A to Z Classes
Cbse, ncert and icse solution online, class 6 science case study question, case study question class 6 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science.
There are total 16 chapter Food Where Does It Come From, Components of Food, Fibre to Fabric, Sorting Materials Into Groups, Separation of Substances, Changes Around Us, Getting to Know Plants, Body Movements, The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings, Motion and Measurement of Distances, Light Shadows and Reflection, Electricity and Circuits, Fun with Magnets, Water, Air Around Us, Garbage In Garbage Out.
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.

CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question
Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question
Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question
Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question
Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question
Chapter 9 The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question
Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question
Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question
Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 6 Book Solution
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Science
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Case Based Questions - Body Movements
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Case 1: Skeletal System
Sarah is a 10-year-old girl who loves to play sports. Recently, she fell during a game and injured her rib cage. She's curious about the bones in her body.
Q1: Explain to Sarah what the rib cage is and its function. Ans: The rib cage is a cone-shaped bony cage formed by 12 pairs of ribs that are attached to the vertebral column. It protects vital organs like the lungs and heart. Q2: Sarah wants to know why her rib cage is important. How would you explain it to her? Ans: Your rib cage is important because it acts like armor, keeping your delicate organs safe from harm. Q3: Which type of joint allows movement in all directions? (a) Hinge joint (b) Gliding joint (c) Ball and socket joint (d) Fixed joint Ans: (c) Ball and socket joint
Case 2: Animal Locomotion
John is studying different animals and their methods of locomotion for his science project.
Q4: Describe how an earthworm moves and the role of its bristles. Ans: Earthworms move by contracting and expanding alternate portions of their body. Bristles on the ventral surface help them grip the ground. Q5: Explain why an earthworm contracts and expands alternate portions of its body during movement. Ans: Earthworms contract the front part, grip the ground with bristles, and then drag the posterior portion forward, repeating this process to move. Q6: What type of joint allows only one-plane movement of up to 180⁰? (a) Ball and socket joint (b) Pivot joint (c) Hinge joint (d) Gliding joint Ans: (c) Hinge joint
Case 3: Bird Adaptations
Emma is fascinated by birds and wants to learn how they are adapted for different forms of locomotion.
Q7: Describe the adaptations of a bird's skeleton for both walking and flying. Ans: A bird's skeleton is adapted for walking with light and strong bones. For flying, they have wings and tail feathers. Q8: Explain the role of feathers in a bird's ability to fly. Ans: Feathers provide lift and help birds control their direction during flight. Q9: What helps a snake move forward by making loops on its sides? (a) Wings (b) Muscles (c) Ribs (d) Bristles Ans: (b) Muscles
Case 4: Fish Locomotion
Alex is studying fish and their swimming techniques for his biology project.
Q10: Describe the streamlined body of a fish and its importance in swimming. Ans: Fish have streamlined bodies to reduce water resistance while swimming. Q11: Explain how the tail fin of a fish aids in changing direction during swimming. Ans: The tail fin of a fish helps change direction by adjusting its position in the water. Q12: What type of joint allows movements in many planes, such as up and down and side to side? (a) Hinge joint (b) Gliding joint (c) Pivot joint (d) Ball and socket joint Ans: (c) Pivot joint
Case 5: Skeletal Protection
Lily is learning about the protective functions of the human skeleton.
Q13: Explain how the rib cage protects vital organs like the lungs and heart. Ans: The rib cage protects the lungs and heart by forming a bony cage around them. Q14: Describe the role of the vertebral column in providing support to the body. Ans: The vertebral column provides support and allows flexibility for movements. Q15: How does a snail primarily achieve locomotion? (a) Muscular foot (b) Wings (c) Jointed legs (d) Slithering movement Ans: (a) Muscular foot
| |205 docs|48 tests |
Top Courses for Class 6
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
Semester Notes
Important questions, mock tests for examination, extra questions, study material, practice quizzes, shortcuts and tricks, sample paper, video lectures, viva questions, past year papers, objective type questions, previous year questions with solutions.

Case Based Questions: Body Movements Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: body movements, case based questions: body movements notes, case based questions: body movements class 6, study case based questions: body movements on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances
- Class 6 Important Question
- Chapter 5: Separation Of Substances

CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books . Register Online for NCERT Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions | ||
Sl.No | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
1 | Chapter 1 |
|
2 | Chapter 2 |
|
3 | Chapter 3 |
|
4 | Chapter 4 |
|
5 | Chapter 5 | Separation of Substances |
6 | Chapter 6 |
|
7 | Chapter 7 |
|
8 | Chapter 8 |
|
9 | Chapter 9 |
|
10 | Chapter 10 |
|
11 | Chapter 11 |
|
12 | Chapter 12 |
|
13 | Chapter 13 |
|
14 | Chapter 14 |
|
15 | Chapter 15 |
|
16 | Chapter 16 |
|
Study Important Questions For Class 6 Science Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances
Very Short Answer Questions: 1 mark 1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Name one method for separation of substances ________.
Ans: Winnowing
(ii) Separation of fine particles from bigger particles using a sieve ___________.
Ans: Sieving
(iii) Name on method used to separate sand and water _____________.
Ans: Sedimentation
(iv) Salt is obtained from seawater by a process known as __________.
Ans: Evaporation
(v) The process of separating cream from the milk is known as ___________.
Ans: Filtration
Short Answer Questions 3 marks 2. Define winnowing.
Ans: Winnowing is the process of separating heavy components from lighter components with the help of wind.
3. What is sieving?
Ans: Sieving is the process of separating tiny particles from larger particles by the use of holes in a sieve.
4. Define threshing.
Ans: The term "threshing" refers to the process of removing grains from their stalks. The stalks are beaten to liberate the grain seeds in this process.
5. Define sedimentation.
Ans: Sedimentation is the process in which heavier components settle down at the bottom of the container. E.g. Water mixed with mud or sand.
6. Define decantation.
Ans: Decantation is the process of taking out clear water into a new container after sedimentation. The water after decantation is clear but it is still not fit for drinking.
7. Define evaporation.
Ans: Evaporation is the process of converting water into water vapour.
8. Define condensation.
Ans: Condensation is the process of turning water vapour into liquid. Example: Melting of ice.
9. Define saturated solution.
Ans: Saturated solution is a solution in which no more of a substance/solute can be dissolved.
10. Name 5 methods used for separating substances from their mixtures?
Ans: Five methods used for separating substances are:
Handpicking
Decantation
11. Give one importance of separating substances from the mixtures.
Ans: It is important to separate substances from mixtures to obtain pure substances differently for various purposes.
Long Answer Questions 5 marks 12. How do you separate sugar mixed with wheat flour?
Ans: The method of sieving is used to separate the sugar and wheat flour mixture. First, the mixture is filtered through a sieve. Wheat flour particles will pass through, while the large sugar particles will be trapped by the sieve.
13. Explain the method used to separate the sand and water from their mixture?
Ans: A combination of sedimentation and decantation is used to separate sand and water.
A mixture of sand and water is taken in a glass/container and left for some time.
Sand settles at the bottom of the container during this process because it is heavier. This is called sedimentation.
The clean water is then gradually moved to another container slowly leaving the sand in the original container. This process is called decantation.
14. What is winnowing and why is it needed?
Ans: Winnowing is the process of separating heavy particles from lighter particles using wind. For example, winnowing can be used to separate husk particles from heavier grains such as wheat or patty. The husk particles will be carried away by the wind leaving large grains in a different pile. For winnowing, fast-moving air is the most important factor.
Advantage of Winnowing: The operation of this method does not involve the use of any machines. It is entirely reliant on human activity; hence it takes less time to process and is unquestionably inexpensive.
Disadvantage of Winnowing: Winnowing is a way of separating heavy components of a mixture from lighter components using wind, but this procedure does not work for items heavier than grains, such as stones.
Benefits of Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances
The benefits of having a set of important questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5, "Separation of Substances," are manifold. These questions offer a structured approach to learning, helping students identify and focus on key concepts related to separation techniques. They stimulate critical thinking by presenting thought-provoking queries that encourage students to apply their knowledge practically. Moreover, important questions act as effective tools for exam preparation, guiding students towards the most relevant topics and providing a platform for self-assessment. They enhance problem-solving skills and deepen the understanding of scientific processes, fostering a lifelong appreciation for the subject. In essence, important questions enrich the learning experience, making science more accessible and fostering valuable skills for both academics and everyday life.
Important Related Links for CBSE 6 Science
CBSE Class 6 Science Study Materials |
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
The compilation of important questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5, "Separation of Substances," is a valuable educational asset. These questions serve as essential aids for students, offering a structured approach to mastering the concepts related to separating substances. They encourage critical thinking and problem-solving skills by posing thought-provoking inquiries. Importantly, they serve as effective tools for exam preparation, enabling students to focus on the most significant topics and evaluate their own understanding. Beyond academics, these important questions foster an appreciation for scientific processes and their practical applications in daily life. In essence, they enrich the learning journey, making science more engaging and accessible while equipping students with valuable skills for both the classroom and the real world.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances
1. Why is the separation of substances necessary? State 3 points.
Separating substances are really important in our day-to-day lives. Most of the time, a substance is always mixed and is in an impure state. The following points help state the necessity of separating different substances;
Impure substances cannot be used for many purposes. Therefore, separating unwanted or useless components is important.
Separating components help increase the quality, purity, strength, and utilities of various substances.
Finally, estimation of ratios of different substances is also possible when substances are separated.
2. Does ink lose its properties when mixed with water?
Yes, ink loses its properties when mixed with water because its ratio gets changed, and hence, the property is lost. Once the ink is dropped in water, diffusion happens and it gets evenly spread throughout the water particles. This happens because of the random motion of both water and ink particles. The chapter can get quite confusing for class 6 students with topics like these especially. Important Questions for chapter 5 can guide students by providing an easy explanation.
3. How do you teach the separation of substances?
Chapter 5 is about ‘Separation of Substances’. It mainly deals with different types of separation methods, the necessity of separating various substances, properties of different mixtures, and other related topics. By using Important Questions for chapter 5, important areas in the chapter can be selected and taught to students by putting more emphasis. The ideas are conveyed in a simple and legible format, so students can easily grasp hold of the information to score a perfect result.
4. Why do we need to separate substances Class 6?
There is always a need to separate substances for various purposes. The majority of the time, a substance is always mixed and impure. The following points will help students understand why it is important to separate substances:
Many things can't be done with impure substances. As a result, it's critical to remove undesirable elements from substances.
The quality, strength, etc. of substances can be improved through separation.
When substances are separated, estimation of ratios of distinct substances is achievable.
To know more students can download the vedantu app.
5. What is the basis of the separation of components of mixture Class 6?
The basis of chapter 5 is to make students understand why the separation of various substances is essential and of importance. Thereby, they are introduced to different methods of separation like winnowing, threshing, sieving, etc. All these concepts lead students back to the basic concept which is addressed in the chapter. Separating substances are useful in daily lives for a lot of purposes. The Important Questions created for this chapter are available free of cost in the form of PDF from the vedantu website (vedantu.com). It will help to strengthen the basic concept by focusing on necessary areas.
Chapter wise Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science
Cbse study materials.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 5 Class 6 - Separation of Substances
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Separation of Substances is the fifth chapter which we will study in Class 6 Science.
In this chapter, Teachoo provides NCERT Solutions, Notes, Worksheets, MCQ, 1 Mark questions (with solutions).
On Teachoo , you can find explanations of various concepts , NCERT questions and extra questions prepared by experts which can be your one stop solution to all the doubts.
In the chapter 5 , Separation of substances , as the name suggests, you will learn about separating one component from the other in order to remove any harmful substance or impurity from the main substance that you are going to consume .
Separation of these impurities is necessary for humans as the impurities are harmful for the human body and can cause health complications if consumed.
Firstly, you will learn about what are these impurities or substances that are to be separated.
Substances like
- Tea leaves from tea ;
- Small stones from rice and ;
- Grains from stalks
Are few examples of harmful substances
Along with impurities, even other useful components can be obtained through separation. For example - Butter is obtained from milk after using a certain technique known as churning .
There are also other techniques that you are going to learn in this chapter and they are -
- Hand picking
- Evaporation
Sedimentation, Filtration and Decantation
Just click on a link below to start doing the chapter.
NCERT Questions
Teachoo questions.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Extra Questions
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download the PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Separation of Substances Class 6 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short answer questions.
1. What is strainer? Answer: Strainer is a kind of sieve which is used to separate a liquid from solid.
2. Name the method used to separate cream from curd. Answer: Centrifugation.
3. How will you separate mango from a mixture of mango and apple? Answer: By picking.
4. You are given a mixture of salt and sand. Can you separate them by picking? Answer: No, we cannot separate them by picking.
5. Name the method used to separate the pieces of stone from grain. Answer: Handpicking.
6. How can you separate grains from stalk? Answer: We separate grains from stalk by threshing.
7. What types of material can we separate by using handpicking? Answer: The materials having different size and colour can be separated by handpicking.
8. Name the other methods used to separate solid materials of different size. Answer: Sieving.
9. Name the process used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture. Answer: Winnowing.
10. Can the above stated method be used if both the components have same weight? Answer: No, this method cannot be used.
11. What is evaporation? Answer: The process of conversion of water into vapour is called evaporation.
12. Name the method by which we get salt from ocean water. Answer: Evaporation.
13. Define condensation. Answer: The process of conversion of water vapour into liquid form is called condensation.
14. Write opposite process of evaporation. Answer: Condensation.
Short Type Questions and Answers
1: What is done in threshing? How it can be done?
Answer: In threshing, the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Threshing can be done with the help of bullocks or machines.
2: Which type of impurities can be separated by hand picking?
Answer: Hand picking is used to separate slightly large sized impurities. It is used when the quantity of impurities is not very large.
3: Why is separating different components of a mixture necessary? Answer: a) To separate two different but useful components. b) To remove impurities or non-useful component from a mixture.
4: What do you mean by winnowing? Explain with example
Answer: Winnowing is separating the heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air. For example-separating mixture of saw dust and sand.
5: How is sieving use to separate particles of a mixture? Give example.
Answer: Sieving allows the fine particles to pass through the holes of a sieve while bigger impurities remain on sieve. E.g. separating bran from flour.
6: What is a saturated solution?
Answer: When no more solute (e.g. Salt) can be dissolved in the amount of solvent (e.g. Water) taken, the solution is said to be saturated solution.
7: What happens when steam comes in contact with the metal plate cooled with ice?
Answer: When steam comes in contact with the metal plate cooled with ice, it condenses and forms liquid water.
8: What is condensation?
Answer: The process of conversation of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
9: By which process salt, sand and water can be separated?
Answer: Salt, sand and water can be separated by decantation, filtration, evaporation followed by condensation.
10: What is the difference between evaporation and condensation?
Answer: The process of conversion of water into its vapour is called evaporation. The process of conversation of water vapour into its liquid form is called condensation.
11: What is sedimentation?
Answer: When the heavier component of a mixture settles after water is added to it, the process is called sedimentation
12: Write the name of method for separating
a) Salt from salt water solution. b) Wheat from mixture of wheat and rice. Answer: a). Evaporation b). handpicking.
13: Which of the following is true : a) Flour is sieved to separate impurities. b) Threshing is used to separate grains from stalk. c) Winnowing is used to separate component of same weight.
Answer: a) True b) true c) false.
14. What is mixture? Answer: When two or more than two substances are mixed together in any ratio then it is called a mixture.
15. Write various methods of separation of components from their mixture.
- Handpicking
- Sedimentation
- Decantation
- Evaporation
- Condensation
16. Define the term handpicking.
Answer: The process used to separate slightly larger particles from a mixture by hand is called handpicking. For example: Stone pieces can be separated from wheat or rice by handpicking.
17. What do you mean by threshing? Where is it used?
Answer: Threshing is a process in which we separate grain from stalks. This process is used by farmer to separate gram, wheat, rice, mustard seeds in his field.
18. How will you separate oil and water from their mixture?
Answer: Oil, being lighter than water, will float on it. Two distinct layers are formed and slowly oil is allowed to flow into another container and is separated from water. Separating funnel can also be used to separate the two.
19. What is evaporation?
Answer: The process of conversion of water into vapour is called evaporation. This process takes place continuously where water is present. Common salt from sea water is obtained using this method.
20. Define winnowing.
Answer: The process is used to separate components from a mixture in which one component is heavier or lighter than other is called winnowing. Winnowing is done with the help of wind or by blowing air.
21. What do you mean by sieving? Give an example.
Answer: Sieving allows the fine flour particles to pass through the holes of the sieve while the bigger particles or impurities remain on the sieve. For example, in a flour mill, impurities like husk and stones are removed from wheat before grinding it.
22. Name and describe briefly a method which can be helpful in separating a mixture of husk from grains. What is the principle of this method?
Answer: Winnowing is the method used for separating a mixture of husk from grains. It is based on the principle that the lighter husk particles are carried away by the wind leaving behind the grains.
23. How do we get salt from sea water?
Answer: First sea water is collected in shallow pits and due to heat of the Sun, water starts evaporating. After few days, the water evaporates completely leaving behind solid salt.
24. Why does visibility increase after rain?
Answer: Rain dissolves all the dust particles in atmosphere and brings them down to earth, thus increasing visibility.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. What is threshing?
Answer: Threshing is a process that is used to separate grain from stalks. In this process the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Sometimes threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used to thresh large quantities of grain.
2. Describe the method to obtain salt from sea water.
Answer: Sea water contains many salts mixed in it. One of them is common salt, when sea water is allowed to stand in shallow pits, water gets evaporated by sunlight and slowly turns into water vapour. In a few days, the water evaporates completely leaving behind the solid salts. Common salt is then obtained from this mixture of salts by further purification.
3. What is decantation?
Answer: Decantation is a process, of separation of insoluble solids from liquid. The suspension of solid particles in liquid is allowed to stand for some time. The solid particles then settle down at the bottom of the container and clean water goes up. Without disturbing the settled particles the clean water is transferred into other container.
4. Where is decantation used? Give two examples.
Answer: (i) Decantation is used to separate insoluble solids or liquid from liquid. Rain water is a mixture of mud and water. It is purified by decantation. (ii) Oil and water also get separated by this method because oil floats up.
5. How will you prepare cheese (paneer)?
Answer: For making paneer, a few drops of lemon juice sire added to milk as it boils. This gives a mixture of particles of solid paneer and liquid. The paneer is then separated by filtering the mixture through a fine cloth or strainer.
6. Explain the method that can be used for separating the following mixture: (i) Sand and husk (ii) Wheat, sugar and stalk (iii) Water and petrol (iv) Rice and salt (v) Sand and salt
Answer: (i) Mixture of sand and husk: Sand and husk can be separated by the method of winnowing.
(ii) Mixture of wheat, sugar and stalk: For separating stalk from the mixture we should follow the winnowing method because milk is lighter than other two components and get separated. Wheat and sugar can be separated by sieving because they are in different sizes.
(iii) Mixture of water and petrol: Water does not dissolve in petrol. So, it can be separated by the use of separating funnel.
(iv) Mixture of rice and salt: Rice and salt can be separated by sieving.
(v) Mixture of sand and salt: Sand and salt is mixed with water, salt dissolves in water and sand can be separated solution by sedimentation and decantation followed by filtration. After that using evaporation common salt is separated.
7: How is common salt obtained from sea?
Answer: Sea water contains many salts mixed in it. When sea water is allowed to stand in shallow pits, water gets heated by sunlight and slowly turns into water vapour, through evaporation. In few days water is evaporated completely leaving behind solid salts. Common salt is obtained from mixture of salts by further purification.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Separation of Substances Class 6 Extra Questions Science Chapter 5
September 11, 2019 by Bhagya
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Methods of separation
Question 1. When is handpicking used? Answer: Handpicking is used to separate undesirable component when present in small amount.
Question 2. What is threshing? How is it done? Answer: The process that is used to separate the grain from stalks is threshing. In this process, the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Sometimes, threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used to thresh large quantities of grain.
Question 3. Which type of separation is used in cashew nut factories? Answer: Sieving.
Question 4. Give one example of sieving used in everyday life. Answer: Separation of barn (choker) from flour.
Question 5. Name some materials that are used as filters. Answer: Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, filter paper.
Question 6. Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids. Answer: By using separating funnel or by decantation.
Question 7. Which substance is used for loading? Answer: Alum (phitkari).
Question 8. What is the use of alum in loading? Answer: Alum is used to make the sedimentation faster. Bv adding alum the clay particles settle down rapidly.
Question 9. Which process is used to separate bacteria from water? Answer: Filtration, by using special filters, i.e., bacteria proof filter.

Question 11. What is the use of decantation? Answer: Decantation is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids. Two immiscible liquids are also separated by this process.
Question 12. What is filtration? Answer: When one component of a mixture is soluble in water and other component is insoluble in water, the soluble component gets dissolved and insoluble one is separated by filtering the solution.

