

Essay on Man Made Disaster

Introduction to Man Made Disaster
Man-made disaster, a sobering reality of our modern world, stem from human activities and errors, often resulting in catastrophic consequences. Unlike natural disasters, which arise from uncontrollable forces, man-made disasters are largely preventable and thus require a more profound understanding to mitigate their occurrence and impact. Ranging from industrial accidents to acts of terrorism, these events disrupt communities, devastate ecosystems, and challenge societal resilience. Recognizing the importance of comprehending the causes, impacts, and prevention measures of man-made disasters, this essay seeks to explore their various facets, fostering awareness and advocating for proactive solutions in safeguarding lives and the environment.

Types of Man Made Disaster

Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
Man-made disasters result from human actions, negligence, or error, significantly harming human life, property, and the environment. These disasters can vary widely in their causes and effects. Here are some types of man made disasters, along with detailed explanations:
1. Industrial Accidents
Industrial accidents typically occur in manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, refineries, and other industrial settings. These accidents can result from equipment failures, human error, improper maintenance, or inadequate safety protocols.
Examples include:
- Chemical Spills : Chemical spills happen when industrial facilities release hazardous substances into the environment due to accidents, equipment failures, or human error. These spills can contaminate soil, water , and air, leading to adverse health effects and environmental damage.
- Nuclear Accidents : Nuclear accidents involve the release of radioactive materials from nuclear power plants or other facilities. Events like meltdowns, leaks, or explosions can result in radiation exposure, widespread contamination, and long-term health risks for nearby populations.
- Explosions : Industrial explosions, such as those in factories, chemical plants, or storage facilities, can cause extensive damage to property and infrastructure. They may also result in injuries or fatalities among workers and nearby residents.
2. Transportation Accidents
Transportation accidents involve moving people or goods by air, land, or sea. Factors contributing to transportation accidents may include human error, mechanical failures, adverse weather conditions, and inadequate infrastructure.
- Plane Crashes : Aviation accidents involving commercial or private aircraft can lead to loss of life, property damage, and disruptions to transportation systems. Causes may include mechanical failures, pilot error, or adverse weather conditions.
- Train Derailments : Train derailments can occur due to track defects, equipment malfunctions, or human error. These accidents can result in train collisions, spills of hazardous materials, and damage to surrounding communities.
- Vehicle Collisions : Automobile accidents, including collisions between cars, trucks, and buses, can cause injuries, fatalities, and traffic congestion. Factors such as speeding, distracted driving, and impaired driving contribute to the occurrence of these accidents.
3. Environmental Pollution
Environmental pollution refers to introducing harmful contaminants into the natural environment, causing adverse effects on ecosystems, human health, and the overall quality of life. Human activities, including industrial processes, transportation, agriculture, and improper waste disposal, primarily drive this widespread issue.
Types of environmental pollution include:
- Air Pollution : Air pollution results from releasing harmful gases, particulate matter, and pollutants into the atmosphere from sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and power plants. Prolonged exposure to air pollution can lead to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and environmental degradation.
- Water Pollution : Water pollution occurs when contaminants enter water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans, through industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, or improper waste disposal. Pollution can harm aquatic ecosystems, threaten public health, and limit access to clean drinking water.
- Soil Contamination : Soil contamination arises from the deposition of toxic substances, heavy metals, or chemicals in the soil due to industrial activities, improper waste disposal, or agricultural practices. Contaminated soil can affect plant growth, leach into groundwater, and pose risks to human health through food chain contamination.
4. Terrorist Attacks
Terrorist attacks are deliberate acts of violence carried out by individuals, groups, or organizations with political, ideological, religious, or social motives to instill fear, intimidate, or coerce governments, societies, or specific populations. These attacks target civilians, infrastructure, and symbolic locations to achieve their objectives.
Example Include:
- Bombings : Terrorist bombings target public spaces, transportation systems, or critical infrastructure to instill fear, cause casualties, and disrupt societal functioning. In crowded areas, government buildings, or places of worship, individuals may detonate explosive devices.
- Cyber Attacks : Cyber attacks involve the unauthorized access, disruption, or manipulation of computer systems, networks, or information systems for political, economic, or ideological motives. These attacks can lead to data breaches, financial losses, and disruptions to essential services.
- Biological Attacks : Biological attacks involve deliberately releasing pathogens, toxins, or infectious agents to cause illness, death, or widespread panic among populations. Biological weapons may target food supplies, water sources, or public spaces, posing significant public health threats.
5. Structural Failures
Ensuring the safety and resilience of infrastructure requires adherence to building codes and standards, regular inspections, routine maintenance, and investment in infrastructure upgrades and retrofits.
Examples Include:
- Building Collapses : Structural failures in buildings and infrastructure can occur due to poor construction practices, inadequate maintenance, or natural disasters such as earthquakes or floods. Collapses can result in significant loss of life, injuries, and property damage.
- Bridge Failures : Bridges may collapse due to design flaws, material deterioration, or overloading. Bridge failures can disrupt transportation networks, cause accidents, and impede economic activities in affected areas.
6. Urban Fires
Urban fires, often exacerbated by densely populated areas, can result from various sources such as electrical faults, arson, or industrial accidents. These disasters lead to property destruction and displacement of communities and pose challenges to firefighting efforts.
- High-rise Fires : Fires in high-rise buildings present unique challenges for firefighting and evacuation due to limited access, vertical spread, and potential for rapid fire growth. High-rise fires can lead to multiple casualties, property damage, and complications in rescue operations.
- Industrial Fires : Industrial facilities, such as warehouses, factories, and chemical plants, are susceptible to fires caused by equipment malfunctions, electrical faults, or chemical reactions. Industrial fires may release toxic smoke, hazardous fumes, and pollutants into the environment, posing risks to public health and safety.
7. Mass Gatherings and Stampedes
Mass gatherings and stampedes represent a specific type of man-made disaster characterized by the convergence of large crowds in a confined space, often leading to chaotic situations and the loss of life.
- Concerts and Events : Large gatherings, concerts, festivals, and sporting events can experience overcrowding, insufficient crowd control measures, or panic situations leading to stampedes, trampling incidents, and injuries. Inadequate crowd management and emergency preparedness can exacerbate the impact of such incidents.
- Religious Festivals : Religious gatherings and pilgrimages, particularly in densely populated areas, may face challenges related to crowd management, crowd dynamics, and infrastructure limitations. Stampedes and overcrowding incidents can occur during religious festivals, resulting in fatalities and injuries.
8. Oil Spills
Oil spills occur when industrial facilities release crude oil or refined petroleum products into the environment. Spills can happen during transportation by tanker ships, pipelines, or offshore drilling operations.
- Marine Oil Spills : Oil spills from maritime accidents, offshore drilling operations, or tanker collisions can devastate marine ecosystems, coastal communities, and wildlife. Spilled oil can contaminate waterways, coat shorelines, and harm aquatic organisms, fisheries, and habitats.
- Pipeline Leaks : Pipeline ruptures, leaks, or breaches can release large volumes of oil and petroleum products into the environment, posing risks to soil, groundwater, and surface water quality. Pipeline spills may occur due to corrosion, equipment failure, or human error during transportation and distribution activities.
Causes of Man-Made Disasters
The causes of man-made disasters are varied and often interconnected, involving human error, negligence, or deliberate actions. Understanding these causes is crucial for implementing effective prevention measures. Here are some key factors contributing to man-made disasters:
- Human Error: Mistakes made by individuals or groups during operations, maintenance, or decision-making processes can lead to disasters. These errors may stem from insufficient training, fatigue, or miscommunication among personnel.
- Negligence: Failure to adhere to safety protocols, regulations, or industry standards can increase the risk of disasters. Negligence may involve shortcuts in procedures, inadequate maintenance of equipment or infrastructure, or disregard for warning signs and safety precautions.
- Violations of Safety Regulations: Non-compliance with safety regulations and guidelines set by regulatory authorities or governing bodies can create conditions conducive to disasters. Companies or individuals may prioritize cost-cutting over safety measures, leading to increased risks.
- Lack of Preparedness: Inadequate planning, training, and emergency response protocols can exacerbate the impact of disasters. Failure to anticipate potential risks or develop contingency plans leaves communities and organizations vulnerable to unforeseen events.
- Intentional Acts: Deliberate acts of sabotage, terrorism, or vandalism aimed at causing harm or disruption can result in man-made disasters. These malicious actions may target critical infrastructure, public spaces, or vulnerable populations, leading to widespread devastation and loss of life.
- Environmental Degradation: Human activities such as deforestation , industrial pollution, and resource extraction can contribute to environmental degradation, increasing the likelihood of disasters such as chemical spills, land degradation, and habitat destruction.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic disparities, unequal access to resources, and systemic injustices can exacerbate the vulnerability of specific communities to man-made disasters. Marginalized populations often bear the brunt of disasters due to limited resources, inadequate infrastructure, and reduced access to information and support services.
- Technological Complexity: Advances in technology have introduced new risks and vulnerabilities, particularly in complex systems such as nuclear power plants, transportation networks, and information technology infrastructure. Malfunctions, software glitches, or system failures can trigger cascading and catastrophic consequences.
Impact of Man-Made Disasters
The impact of man-made disasters is profound and far-reaching, affecting various aspects of society, the environment, and the economy. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective response, recovery, and mitigation efforts. Here are some key dimensions of the effects of man-made disasters:
- Loss of Life and Injury: Man-made disasters often result in significant loss of life, causing immense human suffering and trauma. Injuries ranging from minor to severe can lead to long-term physical disabilities and psychological distress among survivors. The loss of loved ones and community members can have enduring emotional and social repercussions.
- Environmental Degradation: Man-made disasters can cause widespread environmental pollution and degradation, threatening ecosystems, wildlife, and natural resources. Chemical spills, industrial accidents, and oil spills can contaminate water bodies, soil, and air, disrupting ecological balance and endangering biodiversity. Long-term environmental impacts may include soil erosion, habitat destruction, and contamination of food chains.
- Economic Consequences: Man-made disasters impose significant economic burdens on affected communities, industries, and governments. Direct costs include expenses related to emergency response, search and rescue operations, and infrastructure repair. Indirect costs encompass loss of productivity, reduced consumer confidence, and damage to businesses and livelihoods. Recovery and reconstruction efforts require substantial financial resources and may strain public budgets and insurance systems.
- Social Disruption: Man-made disasters disrupt social cohesion and community resilience, undermining trust and cooperation among individuals and groups. Displacement of populations, loss of homes, and disruption of essential services can lead to social instability and vulnerability. Communities may experience social unrest, conflict, and tensions exacerbated by disparities in access to resources and support.
- Psychological Effects: Man-made disasters can profoundly impact survivors, responders, and affected communities. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety , depression, and other mental health issues may emerge in the aftermath of traumatic events. Emotional distress, grief, and feelings of helplessness and vulnerability can persist long after the disaster has occurred. Access to mental health services, social support networks, and psychosocial interventions is critical for addressing psychological trauma and promoting resilience.
Case Studies of Notable Man Made Disasters
Case studies of notable man-made disasters offer valuable insights into the causes, consequences, and lessons learned from these tragic events. Here are several examples:
1. Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster (1986): The Chernobyl disaster remains one of the most catastrophic nuclear accidents in history. On April 26, 1986, during a safety test at the Chornobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Pripyat, Ukraine, a reactor exploded, releasing a massive amount of radioactive materials into the atmosphere.
- Cause: A flawed reactor design and operator error led to a catastrophic explosion and fire during a safety test.
- Consequences: The release of radioactive materials contaminated vast areas of land, forcing the evacuation of thousands of people and causing long-term health effects.
- Lessons Learned: Highlighted the importance of stringent safety protocols, transparent communication, and international cooperation in nuclear energy regulation.
2. Bhopal Gas Tragedy (1984): The Bhopal Gas Tragedy, also known as the Union Carbide disaster, occurred on December 2-3, 1984, in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. It stands as one of the world’s deadliest industrial disasters, involving releasing toxic gas from the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant.
- Cause: A toxic gas leak from a pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide Corporation resulted from equipment malfunction, maintenance deficiencies, and safety violations.
- Consequences: Thousands of people died, and hundreds of thousands suffered from respiratory ailments, eye problems, and other health issues due to exposure to methyl isocyanate gas.
- Lessons Learned: Emphasized the need for corporate responsibility , regulatory oversight, and emergency preparedness in hazardous industries.
3. Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill (2010): The Deepwater Horizon oil spill, also known as the BP oil spill, was an environmental disaster that unfolded in the Gulf of Mexico. The incident originated with the explosion and sinking of the Deepwater Horizon offshore drilling rig on April 20, 2010, and resulted in one of the largest marine oil spills in history.
- Cause: An explosion and subsequent oil spill occurred during drilling operations at the Deepwater Horizon offshore oil rig, leading to history’s most significant marine oil spill.
- Consequences: Massive environmental damage, including the loss of marine life, contamination of coastal ecosystems, and economic impacts on fishing and tourism industries.
- Lessons Learned: Highlighted the risks associated with offshore drilling, the importance of robust safety standards, and the need for adequate spill response measures and environmental monitoring.
4. 9/11 Terrorist Attacks (2001): The September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks were a series of coordinated suicide hijackings carried out by the extremist group al-Qaeda against targets in the United States. It remains one of the deadliest terrorist attacks in history and a defining moment of the 21st century.
- Cause: Coordinated terrorist attacks by the extremist group al-Qaeda involving the hijacking of commercial airplanes and their subsequent crashes into the World Trade Center towers, the Pentagon, and a field in Pennsylvania.
- Consequences: Nearly 3,000 people died, and thousands more were injured. The attacks prompted significant changes in security policies, counterterrorism efforts, and international relations.
- Lessons Learned: Demonstrated the vulnerability of modern societies to asymmetric threats and underscored the importance of intelligence-sharing, border security, and resilience planning.
5. Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster (2011): The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster occurred on March 11, 2011, following a powerful undersea earthquake off the northeastern coast of Japan. The earthquake triggered a massive tsunami that inundated the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, leading to a complex nuclear crisis.
- Cause: A massive earthquake and tsunami triggered meltdowns and releases of radioactive material at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, resulting from design flaws, inadequate safety measures, and regulatory failures.
- Consequences: Forced evacuations, land and water contamination, and long-term health concerns for residents exposed to radiation.
- Lessons Learned: Highlighted the need for robust nuclear safety standards, emergency response capabilities, and risk assessments in disaster-prone regions.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Prevention and mitigation strategies are essential for minimizing the occurrence and impact of man-made disasters. These strategies encompass proactive measures to identify and address risks before they escalate into crises. Here are some key prevention and mitigation strategies:
- Risk Assessment and Management: Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential hazards, vulnerabilities, and exposures. Implement risk management frameworks to prioritize and address high-risk areas and activities. Develop contingency plans and response protocols for different types of disasters.
- Regulatory Compliance and Enforcement: Establish and enforce stringent safety regulations, building codes, and environmental standards. Conduct regular inspections, audits, and evaluations to ensure compliance with regulations and best practices. Hold accountable individuals and organizations that violate safety protocols or endanger public welfare.
- Investment in Infrastructure Resilience: Invest in resilient infrastructure designs that withstand natural disasters, technological failures, and security threats. Enhance critical infrastructure systems, including transportation networks, utilities, and communication systems, to improve reliability and redundancy. Incorporate climate resilience and adaptation measures into infrastructure planning and development.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Develop and regularly update emergency response plans at the organizational, community, and governmental levels. Conduct training exercises, drills, and simulations to test emergency response capabilities and improve stakeholder coordination. Establish communication protocols and information-sharing mechanisms to facilitate timely and effective response efforts.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raise awareness among the public about potential risks, hazards, and emergency procedures through outreach campaigns, educational programs, and community engagement. Promote disaster preparedness and resilience-building initiatives at the individual, household, and community levels. Provide accessible and accurate information about preventive measures, evacuation routes, and emergency shelters.
- Technological Innovations and Advances: Leverage technological innovations, such as early warning systems, remote sensing technologies, and predictive analytics, to enhance disaster preparedness and response. Invest in research and development of new hazard monitoring, detection, and mitigation technologies. Foster collaborations between academia, industry, and government agencies to harness the potential of emerging technologies in disaster risk reduction.
- International Cooperation and Collaboration: To address transboundary threats and shared vulnerabilities, Foster partnerships and cooperation among countries, regions, and international organizations. Exchange best practices, lessons learned, and expertise in disaster management, capacity building, and resource sharing. Support multilateral initiatives and frameworks for disaster risk reduction, resilience-building, and sustainable development.
- Community Engagement and Participation: Empower local communities to actively participate in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. Foster community resilience through social networks, mutual assistance groups, and grassroots initiatives. Involve community stakeholders in decision-making processes and resource allocation for disaster risk reduction and mitigation.
Initiatives taken by Governments across the world
Governments worldwide have implemented various initiatives to address the challenges posed by man-made disasters and enhance resilience in their respective regions. These initiatives encompass legislative reforms, policy frameworks, capacity-building programs, and international collaborations. Here are some examples of initiatives taken by governments across the world:
1. Legislative Reforms and Policy Frameworks
- United States : The U.S. government has enacted legislation like the Robert T. Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance Act, establishing the federal disaster response and recovery efforts framework.
- Japan : Japan has implemented comprehensive disaster management laws and policies, including the Basic Act on Disaster Management, to enhance preparedness, response, and recovery capabilities.
- European Union : The European Union has developed the Civil Protection Mechanism, which facilitates cooperation among member states in disaster response and provides financial assistance for emergency operations.
2. National Disaster Management Agencies
- India : The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) in India coordinates disaster preparedness, mitigation, and response efforts at the national level, focusing on building community resilience and capacity.
- Australia : The Australian Government’s Department of Home Affairs oversees emergency management and disaster response activities, working closely with state and territory governments through the Australian Disaster Resilience Framework.
3. Early Warning Systems and Technologies
- Indonesia : Indonesia has implemented the Indonesian Tsunami Early Warning System (InaTEWS) to detect and disseminate timely warnings of tsunamis and seismic events, helping to mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
- Mexico : The Mexican government operates the Sistema de Alerta Sísmica Mexicano (SASMEX), a seismic early warning system that alerts vulnerable populations during earthquakes.
4. Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction Programs
- Philippines : The Philippines has implemented community-based disaster risk reduction and management (CBDRRM) programs, empowering local communities to identify risks, develop preparedness plans, and undertake mitigation measures.
- Bangladesh : Bangladesh has established community-based flood early warning systems and cyclone shelters, supported by government initiatives and international partnerships, to enhance resilience to recurring natural disasters.
5. International Collaborations and Partnerships
- United Nations : The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) works with governments and stakeholders worldwide to promote disaster risk reduction, resilience-building, and the implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
- International Monetary Fund (IMF) : The IMF provides technical assistance and capacity-building support to countries to strengthen their disaster risk management frameworks, enhance fiscal resilience, and develop contingency planning mechanisms.
6. Research and Innovation Initiatives
- Singapore : Singapore invests in research and innovation initiatives through organizations like the Centre for Climate Research Singapore (CCRS) to enhance understanding of climate change impacts and develop adaptive strategies for disaster resilience.
- South Korea : South Korea supports research and development projects in disaster management and technology innovation, fostering collaborations between government agencies, academia, and industry stakeholders.
Man-made disasters represent profound challenges to societies worldwide, necessitating vigilant preparedness and proactive measures to mitigate their impact. These events, from industrial accidents to environmental catastrophes, underscore the critical importance of robust regulatory frameworks, effective risk management strategies, and international collaboration. By prioritizing safety, resilience, and sustainability, governments and stakeholders can work together to prevent and mitigate the occurrence of man-made disasters. Through continuous innovation, community engagement, and shared responsibility, we can strive actively to build a safer, more resilient world where we minimize the potential for human-induced catastrophes and safeguard the well-being of all individuals and ecosystems.

