- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.

Hypothesis Sentence Examples
Their hypothesis explains so many facts.
An unproven hypothesis of the existence of things can be useful.
There is no data to accept or refute this hypothesis .
At any rate this hypothesis suggests an explanation of many hitherto inexplicable facts.
The schedule now called for hypothesis testing.
The Chemistry of the Sun (1887) is an elaborate treatise on solar spectroscopy based on the hypothesis of elemental dissociation through the intensity of solar heat.
His silent votes were all given on that hypothesis .
A detective's work consists largely in forming and testing hypothesis .
A third hypothesis is that advanced by Karl Rieder (Der Gottesfreund von Oberland, Innsbruck, 1905), who thinks that not even Merswin himself wrote any of the literature, but that his secretary and associate Nicholas of Lowen, head of the House of St John at Griinenworth, the retreat founded by Merswin for the circle, worked over all the writings which emanated from different members of the group but bore no author's names, and to glorify the founder of the house attached Merswin's name to some of them and out of his imagination created "the Friend of God from the Oberland," whom he named as the writer of the others.
Such are to be explained on the "sources hypothesis ."
The degree of smoothness or consistency which is to be expected on the hypothesis of a single author will be determined by taste rather than argument.
It seems clear, however, that the hypothesis of epics such as the Iliad and Odyssey having been formed by putting together or even by working up shorter poems finds no support from analogy.
Herbert Spencer, again, before the decline in question set in, put forward the hypothesis that "the ability to maintain individual life and the ability to multiply vary inversely"; in other words, the strain upon the nervous system involved in the struggle for life under the conditions of modern civilization, by reacting on the reproductive powers, tends towards comparative sterility.
According to the hypothesis of Waldeyer and Thiersch there is perfect equilibrium between the normal epithelium and its supporting structure, the connective tissue, but with advancing age this balance is upset owing to the connective tissue gradually losing its restraining power.
As the word " interpolation " implies, Hermann did not maintain the hypothesis of a congeries of independent " lays."
This line of hypothesis and demonstration is typical of the palaeogeographic methods generally - namely, that vertebrate palaeontologists, impressed by the sudden appearance of extinct forms of continental life, demand land connexion or migration tracts from common centres of origin and dispersal, while the invertebrate palaeontologist alone is able to restore ancient coast-lines and determine the extent and width of these tracts.
This hypothesis Clifford connected with the hypothesis of psychophysical parallelism.
The latter hypothesis seems more probable, upon the whole, although there is little to choose between the two.
But this hypothesis cannot be accepted as furnishing a satisfactory explanation of the likeness.
The hypothesis that Beowulf is in whole or in part a translation from a Scandinavian original, although still maintained by some scholars, introduces more difficulties than it solves, and must be dismissed as untenable.
In the motion consequent on any slight disturbance the total energy T+V is constant, and since T is essentially positive it follows that V can never exceed its equilibrium value by more than a slight amount, depending on the energy of the disturbance, This implies, on the present hypothesis , that there is an upper limit to the deviation of each co-ordinate from its equilibrium value; moreover, this limit diminishes indefinitely with the energy of the original disturbance.
This leads to a determinantal equation in X whose 2n roots are either real and negative, or complex with negative real parts, on the present hypothesis that the functions T, V, F are all essentially positive.
It is sometimes known as the "expectation of life," a term, however, which involves a mathematical hypothesis now discarded.
Stubbs's edition of the Itinerarium (Rolls Series, 1864), in which the contrary hypothesis is maintained, appeared before Gaston Paris published his discovery.
It follows that, for the thinking mind, matter is a necessary hypothesis .
It follows that philosophy is in a sense both dualist and monist; it is a cosmic dualism inasmuch as it admits the possible existence of matter as a hypothesis , though it denies the possibility of any true knowledge of it, and is hence in regard of the only possible knowledge an idealistic monism.
Both laws were of paramount importance, as direct evidence of Darwin's theory of descent, which, it will be remembered, was at the time regarded merely as an hypothesis .
In Kowalevsky's Versuch einer natiirlichen Classification der Fossilen Hufthiere (1873) we find a model union of detailed inductive study with theory and working hypothesis .
Brocchi and Daniel Rosa (1899) have developed the hypothesis of the progressive reduction of variability.
