

Resources For Educators
Welcome to Making Caring Common’s Resources for Educators, Teachers, Counselors, School Administrators, and School Leaders!
We offer strategies, resources lists, audits, surveys, discussion guides, and more, which we hope you will use in your school. You can review the list of resources below or click to sort by topic.
- Caring and Empathy
- College Admissions
- Current Events
- Mental Health
- Moral and Ethical Development
- Relationship Mapping
- Romantic Relationships
- Social-Emotional Learning
Gender Bias Case Study
Despite the progress girls and women have made in school and the workplace in the past few decades, a gender gap still persists, and our research suggests that biases could be at the root of this gap., gender bias and discrimination is surprisingly common in many schools and sometimes happens beneath school staff’s radar. as adults, we can shed light on these important topics that often go undiscussed at school. these discussions can be challenging. for some youth, this is an immensely personal or even heated topic that brings up questions of equality and privilege. others may question whether gender biases even exist. finally, the idea that biases can be implicit—and discrimination unconscious—may itself be a novel concept to some teenagers., fortunately, the payoff in broaching these topics is huge. by allowing children to explore this topic, share ideas for improvement, and participate in community-building and empathy-promoting activities, you are taking steps towards ensuring that your classroom or school is a place where everyone is respected, supported, and empowered..

Overview For: Educators Ages: Middle School and High School Resource Type: Case Study
Related Research + Initiatives
Case Study and Discussion
The following reading exercise includes three short stories of bias and discrimination that are common in many high schools. These stories are designed to facilitate discussion about the effects of gender bias and discrimination and promote empathy and perspective taking skills. Have students read the case study and then use the questions to facilitate a follow-up discussion.
Adams High School: A Case Study
Jessica had loved playing soccer since she was a little kid, and she was the star player on the co-ed soccer team at her school. When she transferred to Adams High School in the middle of her junior year, she was surprised to hear there was no co-ed team—instead she would play on the all girls’ team. While Jessica enjoyed playing on the girls’ team and met some really talented players there, she quickly realized that the boys’ team had much nicer uniforms, had the best practice spaces, and were the ones that were celebrated in school announcements and rallies. The girls were good too, but got way less attention. In gym class, Jessica had her chance to take on the boys on the field, though. She was better than almost everyone and pretty regularly scored tough goals against the varsity boys’ teams’ star player, Jeremy. After one particularly brutal game where Jessica scored several goals against the boys, Jeremy and his soccer friends decided that they didn’t want to play against Jessica any more. In front of the entire gym class, Jeremy called Jessica “the beast” and made cracks about her being too athletic for any guy at Adams to date. The other students in the class giggled nervously, but no one said anything.
Nate was a junior at Adams and was trying to figure out what he wanted to do after high school. He had decided not to go into his father’s restaurant business and was exploring career options. He had a bunch of younger cousins that he sometimes watched and he knew that he had always gotten along well with kids. He thought sometimes about joining the for-credit childcare program at Adams to see if professional childcare might be a good fit, but he always decided against it; those programs only had girls in them. If he joined the childcare program the other guys in school would never let it go. He signed up for shop class instead—it was less interesting to him, but at least he’d be with the guys and wouldn’t get teased.
Ms. Phillips
Ms. Phillips was the guidance counselor at Adams. She had been trying to set up a visit from the CEO of the biggest tech firm in town for almost two months. Many Adams students wanted to work there after college and Ms. Phillips wanted the CEO to talk with the students about the company and the type of employees it hired. On the day of the event, Ms. Phillips was not surprised when over 30 students showed up. All but two were boys. As they waited for the CEO to arrive, the students chatted about what the CEO would say—what type of advice would he give? Where would he recommend they go to college and what would he say they should study? What kind of fancy car would he drive to the school? When the CEO arrived in the classroom, all of the students looked surprised and a few looked confused. A few even made snide comments under their breath. The person standing in front of them was a woman.
Discussion Tips
Once students have read the case study, use the following questions to facilitate a discussion that will help students understand how common and harmful gender-related biases and discrimination can be, and allow students to think about solutions. In your discussion, encourage students to think about each character’s perspective and to understand and appreciate their feelings (empathy).
Understanding others’ feelings is just the beginning, though—it is important to encourage students to act upon those feelings of empathy and to reach out to those who are victims of gender bias. As your students read the case and answer the questions, encourage them to think about what their best or “ideal” selves would do in this case, as opposed to what they would actually do. Ask them to think about why there is a gap between their “ideal” selves and their actual behavior. What gets in the way of them doing the right thing? Ask them to consider how they might close this gap.
Potential Obstacles and Tips
Students don’t take the cases seriously or don’t show empathy for the characters. Remind students that everyone has felt mistreated or discriminated against for some reason at one point or another. It may be helpful to have students engage in a reflective exercise where they think or write about a time when they have felt judged or mistreated by their peers. Ask students how they would have liked to have been treated in their own situation.
Students seem to care about the characters’ feelings, but they don’t know how to help. Try opening up a class brainstorm session about ways to help or support the characters in this story—for example, they could stick up for Jessica when she is harassed, or they could encourage Nate to join the childcare course.
Students’ responses suggest they care about the characters, but their everyday actions suggest that they don’t care about actual gender discrimination in real life. Try asking students to reflect silently on instances in their own lives where they have seen other students treated differently or badly based on gender. Ask students to reflect on what they could have done to improve the situation.
Students start sharing personal stories aloud. From the beginning of the discussion, encourage students to focus on the case and questions, rather than sharing many personal stories aloud. The sharing of personal stories can be emotionally triggering for some students and can be difficult to manage in a classroom setting. If students attempt to tell many personal stories or the conversation becomes too heated or emotional, re-direct the conversation to focus on the case. If very personal or emotional content is brought up and re-directed, make sure to follow up with individual students after the class period, as needed. It is important that students know that you care about their concerns and experiences.
Discussion Questions
What is going on at Adams? Is Adams an extreme example of gender discrimination or is it just a typical school? How is your school the same or different than Adams?
Why did no one stand up for Jessica when she was teased? What would you do? What would your best self-have done in this scenario?
Jessica felt that the girls’ team was treated differently than the boys’ team. Why would girls’ teams be treated differently? Why is this a problem? What would you do if you were running sports programs at your school? Would you have co-ed teams?
Nate assumed that the other guys at Adams would tease him about joining a childcare program. Is Nate’s decision harmful? To himself? To others? Why? What would you have done if you were Nate? Why? Have you ever not done an activity because you worried about what others would think?
We’re you surprised that the CEO of the tech company that visited Adams was a woman? Why or why not? Why is it problematic to make assumptions about a person’s gender based on their job or title?
Why is it problematic that so few women are CEOs and that so few are involved in technology development?
What are ways that boys and girls are treated differently in your school? Are any of these ways problematic? If so, why are they problems? What can be done to fix them?
If you were the principal of Adams, what would you do to challenge the gender biases in the school?
Last reviewed October 2018.
Related Resources


Case Study: Gender Equality, Anti-Discrimination at Tokyo 2020
Author - Centre for Sport and Human Rights
The Tokyo 2020 Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games, postponed by one year due to the Covid-19 pandemic, took place in a highly unique context and served as an opportunity to bring people back together. In its 2016 Action and Legacy Plan , the Tokyo Organising Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games (TOCOG) highlighted “Achieving Personal Best, Unity in Diversity and Connecting to Tomorrow” as its main legacy objectives. This legacy plan highlighted five pillars to achieve this goal. The Centre for Sport and Human Rights collaborated with TOCOG specifically on the “Unity in Diversity” aspect, and supporting TOCOG who wanted to embody diversity and inclusion (D&I), and ensure that nobody would experience discrimination throughout the preparation and operation of the Games.
Like many countries, Japan has long had a paternalistic culture creating gender equality issues and sexism. While preparing to host the Games, Japan recognised that this culture needed to change – for example, despite business and human rights being a relatively new topic in Japan, TOCOG was determined to leave a legacy based on human rights setting ‘human rights, labour and fair business practices’ as one of the key priorities in its pre-Games Sustainability Report .
The Centre supported TOCOG in two key ways toward realising this objective – the first was in providing access to a network of D&I experts and reviewing guidelines and training materials that were being developed. The second was offering support on further promoting gender equality.
Focus on Anti-Discrimination :
D&I was a relatively new topic in Japan, which is why TOCOG decided to use the opportunity of the Games to shine a spotlight on anti-discrimination and D&I efforts. Before the Games, workshops were organised for volunteers to train them on guidelines around anti-discrimination, including outlining scenarios of what could happen, how to react and how to respond to the situation and questions related to it. The Operational Readiness Program provided information on all the different venues, including information from test events and each department was required to be aware of the guidelines and how to implement them. This Program helped identify football for example as a higher risk sport regarding discrimination, which meant special training for the venue, sports team, staff, and others. Different training was offered to staff (who followed all guidelines) and volunteers (who were given general training and additional training depending on the venue)
The Centre supported TOCOG in its anti-discrimination efforts by first providing a briefing to TOCOG on the human rights that could be infringed upon by discriminatory practices, as well as good examples from other sport federations to give an idea on how to respond. The Centre also connected TOCOG with corporate partners who had a long history of implementing anti-discrimination within their workplaces. These corporates shared materials they used to train staff. Finally, the Centre connected TOCOG with other sport federations, as well as the FARE Network – international experts in anti-discrimination in sport. Together, they were able to identify a list of potentially offensive banners, flags and phrases that volunteers should look out for during the event. One example of where this training was used was during the Games, there was an incident with a spectator waving a “Rising Sun” flag (seen as a symbol of Japanese militarism and colonialism during World War II, and therefore considered discriminatory by affected populations). Security was able to talk to the spectator in question and after understanding the situation, put away the flag. This was a good example of a calm, appropriate response to a potentially defamatory situation. Whilst many of the potential benefits were denied by the lack of spectators, a lasting legacy was still realised by those who received the training.
Focus on Gender Equality :
In February 2021, just a few months before the start of the Games, then President of TOCOG Yoshiro Mori caused chaos in Japanese society by making a sexist comment which had a huge impact on the media, young Japanese people, and the public who called for it to be an opportunity to change Japanese culture. TOCOG itself recognised in its post-Games inclusion case study that they had work to do on gender, noting that the country had ranked 101 out of 135 on WEF’s Gender Gap Index. Following this scandal, a female president was put in place at TOCOG, alongside female Directors who were added to the Board. Whilst there was criticism from some NGOs that these posts were simply for show, it still sent a strong message to Japanese society. This was complemented with several programmes put in place by TOCOG to accelerate gender equality. Some positive examples include:
- TOCOG established a Gender Equality Promotion Team.
- The Tokyo Games were the most gender-balanced in history with 48% of all athletes competing in the Olympics being female and 42% in the Paralympics
- The Tokyo Games were also the first that insisted on having both a male and female flag bearer for each country
- TOCOG ensured the prohibition of photography taken that could lead to sexual harassment and requested gender-equal and fair reporting of all athletes.
The Centre also provided a briefing to TOCOG suggesting ways in which it could capitalise on the opportunity to use these Games as an opportunity to advance gender equality in Japan and the wider region.

- athletes competing in the Olympics being female : 48%
- athletes competing in the Paralympics being female : 42%
Key Takeaways :
- Despite the success of the Games, Covid-19 limited the opportunities to present the accomplishments and the preparations made ahead of the Games in order to build a society where unity in diversity and inclusion are part of the reality.
- Collaboration and open management were emphasised by organisers as a key point and the Centre for Sport and Human Rights (CSHR) was recognised as a constructive partner introducing TOCOG to organisations like FIFA, FARE, and others.
- It was also emphasised that every host has its own culture and needs to adapt to different elements of the Games.
- Throughout the preparation and the delivery of the Games, communication was one of the most powerful elements of it – it was necessary at every interface, including with the stakeholders.
- Finally, it is important to recognise that one can never get everything right, but organisers can share mistakes and lessons with partners to continue to grow
Related Articles

The Impact of a Sport Mega Event in the Right to Access Public Education: The Case of the Porto Alegre Communities Affected by the 2014 Brazil World Cup

Sport Ecosystem Responses to the Invasion of Ukraine

Case Study: Tokyo 2020 Pro Bono Legal Mechanism

Case Study: Managing Acts of Discrimination and Activism at Mega-Sporting Events
- Publications
What Works in Gender and Health in the United Nations – Case Study Series
Explore gender mainstreaming in health across five UN agencies, detailing 14 case studies of programmatic and institutional achievements.
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
Welcome to the What Works in Gender and Health in the United Nations Case Study Series page. The United Nations University International Institute for Global Health (UNU-IIGH) co-produced with partners a report documenting practice-based lessons across five UN agencies working in global health analyzing what has worked, where, for whom, why and how, to promote gender equality in health. The research involved in-depth analyses of 14 case studies that were considered examples of successful programmatic and institutional gender mainstreaming across five UN agencies (UNAIDS, UNDP, UNFPA, UNICEF, WHO). Each brief presents further details about each case study, including the successful outcomes achieved, the pre-existing contextual factors that enabled success, the factors that triggered positive change, and the mechanisms that sustained these changes over time.
Additionally, a complimentary Compendium detailing the history of gender mainstreaming across the five UN institutes, and an executive summary giving an overview of the findings are found below. For case study details, this page outlines the key takeaways and recommendations based on this project's findings.
Download the 14 Case studies here .
Download the Compendium here .
Download the Executive Summary here .
Case Reports
This Case Study Series consists of individual briefs for each of the 14 successful cases analyzed as part of the “What Works in Gender and Health in the UN” report. The case studies categorized into three groups based on the types of successful outcomes achieved, reflecting the different levels that UN agencies work on and illustrating the capabilities and strengths of the UN system, namely those that:
- empowered women and girls to resist harmful gender norms and practices and advocate for their own health needs;
- put gender and health issues on the global agenda;
- embedded gender equality issues in institutional processes and structures that supported gender equality in health programming.
Key Takeaways
Cases that empowered women and girls to resist harmful gender norms and practices and advocate for their own health needs:.
- Case study 1 : Empowering girls and women to challenge harmful gender norms to improve menstrual health and hygiene, implemented as part of a WASH programme (UNICEF)
- Case study 2 : Empowering women and girls to resist gender and social norms that encourage female genital mutilation, promote positive masculinities, and strive for more equal gender power relations (Phase 3 of UNFPA-UNICEF Joint Programme on the Abandonment of FGM)
- Case study 3 : Empowering women and marginalised groups living with HIV in MENA (UNAIDS Secretariat, regional team).
Cases that put gender and health issues on the global agenda:
- Case study 4 : HIV reduction and the empowerment of adolescent girls and young women in decision-making through the adoption and implementation of comprehensive HIV programmes in South Africa (UNAIDS Secretariat country office)
- Case study 5 : Violence against women acknowledged as a global public health priority through sustained strategic leveraging of opportunities by WHO gender experts
- Case study 6 : GBV in humanitarian settings prioritised in the global agenda through UNFPA’s leadership and advocacy.
Cases that embedded gender equality issues in institutional processes and structures that supported gender equality in health programming:
- Case study 7 : Enabling the rights of women and girls through enhanced legal, policy and regulatory environments in the context of HIV (supported by the UNDP HIV, Health and Development group)
- Case study 8 : Institutional integration of gender across all technical programmes, Member State health programmes, and the Pan American Health Organization
- Case study 9 : Institutional integration of gender at global, regional and country levels, including in health (UNICEF)
- Case study 10 : Member State implementation of gender-responsive programmes, including in the health sector, through the strategic use of Gender Programmatic Reviews Central (UNICEF regional and country offices, Europe and Central Asia)
- Case study 11 : Changes in institutional culture within UNAIDS Secretariat to support gender equality brought about by the Independent Expert Panel
- Case study 12 : Adequate financial allocations for programmes advancing gender equality and women’s empowerment through effective use of the Gender Equality Marker (UNFPA)
- Case study 13 : Integration of gender into the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases (WHO)
- Case study 14 : Improved institutional and programmatic gender mainstreaming through increased participation in the Gender Equality Seal (UNDP)
Download all figures here .
Related content

KNOW your rights
09 Aug 2024

Case Study: Hate Speech
30 Jul 2024

Case Study: The Democratic Republic of the Congo
Applying the un human rights due diligence policy in peacebuilding.
26 Jul 2024
Latest at Reach

Fostering Connections in New York: Youth Leadership and the Power of Global Change
The reach alliance.
Munk School of Global Affairs & Public Policy at the University of Toronto
1 Devonshire Place, Toronto, Ontario, M5S 3K7 Canada
General Inquiries
reachalliance.munk@utoronto.ca
Case Studies

The Reach Alliance is committed to being a prominent hub of inclusive knowledge production. We prioritize knowledge, knowers, and ways of knowing that have been traditionally disengaged and marginalized from ‘legitimate’ academic knowledge. We work with research collaborators to share findings with the global insight community, project implementers, those that contributed to the research, and those that can benefit from the research directly. We do so in ways that amplify the perspectives of those who have historically been left out or silenced in these discussions.

Academic Partner
Research Status
Research year.

Case Study India
Cutting Through the Grass Ceiling: Supporting Women Smallholder Farmers with the Collective Power of Community, Participatory Learning, and Trust
SDG 1 SDG 3 SDG 5 SDG 13

Case Study Mali
Social Art for Behavioural Change (SABC): Promoting WASH in Mali
SDG 3 SDG 5 SDG 6 SDG 8 SDG 9 SDG 11

Case Study Mexico
Strengthening Small Family Businesses in Tequila, Mexico
SDG 5 SDG 8 SDG 10

The City Seen By Women: The Appropriation of Public Spaces from a Gender Perspective
SDG 5 SDG 10 SDG 16

Case Study United Kingdom
Accessing Maternal Healthcare in a Hostile Environment
SDG 3 SDG 5 SDG 10

Case Study Morocco
Water in the Desert: Dar Si Hmad’s Fog-Harvesting Program
SDG 5 SDG 9 SDG 11 SDG 12 SDG 6 SDG 15 SDG 13

Case Study Nepal
Empowered Community and Local Ownership: The Hariyo Ban “Green Forest” Project
SDG 10 SDG 5 SDG 11 SDG 13

The “Kolombia Regia”: Social Vindication in the Face of Stigma and Violence in Monterrey
SDG 1 SDG 10 SDG 16 SDG 5

Women Defenders of Jalisco: Combatting Land Deterioration
SDG 5 SDG 11 SDG 12 SDG 15 SDG 6

Maternal Healthcare for Women with Disabilities in Nepal
SDG 3 SDG 10 SDG 5

Case Study South Africa
Access to Maternal Healthcare Services for Women Who are Unhoused in Cape Town, South Africa

Incarceration and Innocence: Early childhood development of children of imprisoned women living in the Mexican penitentiary system
SDG 10 SDG 5 SDG 3 SDG 4
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 25 Jun 2024
- Research & Ideas
Rapport: The Hidden Advantage That Women Managers Bring to Teams
Lack of communication between managers and their employees can hurt productivity and even undermine the customer experience. Female managers are more adept at building rapport among mixed-gender teams, which can improve an organization’s performance, says research by Jorge Tamayo.
- 18 Jun 2024
What Your Non-Binary Employees Need to Do Their Best Work
How can you break down gender boundaries and support the non-binary people on your team better? A study by Katherine Coffman reveals the motivations and aspirations of non-binary employees, highlighting the need for greater inclusion to unlock the full potential of a diverse workforce.

- 04 Mar 2024
Want to Make Diversity Stick? Break the Cycle of Sameness
Whether on judicial benches or in corporate boardrooms, white men are more likely to step into roles that other white men vacate, says research by Edward Chang. But when people from historically marginalized groups land those positions, workforce diversification tends to last. Chang offers three pieces of advice for leaders striving for diversity.

- 14 Sep 2023
Working Moms Are Mostly Thriving Again. Can We Finally Achieve Gender Parity?
The pandemic didn't destroy the workplace advancements moms had achieved. However, not all of the positive changes forced by the crisis and remote work have stuck, says research by Kathleen McGinn and Alexandra Feldberg.

- 26 Jul 2023
STEM Needs More Women. Recruiters Often Keep Them Out
Tech companies and programs turn to recruiters to find top-notch candidates, but gender bias can creep in long before women even apply, according to research by Jacqueline Ng Lane and colleagues. She highlights several tactics to make the process more equitable.

- 18 Jul 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
Diversity and Inclusion at Mars Petcare: Translating Awareness into Action
In 2020, the Mars Petcare leadership team found themselves facing critically important inclusion and diversity issues. Unprecedented protests for racial justice in the U.S. and across the globe generated demand for substantive change, and Mars Petcare's 100,000 employees across six continents were ready for visible signs of progress. How should Mars’ leadership build on their existing diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts and effectively capitalize on the new energy for change? Harvard Business School associate professor Katherine Coffman is joined by Erica Coletta, Mars Petcare’s chief people officer, and Ibtehal Fathy, global inclusion and diversity officer at Mars Inc., to discuss the case, “Inclusion and Diversity at Mars Petcare.”

- 03 Mar 2023
When Showing Know-How Backfires for Women Managers
Women managers might think they need to roll up their sleeves and work alongside their teams to show their mettle. But research by Alexandra Feldberg shows how this strategy can work against them. How can employers provide more support?

- 31 Jan 2023
Addressing Racial Discrimination on Airbnb
For years, Airbnb gave hosts extensive discretion to accept or reject a guest after seeing little more than a name and a picture, believing that eliminating anonymity was the best way for the company to build trust. However, the apartment rental platform failed to track or account for the possibility that this could facilitate discrimination. After research published by Professor Michael Luca and others provided evidence that Black hosts received less in rent than hosts of other races and showed signs of discrimination against guests with African American sounding names, the company had to decide what to do. In the case, “Racial Discrimination on Airbnb,” Luca discusses his research and explores the implication for Airbnb and other platform companies. Should they change the design of the platform to reduce discrimination? And what’s the best way to measure the success of any changes?

- 03 Jan 2023
Confront Workplace Inequity in 2023: Dig Deep, Build Bridges, Take Collective Action
Power dynamics tied up with race and gender underlie almost every workplace interaction, says Tina Opie. In her book Shared Sisterhood, she offers three practical steps for dismantling workplace inequities that hold back innovation.

- 29 Nov 2022
How Will Gamers and Investors Respond to Microsoft’s Acquisition of Activision Blizzard?
In January 2022, Microsoft announced its acquisition of the video game company Activision Blizzard for $68.7 billion. The deal would make Microsoft the world’s third largest video game company, but it also exposes the company to several risks. First, the all-cash deal would require Microsoft to use a large portion of its cash reserves. Second, the acquisition was announced as Activision Blizzard faced gender pay disparity and sexual harassment allegations. That opened Microsoft up to potential reputational damage, employee turnover, and lost sales. Do the potential benefits of the acquisition outweigh the risks for Microsoft and its shareholders? Harvard Business School associate professor Joseph Pacelli discusses the ongoing controversies around the merger and how gamers and investors have responded in the case, “Call of Fiduciary Duty: Microsoft Acquires Activision Blizzard.”

- 10 Nov 2022
Too Nice to Lead? Unpacking the Gender Stereotype That Holds Women Back
People mistakenly assume that women managers are more generous and fair when it comes to giving money, says research by Christine Exley. Could that misperception prevent companies from shrinking the gender pay gap?

- 08 Nov 2022
How Centuries of Restrictions on Women Shed Light on Today's Abortion Debate
Going back to pre-industrial times, efforts to limit women's sexuality have had a simple motive: to keep them faithful to their spouses. Research by Anke Becker looks at the deep roots of these restrictions and their economic implications.

- 01 Nov 2022
Marie Curie: A Case Study in Breaking Barriers
Marie Curie, born Maria Sklodowska from a poor family in Poland, rose to the pinnacle of scientific fame in the early years of the twentieth century, winning the Nobel Prize twice in the fields of physics and chemistry. At the time women were simply not accepted in scientific fields so Curie had to overcome enormous obstacles in order to earn a doctorate at the Sorbonne and perform her pathbreaking research on radioactive materials. How did she plan her time and navigate her life choices to leave a lasting impact on the world? Professor Robert Simons discusses how Marie Curie rose to scientific fame despite poverty and gender barriers in his case, “Marie Curie: Changing the World.”

- 18 Oct 2022
When Bias Creeps into AI, Managers Can Stop It by Asking the Right Questions
Even when companies actively try to prevent it, bias can sway algorithms and skew decision-making. Ayelet Israeli and Eva Ascarza offer a new approach to make artificial intelligence more accurate.

- 29 Jul 2022
Will Demand for Women Executives Finally Shrink the Gender Pay Gap?
Women in senior management have more negotiation power than they think in today's labor market, says research by Paul Healy and Boris Groysberg. Is it time for more women to seek better opportunities and bigger pay?

- 24 May 2022
Career Advice for Minorities and Women: Sharing Your Identity Can Open Doors
Women and people of color tend to minimize their identities in professional situations, but highlighting who they are often forces others to check their own biases. Research by Edward Chang and colleagues.

