- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial

Basic Applications of Computers
The term computer was taken from the Greek word compute means calculation and the computer was a person or device that did computation. In this article, we will learn what exactly a computer is, how it affects our lives, and the applications of computers in our life.
What is a Computer?
A computer is a machine used to manipulate data or information and perform mathematical and logical operations. Modern computers perform a wide range of tasks, store retrieve, and process information. Using a computer we can create/modify documents, send/receive emails, browse information on the internet , and play video games. After the invention of computer science and technology became too advanced. Today we can not imagine growing our technology without computers.
Components of the Computer System
The various components of the computer system are classified into two groups.
1. Hardware
Hardware is the physical tangible component of the computer system. This type of component is touchable. CPU , Mouse, Keyboard are examples of hardware components. So, the hardware of the computer system are:
- Input Device: Input devices allow the user to enter data/information in the CPU (Central Processing Unit). Mouse, Keyboard, scanner, barcode reader are general examples of input devices.
- Output Device: Output devices input the processed data/information into human-readable form. Monitor, speaker, projector, printer are general examples of output devices.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is referred to as the brain of a computer system. It is used to processed data/information and provides output to output devices. The CU (control unit), ALU (arithmetic and logical unit), and registers are components of the CPU.
- Storage: In a computer, storage devices are used to store the data or information that entered into the computer system and the output comes from processing the information or data.
2. Software:
Software is a collection of programs (set of instructions), data, and protocols. It is not in material form so we can not touch such types of components. The execution of software programs is performed by hardware. Firmware , operating systems , applications are examples of software.
Features of Computer
Now we will discuss the features of the computer:
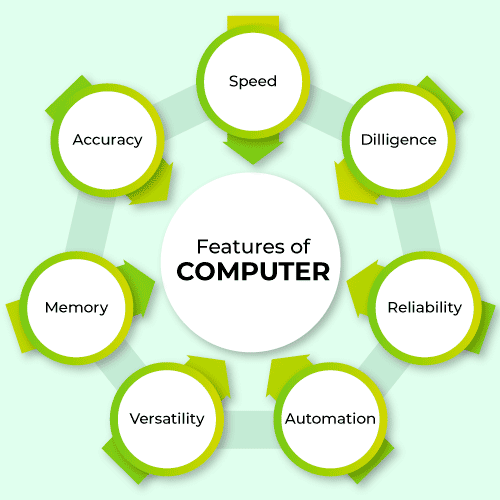
- Speed: A computer is a time-saving device. It performs several calculations and tasks in few seconds that we take hours to solve. The speed of a computer is measure in terms of GigaHertz and MegaHertz.
- Accuracy: A calculation or task performed by a computer is accurate the chances of occurring errors are minimal. The errors occur in a computer by entering wrong data by a human being. A computer performs several tasks and calculations so quickly and accurately.
- Memory: A computer can store billions of records as per requirement and these records can easily accessible with full accuracy. The storing capacity of computer memory is measured in terms of Bytes, Kilobytes (KB), Megabytes (MB), Gigabyte(GB), and Terabyte(TB).
- Versatility: A computer can perform more than one task at the same time, this feature is called versatility. For example, we can create our project using PowerPoint and Wordpad while listening to music or we can design a website while listening to music.
- Automation: Today the world is moving toward AI (Artificial Intelligence) based technology. Once instructions are programmed, a computer can perform work automatically. This feature of the computer replaces thousands of workers by performing tasks automatically.
- Reliability: A computer is a reliable device. The output results never differ until the input is different. If an input is the same then output won’t be different.
- Diligence: A human can not work for several hours without taking a rest whereas a computer device never gets tired. A computer can perform millions of calculations constantly with full accuracy without taking a rest.
Computers are used in every field of life, such as homes, businesses, educational institutions, research organizations, the medical field, government offices, entertainment, etc. Today we can not imagine growing our technology without computers. The various field where the computer is very essential are:
Today computer is the primary work tool in the field of science. It is the best-suited machine for collecting, analyzing, classifying, and storing data. It becomes the most essential medium to spread knowledge internally and internationally. It allows scientists from different locations to work together and share ideas on the same project.
Defence System
A computer performs a vital to control defense system. Computers are used to track airplanes, missiles, tanks, and different kinds of weapons. Once the radar system tracks a missile and artificial intelligence is programmed to target a missile and destroy it before it comes on the surface. It also used for GPS tracking, controlling defense vehicles, records of all members of the military.
The computer plays a very important role in medical science such as record patients’ information monitoring heart rate, oxygen level, and blood pressure. To conduct various surgeries junior doctors get the help of another professional doctor by web conferencing. Research is also spread with the help of computers in the health sector.
Today learning becomes easy because of computers. Anyone employed or student can learn any stage of life with the help of a computer. Computers are very crucial for online classes, download study material on the internet . Computers are also used to track student attendance and learning strategies. Coaching and institutes increased their areas by audio-visual aids using computers.
A computer performs a crucial role in banking sectors, by storing several account holder details on a bank server. All transactions such as deposits and withdrawals perform by a computer. A banking company can easily monitor all ATMs and passbook printing machines.
Government Sectors
Government can easily monitor government sectors such as road services, railway, development, and other rising funds. The information of every citizen is stored on the server through the computer.
Entertainment
Today most people are so busy and they do not easily get time to fresh their mind. We can play various interesting video games using a computer. We can watch movies, TV shows, and reality shows on the computer. A computer is also used to create sarcastic memes and make us happy.
FAQs on Basic Applications of Computers
Q.1: what is a computer program.
A computer is a machine used to manipulate data or information and perform mathematical and logical operations. computer system execute or perform some operation and gave the result that operation is called program.
Q.2: Write three components of computer hardware?
These are the following three main components of computer hardware. Input Device Output Device CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Q.3: How have computers impacted education?
Now a days, computers used in education sector by providing E-learning platforms, online classes, and video conferencing tools. By using these technologies you can access to courses, learning content, and interactive learning experiences, making education more interactive.
Q.4: Write three popular operating systems of computer?
These are the following three popular operating systems. Microsoft Window Ubuntu Mac OS

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Programming
- Top Android Apps for 2024
- Top Cell Phone Signal Boosters in 2024
- Best Travel Apps (Paid & Free) in 2024
- The Best Smart Home Devices for 2024
- 15 Most Important Aptitude Topics For Placements [2024]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Introduction to Computer Application
Published by Suparman Lesmana Modified over 7 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Introduction to Computer Application"— Presentation transcript:

4.03 IT PowerPoint Objective 4.03—Understand Information Technology activities and careers.

Slide 1 Program Pasca Sarjana Magister Manajemen Universitas Gunadarma Introduction to Computer Application I Hustinawaty

McGraw-Hill/Irwin ©2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Plug-in B3 HARDWARE & SOFTWARE.

ICS103 Programming in C Lecture 1: Overview of Computers & Programming

Lecture 1: Overview of Computers & Programming

Essential Introduction to Computers. What is a Computer? An electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory, that.

Data Communications and Computer Networks

Chapter 1. What is computer fluency? The knowledge possessed by people who are able to navigate the digital world successfully NOT THIS.

Office 2003 Introductory Concepts and Techniques M i c r o s o f t CPTG104 Intro to Information Systems Dr. Hwang Essential Introduction to Computers.

Computer Parts There are many parts that work together to make a computer work.

Introduction to Computers Essential Understanding of Computers and Computer Operations.

Information Technology Ms. Abeer Helwa. Computer Generations First Generation (Vacuum Tubes) -They relied on the machine language to perform operations.

CS102 Introduction to Computer Programming

Introduction to Computers and Python. What is a Computer? Computer- a device capable of performing computations and making logical decisions at speeds.

CS 161 INTRO TO PROGRAMMING I Dr. Blaise W. Liffick Fall

BASIC COMPUTER CONCEPTS What is a computer? An electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory unit, that can.

Introduction to the Computer System. What is a computer ? A computer is an electronic device that can accept data and instruction, process them or store.

Microsoft Office 2007 Essential Introduction to Computers.

Computer Parts. Two Basic Parts Hardware & Software.

