career advancements, relocation to a new institution, or joining a collaborative project with colleagues from different organizations.
Imagine a scenario where Dr. Smith, an esteemed biologist, publishes a groundbreaking study on genetic mutations in cancer cells. The paper, which carries her former institution’s affiliation, receives widespread recognition and becomes a cornerstone in cancer research. However, a year after the publication, Dr. Smith accepts an enticing research opportunity at a leading medical centre. Now, with her scientific journey taking her to a new institution, she realizes the need to update her affiliation on the already published paper, ensuring that her latest work reflects her current professional standing.
In such cases, ensuring accurate and up-to-date affiliations is not only a matter of personal career progression but also a matter of scientific integrity. It’s crucial to maintain an accurate historical record of affiliations, as these affiliations provide valuable insights into the collaborative networks and institutional contributions that shaped the research landscape.
In this blog post, we aim to shed light on the significance of affiliations in research papers and why researchers may need to modify them post-publication. We recognize the challenges researchers might face when attempting to make such changes and the potential impact on their academic standing and future collaborations. To empower researchers in navigating this process, we will provide a step-by-step guide, offering practical advice on how to initiate and implement affiliation changes in published papers.
Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or a budding scholar, understanding the process of updating affiliations is essential for maintaining the accuracy and credibility of your scientific contributions. So, let’s embark on this informative journey and equip ourselves with the knowledge and tools to responsibly manage affiliation changes in the dynamic world of academic research.
I have written articles on the possible corrections an author may want to do to a research paper that is already published. Please visit the articles listed below for further details.
- “ 5 Proven Steps to Change Author Email Id in a Published Research Paper”
- “ How to Change Author Name on a Previously Published Research Paper? “
- “ 4 Easy Steps to Withdraw Author Name from a Research Paper “
How can I change my affiliation in a Published Research Paper?
Step 1: check publication policy.
Before embarking on the process of changing affiliations in an already published research paper, it is vital to familiarize yourself with the publication’s guidelines and policies regarding corrections and updates. Each journal or publication may have specific procedures and requirements for making changes to author affiliations, and understanding these guidelines is crucial to ensure a smooth and successful process.
Journal publications uphold rigorous standards of accuracy and integrity to maintain the credibility of scientific literature. Affiliation details play a significant role in establishing the author’s credibility, expertise, and institutional association with the research presented in the paper. Any changes to affiliations should be done in a manner that preserves the historical record of the paper while reflecting the most current and accurate information.
Let’s consider an example where Dr. Johnson, a researcher in the field of environmental science, published a paper on climate change with her previous institution’s affiliation. Due to her recent appointment as a faculty member at a renowned university, Dr. Johnson now wishes to update the affiliation on the published paper to reflect her current position. However, she is unsure about the correct procedure to follow.
- Journal Website : The publication’s website often contains a dedicated section titled “Instructions for Authors” or “Author Guidelines.” This section outlines the journal’s policies, including instructions on how to correct or update affiliations post-publication.
- Author’s Dashboard : If the paper was submitted through an online manuscript submission system, the author’s dashboard may provide information on how to request affiliation changes.
- Contact the Editorial Office : If the journal’s guidelines are not easily accessible, contacting the editorial office via email or phone is a reliable way to obtain the necessary information. Editorial staff members are well-versed in the publication’s policies and can provide guidance on making affiliation changes.
- Online Resources : Some journals have FAQs or online resources addressing common author queries, including how to correct affiliations. Check the journal’s website or relevant forums for any such resources.
- Publication Agreement : Revisit the publication agreement or copyright transfer form you signed during the submission process. It may contain provisions related to post-publication changes.
Example (Continued):
After some research, Dr. Johnson visits the journal’s website and locates the “Instructions for Authors” page. She discovers a subsection specifically addressing corrections and updates to published papers. Following the provided instructions, she prepares to contact the editorial office to initiate the process of changing her affiliation.
By understanding the publication’s guidelines and following the correct procedure, researchers like Dr. Johnson can navigate the affiliation change process with confidence, ensuring that their contributions are accurately represented in the scientific literature. Remember, each journal may have its own unique guidelines, so it’s essential to be diligent in locating and adhering to the specific instructions for the paper in question.
Step 2: Gather Documentation
Once you have familiarized yourself with the publication’s guidelines and determined the appropriate procedure for changing affiliations, the next crucial step is to gather the necessary documentation to support the affiliation change. Providing proper documentation is essential to validate the updates and ensure the accuracy and credibility of the revised affiliation.
- Official Letters from the New Institution : A formal letter from the new institution confirming your affiliation with them is one of the primary and most important documents. The letter should be on the institution’s official letterhead and signed by an authorized representative, such as the department head, dean, or human resources officer. The letter should include your name, the effective date of the affiliation change, your official title or position at the new institution, and any other relevant details.
Let’s consider Dr. Rodriguez, a postdoctoral researcher in the field of neuroscience, who recently accepted a position at a prestigious research institute. She now needs to update her affiliation on a published paper that was submitted during her previous postdoctoral position. To support the affiliation change, Dr. Rodriguez obtains an official letter from the research institute confirming her employment and new affiliation. The letter contains all the necessary details, including the effective date of the change.
- Employment Contract or Offer Letter : If your affiliation change is due to a new job or employment opportunity, providing a copy of your employment contract or offer letter can be valuable documentation. This document further substantiates the official nature of your affiliation with the new institution and reinforces the validity of the update.
- Acceptance Letters or Invitations to Collaborate : In cases where the affiliation change is the result of a collaboration with researchers from a different institution, you can include acceptance letters or invitations to collaborate as additional supporting documentation. These letters should clearly state the nature of the collaboration and your role in the project.
- Publication Agreement : Including a copy of the publication agreement or copyright transfer form you signed during the initial submission can serve as proof that you are an author associated with the paper.
- CV or Resume : While not a formal document for the affiliation change process, providing an updated CV or resume that includes your new affiliation can be helpful for the editorial office to cross-check and verify the change.
Having received the official letter from the prestigious research institute, Dr. Rodriguez is now ready to initiate the affiliation change process. She gathers all the relevant documentation, including the official letter, her new employment contract, and a copy of the publication agreement signed during the initial submission.
By compiling the necessary documentation, researchers like Dr. Rodriguez ensure that their affiliation change request is well-substantiated and meets the publication’s requirements for validation. Proper documentation adds credibility to the affiliation change, giving the journal’s editorial office confidence in implementing the updates accurately. Remember to provide clear and legible copies of the documents to avoid any delays or complications in the process.
Step 3: Contact the Journal or Publisher
After gathering the necessary documentation to support the affiliation change, the next step is to contact the journal or publisher to initiate the process formally. Professional and courteous communication is essential when reaching out to the editorial office to ensure smooth and efficient handling of your request.
- Locating Contact Information : Start by identifying the appropriate contact information for the journal or publisher. Most reputable journals will have a dedicated editorial office or a contact email specifically for author inquiries or corrections. You can typically find this information on the journal’s website, in the published paper, or in any communications you may have received from the journal during the review process.
- Compose a Clear and Concise Email : When drafting your email, be clear and concise in stating the purpose of your inquiry. Begin by mentioning the title of the published paper, the names of all authors, and the DOI (Digital Object Identifier) or any other identifying information of the paper.
Subject: Request for Affiliation Change – Paper Title: “Advancements in Neural Network Research”
Dear [Journal/Publisher Name],
I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to request a correction to the affiliation associated with the published paper titled “Advancements in Neural Network Research,” authored by [Author Names]. The DOI for the paper is [DOI number].
- Explain the Reason for the Affiliation Change : Briefly explain the reason for the affiliation change and attach the relevant supporting documentation. State the effective date of the affiliation change and provide a clear statement of the updated affiliation details.
As of [Effective Date], I have joined [New Institution Name] as [New Position/Title]. I kindly request to update my affiliation on the published paper to reflect this change accurately. Please find attached the official letter from [New Institution Name] confirming my affiliation with them.
- Express Gratitude and Professionalism : Show appreciation for the journal’s consideration of your request and maintain a professional tone throughout the email.
I understand that the editorial process involves careful attention to detail, and I genuinely appreciate your assistance in making this important correction. Should you require any additional information or have any questions, please do not hesitate to reach out to me.
Thank you for your time and attention to this matter.
Sincerely, [Your Name] [Your Current Affiliation]
- Attach Relevant Documents : Attach the supporting documentation, such as the official letter from the new institution, your updated CV, or any other documents requested by the journal’s guidelines.
Dr. Rodriguez drafts a professional email following the guidelines outlined above. She attaches the official letter from the prestigious research institute and includes her updated CV for reference. After thoroughly reviewing the email for clarity and accuracy, she sends it to the contact email provided by the journal.
By communicating professionally and providing all the necessary information, researchers like Dr. Rodriguez can ensure that their affiliation change request is handled efficiently by the journal’s editorial office. Remember to be patient during this process, as it may take some time for the journal to review and process the request, especially if there are other pending corrections or updates.
Step 4: Submit a Correction or Erratum
Once the journal or publisher has acknowledged your request to change the affiliation on the published paper and provided instructions for correction, it’s time to prepare and submit a formal correction or erratum. A correction is issued to rectify errors or inaccuracies in the published paper, while an erratum is used to address mistakes made by the journal itself.
- Identify the Corrected Information : Clearly state the specific changes that need to be made to the affiliations. Include the updated affiliation details, including the new institution’s name, department, address, and any additional information required by the journal’s guidelines.
The corrected affiliation for Dr. Johnson is as follows: Department of Environmental Science, Prestigious Research Institute, City, Country.
- Title the Correction or Erratum : Use a descriptive title that indicates that the document is a correction or erratum for the published paper. Include the paper’s title and any relevant identifying information, such as the DOI or publication date.
Correction to: “Insights into Climate Change Impact on Biodiversity” – DOI: [DOI number]
- Explain the Reason for the Correction or Erratum : Provide a concise explanation of the reason for the change in affiliations. Mention that the original publication had an outdated affiliation and that this correction aims to update and accurately reflect the author’s current institutional affiliation.
We are issuing this correction to update the author’s affiliation on the published paper to reflect her current position at the Prestigious Research Institute. The previous affiliation listed was based on her previous postdoctoral position.
- Reference the Original Paper : Include the full citation or reference to the original published paper that requires the correction or erratum. This will help readers and indexers connect the corrected version to the original work.
Original Paper: [Author Names]. (Year). “Insights into Climate Change Impact on Biodiversity.” Journal of Environmental Science, Volume(X), Page Range. DOI: [DOI number]
- Attach Supporting Documentation : Include the relevant supporting documentation that validates the affiliation change. Attach the official letter from the new institution or any other documents required by the journal’s guidelines.
Following the journal’s instructions, Dr. Johnson prepares the correction document. She includes the updated affiliation information, the title indicating the document as a correction, and a concise explanation of the reason for the change. Dr. Johnson references the original paper with its full citation and attaches the official letter from the prestigious research institute.
- Submit the Correction or Erratum : Follow the journal’s specific instructions for submission. Some journals may have a dedicated online platform for corrections or errata, while others may require submission via email.
Dr. Johnson submits the correction document, along with the required attachments, through the journal’s online submission system as per their guidelines.
By submitting a well-organized and clear correction or erratum document, researchers like Dr. Johnson ensure that the journal’s readership and indexing services have access to the accurate and updated affiliation information. This process upholds the integrity of the published scientific literature and ensures that researchers’ contributions are appropriately recognized with their current institutional affiliations.
Step 5: Review and Approval
After submitting the correction or erratum to the journal, the document undergoes a review process to ensure its accuracy and validity. The journal’s role in this step is essential as they act as gatekeepers of scientific integrity, maintaining the credibility of the published literature.
Journal’s Role in Reviewing the Correction or Erratum:
- Verification of Information : The journal’s editorial team carefully reviews the submitted correction or erratum to verify the accuracy of the requested changes. They cross-reference the provided documentation with the original publication and ensure that the updated affiliation information aligns with the supporting evidence.
In Dr. Johnson’s case, the journal’s editorial team compares the correction document with the original paper titled “Insights into Climate Change Impact on Biodiversity” to validate the affiliation change from her previous institution to the prestigious research institute.
- Adherence to Publication Policies : The journal’s editorial team ensures that the correction or erratum complies with the publication’s policies and guidelines. They confirm that the document follows the correct formatting, includes the necessary information, and adheres to ethical standards.