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW
Pen2Print Services
Get Pen2Print services from our Educational Platform for scholars.
- _Published Books
- Conferences
- Conference Proceedings
- Edited Books
- Cover Design
Search more articles
Short essay on 'man made disaster' (200 words).

Featured post
How to write effective literature review.
A literature review is an essential component of any research project or academic paper. It involves identifying, evaluating, and summarizin...

- Book Chapters

Services Tags
- Audio Books
- Book Chapter Publication
- Book Chapters Publication
- Book Publication
- Book Publishing
- Book review
- Book Series
- Book-Chapters
- Book-Cover-Design
- Call for Book Chapters
Call for Papers
- Conference-Proceedings
- Content Writing
- Copywriting
- Creative Writing
- Edited-Books
- Pen2Print Publication
- Pen2print Services
- Physical Educational Books
- Publications
- Research Papers
- Research Publication
- Website Development
- Writing Services
Readers of the Forum
Search this website.
Our YouTube channel crossed 10k subs!
- Publication
Popular Posts

Get More Services
Welcome to Books and Book Chapters, if you wish to get your scholarly books and book chapters published then you are at the right place.

Send mail to [email protected]

Essay on Man Made Disasters
Students are often asked to write an essay on Man Made Disasters in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Man Made Disasters
What are man made disasters.
Man made disasters are terrible events caused by human actions. These can be accidents like oil spills, or on purpose like wars. They hurt people, animals, and the environment. Unlike natural disasters, these tragedies come from mistakes or bad choices by people.
Examples of Man Made Disasters
Some common examples include factory explosions, chemical leaks, and forest fires started by humans. Pollution from cars and industries is also a big problem. It makes the air dirty and can make people sick.
Effects on Life and Nature
These disasters can destroy homes and take away people’s jobs. They can also kill plants and animals, making it hard for nature to recover. Clean water can become scarce, and food supplies may be affected, too.
Preventing Disasters
To stop these disasters, we must be careful with technology and chemicals. Laws should be strict to protect our world. Everyone has a part to play in keeping the planet safe for future generations.
250 Words Essay on Man Made Disasters
What are man made disasters, types of man made disasters.
There are many kinds of man made disasters. Pollution is a big one, where harmful chemicals get into the air, water, or land. Accidents at factories or plants can release dangerous substances. Wars and bombings destroy cities and hurt innocent people. Then there are fires that can start by someone’s error and burn forests and homes.
Effects on People and Nature
These disasters can make people sick, leave them without homes, or worse. Nature suffers too. Animals lose their homes, and beautiful places can get ruined. Sometimes, the damage is so bad that it takes a very long time for things to get better.
The good news is that we can do things to stop many man made disasters. Making strict rules for factories, using less harmful stuff, and being careful can help a lot. Everyone has a part to play, from big companies to regular folks like you and me.
In conclusion, man made disasters are a big problem, but we can fight against them. By understanding what they are and how they happen, we can work together to keep our world safe and beautiful for everyone.
500 Words Essay on Man Made Disasters
Man made disasters are terrible events that happen because of human actions. These actions can be mistakes or things people do on purpose. Unlike natural disasters like earthquakes or hurricanes, man made disasters are not caused by nature. They often come from not following safety rules or fighting among people. These disasters can hurt people, damage homes, and make the environment dirty.
Industrial Accidents
Industrial accidents happen when something goes wrong in places like factories or power plants. A famous example is the Chernobyl disaster, where a nuclear power plant exploded and sent harmful radiation into the air. This radiation made many people ill and left a large area unsafe to live in for a long time.
Chemical Spills
Chemical spills are when harmful chemicals leak and get into the ground, water, or air. This can happen if a tank or truck carrying chemicals breaks. These spills can kill plants and animals, make water unsafe to drink, and cause health problems for people.
Wars and Conflicts
Preventing man made disasters.
To stop man made disasters, it is important to follow safety rules and be careful with dangerous materials. Governments and companies should work together to make sure everything is safe and to teach people about the dangers. It’s also important for countries to talk to each other and solve problems without fighting.
What Can We Do?
Everyone can help prevent man made disasters. We can learn about safety and be careful with things that can cause harm. We can also tell others about the importance of peace and taking care of our world. If a disaster does happen, we can help those who are hurt by giving support and aid.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Man-made disasters are occurrences that come about due to man’s activities on the earth’s surface. They can be intentional or accidental, but in either case, they can cause great harm to human beings, animals, property and the environment at large. Some examples of man-made disasters include global warming which has been caused by excessive burning of fossils and deforestation or land cultivation this exposing the settlements to landslides, soil erosion, and desertification. Some disasters caused by man intentionally include terrorism and war (Schein 2006).
On the other hand, natural disasters occur naturally and can cause severe losses to humans, directly or indirectly, and also environmental destruction. Some of these include earthquakes, floods, tsunamis, eruptions, and hurricanes. For example, the Spanish flu of 1918-1919, that killed millions of people even more than the First World War which was before it (James, 1996). Effects of such disasters can be very devastating since they occur naturally without man’s prior knowledge hence the need to be prepared through prior planning.
Other disasters can be classified as both man-made and natural since they occur due to a combination of the two factors. For example, mine collapse can be said to occur naturally due to earth’s shifts and at the same can be man-made due to poor construction of mines by man.
Whether natural or man-made, the effects of such disasters can be very devastating to mankind, either physically or psychologically. The reactions of people at the individual and community level may also differ in either case. A natural disaster model proposed by Chapman 1962 (as cited in James, 1996, p. 102) reveals that there are stages that follow before a disaster occurs. Before a natural disaster strikes, there is the ‘warning stage’ where warnings may be sent to people, though some may ignore or probably may not get the information. By the time it gets to ‘threat stage’, signs of an impending danger begin to be felt, although in this case, some disasters have little or no prior warning. When a disaster finally strikes – ‘impact stage’, there is a lot of anxiety amongst people close to it or those who had a prior experience of a similar occurrence. At ‘inventory’ and ‘rescue’ stages, rescue efforts by those near begin while others access the losses. In many cases, government and other agencies intervene to offer some help to the survivors thus giving them some hope of survival, ‘remedy’ stage. In a case where the intensity of the disaster is very high, the survivors may start feeling discouraged and abandoned especially when some of the help groups start pulling out of the rescue exercise. At the recovery stage which may be several months or years, people tart rebuilding their property and psychological lives, though it is usually a slow and bumpy process. Similarly, this also happens in the case of a manmade disaster (James, 1996).
In both cases, the psychological impacts may have long-term effects on the victims such as, believe that similar phenomena might occur again and affect an individual. People also tend to think and discuss so much on the happenings and this results in increased fears. Resulting deaths and property loss tend to trouble people as they feel prone to a similar disaster in the future and their inability to protect themselves. A disaster where with no prior warning and one that seems to be out of control with so much trauma has a more harsh impact on the victims and more long-term psychological effects. All these are characteristic of both natural and technological disasters.
The psychological and emotional effects are more severe and tend to last longer when several people are victims of a disaster. Those involved at a personal level may suffer most but survivors as well may have long and short-term effects. When a disaster involves victimizations of the victims, the reactions tend to be tenser for the people involved and even the response groups find it quite challenging to offer relief. This mostly happens if the crime was man-made and moreover intentional (Danieli & Brom 2005). The government’s response in such a case is more intricate, stressful and the area is branded a crime scene where movements may be limited. This is unlike in the case of a natural disaster where relief efforts are done with several agencies offering to help
According to Ursano and Norwood (2003), stress experienced when a natural disaster occurs is mostly related to lack of prior warning, loss of property and lives and separation from loved ones. This may be experienced for some time but heal in 18months time unless the intense and number of sufferers was quite extreme. In the case of a man-made disaster, the post-traumatic stress disorder associated with the threat to life may be long-lasting and take a lot of time to heal.
Ted and Theodore (2006) say that in an occurrence of a natural disaster, spiritual beliefs may be distorted where some people may start to lose faith in God for allowing such a thing to happen. Others feel a bit insecure as they realize that no one is indestructible by such an act of nature. On the other hand, a technological disaster may bring about distrust among people on realizing that the world is no longer secure and that one cannot keep away from danger. Survivors of such an act may tend to be withdrawn as they feel that no one around can be trusted.
Most natural disasters tend to affect poor people or low-income earners since they live in places that are prone to such disasters as landslides and floods. Victims from certain groups like the disabled, orphans or some ethnic groups tend to take more time to heal thus making them feel more stigmatized and increasing psychological stress. Victims of a technological disaster on the other hand may start feeling guilty and humiliated especially if they are not in a position to offer help. Family, friends and the community may stay away on realizing that a mishap can happen to anybody. Continued encouragement of those affected to carry on with their live may make them feel as if they are wrong for their suffering (Ted and Theodore 2006).
Victims of a technological disaster tend to feel helpless in pursuit of justice or compensation from the concerned authorities since the process is sometimes long, bureaucratic and frustrating. At times, they feel that the penalty enforced on the culprits is not worth enough compared to the suffering they undergo. Sufferers of a natural disaster on the other hand may feel disheartened as all their needs may not be met by the assisting agencies due to the long procedures involved in channeling of resources or even the inadequacy of the resources themselves (Ursano, McCaughey and Rhaphael 1995).
In conclusion, the effects of a disaster, whether natural or technological have severe impact on the victims, some of which might be short-lived while others may be experienced as long as one lives. Proper plans should therefore be made in advance on issues relating to preparedness, response and recovery so as to counter the effects of a future calamity. Such plans do not necessarily prevent a disaster from occurring but they help in managing the damages caused with much ease.
Danieli Y., Brom D. & Sills J. (2005). The trauma of terrorism: sharing knowledge and shared care, an international handbook. Routledge
James K. Mitchell (Ed.) (1996). The long road to recovery: Community responses to industrial disaster . United Nations University Press
Schein A. L., (2006) Psychological effects of catastrophic disasters: group approaches to treatment . Routledge
Ted S. & Theodore S. (2006). Acts of God: the unnatural history of natural disaster in America (2 nd ed.) Oxford University Press
Ursano J. R., McCaughey G. B. & Rhaphael B. (1995) Individual and Community Responses to Trauma and Disaster: The Structure of Human Chaos . Cambridge University Press
Ursano J. R., & Norwood A. E. (2003 ). Trauma and disaster responses and management . Cambridge University Press.
- Earthquake Impacts: A Case Study of the 2010 Haiti Earthquake
- Community and Authority Response to Volcanic Eruptions
- Returns to Investment in Education
- Los Angeles International Airport's Environmental Impacts
- Urban Form Determinants of Rome
- Government Response to Natural Disasters – Hurricane Katrina
- Crisis Intervention of Natural Disasters
- Famine in Africa in “Surrender or Starve” by Robert Kaplan
- City of Jeddah’s Flood: Cause and Disastrous Effects
- Physical Aspect of Tsunami
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, December 16). Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-made-and-natural-disasters-comparison/
"Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison." IvyPanda , 16 Dec. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/human-made-and-natural-disasters-comparison/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison'. 16 December.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison." December 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-made-and-natural-disasters-comparison/.
1. IvyPanda . "Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison." December 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-made-and-natural-disasters-comparison/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Human-Made and Natural Disasters Comparison." December 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-made-and-natural-disasters-comparison/.
- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
Natural Disaster Essay: How to Write, Topics, & Examples
What would you do if someone told you that a tsunami would wipe out your house tomorrow afternoon? You won’t believe them. It always seems that natural disasters happen in someone else’s life. But every year, millions of people worldwide suffer from various natural calamities. This article attempts to systemize the chaos of nature for you to write an impressive natural disaster essay. You will get acquainted with the seven types of disasters, get a long list of topics and examples of natural disaster essay in 200 words and 300 words.
- 🌪️ Natural Disaster: The Basics
- 💡 114 Essay Topics
- 📑 Outlining Your Essay
- 🌊 Essay Sample (200 Words)
- 🏜️ Essay Sample (300 Words)
🌪️ Natural Disaster Essay: What Is It About?
A natural disaster is a large-scale meteorological or geological event that can to cause loss of life or massive damage to people’s property. Floods and severe storms are the most reported acts of nature in the US, but other incidents also happen from time to time. That is why you can dedicate your essay on natural disasters to earthquakes, droughts, wildfires, floods, tsunamis, hurricanes, or tornadoes.