1 California State University, Fullerton Chapter 1 Information Systems in Business.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Computer Fundamentals and Programming in C
Reema Thareja, Assistant Professor, Institute of Information Technology and Management
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
1 st gen-1940-56
2 nd gen 1956-63
3 rd -64-71
4 th —72-89
5 th -mordern day
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SOFTWARE
- A computer is a machine that takes instructions and performs computations based on those instructions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS
The word generation means the state of improvement in the product development process. Similarly, computer generation refers to the different advancements of new computer technology.
First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes
The first generation computers used very large number of vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory.
UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are prime examples of first-generation computing devices.
Advantages: Fastest calculating device of their time
Disadvantages:
1. Dissipate a lot of heat
2. Consume a lot of electricity
3. Very bulky in size
4. These computers were frequently down due to hardware failures.
5. These computers needed constant maintenance because of low mean time between failures
6. Limited commercial use because these computers were difficult to program
7. Very expensive
Second Generation (1956-1963) Transistors
- The second generation computers were manufactured using transistors.
- While first generation computers were programmed using machine language, second generation computers moved towards symbolic, or assembly languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words.
- At this time, high-level programming languages like COBOL, FORTRAN, ALGOL and SNOBOL were also being developed.
- Second generation computers were first to store instructions in memory, which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology.
- Second generation computers were first developed for the atomic energy industry.
Advantages:
1. Consumed less electricity and thus dissipated less heat as compared to first generation computers
2. Faster, cheaper smaller and more reliable than first generation computers
3. Could be programmed using assembly language and high level languages
4. These computers had faster primary memory and a larger secondary memory
1. Second generation computers were manufactured using transistors that had to be assembled manually. This made commercial production of computers difficult and expensive.
Third Generation (1964-1971) Integrated Circuits
- The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
- These computers had few megabytes of main memory and magnetic disks which could store few tens of megabytes of data per disk drive.
- High level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were standardized by ANSI
- Some more high level programming languages like PL/I PASCAL and BASIC were introduced at this time.
- Third generation computers were the first to implement time sharing operating systems.
- Input to these computers could now be provided using keyboards and mouse.
- Faster than second generation computers and could perform 1 million transactions per second.
2. Smaller, cheaper and more reliable than their predecessors
3. These computers had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They were widely used for scientific as well as business applications
5. During this generation of computers, standardization of existing high level languages and invention of new high level languages was done
6. These computers had time sharing operating system which allowed interactive use of computer by one or more users simultaneously thereby improving the productivity of the users.
Fourth Generation (1971-1989) Microprocessors
- The microprocessor started the fourth generation of computers with thousands of integrated circuits built onto a single silicon chip.
- Semi-conductor memories were used which were very fast, even the hard disks became cheaper, smaller in size and larger in capacity.
- For input, floppy disks (in addition to magnetic tapes) were used to port data and programs from one computer to another.
- During this period many new operating systems were developed like MS-DOS MS-Windows UNIX and Apple’s proprietary operating system.
- Development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
- In this period, several word processing packages, spreadsheet packages and graphics packages were introduced.
1. Smaller, cheaper, faster and more reliable
2. Consumed less electricity and therefore dissipated less heat
3. They had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They could be used as general purpose computers.
5. GUIs enabled people to learn to work with computers very easily. So the use of computers in both office and home became widespread.
6. Networks allowed sharing of resources thereby efficient utilization of computer hardware and software
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond) Artificial Intelligence
- The fifth generation computers are completely based on a new concept of artificial intelligence.
- Although such computers are still in development, there are certain applications like voice recognition which is widely being used today.
- In the fifth generation of computers the aim is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
- The two most common are LISP and Prolog.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold and price.
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold, and price .
Classification of Computers
Super Computer
Mini Computers
Mainframe Computers
Micro Computers
Intelligent Terminal
Dumb Terminal
Workstation
Cellular Telephones
H/PC Pro Devices
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS
- Word Processing
- Digital Audio or Video Composition
- Desktop Publishing
- Traffic Control
- Legal System
- Retail Business
- Travel and Tourism
- Business and Industry
- Weather Forecasting
- Online Banking
- Industry and Engineering
- Decision Support Systems
- Expert Systems
BASIC ORGANIZATION OF A COMPUTER
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes:
1) accepts data or instructions (input)
2) stores data
3) process data
4) displays results (output) and
5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer
CONTROL UNIT
ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT
Data and instructions
Flow of data and instructions
Control exercised by control unit

Computers and Applications
Mar 23, 2019
3.28k likes | 7.95k Views
Computers and Applications. CCNA Discovery: Chapter 1. Contents. Section 1-1: Computer Systems Applications Types of Computers Binary Numbers Section 1-2 Computer System Requirements Computing Devices Installations and Upgrades. Computer Systems.
Share Presentation
- binary number
- network applications
- portable devices
- section 1 1
- 000 mb hard drives