The journal confirms that Dr. Johnson’s correction document includes all the required elements, such as the corrected affiliation, a clear explanation of the change, and a reference to the original paper. They also verify that the supporting documentation provided by Dr. Johnson meets the journal’s requirements.
- Communication with the Author : If any discrepancies or questions arise during the review process, the journal’s editorial team may communicate with the author to seek clarification or additional information. Open communication helps ensure the accuracy and completeness of the correction or erratum.
The journal contacts Dr. Johnson to inquire about a minor formatting issue in the correction document. Dr. Johnson promptly addresses the matter, providing the necessary adjustments.
- Approval and Publication : Once the review process is complete, and the correction or erratum is deemed accurate and valid, the journal approves the document for publication. The updated affiliation is then published in a subsequent issue, either as a standalone correction or as part of an erratum section.
After conducting a thorough review and confirming the validity of Dr. Johnson’s correction document, the journal’s editorial team approves it for publication. The corrected affiliation of Dr. Johnson is scheduled to be published in the upcoming issue of the journal.
It is crucial to underscore that accuracy and validity are paramount when making corrections or issuing errata. The journal’s role in reviewing and approving such changes ensures that the scientific record remains reliable and up-to-date. By maintaining strict quality control measures, journals safeguard against potential inaccuracies and contribute to the integrity of the research community.
As researchers, authors, and readers, we share the collective responsibility to uphold the accuracy of published work. Collaboration between authors and journal teams in the correction process reinforces the commitment to transparent and accurate scientific communication. With these rigorous standards in place, the scientific literature continues to be a reliable foundation for advancing knowledge and shaping the future of research.
Step 6: Notify Indexing Services (if applicable)
After the correction or erratum has been approved and published by the journal, it is essential to notify indexing services about the affiliation change. Indexing services, such as PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and others, play a crucial role in organizing and providing access to the vast amount of scientific literature. Informing them about the affiliation change ensures that the updated information is accurately reflected in their databases, facilitating proper attribution and discoverability of the research.
- Accurate Attribution : Indexing services use affiliations to attribute research to specific institutions or organizations accurately. Keeping this information up to date is essential to ensure that researchers are credited appropriately for their work and that institutions receive proper recognition for their contributions.
When Dr. Rodriguez’s affiliation is updated to the prestigious research institute in the journal’s published correction, notifying indexing services like PubMed about this change ensures that her research contributions are accurately linked to her new institution in their database. This allows other researchers and institutions to recognize her affiliation with the prestigious research institute when accessing her publications.
- Discoverability and Accessibility : Correctly indexed affiliations help researchers and readers easily discover relevant literature from specific institutions or researchers. This enhances the accessibility and visibility of research from particular institutions or research groups.
If a reader searches for publications from the prestigious research institute, the correct indexing of Dr. Rodriguez’s research under her new affiliation will lead to more accurate and relevant search results, making it easier for readers to find her latest work.
- Research Evaluations and Rankings : Some institutions and funding agencies use publication records to assess research productivity and impact. Ensuring accurate affiliations is crucial for fair evaluations and rankings, which can influence funding decisions and institutional recognition.
The prestigious research institute’s ranking and reputation may be positively affected by the accurate affiliation indexing of its researchers, such as Dr. Rodriguez. This can lead to increased opportunities for research funding and collaborations.
Each indexing service has its own procedures for updating affiliations. It may involve contacting the indexing service directly, filling out a form, or following specific instructions on their website. Journals or publishers might also have direct communication channels with indexing services to facilitate such updates.
After the publication of the correction with Dr. Rodriguez’s updated affiliation, the journal’s editorial team takes the initiative to notify indexing services about the change. They ensure that the corrected information is communicated accurately to the relevant indexing databases.
By proactively notifying indexing services about affiliation changes, journals, researchers, and institutions contribute to maintaining the accuracy and integrity of research records worldwide. It also ensures that researchers receive proper recognition and that their contributions are accurately represented in the scientific community.
Step 7: Update Personal Profiles
After the affiliation change has been approved and published in the journal, it is crucial for the author to update their personal profiles to reflect the new affiliation. This step helps maintain consistency across various platforms and ensures that the author’s current institutional association is accurately represented in the academic community.
- Researcher Profile Websites : If you have a researcher profile on platforms like ResearchGate, Academia.edu , Google Scholar , or ORCID , log in to your account and update your affiliation information.
Dr. Smith, who recently changed her affiliation to a new university, visits her ResearchGate profile and updates the “Affiliation” section with her new institution’s details. This change is automatically reflected on her ResearchGate profile, which is viewed by researchers worldwide.
- University/Institution Websites : If your new institution hosts researcher profiles on its website, update your affiliation information there as well. This ensures that your profile is consistent with the official records of your institution.
Dr. Johnson, who is now affiliated with the prestigious research institute, visits the institute’s website and navigates to her faculty profile. She updates the “Affiliation” field on her profile page, providing her new position and affiliation details.
- Social and Professional Networking Sites : Platforms like LinkedIn are widely used for professional networking. Make sure to update your LinkedIn profile to reflect the correct affiliation, as this information is visible to potential collaborators, employers, and colleagues.
Dr. Rodriguez, now affiliated with the prestigious research institute, logs in to her LinkedIn account and edits her “Experience” section, adding her new position and affiliation. This update is visible to her connections and professional network.
- Publication Records : If you maintain a personal publication list on your website or other platforms, update the affiliation information for your published papers to match the corrected version in the journal.
Dr. Smith manages her personal website, where she maintains a list of her publications. She updates the affiliation for the published paper to reflect her new institution and provides a link to the corrected version of the paper on the journal’s website.
- Provide Links to the Corrected Paper : When updating your personal profiles, consider providing links to the corrected version of the published paper, especially if it is available online. This allows readers and colleagues to access the accurate and updated version of your work.
Dr. Johnson updates her ResearchGate profile and includes a link to the corrected version of her paper, “Advancements in Neural Network Research,” on the journal’s website. This way, readers who visit her profile can access the most recent and accurate information about her research.
By updating personal profiles with the correct affiliation and providing links to the corrected version of the published paper, researchers ensure that their professional information is current and consistent across different platforms. This contributes to establishing a reliable and accurate academic identity, allowing colleagues and collaborators to find and connect with them easily.
Subject: Request for Affiliation Change in Published Paper
I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to request a correction to the affiliation associated with the published paper titled “[Paper Title]” authored by [Author Names]. The paper’s DOI is [DOI number], and it was published in [Journal Name], [Volume], [Issue], [Publication Year].
I recently experienced a change in my institutional affiliation, and I wish to update the information in the published paper to reflect my current position. The correction is necessary to ensure the accuracy and credibility of the scientific literature and to properly credit my research contributions to the institution with which I am currently affiliated.
I kindly request to update my affiliation as follows:
Old Affiliation: [Old Institution Name], [Old Department], [Old City], [Old Country]
New Affiliation: [New Institution Name], [New Department], [New City], [New Country]
To support this affiliation change, I have attached an official letter from [New Institution Name] confirming my current association with them. The letter is on the institution’s official letterhead and is signed by [Name and Designation of Authorized Representative].
I assure you that the affiliation change has no impact on the content, results, or conclusions presented in the published paper. All co-authors have been informed of this request, and they fully support this correction.
Please let me know if you require any additional information or documentation to proceed with the affiliation change process. I am more than willing to provide any further details necessary.
Thank you for your attention to this matter. I greatly appreciate your cooperation in updating my affiliation in the published paper. I look forward to your positive response.
[Your Name] [Your Current Affiliation] [Contact Email] [Contact Phone Number]
The journey of academic research is one paved with innovation, collaboration, and growth. As researchers, our affiliations serve as critical milestones, connecting us to the institutions and organizations that shape our contributions to the scientific community. However, the dynamic nature of our careers can lead to situations where updating affiliations in already published research papers becomes necessary.
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the step-by-step process of changing affiliations in published papers, emphasizing the importance of accuracy, transparency, and integrity. Understanding the publication’s guidelines, gathering the right documentation, and maintaining professional communication with the journal’s editorial team are the initial keystones to navigating this process.
We have witnessed the significance of notifying indexing services to ensure accurate records, enhance discoverability, and preserve the credit and recognition researchers deserve. Updating personal profiles with the correct affiliations reinforces a consistent and reliable academic identity, making it easier for colleagues and collaborators to connect and engage.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- Best 5 Journals for Quick Review and High Impact in August 2024
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- Journal Article Publishing Support Center
To post social content, you must have a display name. The page will refresh upon submission. Any pending input will be lost.
What affiliations should I use?
Authors should use their current or recent affiliation in Author forms, and the affiliation that applied mostly when the manuscript was being prepared/ research was undertaken in the proofs of the paper.
Proof Central makes it possible to change the author list, including the affiliations and the associated footnotes. To do so, click on the 'pencil' icon to open the edit screen in the right pane. Here you can add, remove or edit author names, the author’s associated affiliations and footnotes. Changes made to the author group will always be reviewed and require approval from the journal editor, to make sure no invalid correction is being made by the corresponding author.
Was this answer helpful?
Thank you for your feedback, it will help us serve you better. If you require assistance, please scroll down and use one of the contact options to get in touch.
Help us to help you:
Thank you for your feedback!
- Why was this answer not helpful?
- It was hard to understand / follow.
- It did not answer my question.
- The solution did not work.
- There was a mistake in the answer.
- Feel free to leave any comments below: Please enter your feedback to submit this form
Related Articles:
- What should I do if my organization (i.e. affiliation or funder) is not found when I am requested to add this information when completing the Rights and Access form?
- Author Guide to the Publication Process (Post-Acceptance)
- What should I do if the proof is incorrect or incomplete?
- Will I get to check my proofs again?
- Can I make a correction to my typeset article after I have returned my proofs?
For further assistance:
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Research papers should...
- Authors’ affiliations in Research Papers: To Include or not
Rapid response to:
Research papers should omit their authors’ affiliations
- Related content
- Article metrics
- Rapid responses
Rapid Response:
The fact that the affiliation of authors could influence readers/reviewers has been highlighted by Matthew Harris in a Personal View (1). It has also been suggested that research papers should omit their authors’ affiliations. Nevertheless, we assume that, although the presence of authors’ affiliations in the articles could impose the concept that the study is well-conducted or more immediately relevant to the context of the reader, their elimination would violate the freedom of the readers.
Furthermore, when it comes to the medical sciences and the lives that could be either saved thanks to an excellent study or lost due to a fabricated or biased study, the editors and reviewers ought to be more cautious. The emerging discipline of “reverse innovation” is extremely appealing yet it neglects a crucial fact. In case of detection of any conflict, bias, mistake or fabrication in the studies from within developed countries, they are ultimately retracted from the databases; this is not an uncommon phenomenon these days, especially in the leading journals (2, 3). Consequently, the authors shoulder the responsibility; appropriate legislation is ready to be promptly implemented and the losses caused due to the flawed study are compensated to some extents. One might skeptically pose the question whether this would be true for all authors from every corner of the world.
References:
1. BMJ 2014;349:g6439 2. Shafer SL. Editor's Note: Notice of Retraction. Anesth Analg. 2014;119(5):1225. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000417. 3. Lancet Editors. Retraction--Valsartan in a Japanese population with hypertension and other cardiovascular disease (Jikei Heart Study): a randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint morbidity-mortality study. Lancet. 2013; 7;382(9895):843. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61847-4.
Competing interests: No competing interests
- Find guidance
- Our organisation
- Core Practices
- Find a member
- Become a member
- Work with us
You are here
Home Resources Forum discussion topics
Claiming institutional affiliations
December 2023
Watch the introduction to "Claiming institutional affiliations" with Ana Marušić
Standards and guidance on "institutional authorship"
Authorship is the currency of research and academia. But what about author affiliations? Research assessment and university ranking systems, as well as national accreditation systems, put demands on institutions and researchers to boost publication productivity. This has led to an increasing practice of inflating the number of affiliations claimed by an author on their publications, which is not solely due to increased research collaboration or mobility.
Journals and research institutions rarely provide guidance or standards on the definition of “deserving” affiliations or the number of affiliations per author on a publication. Multiple undeserved affiliations may be considered as research malpractice and may affect different stakeholders and the integrity of the published record.
During this Forum we will engage in a discussion on “institutional authorship” – the definition of affiliation on a publication, standards and guidance on their number and challenges to trustworthy institutional representation on publications. We welcome your thoughts and feedback.