| It is a powerful funnel-shaped cloud that rotates and demolishes buildings, hurls cars, and uproots trees. Tornadoes appear from cumulonimbus clouds, pending with their smaller part to the ground. This column of air has a wind speed of up to 300 mph. In your disaster management essay, you can suggest reasonable precautions to save as many people and property as possible in a tornado area. | |
| It is a tropical cyclone that affects the coastal population of the southern Atlantic Ocean, eastern , Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. These acts of nature may include heavy winds, floods, and tornadoes. For this reason, you can describe natural disasters’ impact on human life in the essay. | |
| Floods are the most common natural disaster in the US. They usually occur when the volume of water in a stream is larger than the channel’s capacity. Then, the land that is typically dry gets submerged. Streamflow depends on numerous factors making floods hard to predict. | |
| This Japanese word (‘tsu’ for harbor and ‘nami’ for wave) denominates powerful waves caused by an underwater earthquake, land slumping, landslides on the seafloor, meteorite impact, or volcanic eruption in the ocean. In a tsunami disaster essay, you could describe a historical tragedy and analyze its causes. | |
| This type of disaster starts when lightning hits a tree in the wood or due to man-made causes. It is an unplanned and uncontrolled spread of fire in natural areas with combustible vegetation. | |
| It is an extended lack of water in a given region. A drought can happen due to the below-normal precipitation. It causes crop damage and water shortage in the area. It can last for years or end in weeks. | |
| It is the result of seismic waves in the Earth’s crust. Tectonic plates shake or move, damaging everything that stands or lives on them. Some of them may be caused by anthropogenic factors. |
💡 114 Natural Disasters Essay Topics
What could you write in a natural disaster essay? You can invent your own topic about various types of natural disasters, their causes, and aftermath, or their impact on human life and the economy. Depending on the discipline, you can also describe historic calamities that changed the direction of human civilization. Alternatively, choose one from our comprehensive list below.
- Why are the Great Plains of the central US ideal for tornado formation?
- Global Warming and Climate Change Legislation.
- Research the atmospheric parameters inside a tornado.
- Energy, Technology and Climate Change.
- Why are the boundaries of Tornado Alley in the US so debatable?
- The global climate change as a manmade disaster.
- Which actions should you never do when a tornado is nearby?
- Volunteers’ Role During Disasters.
- Suggest your opinion on the best action strategy in a hurricane.
- The Columbia Disaster and safety violations.
- What were the causes and effects of a flood?
- Analysis on Climate Change and Global Impact.
- Describe the most devastating wildfires in the US and find their common features.
- Earthquake Engineering Considerations and Methods.
- Brainstorm ideas to prevent wildfires.
- Global warming and the greenhouse effect.
- How can building dams cause earthquakes?
- Climate Change and Its Impact on Freshwater.
- Analyze the impact of droughts on tourism.
- Climate Change Effect on Coral Reef Communities.
- Describe the most extended droughts in human history.
- Marine and Coastal Climate Change in Australia.
- Write an essay on natural disasters and earthquakes in particular.
- Air pollution and mortality rates
- What are the distinctive features of droughts in third-world countries?
- Global Warming, Climate Change, and Society’s Impact on the Environment.
- Study the relationship between global warming and droughts.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder After a Hurricane.
- Evaluate the damage caused by Hurricane Maria in 2017.
- Social Media’s Role in Disaster Response.
- Classify the effects of natural disasters in an essay.
- Sustainability and Climate Change.
- Describe the 1815 volcanic eruption of Mt. Tambora, Indonesia.
- Hurricane Katrina: Overview, Impact, Response.
- Each new leap of civilization causes new responses of nature.
- Animal Exploitation. Animal Agriculture and Climate Change.
- Think of any positive effects a volcanic eruption may have.
- In Arizona, Collaboration Averts Water Disaster.
- Children are the poorest victims of any disaster.
- A Solution to Remedy Climate Change.
- Which ways of disaster risk reduction do you know?
- An Emergency Operations Center During Hurricane Harvey.
- Research the current problems in disaster management.
- Disaster Recovery Plan for Information Technology Organizations.
- Analyze ineffective disaster management in an essay about hurricane Katrina.
- Nurse Competencies and Scope of Practice in Disaster.
- What should a household have at home in the case of a disaster?
- Hurricane Katrina: The Powerful Natural Disaster.
- Describe the humanitarian disaster during the drought in Somalia.
- Technology in Disaster Preparedness.
- Can man-made disasters entail natural calamities?
- Disaster Management in Philadelphia.
- Review the criteria for disaster classification.
- Jeddah Floods and Adaptation Strategies in the City of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Search for real examples of hybrid disasters.
- Natural Disasters Prevention: A Tabletop Exercise.
- Who is responsible for casualties after a natural disaster?
- The Sand Storms: Remote Sensing and Meteorological Variables.
- List the lessons we could learn from our past disaster experience.
- Fire Development, Growth, and Spreads.
- The ice storm and silver thaw: A gentle disaster.
- Fire Crisis Management in the UAE.
- Rockslides: A pressing issue for rural areas.
- 1d – 2d Flood Modeling Using PCSWMM.
- What are the psychological benefits of disaster preparedness?
- Structural Control and Origin of Volcanism in the Taupo Volcanic Zone.
- When does a blizzard become a disaster?
- Extreme Weather Events + Geographies of Globalization.
- Research the causes of dust storms and name the affected areas.
- Strategies for Sustainable Integrated Oil Disaster Management in West Africa.
- Why did the San Francisco earthquake (1906) cause devastating fires?
- Causes of Climate Change.
- What could be done to help people who lost their homes in an earthquake?
- Book Review: Energy and Global Climate Change.
- Analyze the role of World Vision in humanitarian aid after disasters.
- Tangshan earthquake of 1976 showed that high population density is disastrous.
- The Role of Carbon Dioxide in Climate Change.
- Rock avalanche: Why water is the most powerful geological agent.
- Aspects of Climate Change.
- When do extreme weather conditions turn into a disaster?
- Climate Change: Reasons, Kyoto Protocol.
- Write an article on shelter-providing organizations for disaster victims.
- Establishing an IT Disaster Recovery Plan.
- Describe earthquake cycles in Haiti.
- Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture and Food.
- How can nature damage ecology in natural disasters?
- Climate Change. Problems. Effects.
- Disaster management should include psychological help to the survivors.
- Climate Change Causes: Position and Strategies.
- Suggest ways to prevent damage caused by debris flow.
- HAT 4: Disaster in Franklin Country.
- How did the lack of evacuation after the Bhola cyclone (1970) result in the massive death toll?
- The Effects of Climate Change.
- The most significant Yellow River flood: 2 million deaths in 1887.
- Resilience Building Against Natural Disasters in the Caribbean Islands.
- Sinkholes: A natural disaster or attraction for cavers and water-divers?
- Global Climate Change and Health.
- Describe the dynamics of landslides in California.
- Which early-warning systems to detect avalanches do you know?
- Los Angeles Regional Collaborative for Climate Action.
- Pyroclastic flow: The deadliest volcanic hazard.
- Communication During Disaster Response.
- Describe the volcano eruption of Vesuvius that destroyed the Herculaneum and Pompeii.
- Disaster Planning for Families.
- Disaster prevention measures: Investments that save millions of lives.
- Natural Disaster Management and Historical Prospective Study in the UAE.
- Research the PTSD in survivors of natural disasters.
- Are the latest disasters the nature’s fightback to humanity?
- Estimate the human impact on natural disasters.
- List the countries with the largest number of disasters and find their standard features.
- Everyday Communication on Climate Change.
- Insurance coverage against disasters: Our inevitable future.
- Emergency Planning Before and After Hurricane Katrina.
- One natural disaster could bring the world to its end.
Haven’t found a suitable topic in the list above? Use our essay topic generator to get more ideas.
📑 Natural Disaster Essay Outline
Outlines differ, depending on the assigned length and essay type. It is a reference sample. Feel free to modify it, extending some points and narrowing the others. Still, the overall structure should remain the same. We have chosen the “Causes of Earthquakes” essay topic for demonstrative purposes.
- Hook . There are millions of possible ways to start your essay, from a rhetorical question to any imaginable scenario. The point is to grab the reader’s attention, showing them that your writing is unique and creative. For example: We are always concerned with the consequences of a natural disaster. But what brought us into such a calamity in the first place?
- Concepts. Natural disasters can be studied in the framework of various disciplines. But in all cases, they are linked with geology, biology, chemistry, geography, and some other subjects with broad and complicated terminology. Explain the terms that could be elusive for your readers here. For example: For the purposes of this essay, an earthquake is a sudden displacement of the land surface.
- Background. How did you come to think of this problem? Why is it topical? The causes of earthquakes are numerous and often unrelated. To understand them as a system, we need a strict classification.
- Thesis statement . Clearly state the aim of your essay. This essay attempts to group the causes of earthquakes to determine which factors can be tackled by human forces.
- Transition sentence. It comes in the previous sentence (for paragraphs 2 and 3) and ensures smooth reading. E.g.: Tectonic movements are the most powerful causes of earthquakes, and we cannot influence them. But still, there is something we could do.
- Topic sentence . What will you explain in this paragraph? Human interference with nature can also cause earthquakes.
- Evidence. How can you confirm the topic sentence? Heavy clubbing of dam water can disturbance the crustal balance. Nuclear bombing causes shockwaves that penetrate the surface, changing the tectonic plates and their natural alignment. Mining can also cause earthquakes by removing extensive volumes of stone from under the ground.
- Warrant. Why does the reader need this information, and how does it relate to the thesis statement? Knowing these facts can help us change the old-fashioned approaches and lessen the ecological damage to our planet.
- Summary. Collect and summarize all your arguments here. Tectonic movements, volcano eruptions, and geological faults cause a significant part of earthquakes worldwide. But various man-made causes bring us to the same result.
- Rephrased thesis. We cannot stop the tectonic movements or hinder volcanic eruptions, but we can use natural resources with more care.
🌊 Natural Disaster Essay 200 Words
Below you will find a short natural disaster essay for 200 words. It explores the causes and effects of the tsunami in Japan in 2011.
Tsunami in Japan: Causes and Effects The proximity of the deadliest disasters is often unpredictable. As a result, the consequences of a tsunami can exceed any possible expectations. This essay looks for the decisive factors that caused the tsunami in Japan in 2011 and its results for the local population and other countries. The causes were out of human control and could not be predicted. The Pacific plate moved in the horizontal and vertical plane, advancing beneath the Eurasian Plate. It displaced the seawater above and entailed several destructive waves. The disaster had enormous consequences for the Japanese people and their economy. It killed almost 16,000 people, although the country had a sophisticated alarming system. Besides, the earthquake caused fires and explosions at oil factories. The cooling system of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant went out of service. Two people were lost, and many were injured. Nissan, like many other large corporations, had to suspend the operation of its four factories. The economic losses due to the catastrophe amounted to 300 billion dollars. But the disaster moved to other places. On 24 March 2011, the earthquake in the east of Myanmar claimed the lives of 60 people and destroyed 300 buildings. As we can see, everything is linked on our planet. Movements of the earth’ crust in any part of the world bring about earthquakes and tsunami in other countries. The series of waves in Japan was caused by the underwater earthquake and had horrible consequences.
🏜️ Natural Disaster Essay 300 Words
If your assignment is longer, you will have to provide your opinion in the essay. Or, you can make your argumentation more detailed. Below you can check our 300-word sample of a disaster essay.
The Economic Effects of the Dust Bowl Drought When someone says “a natural disaster,” we usually imagine an earthquake or a tsunami. Buildings are destroyed, and property is lost. But imagine a scenario of a devastating drought, which happened in the US in the 1930s. Its effect is less visible because it lies in the domain of the national economy. This essay reveals the economic consequences of the Dust Bowl drought. During the third decade of the XX century, strong winds raised choking dust in the southern states, from Texas to Nebraska. People and animals died as the crops failed in the area for several years in a row. The Dust Bowl lasted for almost a decade and was also called “the Dirty Thirties.” This drought intensified the impact of the Great Depression. Local farmers had to migrate to urban areas in search of better conditions and other sources of living. About 2.5 million people moved West from the worst-hit states, namely New Mexico, Texas, Nebraska, Oklahoma, and Kansas. But they found only discrimination, meager salaries, and inhuman working conditions. Many had to live in tents near irrigation ditches. They were called “Okies,” a disdainful name for migrants of any state. Regular rains returned to the southern states by the end of 1939, closing the drought. However, the economic aftermath persisted. The counties that suffered the most failed to recover the agricultural value of their land till the 1950s. Thus, the local population kept decreasing for twenty years. Although a drought does not ruin property, it can tangibly lower human life levels. The Dust Bowl threw people into a lose-lose situation. Their farms were unfit for gaining any profit, and the new places of living gave them no better opportunities. It took two decades to restore public wellbeing in the Southern States.
Researching the worst acts of nature can teach you to value what you have. We hope that this article has made your creative writing more manageable and pleasurable. You can write an essay of any length by simply following our outline. All you will need to do after that is make a cover page for it.
Please share your natural disaster essay ideas in the comments below.
❓ Natural Disaster Essay FAQ
How to write an essay about natural disaster.
Your approach should depend on the discipline. But in any case, you can discuss the types of disasters, their consequences, characteristics, and preconditions. The excellent idea is to select a past disastrous event and analyze it from the economic, social, or individual point of view.
What Is a Disaster Essay?
A disaster essay explores the stages of a natural or man-made calamity and seeks the possible ways to prevent similar emergencies in the future. An article on disaster management studies the correct and efficient activities to lower the casualties and property loss after a disaster.
What Is Disaster Preparedness Essay?
This type of writing analyzes the level of readiness of a region or municipality to an unexpected natural disaster. You can highlight the vulnerable groups of the population that will suffer the most. Or, you may invent measures that could reduce the disaster response and coping time. Such assignments teach you strategic thinking and a systematic approach to problem-solving.
How to Describe a Natural Disaster for an Essay?
You should specify that the event was unexpected and led to many deaths and property loss. The most critical things include the causes of the disaster, its progress and duration, and the negative consequences for the locals. You can also specify the negative effect on the economy and humanitarian condition of the area.
🔗 References
- Natural Disasters and Severe Weather | CDC
- Types of Disasters | SAMHSA
- Natural Disaster – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Natural Disasters – National Geographic
- What Is Disaster Management: Prevention and Mitigation
Essays on Economics of Man-Made Disasters
Journal Title
Journal issn, volume title, repository usage stats.
The severity of man-made disasters has been increasing recently and is expected to further increase with climate change. For example, the number of conflicts and their associated fatalities have risen by 105\% and 286\% since 2010, respectively. With the internet and technological advancement, disasters significantly affect individual welfare both directly and indirectly. I study how the end of a man-made disaster affects labor market outcomes over time and how disasters affect risk preferences in the long run and time use in the short run. In Chapter 1, I study the causal impact of peace on labor market outcomes using the sudden and unexpected end of the Aceh Insurgency in Indonesia in a difference-in-differences framework. In Chapter 2, the intergenerational effects of early life exposure to the Korean War on risk preferences are examined in a difference-in-differences-type model with both structural and reduced-form estimation methods. In Chapter 3, I take the 2014 $Sewol$ ferry disaster as a natural experiment to examine the causal effects of an exogenous psychological shock on time use.
Description
Kim, Dongyoung (2023). Essays on Economics of Man-Made Disasters . Dissertation, Duke University. Retrieved from https://hdl.handle.net/10161/27656 .
Collections

