- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff


News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School’s In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
Discover the latest in science, tech, and space with over 100,000 subscribers who rely on Phys.org for daily insights. Sign up for our free newsletter and get updates on breakthroughs, innovations, and research that matter— daily or weekly .
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Man scouring Google Earth found a mysterious scar in the Australian outback. Now we know what caused it
21 minutes ago

Slender-billed Curlew may be extinct, marking the disappearance of a third bird species from the Western Palaearctic

WEAVE spectrograph uncovers dual nature of galaxy shock
3 hours ago

Scientists seek miracle pill to stop methane cow burps
9 hours ago

Sustainable method can electrosynthesize important chemical for synthetic rubber production
Nov 23, 2024

Healthy elbow room: Social distancing in Neolithic mega-settlements

First successful test of wild minke whales reveals they have ultrasonic hearing

Extending classical black hole inequalities into the quantum realm

Saturday Citations: Sweaty, remarkable humans; ocean level rise projections; closeup of a star in another galaxy

Earliest fish-trapping facility in Central America discovered in Maya lowlands
Nov 22, 2024
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Extension resource for advanced high school / pre-university students.
Nov 19, 2024
Sources to study basic logic for precocious 10-year old?
Nov 12, 2024
Stephen Wolfram explains how ChatGPT works
Nov 2, 2024
Is the AAPT 2023 Physics Bowl Answer Key Incorrect?
Oct 30, 2024
How to explain AI to middle schoolers?
Oct 25, 2024
Help with math terminology in tutorial
Oct 19, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Race-blind college admissions harm diversity without improving quality, study finds
Nov 21, 2024

Math-selective US universities reduce gender gap in STEM fields, analysis finds

Be humble: Studies reveal how to increase perceived trustworthiness of scientists
Nov 18, 2024

Teaching methods must change to address globally poor reading skills, experts say
Nov 11, 2024

Kindness in academic workplaces tied to stronger institutional identity and well-being
Nov 8, 2024

Survey highlights 'publish or perish' culture as key factor in research irreproducibility
Nov 5, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.

Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- How It Works
- Sleep Meditation
- VA Workers and Veterans

- How It Works 01
- Sleep Meditation 02
- Mental Fitness 03
- Neurofeedback 04
- Healium for Business 05
- VA Workers and Veterans 06
- Sports Meditation 07
- VR Experiences 08
- Social Purpose 11
Does Homework Cause Stress? Exploring the Impact on Students’ Mental Health
How much homework is too much?
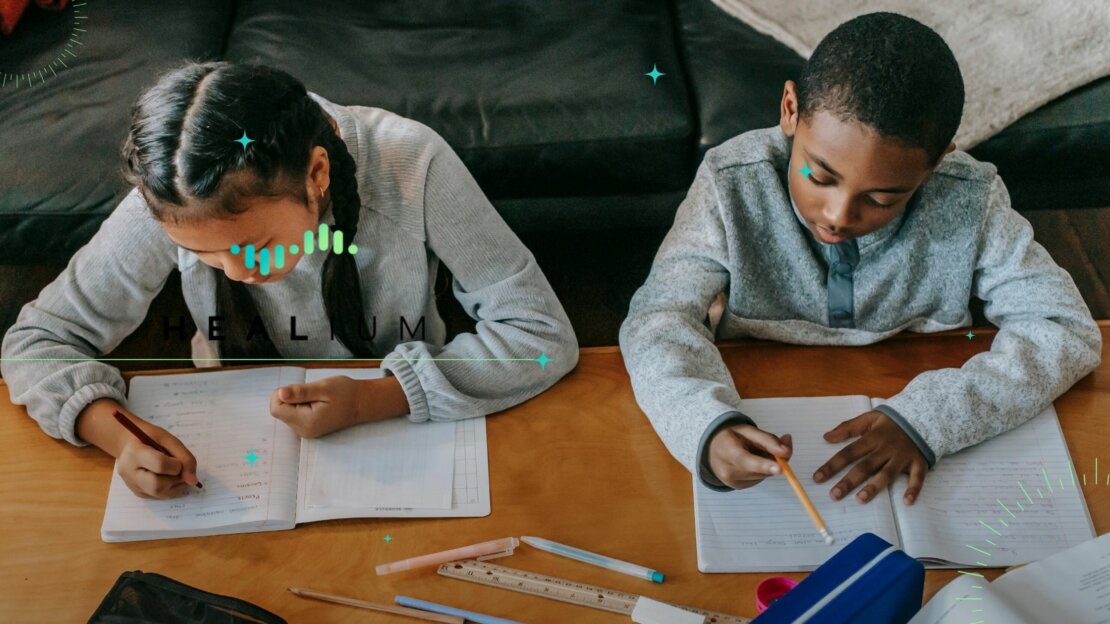