The net result of observation is not favourable to the essentially Darwinian view that the adaptive arises out of the fortuitous by selection, but is rather favourable to the hypothesis of the existence of some quite unknown intrinsic law of life which we are at present totally unable to comprehend or even conceive.
The resemblance of this to some versions of the Hindu doctrine of the four ages or yuga is hardly to be accounted for except on the hypothesis that the Mexican theology contains ideas learnt from Asiatics.
This view, generally known as "Prout's hypothesis ," at least had the merit of stimulating inquiry, and many of the most careful determinations of atomic weights undertaken since its promulgation have been provoked by the desire to test its validity.
In 1902, in an "attempt at a chemical conception of the ether," he put forward the hypothesis that there are in existence two elements of smaller atomic weight than hydrogen, and that the lighter of these is a chemically inert, exceedingly mobile, all-penetrating and all-pervading gas, which constitutes the aether.
The occasional similarities of thought and expression between them and the Lucan writings suggest that the period of their origin lies within a quarter of a century after Paul's death, and, when one or two later accretions are admitted, the internal evidence, either upon the organization of the church 1 or upon the errors controverted, tallies with this hypothesis .
But Aristotle was an author as well as a lecturer; for the hypothesis that the Aristotelian writings are notes of his lectures taken down by his pupils is contradicted by the tradition of their learning while walking, and disproved by the impossibility of taking down such complicated discourses from dictation.
Such in brief is the Platonism of the written dialogues; where the main doctrine of forms is confessedly advanced never as a dogma but always as a hypothesis , in which there are difficulties, but without which Plato can explain neither being, nor truth nor goodness, because throughout he denies the being of individual things.
Plato's hypothesis of supernatural forms, and advance his own.
Here, too, he examined the hypothesis of Eudoxus that things are caused by mixture of forms, a hypothesis which formed a kind of transition to - his own later views, but failed to satisfy him on account of its diffi - culties.
He rejected the Platonic hypothesis of forms, and affirmed that they are not separate but common, without however as yet having advanced to a constructive metaphysics of his own; while at the same time, after having at first adopted his master's dialectical treatment of metaphysical problems, he soon passed from dialogues to didactic works,, which had the result of separating metaphysics from dialectic. The all-important consequence of this first departure from Platonism was that Aristotle became and remained primarily a metaphysician.
During his master's life, in the second period of his own life, he protested against the Platonic hypothesis of forms, formal numbers and the one as the good, and tended to separate metaphysics from dialectic by beginning to pass from dialogues to didactic works.
There is a further hypothesis that the Aristotelian works were not originally treatises, but notes of lectures either for or by his pupils.
We have seen how anxious Aristotle was to be considered one of the Platonists, how reluctant he was to depart from Plato's hypothesis of forms, and how, in denying the separability, he retained the Platonic belief in the reality and even in the unity of the universal.
The hypothesis of inherence gives an inadequate account of the dependence of an attribute on a substance, and is a kind of half-way house between separation and predication.
These considerations make it probable that the author of all three treatises was Aristotle himself; while the analysis of the treatises favours the hypothesis that he wrote the Eudemian Ethics and the Magna Moralia more or less together as the rudimentary first drafts of the mature Nicomachean Ethics.
At first he adopted the somewhat ascetic views of his master about soul and body, and about goods of body and estate; but before Plato's death he had rejected the hypothesis of forms, formal numbers and the form of the good identified with the one, by which Plato tried to explain moral phenomena; while his studies and teaching on rhetoric and poetry soon began to make him take a more tolerant view than Plato did of men's passions.
The hypothesis that the Eudemian Ethics, and by consequence the Magna Moralia, are later than Aristotle has arisen from a simple misconception, continued in a Scholium attributed to Aspasius, who lived in the 2nd century A.D.
According to a probable hypothesis it is a continuation of the above-mentioned river Reka, which is lost near Sankt Kanzian.
The hypothesis (Schlatter, Das neugefundene hebrdische Stuck des Sirach) that it was from Aristobulus that the philosophy of Ecclesiasticus was derived is not generally accepted.
The structure of the Mollusca in the greater number of cases agrees with the hypothesis that the primitive form was unsegmented, and therefore had but one pair of coelomic ducts and one pair of nephridia.
The former hypothesis with its variants may be called the Trochosphere- hypothesis , the latter the Gastraea- hypothesis .