Dukes student scholarship is made available to the public using a Creative Commons Attribution / Non-commercial / No derivative (CC-BY-NC-ND) license .
- BiologyDiscussion.com
- Follow Us On:
- Google Plus
- Publish Now

Natural and Man-Made Disaster and their Impact on Environment
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Earthquakes, floods and landslides, etc. are natural environmental hazards of disastrous consequences.
In recent years these hazards took toll of thousands of lives and caused massive destruction of property.
These have adversely affected the vital sectors of our development as agriculture, communication, irrigation, power projects and rural and urban settlements.
The time and cost overrun in some cases have been enormous but their indirect impact on our economy has never been calculated. India is among the world’s most disaster prone areas and a large part of the country is exposed to natural hazards, which often turn into disasters causing loss of life and property. The unique geo-climatic conditions have exposed this country to natural catastrophes.
Disasters can be defined as a sudden, accidental event of great magnitude that causes considerable damage to life and property. They are sudden, drastic and normally occur without any alarm or warning. Some disasters may be short lived such as earthquakes and some other may be of long duration, such as floods.
However, irrespective of the duration of a disaster, the damage in the form of deaths, injuries and losses of property is immense. The magnitude of the disasters can be judged by the fact that only during the past two decades, occurrences of floods, earthquakes, landslides, cyclones, etc. have killed several million people.
Most of the disasters have a natural origin, however, some disasters are manmade as well. On this basis, disasters can be broadly classified into two groups:
Natural disasters:
When disasters occur due to natural forces they are called natural disasters, over which man has hardly any control. Some common natural disasters are earthquakes, landslides floods, droughts, cyclones, etc. Tsunamis, volcanic eruptions and wildfires are also included under natural disasters. These disasters cause enormous loss to life and property.
Man-made disasters:
When the disasters are due to carelessness of human or mishandling of dangerous equipment’s they are called man-made disasters. Common examples of these disasters are train accidents, aero plane crashes, collapse of buildings, bridges, mines, tunnels, etc.
Natural Disasters :
Some of the common natural disasters, their impact on environment, and their prevention, control and mitigation are discussed below:
Earthquakes :
An earthquake is the shaking of the earth’s surface caused by rapid movement of the earth’s crust or outer layer. Ever since it came into existence 4.6 billion years ago, the earth has been a dynamic, evolving system. The position of the different continents and oceans that we see today, has changed a number of times in the earth’s history.
The earth is primarily composed of three layers:
1. The outer crust,
2. The middle mantle, and
3. The inner core
The Earth’s outer layer or crust is made up of a number of zig-saw pieces like structures that interlock into one another. These pieces are called tectonic plates. These plates are in continuous motion over the mantle, which is known as tectonic movements. These tectonic processes are also responsible for the mountain building processes.
The plates that are moving past over one another are slowed by friction along their boundaries. Due to this, the rocks are under strain. When the stress on the rocks exceeds certain limits, the rocks rupture and form a fault along which the rocks are displaced during tectonic movements. This sudden rupture of the rocks releases energy in the form of earthquake waves (Fig. 18.1).
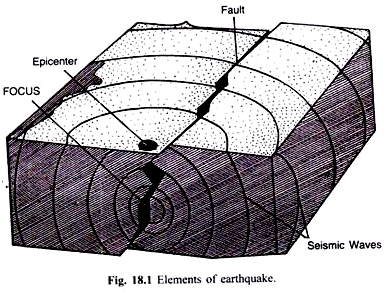
Thus earthquake is a form of energy, which is transmitted to the surface of the earth in the form of waves called seismic waves. The study of earthquakes and the waves they create is called seismology (from the Greek seismos, “to shake”). Scientists who study earthquakes are called seismologists. The instrument that records the seismic waves is called seismograph.
The exact spot under the earth surface at which an earthquake originates is called the focus or hypocenter. The point on the earth surface above the focus is called the epicenter. The Richter scale is used to measure the intensity of earthquakes. The intensity is measured on a scale of 0 to 8 and above (Table 18.1).
Impact of Earthquake on the Environment :
The destruction, an earthquake causes, depends on its magnitude and duration or the amount of shaking that occurs. In the last 500 years, earthquakes around the world have killed several million people. Earthquake is one of the most catastrophic natural disasters. Massive loss of life and property occurs due to collapse of buildings. Besides, roads, bridges, canals, electric poles, etc. are severely damaged. Certain regions of the earth are more prone to earthquakes.
These are places located in the unstable regions of the earth crust, which are subjected to tectonic activities. Countries like Japan, parts of Southeast Asia, Turkey, Iran, Mexico, etc. are affected by severe earthquakes. In India, the entire Himalayan region, parts of the Gangetic Plain, Kutch and Andaman and Nicobar islands are in the earthquake hazard zone (Table 18.2).
The major impacts of earthquakes are as follows:

Shaking of the ground and surface rupture:
This is the main cause of destruction in which buildings, bridges, roads, canals and other structures are damaged.
Liquefaction:
Earthquakes make sands and silts to transform from a solid to liquid state. This also results in building collapse.
Landslides:
Earthquakes of high intensity often trigger many landslides in the hilly regions.
It is a major hazard associated with earthquakes. The shakings of the ground and building damage often break the gas pipes and electric lines that cause fires.
Changes in the land elevation:
The surface topography of a region and groundwater conditions are altered after an earthquake.
It is a Japanese term meaning ‘harbour waves’. Tsunamis are massive sea waves that are mainly caused due to earthquakes in the ocean floor or possibly due to an undersea landslide or volcanic eruption. When the ocean floor is tilted or offset during an earthquake a set of waves is created similar to the concentric waves generated by an object dropped into the water.
These waves are massive in size and gain height as they approach the seashore. Tsunamis up to the height of 30 m are recorded (Fig. 18.2). Tsunamis are the most catastrophic among natural disasters as they affect a very wide geographical area. The tsunami of 26 December, 2004 killed around three lakh people and affected parts of Indonesia, Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India, Sri Lanka and even Somalia.
Prevention and Mitigation :
Despite the advances made by modem science, the exact time and place where an earthquake may strike cannot be predicted. Hence, the occurrence of an earthquake cannot be prevented. However, there are certain regions that are earthquakes prone and so the administration must work before hand to minimize the damages due to occurrence of earthquakes in such areas. The control and mitigation measures in earthquake prone regions include hazard reduction programmes, development of critical facilities and proper land use planning.
Hazard reduction programmes:
These include the following:
i. Earthquake education and evacuation plans.
ii. Use of proper construction material that is not injurious even if the structures collapse.
iii. Construction of quake resistant buildings having proper structural design.
Development of critical facilities:
i. Establishment of earthquake regulatory agencies for fast relief.
ii. Establishment of specific health care units for treating earthquake injuries Proper land use planning.
iii. Mapping of faults and weak zones in earthquake prone areas.
iv. Buildings such as schools, hospitals, offices, etc. should be in areas away from active faults.
Floods refer to the ‘inundation of large parts of land which otherwise remain dry by water for some duration of time’. Floods are one of the most common natural disasters occurring in many parts of the world every year. Floods occur due to heavy rainfall within a short duration of time in a particular region which causes the rivers and streams to overflow.
Since most of the precipitation occurs within span of two to three months during the rainy season, most floods occur during that time. The floods in the mountainous regions due to cloudbursts or damming of streams are referred to as flash-floods. In flash-floods, the water drains away quickly but only after causing extensive damage. The plain areas of a region which are drained by a number of rivers, are the places most affected by floods.
In India, states like Assam, Bihar and parts of Gangetic Uttar Pradesh are quite prone to floods during the rainy season (Fig. 18.3). The Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers and their tributaries are most susceptible to floods. However, heavy rains cause occasional floods in parts of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. Flooding, in India, is a major problem and some part or the other is affected by the fury of floods usually during the months from July to September.
Floods cause untold miseries to the affected regions in the form of huge losses of life and property. There is great damage to agriculture and livestock. Flood affected areas face acute shortages of food and drinking water. Besides, floods cause a number of water borne diseases such as diarrhea, gastroenteritis, jaundice, malaria, etc.
Impact on the Environment :
Though the lives lost in floods may not be as high as in case of earthquakes or cyclones, the damage to the environment is immense. The problem is further aggravated if the floods last for a longer duration of time.
Floods not only damage property and endanger if lives of humans and animals, but have other effects as well, such as:
1. Floods cause the spread of many epidemic diseases.
2. Rapid runoff causes soil erosion.
3. Wildlife habitat and forests are often destroyed.
4. Manmade structures like buildings, bridges, roads, sewer lines, power lines, etc. are damaged.
5. Floods cause widespread damage to the standing crops and degrade the agricultural land.
6. Flood affected areas are faced with acute shortage of food and drinking water.
Prevention, Control and Mitigation :
Though floods are a natural hazard, it is sometimes intensified due to undesirable human activities. The measures that can be taken to control the extent of flood damage include land use planning, building of physical barriers, preventing human encroachment and use of technology for relief.
Land use planning:
Proper land use planning in flood prone areas includes:
1. Demarcation of the flood-prone areas that are first inundated during floods.
2. Construction work and concentration of human population should be avoided in the floodplains.
3. Afforestation on the upper reaches of the river (catchment areas) to control soil erosion and excessive runoff.
Building of physical barriers:
Flood can be prevented by building certain structures, such as:
1. Embankments along the banks of rivers in densely populated areas.
2. Building of reservoirs to collect excess water during floods.
3. The construction of channels that divert floodwater.
Preventing human encroachment:
Human encroachment should be avoided in the following areas:
1. Floodplains and catchment areas.
2. This would control deforestation and soil erosion which would prevent excessive runoff.
Use of technology for relief:
Advanced technology can be used in the following ways:
1. Advanced communication techniques for flood forecasting and warning.
2. Fast evacuation of people.
3. To provide relief in temporary shelters.
4. Immediate supply of medicines, drinking water, food and clothes.
5. Epidemic diseases must be controlled through spraying, vaccination, etc.
Drought is a condition of abnormally dry weather within a geographic region. Drought refers to the lack or insufficiency of rain for an extended period of time in a specific region. During droughts, rainfall is less than normal causing a water imbalance and resultant water shortage. It occurs when the rate of evaporation and transpiration exceeds precipitation for a considerable period. Drought should not be confused with dry climate, as in the Sahara or Thar Desert. It is marked by an unusual scarcity of water and food for the humans as well as animals.
Certain regions of the world, such as parts of Central Africa, are characterized by low amount of rainfall resulting in perennial drought-like conditions. Some part of India is often affected by drought even during the rainy season. As India is primarily an agricultural country, droughts cause untold miseries to the common people.
Many Indian farmers are still totally dependent on rainfall for irrigation and because of abnormally dry spells there is extensive crop damage. The main drought prone areas of the country are parts of Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Orissa, Tamil Nadu and Chhattisgarh. However, sometimes drought-like conditions also prevail in the Gangetic Plain also.
The severity of the drought is gauged by the degree of moisture deficiency, its duration, and the size of the area affected. If the drought is brief, it is known as a dry spell or partial drought.
Drought causes serious environmental imbalances, which are summarized below:
1. Water-supply reservoirs become empty, wells dry up and there is acute water shortage.
2. Groundwater level is also depleted because of less recharge.
3. Soil degradation and erosion occurs. Soil cracks because of shrinkage during desiccation (Fig. 18.4).
4. There is extensive crop damage.
5. People become impoverished and there are diseases due to malnutrition.
6. Widespread damage to flora and fauna air including domestic animals.
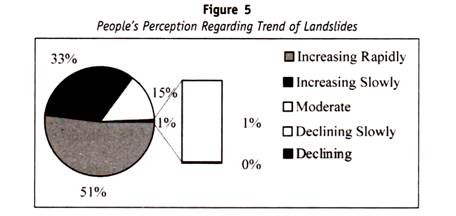
Prevention, control and mitigation :
Rains are caused by a number of natural factors like air currents, wind direction, etc. Thus, droughts are a natural phenomenon, beyond human control and prevention. Though, global warming may have changed the pattern of rainfall in the recent times. In modem times, by the use of satellites, we can predict the weather pattern over a particular area. Drought-like conditions can be overcome by better water harvesting techniques. Certain precautions can be taken in drought prone areas, which relate to management of water resources, proper agricultural techniques and relief by different agencies.
Management of water resources:
1. Conservation of water through rainwater harvesting, building check dams, bunds, etc.
2. Construction of reservoirs to hold emergency water supplies.
Proper agricultural techniques:
1. Increased use of drought resistant crops.
2. Proper irrigation techniques, such as drip and trickle irrigation that minimize the use of water.
3. Over-cropping and overgrazing should be avoided.
Relief measures:
Immediate relief to the drought-affected people should be provided in the form of:
1. Employment generation programmes, like ‘food for work’ in the drought affected areas.
2. To provide fodder for domestic animals.
Cyclone is an area of low atmospheric pressure surrounded by a wind system blowing in anti-clockwise direction, formed in the northern hemisphere. In common terms, cyclone can be described as a giant circular storm system. In a cyclone, the wind speed must be more than 119 km/hr. Cyclones generate in the seas and oceans and move with a very high speed towards the land.
Cyclones form when moisture evaporates from the warm oceans during the hot season. The air rises, condenses and gathers momentum as it moves over the ocean. Due to the extreme low pressure in the centre, more and more air rushes inwards and it grows to a considerable size and intensity.
It strikes the land with a devastating force and gradually withers off on land when they are cut from their source of ocean moisture. Cyclones are named variously depending on their source of origin. They are called hurricanes in the Atlantic, typhoons in the Pacific, cyclones in the Indian Ocean and willy-willies aroimd Australia.
Cyclones are quite common in the Bay of Bengal and often cause much damage in Bangladesh and coastal areas of West Bengal, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. Bangladesh has been devastated by cyclones a number of times. In November 1970, a severe cyclone caused a 6 m rise in sea-level and the consequent flooding killed approximately three lakh people.
Another cyclone in 1971 killed more than one lakh people. The cyclone that hit Orissa in 1999, is the worst recorded natural disaster in India. Even an advanced country like America recorded more than 10,000 deaths and huge financial losses when New Orleans was hit by a hurricane named Katrina, during August 2005. Cyclones cause devastation when they hit the landmass in the form of very strong winds, heavy rains and storm tides.
The impact on the environment is severe, some of which are as under (Fig. 18.5):
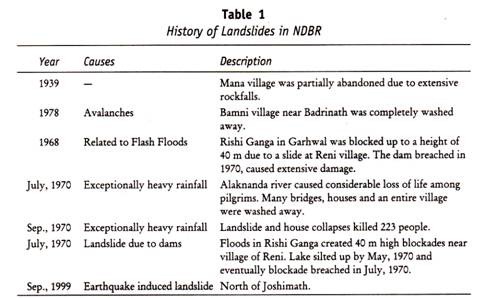
1. The coastal low lying areas are most affected.
2. The affected areas are inundated both with rainfall and the surge of seawater.
3. Devastation is also increased due to the accompanying high velocity winds.
4. Widespread damage in the form of uprooted trees, blown-off roof tops, standing crops, injuries and death to humans and animals.
5. Many shipwrecks occur during cyclonic storms.
6. The affected areas are impoverished and are followed by spread of epidemic and diseases.
The occurrence of cyclones is a natural phenomenon, over which humans have no control, hence it cannot be prevented. However, some scientists have speculated that rise in global warming may cause an increased occurrences of cyclones. The devastating effects of cyclones can only be controlled and mitigated through some effective policies such as use of advanced technology, hazard reduction initiatives and relief measures.
Use of Advanced Technology:
1. Satellites can easily forecast the origin of cyclones in advance.
2. Satellite images can track the movement and intensity of cyclones.
3. Installation of early warning systems in the coastal areas.
Hazard reduction initiatives :
1. Increasing public awareness regarding cyclones.
2. Increasing the public response to cyclone warnings through training.
3. Development of underground shelter belts in the cyclone prone areas.
1. Rushing relief to the affected areas in the form of medicines, food, clothes, etc.
2. Checking the spread of epidemic water borne diseases as cyclones are generally accompanied by flooding.
Landslides :
Landslides refer to a rapid down-slope movement of rocks or soil mass under the force of gravity. It is also known as slope failure and mass wasting. Landslides may be typed as mudflow where there is down-slope movement of soil and debris flow, which is the down-slope movement of coarse material and rocks. Landslides may occur when water from rain and melting snow, seeps through the earth on a sloppy surface and encounters a layer of loose, unstable material such as clay.
Landslides mostly occur on unstable hillsides by the action of rain or snow that seep through the soils and rocks (Figs. 18.6 and 18.7). This results in the sliding of earth and rock masses down the hill slopes. These are further triggered due to deforestation and human encroachment on unstable slopes. All the hilly regions of our country are prone to landslides.
The important factors responsible for landslide occurrence are as follows:
1. Stability of slopes
2. The type of earth and rock material
3. The type of vegetation
4. The role of ground water conditions and precipitation
5. Presence of streams, etc.
It is a type of landslide involving a large mass of snow, ice and rock debris that slides and fall rapidly down a mountainside. Avalanches are initiated when a mass of snow and ice begins to rapidly move downhill because of the overload caused due to a large volume of new snowfall. This result in internal changes of the snow pack, producing zones of weakness along which fissure occurs.
Landslides, though local in nature, occur quite often in many parts of the world. Landslides occur in the hilly regions; the Himalayan region in India is particularly prone to landslides. Every year landslides occur, especially during the monsoon season and cause much damage to life and property. For example, Malpa landslide in 1999 in the Kumaon hills, took the lives of many pilgrims who were going to Mansarovar in Tibet.
The impact on the environment is manifested in the form of:
1. Uprooted trees and degraded soil
2. Buried building and settlements
3. Damage to crops and plantation
4. Frequent roadblocks in the hilly areas
5. Injuries and death to humans and animals
Though landslides are a natural phenomenon and may occur without human interference, in certain cases human activities like deforestation, mining, etc. can also induce landslides. Landslides can be controlled, to some extent, by adopting initiatives, such as providing slope support and minimizing human encroachment.
Providing slope support :
i. By building retaining walls made of concrete, gabions (stone filled wire blocks) and wooden and steel beams, etc.
ii. By providing drainage control measures so that water may not infiltrate into the slope
Minimizing human encroachment:
i. Mining activities should be monitored in the hilly, unstable regions.
ii. Plantation of trees should be undertaken on the unstable hilly slopes.
iii. By preventing human encroachment in the form of buildings, roads, agriculture, grazing, etc. on unstable slopes.
Man-Made Disasters :
Man-made disasters are the result of carelessness or human errors during technological and industrial use. The disasters are in the form of accidents, which occur all of a sudden and take a huge toll on life and property. Mostly such disasters cause injuries, diseases and casualties where they occur.
Man-made disasters are mainly of two types:
Local disasters:
These are small-scale disasters such as train accidents, plane crashes and shipwrecks.
Industrial and technological disasters:
These are much larger in scale and are the result of technology failures or industrial accidents. Such disasters affect both local population and may even cover a much larger area. Industrial disasters result due to accidental leakage of water or air pollutants. Many of the chemicals are extremely toxic and carcinogenic which affect the human population in an adverse way. Some people die instantly while others are crippled for whole life in the form of blindness, paralysis and many other chronic diseases.
Impact on the environment:
Leakage of toxic chemicals from the industries and accidents in the nuclear reactors has short-term and long-term effects on the environment and human health. Short-term effects on human health relate to casualties and diseases like blindness, cancer, paralysis, heart trouble, gastric and respiratory abnormalities. Long-term effects include genetic imbalances in humans and its impact on the future generations. Soil and water sources also remain polluted for long durations of time.
Man-made disasters can be minimized to a large extent by adopting the following measures:
1. Proper training of personnel working in the hazardous industries.
2. Proper maintenance and care of safety measures.
3. Removing human encroachments around hazardous industries.
4. Making the people aware about the first-aid methods in case of accidents.
5. Applying wet cloth over the mouth and nose in case of gas leakages minimizes the health hazards.
6. Remaining indoors in case of radioactive accidents.
7. Providing the people with proper medical care, in some cases throughout their life.
8. Providing adequate compensation to the affected people by way of money and employment.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy (BGT) :
The most serious industrial disaster occurred on December 3, 1984 at Bhopal, India, which is known as the Bhopal Gas Tragedy (BGT). The Bhopal gas tragedy occurred due to leakage of methyl isocyanide (MIC) gas from the factory of Union Carbide of India Ltd. MIC gas is used as an ingredient in pesticides.
It leaked from the factory and formed the deadly cloud over Bhopal. People living in slums in the vicinity of the factory were the most affected and more than 5000 people were killed, half of them due to direct exposure and other half due to after affects. MIC is a colourless gas which causes severe irritation, violent coughing, swelling of the lungs, bleeding and death due to direct inhalation. It also caused loss of eye-sight in more than 1000 people. More than 50,000 people were affected with respiratory, eye, gastric, neurological and gynaecological problems (Figs. 18.8 and 18.9).