- 08 Mar 2022
Representation Matters: Building Case Studies That Empower Women Leaders
The lessons of case studies shape future business leaders, but only a fraction of these teaching tools feature women executives. Research by Colleen Ammerman and Boris Groysberg examines the gender gap in cases and its implications. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 22 Feb 2022
Lack of Female Scientists Means Fewer Medical Treatments for Women
Women scientists are more likely to develop treatments for women, but many of their ideas never become inventions, research by Rembrand Koning says. What would it take to make innovation more equitable? Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 01 Sep 2021
How Women Can Learn from Even Biased Feedback
Gender bias often taints performance reviews, but applying three principles can help women gain meaningful insights, says Francesca Gino. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 23 Jun 2021
One More Way the Startup World Hampers Women Entrepreneurs
Early feedback is essential to launching new products, but women entrepreneurs are more likely to receive input from men. Research by Rembrand Koning, Ramana Nanda, and Ruiqing Cao. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 06 September 2023
Gender equality: the route to a better world
You have full access to this article via your institution.
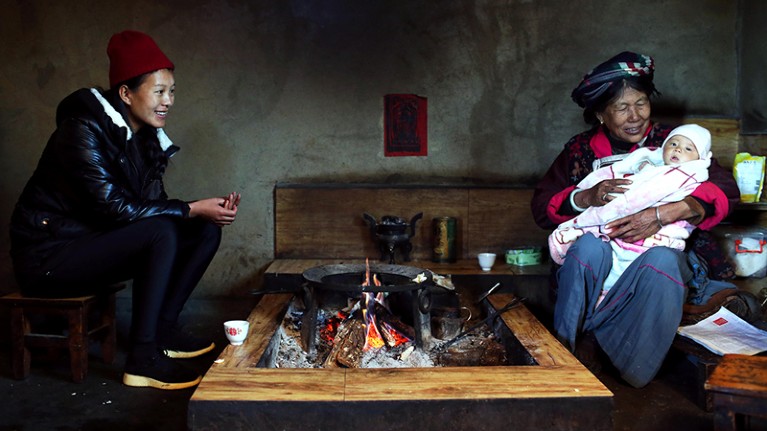

The Mosuo people of China include sub-communities in which inheritance passes down either the male or the female line. Credit: TPG/Getty
The fight for global gender equality is nowhere close to being won. Take education: in 87 countries, less than half of women and girls complete secondary schooling, according to 2023 data. Afghanistan’s Taliban continues to ban women and girls from secondary schools and universities . Or take reproductive health: abortion rights have been curtailed in 22 US states since the Supreme Court struck down federal protections, depriving women and girls of autonomy and restricting access to sexual and reproductive health care .
SDG 5, whose stated aim is to “achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls”, is the fifth of the 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, all of which Nature is examining in a series of editorials. SDG 5 includes targets for ending discrimination and violence against women and girls in both public and private spheres, eradicating child marriage and female genital mutilation, ensuring sexual and reproductive rights, achieving equal representation of women in leadership positions and granting equal rights to economic resources. Globally, the goal is not on track to being achieved, and just a handful of countries have hit all the targets.

How the world should oppose the Taliban’s war on women and girls
In July, the UN introduced two new indices (see go.nature.com/3eus9ue ), the Women’s Empowerment Index (WEI) and the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI). The WEI measures women’s ability and freedoms to make their own choices; the GGPI describes the gap between women and men in areas such as health, education, inclusion and decision making. The indices reveal, depressingly, that even achieving a small gender gap does not automatically translate to high levels of women’s empowerment: 114 countries feature in both indices, but countries that do well on both scores cover fewer than 1% of all girls and women.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made things worse, with women bearing the highest burden of extra unpaid childcare when schools needed to close, and subjected to intensified domestic violence. Although child marriages declined from 21% of all marriages in 2016 to 19% in 2022, the pandemic threatened even this incremental progress, pushing up to 10 million more girls into risk of child marriage over the next decade, in addition to the 100 million girls who were at risk before the pandemic.
Of the 14 indicators for SDG 5, only one or two are close to being met by the 2030 deadline. As of 1 January 2023, women occupied 35.4% of seats in local-government assemblies, an increase from 33.9% in 2020 (the target is gender parity by 2030). In 115 countries for which data were available, around three-quarters, on average, of the necessary laws guaranteeing full and equal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights had been enacted. But the UN estimates that worldwide, only 57% of women who are married or in a union make their own decisions regarding sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Systemic discrimination against girls and women by men, in many contexts, remains a colossal barrier to achieving gender equality. But patriarchy is not some “natural order of things” , argues Ruth Mace, an anthropologist at University College London. Hundreds of women-centred societies exist around the world. As the science writer Angela Saini describes in her latest book, The Patriarchs , these are often not the polar opposite of male-dominated systems, but societies in which men and women share decision making .

After Roe v. Wade: dwindling US abortion access is harming health a year later
One example comes from the Mosuo people in China, who have both ‘matrilineal’ and ‘patrilineal’ communities, with rights such as inheritance passing down either the male or female line. Researchers compared outcomes for inflammation and hypertension in men and women in these communities, and found that women in matrilineal societies, in which they have greater autonomy and control over resources, experienced better health outcomes. The researchers found no significant negative effect of matriliny on health outcomes for men ( A. Z. Reynolds et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 30324–30327; 2020 ).
When it comes to the SDGs, evidence is emerging that a more gender-equal approach to politics and power benefits many goals. In a study published in May, Nobue Amanuma, deputy director of the Integrated Sustainability Centre at the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies in Hayama, Japan, and two of her colleagues tested whether countries with more women legislators, and more younger legislators, are performing better in the SDGs ( N. Amanuma et al. Environ. Res. Lett. 18 , 054018; 2023 ). They found it was so, with the effect more marked for socio-economic goals such as ending poverty and hunger, than for environmental ones such as climate action or preserving life on land. The researchers recommend further qualitative and quantitative studies to better understand the reasons.
The reality that gender equality leads to better outcomes across other SDGs is not factored, however, into most of the goals themselves. Of the 230 unique indicators of the SDGs, 51 explicitly reference women, girls, gender or sex, including the 14 indicators in SDG 5. But there is not enough collaboration between organizations responsible for the different SDGs to ensure that sex and gender are taken into account. The indicator for the sanitation target (SDG 6) does not include data disaggregated by sex or gender ( Nature 620 , 7; 2023 ). Unless we have this knowledge, it will be hard to track improvements in this and other SDGs.
The road to a gender-equal world is long, and women’s power and freedom to make choices is still very constrained. But the evidence from science is getting stronger: distributing power between genders creates the kind of world we all need and want to be living in.
Nature 621 , 8 (2023)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-02745-9
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Sustainability
- Public health

Waste management won’t solve the plastics problem — we need to cut consumption
News & Views 04 SEP 24

Light bulbs have energy ratings — so why can’t AI chatbots?
Comment 21 AUG 24
Monitor soil health using advanced technologies
Correspondence 23 JUL 24

Mpox is spreading rapidly. Here are the questions researchers are racing to answer
News Explainer 28 AUG 24
What accelerates brain ageing? This AI ‘brain clock’ points to answers
News 27 AUG 24

Mysterious Oropouche virus is spreading: what you should know
News Q&A 26 AUG 24

Brazil’s ban on X: how scientists are coping with the cutoff
News 06 SEP 24

The Taliban said women could study — three years on they still can’t
News 14 AUG 24

Who is legally responsible for climate harms? The world’s top court will now decide
Editorial 13 AUG 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Genetic Epidemiology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
NOMIS Foundation ETH Postdoctoral Fellowship
The NOMIS Foundation ETH Fellowship Programme supports postdoctoral researchers at ETH Zurich within the Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life ...
Zurich, Canton of Zürich (CH)
Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life at ETH Zurich
13 PhD Positions at Heidelberg University
GRK2727/1 – InCheck Innate Immune Checkpoints in Cancer and Tissue Damage
Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg (DE) and Mannheim, Baden-Württemberg (DE)
Medical Faculties Mannheim & Heidelberg and DKFZ, Germany
Postdoctoral Associate- Environmental Epidemiology
Open faculty positions at the state key laboratory of brain cognition & brain-inspired intelligence.
The laboratory focuses on understanding the mechanisms of brain intelligence and developing the theory and techniques of brain-inspired intelligence.
Shanghai, China
CAS Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Explainer: How gender inequality and climate change are interconnected
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to E-mail

Gender inequality coupled with the climate crisis is one of the greatest challenges of our time. It poses threats to ways of life, livelihoods, health, safety and security for women and girls around the world.
Historically, climate change scientists, researchers and policymakers have struggled with how to make the vital connections between gender, social equity, and climate change. As more and more data and research reveal their clear correlation, it’s time to talk about the disparate impacts of climate change and the linkages between women’s empowerment and effective, global climate action.
On International Women’s Day, we take a look at how climate change impacts women and girls, why gender equality is key to climate action, and what you can do to support solutions for women, by women.

How does climate change impact women and girls?
The climate crisis is not “gender neutral”. Women and girls experience the greatest impacts of climate change, which amplifies existing gender inequalities and poses unique threats to their livelihoods, health, and safety.
Across the world, women depend more on, yet have less access to, natural resources. In many regions, women bear a disproportionate responsibility for securing food, water, and fuel. Agriculture is the most important employment sector for women in low- and lower-middle income countries, during periods of drought and erratic rainfall, women, as agricultural workers and primary procurers, work harder to secure income and resources for their families. This puts added pressure on girls, who often have to leave school to help their mothers manage the increased burden.

Climate change is a “threat multiplier”, meaning it escalates social, political and economic tensions in fragile and conflict-affected settings. As climate change drives conflict across the world, women and girls face increased vulnerabilities to all forms of gender-based violence, including conflict-related sexual violence, human trafficking, child marriage, and other forms of violence.
When disasters strike, women are less likely to survive and more likely to be injured due to long standing gender inequalities that have created disparities in information, mobility, decision-making, and access to resources and training. In the aftermath, women and girls are less able to access relief and assistance, further threatening their livelihoods, wellbeing and recovery, and creating a vicious cycle of vulnerability to future disasters.
Women’s and girls’ health is endangered by climate change and disasters by limiting access to services and health care, as well as increasing risks related to maternal and child health. Research indicates that extreme heat increases incidence of stillbirth, and climate change is increasing the spread of vector-borne illnesses such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus, which are linked to worse maternal and neonatal outcomes .

How does climate change intersect with other inequalities for women and girls?
While women and girls experience disproportionate impacts from climate change at the global level, the effects are not uniform. Looking at climate change through the lens of intersectional feminism , the way in which various forms of inequality often operate together and exacerbate each other, it is clear that climate change risks are acute for indigenous and Afro-descendent women and girls, older women, LGBTIQ+ people, women and girls with disabilities, migrant women, and those living in rural, remote, conflict and disaster-prone areas.

“If you are invisible in everyday life, your needs will not be thought of, let alone addressed, in a crisis situation,” says Matcha Phorn-In , a lesbian feminist human-rights defender who works to empower stateless and landless Indigenous women, girls and young LGBTIQ+ people in Thailand’s Chiang Mai, Mae Hong Son, and Tak provinces. “Humanitarian programmes tend to be heteronormative and can reinforce the patriarchal structure of society if they do not take into account sexual and gender diversity,” Phorn-in explains. “In addressing structural change, we are advocating for and working towards equality of all kinds.”

In the Brazilian Amazon, Dandara Rudsan , a Black and trans activist and an environmental racism specialist in the Public Defender’s Office of Pará State, knows firsthand that centering the experiences and challenges faced by different groups illuminates the connections between all fights for justice and liberation.
“In the Amazon, defending human rights means fighting for the survival of people and the rainforest every day, but there is no hierarchy between agendas… To finance social movements in the Amazon is to finance the survival of these communities, these people, and the rainforest.”
- Climate change
- Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, intersex (LGBT) rights
Related content

‘You have the power to change’ – Young women in South Africa break through stigma and poverty and inspire others

In search of safety – LGBTIQ+ people on the move


LGBTIQ+ migrants face unique risks, starting with the perception that they are second-class citizens – Interview with migrant rights activist Rey Perez Asis from The Philippines
Target Gender Equality Case Studies & Profiles
Check out how leaders move the needle for gender equality, target gender equality case studies.
Europe & North America
- Starlight Media - Aligning with WEPs to achieve gender equality internally and externally
- Calik Denim - Inspiring ideas across the board with well-framed human resource practices
- Domino Tekstil - Building innovative solutions by incorporating women in production
- Yildiz Holding - Creating opportunities through inclusion, equality and pluralism in the workplace
- Caixabank - Developing diversity to improve gender equality
- Solunion Seguros - Promoting equality by eliminating discrimination in the workplace
- BIOAZUL - Creating a balanced workplace to prevent gender-based discrimination
For more stories of local impact, check out our past newsletters .

- East African Breweries Ltd . - Reflecting the diversity of the communities they serve
- RA International - Tailoring programs for women to equalize opportunities

- Capgemini India - Tackling gender bias to enhance inclusion
- Martha Tilaar Group - Harnessing the power of women by providing equal opportunities
- MAS Holdings - Empowering women to yield growth-oriented results

Latin America and the Caribbean
- Ripipsa - Cultivating an inclusive work environment by promoting female leadership
- Special Dog Company - Utilizing different perspectives from a diverse workforce
- BBVA Mexico - Achieving gender parity in leadership positions
- Solunion Seguros - Promoting equality by eliminating discrimination in the workplace
- Mutualista Pinchicha - Utilizing the Women’s Empowerment Principles to generate positive impacts everywhere
- Enagás - Reducing the gender gap by keeping female talent at the forefront
- Natura & Co. - Closing the gender gap using accountability and transparency
- Enagás - Enagás has undertaken internal and external communication initiatives to put on the map its activity and to attract female talent through testimonials from leading women at Enagás.

Profiles of Target Gender Equality Leaders

Instead of focusing on what we failed, focus on what we achieved.

Don’t ever doubt yourself. You probably know more than you think. All you have to do is just give it a shot.

At ReNew Power, Vaishali Nigam Sinha implements impact-oriented sustainability and gender parity across all levels of her organization

Proper mentorship and support from male counterparts increases female leadership in the workplace, says Tahmina Zaman Khan of Mutual Trust Bank

At Absa Bank, Jane Waiyaki embodies the spirit of capacity building and transformational change when it comes to gender equality.

Training tailored for women goes a long way in evening out system-built skill disparities between men and women, says Sharon Thuku of Ends International

At SuperHuman Race, Gagandeep K. Bhullar empowers people from all walks of life, genders, and ethnic groups to drive forward equality at every level

Promoting education, equality and diversity helps unlock human potential and organizational growth for Marijana Bačić at Hrvatski Telekom

Eva Muñoz strategically implements small changes to create a trickle-down effect towards normalizing the broader SDGs in the work culture at Solunion Seguros

At the UNGC Lebanon Network, Bruno Elias creates change by striving to break structural and cultural barriers to women’s labor-market participation

For Catherine Haslam, actively setting goals and targets accelerates the pace of change in achieving gender equality at DWF

Pilaar Zapata Aranda implements the principles of a circular economy at BIOAZUL S.L. to drive forward sustainable change in the long run

Sara Hernández advocates for more female mentors to create an impact on young women’s career trajectories at BIOAZUL S.L

Diversity and inclusion go a long way in creating a growth-oriented work culture, says Harriet Quiney from DWF

For Marisol Amo, education, trust, and awareness are vital towards establishing a diverse work culture at Europa Mundo Vaccaciones

Promoting family-oriented work models based on productivity & flexible timing for men and women is crucial for Ana Belén Montosa at BIOAZUL S.L.

At the Central Bank of Egypt, May Abulnaga helps save women by increasing their access to financial inclusion and fighting the uphill battle against typical Egyptian gender norms

As a Member of Parliament in Namibia, Emma Inamutila Theofelus is doing her part in overturning patriarchal systems by advocating for women’s representation in public offices and political decision-making processes

For Angela Magno Malagón, utilizing women’s unique perspectives and capacity for analysis is paramount for achieving success at BIOAZUL S.L.

At Sasini PLC, Martin Ochien’g is actively achieving gender equity not just in leadership but also at all levels of his organization by setting ambitious goals that trickle down from the top to the bottom

At JKH, Krishan Balendra upholds the values of gender equality and sustainability by breaking typical gender norms in hotel businesses while also advocating for sustainable practices through his recycling projects

We, men, sometimes don't understand something because we don't live it. We don’t suffer that discrimination and sexist jokes. How men and women interact is different now than three years ago when we started our efforts. It’s more like a partnership.

When you start to pay attention, you really see inequality, but more importantly, you see how men could play an important role.

Diversity is one of the best tools that we have to achieve our goals as an organization.

It’s about human capital as much as it is around natural capital. As a business, it's going to help us be more successful, and ultimately it’s going to help our clients be more successful.

Among the most successful and pragmatic strategies at International SOS has been mentoring and training promising female talent around the world to put them on a leadership track.

As Chairperson of the Board of Directors, I led the remarkable turnaround and return to profitability of the 20-year FBN Insurance Brokers.

Our company, Europamundo, and Kuoni Tulmare, our partner organization, both belong to the JTB Group, the biggest travel agency in Japan.
- TECHNOLOGY BUSINESS ENTERPRISE COMMS START-UPS ALL
- SCIENCE INNOVATION MACHINES CLIMATE ALL
- CAREERS ADVICE PEOPLE EMPLOYERS JOBS NEWS ALL
- FUTURE HUMAN
- MORE VIDEO ADVERTISE FOLLOW US CONTACT ABOUT COOKIE & PRIVACY POLICY
5 case studies of companies trying to correct the gender gap
by Eva Short
28 Nov 2018
The gender gap is one of the most contentious diversity issues in the world of work. These are just a few of the companies who have taken action to try and correct the issue.
It is no secret that the tech industry has struggled with a diversity problem. The problem spans all levels of business, from how female and minority employees are compensated, to their representation at all employee levels. However, the promise of a turning point is on the horizon as more companies start to pay attention and address the issue.
Research has continually shown that diverse teams outperform non-diverse teams financially. Knowing this, HR professionals at top firms have started to prioritise diversity in recruitment above all else.
In April 2018, the first slew of gender pay gap data was released in the UK following a law that was passed mandating large enterprises to do so. Prior to this, Iceland brought in legislation requiring organisations to provide proof that men and women are being compensated fairly, or face daily fines .
Many companies have taken steps to address gender gap issues. In a few cases, such as with tech giant Google , the efforts were found to be lacking. Yet in other cases, changes made have led to significant progress in addressing gender disparity. Here are some of the companies who have recently made inroads in this area, and how they did it.
Duolingo CEO and co-founder Luis von Ahn took to Twitter in October to highlight how the company had achieved a 50:50 ratio for new software engineer hires. Grimly, yet perhaps unsurprisingly, the response the company received was dominated by, in Von Ahn’s words, “men angrily arguing discrimination, and that we should hire the best people instead”.
Duolingo just tweeted about how we achieved a 50% female ratio of new engineering college graduate hires. We're very proud of this. I'm disappointed that the top comments were all from men angrily arguing discrimination, and that we should hire the best people instead. Idiots. https://t.co/WHjq2WnKzH — Luis von Ahn (@LuisvonAhn) October 11, 2018
The co-founder took great issue with this idea that promoting diversity somehow compromises quality. According to Von Ahn, all female hires had “either perfect or near-perfect GPAs from the best universities in the world, with stellar recommendations, and aced our very thorough interview process”.
Duolingo achieved its 50:50 ratio through a multipronged, data-driven approach. It only recruited from colleges with more than the US national average (18pc) of women enrolled in their computer science programmes, such as Duke, Cornell, Harvard and MIT. It then reached out to the women groups at each school and went along to any network events it held. It sponsored the 2017 Grace Hopper Conference and had all its female engineers attend. Finally, Duolingo says it put all its interviewers through unconscious bias training.
Duolingo has expressed a continued commitment to promoting diversity and gender parity in the workplace through both internal and external action.
Since Salesforce started examining its pay gap in 2016, it has shelled out $6m in order to correct compensation imbalances.
Join us to create the technology of tomorrow
Make work more human
Think for impact with Liberty IT. Delivering global software solutions
Join us to start Caring. Connecting. Growing together
This action aligns with promises that Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff made in 2015 in an interview with HuffPost. “My job is to make sure that women are treated 100pc equally at Salesforce in pay, opportunity and advancement,” Benioff said, noting that while he did not know what the gender pay gap was at the time, he was determined to find out and act accordingly.
Salesforce committed to undertaking regular pay audits, reflecting the fact that pay equity is, as executive VP of global employee success Cindy Robbins put it , “a moving target”.
In March 2018, Bloomberg editor in chief John Micklethwait announced a new staff policy regarding outside speaking engagement. So as to promote gender equality both within the newsroom and outside it, it is now a requirement that at least one woman is on any panel in order for a Bloomberg journalist to participate. “At the risk of stating the obvious, the woman could be you,” Micklethwait noted.
If this condition is not met, journalists will be required to decline, though there seems to be an appeals system in place if a journalist feels their participation on an all-male panel is necessary. “But I think this is a standard that we should be able to uphold on the vast majority of occasion,” Micklethwait concluded.
At cloud-based HR and payroll software company Gusto, the journey to gender parity began when software engineer Julia Lee asked Gusto co-founder and chief technology officer Edward Kim for a meeting. In it, she flagged that she was the only woman on the engineering team and disclosed her previous experiences of being dismissed due to her gender. Kim was receptive, and made a point to examine the gender breakdowns of other tech companies.
The results were dismal to say the least, so Kim met with Gusto’s HR team to come up with a strategy to address the issue. First, it elected to move away from using ‘masculine’ phrases such as “ninja rockstar coder” in its job ads. For the first six months of 2018, it focused solely on recruiting female engineers, though made a point to equally consider any men who approached the company so it would not breach anti-discrimination laws.
Like Duolingo, it sent representatives to the Grace Hopper conference. Now, Gusto reports that 51pc of its staff are women and more than 24pc of its engineers are women.
It also submitted to gender pay auditing by human resources firm Mercer, which found no disparity. It offers 16 weeks’ paid leave complete with generous grocery and housecleaning benefits for a primary parent.
Nike has had a year peppered with controversy in the world of gender, culminating when four women hit the sportswear company with a lawsuit over alleged discrimination. The women maintain that Nike violated US equal pay laws and fostered a work environment that allowed for sexual harassment, The Guardian reported in August of this year.
Prior to the suit being filed, Nike responded to the issues raised by ousting a number of high-profile executives in what was termed a “ harassment reckoning ”. A month before the suit was filed, Nike HR chief Monique Matheson admitted in a staff memo obtained by The Wall Street Journal that the company had failed women and that it wants to “to create a culture of true inclusion” and that, in order to do this, it needs to “improve representation of women and people of colour”. That same month, the company revealed that it planned to adjust the pay of 7,000 of its employees after an internal compensation review in order to address pay disparities.
Nike is arguably in the more nascent stages of dealing with its issues. These steps are more about putting out fires than they are about instituting structural change, but it’s an excellent start from the footwear giant.
Related: equality , software engineers , Salesforce , diversity
Eva Short was a journalist at Silicon Republic, specialising in the areas of tech, data privacy, business, cybersecurity, AI, automation and future of work, among others.
10 things you need to know, direct to your inbox
Sign up for the Daily Brief, Silicon Republic's weekday digest of essential sci-tech news
More from careers
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Twenty years of gender equality research: A scoping review based on a new semantic indicator
Contributed equally to this work with: Paola Belingheri, Filippo Chiarello, Andrea Fronzetti Colladon, Paola Rovelli
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell’Energia, dei Sistemi, del Territorio e delle Costruzioni, Università degli Studi di Pisa, Largo L. Lazzarino, Pisa, Italy
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Department of Engineering, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy, Department of Management, Kozminski University, Warsaw, Poland
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Faculty of Economics and Management, Centre for Family Business Management, Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, Bozen-Bolzano, Italy
- Paola Belingheri,
- Filippo Chiarello,
- Andrea Fronzetti Colladon,
- Paola Rovelli