The careful study of the development of one Acoelous form and of certain Rhabdocoels has strengthened this hypothesis by showing that no definite enteron or gut is at first laid down, but that certain embryonic syncytial tracts become digestive tracts, others excretory, others again muscular.
And in general it may be stated that the hypothesis of such an intermixture of forms from neighbouring dialects has been rendered in recent years far more credible by the striking evidence of such continual intermixture going on within quite modern periods of time afforded by the Atlas linguistique de la France, even in the portion which has already been published.
Even the Cartesian school, as it came more and more to feel the difficulty of explaining the interaction of body and mind, and, indeed, any efficient causation whatever, gradually tended to the hypothesis that the real cause is God, who, on the occasion of changes in body, causes corresponding changes in mind, and vice versa.
Avenarius (q.v.) is the hypothesis of the inseparability of subject and object, or, to use his own phraseology, of ego and environment, in purely empirical, or a posteriori form.
He considered that the whole hypothesis that an outer physical thing causes a change in one's central nervous system, which again causes another change in one's inner psychical system or soul, is a departure from the natural view of the universe, and is due to what he called " introjection," or the hypothesis which encloses soul and its faculties in the body, and then, having created a false antithesis between outer and inner, gets into the difficulty of explaining how an outer physical stimulus can impart something into an inner psychical soul.
It is curious that Avenarius should have brought forward this artificial hypothesis as the natural view of the world, without reflecting that on the one hand the majority of mankind believes that the environment (R) exists, has existed, and will exist, without being a counterpart of any living being as central part (C); and that on the other hand it is so far from being natural to man to believe that sensation and thought (E) are different from, and merely dependent on, his body (C), that throughout the Homeric poems, though soul is required for other purposes, all thinking as well as sensation is regarded as a purely bodily operation.
He starts as a phenomenalist from the hypothesis , which we have just described, that knowledge is ex Wundt.
Between Hume's a posteriori and Kant's a priori hypothesis he proposes a logical theory of the origin of notions beyond experience.
Wundt, however, having satisfied himself of the power of mere logical thought beyond experience, goes on to further apply his hypothesis , and supposes that, in dealing with the physical world, logical thinking having added to experience the " supplementary notion " of causality as the connexion of appearances which vary together, adds also the " supplementary notion " of substance as substratum of the connected appearances.
Taken for granted the Kantian hypothesis of a sense of sensations requiring synthesis by understanding, and the Kantian conclusion that Nature as known consists of phenomena united by categories as objects of experience, Green argued, in accordance with Kant's first position, that knowledge, in order to unite the manifold of sensations by relations into related phenomena, requires unifying intelligence, or what Kant called synthetic unity of apperception, which cannot itself be sensation, because it arranges sensations; and he argued, in accordance with Kant's second position, that therefore Nature itself as known requires unifying intelligence to constitute the relations of its phenomena, and to make it a connected world of experience.
Rejecting everything in the Kritik which savoured of the " metempirical," he yet sympathized so far with Hegel's noumenalism as to accept the identification of cause and effect, though he interpreted the hypothesis phenomenalistically by saying that cause and effect are two aspects of the same phenomenon.
But his main sympathy was with Fechner, the gist of whose " inner psychophysics " he adopted, without, however, the hypothesis that what is conscious in us is conscious in the all-embracing spirit of God.
Clifford (q.v.) was working out the hypothesis of psychophysical parallelism to a conclusion different from that of Lewes, and more allied to that of Leibnitz, the prime originator of all these hypotheses.
He disagrees with Fechner's hypothesis of a world-soul, the highest spirit, God, who embraces all psychophysical processes.
James Ward, in Naturalism and Agnosticism (1899), starts from the same phenomenalistic views of Mach and Kirchhoff about mechanics; he proceeds to the hypothesis of duality within experience, which we have traced in James Ward.
These sudden appearances of vast bodies of lemmings, and their singular habit of persistently pursuing the same onward course of migration, have given rise to various speculations, from the ancient belief of the Norwegian peasants, shared by Olaus Magnus, that they fall down from the clouds, to the hypothesis that they are acting in obedience to an instinct inherited from ancient times, and still seeking the congenial home in the submerged Atlantis, to which their ancestors of the Miocene period were wont to resort when driven from their ordinary dwelling-places by crowding or scarcity of food.