Homework has become a matter of concern for educators, parents, and researchers due to its potential effects on students’ stress levels. It’s no secret students often find themselves grappling with high levels of stress and anxiety throughout their academic careers, so understanding the extent to which homework affects those stress levels is important.
By delving into the latest research and understanding the underlying factors at play, we hope to curate insights for educators, parents, and students who are wondering whether homework causing stress in their lives?
The Link Between Homework and Stress: What the Research Says
Over the years, numerous studies investigated the relationship between homework and stress levels in students.
One study published in the Journal of Experimental Education found that students who reported spending more than two hours per night on homework experienced higher stress levels and physical health issues . Those same students reported over three hours of homework a night on average.
This study, conducted by Stanford lecturer Denise Pope, has been heavily cited throughout the years, with WebMD producing the below video on the topic– part of their special report series on teens and stress :
Additional studies published by Sleep Health Journal found that long hours on homework on may be a risk factor for depression , suggesting that reducing workload outside of class may benefit sleep and mental fitness .
Homework’s Potential Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Homework-induced stress on students can involve both psychological and physiological side effects.
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Anxiety: The pressure to perform well academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming.
• Sleep Disturbances : Homework-related stress can disrupt students’ sleep patterns, leading to sleep anxiety or sleep deprivation, both of which can negatively impact cognitive function and emotional regulation.
• Reduced Motivation: Excessive homework demands could drain students’ motivation, causing them to feel fatigued and disengaged from their studies. Reduced motivation may lead to a lack of interest in learning, hindering students’ overall academic performance.
2. Potential Physiological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Impaired Immune Function: Prolonged stress could weaken the immune system, making students more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
• Disrupted Hormonal Balance : The body’s stress response triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which, when chronically elevated due to stress, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance and lead to various health issues.
• Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Stress has been known to affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as stomachaches, nausea, and other digestive problems.
• Cardiovascular Impact: The increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure associated with stress can strain the cardiovascular system, potentially increasing the risk of heart-related issues in the long run.
• Brain impact: Prolonged exposure to stress hormones may impact the brain’s functioning , affecting memory, concentration, and other cognitive abilities.
The Benefits of Homework
It’s important to note that homework also offers many benefits that contribute to students’ academic growth and development, such as:
• Development of Time Management Skills: Completing homework within specified deadlines encourages students to manage their time efficiently. This valuable skill extends beyond academics and becomes essential in various aspects of life.
• Preparation for Future Challenges : Homework helps prepare students for future academic challenges and responsibilities. It fosters a sense of discipline and responsibility, qualities that are crucial for success in higher education and professional life.
• Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Homework often presents students with challenging problems to solve. Tackling these problems independently nurtures critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
While homework can foster discipline, time management, and self-directed learning, the middle ground may be to strike a balance that promotes both academic growth and mental well-being .
How Much Homework Should Teachers Assign?
As a general guideline, educators suggest assigning a workload that allows students to grasp concepts effectively without overwhelming them . Quality over quantity is key, ensuring that homework assignments are purposeful, relevant, and targeted towards specific objectives.
Advice for Students: How to balance Homework and Well-being
Finding a balance between academic responsibilities and well-being is crucial for students. Here are some practical tips and techniques to help manage homework-related stress and foster a healthier approach to learning:
• Effective Time Management : Encourage students to create a structured study schedule that allocates sufficient time for homework, breaks, and other activities. Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can prevent last-minute rushes and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed.
• Break Tasks into Smaller Chunks : Large assignments can be daunting and may contribute to stress. Students should break such tasks into smaller, manageable parts. This approach not only makes the workload seem less intimidating but also provides a sense of accomplishment as each section is completed.
• Find a Distraction-Free Zone : Establish a designated study area that is free from distractions like smartphones, television, or social media. This setting will improve focus and productivity, reducing time needed to complete homework.
• Be Active : Regular exercise is known to reduce stress and enhance mood. Encourage students to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, whether it’s going for a walk, playing a sport, or doing yoga.
• Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques : Encourage students to engage in mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to alleviate stress and improve concentration. Taking short breaks to relax and clear the mind can enhance overall well-being and cognitive performance.
• Seek Support : Teachers, parents, and school counselors play an essential role in supporting students. Create an open and supportive environment where students feel comfortable expressing their concerns and seeking help when needed.
How Healium is Helping in Schools
Stress is caused by so many factors and not just the amount of work students are taking home. Our company created a virtual reality stress management solution… a mental fitness tool called “Healium” that’s teaching students how to learn to self-regulate their stress and downshift in a drugless way. Schools implementing Healium have seen improvements from supporting dysregulated students and ADHD challenges to empowering students with body awareness and learning to self-regulate stress . Here’s one of their stories.
By providing students with the tools they need to self-manage stress and anxiety, we represent a forward-looking approach to education that prioritizes the holistic development of every student.
To learn more about how Healium works, watch the video below.
About the Author