Question 13. What is the drawback of evaporation? Answer: The liquid in the mixture is evaporated off into the air and is not recovered.
Question 14. Name the process to obtain salt from seawater. Answer: Evaporation.
Question 15. Which types of mixtures are separated by evaporation? Answer: Evaporation is used to separate solids dissolved in liquid.
Question 16. Describe the method to obtain pure salt from rock salt. Answer: First, the mixture is crushed and grinded. Water is then added and filtered. Pure salt is collected as filtrate which is heated for evaporation. Water evaporates off and pure salt is left.
Question 17. How will you separate pure water from a solution of salt in water? Answer: We can separate pure water from a solution of salt in water, by the process of distillation that is by evaporation and followed by condensation.
Question 18. Write opposite process of condensation. Answer: Evaporation.
Question 19. How is common salt obtained from seawater? Answer: When seawater is allowed to evaporate in shallow pits, water gets heated by sunlight and changes into water vapour by the process of evaporation leaving behind impure solid salts. Now, the lumps of impure common salt are crushed to get powdered salt. The powdered common salt is dissolved in water to prepare a solution. Now the solution of common salt is filtered to remove insoluble impurities. The clear solution is evaporated by heating to remove the water content to obtain a concentrated solution of common salt. The hot and concentrated solution is allowed to cool. On cooling, crystallization takes place and crystals of pure common salt are obtained.

Question 21. What do you mean by solubility? Answer: The maximum mass of a solute that can be dissolved in 100 g of the solvent at any specific temperature is called solubility.
Question 22. Why is water a universal solvent? Answer: Water can dissolve different kinds of substances. That is why water is commonly called as a universal solvent.
Question 23. What is the effect of temperature on solubility? Answer: Solubility increases when the increase in temperature takes place.
Question 24. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated solutions. Answer: Saturated solution: A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. Unsaturated solution: A solution in which more solute can be dissolved at any temperature.
Question 25. During centrifugation, which particles settle down at the bottom? Answer: Heavy particles settle down at the bottom and lighter particles float at the top of the liquid.
Question 26. Name the method by which you can separate butter from milk. Answer: Centrifugation.

Question 28. Why does visibility increase after rains? Answer: After rains, the objects at a distance are seen more clearly, because the fine dust particles that were present in air settle down due to loading by rain drops.

- salt and camphor
- wheat and husk
- iron fillings and saw-dust
- coconut oil and water.
- sublimation
- magnetic separation
- separating funnel.
Question 31. Mention the methods that can be used for the separation of the following mixtures:
- wheat, sugar and husk
- rice, gram and iron fillings
- sand, Mack gram (urad) and husk.
Answer: 1. Mixture of wheat, sugar and husk.
- For separating husk from the mixture, we should follow the winnowing method as husk is lighter than other two components.
- Wheat and sugar can be separated by sieving as they have different sizes.
2. Mixture of rice, gram and iron fillings.
- For separating iron fillings, we can use a magnet.
- Rice and gram can be separated either by sieving or by handpicking.
3. Sand, black gram (urad) and husk.
- For separating sand from the mixture, we can sieve the mixture.
- Black gram (urad) and husk can be separated by the method of winnowing.
Question 32. Write various methods of separation of compounds from their mixture. Answer:
- Handpicking
- Sedimentation
- Decantation
- Evaporation
- Condensation.
Question 33. How will you Separate a mixture of common salt and chalk powder? Answer: We know that common salt is soluble in water while chalk is sparingly, soluble. So on the basis of different solubility, we can separate the common salt and chalk powder as follows: 1. First, some water is mixed with the mixture of common salt and chalk powder, stir the solution well. Filter the solution by using filter paper. On filtering, chalk powder is obtained as a residue on the filter paper and salt solution is obtained.
2. Now filtrate is evaporated and dry common salt is left behind.
Activity 2. Bring a packet of food grain purchased from a shop to the classroom. Now, spread the grains on a sheet of paper. Do you find only one kind of grain on the sheet of paper? Are there pieces of stone, husks, broken grain and particles of any other grain in it? No. There are pieces of stone, husks, broken grain, etc., in it.
Activity 3. Make a mixture of dry sand with sawdust or powdered dry leaves. Keep this mixture on a plate or a newspaper. Look at this mixture carefully. Can the two different components be made out easily? Are the sizes of particles of the two; components similar? Would it be possible to separate the components by handpicking? Yes, we can separate two components from the mixture. Dry sand and sawdust have different sizes of particles, we cannot separate out the components by handpicking.
Now, take your mixture to an open ground and stand on a raised platform. Put the mixture in a plate or sheet of paper. Hold the plate or the sheet of paper containing the mixture, at your shoulder height. Tilt it slightly, so that the mixture slides out slowly.
What happens? Do both the components – sand and sawdust (or powdered leaves) fall at the same place? Is there a component that blows away? Did the wind manage to separate the two components? : No, sawdust will fall far from the sand as it is lighter. Sand dust blows away with the wind.
Activity 4. Bring a sieve and a small quantity of flour from home, to the class. Sieve the flour to separate any impurities in it. Now, make a fine powder of chalk pieces and mix it with the flour. Can we separate the flour and the powdered chalk by sieving? No, the flour and the powdered chalk cannot be separated by sieving because their particles are of the same size.
Activity 5. Collect some muddy water from a pond or a river. If it is not available, mix some l soil to water in a glass. Let it stand for half an hour. Observe the water carefully ‘ and note your observations. Does some soil settle at the bottom of water? Why? What will you call this j process? Yes, some heavier soil particles settle at the bottom of the water. This process is called sedimentation.
Activity 6. Heat a beaker containing some water. Allow the water to boil. If you continue heating, would the water turn into steam and disappear completely? Yes, the water will disappear completely.

Activity 10. Take two glasses and pour half a cup of water in each of them. Add a teaspoon of salt to one glass and stir till the salt dissolves. Go on adding salt, one teaspoon at a time, till the solution saturates. Record the number of spoons of salt that dissolved in the water, in Table 5.2. Now, repeat the same activity with sugar. Repeat this with some other substances that are soluble in water.
What do you notice from Table 5.2? Do you find that water dissolves different substances in different amounts? Table 5.2
| Salt | 1 spoon of salt in 100 gm water at 25°C |
| Sugar | 4 spoons of sugar in 100 gm water at 25°C |
| Copper sulphate | Nearly 4 spoon of copper sulphate in 100 gm of water at 25°C |
We notice from the table that different substances dissolve in water in different amounts.
Objective Type Questions
Question 1. Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
| (a) Handpicking | (i) Conversion of water vapours into liquids |
| (b) Threshing | (ii) Separating bran from flour |
| (c) Winnowing | (iii) Separating larger size impurities |
| (d) Sieving | (iv) Separating butter from milk |
| (e) Sedimentation | (v) Conversion of water into Us vapours |
| (f) Evaporation | (vi) Separating grains from its stalks |
| (g) Condensation | (vii) Settling of heavier components at bottom |
| (h) Churning | (viii) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| (a) Handpicking | (iii) Separating larger size impurities |
| (b) Threshing | (iv) Separating grains from its stalks |
| (c) Winnowing | (viii) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| (d) Sieving | (ii) Separating bran from flour |
| (e) Sedimentation | (vii) Settling of heavier components at bottom |
| (f) Evaporation | (v) Conversion of water into its vapours |
| (g) Condensation | (i) Conversion of water vapours into liquids |
| (h) Churning | (iv) Separating butter from milk |
Question 2. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
- Peanuts are separated from a mixture of wheat and peanut by …………… .
- ………………. is used to separate husk from wheat.
- Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by ……………. .
- Glass is a ………….. .
- Compounds have ……………….. melting points.
- Milk has a ……………………….. boiling point.
- Boiling point of pure water is …………………. than that of impure water.
- Mixture may be solid, liquid or …………… .
- Butter is a component of …………….. .
- Sugarcane juice is a mixture of …………………………, water and many other substances.
- Separation of components is done to obtain a …………………….. substance.
- Components retain their properties in a ……………… .
- handpicking
- butter milk
Question 3. State whether the statements given below are True or False:
- Butter is separated from butter milk by churning.
- Separation of components of a mixture is a useful process.
- Ink loses its properties when mixed in water.
- ‘Sharbat’ is a mixture of sugar and water.
- Rocks are pure substances.
- Milk is a mixture.
- Common salt is ai pure substance.
- Mixture has properties different from its components.
- Tap water and pond water are alike.
- Elements are pure substances.
- A pure substance has a fixed melting and boiling points.
- Condensation method is used for separating substances which on heating change directly into vapour.
Question 4. Choose the correct option in the following questions:
(i)Butter is separated from milk by (a) sedimentation (b) filtration (c) churning (d) decantation Answer: (c) Butter is separated by churning.
(ii) Filtration is a method to separate the components of a (a) solution (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance (c) both (a) and (b) (d) pure substance Answer: (b) Components of solution cannot be separated by this method.
(iii) Threshing is done by (a) beating (b) bullocks (c) machines (d) all of these Answer: (d.) All the three methods can be used for threshing.
(iv) Which method is used to separate pebbles and stones from sand? (a) Handpicking (b) Winnowing (c) Sieving (d) Any of these Answer: (c) Handpicking will require more time while winnowing is not fit at all.
(v) The components of a solution (say sugar in water) can be separated by (a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation Answer: (b) By evaporation, the volatile component is evaporated which is then condensed.
(vi) Sand from water is separated by (a) sieving (b) evaporation (c) filtration (d) sedimentation and decantation Answer: (d) It can be done by evaporation and filtration also but sedimentation and decantation are easier ways.
(vii) The process of conversion of water vapours into liquid is called (a) condensation (b) decantation (c) sedimentation (d) evaporation Answer: (a) Water vapours changing into liquid is called condensation.
(viii) The process of conversion of water into its vapours is called (a) evaporation (b) condensation (c) guttation (d) transpiration Answer: (a) The conversion of water into vapours is called evaporation.
(ix) A mixture of ammonium chloride and sand is separated by (a) evaporation (b) decantation (c) sublimation (d) filtration Answer: (c) Ammonium chloride is separated by sublimation process.
(x) The property which forms the basis of sieving (a) difference in weight (b) difference in colour (c) difference in shape (d) difference in size Answer: (d) Sieving method is used for separating solid constituents of a mixture which differ in their size.
Extra Questions for Class 6 Science
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
Register here
In case you want to be notified about school in your locality then please register here.
- Are you a Parent or Student?
- Are you a Teacher?
- Are you a School Supplier?