Questions for the Forum discussion
1) Is there a definition of institutional affiliation i.e. institutional authorship, on a publication?
2) When does institutional support merit inclusion as an author affiliation on a publication?
3) Are there accepted standards on the number of reported institutional affiliations per author on a publication?
4) Who should create such standards?
Comments from the COPE Forum, December 2023
NOTE, comments do not imply formal COPE advice or consensus
- In many institutions the first and last place in the authorship list have particular prestige as they denote the lead author and a senior author respectively. This can lead to authors being encouraged to include their affiliation by several different institutions.
- For authors, the institution can be the current employer, the place where the most substantial part of the research was done, or the body who provided the funding. It may not be as clear-cut as ‘where the research was done’.
- For journals, however, it is important to be clear which is the institution that has given ethics approval, will pay any publication fees, and will be the point of contact for any issues with the publication.
- Definitions of eligible affiliations are still rare. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association says that only organisations that have made some substantial contribution to the work should be included.
- Journals could be clearer in how they define the institutional affiliation.
- Some journals do not permit more than one affiliation to be given per author.
- Some of the strain in the system arises from increasing use of affiliations by corresponding authors to claim eligibility for publishers’ Open Access funding schemes. Should publishers be using something other than institutional affiliation to determine eligibility for this funding? It might be helpful for publishers to specify corresponding or billing affiliation instead.
- Are affiliations as important for non-research articles? Who is accountable for opinion pieces or editorials, or for articles signed only on behalf of the journal?
- Affiliations matter to institutions who rely on rankings to boost their recruitment and income. Demanding that authors include them as an affiliation is a way to boost their indicators of productivity. However, it can become a case of gift authorship if it does not accurately represent where the work was done or where responsibility for it lies.
- Researchers who are at an early career stage may legitimately have several affiliations because of institutional mobility, or they may have no permanent affiliation. ‘Current affiliation’ may be a more useful way to declare their status.
- Researchers who are retired or who are not attached to any institution (independent scholars) are not well served by the emphasis on affiliation and may feel discriminated against.
- Should authors be expected to declare how much of the work was done at each institution listed? Or which institution is the employer and which funded the research if these are different?
- The issue goes beyond authors and publishers: author affiliations and funding organisations are treated separately by some indexing and registration databases such as CrossRef. Publishers need to be clear in what they are collecting so that the data can be registered accurately.
- Databases of persistent identifiers such as the Ringgold Identity Database may be of use to publishers in tracking and identifying institutional affiliations. Ringgold Database identifiers can be linked to the International Standard Name Identifier database and via that, to The Research Organization Registry .
- More guidance on affiliations would be welcome since it has become so important as an indicator of research output, quality, credit, and prestige.
Further reading
What’s in a name? How false author affiliations are damaging academic research Vivienne C. Bachelet, LSE Blog
Misrepresentation of institutional affliations: The results from an exploratory case study of Chilean authors Research article
- Octopus affiliations Khaled Moustafa, Arabixiv Papers
A summary of the discussion at the virtual Forum event will be added to this page shortly.
Page updated: 12 December 2023
We welcome comments on this discussion from COPE Members and non-members here:
Your comments
You must be logged in to leave a comment on the COPE website. If you are not a member of COPE you can register to create a guest account .
Comments will not appear immediately. We review comments on our website before publishing them, to ensure they are respectful and relevant.
- Login to your account or register to post comments
- Posted by Kevin McCurley , 11/11/2023 2.30am
There is another possible problem that you didn't mention, namely a concealed affiliation. Affiliations are often thought of as an employment or student relationship, but they can also come in the form of financial support or non-employment membership in an organization. Some research has been criticized in the past for having been motivated by concealed funding. Examples include funding by tobacco industry to dispute health concerns, or funding by the petroleum industry to combat competing climate change research.
It feels like affiliations could use a taxonomy, much like the CRediT taxonomy for contributor roles. That way we could cover things like "research started while employed at..." or "research concluded while employed by..." or "research conducted while visiting ..." or even "Research independent of the author relationship to...". The exact taxonomy would require considerable discussion.
- Posted by Pekka Nygren , 27/11/2023 9.41am
I feel somewhat symphatic with this proposal yet it is quite bureaucratic. The same could be done by adding short explanations to the affiliation list, like "current address" for the contact address of an author while the affiliation during the actual research would be plain. If the author has been a visiting scholar during much of the research, again plain affiliation to the organisation where the work was done with the contact address with note "permanent address". I think that accepting two affiliation is totally valid e.g., in cases like above. More would need a justification. Funding does not make affiliation. The scientists working in a research organisation on a foundation grant (quite common in my home country) should list the organisation where they work as the affiliation even in the case they do not have an employer status.
- Posted by Dr. B. J. C. Perera , 20/11/2023 1.03am
I believe that only the major primary affiliation should be included in research papers. All other ancillary connections and vaguely related positions should not be listed in the publication. If a free-for-all facility is provided by journals, there will not be a limit to which authors possibly could go to.
There should be agreed concensus on the part of journals in this regard.
- Posted by Gerta Rücker , 20/11/2023 12.45pm
At our journal we discussed the problem of submissions from paper mills and faked affiliations. During this discussion the suggestion came up that submissions should be admitted only if coming from well known academic or industry affiliations. This, however, makes a big problem for independent researchers, for example retired academics or people like me, when I was unemployed in maternal leave, working from my kitchen table in Chemical Graph Theory together with my husband and using his academic affiliation, which was not a problem at that time (the nineties). I will have the same problem in near future when I'll loose my academic affiliation because I am retired. My opinion is that freedom of research allows every researcher publishing their research in academic journals, independently of affiliation.
- Posted by Lee Harvey , 20/11/2023 4.12pm
I'm not sure what the problem is here. We permit author to simply insert their department/reserch unit and university/college (inc town/city and country). On the rare occasions that the contributor works outside higher education we note as appropriate.
- Posted by Ahmed Al-Tabbakh , 20/11/2023 8.58pm
authors must be affiliated with the institution/organization where they primarily work. This is because every moment they spend contributing to a publication is ultimately acknowledged, rewarded and supported (completely or partially) by this affiliation body. If the author receives financial support from another institution/organization/company, he/she should acknowledge this support. But this does not grant the author the right to affiliation. if the author is hosted as a contributing researcher in one of the institution /organization laboratories, then he/she has the right to claim affiliation (maybe a second affiliation). Claiming more than one affiliation must be justified by the author and acknowledged by the affiliation body. Journals may generate a system for the verification of the affiliation of the contributing authors in which the head of the department/the manager / the director has to verify this piece of information (the author affiliation).
- Posted by João de Deus Ba... , 20/11/2023 9.53pm
In our portal (BAHIANA Journals, Brazil), are considered proper afilliations only those with which the author maintains formal contractual ties of employment either for teaching, research activities and/or clinical practice. Independent researchers may submit papers and are permitted to declare themselves as such. For those authors who do not have an employment relationship with educational and/or research institutions, the student relationship may be considered, usually the highest academic rank to be obtained by the author at the time of submission (i.e., doctoral student, master's student, undergraduate student). Laboratories, research groups and institutions in which the author is a postdoctoral fellow, visiting professor or consultant are not considered as affiliations for the purposes of publication in order to avoid having authors taking advantage of the status of institutions where they might be working on in a short-term basis and/or without contractual ties. The authors are requested to comply with that at the time of submission. As we are unable to verify all claims, we have made ORCID authentication mandatory for all authors of any given submission to any of the journals of our portal, allowing for the independent verification of the authorship claims. Mandatory ORCID authentication for all authors may also be effective in curbing ghost authorship.
- Posted by Ruslan Saygitov , 13/2/2024 2.18pm
Starting point: whether we should indicate the authors' affiliation (or independence from their involvement) at all, and if so, on what basis. Why is it important/mandatory? For whom is it important (stakeholder perspectives)? And only after that move on to the definition (if required).
- Authorship and contributorship
- Journal management

Style and Grammar Guidelines
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps writers present their ideas in a clear, concise, and inclusive manner. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably. People are described using language that affirms their worth and dignity. Authors plan for ethical compliance and report critical details of their research protocol to allow readers to evaluate findings and other researchers to potentially replicate the studies. Tables and figures present information in an engaging, readable manner.
The style and grammar guidelines pages present information about APA Style as described in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition and the Concise Guide to APA Style, Seventh Edition . Any updates to APA Style are noted on the applicable topic pages. If you are still using the sixth edition, helpful resources are available in the sixth edition archive .
Looking for more style?

- Accessibility of APA Style
- Line Spacing
- Order of Pages
- Page Header
- Paragraph Alignment and Indentation
- Sample Papers
- Title Page Setup
- Appropriate Level of Citation
- Basic Principles of Citation
- Classroom or Intranet Sources
- Paraphrasing
- Personal Communications
- Quotations From Research Participants
- Secondary Sources
- Abbreviations
- Capitalization
- Italics and Quotation Marks
- Punctuation
- Spelling and Hyphenation
- General Principles for Reducing Bias
- Historical Context
- Intersectionality
- Participation in Research
- Racial and Ethnic Identity
- Sexual Orientation
- Socioeconomic Status
- Accessible Use of Color in Figures
- Figure Setup
- Sample Figures
- Sample Tables
- Table Setup
- Archival Documents and Collections
- Basic Principles of Reference List Entries
- Database Information in References
- DOIs and URLs
- Elements of Reference List Entries
- Missing Reference Information
- Reference Examples
- References in a Meta-Analysis
- Reference Lists Versus Bibliographies
- Works Included in a Reference List
- Active and Passive Voice
- Anthropomorphism
- First-Person Pronouns
- Logical Comparisons
- Plural Nouns
- Possessive Adjectives
- Possessive Nouns
- Singular “They”
- Adapting a Dissertation or Thesis Into a Journal Article
- Correction Notices
- Cover Letters
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- Open Science
- Response to Reviewers
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Add affiliations to the authors' name in the article class
I am using the \documentclass{article} to write an article. how can I add the affiliation to the author's name like the following picture?

And, this document class has a date under the names. Can I omit it?
3 Answers 3
Using authblk maybe it's better to do something like:
This way, you can mix affiliations.
- Thanks @Harish Kumar for very helpful answer. I do a have a similar question here . Would highly appreciate if you have a look on this and provide any answer. Thanks – MYaseen208 Commented Apr 15, 2016 at 16:21
- It doesn't work in amsart class. Wasted a lot of time on this. – user2679290 Commented Oct 29, 2019 at 17:05
- 5 Could you explain why you changed the Maxaffil counter? I don't really see the purpose. – FWDekker Commented May 11, 2021 at 9:25
When I've needed to use \maketitle , a trick I've used is to abuse \date{} :

- 7 Quick and dirty, but quite effective (!). Thanks – loved.by.Jesus Commented Jul 10, 2017 at 21:10
- This is really handy! – Raul Guarini Riva Commented Nov 28, 2017 at 23:50
- 1 I normally manipulate the author field to add affiliations, but I think the date manipulation works better. In the author field, you can't increase spacing between name and additional objects. – cryptic0 Commented Feb 22, 2019 at 14:12
- Hi, I am using the above but "No institute given" text is comming after the names of the authors. – user132638 Commented Feb 25, 2020 at 5:31
I always use a trick I learned from Anthony Liekens , which is used for showing multiple affiliations per author. Omitting the date is as easy as using \date{} .

- 1 I feel this should be the answer. – lkahtz Commented Jan 31, 2020 at 3:40
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged article ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Where does Postgres fit in a world of GenAI and vector databases?
- Featured on Meta
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
Hot Network Questions
- Are there different conventions for 'rounding to even'?
- Simple casino game
- Is it advisable to contact faculty members at U.S. universities prior to submitting a PhD application?
- How Can this Limit be really Evaluated?
- Why are AAVs not a replacement for through-roof vent pipe?
- What did the Ancient Greeks think the stars were?
- Stealth Mosquitoes?
- DATEDIFF Rounding
- Why does a halfing's racial trait lucky specify you must use the next roll?
- Purpose of burn permit?
- Why is Emacs recompiling some packages on every startup?
- What is the significance of bringing the door to Nippur in the Epic of Gilgamesh?
- I'm trying to remember a novel about an asteroid threatening to destroy the earth. I remember seeing the phrase "SHIVA IS COMING" on the cover
- On a 3D Gagliardo-Nirenberg inequality
- What I have to do more to improve my regression model in r
- Is there any video of an air-to-air missile shooting down an aircraft?