- Published: September 21, 2021
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474
- Reader Comments
9 Nov 2021: The PLOS ONE Staff (2021) Correction: Twenty years of gender equality research: A scoping review based on a new semantic indicator. PLOS ONE 16(11): e0259930. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259930 View correction
Gender equality is a major problem that places women at a disadvantage thereby stymieing economic growth and societal advancement. In the last two decades, extensive research has been conducted on gender related issues, studying both their antecedents and consequences. However, existing literature reviews fail to provide a comprehensive and clear picture of what has been studied so far, which could guide scholars in their future research. Our paper offers a scoping review of a large portion of the research that has been published over the last 22 years, on gender equality and related issues, with a specific focus on business and economics studies. Combining innovative methods drawn from both network analysis and text mining, we provide a synthesis of 15,465 scientific articles. We identify 27 main research topics, we measure their relevance from a semantic point of view and the relationships among them, highlighting the importance of each topic in the overall gender discourse. We find that prominent research topics mostly relate to women in the workforce–e.g., concerning compensation, role, education, decision-making and career progression. However, some of them are losing momentum, and some other research trends–for example related to female entrepreneurship, leadership and participation in the board of directors–are on the rise. Besides introducing a novel methodology to review broad literature streams, our paper offers a map of the main gender-research trends and presents the most popular and the emerging themes, as well as their intersections, outlining important avenues for future research.
Citation: Belingheri P, Chiarello F, Fronzetti Colladon A, Rovelli P (2021) Twenty years of gender equality research: A scoping review based on a new semantic indicator. PLoS ONE 16(9): e0256474. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474
Editor: Elisa Ughetto, Politecnico di Torino, ITALY
Received: June 25, 2021; Accepted: August 6, 2021; Published: September 21, 2021
Copyright: © 2021 Belingheri et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its supporting information files. The only exception is the text of the abstracts (over 15,000) that we have downloaded from Scopus. These abstracts can be retrieved from Scopus, but we do not have permission to redistribute them.
Funding: P.B and F.C.: Grant of the Department of Energy, Systems, Territory and Construction of the University of Pisa (DESTEC) for the project “Measuring Gender Bias with Semantic Analysis: The Development of an Assessment Tool and its Application in the European Space Industry. P.B., F.C., A.F.C., P.R.: Grant of the Italian Association of Management Engineering (AiIG), “Misure di sostegno ai soci giovani AiIG” 2020, for the project “Gender Equality Through Data Intelligence (GEDI)”. F.C.: EU project ASSETs+ Project (Alliance for Strategic Skills addressing Emerging Technologies in Defence) EAC/A03/2018 - Erasmus+ programme, Sector Skills Alliances, Lot 3: Sector Skills Alliance for implementing a new strategic approach (Blueprint) to sectoral cooperation on skills G.A. NUMBER: 612678-EPP-1-2019-1-IT-EPPKA2-SSA-B.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The persistent gender inequalities that currently exist across the developed and developing world are receiving increasing attention from economists, policymakers, and the general public [e.g., 1 – 3 ]. Economic studies have indicated that women’s education and entry into the workforce contributes to social and economic well-being [e.g., 4 , 5 ], while their exclusion from the labor market and from managerial positions has an impact on overall labor productivity and income per capita [ 6 , 7 ]. The United Nations selected gender equality, with an emphasis on female education, as part of the Millennium Development Goals [ 8 ], and gender equality at-large as one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to be achieved by 2030 [ 9 ]. These latter objectives involve not only developing nations, but rather all countries, to achieve economic, social and environmental well-being.
As is the case with many SDGs, gender equality is still far from being achieved and persists across education, access to opportunities, or presence in decision-making positions [ 7 , 10 , 11 ]. As we enter the last decade for the SDGs’ implementation, and while we are battling a global health pandemic, effective and efficient action becomes paramount to reach this ambitious goal.
Scholars have dedicated a massive effort towards understanding gender equality, its determinants, its consequences for women and society, and the appropriate actions and policies to advance women’s equality. Many topics have been covered, ranging from women’s education and human capital [ 12 , 13 ] and their role in society [e.g., 14 , 15 ], to their appointment in firms’ top ranked positions [e.g., 16 , 17 ] and performance implications [e.g., 18 , 19 ]. Despite some attempts, extant literature reviews provide a narrow view on these issues, restricted to specific topics–e.g., female students’ presence in STEM fields [ 20 ], educational gender inequality [ 5 ], the gender pay gap [ 21 ], the glass ceiling effect [ 22 ], leadership [ 23 ], entrepreneurship [ 24 ], women’s presence on the board of directors [ 25 , 26 ], diversity management [ 27 ], gender stereotypes in advertisement [ 28 ], or specific professions [ 29 ]. A comprehensive view on gender-related research, taking stock of key findings and under-studied topics is thus lacking.
Extant literature has also highlighted that gender issues, and their economic and social ramifications, are complex topics that involve a large number of possible antecedents and outcomes [ 7 ]. Indeed, gender equality actions are most effective when implemented in unison with other SDGs (e.g., with SDG 8, see [ 30 ]) in a synergetic perspective [ 10 ]. Many bodies of literature (e.g., business, economics, development studies, sociology and psychology) approach the problem of achieving gender equality from different perspectives–often addressing specific and narrow aspects. This sometimes leads to a lack of clarity about how different issues, circumstances, and solutions may be related in precipitating or mitigating gender inequality or its effects. As the number of papers grows at an increasing pace, this issue is exacerbated and there is a need to step back and survey the body of gender equality literature as a whole. There is also a need to examine synergies between different topics and approaches, as well as gaps in our understanding of how different problems and solutions work together. Considering the important topic of women’s economic and social empowerment, this paper aims to fill this gap by answering the following research question: what are the most relevant findings in the literature on gender equality and how do they relate to each other ?
To do so, we conduct a scoping review [ 31 ], providing a synthesis of 15,465 articles dealing with gender equity related issues published in the last twenty-two years, covering both the periods of the MDGs and the SDGs (i.e., 2000 to mid 2021) in all the journals indexed in the Academic Journal Guide’s 2018 ranking of business and economics journals. Given the huge amount of research conducted on the topic, we adopt an innovative methodology, which relies on social network analysis and text mining. These techniques are increasingly adopted when surveying large bodies of text. Recently, they were applied to perform analysis of online gender communication differences [ 32 ] and gender behaviors in online technology communities [ 33 ], to identify and classify sexual harassment instances in academia [ 34 ], and to evaluate the gender inclusivity of disaster management policies [ 35 ].
Applied to the title, abstracts and keywords of the articles in our sample, this methodology allows us to identify a set of 27 recurrent topics within which we automatically classify the papers. Introducing additional novelty, by means of the Semantic Brand Score (SBS) indicator [ 36 ] and the SBS BI app [ 37 ], we assess the importance of each topic in the overall gender equality discourse and its relationships with the other topics, as well as trends over time, with a more accurate description than that offered by traditional literature reviews relying solely on the number of papers presented in each topic.
This methodology, applied to gender equality research spanning the past twenty-two years, enables two key contributions. First, we extract the main message that each document is conveying and how this is connected to other themes in literature, providing a rich picture of the topics that are at the center of the discourse, as well as of the emerging topics. Second, by examining the semantic relationship between topics and how tightly their discourses are linked, we can identify the key relationships and connections between different topics. This semi-automatic methodology is also highly reproducible with minimum effort.
This literature review is organized as follows. In the next section, we present how we selected relevant papers and how we analyzed them through text mining and social network analysis. We then illustrate the importance of 27 selected research topics, measured by means of the SBS indicator. In the results section, we present an overview of the literature based on the SBS results–followed by an in-depth narrative analysis of the top 10 topics (i.e., those with the highest SBS) and their connections. Subsequently, we highlight a series of under-studied connections between the topics where there is potential for future research. Through this analysis, we build a map of the main gender-research trends in the last twenty-two years–presenting the most popular themes. We conclude by highlighting key areas on which research should focused in the future.
Our aim is to map a broad topic, gender equality research, that has been approached through a host of different angles and through different disciplines. Scoping reviews are the most appropriate as they provide the freedom to map different themes and identify literature gaps, thereby guiding the recommendation of new research agendas [ 38 ].
Several practical approaches have been proposed to identify and assess the underlying topics of a specific field using big data [ 39 – 41 ], but many of them fail without proper paper retrieval and text preprocessing. This is specifically true for a research field such as the gender-related one, which comprises the work of scholars from different backgrounds. In this section, we illustrate a novel approach for the analysis of scientific (gender-related) papers that relies on methods and tools of social network analysis and text mining. Our procedure has four main steps: (1) data collection, (2) text preprocessing, (3) keywords extraction and classification, and (4) evaluation of semantic importance and image.
Data collection
In this study, we analyze 22 years of literature on gender-related research. Following established practice for scoping reviews [ 42 ], our data collection consisted of two main steps, which we summarize here below.
Firstly, we retrieved from the Scopus database all the articles written in English that contained the term “gender” in their title, abstract or keywords and were published in a journal listed in the Academic Journal Guide 2018 ranking of the Chartered Association of Business Schools (CABS) ( https://charteredabs.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/AJG2018-Methodology.pdf ), considering the time period from Jan 2000 to May 2021. We used this information considering that abstracts, titles and keywords represent the most informative part of a paper, while using the full-text would increase the signal-to-noise ratio for information extraction. Indeed, these textual elements already demonstrated to be reliable sources of information for the task of domain lexicon extraction [ 43 , 44 ]. We chose Scopus as source of literature because of its popularity, its update rate, and because it offers an API to ease the querying process. Indeed, while it does not allow to retrieve the full text of scientific articles, the Scopus API offers access to titles, abstracts, citation information and metadata for all its indexed scholarly journals. Moreover, we decided to focus on the journals listed in the AJG 2018 ranking because we were interested in reviewing business and economics related gender studies only. The AJG is indeed widely used by universities and business schools as a reference point for journal and research rigor and quality. This first step, executed in June 2021, returned more than 55,000 papers.
In the second step–because a look at the papers showed very sparse results, many of which were not in line with the topic of this literature review (e.g., papers dealing with health care or medical issues, where the word gender indicates the gender of the patients)–we applied further inclusion criteria to make the sample more focused on the topic of this literature review (i.e., women’s gender equality issues). Specifically, we only retained those papers mentioning, in their title and/or abstract, both gender-related keywords (e.g., daughter, female, mother) and keywords referring to bias and equality issues (e.g., equality, bias, diversity, inclusion). After text pre-processing (see next section), keywords were first identified from a frequency-weighted list of words found in the titles, abstracts and keywords in the initial list of papers, extracted through text mining (following the same approach as [ 43 ]). They were selected by two of the co-authors independently, following respectively a bottom up and a top-down approach. The bottom-up approach consisted of examining the words found in the frequency-weighted list and classifying those related to gender and equality. The top-down approach consisted in searching in the word list for notable gender and equality-related words. Table 1 reports the sets of keywords we considered, together with some examples of words that were used to search for their presence in the dataset (a full list is provided in the S1 Text ). At end of this second step, we obtained a final sample of 15,465 relevant papers.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.t001
Text processing and keyword extraction
Text preprocessing aims at structuring text into a form that can be analyzed by statistical models. In the present section, we describe the preprocessing steps we applied to paper titles and abstracts, which, as explained below, partially follow a standard text preprocessing pipeline [ 45 ]. These activities have been performed using the R package udpipe [ 46 ].
The first step is n-gram extraction (i.e., a sequence of words from a given text sample) to identify which n-grams are important in the analysis, since domain-specific lexicons are often composed by bi-grams and tri-grams [ 47 ]. Multi-word extraction is usually implemented with statistics and linguistic rules, thus using the statistical properties of n-grams or machine learning approaches [ 48 ]. However, for the present paper, we used Scopus metadata in order to have a more effective and efficient n-grams collection approach [ 49 ]. We used the keywords of each paper in order to tag n-grams with their associated keywords automatically. Using this greedy approach, it was possible to collect all the keywords listed by the authors of the papers. From this list, we extracted only keywords composed by two, three and four words, we removed all the acronyms and rare keywords (i.e., appearing in less than 1% of papers), and we clustered keywords showing a high orthographic similarity–measured using a Levenshtein distance [ 50 ] lower than 2, considering these groups of keywords as representing same concepts, but expressed with different spelling. After tagging the n-grams in the abstracts, we followed a common data preparation pipeline that consists of the following steps: (i) tokenization, that splits the text into tokens (i.e., single words and previously tagged multi-words); (ii) removal of stop-words (i.e. those words that add little meaning to the text, usually being very common and short functional words–such as “and”, “or”, or “of”); (iii) parts-of-speech tagging, that is providing information concerning the morphological role of a word and its morphosyntactic context (e.g., if the token is a determiner, the next token is a noun or an adjective with very high confidence, [ 51 ]); and (iv) lemmatization, which consists in substituting each word with its dictionary form (or lemma). The output of the latter step allows grouping together the inflected forms of a word. For example, the verbs “am”, “are”, and “is” have the shared lemma “be”, or the nouns “cat” and “cats” both share the lemma “cat”. We preferred lemmatization over stemming [ 52 ] in order to obtain more interpretable results.
In addition, we identified a further set of keywords (with respect to those listed in the “keywords” field) by applying a series of automatic words unification and removal steps, as suggested in past research [ 53 , 54 ]. We removed: sparse terms (i.e., occurring in less than 0.1% of all documents), common terms (i.e., occurring in more than 10% of all documents) and retained only nouns and adjectives. It is relevant to notice that no document was lost due to these steps. We then used the TF-IDF function [ 55 ] to produce a new list of keywords. We additionally tested other approaches for the identification and clustering of keywords–such as TextRank [ 56 ] or Latent Dirichlet Allocation [ 57 ]–without obtaining more informative results.
Classification of research topics
To guide the literature analysis, two experts met regularly to examine the sample of collected papers and to identify the main topics and trends in gender research. Initially, they conducted brainstorming sessions on the topics they expected to find, due to their knowledge of the literature. This led to an initial list of topics. Subsequently, the experts worked independently, also supported by the keywords in paper titles and abstracts extracted with the procedure described above.
Considering all this information, each expert identified and clustered relevant keywords into topics. At the end of the process, the two assignments were compared and exhibited a 92% agreement. Another meeting was held to discuss discordant cases and reach a consensus. This resulted in a list of 27 topics, briefly introduced in Table 2 and subsequently detailed in the following sections.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.t002
Evaluation of semantic importance
Working on the lemmatized corpus of the 15,465 papers included in our sample, we proceeded with the evaluation of semantic importance trends for each topic and with the analysis of their connections and prevalent textual associations. To this aim, we used the Semantic Brand Score indicator [ 36 ], calculated through the SBS BI webapp [ 37 ] that also produced a brand image report for each topic. For this study we relied on the computing resources of the ENEA/CRESCO infrastructure [ 58 ].
The Semantic Brand Score (SBS) is a measure of semantic importance that combines methods of social network analysis and text mining. It is usually applied for the analysis of (big) textual data to evaluate the importance of one or more brands, names, words, or sets of keywords [ 36 ]. Indeed, the concept of “brand” is intended in a flexible way and goes beyond products or commercial brands. In this study, we evaluate the SBS time-trends of the keywords defining the research topics discussed in the previous section. Semantic importance comprises the three dimensions of topic prevalence, diversity and connectivity. Prevalence measures how frequently a research topic is used in the discourse. The more a topic is mentioned by scientific articles, the more the research community will be aware of it, with possible increase of future studies; this construct is partly related to that of brand awareness [ 59 ]. This effect is even stronger, considering that we are analyzing the title, abstract and keywords of the papers, i.e. the parts that have the highest visibility. A very important characteristic of the SBS is that it considers the relationships among words in a text. Topic importance is not just a matter of how frequently a topic is mentioned, but also of the associations a topic has in the text. Specifically, texts are transformed into networks of co-occurring words, and relationships are studied through social network analysis [ 60 ]. This step is necessary to calculate the other two dimensions of our semantic importance indicator. Accordingly, a social network of words is generated for each time period considered in the analysis–i.e., a graph made of n nodes (words) and E edges weighted by co-occurrence frequency, with W being the set of edge weights. The keywords representing each topic were clustered into single nodes.
The construct of diversity relates to that of brand image [ 59 ], in the sense that it considers the richness and distinctiveness of textual (topic) associations. Considering the above-mentioned networks, we calculated diversity using the distinctiveness centrality metric–as in the formula presented by Fronzetti Colladon and Naldi [ 61 ].
Lastly, connectivity was measured as the weighted betweenness centrality [ 62 , 63 ] of each research topic node. We used the formula presented by Wasserman and Faust [ 60 ]. The dimension of connectivity represents the “brokerage power” of each research topic–i.e., how much it can serve as a bridge to connect other terms (and ultimately topics) in the discourse [ 36 ].
The SBS is the final composite indicator obtained by summing the standardized scores of prevalence, diversity and connectivity. Standardization was carried out considering all the words in the corpus, for each specific timeframe.
This methodology, applied to a large and heterogeneous body of text, enables to automatically identify two important sets of information that add value to the literature review. Firstly, the relevance of each topic in literature is measured through a composite indicator of semantic importance, rather than simply looking at word frequencies. This provides a much richer picture of the topics that are at the center of the discourse, as well as of the topics that are emerging in the literature. Secondly, it enables to examine the extent of the semantic relationship between topics, looking at how tightly their discourses are linked. In a field such as gender equality, where many topics are closely linked to each other and present overlaps in issues and solutions, this methodology offers a novel perspective with respect to traditional literature reviews. In addition, it ensures reproducibility over time and the possibility to semi-automatically update the analysis, as new papers become available.
Overview of main topics
In terms of descriptive textual statistics, our corpus is made of 15,465 text documents, consisting of a total of 2,685,893 lemmatized tokens (words) and 32,279 types. As a result, the type-token ratio is 1.2%. The number of hapaxes is 12,141, with a hapax-token ratio of 37.61%.
Fig 1 shows the list of 27 topics by decreasing SBS. The most researched topic is compensation , exceeding all others in prevalence, diversity, and connectivity. This means it is not only mentioned more often than other topics, but it is also connected to a greater number of other topics and is central to the discourse on gender equality. The next four topics are, in order of SBS, role , education , decision-making , and career progression . These topics, except for education , all concern women in the workforce. Between these first five topics and the following ones there is a clear drop in SBS scores. In particular, the topics that follow have a lower connectivity than the first five. They are hiring , performance , behavior , organization , and human capital . Again, except for behavior and human capital , the other three topics are purely related to women in the workforce. After another drop-off, the following topics deal prevalently with women in society. This trend highlights that research on gender in business journals has so far mainly paid attention to the conditions that women experience in business contexts, while also devoting some attention to women in society.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.g001
Fig 2 shows the SBS time series of the top 10 topics. While there has been a general increase in the number of Scopus-indexed publications in the last decade, we notice that some SBS trends remain steady, or even decrease. In particular, we observe that the main topic of the last twenty-two years, compensation , is losing momentum. Since 2016, it has been surpassed by decision-making , education and role , which may indicate that literature is increasingly attempting to identify root causes of compensation inequalities. Moreover, in the last two years, the topics of hiring , performance , and organization are experiencing the largest importance increase.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.g002
Fig 3 shows the SBS time trends of the remaining 17 topics (i.e., those not in the top 10). As we can see from the graph, there are some that maintain a steady trend–such as reputation , management , networks and governance , which also seem to have little importance. More relevant topics with average stationary trends (except for the last two years) are culture , family , and parenting . The feminine topic is among the most important here, and one of those that exhibit the larger variations over time (similarly to leadership ). On the other hand, the are some topics that, even if not among the most important, show increasing SBS trends; therefore, they could be considered as emerging topics and could become popular in the near future. These are entrepreneurship , leadership , board of directors , and sustainability . These emerging topics are also interesting to anticipate future trends in gender equality research that are conducive to overall equality in society.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.g003
In addition to the SBS score of the different topics, the network of terms they are associated to enables to gauge the extent to which their images (textual associations) overlap or differ ( Fig 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.g004
There is a central cluster of topics with high similarity, which are all connected with women in the workforce. The cluster includes topics such as organization , decision-making , performance , hiring , human capital , education and compensation . In addition, the topic of well-being is found within this cluster, suggesting that women’s equality in the workforce is associated to well-being considerations. The emerging topics of entrepreneurship and leadership are also closely connected with each other, possibly implying that leadership is a much-researched quality in female entrepreneurship. Topics that are relatively more distant include personality , politics , feminine , empowerment , management , board of directors , reputation , governance , parenting , masculine and network .
The following sections describe the top 10 topics and their main associations in literature (see Table 3 ), while providing a brief overview of the emerging topics.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.t003
Compensation.
The topic of compensation is related to the topics of role , hiring , education and career progression , however, also sees a very high association with the words gap and inequality . Indeed, a well-known debate in degrowth economics centers around whether and how to adequately compensate women for their childbearing, childrearing, caregiver and household work [e.g., 30 ].
Even in paid work, women continue being offered lower compensations than their male counterparts who have the same job or cover the same role [ 64 – 67 ]. This severe inequality has been widely studied by scholars over the last twenty-two years. Dealing with this topic, some specific roles have been addressed. Specifically, research highlighted differences in compensation between female and male CEOs [e.g., 68 ], top executives [e.g., 69 ], and boards’ directors [e.g., 70 ]. Scholars investigated the determinants of these gaps, such as the gender composition of the board [e.g., 71 – 73 ] or women’s individual characteristics [e.g., 71 , 74 ].
Among these individual characteristics, education plays a relevant role [ 75 ]. Education is indeed presented as the solution for women, not only to achieve top executive roles, but also to reduce wage inequality [e.g., 76 , 77 ]. Past research has highlighted education influences on gender wage gaps, specifically referring to gender differences in skills [e.g., 78 ], college majors [e.g., 79 ], and college selectivity [e.g., 80 ].
Finally, the wage gap issue is strictly interrelated with hiring –e.g., looking at whether being a mother affects hiring and compensation [e.g., 65 , 81 ] or relating compensation to unemployment [e.g., 82 ]–and career progression –for instance looking at meritocracy [ 83 , 84 ] or the characteristics of the boss for whom women work [e.g., 85 ].
The roles covered by women have been deeply investigated. Scholars have focused on the role of women in their families and the society as a whole [e.g., 14 , 15 ], and, more widely, in business contexts [e.g., 18 , 81 ]. Indeed, despite still lagging behind their male counterparts [e.g., 86 , 87 ], in the last decade there has been an increase in top ranked positions achieved by women [e.g., 88 , 89 ]. Following this phenomenon, scholars have posed greater attention towards the presence of women in the board of directors [e.g., 16 , 18 , 90 , 91 ], given the increasing pressure to appoint female directors that firms, especially listed ones, have experienced. Other scholars have focused on the presence of women covering the role of CEO [e.g., 17 , 92 ] or being part of the top management team [e.g., 93 ]. Irrespectively of the level of analysis, all these studies tried to uncover the antecedents of women’s presence among top managers [e.g., 92 , 94 ] and the consequences of having a them involved in the firm’s decision-making –e.g., on performance [e.g., 19 , 95 , 96 ], risk [e.g., 97 , 98 ], and corporate social responsibility [e.g., 99 , 100 ].
Besides studying the difficulties and discriminations faced by women in getting a job [ 81 , 101 ], and, more specifically in the hiring , appointment, or career progression to these apical roles [e.g., 70 , 83 ], the majority of research of women’s roles dealt with compensation issues. Specifically, scholars highlight the pay-gap that still exists between women and men, both in general [e.g., 64 , 65 ], as well as referring to boards’ directors [e.g., 70 , 102 ], CEOs and executives [e.g., 69 , 103 , 104 ].
Finally, other scholars focused on the behavior of women when dealing with business. In this sense, particular attention has been paid to leadership and entrepreneurial behaviors. The former quite overlaps with dealing with the roles mentioned above, but also includes aspects such as leaders being stereotyped as masculine [e.g., 105 ], the need for greater exposure to female leaders to reduce biases [e.g., 106 ], or female leaders acting as queen bees [e.g., 107 ]. Regarding entrepreneurship , scholars mainly investigated women’s entrepreneurial entry [e.g., 108 , 109 ], differences between female and male entrepreneurs in the evaluations and funding received from investors [e.g., 110 , 111 ], and their performance gap [e.g., 112 , 113 ].
Education has long been recognized as key to social advancement and economic stability [ 114 ], for job progression and also a barrier to gender equality, especially in STEM-related fields. Research on education and gender equality is mostly linked with the topics of compensation , human capital , career progression , hiring , parenting and decision-making .
Education contributes to a higher human capital [ 115 ] and constitutes an investment on the part of women towards their future. In this context, literature points to the gender gap in educational attainment, and the consequences for women from a social, economic, personal and professional standpoint. Women are found to have less access to formal education and information, especially in emerging countries, which in turn may cause them to lose social and economic opportunities [e.g., 12 , 116 – 119 ]. Education in local and rural communities is also paramount to communicate the benefits of female empowerment , contributing to overall societal well-being [e.g., 120 ].
Once women access education, the image they have of the world and their place in society (i.e., habitus) affects their education performance [ 13 ] and is passed on to their children. These situations reinforce gender stereotypes, which become self-fulfilling prophecies that may negatively affect female students’ performance by lowering their confidence and heightening their anxiety [ 121 , 122 ]. Besides formal education, also the information that women are exposed to on a daily basis contributes to their human capital . Digital inequalities, for instance, stems from men spending more time online and acquiring higher digital skills than women [ 123 ].
Education is also a factor that should boost employability of candidates and thus hiring , career progression and compensation , however the relationship between these factors is not straightforward [ 115 ]. First, educational choices ( decision-making ) are influenced by variables such as self-efficacy and the presence of barriers, irrespectively of the career opportunities they offer, especially in STEM [ 124 ]. This brings additional difficulties to women’s enrollment and persistence in scientific and technical fields of study due to stereotypes and biases [ 125 , 126 ]. Moreover, access to education does not automatically translate into job opportunities for women and minority groups [ 127 , 128 ] or into female access to managerial positions [ 129 ].
Finally, parenting is reported as an antecedent of education [e.g., 130 ], with much of the literature focusing on the role of parents’ education on the opportunities afforded to children to enroll in education [ 131 – 134 ] and the role of parenting in their offspring’s perception of study fields and attitudes towards learning [ 135 – 138 ]. Parental education is also a predictor of the other related topics, namely human capital and compensation [ 139 ].
Decision-making.
This literature mainly points to the fact that women are thought to make decisions differently than men. Women have indeed different priorities, such as they care more about people’s well-being, working with people or helping others, rather than maximizing their personal (or their firm’s) gain [ 140 ]. In other words, women typically present more communal than agentic behaviors, which are instead more frequent among men [ 141 ]. These different attitude, behavior and preferences in turn affect the decisions they make [e.g., 142 ] and the decision-making of the firm in which they work [e.g., 143 ].
At the individual level, gender affects, for instance, career aspirations [e.g., 144 ] and choices [e.g., 142 , 145 ], or the decision of creating a venture [e.g., 108 , 109 , 146 ]. Moreover, in everyday life, women and men make different decisions regarding partners [e.g., 147 ], childcare [e.g., 148 ], education [e.g., 149 ], attention to the environment [e.g., 150 ] and politics [e.g., 151 ].
At the firm level, scholars highlighted, for example, how the presence of women in the board affects corporate decisions [e.g., 152 , 153 ], that female CEOs are more conservative in accounting decisions [e.g., 154 ], or that female CFOs tend to make more conservative decisions regarding the firm’s financial reporting [e.g., 155 ]. Nevertheless, firm level research also investigated decisions that, influenced by gender bias, affect women, such as those pertaining hiring [e.g., 156 , 157 ], compensation [e.g., 73 , 158 ], or the empowerment of women once appointed [ 159 ].
Career progression.
Once women have entered the workforce, the key aspect to achieve gender equality becomes career progression , including efforts toward overcoming the glass ceiling. Indeed, according to the SBS analysis, career progression is highly related to words such as work, social issues and equality. The topic with which it has the highest semantic overlap is role , followed by decision-making , hiring , education , compensation , leadership , human capital , and family .
Career progression implies an advancement in the hierarchical ladder of the firm, assigning managerial roles to women. Coherently, much of the literature has focused on identifying rationales for a greater female participation in the top management team and board of directors [e.g., 95 ] as well as the best criteria to ensure that the decision-makers promote the most valuable employees irrespectively of their individual characteristics, such as gender [e.g., 84 ]. The link between career progression , role and compensation is often provided in practice by performance appraisal exercises, frequently rooted in a culture of meritocracy that guides bonuses, salary increases and promotions. However, performance appraisals can actually mask gender-biased decisions where women are held to higher standards than their male colleagues [e.g., 83 , 84 , 95 , 160 , 161 ]. Women often have less opportunities to gain leadership experience and are less visible than their male colleagues, which constitute barriers to career advancement [e.g., 162 ]. Therefore, transparency and accountability, together with procedures that discourage discretionary choices, are paramount to achieve a fair career progression [e.g., 84 ], together with the relaxation of strict job boundaries in favor of cross-functional and self-directed tasks [e.g., 163 ].
In addition, a series of stereotypes about the type of leadership characteristics that are required for top management positions, which fit better with typical male and agentic attributes, are another key barrier to career advancement for women [e.g., 92 , 160 ].
Hiring is the entrance gateway for women into the workforce. Therefore, it is related to other workforce topics such as compensation , role , career progression , decision-making , human capital , performance , organization and education .
A first stream of literature focuses on the process leading up to candidates’ job applications, demonstrating that bias exists before positions are even opened, and it is perpetuated both by men and women through networking and gatekeeping practices [e.g., 164 , 165 ].
The hiring process itself is also subject to biases [ 166 ], for example gender-congruity bias that leads to men being preferred candidates in male-dominated sectors [e.g., 167 ], women being hired in positions with higher risk of failure [e.g., 168 ] and limited transparency and accountability afforded by written processes and procedures [e.g., 164 ] that all contribute to ascriptive inequality. In addition, providing incentives for evaluators to hire women may actually work to this end; however, this is not the case when supporting female candidates endangers higher-ranking male ones [ 169 ].
Another interesting perspective, instead, looks at top management teams’ composition and the effects on hiring practices, indicating that firms with more women in top management are less likely to lay off staff [e.g., 152 ].
Performance.
Several scholars posed their attention towards women’s performance, its consequences [e.g., 170 , 171 ] and the implications of having women in decision-making positions [e.g., 18 , 19 ].
At the individual level, research focused on differences in educational and academic performance between women and men, especially referring to the gender gap in STEM fields [e.g., 171 ]. The presence of stereotype threats–that is the expectation that the members of a social group (e.g., women) “must deal with the possibility of being judged or treated stereotypically, or of doing something that would confirm the stereotype” [ 172 ]–affects women’s interested in STEM [e.g., 173 ], as well as their cognitive ability tests, penalizing them [e.g., 174 ]. A stronger gender identification enhances this gap [e.g., 175 ], whereas mentoring and role models can be used as solutions to this problem [e.g., 121 ]. Despite the negative effect of stereotype threats on girls’ performance [ 176 ], female and male students perform equally in mathematics and related subjects [e.g., 177 ]. Moreover, while individuals’ performance at school and university generally affects their achievements and the field in which they end up working, evidence reveals that performance in math or other scientific subjects does not explain why fewer women enter STEM working fields; rather this gap depends on other aspects, such as culture, past working experiences, or self-efficacy [e.g., 170 ]. Finally, scholars have highlighted the penalization that women face for their positive performance, for instance when they succeed in traditionally male areas [e.g., 178 ]. This penalization is explained by the violation of gender-stereotypic prescriptions [e.g., 179 , 180 ], that is having women well performing in agentic areas, which are typical associated to men. Performance penalization can thus be overcome by clearly conveying communal characteristics and behaviors [ 178 ].
Evidence has been provided on how the involvement of women in boards of directors and decision-making positions affects firms’ performance. Nevertheless, results are mixed, with some studies showing positive effects on financial [ 19 , 181 , 182 ] and corporate social performance [ 99 , 182 , 183 ]. Other studies maintain a negative association [e.g., 18 ], and other again mixed [e.g., 184 ] or non-significant association [e.g., 185 ]. Also with respect to the presence of a female CEO, mixed results emerged so far, with some researches demonstrating a positive effect on firm’s performance [e.g., 96 , 186 ], while other obtaining only a limited evidence of this relationship [e.g., 103 ] or a negative one [e.g., 187 ].
Finally, some studies have investigated whether and how women’s performance affects their hiring [e.g., 101 ] and career progression [e.g., 83 , 160 ]. For instance, academic performance leads to different returns in hiring for women and men. Specifically, high-achieving men are called back significantly more often than high-achieving women, which are penalized when they have a major in mathematics; this result depends on employers’ gendered standards for applicants [e.g., 101 ]. Once appointed, performance ratings are more strongly related to promotions for women than men, and promoted women typically show higher past performance ratings than those of promoted men. This suggesting that women are subject to stricter standards for promotion [e.g., 160 ].
Behavioral aspects related to gender follow two main streams of literature. The first examines female personality and behavior in the workplace, and their alignment with cultural expectations or stereotypes [e.g., 188 ] as well as their impacts on equality. There is a common bias that depicts women as less agentic than males. Certain characteristics, such as those more congruent with male behaviors–e.g., self-promotion [e.g., 189 ], negotiation skills [e.g., 190 ] and general agentic behavior [e.g., 191 ]–, are less accepted in women. However, characteristics such as individualism in women have been found to promote greater gender equality in society [ 192 ]. In addition, behaviors such as display of emotions [e.g., 193 ], which are stereotypically female, work against women’s acceptance in the workplace, requiring women to carefully moderate their behavior to avoid exclusion. A counter-intuitive result is that women and minorities, which are more marginalized in the workplace, tend to be better problem-solvers in innovation competitions due to their different knowledge bases [ 194 ].
The other side of the coin is examined in a parallel literature stream on behavior towards women in the workplace. As a result of biases, prejudices and stereotypes, women may experience adverse behavior from their colleagues, such as incivility and harassment, which undermine their well-being [e.g., 195 , 196 ]. Biases that go beyond gender, such as for overweight people, are also more strongly applied to women [ 197 ].
Organization.
The role of women and gender bias in organizations has been studied from different perspectives, which mirror those presented in detail in the following sections. Specifically, most research highlighted the stereotypical view of leaders [e.g., 105 ] and the roles played by women within firms, for instance referring to presence in the board of directors [e.g., 18 , 90 , 91 ], appointment as CEOs [e.g., 16 ], or top executives [e.g., 93 ].
Scholars have investigated antecedents and consequences of the presence of women in these apical roles. On the one side they looked at hiring and career progression [e.g., 83 , 92 , 160 , 168 , 198 ], finding women typically disadvantaged with respect to their male counterparts. On the other side, they studied women’s leadership styles and influence on the firm’s decision-making [e.g., 152 , 154 , 155 , 199 ], with implications for performance [e.g., 18 , 19 , 96 ].
Human capital.
Human capital is a transverse topic that touches upon many different aspects of female gender equality. As such, it has the most associations with other topics, starting with education as mentioned above, with career-related topics such as role , decision-making , hiring , career progression , performance , compensation , leadership and organization . Another topic with which there is a close connection is behavior . In general, human capital is approached both from the education standpoint but also from the perspective of social capital.
The behavioral aspect in human capital comprises research related to gender differences for example in cultural and religious beliefs that influence women’s attitudes and perceptions towards STEM subjects [ 142 , 200 – 202 ], towards employment [ 203 ] or towards environmental issues [ 150 , 204 ]. These cultural differences also emerge in the context of globalization which may accelerate gender equality in the workforce [ 205 , 206 ]. Gender differences also appear in behaviors such as motivation [ 207 ], and in negotiation [ 190 ], and have repercussions on women’s decision-making related to their careers. The so-called gender equality paradox sees women in countries with lower gender equality more likely to pursue studies and careers in STEM fields, whereas the gap in STEM enrollment widens as countries achieve greater equality in society [ 171 ].
Career progression is modeled by literature as a choice-process where personal preferences, culture and decision-making affect the chosen path and the outcomes. Some literature highlights how women tend to self-select into different professions than men, often due to stereotypes rather than actual ability to perform in these professions [ 142 , 144 ]. These stereotypes also affect the perceptions of female performance or the amount of human capital required to equal male performance [ 110 , 193 , 208 ], particularly for mothers [ 81 ]. It is therefore often assumed that women are better suited to less visible and less leadership -oriented roles [ 209 ]. Women also express differing preferences towards work-family balance, which affect whether and how they pursue human capital gains [ 210 ], and ultimately their career progression and salary .
On the other hand, men are often unaware of gendered processes and behaviors that they carry forward in their interactions and decision-making [ 211 , 212 ]. Therefore, initiatives aimed at increasing managers’ human capital –by raising awareness of gender disparities in their organizations and engaging them in diversity promotion–are essential steps to counter gender bias and segregation [ 213 ].
Emerging topics: Leadership and entrepreneurship
Among the emerging topics, the most pervasive one is women reaching leadership positions in the workforce and in society. This is still a rare occurrence for two main types of factors, on the one hand, bias and discrimination make it harder for women to access leadership positions [e.g., 214 – 216 ], on the other hand, the competitive nature and high pressure associated with leadership positions, coupled with the lack of women currently represented, reduce women’s desire to achieve them [e.g., 209 , 217 ]. Women are more effective leaders when they have access to education, resources and a diverse environment with representation [e.g., 218 , 219 ].
One sector where there is potential for women to carve out a leadership role is entrepreneurship . Although at the start of the millennium the discourse on entrepreneurship was found to be “discriminatory, gender-biased, ethnocentrically determined and ideologically controlled” [ 220 ], an increasing body of literature is studying how to stimulate female entrepreneurship as an alternative pathway to wealth, leadership and empowerment [e.g., 221 ]. Many barriers exist for women to access entrepreneurship, including the institutional and legal environment, social and cultural factors, access to knowledge and resources, and individual behavior [e.g., 222 , 223 ]. Education has been found to raise women’s entrepreneurial intentions [e.g., 224 ], although this effect is smaller than for men [e.g., 109 ]. In addition, increasing self-efficacy and risk-taking behavior constitute important success factors [e.g., 225 ].
Finally, the topic of sustainability is worth mentioning, as it is the primary objective of the SDGs and is closely associated with societal well-being. As society grapples with the effects of climate change and increasing depletion of natural resources, a narrative has emerged on women and their greater link to the environment [ 226 ]. Studies in developed countries have found some support for women leaders’ attention to sustainability issues in firms [e.g., 227 – 229 ], and smaller resource consumption by women [ 230 ]. At the same time, women will likely be more affected by the consequences of climate change [e.g., 230 ] but often lack the decision-making power to influence local decision-making on resource management and environmental policies [e.g., 231 ].
Research gaps and conclusions
Research on gender equality has advanced rapidly in the past decades, with a steady increase in publications, both in mainstream topics related to women in education and the workforce, and in emerging topics. Through a novel approach combining methods of text mining and social network analysis, we examined a comprehensive body of literature comprising 15,465 papers published between 2000 and mid 2021 on topics related to gender equality. We identified a set of 27 topics addressed by the literature and examined their connections.
At the highest level of abstraction, it is worth noting that papers abound on the identification of issues related to gender inequalities and imbalances in the workforce and in society. Literature has thoroughly examined the (unconscious) biases, barriers, stereotypes, and discriminatory behaviors that women are facing as a result of their gender. Instead, there are much fewer papers that discuss or demonstrate effective solutions to overcome gender bias [e.g., 121 , 143 , 145 , 163 , 194 , 213 , 232 ]. This is partly due to the relative ease in studying the status quo, as opposed to studying changes in the status quo. However, we observed a shift in the more recent years towards solution seeking in this domain, which we strongly encourage future researchers to focus on. In the future, we may focus on collecting and mapping pro-active contributions to gender studies, using additional Natural Language Processing techniques, able to measure the sentiment of scientific papers [ 43 ].
All of the mainstream topics identified in our literature review are closely related, and there is a wealth of insights looking at the intersection between issues such as education and career progression or human capital and role . However, emerging topics are worthy of being furtherly explored. It would be interesting to see more work on the topic of female entrepreneurship , exploring aspects such as education , personality , governance , management and leadership . For instance, how can education support female entrepreneurship? How can self-efficacy and risk-taking behaviors be taught or enhanced? What are the differences in managerial and governance styles of female entrepreneurs? Which personality traits are associated with successful entrepreneurs? Which traits are preferred by venture capitalists and funding bodies?
The emerging topic of sustainability also deserves further attention, as our society struggles with climate change and its consequences. It would be interesting to see more research on the intersection between sustainability and entrepreneurship , looking at how female entrepreneurs are tackling sustainability issues, examining both their business models and their company governance . In addition, scholars are suggested to dig deeper into the relationship between family values and behaviors.
Moreover, it would be relevant to understand how women’s networks (social capital), or the composition and structure of social networks involving both women and men, enable them to increase their remuneration and reach top corporate positions, participate in key decision-making bodies, and have a voice in communities. Furthermore, the achievement of gender equality might significantly change firm networks and ecosystems, with important implications for their performance and survival.
Similarly, research at the nexus of (corporate) governance , career progression , compensation and female empowerment could yield useful insights–for example discussing how enterprises, institutions and countries are managed and the impact for women and other minorities. Are there specific governance structures that favor diversity and inclusion?
Lastly, we foresee an emerging stream of research pertaining how the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic challenged women, especially in the workforce, by making gender biases more evident.
For our analysis, we considered a set of 15,465 articles downloaded from the Scopus database (which is the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature). As we were interested in reviewing business and economics related gender studies, we only considered those papers published in journals listed in the Academic Journal Guide (AJG) 2018 ranking of the Chartered Association of Business Schools (CABS). All the journals listed in this ranking are also indexed by Scopus. Therefore, looking at a single database (i.e., Scopus) should not be considered a limitation of our study. However, future research could consider different databases and inclusion criteria.
With our literature review, we offer researchers a comprehensive map of major gender-related research trends over the past twenty-two years. This can serve as a lens to look to the future, contributing to the achievement of SDG5. Researchers may use our study as a starting point to identify key themes addressed in the literature. In addition, our methodological approach–based on the use of the Semantic Brand Score and its webapp–could support scholars interested in reviewing other areas of research.
Supporting information
S1 text. keywords used for paper selection..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256474.s001
Acknowledgments
The computing resources and the related technical support used for this work have been provided by CRESCO/ENEAGRID High Performance Computing infrastructure and its staff. CRESCO/ENEAGRID High Performance Computing infrastructure is funded by ENEA, the Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development and by Italian and European research programmes (see http://www.cresco.enea.it/english for information).
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 9. UN. Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. General Assembley 70 Session; 2015.
- 11. Nature. Get the Sustainable Development Goals back on track. Nature. 2020;577(January 2):7–8
- 37. Fronzetti Colladon A, Grippa F. Brand intelligence analytics. In: Przegalinska A, Grippa F, Gloor PA, editors. Digital Transformation of Collaboration. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland; 2020. p. 125–41. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233276 pmid:32442196
- 39. Griffiths TL, Steyvers M, editors. Finding scientific topics. National academy of Sciences; 2004.
- 40. Mimno D, Wallach H, Talley E, Leenders M, McCallum A, editors. Optimizing semantic coherence in topic models. 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; 2011.
- 41. Wang C, Blei DM, editors. Collaborative topic modeling for recommending scientific articles. 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining 2011.
- 46. Straka M, Straková J, editors. Tokenizing, pos tagging, lemmatizing and parsing ud 2.0 with udpipe. CoNLL 2017 Shared Task: Multilingual Parsing from Raw Text to Universal Dependencies; 2017.
- 49. Lu Y, Li, R., Wen K, Lu Z, editors. Automatic keyword extraction for scientific literatures using references. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Innovative Design and Manufacturing (ICIDM); 2014.
- 55. Roelleke T, Wang J, editors. TF-IDF uncovered. 31st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval—SIGIR ‘08; 2008.
- 56. Mihalcea R, Tarau P, editors. TextRank: Bringing order into text. 2004 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; 2004.
- 58. Iannone F, Ambrosino F, Bracco G, De Rosa M, Funel A, Guarnieri G, et al., editors. CRESCO ENEA HPC clusters: A working example of a multifabric GPFS Spectrum Scale layout. 2019 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation (HPCS); 2019.
- 60. Wasserman S, Faust K. Social network analysis: Methods and applications: Cambridge University Press; 1994.
- 141. Williams JE, Best DL. Measuring sex stereotypes: A multination study, Rev: Sage Publications, Inc; 1990.
- 172. Steele CM, Aronson J. Stereotype threat and the test performance of academically successful African Americans. In: Jencks C, Phillips M, editors. The Black–White test score gap. Washington, DC: Brookings; 1998. p. 401–27
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection
- PMC10100361