Another technological disaster is due to the potential damages of nuclear fallout. An example is the Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster.
Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster :
This nuclear disaster occurred at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, which was one of the largest power plants in the Ukrainian Republic of erstwhile USSR, on April 26, 1986. It is the worst nuclear disaster recorded in a nuclear power plant. This nuclear power plant had four reactors of 1000 megawatt each for electricity generation. A sudden power surge resulted in two explosions, which destroyed the reactor core and blasted a large hole in the roof of the reactor building.
The Radioactive debris moved up through that hole to heights of 1 km. Approximately 100 to 150 million curies of radiation (radioactive isotopes of iodine and caesium) escaped into the atmosphere. To reduce emissions, the rescue team bombarded the reactor with 5,000 metric tonnes of shielding material consisting of lead, boron, sand and clay. Soviet officials placed the toll of human lives to 31.
However, according to western estimates, 2000 people were killed. Large areas of the Ukrainian, Byelorussia Republics of the USSR and even parts of Poland, Denmark and Sweden were contaminated. Around 200,000 people had to be evacuated and resettled. The after affects lasted for many years and a rise in the incidence of thyroid and blood cancer has been observed in a wide group of people. Other affects on the human health included skin diseases, hair loss, nausea, anemia, respiratory and reproductive diseases.
Related Articles:
- Impact of Global Warming on Ecosystem
- Impact of Floods on Biodiversity in the Brahmaputra Valley
- Anybody can ask a question
- Anybody can answer
- The best answers are voted up and rise to the top
Forum Categories
- Animal Kingdom
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Biology An Introduction 11
- Biology An Introduction
- Biology in Human Welfare 175
- Biomolecules
- Biotechnology 43
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Cell- Structure and Function
- Chemical Coordination
- Digestion and Absorption
- Diversity in the Living World 125
- Environmental Issues
- Excretory System
- Flowering Plants
- Food Production
- Genetics and Evolution 110
- Human Health and Diseases
- Human Physiology 242
- Human Reproduction
- Immune System
- Living World
- Locomotion and Movement
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Mineral Nutrition
- Molecualr Basis of Inheritance
- Neural Coordination
- Organisms and Population
- Photosynthesis
- Plant Growth and Development
- Plant Kingdom
- Plant Physiology 261
- Principles and Processes
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Reproduction 245
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Reproductive Health
- Respiration
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Transport in Plants
- Trending 14
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Disaster Management in 500 Words

- Updated on
- Feb 1, 2024

Disaster management is the practice of managing and organizing resources to deal with disasters or hazardous events. Depending on the type and intensity of a disaster, its coping strategies or methods can vary. In India, the National Disaster Management Authority is the apex body to govern all types of natural disasters. Before knowing what disaster management is and how the coping strategies are implemented, it’s important to understand the types of disasters that have occurred. Some of the most prevalent disasters are Earthquakes , tsunamis, floods, wars, and many more.
One day State-level Policy Cafe on Integration of Health, Nutrition, WASH in Disasters and Emergencies, organized jointly by @CcdrrCentreNIDM, @nidmmhaindia along with HPSDMA and @balrakshabharat Save the Date: 15th December 2023 Join Zoom Meeting https://t.co/IZpKZR5BJS pic.twitter.com/V0Xmno5gFW — National Institute of Disaster Management (@nidmmhaindia) December 15, 2023
Also Read: Essay on Water Conservation
Types of Disaster Management
There are different types of disaster management practices adopted by concerned authorities. The National Disaster Management Authority has set out certain mitigation strategies, policies, and guidelines depending on what type of disaster has occurred.
Disasters are of two types: Natural and Man-made.
- Natural Disasters include earthquakes, cyclones, heat waves, landslides , urban floods and floods, and volcanic eruptions.
- Man-made disasters include terrorist activities and wars, chemical, biological, and Nuclear hazards.
To deal effectively with disasters, NDMA has five major divisions: Policy & Plans, Mitigation, Operations & Communications & Information & Technology , Administration and Finance.
Let us have a look at these 5 major divisions:
- Policy and plans include risk assessment, preparedness measures, and response and relief strategies.
- Mitigation measures include land-use planning, building codes and regulations, infrastructure improvements, and environmental conservation measures.
- Operations and Communication for public safety, managing expectations, and coordinating relief efforts.
- Information and Technology includes early warning systems with the help of satellite imagery, weather forecasting, and sensors.
- Administration and Finance to manage all the disaster management practices.
Also Read: World Tsunami Awareness Day 2023
Effects of Disaster Management
A disaster not only damages life and property but causes significant economic impacts in the affected areas. Therefore, proper and effective disaster management practices are necessary for timely response and to reduce the damage of the disaster.
To learn more about important Disaster Management Practices, let us consider the following points:
- Early warning and evacuation plans are necessary to reduce loss of life and injury.
- Mitigation measures like risk assessments, resilient infrastructure planning, and pre-disaster mitigation measures can help minimize the damage to buildings, roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure.
- Disaster management planning facilitates the recovery and reconstruction process so that developmental activities are not on halt for long.
- Enhanced community resilience can withstand and recover from the impacts of disasters. This can be done by proper training and education programs.
Also Read: Environment Conservation Speech
National Disaster Management Authority
The NDMA not only manages all the disaster management practices but also makes people aware of what disasters are and how to act to reduce their impacts. The Prime Minister of India is the Chairman of the NDMA. The sustained and collective efforts by NDMA are meant to mitigate the damage and destruction caused by natural and man-made disasters.
NDMA has laid down guidelines to mitigate all types of disasters. For example, the mitigation methods for floods are:
- Install check valves in sewer traps to prevent flood water backup.
- You can construct an interior barrier to stop floodwater from entering your home and basements.
- Elevate all electronic items like air conditioners, water heaters, etc.
- Make your basement walls waterproof by sealing them with compounds to avoid seepage.
Also Read: World Environment Health Day 2023
Also Read: How to Prepare for UPSC in 6 Months?
Paragraph on Disaster Management
| Disaster Management is the practice of coping with natural and man-made disasters. There are multiple tasks involved in disaster management, such as planning, organizing, coordinating, and implementing measures to prepare for, respond to, recover from, and mitigate the impact of disasters. There are four main phases of disaster management: Preparedness, Response, Recovery, and Mitigation. Every country has its disaster management authority. In India, the National Disaster Management Authority is the apex body to govern and manage all types of disaster-related activities. In the USA, the manages and promotes disaster management practices. In recent years, the frequency of natural disasters has increased, which not only causes loss of life and property but leads to significant economic and psychological impacts on the people. Therefore, it is necessary to plan and implement effective disaster management practices. |
Also Read: Environmental Conservation
Ans: Disaster management is the practice of managing and organizing resources to deal with disasters or hazardous events. Depending on the type and intensity of a disaster, its coping strategies or methods can vary. There are 4 disaster managing practices: Preparedness, Response, Recovery, and Mitigation. It is important to implement necessary disaster management practices to mitigate and faster recovery from any calamity.
Ans: The disaster management practices are Preparedness, Response, Recovery, and Mitigation.
Ans: The Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, is the head of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
Related Articles
For more information on such informative articles for your school, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test

Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
INTERACTIVE
Humans induce and reduce environmental disasters.
Environmental disasters from 1970 to 2019 led to new developments in science, engineering, and policy. Explore disasters that have occurred over the last fifty years on land, in water, and in the atmosphere, as well as envision solutions to prevent or minimize further disasters.
Biology, Ecology, Conservation, Earth Science, Climatology, Oceanography, Geography, Human Geography

View full screen here .
Base map may not reflect National Geographic's current map policy.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
Read The Diplomat , Know The Asia-Pacific
- Central Asia
- Southeast Asia
- Environment
- Asia Defense
- China Power
- Crossroads Asia
- Flashpoints
- Pacific Money
- Tokyo Report
- Trans-Pacific View
Photo Essays
- Write for Us
- Subscriptions
Pakistan’s Floods Are a Man-Made Disaster
Recent features.