Presentation Transcript
Computers and Applications CCNA Discovery: Chapter 1
Contents Section 1-1: • Computer Systems • Applications • Types of Computers • Binary Numbers Section 1-2 • Computer System Requirements • Computing Devices • Installations and Upgrades
Computer Systems • In order for a computer system to operate, these 3 components must work together • Hardware • Operating System software • Application Software
Hardware • Hardware- the physical components of the computer, or the electronic pieces that make up a computer system • Hardware includes external and internal components
Software • Software - the programs that tell the computer what to do • Operating System software is a set of computer programs that manages the hardware of a computer. • An operating system controls the resources on a computer, including memory and disk storage. • Examples: Windows XP, Windows Vista, Linux, Mac OS
Application Software • Application software is a program loaded on the computer that performs a specific task for a user or another application. • Examples: word processor, web browser, graphics editor, spreadsheet, mail reader
Applications • The computer is only as useful as the program or application on it. • Applications can be divided into two general categories: • Business/Industry Software – designed to be used by specific businesses • Examples: The Medical industry, CAD programs • General Use Software – designed for a wide range of users • Example: Graphic Editors, Office Suites
Local vs. Network Applications • Local applications - Programs, such as word processors, that are stored on the hard disk of the computer. • The application runs only on that computer. • Network applications – Programs that are designed to run over a network, such as the Internet. • A network application has two components, one that runs on the local computer and one that runs on a remote computer. • Server: runs on the remote computer • Client: runs on the local computer • Examples: Email, Web browser, FTP, File Sharing • Most computers have a combination of local and network applications installed.
Classes of Computers • There are many different types of computers available including: • Mainframes • Servers • Desktops • Workstations • Laptops • Hand-held portable devices • Each type of computer is designed with a particular purpose in mind
Mainframes • Mainframes: a mainframe is a large, powerful computer stored in a secure location, which allows users access through dumb terminals • Dumb terminals usually consist of just a monitor, keyboard, and a communication port to the mainframe • Mainframes are very secure because management is centralized and users have very little control over the system • Although mainframes are expensive, the use of dumb terminals can be a low cost alternative to providing users with complete computer systems
Servers • Servers are high performance computers used in businesses and other organizations. • Servers provide services to many end users or clients. • Services: file storage, email storage, web pages, print sharing • Servers usually have specialized hardware that is optimized for quick response time to multiple network requests. • multiple Central Processing Units (CPUs) • large amounts of Random Access Memory (RAM) • multiple high capacity disk drives
Redundancy and Security • The services provided by a server are often important and may need to be available to users at all times. • Servers, therefore, often contain duplicate, or redundant, parts to prevent them from failing. • Automatic and manual backups of data are also usually done on a regular basis. • Servers are usually kept in secure areas where access is controlled.
Server Design • Servers come in many different designs • standalone tower design • rack mounted • blade design. • A server is typically used as a storage point and not a day-to-day end-user device, so it may not have a monitor or keyboard, or may share a monitor and keyboard with other devices
Desktops • Desktop PCs: a desktop PC is a stand-alone computer, that is not dependent on other computers to operate • Desktop PCs are cheaper than mainframe systems, and allow users to use a GUI (graphical user interface) instead of text-based entry • They are also standardized in terms of hardware and operating systems • Desktops support many different types of hardware and application software
Workstations • Workstations are high-powered business computers that are designed for specialized, high-end applications • Engineering programs like CAD • 3-D graphics design • Video animation • Virtual reality simulation. • They may also be used as management stations for telecommunications or medical equipment. • Workstation Hardware is usually more advanced than a desktop PC: • multiple CPUs • large amounts of RAM • multiple, high-capacity disk drives • powerful graphics capabilities • large monitor or multiple monitors
Portable Devices Portable devices vary in size, power and graphic capability: • Laptop or notebook PC • Tablet PC • Pocket PC • Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) • Gaming device • Cell phones • Laptops are comparable to desktops in usage and processing capability. • Built to be lightweight and use less power • Many hardware is built-in: mouse, monitor and keyboard • Have a limited number of configurations available, such as video options and connection types • Not as easily upgradeable as the desktop
PDAs and Pocket PCs • PDAs and pocket PCs have less hardware capabilities • less powerful CPUs than a laptop • less RAM than a laptop • small screens with limited display capabilities • small input keyboard. • Multi-Function Devices: • combines a PDA, cell phone, digital camera, and music player • provides Internet access and wireless networking capability • limited processing power similar to the PDA • Advantages of Portable Computers: • information and services are available immediately, almost anywhere
Binary • In a computer, information is represented and stored in a digital binary format. • Computers are electronic devices, made up of millions of tiny circuits, which act like switches • Each switch can have 2 states: on or off • A computer relies on the binary number system to process data: it uses the numbers 1 and 0 to represent on and off • Everything that is done on a computer must be translated into a series of 1’s and 0’s, so the computer can interpret it • The term bit is an abbreviation of binary digit and represents the smallest piece of data – a 1 or 0
ASCII Code • Computers use binary codes to represent and interpret letters, numbers and special characters with bits. • The ASCII Code is used to represent each character as a string of bits. • Each character is assigned a number, which is then converted to binary • Capital letter: A = 01000001 • Number: 9 = 00111001 • Special character: # = 00100011
ASCII Chart
Data Capacity • Information or data capacity in computers is measured in terms of the bit • Each group of eight bits, such as the representations of letters and numbers, is known as a byte. Unit Measurement Used to measure bit a 0 or 1 a binary decision byte 8 bits 1 character Kilobyte (KB) 1,000 bytes text documents Megabtye (MB) 1 million bytes (1,000 kb) multimedia files, RAM Gigabyte (GB) 1 billion bytes (1,000 mb) hard drives, DVDs Terabyte (TB) 1 trillion bytes (1,000 gb) High capacity drive Petabyte (PB) 1,000 terabytes (250 bytes) National databases Exabyte (EB) 1 billion GB (1 quintillion bytes) all words ever spoken = 5 EB Note: 1kb = 1 kilobit while 1KB = 1 kilobyte
Bandwidth • Bandwidth is a measurement of how much information can be transferred within a particular period of time • Bandwidth is measured in terms of bits per second Kilobits per Second (Kbps) KiloBytes per Second (KBps) Megabits per Second (Mbps) MegaBytes per Second (MBps) Gigabits per Second (Gbps) GigaBytes per Second (GBps)
Bandwidth Calculations: Download Time = Size of File Bandwidth Example: How long would it take to transfer a 10 MB file over 1.54 Mbps connection? Time =10 MB 1.54 Mbps (10 MB x 8) = 80 Mb 1.54 Mb/s Time =80 Mb 1.54 Mb/s Time =80 1.54 s Time =52 seconds
Decimal Numbering System Example: 2134 = (2x103) + (1x102) + (3x101) + (4x100)
Binary Numbers • The binary number system uses only two symbols – 0 and 1 – instead of the ten symbols used in the decimal numbering system. • The position, or place, of each digit represents the number 2 – the base number – raised to a power (exponent), based on its position (20, 21, 22, 23, 24, etc.)
Binary Numbering System
256: The magic number • How many different number combinations can be made with 8 bits? • If you do the math you will see that 8 bits, or 1 byte, can represent 256 different values • The numbers 0 to 255 = 256 possible values • The number 256 is important in computing: • the RGB color scheme contains 256 values for each of red, green, and blue.
Binary to Decimal Conversion 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 10011001 = • Write out each bit in the binary number over its place value • Multiply out each bit value (0 or 1) by its place value (ex. 1 x 128) • Add up all the numbers to get the decimal equivalent = (1 x 128) + (0 x 64) + (0 x 32) + (1 x 16) + (1 x 8) + (0 x 4) + (0 x 2) + (1 x 1) = 128 + 0 + 0 + 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 153
Decimal to Binary Conversion • Divide the Decimal number by the highest order bit in the 8-bit binary number (the 128th place) • If the decimal number can be divided at least once by the place value (ex. 200 / 128), then put a 1 in that place value, and carry the remainder • If the number can not be divided by the place value, put a 0 in that place value and carry the remainder • Continue to divide the decimal number by each binary place value, until you get to the 1’s place Example: Convert the decimal number 199 to a binary number. R71 R7 R3 R1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 199 =
Counting in Binary • It is very useful to be able to count in binary, at least up to the number 15, when working with computers and networks • Counting in binary is usually done using only the 4 least-order bits • the first 4 bits on the right side of an 8 bit number are called the least-order bits • These represent the 8’s, 4’s, 2’s and 1’s place • The 4 high-order bits on the left (128, 64, 32 and 16 place) are assumed to be all 0’s, therefore they can be left out.
Binary Counting Full Binary Decimal Binary Counting 00000000 0 0000 00000001 1 0001 00000010 2 0010 00000011 3 0011 00000100 4 0100 00000101 5 0101 00000110 6 0110 00000111 7 0111 00001000 8 1000 00001001 9 1001 00001010 10 1010 00001010 11 1011 00001100 12 1100 00001101 13 1101 00001110 14 1110 00001111 15 1111
Bit Patterns • As you start working with IP addresses and subnets, it will be very useful to learn to recognize some common bit patterns that are used in computing and networking. • Common bit Patterns in Networking: • 10000000 = 128 • 11000000 = 192 • 11100000 = 224 • 11110000 = 240 • 11111000 = 248 • 11111100 = 252 • 11111110 = 254 • 11111111 = 255
Computer System Requirements • There are many types of computers. • What makes one computer better for a certain task are the components and peripherals that make up the computer system. • It is important to determine the intended uses for a computer before deciding on the type of computer and components to purchase. • The final product must match the requirements of the end user.
Important Components • Important components to consider when purchasing a computer: • Motherboard • Processor • RAM • Storage • Adapter cards • Case • Power Supply
Purchase Options When purchasing a computer, there are 2 main options: • Preassembled computers • Custom Built computers Each option has its advantages and its disadvantages
Preassembled Computers Advantages: • Lower cost • Adequate to perform most applications • No waiting period for assembly • Typically used by less knowledgeable consumers who do not require special needs Disadvantages: • Often lack the performance level that can be obtained from custom built computers
Custom Built Computers Advantages: • The end-user can specify exact components that meet user needs • Generally support higher performance applications such as graphics, gaming, and server applications Disadvantages: • Generally more costly than a preassembled device • Longer waiting periods for assembly
Computing Devices • A computer performs 4 main tasks, and each requires a different type of hardware device • Input Devices: • Allow the user to give data to the computer • Input devices include: keyboard, mouse, scanner, tablet, microphone • Processing Device: • Reads and executes data and instructions • Data must be read, organized and checked for accuracy • The CPU (central processing unit) performs this task • Output Devices • Allow the computer to give data back to the user • Output devices include: monitor, printer, speakers • Storage Devices • Allows data to be stored for use at a later date • Storage devices include :hard drive, floppy drive, CD/DVD burner, flash drives, tape backups
Types of Computing Devices There are 4 types of Computing Devices: Input Output storage networking devices Examples: Input devices - trackball, joystick, scanner, digital camera, digitizer, barcode reader, microphone Output devices - printer, plotter, speakers, headphones Storage devices - secondary hard drive, external CD/DVD devices, flash drives Networking - external modems, external NIC
Motherboard • The motherboard is a large circuit board used to connect the electronics and circuitry that make up the computer system. • Motherboards contain connectors which allow major system components such as the CPU and RAM to attach to the board. • The motherboard moves data between the various connections and system components. • A motherboard can also contain connector slots for network, video and sound cards. • Many motherboards now come equipped with these features as integrated components.
Choosing a Motherboard When selecting a motherboard it must: • Support the selected CPU type and speed • Support the amount and type of system RAM required by the applications • Have sufficient slots of the correct type to accept all required interface cards • Have sufficient interfaces of the correct type
Central Processing Unit (CPU) • The CPU is the nerve center of the computer system. • It is the component that processes all of the data within the machine. • The type of CPU should be the first decision made when building or updating a computer system. • Important factors when selecting a CPU are: • processor speed • bus speed • Socket type – must be compatible with the mobo
Processor Speed • Processor speed measures how fast a CPU cycles information • Usually measured in MHz or GHz • The higher the speed the faster the performance • Faster processors consume more power and create more heat • Mobile devices, such as laptop computers, typically use processors that are slower and consume less power in order to extend the time they can operate using batteries.
Bus Speed • CPUs transfer data between various types of memory on the system board during its operation. • The Bus is the pathway for this movement of data • The faster the bus, the faster the computer will be
Choosing a CPU • When selecting a CPU, keep in mind that applications continue to evolve, if the CPU is not sufficiently fast, the overall performance, measured in terms of response time, will be slower. • The CPU is mounted through a socket on the motherboard and is normally the largest component on the board. • The motherboard must be equipped with a compatible socket to accept the selected CPU.
Random Access Memory (RAM) • RAM is the temporary data storage in a computer • It is used to store data and instructions that are currently being processed by the CPU. • Data in RAM is accessed in any order, or at random, as needed. • All computer programs run from RAM. • Besides the CPU, the amount of RAM is the most important factor in computer performance.
Choosing RAM • When choosing how much RAM to put in a computer, you should consider the following: • The amount of Multi-Tasking required • Most computers are capable of running multiple applications simultaneously, or multi-tasking. • All of these applications require memory. • The more applications that need to run simultaneously, the more RAM required. • How many processors the system has • More RAM is needed for multiple processor systems • CPU and bus speed • A faster CPU and bus require more RAM • The RAM configuration that the motherboard will support
Adapter Cards • Adapter cards add functionality to a computer system. • They plug into a connector or slot on the motherboard • Many motherboards have built-in components that perform the same functions as adapter cards • On-Board components do not usually produce the same level of performance as adapter cards
Adapter Cards Common adapter cards: • Video cards • Sound cards • Network interface cards • Modems • Interface cards • Controller cards Sound Card Video Card NIC
NICs • A Network Interface Card (NIC) is the computer's interface with the LAN. • The NIC communicates with the network through serial connections and communicates with the computer through parallel connections. • NICs are expansion cards (PCI or ISA) that can be installed in one of the computer's expansion slots. • The network cable plugs in to the computer through the adapter card or NIC.
- More by User

