What is Research Design? Characteristics, Types, Process, & Examples
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

Your search has come to an end!
Ever felt like a hamster on a research wheel fast, spinning with a million questions but going nowhere? You've got your topic; you're brimming with curiosity, but... what next? So, forget the research rut and get your papers! This ultimate guide to "what is research design?" will have you navigating your project like a pro, uncovering answers and avoiding dead ends. Know the features of good research design, what you mean by research design, elements of research design, and more.

What is Research Design?
Before starting with the topic, do you know what is research design? Research design is the structure of research methods and techniques selected to conduct a study. It refines the methods suited to the subject and ensures a successful setup. Defining a research topic clarifies the type of research (experimental, survey research, correlational, semi-experimental, review) and its sub-type (experimental design, research problem, descriptive case-study).
There are three main types of designs for research:
1. Data Collection
2. Measurement
3. Data Analysis
Elements of Research Design
Now that you know what is research design, it is important to know the elements and components of research design. Impactful research minimises bias and enhances data accuracy. Designs with minimal error margins are ideal. Key elements include:
1. Accurate purpose statement
2. Techniques for data collection and analysis
3. Methods for data analysis
4. Type of research methodology
5. Probable objections to research
6. Research settings
7. Timeline
8. Measurement of analysis
Got a hang of research, now book yout student accommodation with one click!
Book through amber today!
Characteristics of Research Design
Research design has several key characteristics that contribute to the validity, reliability, and overall success of a research study. To know the answer for what is research design, it is important to know the characteristics. These are-
1. Reliability
A reliable research design ensures that each study’s results are accurate and can be replicated. This means that if the research is conducted again under the same conditions, it should yield similar results.
2. Validity
A valid research design uses appropriate measuring tools to gauge the results according to the research objective. This ensures that the data collected and the conclusions drawn are relevant and accurately reflect the phenomenon being studied.
3. Neutrality
A neutral research design ensures that the assumptions made at the beginning of the research are free from bias. This means that the data collected throughout the research is based on these unbiased assumptions.
4. Generalizability
A good research design draws an outcome that can be applied to a large set of people and is not limited to the sample size or the research group.
Research Design Process
What is research design? A good research helps you do a really good study that gives fair, trustworthy, and useful results. But it's also good to have a bit of wiggle room for changes. If you’re wondering how to conduct a research in just 5 mins , here's a breakdown and examples to work even better.
1. Consider Aims and Approaches
Define the research questions and objectives, and establish the theoretical framework and methodology.
2. Choose a Type of Research Design
Select the suitable research design, such as experimental, correlational, survey, case study, or ethnographic, according to the research questions and objectives.
3. Identify Population and Sampling Method
Determine the target population and sample size, and select the sampling method, like random, stratified random sampling, or convenience sampling.
4. Choose Data Collection Methods
Decide on the data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments, and choose the appropriate instruments for data collection.
5. Plan Data Collection Procedures
Create a plan for data collection, detailing the timeframe, location, and personnel involved, while ensuring ethical considerations are met.
6. Decide on Data Analysis Strategies
Select the appropriate data analysis techniques, like statistical analysis, content analysis, or discourse analysis, and plan the interpretation of the results.
What are the Types of Research Design?
A researcher must grasp various types to decide which model to use for a study. There are different research designs that can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research identifies relationships between collected data and observations through mathematical calculations. Statistical methods validate or refute theories about natural phenomena. This research method answers "why" a theory exists and explores respondents' perspectives.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is essential when statistical conclusions are needed to gather actionable insights. Numbers provide clarity for critical business decisions. This method is crucial for organizational growth, with insights from complex numerical data guiding future business decisions.
Qualitative Research vs Quantitative Research
While researching, it is important to know the difference between qualitative and quantitative research. Here's a quick difference between the two:
| Aspect | Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. | Numerical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. |
| Purpose | To understand concepts, thoughts, or experiences. | To test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions. |
| Data Collection | Common methods include interviews with open-ended questions, observations described in words, and literature reviews. | Common methods include surveys with closed-ended questions, experiments, and observations recorded as numbers. |
| Data Analysis | Data is analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis. | Data is analyzed using statistical methods. |
| Outcome | Produces rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and uncovers new insights and meanings. | Produces objective, empirical data that can be measured. |
The research types can be further divided into 5 categories:
1. Descriptive Research
Descriptive research design focuses on detailing a situation or case. It's a theory-driven method that involves gathering, analysing, and presenting data. This approach offers insights into the reasons and mechanisms behind a research subject, enhancing understanding of the research's importance. When the problem statement is unclear, exploratory research can be conducted.
2. Experimental Research
Experimental research design investigates cause-and-effect relationships. It’s a causal design where the impact of an independent variable on a dependent variable is observed. For example, the effect of price on customer satisfaction. This method efficiently addresses problems by manipulating independent variables to see their effect on dependent variables. Often used in social sciences, it involves analysing human behaviour by studying changes in one group's actions and their impact on another group.
3. Correlational Research
Correlational research design is a non-experimental technique that identifies relationships between closely linked variables. It uses statistical analysis to determine these relationships without assumptions. This method requires two different groups. A correlation coefficient between -1 and +1 indicates the strength and direction of the relationship, with +1 showing a positive correlation and -1 a negative correlation.
4. Diagnostic Research
Diagnostic research design aims to identify the underlying causes of specific issues. This method delves into factors creating problematic situations and has three phases:
- Issue inception
- Issue diagnosis
- Issue resolution
5. Explanatory Research
Explanatory research design builds on a researcher’s ideas to explore theories further. It seeks to explain the unexplored aspects of a subject, addressing the what, how, and why of research questions.
Benefits of Research Design
After learning about what is research design and the process, it is important to know the key benefits of a well-structured research design:
1. Minimises Risk of Errors: A good research design minimises the risk of errors and reduces inaccuracy. It ensures that the study is carried out in the right direction and that all the team members are on the same page.
2. Efficient Use of Resources: It facilitates a concrete research plan for the efficient use of time and resources. It helps the researcher better complete all the tasks, even with limited resources.
3. Provides Direction: The purpose of the research design is to enable the researcher to proceed in the right direction without deviating from the tasks. It helps to identify the major and minor tasks of the study.
4. Ensures Validity and Reliability: A well-designed research enhances the validity and reliability of the findings and allows for the replication of studies by other researchers. The main advantage of a good research design is that it provides accuracy, reliability, consistency, and legitimacy to the research.
5. Facilitates Problem-Solving: A researcher can easily frame the objectives of the research work based on the design of experiments (research design). A good research design helps the researcher find the best solution for the research problems.
6. Better Documentation: It helps in better documentation of the various activities while the project work is going on.
That's it! You've explored all the answers for what is research design in research? Remember, it's not just about picking a fancy method – it's about choosing the perfect tool to answer your burning questions. By carefully considering your goals and resources, you can design a research plan that gathers reliable information and helps you reach clear conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key components of a research design, how can i choose the best research design for my study, what are some common pitfalls in research design, and how can they be avoided, how does research design impact the validity and reliability of a study, what ethical considerations should be taken into account in research design.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts

Top 10 Film Schools in New York in 2024!

Explore 15 Best Short Certificate Programs That Pay Well in 2024!

Education As An Investment: 12 Key Reasons to Consider in 2024

amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students

Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
Grounded Theory Research Design
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.

Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
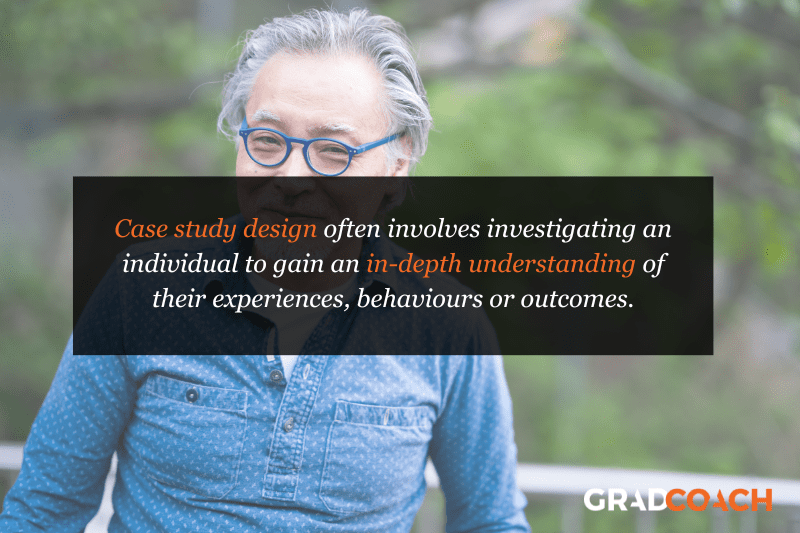
Case Study Design
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
13 Comments
Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
This post is really helpful.
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
how can I put this blog as my reference(APA style) in bibliography part?
This post has been very useful to me. Confusing areas have been cleared
This is very helpful and very useful!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
The Four Types of Research Design — Everything You Need to Know
Updated: July 23, 2024
Published: January 18, 2023
When you conduct research, you need to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve and how to accomplish it. A good research design enables you to collect accurate and reliable data to draw valid conclusions.