The Rise, Decline, and Possible Resurrection of China’s Confucius Institutes

Nowhere to Go: Myanmar’s Exiled Journalists in Thailand

Trump 2.0 Would Get Mixed Responses in the Indo-Pacific

Why Thaksin Could Help Hasten a Middle-Class Revolution in Thailand

Can the Bangladesh Police Recover?

The Lingering Economic Consequences of Sri Lanka’s Civil War

What’s Driving Lithuania’s Challenge to China?

Hun Manet: In His Father’s Long Shadow

Afghanistan: A Nation Deprived, a Future Denied

In Photos: Life of IDPs in Myanmar’s Rakhine State

Indian Government’s Intensifying Attack on Scientific Temperament Worries Scientists

Beyond Tariffs: Unveiling the Geopolitics of Electric Vehicles Through Supply Chains
The debate | opinion.
It’s not just climate change – corruption, bad governance, poor planning, and faulty water management are also to blame for the scale of the current disaster.

A man looks for salvageable belongings from his flooded home in the Shikarpur district of Sindh Province, Pakistan, September 1, 2022.
Unprecedented torrential rains followed by floods in one-third of Pakistan have caused more than $30 billion in damage, killed 1,596 people, and directly impacted more than 33 million, according to the country’s National Disaster Management Authority. Pakistan’s most impoverished provinces, southwestern Balochistan and southern Sindh, are the worst affected.
In Sindh , Pakistan’s second largest provinces, but one of its poorest, an estimated 10 million people have been affected by the floods. They are in desperate need of shelter and emergency medical assistance. The situation is similar in restive southwestern Balochistan province, where 300 people have died due to floods since June. The fragile provincial government declared 32 out of 34 districts “calamity-hit.”
Balochistan is the second-most affected province after Sindh, with more than 9 million out of its population of 12 million affected.
Pakistan, especially its northern areas, is not unfamiliar with monsoon rain. However, what was uncommon this year was that the country’s southern arid region experienced five times more than the average annual rainfall, which led to the overflowing of traditional unmaintained canals and the destruction of protective embankments, which had been built poorly with mud and sand.
The lack of proper water management exacerbated the accumulation of water. As a result, many poor towns and villages in Balochistan and Sindh found themselves under water. In several parts of Sindh, standing water reached as high as three to six meters. The same happened in Balochistan. Water accumulation and encroachment at some places caused flash floods, which washed away roads, bridges, houses, and hundreds of thousands of acres of crops.
In the aftermath of the current floods, there has been much discussion about the impacts of climate change in Pakistan. Many, including Pakistan’s climate minister, Sherry Rehman , have described it as a “climate catastrophe.” Rehman says that climate change caused the loss of life of nearly 1,600 people and displaced millions of others in Pakistan. She has also been demanding reparations from wealthy industrialized nations for their carbon emissions. She argues that Pakistan contributes less than 1 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions but is paying the price for climate change; thus, it deserves compensation from richer industrialized countries.
What Rehman doesn’t like to mention or talk about is her government’s unpreparedness and its poor regulation of floodplains. She also failed to cite the inadequate infrastructure and lack of proper water management system in her native Sindh province.
Rehman belongs to the Pakistan People’s Party (PPP), currently in power in Sindh and part of the ruling coalition in the central government. The PPP was founded by Zulfikar Ali Bhutto from Sindh, and the party has been in power in the province for over four decades. The Bhutto family is Pakistan’s most ambitious and powerful political clan, as British journalist Owen Bennet Jones wrote in his book “The Bhutto Dynasty.”
Pakistan’s foreign minister, the young Bilawal Bhutto, a history graduate from the Christ Church College at Oxford, has become the fifth in his family to run his native Sindh province. His great grandfather, grandfather, mother, and father had been in power in the past. “The Bhuttos’ story is so full of passion, talent, suffering, courage, violence, and money that it never lacks a strong narrative thrust,” Bennet-Jones wrote
Still, Sindh is judged food insecure and engulfed by many problems ranging from poor governance to corruption, and from deplorable infrastructure to a lack of basic health facilities.
The flash floods that hit Sindh and Balochistan weren’t only the result of climate change, as claimed repeatedly by Rehman and others. One cannot deny the impacts of climate change in Pakistan; for instance, heat extremes, including an all-time record temperature of 53.5 Celsius in Balochistan’s Turbat in May 2017 , and the glaciers of the Himalayan mountains melting down at an alarming level. Still, the lack of proper floodplains and abysmal infrastructure have contributed to the gravity of the flooding.
Now the country’s poor to nonexistent health infrastructure and lack of capacity to drain the accumulated floodwaters in some areas pose a severe health threat to millions. Two weeks ago, Sindh’s chief minister said it would take his provincial government three to six months to drain water from the flood-hit areas. This shows its level of preparedness in tackling disasters.
As a result, there has already been an increase in waterborne diseases, dengue, malaria, and diarrhea. Last week, nine people died from such diseases in Sindh. UNICEF said that millions of children and women are prone to water-borne diseases, mostly in Balochistan and Sindh, the worst-affected provinces. There is widespread anger among the locals of these provinces against the government for failing to provide them with timely assistance.
The floods also struck several parts of Balochistan province, bringing life to a crippling halt. The districts of Lasbela, Jhaffarabad, Naseerabad, Jhal Magsi, and Dera Murad Jamali have been the worst hit. All these areas are ruled by tribal chieftains, who have been in power since the formation of Pakistan in 1947. The flood wreaked havoc in these areas, as either there was no plan in place to tackling such unprecedented rainfall or the leaders did not correctly plan while building dams, rivers, and bridges.
For instance, heavy floods in Lasbela could have been mitigated or diverted had a protective embankment called Tharra been built with solid materials. The poor quality of the construction couldn’t resist the flood water for long. Similarly, if work on the Porali River, a project of the World Bank , had done with the proper planning, the damages caused by the current flood in Lasbela would have been much reduced.
In addition, the emphasis on building infrastructure and housing ventures in natural floodplains also played its part in causing more damage – not only to the natural environment but to the public too. We saw this in Swat , where luxury hotels and restaurants were swept away by floodwater in seconds.
Floods and torrential rainfall aren’t unusual in Balochistan and Sindh. Both provinces have experienced severe floods in the last two decades. These natural calamities killed thousands of people, destroyed livelihoods, and killed thousands of animals in 2007, 2010, 2012, and now. What was uncommon was the unpreparedness of the Balochistan and Sindh governments in tackling a disaster-like situation.
The current flooding is the worst and deadliest in Pakistan’s 75 years of history, and there are multiple reasons for that. Despite having experienced similar catastrophes in 2007, 2010, and 2012, the government was not prepared to deal with a major flooding event. This time the lack of unpreparedness and proper planning increased the disaster’s impact, which will further escalate unless the water accumulated in flood-hit areas dries up.
More children and women vulnerable to infectious diseases are likely to suffer. The government still doesn’t have a plan to rehabilitate or at least settle these displaced people in temporary shelters – many are living on their own on roadsides under the open sky. Resettling 33 million people remains a daunting task for the current government.
Climate change is a reality, and Pakistan isn’t an exceptional victim of it. But despite the warnings and disasters we have experienced in the past, we still don’t have proper planning to tackle it. We risk missing a crucial point if we lay the blame on climate change alone. Corruption, bad governance, poor planning, and faulty water management can equally be blamed for the current disaster.
Climate change undoubtedly played a role, but Pakistan’s current flood is also a man-made disaster, requiring man-made and long-lasting solutions.

Pakistan Shouldn’t Get ‘Aid’ After Its Devastating Flood. It Is Owed Climate Reparations.
By zareen zahid qureshi.

Pakistan and the Global North’s Climate-linked Trade Policy
By maryam khan.

The Anatomy of Pakistan’s 2022 Floods
By mariyam suleman anees.

A Plea From Pakistan’s Sindh: ‘Our Village Drowned. You Might Still Have Time to Save Yours.’
By morial shah.

By Aleksander Lust

A Gen-Z Revolution in Pakistan Will Have to Wait
By abdul basit.

Indonesia’s Bold Bid to Become a Semiconductor Hub
By patrick kurniawan.

By Rajeev Bhattacharyya

By Si-yuan Li and Kenneth King

By Hailun Li

By Derek Grossman

By Jason Johnson
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Disaster Management Essay

Essay on Disaster Management
Disaster Management is the arrangement and management of the resources following a disaster, be it natural or man-made. There are so many organizations who are dealing with various types of disastrous situations from the humanitarian aspect. Some disasters are just the consequences of human hazards and some are caused by natural calamity. However, we can prevent them by taking the necessary emergency measures to save and preserve lives. As natural disasters cannot be predicted, they can take place anywhere at any time.
Vedantu has provided an essay on Disaster management on this page. Students who have received an assignment to write an essay on Disaster Management or preparing an essay for examination can refer to this page to understand the pattern. Any student or parent can directly visit Vedantu site or download the app on the phone to get access to the study materials.
Disaster Management’ is the simple term of management which embraces loads of disaster-related activities. Disaster occurs frequently in some parts of the world. Japan is the best example of it. Japanese people are annoyed on Tsunamis and earthquakes. The local scene is not much different from the global one. No one could forget the cyclone in Orissa, Earthquake in Gujarat or even the Mumbai Terrorist Attack.
Natural and man-made are the two categories of the disaster. Natural disasters are those which occurred due to sudden changes in the environment or topography causing uncountable human as well as economic loss. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods and cloudbursts are few of the natural disasters. Manual intentional made disasters are man-made disasters. For example, Gas leakage, terrorist attacks, fire, oil spills. Man-made disasters are the result of human intentions or might be because of workmanship or technical errors. The count of man-made and natural disasters is rising rapidly.
Here are a few things which will help us to deal with earthquakes. The significant information about Natural calamities is predicted easier and is being shared within the public by the central bureau. Furthermore, earthquake-resistant structures are constructed considering, ‘Precaution is Better Than Cure’. Reflexes are made so strong that cover of solid platforms such as a table and chair should be taken as soon as the danger is sensible while the cover of trees, electric poles or buildings is avoided as far as possible. Keep in touch with local news during heavy rainy days. Any flood is preceded with significant time. Making proper use of divine buffer time for safety is advisable. Strategically planning of water reservoirs, land uses, tree plantation, rainwater harvesting techniques help us increase immunity power to fight against the drought.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), American Red Cross, Federal Emergency Management Agency, International Association of Emergency Managers etc. are the best disaster management authorities. NDMA is a core body which obeys the law of Disaster Management. The reputed disaster managers are stuck in finding plans for rescuing from the loss of disaster. Moreover, to counteract the effect of disaster Rajya Sabha passed the ‘Disaster Management Act’ on 23 December 2005 which includes 11 chapters and 79 sections in it. Honourable Prime Minister of India Mr Narendra Modi holds the position of chairman of it.
Youngsters should motivate themselves to learn and practice plenty of disaster management techniques and arrange the camps regarding it. Today, everyone is fighting against one of the breathtaking disasters named COVID-19 which is as big as fighting in world war. Avoiding the crowd, wearing the mask are the basic precautions suggested by the World Health Organization (WHO) during this period of fighting. This disease spreads mostly amongst the people who come in close contact with the infected one. So, it's suggested to keep a safe distance of around 3 meters within the others. This is being termed as ‘Social Distancing’. Nature is not cruel nor is it human. Just small management skills help us withstand before, in and after disasters. Uncountable suggestions and instructions in disaster management but few which apply every time must be followed.
Stages of Disaster Management
With proper implementation and structured action, we can prevent or lessen the impact of natural or man-made disasters. There are certain stages involving the cycle for disaster management plan which incorporates policies and emergency responses required for a prospectively complete recovery. The stages are –
The most preferred way to deal with disasters is to be proactive in their prevention rather than rushing later for their cure. This implies recognition of potential hazards and working towards infrastructure to mitigate their impact. This stage in the management cycle involves setting up permanent measures to minimize disaster risk.
Setting up an evacuation plan in a school, training the teachers to lead the students towards safe structures in the event of earthquake, tornado or fire, planning a strong base for high raised sky-scrapers to prepare for earthquakes and designing a city in such a manner that reduces the risk of flooding are some examples of measures takes for disaster prevention.
Mitigation is the first and the foremost attempt to save human lives during the time of disaster or their recovery from the aftermath. The measures which are taken can be both structural and non-structural.
Structural mitigation measures could include transforming the physical characteristics of a building or the surroundings to curb the effect, for example, clearing out of the trees around your house, ensuring that storms don’t knock down the trees and send them crashing into the house. Non-structural measures could include amending the building or locality codes to enhance safety and prevent disasters.
Preparedness
Preparedness is a process that involves a social community where the trained, or the head of the community, businesses and institutions demonstrate the plan of action which is supposed to be executed during the event of a disaster. It is an ongoing continuous process with anticipation of a calamity, which involves training, evaluating and taking corrective action with the highest level of alertness. Some examples of such prevention measures are fire drills, shooter drills and evacuation rehearsals.
The response is the action taken after the disaster has occurred to retrieve some life from it. It includes short-term and long-term responses. In ideal situations, the disaster-management leader will coordinate the use of resources in the restoration process and minimize the risk of further property damage.
During this stage, the area of the calamity is cleared if it poses any further threat to human as well as environmental life. For example, evacuation of the city of Chernobyl, Ukraine, is a responsive action against a disaster.
The fifth and last stage in the process of the disaster management plan is the recovery stage. This can sometimes take years or decades to happen. The larger mass of a city is also sometimes part of the recovery from a disaster. The greatest and the most infamous example of this is the Hiroshima and Nagasaki nuclear attacks on Japan, it took the people of those cities years and decades to recover from that man-made calamity.
It took years of effort to stabilize the area and restore essential community or individual functions. The recovery stage prioritizes the basic essential needs of human survival like food, drinkable water, utilities, transportation and healthcare over less-essential services. Eventually, this stage is all about coordinating with individuals, communities and businesses to help each other to restore a normal or a new normal, as in the case of Covid-19.
How to Act as a Responsible Person During a Time of Disaster?
Some people have more experience than others with managing natural or man-made disasters and their prevention of them. Although this is that subject of life which should be studied and implemented by every business or community. As it is said rightly, “prevention is better than cure”, and any organization or an individual or a community can be hit by a disaster sooner or later, whether it's something as minor as a prolonged power cut or a life-threatening hurricane or an earthquake. Usually, the pandemics train us, as a social and political community, to deal with natural calamities and compel the organizations responsible for it, to build an infrastructure for its prevention.
To act responsibly and pro-actively during the event of a disaster, we have got to be prepared and equipped as a nation, individually and as a social community. To be well-educated and read with the aspects of disaster management is to be responsible for the handling of it.