Addressing workplace gender inequality: Using the evidence to avoid common pitfalls
Michelle k. ryan.
1 Global Institute for Women's Leadership, The Australian National University, Canberra Australian Capital Territory, Australia
2 Faculty of Business and Economics, University of Groningen, Groningen The Netherlands
In this Landmark article I outline four common missteps that are made when designing and implementing workplace gender equality initiatives: (1) when we don't go beyond describing the numbers; (2) when we try to ‘fix’ women rather than fix systems; (3) when we are overly optimistic about the progress we have made; and (4) when we fail to recognise the intersectionality of the experiences that women face. I will briefly consider each of these missteps in term, presenting research that suggests alternative ways of approaching gender equality initiatives.
INTRODUCTION
Despite much progress in the past 50 years, workplace gender inequality remains a persistent problem. Worldwide, women only occupy about 37 per cent of leadership roles (World Economic Forum, 2022 ), the pay gap sits at approximately 20 per cent (International Labour Oragnisation, 2022 ), and women remain concentrated in low‐status, low‐paid jobs (UN Women, 2022 ). There are countless initiatives designed to address workplace gender equality—those that try to attract women to certain professions and roles where they are under‐represented, those that try to support women's career trajectories, and the those that try to retain women in the workforce. While the impetus behind these initiatives is generally positive, many of these interventions are not based on evidence, in terms of their design, their implementation or in the evaluation of their efficacy.
Most infamous in this space are those initiatives that build on an understanding that much gender discrimination (but certainly not all) is a result unconscious bias. The research most cited to underpin unconscious bias training is work on implicit prejudice and implicit associations (e.g. Devine, 1989 ; Greenwald et al., 1998 ; Greenwald & Banaji, 1995 ). While there has been theoretical, methodological and psychometric debate about the utility of implicit tests such as the IAT (e.g. Blanton & Jaccard, 2006 ; Nosek & Sriram, 2007 ; see also Jost, 2019 ) what is of more interest here is the utility of unconscious bias training itself. While unconscious bias training is good at awareness raising, it is less effectual at achieving behaviour change or increased gender equality (e.g. Atewologun et al., 2018 ; Bezrukova et al., 2016 ; Kalev et al., 2006 ) and has been shown to have unintended negative consequences such as backfiring or feelings of false progress (e.g. Dover et al., 2020 ; Leslie, 2019 ).
In my current role, as the Director of the Global Institute for Women's Leadership at The Australian National University, I have three key responsibilities (1) to conduct research to better understand gender inequality, (2) to work with organizations and government to translate the evidence base into effective policy and practice and (3) to advocate for social change and gender equality. It is at the nexus of these three endeavours that I can see where we get it right, and where we, unfortunately, get it wrong.
In this Landmark article I outline four common missteps that are made when designing and implementing workplace gender equality initiatives: (1) when we do not go beyond describing the numbers; (2) when we try to ‘fix’ women rather than fix systems; (3) when we are overly optimistic about the progress we have made; and (4) when we fail to recognize the intersectionality of the experiences that women face. I will briefly consider each of these missteps in term, presenting research that suggests alternative ways of approaching gender equality initiatives. 1
WHEN NUMBERS JUST AREN'T ENOUGH
One of the first steps in many gender equality action plans is to do an audit of the representation of women. How many women are in the organization? How many women are in decision‐making roles? How many women are there in senior management and on the boards of directors? This number crunching extends to describing other inequalities: How big is the gender pay gap? How many women were promoted in the last promotions round? What is the success rate of female job applicants? This approach is common in many internal organizational gender equality plans (Ely & Thomas, 2020 ), and as part of many external accreditation programmes (e.g. Rosser et al., 2019 ). Understanding representation and understanding key metrics of gender equality are a necessary part of achieving gender equality—but they are not sufficient. Such numbers are a great starting point as they identify problem areas to be rectified. But they do not tell the whole story.
In this section, I will outline a body of research on women in leadership and the glass cliff (Haslam & Ryan, 2008 ; Ryan & Haslam, 2005 , 2007 ) that illustrates why we cannot just stop at descriptive numbers. This work suggests that it is not enough to know whether women are in leadership positions, but when they are in leadership positions. It also illustrates the importance of looking at women's experiences in such positions. And finally, it illustrates the importance of understanding the psychological processes behind the appointment of women to leadership positions.
This body of research builds on the metaphor of the glass ceiling, that describes the under‐representation of women in leadership positions, to examine the conditions under which women are likely to be appointed to leadership positions. Almost 20 years of research has demonstrated the phenomenon whereby women are more likely to be appointed to leadership roles during times of crisis (see Morgenroth et al., 2020 , & Ryan et al., 2016 , for meta‐analyses and an overview). With the extension of the glass ceiling metaphor—the glass cliff—we hoped to capture the riskiness and precarity of such leadership positions: to give a sense of occupying a position up on high, yet of teetering on the edge.
The phenomenon of the glass cliff was first uncovered as a reaction to a newspaper article in The Times (Judge, 2003 ). This article presented evidence that companies that had more women on their boards of directors, had poorer share prices, and thus the increasing number of women on UK corporate board was ‘wreaking havoc’ on corporate Britain (p. 21). In response, Ryan and Haslam ( 2005 ) proposed an alternative analysis, whereby rather than women causing poor company performance, it was poor company performance that led to women being appointed to boards of directors. We conducted nuanced analysis of board appointments and monthly changes in company share prices that showed that this alternative explanation was indeed the case—(the small number of) women who were appointed to boards of directs, were appointed after a prolonged period of poor share price performance. Share price afterwards did not differ from their male counterparts.
Since this first discovery of the phenomenon, a global body of research on the glass cliff has emerged, one that uses multiple methodologies (archival analyses, experimental studies, case studies, qualitative work) to demonstrate the nuance and underlying processes associated with the glass cliff phenomenon (Morgenroth et al., 2020 ; Ryan et al., 2016 ). The glass cliff is not restricted to corporate settings, and has also been found in (a) the political sphere (e.g. Kulich et al., 2015 ; Ryan et al., 2010 )—as illustrated by all three of the UK's female Prime ministers: Thatcher (1980s recession), May (Brexit) and Truss (energy crisis and spiralling inflation); (b) sporting contexts (e.g. Wicker et al., 2019 ); and (c) in non‐government, third sector organizations (e.g., Bogacz‐Wojtanowska et al., 2018 ).
The importance of the glass cliff here is that it points to the necessity of looking beyond simply the number of women in leadership positions, to understand the circumstances under which women are likely to be appointment to such positions. If we just take the proportion of women in leadership roles as a measure of gender equality, then glass cliff appointments may be seen as an example of progress towards gender equality. But in reality, the opposite may be the case.
The context in which the glass cliff occurs can lead to such positions representing a new and subtle form of sexism or gender discrimination. Such a poisoned chalice potentially sets women up for additional scrutiny, stress and risk of failure. Indeed, the very risk and precarity experienced by those in glass cliff positions may hinder progress towards gender equality. Women in glass cliff positions are likely to face greater challenges in their leadership roles, such as (a) being blamed for negative conditions that were set in train long before they were appointed (Ryan & Haslam, 2005 ), shorter tenure (Glass & Cook, 2016 ) or (c) stress and burnout (Ryan et al., 2009 ). These additional difficulties may contribute to the stagnation of women's representation in leadership positions, reinforcing stereotypes that women are not suited to leadership.
The glass cliff is just one example where the complexity of gender equality might be hidden behind the top‐line numbers. Understanding the subtlety and nuance behind the numbers gives us a truer sense of our progress towards gender equality. We can think of these in terms of who, when, why and where questions. For example, who bears the brunt of gender inequality—we know that gender inequality is fundamentally intersectional, being exacerbated by other group memberships (see Section ‘ When we are overly optimistic ’, below). When and where does inequality occur. And the big question for us as psychologists, is the why —what are the processes sitting behind the numbers, what drives inequality, and in turn, what do we need to do to help mitigate it.
Exploring beyond the numbers can also help inform us of the most effective ways to attack those problems. In the case of the glass cliff, looking beyond the number of appointments raises a whole new set of research questions to be asked (and answered). Are women preferentially selected by others for leadership in times crisis (yes, according to Haslam & Ryan, 2008 )? Are women appointed because we think they are good at dealing with crisis (no, according to Kulich et al., 2015 ; Ryan et al., 2011 ). Do women select these positions because they like a challenge (also no, according to Rink et al., 2012 )?
WHEN WE TRY TO FIX WOMEN
The question of whether women self‐select into glass cliff positions leads us nicely into our next misstep—the tendency to focus on women when trying to solve the problem of gender inequality. Many of the approaches to improving gender equality recognize that the issues arise from inequalities embedded in our social and organizational structures and systems. Key here are the traditional gender stereotypes about what women and men are like (Ellemers, 2018 ) and what they should be like (Heilman, 2012 ). In particular, many workplace inequalities arise because the societal view of women's warmth is incompatible with societal views of leadership and success that prioritize notions of agency and competence (e.g. Koenig et al., 2011 ; Schein, 1973 ). Importantly our social and organizational structures and systems are predicated on these gender norms and stereotypes (Eagly et al., 2000 ), including recruitment, promotion and reward practices; parental leave and childcare policies; and educational systems.
However, this acknowledgement of systemic basis of gender equality often dissipates when it comes to actually implementing interventions and initiatives. There is a relatively consistent underlying assumption within these initiatives that gender inequalities can be addressed with a focus on individual competencies. From this perspective, we can narrow the gender equality gaps by providing women with additional skills and training. For example, initiatives to encourage girls and women in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM) are often focused on boosting their engagement and ambition (Liben & Coyle, 2014 ). Leadership training courses often focus on teaching women ‘girl boss’ leadership skills (Atir, 2022 ) and encouraging them to take greater risks and make bigger sacrifices, overcome impostor symptom, be authentic at work and negotiate the next promotion or pay rise (Hackworth et al., 2018 ). This approach is epitomized by the ‘lean in’ approach to gender equality (Sandberg, 2013 ), which seeks to encourage women to make the right choices and have the right mindset.
All of these approaches have, as their implicit theory of change, an understanding that women are in some way broken and not up to the task. The solution is, therefore, seen to be to ‘fix’ them—to change their behaviours, address their skills deficit, remedy their mindset. But the evidence is very clear on this point—it is not women that need fixing, but the deeply entrenched systems of gender inequality that structure our organizations and structure society more broadly.
Below I outline some illustrative research that demonstrates that women's engagement and belonging, their feelings of impostor syndrome and their willingness to take risks are not individual‐level problems that renders them needing to be fixed. Rather, these issues are a direct product of organizational and societal systems, and their experiences in these systems and thus require structural solutions.
Engagement and belonging
One area in which this approach is highly visible is trying to attract and retain girls and women in male‐dominated sectors, such as STEM, finance and construction. Many of initiatives designed to increase gender inequality in these spaces focus on trying to increase girls' and women's interest for and engagement with these sectors (McKinnon, 2022 ), such as the heavily criticized campaign—Science: It's a Girl Thing—from the European Commission, which featured women in fashionable PPE making lipstick (Grosu, 2013 ). What is implicit here is that there is some sort of inherent lack of enthusiasm in women, that needs to be addressed, rather than the fact that women and girls are responding to very real cultural and normative barriers that exclude them (Saucerman & Vasquez, 2014 ).
In a series of studies looking at women in surgery—where women make up less than 25% per cent of the profession—Peters et al. ( 2012 ) examined whether the under‐representation of women may be explained, at least in part, by women's perceptions of, and experiences within, the profession. Across two studies we demonstrated that female surgical trainees perceived a lack of fit between themselves and the prototypical masculine surgeon. In turn, this perceived lack of fit was associated with a reduction in identification with the profession and an increased desire to opt out of the profession.
Similarly, work by Meeussen et al. ( 2022 ) demonstrate than in male‐dominated careers, such as surgery and the veterinary profession, women (compared to men) report less career engagement because of their more frequent experiences of gender discrimination and lower perceived fit with those higher up the career ladder. In turn, these barriers predicted reduced expectations of success in their field and expected success of their sacrifices, which in turn predicted lower willingness to make sacrifices.
Together, these studies suggest the role that external barriers, such as experiences of discrimination and perceptions of fit, play in women's career decision making in male‐dominated professions. Thus, trying to attract and retain women in these spaces by focusing on women themselves is unlikely to be fruitful. Rather, interventions need to address the root of the problem, discriminatory environments and a lack of role models if they want women to come and women to stay (see Casad et al., 2018 ).
Imposter syndrome
Another area in which has received a lot of attention when it comes to women in the workplace are initiatives that seek to address impostor syndrome. This concept is used to describe individuals who express doubts about their self‐worth, failing to take credit for their successes or attributing their successes to luck. Such individuals worry that others will see them as impostors or frauds. The very use of the term ‘syndrome’ suggests that this experience is an individual‐level problem—a condition that requires diagnosis and treatment and fixing. And indeed, there will be no surprise to find out that there are many initiatives out there that are designed to help individuals, and in particular women, to overcome ‘their’ impostor syndrome. For example, such interventions seek to increase women's confidence, reduce their perfectionism and change their mindsets (Chandra et al., 2019 ).
However, as Feenstra et al. ( 2020 ) argue, rather than being seen as a personal problem that plagues individual women, it is critical to acknowledge the role that the social and organizational context plays in eliciting feelings of impostorism (see also Kark et al., 2022 ). Indeed, a series of studies by Begeny et al. ( 2022 ) demonstrate that impostor feelings can be seen as is a direct response to how one is treated by others. In a longitudinal study, we showed that that experiencing fewer expressions of distinctive treatment, such as being asked for advice, resulted in a significant increase in impostor feelings over time. Moreover, in experimental studies we showed that when individuals experience positive distinctive treatment from work colleagues, this significantly reduces impostor feelings.
In this way, characterizing impostor feelings at an individual level is unlikely to be useful, both in terms of running the risk of pathologizing these feelings and in terms of understanding where they come from. Thinking of impostor feelings as a context‐dependent outcome of workplace experiences has clear implications for how we ‘treat’ impostor syndrome. Rather than putting the onus on employees, particularly women, to overcome their own impostor feelings—being more confident and ‘faking it until you make it’—we need to implement more systemic approaches, creating cultures where colleagues are valued and treated with respect.
Risk taking
One common explanation for the persistence of workplace gender inequalities is that women are less willing to take career‐enhancing risks, such as asking for a pay rise or taking on a new position (Byrnes et al., 1999 ). Indeed, women's risk aversion is a persistent aspect of gender stereotypes, with many arguing that this is an innate difference aspect of gender (Bem, 1974 ). Such an analysis has a number of issues, including the assumption that risk taking is inherent desirable and necessarily career enhancing, and because it fails to recognize the types of risks that women do take in everyday life (Morgenroth et al., 2018 ). But nonetheless, a key facet of the lean in approach to fixing women is encouraging women to take more risks, including memetic advice such as ‘if you are offered a seat on a rocket ship, do not ask what seat, just get on’ and ‘fortune does favour the bold, and you never know what you are capable of if you do not try’ (Sandberg, 2013 ).
However, research demonstrates that far from being innate, women's willingness to take risks is dependent of their experiences in the workplace. Research conducted by Morgenroth et al. ( 2022 ) looks at gender differences in risk taking through a lens of the anticipated and experienced consequences of risk taking. Across three studies, there was no evidence for gender differences in initial risk taking or in the anticipation of consequences for the risks with which women and men had no prior experience. However, when we looked at actual experiences of risk taking in the workplace—such as taking on a difficult task, speaking up or quitting your job for a new job—men reported more positive consequences for taking risks than women, and as a result, anticipated having a greater likelihood of taking the same risks in the future.
Studies like this question the assumption that it is women's innate risk aversion that underlies workplace gender inequalities. Rather they demonstrate that any aversions women have are likely to be a consequence of their workplace experiences, and indeed, are likely to be informed by the gendered, negative experiences they have when attempting to take risks. For this reason, gender equality initiatives that focus on encouraging women to take more risks are unlikely to succeed, and it is the gendered costs and benefits for risk that need to be addressed.
Taken together, this exploration of some of the common ways in which initiatives target gender equality issues—engagement, impostor syndrome and risk taking—suggest that framing these as individual‐level problems is unlikely to be fruitful. At best, such an approach may provide those individual women who are targeted by such initiatives, usually women that hold a certain amount of privilege (see Section 4) with a short‐term advantage. At worst, such attempts to fix women reinforce the stereotypes and norms that form the basis of structural gender inequalities and become yet another demand on women's time. Interventions should, instead, target the foundational causes of inequality: organizational systems and culture.
WHEN WE ARE OVERLY OPTIMISTIC
If we compare where we are now on the workplace gender equality front, compared to where we have been historically, it is clear that there have been many positive changes—better gender representation, safer working conditions and more equality in terms of pay. But such changes are not linear, and neither are they inevitable. Indeed, over more recent time periods we have seen stagnation in these advances, in in some cases even backsliding (Word Economic Forus, 2022 ). Indeed, current forecasts suggest it will be at anywhere between 132 (Word Economic Forus, 2022 ) and 300 (UN Women, 2022 ) years before we reach global gender equality.
Part of the tension here lies in the degree to which we recognize and celebrate our gender equality accomplishments, and to what extent are we realistic about how much we still have to achieve. This decision is not just about whether or not one wants to be an optimistic person. An understanding of the degree to which gender inequalities persist, and in particular the denial of gender inequality, forms a key aspect of sexist attitudes, such as those captured by the modern sexism scale (Swim et al., 1995 ). Indeed, there are a number of very real consequences of failing to acknowledge the persistence of gender inequality.
Begeny et al. ( 2020 ) looked at what happens when traditionally male‐occupied professions, such as the veterinary profession, attract more women. While having a greater representation of women is clearly progress, some may take it as an indication that the discrimination is no longer a problem. We demonstrated that despite women being the majority of veterinary students and junior vets, female vets still report experiencing discrimination. In a follow‐up experimental study, we illustrated one way in which this discrimination manifests itself. Vets with managerial responsibilities evaluated a male vet as more competent and suggested paying him 8 per cent more than an equally qualified female vet. Key here, these discriminatory evaluations were evident primarily among those who believed women no longer face discrimination in the profession. Thus, even when positive change occurs, discrimination persists, ironically perpetuated by those who believe it is no longer a problem.
Research also demonstrates that progress towards gender equality may be hampered by those who overestimate the rate of progress. A study by Begeny et al. ( 2022 ) surveyed doctors in the United Kingdom who were asked to estimate the representation of women across a number of roles in the medical profession. Both male and female doctors consistently overestimated the number of women in medicine. However, while those women who over‐estimated female representation still supported gender‐equality initiatives, such as initiatives run by the Royal College of Surgeons and the General Medical Council, those men who were over‐optimistic about progress showed significantly lower levels of support. Thus, men who overestimated progress towards gender equality were at highest risk of undermining it (see also Coffé & Reiser, 2021 ).
Recognizing and celebrating progress towards gender equality is important for a sense of hope and collective efficacy, both necessary for continued motivation for change (e.g. Cohen‐Chen & Van Zomeren, 2018 ; Van Zomeren, 2013 ). However, studies like these suggest that there is potentially a fine line between optimism and a failure to recognize persistent inequalities. If we are to close the gap, and it would be nice if we could do so in less than a century, we need a healthy dose of realism and we need to acknowledge what still remains to be done.
WHEN WE AREN'T INTERSECTIONAL
A final common misstep that is taken when trying to address gender inequalities is to treat women as if they are a monolithic, homogenous group. There is often a ‘one size fits all’ approach to interventions and change (Tzanakou, 2019 ). But the experiences within women—between individuals and between different groups of women—are often more varied than the experiences between women and men. There is a need to understand this variety in women's experiences, and how this is determined by other intersecting identities, especially those that are marginalized or stigmatized (e.g. Crenshaw, 1991 ).
What is most troublesome about the one size fits all approach, is that gender interventions and initiatives are most often based on the experiences of the dominant group—such as those women who are white, middle‐class or straight. This is problematic, both because the experiences of such women are by no means universal, and because women not included in this group—for example culturally and linguistically diverse women, working‐class women, and LGBTQI+ women and gender diverse people, often face the greatest inequalities.
For example, research by Opara et al. ( 2020 ) identified that Black and minoritized women's workplaces experienced were very much influenced by their racial identities, including having stereotypes and expectations imposed upon them. Indeed, research demonstrates that Black women are treated on the basis of negative stereotypes that question their competence and their legitimacy (e.g. Williams & Dempsey, 2014 ) or see them as aggressive and masculine (Hall et al., 2019 ). In contrast, Asian women may be affected by the model minority myth (Cheng et al., 2017 ) and be seen as hyper‐competent (Liang & Peters‐Hawkins, 2017 ), but at the same time face stereotypes of low agency (Ghavami & Peplau, 2013 ) and hyper‐femininity (Mukkamala & Suyemoto, 2018 ).
These differential experiences mean that homogenous workplace gender equality initiatives are unlikely to be effective. Indeed, Wong et al. ( 2022 ) argue that diversity interventions tend not to take into account the wide variety of women's experiences. Across three studies we demonstrate that women who are racially marginalized need different things from their diversity interventions than do White women. More specifically we found that while White women focused on the needs of initiatives address issues of women's agency, Black women overtly reported the need for initiatives to take into account intersectional differences, such as racialized gender stereotypes where Black women are seen as pushy or overly assertive. Similarly, Asian women reported the need to address challenges to their authority which stem from racialized stereotypes of Asian women as passive and submissive. Importantly, our textual analysis of gender equality websites showed that organizations were less likely to represent the needs of Black and Asian women—a form of intersectional invisibility (Purdie‐Vaughns & Eibach, 2008 )—such that their gender equality advocacy tended to focus on (White women's) issues of agency, rather than issues of racialized stereotyping reported by Black and Asian women.
These findings suggest that if gender equality initiatives are going to be successful, they must take into account the wide variety of women's experiences and needs. Catering for just one group of women is unhelpful, particularly if that group of women as a whole are likely to experience less disadvantage. Interventions need to overtly address the issues faced by all women, not just those in the majority or those with the most privilege. This points to the importance of understanding the intersectional nature of gender inequality—taking into account that these inequalities are exacerbated and qualified by multiple forms of oppression, such as those based on race, ethnicity, class, sexuality, disability, age and linguistic diversity.
CONCLUSIONS
While the majority of gender equality initiatives are founded on good intentions, this in and of itself is not enough to bring about significant and lasting change. As we have seen above, interventions need to be based on a clear evidence base, one that (1) looks beyond the top line numbers to the complexity and nuance of gender inequality; (2) aims to fix the things that actually needs fixing (systems and structures) rather than trying to fix women; (3) celebrates change while at the same time being realistic about the challenges that are to come; and (4) understands the inherently intersectional nature of gender inequality.
The good news is that social psychology is perfectly situated to rise to all of these challenges. First, we are well placed to understand the processes and contexts that sit behind the top line numbers. For example, as we have seen, social psychological theories can help us understanding the gendered stereotypes than underlie our social and organizational policies and practices (e.g. Eagly et al., 2000 ; Ellemers, 2018 ; Heilman, 2012 ; Koenig et al., 2011 ). They can also help us understanding how workplace experiences can affect gendered workplace choices (e.g. Begeny et al., 2022 ; Meeussen et al., 2022 ; Morgenroth et al., 2022 ).
Second, within our theories we have the ability to ensure we are asking the appropriate questions and that we are framing our questions at the right level of analysis—at the level of the individual, the group or at a societal level—and an understanding that the individual level is not always the most appropriate. For example, the social identity approach (Tajfel & Turner, 1979 ; Turner et al., 1987 ) provides a clear framework to examine how our group memberships, and the contexts in which we are embedded, may impact upon our attitudes and behaviours, particularly at work (Haslam, 2004 ).
Third, through concepts like modern sexism (Swim et al., 1995 ), social psychology can provide an understanding of the perniciousness of the denial of sexism and the subsequent outcomes, such as continued gender discrimination and a lack of support for gender equality initiatives (see Begeny et al., 2020 , 2022 ). This is particularly important as such views provide a strong basis to the backlash that is levelled against gender equality initiatives (Flood et al., 2021 ). Indeed, more recent theories of sexism, such as the belief in sexism shift (Zehnter et al., 2021 ), indicate that there are increasingly prevalent views that men are now the key victims of sexism (Ryan & Zehnter, 2022 ), a view that is likely to exacerbate resistance to change.
Finally, while not yet an integrated part of social psychology, there are some excellent examples of how to make our research more intersectional (Bowleg, 2017 ; Cole, 2009 ; Rosenthal, 2016 ). This intersectionality can be implemented in terms of the types of research questions we ask and the make‐up of our samples (Purdie‐Vaughns & Eibach, 2008 ; Remedios & Snyder, 2015 ) and even the way we do open science (Sabik et al., 2021 ). Importantly, while much of the intersectional advances have been made at the intersection of gender and race; there is still much to be done in acknowledging other intersectional identities, such as those based on age, class, disability and sexuality.
Taken together, while the evidence shows us that there have clearly been missteps on the way, the evidence also demonstrates that social psychology is in an excellent position to play an important role as we stride forward towards gender equality.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Landmark articles are, by tradition, single authored papers, but of course the work that is discussed in the paper could only have been conducted in collaboration. Thanks to all my terrific colleagues with whom I've had the pleasure to work with, in particular to Thekla Morgenroth, Chris Begeny, Alex Haslam and Kim Peters whose work contributed significantly to the ideas in this paper. This paper was supported in part by a European Research Council consolidator Grant (725128).
Ryan, M. K. (2023). Addressing workplace gender inequality: Using the evidence to avoid common pitfalls . British Journal of Social Psychology , 62 , 1–11. 10.1111/bjso.12606 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
1 This Landmark Article builds on a short opinion piece I wrote for Nature: Ryan ( 2022 )
- Atewologun, D. , Cornish, T. , & Tresh, F. (2018). Unconscious bias training: An assessment of the evidence for effectiveness . Equality and Human Rights Commission Research Report Series.
- Atir, S. (2022). Girlboss? Highlighting versus downplaying gender through language . Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 8 , 623–625. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blanton, H. , & Jaccard, J. (2006). Arbitrary metrics in psychology . American Psychologist , 61 , 27–41. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Begeny, C. T. , Grossman, R. C. , & Ryan, M. K. (2022). Overestimating women's representation in medicine and support for gender‐equality initiatives . British Medical Journal (Open) , 12 , e054769. 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054769 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Begeny, C. T. , Ryan, M. K. , Moss‐Racusin, C. A. , & Ravetz, G. (2020). In some professions women have become well‐represented, yet gender bias persists – Perpetuated by those who think it is not happening . Science Advances , 6 , eaba7814. 10.1126/sciadv.aba7814 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bem, S. L. (1974). The measurement of psychological androgyny . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 42 , 155–162. 10.1037/h0036215 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bezrukova, K. , Spell, C. S. , Perry, J. L. , & Jehn, K. A. (2016). A meta‐analytical integration of over 40 years of research on diversity training evaluation . Psychological Bulletin , 142 , 1227–1274. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bogacz‐Wojtanowska, E. , Peter‐Bombik, K. , & Wrona, S. (2018). Women on the Glass cliff: Managing local funds . Journal of Business Diversity , 18 , 58–69. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bowleg, L. (2017). Intersectionality: An underutilized but essential theoretical framework for social psychology. In McLeod J. D., Lawler E. J., & Schwalbe M. (Eds.), The Palgrave handbook of critical social psychology (pp. 507–529). Palgrave Macmillan. [ Google Scholar ]
- Byrnes, J. P. , Miller, D. C. , & Schafer, W. D. (1999). Gender differences in risk taking: A meta‐analysis . Psychological Bulletin , 125 ( 3 ), 367–383. 10.1037/0033-2909.125.3.367 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Casad, B. J. , Oyler, D. L. , Sullivan, E. T. , McClellan, E. M. , Tierney, D. N. , Anderson, D. A. , … Flammang, B. J. (2018). Wise psychological interventions to improve gender and racial equality in STEM . Group Processes and Intergroup Relations , 21 , 767–787. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chandra, S. , Huebert, C. A. , Crowley, E. , & Das, A. M. (2019). Impostor syndrome: Could it be holding you or your mentees back? Chest , 156 , 26–32. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheng, A. W. , Chang, J. , O'Brien, J. , Budgazad, M. S. , & Tsai, J. (2017). Model minority stereotype: Influence on perceived mental health needs of Asian Americans . Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health , 19 , 572–581. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coffé, H. , & Reiser, M. (2021). How perceptions and information about women's descriptive representation affect support for positive action measures . International Political Science Review 0192512121995748. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen‐Chen, S. , & Van Zomeren, M. (2018). Yes we can? Group efficacy beliefs predict collective action, but only when hope is high . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 77 , 50–59. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cole, E. R. (2009). Intersectionality and research in psychology . American Psychologist , 64 , 170–180. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crenshaw, K. (1991). Mapping the margins: Intersectionality, identity politics, and violence against women of color . Stanford Law Review , 43 , 1241–1299. 10.2307/1229039 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Devine, P. G. (1989). Stereotypes and prejudice: Their automatic and controlled components . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 56 , 5–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dover, T. L. , Kaiser, C. R. , & Major, B. (2020). Mixed signals: The unintended effects of diversity initiatives . Social Issues and Policy Review , 14 , 152–181. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eagly, A. H. , Wood, W. , & Diekman, A. B. (2000). Social role theory of sex differences and similarities: A current appraisal. In Eckes T. & Trautner H. M. (Eds.), The developmental social psychology of gender (pp. 123–174). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellemers, N. (2018). Gender stereotypes . Annual Review of Psychology , 69 , 275–298. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ely, R. J. , & Thomas, D. A. (2020). Getting serious about diversity . Harvard Business Review , 98 , 114–122. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feenstra, S. , Begeny, C. T. , Ryan, M. K. , Rink, F. A. , Stoker, J. I. , & Jordan, J. (2020). Contextualizing the impostor “syndrome” . Frontiers in Psychology , 11 , 1–6. 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.575024 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flood, M. , Dragiewicz, M. , & Pease, B. (2021). Resistance and backlash to gender equality . Australian Journal of Social Issues , 56 , 393–408. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghavami, N. , & Peplau, L. A. (2013). An intersectional analysis of gender and ethnic stereotypes: Testing three hypotheses . Psychology of Women Quarterly , 37 , 113–127. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glass, C. , & Cook, A. (2016). Leading at the top: Understanding women's challenges above the Glass ceiling . The Leadership Quarterly , 27 , 51–63. [ Google Scholar ]
- Greenwald, A. G. , & Banaji, M. R. (1995). Implicit social cognition: Attitudes, self‐esteem, and stereotypes . Psychological Review , 102 , 4–27. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greenwald, A. G. , McGhee, D. E. , & Schwarz, J. L. K. (1998). Measuring individual differences in implicit cognition: The implicit association test . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 74 , 1464–1480. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grosu, I. (2013). Science: it's a girl thing should start with adequate toys . Open Journal of Education , 2013 ( 1 ), 139–142. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hackworth, J. , Steel, S. , Cooksey, E. , DePalma, M. , & Kahn, J. A. (2018). Faculty members' self‐awareness, leadership confidence, and leadership skills improve after an evidence‐based leadership training program . The Journal of Pediatrics , 199 , 4–6. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall, E. V. , Hall, A. V. , Galinsky, A. D. , & Phillips, K. W. (2019). MOSAIC: A model of stereotyping through associated and intersectional categories . Academy of Management Review , 44 , 643–672. 10.5465/amr.2017.0109 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haslam, S. A. (2004). Psychology in organizations: The social identity approach (2nd ed.). Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haslam, S. A. , & Ryan, M. K. (2008). The road to the glass cliff: Differences in the perceived suitability of men and women for leadership positions in succeeding and failing organizations . Leadership Quarterly , 19 , 530–546. 10.1016/j.leaqua.2008.07.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heilman, M. E. (2012). Gender stereotypes and workplace bias . Research in Organizational Behavior , 32 , 113–135. [ Google Scholar ]
- International Labour Oragnisation . (2022). Pay transparency legislation: Implications for employers’ and workers’ organizations . https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_protect/---protrav/---travail/documents/publication/wcms_849209.pdf
- Jost, J. T. (2019). The IAT is dead, long live the IAT: Context‐sensitive measures of implicit attitudes are indispensable to social and political psychology . Current Directions in Psychological Science , 28 , 10–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Judge, E. (2003). Women on board: Help or hindrance? The Times. 11 November. p21 .
- Kalev, A. , Dobbin, F. , & Kelly, E. (2006). Best practices or best guesses? Assessing the efficacy of corporate affirmative action and diversity policies . American Sociological Review , 71 , 589–617. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kark, R. , Meister, A. , & Peters, K. (2022). Now you see me, now you don't: A conceptual model of the antecedents and consequences of leader impostorism . Journal of Management , 48 , 1948–1979. [ Google Scholar ]
- Koenig, A. M. , Eagly, A. H. , Mitchell, A. A. , & Ristikari, T. (2011). Are leader stereotypes masculine? A meta‐analysis of three research paradigms . Psychological Bulletin , 137 , 616–642. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kulich, C. , Lorenzi‐Cioldi, F. , Iacoviello, V. , Faniko, K. , & Ryan, M. K. (2015). Signaling change during a crisis: Refining conditions for the glass cliff . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 61 , 96–103. 10.1016/j.jesp.2015.07.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leslie, L. M. (2019). Diversity initiative effectiveness: A typological theory of unintended consequences . Academy of Management Review , 44 , 538–563. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liang, J. G. , & Peters‐Hawkins, A. L. (2017). “I am more than what I look alike” Asian American women in public school administration . Educational Administration Quarterly , 53 , 40–69. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liben, L. S. , & Coyle, E. F. (2014). Developmental interventions to address the STEM gender gap: Exploring intended and unintended consequences. In Liben L. S. & Bigler R. S. (Eds.), Advances in child development and behavior, Vol. 47. The role of gender in educational contexts and outcomes (pp. 77–115). Elsevier Academic Press. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McKinnon, M. (2022). The absence of evidence of the effectiveness of Australian gender equity in STEM initiatives . Australian Journal of Social Issues , 57 , 202–214. [ Google Scholar ]
- Meeussen, L. , Begeny, C. T. , Peters, K. , & Ryan, M. K. (2022). Why are women less willing to make sacrifices for their career? How discrimination and lack of fit with those higher up the ladder reduce the perceived benefits of sacrifices . Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 8 , 588–601. 10.1111/jasp.12750 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgenroth, T. , Fine, C. , Ryan, M. K. , & Genat, A. (2018). Sex, drugs, and reckless driving: Are measures biased toward identifying risk‐taking in men? Social Psychological and Personality Science , 9 , 744–753. 10.1177/1948550617722833 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgenroth, T. , Kirby, T. A. , Ryan, M. K. , & Sudkaemper, A. (2020). The who, when, and why of the glass cliff phenomenon: A meta‐analysis of appointments to precarious leadership positions . Psychological Bulletin , 146 , 797–829. 10.1037/bul0000234 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgenroth, T. , Ryan, M. K. , & Fine, C. (2022). Who takes workplace risks and why? Gender differences in the consequences of risk‐ taking . Psychology of Women Quarterly. , 46 , 257–277. 10.1177/03616843221084048 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nosek, B. A. , & Sriram, N. (2007). Faulty assumptions: A comment on Blanton, Jaccard, Gonzales, and Christie (2006) . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 43 , 393–398. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mukkamala, S. , & Suyemoto, K. L. (2018). Racialized sexism/sexualized racism: A multimethod study of intersectional experiences of discrimination for Asian American women . Asian American Journal of Psychology , 9 , 32–46. [ Google Scholar ]
- Opara, V. , Sealy, R. , & Ryan, M. K. (2020). The workplace experiences of BAME professional women: Understanding experiences at the intersection . Gender, Work and Organization , 27 , 1192–1213. 10.1111/gwao.12456 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peters, K. , Ryan, M. K. , Haslam, S. A. , & Fernandes, H. (2012). To belong or not to belong: Evidence that women's occupational disidentification is promoted by lack of fit with masculine occupational prototypes . Journal of Personnel Psychology , 3 , 148–158. 10.1027/1866-5888/a000067 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Purdie‐Vaughns, V. , & Eibach, R. P. (2008). Intersectional invisibility: The distinctive advantages and disadvantages of multiple subordinate‐group identities . Sex Roles , 59 , 377–391. [ Google Scholar ]
- Remedios, J. D. , & Snyder, S. H. (2015). Where do we go from here? Toward an inclusive and intersectional literature of multiple stigmatization . Sex Roles , 73 , 408–413. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rink, F. , Ryan, M. K. , & Stoker, J. I. (2012). Influence in times of crisis: Exploring how social and financial resources affect men's and women's evaluations of glass cliff positions . Psychological Science , 11 , 1306–1313. 10.1177/0956797612453115 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal, L. (2016). Incorporating intersectionality into psychology: An opportunity to promote social justice and equity . American Psychologist , 71 , 474–485. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosser, S. V. , Barnard, S. , Carnes, M. , & Munir, F. (2019). Athena SWAN and ADVANCE: Effectiveness and lessons learned . The Lancet , 393 , 604–608. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. (2022). To advance equality for women, use the evidence . Nature , 604 ( 7906 ), 403. 10.1038/d41586-022-01045-y [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , & Haslam, S. A. (2005). The glass cliff: Evidence that women are over‐represented in precarious leadership positions . British Journal of Management , 16 , 81–90. 10.1111/j.1467-8551.2005.00433.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , & Haslam, S. A. (2007). The glass cliff: Exploring the dynamics surrounding women's appointment to precarious leadership positions . Academy of Management Review , 32 , 549–572. 10.5465/amr.2007.24351856 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , Haslam, S. A. , Hersby, M. D. , & Bongiorno, R. (2011). Think crisis–think female: Glass cliffs and contextual variation in the think manager–think male stereotype . Journal of Applied Psychology , 96 , 470–484. 10.1037/a0022133 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , Haslam, S. A. , Morgenroth, T. , Rink, F. , Stoker, J. I. , & Peters, K. (2016). Getting on top of the glass cliff: Reviewing a decade of evidence, explanations, and impact . Leadership Quarterly , 3 , 446–455. 10.1016/j.leaqua.2015.10.008 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , Haslam, S. A. , Hersby, M. D. , Kulich, C. , & Wilson‐Kovacs, M. D. (2009). The stress of working on the edge: Implications of glass cliffs for both women and organizations. In Barreto M., Ryan M. K., & Schmitt M. T. (Eds.), The Glass ceiling in the 21st century: Understanding barriers to gender equality (pp. 153–169). American Psychological Association. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , Haslam, S. A. , & Kulich, C. (2010). Politics and the glass cliff: Evidence that women are preferentially selected to contest hard‐to‐win seats . Psychology of Women Quarterly , 34 , 56–64. 10.1111/j.1471-6402.2009.01541.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan, M. K. , & Zehnter, M. K. (2022). Sexism today: Tools in the patriarchy's toolbox. In Gillar J. (Ed.), Not now not ever, ten years on from the misogyny speech (pp. 99–120). Vintage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabik, N. J. , Matsick, J. L. , McCormick‐Huhn, K. , & Cole, E. R. (2021). Bringing an intersectional lens to “open” science: An analysis of representation in the reproducibility project . Psychology of Women Quarterly , 45 , 475–492. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandberg, S. (2013). Lean in: Women, work, and the will to lead . Random House. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saucerman, J. , & Vasquez, K. (2014). Psychological barriers to STEM participation for women over the course of development . Adultspan Journal , 13 , 46–64. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schein, V. E. (1973). The relationship between sex role stereotypes and requisite management characteristics . Journal of Applied Psychology , 57 , 95–100. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swim, J. K. , Aikin, K. J. , Hall, W. S. , & Hunter, B. A. (1995). Sexism and racism: Old‐fashioned and modern prejudices . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 68 , 199–214. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tajfel, H. , & Turner, J. C. (1979). An integrative theory of intergroup conflict. In Austin W. G. & Worchel S. (Eds.), The social psychology of intergroup relations (pp. 33–47). Brooks/Cole. [ Google Scholar ]
- Turner, J. C. , Hogg, M. A. , Oakes, P. J. , Reicher, S. D. , & Wetherell, M. S. (1987). Rediscovering the social group: A self‐categorization theory . Blackwell. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tzanakou, C. (2019). Unintended consequences of gender‐equality plans . Nature , 570 , 277–278. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UN Women . (2022). Progress on the Sustainable Development Goals: The Gender Snapshot . https://www.unwomen.org/sites/default/files/2022‐09/Progress‐on‐the‐sustainable‐development‐goals‐the‐gender‐snapshot‐2022‐en_0.pdf
- Van Zomeren, M. (2013). Four core social‐psychological motivations to undertake collective action . Social and Personality Psychology Compass , 7 , 378–388. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wicker, P. , Cunningham, G. B. , & Fields, D. (2019). Head coach changes in women's college soccer: An investigation of women coaches through the lenses of gender stereotypes and the glass cliff . Sex Roles , 81 , 797–807. [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams, J. , & Dempsey, R. (2014). What works for women at work . New York University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wong, C. Y. , Kirby, T. A. , Rink, F. , & Ryan, M. K. (2022). Intersectional invisibility in women's diversity interventions . Frontiers in Psychology , 13 . 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.791572 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Word Economic Forus . (2022). Global gender gap report . https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GGGR_2022.pdf
- Zehnter, M. K. , Manzi, F. , Shrout, P. E. , & Heilman, M. E. (2021). Belief in sexism shift: Defining a new form of contemporary sexism and introducing the belief in sexism shift scale (BSS scale) . PloS One , 16 , e0248374. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Open access
- Published: 01 November 2022
A qualitative study on gender inequality and gender-based violence in Nepal
- Pranab Dahal 1 ,
- Sunil Kumar Joshi 2 &
- Katarina Swahnberg 1
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 2005 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
86k Accesses
26 Citations
Metrics details
Gender inequality and violence are not mutually exclusive phenomena but complex loops affecting each other. Women in Nepal face several inequalities and violence. The causes are diverse, but most of these results are due to socially assigned lower positioning of women. The hierarchies based on power make women face subordination and violence in Nepal. The study aims to explore participants' understanding and experience to identify the status of inequality for women and how violence emerges as one of its consequences. Furthermore, it explores the causes of sex trafficking as an example of an outcome of inequality and violence.
The study formulated separate male and female groups using a purposive sampling method. The study used a multistage focus group discussion, where the same groups met at different intervals. Six focus group discussions, three times each with male and female groups, were conducted in a year. Thirty-six individuals, including sixteen males and twenty females, were involved in the discussions. The study used constructivist grounded theory for the data analysis.
The study participants identify that a power play between men and women reinforce inequality and increases the likelihood of violence for women. The findings suggest that the subjugation of women occurs due to practices based on gender differences, constricted life opportunities, and internalization of constructed differences among women. The study identifies that interpersonal and socio-cultural violence can result due to established differences between men and women. Sex trafficking, as an example of the outcome of inequality and violence, occurs due to the disadvantageous position of women compounded by poverty and illiteracy. The study has developed a concept of power-play which is identified as a cause and consequence of women's subordination and violence. This power play is found operative at various levels with social approval for men to use violence and maintain/produce inequality.
The theoretical concept of power play shows that there are inequitable power relations between men and women. The male-centric socio-cultural norms and practices have endowed men with privilege, power, and an opportunity to exploit women. This lowers the status of women and the power-play help to produce and sustain inequality. The power-play exposes women to violence and manifests itself as one of the worst expressions used by men.
Peer Review reports
Violence against women is identified as an attempt by men to maintain power and control over women [ 1 ] and is manifested as a form of structural inequality. This structural inequality is apparent with greater agency among men [ 2 ]. The differences between sexes are exhibited in the attainment of education and professional jobs, ownership of assets, the feminization of poverty, etc., and these differences increase the risk of violence towards women [ 3 ]. The global estimate identifies that thirty percent of women experience physical and/or sexual violence during their lifetime, illustrating the enormity of this problem [ 4 ]. From a feminist perspective, lending ideas of patriarchy [ 5 ] and gender performativity [ 6 ], the understanding of gender roles prescribed by male-dominated social structures and processes helps further explore the violence and abuse faced by women [ 7 ]. According to Heise [ 8 ], men who adhere to traditional, rigid, and misogynistic views on gender norms, attitudes, and behaviors are more likely to use violence towards women. The individual and collective attitudes of men toward different established gender norms, and their reproduction explain men’s use of violence toward women [ 9 ]. It is known that gender norms influence violence, but at the same time violence also directs and dictates gender performance with fear, sanction, and corrective measures for enacting respective prescribed gender functions [ 10 ].
It is difficult for women subjected to violence to enjoy legitimate rights, as most of the infringement of their rights and violence takes place inside a private sphere of the home [ 11 , 12 ]. Violence against women is the major cause of death and disability for women [ 13 ] and globally a major public health concern [ 14 ]. Establishing gender equality is fundamental for fostering justice and attaining sustainable development [ 15 ]; moreover, violence against women has to be acknowledged as a fundamental abuse of human rights [ 16 ]. A report on global violence has identified that violence against women exists at all levels of the family, community, and state. The report recommended the development of frameworks for respecting, protecting, and fulfilling women’s rights [ 17 ]. Fifteen years later, a review of the same identifies that violence continues with impunity, reaffirming violence as a major obstacle to the attainment of justice [ 18 ].
The inclusion of the gender lens to violence against women has provided more contextual evidence to explore these processes of violence. This requires the identification of unequal power relationships and an inquiry into the differences-producing various gender stereotypes [ 19 ]. This analysis of violence requires an understanding of behaviors that promote women’s subordination and factors that favor men to sustain these malpractices [ 8 ]. A closer look at the male-centric structural arrangements embedded in the social, political, and economic organization of life reveals that these structures provide lesser access and lower accountability toward women, promote systemic subordination, and create hierarchies, resulting in the increase of violence against women [ 20 ]. This unequal gender power relationship reinforced and manifested by social approval of men’s authority over women is found operative at multiple levels and helps to produce diversities of inequalities and violence [ 21 , 22 ].
The inequalities faced by women in Nepal majorly stem from socio-cultural, economic, and religious factors and influencers that define traditional roles and responsibilities between men and women [ 23 ]. The inequalities are more evident and pronounced in settings exhibiting prominent patriarchal norms restricting advantages and opportunities for the majority of women [ 24 ]. Women in Nepal are restricted inside their homes, have lesser access to life opportunities, and have limited or no involvement in decision-making on important issues directly affecting their lives [ 25 , 26 ]. Figures indicative of women’s inequalities in Nepal suggest that one-third of women have no education, fifty-two percent of women are involved in non-paid jobs, and women are less likely than men to own a home or land [ 27 ]. The men in Nepalese society are positioned higher and are expected to be the breadwinner and protectors of their families. Most of these men intend to earn respect and obedience from women and are socially expected to discipline women to achieve it [ 28 ]. Many societies across the world including Nepal, recognizes violence as a private affair requiring discussion only within a family. This has led to a serious underreporting of violence committed toward women in Nepal [ 29 ]. The national gender data in Nepal is scarce, the available Nepal Demographic Health Survey 2016 identifies that since the age of fifteen, twenty-two percent of women and seven percent of women experience physical and sexual violence, respectively in the past twelve months [ 27 ].
The contributing factors for violence against women in Nepal include the lower social status of women, illiteracy, economic dependency, patriarchal society, sex trafficking, alcohol-related abuse, dowry-related violence, infidelity, extramarital affairs of husband, unemployment, and denial of sex with husband [ 30 , 31 , 32 ]. Nepalese women have been repressing violence with silence due to the fear of breaking relationships, receiving less love and affection from family, fear of social norms by going against men, lack of faith in the justice system, and the threat of increased violence [ 33 ]. Women and girls in Nepal are sex trafficked to various countries. Sex trafficking in Nepal is prevalent due to persistent gender inequality, violence, stigma, and discriminatory socio-cultural structures; however, the actual extent of sex trafficking is still undetermined [ 17 , 34 , 35 ].
The recent trends in Nepal with the increasing number of out-migration of men for employment have provided women with temporary autonomy, and a shift in the gender roles. Earlier research has identified that migration of male spouses has provided a resistance to the power dynamics for women on the other hand it has limited their mobility, required them to share decision-making with household structures, face continued social vigilance on the money received from remittance, and get central attention with their personal sexual lives [ 36 , 37 ].
Morang district lies in the eastern region of Nepal. A district profile report based on a census survey [ 38 ] identifies that the place is inhabited by a close to a million population, out of which ethnic groups ( close to forty percent) live in the district with a majority (seventy-eight percent) of its population living in the rural areas. Tharu an ethnic group is one of the dominant population in the study area and all study participants for this study were from same Tharu population. A close to thirty-six percent of women in the district are illiterate and the average age of marriage is eighteen years. The report identifies that only twenty-three percent of women engage in economic activities apart from agricultural work and less than fourteen percent of women head the household. Almost eighty percent of the population in the district practice Hinduism.
This study is a part of a large intervention project and it was focused to establish a qualitative baseline of the gender status in the study area. This study aimed to explore participants’ experiences and understanding of gender inequality, violence against women, and information on sex trafficking in the Morang district of eastern Nepal. The selection of sex trafficking topic was motivated to assess the respondents’ general understanding of one of the consequences of inequality and violence faced by women. The study focused to explore factors that help to produce and sustain the practice of gender inequality and violence against women in the local community.