In this he gave equations resulting from the hypothesis that the magnetism of a ship is partly due to the permanent magnetism of hard iron and partly to the transient induced magnetism of soft iron; that the latter is proportional to the intensity of the inducing force, and that the length of the needle is infinitesimally small compared to the distance of the surrounding iron.
Cuenot, in order to explain certain features in the hereditary transmission of coat colour in mice, postulated the hypothesis that the grey colour of the wild mouse (which is known to be a compound of black, chocolate and yellow pigments) may be due either to the interaction of a single ferment and three chromogens, or vice versa, to one chromogenic substance and three ferments.
Simplicius's further suggestion that Thales conceived the element to be modified by thinning and thickening is plainly inconsistent with the statement of Theophrastus that the hypothesis in question was peculiar to Anaximenes.
On the whole, a common origin in the north for at least the arcticoaltaic group of alpine plants seems to be the most reasonable hypothesis .
On this basis, with other interesting morphological comparisons, Brefeld erected his hypothesis , now untenable, that the Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes diverge from the Zygomycetes, the former having particularly specialized the ascus (sporangial) mode of reproduction, the latter having specialized the conidial (indehiscent one-spored sporangiole) mode.
The isolation of these compounds is a powerful argument in favour of the Hantzsch hypothesis which requires the existence of these three different types, whilst the Bamberger-Blomstrand view only accounts for the forma tion of two isomeric cyanides, namely, one of the normal diazonium type and one of the iso-diazocyanide type.
Cleanthes's view is, therefore, an hypothesis , and in no sense an inference.
The phenomenon of isomerism will probably supply the crucial test, at least for the chemist, and the question will be whether the Ostwaldian conception, while substituting the Daltonian hypothesis , will also explain isomerism.
But this hypothesis is apparently without foundation.
Poulton, in an admirable discussion of contemporary views regarding species (presidential address to the Entomological Society of London 1904), has shown that Darwin did not believe in the objective existence of species, not only because he was led to discard the hypothesis of special creation as the explanation of the polymorphism of life, but because in practice as a working systematist he could neither find for himself nor ascertain from other systematists any settled criteria by which a group of specimens could be elevated into a genus, accepted as a species, or regarded as a variety.
Malthus has in more modern times derived a certain degree of reflected lustre from the rise and wide acceptance of the Dar, winian hypothesis .
Starting from the hypothesis that Sweden was "DenmarkNorway's most active and irreconcilable enemy," Bernstorff logically included France, the secular ally of Sweden, among the hostile powers with whom an alliance was to be avoided, and drew near to Great Britain as the natural foe of France, especially during the American War of Independence, and this too despite the irritation occasioned in Denmark-Norway by Great Britain's masterful interpretation of the expression "contraband."
Weber's hypothesis of electric atoms, capable of diffusing through metallic bodies and conductors of electricity, but capable of vibration only in non-conductors, it is possible that the ultimate mechanism of conduction may be reduced in all cases to that of diffusion in metallic bodies or internal radiation in dielectrics.
But without following the explanation into the details in which it revels, it may be enough to say that the whole hypothesis is but an attempt to exclude the occult conception of action at a distance, and substitute a familiar phenomenon.
Birkeland (19), who has made a special study of magnetic disturbances in the Arctic, proceeding on the hypothesis that they arise from electric currents in the atmosphere, and who has thence attempted to deduce the position and intensity of these currents, asserts that whilst in the case of many storms the data were insufficient, when it was possible to fix the position of the mean line of flow of the hypothetical current relatively to an auroral arc, he invariably found the directions coincident or nearly so.
The height has also been calculated on the hypothesis that auroral light has its source where the atmospheric pressure is similar to that at which most brilliancy is observed when electric discharges pass in vacuum tubes.
By modifying the hypothesis as to the size and density, times appreciably longer or shorter than the above would be obtained.
The Achaeans, or Hellenes, as they were later termed, were on this hypothesis one of the fair-haired tribes of upper Europe known to the ancients as Keltoi (Celts), who from time to time have pressed down over the Alps into the southern lands, successively as Achaeans, Gauls, Goths and Franks, and after the conquest of the indigenous small dark race in no long time died out under climatic conditions fatal to their physique and morale.
To regard these letters as ciphers is a precarious hypothesis , for the simple reason that cryptography is not to be looked for in the very infancy of Arabic writing.
Their connection with Semitic and Egyptian, therefore, remains at present an obscure though probable hypothesis .