In this blog post, we'll outline the key features of the four common types of research design with real-life examples from UnderArmor, Carmex, and more. Then, you can easily choose the right approach for your project.
Table of Contents
What is research design?
The four types of research design, research design examples.
Research design is the process of planning and executing a study to answer specific questions. This process allows you to test hypotheses in the business or scientific fields.
Research design involves choosing the right methodology, selecting the most appropriate data collection methods, and devising a plan (or framework) for analyzing the data. In short, a good research design helps us to structure our research.
Marketers use different types of research design when conducting research .
There are four common types of research design — descriptive, correlational, experimental, and diagnostic designs. Let’s take a look at each in more detail.
Researchers use different designs to accomplish different research objectives. Here, we'll discuss how to choose the right type, the benefits of each, and use cases.
Research can also be classified as quantitative or qualitative at a higher level. Some experiments exhibit both qualitative and quantitative characteristics.
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Experimental
An experimental design is used when the researcher wants to examine how variables interact with each other. The researcher manipulates one variable (the independent variable) and observes the effect on another variable (the dependent variable).
In other words, the researcher wants to test a causal relationship between two or more variables.
In marketing, an example of experimental research would be comparing the effects of a television commercial versus an online advertisement conducted in a controlled environment (e.g. a lab). The objective of the research is to test which advertisement gets more attention among people of different age groups, gender, etc.
Another example is a study of the effect of music on productivity. A researcher assigns participants to one of two groups — those who listen to music while working and those who don't — and measure their productivity.
The main benefit of an experimental design is that it allows the researcher to draw causal relationships between variables.
One limitation: This research requires a great deal of control over the environment and participants, making it difficult to replicate in the real world. In addition, it’s quite costly.
Best for: Testing a cause-and-effect relationship (i.e., the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable).
Correlational
A correlational design examines the relationship between two or more variables without intervening in the process.
Correlational design allows the analyst to observe natural relationships between variables. This results in data being more reflective of real-world situations.
For example, marketers can use correlational design to examine the relationship between brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. In particular, the researcher would look for patterns or trends in the data to see if there is a relationship between these two entities.
Similarly, you can study the relationship between physical activity and mental health. The analyst here would ask participants to complete surveys about their physical activity levels and mental health status. Data would show how the two variables are related.
Best for: Understanding the extent to which two or more variables are associated with each other in the real world.
Descriptive
Descriptive research refers to a systematic process of observing and describing what a subject does without influencing them.
Methods include surveys, interviews, case studies, and observations. Descriptive research aims to gather an in-depth understanding of a phenomenon and answers when/what/where.
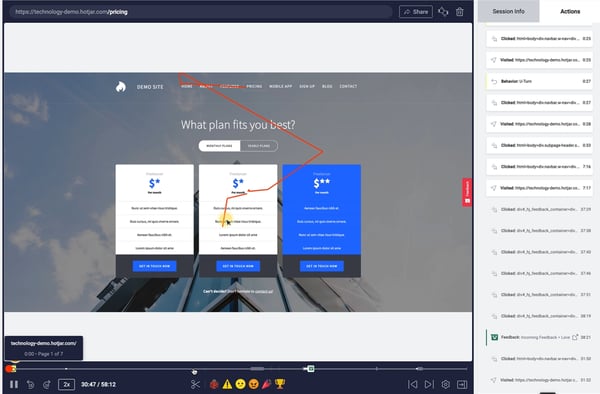
SaaS companies use descriptive design to understand how customers interact with specific features. Findings can be used to spot patterns and roadblocks.
For instance, product managers can use screen recordings by Hotjar to observe in-app user behavior. This way, the team can precisely understand what is happening at a certain stage of the user journey and act accordingly.
Brand24, a social listening tool, tripled its sign-up conversion rate from 2.56% to 7.42%, thanks to locating friction points in the sign-up form through screen recordings.
Carma Laboratories worked with research company MMR to measure customers’ reactions to the lip-care company’s packaging and product . The goal was to find the cause of low sales for a recently launched line extension in Europe.
The team moderated a live, online focus group. Participants were shown w product samples, while AI and NLP natural language processing identified key themes in customer feedback.
This helped uncover key reasons for poor performance and guided changes in packaging.
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities – start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
| Qualitative approach | Quantitative approach |
|---|---|
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships, while descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Experimental | |
| Quasi-experimental | |
| Correlational | |
| Descriptive |
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends, and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analysing the data.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | |
| Phenomenology |
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region, or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalise your results to the population as a whole.
| Probability sampling | Non-probability sampling |
|---|---|
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study, your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalise to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question.
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviours, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews.
| Questionnaires | Interviews |
|---|---|
Observation methods
Observations allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviours, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
| Quantitative observation | |
|---|---|
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
| Field | Examples of data collection methods |
|---|---|
| Media & communication | Collecting a sample of texts (e.g., speeches, articles, or social media posts) for data on cultural norms and narratives |
| Psychology | Using technologies like neuroimaging, eye-tracking, or computer-based tasks to collect data on things like attention, emotional response, or reaction time |
| Education | Using tests or assignments to collect data on knowledge and skills |
| Physical sciences | Using scientific instruments to collect data on things like weight, blood pressure, or chemical composition |
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected – for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are reliable and valid.
Operationalisation
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalisation means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in – for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced , while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
| Reliability | Validity |
|---|---|
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method, you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample – by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method, it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method, how will you avoid bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organising and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymise and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well organised will save time when it comes to analysing them. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings.
On their own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyse the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarise your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarise your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
| Approach | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Thematic analysis | |
| Discourse analysis |
There are many other ways of analysing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, March 20). Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
What are the different types of research design?
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Research design is the strategy or plan you use to gather that data and make sense of it in a way that seems understandable, logical, and actionable.
Consider your research design the roadmap of data collection and measurement. Various types of design allow you to systematically gather and interpret data to be most beneficial to you. Let’s dive into the ins and outs of research design.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What are the elements of research design?
While there are many types of research design, some elements are essential to all types. For your research to be impactful, pay special attention to keeping the margin of error minimal.
Here are the key elements:
A stated purpose
Method for collecting the data
Method for analyzing the data
Established type of research methodology
The number of participants necessary
To what capacity (time, data, permissions) you’ll require participants
The probable and expected goal for research (the questions you’ll answer)
Study setting
Established timeline for the entire study
Statistics of study (what you’re studying vs. statistically accurate sample representation)
Approved budget of study for compensation for participants and survey responses
Characteristics of research design
Generally, four characteristics of research design will set your study up for success:
Neutrality : Keep your projected study results unbiased and neutral.
Reliability : Standardize your design to handle each research segment the same each time.
Validity : Use the correct measuring tools to gauge the results.
Generalization : Your research results should apply to a generalized segment, not just a small select sample.
Making sure your research is without bias means your survey must meet these four criteria.
When planning your research design strategy, you need to consider two perspectives: Quantitative and qualitative . Understanding how these two work and how they pertain to your study will give you a better idea of how to implement your project in the research design.
Quantitative research design
In quantitative research design, you use numerous variables to analyze the findings, such as numbers and statistics.
Quantitative research design is absolute and often uses graphs, charts, and statistics to demonstrate the findings. These findings typically answer “ what is happening? ”
You can use online questionnaires, surveys, or polls to gather quantitative information. Most surveys are multiple-choice, limiting open-ended questions. Researchers usually carry them out on a large statistically relevant group of respondents.
Qualitative research design
Qualitative research determines the hows and the whys of how people think or respond to questions. This research design uses open-ended questions and conversational responses in virtual call conversations or face-to-face interviews.
Qualitative research focuses on generating ideas and developing theories. You can do this with fewer but more in-depth sessions with respondents than with a quantitative research design.
- What are the different types of research designs?
There are thirteen different types of research design. Researchers familiar with these types will find it easier to gather the data they need to complete their study. Each type differs in how you collect, analyze, or use data.
Action research design
Action research can be quantitative, qualitative, or a combination. It addresses a specific issue and seeks to solve it. Because the action research design is cooperative and adaptive, it works well in employment and community situations. It can increase the chances of learning from the participant's overall experience.
Case study research design
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject. Case study research design is usually qualitative but can also sometimes use quantitative methods.
These studies are excellent for evaluating and understanding the different facets of a research problem. Case study research designs narrow down a significant problem into more easily researchable problems.
Researchers sometimes use them to describe rare cases, and social scientists test situations with case study research. Sometimes, case studies use small samplings, which can call the research’s reliability and generality into question.
Causal research design
Causal research works to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables. Many companies use this research design to determine the impact a change in a product or process will make.
Sometimes called explanatory research or causal-comparative research, it can be challenging to perform, especially when the research deals with opinions or emotions.
Companies often use causal research during the later stages of decision-making rather than initial research designs. That’s because it’s usually assessing the impact of a change in an existing product.
Cohort research design
Cohort design is an observational research design that sometimes follows participants over an extended period. The health and medical fields regularly use this research to evaluate the outcome of a particular drug or the occurrence of a reaction. The researcher selects participants that have things in common.
Open or closed cohort research types depend on the size and scope of the study. Closed studies involve participants who enter the study at the same time and involve a specific population. Though cohort studies are flexible, they are often lengthy.
Cross-sectional research design
Biological or medical applications use cross-sectional research when they require data from a population or representative sample at a specific point in time. Surveys are the usual data collection method, so it is less expensive than other research designs. Sometimes participants are difficult to find, and a narrow timeframe sometimes makes information hard to get.
Descriptive research design
In descriptive research design, the intent is to describe a situation or case by systematically obtaining data to describe the phenomenon, population, or event.
It can help others further understand the need for research by answering the what : Questions as to how, when, or why require further research.
Experimental research design
You conduct experimental research in an objective and controlled manner to ensure precision. This also enables you to draw conclusions that establish one variable's effect on another. In other words, it uses a control group to compare with the experimental group.
This type of research has numerous applications, and several industries use it. It can deliver a high level of evidence based on the research and determine cause and effect in many situations. You can manipulate the variables and monitor the effect of the changes.
Exploratory research design
As it sounds, exploratory research design explores areas researchers have not studied before. Often, exploratory research determines if further research is necessary. Exploratory research attempts to answer the what, why, and how while setting up additional research needs. Usually qualitative by design, you could also set up larger studies as quantitative.
Historical research design
Historical research design pulls historical data from past studies. You collect, evaluate, and present that data based on the outcomes. This usually requires you to combine data from several sources and present it as one research hypothesis.
For example, you could pull information from timesheets, logs, news reports, maps, or other archived or current information. Many industries use it in trend analysis.
Longitudinal research design
This type of research design makes multiple observations and experiments. Longitudinal research tends to interview the same group over an extended period.
Behavioral and psychological research uses this type of study to track the behavior of specific groups and identify the variables that changed their behavior.
This type of research takes a long time to complete, and sometimes the original sample changes over time. It is an observational study that we can also refer to as a panel study.
Observational research design
Observational research design is where you observe participants with or without their knowledge. You’ll usually perform it in natural settings to observe how the respondents make choices or respond to certain situations. They are reasonably flexible types of research, and you can correlate the results to reflect real-life events.
Philosophical research design
Philosophical research design is a broader approach to researching a problem. You use this design to make assumptions in areas you’re researching.
In essence, researchers use logic and information from models and theories to analyze and create a basis for:
Practical decision-making
Refining established concepts
Giving clarity and definition to ideas and concepts
Sequential research design
Of course, this type of research design is sequential. This means you must finish one research stage before moving on to the next stage or sequence.
These sequences continue until you’ve collected enough data to fulfill the research. Sequential research includes some elements from cross-sectional and longitudinal designs.
- How to create a research design
To create a research design, you must be sure your chosen methods match your research intent. Not all types are suitable for all research analysis and data collection.
When creating your research design, consider your overall objectives, how you plan to sample, and how you intend to collect and analyze your data. Determine which methods are the most appropriate for the research you’ll be doing.
Keep the following steps in mind when creating your research design:
1. Consider your aims and approach
Before anything else, determine the question you want to answer. Without this information, it is hard to formulate the research you need, the length of time for your study, and the desired result. Sometimes, people get so wrapped up in the details that they can lose sight of the goal.
Knowing what type of information you are collecting and why you need the data is important. Being concise and to the point can save your stakeholders time and money and prevent you from getting lost.
2. Choose a type of research design
Look at the type of research designs above and decide on the design that best fits your needs. Each provides a framework for you to move forward with your research. Decide if your research should be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.
Will you need online surveys to collect your data? Will you conduct in-person interviews, asking open-ended questions that give respondents a chance to voice their opinions? Or maybe a more scientific, quantitative approach is what you are looking for.
3. Identify your population and sampling method
By now, you’ve determined who or what your research will focus on and how you will choose your respondents. Now you need to focus on your population.
In research talk, population is the whole group that you are aiming your research at. Samples are the ones you actually peg as your participants from that group. They will provide you with the relevant data to form accurate theories.
Decide what makes up your population specifically. If you are researching all students who are attending college, you will identify that as your target population. You narrow the population if you want to target all students in a state university. You've defined the population further if you’re researching students studying literature at Arizona State University. The more precise your definition, the easier it will be to get a reliable sample.
4. Choose your data collection methods
The way you gather your information is vital to your overall results. You need a method that’s manageable for your project.
Several methods effectively collect data, and you can use some in combination for the best results:
Surveys are helpful in collecting information on opinions, behaviors, and characteristics. You can acquire the data through questionnaires with multiple-choice questions. It’s best to analyze this option as quantitative data.
Observation
Observation lets you observe the participants, their reactions, choices, and interactions. You can do this with or without their knowledge. In addition to observing in real-time, you can collect some qualitative data through recordings and in-app behavior analytics.
Historical data
You can collect historical data from an assortment of sources if combining the data helps you get to your desired study results.
5. Plan your data collection procedures
Data collection procedures mean more than just writing up a survey and asking a few questions. You must ensure your data is accurate, unbiased, and the same data you use throughout your sample. It’s essential to be consistent in collecting the information.
It may be easy to ask your sample population the same questions on the same survey, but are there variables you must consider? If using observation, how do you maintain a neutral position if it’s impossible to observe every single detail?
This is where you should determine:
The size of your sample
The length of the survey or interview
The resources (financial or human) needed to conduct your study
Is the location secured for your research to be conducted?
Organizational skills are necessary regardless of which research design you use. Often, stakeholders will want to know upfront the costs and resources involved in a study.
For the collected data to meet the requirements of neutrality, reliability, validity, and generalization, you must ensure your data collection is consistent, unbiased, and accurate.
6. Decide on your data analysis strategies
If you have decided on a quantitative research design, you may want to prepare your analysis using statistics and numbers. You may present your findings in pie charts, graphs, and other statistical visual methods.
Qualitative research design relies on opinions and ideas and may be more challenging to represent. You will have to weed through your information, compile it to meet the objectives, and only extract relevant facts.
- What makes a good research design?
A good research design fulfills the needs of the study. While that’s a broad definition, the research design that’s right for you should always have the end in sight.
In summary, your research should always be:
Within your budget
Appropriate
Packed with valid information from appropriate and trustworthy data collection
A large enough sample to represent the larger population you are researching
By applying these guidelines to your next research design, you’ll be able to craft a winning formula.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is Research Design? Understand Types of Research Design, with Examples
Have you been wondering “ what is research design ?” or “what are some research design examples ?” Are you unsure about the research design elements or which of the different types of research design best suit your study? Don’t worry! In this article, we’ve got you covered!
Table of Contents
What is research design?
Have you been wondering “ what is research design ?” or “what are some research design examples ?” Don’t worry! In this article, we’ve got you covered!
A research design is the plan or framework used to conduct a research study. It involves outlining the overall approach and methods that will be used to collect and analyze data in order to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A well-designed research study should have a clear and well-defined research question, a detailed plan for collecting data, and a method for analyzing and interpreting the results. A well-thought-out research design addresses all these features.
Research design elements
Research design elements include the following:
- Clear purpose: The research question or hypothesis must be clearly defined and focused.
- Sampling: This includes decisions about sample size, sampling method, and criteria for inclusion or exclusion. The approach varies for different research design types .
- Data collection: This research design element involves the process of gathering data or information from the study participants or sources. It includes decisions about what data to collect, how to collect it, and the tools or instruments that will be used.
- Data analysis: All research design types require analysis and interpretation of the data collected. This research design element includes decisions about the statistical tests or methods that will be used to analyze the data, as well as any potential confounding variables or biases that may need to be addressed.
- Type of research methodology: This includes decisions about the overall approach for the study.
- Time frame: An important research design element is the time frame, which includes decisions about the duration of the study, the timeline for data collection and analysis, and follow-up periods.
- Ethical considerations: The research design must include decisions about ethical considerations such as informed consent, confidentiality, and participant protection.
- Resources: A good research design takes into account decisions about the budget, staffing, and other resources needed to carry out the study.
The elements of research design should be carefully planned and executed to ensure the validity and reliability of the study findings. Let’s go deeper into the concepts of research design .

Characteristics of research design
Some basic characteristics of research design are common to different research design types . These characteristics of research design are as follows:
- Neutrality : Right from the study assumptions to setting up the study, a neutral stance must be maintained, free of pre-conceived notions. The researcher’s expectations or beliefs should not color the findings or interpretation of the findings. Accordingly, a good research design should address potential sources of bias and confounding factors to be able to yield unbiased and neutral results.
- Reliability : Reliability is one of the characteristics of research design that refers to consistency in measurement over repeated measures and fewer random errors. A reliable research design must allow for results to be consistent, with few errors due to chance.
- Validity : Validity refers to the minimization of nonrandom (systematic) errors. A good research design must employ measurement tools that ensure validity of the results.
- Generalizability: The outcome of the research design should be applicable to a larger population and not just a small sample . A generalized method means the study can be conducted on any part of a population with similar accuracy.
- Flexibility: A research design should allow for changes to be made to the research plan as needed, based on the data collected and the outcomes of the study
A well-planned research design is critical for conducting a scientifically rigorous study that will generate neutral, reliable, valid, and generalizable results. At the same time, it should allow some level of flexibility.
Different types of research design
A research design is essential to systematically investigate, understand, and interpret phenomena of interest. Let’s look at different types of research design and research design examples .
Broadly, research design types can be divided into qualitative and quantitative research.
Qualitative research is subjective and exploratory. It determines relationships between collected data and observations. It is usually carried out through interviews with open-ended questions, observations that are described in words, etc.
Quantitative research is objective and employs statistical approaches. It establishes the cause-and-effect relationship among variables using different statistical and computational methods. This type of research is usually done using surveys and experiments.
Qualitative research vs. Quantitative research
| Deals with subjective aspects, e.g., experiences, beliefs, perspectives, and concepts. | Measures different types of variables and describes frequencies, averages, correlations, etc. |
| Deals with non-numerical data, such as words, images, and observations. | Tests hypotheses about relationships between variables. Results are presented numerically and statistically. |
| In qualitative research design, data are collected via direct observations, interviews, focus groups, and naturally occurring data. Methods for conducting qualitative research are grounded theory, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis.
| Quantitative research design is empirical. Data collection methods involved are experiments, surveys, and observations expressed in numbers. The research design categories under this are descriptive, experimental, correlational, diagnostic, and explanatory. |
| Data analysis involves interpretation and narrative analysis. | Data analysis involves statistical analysis and hypothesis testing. |
| The reasoning used to synthesize data is inductive.
| The reasoning used to synthesize data is deductive.
|
| Typically used in fields such as sociology, linguistics, and anthropology. | Typically used in fields such as economics, ecology, statistics, and medicine. |
| Example: Focus group discussions with women farmers about climate change perception.
| Example: Testing the effectiveness of a new treatment for insomnia. |
Qualitative research design types and qualitative research design examples
The following will familiarize you with the research design categories in qualitative research:
- Grounded theory: This design is used to investigate research questions that have not previously been studied in depth. Also referred to as exploratory design , it creates sequential guidelines, offers strategies for inquiry, and makes data collection and analysis more efficient in qualitative research.
Example: A researcher wants to study how people adopt a certain app. The researcher collects data through interviews and then analyzes the data to look for patterns. These patterns are used to develop a theory about how people adopt that app.
- Thematic analysis: This design is used to compare the data collected in past research to find similar themes in qualitative research.
Example: A researcher examines an interview transcript to identify common themes, say, topics or patterns emerging repeatedly.
- Discourse analysis : This research design deals with language or social contexts used in data gathering in qualitative research.
Example: Identifying ideological frameworks and viewpoints of writers of a series of policies.
Quantitative research design types and quantitative research design examples
Note the following research design categories in quantitative research:
- Descriptive research design : This quantitative research design is applied where the aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, and categories. It may not often begin with a hypothesis. The basis of this research type is a description of an identified variable. This research design type describes the “what,” “when,” “where,” or “how” of phenomena (but not the “why”).
Example: A study on the different income levels of people who use nutritional supplements regularly.
- Correlational research design : Correlation reflects the strength and/or direction of the relationship among variables. The direction of a correlation can be positive or negative. Correlational research design helps researchers establish a relationship between two variables without the researcher controlling any of them.
Example : An example of correlational research design could be studying the correlation between time spent watching crime shows and aggressive behavior in teenagers.
- Diagnostic research design : In diagnostic design, the researcher aims to understand the underlying cause of a specific topic or phenomenon (usually an area of improvement) and find the most effective solution. In simpler terms, a researcher seeks an accurate “diagnosis” of a problem and identifies a solution.
Example : A researcher analyzing customer feedback and reviews to identify areas where an app can be improved.
- Explanatory research design : In explanatory research design , a researcher uses their ideas and thoughts on a topic to explore their theories in more depth. This design is used to explore a phenomenon when limited information is available. It can help increase current understanding of unexplored aspects of a subject. It is thus a kind of “starting point” for future research.
Example : Formulating hypotheses to guide future studies on delaying school start times for better mental health in teenagers.
- Causal research design : This can be considered a type of explanatory research. Causal research design seeks to define a cause and effect in its data. The researcher does not use a randomly chosen control group but naturally or pre-existing groupings. Importantly, the researcher does not manipulate the independent variable.
Example : Comparing school dropout levels and possible bullying events.
- Experimental research design : This research design is used to study causal relationships . One or more independent variables are manipulated, and their effect on one or more dependent variables is measured.
Example: Determining the efficacy of a new vaccine plan for influenza.
Benefits of research design
T here are numerous benefits of research design . These are as follows:
- Clear direction: Among the benefits of research design , the main one is providing direction to the research and guiding the choice of clear objectives, which help the researcher to focus on the specific research questions or hypotheses they want to investigate.
- Control: Through a proper research design , researchers can control variables, identify potential confounding factors, and use randomization to minimize bias and increase the reliability of their findings.
- Replication: Research designs provide the opportunity for replication. This helps to confirm the findings of a study and ensures that the results are not due to chance or other factors. Thus, a well-chosen research design also eliminates bias and errors.
- Validity: A research design ensures the validity of the research, i.e., whether the results truly reflect the phenomenon being investigated.
- Reliability: Benefits of research design also include reducing inaccuracies and ensuring the reliability of the research (i.e., consistency of the research results over time, across different samples, and under different conditions).
- Efficiency: A strong research design helps increase the efficiency of the research process. Researchers can use a variety of designs to investigate their research questions, choose the most appropriate research design for their study, and use statistical analysis to make the most of their data. By effectively describing the data necessary for an adequate test of the hypotheses and explaining how such data will be obtained, research design saves a researcher’s time.
Overall, an appropriately chosen and executed research design helps researchers to conduct high-quality research, draw meaningful conclusions, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Research Design
Q: What are th e main types of research design?
Broadly speaking there are two basic types of research design –
qualitative and quantitative research. Qualitative research is subjective and exploratory; it determines relationships between collected data and observations. It is usually carried out through interviews with open-ended questions, observations that are described in words, etc. Quantitative research , on the other hand, is more objective and employs statistical approaches. It establishes the cause-and-effect relationship among variables using different statistical and computational methods. This type of research design is usually done using surveys and experiments.
Q: How do I choose the appropriate research design for my study?
Choosing the appropriate research design for your study requires careful consideration of various factors. Start by clarifying your research objectives and the type of data you need to collect. Determine whether your study is exploratory, descriptive, or experimental in nature. Consider the availability of resources, time constraints, and the feasibility of implementing the different research designs. Review existing literature to identify similar studies and their research designs, which can serve as a guide. Ultimately, the chosen research design should align with your research questions, provide the necessary data to answer them, and be feasible given your own specific requirements/constraints.
Q: Can research design be modified during the course of a study?
Yes, research design can be modified during the course of a study based on emerging insights, practical constraints, or unforeseen circumstances. Research is an iterative process and, as new data is collected and analyzed, it may become necessary to adjust or refine the research design. However, any modifications should be made judiciously and with careful consideration of their impact on the study’s integrity and validity. It is advisable to document any changes made to the research design, along with a clear rationale for the modifications, in order to maintain transparency and allow for proper interpretation of the results.
Q: How can I ensure the validity and reliability of my research design?
Validity refers to the accuracy and meaningfulness of your study’s findings, while reliability relates to the consistency and stability of the measurements or observations. To enhance validity, carefully define your research variables, use established measurement scales or protocols, and collect data through appropriate methods. Consider conducting a pilot study to identify and address any potential issues before full implementation. To enhance reliability, use standardized procedures, conduct inter-rater or test-retest reliability checks, and employ appropriate statistical techniques for data analysis. It is also essential to document and report your methodology clearly, allowing for replication and scrutiny by other researchers.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Back to School – Lock-in All Access Pack for a Year at the Best Price