Statistics and Computers
Statistics and Computers. By Jordan Neuzil. Statistics. Statistics is the mathematics of the collection, organization, and interpretation of numerical data, especially the analysis of population characteristics by inference from sampling. . Statistics Today.
2.36k views • 17 slides

Applications of Computers Lecture-3
Applications of Computers Lecture-3 E-Commerce Almost all major companies have their homes on the web, mainly for advertising Companies were reluctant towards e-commerce but now it is picking up The most revolutionary e-commerce is between business and customer
613 views • 18 slides

Computers and Humor
Computers and Humor by Don L. F. Nilsen and Alleen Pace Nilsen High Learning Curve IT Support How Computers Have Affected the World Bill Gates Computer Generated Humor: Apple’s Joke Teller Given the command, “Computer, tell me a joke,” this is one response: COMPUTER: Knock, knock.
1.64k views • 93 slides

Applications of Computers
Applications of Computers . We talk about databases and their implementation Implementation of databases involves trees therefore we introduce trees E-commerce (BTC) allows web-based access of inventory and orders Where are the inventory and orders stored? In the corporate database.
663 views • 41 slides

Classification of Digital Computers & Applications of Computers
Classification of Digital Computers & Applications of Computers. Classification. Personal Computers Laptops Network Computers Mini and Microcomputers PDAs Workstations Servers Mainframes Supercomputers. Personal Computers. Used at home
1.4k views • 30 slides

Applications of Computers in pharmacy
Applications of Computers in pharmacy. MADE BY: SIR NASEEM AHMED KHAN DOW VOCATIONAL & TECHNICAL TRAINING CENTRE. What are the applications of Computers in pharmacy?.
4.11k views • 12 slides

Computers, computers!
Computers, computers!. It’s quicker to count them by foot!. Dr Mark Abrams (1906 –1994). (Director, SSRC Survey Unit, 1970-76, always kept a slide-rule on his desk). He also said,. "Don’t get it right: get it written!". …and, "If it’s worth saying, you can say it in percentages.".
557 views • 34 slides

Parallel Programming: Techniques and Applications Using Networked Workstations and Parallel Computers
Parallel Programming: Techniques and Applications Using Networked Workstations and Parallel Computers. Barry Wilkinson and Michael Allen. Chapter 7: Load Balancing and Termination Detection Sec 7.4: Program Example. Modified 5/10/05 by T. O’Neil for 3460:4/577, Fall 2005, Univ. of Akron.
649 views • 31 slides
Quantum Computers: Fundamentals, Applications and Implementation
Quantum Computers: Fundamentals, Applications and Implementation. ˆ. z = |0 >. | ψ >. θ. ˆ. y. Ben Feldman, Harvard University Big Techday Conference June 14, 2013. φ. ˆ. x. ˆ. -z = |1 >. Image: Introduction to quantum information processing review, Science 339 , 1163 (2013).
173 views • 0 slides

Computers, Applications, and Java
Computers, Applications, and Java. Based on slides from Deitel & Associates, Inc. Modified and enhanced by T. A. Yang. Outline. Computers Programs and Software Applications Programming languages Java. Chapter organization. 1.1 Introduction.
801 views • 60 slides

Personal Computers and Applications
Personal Computers and Applications. Networking for Home and Small Businesses – Chapter 1. Objectives. Purpose and use of personal computers. Differentiate local and network applications. Different types of computing devices and usage. Binary Arithmetic and Character representation.
581 views • 27 slides

Personal Computers and Applications. Networking for Home and Small Businesses – Chapter 1. Objectives. Identify the purpose and uses of personal computers and describe local and network applications. Compare and contrast different types of computing devices.
396 views • 25 slides

Introduction to Computers and their Applications
Introduction to Computers and their Applications. Course Introduction Professor Pepper. Major Course Objectives. Create web sites Know some of Office Able to specify your own PC Familiarity with IT terminology Investigate IT ethical issues Become familiar with Online methods of learning
382 views • 25 slides

Evolution of computers and Computers Today
Evolution of computers and Computers Today. www.apepanthiya.com. History.
1.68k views • 88 slides

Lecture#2 Introduction to Computers, HISTORY AND applications
Lecture#2 Introduction to Computers, HISTORY AND applications. Instructor: M. Mateen Yaqoob. Contents. History of Computers. Blaise Pascal invented the first mechanical adding machine in 1642 Baron Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz invented the first calculator for multiplication in 1671
382 views • 22 slides

178 views • 11 slides

CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications
CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications. Information Literacy Lecture 3 – Information Resources. Information Resources. The library remains our most important information resource, although the manner in which we get our information has changed.
191 views • 17 slides

Basics of Computers: Classification, Applications, advantages and Limitations.
Basics of Computers: Classification, Applications, advantages and Limitations. Chapter 2. Classification of computers. Computers based on technology. Digital computer :- using only 0’s and 1’s. 8 bits called a byte. 2. Analog computer :- values keep changing with time.
261 views • 18 slides

271 views • 25 slides

Introduction to Computers and their Applications Structure and Grading
Introduction to Computers and their Applications Structure and Grading. Course Introduction Professor Pepper. Projects / Grading. 10% off for late work when allowed late at all I encourage redoing work when I comment to say you can fix it. Computer Equipment Required. NONE
131 views • 10 slides
Applications of Computers Lectures 1 and 2
Applications of Computers Lectures 1 and 2. Let us revise “indexing into the arrays” Later, we will look at databases and their applications Databases have wide-spread applications in all walks of life We will introduce network model and relational model of database. Indexing into arrays.
538 views • 47 slides

Introduction to Computers and their Applications Objectives and Grading
Introduction to Computers and their Applications Objectives and Grading. Course Introduction Professor Pepper. Major Course Objectives. Create web sites Know some of Office Able to specify your own PC Investigate IT ethical issues Improve ability to research and evaluate sources
115 views • 6 slides

- Computer Concepts Tutorial
- Computer Concepts - Home
- Introduction to Computer
- Introduction to GUI based OS
- Elements of Word Processing
- Spread Sheet
- Introduction to Internet, WWW, Browsers
- Communication & Collaboration
- Application of Presentations
- Application of Digital Financial Services
- Computer Concepts Resources
- Computer Concepts - Quick Guide
- Computer Concepts - Useful Resources
- Computer Concepts - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Basic Applications of Computer
Computers play a role in every field of life. They are used in homes, business, educational institutions, research organizations, medical field, government offices, entertainment, etc.
Computers are used at homes for several purposes like online bill payment, watching movies or shows at home, home tutoring, social media access, playing games, internet access, etc. They provide communication through electronic mail. They help to avail work from home facility for corporate employees. Computers help the student community to avail online educational support.
Medical Field
Computers are used in hospitals to maintain a database of patients’ history, diagnosis, X-rays, live monitoring of patients, etc. Surgeons nowadays use robotic surgical devices to perform delicate operations, and conduct surgeries remotely. Virtual reality technologies are also used for training purposes. It also helps to monitor the fetus inside the mother’s womb.
Entertainment
Computers help to watch movies online, play games online; act as a virtual entertainer in playing games, listening to music, etc. MIDI instruments greatly help people in the entertainment industry in recording music with artificial instruments. Videos can be fed from computers to full screen televisions. Photo editors are available with fabulous features.
Computers are used to perform several tasks in industries like managing inventory, designing purpose, creating virtual sample products, interior designing, video conferencing, etc. Online marketing has seen a great revolution in its ability to sell various products to inaccessible corners like interior or rural areas. Stock markets have seen phenomenal participation from different levels of people through the use of computers.
Computers are used in education sector through online classes, online examinations, referring e-books, online tutoring, etc. They help in increased use of audio-visual aids in the education field.
In government sectors, computers are used in data processing, maintaining a database of citizens and supporting a paperless environment. The country’s defense organizations have greatly benefitted from computers in their use for missile development, satellites, rocket launches, etc.
In the banking sector, computers are used to store details of customers and conduct transactions, such as withdrawal and deposit of money through ATMs. Banks have reduced manual errors and expenses to a great extent through extensive use of computers.
Nowadays, computers are totally integrated into business. The main objective of business is transaction processing, which involves transactions with suppliers, employees or customers. Computers can make these transactions easy and accurate. People can analyze investments, sales, expenses, markets and other aspects of business using computers.
Many organizations use computer-based training to train their employees, to save money and improve performance. Video conferencing through computers allows saving of time and travelling costs by being able to connect people in various locations.
Computers are extensively used in dance, photography, arts and culture. The fluid movement of dance can be shown live via animation. Photos can be digitized using computers.
Science and Engineering
Computers with high performance are used to stimulate dynamic process in Science and Engineering. Supercomputers have numerous applications in area of Research and Development (R&D). Topographic images can be created through computers. Scientists use computers to plot and analyze data to have a better understanding of earthquakes.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Exclusive access to over 200,000 completely editable slides.
- Diagram Finder
- Free Templates
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Timelines & Planning
- Health & Wellness
- Environment
- Cause & Effect
- Executive Summary
- Customer Journey
- 30 60 90 Day Plan
- Social Media
- Escalation Matrix
- Communication
- Go to Market Plan/Strategy
- Recruitment
- Pros and Cons
- Business Plan
- Risk Management
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Mental Health
- ISO Standards
- Process Diagrams
- Puzzle Diagrams
- Organizational Charts
- Arrow Diagrams
- Infographics
- Tree Diagrams
- Matrix Charts
- Stage Diagrams
- Text Boxes & Tables
- Data Driven Charts
- Flow Charts
- Square Puzzle
- Circle Puzzle
- Circular Arrows
- Circle Segments
- Matrix Table
- Pillar Diagrams
- Triangle Puzzle
- Compare Diagrams
- Ladder Diagrams
- Google Slides
- North America Maps
- United States (US) Maps
- Europe Maps
- South America Maps
- Apple Keynote
- People & Objects
- Trending Products
- PowerPoint Templates
Applications of Computer PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(2 Editable Slides)
Download Now
This template is part of our Pro Plan.
Gain access to over 200,000 slides with pro plan..
Upgrade Now
Already a Pro customer? Login