- Our other Domains Olympiad Preparation Math Square Science Square English Square Cyber Square School Square Scholar Square Global Olympiads NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers
- Join WhatsApp Channel
- Apply for CREST Olympiads

Chapter 5: Separation of Substances
(www.olympiadsuccess.com)
Class: VI
Exemplar Solutions
Multiple Choice Questions
Paheli bought some vegetables such as french beans, lady’s finger, green chillies, brinjals and potatoes all mixed in a bag. Which of the following methods of separation would be most appropriate for her to separate them?
(a) Winnowing
(b) Sieving
(c) Threshing
(d) Hand picking
Boojho’s grandmother is suffering from diabetes. Her doctor advised her to take ‘ Lassi ’ with less fat content. Which of the following methods would be most appropriate for Boojho to prepare it?
(a) Filtration
(b) Decantation
(c) Churning
(d) Winnowing
Which of the following mixtures would you be able to separate using the method of filtration?
(a) Oil in water
(b) Cornflakes in milk
(c) Salt in water
(d) Sugar in milk
Which amongst the following methods would be most appropriate to separate grains from bundles of stalks?
(a) Hand picking
(b) Winnowing
(c) Sieving
(d) Threshing
Four mixtures are given below
(i) Kidney beans and chick peas
(ii) Pulses and rice
(iii) Rice flakes and corn
(iv) Potato wafers and biscuits
Which of these can be separated by the method of winnowing?
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
While preparing chapattis, Paheli found that the flour to be used was mixed with wheat grains. Which out of the following is the most suitable method to separate the grains from the flour?
(a) Threshing
(c) Winnowing
(d) Filtration
You might have observed the preparation of ghee from butter and cream at home. Which method(s) can be used to separate ghee from the residue?
(i) Evaporation
(ii) Decantation
(iii) Filtration
(iv) Churning
Which of the following combination is the correct answer?
(c) (ii) and (iv) (d) (iv) only
In an activity, a teacher dissolved a small amount of solid copper sulphate in a tumbler half filled with water. Which method would you use to get back solid copper sulphate from the solution?
(a) Decantation
(b) Evaporation
(c) Sedimentation
(d) Condensation
During summer, Boojho carries water in a transparent plastic bottle to his school. One day he left his bottle in the school. The bottle still had some water left in it. The following day, he observed some water droplets on the inner surface of the empty portion of the bottle. These droplets of water were formed due to
(a) boiling and condensation.
(b) evaporation and saturation.
(c) evaporation and condensation.
(d) condensation and saturation.
Question 10
Paheli asked for a glass of water from Boojho. He gave her a glass of ice cold water. Paheli observed some water droplets on the outer surface of the glass and asked Boojho how these droplets of water were formed? Which of the following should be Boojho’s answer?
(a) Evaporation of water from the glass.
(b) Water that seeped out from the glass.
(c) Evaporation of atmospheric water vapor.
(d) Condensation of atmospheric water vapor.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 11
Sheela, Saima and Ravi have to dissolve maximum amount of sugar in the same amount of milk so as to win in a game. Ravi took hot boiling milk while Saima took ice cold milk. Sheela managed to get milk at room temperature. Whom do you think would win the game and why?
Milk at higher temperature would dissolve more sugar so Ravi would win the game.
Question 12
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
(i) Small pieces of stone can be removed from rice by __________.
(ii) ___________ are obtained from stalks by threshing.
(iii) Husk from wheat flour is generally removed by __________.
(iv) The process of settling of heavier particles is called __________.
(iv) Filtration is helpful in separating an insoluble __________ from a __________.
(i) hand picking; (ii) grains; (iii) sieving; (iv) sedimentation; (v) solid, liquid.
Question 13
State whether the following statements are true or false .
(a) A mixture of oil and water can be separated by filtration.
(b) Water can be separated from salt by evaporation.
(c) A mixture of wheat grains and wheat flour can be separated by sieving.
(d) A mixture of iron filings and rice flour can be separated by magnet.
(e) A mixture of wheat grains and rice flakes can be separated by winnowing.
(f) A mixture of tea leaves and milk can be separated by decantation.
(a) False (b) True
(c) True (d) True
(e) True (f) True
Short Answer Questions
Question 14
Name and describe briefly a method which can be helpful in separating a mixture of husk from grains. What is the principle of this method?
Winnowing. This method is based on the principle that the lighter particles are carried away by the wind.
Question 15
Match the mixtures in Column I with their method of separation in Column II .
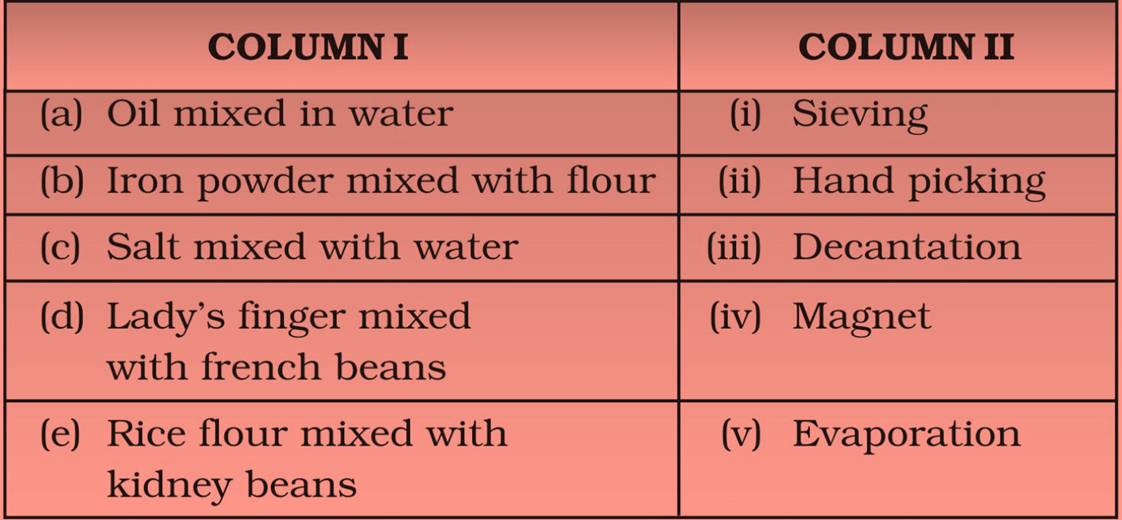
(a) – (iii)
(b) – (iv)
(c) – (v)
(d) – (ii)
(e) – (i)
Long Answer Questions
Question 16
Both Sarika and Mohan were asked to make salt solution. Sarika was given a teaspoonful of salt and half a glass of water, whereas Mohan was given twenty teaspoons full of salt and half a glass of water.
(a) How would they make salt solutions?
(b) Who would be able to prepare saturated solution?
(a) They will mix salt with water to make salt solution.
(b) Mohan’s solution would be saturated because in Mohan’s case some salt would remain
undissolved and settle at the bottom of the glass.
Question 17
Paheli was feeling thirsty but there was only a pot of water at home which was muddy and unfit for drinking. How do you think Paheli would have made this water fit for drinking if the following materials were available to her.
Alum, tub, muslin cloth, gas stove, thread, pan and lid.
(i) Filtration using muslin cloth.
(ii) Swirl with alum and leave water undisturbed for some time.
(iii) Decantation.
(iv) Boil for 10 minutes in covered pan.
(v) Cool, filter and now it is fit for drinking.
Question 18
Read the story titled "WISE FARMER" and tick the correct option to complete the story.
A farmer was sad/happy to see his healthy wheat crop ready for harvest. He harvested the crops and left it under the sun/rain to dry the stalks. To separate the seeds from the bundles of the stalk he handpicked/threshed them. After gathering the seed grains he wanted to separate the stones and husk from it. His wife winnowed/threshed them to separate the husk and later sieved/hand picked to remove stones from it. She ground the wheat grains and sieved/ filtered the flour. The wise farmer and his wife got a good price for the flour. Can you tell why?
(iii) threshed
(iv) winnowed
(v) handpicked
(vi) sieved
They got a good price as they used appropriate methods of separation to get good quality of flour.
Question 19
You are provided with a mixture of salt, sand, oil and water. Write the steps involved for the separation of salt, sand and oil from the mixture by giving an activity along with the diagram.
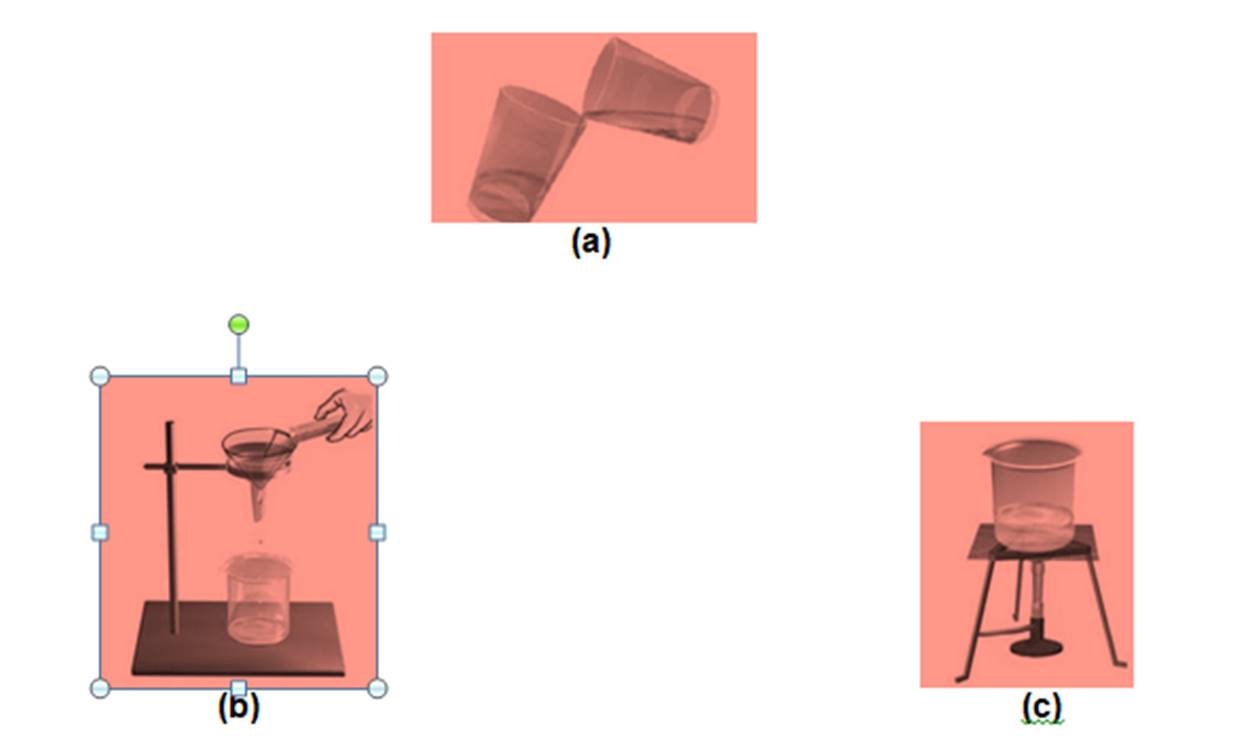
(a) Decantation – to separate oil
(b) Filtration – to separate sand
(c) Evaporation – to separate salt
Question 20
A mixture of iron nails, salt, oil and water is provided to you. Give stepwise methods to separate each component from this mixture?
(a) Iron nails – hand picking/magnet
(b) Oil – decantation
(c) Salt, water – evaporation and condensation
Other Chapters
- Chapter 1: Food - Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2: Components of Food
- Chapter 3: Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4: Sorting Materials and Groups
- Chapter 6: Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7: Getting To Know Plants
- Chapter 8: Body Movements
- Chapter 9: The Living Organisms and their Surroundings
- Chapter 10: Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11: Light, Shadows and Reflections
- Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13: Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14: Water
- Chapter 15: Air Around Us
- Chapter 16: Garbage in, Garbage out