Journal Turnaround Time: Researcher.Life and Scholarly Intelligence Join Hands to Empower Researchers with Publication Time Insights
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Design
Definition:
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study. Research design is important because it guides the entire research process and ensures that the study is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner.
Types of Research Design
Types of Research Design are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
This type of research design is used to describe a phenomenon or situation. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations. The aim of descriptive research is to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a particular group, event, or situation. It can be useful in identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. This type of research design involves collecting data from participants and analyzing the relationship between the variables using statistical methods. The aim of correlational research is to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable. The aim of experimental research is to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. This type of research design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to conduct a true experiment.
Case Study Research Design
Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The aim of case study research is to provide an in-depth understanding of a particular case or situation.
Longitudinal Research Design
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
Structure of Research Design
The format of a research design typically includes the following sections:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem, the research questions, and the importance of the study. It also includes a brief literature review that summarizes previous research on the topic and identifies gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: This section identifies the specific research questions or hypotheses that the study will address. These questions should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Research Methods : This section describes the methods that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes details about the study design, the sampling strategy, the data collection instruments, and the data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This section describes how the data will be collected, including the sample size, data collection procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: This section describes how the data will be analyzed, including the statistical techniques that will be used to test the research questions or hypotheses.
- Results : This section presents the findings of the study, including descriptive statistics and statistical tests.
- Discussion and Conclusion : This section summarizes the key findings of the study, interprets the results, and discusses the implications of the findings. It also includes recommendations for future research.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research design.
Example of Research Design
An Example of Research Design could be:
Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school students?
Research design:
- Research approach : The research approach will be quantitative as it involves collecting numerical data to test the hypothesis.
- Research design : The research design will be a quasi-experimental design, with a pretest-posttest control group design.
- Sample : The sample will be 200 high school students from two schools, with 100 students in the experimental group and 100 students in the control group.
- Data collection : The data will be collected through surveys administered to the students at the beginning and end of the academic year. The surveys will include questions about their social media usage and academic performance.
- Data analysis : The data collected will be analyzed using statistical software. The mean scores of the experimental and control groups will be compared to determine whether there is a significant difference in academic performance between the two groups.
- Limitations : The limitations of the study will be acknowledged, including the fact that social media usage can vary greatly among individuals, and the study only focuses on two schools, which may not be representative of the entire population.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations will be taken into account, such as obtaining informed consent from the participants and ensuring their anonymity and confidentiality.
How to Write Research Design
Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a research question or hypothesis. Here are some steps to help you write a research design:
- Define the research question or hypothesis : Before beginning your research design, you should clearly define your research question or hypothesis. This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods.
- Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
- Develop a sampling plan : If your research involves collecting data from a sample, you will need to develop a sampling plan. This should outline how you will select participants and how many participants you will include.
- Define variables: Clearly define the variables you will be measuring or manipulating in your study. This will help ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Choose data collection methods : Decide on the data collection methods you will use to gather information. This may include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data sources.
- Create a data analysis plan: Develop a plan for analyzing your data, including the statistical or qualitative techniques you will use.
- Consider ethical concerns : Finally, be sure to consider any ethical concerns related to your research, such as participant confidentiality or potential harm.
When to Write Research Design
Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Ideally, the research design should be developed as early as possible in the research process, before any data is collected. This allows the researcher to carefully consider the research question, identify the most appropriate research methodology, and plan the data collection and analysis procedures in advance. By doing so, the research can be conducted in a more efficient and effective manner, and the results are more likely to be valid and reliable.
Purpose of Research Design
The purpose of research design is to plan and structure a research study in a way that enables the researcher to achieve the desired research goals with accuracy, validity, and reliability. Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis.
Some of the key purposes of research design include:
- Providing a clear and concise plan of action for the research study.
- Ensuring that the research is conducted ethically and with rigor.
- Maximizing the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
- Minimizing the possibility of errors, biases, or confounding variables.
- Ensuring that the research is feasible, practical, and cost-effective.
- Determining the appropriate research methodology to answer the research question(s).
- Identifying the sample size, sampling method, and data collection techniques.
- Determining the data analysis method and statistical tests to be used.
- Facilitating the replication of the study by other researchers.
- Enhancing the validity and generalizability of the research findings.
Applications of Research Design
There are numerous applications of research design in various fields, some of which are:
- Social sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, research design is used to investigate human behavior and social phenomena. Researchers use various research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and correlational designs, to study different aspects of social behavior.
- Education : Research design is essential in the field of education to investigate the effectiveness of different teaching methods and learning strategies. Researchers use various designs such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and case study designs to understand how students learn and how to improve teaching practices.
- Health sciences : In the health sciences, research design is used to investigate the causes, prevention, and treatment of diseases. Researchers use various designs, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to study different aspects of health and healthcare.
- Business : Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey research, experimental research, and case studies, to study different aspects of the business world.
- Engineering : In the field of engineering, research design is used to investigate the development and implementation of new technologies. Researchers use various designs, such as experimental research and case studies, to study the effectiveness of new technologies and to identify areas for improvement.
Advantages of Research Design
Here are some advantages of research design:
- Systematic and organized approach : A well-designed research plan ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner, which makes it easier to manage and analyze the data.
- Clear objectives: The research design helps to clarify the objectives of the study, which makes it easier to identify the variables that need to be measured, and the methods that need to be used to collect and analyze data.
- Minimizes bias: A well-designed research plan minimizes the chances of bias, by ensuring that the data is collected and analyzed objectively, and that the results are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or preferences.
- Efficient use of resources: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the resources (time, money, and personnel) are used efficiently and effectively, by focusing on the most important variables and methods.
- Replicability: A well-designed research plan makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study, which enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings.
- Validity: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings are valid, by ensuring that the methods used to collect and analyze data are appropriate for the research question.
- Generalizability : A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or situations, which increases the external validity of the study.
Research Design Vs Research Methodology
| Research Design | Research Methodology |
|---|---|
| The plan and structure for conducting research that outlines the procedures to be followed to collect and analyze data. | The set of principles, techniques, and tools used to carry out the research plan and achieve research objectives. |
| Describes the overall approach and strategy used to conduct research, including the type of data to be collected, the sources of data, and the methods for collecting and analyzing data. | Refers to the techniques and methods used to gather, analyze and interpret data, including sampling techniques, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. |
| Helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic, rigorous, and valid way, so that the results are reliable and can be used to make sound conclusions. | Includes a set of procedures and tools that enable researchers to collect and analyze data in a consistent and valid manner, regardless of the research design used. |
| Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, and descriptive studies. | Common research methodologies include qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods approaches. |
| Determines the overall structure of the research project and sets the stage for the selection of appropriate research methodologies. | Guides the researcher in selecting the most appropriate research methods based on the research question, research design, and other contextual factors. |
| Helps to ensure that the research project is feasible, relevant, and ethical. | Helps to ensure that the data collected is accurate, valid, and reliable, and that the research findings can be interpreted and generalized to the population of interest. |
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and...

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Business Research Design: Exploratory, Descriptive and Causal Designs
- First Online: 01 January 2013
Cite this chapter

- S. Sreejesh 4 ,
- Sanjay Mohapatra 5 &
- M. R. Anusree 6
24k Accesses
4 Citations
The objective of this chapter is to define and explain research design in detail. In this chapter, we discussed three major types of research designs, such as exploratory, descriptive and causal research designs. We also explained the mode of data used in each of these designs and the techniques to collect these data, which would ultimately helps the researcher to decide appropriate analysis technique. This chapter concludes with budgeting and scheduling of a business research project and elaborated the guidelines for writing a business research proposal. This chapter designed in such a way that the reader can appreciate these concepts by considering the examples and cartoon illustrations, which would better elicit and convince the concept understanding.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

The Use of Experiments in Business Research

Basic Research Methods

Design of the Empirical Study
By David Voreacos, Alex Nussbaum and Greg Farrel, Johnson and Johnson reaches a band-aid, Bloomberg Business week.
Due of lack of representativeness it is not possible to compare the results from different groups in a strict quantitative sense.
See Ref. Sudman ( 1980 ).
See Ref. Cook and Campbell ( 1979 ).
ASQ Statistics Division Newsletter (2000), vol 19(issue 2)
Google Scholar
Beri GC (1989) Marketing research, 1st edn. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Cook T, Campbell D (1979) Quasi experimentation: design and analysis issues for field settings. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston
Sudman S (1980) Improving the quality of shopping centre sampling. J Mark Res 17:423–431
Zikmund WG (2003) Business research methods, 7th edn. Thomson South-Western, Singapore, p 281
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
IBS Hyderabad, IFHE University, Hyderabad, 501504, India
S. Sreejesh
Xavier Institute of Management, Xavier Road, Bhubaneswar, Orissa, 751013, India
Sanjay Mohapatra
Department of Statistics, University of Kerala, Trivandrum, Kerala, 695581, India
M. R. Anusree
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to S. Sreejesh .
In an experimental design, the primary goal is to isolate and identify the effects produced by the…
Dependent variable
Extraneous variable
Independent variable
An experiment has high… if one has confidence that the experiential treatment has been the source of change in the dependent variable.
Internal validity
External validity
Internal and external validity
Internal and external reliability
Which of the following is a threat to internal validity of an experimental design
Interaction of setting and treatment
Interaction effects of pre-testing
Reactive effects of experimental design
Which of the following effect in internal validity occurs when test units with extreme scores move closer to the average score during the course of the experiment
Statistical Regression
Selection bias
Instrumentation
Which of the following statement is incorrect with respect to ‘An experimental design is a set of procedures specifying
How to test units (subjects) are divided into homogeneous sub samples
What independent variables or treatments are to be measured
What dependent variables are to be measured
How the extraneous variables are to be controlled
Randomization of test units is a part of…
A characteristic that distinguishes true experiments from weaker experimental designs is that true experiments include
Random assignment
Repeated measurements of the dependent variable
Random sampling
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Sreejesh, S., Mohapatra, S., Anusree, M.R. (2014). Business Research Design: Exploratory, Descriptive and Causal Designs. In: Business Research Methods. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00539-3_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00539-3_3
Published : 01 August 2013
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-00538-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-00539-3
eBook Packages : Business and Economics Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Research Design: What it is, Elements & Types

Can you imagine doing research without a plan? Probably not. When we discuss a strategy to collect, study, and evaluate data, we talk about research design. This design addresses problems and creates a consistent and logical model for data analysis. Let’s learn more about it.
What is Research Design?
Research design is the framework of research methods and techniques chosen by a researcher to conduct a study. The design allows researchers to sharpen the research methods suitable for the subject matter and set up their studies for success.
Creating a research topic explains the type of research (experimental, survey research , correlational , semi-experimental, review) and its sub-type (experimental design, research problem , descriptive case-study).
There are three main types of designs for research:
- Data collection
- Measurement
- Data Analysis
The research problem an organization faces will determine the design, not vice-versa. The design phase of a study determines which tools to use and how they are used.
The Process of Research Design
The research design process is a systematic and structured approach to conducting research. The process is essential to ensure that the study is valid, reliable, and produces meaningful results.
- Consider your aims and approaches: Determine the research questions and objectives, and identify the theoretical framework and methodology for the study.
- Choose a type of Research Design: Select the appropriate research design, such as experimental, correlational, survey, case study, or ethnographic, based on the research questions and objectives.
- Identify your population and sampling method: Determine the target population and sample size, and choose the sampling method, such as random , stratified random sampling , or convenience sampling.
- Choose your data collection methods: Decide on the data collection methods , such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments, and select the appropriate instruments or tools for collecting data.
- Plan your data collection procedures: Develop a plan for data collection, including the timeframe, location, and personnel involved, and ensure ethical considerations.
- Decide on your data analysis strategies: Select the appropriate data analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis , content analysis, or discourse analysis, and plan how to interpret the results.
The process of research design is a critical step in conducting research. By following the steps of research design, researchers can ensure that their study is well-planned, ethical, and rigorous.
Research Design Elements
Impactful research usually creates a minimum bias in data and increases trust in the accuracy of collected data. A design that produces the slightest margin of error in experimental research is generally considered the desired outcome. The essential elements are:
- Accurate purpose statement
- Techniques to be implemented for collecting and analyzing research
- The method applied for analyzing collected details
- Type of research methodology
- Probable objections to research
- Settings for the research study
- Measurement of analysis
Characteristics of Research Design
A proper design sets your study up for success. Successful research studies provide insights that are accurate and unbiased. You’ll need to create a survey that meets all of the main characteristics of a design. There are four key characteristics:

- Neutrality: When you set up your study, you may have to make assumptions about the data you expect to collect. The results projected in the research should be free from research bias and neutral. Understand opinions about the final evaluated scores and conclusions from multiple individuals and consider those who agree with the results.
- Reliability: With regularly conducted research, the researcher expects similar results every time. You’ll only be able to reach the desired results if your design is reliable. Your plan should indicate how to form research questions to ensure the standard of results.
- Validity: There are multiple measuring tools available. However, the only correct measuring tools are those which help a researcher in gauging results according to the objective of the research. The questionnaire developed from this design will then be valid.
- Generalization: The outcome of your design should apply to a population and not just a restricted sample . A generalized method implies that your survey can be conducted on any part of a population with similar accuracy.
The above factors affect how respondents answer the research questions, so they should balance all the above characteristics in a good design. If you want, you can also learn about Selection Bias through our blog.
Research Design Types
A researcher must clearly understand the various types to select which model to implement for a study. Like the research itself, the design of your analysis can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative.
Qualitative research
Qualitative research determines relationships between collected data and observations based on mathematical calculations. Statistical methods can prove or disprove theories related to a naturally existing phenomenon. Researchers rely on qualitative observation research methods that conclude “why” a particular theory exists and “what” respondents have to say about it.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is for cases where statistical conclusions to collect actionable insights are essential. Numbers provide a better perspective for making critical business decisions. Quantitative research methods are necessary for the growth of any organization. Insights drawn from complex numerical data and analysis prove to be highly effective when making decisions about the business’s future.
Qualitative Research vs Quantitative Research
Here is a chart that highlights the major differences between qualitative and quantitative research:
| Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|
| Focus on explaining and understanding experiences and perspectives. | Focus on quantifying and measuring phenomena. |
| Use of non-numerical data, such as words, images, and observations. | Use of numerical data, such as statistics and surveys. |
| Usually uses small sample sizes. | Usually uses larger sample sizes. |
| Typically emphasizes in-depth exploration and interpretation. | Typically emphasizes precision and objectivity. |
| Data analysis involves interpretation and narrative analysis. | Data analysis involves statistical analysis and hypothesis testing. |
| Results are presented descriptively. | Results are presented numerically and statistically. |
In summary or analysis , the step of qualitative research is more exploratory and focuses on understanding the subjective experiences of individuals, while quantitative research is more focused on objective data and statistical analysis.
You can further break down the types of research design into five categories:
1. Descriptive: In a descriptive composition, a researcher is solely interested in describing the situation or case under their research study. It is a theory-based design method created by gathering, analyzing, and presenting collected data. This allows a researcher to provide insights into the why and how of research. Descriptive design helps others better understand the need for the research. If the problem statement is not clear, you can conduct exploratory research.
2. Experimental: Experimental research establishes a relationship between the cause and effect of a situation. It is a causal research design where one observes the impact caused by the independent variable on the dependent variable. For example, one monitors the influence of an independent variable such as a price on a dependent variable such as customer satisfaction or brand loyalty. It is an efficient research method as it contributes to solving a problem.
The independent variables are manipulated to monitor the change it has on the dependent variable. Social sciences often use it to observe human behavior by analyzing two groups. Researchers can have participants change their actions and study how the people around them react to understand social psychology better.
3. Correlational research: Correlational research is a non-experimental research technique. It helps researchers establish a relationship between two closely connected variables. There is no assumption while evaluating a relationship between two other variables, and statistical analysis techniques calculate the relationship between them. This type of research requires two different groups.
A correlation coefficient determines the correlation between two variables whose values range between -1 and +1. If the correlation coefficient is towards +1, it indicates a positive relationship between the variables, and -1 means a negative relationship between the two variables.
4. Diagnostic research: In diagnostic design, the researcher is looking to evaluate the underlying cause of a specific topic or phenomenon. This method helps one learn more about the factors that create troublesome situations.
This design has three parts of the research:
- Inception of the issue
- Diagnosis of the issue
- Solution for the issue
5. Explanatory research : Explanatory design uses a researcher’s ideas and thoughts on a subject to further explore their theories. The study explains unexplored aspects of a subject and details the research questions’ what, how, and why.
Benefits of Research Design
There are several benefits of having a well-designed research plan. Including:
- Clarity of research objectives: Research design provides a clear understanding of the research objectives and the desired outcomes.
- Increased validity and reliability: To ensure the validity and reliability of results, research design help to minimize the risk of bias and helps to control extraneous variables.
- Improved data collection: Research design helps to ensure that the proper data is collected and data is collected systematically and consistently.
- Better data analysis: Research design helps ensure that the collected data can be analyzed effectively, providing meaningful insights and conclusions.
- Improved communication: A well-designed research helps ensure the results are clean and influential within the research team and external stakeholders.
- Efficient use of resources: reducing the risk of waste and maximizing the impact of the research, research design helps to ensure that resources are used efficiently.
A well-designed research plan is essential for successful research, providing clear and meaningful insights and ensuring that resources are practical.
QuestionPro offers a comprehensive solution for researchers looking to conduct research. With its user-friendly interface, robust data collection and analysis tools, and the ability to integrate results from multiple sources, QuestionPro provides a versatile platform for designing and executing research projects.
Our robust suite of research tools provides you with all you need to derive research results. Our online survey platform includes custom point-and-click logic and advanced question types. Uncover the insights that matter the most.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS
Interactive Forms: Key Features, Benefits, Uses + Design Tips
Sep 4, 2024