FAQs on Disaster Management Essay
1. What is Disaster Management?
In simpler words, disaster management can be defined as the arrangement of resources and precautions to deal with all humanitarian aspects during an emergency. Disasters are the consequences of natural or human hazards. Earthquakes, floods, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes are some of the deadliest natural disasters to name a few. Examples of man-made disasters are bomb blast, radiations, transport accidents, terrorist attacks etc.
2. What is the Main Aim of Disaster Management?
The main aim of disaster management is prevention, rescue and recovery from the trauma, and development.
3. How to Write an Essay on Disaster Management?
Disaster management refers to the response to an emergency situation to make it as normal as possible. While writing an essay on Disaster Management, you can start with an introduction, then go on with the definition, the types of disaster management, a little in-depth explanation along with examples, and finish it off with a conclusion.
4. Can I Get a Sample Essay on Disaster Management from Vedantu?
Yes, the essay mentioned on this page is about Disaster Management. This essay has been written by the experts of Vedantu keeping the understanding ability of the students of each class.
5. What are the career opportunities in the field of Disaster management?
People looking for career opportunities in the field of disaster management have many pathways to approach it. Some examples of the jobs relating to this line of work are crisis-management leader, disaster-assistance specialist and emergency-planning coordinator. These are the roles which call for varying levels of responsibility in preparing a city or a company for catastrophic events. The job roles can be approached with earning a master’s degree in emergency and crisis management.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Disaster Management Essay | Essay on Disaster Management for Students and Children in English
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Disaster Management Essay: Every country should have a plan and an outlay to maintain or mitigate the cause of disasters, both man-made and natural. Disaster management is a term that is usually referred to as the management of resources and responsibilities in dealing with the losses of life and property in a disaster like an earthquake, volcanic eruptions, epidemics and pandemics. The whole world is in the disaster management mode due to the COVID-19 pandemic that has gripped the whole world from the past few months. But this essay on disaster management is not confined to that aspect.
Countries that were disaster-ready are coping up with the pandemic relatively well than the countries that had neglected the importance of disaster management.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short essay on Disaster Management for school Students and Kids in English
In this article, we have provided a disaster management Essay of 500-word as well as a 200-word short essay on disaster management that students can use in their project work, tests, exams, assignment and essay writing competitions.
Long essay on Disaster Management in English 500 words
Disaster can be of both man-made as well of natural causes. Earthquakes, floods and volcanic eruptions are usually considered as natural disasters while bomb explosion, gas leakage and wars are considered as man-made disasters. These categorizations of disaster as man-made and natural are in itself a dispute because certain natural calamities are directly linked to the man-made drudgery. In this essay on disaster management, we will be talking about the importance of disaster management as well as how well countries are prepared for the upcoming disasters.
What is the importance of disaster management?
The crux of the essay on disaster management lies in understanding the importance of why disaster management is necessary for every country. Therefore, we have provided three main reasons why every country should have robust policies on disaster management
Reduce the potential loss of lives
Organizations such as the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) are the ones that take necessary actions during and before disasters. In fact, there is nothing that we as humans can do during a disaster, like the one that’s e are living in, COVID-19 pandemic. Disaster management always should have long term planning and everything should be in place well before the occurrence of disasters. This robust planning beforehand will reduce the losses to life and property.
As we have seen the cyclone Amphan that has hit India and Bangladesh on the Bay of Bengal coast, the preparedness of the authorities led to the mass evacuation of people in the red zones, which helped save millions of lives. If proper planning is not in place, then millions of lives will be lost, like we have seen in the USA, Italy or Spain due to the COVID 19 pandemic. The healthcare systems were not able to cope up with the number of coronavirus infected people rushing to the hospitals as a result of which, millions of lives were lost, which would have otherwise been saved if proper disaster management policies were in place.
Rehabilitation programs
There are certain disasters whose effect on loss on lives cannot be averted even if proper disaster management policies are in place because, let us accept it, nature keeps throwing surprises at us all the time. But disaster management policies are not framed to just prevent the loss, but how to overcome losses. In the case of floods or earthquakes, many families and in certain cases, entire communities will be displaced and their basic livelihoods will be affected. A proper rehabilitation program should be in place to help them get back on their feet to lead a normal life again. The government should provide employment opportunities to the affected people along with health and monetary befits to the families of the lost ones.
Saving environment
As the saying goes prevention is better than cure, a good disaster management policy will have an efficient long term plan to prevent the disaster from happening in the first place. While this particular essay on disaster management covers measures to save human life, we should also be talking about saving the environment, without which a good essay on disaster management will not be complete.
Many of the so-called natural disasters that are happening around us such as floods and earthquakes are a result of man’s greed and exploitation of nature. Increased agriculture, deforestation, globalization, carbon emissions are some of the things that man has done that indirectly or directly results in floods, famines and pandemics in the world.
While disaster can be prevented if the man is responsible for nature, even if it cannot be prevented, at least every government in the world should have efficient disaster management policies in place to prevent the impact of the disaster on human beings as well as nature.
Short essay on disaster management in English 200 words
Find below a 200-word short essay on disaster management which can be used by children in school and college essay writing competition.
Disasters can come anytime and anywhere without warnings. It is the responsibility of the government to have proper disaster management laws and policies in the country so that when the disasters do occur, the prevention of lives and property will be easier. Disaster management also includes the prevention of disaster in the first place.
But this is easier said than done. All the stakeholders including the common citizen should come together to prevent this from happening. Planning, organizing, reducing and implementing are some of the core functionalities of a disaster management relief force.
Climate change, global warming, globalization, rapid industrialization, agriculture expansion, deforestation and population explosion are some of the problems that disaster management policies should address. At the same time, disaster management is not just about saving human lives, it should also include plans to save animal and wildlife as well as forests and other such natural resources.
Read More: How To Prevent Natural Disasters Essay
10 Lines on Essay on Disaster Management
- Good disaster management should include both prevention and cure for the aftereffects of a disaster
- The governing body in India with regard to disaster management is the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- Disaster are mostly two types, man-made and natural disaster
- Disaster need to be predicted and people near the vicinity of the location of diaster should be given relief measure immediately
- Preparedness, response and recovery are the three main core values governing a disaster management policy
- Some of the deadliest disasters are earthquakes, floods, volcanic eruptions, storms, pandemics and hurricanes
- Man-made disasters include wars, chemical explosions, gas leakages, forest fires and oil spills
- When a disaster like COVID 19 occurs, each country should support each other in the time of need
- Long term planning and vision is necessary to prevent disaster from happening
- Globalization, population, deforestation are some of the reasons for the natural occurrence of disasters like floods, famine and earthquakes
FAQ’s on Disaster Management Essay
Question 1. What are the types of natural disasters?
Answer: Geophysical, hydrological, climatological, meteorological and biological disasters are the types of natural disasters
Question 2. What is the main aim of disaster management?
Answer: Prevention, rescue and recover are the main aims of disaster management
Question 3. Which is the worst disaster in the world?
Answer: The 1931 China floods in considered to be the worst disaster in the world with more than 4 million people killed because of it
Question 4. When is the world disaster day?
Answer: 13th October is considered as the international day for natural disaster reduction
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Natural Disasters — Natural Disasters: Causes and Impacts
Natural Disasters: Causes and Impacts
- Categories: Natural Disasters
About this sample

Words: 682 |
Published: Jan 31, 2024
Words: 682 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, definition of natural disasters, causes of natural disasters, environmental effects of natural disasters, economic effects of natural disasters, social effects of natural disasters, mitigation and preparedness measures.
- Callaghan, K., & Alexander, M. (2018). Hurricane Harvey on the Gulf Coast: A Comprehensive Analysis of Impacts. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Kennedy School.
- IPCC. (2014). Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Cambridge University Press.
- McMahon, J., & Keefer, J. (2016). Social Vulnerability and Tropical Cyclones in Sint Maarten. Journal of Water and Climate Change , 7(2), 396-408.
- UNDRR. (2017). Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction. United Nations.
- Vos, F., Dykes, J., & Pierce, L. (2017). Flood Preparedness and Early-warning System Effectiveness in the Philippines. Disasters, 41(S1), S16-S37.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 927 words
4 pages / 1774 words
7 pages / 3050 words
3 pages / 1325 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Natural Disasters
Ulmer, Robert R., et al. Effective Crisis Communication: Moving from Crisis to Opportunity. SAGE Publications, 2019.U.S. Tornadoes. “May 4, 2007: The Night That Made Maps of Greensburg, Kansas Have to Be Redrawn.” U.S. [...]
The sinking of the RMS Lusitania on May 7, 1915, stands as one of the most significant maritime disasters in history, not only due to the tragic loss of life but also because of its profound geopolitical ramifications. As a [...]
Natural disasters have the potential to cause widespread devastation and leave lasting impacts on communities. In recent history, Hurricanes Katrina and Harvey stand out as two of the most destructive and costly hurricanes to [...]
Volcanoes are an inescapable part of our planet's geologic makeup, and their eruptions can have devastating consequences for the environment. In this essay, I will explore the myriad ways in which volcanoes affect the [...]
Have you ever been present in a category 5 hurricane? If the answer is no let me tell you that I just wish you never had to go through an experience like that. In September 20 Hurricane Maria struck Puerto Rico. All the [...]
Natural Disasters are never a good thing. In areas where they happen, they affect everything in a negative way. They can destroy whole town, cities, the economy, infrastructure, and in some cases the human population. They wreak [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- School Guide
- CBSE Notes for Class 8
- CBSE Notes for Class 9
- CBSE Notes for Class 10
- CBSE Notes for Class 11
- CBSE Notes for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions
- English Grammar
- Basic Maths Formulas
500+ Words Essay on Natural Disasters For Students
From the towering walls of water that sweep across coastlines to the ground-shaking tremors that ripple through the earth’s surface, natural disasters are a stark reminder of the immense power of nature and the fragility of our existence. These catastrophic events strike without warning, leaving in their wake a trail of destruction, displacement, and heartbreak.
Table of Content
Types of Natural Disasters
Causes of natural disasters, effects of natural disasters, precautions and preparedness, 500 words essay on natural disasters.
Natural disasters can take many forms, each with its unique characteristics and consequences. Some of the most devastating types include:
1. Earthquakes: Triggered by the sudden release of energy within the Earth’s crust, earthquakes can cause massive structural damage, trigger tsunamis, and disrupt vital infrastructure.
2. Tsunamis: Towering waves generated by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, tsunamis can inundate coastal regions with incredible force, sweeping away everything in their path.
3. Hurricanes and Cyclones: These powerful rotating storm systems, fueled by warm ocean waters, bring destructive winds, torrential rain, and storm surges that can devastate entire communities.
4. Floods : Caused by excessive rainfall, melting snow, or dam failures, floods can submerge vast areas, disrupting lives and destroying property.
5. Wildfires: Driven by dry conditions, high winds, and human activities, wildfires can consume vast swaths of land, threatening lives, homes, and natural habitats.
6. Volcanic Eruptions: The explosive release of molten rock, ash, and gases from the Earth’s interior can bury entire regions in a blanket of destruction.
7 . Droughts : Prolonged periods of abnormally low rainfall can lead to water scarcity, crop failures, and even famine in some regions.
While some natural disasters are triggered by geological processes deep within the Earth, others are influenced by human activities and the changing climate. Factors such as deforestation, urbanization, and the burning of fossil fuels can increase the risk and intensity of certain disasters.
Climate change, in particular, is playing an increasingly significant role in the frequency and severity of many natural disasters. Rising global temperatures are contributing to more intense hurricanes, prolonged droughts, and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, which can exacerbate coastal flooding.
The impact of natural disasters can be catastrophic, affecting every facet of human life and the environment. Some of the most significant effects include:
1. Loss of Life: Natural disasters can claim countless lives, leaving families and communities devastated by the loss of loved ones.
2. Destruction of Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, buildings, and critical infrastructure can be severely damaged or destroyed, hampering relief efforts and hindering recovery.
3. Economic Losses: The damage caused by natural disasters can result in staggering economic losses, affecting businesses, industries, and entire economies.
4. Displacement of Populations: Disasters often force people to abandon their homes and seek shelter elsewhere, leading to humanitarian crises and long-term displacement.
5. Environmental Degradation: Natural disasters can disrupt ecosystems, pollute water sources, and contribute to soil erosion and habitat loss, threatening biodiversity and natural resources.
6. Psychological Trauma: Survivors of natural disasters often grapple with the psychological toll, including post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, and anxiety.
While it is impossible to prevent many natural disasters, proactive measures can be taken to mitigate their impact and enhance preparedness. Some of these measures include:
1. Effective Early Warning Systems: Developing and implementing robust early warning systems can provide valuable lead time for evacuation and emergency response efforts.
2. Disaster Risk Reduction: Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities through measures such as land-use planning, building codes, and infrastructure improvements can minimize potential damages.
3. Community Preparedness: Educating and empowering communities on disaster preparedness, including emergency plans, evacuation routes, and survival skills, can save lives and facilitate quicker recovery.
4. Resilient Infrastructure: Investing in resilient infrastructure, such as earthquake-resistant buildings and flood control systems, can reduce the impact of natural disasters.
5. Environmental Protection: Conserving and restoring natural ecosystems, such as wetlands and forests, can act as natural buffers against certain disasters and mitigate their effects.
6. International Cooperation: Fostering global partnerships and collaborations can facilitate knowledge-sharing, resource allocation, and coordinated response efforts during disasters.
Throughout human history, civilizations have grappled with the unpredictable and often merciless power of nature. Natural disasters, ranging from earthquakes and tsunamis to hurricanes and wildfires, have left indelible scars on communities worldwide, reminding us of our fragility in the face of nature’s might.
At their core, natural disasters are events triggered by the Earth’s natural processes, such as tectonic shifts, atmospheric disturbances, or geological phenomena. However, their consequences extend far beyond the physical realm, profoundly impacting lives, livelihoods, and the very fabric of societies.
The destructive force of these events is unparalleled. Earthquakes can reduce towering structures to rubble in mere seconds, while hurricanes and cyclones unleash winds of incredible ferocity, capable of obliterating entire coastlines. Wildfires, fueled by dry conditions and strong winds, consume everything in their path, leaving smoldering landscapes and displaced communities in their wake.
The human toll of natural disasters is staggering. Lives are tragically lost, families are torn apart, and survivors are left to grapple with the psychological trauma of witnessing such overwhelming devastation. Beyond the immediate loss of life, the aftermath often brings a cascade of challenges, including displacement, lack of access to essential resources, and the daunting task of rebuilding shattered communities.
The economic impact of natural disasters is equally profound. Infrastructure is crippled, businesses are disrupted, and entire industries can be brought to a standstill. The ripple effects of these events can reverberate throughout local and global economies, hampering recovery efforts and exacerbating existing vulnerabilities.
Moreover, the environmental consequences of natural disasters are far-reaching. Ecosystems are disrupted, delicate habitats are destroyed, and biodiversity is threatened as species struggle to adapt to the altered landscapes. The long-term effects on the natural world can be felt for generations, further compounding the challenges faced by impacted communities.
Addressing the threat posed by natural disasters requires a multifaceted approach that spans prevention, preparedness, and resilience-building efforts. Investing in robust early warning systems, fortifying infrastructure, and promoting disaster risk reduction strategies are crucial steps in minimizing the impact of these events.
Furthermore, addressing the underlying drivers of climate change is paramount, as many natural disasters are exacerbated by the effects of global warming. By transitioning towards more sustainable practices and reducing our carbon footprint, we can mitigate the intensity and frequency of certain disasters, safeguarding both human and environmental well-being.
Ultimately, natural disasters serve as a humbling reminder of the immense power of nature and the fragility of our existence. While we cannot control the forces that give rise to these events, we can cultivate resilience, foster global cooperation, and prioritize preparedness efforts to better withstand their fury.
As we navigate the unpredictable landscape of natural disasters, let us embrace our shared responsibility to protect lives, safeguard communities, and forge a more sustainable relationship with the natural world. By doing so, we can forge a path towards a future where the devastating impacts of these events are minimized, and humanity emerges stronger and more resilient in the face of nature’s challenges.
Also Read: My Aim in Life Essay For Students: 100, 200 & 500 Words Essay My Village Essay in English For Students 500+ Words Essay on Importance of Education in English
Natural disasters underscore our need for resilience and preparedness. By bolstering infrastructure, safeguarding the environment, and addressing climate change, we can lessen their impact. Emphasizing risk reduction and sustainable practices, we aim to protect lives, economies, and ecosystems. Together, through resilience and cooperation, we can build a future where communities coexist with nature’s forces.
Essay on Natural Disasters- FAQs
What is disaster 1 paragraph.
A disaster is a major disturbance in the operation of a community or society resulting in widespread human, material, economic, or environmental losses and impacts that surpass the afflicted community’s or society’s ability to manage using its own resources.
What are the 2 main types of disasters?
Disasters are typically divided into two categories: natural and man-made. Natural catastrophes are typically related with weather and geological occurrences such as severe temperatures, floods, storms, earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and drought.
What are 5 man-made disasters?
A. Man-made disasters involve human intent, neglect, or error in the breakdown of a man-made system, as opposed to natural disasters caused by natural hazards. Such man-made calamities include crime, arson, civil unrest, terrorism, war, biological/chemical threats, cyber-attacks, and so on.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School English
- Essay Writing
- school blogs
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Disaster Management Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on disaster management.
Nature has various manifestations both gentle as well as aggressive. We see how sometimes it is so calm while the other times it becomes fierce. The calm side is loved by everyone, of course, however, when the ferocious side is shown, devastation happens. As humans cannot control everything, certain things of nature are out of our control.