- What are the risks of a compromised top tube and of attempts to repair it?
- How do I alter a table by using AFTER in hook update?
- Why does my PC take a long time to start, then when it's at the login screen it jumps to the desktop instantly?
- How would increasing atomic bond strength affect nuclear physics?
- My colleagues and I are travelling to UK as delegates in an event and the company is paying for all our travel expenses. what documents are required
- Why is one of the Intel 8042 keyboard controller outputs inverted?
- What is the difference between using a resistor or a capacitor as current limiter?
- What would be non-slang equivalent of "copium"?
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 22 July 2024
Neural general circulation models for weather and climate
- Dmitrii Kochkov ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3846-4911 1 na1 ,
- Janni Yuval ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7519-0118 1 na1 ,
- Ian Langmore 1 na1 ,
- Peter Norgaard 1 na1 ,
- Jamie Smith 1 na1 ,
- Griffin Mooers 1 ,
- Milan Klöwer 2 ,
- James Lottes 1 ,
- Stephan Rasp 1 ,
- Peter Düben ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4610-3326 3 ,
- Sam Hatfield 3 ,
- Peter Battaglia 4 ,
- Alvaro Sanchez-Gonzalez 4 ,
- Matthew Willson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8730-1927 4 ,
- Michael P. Brenner 1 , 5 &
- Stephan Hoyer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5207-0380 1 na1
Nature ( 2024 ) Cite this article
53k Accesses
3 Citations
678 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Atmospheric dynamics
- Climate and Earth system modelling
- Computational science
General circulation models (GCMs) are the foundation of weather and climate prediction 1 , 2 . GCMs are physics-based simulators that combine a numerical solver for large-scale dynamics with tuned representations for small-scale processes such as cloud formation. Recently, machine-learning models trained on reanalysis data have achieved comparable or better skill than GCMs for deterministic weather forecasting 3 , 4 . However, these models have not demonstrated improved ensemble forecasts, or shown sufficient stability for long-term weather and climate simulations. Here we present a GCM that combines a differentiable solver for atmospheric dynamics with machine-learning components and show that it can generate forecasts of deterministic weather, ensemble weather and climate on par with the best machine-learning and physics-based methods. NeuralGCM is competitive with machine-learning models for one- to ten-day forecasts, and with the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ensemble prediction for one- to fifteen-day forecasts. With prescribed sea surface temperature, NeuralGCM can accurately track climate metrics for multiple decades, and climate forecasts with 140-kilometre resolution show emergent phenomena such as realistic frequency and trajectories of tropical cyclones. For both weather and climate, our approach offers orders of magnitude computational savings over conventional GCMs, although our model does not extrapolate to substantially different future climates. Our results show that end-to-end deep learning is compatible with tasks performed by conventional GCMs and can enhance the large-scale physical simulations that are essential for understanding and predicting the Earth system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks
Deep learning for twelve hour precipitation forecasts
Skilful predictions of the Asian summer monsoon one year ahead
Solving the equations for Earth’s atmosphere with general circulation models (GCMs) is the basis of weather and climate prediction 1 , 2 . Over the past 70 years, GCMs have been steadily improved with better numerical methods and more detailed physical models, while exploiting faster computers to run at higher resolution. Inside GCMs, the unresolved physical processes such as clouds, radiation and precipitation are represented by semi-empirical parameterizations. Tuning GCMs to match historical data remains a manual process 5 , and GCMs retain many persistent errors and biases 6 , 7 , 8 . The difficulty of reducing uncertainty in long-term climate projections 9 and estimating distributions of extreme weather events 10 presents major challenges for climate mitigation and adaptation 11 .
Recent advances in machine learning have presented an alternative for weather forecasting 3 , 4 , 12 , 13 . These models rely solely on machine-learning techniques, using roughly 40 years of historical data from the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) reanalysis v5 (ERA5) 14 for model training and forecast initialization. Machine-learning methods have been remarkably successful, demonstrating state-of-the-art deterministic forecasts for 1- to 10-day weather prediction at a fraction of the computational cost of traditional models 3 , 4 . Machine-learning atmospheric models also require considerably less code, for example GraphCast 3 has 5,417 lines versus 376,578 lines for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s FV3 atmospheric model 15 (see Supplementary Information section A for details).
Nevertheless, machine-learning approaches have noteworthy limitations compared with GCMs. Existing machine-learning models have focused on deterministic prediction, and surpass deterministic numerical weather prediction in terms of the aggregate metrics for which they are trained 3 , 4 . However, they do not produce calibrated uncertainty estimates 4 , which is essential for useful weather forecasts 1 . Deterministic machine-learning models using a mean-squared-error loss are rewarded for averaging over uncertainty, producing unrealistically blurry predictions when optimized for multi-day forecasts 3 , 13 . Unlike physical models, machine-learning models misrepresent derived (diagnostic) variables such as geostrophic wind 16 . Furthermore, although there has been some success in using machine-learning approaches on longer timescales 17 , 18 , these models have not demonstrated the ability to outperform existing GCMs.
Hybrid models that combine GCMs with machine learning are appealing because they build on the interpretability, extensibility and successful track record of traditional atmospheric models 19 , 20 . In the hybrid model approach, a machine-learning component replaces or corrects the traditional physical parameterizations of a GCM. Until now, the machine-learning component in such models has been trained ‘offline’, by learning parameterizations independently of their interaction with dynamics. These components are then inserted into an existing GCM. The lack of coupling between machine-learning components and the governing equations during training potentially causes serious problems, such as instability and climate drift 21 . So far, hybrid models have mostly been limited to idealized scenarios such as aquaplanets 22 , 23 . Under realistic conditions, machine-learning corrections have reduced some biases of very coarse GCMs 24 , 25 , 26 , but performance remains considerably worse than state-of-the-art models.
Here we present NeuralGCM, a fully differentiable hybrid GCM of Earth’s atmosphere. NeuralGCM is trained on forecasting up to 5-day weather trajectories sampled from ERA5. Differentiability enables end-to-end ‘online training’ 27 , with machine-learning components optimized in the context of interactions with the governing equations for large-scale dynamics, which we find enables accurate and stable forecasts. NeuralGCM produces physically consistent forecasts with accuracy comparable to best-in-class models across a range of timescales, from 1- to 15-day weather to decadal climate prediction.
Neural GCMs
A schematic of NeuralGCM is shown in Fig. 1 . The two key components of NeuralGCM are a differentiable dynamical core for solving the discretized governing dynamical equations and a learned physics module that parameterizes physical processes with a neural network, described in full detail in Methods , Supplementary Information sections B and C , and Supplementary Table 1 . The dynamical core simulates large-scale fluid motion and thermodynamics under the influence of gravity and the Coriolis force. The learned physics module (Supplementary Fig. 1 ) predicts the effect of unresolved processes, such as cloud formation, radiative transport, precipitation and subgrid-scale dynamics, on the simulated fields using a neural network.
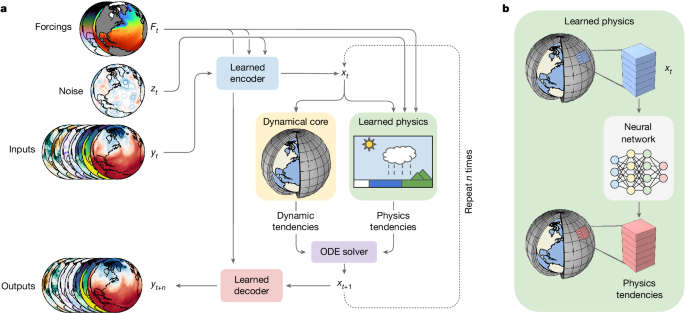
a , Overall model structure, showing how forcings F t , noise z t (for stochastic models) and inputs y t are encoded into the model state x t . The model state is fed into the dynamical core, and alongside forcings and noise into the learned physics module. This produces tendencies (rates of change) used by an implicit–explicit ordinary differential equation (ODE) solver to advance the state in time. The new model state x t +1 can then be fed back into another time step, or decoded into model predictions. b , The learned physics module, which feeds data for individual columns of the atmosphere into a neural network used to produce physics tendencies in that vertical column.
The differentiable dynamical core in NeuralGCM allows an end-to-end training approach, whereby we advance the model multiple time steps before employing stochastic gradient descent to minimize discrepancies between model predictions and reanalysis (Supplementary Information section G.2 ). We gradually increase the rollout length from 6 hours to 5 days (Supplementary Information section G and Supplementary Table 5 ), which we found to be critical because our models are not accurate for multi-day prediction or stable for long rollouts early in training (Supplementary Information section H.6.2 and Supplementary Fig. 23 ). The extended back-propagation through hundreds of simulation steps enables our neural networks to take into account interactions between the learned physics and the dynamical core. We train deterministic and stochastic NeuralGCM models, each of which uses a distinct training protocol, described in full detail in Methods and Supplementary Table 4 .
We train a range of NeuralGCM models at horizontal resolutions with grid spacing of 2.8°, 1.4° and 0.7° (Supplementary Fig. 7 ). We evaluate the performance of NeuralGCM at a range of timescales appropriate for weather forecasting and climate simulation. For weather, we compare against the best-in-class conventional physics-based weather models, ECMWF’s high-resolution model (ECMWF-HRES) and ensemble prediction system (ECMWF-ENS), and two of the recent machine-learning-based approaches, GraphCast 3 and Pangu 4 . For climate, we compare against a global cloud-resolving model and Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project (AMIP) runs.
Medium-range weather forecasting
Our evaluation set-up focuses on quantifying accuracy and physical consistency, following WeatherBench2 12 . We regrid all forecasts to a 1.5° grid using conservative regridding, and average over all 732 forecasts made at noon and midnight UTC in the year 2020, which was held-out from training data for all machine-learning models. NeuralGCM, GraphCast and Pangu compare with ERA5 as the ground truth, whereas ECMWF-ENS and ECMWF-HRES compare with the ECMWF operational analysis (that is, HRES at 0-hour lead time), to avoid penalizing the operational forecasts for different biases than ERA5.
Model accuracy
We use ECMWF’s ensemble (ENS) model as a reference baseline as it achieves the best performance across the majority of lead times 12 . We assess accuracy using (1) root-mean-squared error (RMSE), (2) root-mean-squared bias (RMSB), (3) continuous ranked probability score (CRPS) and (4) spread-skill ratio, with the results shown in Fig. 2 . We provide more in-depth evaluations including scorecards, metrics for additional variables and levels and maps in Extended Data Figs. 1 and 2 , Supplementary Information section H and Supplementary Figs. 9 – 22 .
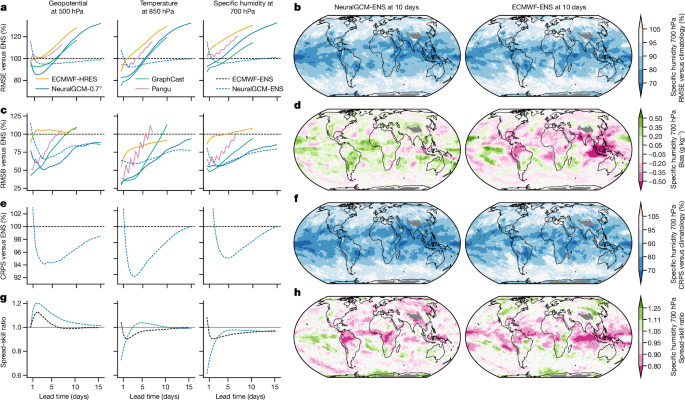
a , c , RMSE ( a ) and RMSB ( c ) for ECMWF-ENS, ECMWF-HRES, NeuralGCM-0.7°, NeuralGCM-ENS, GraphCast 3 and Pangu 4 on headline WeatherBench2 variables, as a percentage of the error of ECMWF-ENS. Deterministic and stochastic models are shown in solid and dashed lines respectively. e , g , CRPS relative to ECMWF-ENS ( e ) and spread-skill ratio for the ENS and NeuralGCM-ENS models ( g ). b , d , f , h , Spatial distributions of RMSE ( b ), bias ( d ), CRPS ( f ) and spread-skill ratio ( h ) for NeuralGCM-ENS and ECMWF-ENS models for 10-day forecasts of specific humidity at 700 hPa. Spatial plots of RMSE and CRPS show skill relative to a probabilistic climatology 12 with an ensemble member for each of the years 1990–2019. The grey areas indicate regions where climatological surface pressure on average is below 700 hPa.