Related Products
Person on Computer Icons for PowerPoint and Google Slides

Computerized Maintenance Management System PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
Working on Computer Icons for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Computer Hack Icons for PowerPoint and Google Slides

Computer Forensics PowerPoint and Google Slides Template

Person in Front of a Computer Illustration for PowerPoint and Google Slides
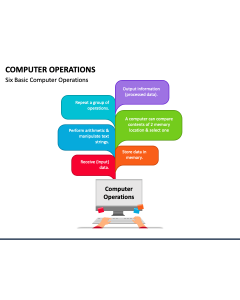
Computer Operations PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
Computer Programmer Icons for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Download our Applications of Computer PowerPoint and Google Slides template to describe how computers have transformed today’s digital landscape. You can also use this deck to present computers’ versatile features and dynamic capabilities and explain their role in modern-day communication, information sharing, and numerous other functionalities across industries and domains. Technology enthusiasts can also use this set to explain how regular technological advancements will drive endless computer applications.
The slides feature a circular infographic and serial-numbered textual boxes presenting the wide range of applications of computers. The vibrant color schemes will help you maintain visual coherence in your presentation and get the full attention of the audience.
Distinctive Features
- The deck offers hassle-free editing; hence, the users can quickly mold the elements to suit their presentation’s theme.
- You can scale the graphics on screens of all sizes without disturbing the resolution.
- Everything has been thoughtfully crafted to prevent copyright issues.
- Our support staff is accessible 24*7.
Make your presentations shine and convey your message with more impact by downloading this graphic-rich PPT!
Create compelling presentations in less time
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Brandon Leshchinskiy
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Artificial Intelligence
Learning Resource Types
Presentation slide deck (pdf - 3 mb).

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
Analog computers
Mainframe computer.
- Supercomputer
- Minicomputer
- Microcomputer
- Laptop computer
- Embedded processors
- Central processing unit
- Main memory
- Secondary memory
- Input devices
- Output devices
- Communication devices
- Peripheral interfaces
- Fabrication
- Transistor size
- Power consumption
- Quantum computing
- Molecular computing
- Role of operating systems
- Multiuser systems
- Thin systems
- Reactive systems
- Operating system design approaches
- Local area networks
- Wide area networks
- Business and personal software
- Scientific and engineering software
- Internet and collaborative software
- Games and entertainment
- Analog calculators: from Napier’s logarithms to the slide rule
- Digital calculators: from the Calculating Clock to the Arithmometer
- The Jacquard loom
- The Difference Engine
- The Analytical Engine
- Ada Lovelace, the first programmer
- Herman Hollerith’s census tabulator
- Other early business machine companies
- Vannevar Bush’s Differential Analyzer
- Howard Aiken’s digital calculators
- The Turing machine
- The Atanasoff-Berry Computer
- The first computer network
- Konrad Zuse
- Bigger brains
- Von Neumann’s “Preliminary Discussion”
- The first stored-program machines
- Machine language
- Zuse’s Plankalkül
- Interpreters
- Grace Murray Hopper
- IBM develops FORTRAN
- Control programs
- The IBM 360
- Time-sharing from Project MAC to UNIX
- Minicomputers
- Integrated circuits
- The Intel 4004
- Early computer enthusiasts
- The hobby market expands
- From Star Trek to Microsoft
- Application software
- Commodore and Tandy enter the field
- The graphical user interface
- The IBM Personal Computer
- Microsoft’s Windows operating system
- Workstation computers
- Embedded systems
- Handheld digital devices
- The Internet
- Social networking
- Ubiquitous computing

What is a computer?
Who invented the computer, what can computers do, are computers conscious, what is the impact of computer artificial intelligence (ai) on society.

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- University of Rhode Island - College of Arts and Sciences - Department of Computer Science and Statistics - History of Computers
- LiveScience - History of Computers: A Brief Timeline
- Computer History Museum - Timeline of Computer history
- Engineering LibreTexts - What is a computer?
- Computer Hope - What is a Computer?
- computer - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- computer - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

A computer is a machine that can store and process information . Most computers rely on a binary system , which uses two variables, 0 and 1, to complete tasks such as storing data, calculating algorithms, and displaying information. Computers come in many different shapes and sizes, from handheld smartphones to supercomputers weighing more than 300 tons.
Many people throughout history are credited with developing early prototypes that led to the modern computer. During World War II, physicist John Mauchly , engineer J. Presper Eckert, Jr. , and their colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania designed the first programmable general-purpose electronic digital computer, the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC).
What is the most powerful computer in the world?
As of November 2021 the most powerful computer in the world is the Japanese supercomputer Fugaku, developed by RIKEN and Fujitsu . It has been used to model COVID-19 simulations.
How do programming languages work?
Popular modern programming languages , such as JavaScript and Python, work through multiple forms of programming paradigms. Functional programming, which uses mathematical functions to give outputs based on data input, is one of the more common ways code is used to provide instructions for a computer.
The most powerful computers can perform extremely complex tasks, such as simulating nuclear weapon experiments and predicting the development of climate change . The development of quantum computers , machines that can handle a large number of calculations through quantum parallelism (derived from superposition ), would be able to do even more-complex tasks.
A computer’s ability to gain consciousness is a widely debated topic. Some argue that consciousness depends on self-awareness and the ability to think , which means that computers are conscious because they recognize their environment and can process data. Others believe that human consciousness can never be replicated by physical processes. Read one researcher’s perspective.
Computer artificial intelligence's impact on society is widely debated. Many argue that AI improves the quality of everyday life by doing routine and even complicated tasks better than humans can, making life simpler, safer, and more efficient. Others argue AI poses dangerous privacy risks, exacerbates racism by standardizing people, and costs workers their jobs leading to greater unemployment. For more on the debate over artificial intelligence, visit ProCon.org .
Recent News
computer , device for processing, storing, and displaying information.
Computer once meant a person who did computations, but now the term almost universally refers to automated electronic machinery . The first section of this article focuses on modern digital electronic computers and their design, constituent parts, and applications. The second section covers the history of computing. For details on computer architecture , software , and theory, see computer science .
Computing basics
The first computers were used primarily for numerical calculations. However, as any information can be numerically encoded, people soon realized that computers are capable of general-purpose information processing . Their capacity to handle large amounts of data has extended the range and accuracy of weather forecasting . Their speed has allowed them to make decisions about routing telephone connections through a network and to control mechanical systems such as automobiles, nuclear reactors, and robotic surgical tools. They are also cheap enough to be embedded in everyday appliances and to make clothes dryers and rice cookers “smart.” Computers have allowed us to pose and answer questions that were difficult to pursue in the past. These questions might be about DNA sequences in genes, patterns of activity in a consumer market, or all the uses of a word in texts that have been stored in a database . Increasingly, computers can also learn and adapt as they operate by using processes such as machine learning .