Sarah Hill , a former interactive TV news journalist at NBC, ABC, and CBS affiliates in Missouri, gained recognition for pioneering interactive news broadcasting using Google Hangouts. She is now the CEO of Healium, the world’s first biometrically powered immersive media channel, helping those with stress, anxiety, insomnia, and other struggles through biofeedback storytelling. With patents, clinical validation, and over seven million views, she has reshaped the landscape of immersive media.

- General Categories
- Mental Health
- IQ and Intelligence
- Bipolar Disorder

The Dark Side of Homework: Why It’s Harmful and What the Statistics Say
Pencils down, backpacks zipped—the after-school battle that’s eroding our children’s well-being and widening educational gaps has a name: homework. This seemingly innocuous academic tradition has become a contentious issue in recent years, sparking debates among educators, parents, and policymakers alike. As we delve into the dark side of homework, we’ll explore its history, examine its impact on students, and consider alternatives that could reshape the future of education.
The practice of assigning homework has been a cornerstone of education for centuries, with its roots tracing back to the early days of formal schooling. Initially conceived as a way to reinforce classroom learning and instill discipline, homework has evolved into a complex and often controversial aspect of modern education. Today, the homework debate rages on, with proponents arguing for its necessity in academic achievement and critics pointing to its detrimental effects on student well-being and family life.
The importance of examining homework’s impact on students cannot be overstated. As our understanding of child development and learning processes advances, it’s crucial to reevaluate long-standing educational practices. The homework question touches on fundamental issues of equity, mental health, and the very purpose of education itself. By critically analyzing the role of homework in our educational system, we can work towards creating more effective and supportive learning environments for all students.
The Negative Effects of Homework on Student Well-being
One of the most significant concerns surrounding homework is its impact on student well-being. The Alarming Reality: What Percent of Students Are Stressed by Homework? reveals that a staggering number of students experience stress and anxiety related to their after-school assignments. This stress can manifest in various ways, from physical symptoms like headaches and stomach aches to emotional distress and feelings of overwhelm.
The pressure to complete homework often comes at the expense of valuable family time and social interactions. As students struggle to balance their academic responsibilities with extracurricular activities and personal interests, family dinners become rushed affairs, and quality time with loved ones becomes a luxury. This erosion of family connections can have long-lasting effects on a child’s emotional development and sense of security.
Moreover, the time-consuming nature of homework can significantly impact students’ sleep patterns and physical health. Late nights spent completing assignments lead to sleep deprivation, which in turn affects cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall well-being. Understanding Homeostatic Imbalance and Stress: A Comprehensive Guide with Worksheet Answers sheds light on how disrupted sleep patterns can contribute to a cascade of health issues.
Perhaps most concerning is the potential for homework to diminish students’ interest in learning and contribute to academic burnout. When learning becomes synonymous with tedious, repetitive tasks, students may lose their natural curiosity and enthusiasm for education. This disengagement can have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only academic performance but also future career aspirations and lifelong learning attitudes.
Homework and Academic Performance: A Surprising Relationship
Contrary to popular belief, the relationship between homework and academic achievement is not as straightforward as one might assume. Numerous studies have shown a limited correlation between homework and improved performance, particularly for younger students. This surprising finding challenges the long-held assumption that more homework inevitably leads to better academic outcomes.
The law of diminishing returns applies to homework as well. While some homework may be beneficial, there comes a point where additional assignments yield little to no academic benefit. This threshold varies depending on the student’s age, with high school students generally able to handle more homework than elementary or middle school students. However, even for older students, excessive homework can lead to burnout and decreased motivation.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of homework differs across age groups. For younger children, homework has been shown to have minimal impact on academic achievement. As students progress through middle and high school, homework can become more beneficial, but only when it’s carefully designed and appropriately challenging.