Participants
This study was part of a larger control-comparison project that used Forum Theatre interventions to promote gender equality, reduce violence against women, and increase awareness of sex trafficking [ 39 , 40 ]. The participants for the focus group discussion included the intervention population from one of the randomly sampled intervention sites. A multistage focus group discussion [ 41 ] was used involving the same participants discussing various emerging topics at different periods. The participants were recruited voluntarily during an earlier quantitative data collection for the project. The study used a purposive sampling method for the selection of participants. The local field staff at the study site facilitated the recruitment of the participants. The study formulated separate male and female groups. A total of six focus groups, three each with male and female groups were conducted over twelve months. Two inclusion criteria were set for participation. First, the participants had to be part of the population of the larger study. Secondly, they had to witness and/or participate in the Forum Theatre interventions conducted in between the study. The set inclusion criteria served a dual purpose of understanding the causes of inequality and violence and further helped to develop and determine the efficacy of participatory Forum Theater intervention for awareness-raising among the study intervention groups [ 39 ].
A total of thirty-six participants consisting of sixteen males and twenty females joined the discussions. The first discussion consisted of eight participants each from groups while the second and the third discussion missed two female and four male participants respectively. The majority of the participants were 20–29 years old. Tharu, an ethnic community of Nepal, is a dominant population in the study area, and all the participants belonged to the same Tharu community. Only one female participant was unmarried, and a single married male participated in the discussions. All participants were literate, with four males completing a bachelor's level of education. Seven female participants had education below the high school level. The nuclear family with parents and their children was the major family type identified in both male and female groups. Table 1 provides the detail of the participants.
The focus group discussions were conducted in January 2017, April–May 2017, and January 2018. The discussions were conducted in a place recommended by the participants. An isolated place in an open setting at the premise of a local temple was used for conducting all discussions. The participants were briefed about the objectives of the discussion and written consent was obtained for their participation. Verbal consent was taken for the audio recording of the discussions. Each participant was assigned a unique numerical code before the discussions to ensure anonymity during recording, note-taking, and analysis. The discussions averaged ninety minutes during each session. The discussions were conducted with the same participants and no new participants were added during the follow-ups. A single male and female participant were missing in the second follow up and two male participants missed the final follow-up. The reason for missing participants was due to their unavailability as they were out of the village due to personal reasons.
The discussions were conducted in the Nepali language. The first author moderated all six discussions, a support field staff member took the notes, and the last author observed the discussions. The audio recordings were translated into English, and the transcriptions were checked with the recordings to verify accuracy. The field and the discussion notes were used during various stages of data analysis. The notes provided information on the discussion setting, as well as the verbal and nonverbal expressions of the participants. The notes helped to assess the impressions, emphasis, and feelings of the participants during the discussions.
The discussions used pre-formulated discussion guides with open-ended questions on inequalities, gender practices, violence, and sex trafficking. The guiding questions were based on the theoretical premise of discrimination, patriarchy, oppression, hegemony, and participation of women. Three separate discussion guides were developed for each of discussions. The guides were developed by the first and last authors. Probing was done on several occasions during the discussion to gain more clarity on the issue. Cross-checking among the participants and between the groups was done to triangulate received information. Any topic deemed appropriate for discussions and/or any unclear issues identified during the initial data analysis came up subsequently in the discussion guide during the follow-ups.
Data analysis
This study used the constructivist grounded theory method. This method adheres to a constructivist philosophical approach wherein both researchers and participants mutually co-construct the meaning of a phenomenon [ 42 ]. This interaction is important since it helps to impart the meaning of shared experiences [ 42 ]. The constructivist grounded theory made it possible to (re) discover gender issues, important for both the researcher and the study participants. This method allowed the study to progress with responsiveness to emerging issues with an in-depth exploration of the identified issues. This clarity was achieved through repeated interactive discussions, analysis of explanations, and sharing of emergent findings with the study participants.
The audio recordings were translated and transcribed into English. Six transcripts from discussions were initially analyzed using a line-by-line coding process. The coding process helped with the fragmentation of data through interactive comparisons. Fifty-two initial codes such as gender differences, restricting women, alcohol-related violence, underreporting of sexual violence, coping, etc. were identified. The later stage of focused coding helped to achieve categorized data, providing logical sense to the developed initial codes. Three focused codes, namely, the subjugation of women, violence, and chasing dreams were formulated during the analysis. The abductive reasoning from the codes, memos, and discussion notes helped to develop the theoretical concept. The development of conceptual abstraction involved an iterative comparison of the data, codes, categories, memos, and discussion notes.
The constant communication between the authors during the stages of data analysis such as the formulation of codes, explanations of concepts, and categories helped to refine the analysis. The shared experiences of the participants and the description of the data collection and analysis included substantial details, enabling comparisons for future research and application to other similar contexts. The reliability of the study is warranted by the theoretical saturation [ 42 ] achieved by this study. This is supported by prolonged engagement with the study participants with communication on the emerging findings, and triangulation.
Reflexivity has a greater significance for the constructivist approach. The first and the second author of Nepalese origin were aware of the socio-cultural norms, stereotypes, values, and stigmas associated with gender in the local context. This helped the study to ascertain the depth of inquiry within the acceptable local normative limits. The non-Nepalese author, familiar with the study participants and Nepalese contexts, witnessed the discussions as an observer. The prior knowledge of the authors helped to critically assess different schemas, perspectives, and explanations shared by the participants. The universality of gender inequality and violence against women and its re-examination in the local context helped the authors to build upon existing knowledge by providing contextual explanations. The diversities among the authors and research participants established a basis for co-creating the perceived and observed realities.
The section below describes the participants’ perceptions and understanding of inequality and violence. The section contains subheadings that were derived as themes in the data analysis. The first theme subjugation of women; discusses how norms, beliefs, and practices produce inferior status and positions for women. The second theme domestic and gender violence; provides a narrative of interpersonal and socio-cultural violence present in the study area. The theme of chasing dreams; discusses the process of sex trafficking as an outcome of violence. The theoretically abstracted concept of power-play identifies the cause for the generation of power imbalance producing inequality and the use of violence by men.
Subjugation of women
The subjugation of women reflected practices and beliefs imparting positional differences for women and their social situation compared to men. The participants shared a common understanding that belief systems adhering to male supremacy have positioned women in a lower status. They provided examples of social practices of male supremacy such as males being considered as the carrier of a family name, legacy, and heritage, while women were referred to as someone else’s property. The socialization of the idea that girls will be married off to a husband and relocate themselves to their homes was identified as the major reason for instilling and perpetuating early gender differences. The participants mentioned that discriminatory practices and seclusion have situated women at the bottom rung of the gender hierarchy, establishing them as socially incompetent individuals or groups. Moreover, they inferred that selective preferences provided preparatory grounds for inequalities, and they remain attached to women throughout their lives. The participants provided examples of unequal access to education and life opportunities as a practice of selective preferences occurring in the community. They mentioned that socialization with these discriminatory beliefs and their practice helped to develop specialized gender roles from an early age. The participants provided an example of how gender intersected with mobility and resource generation in the community, it was clear from the discussions that this has restricted women inside homes but provided freedom and opportunities for men. A female participant expressed,
A woman from a poor family is more than willing to work and support her family. But she is not allowed by the men in the family to work outside of the home.
The participants informed that differences between the sexes were visible for women from a young age. Sharing practical examples from the community, the participants from both groups stated that girls received education mostly in low-cost government and community schools, while boys were enrolled in expensive private schools. They raised concerns that this selective investment for education, cited as the ‘building block of life’ by the participants, installed lesser capacity, and negotiating abilities in girls. A female participant stated,
There are differences in educational opportunities for boys and girls in our community. Family provides more support for a boy’s education by enrolling him in private schools, while a girl mostly gets her education in a community school together with engagement in household work.
The discussions revealed that women required several male anchors for their survival during their various stages of life. The participants provided examples of the shift of anchors for women which traversed from a father to a husband during marriage and later to the male child during her old age. They believed that this tradition of transferring women’s identity established men as a higher social category and stripped women of their individuality and identity. A male participant added,
Women have to remain dependent on men throughout their lives, first with their fathers and later with their husbands. They remain completely dependent as they are not economically active. This makes men believe that they have higher authority.
The female participants provided an example of marriage to illustrate how someone else’s decision-making had been affecting women’s lives. A participant explained that women were held responsible for household activities after marriage and any support for career progression or education was restricted despite her desire for its continuation. It was inferred that women had to drop their hopes and aspirations as the husband and his family made decisions for them. The female participants agreed that this continuous exposure to the ideas of male supremacy makes them start to believe and internalize the idea that women have lesser cognitive abilities and intelligence compared to men. A female participant stated,
Men and women certainly have different mental abilities. Men think and act differently often in a smart way compared to women.
The participants from both groups expressed that youth in the community were developing flexible attitudes and beliefs towards gender roles and responsibilities. They agreed that both young men and women were observed altering their roles and responsibilities shifting from traditional gender ideologies. The participants expressed that instilling these fluidity and flexible approaches in the older generation was impossible as they strictly followed traditional beliefs and practices. Few of the female participants admitted that at times young women also fail to accommodate the situation and reap benefits from available opportunities. The discussions revealed that a few of the women in the community received opportunities for independence and economic empowerment. These women had received entrepreneurial training and various skill development activities for sustaining livelihoods with practical skill-based training in tailoring, beautician, and doll-making. The female participants expressed that opportunities for independence and growth slipped away from them due to a lack of family support, financial constraints, and self-passivity. They explained that starting a business required approval from a family which was difficult to obtain. Moreover, if women made a self-decision to start up on their own, they lacked the initial capital and had to rely on men for obtaining resources. The participants further explained that the denial of men to support women were majorly due to the fear that norms of staying indoors for women will be breached and economic independence may enable women to have a similar financial footing as men. The participants stated that self-passivity in women emerged due to their engagement in household multiple roles, dependency upon males, and lack of decision-making power and abilities. A female participant summed it up by stating,
Some of us women in the community have received entrepreneurial skills training, but we have not been able to use our skills for our growth and development. Once the training finishes, we get back to our household chores and taking care of the children.
The female participants admitted that acceptance of belief systems requiring women to be docile, unseen, and unheard were the reasons for this self-passivity. The female participants resonated that the external controlling and unfavorable environment influenced by practices of discriminatory norms and beliefs developed self-passivity for women. A female participant expressed the cause and consequence of self-passivity as,
Women have inhibitions to speaking their minds; something stops us from making our position clear, making us lose all the time.
The discussions identified that gender norms were deeply engraved in various social interactions and daily life, and any deviance received strict criticism. The participants shared common examples of sanctions for women based on rigid norms like restrictive movements for women, social gossiping when women communicated with outsider men, prohibition for opinion giving in public, and lesser involvement during key decision-making at home. The participants shared that norms dictating gender roles were in place for both men and women with social sanctions and approval for their performance. A male discussion participant who occasionally got involved with cooking which was a so-called “women’s job” faced outright disapproval from his female relatives and neighbors. The male participant stated,
If I cook or get engaged in any household jobs, it is mostly females from the home and neighborhood who make fun of me and remind me that I am a man and that I should not be doing a woman’s job.
The foreign migration of youth looking for job opportunities has affected the Tharu community. It was known that a large number of men were absent from the community. The participants stated that women in such households with absent men had gained authority and control over resources, moreover, these women have been taking some of the men’s roles. The participants disclosed that these women had greater access and control over resources and were involved in the key decision-making positioning them in a relatively higher position compared to other women. It was known that this higher position for women came with a price, they were under higher social vigilance and at higher risk of abuse and violence due to the absence of ‘protective men’. It was known that women's foreign employment was associated with myths and sexist remarks. The participants shared that women had to face strict social criticisms and that their plans for livelihood and independence were related to an issue of sexual immorality and chastity. The participants from both groups strictly opposed the norms that associated women with sexual immorality but lamented that it continues. A male participant provided an insight into the social remarks received by women if she dares to go for foreign employment,
If a woman wants to go for a foreign job, she is considered to be of loose character. The idea that she is corrupt and will get involved in bad work will be her first impression of anyone.
Although the participant did not explicitly describe what bad work referred to as but it was inferred that he was relating it to sex work.
Domestic and gender violence
The participants identified violence as control, coercion, and use of force against someone will occurring due to unequal status. They primarily identified men as the perpetrators and women as the victims of violence. They explained that two types of violence were observed in the community. The first type occurred in an interpersonal relationship identified as physical, emotional, and sexual violence. The second type, as explained by the participants had its roots in socio-cultural belief systems. They provided examples of dowry exchange and witchcraft accusations for the latter type. The participants identified women as primary victims and listed both men and women as the perpetrators of both types of violence. They reported that physical violence against women by men under the influence of alcohol was the most commonly occurring violence in the community. The participants from both groups confirmed that wife-beating, verbal abuse, and quarrel frequently occurred in the community. It was known from discussions that alcohol consumption among men was widespread, and its cultural acceptance was also increasing episodes of violence. One of the female participants clarified further,
The most common violence occurring in our society is wife-beating by a husband under the influence of alcohol. We see it every day.
The participants reported the occurrence of sexual violence in the community but also pointed out that people refrained from discussing it considering it a taboo and private affair. The participants had hesitation to discuss freely on sexual violence. During the discussions, participants from both groups informed only of rape and attempted rape of women by men as sexual violence present in the community. Despite repeated probing, on several occasions, none of the participants from either group brought up issues and discussions about any other forms of sexual violence. Participants from both groups confirmed that stories about incidents of rape or attempted rape emerged only after cases were registered with the local police. The participants presumed that incidents of rape and attempted rape were not known to the wider community. A female participant stated,
Sexual violence does occur in our community, but people mostly do not report or disclose it, but they tend to keep it amongst themselves and their families.
The participants explained the identity of the rape perpetrator and victim. They identified the perpetrator as a rich, influential, and relatively powerful man from the community. The victim was portrayed as a poor and isolated woman which lesser social ties. It was known from the discussions that most of the rape cases in the community were settled with financial negotiations and monetary compensations for the victim rather than finding legal remedies. It can be inferred that the victimization of women intersects with gender, wealth, social stature, and affluence. The participants feared that this practice of settlement of rape with money could make rape a commodity available for the powerful, rich, and affluent men to exploit and victimize women. A male participant clarifies,
Recently, a man in his sixties raped a young girl near our village. The victim's family was ready to settle with monetary compensation offered by the rapist, but the involvement of the community stopped it and the rapist was handed over to the police.
The participants shared available coping mechanisms against violence practiced in the community by women. It was learned that the victim of household violence mostly used community consultation and police reporting to evade further violence. They divulged that community consultation and police reporting resulted in decisions in favor of victim women, directing abusive husbands to show decency and stop committing violence. The fear of legal repercussions such as spending time in police custody and getting charged under domestic violence cases was understood as the reasons for husbands to stop abuse and violence. The discussions revealed that women who file a formal complaint about their husband’s violent behavior could face an increased risk of violence. The participants disclosed that sharing such incidents publicly brought shame to some of the men and increased their anger, and often backlashed with increased violence. The participants in both groups stated that not all women in the community reported violence. They identified that women tend to be quiet despite facing continuous violence due to the fear of encountering more violence and to keeping their families together. A female participant clarifies,
Lodging public complaints against the abusive husband can sometimes escalate the violence. The husband’s anger for being humiliated in public must be faced by the woman inside the closed doors of the house with more violence and the men’s threat of abandoning the relationship.
The participants stated that socio-cultural violence against women in dowry-related cases was widespread and increasing. The dowry exchange was explained as a traditional practice with the family of the bride paying cash and kind to the groom's family. The participants clarified that the practice of dowry in the earlier days must have been an emergency fund for the newly wedded bride in a newer setting. According to the participants, the system of dowry has now developed and evolved as a practice of forced involuntary transfer of goods and cash demanded by the groom’s family. The discussions disclosed that the demands for dowry were increasing with time and failing to provide as promised immediately resulted in violence for the newly wedded bride. The participants described that dowry-related violence starts with taunts and progresses to withholding of food, verbal abuse, and finally, physical violence. They added that perpetrators of such violence were both men and women from the groom’s family. They stated that due to poverty not all bride families in the community were able to supply all demanded dowry which has exposed a large number of women to face dowry-related abuse and violence. The discussions also informed of a newer trend among girls by demanding goods during their wedding. It was shared that this new emerging trend had increased a two-fold financial burden on the bride’s family with heavy marriage debts. The male participants when questioned about the dowry demands cunningly shifted the responsibilities towards family and stated that it was not the groom but their families who were making such dowry demands. The discussions verified that dowry practice was so engraved in the community that it was impossible to even imagine a marriage without any dowry. A male participant reflected,
If I marry without any dowry, my family, neighbors, and all whom I know would consider that I am insane.
The participants also discussed and identified harmful traditional practices present in the community. The participants informed a common practice of accusing women of as witches existed in the community. It was mentioned that women faced witchcraft allegations in different situations. They provided examples of witchcraft allegations in common situations such as when someone’s cow stops producing milk when a child has a sore eye, when someone is bedridden due to sickness for days, or when a woman undergoes a miscarriage, etc. The participants stated that women accused of witch were always elderly/single women living in seclusion, poverty, and with fewer social ties. They also shared that the witch doctors, who ascertain whether a woman is a witch or not, were surprisingly mostly always men and hold higher status, respect, and social recognition. The consequences of being labeled as a witch, as explained by the participants, haunted victim women with torture, name-calling, social boycott, and extremes of physical violence. The participants informed that inhumane practices such as forceful feeding of human excreta prevailed during the witch cleansing sessions. A female participant explaining the witchcraft situation stated,
Witchcraft accusation is very real in our community; I know someone who has tortured his mother, citing reasons for his wife being childless. The old woman was called names, beaten, and later thrown out of the home.
The participants felt that men’s use of violence and its legitimization primarily existed due to gender hierarchy and internalization of the belief that violence was the best method to resolve any conflict. They inferred that men’s use of violence was further reinforced by women's acceptance and belief that violence had occurred due to their faults and carelessness. The female participants shared examples of common household situations that could result in an episode of violence such as women cooking distasteful food, failing to provide timely care to children and the elderly due to workload, and forgetting to clean rooms. These incidents make women believe that violence majorly occurred due to their mistakes. Furthermore, the participants believed that this self-blaming of the victim resulted due to constant exposure to violence and a non-negotiable social positioning of women for raising questions. The participants stated that beliefs instilled by religion increased the likelihood of victimization for women. They explained that religious practices and ideologies required women to refer to their husbands as godly figures, and a religious belief that anything said or done against husbands was a disgrace bringing sin upon her and family positioned women in an inferior position. A male participant added,
We belong to a culture where females worship their husbands as a god, and this might be an important reason for men to feel powerful as a god to exploit and abuse women.
The discussions put forward the idea that the existence of discriminatory beliefs, reinforcement of such beliefs, and a blind following of such practices produced differences and violence. The male participants acknowledged that the idea of male supremacy not only produced violence but also established a belief system that considered violence as an indispensable way to treat deviated women. One male participant stated this idea of male supremacy and privilege as,
The language of the feet is essential when words fail.
The participants also discussed violence committed toward men by women. The male participants burst into laughter when they stated that some men were beaten by their wives when they were drunk. The male participants admitted that intoxication reduced their strength and they got beaten. The female participants, on the other hand, assumed that women hit intoxicated men due to frustration and helplessness. They further clarified that the act of husband beating was a situational reaction towards men who had spent all of their daily earnings on alcohol. They stated that women with the responsibility to cook and feed family find themselves in an utterly helpless situation by the irresponsible drinking behavior of men. The male participants shared incidences of violence against men due to foreign migration. It was revealed in the discussions that some of the migrating men’s wives had run away with remitted money, abandoning marriage, and breaking up the family. The male participants identified this as a form of victimization of men, furthermore, the spreading of rumors and gossip caused emotional instability in those men. The female participants confirmed that some returning men failed to find their homes, property, money, and/or their wives. The discussion participants in both groups identified that this practice was on the rise in the community. It became apparent from the discussions that this increasing trend of women running away with the money and breaking away from family was a personal issue requiring social remedies.
Chasing dreams
The participants referred to sex trafficking as the exploitation of women, arising from poverty, illiteracy, and deceit. Explaining the causes of trafficking, the participants stated that women living in poverty, having dreams of prosperity and abundance were tricked by the traffickers making them victims of sex trafficking. The participants mentioned that women who had dreams larger than life and yearned for a comfortable and luxurious life in a short time were at a greater risk for sex trafficking. The participants from both groups resonated that the traffickers had been manipulating the dreams of poor women and deceiving them into trafficking. A female participant elaborated,
Women in poverty can be fooled easily with dreams. She can be tricked by a trafficker by saying I will find you employment with good pay abroad, and she gets into the trap easily.
A male participant further clarified,
Women readily fall into fraud and trickery shown by the traffickers who assure of luxurious life with foreign employment and this bait often leads to sex trafficking.
They identified that false hopes for foreign jobs were primarily used as an entry point by the traffickers to trap potential victims. Besides, they stated that some traffickers tricked women with false romantic relationships and marriages to win over their trust enabling traffickers to maneuver women as they wished.
It was identified that traffickers were not always strangers but known and familiar faces from the community, allowing the traffickers to gain the victim’s trust. The discussions divulged that traffickers strategically chose women who were less educated and poor. The participants explained that sex trafficking mostly occurred among women from a lower caste (the caste system is hierarchy-based in Hindu society which is determined by birth and unchangeable). They further explained that if one of these lower caste women went missing, it seldom raised any serious concerns in society, making these women easy targets for the traffickers. The discussions revealed that life for the survivors of sex trafficking was difficult. They identified that the survivor had to face strong stigmas and stereotypes which further increased their risk for re-victimization. The participants explained that the social acceptance of the trafficking survivors was minimal and finding a job for survival was very difficult. It was reported that social beliefs, norms, and practices were rigid for sex trafficking survivors and provided lesser opportunities for complete social integration. A female participant stated,
The story of a sex-trafficked woman does not end after her rescue. It is difficult for her to live in society, and this increases her chances of being a further victim.
The discussions in both groups highlighted that education and awareness were important for reducing sex trafficking. The participants felt that securing a livelihood for women was essential, but they identified it as a major challenge. The female participants recommended the use of education and awareness for reducing sex trafficking. They demanded effective legal actions and stringent enforcement of the law with maximum punishment for offending sex traffickers. They mentioned that the fear of law with maximum punishment for culprits could help decrease cases of trafficking.
The theoretical concept of power play
The discussions identified that gender inequality and violence against women occurred as men possessed and exercised greater authority. The participants explained that the authority emerging from male-centric beliefs was reinforced through established socio-cultural institutions. It was known that oppressive practices toward women in both public and private life have led to the domination and devaluation of women. The differences between men and women were known to be instilled by evoking discriminatory beliefs and due to internalization of them as fundamental truths by women which further helps to sustain these created differences.
The concept of power-play developed from the study has its roots in the belief systems and was found constantly used by men to maintain created differences. The power-play rise due to patriarchy, guiding discriminatory norms and unequal gender practices. These norms and practices in the canopy of patriarchy positions women inferior to men and impose control and restrictions. The power play possessed multi-dimensional effects on women such as creating further barriers, restricted life opportunities, the need for men-centered anchoring systems, and exclusion from the public arena. The power play gains its strength from the strict enforcement of stereotypical practices and committed adherence to gender performances. This leads to internalization of subordination as a natural occurrence by women. These further isolate women putting them into several non-negotiating positions. The power play at an individual level provides restrictive movement for women, barring them from quality education and other life opportunities, and is exhibited in alcohol-related assault and sexual violence. At the structural level, this power play limits women from economic opportunities, access to resources, and decision-making, and induces socio-cultural inequality exhibited in dowry and cases of witchcraft. The socio-cultural acceptance of power-play allows men to use violence as a misuse of power and use it as an effort to maintain authority. The use of power-play for committing violence was identified as the worst display of exercised power play.
Figure 1 describes the concept of power-play developed from the study. The power-play model is based on discussions and inferences made from data analysis. The model provides a description and explanation of how women are subjected to inequality and face violence. The concept of power play derives its strength from the subjugated status of women which are based on selective treatment, self-embodiment of inferiority, imposed restrictions and due to lesser life opportunities. The power play gain legitimacy through social approval of the status differences between men and women and through social systems and institutions majorly developed and favoring men. The status difference between men and women and its approval by developed social institutions and processes give rise to the concept of powerplay. It identifies that status differences allow men to gain and (mis)use power play not only to maintain differences but also enable men to use violence. The use of power-play exists at both interpersonal and cultural levels. Further, the model elaborates on influencers causing subjugation of women, display of power-play, and violence. The model identified that lodging public complaints and seeking legal remedies are the influencers that suppress violence against women. The influence of Forum Theater was perceived to have greater influence for victim, perpetrator, and bystanders. The influencers that aggravate violence are fear of further violence, the nature of the interpersonal relationship, alcohol-related abuse, and remaining silent especially on sexual violence. The cultural violence mentioned in the model refers to dowry and witchcraft-related violence and stands as systemic subordination. In the model, sex trafficking is depicted as one of the outcomes of inequality and violence faced by women majorly occurring due to deceit and fraud.
The theoretical concept of power-play developed in this study identifies that inequality produces violence and violence further reinforces inequality, creating a vicious circle. The power play situates hierarchy based on gender as the primary cause and identifies violence as an outcome of this power asymmetry. The authority to use power by men is received by social approval from embedded structures and institutions. The functioning of associated structures and norms is designed and run by men helping to perpetuate the dominance and subjugation of women. The study identifies that both interpersonal and socio-cultural violence emerges due to the positional differences and use of power. The study found that an element of control exists in interpersonal violence. The findings show that few victim women in the community took advantage of consultations and rely on the law to evade and /or cope during the occurrence of interpersonal violence. A large number of victims women however suffer silently as they are unable and unwilling to take a stand on violence due to their perceived positional differences and strict norms following. The study finds that violence originating from socio-cultural systems is widely accepted and no established means of control exists. The practice of heinous acts against a fellow human during witchcraft allegations and dowry exchanges is prohibited by the law of Nepal but is widespread. This situates that practices which are based on belief systems are more effective than prevailing national laws which try to stop them. Sex trafficking as a form of sexual violence use deceit and fraud against women. Poverty and illiteracy compel women to search for alternatives, and they become easy victims of sex trafficking when their dreams of a better life are manipulated by the traffickers. The false promise of a better life and highly paid job put women in a non-negotiating position with traffickers. The cherished dream of escaping the prevailing status-quo of oppression, subordination, violence, and poverty mesmerizes women to take risky decisions, falling into the risk and trap of sex trafficking.
The socio-cultural norms are the unwritten script of social operatives and functioning. These social norms function as codes of operation and are a major determinant for behavior and interactions between people [ 43 ]. The study has found that these norms were skewed, and most favored men, giving rise to status differences and producing inequalities for women. This is observed with lesser life opportunities, lower participation in decision-making, and a constant need to anchor women. This further helps men to maintain their hierarchical positional status and use violence. The subjugation of women does not occur in a linear process, it is influenced by the internalization of discrimination resulting in lower self-esteem, suppression, and domination of women based on norms and unequal practices. Earlier research has identified that norms and beliefs encourage men to control women, and direct them to use force to discipline women which increases the risk of violence occurrence [ 44 , 45 ]. An earlier study shows that traits of masculinity require men to become controlling, aggressive, and dominant over women to maintain status differences [ 46 ]. The study confirms that men upon receiving both normative and social approval for using violence against women can do so without hesitation.
Violence against women in Nepal mostly occurs inside the home and is only reported when it reaches higher levels of severity. The acceptance of violence as a private affair has restricted women from seeking support and discourages them from communicating their problems with outsiders [ 47 ] this increases more likelihood for men to use violence. The study finds issues related to sex and sexual violence is a taboo and are seldom reported. The study could only identify cases of sexual assault registered with the police and other cases known to the wider community as sexual violence. A community with known incidents of rape may have other cases of abuse, harassment, incest, forceful sexual contact, etc. Failure to report incidents of sexual violence infer that a large number of women could be suffering in silence. Earlier research identifies that increased stigmatization associated with sexual violence, and fear of seclusion cause reluctance in victims to report or seek support [ 48 ]. This silencing of victims provides men with greater sexual control over women [ 49 ] increasing more likelihood of use of violence. Gender-based inequality and violence intersect structures, institutions, and socio-cultural processes, making inequality and violence visible at all levels. The dowry-related violence and witchcraft allegation intersect interpersonal and structural violence. This cultural violence forces women to be a victim of lifelong abuse and trauma. The intersecting relationship between gender norms, social structures, and individual is so closely knitted that it produces varieties of inequality and violence at all levels [ 50 ]. Emotional violence in this study only emerged as a type of violence, during discussions in both groups. It did not emerge as a major concern for the participants except for dowry-related violence and violence against men. The intertwined nature of emotional violence and its occurrence with each abusive, exploitative, and violent situation may have influenced the participants understand it as a result, rather than as a specific type of violence.
The power play between sexes was found in synchronicity with the established norms and prevailing stereotypes, helping to perpetuate gender power imbalance. The gender system is influenced and governed by norms and the social arena becomes the site of its reproduction through the interaction and engagement of people. This interaction provides approval to the institutions and processes that are based on constructed differences between men and women [ 51 ]. The power, as identified by Fricker [ 52 ], controls a social group and operates and operates through the agent or established social structures. A man can actively use the vested power to either patronize and/or abuse women while passively women’s internalization of social settings and embedded norms can put them docile. The social controls as reported by Foucault [ 53 ] work with the embedded systems of internalization, discipline, and social monitoring and uses coercion rather than inflicting pain. The internalization of status differences among women as indicated by the study confirms this schema of social control. The dominance of men over women with patriarchal beliefs establishes the significance of male-centered kinship. This requires women to constantly anchor with men providing grounds for inequalities to perpetuate further. This idealizes men and reinforces the belief that women are non-existent without their presence. The requirement for male anchorage has an attachment to prevailing structural inequality. The family property and resources are mostly controlled by men and it usually transfers from father to son limiting inheritance to women [ 51 ]. These glorified idealizations of men's competence as described by Ridgeway [ 54 ] idealize men as individuals with abilities, status, power, and influences. The need for women to rely on men as anchors, fear of going against the norms and social sanctions explains the positional difference and show that men possess greater competencies. The internalization of men-centric superior beliefs by women occurs due to self-passivity and devalues women creating false impressions of their abilities. The gender roles and responsibilities were strict for both sexes but provided greater flexibility, privilege, and opportunity for men. Earlier studies in congruence with this study find that socio-cultural expectations limit women from deviation, and strictly adhere to their prescribed role and expectations [ 55 , 56 ] providing an upper hand to the men. The unequal social positioning of women, as defined by a few of the participants, can help define men's use of violence. As inferred by Kaufman [ 57 ], the disadvantageous position of women and support from the established structures enable men to use aggression and violence with considerable ease. The concept of power-play derived from this study also reflects that inequalities not only create hierarchies, putting women into a subordinating position but also legitimize norms of harmful masculinity and violence [ 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ] creating a vicious cycle of inequality and violence. The concept of power-play developed by this study requires further exploration of gender relations, injustice, and patriarchy to identify multiple operatives of power with an outcome of inequality and violence.
Strengths and limitations of the study
The study followed the same participants over a period, which helped the study to achieve clarity on the topics through constant engagement. The data collection and the initial data analysis of the study were conducted by the same person, which reduced the risk of misrepresented findings. The study used follow-up discussions, which provided an opportunity to meet the participants again to resolve any ambiguities. The constant engagement with the participants helped to develop rapport and trust, which is essential to enable meaningful discussions. The study gathered rich data for developing the theory of power play in the Nepalese context. The study has attempted to explain the interplay of men’s use of power play, gender inequality, and violence against women, which, in itself, is a complex, but important issue. The study helped to develop a platform by identifying a level of awareness and needs for a Forum Theatre intervention study, a first of its kind in Nepal.
The major limitation of the study is that it was conducted with only one of the ethnic populations of Nepal; thus, the findings from this study cannot be generalized to a completely different setting. However, the transferability of the study is possible in a similar setting. The incidences of inequality and violence shared by the participants were self-reported, and no other means of verification were available to crosscheck those claims. The differences among the participants both in and between groups based on education and marital status might have influenced the study participants to understand, observe, and experience the phenomenon. The possibility of social desirability bias remains with the study, as a constant engagement with the study participants might have influenced them to answer differently. Furthermore, the discussions were conducted in groups, and participants might have had hesitation to bring up any opposing views. The study relied on collecting information on social norms and individual experiences and the perceptions of the study participants. It cannot be claimed that the study is devoid of any data rigidity as participants were free to choose what they wanted to share and express.
Study implications
The study explains gender practices, norms, violence against women, and sex trafficking in Nepal. The study helps to increase the understanding of how gender systems are operative in the daily lives of the Tharu community in the Morang district of Nepal. Future studies can explore the established linkages of interpersonal and socio-cultural violence. Like the complex link existing between gender inequality and violence against women, interpersonal violence and socio-cultural violence cannot be studied in isolation. The study provides an opportunity for future research on exploring how changing norms have been altering the position and victimization of women. The study finds that changing gender norms and responsibilities have, on the one hand, provided agency and empowerment for women, but on the other hand, they have also increased their risk of being a victim, an area that requires further exploration. The study has identified that constant engagement with the study participants through follow-up studies ensures the richness of data, which can be useful information for a future research study design. The study can be helpful for policy development, social activists, leaders, and researchers as it discusses prevalent gender oppressions and victimization, which need to be addressed. The findings from the study can be helpful for dialogue imitation and for designing intervention projects aimed at providing justice and equality to women.
The study identifies the presence of gender inequalities and violence against women in the study area. The positional differences based on norms, institutions, and practices have assigned greater privileges to men. The concept of power-play devised by the study ascertains the maintenance of gender hierarchy to produce inequality further and victimization of women. The subjugation of women based on the social-cultural process, embedded belief systems, and norms prevent women from life opportunities and dignified life. It situates men at the highest rung of the gender and social ladder providing a comparative advantage for men to use power. Violence emerges as men’s use of power play and as a strategy for the continued subjugation of women. Sex trafficking as a consequence of inequality and violence has its origins in illiteracy and poverty with women falling prey to the deceit of traffickers. It is important that dreams for progression provide motivation for women to develop further but at the same time, dreams should not be exchanged with trickery and fraud offered by the traffickers. Awareness and attitudinal changes are imperative to challenge unequal norms, and practices, and reduce the risks of sex trafficking. This can help to develop negotiations for power-sharing which helps to reduce inequality, violence, and preparedness in chasing dreams. Changes at both individual and societal levels are necessary to develop a collective action for establishing belief systems and practices providing women with an equal position and reducing the risk of violence.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to privacy but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Felson RB, Outlaw MC. The control motive and marital violence. Violence Vict. 2007;22:387–407.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wamala S, Ågren G. Gender inequity and public health: Getting down to real issues. European Journal of Public Health. 2002.
World Health Organization. Promoting gender equality to prevent violence against women. World Health Organization. 2009.
Devries K, Maki J, Garcia-Moreno C, Petzold M, Child J, Falder G, et al. The Global Prevalence of Intimate Partner Violence Against Women. Science (80- ). 2013;340(6140):1527–38.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Walby S. Theorising patriarchy. Sociology. 1989;
Butler J. Undoing gender. Routledge. 2004.
Yllo K. Through a Feminist Lens: Gender, Diversity, and Violence: Extending the Feminist Framework In Current Controversies on Family Violence. California: Sage Publication; 2005.
Google Scholar
Heise L. Violence against women: An integrated, ecological framework. Violence Against Women. 1998;4:262–90.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Pulerwitz J, Barker G. Measuring attitudes toward gender norms among young men in Brazil: Development and psychometric evaluation of the GEM Scale. Men Masculinities. 2008;10:322–38.
Article Google Scholar
Jakobsen H. What’s Gendered about Gender-Based Violence?: An Empirically Grounded Theoretical Exploration from Tanzania. Gend Soc [Internet]. 2014;28(4):537–61. Available from: ( http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0891243214532311 ).
Cook RJ. Gender, Health and Human Rights. Heal Hum Rights Quart. 1995;350–68.
Freeman MA. Reservations to CEDAW: An Analysis for UNICEF. Discussion Pper [Internet]. UNICEF; 2009. Available from: http://www.unicef.org/gender/files/Reservations_to_CEDAW-an_Analysis_for_UNICEF.pdf
UNIFEM. Facts and figures: Violence against women [Internet]. 2007. Available from: https://asiapacific.unwomen.org/en/focus-areas/end-violence-against-women/evaw-facts-and-figures .
WHO. Multi-country study on women’s health and violence against women [Internet]. World Health Organization: Geneva; 2005. Available from: http://www.who.int/gender/violence/whomulticountry-study/en/ .
UN Women. World Survey on the Role of Women in Development. Gender Equality and Sustainable Development. New York: United Nations; 2014.
Thomas D, Beasley M. Domestic Violence as a Human Rights Issue. Albany Law Rev. 1995;58:1119–47.
Coomaraswamy R. Special Rapporteur on Violence against Women, its Causes and Consequences, Integration of the Human Rights of Women and the Gender Perspective: Violence U.N. Doc. E/CN.4/1999/68 Against Women: Violence against women in the family [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland; 2002. Available from: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/459009?ln=en
OHCHR. 15 Years of the United Nations Special Rapporteur on Violence against Women (1994–2009)-A Critical Review [Internet]. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR); 2009. Available from: https://www.ohchr.org/Documents/Issues/Women/15YearReviewofVAWMandate.pdf
Stephanie Rose M. The role of structural and interpersonal violence in the lives of women: a conceptual shift in prevention of gender-based violence. BMC Women Heal. 2015;15:93.
Farmer PE, Nizeye B, Stulac S, Keshavjee S. Structural violence and clinical medicine. Plos Med. 2006;3(10):e449.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
WHO. World Report on Violence and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002.
Connell RW. Hegemonic Masculinity. Jackson S, Scott S, editors. Gender: A Sociological Reader. London: Routledge; 1987.
UNFPA. Overcoming violence against women through an integrated and community-based approach Vol. 2, Programming to Address Violence Against Women. 8 Case Studies. 2008.
Pigg S. Inventing Social Categories through Place: Social Representations and Development in Nepal. Comp Stud Soc Hist. 1992;34(3):491–513.
Lamichhane P, Puri M, Tamang J, Dulal B. Women’s Status and Violence against Young Married Women in Rural Nepal. BMC Womens Health. 2011;11:19.
Atteraya MS, Gnawali S, Song IH. Factors Associated With Intimate Partner Violence Against Married Women in Nepal. J Interpers Violence. 2015;30(7):1226–46.
Ministry of Health N, New Era. Nepal Demographic and Health Survey 2016 [Internet]. Kathmandu, Nepal: MOH/Nepal, New ERA, and ICF; 2017. Available from: http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR336/FR336.pdf
Ghimire DJ, Axinn WG, Smith-Greenaway E. Impact of the spread of mass education on married women’s experience with domestic violence. Soc Sci Res. 2015;
Joshi S, Kharel J. Violence against Women in Nepal -- An Overview. Free Libr. 2008;
Government of Nepal. A study on gender based violence conducted in selected rural districts of Nepal. Kathmandu, Nepal: Office of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers; 2012.
Deuba K, Mainali A, Alvesson HM, Karki DK. Experience ofintimate partner violence among young pregnant women in urban slums of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: a qualitative study. BMC Women’s Heal. 2016;16:11.
Sharma S, SRIF/SNV. Domestic violence in Nepali society: root cause and consequences a research report. Social Inclusion Research Fund; 2007.
Joshi SK. Violence Against Women (VAW) in Nepal: Role of Health Care Workers. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2009;7(2):89–91.
Dahal P, Kumar Joshi S, Swahnberg K. “We are looked down upon and rejected socially”: A qualitative study on the experiences of trafficking survivors in nepal. Glob Health Action. 2015;8:29267.
Huda S. Sex trafficking in South Asia. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2006;94(3):374–81.
Hendrickson ZM, Owczarzak J, Lohani S, Thapaliya Shrestha B, Underwood CR. The (re)productive work of labour migration: the reproductive lives of women with an absent spouse in the central hill region of Nepal. Cult Heal Sex. 2019;21(6):684–700.
Hendrickson ZM, Lohani S, Thapaliya Shrestha B, Underwood CR. Talking about reproduction with a migrating spouse: Women’s experiences in Dhading. Nepal Health Care Women Int. 2018;39(11):1234–58.
DDC. District Profile Morang 2070 [Internet]. Biratnagar, Morang; 2013. Available from: http://ddcmorang.gov.np/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/District-profile-2070.pdf
Dahal P, Joshi SK, Swahnberg K. Does Forum Theater Help Reduce Gender Inequalities and Violence? Findings From Nepal. J Interpers Violence [Internet]. 2021 Mar 4;0886260521997457. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260521997457
Dahal P, Joshi SK, Swahnberg K. The Prevalence of gender inequalities and gender based violence in eastern Nepal. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2019;17(4 [ISSUE 68|OCT.-DEC).
Hummelvol JK. The Multistage Focus Group Interview A Relevant and Fruitful Method in Action Research Based on a Co-operative Inquiry Perspective. Nor Tidsskr Sykepl. 2008;10.
Chamraz K. Constructing Grounded Theory A Practical Guide Through Qualitative Analysis. London, Thousand Oaks, New Delhi: SAGE Publications; 2010.
Darlauf SN, Blume LE. New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Second. London: Macmillan; 2008.
Book Google Scholar
Ilika AL. Women’s Perception of Partner Violence in a Rural Igbo Community. Afr J Reprod Health. 2005;9:77–88.
Mitra A, Singh P. Human Capital Attainment and Gender Empowerment: The Kerela Paradox. Soc Sci Q. 2007;88:1227–42.
Niaz U. Violence against women in South Asian countries. Arch Women’s Ment Heal. 2003;6(3):173–84.
Khan H. Women’s perceptions and experiences of sexual violence in marital relationships and its effect on reproductive health. Health Care Women Int. 2008;29:468–83.
Sable M, Danis F, Mauzy D, Gallagher SK. Barriers to reporting sexual assault for women and men: perspectives of college students. J Am Coll Heal. 2006;55:157–62.
Flood M, Pease B. Factors Influencing Attitudes To Violence Against Women. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2009;10(2):125–42.
Jewkes R, Penn KL, Rose JH. ‘‘If they rape me, I can’t blame them”: Reflections on gender in the social context of child rape in South Africa and Namibia. Soc Sci Med. 2005;61:1809–20.
Cislaghi B, Heise L. Using social norms theory for health promotion in low-income countries. Heal Promot Int. 2019;34(3):616–23.
Fricker M. Epistemic Injustice: Power and the Ethics of Knowing. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2007.
Foucault M. Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison. New York: Vintage Books; 1995.
Ridgeway CL. Framed Before We Know It: How Gender Shapes Social Relations. Gend Soc. 2009;23(2):145–60.
Hollander J. Demand More of People: Accountability, Interaction, and Gender Change. Gend Soc. 2013;27(1):5–29.
West C, Zimmerman D. Doing Gender. Gend Soc. 1987;1(2):125–51.
Kaufman M. The Construction of Masculinity and the Triad of Men’s Violence. Beyond Patriarchy: Essays by Men on Pleasure, Power, and Change. Canada: Oxford University Press; 1987.
Connell R. Masculinities. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1995.
Courtenay WH. Constructions of masculinity and their influence on men’s well-being: a theory of gender and health. Soc Sci Med [Internet]. 2000;50(10):1385–401. Available from: ( http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0277953699003901 ).
Jakobsen H. What’s Gendered about Gender-Based Violence? Gend Soc. 2014;28(4):537–61.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all the focus group discussion participants. The authors are indebted to Bhojraj Sharma, Deekshya Chaudhary, Subham Chaudhary, and Dev Kala Dhungana for their coordination and facilitation in reaching the discussion participants.
Open access funding provided by Linnaeus University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health and Caring Science, Linnaeus University, 391 82, Kalmar, Sweden
Pranab Dahal & Katarina Swahnberg
Department of Community Medicine, Kathmandu Medical College, 446 00, Kathmandu, Nepal
Sunil Kumar Joshi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
PD, SKJ, and KS were involved in the study design. PD and KS developed the discussion guides. PD was responsible for the data collection and the data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pranab Dahal .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The ethical clearance for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Committee, Kathmandu Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu. All protocols were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants for the study and verbal consent was sought for the audio recording of the discussions.
Consent for publication
All the participants provided Informed consent for the publication of their data.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Dahal, P., Joshi, S.K. & Swahnberg, K. A qualitative study on gender inequality and gender-based violence in Nepal. BMC Public Health 22 , 2005 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14389-x
Download citation
Received : 18 February 2021
Accepted : 19 October 2022
Published : 01 November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14389-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Constructivist grounded theory
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty.
Established in 1966, it is owned by 68 members—49 from the region..