The memorandum of the adjutant-general above referred to was based on the hypothesis that Khartum could not hold out beyond the 15th of November, and that the expedition should reach Berber by the 20th of October.
Or again, the process of scientific induction is a threefold chain; the original hypothesis (the first unification of the fact) seems to melt away when confronted with opposite facts, and yet no scientific progress is possible unless the stimulus of the original unification is strong enough to clasp the discordant facts and establish a reunification.
The unanimous recognition on the part of all biblical scholars that the Old Testament cannot be taken as it stands as a trustworthy account of the history with which it deals, necessitates a hypothesis or, it may be, a series of hypotheses, which shall enable one to approach the more detailed study of its history and religion.
Material forces are, by hypothesis , capable of feeling; matter also must have been from the first endowed with consciousness.
In 1754 Euler communicated to the Berlin Academy a further memoir, in - which, starting from the hypothesis that light consists of vibrations excited in an elastic fluid by luminous bodies, and that the difference of colour of light is due to the greater or less frequency of these vibrations in a given time, he deduced his previous results.
The correctness cf this hypothesis has long been under suspicion, but it has generally been accepted as the best simple approximation to the actual distribution of the motions that could be made.
But, whilst recognizing the existence of local drifts and systems, and admitting the possibility of relative motion between the nearer and more distant, or other classes of stars, it is;only recently that astronomers have seriously doubted the correctness of the hypothesis of random distribution of stellar motions as at least a rough representation of the truth.
This hypothesis of two star-drifts does not imply that all the stars move in one or other of two directions.
The older one - which may be called the " one-drift " hypothesis , since according to it the stars appear to form a single drift moving away from the solar apex - requires that the apparent directions of motion should be so distributed that fewest stars are moving directly towards the solar apex, and most stars along the great circle away from the solar apex, the number decreasing symmetrically, for directions inclined on either side of this great circle, according to a law which can be calculated.
Until the hypothesis has been thoroughly tested by an examination of the line-of-sight velocities of stars from the same point of view, this physical interpretation must be received with some degree of caution; but there can be no doubt of the reality of the anomalies in the statistical distribution of proper motions of the stars, and of these it offers a simple and adequate explanation.
But the crowning absurdity is that, if all universals were hypothetical, Barbara in the first figure would become a purely hypothetical syllogism - a consequence which seems innocent enough until we remember that all universal affirmative conclusions in all sciences would with their premises dissolve into mere hypothesis .
But his account of the first is imperfect, because in ancient analysis the more general propositions, with which it concludes, are not mere consequences, but the real grounds of the given proposition; while his addition of the second reduces the nature of analysis to the utmost confusion, because hypothetical deduction is progressive from hypothesis to consequent facts whereas analysis is regressive from consequent facts to real ground.
It is noticeable that Wundt quotes Newton's discovery of the centripetal force of the planets to the sun as an instance of this supposed hypothetical, analytic, inductive method; as if Newton's analysis were a hypothesis of the centripetal force to the sun, a deduction of the given facts of planetary motion, and a verification of the hypothesis by the given facts, and as if such a process of hypothetical deduction could be identical with either analysis or induction.
Hence it is that Jevons, followed by Sigwart and Wundt, reduces it to deduction from a hypothesis in the form "Let every M be P, S is M,.
As we have seen, Jevons, Sigwart and Wundt all think that induction contains a belief in causation, in a cause, or ground, which is not present in the particular facts of experience, but is contributed by a hypothesis added as a major premise to the particulars in order to explain them by the cause or ground.
Not, however, that all induction is causal; but where it is not, there is still less reason for making it a deduction from hypothesis .
It is, then, a fair working hypothesis as to the structure of the Organon to place the Topics, which deal with dialectical reasoning, before the Analytics.
The conjunction was by hypothesis not given, and is a new result by no_ means to be reached, apart from direct perception save by use of at least two given conjunctions.
The positive procedure by hypothesis and verification is rejected by Bacon, who thinks of hypothesis as the will o' the wisp of science, and prefers the cumbrous machinery of negative reasoning.
The hypothesis of the collector, the man who keeps a rain-gauge, or the missionary among savages, is to be discounted from as a source of error.
In especial he showed clear understanding of the functions of hypothesis and verification in the investigations of the solitary worker, with his facts still in course of accumulation and needing to be lighted up by the scientific imagination.