Computers also have limitations, some of which are theoretical. For example, there are undecidable propositions whose truth cannot be determined within a given set of rules, such as the logical structure of a computer. Because no universal algorithmic method can exist to identify such propositions, a computer asked to obtain the truth of such a proposition will (unless forcibly interrupted) continue indefinitely—a condition known as the “ halting problem .” ( See Turing machine .) Other limitations reflect current technology . For example, although computers have progressed greatly in terms of processing data and using artificial intelligence algorithms , they are limited by their incapacity to think in a more holistic fashion. Computers may imitate humans—quite effectively, even—but imitation may not replace the human element in social interaction. Ethical concerns also limit computers, because computers rely on data, rather than a moral compass or human conscience , to make decisions.
Analog computers use continuous physical magnitudes to represent quantitative information. At first they represented quantities with mechanical components ( see differential analyzer and integrator ), but after World War II voltages were used; by the 1960s digital computers had largely replaced them. Nonetheless, analog computers, and some hybrid digital-analog systems, continued in use through the 1960s in tasks such as aircraft and spaceflight simulation.

One advantage of analog computation is that it may be relatively simple to design and build an analog computer to solve a single problem. Another advantage is that analog computers can frequently represent and solve a problem in “real time”; that is, the computation proceeds at the same rate as the system being modeled by it. Their main disadvantages are that analog representations are limited in precision—typically a few decimal places but fewer in complex mechanisms—and general-purpose devices are expensive and not easily programmed.
Digital computers
In contrast to analog computers, digital computers represent information in discrete form, generally as sequences of 0s and 1s ( binary digits, or bits). The modern era of digital computers began in the late 1930s and early 1940s in the United States , Britain, and Germany . The first devices used switches operated by electromagnets (relays). Their programs were stored on punched paper tape or cards, and they had limited internal data storage. For historical developments, see the section Invention of the modern computer .
During the 1950s and ’60s, Unisys (maker of the UNIVAC computer), International Business Machines Corporation (IBM), and other companies made large, expensive computers of increasing power . They were used by major corporations and government research laboratories, typically as the sole computer in the organization. In 1959 the IBM 1401 computer rented for $8,000 per month (early IBM machines were almost always leased rather than sold), and in 1964 the largest IBM S/360 computer cost several million dollars.
These computers came to be called mainframes, though the term did not become common until smaller computers were built. Mainframe computers were characterized by having (for their time) large storage capabilities, fast components, and powerful computational abilities. They were highly reliable, and, because they frequently served vital needs in an organization, they were sometimes designed with redundant components that let them survive partial failures. Because they were complex systems, they were operated by a staff of systems programmers, who alone had access to the computer. Other users submitted “batch jobs” to be run one at a time on the mainframe.
Such systems remain important today, though they are no longer the sole, or even primary, central computing resource of an organization, which will typically have hundreds or thousands of personal computers (PCs). Mainframes now provide high-capacity data storage for Internet servers, or, through time-sharing techniques, they allow hundreds or thousands of users to run programs simultaneously. Because of their current roles, these computers are now called servers rather than mainframes.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 6. Basic computer terminologies
Topic A: Application programs
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Word Processors and Spreadsheets
Application program – a computer program that provides users with tools to accomplish a specific task.
Examples of application programs include those for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, and database management, as well as Internet browsers, email programs, media players, accounting software, and programs that help with pronunciation, translation, desktop publishing, enterprise.
Microsoft Office – A group of productivity software applications developed by Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Office 2016 includes such programs as Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Word processors
Word processor – a program that allows users to create, save, edit, format, print, and retrieve documents.
Word processing programs can be used to create all types of text-based documents, such as:
- Assignments
- Newsletters
- Short stories
- Books (with tables, diagrams, photos, links, etc.)
Examples of word processing programs include Microsoft Word, Google Docs, Apple Pages, and LibreOffice Writer.

Spreadsheets
Spreadsheet (electronic worksheet) – a program that organizes data into rows and columns, also known as tabular form. This data can then be arranged, sorted, calculated (using formulas and functions), analyzed, or illustrated using graphical representations.
Among many other things, a spreadsheet program can be used to:
- Create budgets
- Calculate grades
- Balance bank accounts
- Calculate loan payments
- Calculate tax
- Prepare payrolls
- Analyze business performance numbers and results
- Produce charts
- Calculate revenues
Examples of spreadsheet programs include Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, Apple Numbers, and LibreOffice Calc.
Presentation and Database Programs
Presentation programs.

Presentation program – a program that is designed to present information in the form of a slideshow, using multimedia formats such as pictures, sounds, videos, and text. Such a program is commonly used in education, training, business meetings, etc., to create powerful presentations.
Presentation programs are commonly used to:
- Create slideshow presentations
- Create lectures and tutorials
- Make photo slideshows
- Design websites with hyperlinks and interactivity
- Make photo albums
- Create animated videos (with voice and animation)
Examples of presentation programs include Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Apple Keynote, Prezi, CustomShow, SlideDog, and Powtoon.
Database programs
Database program (database management system) – A program that is designed for creating, editing, updating, maintaining databases, and managing organized information stored in them.
Databases are useful for keeping track of customers, users, employees, students, inventory, product purchases, ISBN numbers, etc. Database programs are used in the following fields:
- Airline/railway reservation
- Library management
- Human resource management
Examples of database programs include Microsoft Access, Oracle Database, Knack, TablePlus, and TeamDesk.
Launch and Terminate a Program
Launch an application program.
- Click the name of the program that you wish to start (e.g., Word 2016).
- Click the name of the program that you want to launch.
- Double-click a program shortcut icon on the desktop, if there is one.
Close (exit) a program (close an active open window)
- Click the Close icon (x) in the upper-right corner of the window.

Method 2 (Apple)
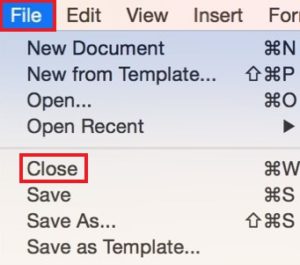
- Click Close .
Force close a frozen program
- Click Alt + F4 .
- Click Ctrl + Alt + Delete to open Task Manager .
- Select the unresponsive program and click End Task .
a computer program that provides users with tools to accomplish a specific task.
a group of productivity software applications developed by Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Office 2016 includes such programs as Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, etc.
a program that allows users to create, save, edit, format, print, and retrieve documents.
a program that organizes data into rows and columns, also known as tabular form. This data can then be arranged, sorted, calculated (using formulas and functions), analyzed, or illustrated using graphical representations.
a program that is designed to present information in the form of a slideshow, using multimedia formats such as pictures, sounds, videos, and text.
a program that is designed for creating, editing, updating, and maintaining databases and managing organized information stored in them.
Key Concepts of Computer Studies Copyright © 2020 by Meizhong Wang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
28 Free Technology PowerPoint Templates for Presentations from the Future
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
By Lyudmil Enchev
in Freebies
3 years ago
Viewed 270,217 times
Spread the word about this article:
If you’re amongst the science and technology teachers, students, or businesses in the field; we have something for you. We deep-dived to find the best free technology PowerPoint templates for your presentation, so today’s collection has 28 amazing designs to choose from.
The following selection has templates related to science, technology, cybersecurity, search engines, bitcoin, networking, programming, and engineering, so there’s something for everyone.
1. Computer Hardware Free Technology PowerPoint Template
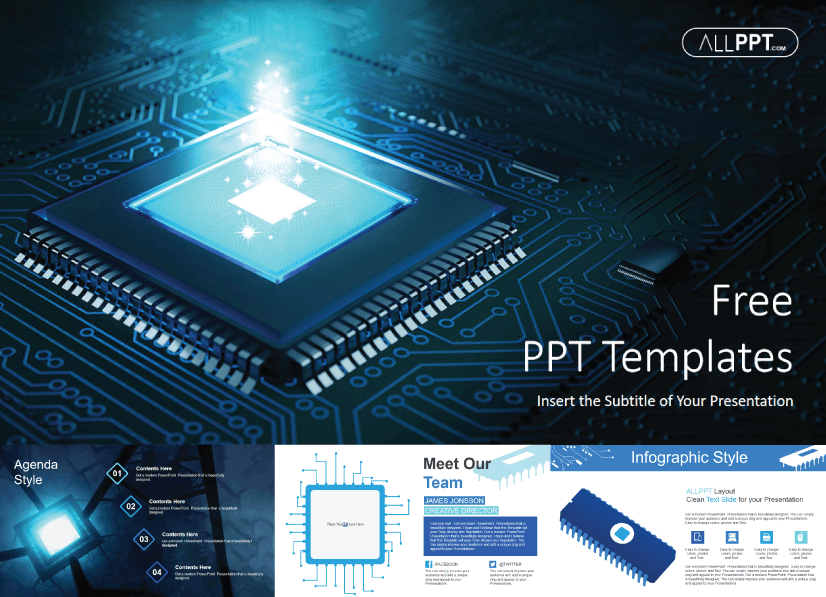
This template sports a cool design with a bright light of a microchip processor and a blue background. Ideal for explaining concepts such as semiconductors, databases, and central computer processors.
- Theme : Technology, Hardware
- Slides : 48
- Customization : Fully editable + 136 editable icons
- Graphics : Vector
- Aspect Ratio : 16:9
- License : Free for Personal and Commercial Use │ Do Not Redistribute Any Components of the Template
2. Space Science Free Technology Powerpoint Templates
This free template has 3D spaceship graphics and blue background color. It’s great for presentations on astronomy.
- Theme : Technology, Cosmos
- Slides : 25
- Customization : Fully editable
- Resolution : 1920×1080
3. 5G Technology Speed Free Powerpoint Templates