- Annual Reports
- Policies and Strategies
ORGANIZATION
- Board of Governors
- Board of Directors
- Departments and Country Offices
ACCOUNTABILITY
- Access to Information
- Accountability Mechanism
- ADB and Civil Society
- Anticorruption and Integrity
- Development Effectiveness
- Independent Evaluation
- Administrative Tribunal
- Ethics and Conduct
- Ombudsperson
Strategy 2030
Annual meetings, adb supports projects in developing member countries that create economic and development impact, delivered through both public and private sector operations, advisory services, and knowledge support..

ABOUT ADB PROJECTS
- Projects & Tenders
- Project Results and Case Studies
PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
- Public Sector Financing
- Private Sector Financing
- Financing Partnerships
- Funds and Resources
- Economic Forecasts
- Publications and Documents
- Data and Statistics
- Asia Pacific Tax Hub
- Development Asia
- ADB Data Library
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Climate Change
- Digital Technology
- Environment
- Finance Sector
- Fragility and Vulnerability
- Gender Equality
- Markets Development and Public-Private Partnerships
- Regional Cooperation
- Social Development
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Urban Development
REGIONAL OFFICES
- European Representative Office
- Japanese Representative Office | 日本語
- North America Representative Office
LIAISON OFFICES
- Pacific Liaison and Coordination Office
- Pacific Subregional Office
- Singapore Office
SUBREGIONAL PROGRAMS
- Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines East ASEAN Growth Area (BIMP-EAGA)
- Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation (CAREC) Program
- Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) Program
- Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand Growth Triangle (IMT-GT)
- South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
With employees from more than 60 countries, ADB is a place of real diversity.
Work with us to find fulfillment in sharing your knowledge and skills, and be a part of our vision in achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable asia and the pacific., careers and scholarships.
- What We Look For
- Career Opportunities
- Young Professionals Program
- Visiting Fellow Program
- Internship Program
- Scholarship Program
FOR INVESTORS
- Investor Relations | 日本語
- ADB Green and Blue Bonds
- ADB Theme Bonds
INFORMATION ON WORKING WITH ADB FOR...
- Consultants
- Contractors and Suppliers
- Governments
- Executing and Implementing Agencies
- Development Institutions
- Private Sector Partners
- Civil Society/Non-government Organizations
PROCUREMENT AND OUTREACH
- Operational Procurement
- Institutional Procurement
- Business Opportunities Outreach
Gender Equality Results Case Study: India - Enhancing Energy-Based Livelihoods for Women Micro-Entrepreneurs
Share this page.