Whether the tradition which makes Ararat the resting-place of Noah's Ark is of any historical value or not, there is at least poetical fitness in the hypothesis , inasmuch as this mountain is about equally distant from the Black Sea and the Caspian, from the Mediterranean and the Persian Gulf.
Later and more accurate experiments have confirmed the experimental value, and have shown that the limiting value of the specific heat should consequently be somewhat smaller than that given by Maxwell's hypothesis .
In all such systems, God is the terminus ad quem, a direct knowledge of whom is not claimed, but who is, as it were, the hypothesis adopted, with varying degrees of certainty in different thinkers, for the explanation of the facts before them.
Moreover, as this complication was a marked feature in certain epidemics of plague in India, the hypothesis has been framed by Hirsch that a special variety of plague, pestis indica, still found in India, is that which overran the world in the 14th century.
Further, to make out a case for dependence at all, one must assume the mistaken order (as it may be) in Gamaliel's speech as due to gross carelessness in the author of Acts - an hypothesis unlikely in itself.
Coulomb experimentally proved that the law of attraction and repulsion of simple electrified bodies was that the force between them varied inversely as the square of the distance and thus gave mathematical definiteness to the two-fluid hypothesis .
Berzelius early in the 19th century had advanced the hypothesis that chemical combination was due to electric attractions between the electric charges carried by chemical atoms. The notion, however, that electricity is atomic in structure was definitely put forward by Hermann von Helmholtz in a well-known Faraday lecture.
Varley had advanced tentatively the hypothesis that it consisted in an actual projection of electrified matter from the cathode, and Crookes was led by his researches in 1870, 1871 and 1872 to embrace and confirm this hypothesis in a modified form and announce the existence of a fourth state of matter, which he called radiant matter, demonstrating by many beautiful and convincing experiments that there was an actual projection of material substance of some kind possessing inertia from the surface of the cathode.
The final outcome of these investigations was the hypothesis that Thomson's corpuscles or particles composing the cathode discharge in a high vacuum tube must be looked upon as the ultimate constituent of what we call negative electricity; in other words, they are atoms of negative electricity, possessing, however, inertia, and these negative electrons are components at any rate of the chemical atom.
Thomson also developed this hypothesis in a profoundly interesting manner, and we may therefore summarize very briefly the views held on the nature of electricity and matter at the beginning of the 10th century by saying that the term electricity had come to be regarded, in part at least, as a collective name for electrons, which in turn must be considered as constituents of the chemical atom, furthermore as centres of certain lines of self-locked and permanent strain existing in the universal aether or electromagnetic medium.
Larmor and many others, the electronic hypothesis of matter and of electricity has been developed in great detail and may be said to represent the outcome of modern researches upon electrical phenomena.
But although the rigorous requirements of science could only be fulfilled by the employment of all these means, yet in their absence it was permissible to draw from the tables and the exclusion a hypothetical conclusion, the truth of which might be verified by the use of the other processes; such an hypothesis is called fantastically the First Vintage (Vindemiatio).
The true scientific procedure is by hypothesis followed up and tested by verification; the most powerful instrument is the deductive method, which Bacon can hardly be said to have recognized.
The power of framing hypothesis points to another want in the Baconian doctrine.
But he was certainly not ignorant of what may be called a deductive method, and of a kind of hypothesis .
Progress in scientific discovery is made mainly, if not solely, by the employment of hypothesis , and for that no code of rules can be laid down such as Bacon had devised.
Yet the framing of hypothesis is no mere random guesswork; it is left not to the imagination alone, but to the scientific imagination.
Not content with the barren assertion that the understanding makes nature, and that we can construct science only on the hypothesis that there is reason in the world, they proceeded to show how the thing was actually done.
Hume's casual allusion to "this famous atheist" and his "hideous hypothesis " is a fair specimen of the tone in which he is usually referred to; people talked about Spinoza, Lessing said, "as if he were a dead dog."
Lake San Martin lies in a crooked deeply cut passage through the Andes, and the divide between its southern extremity (Laguna Tar) and Lake Viedma, which discharges through the Santa Cruz river into the Atlantic, is so slight as to warrant the hypothesis that this was once a strait between the two oceans.