Deterministic models that produce a single weather forecast for given initial conditions can be compared effectively using RMSE skill at short lead times. For the first 1–3 days, depending on the atmospheric variable, RMSE is minimized by forecasts that accurately track the evolution of weather patterns. At this timescale we find that NeuralGCM-0.7° and GraphCast achieve best results, with slight variations across different variables (Fig. 2a ). At longer lead times, RMSE rapidly increases owing to chaotic divergence of nearby weather trajectories, making RMSE less informative for deterministic models. RMSB calculates persistent errors over time, which provides an indication of how models would perform at much longer lead times. Here NeuralGCM models also compare favourably against previous approaches (Fig. 2c ), with notably much less bias for specific humidity in the tropics (Fig. 2d ).
Ensembles are essential for capturing intrinsic uncertainty of weather forecasts, especially at longer lead times. Beyond about 7 days, the ensemble means of ECMWF-ENS and NeuralGCM-ENS forecasts have considerably lower RMSE than the deterministic models, indicating that these models better capture the average of possible weather. A better metric for ensemble models is CRPS, which is a proper scoring rule that is sensitive to full marginal probability distributions 28 . Our stochastic model (NeuralGCM-ENS) running at 1.4° resolution has lower error compared with ECMWF-ENS across almost all variables, lead times and vertical levels for ensemble-mean RMSE, RSMB and CRPS (Fig. 2a,c,e and Supplementary Information section H ), with similar spatial patterns of skill (Fig. 2b,f ). Like ECMWF-ENS, NeuralGCM-ENS has a spread-skill ratio of approximately one (Fig. 2d ), which is a necessary condition for calibrated forecasts 29 .
An important characteristic of forecasts is their resemblance to realistic weather patterns. Figure 3 shows a case study that illustrates the performance of NeuralGCM on three types of important weather phenomenon: tropical cyclones, atmospheric rivers and the Intertropical Convergence Zone. Figure 3a shows that all the machine-learning models make significantly blurrier forecasts than the source data ERA5 and physics-based ECMWF-HRES forecast, but NeuralCGM-0.7° outperforms the pure machine-learning models, despite its coarser resolution (0.7° versus 0.25° for GraphCast and Pangu). Blurry forecasts correspond to physically inconsistent atmospheric conditions and misrepresent extreme weather. Similar trends hold for other derived variables of meteorological interest (Supplementary Information section H.2 ). Ensemble-mean predictions, from both NeuralGCM and ECMWF, are closer to ERA5 in an average sense, and thus are inherently smooth at long lead times. In contrast, as shown in Fig. 3 and in Supplementary Information section H.3 , individual realizations from the ECMWF and NeuralGCM ensembles remain sharp, even at long lead times. Like ECMWF-ENS, NeuralGCM-ENS produces a statistically representative range of future weather scenarios for each weather phenomenon, despite its eight-times-coarser resolution.
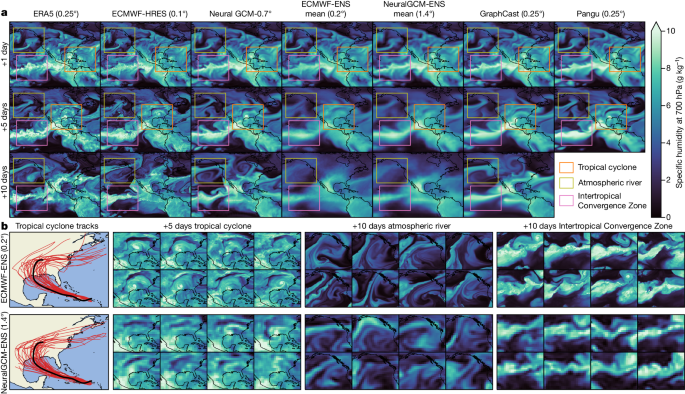
All forecasts are initialized at 2020-08-22T12z, chosen to highlight Hurricane Laura, the most damaging Atlantic hurricane of 2020. a , Specific humidity at 700 hPa for 1-day, 5-day and 10-day forecasts over North America and the Northeast Pacific Ocean from ERA5 14 , ECMWF-HRES, NeuralGCM-0.7°, ECMWF-ENS (mean), NeuralGCM-ENS (mean), GraphCast 3 and Pangu 4 . b , Forecasts from individual ensemble members from ECMWF-ENS and NeuralGCM-ENS over regions of interest, including predicted tracks of Hurricane Laura from each of the 50 ensemble members (Supplementary Information section I.2 ). The track from ERA5 is plotted in black.
We can quantify the blurriness of different forecast models via their power spectra. Supplementary Figs. 17 and 18 show that the power spectra of NeuralCGM-0.7° is consistently closer to ERA5 than the other machine-learning forecast methods, but is still blurrier than ECMWF’s physical forecasts. The spectra of NeuralGCM forecasts is also roughly constant over the forecast period, in stark contrast to GraphCast, which worsens with lead time. The spectrum of NeuralGCM becomes more accurate with increased resolution (Supplementary Fig. 22 ), which suggests the potential for further improvements of NeuralGCM models trained at higher resolutions.
Water budget
In NeuralGCM, advection is handled by the dynamical core, while the machine-learning parameterization models local processes within vertical columns of the atmosphere. Thus, unlike pure machine-learning methods, local sources and sinks can be isolated from tendencies owing to horizontal transport and other resolved dynamics (Supplementary Fig. 3 ). This makes our results more interpretable and facilitates the diagnosis of the water budget. Specifically, we diagnose precipitation minus evaporation (Supplementary Information section H.5 ) rather than directly predicting these as in machine-learning-based approaches 3 . For short weather forecasts, the mean of precipitation minus evaporation has a realistic spatial distribution that is very close to ERA5 data (Extended Data Fig. 4c–e ). The precipitation-minus-evaporation rate distribution of NeuralGCM-0.7° closely matches the ERA5 distribution in the extratropics (Extended Data Fig. 4b ), although it underestimates extreme events in the tropics (Extended Data Fig. 4a ). It is noted that the current version of NeuralGCM directly predicts tendencies for an atmospheric column, and thus cannot distinguish between precipitation and evaporation.
Geostrophic wind balance
We examined the extent to which NeuralGCM, GraphCast and ECMWF-HRES capture the geostrophic wind balance, the near-equilibrium between the dominant forces that drive large-scale dynamics in the mid-latitudes 30 . A recent study 16 highlighted that Pangu misrepresents the vertical structure of the geostrophic and ageostrophic winds and noted a deterioration at longer lead times. Similarly, we observe that GraphCast shows an error that worsens with lead time. In contrast, NeuralGCM more accurately depicts the vertical structure of the geostrophic and ageostrophic winds, as well as their ratio, compared with GraphCast across various rollouts, when compared against ERA5 data (Extended Data Fig. 3 ). However, ECMWF-HRES still shows a slightly closer alignment to ERA5 data than NeuralGCM does. Within NeuralGCM, the representation of the geostrophic wind’s vertical structure only slightly degrades in the initial few days, showing no noticeable changes thereafter, particularly beyond day 5.
Generalizing to unseen data
Physically consistent weather models should still perform well for weather conditions for which they were not trained. We expect that NeuralGCM may generalize better than machine-learning-only atmospheric models, because NeuralGCM employs neural networks that act locally in space, on individual vertical columns of the atmosphere. To explore this hypothesis, we compare versions of NeuralCGM-0.7° and GraphCast trained to 2017 on 5 years of weather forecasts beyond the training period (2018–2022) in Supplementary Fig. 36 . Unlike GraphCast, NeuralGCM does not show a clear trend of increasing error when initialized further into the future from the training data. To extend this test beyond 5 years, we trained a NeuralGCM-2.8° model using only data before 2000, and tested its skill for over 21 unseen years (Supplementary Fig. 35 ).
Climate simulations
Although our deterministic NeuralGCM models are trained to predict weather up to 3 days ahead, they are generally capable of simulating the atmosphere far beyond medium-range weather timescales. For extended climate simulations, we prescribe historical sea surface temperature (SST) and sea-ice concentration. These simulations feature many emergent phenomena of the atmosphere on timescales from months to decades.
For climate simulations with NeuralGCM, we use 2.8° and 1.4° deterministic models, which are relatively inexpensive to train (Supplementary Information section G.7 ) and allow us to explore a larger parameter space to find stable models. Previous studies found that running extended simulations with hybrid models is challenging due to numerical instabilities and climate drift 21 . To quantify stability in our selected models, we run multiple initial conditions and report how many of them finish without instability.
Seasonal cycle and emergent phenomena
To assess the capability of NeuralGCM to simulate various aspects of the seasonal cycle, we run 2-year simulations with NeuralGCM-1.4°. for 37 different initial conditions spaced every 10 days for the year 2019. Out of these 37 initial conditions, 35 successfully complete the full 2 years without instability; for case studies of instability, see Supplementary Information section H.7 , and Supplementary Figs. 26 and 27 . We compare results from NeuralGCM-1.4° for 2020 with ERA5 data and with outputs from the X-SHiELD global cloud-resolving model, which is coupled to an ocean model nudged towards reanalysis 31 . This X-SHiELD run has been used as a target for training machine-learning climate models 24 . For comparison, we evaluate models after regridding predictions to 1.4° resolution. This comparison slightly favours NeuralGCM because NeuralGCM was tuned to match ERA5, but the discrepancy between ERA5 and the actual atmosphere is small relative to model error.
Figure 4a shows the temporal variation of the global mean temperature to 2020, as captured by 35 simulations from NeuralGCM, in comparison with the ERA5 reanalysis and standard climatology benchmarks. The seasonality and variability of the global mean temperature from NeuralGCM are quantitatively similar to those observed in ERA5. The ensemble-mean temperature RMSE for NeuralGCM stands at 0.16 K when benchmarked against ERA5, which is a significant improvement over the climatology’s RMSE of 0.45 K. We find that NeuralGCM accurately simulates the seasonal cycle, as evidenced by metrics such as the annual cycle of the global precipitable water (Supplementary Fig. 30a ) and global total kinetic energy (Supplementary Fig. 30b ). Furthermore, the model captures essential atmospheric dynamics, including the Hadley circulation and the zonal-mean zonal wind (Supplementary Fig. 28 ), as well as the spatial patterns of eddy kinetic energy in different seasons (Supplementary Fig. 31 ), and the distinctive seasonal behaviours of monsoon circulation (Supplementary Fig. 29 ; additional details are provided in Supplementary Information section I.1 ).
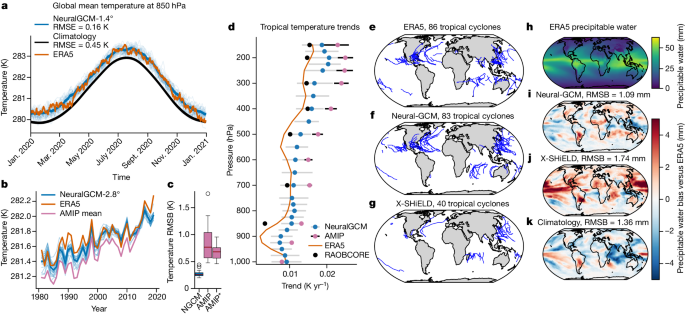
a , Global mean temperature for ERA5 14 (orange), 1990–2019 climatology (black) and NeuralGCM-1.4° (blue) for 2020 using 35 simulations initialized every 10 days during 2019 (thick line, ensemble mean; thin lines, different initial conditions). b , Yearly global mean temperature for ERA5 (orange), mean over 22 CMIP6 AMIP experiments 34 (violet; model details are in Supplementary Information section I.3 ) and NeuralGCM-2.8° for 22 AMIP-like simulations with prescribed SST initialized every 10 days during 1980 (thick line, ensemble mean; thin lines, different initial conditions). c , The RMSB of the 850-hPa temperature averaged between 1981 and 2014 for 22 NeuralGCM-2.8° AMIP runs (labelled NGCM), 22 CMIP6 AMIP experiments (labelled AMIP) and debiased 22 CMIP6 AMIP experiments (labelled AMIP*; bias was removed by removing the 850-hPa global temperature bias). In the box plots, the red line represents the median. The box delineates the first to third quartiles; the whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range (Q1 − 1.5IQR and Q3 + 1.5IQR), and outliers are shown as individual dots. d , Vertical profiles of tropical (20° S–20° N) temperature trends for 1981–2014. Orange, ERA5; black dots, Radiosonde Observation Correction using Reanalyses (RAOBCORE) 41 ; blue dots, mean trends for NeuralGCM; purple dots, mean trends from CMIP6 AMIP runs (grey and black whiskers, 25th and 75th percentiles for NeuralGCM and CMIP6 AMIP runs, respectively). e – g , Tropical cyclone tracks for ERA5 ( e ), NeuralGCM-1.4° ( f ) and X-SHiELD 31 ( g ). h – k , Mean precipitable water for ERA5 ( h ) and the precipitable water bias in NeuralGCM-1.4° ( i ), initialized 90 days before mid-January 2020 similarly to X-SHiELD, X-SHiELD ( j ) and climatology ( k ; averaged between 1990 and 2019). In d – i , quantities are calculated between mid-January 2020 and mid-January 2021 and all models were regridded to a 256 × 128 Gaussian grid before computation and tracking.