This gender equality case study presents the contributions of the ADB-India project in providing 24-hour power supply to rural households in Madhya Pradesh and how it has opened opportunities for women entrepreneurs in the energy sector.
Download (Free : 2 available)
- PDF File (668.17 KB)
- ePub (2.13 MB)
- US$19.00 (paperback)
- http://dx.doi.org/10.22617/TCS178994-2
Reliable supply of 24-hour electricity in the State of Madhya Pradesh since 2014 has transformed the lives of many, including women from low-income households. An Asian Development Bank project—Enhancing Energy-Based Livelihoods for Women Micro-Entrepreneurs—validates how women can be empowered through capacity development in efficient use of electricity and energy-based enterprises, and provision of business development services. The case study builds up on the project progress so far, showcasing women who, along with their sense of personal empowerment, have increased their incomes and savings through microenterprises. The case study reaffirms that a steady supply of electricity, coupled with capacity development, helps create an arena where men and women are accorded equal participation in business opportunities.
- Introduction
- Project Aims and Expected Outcomes
- Gender Equality Issues in Energy Development
- Approaches to Address Gender Equality Issues
- Gender Equality Results: Project Achievements
- Project Features that Contributed to the Achievement of Gender Equality Results
- Challenges Encountered
- Lessons Learned and Ways Forward
Additional Details
| Type | |
| Series | |
| Subjects | |
| Countries | |
| Pages | |
| Dimensions | |
| SKU | |
| ISBN |
- India: Madhya Pradesh Energy Efficiency Improvement Investment Program (Facility Concept)
- More on gender and development
- More on energy
- More on ADB's work in India
Also in this Series
- Gender Equality Results Case Study: India – Rural Connectivity Investment Program
- Gender Equality Results Case Study: India – Infrastructure Development Investment Program for Tourism in Himachal Pradesh and Punjab
- Gender Equality Results Case Study: Nepal – Gender Equality and Empowerment of Women Project
- ADB funds and products
- Agriculture and natural resources
- Capacity development
- Climate change
- Finance sector development
- Gender equality
- Governance and public sector management
- Industry and trade
- Information and Communications Technology
- Private sector development
- Regional cooperation and integration
- Social development and protection
- Urban development
- Central and West Asia
- Southeast Asia
- The Pacific
- China, People's Republic of
- Lao People's Democratic Republic
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Learning materials Guidelines, toolkits, and other "how-to" development resources
- Books Substantial publications assigned ISBNs
- Papers and Briefs ADB-researched working papers
- Conference Proceedings Papers or presentations at ADB and development events
- Policies, Strategies, and Plans Rules and strategies for ADB operations
- Board Documents Documents produced by, or submitted to, the ADB Board of Directors
- Financing Documents Describes funds and financing arrangements
- Reports Highlights of ADB's sector or thematic work
- Serials Magazines and journals exploring development issues
- Brochures and Flyers Brief topical policy issues, Country Fact sheets and statistics
- Statutory Reports and Official Records ADB records and annual reports
- Country Planning Documents Describes country operations or strategies in ADB members
- Contracts and Agreements Memoranda between ADB and other organizations
Subscribe to our monthly digest of latest ADB publications.
Follow adb publications on social media..