In the cuneiform letters from Tell el-Amarna in Egypt (1400 B.C.), we find among the princelings of Syria and Palestine names like Artamanya, Arzawiya, Shuwardata, a name terminating in -warzana, &c.; while the kings of Mitanni on the Euphrates are Artatama, Shutarna, Artashumara, and Dushratt anames too numerous and too genuinely Iranian to allow of the hypothesis of coincidence.
To him is also due the discovery of the power of rotatory polarization exhibited by quartz, and last of all, among his many contributions to the support of the undulatory hypothesis , comes the experimentum crucis which he proposed to carry out for comparing directly the velocity of light in air and in water or glass.
The hypothesis that a saying of Jesus is loosely added here to an Old Testament citation is very forced, and the inference is that by the time the author wrote, Luke's gospel was reckoned as This would be explicable if Luke could be assumed to have been the author, in whole or part, of the pastorals.
The fundamental doctrine of this work is that, on the hypothesis of free competition, exchange value is determined by the labour expended in production, - a proposition not new, nor, except with considerable limitation and explanation, true, and of little practical use, as "amount of labour" is a vague expression, and the thing intended is incapable of exact estimation.
The next step is to deduce this surface-tension from a hypothesis as to the molecular constitution of the liquid and of the bodies that surround it.
He proceeded to an investigation of the equilibrium of a fluid on the hypothesis of uniform density, and arrived at the conclusion that on this hypothesis none of the observed capillary phenomena would take place, and that, therefore, Laplace's theory, in which the density is supposed uniform, is not only insufficient but erroneous.
On the hypothesis of uniform density we shall find that this is true for films whose thickness exceeds The symbol x is defined as the energy of unit of mass of the substance.
In this assertion we think he was mathematically wrong, though in his own hypothesis that the density does actually vary, he was probably right.
This hypothesis was suggested by Laplace, and may conveniently be named after him.
It was also tacitly adopted by Young, in connexion with the still more special hypothesis which Young probably had in view, namely that the force in each case was constant within a limited range, the same in all cases, and vanished outside that range.
As an immediate consequence of this hypothesis we have from (28) K = Koo' 2, where Ko, To are the same for all bodies.
We are thus led to the important conclusion that according to this hypothesis Neumann's triangle is necessarily imaginary, that one of three fluids will always spread upon the interface of the other two.
So far the results of Laplace's hypothesis are in marked accordance with experiment; but if we follow it out further, discordances begin to manifestthemselves.
What is more, (52) shows that according to the hypothesis T12 is necessarily positive; 23 FIG.
This idiom could, of course, be explained on the hypothesis of an Aramaic original.
The hypothesis has won very wide acceptance, but several editors and critics (including Harnack, Zahn and Clemen) remain unconvinced.
If the hypothesis already outlined is set aside, it is open to the critic to regard large portions of the canonical Romans as having originally occupied a separate setting,5 or to ascribe the textual variations to the exigencies of church reading after the formation of the canon (which might explain the absence of Ev `Pt)t7j in i.
With regard to his birth, parentage, youth, and education everything depends upon this tradition, and it is not until he was according to one extreme hypothesis thirty-six, according to the other extreme twenty-four, that we have solid testimony respecting him.
The second book, which introduces the principal hero of the whole, Pantagruel, Gargantua's son, is, on any other hypothesis but that already suggested of its prior composition, very difficult to explain, but in itself it is intelligible enough.
They are always written in the author's highest style, a style perfectly eloquent and unaffected; they can only be interpreted (on the free-thinking hypothesis ) as allegorical with the greatest difficulty and obscurity, and it is pretty certain that no one reading the book without a thesis to prove would dream of taking them in a non-natural sense.
Possibly, however, many of the royal families may have contained an element of Scandinavian blood, a hypothesis which would well accord with the social conditions of the migration period, as illustrated, e.g., in Volsunga Saga and in Hervarar Saga ok Heib'reks Konungs.
A hypothesis favoured by Dr Frazer, that the victim is usually a divine man, a priest-king 4 Pliny, Nat.
More recently he expressed his dissatisfaction with the hypothesis of "sexual selection" by which Darwin sought to explain the conspicuous characters which are displayed during the courtship of animals.
Bellarmine did not proscribe the Copernican system, as has been maintained by Reusch (Der Process Galilei's and die Jesuiten, Bonn, 1879, p. 125); all he claimed was that it should be presented as an hypothesis until it should receive scientific demonstration.