Design with twinkling rays of geometric shapes is perfect for presentations on technology topics such as internet networking, intranet, and communication technology.
- Theme : Technology, Networking, 5G
- Customization : Editable
4. Start-Up Tech Corporation Free Powerpoint Template
This free tech corporation template is great for presentations on tech business startups.
- Theme : Technology, Tech Business, Start-Up Companies
5. App Startup Free Powerpoint Technology Template
This design is great for presentations on communication, mobile technology, and other digital devices used for the PPT presentations.
- Theme : Technology, Apps, Software
6. Cloud Technology Free Powerpoint Template
A technology template with a clean and modern design for your presentations about cloud computing and other computing services.
- Theme : Cloud Technlogy
7. Artificial Intelligence High Technology Free PowerPoint Template
This template represents artificial intelligence as an illustration . It also includes related shapes to allow for a variety of expressions.
- Theme : Technology, Artificial Intelligence
8. Search Engine Optimization PowerPoint Template
The template is SEO-themed but you can adapt it to any presentation related to marketing and search engines.
- Theme : Technology, Marketing, SEO
9. Binary Code Free PowerPoint Template
The cool binary code design makes this template perfect for any presentation on computer science.
- Theme : Computer Science, Programming
10. Network Free Technology PowerPoint Template

Sporting design with crags and electric rays in many angles are representing networking around the globe, the template is suitable for presentations on communication, networking, technology, and crag wheels.
- Theme : Technology, Networking
11. Hexagonal Design Free PowerPoint Template

Here we have a free template with hexagons and icons pattern for techy content. Its dark background and bright blue color palette give a professional look.
- Theme : Technology
12. Technology Pixels Free PowerPoint Template

A technology-themed template for presentations on consulting, IT, software, and other related subjects. The pixel pattern is grouped by tones which you can change from the master slides.
13. Connections and Networking Free PowerPoint Template

This free Powerpoint template is perfect for a presentation about the internet, blockchain, machine learning, cybersecurity, or cloud computing.
14. Isometric Free Technology PowerPoint Template

Here we have an amazing isometric design and high-tech background with gradients. Ideal for subjects like cloud computing, SaaS development, servers, and networks, or cybersecurity.
- Theme : Networking, Programming
15. Free PowerPoint Template with Techy Contour Lines
This design has an abstract contour lines background in a dark green color. Ideal for subjects like geography, technology, video games, or even military affairs.
- Theme : Technology, Gaming

16. Marketing and Technology Free PowerPoint Template
The isometric design has illustrations on business, marketing, and technology topics that will make every slide stand out.
- Theme : Technology, Marketing
17. Purple Hexagons Free PowerPoint Template

For presentations related to scientific or technological topics, with professional hexagonal design.
- Theme : Technology, Science
18. Rockets Taking Off Free PowerPoint Template

Rockets taking off is a great metaphor for growing businesses. It’s also a symbol of progress and technology.
- Slides : 35
19. IOT Smart City Free PowerPoint Template
Smart City offers a futuristic design for subjects such as internet communication, smart city concepts, and tech innovation.
- Theme : Technology, Smart City
20. Cyber Security Free PowerPoint Template

The perfect template for presentations on cybersecurity, antivirus software, and other related topics.
- Theme : Technology, Cyber Security
21. BlockChain Free PowerPoint Templates
This template is a 3D rendering design of blockchain technology and you can use it for a variety of purposes.
Presentation Design Tips You Wish You Knew Earlier:
The shorter you keep the text, the better. In fact, some specialists suggest that you shouldn’t use more than 5-6 words per slide . And sometimes, a single word combined with a powerful visual is enough to nail the attention of the people sitting in front of you and make them listen to what you have to say.
22. BitCoin Themed Free PowerPoint Template

A very versatile template that includes 20 semi-transparent illustrations of different concepts: security, social networks, programming, bitcoin.
- Theme : Technology, Bitcoin
23. Technical Blueprint Free Technology PowerPoint Template

This template uses a blueprint style and a monospaced font to emulate the technical drawings used in construction and industry.
- Theme : Technology, Engineering
24. Blue Connections Free PowerPoint Template

The design of this free template fits social media, connection, internet, cloud computing, and science-related topics.
- Theme : Technology, Social Media
25. Cute Robots Free PowerPoint Template

Here we have a colorful design with beautifully illustrated robots for presentation on technology, science, and physics.
- Theme : Technology, Physics
26. Green Circuit Free PowerPoint Template

This is a free template with futuristic vibes that you can use for your tech presentations both in PowerPoint and Google Slides.
27. Data Particles Free Technology PowerPoint Template

The design with particle lines gives it a modern and slightly technological look.
28. Science Hexagons Free Technology PowerPoint Template

The background gradients highlight the white text, and the hexagons give it a techie style.
Final Words
That’s it. Today’s collection covered the best free technology PowerPoint templates that you can download and adapt to your presentations related to science, technology, programming, engineering, and physics. Now all you need to do is open your PowerPoint and make the most amazing presentation your viewers have ever seen.
For more freebies, you can check the Best Free Powerpoint Templates of 2022 or see these related articles:
36 Free Food PowerPoint Templates For Delicious Presentations
- 31 Free Modern Powerpoint Templates for Your Presentation
- 25 Free Education PowerPoint Templates For Lessons, Thesis, and Online Lectures

Add some character to your visuals
Cartoon Characters, Design Bundles, Illustrations, Backgrounds and more...
Like us on Facebook
Subscribe to our newsletter
Be the first to know what’s new in the world of graphic design and illustrations.
- [email protected]
Browse High Quality Vector Graphics
E.g.: businessman, lion, girl…
Related Articles
Where to find free vector images for commercial use, free oktoberfest graphics collection to make you see double, 30 free marketing presentation templates with modern design, the best free powerpoint templates to download in 2019, free gifs for powerpoint to animate your killer presentation, 500+ free and paid powerpoint infographic templates:, enjoyed this article.
Don’t forget to share!
- Comments (0)

Lyudmil Enchev
Lyudmil is an avid movie fan which influences his passion for video editing. You will often see him making animations and video tutorials for GraphicMama. Lyudmil is also passionate for photography, video making, and writing scripts.

Thousands of vector graphics for your projects.
Hey! You made it all the way to the bottom!
Here are some other articles we think you may like:

Free Vectors
100 free cartoon background vectors for all your projects.
by Iveta Pavlova

by Al Boicheva

800+ Free Silhouette Graphics to Download Now
by Lyudmil Enchev
Looking for Design Bundles or Cartoon Characters?
A source of high-quality vector graphics offering a huge variety of premade character designs, graphic design bundles, Adobe Character Animator puppets, and more.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Computer Basics - What is a Computer?
Computer basics -, what is a computer, computer basics what is a computer.

Computer Basics: What is a Computer?
Lesson 2: what is a computer.
/en/computerbasics/about-this-tutorial/content/
What is a computer?
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store , retrieve , and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents , send email , play games , and browse the Web . You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets , presentations , and even videos .
Watch the video below to learn about different types of computers.
Looking for the old version of this video? You can still view it here .
Hardware vs. software
Before we talk about different types of computers, let's talk about two things all computers have in common: hardware and software .

Everything you do on your computer will rely on both hardware and software. For example, right now you may be viewing this lesson in a web browser (software) and using your mouse (hardware) to click from page to page. As you learn about different types of computers, ask yourself about the differences in their hardware. As you progress through this tutorial, you'll see that different types of computers also often use different types of software.
What are the different types of computers?
When most people hear the word computer , they think of a personal computer such as a desktop or laptop . However, computers come in many shapes and sizes, and they perform many different functions in our daily lives. When you withdraw cash from an ATM, scan groceries at the store, or use a calculator, you're using a type of computer.

Desktop computers

Many people use desktop computers at work, home, and school. Desktop computers are designed to be placed on a desk, and they're typically made up of a few different parts, including the computer case , monitor , keyboard , and mouse .
Laptop computers

The second type of computer you may be familiar with is a laptop computer , commonly called a laptop. Laptops are battery-powered computers that are more portable than desktops, allowing you to use them almost anywhere.
Tablet computers

Tablet computers —or tablets —are handheld computers that are even more portable than laptops. Instead of a keyboard and mouse, tablets use a touch-sensitive screen for typing and navigation. The iPad is an example of a tablet.