Closed-Loop Management: The Key to Customer Centricity
Sep 3, 2024

Net Trust Score: Tool for Measuring Trust in Organization
Sep 2, 2024

Why You Should Attend XDAY 2024
Aug 30, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Business Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Business research: definition, types & methods.
10 min read What is business research and why does it matter? Here are some of the ways business research can be helpful to your company, whichever method you choose to carry it out.
What is business research?
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad – it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market. It could focus on customer experience and assess customer satisfaction levels. Or it could involve sizing up the competition through competitor research.
Often when carrying out business research, companies are looking at their own data, sourced from their employees, their customers and their business records. However, business researchers can go beyond their own company in order to collect relevant information and understand patterns that may help leaders make informed decisions. For example, a business may carry out ethnographic research where the participants are studied in the context of their everyday lives, rather than just in their role as consumer, or look at secondary data sources such as open access public records and empirical research carried out in academic studies.
There is also a body of knowledge about business in general that can be mined for business research purposes. For example organizational theory and general studies on consumer behavior.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
Why is business research important?
We live in a time of high speed technological progress and hyper-connectedness. Customers have an entire market at their fingertips and can easily switch brands if a competitor is offering something better than you are. At the same time, the world of business has evolved to the point of near-saturation. It’s hard to think of a need that hasn’t been addressed by someone’s innovative product or service.
The combination of ease of switching, high consumer awareness and a super-evolved marketplace crowded with companies and their offerings means that businesses must do whatever they can to find and maintain an edge. Business research is one of the most useful weapons in the fight against business obscurity, since it allows companies to gain a deep understanding of buyer behavior and stay up to date at all times with detailed information on their market.
Thanks to the standard of modern business research tools and methods, it’s now possible for business analysts to track the intricate relationships between competitors, financial markets, social trends, geopolitical changes, world events, and more.
Find out how to conduct your own market research and make use of existing market research data with our Ultimate guide to market research
Types of business research
Business research methods vary widely, but they can be grouped into two broad categories – qualitative research and quantitative research .
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative business research deals with non-numerical data such as people’s thoughts, feelings and opinions. It relies heavily on the observations of researchers, who collect data from a relatively small number of participants – often through direct interactions.
Qualitative research interviews take place one-on-one between a researcher and participant. In a business context, the participant might be a customer, a supplier, an employee or other stakeholder. Using open-ended questions , the researcher conducts the interview in either a structured or unstructured format. Structured interviews stick closely to a question list and scripted phrases, while unstructured interviews are more conversational and exploratory. As well as listening to the participant’s responses, the interviewer will observe non-verbal information such as posture, tone of voice and facial expression.
Focus groups
Like the qualitative interview, a focus group is a form of business research that uses direct interaction between the researcher and participants to collect data. In focus groups , a small number of participants (usually around 10) take part in a group discussion led by a researcher who acts as moderator. The researcher asks questions and takes note of the responses, as in a qualitative research interview. Sampling for focus groups is usually purposive rather than random, so that the group members represent varied points of view.
Observational studies
In an observational study, the researcher may not directly interact with participants at all, but will pay attention to practical situations, such as a busy sales floor full of potential customers, or a conference for some relevant business activity. They will hear people speak and watch their interactions , then record relevant data such as behavior patterns that relate to the subject they are interested in. Observational studies can be classified as a type of ethnographic research. They can be used to gain insight about a company’s target audience in their everyday lives, or study employee behaviors in actual business situations.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is an immersive design of research where one observes peoples’ behavior in their natural environment. Ethnography was most commonly found in the anthropology field and is now practices across a wide range of social sciences.
Ehnography is used to support a designer’s deeper understanding of the design problem – including the relevant domain, audience(s), processes, goals and context(s) of use.
The ethnographic research process is a popular methodology used in the software development lifecycle. It helps create better UI/UX flow based on the real needs of the end-users.
If you truly want to understand your customers’ needs, wants, desires, pain-points “walking a mile” in their shoes enables this. Ethnographic research is this deeply rooted part of research where you truly learn your targe audiences’ problem to craft the perfect solution.
Case study research
A case study is a detailed piece of research that provides in depth knowledge about a specific person, place or organization. In the context of business research, case study research might focus on organizational dynamics or company culture in an actual business setting, and case studies have been used to develop new theories about how businesses operate. Proponents of case study research feel that it adds significant value in making theoretical and empirical advances. However its detractors point out that it can be time consuming and expensive, requiring highly skilled researchers to carry it out.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research focuses on countable data that is objective in nature. It relies on finding the patterns and relationships that emerge from mass data – for example by analyzing the material posted on social media platforms, or via surveys of the target audience. Data collected through quantitative methods is empirical in nature and can be analyzed using statistical techniques. Unlike qualitative approaches, a quantitative research method is usually reliant on finding the right sample size, as this will determine whether the results are representative. These are just a few methods – there are many more.
Surveys are one of the most effective ways to conduct business research. They use a highly structured questionnaire which is distributed to participants, typically online (although in the past, face to face and telephone surveys were widely used). The questions are predominantly closed-ended, limiting the range of responses so that they can be grouped and analyzed at scale using statistical tools. However surveys can also be used to get a better understanding of the pain points customers face by providing open field responses where they can express themselves in their own words. Both types of data can be captured on the same questionnaire, which offers efficiency of time and cost to the researcher.
Correlational research
Correlational research looks at the relationship between two entities, neither of which are manipulated by the researcher. For example, this might be the in-store sales of a certain product line and the proportion of female customers subscribed to a mailing list. Using statistical analysis methods, researchers can determine the strength of the correlation and even discover intricate relationships between the two variables. Compared with simple observation and intuition, correlation may identify further information about business activity and its impact, pointing the way towards potential improvements and more revenue.
Experimental research
It may sound like something that is strictly for scientists, but experimental research is used by both businesses and scholars alike. When conducted as part of the business intelligence process, experimental research is used to test different tactics to see which ones are most successful – for example one marketing approach versus another. In the simplest form of experimental research, the researcher identifies a dependent variable and an independent variable. The hypothesis is that the independent variable has no effect on the dependent variable, and the researcher will change the independent one to test this assumption. In a business context, the hypothesis might be that price has no relationship to customer satisfaction. The researcher manipulates the price and observes the C-Sat scores to see if there’s an effect.
The best tools for business research
You can make the business research process much quicker and more efficient by selecting the right tools. Business research methods like surveys and interviews demand tools and technologies that can store vast quantities of data while making them easy to access and navigate. If your system can also carry out statistical analysis, and provide predictive recommendations to help you with your business decisions, so much the better.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design , you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.
There are many ways to categorize different types of research. The words you use to describe your research depend on your discipline and field. In general, though, the form your research design takes will be shaped by:
- The type of knowledge you aim to produce
- The type of data you will collect and analyze
- The sampling methods , timescale and location of the research
This article takes a look at some common distinctions made between different types of research and outlines the key differences between them.
Table of contents
Types of research aims, types of research data, types of sampling, timescale, and location, other interesting articles.
The first thing to consider is what kind of knowledge your research aims to contribute.
| Type of research | What’s the difference? | What to consider |
|---|---|---|
| Basic vs. applied | Basic research aims to , while applied research aims to . | Do you want to expand scientific understanding or solve a practical problem? |
| vs. | Exploratory research aims to , while explanatory research aims to . | How much is already known about your research problem? Are you conducting initial research on a newly-identified issue, or seeking precise conclusions about an established issue? |
| aims to , while aims to . | Is there already some theory on your research problem that you can use to develop , or do you want to propose new theories based on your findings? |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The next thing to consider is what type of data you will collect. Each kind of data is associated with a range of specific research methods and procedures.
| Type of research | What’s the difference? | What to consider |
|---|---|---|
| Primary research vs secondary research | Primary data is (e.g., through or ), while secondary data (e.g., in government or scientific publications). | How much data is already available on your topic? Do you want to collect original data or analyze existing data (e.g., through a )? |
| , while . | Is your research more concerned with measuring something or interpreting something? You can also create a research design that has elements of both. | |
| vs | Descriptive research gathers data , while experimental research . | Do you want to identify characteristics, patterns and or test causal relationships between ? |
Finally, you have to consider three closely related questions: how will you select the subjects or participants of the research? When and how often will you collect data from your subjects? And where will the research take place?
Keep in mind that the methods that you choose bring with them different risk factors and types of research bias . Biases aren’t completely avoidable, but can heavily impact the validity and reliability of your findings if left unchecked.
| Type of research | What’s the difference? | What to consider |
|---|---|---|
| allows you to , while allows you to draw conclusions . | Do you want to produce knowledge that applies to many contexts or detailed knowledge about a specific context (e.g. in a )? | |
| vs | Cross-sectional studies , while longitudinal studies . | Is your research question focused on understanding the current situation or tracking changes over time? |
| Field research vs laboratory research | Field research takes place in , while laboratory research takes place in . | Do you want to find out how something occurs in the real world or draw firm conclusions about cause and effect? Laboratory experiments have higher but lower . |
| Fixed design vs flexible design | In a fixed research design the subjects, timescale and location are begins, while in a flexible design these aspects may . | Do you want to test hypotheses and establish generalizable facts, or explore concepts and develop understanding? For measuring, testing and making generalizations, a fixed research design has higher . |
Choosing between all these different research types is part of the process of creating your research design , which determines exactly how your research will be conducted. But the type of research is only the first step: next, you have to make more concrete decisions about your research methods and the details of the study.
Read more about creating a research design
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/types-of-research/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

What is Research Design? Features, Components
- Post last modified: 13 August 2023
- Reading time: 15 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

What is Research Design?
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan that a researcher outlines to conduct a study and gather relevant data to address a research question or test a hypothesis. It serves as a blueprint for the entire research process, providing a structure and guidance for the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
In the field of research, the major purpose of research is to find a solution for a given research problem. The researcher can find a solution to a research problem by ensuring that he/she uses an appropriate research design.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Research Design?
- 2 Concept of Research Design
- 3 Need and Features of Research Design
- 4.1 Neutrality
- 4.2 Reliability
- 4.3 Performance
- 4.4 General practice
- 4.5 Qualitative
- 4.6 Quantitative
- 5.1 Research questions
- 5.2 Course suggestions
- 5.3 Unit analysis
- 5.4 Data linking and propositions
- 5.5 Interpretation of findings from the study
The chances of success of a research project depend on how the researcher has taken care to develop a research design that is in line with the research problem. A research design is created or developed when the researcher prepares a plan, structure and strategy for conducting research.
Research design is the base over which a researcher builds his research. A good research design provides vital information to a researcher with respect to a research topic, data type, data sources and techniques of data collection used in the research. In this chapter, you will study about the concept of research design, its need, features, components, etc.
Next, the chapter will describe the types of research design, research design framework, and types of errors affecting research design. Towards the end, you will study about the meaning of experiments and types of experiments.
Concept of Research Design
The research design refers to the framework of research methods and techniques selected by a researcher. The design chosen by the researchers allows them to use appropriate methods to study and plan their studies effectively and in the future. The descriptive research method focuses primarily on defining the nature of a class of people, without focusing on the “why” of something happening.
In other words, it “explains” the topic of research, without covering why “it” happens. Let us study in detail about the concept of research design, its requirements, features or characteristics, designing research framework its related case studies and observations.
Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies, casual research and errors arising while designing the research which are related to improper selection of respondents. This is a framework for determining the research methods and techniques to be used. This design enables researchers to set the research methods that are most relevant to the subject.
The design of the research topic describes the type of research (testing, research, integration, experimentation, review) and its sub-type (test design, research problem, descriptive case study). Research design can also be considered as the blueprint for collection, measurement and analysis of data.
The type of research problem the organisation is facing will determine the structure of the research and not the other way around. The study design phase determines which tools to use and how to use them. Impact studies often create less bias in the data and increase confidence in the accuracy of the data collected. A design that produces a small error limit in test studies is usually considered to be the desired result.
In research, the important things are:
- A specific statement of intent
- Strategies used to collect and analyse data
- Type of research methodology
- Potential objections to research
- Research study settings
- Analysis rating
Need and Features of Research Design
Much of what we do in our daily lives is based on understanding, what we have learned from others, or what we have learned through personal experience or observation. Sometimes, there are conflicting ideas about what is good or what works in a particular situation.
In addition, what works in one situation or situation may be ineffective or even harmful in another, or it may be combined with other measures. Psychological techniques ignore the impact of external factors that can influence what is seen. Even in health care settings, there are gaps in knowledge, ideas about how something can work better and ideas for improvement.
Since health professionals cannot afford to be risky, research is needed. For clinical trials, this is also a legal requirement that pharmaceutical companies cannot obtain marketing authorisation (i.e., permission to sell their new drugs) until they are approved by the relevant authorities.
Another advantage of doing research is that in most studies, the findings can be statistically recorded and statistically evaluated to determine if the findings are significant (meaning how much they can be called with a certain degree of certainty that they are not just a risk factor).
With limited studies, results can usually be performed in a broader population (for example, in people with dementia, caregivers, GPs, or generalised individuals, depending on the study group). This is because steps would be taken to ensure that the group of participants in the study, represented other people in that category, as far as possible.
The advantage of many quality studies is that they allow for a thorough investigation of a particular aspect of the human experience. They give people the opportunity to express in their own words how they feel, what they think, and how they make sense of the world around them.
In some cases, the results may be passed on to others as conditions. However, the advantage of quality studies is that it provides rich, logical and insightful information on the complexity of human experience with all the contradictions, differences and idiosyncrasies. Others discuss topics that have not been researched before and maybe facing issues that are controversial, critical, or illegal.Some courses also work to give voice to vulnerable or small groups
Features of Research Design
Proper research design makes your study a success. Effective research provides accurate and impartial information. You will need to create a survey that meets all the key design features. Key features of a good research design are:
When planning your study, you may need to think about the details you are going to collect. The results shown in the study should be fair and impartial. Understand the ideas about the last scores tested and the conclusions from most people and consider those who agree with the results obtained.
Reliability
With regular research, the researcher involved expects the same results regularly. Research design should be developed in a way that good research questions are developed and quality results are ensured. You will only be able to access the expected results if your design is reliable.
Performance
There are many measuring tools available. However, the only valid measurement tools are those that assist the researcher in measuring results according to the research purpose. The list of questions created from this project will be valid.
General practice
The effect of your design should apply to people and not just to the restricted sample. A comprehensive design means that your survey can be done on any part of the people with the same accuracy. The above factors affect the way respondents respond to research questions and therefore all of the above factors should be balanced in good design. The researcher must have a clear understanding of the different types of study design in order to choose which model to use in the study.
Qualitative
Quality research helps in understanding the problem and to develop hypothesis. Researchers rely on high-quality research methods that conclude “why” a certain idea exists and what “responders” say.
Quantitative
A quantitative study is one of the situations in which statistical conclusions are arrived at on the basis of collected data. Numbers provide a better idea of how to make critical business decisions. Research is needed for the growth of any organisation. The information taken from the data and the analysis of the hard data is very effective in making decisions related to the future of the business.
Components of Research Design
The main purpose behind the design of the study is to help avoid a situation where the evidence does not address the main research questions. The research design is about a logical problem and not a planning problem.
The five main components of a research design are:
Research questions
Course suggestions.
- Units of analysis
- Linking data to propositions
- Interpretation of the findings of the study
The components of research design apply to all types of standardised, extra-terrestrial research, whether physical or social sciences.
This first item raises the type of question – about “who,” “what,” “where,” “how,” and “why” – provides important clues as to the proper research methodology used. Use three paragraphs: First, use the books to reduce your interest in one or two topics. In 2nd paragraph, take a closer look — or cut — a few key lessons from your favorite topic. Find questions in those few studies and conclude with new questions for future research. In the 3rd paragraph, check out another science group on the same topic. They may offer support for your potential questions or suggest ways to sharpen it.
Each suggestion directs the focus to something needed to be tested within the study. Only if you are forced to give some suggestions will you go the right way. For example, you would think that businesses are cooperating as they receive the same benefits. This suggestion, in addition to highlighting an important theoretical issue (that some corporate incentives do not exist or do not matter), also begins to tell you where to look for related evidence (defining and determining the magnitude of specific benefits in each business).
Unit analysis
It is associated with the basic problem of defining what “case” is – a problem that has affected many researchers at the beginning of the study. Take the example of medical patients. In this case, the person is being studied, and that person is an important unit of analysis.
Information about the right person will be collected, and few such people can be part of a multidisciplinary investigation. You will need study questions and suggestions to help you find the right information to collect about this person or people. Without such questions and suggestions, you may be tempted to cover “everything” about the person (s), which is not possible.
Data linking and propositions
Data linking methods and propositions such as pattern, definition structure, time series analysis, logic models and cross-case synthesis. The actual analysis will require you to compile or calculate your study data as a direct indication of your initial study suggestions.
Interpretation of findings from the study
Statistical analysis determines whether the research results support the hypothesis. Several statistical tests, for example, T-tests (determining whether two groups are statistically different from each other), Chi-square tests (where data is compared with the expected result), and oneway analysis of variance (provides multiple group comparisons), are performed by data type, number, and types of variables and data categories.
Statistical analysis provides some clear ways to translate. For example, according to the agreement, social science looks at a level below -55 to show that perceived differences are “statistically significant.” On the other hand, the analysis of many cases will not depend on the use of statistics and therefore focuses on alternative approaches to these approaches.
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
- What is Hypothesis?
- Sampling Method
- Research Methods
Data Collection in Research
Methods of collecting data.
- Application of Business Research
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
- Hypothesis Testing
Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
What is literature review importance, functions, process,, data analysis in research, what is hypothesis testing procedure, what is descriptive research types, features, steps in questionnaire design, what is measure of central tendency, what is scaling techniques types, classifications, techniques, what is research problem components, identifying, formulating,, what is hypothesis definition, meaning, characteristics, sources, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal Growth