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study and Discussion. The following reading exercise includes three short stories of bias and discrimination that are common in many high schools. These stories are designed to facilitate discussion about the effects of gender bias and discrimination and promote empathy and perspective taking skills. Have students read the case study and ...
The Tokyo Games were the most gender-balanced in history with 48% of all athletes competing in the Olympics being female and 42% in the Paralympics. The Tokyo Games were also the first that insisted on having both a male and female flag bearer for each country. TOCOG ensured the prohibition of photography taken that could lead to sexual ...
Welcome to the What Works in Gender and Health in the United Nations Case Study Series page. The United Nations University International Institute for Global Health (UNU-IIGH) co-produced with partners a report documenting practice-based lessons across five UN agencies working in global health analyzing what has worked, where, for whom, why and how, to promote gender equality in health.
We do so in ways that amplify the perspectives of those who have historically been left out or silenced in these discussions. UN SDGs. SDG 1: No Poverty SDG 2: Zero Hunger SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being SDG 4: Quality Education SDG 5: Gender Equality SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy SDG 8: Decent Work and ...
Articles, Research, & Case Studies on Gender
Global State of Democracy 2023 Report. This Case Study is part of The Global State of Democracy 2023 Report. At the end of 2022, Gender Equality scores in the Global State of Democracy (GSoD) dataset were decidedly mid-range. Although mid-range global scores have long been the norm (since 1983), it is important to note that there has been slow ...
THE STATUS OF GENDER EQUALITY At the end of 2022, Gender Equality scores in the Global State of Democracy (GSoD) dataset were decidedly mid-range (Figure 1). Although mid-range global scores have long been the norm (since 1983), it is important to note that there has been slow improvement over time. CASE STUDY: GENDER EQUALITY
The road to a gender-equal world is long, and women's power and freedom to make choices is still very constrained. But the evidence from science is getting stronger: distributing power between ...
Women and girls experience the greatest impacts of climate change, which amplifies existing gender inequalities and poses unique threats to their livelihoods, health, and safety. Across the world, women depend more on, yet have less access to, natural resources. In many regions, women bear a disproportionate responsibility for securing food ...
Profiles of Target Gender Equality Leaders. Alejandra Reynoso Barral, Chairwoman, ccNSO Council, Instead of focusing on what we failed, focus on what we achieved. Learn More >>. Shaima Abd Alghafoor, Founder and Commercial Head, Dukkan Alfreej. Don't ever doubt yourself. You probably know more than you think.
Gender Equality Results Case Study: India - Enhancing Energy-Based Livelihoods for Women Micro-Entrepreneurs. This gender equality case study presents the contributions of the ADB-India project in providing 24-hour power supply to rural households in Madhya Pradesh and how it has opened opportunities for women entrepreneurs in the energy sector.
A multiple case study design requires the selection of cases (i.e., families) who have a similar connection to a phenomenon (i.e., TGD healthcare) but with different contexts or situations . We aimed to recruit and retain four families who lived in the sampled state and had at least one child under the age of 18 who identified as transgender ...
This report on "Gender Results Case Study on Enhancing Energy-Based Livelihoods for Women Micro Entrepreneurs" is a microcosm of these priorities. The case study builds up on the progress achieved so far and to showcase how women can be empowered by supporting energy-based enterprises and business development. The report reaffirms the
Many companies have taken steps to address gender gap issues. In a few cases, such as with tech giant Google, the efforts were found to be lacking. Yet in other cases, changes made have led to ...
A further reading of the projects led to a short list of 219 projects that had explicitly integrated gender in the implementation. From this pool, 42 were randomly selected for deeper review to determine which were gender transformative. ... By applying the Gender at Work framework, the six case studies examined gender inequality at the ...
In this paper, the fourth in a Series on gender equality, norms, and health, we examine how to address restrictive norms and inequalities in health systems, through recognition and disruptive solutions. We used intersectional feminist theory to guide our approach, 9, 10 reviewing the literature and doing new empirical analyses.
Gender equality is a major problem that places women at a disadvantage thereby stymieing economic growth and societal advancement. In the last two decades, extensive research has been conducted on gender related issues, studying both their antecedents and consequences. However, existing literature reviews fail to provide a comprehensive and clear picture of what has been studied so far, which ...
An understanding of the degree to which gender inequalities persist, and in particular the denial of gender inequality, forms a key aspect of sexist attitudes, such as those captured by the modern sexism scale (Swim et al., 1995). Indeed, there are a number of very real consequences of failing to acknowledge the persistence of gender inequality.
Abstract. The study investigated undergraduate students' perceptions of gender equality, their practices and perceived strategies to promote gender equality in Afghanistan. It also examined the impact of the participants' gender on their responses. The authors used an online questionnaire to collect data from 448 students using snowball ...
A qualitative study on gender inequality and gender-based ...
This gender equality case study presents the contributions of the ADB-India project in providing 24-hour power supply to rural households in Madhya Pradesh and how it has opened opportunities for women entrepreneurs in the energy sector. Download (Free : 2 available) PDF File (668.17 KB)