Quick Links

SchoolPlus Program
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.

Olympiad Exam Dates
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.

LIVE Classes for Olympiads
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.

Olympiad Test Series
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.

India’s First Summer Olympiads
Know your true potential by participating in Unicus Olympiads for classes 1-11.
Asia’s Biggest Winter Olympiads
Give wings to your innovation by appearing in CREST Olympiads for Prep/KG to classes 1-10.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances are given below in an easy-to-understand way for CBSE Class 6 Science students. Students can find the full solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 here
January 22, 2024

Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 5: NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances guides students in addressing various questions related to methods of separating different substances.
These solutions are conveniently available in PDF format for downloading and easy access. This study material holds importance for CBSE Class 6 examinations, and to achieve good marks, it is recommended to thoroughly study the provided solutions.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science serve as crucial study resources, assisting learners in clarifying doubts related to the CBSE syllabus Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science. Answering fill-in-the-blanks, true or false questions, long-answer questions, and practical-based questions will enhance their understanding of important concepts for future studies.
Access the PDF of this chapter’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science through the provided link below.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 5 PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Overview
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 6 acquaints students with various separation methods, including hand-picking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, sedimentation, decantation, filtration, and evaporation.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science for this chapter aim to enhance understanding through real-life examples, like separating husks and stones from grains, as well as the separation of solids from liquids. These solutions provide a comprehensive grasp of the separation processes discussed in the chapter.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Exercise
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances are provided here with simple step-by-step explanations.
Exercise Questions
1. Why do we need to separate different components of a mixture? Give two examples.
When two or more substances are mixed together, they form a mixture. Components of a mixture should be separated because some components may not be useful or may spoil the useful component of the mixture.
Examples: Tea leaves are separated from the liquid with a strainer while preparing tea. Removal of stone pieces from wheat, rice or pulses by hand.
2. What is winnowing? Where is it used?
The method of separating the components from a mixture is known as winnowing. In this method, heavier and lighter components of a mixture are separated by wind or by blowing air. This method is used by farmers to separate lighter husk particles from heavier seeds of grain.
3. How will you separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses before cooking?
Husk and dirt particles are separated from pulses by winnowing.
4. What is sieving? Where is it used?
Sieving is a method in which fine particles are sieved through holes in the sieve while the bigger impurities remain on the sieve. Sieving is used in a flour mill to separate impurities like husk and stones from wheat before grinding it. It is also used at construction sites to separate pebbles and stones from sand.
5. How will you separate sand and water from their mixture?
Sand and water are separated from their mixture by the following steps:
a) The mixture is allowed to stand without any disturbances.
b) Now, sand settles down.
c) Slowly pour the water into another container to obtain sand in the bottom.
6. Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it?
Yes, it is possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour by the following method:
a) Mix sugar and wheat flour in water.
b ) Stir the solution to allow the sugar to dissolve.
c) Now, filter the mixture.
d ) Filtrate contains the sugar solution, and the residue will be wheat flour.
7. How would you obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water?
The following process should be carried out to obtain clear water from muddy water:
i) Allow muddy water to stand.
ii) Mud gets settled down in the water.
iii) Slowly pour water into another container.
8. Fill in the blanks.
(a) The method of separating the seeds of paddy from its stalks is called ___________.
(b) When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth, the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of ___________.
(c) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of ___________.
(d) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called ___________.
(a) The method of separating the seeds of paddy from its stalks is called threshing.
(b) When milk cooled after boiling is poured onto a piece of cloth, the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of filtration.
(c) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of evaporation.
(d) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called decantation.
9. True or false.
(a) A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration.
(b) A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by the process of winnowing
(c) Separation of sugar from tea can be done with filtration.
(d) Grain and husk can be separated with the process of decantation.
10. Lemonade is prepared by mixing lemon juice and sugar in water. You wish to add ice to cool it. Should you add ice to the lemonade before or after dissolving sugar? In which case would it be possible to dissolve more sugar?
Solution: Ice should be added to lemonade after dissolving sugar. It is possible to add more sugar before adding ice.
CBSE Admit Card 2024
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 offer numerous benefits to students, aiding in their understanding and mastery of the subject matter. Here are some detailed benefits:
1. Concept Clarity: The solutions provided in Chapter 5 aim to clarify fundamental concepts related to the separation of substances. Through detailed explanations, students gain a clearer understanding of the methods involved in separating different substances.
2. Comprehensive Coverage: The NCERT Solutions comprehensively cover all topics and subtopics of Chapter 5, ensuring that students are well-prepared for examinations. Various types of questions, including fill-in-the-blanks, true or false, long-answer, and practical-based questions, are addressed to provide a holistic learning experience.
3. Real-life Examples: The solutions incorporate real-life examples, such as separating husks and stones from grains, making the learning experience more relatable and practical for students. These examples help students connect theoretical knowledge with everyday situations, enhancing their understanding of the application of separation methods.
4. Easy Accessibility: The NCERT Solutions are readily available in PDF format, making them easily accessible for students to download and study at their convenience. This accessibility ensures that students can refer to the solutions both online and offline, facilitating flexible learning.
5. Exam Preparation: The solutions serve as an excellent resource for exam preparation, providing a thorough revision of the chapter. By studying these solutions, students can gain confidence in answering different types of questions that may be asked in the examinations.
6. CBSE Curriculum Alignment: The NCERT Solutions align with the CBSE curriculum, ensuring that students cover the prescribed syllabus effectively. This alignment is crucial for students preparing for CBSE Class 6 examinations, as it helps them focus on the essential topics outlined by the educational board.
7. Self-assessment and Improvement: The solutions enable students to self-assess their understanding of the chapter by attempting various types of questions. Through self-assessment, students can identify areas of improvement and focus on reinforcing their knowledge in those specific areas.
8. Facilitation of Active Learning: The solutions encourage active learning by prompting students to think critically and apply their knowledge to solve problems. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and promotes a more engaged learning experience.
CBSE Board Exam Centre List 2024
How to Prepare With NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5
Preparing with NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 can significantly enhance your understanding of the subject. Here’s a detailed guide on how to effectively prepare using these solutions:
1. Familiarise Yourself with the Chapter: Begin by reading Chapter 5 thoroughly to understand the concepts related to the separation of substances. Pay attention to definitions, processes, and examples provided in the chapter.
2. Systematic Reading of NCERT Solutions: Start with the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5, going through each question and its corresponding solution systematically. Understand the step-by-step explanations and reasoning behind each solution.
3. Active Participation: Engage actively with the solutions by attempting to solve the questions before referring to the provided answers. This approach enhances your problem-solving skills and ensures a more effective learning experience.
4. Focus on Real-life Examples: Concentrate on the real-life examples given in the solutions, such as the separation of husks and stones from grains. Relate these examples to practical scenarios, reinforcing your understanding of how separation methods are applied.
5. Practise Different Question Types: NCERT Solutions cover various question types, including fill-in-the-blanks, true or false, long-answer, and practical-based questions. Practice solving each type to be well-prepared for the diverse questions that may appear in examinations.
6. Use Visual Aids: If applicable, use diagrams and visual aids to represent separation methods, helping you grasp concepts more easily. Visualising the processes can enhance your understanding and make the learning experience more enjoyable.
7. Self-assessment and Review: Regularly assess your understanding by attempting self-assessment quizzes and review questions provided in the NCERT Solutions. Identify areas where you may need further clarification and revisit those sections for reinforcement.
8. Consistent Revision: Plan a schedule for consistent revision of the chapter to reinforce your learning. Regular revision ensures that the concepts stay fresh in your memory, making it easier to recall information during exams.
9. Utilise Additional Resources: While NCERT Solutions are comprehensive, you can supplement your learning with additional resources, such as reference books or online tutorials, to gain a more in-depth understanding.
10. Seek Clarification: If you encounter difficulties or have doubts, don’t hesitate to seek clarification from your teacher, classmates, or online resources. Understanding each concept thoroughly is crucial for effective preparation.
11. Simulate Exam Conditions: To enhance exam readiness, simulate exam conditions by practising with a time limit and adhering to the exam pattern. This practice helps you manage time effectively during the actual examination.
12. Reflect and Improve: Reflect on your performance in practice tests and identify areas for improvement. Focus on refining your problem-solving skills and addressing any weaknesses in your understanding of the chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances
Important topics.
In NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 5, Separation of Substances, students will learn essential concepts, including:
- Methods of separation
- Hand-picking
- Sedimentation, decantation, and filtration
- Evaporation
- Use of more than one method of separation
- Can water dissolve any amount of a substance?
Related Links –
|
| |
Important Points
- Separation is the process of isolating one or more components from a mixture.
- Handpicking is a common method for separating large-sized impurities like dirt, husk, and stones from pulses, wheat, and rice.
- Threshing involves beating stalks to separate grains from harvested crops, either using machines or manually.
- Sieving separates larger particles, typically impurities, by passing the mixture through a filter or sieve.
- Filtration removes solid particles from the fluid component of a mixture using a filter.
- Sedimentation settles heavier components in a mixture after adding water, and decantation is used to remove water along with impurities.
5.1 Methods of Separation
NCERT solution for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 simplifies the different separation methods, including hand-picking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, evaporation, sedimentation, and filtration.
- Hand-picking is a basic method for separating large substances, like removing rocks from garden soil or plastic from debris.
- Threshing separates grains from stalks, commonly used for rice or wheat, involving thrashing stalks on a stone or wooden slab.
- Winnowing separates heavier from lighter substances, demonstrated by villagers separating seeds from seed covers using wind.
- Sieving separates smaller substances from larger ones by passing the mixture through a mesh or sieve.
- Sedimentation separates suspended solids from a liquid, and decantation removes water with impurities.
- Filtration uses gravitational force to separate finer particles from a liquid through a filter paper.
- Evaporation separates dissolved particles from a liquid by applying heat, converting the liquid into gas, and leaving particles in the container.
Multiple methods can be employed for separation, such as winnowing or sieving for sand and salt, or using water to dissolve salt, which can be separated from sand through evaporation. Water, considered a universal solvent, has limited solubility for substances, leading to saturated solutions beyond a certain concentration.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 FAQs
Separation of substances in Class 6 Science involves various methods to isolate different components, such as solids from liquids, through techniques like filtration, evaporation, etc.
In Class 6, sieving is a separation method where a sieve or mesh is utilised to separate larger particles from smaller ones based on their size.
Winnowing in Class 6 refers to the process of separating grains from chaff by letting them be blown away by the wind.
In Class 6, a strainer is a device with holes or a mesh used for separating solid particles from liquids by allowing the liquid to pass through while holding back the solid particles.
Size separation in Class 6 involves sorting particles based on their sizes using methods like sieving or filtration to separate larger particles from smaller ones.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
HPBOSE 10th Admit Card 2024, Download HPBOSE Class 10 Hall Ticket