The quality of homework assignments is far more important than quantity. Meaningful, engaging tasks that reinforce classroom learning or encourage independent exploration are more likely to yield positive results than rote memorization or busywork. Educators and policymakers must focus on creating homework policies that prioritize quality over quantity, ensuring that out-of-school assignments truly contribute to student learning and growth.
Stress and Homework: What the Statistics Reveal
The statistics surrounding homework-related stress are alarming. Studies have consistently shown that a high percentage of students report experiencing stress and anxiety due to homework demands. In some surveys, as many as 70-80% of students indicate that homework is a significant source of stress in their lives.
When comparing stress levels across different educational systems, it becomes clear that homework practices vary widely. Countries with high-performing education systems, such as Finland, often assign less homework than their counterparts, challenging the notion that more homework equates to better academic outcomes. These international comparisons provide valuable insights into alternative approaches to education that prioritize student well-being alongside academic achievement.
The long-term effects of academic stress on mental health are a growing concern among researchers and mental health professionals. Chronic stress during childhood and adolescence can lead to increased risk of anxiety disorders, depression, and other mental health issues later in life. Overcoming Math Stress: Strategies for Confidence and Success in Mathematics explores how subject-specific stress, such as math anxiety, can have lasting impacts on students’ academic and personal lives.
Interestingly, gender differences in homework-related stress have been observed in various studies. Girls often report higher levels of stress and anxiety related to homework compared to boys. This disparity may be attributed to societal expectations, differences in coping strategies, or other factors that require further investigation to fully understand and address.
The Equity Issue: How Homework Perpetuates Inequality
One of the most troubling aspects of homework is its potential to exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Students from different socioeconomic backgrounds often face vastly different circumstances when it comes to completing homework assignments. Disparities in home resources and support can significantly impact a student’s ability to succeed academically.
For students from low-income families, homework can present numerous challenges. Limited access to technology, quiet study spaces, or academic resources can make completing assignments difficult or impossible. Parents working multiple jobs may have less time to assist with homework, putting their children at a disadvantage compared to peers with more available parental support. The Pervasive Daily Stress of Poverty: Unraveling Its Impact on Brain Development highlights how these socioeconomic factors can have far-reaching effects on a child’s cognitive development and academic potential.
Homework’s role in widening the achievement gap is a critical concern. As students from privileged backgrounds benefit from additional resources and support, those from disadvantaged backgrounds may fall further behind. This cycle can perpetuate and even amplify existing inequalities, making it increasingly difficult for students from low-income families to achieve academic success and social mobility.
Cultural biases in homework assignments can further compound these issues. Assignments that assume certain cultural knowledge or experiences may inadvertently disadvantage students from diverse backgrounds. Educators must be mindful of these potential biases and strive to create inclusive, culturally responsive homework practices that support all students’ learning and growth.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
As the drawbacks of traditional homework become increasingly apparent, educators and researchers are exploring alternative approaches to out-of-school learning. Project-based learning approaches offer one promising alternative, encouraging students to engage in long-term, interdisciplinary projects that foster creativity, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving skills.