Next, we compare the annual biases of a single NeuralGCM realization with a single realization of X-SHiELD (the only one available), both initiated in mid-October 2019. We consider 19 January 2020 to 17 January 2021, the time frame for which X-SHiELD data are available. Global cloud-resolving models, such as X-SHiELD, are considered state of the art, especially for simulating the hydrological cycle, owing to their resolution being capable of resolving deep convection 32 . The annual bias in precipitable water for NeuralGCM (RMSE of 1.09 mm) is substantially smaller than the biases of both X-SHiELD (RMSE of 1.74 mm) and climatology (RMSE of 1.36 mm; Fig. 4i–k ). Moreover, NeuralGCM shows a lower temperature bias in the upper and lower troposphere than X-SHiELD (Extended Data Fig. 6 ). We also indirectly compare precipitation bias in X-SHiELD with precipitation-minus-evaporation bias in NeuralGCM-1.4°, which shows slightly larger bias and grid-scale artefacts for NeuralGCM (Extended Data Fig. 5 ).
Finally, to assess the capability of NeuralGCM to generate tropical cyclones in an annual model integration, we use the tropical cyclone tracker TempestExtremes 33 , as described in Supplementary Information section I.2 , Supplementary Fig. 34 and Supplementary Table 6 . Figure 4e–g shows that NeuralGCM, even at a coarse resolution of 1.4°, produces realistic trajectories and counts of tropical cyclone (83 versus 86 in ERA5 for the corresponding period), whereas X-SHiELD, when regridded to 1.4° resolution, substantially underestimates the tropical cyclone count (40). Additional statistical analyses of tropical cyclones can be found in Extended Data Figs. 7 and 8 .
Decadal simulations
To assess the capability of NeuralGCM to simulate historical temperature trends, we conduct AMIP-like simulations over a duration of 40 years with NeuralGCM-2.8°. Out of 37 different runs with initial conditions spaced every 10 days during the year 1980, 22 simulations were stable for the entire 40-year period, and our analysis focuses on these results. We compare with 22 simulations run with prescribed SST from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) 34 , listed in Supplementary Information section I.3 .
We find that all 40-year simulations of NeuralGCM, as well as the mean of the 22 AMIP runs, accurately capture the global warming trends observed in ERA5 data (Fig. 4b ). There is a strong correlation in the year-to-year temperature trends with ERA5 data, suggesting that NeuralGCM effectively captures the impact of SST forcing on climate. When comparing spatial biases averaged over 1981–2014, we find that all 22 NeuralGCM-2.8° runs have smaller bias than the CMIP6 AMIP runs, and this result remains even when removing the global temperature bias in CMIP6 AMIP runs (Fig. 4c and Supplementary Figs. 32 and 33 ).
Next, we investigated the vertical structure of tropical warming trends, which climate models tend to overestimate in the upper troposphere 35 . As shown in Fig. 4d , the trends, calculated by linear regression, of NeuralGCM are closer to ERA5 than those of AMIP runs. In particular, the bias in the upper troposphere is reduced. However, NeuralGCM does show a wider spread in its predictions than the AMIP runs, even at levels near the surface where temperatures are typically more constrained by prescribed SST.
Lastly, we evaluated NeuralGCM’s capability to generalize to unseen warmer climates by conducting AMIP simulations with increased SST (Supplementary Information section I.4.2 ). We find that NeuralGCM shows some of the robust features of climate warming response to modest SST increases (+1 K and +2 K); however, for more substantial SST increases (+4 K), NeuralGCM’s response diverges from expectations (Supplementary Fig. 37 ). In addition, AMIP simulations with increased SST show climate drift, underscoring NeuralGCM’s limitations in this context (Supplementary Fig. 38 ).
NeuralGCM is a differentiable hybrid atmospheric model that combines the strengths of traditional GCMs with machine learning for weather forecasting and climate simulation. To our knowledge, NeuralGCM is the first machine-learning-based model to make accurate ensemble weather forecasts, with better CRPS than state-of-the-art physics-based models. It is also, to our knowledge, the first hybrid model that achieves comparable spatial bias to global cloud-resolving models, can simulate realistic tropical cyclone tracks and can run AMIP-like simulations with realistic historical temperature trends. Overall, NeuralGCM demonstrates that incorporating machine learning is a viable alternative to building increasingly detailed physical models 32 for improving GCMs.
Compared with traditional GCMs with similar skill, NeuralGCM is computationally efficient and low complexity. NeuralGCM runs at 8- to 40-times-coarser horizontal resolution than ECMWF’s Integrated Forecasting System and global cloud-resolving models, which enables 3 to 5 orders of magnitude savings in computational resources. For example, NeuralGCM-1.4° simulates 70,000 simulation days in 24 hours using a single tensor-processing-unit versus 19 simulated days on 13,824 central-processing-unit cores with X-SHiELD (Extended Data Table 1 ). This can be leveraged for previously impractical tasks such as large ensemble forecasting. NeuralGCM’s dynamical core uses global spectral methods 36 , and learned physics is parameterized with fully connected neural networks acting on single vertical columns. Substantial headroom exists to pursue higher accuracy using advanced numerical methods and machine-learning architectures.
Our results provide strong evidence for the disputed hypothesis 37 , 38 , 39 that learning to predict short-term weather is an effective way to tune parameterizations for climate. NeuralGCM models trained on 72-hour forecasts are capable of realistic multi-year simulation. When provided with historical SSTs, they capture essential atmospheric dynamics such as seasonal circulation, monsoons and tropical cyclones. However, we will probably need alternative training strategies 38 , 39 to learn important processes for climate with subtle impacts on weather timescales, such as a cloud feedback.
The NeuralGCM approach is compatible with incorporating either more physics or more machine learning, as required for operational weather forecasts and climate simulations. For weather forecasting, we expect that end-to-end learning 40 with observational data will allow for better and more relevant predictions, including key variables such as precipitation. Such models could include neural networks acting as corrections to traditional data assimilation and model diagnostics. For climate projection, NeuralGCM will need to be reformulated to enable coupling with other Earth-system components (for example, ocean and land), and integrating data on the atmospheric chemical composition (for example, greenhouse gases and aerosols). There are also research challenges common to current machine-learning-based climate models 19 , including the capability to simulate unprecedented climates (that is, generalization), adhering to physical constraints, and resolving numerical instabilities and climate drift. NeuralGCM’s flexibility to incorporate physics-based models (for example, radiation) offers a promising avenue to address these challenges.
Models based on physical laws and empirical relationships are ubiquitous in science. We believe the differentiable hybrid modelling approach of NeuralGCM has the potential to transform simulation for a wide range of applications, such as materials discovery, protein folding and multiphysics engineering design.
Differentiable atmospheric model
NeuralGCM combines components of the numerical solver and flexible neural network parameterizations. Simulation in time is carried out in a coordinate system suitable for solving the dynamical equations of the atmosphere, describing large-scale fluid motion and thermodynamics under the influence of gravity and the Coriolis force.
Our differentiable dynamical core is implemented in JAX, a library for high-performance code in Python that supports automatic differentiation 42 . The dynamical core solves the hydrostatic primitive equations with moisture, using a horizontal pseudo-spectral discretization and vertical sigma coordinates 36 , 43 . We evolve seven prognostic variables: vorticity and divergence of horizontal wind, temperature, surface pressure, and three water species (specific humidity, and specific ice and liquid cloud water content).
Our learned physics module uses the single-column approach of GCMs 2 , whereby information from only a single atmospheric column is used to predict the impact of unresolved processes occurring within that column. These effects are predicted using a fully connected neural network with residual connections, with weights shared across all atmospheric columns (Supplementary Information section C.4 ).
The inputs to the neural network include the prognostic variables in the atmospheric column, total incident solar radiation, sea-ice concentration and SST (Supplementary Information section C.1 ). We also provide horizontal gradients of the prognostic variables, which we found improves performance 44 . All inputs are standardized to have zero mean and unit variance using statistics precomputed during model initialization. The outputs are the prognostic variable tendencies scaled by the fixed unconditional standard deviation of the target field (Supplementary Information section C.5 ).
To interface between ERA5 14 data stored in pressure coordinates and the sigma coordinate system of our dynamical core, we introduce encoder and decoder components (Supplementary Information section D ). These components perform linear interpolation between pressure levels and sigma coordinate levels. We additionally introduce learned corrections to both encoder and decoder steps (Supplementary Figs. 4–6 ), using the same column-based neural network architecture as the learned physics module. Importantly, the encoder enables us to eliminate the gravity waves from initialization shock 45 , which otherwise contaminate forecasts.
Figure 1a shows the sequence of steps that NeuralGCM takes to make a forecast. First, it encodes ERA5 data at t = t 0 on pressure levels to initial conditions on sigma coordinates. To perform a time step, the dynamical core and learned physics (Fig. 1b ) then compute tendencies, which are integrated in time using an implicit–explicit ordinary differential equation solver 46 (Supplementary Information section E and Supplementary Table 2 ). This is repeated to advance the model from t = t 0 to t = t final . Finally, the decoder converts predictions back to pressure levels.
The time-step size of the ODE solver (Supplementary Table 3 ) is limited by the Courant–Friedrichs–Lewy condition on dynamics, and can be small relative to the timescale of atmospheric change. Evaluating learned physics is approximately 1.5 times as expensive as a time step of the dynamical core. Accordingly, following the typical practice for GCMs, we hold learned physics tendencies constant for multiple ODE time steps to reduce computational expense, typically corresponding to 30 minutes of simulation time.
Deterministic and stochastic models
We train deterministic NeuralGCM models using a combination of three loss functions (Supplementary Information section G.4 ) to encourage accuracy and sharpness while penalizing bias. During the main training phase, all losses are defined in a spherical harmonics basis. We use a standard mean squared error loss for prompting accuracy, modified to progressively filter out contributions from higher total wavenumbers at longer lead times (Supplementary Fig. 8 ). This filtering approach tackles the ‘double penalty problem’ 47 as it prevents the model from being penalized for predicting high-wavenumber features in incorrect locations at later times, especially beyond the predictability horizon. A second loss term encourages the spectrum to match the training data using squared loss on the total wavenumber spectrum of prognostic variables. These first two losses are evaluated on both sigma and pressure levels. Finally, a third loss term discourages bias by adding mean squared error on the batch-averaged mean amplitude of each spherical harmonic coefficient. For analysis of the impact that various loss functions have, refer to Supplementary Information section H.6.1 , and Supplementary Figs. 23 and 24 . The combined action of the three training losses allow the resulting models trained on 3-day rollouts to remain stable during years-to-decades-long climate simulations. Before final evaluations, we perform additional fine-tuning of just the decoder component on short rollouts of 24 hours (Supplementary Information section G.5 ).
Stochastic NeuralGCM models incorporate inherent randomness in the form of additional random fields passed as inputs to neural network components. Our stochastic loss is based on the CRPS 28 , 48 , 49 . CRPS consists of mean absolute error that encourages accuracy, balanced by a similar term that encourages ensemble spread. For each variable we use a sum of CRPS in grid space and CRPS in the spherical harmonic basis below a maximum cut-off wavenumber (Supplementary Information section G.6 ). We compute CRPS on rollout lengths from 6 hours to 5 days. As illustrated in Fig. 1 , we inject noise to the learned encoder and the learned physics module by sampling from Gaussian random fields with learned spatial and temporal correlation (Supplementary Information section C.2 and Supplementary Fig. 2 ). For training, we generate two ensemble members per forecast, which suffices for an unbiased estimate of CRPS.