Development
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Crit Care Med
- v.23(Suppl 4); 2019 Dec
Understanding Research Study Designs
Priya ranganathan.
Department of Anesthesiology, Critical Care and Pain, Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
In this article, we will look at the important features of various types of research study designs used commonly in biomedical research.
How to cite this article
Ranganathan P. Understanding Research Study Designs. Indian J Crit Care Med 2019;23(Suppl 4):S305–S307.
We use a variety of research study designs in biomedical research. In this article, the main features of each of these designs are summarized.
TERMS USED IN RESEARCH DESIGNS
Exposure vs outcome.
Exposure refers to any factor that may be associated with the outcome of interest. It is also called the predictor variable or independent variable or risk factor. Outcome refers to the variable that is studied to assess the impact of the exposure on the population. It is also known as the predicted variable or the dependent variable. For example, in a study looking at nerve damage after organophosphate (OPC) poisoning, the exposure would be OPC and the outcome would be nerve damage.
Longitudinal vs Transversal Studies
In longitudinal studies, participants are followed over time to determine the association between exposure and outcome (or outcome and exposure). On the other hand, in transversal studies, observations about exposure and outcome are made at a single point in time.
Forward vs Backward Directed Studies
In forward-directed studies, the direction of enquiry moves from exposure to outcome. In backward-directed studies, the line of enquiry starts with outcome and then determines exposure.
Prospective vs Retrospective Studies
In prospective studies, the outcome has not occurred at the time of initiation of the study. The researcher determines exposure and follows participants into the future to assess outcomes. In retrospective studies, the outcome of interest has already occurred when the study commences.
CLASSIFICATION OF STUDY DESIGNS
Broadly, study designs can be classified as descriptive or analytical (inferential) studies.
Descriptive Studies
Descriptive studies describe the characteristics of interest in the study population (also referred to as sample, to differentiate it from the entire population in the universe). These studies do not have a comparison group. The simplest type of descriptive study is the case report. In a case report, the researcher describes his/her experience with symptoms, signs, diagnosis, or treatment of a patient. Sometimes, a group of patients having a similar experience may be grouped to form a case series.
Case reports and case series form the lowest level of evidence in biomedical research and, as such, are considered hypothesis-generating studies. However, they are easy to write and may be a good starting point for the budding researcher. The recognition of some important associations in the field of medicine—such as that of thalidomide with phocomelia and Kaposi's sarcoma with HIV infection—resulted from case reports and case series. The reader can look up several published case reports and case series related to complications after OPC poisoning. 1 , 2
Analytical (Inferential) Studies
Analytical or inferential studies try to prove a hypothesis and establish an association between an exposure and an outcome. These studies usually have a comparator group. Analytical studies are further classified as observational or interventional studies.
In observational studies, there is no intervention by the researcher. The researcher merely observes outcomes in different groups of participants who, for natural reasons, have or have not been exposed to a particular risk factor. Examples of observational studies include cross-sectional, case–control, and cohort studies.
Cross-sectional Studies
These are transversal studies where data are collected from the study population at a single point in time. Exposure and outcome are determined simultaneously. Cross-sectional studies are easy to conduct, involve no follow-up, and need limited resources. They offer useful information on prevalence of health conditions and possible associations between risk factors and outcomes. However, there are two major limitations of cross-sectional studies. First, it may not be possible to establish a clear cause–benefit relationship. For example, in a study of association between colon cancer and dietary fiber intake, it may be difficult to establish whether the low fiber intake preceded the symptoms of colon cancer or whether the symptoms of colon cancer resulted in a change in dietary fiber intake. Another important limitation of cross-sectional studies is survival bias. For example, in a study looking at alcohol intake vs mortality due to chronic liver disease, among the participants with the highest alcohol intake, several may have died of liver disease; this will not be picked up by the study and will give biased results. An example of a cross-sectional study is a survey on nurses’ knowledge and practices of initial management of acute poisoning. 3
Case–control Studies
Case–control studies are backward-directed studies. Here, the direction of enquiry begins with the outcome and then proceeds to exposure. Case–control studies are always retrospective, i.e., the outcome of interest has occurred when the study begins. The researcher identifies participants who have developed the outcome of interest (cases) and chooses matching participants who do not have the outcome (controls). Matching is done based on factors that are likely to influence the exposure or outcome (e.g., age, gender, socioeconomic status). The researcher then proceeds to determine exposure in cases and controls. If cases have a higher incidence of exposure than controls, it suggests an association between exposure and outcome. Case–control studies are relatively quick to conduct, need limited resources, and are useful when the outcome is rare. They also allow the researcher to study multiple exposures for a particular outcome. However, they have several limitations. First, matching of cases with controls may not be easy since many unknown confounders may affect exposure and outcome. Second, there may be biased in the way the history of exposure is determined in cases vs controls; one way to overcome this is to have a blinded assessor determining the exposure using a standard technique (e.g., a standardized questionnaire). However, despite this, it has been shown that cases are far more likely than controls to recall history of exposure—the “recall bias.” For example, mothers of babies born with congenital anomalies may provide a more detailed history of drugs ingested during their pregnancy than those with normal babies. Also, since case-control studies do not begin with a population at risk, it is not possible to determine the true risk of outcome. Instead, one can only calculate the odds of association between exposure and outcome.
Kendrick and colleagues designed a case–control study to look at the association between domestic poison prevention practices and medically attended poisoning in children. They identified children presenting with unintentional poisoning at home (cases with the outcome), matched them with community participants (controls without the outcome), and then elicited data from parents and caregivers on home safety practices (exposure). 4
Cohort Studies
Cohort studies resemble clinical trials except that the exposure is naturally determined instead of being decided by the investigator. Here, the direction of enquiry begins with the exposure and then proceeds to outcome. The researcher begins with a group of individuals who are free of outcome at baseline; of these, some have the exposure (study cohort) while others do not (control group). The groups are followed up over a period of time to determine occurrence of outcome. Cohort studies may be prospective (involving a period of follow-up after the start of the study) or retrospective (e.g., using medical records or registry data). Cohort studies are considered the strongest among the observational study designs. They provide proof of temporal relationship (exposure occurred before outcome), allow determination of risk, and permit multiple outcomes to be studied for a single exposure. However, they are expensive to conduct and time-consuming, there may be several losses to follow-up, and they are not suitable for studying rare outcomes. Also, there may be unknown confounders other than the exposure affecting the occurrence of the outcome.
Jayasinghe conducted a cohort study to look at the effect of acute organophosphorus poisoning on nerve function. They recruited 70 patients with OPC poisoning (exposed group) and 70 matched controls without history of pesticide exposure (unexposed controls). Participants were followed up or 6 weeks for neurophysiological assessments to determine nerve damage (outcome). Hung carried out a retrospective cohort study using a nationwide research database to look at the long-term effects of OPC poisoning on cardiovascular disease. From the database, he identified an OPC-exposed cohort and an unexposed control cohort (matched for gender and age) from several years back and then examined later records to look at the development of cardiovascular diseases in both groups. 5
Interventional Studies
In interventional studies (also known as experimental studies or clinical trials), the researcher deliberately allots participants to receive one of several interventions; of these, some may be experimental while others may be controls (either standard of care or placebo). Allotment of participants to a particular treatment arm is carried out through the process of randomization, which ensures that every participant has a similar chance of being in any of the arms, eliminating bias in selection. There are several other aspects crucial to the validity of the results of a clinical trial such as allocation concealment, blinding, choice of control, and statistical analysis plan. These will be discussed in a separate article.
The randomized controlled clinical trial is considered the gold standard for evaluating the efficacy of a treatment. Randomization leads to equal distribution of known and unknown confounders between treatment arms; therefore, we can be reasonably certain that any difference in outcome is a treatment effect and not due to other factors. The temporal sequence of cause and effect is established. It is possible to determine risk of the outcome in each treatment arm accurately. However, randomized controlled trials have their limitations and may not be possible in every situation. For example, it is unethical to randomize participants to an intervention that is likely to cause harm—e.g., smoking. In such cases, well-designed observational studies are the only option. Also, these trials are expensive to conduct and resource-intensive.
In a randomized controlled trial, Li et al. randomly allocated patients of paraquat poisoning to receive either conventional therapy (control group) or continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (intervention). Patients were followed up to look for mortality or other adverse events (outcome). 6
Researchers need to understand the features of different study designs, with their advantages and limitations so that the most appropriate design can be chosen for a particular research question. The Centre for Evidence Based Medicine offers an useful tool to determine the type of research design used in a particular study. 7
Source of support: Nil
Conflict of interest: None
Research: When Bonuses Backfire
by Dirk Sliwka and Timo Vogelsang

Summary .
Why do bonuses sometimes backfire? It’s because each incentive design choice both signals information about your own beliefs and intentions as an employer and shapes the signaling value of employee behavior within the organization. If you don’t think through these signals carefully, you may end up approving a bonus scheme with results that are the opposite of what you intend. This article offers a way to help you align the signals your incentive scheme sends with your performance goals.
More than 30 years ago, author and lecturer Alfie Kohn, in a rather controversial but often cited HBR article , claimed that “rewards typically undermine the very processes they are intended to enhance.” Yet until recently, nearly all scientific studies that have documented such “backfiring” effects have been confined to laboratory experiments or field settings outside of the firm. This may cause some to question whether these effects are really present in commercial contexts. Our new research, which consists of two large field experiments in retail organizations, demonstrates that they do indeed occur.
Partner Center

- How it works
- Video tutorials
Watch video tutorials

Online Usability Testing
Understand user behavior on your website.
Mobile & Tablet UX Testing
Test usability on mobile devices and tablets.
Moderated Testing
Conduct live, guided user testing sessions.
Information Architecture Testing
Design or refine your information architecture.
Unmoderated Testing
Allow users to test without assistance.
True Intent Studies
Understand visitors’ goals and satisfaction.
A/B Testing
Determine which design performs better.
UX Benchmarking
Analyze your website against competitors.
Prototype Testing
Optimize design before development.
Search Engine Findability
Measure ease of finding your online properties.
Explore all Loop11 features →
Reporting Features
AI Insights
Gain deeper insights using the power of AI.
Clickstream Analytics
Track users’ clicks and navigation patterns.
Heatmap Analysis
Visualize user engagement and interaction.
User Session Recording & Replay
Capture user interactions for usability analysis.
Get access to all Loop11 features for free. Start free trial

- Clients & Testimonials
Written by Syed Balkhi
3 September, 2024

Do you ever wonder how websites and apps seem to know exactly what you want? The truth is, this is in large part due to AI in UX design.
There’s no question that AI has fundamentally changed how companies across all industries operate. According to Forbes, the AI industry is expected to hit $407 billion by 2027! For more context, research shows that around 73% of online businesses in the U.S. are already using AI in some way.
And it’s no wonder why. AI saves marketers about 2.5 hours a day – that’s 25 whole days a year!
But if you want to get the most from AI, you need to start thinking about how you can use it in UX research. With the right knowledge and resources, you can continuously streamline your design process, which will ultimately lead to more engagement, clicks, and, most importantly, sales.
Today, we are going to show you how AI is improving UX research and design and how you can use it to your advantage.
Let’s get started!
How AI Enhances UX Research and the Design Process
Let’s start by exploring a few key benefits of adding AI to your existing design process.
- Speed Things Up – AI tools can crunch data faster than any human. With the right tool, you can quickly and accurately gather actionable data about your target audience and campaigns.
- Make Smarter Choices – Instead of guessing or “going with your gut,” you can use hard data to make decisions that line up with your visitors’ needs, goals, and pain points.
- Get Personal – People love it when things feel made just for them. In fact, 80% of people prefer to engage with brands that personalize content and offers. Since you now know what your visitors like, it’s easy to understand how AI can help you build rapport and get to know your audience.
- Include Everyone – AI can spot accessibility issues that humans might miss. Automated accessibility checks ensure that designs are inclusive, which will broaden your audience and improve user experiences for all.
- Save Money – By reducing the need for extensive manual testing and analysis, AI helps businesses optimize their UX research budget and allocate resources more effectively.
7 Practical AI Applications in User Testing and Research
Now that you know a little more about the benefits, let’s talk about some of the specific, practical applications for AI in both user testing and research.
1. AI-Driven User Testing and Analytics
Automated user behavior analysis makes it easier to see how your audience interacts with your product. AI can track and analyze every click, scroll, and hover, things that would take humans much longer to uncover. Since all of this information is at your fingertips in minutes, you can quickly identify patterns and take action.
It can handle a whole lot of data at once, which makes large-scale user testing more manageable than ever before. Traditional user testing often limits the number of participants due to logistical constraints. But with AI, you can test with thousands or even millions of users, which means your data will be statistically significant and reliable.
By finding subtle trends and anomalies in the big picture, AI helps you understand user behavior and needs better, which means you can make data-driven decisions that improve user satisfaction and overall experience.
2. Intelligent A/B Testing
A/B testing is a proven way to see which version of a web page or app performs better based on a number of different metrics. This strategy is also called split-testing, and it’s been around since long before AI.
But there’s no question that machine learning makes this process even better by optimizing it in new and exciting ways. For example, AI algorithms are very good at analyzing different versions of a landing page or offer, which will help you find the best ways to connect with your audience.
Predictive analytics is another element of A/B testing that you should know about. By using historical data and learned patterns, AI can predict which version will perform better even before the testing is complete. This means faster decision-making and better version implementation, so you waste less time and resources on testing.
Ultimately, AB testing helps you deliver the best possible experience based on data, not guesswork or intuition. AI can make it even better.
3. AI-Assisted Prototyping
Brainstorming for new designs is important but time-consuming. Instead of spending hours at meetings, you can use AI to speed up this process.
Basically, you can ‘feed’ your program different designs and campaigns that worked well in the past. The AI-powered software can look through this information and pull out key elements that it can then use to build new campaigns.
Doing this can help you generate a library of great-looking templates and concepts that you can discuss with your design team. Much like traditional brainstorming, not every idea will be a winner. But there’s no question that you’ll save a significant chunk of time by using AI to come up with a pool of ideas.
Rapid iteration on an existing campaign is also possible with AI-driven prototyping, which actually leads back to A/B testing. Instead of spending weeks or months on one prototype, AI tools can generate multiple versions in minutes that you can experiment with on your site or social media.
Trying out different concepts is important for creative growth, and AI makes it possible to experiment more. By making it easy to test and discard many ideas, AI creates an environment where prototype testing can flourish.
4. Automated Accessibility Compliance
Making your product accessible to all users is not only the right thing to do, but it also dramatically expands your audience.
AI-driven accessibility checks can automatically scan your design for issues that will hinder users with disabilities. For example, there are tests to determine if a site is color-blind friendly, with different versions for each type of colorblindness. In my experience, this proactive approach helps you identify and fix problems early in the design process.
There’s no doubt that AI can check for accessibility issues faster and more accurately than manual testing. Since AI is working on this part of your site, the design team can focus on other important parts of the user experience while knowing accessibility is being taken care of.
Using AI for periodic checks makes sure no one is left out. It promotes a welcoming design approach so all users, regardless of ability, can have a good experience with your product. This not only increases user satisfaction but also your brand’s reputation for inclusivity .
5. Personalized User Experiences
Did you know that 74% of shoppers say they’ve felt frustrated by a shopping experience because the content didn’t match their interests? This is exactly why personalization is the key to user engagement. People are more likely to take action on your site if you show them things that are relevant to their interests.
AI can supercharge this concept by automatically adapting content and promotions to each user’s preferences. It can do this by analyzing user behavior, determining what content users will find most interesting based on their actions, and tailoring the experience accordingly. This will create a more engaging experience for every single person who lands on your site.
Cool, right?
AI-driven personalization at scale is especially useful for growing businesses. As your user base grows, it admittedly gets hard to add a personal touch to everything you do. AI is able to process huge amounts of data, which means it can hone in and deliver personalized experiences to millions of users without compromising on quality.
The bottom line is people will engage with content that feels tailored to them, which means a big boost in retention and satisfaction. When you add AI to the mix, it creates a win-win situation for you and your customers.
6. Predictive UX Modeling
Knowing what users want and need is a powerful way to improve the user experience. With the right data, AI can predict what someone might want or do next by looking at past behavior and trends. This foresight will help you design interfaces and interactions that are more intuitive and meet each customer’s expectations.
For example, a streaming service like Max will show each person shows and movies they might like based on their watch history.
In the old days, you’d have to wait weeks, sometimes months, and read through tons of user feedback before you could make actionable changes to your campaigns. With AI, you can make these changes essentially in real time based on how people are engaging with your content or offers.
By knowing what they need before they even realize they have a problem, you can offer solutions that add value to their lives. This proactive approach builds loyalty as users feel understood and valued by your brand.
7. AI-Enhanced Design Systems
Consistency is a massive part of creating a positive user experience. People want to feel comfortable with a brand, whether they’re browsing their blog or buying their products.
AI can help with this by generating style guides across your entire brand, including products, landing pages, and social media profiles. As a result, all the different parts of your product will have an original look and feel that your customers will recognize.
In this instance, AI will save you a lot of time. Instead of manually checking each component, like color hex codes, against the style guide, AI can do this for you. This reduces the chances of inconsistencies and makes sure every part of the product aligns with your brand.
Final Thoughts: The Human Touch in an AI World
It’s more clear than ever before that AI is having a huge impact on UX research and design. It’s making things faster, smarter, and more personal.
One of the misconceptions I see around this topic is that it’s meant to replace humans. The truth is, that tools like this actually give designers and researchers better tools to do their job.
The best UX still comes from a mix of AI smarts and human creativity. AI can crunch the numbers and spot patterns, but it takes human insight to turn those insights into experiences that truly connect with users.If you’re ready to bring AI design and research tools to your business, there’s no time like right now to start. Artificial intelligence is getting more helpful every day, so why not take advantage of this remarkable and effective tool today?
- Recent Posts
- AI for UX Research: How Artificial Intelligence is Changing the Design Game -
- 9 Challenging Participant Types -
Were sorry to hear about that, give us a chance to improve.
Article contents
Related articles