The flipped classroom model is another innovative approach that reimagines the role of homework. In this model, students engage with instructional content at home through videos or readings, while class time is devoted to collaborative problem-solving and hands-on activities. This approach allows for more personalized instruction and support during school hours, potentially reducing the need for extensive homework assignments.
Personalized learning strategies, facilitated by advancements in educational technology, offer yet another alternative to traditional homework. These approaches tailor assignments to individual students’ needs, interests, and learning styles, potentially increasing engagement and reducing unnecessary stress. Gloria’s Study Challenge: The Impact of One More Hour and the Hidden Costs of Interruptions explores how personalized study strategies can impact learning outcomes.
Emphasizing in-class practice and collaboration is another way to reduce the burden of homework while still promoting learning and skill development. By providing more opportunities for guided practice during school hours, teachers can ensure that students receive immediate feedback and support, potentially reducing the need for extensive at-home practice.
Conclusion: Rethinking Homework for a Better Educational Future
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the traditional approach to homework is fraught with challenges. From its negative impact on student well-being to its potential to exacerbate educational inequalities, homework as we know it may be doing more harm than good. The limited correlation between homework and academic achievement, particularly for younger students, further calls into question the value of extensive out-of-school assignments.
A balanced approach to out-of-school learning is crucial. While some form of independent practice and exploration outside of school hours may be beneficial, it’s essential to consider the quality, quantity, and purpose of these assignments. Educators and policymakers must prioritize student well-being, equity, and meaningful learning experiences when developing homework policies.
The need for education reform and policy changes is clear. Is Homework Necessary? Examining the Debate and Its Impact on Student Well-being delves deeper into this question, challenging long-held assumptions about the role of homework in education. As we move forward, it’s crucial to consider alternative approaches that support student learning without sacrificing their mental health, family time, or love of learning.
Encouraging further research and discussion on homework practices is essential for developing evidence-based policies that truly serve students’ best interests. By critically examining our current practices and remaining open to innovative approaches, we can work towards an educational system that nurtures well-rounded, engaged, and lifelong learners.
As we conclude this exploration of the dark side of homework, it’s clear that the time has come to reevaluate our approach to out-of-school learning. By addressing the stress, inequity, and limited benefits associated with traditional homework, we can pave the way for a more effective, equitable, and student-centered education system. The Power of Playtime: How Recess Reduces Stress in Students reminds us of the importance of balance in education, highlighting the need for policies that support both academic growth and overall well-being.
The homework debate is far from over, but by continuing to question, research, and innovate, we can work towards educational practices that truly serve the needs of all students. As parents, educators, and policymakers, it’s our responsibility to ensure that our children’s education nurtures their curiosity, supports their well-being, and prepares them for success in an ever-changing world. Let’s reimagine homework not as a nightly battle, but as an opportunity for meaningful learning, growth, and discovery.
References:
1. Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76(1), 1-62.
2. Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81(4), 490-510.
3. OECD (2014). Does homework perpetuate inequities in education? PISA in Focus, No. 46, OECD Publishing, Paris.
4. Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2000). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning. Beacon Press.
5. Marzano, R. J., & Pickering, D. J. (2007). Special topic: The case for and against homework. Educational Leadership, 64(6), 74-79.
6. Vatterott, C. (2018). Rethinking homework: Best practices that support diverse needs. ASCD.
7. Kohn, A. (2006). The homework myth: Why our kids get too much of a bad thing. Da Capo Press.
8. Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy, 43(4), 297-313.
9. Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
10. Sahlberg, P. (2015). Finnish lessons 2.0: What can the world learn from educational change in Finland? Teachers College Press.
Was this article helpful?
Would you like to add any comments (optional), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Related Resources