A server is a computer that serves up information to other computers on a network. For example, whenever you use the Internet, you're looking at something that's stored on a server. Many businesses also use local file servers to store and share files internally.
Other types of computers
Many of today's electronics are basically specialized computers , though we don't always think of them that way. Here are a few common examples.
- Smartphones : Many cell phones can do a lot of things computers can do, including browsing the Internet and playing games. They are often called smartphones .
- Wearables : Wearable technology is a general term for a group of devices —including fitness trackers and smartwatches —that are designed to be worn throughout the day. These devices are often called wearables for short.
- Game consoles : A game console is a specialized type of computer that is used for playing video games on your TV.
- TVs : Many TVs now include applications —or apps —that let you access various types of online content. For example, you can stream video from the Internet directly onto your TV.
PCs and Macs
Personal computers come in two main styles: PC and Mac . Both are fully functional, but they have a different look and feel, and many people prefer one or the other.

This type of computer began with the original IBM PC that was introduced in 1981. Other companies began creating similar computers, which were called IBM PC Compatible (often shortened to PC ). Today, this is the most common type of personal computer, and it typically includes the Microsoft Windows operating system.

The Macintosh computer was introduced in 1984, and it was the first widely sold personal computer with a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey ). All Macs are made by one company ( Apple ), and they almost always use the Mac OS X operating system.
/en/computerbasics/basic-parts-of-a-computer/content/
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

35 templates

108 templates

32 templates

50 templates

mid autumn festival
18 templates
11 templates
Computing Presentation templates
There are only 10 kinds of people in this world: those who know binary and those who don’t. if you’re among the ones who can, this selection of templates is the perfect match for you with these modern designs you can speak about data science, coding, computers or engineering in a modern, creative way that even the end users will understand.
- Calendar & Weather
- Infographics
- Marketing Plan
- Project Proposal
- Social Media
- Thesis Defense
- Black & White
- Craft & Notebook
- Floral & Plants
- Illustration
- Interactive & Animated
- Professional
- Instagram Post
- Instagram Stories

It seems that you like this template!

Register for free and start downloading now
Computer science degree for college.
Computer science degrees prepare students for the jobs of the future (and the present!). If you are interested in getting an education about coding, math, computers, and robots, this is the degree for you! Speak about it with this futuristic template that will take the viewers to another digital dimension....

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Interactive Classroom Icebreakers
Download the Interactive Classroom Icebreakers presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and make the learning experience more enjoyable and...

Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides, web project proposal.
We live in the internet era, which means that web design is currently one of the most demanded skills. This free template is perfect for those designers who want to present their web project proposal to their clients and see a preview of the final work.

AI Tech Types and Tools
Download the AI Tech Types and Tools presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The world of business encompasses a lot of things! From reports to customer profiles, from brainstorming sessions to sales—there's always something to do or something to analyze. This customizable design, available for Google Slides and PowerPoint, is...

Virtual Slides for Education Day
Digital learning is making its way into the world of education. For this reason, we've designed this new template so that the slides look like the screen of a laptop (complete with reflections!). Apart from graphs and infographics, the font is quite "computer-esque" and a perfect fit for this theme....

Soft Colors UI Design for Agencies
Agencies have the most creative employees, so having boring meetings with traditional Google Slides & PowerPoint presentations would be a waste. Make the most out of this potential with this creative design full of editable resources and beautiful decorations in calming, pastel tones. Let the creativity of your agency be...

Multimedia Software Pitch Deck
Download the "Multimedia Software Pitch Deck" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Whether you're an entrepreneur looking for funding or a sales professional trying to close a deal, a great pitch deck can be the difference-maker that sets you apart from the competition. Let your talent shine out thanks to...

Software Testing Company
Software testing might not be the sexiest part of coding, but that doesn't mean it lacks intrigue or importance. After all, who wants to use a buggy app? It's software testing that ensures smooth operation and prevents annoying glitches from making it into the final product. Without it, our lives...

Computer Science & Mathematics Major For College: Computer Science & Programming
Show future students the wonders of computer science and what they can achieve if they join a career in this incredible degree. With these slides you can speak about both technical and simple concepts and they will all be quickly understood! Editing them is as easy as printing Hello world!...

Videogames Lesson!
Download the Videogames Lesson! presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The education sector constantly demands dynamic and effective ways to present information. This template is created with that very purpose in mind. Offering the best resources, it allows educators or students to efficiently manage their presentations and engage audiences. With...

Tech Startup Newsletter
Download the "Tech Startup Newsletter" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Attention all marketers! Are you looking for a way to make your newsletters more creative and eye-catching for your target audience? This amazing template is perfect for creating the perfect newsletter that will capture your audience's attention from the...

Software Development Business Plan
People in the IT sector will be glad to know that Slidesgo has created a new template especially for them! Describe in these slides your software development business plan and try to convince possible partners of the viability of your idea. The palette is composed of cool colors, which are...

Software Engineering Business Plan
Download the "Software Engineering Business Plan" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Conveying your business plan accurately and effectively is the cornerstone of any successful venture. This template allows you to pinpoint essential elements of your operation while your audience will appreciate the clear and concise presentation, eliminating any potential...
Silicon Valley Programmer Portfolio
Download the "Silicon Valley Programmer Portfolio" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. When a potential client or employer flips through the pages of your portfolio, they're not just looking at your work; they're trying to get a sense of who you are as a person. That's why it's crucial to...

All About Programming in Java
Download the All About Programming in Java presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template’s design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow space for research or group projects—the possibilities of...

IT Security Hacker Pitch Deck
Download the IT Security Hacker Pitch Deck presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Whether you're an entrepreneur looking for funding or a sales professional trying to close a deal, a great pitch deck can be the difference-maker that sets you apart from the competition. Let your talent shine out thanks...

Data Analysis for Business
Download the Data Analysis for Business presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic...

Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics
Download the "Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides to get the most out of infographics. Whether you want to organize your business budget in a table or schematically analyze your sales over the past year, this set of infographic resources will be of great...
- Page 1 of 36
Register for free and start editing online

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Basic Applications of Computers. Computers are used in every field of life, such as homes, businesses, educational institutions, research organizations, the medical field, government offices, entertainment, etc. Today we can not imagine growing our technology without computers. The various field where the computer is very essential are: Science ...
Download ppt "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer". Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
This action is not available. Covers the basics of computer hardware, software, and networking and helps students develop basic skills in using Windows and Microsoft Office, and creating web pages. Students also learn how to use ….
Download ppt "Introduction to Computer Application". Outline Introduction to the computer Hardware development Software development Language Programming Operating System Software Application Presentation Multimedia Internet Image Processing.
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes: 1) accepts data or instructions (input) 2) stores data. 3) process data. 4) displays results (output) and. 5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer. .
Application Software • Application software is a program loaded on the computer that performs a specific task for a user or another application. • Examples: word processor, web browser, graphics editor, spreadsheet, mail reader. Applications • The computer is only as useful as the program or application on it.
Computers are used in hospitals to maintain a database of patients' history, diagnosis, X-rays, live monitoring of patients, etc. Surgeons nowadays use robotic surgical devices to perform delicate operations, and conduct surgeries remotely. Virtual reality technologies are also used for training purposes. It also helps to monitor the fetus ...
This presentation describes the Computer and its Applications in different parts of our activity. This is a course ppt slide prepared for first year university students.
4:3. Tags. App. Download our Applications of Computer PowerPoint and Google Slides template to describe how computers have transformed today's digital landscape. You can also use this deck to present computers' versatile features and dynamic capabilities and explain their role in modern-day communication, information sharing, and numerous ...
Electrical Engineering and Computer Science; As Taught In Fall 2021 Level Undergraduate. Topics Engineering. Computer Science. Artificial Intelligence; Learning Resource Types ... Presentation Slide Deck (PDF - 3 MB) pdf. 3 MB Presentation Slide Deck (PDF - 3 MB) Download File DOWNLOAD. Course Info Instructor ...
computer, device for processing, storing, and displaying information. Computer once meant a person who did computations, but now the term almost universally refers to automated electronic machinery. The first section of this article focuses on modern digital electronic computers and their design, constituent parts, and applications.
Download the Referral Program MK Campaign presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Improve your campaign management with this template that will definitely make a difference. It will empower you to organize, execute, and track the effectiveness of your campaign. Enriched with innovative resources, it facilitates seamless communication ...
Word Processors and Spreadsheets. Application program - a computer program that provides users with tools to accomplish a specific task. Examples of application programs include those for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, and database management, as well as Internet browsers, email programs, media players, accounting software, and ...
1. Computer Hardware Free Technology PowerPoint Template. This template sports a cool design with a bright light of a microchip processor and a blue background. Ideal for explaining concepts such as semiconductors, databases, and central computer processors. Theme: Technology, Hardware. Slides: 48.
What is a computer? A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents, send email, play games, and browse the Web. You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, and even videos.
Download the All About Programming in Java presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template's design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow space for research or group ...