How to Drive Sales by Using Video Marketing
Video marketing is one of the most powerful tools for businesses. Here’s how you can drive more sales by optimizing your video marketing strategy.

6-Step Design Process for New Website Development
Websites are the Holy Grail of establishing a stable and fruitful online presence. They play a vital role in your further online business development and can help you take your strategies to new heights, only if you create and design them the right way. Website development and design is an ongoing process that may take […]

How UX Can Help Manage Business Risk
It doesn’t matter what your particular industry, product, or service may be, at the heart of every business is the imperative to provide customers with the best possible experience. And that is why, now more than ever, user experience (UX) is a preeminent concern for tech developers. But optimising UX is about more than winning […]
Create your free trial account
- Free 14-day trial. Easy set-up. Cancel anytime
- No UX or coding experience required
We love sharing interesting UX topics and work by creatives out there. Follow us for weekly UX posts, inspirations and reels!
Follow us on Instagram
Maybe next time!
Trending Topics
- Hersh Goldberg-Polin
Get JTA in your inbox
By submitting the above I agree to the privacy policy and terms of use of JTA.org
At the Jerusalem synagogue where Hersh Goldberg-Polin danced in life, grief and anger reign after his death

JERUSALEM — Three hundred and thirty-two days after Hersh Goldberg-Polin danced in the courtyard next to his Jerusalem synagogue on the holiday of Simchat Torah, more than a thousand people gathered there in grief and prayer to mourn his murder by Hamas terrorists in Gaza.
During the Sunday night vigil, the courtyard railings were lined with oversized yellow ribbons to symbolize advocacy for the hostages, Hapoel Jerusalem soccer flags — the 23-year-old’s favorite team — and posters that read, “We love you, stay strong, survive,” a mantra coined by his mother, Rachel Goldberg-Polin.
Just hours earlier, one of the posters had been hanging over the balcony of the home of Shira Ben-Sasson, a leader of Hakhel, the Goldberg-Polins’ egalitarian congregation in the Baka neighborhood of Jerusalem.
“We were sure we would take it down when he came home,” Ben-Sasson said.
The community wanted to unite while respecting the Goldberg-Polins’ desire for privacy, she said, prompting them to organize the prayer gathering.
“But it’s like a Band-Aid or giving first aid, it’s what you do in an emergency. I don’t know how we go on after this,” she said.

A covered courtyard at the Hakhel congregation was filled with mourners the day after Hersh Goldberg-Polin, whose family are prominent members, was found to have been killed in Gaza. Hundreds of other people crowded outside the gates, Sept. 1, 2024. (Deborah Danan)
She added that the community, which has a large contingent of English-speaking immigrants, was not prepared for the High Holidays, which begin in about a month. She said, “Seeing his empty seat is hard.”
For Ben-Sasson, who wore a T-shirt bearing the Talmudic dictum “There is no greater mitzvah than the redeeming of captives,” the tragedy is especially painful because, she said, it could have been avoided with a ceasefire agreement that freed hostages.
“Hersh was alive 48 hours ago. We think a deal could have saved him. There is no military solution to this,” she said.
That feeling of bereavement, often mixed with betrayal, pervaded gatherings across Israel on Sunday, as the country struggled with the news that six hostages who may have been freed in an agreement were now dead as negotiations continue to stall. Speakers at protests in Tel Aviv blamed Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, who himself apologized for not getting the hostages out alive but blamed Hamas for obstructing a deal. The country’s labor union, the Histadrut, has called a national strike on Monday to demand a deal.
A rare early September rain lashed parts of Israel on Sunday, leading to a widespread interpretation: God, too, was weeping.
Some at the Jerusalem gathering, including the relative of another former hostage, said Netanyahu had chosen defeating Hamas over freeing the captives.

Josef Avi Yair Engel’s grandson Ofir was released from Hamas captivity in November. He paid tribute to Hersh Goldberg-Polin, murdered in captivity, in Jerusalem, Sept. 1, 2024. (Deborah Danan)
Josef Avi Yair Engel, whose grandson Ofir, 18, was released from Hamas captivity in November during that month’s ceasefire deal, expressed shock over Hersh’s murder but said he was not surprised, given the wartime policies of Netanyahu’s government.
“We knew months ago this was going to happen. Bibi’s formula, to dismantle Hamas and return the hostages, wasn’t logical. It’s an either/or situation,” Engel said, referring to Netanyahu by his nickname. “He’s tearing the country apart. I’m afraid that in the coming months there won’t be a state at all.”
Engel said he felt a close bond with Hersh’s father Jon Polin, not only because of their joint activism in the hostage families’ tent outside the Prime Minister’s Residence, but also because of their shared identity as Jerusalemites.
“There aren’t many of us in the hostage circle,” he said. “We’re like family.”
Sarah Mann, who did not know the family personally, said the weekend’s tragedy reminded her of Oct. 7.
“This day has sparks of the seventh, which created numbness and an inability to talk. Just complete shock,” she said.

Mourners left notes at a gathering at Hersh Goldberg-Polin’s family synagogue in Jerusalem. Many of the messages used the Hebrew word for “sorry.” (Deborah Danan)
Part of the reason for that, Mann said, was Rachel, who she described as a “force of faith.” Goldberg-Polin’s mother emerged as the most prominent advocate for the hostages globally and became a symbol in her own right as she crisscrossed the world calling for her son’s freedom.
“Millions of people around the world held onto her. Once that was cut, people’s ability to hold onto faith was knocked out today. But even though this has shattered us, we need to keep holding onto God,” Mann said.
For Susi Döring Preston, the day called to mind was not Oct. 7 but Yom Kippur, and its communal solemnity.
She said she usually steers clear of similar war-related events because they are too overwhelming for her.
“Before I avoided stuff like this because I guess I still had hope. But now is the time to just give in to needing to be around people because you can’t hold your own self up any more,” she said, tears rolling down her face. “You need to feel the humanity and hang onto that.”
Like so many others, Döring Preston paid tribute to the Goldberg-Polins’ tireless activism. “They needed everyone else’s strength but we drew so much strength from them and their efforts, “she said. “You felt it could change the outcome. But war is more evil than good. I think that’s the crushing thing. You can do everything right, but the outcome is still devastating.”

Guy Gordon, with his daughter Maya, added a broken heart to the piece of tape he has worn daily to mark the number of days since the hostage crisis began, Sept. 1, 2024. (Deborah Danan)
Guy Gordon, a member of Hakhel who moved to Israel from Dublin, Ireland, in the mid-1990s, said the efforts towards ensuring Hersh’s safe return have been an anchor for the community during the war. The community knew him as the family described him in its announcement of his funeral on Tuesday, as “a child of light, love and peace” who enjoyed exploring the world and coming home to his family, including his parents and younger sisters, Leebie and Orly.
“It gave us something to hope for, and pray for and to demonstrate for,” he said. “We had no choice but to be unreasonably optimistic. Tragically it transpired that he survived until the very end.”
Gordon, like many others in the crowd, wore a piece of duct tape marked with the number of days since Oct. 7 — a gesture initiated by Goldberg-Polin’s mother. Unlike on previous days, though, his tape also featured a broken red heart beside the number.
Nadia Levene, a family friend, also reflected on the improbability of Hersh’s survival.
“He did exactly what his parents begged him to do. He was strong. He did survive. And look what happened,” Levene said.
She hailed Rachel Goldberg-Polin’s “unwavering strength and belief in God,” adding, “There were times I lost faith. I suppose I was angry with God. But she just kept inspiring us all to pray, pray, pray.”

Leah Silver of Jerusalem examined stickers showing Rachel Goldberg-Polin’s mantra for her son Hersh, who was murdered in captivity in Gaza, at a gathering after Hersh’s death, Sept. 1, 2024. (Deborah Danan)
Jerusalem resident Leah Silver rejected politicizing the hostages’ deaths.
“Everything turns political so quickly. I came here because I felt that before all the protests, we need to just mourn for a moment and to pray. And show respect for each other,” she said. “We’ve become confused about who the enemy is. It’s very sad.”
But not everyone at the gathering joined in to sing Israel’s national anthem at the closing of the prayer gathering.
“I’m sorry, I can’t sing ‘Hatikvah,'” Reza Green, a Baka resident who did not know the Goldberg-Polins personally, said. “I’m too angry. We shouldn’t be here.”
Share this:
Recommended from jta.

Meta panel rules that ‘from the river to the sea’ is not inherently antisemitic

‘I’m gutted,’ Doug Emhoff says about murdered hostages at Washington synagogue vigil

Engagement in campus Jewish life spiked after Oct. 7 but has since dropped down somewhat, Tufts study finds

US Justice Department files criminal charges against Hamas, spurred by Hersh Goldberg-Polin’s murder

As Israel endured a difficult weekend at home, its athletes won several Paralympic medals, bringing Paris total to 7

Hapoel Jerusalem, Hersh Goldberg-Polin’s favorite soccer club, mourns the death of ‘our friend in the stands’
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Positive energy districts: fundamentals, assessment methodologies, modeling and research gaps.