Undue Stress at Work: Navigating and Overcoming Challenges

Workers’ Compensation Mental Health: Your Rights and Options Explained
Motivation, Emotion, and Stress in AP Psychology: Key Concepts Explained

Pablo’s Exam Stress and Overeating: Understanding the Struggle and Finding…

Plate Boundary Landforms: How Tectonic Stress Shapes the Earth

College Student Stress: Major Causes and How to Cope

Nursing School Stress: Effective Coping Strategies for Aspiring Healthcare Professionals

Homework Stress: The Hidden Toll on Students and Its Impact

College Student Stress Crisis: Alarming Statistics and Solutions

College Student Financial Stress: A Practical Guide to Managing Money…
- Second Opinion
- Research & Innovation
- Patients & Families
- Health Professionals
- Recently Visited
- Segunda opinión
- Refer a patient
- MyChart Login
Healthier, Happy Lives Blog
Sort articles by..., sort by category.
- Celebrating Volunteers
- Community Outreach
- Construction Updates
- Family-Centered Care
- Healthy Eating
- Heart Center
- Interesting Things
- Mental Health
- Patient Stories
- Research and Innovation
- Safety Tips
- Sustainability
- World-Class Care
About Our Blog
- Back-to-School
- Pediatric Technology
Latest Posts
- Ask Me Anything About Sports Medicine
- Preschooler Living Seizure-Free With Leading-Edge Medicine
- Stanford Medicine Recycles Every Day
- Bass Center Caregiver Wellness Event Fosters Community and Connection
- Serving Our Nation and Patients

Health Hazards of Homework
March 18, 2014 | Julie Greicius Pediatrics .

A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework “experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.”
Those health problems ranged from stress, headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems, to psycho-social effects like dropping activities, not seeing friends or family, and not pursuing hobbies they enjoy.
In the Stanford Report story about the research, Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Experimental Education , says, “Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good.”
The study was based on survey data from a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in California communities in which median household income exceeded $90,000. Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night.
“It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today’s workplace,” says Neville Golden, MD , chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. “This landmark study shows that excessive homework is counterproductive, leading to sleep deprivation, school stress and other health problems. Parents can best support their children in these demanding academic environments by advocating for them through direct communication with teachers and school administrators about homework load.”
Related Posts

Top-ranked group group in Los Gatos, Calif., is now a part of one of the…

The Stanford Medicine Children’s Health network continues to grow with our newest addition, Town and…
- Julie Greicius
- more by this author...
Connect with us:
Download our App:
ABOUT STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Leadership Team
- Vision, Mission & Values
- The Stanford Advantage
- Government and Community Relations
LUCILE PACKARD FOUNDATION FOR CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Get Involved
- Volunteering Services
- Auxiliaries & Affiliates
- Our Hospital
- Send a Greeting Card
- New Hospital
- Refer a Patient
- Pay Your Bill

Also Find Us on:
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Code of Conduct
- Price Transparency
- Stanford School of Medicine
- Stanford Health Care
- Stanford University

IMAGES
COMMENTS
In 2013, research conducted at Stanford University found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of ...
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
Stress is the body's response to any demand or challenge, triggering a cascade of physiological and psychological reactions. For students, this can manifest as anxiety, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and even physical symptoms like headaches or stomach aches. Homework contributes to student stress levels in various ways.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
Homework-induced stress on students can involve both psychological and physiological side effects. 1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress: • Anxiety: The pressure to perform well academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments ...
The statistics surrounding homework-related stress are alarming. Studies have consistently shown that a high percentage of students report experiencing stress and anxiety due to homework demands. In some surveys, as many as 70-80% of students indicate that homework is a significant source of stress in their lives.
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up." Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
A valid way to evaluate and measure how homework can put stress on students is clearly necessary, as well as what factors can amplify or alleviate said stress. The "Stress around Homework" construct, as proposed by Katz et al. in their 2012 construct validation paper, offers a promising approach to addressing the issue.
Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night. "It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today's workplace," says Neville Golden, MD, chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children's Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. "This ...