.st1{display:none} Related Articles
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 21 Data Handling
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 24 Exercise 24.2 Probability
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 24 Exercise 24.1 Probability
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Volume and Surface Area of Solids
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Exercise 20.3 Volume and Surface Area of Solids
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Exercise 20.2 Volume and Surface Area of Solids
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 20 Exercise 20.1 Volume and Surface Area of Solids
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 19 Exercise 19.2 Three Dimensional Figures
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 19 Three Dimensional Figures
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 19 Exercise 19.1 Three Dimensional Figures

Have doubts?
Our support team will be happy to assist you!
- Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6 Chemistry
- Important Questions Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers
Class 6 chemistry important questions with answers are provided here for Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances. These important questions are based on the CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 6 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 6 important questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 6 annual examinations.
Download Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers PDF by clicking on the button below. Download PDF
Recommended Videos
Separation of substances – complete chapter – mindmap with explanation.

Class 6 Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers
Fill in the blanks.
i.) When a heavier component of a mixture settles after adding water to it, this process is called ____.
ii.) The two liquids that do not mix with each other are called ____ liquids.
iii.) ____ is the opposite of evaporation.
iv.) Chalk powder can be separated from water by ____.
v.) ____ is the essential condition for winnowing.
i.) When a heavier component of a mixture settles after adding water to it, this process is called sedimentation.
ii.) The two liquids that do not mix with each other are called immiscible liquids.
iii.) Condensation is the opposite of evaporation.
iv.) Chalk powder can be separated from water by filtration.
v.) Wind is the essential condition for winnowing.
State True or False
i.) Handpicking should be used only when the quantity of impurities is small.
ii.) At a given temperature, a saturated solution can dissolve more of the solute.
iii.) The sieving method can be used to separate wheat flour from bran.
iv.) Winnowing can separate the heavier and lighter components of a mixture.
v.) Common salt is separated from its solution by decantation.
Match the Following
| a.) Handpicking | i.) Conversion of water vapours into liquids |
|---|---|
| b.) Threshing | ii.) Separating bran from flour |
| c.) Winnowing | iii.) Separating larger size impurities |
| d.) Sieving | iv.) Separating butter from milk |
| e.) Sedimentation | v.) Conversion of water into its vapours |
| f.) Evaporation | vi.) Separating grains from the stalks |
| g.) Condensation | vii.) Settling of heavier components at the bottom |
| h.) Churning | viii.) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| a.) Handpicking | iii.) Separating larger size impurities |
|---|---|
| b.) Threshing | vi.) Separating grains from the stalks |
| c.) Winnowing | viii.) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| d.) Sieving | ii.) Separating bran from flour |
| e.) Sedimentation | vii.) Settling of heavier components at the bottom |
| f.) Evaporation | v.) Conversion of water into its vapours |
| g.) Condensation | i.) Conversion of water vapours into liquids |
| h.) Churning | iv.) Separating butter from milk |
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. What is the use of a strainer in separating substances?
Answer. A strainer is a type of sieve used to separate liquid from solid.
Q2. Which process is used to separate cream from curd?
Answer. Centrifugation.
Q3. List some of the materials that are used as filters.
Answer. Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, and filter paper are some materials used as filters.
Q4. Which method can be used to separate salt from seawater?
Answer. Evaporation.
Q5. Which process is considered the opposite of evaporation?
Answer. Condensation.
Q6. How can husk be removed from wheat?
Answer. By winnowing.
Q7. Which method is used to separate stones from grains?
Answer. Handpicking.
Q8. Which method is used to separate two liquids that do not mix with each other?
Answer. Separating funnel.
Q9. Name the liquid that is known as the universal solvent.
Answer. Water.
Q10. What is the process for separating the heavier and lighter components of a mixture?
Answer. Winnowing.
Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define winnowing.
Answer. Winnowing is the process of separating heavier components of a mixture from lighter components using wind. This method is used to separate grains from the husk after the threshing process.
Q2. Define sedimentation.
Answer. Sedimentation is the separation of solids from liquids. This process is carried out when the heavier component of a mixture settles after water is added to it.
Q3. Define decantation.
Answer. Decantation is the process of separating liquid from solid and other immiscible non-mixing) liquids by removing the liquid layer on top of the solid or liquid layer just below it. The process can be carried out by tilting the mixture after pouring out the top layer.
Q4. What are evaporation and condensation?
Answer. Evaporation is the conversion of a liquid state (water) into a gaseous state (vapour). Condensation is the opposite process that converts gaseous state water (vapour) to a liquid state (water).
Q5. What is a saturated and unsaturated solution?
Answer. A saturated solution is one that cannot dissolve any more solute at that temperature.
An unsaturated solution is one in which the solute can be dissolved at any fixed temperature.
Q6. When is the handpicking method used?
Answer. Handpicking method is used for separating undesirable components that differ in shape, size, and colour and are present in small quantities.
Q7. Define threshing.
Answer. The process of separating grains from the stalk by beating is known as threshing. Since the grains are weakly attached to the stalk, they separate when the stalks are beaten on the ground.
Q8. What is a mixture?
Answer. A mixture is a mixture of two or more substances that do not react with one another. Examples include sugar and water, sugar and sand, and so on.
Q9. Why is it necessary to separate substances from mixtures?
Answer. It is necessary to separate substances from mixtures in order to obtain pure substances for various purposes.
Q10. What are the five methods for separating substances from their mixtures?
Answer. The following are five methods for separating substances:
- Handpicking
- Decantation
Q11. Define handpicking.
Answer. Handpicking is a method of separation in which impurities in a mixture that differ from the useful material are hand-picked and removed.
For example, stone pieces can be separated from wheat or rice by handpicking.
Q12. How will you separate a mixture of oil and water?
Answer. Since oil is lighter than water, it will float on it. Two distinct layers form, and oil is slowly allowed to flow into another container, where it is separated from the water. This method to separate oil and water is called a separating funnel.
Long Answer Questions
Q1 . Differentiate between sedimentation and decantation with a suitable example.
Answer. Sedimentation is the process by which the heavier components of a mixture settle down. For example, when a sand-water mixture is allowed to stand undisturbed for some time and sand settles at the bottom.
Decantation is the process of separating the liquid portion of a mixture when the heavier component settles as sediments at the bottom. In other words, it is the process of moving a liquid from one container to another while leaving the sediments at the bottom alone.
For example, sand settles at the bottom of a container when a mixture of sand and water is allowed to stand. The upper portion of the container contains water. This can be separated from the sand at the bottom simply by pouring it into another container without the use of any other separating device. This is referred to as decantation.
Q2. Describe the process of separating salt from seawater.
Answer. Many salts are present in seawater. When seawater is allowed to stand in shallow pits, sunlight evaporates the water, which slowly turns into water vapour. The water evaporates completely in a few days, leaving behind the solid salts. After further purification, common salt is obtained from this salt mixture.
Q3. Explain how to separate the following mixture:
i.) Sand and husk
ii.) Wheat, sugar and stalk
iii.) Water and petrol
iv.) Rice and salt
v.) Sand and salt
i.) Sand and husk mixture: Sand and husk can be separated using the winnowing method.
ii.) Wheat, sugar, and stalk mixture: The winnowing method can be used to separate the stalk from the mixture because it is lighter than the other two components and separates easily. Because wheat and sugar have different sizes, sieving can be used to separate them.
iii.) Water-petroleum mixture: Water does not dissolve in petrol. As a result, it can be separated using a separating funnel.
iv.) Rice and salt mixture: Rice and salt can be separated by sieving.
v.) Sand and salt mixture: When sand and salt are mixed with water, salt dissolves in water, and sand solution can be separated by sedimentation, decantation, and filtration. The common salt is then separated using evaporation.
Q4. Explain the method of separation of solid-liquid mixtures.
Answer. Filtration is used to separate solid and liquid mixtures when the solid particles are too large to pass through a filter paper.
Solid particles in a liquid can sometimes be so small that they can pass through filter paper. The filtration technique cannot be used to separate such particles. Centrifugation is used to separate such mixtures. Centrifugation is the process of separating insoluble materials from a liquid when filtration does not work well. The centrifugation is determined by the particle size, shape, and density.
Sedimentation and decantation can be used to separate heavy solid particles. If the mixture is left undisturbed for an extended period of time, the solid particles settle to the bottom. They can then be separated from the liquid by decantation.
Q5. What is sieving? Explain how it is done.
Answer. Sieving is a separation method used to separate substances of varying sizes that cannot be separated by handpicking.
The difference in the size of the solid particles is the basis for the principle.
Separation Technique – By passing the mixture through a sieve, large particles are separated from small or finer particles. The sieve is made of wood and has a metal mesh at the bottom. When the sieve is shaken, the mixture is added from the top as the larger particles remain above and the finer particles collect below.
For example, Impurities such as husk and stones are removed from wheat before it is ground in a flour mill.
- Separation of Substances
- Methods of Separation
- Class 6 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 5 Separation of Substances – Set 1
- Class 6 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 5 Separation of Substances – Set 2
- Class 6 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 5 Separation of Substances – Set 3
- Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 Separation of Substances MCQs
- Separation Techniques Questions
- Separation Questions
- Chemistry Concept Questions and Answers
Sieving – Separation of Mixture