Data availability
For training and evaluating the NeuralGCM models, we used the publicly available ERA5 dataset 14 , originally downloaded from https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/ and available via Google Cloud Storage in Zarr format at gs://gcp-public-data-arco-era5/ar/full_37-1h-0p25deg-chunk-1.zarr-v3. To compare NeuralGCM with operational and data-driven weather models, we used forecast datasets distributed as part of WeatherBench2 12 at https://weatherbench2.readthedocs.io/en/latest/data-guide.html , to which we have added NeuralGCM forecasts for 2020. To compare NeuralGCM with atmospheric models in climate settings, we used CMIP6 data available at https://catalog.pangeo.io/browse/master/climate/ , as well as X-SHiELD 24 outputs available on Google Cloud storage in a ‘requester pays’ bucket at gs://ai2cm-public-requester-pays/C3072-to-C384-res-diagnostics. The Radiosonde Observation Correction using Reanalyses (RAOBCORE) V1.9 that was used as reference tropical temperature trends was downloaded from https://webdata.wolke.img.univie.ac.at/haimberger/v1.9/ . Base maps use freely available data from https://www.naturalearthdata.com/downloads/ .
Code availability
The NeuralGCM code base is separated into two open source projects: Dinosaur and NeuralGCM, both publicly available on GitHub at https://github.com/google-research/dinosaur (ref. 50 ) and https://github.com/google-research/neuralgcm (ref. 51 ). The Dinosaur package implements a differentiable dynamical core used by NeuralGCM, whereas the NeuralGCM package provides machine-learning models and checkpoints of trained models. Evaluation code for NeuralGCM weather forecasts is included in WeatherBench2 12 , available at https://github.com/google-research/weatherbench2 (ref. 52 ).
Bauer, P., Thorpe, A. & Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 525 , 47–55 (2015).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Balaji, V. et al. Are general circulation models obsolete? Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119 , e2202075119 (2022).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lam, R. et al. Learning skillful medium-range global weather forecasting. Science 382 , 1416–1421 (2023).
Article ADS MathSciNet CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bi, K. et al. Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks. Nature 619 , 533–538 (2023).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hourdin, F. et al. The art and science of climate model tuning. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 98 , 589–602 (2017).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Bony, S. & Dufresne, J.-L. Marine boundary layer clouds at the heart of tropical cloud feedback uncertainties in climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32 , L20806 (2005).
Webb, M. J., Lambert, F. H. & Gregory, J. M. Origins of differences in climate sensitivity, forcing and feedback in climate models. Clim. Dyn. 40 , 677–707 (2013).
Article Google Scholar
Sherwood, S. C., Bony, S. & Dufresne, J.-L. Spread in model climate sensitivity traced to atmospheric convective mixing. Nature 505 , 37–42 (2014).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Palmer, T. & Stevens, B. The scientific challenge of understanding and estimating climate change. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116 , 24390–24395 (2019).
Fischer, E. M., Beyerle, U. & Knutti, R. Robust spatially aggregated projections of climate extremes. Nat. Clim. Change 3 , 1033–1038 (2013).
Field, C. B. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2012).
Rasp, S. et al. WeatherBench 2: A benchmark for the next generation of data-driven global weather models. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 16 , e2023MS004019 (2024).
Keisler, R. Forecasting global weather with graph neural networks. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.07575 (2022).
Hersbach, H. et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 146 , 1999–2049 (2020).
Zhou, L. et al. Toward convective-scale prediction within the next generation global prediction system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 100 , 1225–1243 (2019).
Bonavita, M. On some limitations of current machine learning weather prediction models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 51 , e2023GL107377 (2024).
Weyn, J. A., Durran, D. R. & Caruana, R. Improving data-driven global weather prediction using deep convolutional neural networks on a cubed sphere. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 12 , e2020MS002109 (2020).
Watt-Meyer, O. et al. ACE: a fast, skillful learned global atmospheric model for climate prediction. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.02074 (2023).
Bretherton, C. S. Old dog, new trick: reservoir computing advances machine learning for climate modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 50 , e2023GL104174 (2023).
Reichstein, M. et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 566 , 195–204 (2019).
Brenowitz, N. D. & Bretherton, C. S. Spatially extended tests of a neural network parametrization trained by coarse-graining. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 11 , 2728–2744 (2019).
Rasp, S., Pritchard, M. S. & Gentine, P. Deep learning to represent subgrid processes in climate models. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115 , 9684–9689 (2018).
Yuval, J. & O’Gorman, P. A. Stable machine-learning parameterization of subgrid processes for climate modeling at a range of resolutions. Nat. Commun. 11 , 3295 (2020).
Kwa, A. et al. Machine-learned climate model corrections from a global storm-resolving model: performance across the annual cycle. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 15 , e2022MS003400 (2023).
Arcomano, T., Szunyogh, I., Wikner, A., Hunt, B. R. & Ott, E. A hybrid atmospheric model incorporating machine learning can capture dynamical processes not captured by its physics-based component. Geophys. Res. Lett. 50 , e2022GL102649 (2023).
Han, Y., Zhang, G. J. & Wang, Y. An ensemble of neural networks for moist physics processes, its generalizability and stable integration. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 15 , e2022MS003508 (2023).
Gelbrecht, M., White, A., Bathiany, S. & Boers, N. Differentiable programming for Earth system modeling. Geosci. Model Dev. 16 , 3123–3135 (2023).
Gneiting, T. & Raftery, A. E. Strictly proper scoring rules, prediction, and estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 102 , 359–378 (2007).
Article MathSciNet CAS Google Scholar
Fortin, V., Abaza, M., Anctil, F. & Turcotte, R. Why should ensemble spread match the RMSE of the ensemble mean? J. Hydrometeorol. 15 , 1708–1713 (2014).
Holton, J. R. An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology 5th edn (Elsevier, 2004).
Cheng, K.-Y. et al. Impact of warmer sea surface temperature on the global pattern of intense convection: insights from a global storm resolving model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49 , e2022GL099796 (2022).
Stevens, B. et al. DYAMOND: the dynamics of the atmospheric general circulation modeled on non-hydrostatic domains. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 6 , 61 (2019).
Ullrich, P. A. et al. TempestExtremes v2.1: a community framework for feature detection, tracking, and analysis in large datasets. Geosc. Model Dev. 14 , 5023–5048 (2021).
Eyring, V. et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 9 , 1937–1958 (2016).
Mitchell, D. M., Lo, Y. E., Seviour, W. J., Haimberger, L. & Polvani, L. M. The vertical profile of recent tropical temperature trends: persistent model biases in the context of internal variability. Environ. Res. Lett. 15 , 1040b4 (2020).
Bourke, W. A multi-level spectral model. I. Formulation and hemispheric integrations. Mon. Weather Rev. 102 , 687–701 (1974).
Ruiz, J. J., Pulido, M. & Miyoshi, T. Estimating model parameters with ensemble-based data assimilation: a review. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn Ser. II 91 , 79–99 (2013).
Schneider, T., Lan, S., Stuart, A. & Teixeira, J. Earth system modeling 2.0: a blueprint for models that learn from observations and targeted high-resolution simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44 , 12–396 (2017).
Schneider, T., Leung, L. R. & Wills, R. C. J. Opinion: Optimizing climate models with process knowledge, resolution, and artificial intelligence. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 24 , 7041–7062 (2024).
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O. & Le, Q. V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27 , 3104–3112 (2014).
Haimberger, L., Tavolato, C. & Sperka, S. Toward elimination of the warm bias in historic radiosonde temperature records—some new results from a comprehensive intercomparison of upper-air data. J. Clim. 21 , 4587–4606 (2008).
Bradbury, J. et al. JAX: composable transformations of Python+NumPy programs. GitHub http://github.com/google/jax (2018).
Durran, D. R. Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics: With Applications to Geophysics Vol. 32, 2nd edn (Springer, 2010).
Wang, P., Yuval, J. & O’Gorman, P. A. Non-local parameterization of atmospheric subgrid processes with neural networks. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 14 , e2022MS002984 (2022).
Daley, R. Normal mode initialization. Rev. Geophys. 19 , 450–468 (1981).
Whitaker, J. S. & Kar, S. K. Implicit–explicit Runge–Kutta methods for fast–slow wave problems. Mon. Weather Rev. 141 , 3426–3434 (2013).
Gilleland, E., Ahijevych, D., Brown, B. G., Casati, B. & Ebert, E. E. Intercomparison of spatial forecast verification methods. Weather Forecast. 24 , 1416–1430 (2009).
Rasp, S. & Lerch, S. Neural networks for postprocessing ensemble weather forecasts. Month. Weather Rev. 146 , 3885–3900 (2018).
Pacchiardi, L., Adewoyin, R., Dueben, P. & Dutta, R. Probabilistic forecasting with generative networks via scoring rule minimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 25 , 1–64 (2024).
Smith, J. A., Kochkov, D., Norgaard, P., Yuval, J. & Hoyer, S. google-research/dinosaur: 1.0.0. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11376145 (2024).
Kochkov, D. et al. google-research/neuralgcm: 1.0.0. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11376143 (2024).
Rasp, S. et al. google-research/weatherbench2: v0.2.0. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11376271 (2023).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Kwa, A. Merose and K. Shah for assistance with data acquisition and handling; L. Zepeda-Núñez for feedback on the paper; and J. Anderson, C. Van Arsdale, R. Chemke, G. Dresdner, J. Gilmer, J. Hickey, N. Lutsko, G. Nearing, A. Paszke, J. Platt, S. Ponda, M. Pritchard, D. Rothenberg, F. Sha, T. Schneider and O. Voicu for discussions.
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Dmitrii Kochkov, Janni Yuval, Ian Langmore, Peter Norgaard, Jamie Smith, Stephan Hoyer
Authors and Affiliations
Google Research, Mountain View, CA, USA
Dmitrii Kochkov, Janni Yuval, Ian Langmore, Peter Norgaard, Jamie Smith, Griffin Mooers, James Lottes, Stephan Rasp, Michael P. Brenner & Stephan Hoyer
Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
Milan Klöwer
European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, UK
Peter Düben & Sam Hatfield
Google DeepMind, London, UK
Peter Battaglia, Alvaro Sanchez-Gonzalez & Matthew Willson
School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA
Michael P. Brenner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.K., J.Y., I.L., P.N., J.S. and S. Hoyer contributed equally to this work. D.K., J.Y., I.L., P.N., J.S., G.M., J.L. and S. Hoyer wrote the code. D.K., J.Y., I.L., P.N., G.M. and S. Hoyer trained models and analysed the data. M.P.B. and S. Hoyer managed and oversaw the research project. M.K., S.R., P.D., S. Hatfield, P.B. and M.P.B. contributed technical advice and ideas. M.W. ran experiments with GraphCast for comparison with NeuralGCM. A.S.-G. assisted with data preparation. D.K., J.Y., I.L., P.N. and S. Hoyer wrote the paper. All authors gave feedback and contributed to editing the paper.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Dmitrii Kochkov , Janni Yuval or Stephan Hoyer .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
D.K., J.Y., I.L., P.N., J.S., J.L., S.R., P.B., A.S.-G., M.W., M.P.B. and S. Hoyer are employees of Google. S. Hoyer, D.K., I.L., J.Y., G.M., P.N., J.S. and M.B. have filed international patent application PCT/US2023/035420 in the name of Google LLC, currently pending, relating to neural general circulation models.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature thanks Karthik Kashinath and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended data fig. 1 maps of bias for neuralgcm-ens and ecmwf-ens forecasts..
Bias is averaged over all forecasts initialized in 2020.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Maps of spread-skill ratio for NeuralGCM-ENS and ECMWF-ENS forecasts.
Spread-skill ratio is averaged over all forecasts initialized in 2020.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Geostrophic balance in NeuralGCM, GraphCast 3 and ECMWF-HRES.
Vertical profiles of the extratropical intensity (averaged between latitude 30°–70° in both hemispheres) and over all forecasts initialized in 2020 of (a,d,g) geostrophic wind, (b,e,h) ageostrophic wind and (c,f,i) the ratio of the intensity of ageostrophic wind over geostrophic wind for ERA5 (black continuous line in all panels), (a,b,c) NeuralGCM-0.7°, (d,e,f) GraphCast and (g,h,i) ECMWF-HRES at lead times of 1 day, 5 days and 10 days.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Precipitation minus evaporation calculated from the third day of weather forecasts.