1. Introduction
State of the art on positive energy districts, 2. methodology.
- Setting: a café-like environment with small, round tables, tablecloths, colored pens, sticky notes and any interaction tool available.
- Welcome and Introduction: the host offers a welcome, introduces the World Café process, and sets the context.
- Small-Group Rounds: three or more twenty-minute rounds of conversations occur in small groups. Participants switch tables after each round, with one person optionally remaining as the “table host” to brief newcomers.
- Questions: each round starts with a context-specific question. Questions may remain constant or be built upon each other to guide the discussion.
- Harvest: participants share their discussion insights with the larger group, often visually represented through graphic recording.
- Objectives of the workshop and preparation. The first step of the World Café approach is to identify the main objectives. For this workshop, there was the need to investigate the current landscape of PED research, as well as to have a benchmark and collect feedback on the current research activities within Annex 83. Questions were structured in order to frame the current state-of-the-art understanding of the topic. A mapping of the potential different stakeholders in the PED design and implementation process was carried out at this stage. As a result, municipalities, community representatives, energy contractors, real estate companies and commercial facilitators, as well as citizens, were identified as main target groups. Later, the follow-up discussions were built around these main actors. Further, the mapping of the stakeholders’ involvement was carried out for better understanding the complexity of relationships, roles and synergies as well as the impact on the design, implementation and operation stages of PEDs.
- Positive Energy Districts’ definitions and fundamentals ( Section 3.1 ).
- Quality-of-life indicators in Positive Energy Districts ( Section 3.2 ).
- Technologies in Positive Energy Districts: development, use and barriers ( Section 3.3 ).
- Positive Energy Districts modeling: what is further needed to model PEDs? ( Section 3.4 ).
- Sustainability assessment of Positive Energy Districts ( Section 3.5 ).
- Stakeholder engagement within the design process ( Section 3.6 ).
- Tools and guidelines for PED implementation ( Section 3.7 ).
3.1. Positive Energy Districts Definitions and Fundamentals
3.2. quality-of-life indicators in positive energy districts, 3.3. technologies in positive energy districts: development, use and barriers, 3.4. positive energy districts modeling: what is further needed to model peds, 3.5. sustainability assessment of positive energy districts, 3.6. stakeholder engagement within the design process, 3.7. tools and guidelines for ped implementation, 4. conclusions, author contributions, data availability statement, acknowledgments, conflicts of interest.
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. 100 Climate-Neutral Cities by 2030—By and for the Citizens ; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs United Nations. 68% of the World Population Projected to Live in Urban Areas by 2050, Says UN. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/en/news/population/2018-revision-of-world-urbanization-prospects.html (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Fatima, Z.; Vacha, T.; Swamygowda, K.; Qubailat, R. Getting Started with Positive Energy Districts: Experience until Now from Maia, Reykjavik, Kifissia, Kladno and Lviv. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 5799. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- OECD. Managing Environmental and Energy Transitions for Regions and Cities ; OECD: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/about/projects/managing-environmental-and-energy-transitions-for-regions-and-cities.html (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Pierce, S.; Pallonetto, F.; De Donatis, L.; De Rosa, M. District energy modelling for decarbonisation strategies development—The case of a University campus. Energy Rep. 2024 , 11 , 1256–1267. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- U.N. SDGs Goal 11|Make Cities and Human Settlements Inclusive, Safe, Resilient and Sustainable. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal11 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Shahmohammad, M.; Salamattalab, M.M.; Sohn, W.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Aghamohmmadi, N. Opportunities and obstacles of blockchain use in pursuit of sustainable development goal 11: A systematic scoping review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024 , 112 , 105620. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Koch, F.; Ahmad, S. How to Measure Progress Towards an Inclusive, Safe, Resilient and Sustainable City? Reflections on Applying the Indicators of Sustainable Development Goal 11 in Germany and India. In Urban Transformations. Future City ; Kabisch, S., Koch, F., Gawel, E., Haase, A., Knapp, S., Krellenberg, K., Nivala, J., Zehnsdorf, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sarvari, H.; Mehrabi, A.; Chan, D.W.M.; Cristofaro, M. Evaluating urban housing development patterns in developing countries: Case study of Worn-out Urban Fabrics in Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021 , 70 , 102941. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gondeck, M.; Triebel, M.-A.; Steingrube, A.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Stryi-Hipp, G. Recommendations for a positive energy district framework—Application and evaluation of different energetic assessment methodologies. Smart Energy 2024 , 15 , 100147. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gohari, S.; Castro Silvia, S.; Ashrafian, T.; Konstantinou, T.; Giancola, E.; Prebreza, B.; Aelenei, L.; Murauskaite, L.; Liu, M. Unraveling the implementation processes of PEDs: Lesson learned from multiple urban contexts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024 , 106 , 105402. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sassenou, L.-N.; Olivieri, L.; Olivieri, F. Challenges for positive energy districts deployment: A systematic review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024 , 191 , 114152. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Good, N.; Martínez Ceseña, E.A.; Mancarella, P. Chapter Two—Energy Positivity and Flexibility in Districts. In Energy Positive Neighborhoods and Smart Energy Districts ; Monti, A., Pesch, D., Ellis, K.A., Mancarella, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 7–30. ISBN 9780128099513. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Derkenbaeva, E.; Halleck Vega, S.; Hofstede, G.J.; van Leeuwen, E. Positive Energy Districts: Mainstreaming Energy Transition in Urban Areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022 , 153 , 111782. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bruck, A.; Díaz Ruano, S.; Auer, H. One Piece of the Puzzle towards 100 Positive Energy Districts (PEDs) across Europe by 2025: An Open-Source Approach to Unveil Favourable Locations of PV-Based PEDs from a Techno-Economic Perspective. Energy 2022 , 254 , 124152. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Vandevyvere, H.; Ahlers, D.; Wyckmans, A. The Sense and Non-Sense of PEDs—Feeding Back Practical Experiences of Positive Energy District Demonstrators into the European PED Framework Definition Development Process. Energies 2022 , 15 , 4491. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Natanian, J.; Magyari, A.; Brunetti, A.; Reith, A.; Guarino, F.; Manapragada, N.; Cellura, S.; de Luca, F.; Naboni, E. Ten Questions on Tools and Methods for Positive Energy Districts. Build. Environ. 2024 , 255 , 111429. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Perera, A.T.D.; Javanroodi, K.; Wang, Y.; Hong, T. Urban Cells: Extending the Energy Hub Concept to Facilitate Sector and Spatial Coupling. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021 , 3 , 100046. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aparisi-Cerdá, I.; Ribó-Pérez, D.; Cuesta-Fernandez, I.; Gómez-Navarro, T. Planning Positive Energy Districts in Urban Water Fronts: Approach to La Marina de València, Spain. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022 , 265 , 115795. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sareen, S.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Aelenei, L.; Reda, F.; Etminan, G.; Andreucci, M.-B.; Kuzmic, M.; Maas, N.; Seco, O.; Civiero, P.; et al. Ten Questions Concerning Positive Energy Districts. Build. Environ. 2022 , 216 , 109017. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mihailova, D.; Schubert, I.; Burger, P.; Fritz, M.M.C. Exploring modes of sustainable value co-creation in renewable energy communities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022 , 330 , 129917. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mihailova, D.; Schubert, I.; Martinez-Cruz, A.L.; Hearn, A.X.; Sohre, A. Preferences for configurations of Positive Energy Districts—Insights from a discrete choice experiment on Swiss households. Energy Policy 2022 , 163 , 112824. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Working Group SET. Plan Temporary SET-Plan ACTION n 3.2 Implementation Plan: Europe to Become a Global Role Model in Integrated, Innovative Solutions for the Planning, Deployment, and Replication of Positive Energy Districts ; 2018. Available online: https://jpi-urbaneurope.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/setplan_smartcities_implementationplan-2.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- JPI Urban Europe/SET Plan Action 3.2. In White Paper on PED Reference Framework for Positive Energy Districts and Neighbourhoods ; 2020. Available online: https://jpi-urbaneurope.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/White-Paper-PED-Framework-Definition-2020323-final.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- ATELIER. Atelier—Positive Energy Districts. Available online: https://smartcity-atelier.eu/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- EURAC Smart-BEEjS—Human-Centric Energy Districts: Smart Value Generation by Building Efficiency and Energy Justice for Sustainable Living. Available online: https://www.eurac.edu/en/institutes-centers/institute-for-renewable-energy/projects/smart-beejs (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Making City Making City—Energy Efficient Pathway for the City Transformation. Available online: https://makingcity.eu/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- +CityxChange. Available online: https://cityxchange.eu/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Uspenskaia, D.; Specht, K.; Kondziella, H.; Bruckner, T. Challenges and Barriers for Net-Zero/Positive Energy Buildings and Districts—Empirical Evidence from the Smart City Project SPARCS. Buildings 2021 , 11 , 78. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hedman, Å.; Rehman, H.U.; Gabaldón, A.; Bisello, A.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Zhang, X.; Guarino, F.; Grynning, S.; Eicker, U.; Neumann, H.-M.; et al. IEA EBC Annex83 Positive Energy Districts. Buildings 2021 , 11 , 130. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gabaldón Moreno, A.; Vélez, F.; Alpagut, B.; Hernández, P.; Sanz Montalvillo, C. How to Achieve Positive Energy Districts for Sustainable Cities: A Proposed Calculation Methodology. Sustainability 2021 , 13 , 710. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aghamolaei, R.; Shamsi, M.H.; Tahsildoost, M.; O’Donnell, J. Review of district-scale energy performance analysis: Outlooks towards holistic urban frameworks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018 , 41 , 252–264. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bottecchia, L.; Gabaldón, A.; Castillo-Calzadilla, T.; Soutullo, S.; Ranjbar, S.; Eicker, U. Fundamentals of Energy Modelling for Positive Energy Districts. In Sustainability in Energy and Buildings ; Littlewood, J.R., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 263, Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, M.; Zhou, N.; Yan, J.; Feng, W.; Yan, R.; You, K.; Zhang, J.; Ke, J. Estimation of Global Building Stocks by 2070: Unlocking Renovation Potential. Nexus 2024 , 1 , 100019. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xiang, X.; Zhou, N.; Ma, M.; Feng, W.; Yan, R. Global transition of operational carbon in residential buildings since the millennium. Adv. Appl. Energy 2023 , 11 , 100145. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yan, R.; Ma, M.; Zhou, N.; Feng, W.; Xiang, X.; Mao, C. Towards COP27: Decarbonization patterns of residential building in China and India. Appl. Energy 2023 , 352 , 122003. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, M.; Zhou, N.; Xie, H.; Ma, Z.; Xiang, X.; Ma, X. Battery electric vehicle charging in China: Energy demand and emissions trends in the 2020s. Appl. Energy 2024 , 365 , 123153. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Orehounig, K.; Evins, R.; Dorer, V. Integration of Decentralized Energy Systems in Neighbourhoods Using the Energy Hub Approach. Appl. Energy 2015 , 154 , 277–289. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pan, Z.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H. Interactions of District Electricity and Heating Systems Considering Time-Scale Characteristics Based on Quasi-Steady Multi-Energy Flow. Appl. Energy 2016 , 167 , 230–243. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, S.; Hensen, J.L.M. An energy paradigm transition framework from negative towards positive district energy sharing networks—Battery cycling aging, advanced battery management strategies, flexible vehicles-to-buildings interactions, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis. Appl. Energy 2021 , 288 , 116606. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Marrasso, E.; Martone, C.; Pallotta, G.; Roselli, C.; Sasso, M. Assessment of energy systems configurations in mixed-use Positive Energy Districts through novel indicators for energy and environmental analysis. Appl. Energy 2024 , 368 , 123374. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bruck, A.; Díaz Ruano, S.; Auer, H. A Critical Perspective on Positive Energy Districts in Climatically Favoured Regions: An Open-Source Modelling Approach Disclosing Implications and Possibilities. Energies 2021 , 14 , 4864. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ali, U.; Shamsi, M.H.; Hoare, C.; Mangina, E.; O’Donnell, J. Review of Urban Building Energy Modeling (UBEM) Approaches, Methods and Tools Using Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis. Energy Build. 2021 , 246 , 111073. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Brunetti, A.; Cellura, S.; Guarino, F.; Longo, S.; Mistretta, M.; Reda, F.; Rincione, R. Development of an Early Design Tool for the Sustainability Assessment of Positive Energy Districts: Methodology, Implementation and Case-Studies. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023 , 2600 , 82020. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Trulsrud, T.H.; Van der Leer, J. Towards a positive energy balance: A comparative analysis of the planning and design of four positive energy districts and neighbourhoods in Norway and Sweden. Energy Build. 2024 , 318 , 114429. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guasselli, F.; Vavouris, A.; Stankovic, L.; Stankovic, V.; Didierjean, S.; Gram-Hanssen, K. Smart energy technologies for the collective: Time-shifting, demand reduction and household practices in a Positive Energy Neighbourhood in Norway. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2024 , 110 , 103436. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aparisi-Cerdá, I.; Ribó-Pérez, D.; Gómez-Navarro, T.; García-Melón, M.; Peris-Blanes, J. Prioritising Positive Energy Districts to achieve carbon neutral cities: Delphi-DANP approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024 , 203 , 114764. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Castillo-Calzadilla, T.; Garay-Martinez, R.; Martin Andonegui, C. Holistic fuzzy logic methodology to assess positive energy district (PathPED). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023 , 89 , 104375. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Derkenbaeva, E.; Jan Hofstede, G.; van Leeuwen, E.; Halleck Vega, S.; Wolfers, J. ENERGY Pro: Spatially explicit agent-based model on achieving positive energy districts. MethodsX 2024 , 12 , 102779. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Eicker, U. Introduction: The Challenges of the Urban Energy Transition. In Urban Energy Systems for Low-Carbon Cities ; Eicker, U., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-0-12-811553-4. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jepsen, B.K.H.; Haut, T.W.; Design, M.J. Modelling and Performance Evaluation of a Positive Energy District in a Danish Island. Future Cities Environ. 2022 , 8 , 1. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guarino, F.; Bisello, A.; Frieden, D.; Bastos, J.; Brunetti, A.; Cellura, M.; Ferraro, M.; Fichera, A.; Giancola, E.; Haase, M.; et al. State of the Art on Sustainability Assessment of Positive Energy Districts: Methodologies, Indicators and Future Perspectives. Sustain. Energy Build. 2021 , 2021 , 479–492. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hearn, A.X.; Sohre, A.; Burger, P. Innovative but Unjust? Analysing the Opportunities and Justice Issues within Positive Energy Districts in Europe. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021 , 78 , 102127. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Haarstad, H.; Wathne, M.W. Are Smart City Projects Catalyzing Urban Energy Sustainability? Energy Policy 2019 , 129 , 918–925. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gouveia, J.P.; Seixas, J.; Palma, P.; Duarte, H.; Luz, H.; Cavadini, G.B.C. Positive Energy District: A Model for Historic Districts to Address Energy Poverty. Front. Sustain. Cities 2021 , 3 , 648473. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bossi, S.; Gollner, C.; Theierling, S. Towards 100 Positive Energy Districts in Europe: Preliminary Data Analysis of 61 European Cases. Energies 2020 , 13 , 6083. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rankinen, J.-A.; Lakkala, S.; Haapasalo, H.; Hirvonen-Kantola, S. Stakeholder Management in PED Projects: Challenges and Management Model. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Plan. Manag. 2022 , 34 , 91–106. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Schiele, H.; Krummaker, S.; Hoffmann, P.; Kowalski, R. The “research world café” as method of scientific enquiry: Combining rigor with relevance and speed. J. Bus. Res. 2022 , 140 , 280–296. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Vandevyvere, H.; Ahlers, D.; Alpagut, B.; Cerna, V.; Cimini, V.; Haxhija, S.; Hukkalainen, M.; Kuzmic, M.; Livik, K.; Padilla, M.; et al. Positive Energy Districts Solution Booklet ; European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Évora—POCITYF. Available online: https://pocityf.eu/city/evora/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Commission, E.; European Climate, I.; Agency, E.E.; Alpagut, B.; Zhang, X.; Gabaldon, A.; Hernandez, P. Digitalization in Urban. Energy Systems—Outlook 2025, 2030 and 2040 ; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [ Google Scholar ]
- Waglé, S.; Singh, J.; Shah, P. Citizen Report Card Surveys: A Note on the Concept and Methodology (English) ; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cimini, V.; Giglio, F.; Carbonari, G. D2.4: Report on Bankability of the Demonstrated Innovations. In +CityxChange—Work Package 2 Task 2.7 ; 2019. Available online: https://cityxchange.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/D2.4-Report-on-Bankability-of-the-Demonstrated-Innovations_v3.0-final.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Cordis—Horizon 2020 Results in Brief. A Collaborative Approach Promotes Net Zero Energy Settlements. In Achieving near Zero and Positive Energy Settlements in Europe Using Advanced Energy Technology ; 2021. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/article/id/430390-a-collaborative-approach-promotes-net-zero-energy-settlements (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Krangsås, S.G.; Steemers, K.; Konstantinou, T.; Soutullo, S.; Liu, M.; Giancola, E.; Prebreza, B.; Ashrafian, T.; Murauskaitė, L.; Maas, N. Positive Energy Districts: Identifying Challenges and Interdependencies. Sustainability 2021 , 13 , 10551. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Prina, M.G.; Manzolini, G.; Moser, D.; Nastasi, B.; Sparber, W. Classification and Challenges of Bottom-up Energy System Models—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020 , 129 , 109917. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Allegrini, J.; Orehounig, K.; Mavromatidis, G.; Ruesch, F.; Dorer, V.; Evins, R. A Review of Modelling Approaches and Tools for the Simulation of District-Scale Energy Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015 , 52 , 1391–1404. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lyden, A.; Pepper, R.; Tuohy, P.G. A Modelling Tool Selection Process for Planning of Community Scale Energy Systems Including Storage and Demand Side Management. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018 , 39 , 674–688. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tozzi, P.; Jo, J.H. A Comparative Analysis of Renewable Energy Simulation Tools: Performance Simulation Model vs. System Optimization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017 , 80 , 390–398. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hall, L.M.H.; Buckley, A.R. A Review of Energy Systems Models in the UK: Prevalent Usage and Categorisation. Appl. Energy 2016 , 169 , 607–628. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ringkjøb, H.-K.; Haugan, P.M.; Solbrekke, I.M. A Review of Modelling Tools for Energy and Electricity Systems with Large Shares of Variable Renewables. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018 , 96 , 440–459. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Neumann, H.M.; Garayo, S.D.; Gaitani, N.; Vettorato, D.; Aelenei, L.; Borsboom, J.; Etminan, G.; Kozlowska, A.; Reda, F.; Rose, J.; et al. Qualitative Assessment Methodology for Positive Energy District Planning Guidelines. In Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies ; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 263, pp. 507–517. [ Google Scholar ]
- Li, L.; Lange, K.W. Planning Principles for Integrating Community Empowerment into Zero-Net Carbon Transformation. Smart Cities 2023 , 6 , 100–122. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Turci, G.; Alpagut, B.; Civiero, P.; Kuzmic, M.; Pagliula, S.; Massa, G.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Seco, O.; Soutullo, S. A Comprehensive PED-Database for Mapping and Comparing Positive Energy Districts Experiences at European Level. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 427. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- PED DB: Map—PED-EU-NET|COST ACTION CA19126. Available online: https://pedeu.net/map/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- European Union. New European Bauhaus. Available online: https://new-european-bauhaus.europa.eu/about/dashboard_en (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Volpe, R.; Gonzalez Alriols, M.; Martelo Schmalbach, N.; Fichera, A. Optimal design and operation of distributed electrical generation for Italian positive energy districts with biomass district heating. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022 , 267 , 115937. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bilić, B.; Šmit, K. Evaluation of the New European Bauhaus in Urban Plans by Land Use Occurrence Indicators: A Case Study in Rijeka, Croatia. Buildings 2024 , 14 , 1058. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fichera, A.; Pluchino, A.; Volpe, R. Local Production and Storage in Positive Energy Districts: The Energy Sharing Perspective. Front. Sustain. Cities 2021 , 3 , 690927. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cellura, M.; Fichera, A.; Guarino, F.; Volpe, R. Sustainable Development Goals and Performance Measurement of Positive Energy District: A Methodological Approach. Conference paper-Book Chapter. In Sustainability in Energy and Buildings ; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 263, pp. 519–527. [ Google Scholar ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Question #1 | Question #2 | Question #3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| | What are the essential PED DNAs? Can generic PED archetypes be created based on them? | What are the categories of quality-of-life indicators relevant for PED development? | How would you use a database tool to learn about PED development process (e.g., using static information for dynamic decision-making)? |