Decantation and The Separation Process

| CHEMISTRY Related Links | |
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. Mixtures need to be separated because (a) to remove undesirable substances (b) to get desirable substances (c) to obtain highly pure substances (d) all of the above
Answer: (d) all of the above

Question 2. The method of separation used to separate stones from rice is (a) handpicking (b) threshing (c) winnowing (d) all of these
Answer: (a) handpicking

Question 3. Butter is separated from milk by (a) sedimentation (b) filtration (c) churning (d) decantation
Answer: (c) churning
Question 4. The separation of grains from husk is done by the process of (a) handpicking (b) sieving (c) winnowing (d) threshing
Answer: (c) winnowing
Question 5. Threshing is done by (a) beating (b) animals (c) machines (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
Question 6. Filtration is a method to separate the components of a (a) solution (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance (c) both (a) & (b) (d) pure substance
Answer: (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance
Question 7. A solid is dissolved in water. Which one of the following methods can be used to separate it? (a) Filtration (b) Decantation (c) Distillation (d) Evaporation
Answer: (d) Evaporation
Question 8. Petroleum contains (a) petrol (b) methanol (c) oil (d) water
Answer: (a) petrol
Question 9. Which of the following method is used when there is a difference in size and colour of desirable and undesirable constituents? (a) Handpicking (b) Threshing (c) Filtration (d) Decantation
Answer: (a) Handpicking
Question 10. The components of a solution of sugar in water can be separated by (a) filtration (b) crystallisation (c) decantation (d) sedimentation
Answer: (b) crystallisation
Question 11. At water treatment plants, the river water is filtered by using (a) filter paper (b) porcelain filters (c) cloth filters (d) sand filters
Answer: (d) sand filters
Question 12. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called (a) handpicking (b) threshing (c) decantation (d) evaporation
Answer: (b) threshing
Question 13. Iodine can be recovered from tincture of iodine by the process of (a) filtration (b) distillation (c) evaporation (d) decantation
Answer: (c) evaporation
Question 14. A mesh which is used to separate things on the basis of their difference in size (a) sieve (b) thresher (c) filter paper (d) none of these
Answer: (a) sieve
Question 15. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called (a) condensation (b) evaporation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) evaporation
Question 16. The process of separation of tea leaves by strainer is called (a) filtration (b) sedimentation (c) evaporation (d) condensation
Answer: (a) filtration
Question 17. Which of the following mixtures cannot be separated by using water as solvent followed by filtration and evaporation? (a) Sand and sugar (b) Salt and chalk powder (c) Sand and sulphur (d) Blue vitriol and sand
Answer: (c) Sand and sulphur
Question 18. The property which forms the basis of sieving is (a) difference in weight (b) difference in colour (c) difference in shape (d) difference in size
Answer: (d) difference in size
Question 19. When no more salt dissolves in water at a particular temperature, then the solution at that temperature is called (a) unsaturated (b) saturated (c) supersaturated (d) none of these
Answer: (b) saturated
Question 20. The separation of insoluble solids from liquids can be done by (a) sedimentation (b) decantation (c) loading (d) all of these
Answer: (a) sedimentation
Question 21. An example of a heterogeneous mixture is (a) fresh air (b) fresh water (c) sugar solution (d) dirty water
Answer: (d) dirty water
Question 22. ………….. is a convenient method of separation. (a) Handpicking (b) Threshing (c) Winnowing (d) Sieving
Question 23. Thresher machines are also used to thresh large quantities of …………….. (a) grain (b) sugar (c) salt (d) sand
Answer: (a) grain
Question 24. A separation funnel is a ……….. bulb to the stem of which is fitted a stopcock. (a) wooden (b) copper (c) glass (d) steel
Answer: (c) glass
Question 25. Distillation is a method of obtaining pure …………….. from a solution. (a) liquid (b) solid (c) gas (d) all of them
Answer: (a) liquid
Question 26. Water present in …………… is in the form of water vapour. (a) soil (b) moist (c) air (d) dry
Answer: (c) air
Question 27. Common salt is recovered from sea water by the process of (a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) sublimation (d) decantation
Question 28. When no more salt dissolves in water at a particular temperature, then the solution at that temperature is called (a) unsaturated (b) saturated (c) super saturated (d) none of the above
Question 29. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called (a) evaporation (b) condensation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (a) evaporation
Question 30. Tincture of iodine is a weak solution of iodine in alcohol. Iodine can be recovered from tincture of iodine by the process of (a) filtration (b) distillation (c) evaporation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) distillation
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. Milk is a mixture of ……………., ……………. and …………….
Answer: milk-proteins, water, cream
Question 2. ……………. substance contains particles of only one type.
Answer: Pure
Question 3. ……………. and ……………. are the types of mixtures.
Answer: Heterogeneous, homogeneous
Question 4. Pebbles can be separated from wheat by …………….
Answer: handpicking
Question 5. ……………. is used to separate husk from wheat.
Answer: Winnowing
Question 6. Glass is a …………….
Answer: mixture
Question 7. Common salt is obtained from sea water by …………….
Answer: evaporation
Question 8. Compounds have ……………. melting points.
Answer: fixed
Question 9. Cream is separated from milk by the process of …………….
Answer: churning
Question 10. The method used to separate the components of different sizes in a mixture using a sieve is called …………….
Answer: sieving
Question 11. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called …………….
Answer: Threshing
Question 12. Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by …………….
Question 13. Breaking of stalks from grains is done by a machine called …………….
Answer: threshers
Question 14. Butter is a component of …………….
Answer: buttermilk
Question 15. Mixture may be solid, liquid or …………….
Answer: gas
Question 16. ……………. is used for separating insoluble substances from a liquid.
Answer: Filtration
Question 17. Sedimentation can be done more quickly by adding ……………. into it.
Answer: alum
Question 18. The used tea-leaves are separated from tea by the method of …………….
Answer: filtration
Question 19. The changing of liquid into vapours is called …………….
Question 20. Components retain their properties in a …………….
Question 21. Peanuts can be separated from a mixture of wheat and peanuts by ………………
Question 22. Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by ………………
Question 23. Compounds have ……………… melting points.
Question 24. Mixture may be solid, liquid or ………………
Question 25. Butter is a component of ………………
Answer: milk
Question 26. Sugarcane juice is a mixture of ……………… water and many other substances.
Answer: sugar
Question 27. Separation of components is done to obtain a ……………… substance.
Answer: pure
Question 28. Components retain their properties in a ………………
Question 29. The solid left behind after filtration is called ………………
Answer: residue
Question 30. The component dissolved in a solvent is called ………………
Answer: solute
True or False
Question 1. Milk is a pure substance.
Answer: False
Question 2. Evaporation is a continuous process.
Answer: True
Question 3. Air is a mixture of gases.
Question 4. Filtration can remove any solid substance which are dissolved in a liquid.
Question 5. A mixture of chalk powder and water is separated by sieving.
Question 6. A mixture of oil and water can be separated by decantation.
Question 7. Rocks are pure substances.
Question 8. Ink loses its properties when mixed in water.
Question 9. Common salt is a pure substance.
Question 10. Loading helps the suspended clay particles to settle down.
Question 11. Separating a mixture of two solids by winnowing is based on the difference in their weights.
Question 12. When no more solute can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature, the solution is said to be unsaturated.
Question 13. Grain and husk can be separated by decantation.
Question 14. Handpicking can be used to separate pulses from a mixture of pulsed and pebbles in a plate.
Question 15. Lemonade is a homogeneous mixture.
Question 16. There are a number of useful minerals present in sea water.
Question 17. The tap water is completely pure and fit for drinking.
Question 18. When a mixture consists of heavier and lighter particles, the lighter particles are separated using winnowing.
Question 19. Winnowing and threshing are same processes.
Question 20. Decantation is generally preceded by sedimentation.
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Purification of water | (a) Threshing |
| 2. Separating butter from curd | (b) Alum |
| 3. Separation of grains from stalks | (c) Churning |
| 4. Separating larger size impurities | (d) Evaporation |
| 5. Separation by wind | (e) Handpicking |
| 6. Separation of common salt from water solution | (f) Winnowing |
| 7. Separating iron particles from dust | (g) Sedimentation |
| 8. Separating bran from flour | (h) Magnet |
| 9. Conversion of water into liquids | (i) Sieving |
| 10. Setting of heavier components at bottom | (j) Condensation |
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Purification of water | (b) Alum |
| 2. Separating butter from curd | (c) Churning |
| 3. Separation of grains from stalks | (a) Threshing |
| 4. Separating larger size impurities | (e) Handpicking |
| 5. Separation by wind | (f) Winnowing |
| 6. Separation of common salt from water solution | (d) Evaporation |
| 7. Separating iron particles from dust | (h) Magnet |
| 8. Separating bran from flour | (i) Sieving |
| 9. Conversion of water into liquids | (j) Condensation |
| 10. Setting of heavier components at bottom | (g) Sedimentation |
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Handpicking | (a) Separating bran from flour |
| 2. Threshing | (b) Separating larger size impurities |
| 3. Winnowing | (c) Separating grains from its stalks |
| 4. Sieving | (d) Settling of heavier components at bottom |
| 5. Sedimentation | (e) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Handpicking | (b) Separating larger size impurities |
| 2. Threshing | (c) Separating grains from its stalks |
| 3. Winnowing | (e) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| 4. Sieving | (a) Separating bran from flour |
| 5. Sedimentation | (d) Settling of heavier components at bottom |
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Category: Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out
Case study questions for class 6 science chapter 15 air around us, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 14 water, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 13 fun with magnets, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 12 electricity and circuits, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 11 light shadow and reflection, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 10 motion and measurement, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 9 living organisms and their surroundings, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 8 body movements, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 7 getting to know plants, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 6 changes around us, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 5 separation of substances, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 4 sorting materials into groups, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 3 fibre to fabric, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 2 components of food, case study questions for class 6 science chapter 1 food – where does it come from.