Similarly, when natural disasters happen, humans cannot control them. However, we can prevent them. In other words, whenever a calamitous situation arises that may disturb the life and ecosystem, we need emergency measures to save and preserve lives. As natural disaster are not predictable, they can take place anywhere at any time. To understand disaster management thoroughly, we need to first identify the types of disasters.
Types of Disasters
If we look at the disasters that have taken place earlier, we can easily say that nature is not merely responsible for them to happen. They happen due to other reasons too. This is why we have classified them in different categories. First comes the natural disasters which are caused by natural processes. They are the most dangerous disaster to happen which causes loss of life and damage to the earth. Some of the deadliest natural disasters are earthquakes , floods, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, and more.

As no country is spared from any kind of disasters, India also falls in the same category. In fact, the geographical location of India makes it a very disaster-prone country. Each year, India faces a number of disasters like floods, earthquakes, tsunami, landslides, cyclones, droughts and more. When we look at the man-made disasters, India suffered the Bhopal Gas Tragedy as well as the plague in Gujarat. To stop these incidents from happening again, we need to strengthen our disaster management techniques to prevent destructive damage.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Disaster Management
Disaster management refers to the efficient management of resources and responsibilities that will help in lessening the impact of the disaster. It involves a well-planned plan of action so we can make effective efforts to reduce the dangers caused by the disaster to a minimum.
Most importantly, one must understand that disaster management does not necessarily eliminate the threat completely but it decreases the impact of the disaster. It focuses on formulating specific plans to do so. The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) in India is responsible for monitoring the disasters of the country. This organization runs a number of programs to mitigate the risks and increase the responsiveness.
Proper disaster management can be done when we make the citizens aware of the precautionary measures to take when they face emergency situations. For instance, everyone must know we should hide under a bed or table whenever there is an earthquake. Thus, the NDMA needs to take more organized efforts to decrease the damage that disasters are causing. If all the citizens learn the basic ways to save themselves and if the government takes more responsive measures, we can surely save a lot of life and vegetation.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the types of disasters?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “There are essentially two types of disasters. One is natural disasters which include floods, earthquake, tsunami, volcanic eruptions and more. The other is man-made disaster including oil spills, fires” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How can we effectively manage disasters?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”We must make people aware of the consequences of disasters. Moreover, we can teach them actions and measures to take when they face emergency situations.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

I'm a middle-aged mom of 3 and I'm going back to Burning Man despite my chaotic first experience last year
- I'm a mom of three, and my husband and I went to Burning Man last year.
- I stressed about what to wear for weeks before going to the Playa.
- I had so many new experiences, which, as a middle-aged woman, is something refreshing.

"Isn't that the thing in the desert for young people on drugs?" My mother-in-law probed when I asked her to stay with our teenage son while my husband and I went to Burning Man. Here I was, a middle-aged mother of three and recovering attorney, setting out to the middle of the Nevada desert without much more than some goggles and bikinis.
I worried I wasn't ready, I wouldn't fit in, or I'd get lost in a dust storm, never to be seen again.
Out of anxiety, I over-prepared for my time in Black Rock City . I needed sun protection, and I couldn't look plain. ("Radical self-expression" is one of the core principles). I bedazzled a hat with ribbon, feathers, and gold paper. The feathers added flare but also symbolized Native America. I am Muscogee (Creek), and I like people to know Native people are still here, living, teaching, and dancing in most communities and, in this case, at Burning Man. I planned to give away feathers to everyone I met.
I had searched for the perfect outfits
Upon my arrival, the Burning Man greeter expressed utter disbelief that I would bring feathers. Worse than plain? Apparently, feathers. They create "moop," Burning Man lingo for litter.
I took these as bad signs: I had no hat, no radical self-expression, and no gifts.
Feeling defeated, I arrived at my Burning Man camp . The camp leaders — including the friend who invited us — are the "tech bros" people love to complain about. They had names like "Cowboy" and "Chaos." One set up my tent and blew up my air mattress, while another made me an ice-cold margarita. "Better Lover" introduced himself, giving us juicy hugs and inviting us to his upcoming wedding on the Playa. There is not a lot that a margarita and a hug can't solve. Slightly refreshed, I went to my tent to change into the first of my many outfits.
Related stories
For weeks before, I searched social media for outfit ideas . What does one wear to a drug-induced dance party in a dust storm with 69,999 of your (soon-to-be) closest friends? The answer is not much .
I donned a purple velvet bra, high-waisted bikini bottoms, a fringed silk kimono, a cowboy hat, and the mandatory goggles. Out on the Playa , I felt strangely conservative in my bra-bikini get-up; most women were showing a lot of ass. When I say a lot, I really mean all . I also noticed the trend of small nipple covers as a shirt.
I loved the social freedom
At night we cruised the desert in an "art car" — a massive truck with a dance floor and DJ booth on top of it, created expressly for hauling not-sober people around the Playa . A young man — wearing only a g-string and a hoodie — boarded our party truck and started grooving with us.
This was one of my favorite parts of the Burner experience : the social freedom people have to meet, talk, dance, and hug strangers, who then become non-strangers and then give you a cold Michelob Ultra. The young guy whispered above the house music, "You are the real art here." He was a bit icky, but the adoration of middle-aged women was a counter-cultural phenomenon that I could get into.
Also, the art was amazing. It's worth a trip to the Playa, even if you aren't into EDM or dirty camping. After a long day of biking through the dirt to see the installations, I said to my husband, "I'd do anything for a lemonade." Not two minutes later, as the dust settled, a yellow lemon, the size of a small house, appeared, offering free ice-cold lemonade to all. I nearly cried.
That night, we attended the wedding of our camp-mates, Better Lover and his bride. In this alternative universe, marriage and monogamy are not really the vibe. But the wedding was beautiful. They declared their commitment — he in gold pants and red fingernails, she in a gold crown and purple braids — as the fading sun turned the desert shades of pink and orange. Even in this upside-down world, love seemed to win after all.
Then the mud came
Then it started raining. Biblical rain and our art car was no ark. After almost 24 hours of deluge, we crawled out of our tent into a strange, barren world of mud . Without options, we began to hike out. The mud caked to my boots so that I carried an extra 10 pounds on each leg.
When we got to the deserted road, they called a "highway," a skinny, well-tanned weed grower from Oregon drove us to the nearest town. There, we stuck out our thumbs. I'm not sure if we manifested it or if Burners are just cool people, but as we sat — muddy, dejected, and hungry — a couple came up to us and said four beautiful words, "You need a ride?"
Talia and Sean had escaped their young twins and rented the single last RV in Reno. Although rejected at the gates of Burning Man because of the rain, they recreated the experience right in that RV. They drove seven of us to Reno, offering kombuchas and snacks along the way. Talia got out her goddess cards, to which we each presented a question. " Should I go back to Burning Man? " I asked. The answer was something about being open to new experiences and seeing where they take you.
Burning Man is more than a drug party in the desert for young people. It's an alternative world where no money is exchanged, age doesn't matter, and art is essential. There is no fitting in because no one fits in — that's the point. I didn't have a spiritual awakening or become a transformed person. But I had a year of new experiences in three days.
In middle age, that is hard to find. I don't think I was ready for all of it last year, but I will be this year. This time I'm hoping for less rain, more love, less moop, and more ass.
Watch: Burning Man ends in massive traffic jam after days of disaster
- Main content

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Therefore, man-made disasters can have severe social and environmental impacts. 500 Words Essay On Man-Made Disaster. Man-made disasters, in contrast to natural disasters, are caused by human activity, whereas natural disasters are caused by natural forces. Man-made disasters can be small, like accidents on the road, or big such as war or ...
500 Words Essay on Man Made Disaster Introduction. Man-made disasters, as the term suggests, are catastrophic events caused directly by human actions. Unlike natural disasters, which occur due to geological or environmental phenomena, man-made disasters result from technological or human hazards. They often lead to severe, large-scale loss of ...
500 Words Essay on Natural And Man-Made Disasters Understanding Disasters. A disaster is a sudden event that causes a lot of damage or loss of life. Disasters can be split into two main types: natural and man-made. Natural disasters are caused by nature, like earthquakes or floods. Man-made disasters are caused by human actions, like wars or ...
Introduction to Man Made Disaster. Man-made disaster, a sobering reality of our modern world, stem from human activities and errors, often resulting in catastrophic consequences. Unlike natural disasters, which arise from uncontrollable forces, man-made disasters are largely preventable and thus require a more profound understanding to mitigate ...
Man-made disasters are disasters due to result of of human intent, negligence or involving a failure of a man-made system that leads to human suffering and environmental damage. Man-made disasters are the consequence of technological or human hazards. Fires, transport accidents, industrial accidents, oil spills and nuclear explosions/ radiation ...
The Bhopal disaster, also referred to as the Bhopal gas tragedy, was a gas leak incident in India, considered one of the world's worst industrial disasters. ... This essay is provided as an example of work produced by students studying towards a environmental sciences degree, ... 1.2 Man Made Disaster: These are mostly caused due to certain ...
100 Words Essay on Man Made Disasters What Are Man Made Disasters? Man made disasters are terrible events caused by human actions. These can be accidents like oil spills, or on purpose like wars. They hurt people, animals, and the environment. Unlike natural disasters, these tragedies come from mistakes or bad choices by people.
Man-made disasters include acts of war, terrorism, cyber-attacks, groundwater contamination, chemical/biological threats, transportation accidents, or fires. Though technological disasters might seem man-made, the significant difference between the two is that technological disasters are highly connected with technical systems and structures ...
Man-made disasters are occurrences that come about due to man's activities on the earth's surface. They can be intentional or accidental, but in either case, they can cause great harm to human beings, animals, property and the environment at large. Some examples of man-made disasters include global warming which has been caused by excessive ...
In a tsunami disaster essay, you could describe a historical tragedy and analyze its causes. Wildfire: This type of disaster starts when lightning hits a tree in the wood or due to man-made causes. It is an unplanned and uncontrolled spread of fire in natural areas with combustible vegetation. Drought: It is an extended lack of water in a given ...
The severity of man-made disasters has been increasing recently and is expected to further increase with climate change. For example, the number of conflicts and their associated fatalities have risen by 105\% and 286\% since 2010, respectively. With the internet and technological advancement, disasters significantly affect individual welfare both directly and indirectly.
500+ Words Essay on Natural Disasters. A Natural disaster is an unforeseen occurrence of an event that causes harm to society. ... Moreover, landslides can cause destruction to man-made things in many ways. Causes: Gravitational pull, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes can cause landslides. Moreover, soil erosion due to deforestation is also a ...
Man-Made Disasters: Man-made disasters are the result of carelessness or human errors during technological and industrial use. The disasters are in the form of accidents, which occur all of a sudden and take a huge toll on life and property. Mostly such disasters cause injuries, diseases and casualties where they occur. ...
Disaster Management is the practice of coping with natural and man-made disasters. There are multiple tasks involved in disaster management, such as planning, organizing, coordinating, and implementing measures to prepare for, respond to, recover from, and mitigate the impact of disasters. There are four main phases of disaster management ...
Explore disasters that have occurred over the last fifty years on land, in water, and in the atmosphere, as well as envision solutions to prevent or minimize further disasters. Environmental disasters from 1970 to 2019 led to new developments in science, engineering, and policy. Explore disasters that have occurred over the last fifty years on ...
Credit: AP Photo/Fareed Khan. Unprecedented torrential rains followed by floods in one-third of Pakistan have caused more than $30 billion in damage, killed 1,596 people, and directly impacted ...
Disaster Management Essay. Disaster Management is the arrangement and management of the resources following a disaster, be it natural or man-made. There are so many organizations who are dealing with various types of disastrous situations from the humanitarian aspect. Some disasters are just the consequences of human hazards and some are caused ...
Man Made Disasters. Man-made disasters are disasters resulting from man-made hazards (threats having an element of human intent, negligence, or error; or involving a failure of a man-made system), as opposed to natural disasters resulting from natural hazards. Man-made hazards or disasters are sometimes referred to as anthropogenic.
To advance this perspective and confront human-made disaster, the profession should promote social development strategies and human rights principles through political practice and within social work education. This would give social work a central role. in preventing human-made disaster and in reconstruction and devel-opment following disaster.
Disaster Management Essay: Every country should have a plan and an outlay to maintain or mitigate the cause of disasters, both man-made and natural. Disaster management is a term that is usually referred to as the management of resources and responsibilities in dealing with the losses of life and property in a disaster like an earthquake ...
The thesis statement for this essay is that natural disasters have wide-ranging effects on various aspects of human life, and it is crucial to understand and take measures to mitigate their impacts. Definition of Natural Disasters. Natural disasters are events caused by environmental factors and are outside of human control.
1. Loss of Life: Natural disasters can claim countless lives, leaving families and communities devastated by the loss of loved ones. 2. Destruction of Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, buildings, and critical infrastructure can be severely damaged or destroyed, hampering relief efforts and hindering recovery. 3.
When we look at the man-made disasters, India suffered the Bhopal Gas Tragedy as well as the plague in Gujarat. To stop these incidents from happening again, we need to strengthen our disaster management techniques to prevent destructive damage. Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Disaster Management
Essay by Shanti Brien. ... The author's first Burning Man experience was a muddy disaster. Courtesy of the author ... while another made me an ice-cold margarita. "Better Lover" introduced himself ...