(a) Tropical (latitudes −20° to 20°) precipitation minus evaporation (P minus E) rate distribution, (b) Extratropical (latitudes 30° to 70° in both hemispheres) P minus E, (c) mean P minus E for 2020 ERA5 14 and (d) NeuralGCM-0.7° (calculated from the third day of forecasts and averaged over all forecasts initialized in 2020), (e) the bias between NeuralGCM-0.7° and ERA5, (f-g) Snapshot of daily precipitation minus evaporation for 2020-01-04 for (f) NeuralGCM-0.7° (forecast initialized on 2020-01-02) and (g) ERA5.
Extended Data Fig. 5 Indirect comparison between precipitation bias in X-SHiELD and precipitation minus evaporation bias in NeuralGCM-1.4°.
Mean precipitation calculated between 2020-01-19 and 2021-01-17 for (a) ERA5 14 (c) X-SHiELD 31 and the biases in (e) X-SHiELD and (g) climatology (ERA5 data averaged over 1990-2019). Mean precipitation minus evaporation calculated between 2020-01-19 and 2021-01-17 for (b) ERA5 (d) NeuralGCM-1.4° (initialized in October 18th 2019) and the biases in (f) NeuralGCM-1.4° and (h) climatology (data averaged over 1990–2019).
Extended Data Fig. 6 Yearly temperature bias for NeuralGCM and X-SHiELD 31 .
Mean temperature between 2020-01-19 to 2020-01-17 for (a) ERA5 at 200hPa and (b) 850hPa. (c,d) the bias in the temperature for NeuralGCM-1.4°, (e,f) the bias in X-SHiELD and (g,h) the bias in climatology (calculated from 1990–2019). NeuralGCM-1.4° was initialized in 18th of October (similar to X-SHiELD).
Extended Data Fig. 7 Tropical Cyclone densities and annual regional counts.
(a) Tropical Cyclone (TC) density from ERA5 14 data spanning 1987–2020. (b) TC density from NeuralGCM-1.4° for 2020, generated using 34 different initial conditions all initialized in 2019. (c) Box plot depicting the annual number of TCs across different regions, based on ERA5 data (1987–2020), NeuralGCM-1.4° for 2020 (34 initial conditions), and orange markers show ERA5 for 2020. In the box plots, the red line represents the median; the box delineates the first to third quartiles; the whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range (Q1 − 1.5IQR and Q3 + 1.5IQR), and outliers are shown as individual dots. Each year is defined from January 19th to January 17th of the following year, aligning with data availability from X-SHiELD. For NeuralGCM simulations, the 3 initial conditions starting in January 2019 exclude data for January 17th, 2021, as these runs spanned only two years.
Extended Data Fig. 8 Tropical Cyclone maximum wind distribution in NeuralGCM vs. ERA5 14 .
Number of Tropical Cyclones (TCs) as a function of maximum wind speed at 850hPa across different regions, based on ERA5 data (1987–2020; in orange), and NeuralGCM-1.4° for 2020 (34 initial conditions; in blue). Each year is defined from January 19th to January 17th of the following year, aligning with data availability from X-SHiELD. For NeuralGCM simulations, the 3 initial conditions starting in January 2019 exclude data for January 17th, 2021, as these runs spanned only two years.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Information (38 figures, 6 tables): (A) Lines of code in atmospheric models; (B) Dynamical core of NeuralGCM; (C) Learned physics of NeuralGCM; (D) Encoder and decoder of NeuralGCM; (E) Time integration; (F) Evaluation metrics; (G) Training; (H) Additional weather evaluations; (I) Additional climate evaluations.
Peer Review File
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kochkov, D., Yuval, J., Langmore, I. et al. Neural general circulation models for weather and climate. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07744-y
Download citation
Received : 13 November 2023
Accepted : 15 June 2024
Published : 22 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07744-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Google ai predicts long-term climate trends and weather — in minutes.
- Helena Kudiabor
Nature (2024)
Weather and climate predicted accurately — without using a supercomputer
- Oliver Watt-Meyer
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: AI and Robotics newsletter — what matters in AI and robotics research, free to your inbox weekly.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How to format multiple authors name, affiliation and email in a paper?
I am writing a paper with my teacher and his teacher. I don't know the standard of writing authors name, affiliation and email in the paper. I am using IEEEtran template for an IEEE conference. If the authors are in different department or university there is no problem we can use column author name like this:
but what if two of them be in a same department and just two of them has a .edu email address? In this situations we can use another style like this:
or it should be like this?
My question is this: What is the right format in this case when different authors with different affiliation, department and email should be on a paper?
In my specific, we all are from the same Univ. and Department but they both have .edu email and I don't have one.
Thanks in advance.
- publications
- affiliation
- Is your question how to format addresses using the IEEEtran template? If so, then this question probably belongs on the TeX Stack Exchange board instead of this one. – aeismail Commented Aug 16, 2013 at 15:30
- @aeismail That was what I had doubt for. but I know how to use tex to write any of those forms. I am looking for the format standard no matter it is latex or word template. – sajjadG Commented Aug 16, 2013 at 15:47
- 3 There is no universal format standard. As F'x suggests, you need to use the format prescribed by the organization you're submitting to (and an organization like IEEE should definitely have one). – aeismail Commented Aug 16, 2013 at 19:23
- 2 I would just do something easy to read and unambiguous. If there are some standards, you'll be informed of those by the editors at some point but, most likely, everything not offending the eye will pass. – fedja Commented Aug 16, 2013 at 21:12
- I don't understand. What's wrong with the first format? So what if Department One and Department Two are identical? Ink is cheap! – JeffE Commented Aug 26, 2013 at 2:25
2 Answers 2
We had a similar complicated case in our paper . I'd suggest this as a good way to do it.
For your own case, add a comma after the braces, followed by your email.
Here's how it would look like:
I am assuming your username tells the reader that it is yours (has your lastname, initials or so). Additionally, do your best to sort the emails such that they follow the same order of authors.
Just look up previous conference proceedings and do the same!
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged publications email authorship affiliation ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Is there a way to skip frames in beamer?
- How Can this Limit be really Evaluated?
- How would increasing atomic bond strength affect nuclear physics?
- What did the Ancient Greeks think the stars were?
- What is this strengthening dent called in a sheet metal part?
- What' the intuition behind Shankar's postulate II?
- How to attach a 4x8 plywood to a air hockey table
- How do I safely remove a mystery cast iron pipe in my basement?
- What happens if all nine Supreme Justices recuse themselves?
- Is it advisable to contact faculty members at U.S. universities prior to submitting a PhD application?
- Story where character has "boomerdisc"
- Can I use "historically" to mean "for a long time" in "Historically, the Japanese were almost vegetarian"?
- ApiVersion 61.0 changes behaviour of inheritance (cannot override private methods in inner class)
- High CPU usage by process with obfuscated name on Linux server – Potential attack?
- Simple casino game
- How are notes named in Japan?
- Are quantum states like the W, Bell, GHZ, and Dicke state actually used in quantum computing research?
- What is the name of the book about a boy dressed in layers of clothes who is actually a mouse?
- Are there any theoretical reasons why we cannot measure the position of a particle with zero error?
- What is the spiritual difference between hungering and thirsting? (Matthew 5:6)
- What would the appropriate cost be for a magical set of full plate with a Cast On and Cast Off property?
- How long does it take to achieve buoyancy in a body of water?
- Sci-fi short story about a dystopian future where all natural resources had been used up and people were struggling to survive
- What would be non-slang equivalent of "copium"?

Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Author affiliation in research papers tells readers where the research was conducted. However, many authors move to a different institution or location after submission and are unsure how to mention changed affiliations for journal publication. This article answers top researcher questions on how to handle author affiliations in research papers.
Author and affiliation. One of the first things to look for is the author or authors. In a research article, the authors will list their affiliation, usually with a university or research institution. In this example, the author's affiliation is clearly shown on the first page of the article. In a research article, you will never have an ...
Convention of Listing Affiliations. Listing affiliations in research papers is a widely recognized convention. It's a practice that is expected within the academic community and publishing industry. When authors adhere to this convention, they demonstrate their commitment to transparency and accountability.
Mentioning affiliation and address. Authors of research papers must keep an important distinction in mind: that an affiliation is not the same thing as a mailing address. The former names the institution at which the work in question was carried out whereas the latter simply supplies the current contact details of the author. For example…
If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the Publication Manual for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). Tracy Reuter 1, Arielle Borovsky 2, and Casey Lew-Williams 1. Author affiliation For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted.
The student version of the APA title page should include the following information (double spaced and centered): Paper title. Author name. Department and university name. Course number and name. Instructor name. Due date of the assignment. The professional title page also includes an author note (flushed left), but not a course name, instructor ...
It is very important to make sure people who have contributed to a paper, are given credit as authors. And also that people who are recognized as authors, understand their responsibility and accountability for what is being published. There are a couple of types of authorship to be aware of. Co-author. Any person who has made a significant ...
Note that publishers seldom allow changes on affiliations once the paper is accepted, and it takes time and effort for both authors and publishers to communicate and rectify the wrong data. Authors are therefore advised to check and display correct affiliation data in their publications to minimise problems with authorship misattribution, paper ...
11. You should be able to put both affiliations on. I assume you are permanently employed, in which case that is more permanent than the academic address. However, if your published work is done as part of your schooling you should put that affiliation first, perhaps listing your job affiliation/address as "permanent" or something describing ...
If authors have multiple affiliations, all affiliations must be entered (as separate entries). This includes multiple departments within the same university/institution/. Do not use short forms or acronyms. Do not abbreviate "Dep." or "Dept.". An affiliation like "Nursing" should be changed into "Department of Nursing", and acronyms like "UHN ...
So, for example, search ing "young adult" is going to search for that intact phrase, whereas search ing young adult, without quotation marks, will look for articles that have young and adult anywhere in the article, regardless of how apart those two words might be in the article (e.g., it could retrieve an article that says, "The young polar ...
Include a cover letter and complete contact information for the corresponding author (affiliation, postal/mail address, email address, and telephone number) ... Example of Research Article. ... The preceding 3 sections are usually combined for accepted papers during the editing process as "Design, Setting, and Participants," but for manuscript ...
Types of Documentation for Affiliation Change: Step 3: Contact the Journal or Publisher. Advice on Contacting the Journal or Publisher: Step 4: Submit a Correction or Erratum. Process of Submitting a Correction or Erratum: Step 5: Review and Approval. Journal's Role in Reviewing the Correction or Erratum:
Authors should use their current or recent affiliation in Author forms, and the affiliation that applied mostly when the manuscript was being prepared/ research was undertaken in the proofs of the paper. Proof Central makes it possible to change the author list, including the affiliations and the associated footnotes.
Speaking very generally, intellectual property is shared between the author (who understands and can reproduce the work) and the affiliation (which paid for it), so it's important to list both. Being affiliated with a well-known research group will lend credibility to your work; the quality of the paper will also reflect on the group.
Rapid Response: The fact that the affiliation of authors could influence readers/reviewers has been highlighted by Matthew Harris in a Personal View (1). It has also been suggested that research papers should omit their authors' affiliations. Nevertheless, we assume that, although the presence of authors' affiliations in the articles could ...
Alternatively, you can list yourself without affiliation (since you currently don't have one) but include a footnote/acknowledgment, "Portions of this research were done while the author was a student at Unseen University and a visitor at Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry."
An example of the later is Elsevier's Energy Economics journal that states: "Present the authors' affiliation ... B but you complete the paper in your research time at affiliation B, then A and B ...
Journals and research institutions rarely provide guidance or standards on the definition of "deserving" affiliations or the number of affiliations per author on a publication. Multiple undeserved affiliations may be considered as research malpractice and may affect different stakeholders and the integrity of the published record.
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps writers present their ideas in a clear, concise, and inclusive manner. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably. People are described using language that affirms their worth and dignity.
Normally, if you are a student, your affiliation will be the school / college / university that you attend (or if you have recently changed institutions, the one you attended when you did the work and wrote the paper).
Stack Exchange Network. Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.. Visit Stack Exchange
For example, NeuralGCM-1.4 ... Authors and Affiliations. Google Research, Mountain View, CA, USA ... I.L., P.N. and S. Hoyer wrote the paper. All authors gave feedback and contributed to editing ...
I am writing a paper with my teacher and his teacher. I don't know the standard of writing authors name, affiliation and email in the paper. I am using IEEEtran template for an IEEE conference. If the authors are in different department or university there is no problem we can use column author name like this:
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about "Trump's Project 2025" agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn't claim the ...