| | Which future technologies would you expect to be adopted in PEDs and cities? | What can be the challenges and the barriers in the future (regarding e.g., control, smart solutions, modeling, technologies) to PED development and diffusion? | What is your expectation for urban and district energy modeling? How can models help to shape PEDs and cities? |
| | What is the impact of stakeholders in the PED design/decision process, what are their interests and how are stakeholders likely to be involved in the overall process? | What costs do you expect to bear and what revenues do you expect to realize from the PED implementation? Which aspects should be included in the organizational/business models? | What would you prioritize in terms of energy aspects or efficiency and social implications of living in a PED? Which aspects are more relevant for you? |
| | Annex 83 together with other PED initiatives is developing a database of PEDs and PED-Labs: what would be your main interest in consulting the database? | Having the outcomes from PED guidelines analysis, what information would be the most interesting for you to see? | Who can benefit from the PED research studies and Annex 83 results? Which stakeholders are interested? |
| Categories | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Facts and Figures | Physical sizes/population size |
| Geographical location | |
| Climate | |
| Density | |
| Built form | |
| Land use | |
| Energy demand | |
| Renewable energy potential | |
| Technologies | Renewable energy supplies |
| Energy-efficiency measures | |
| Energy distribution (e.g., co-generation, district network) | |
| Energy storage | |
| Mobility solutions | |
| Quality of Life | User comfort |
| Social-economic conditions | |
| Health impacts (e.g., air pollution, noise pollution) | |
| Accessibility to green space | |
| Accessibility to services (e.g., bike lane, public transportation) | |
| Local value/sense of community | |
| Others | Regulations/Policies |
| Stakeholder involvement | |
| Local targets and ambitions | |
| Local challenges | |
| Impacts of PEDs |
| Type | Quality Categories | |
|---|---|---|
| Tangible | Indoor and outdoor environmental quality | Physical quality and comfort of the environment |
| Security and safety | ||
| Level and accessibility of servicing | Public and active transport facilities including walkability, energy services (access to affordable energy including access to energy efficiency), sustainable waste management | |
| Access to daily life amenities including education, culture, sports, coworking and study places, provisions for children, but even common gardens or community kitchens | ||
| Aesthetic quality | ||
| Functional mix | ||
| Future-proofness | ||
| Acceptable cost of life (affordability, inclusivity) | ||
| Equity and just transition | ||
| Functional links to realizing circularity and reducing emissions | ||
| Citizen engagement | Involvement in decision-making | |
| Social diversity in participation | ||
| Access to greenery | The possibility to reconnect with nature | |
| Sufficient open space | ||
| Information flow | From creating awareness over enhancing knowledge and literacy up to capacity of control | |
| Transparency on energy flows and information for the end prosumer | ||
| Insight in applicable PED solutions and in healthy lifestyles | ||
| Intangible | Sense of well-being | |
| Quality of social connections | ||
| Sense of personal achievement | ||
| Level of self-esteem | ||
| Sense of community | ||
| Degree of cooperation and engagement for the common interest | ||
| Time spent with friends (outdoor) | ||
| Budget available at the end of the month to spend freely | ||
| Not being aware or realizing of living in a PED | ||
| Technology Groups | Solutions | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy efficiency | New energy-efficient buildings and building retrofitting. | |
| Nature-based solutions (natural sinks) and carbon capture solutions (CCS) | ||
| Efficient resource management | ||
| Efficient water systems for agriculture (smart agriculture, hydroponics, agrivoltaics, etc.) | ||
| Organic photovoltaics and a circular approach (second life materials, like batteries) | ||
| Energy flexibility | Hardware | Storage (long-term and short-term) |
| Monitoring systems (sensors, smart meters, PLCs *, energy management systems, etc.) | ||
| Vehicle to grid | ||
| Heat pumps | ||
| Electronic devices like IoT * technologies | ||
| Buildings fully automated with real time monitoring behind-the-meter and automated actions | ||
| Cybersecurity, data rights and data access | ||
| Demand management and remote control of devices | ||
| Software | Edge computing | |
| Machine learning | ||
| Blockchain | ||
| Digital twins | ||
| 5G | ||
| City management platform and platforms for city planning (space, refurbishment, climate change, etc.) | ||
| E-mobility | Promotion of shared vehicles over individual car use, lift sharing, and alternative ways (like micromobility) to collective transports | |
| Soft mobility | Promotion of a lifestyle that require less use of cars, i.e., “soft mobility” solutions like low emission zones or banning the entrance of some type of car (e.g., Singapore and Iran have policies in place to allow only certain car groups to drive freely in certain periods) | |
| E-vehicle charging stations and vehicle-to-grid solutions | ||
| Low-carbon generation | Photovoltaics | |
| Energy communities | ||
| Electrification of heating and cooling (H&C) using heat pumps, district heating networks utilizing waste heat, or solar thermal technologies | ||
| Virtual production | ||
| Fusion technology | ||
| Challenges and Barriers | Key Topics |
|---|---|
| Capacity building and policy issues | Political and legal barriers |
| Regulatory frameworks and policy constraints | |
| Tailored legislation | |
| Bridging the knowledge gap | |
| Inadequate data sharing practices | |
| Securing sufficient financial resources | |
| Lack of clear regulations defining PED classification | |
| Active involvement of policymakers | |
| Widespread dissemination of knowledge | |
| Collaborative data-sharing efforts | |
| Securing adequate funding | |
| Establishing supportive policies and regulations | |
| Social challenges and considerations | Cultural barriers |
| Access to affordable and sustainable energy for all | |
| Building social agreements and fostering collaboration | |
| Energy literacy | |
| Addressing personal behavior acceptance | |
| Transition strategy for inclusivity | |
| Social inclusion and trust-building | |
| Data sharing and privacy concerns | |
| Overcoming public opposition and promoting knowledge dissemination | |
| Financial barriers | Long-term storage investment and space competition |
| Insufficient investment | |
| High upfront costs | |
| Allocation of costs among stakeholders | |
| Incentives for participation | |
| Addressing investment challenges for different stakeholders | |
| Accounting for battery costs | |
| Data management | Data standardization |
| Data security measures and protocols | |
| Sustainability and maintenance of data infrastructure | |
| Privacy regulations and data anonymization techniques | |
| Sustainable business models and ownership structures | Standardization of control technologies and replication strategies |
| Grid management approaches | |
| Deep penetration of sustainable technologies | |
| Implementation of predictive models Long-term maintenance activities and resident data collection | |
| Balancing diverse requirements | |
| Addressing grid operation challenges | |
| Managing multiple independent energy districts | |
| Inclusivity strategies for digital technology reliance | |
| Managing production peaks and defining the role of buildings and districts | |
| Effective management strategies for grid congestion and stability |
| Categories of Innovation | Innovation Types | Possible Revenues/Advantages in PED Business Model/Governance | Possible Costs/Drawbacks in PED Business Model/Governance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Profit Model | Providing thermal comfort instead of a certain amount of thermal energy to inhabitants | Misconducts or rebound effect |
| Network | Inclusion of the PED into larger projects and international networks, possibility of co-financing and knowledge sharing | Misalignment or delay of the PED project to the original timeline due to constrains related to international activities and networking | |
| Structure | Participation of the real estate companies/investors in the development and management of the energy infrastructure and EV mobility services as well as building management | Lack of knowledge, involvement in activities out of the usual business of investors | |
| Free or almost free thermal energy supply from “waste energy” sources | Failure of the network due to unliteral decisions of a member in ceasing the provision of energy | ||
| Process | Involvement of future inhabitants in the design phase of the energy community since the early stage, to share the sense of belonging and ownership | Reluctancy of inhabitants to participate in additional expenses or being involved in “entrepreneurial” activities or bored by the participation in boards and governance structures | |
| Offering | Product Performance | Investors and companies involved in the PED development take profit from their role of frontrunner placing them before the competitors or entering in new market niches | Hi-tech BA and BEM systems may result costly in O&M, because of digital components, cloud and computing services, rapid aging of technology |
| Product System | Including EV available for PED users may generate new incomes and reduce the need of individual cars. The integration of EV in the energy system may offer “flexibility services” | Lack of knowledge, involvement in activities out of the usual business of investors/real estate companies. Low interest of users in participating to the flexibility market, because of discomfort (unexpected empty battery of the EV) | |
| Experience | Services | Provision of high tech and high-performance buildings, with outstanding energy performances (lower heating/cooling costs) and sophisticated Building Automation and Energy Management systems | Sophisticated Building Automation and Energy Management systems may result “invasive” to users, asking for continuous interaction with complicate systems, or leaving them not enough freedom to choose (e.g., opening the windows is not possible to achieve some energy performance) |
| Channel | The PED is promoted as a rewarding sustainable investment, this allows the city to attract more clean investments (public funds, investment funds, donors), speeding up the energy transition | The communication of the characteristics of the PED is not done in the proper way | |
| Brand | Gold class rated buildings may have an increased value on the market, resulting in higher selling and rental costs, occupancy rate. The high architectural quality is appreciated by the market | The Branding/certification of the PED is not recognized by the market as an added value. | |
| The development of the PED takes longer as expected. Technology failures during the implementation or operation phase create a bad reputation and discourage future similar activities | |||
| Customer Engagement | The PED is available as a digital twin, users are engaged via a dedicated app, allowing interaction, communication, reporting, monitoring of bills, etc. | The PED is perceived by users (e.g., social housing tenants) as a hassle and not responding to their needs, because they have not been involved in the identification of peculiar traits since the beginning |
| Category | Beneficiaries |
|---|---|
| Citizens and communities | Citizens, inhabitants, residents, general public, local communities and neighborhoods, municipalities and provinces, energy communities, and socially disadvantaged groups. |
| City decision-makers and planners | City decision-makers, city planners, local authorities, policy-makers, public administrations, politicians, local and national governments. |
| Research | Scientists, publishers, and research organizations. |
| Private companies and technology developers | Private companies of RES technologies, ICT companies, start-ups and new companies, entrepreneurs, technology developers and other companies involved in local development (tech development and evaluation). |
| Energy providers | Energy providers, grid operators. |
| Education stakeholders | Students and teachers. |
| Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) | NGOs and other civil society groups |
| Category | Comments |
|---|---|
| Strategies | Most comments dealt with the strategies on how to achieve PEDs, that should focus on success factors of PED initiatives, technologies and stakeholders rather than a standardized approach |
| References | Useful information, special attention to Liwen Li, planning principles for integrating community empowerment into zero-carbon transformation |
| Definitions | Help to reduce uncertainty |
| Boundaries | Energy balance calculations, mobility, definition (of buildings) |
| Finance | Financial mechanisms, support schemes |
| Citizen engagement | From engagement to empowerment |
| Management | Process management, organizing involvement, information provision |
| Policy | Incentives, regional policies |
| Flexibility/Grid interaction | Timesteps, credit system |
| Form | Dissemination through video and other forms (not only written information) |
| Category | Comments |
|---|---|
| Lessons learned | Special reference to real life implementation |
| Results | Data analysis and potential research on the field |
| Metadata as the useful information that can the real goal of consultation | |
| Benchmarking to compare PEDs | |
| Need to normalize results depending on a number of factors (size, location…) to really compare different initiatives | |
| Privacy and data protection | |
| Sets of technologies and solutions | - |
| Economic parameters | As a way to benchmark the different PED technologies |
| Citizen engagement | Energy poverty |
| Prosumers | |
| From engagement to empowerment | |
| Definition and boundaries | Need to standardize and have a reference framework to establish the energy balance |
| Contact persons | It is very valuable to have a contact address to ask more about the initiative |
| Regulatory framework | Drivers and Enablers |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Kozlowska, A.; Guarino, F.; Volpe, R.; Bisello, A.; Gabaldòn, A.; Rezaei, A.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Alpagut, B.; Vandevyvere, H.; Reda, F.; et al. Positive Energy Districts: Fundamentals, Assessment Methodologies, Modeling and Research Gaps. Energies 2024 , 17 , 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174425
Kozlowska A, Guarino F, Volpe R, Bisello A, Gabaldòn A, Rezaei A, Albert-Seifried V, Alpagut B, Vandevyvere H, Reda F, et al. Positive Energy Districts: Fundamentals, Assessment Methodologies, Modeling and Research Gaps. Energies . 2024; 17(17):4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174425
Kozlowska, Anna, Francesco Guarino, Rosaria Volpe, Adriano Bisello, Andrea Gabaldòn, Abolfazl Rezaei, Vicky Albert-Seifried, Beril Alpagut, Han Vandevyvere, Francesco Reda, and et al. 2024. "Positive Energy Districts: Fundamentals, Assessment Methodologies, Modeling and Research Gaps" Energies 17, no. 17: 4425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174425
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To know the answer for what is research design, it is important to know the characteristics. These are-. 1. Reliability. A reliable research design ensures that each study's results are accurate and can be replicated. This means that if the research is conducted again under the same conditions, it should yield similar results.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Research design methods refer to the systematic approaches and techniques used to plan, structure, and conduct a research study. The choice of research design method depends on the research questions, objectives, and the nature of the study. Here are some key research design methods commonly used in various fields: 1.
Experimental Research Design. Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables.With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions ...
Put another way, in the honeycomb, the six main elements - namely: (1) research philosophy; (2) research approach; (3) research strategy; (4) research design; (5) data collection and (6) data analysis techniques - come together to form research methodology. This structure is characteristic of the main headings you will find in a methodology ...
In short, a good research design helps us to structure our research. Marketers use different types of research design when conducting research. There are four common types of research design — descriptive, correlational, experimental, and diagnostic designs. Let's take a look at each in more detail.
Typically, a good and well-planned research design consists of the following components, or tasks: 1. Selection of appropriate type of design: Exploratory, descriptive and/or causal design. 2. Identification of specific information needed based problem in hand and the selected design. 3.
Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Frequently asked questions. Introduction. Step 1. Step 2.
Types of Research Design. • Quantitative Research: Focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis to quantify relationships and patterns. Common methods include surveys, experiments, and observational studies. • Qualitative Research: Emphasizes understanding phenomena through in-depth exploration and interpretation of non-numerical data.
In our ultimate guide to research design for businesses, we breakdown the process, including research methods, examples, and best practice tips to help you get started. If you have a business problem that you're trying to solve — from product usage to customer engagement — doing research is a great way to understand what is going wrong.
Data helps you price your product, find your customer, make a better feature, or solve a problem. Research design is the strategy or plan you use to gather that data and make sense of it in a way that seems understandable, logical, and actionable. Consider your research design the roadmap of data collection and measurement.
A well-designed research study should have a clear and well-defined research question, a detailed plan for collecting data, and a method for analyzing and interpreting the results. A well-thought-out research design addresses all these features. Research design elements Research design elements include the following:
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. ... Business: Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the ...
Business research: Definition. Business research is a process of acquiring detailed information on all the areas of business and using such information to maximize the sales and profit of the business. Such a study helps companies determine which product/service is most profitable or in demand. In simple words, it can be stated as the acquisition of information or knowledge for professional or ...
Chapter 3 Business Research Design: Exploratory, Descriptive and Causal Designs. Chapter 3. sLearning ObjectivesAfter reading this chapter, the reader should be able to:Understand the meaning of research design, select an. develop appropriate research design to solve the concerned management dilemma.Understand the basic difference between th.
Research design is the framework of research methods and techniques chosen by a researcher to conduct a study. The design allows researchers to sharpen the research methods suitable for the subject matter and set up their studies for success. Creating a research topic explains the type of research (experimental,survey research,correlational ...
The scope of the term business research is quite broad - it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market. It could focus on customer experience and assess customer satisfaction levels.
Other interesting articles. If you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. Statistics. Normal distribution. Skewness. Kurtosis. Degrees of freedom. Variance. Null hypothesis.
The five main components of a research design are: Research questions. Course suggestions. Units of analysis. Linking data to propositions. Interpretation of the findings of the study. The components of research design apply to all types of standardised, extra-terrestrial research, whether physical or social sciences.
Here are some of the elements of a good research design: Purpose statement. Data collection methods. Techniques of data analysis. Types of research methodologies. Challenges of the research. Prerequisites required for study. Duration of the research study. Measurement of analysis.
for validity and reliability. Design is basically concerned with the aims, uses, purposes, intentions and plans within the. pr actical constraint of location, time, money and the researcher's ...
Ranganathan P. Understanding Research Study Designs. Indian J Crit Care Med 2019;23 (Suppl 4):S305-S307. Keywords: Clinical trials as topic, Observational studies as topic, Research designs. We use a variety of research study designs in biomedical research. In this article, the main features of each of these designs are summarized. Go to:
A design is used to structure the research, to show how all of the major parts of the research project—the samples or groups, measures, treatments or programs, and methods of assignment—work together so as to address the central research questions. From sample results, the researcher generalizes or makes claims about the population.
It's because each incentive design choice both signals information about your own beliefs and intentions as an employer and shapes the signaling value of employee behavior within the organization.
Today, we are going to show you how AI is improving UX research and design and how you can use it to your advantage. Let's get started! How AI Enhances UX Research and the Design Process. Let's start by exploring a few key benefits of adding AI to your existing design process. Speed Things Up - AI tools can crunch data faster than any ...
Josef Avi Yair Engel, whose grandson Ofir, 18, was released from Hamas captivity in November during that month's ceasefire deal, expressed shock over Hersh's murder but said he was not ...
The definition, characterization and implementation of Positive Energy Districts is crucial in the path towards urban decarbonization and energy transition. However, several issues still must be addressed: the need for a clear and comprehensive definition, and the settlement of a consistent design approach for Positive Energy Districts. As emerged throughout the workshop held during the fourth ...