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 6th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances PDF Download
CBSE Class 6th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances are the easiest questions which you see in your question paper and the scoring one all student who attempt it surely get they are just little bit difficult and examine your basic knowledge regarding the particular chapter. Science Value Based Questions for Class 6th are available here at Free of cost. These questions are expected to be asked in the Class 6th board examination. These Science Value Based Questions are from complete CBSE Syllabus.
CBSE Class 6th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances

Most of these Science Value Based Questions are quite easy and students need only a basic knowledge of the chapter to answer these questions. Download CBSE Science Value Based Questions for board examinations. These Science Value Based Questions are prepared by Directorate of Education, Delhi.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions Class 6th Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances PDF
The purpose of the Science Value Based Questions is to make students aware of how basic values are needed in the analysis of different situations and how students require to recognize those values in their daily lives. Some questions are subject related. But even if they are not, that one-minute awareness of what we write about value without any specific preparation is a good step indeed.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 6th Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances download here in PDF format. The most CBSE Science Value Based Questions for annual examination are given here for free of cost. The additional questions for practice the Class 6th exam are collected from various sources. It covers questions asked in previous year examinations.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 6th Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances Free PDF
Class 6th books have many questions. These questions are regularly asked in exams in one or other way. Practising such most CBSE Science Value Based Questions Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances certainly help students to obtain good marks in the examinations.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Case Study Questions Class 6 Science The Living Organisms Characteristics and Habitats
Case study questions class 6 science chapter 9 the living organisms characteristics and habitats.
CBSE Class 6 Case Study Questions Science The Living Organisms Characteristics and Habitats. Important Case Study Questions for Class 6 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions The Living Organisms Characteristics and Habitats.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 6 Science The Living Organisms Characteristics and Habitats
Case study 1.
Let us look at different kinds of fish.The thing that is common in all fishis their streamlined shape, which helps them move inside water. Fish have slippery scales on their bodies. These scales protect the fish and also help in easy movement through water. Fish have flat fins and tails that help them to change directions and keep their body balance in water. Gills present in the fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water.
Que. 2) In water, plants and animals use theair that is dissolved in water.
Que. 3. c) Grills
Que. 4) Answer: The body structure of a camel helps it to survive in desert conditions. Camels have long legs which help to keep their bodies away from the heat of the sand. They excrete small amount of urine, their dung is dry and they do not sweat. Since camels lose very little water from their bodies, they can live for many days without water.
Case study 2
Que.1) Habitat means ……..………………………………………………………………………………..…… .
c) Terrestrial habitat
Case study 3
Que.1. b) False
Case study 4
Mountain habitats are normally very cold and windy. In some areas, snowfall may take place in winters. Here, Trees are normally cone shaped and have sloping branches. The leaves of some of these trees are needle-like. This helps the rainwater and snow to Slide off easily. Animals living in the mountain regions are also adapted to the conditions there. They have thick skin or fur to protect them from cold. For example, yaks have long hair to keep them warm. Snow leopard has thick fur on its body including feet and toes. This protects its feet from the cold when it walks on the snow.
d) None of the above
Que.4) Explain the features that help desert plants to survive in extreme heat?
Que.2. d) Both (a) and (c)
Case study 5
Case study 6.
Que.5) Answer: Exchange of gases in plants mainly takes place through leaves. The leaves take in air through tiny pores in them and use the oxygen. They give out carbon dioxide to the air. The amount of oxygen released in the process of food preparation by plants is much more than the oxygen they use in respiration.
Case study 7
Que.5) Explain the process of excretion in plants?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 22 solutions স্কুলের অনুষ্ঠান করি, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 21 solutions মাঠে টিফিন ভাগ করে খাই, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 20 solutions নিজের খুশিমতো রং করি, jharkhand board solutions class 5 english chapter 8.
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5

Last Updated on August 2, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 9 science chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life.
| The Fundamental Unit of Life | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 9 | |
| Science | |
| Theme | The World of the Living |
| Class 9 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 1:
Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. It is an important process occurring in all living beings. Diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and out of the cells. The molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration becomes equal throughout.
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1. Name the process which is useful for the movement of substances like CO 2 and O 2 across the plasma membrane. a. Osmosis b. Diffusion c. Endocytosis d. Plasmolysis
Q 2. Osmosis is the diffusion of: a. Water b. Free energy c. Solute and solvent d. None of these
Q 3. Diffusion finally stops when: a. concentration of particles of one region becomes higher than the other. b. concentration of particles of one region becomes lower than the other. c. concentration of particles of two regions becomes the same. d. None of the above
Q 4. Which of the following statement defines hypertonic solutions? a. A solution that has a lesser concentration of solutes on the outside of a cell when compared with the inside of a cell. b. A solution that has a greater concentration of solutes on the outside of a cell when compared with the inside of a cell. c. A solution that has same concentration of solutes on the outside of a cell when compared with the inside of a cell. d. None of the above
Q 5. If the two solutions have same concentrations, they are said to be: a. Isotonic b. Hypertonic c. Hypotonic d. Dilute
- (b) Diffusion
- (c) concentration of particles of two regions becomes the same
- (b) A solution that has a greater concentration of solutes on the outside of a cell when compared with the inside of a cell.
- (a) Isotonic
Case study questions for other chapters of class 9 science is given below.
- Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Motion Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Tissues Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Matter in our surroundings class 9 case study questions science chapter 1.
We hope the given case study questions for The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 helps you in your learning.
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Cell as a basic unit of life
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Multicellular organisms
- Cell membrane and cell wall
- Cell organelles and cell inclusions
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Chromosomes – basic structure and number
The egg of an ostrich is the largest known cell of a living animal and an average egg is 15 cm long and 13 cm wide.
he chapter “The Fundamental Unit of Life” in CBSE Class 9 deals with the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms – the cell. This chapter introduces students to the concept of cells as the building blocks of life, offering insights into their discovery, structure, and function
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on The Fundamental Unit of Life Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 9 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 9 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on “The Fundamental Unit of Life” for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on “The Fundamental Unit of Life” class 9 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of “The Fundamental Unit of Life”.
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.

Related Posts

COMMENTS
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Passage-1. You are asked to add two spoons of solid salt to some liquid water taken in a beaker.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer for all Chapter 1 to 16. Class 6 Students can learn Case Type Question from here. 100% FREE Exercise & Practice for CBSE, NCERT and ICSE ... CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question. Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question. Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question. Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question.
The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: Body Movements have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: Body Movements covers topics like Case 1: Skeletal System, Case 2: Animal Locomotion, Case 3: Bird Adaptations, Case 4: Fish Locomotion, Case 5: Skeletal Protection and Case Based ...
Write the steps involved for the separation of salt, sand and oil from the mixture by giving an activity along with the diagram. Solution: A mixture of salt, sand, oil and water can be separated by following steps. Decant the oil from the mixture which is floating - oil is separated. Filter the mixture.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books.Register Online for NCERT Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials ...
CBSETuts.com provides you Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances solved by expert teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All the chapter wise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete CBSE syllabus and score more marks in Your board examinations. NCERT Exemplar Problems Class […]
Below we have complied the Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances important questions with answers. These important questions are divided into three parts. They are - Very short questions, short questions and long important question. CBSE important Questions for Class 6 Science will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Separation of Substances is the fifth chapter which we will study in Class 6 Science. In this chapter, Teachoo provides NCERT Solutions, Notes, Worksheets, MCQ, 1 Mark questions (with solutions). On Teachoo, you can find explanations of various concepts, NCERT questions and extra questions prepared by experts which can be your one stop solution ...
Answer: The materials having different size and colour can be separated by handpicking. 8. Name the other methods used to separate solid materials of different size. Answer: Sieving. 9. Name the process used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture. Answer: Winnowing.
Download Most Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter - 5 Separation of Substances. Download Important Questions PDF. The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science are crucial study sources that will help learners clear all the doubts that occur while studying the CBSE syllabus Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science. Fill in the blanks, true or false ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science - All Chapters. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From. Chapter 2 Components of Food. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups. Chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Chapter 6 Changes Around Us. Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants. Chapter 8 Body Movements.
Give one example of sieving used in everyday life. Separation of barn (choker) from flour. Question 5. Name some materials that are used as filters. Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, filter paper. Question 6. Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids. By using separating funnel or by decantation.
In this page we have Worksheet for Class 6 Science Chapter 5: Separation of Substances. Hope you like them and do not forget to like , social share and comment at the end of the page. ... LONG /SKILL BASED /DIAGRAM-BASED ANSWER TYPE QUESTION. Question 4 Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follows.
Alum, tub, muslin cloth, gas stove, thread, pan and lid. Answer 17. (i) Filtration using muslin cloth. (ii) Swirl with alum and leave water undisturbed for some time. (iii) Decantation. (iv) Boil for 10 minutes in covered pan. (v) Cool, filter and now it is fit for drinking. Question 18.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science serve as crucial study resources, assisting learners in clarifying doubts related to the CBSE syllabus Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science. Answering fill-in-the-blanks, true or false questions, long-answer questions, and practical-based questions will enhance their understanding of important concepts for future ...
Milk or curd is churned to separate the butter (Fig. 5.2). As we learned in Chapter 3, we gin cotton to separate its seeds from the fibre. Perhaps you might have eaten salted daliya or poha. If you found that it had. chillies in it, you may have carefully taken them out before eating. Fig. 5.2 Butter is taken out by churning milk or curds.
By practising these Class 6 important questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 6 annual examinations. Download Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances Important Questions with Answers PDF by clicking on the button below.
Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers. Choose the correct option. Question 1. Mixtures need to be separated because. (a) to remove undesirable substances. (b) to get desirable substances. (c) to obtain highly pure substances. (d) all of the above. Answer.
July 19, 2023 March 4, 2024 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 9 Living Organisms and Their ... July 18, 2023 March 4, 2024 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food - Where Does it Come From. Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1 ...
These ingredients contain components that are needed by our body. These components are called Nutrients. For example- Proteins. Que. 5) Answer: The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Apart from nutrients, food also contains dietary fibres and water.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions Class 6th Chapter 5 Separation Of Substances PDF. The purpose of the Science Value Based Questions is to make students aware of how basic values are needed in the analysis of different situations and how students require to recognize those values in their daily lives. Some questions are subject related.
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 science.
Que.4) Answer: The organisms, both plants and animals, living in a habitat are its biotic components. The non-living things such as rocks, soil, air and water in the habitat constitute its abiotic components. Que.5) Answer: The plants and animals that live on land are said to live in terrestrial habitats.
Reading Time: 7 minutes Last Updated on August 2, 2024 by XAM CONTENT. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board.