In one form or another such a theory of human descent has in our time become part of an accepted framework of zoology, if not as a demonstrable truth, at any rate as a working hypothesis which has no effective rival.
As for the reasoning powers in animals, the accounts of monkeys learning by experience to break eggs carefully, and pick off bits of shell, so as not to lose the contents, or of the way in which rats or martens after a while can no longer be caught by the same kind of trap, with innumerable similar facts, show in the plainest way that the reason of animals goes so far as to form by new experience a new hypothesis of cause and effect which will henceforth guide their actions.
On the other hand it does not follow necessarily from a theory of evolution of species that mankind must have descended from a single stock, for the hypothesis of development admits of the argument, that several simian species may have culminated in several races of man.
Darwin and others having regarded Lord Morton's mare as affording very strong evidence in support of the infection hypothesis , it was considered some years ago desirable to repeat Lord Morton's experiment as accurately as possible.
In conclusion, it may be pointed out that it was only natural for breeders and physiologists in bygone days to account for some of their results by the "infection" hypothesis .
That this endeavour to work into the historical tradition of the life and teaching of Jesus - a hypothesis which had a distinctly foreign origin - led him into serious difficulties is a consideration that must be discussed elsewhere.
He was the first in England to verify Benjamin Franklin's hypothesis of the identity of lightning and electricity, and he made several important electrical discoveries.
The line of pressures as generally given for this dam with the reservoir full, on the hypothesis that the density of the masonry was a little over 2, is shown by long and short dots in fig.
Between ten and eleven years ago there was an hypothesis of mine registered in your books, wherein I hinted a cause of gravity towards the earth, sun and planets, with the dependence of the celestial motions thereon; in which the proportion of the decrease of gravity from the superficies of the planet (though for brevity's sake not there expressed) can be no other than reciprocally duplicate of the distance from the centre.
And I hope I shall not be urged to declare, in print, that I understood not the obvious mathematical condition of my own hypothesis .
Numerous attempts have been made to solve these problems, and to construct a theory of the origin of the Grail story, but so far the difficulty has been to find an hypothesis which would admit of the practically simultaneous existence of apparently contradictory features.
Legends of the part played by Joseph of Arimathea in the conversion of Britain are closely connected with Glastonbury, the monks of which foundation showed, in the 12th century, considerable literary activity, and it seems a by no means improbable hypothesis that the present form of the Grail legend may be due to a monk of Glastonbury elaborating ideas borrowed from Fecamp. This much is certain, that between the Saint-Sang of Fecamp, the Volto Santo of Lucca, and the Grail tradition, there exists a connecting link, the precise nature of which has yet to be determined.
The Buddhist theory, as is well known, is put together without the hypothesis of "soul" at all.
The hypothesis is not free from certain difficulties, one of which will be noticed later.
This hypothesis , however, requires us to suppose that Xerxes had returned from Sardis to Susa by the tenth month of the seventh year of his reign, which is barely credible.
We are prohibited by a general consideration of metamerism in the Arthropoda from adopting the hypothesis of intercalation of somites.
The second book proposes a hypothesis regarding the genesis of our ideas and closes after an elaborate endeavour to verify it.
The hypothesis is, that all human ideas, even the most complex and abstract and sublime, ultimately depend upon " experience."
The " verification " of this hypothesis , offered in the thirteenth and following chapters of the second book, goes to show in detail that even those ideas which are " most abstruse," how remote soever they may seem from original data of outward sense, or of inner consciousness, " are only such as the understanding frames to itself by repeating and joining together simple ideas that it had at first, either from perceiving objects of sense, or from reflection upon its own operations."
The hypothesis , that even our most profound and sublime speculations are all limited to data of the senses and of reflection, is crucially tested by the " modes " and " substances " and " relations " under which, in various degrees of complexity, we somehow find ourselves obliged to conceive those simple phenomena.
The comparative study of the development does not support the hypothesis that the Polyzoa (q.v.) are comparable with Phoronis.
Certainly without some such assumption the hypothesis of an exact correspondence between the series described as parallel becomes, as Professor Ward has shown, unmeaning.
Hedonistic psychology denied the libertarian hypothesis , but it denied also the absoluteness and intuitive character of moral obligation, and attached no validity to the ordinary interpretation of terms like "ought" and duty.
On the contrary, a belief that conduct necessarily results upon the presence of certain motives, and that upon the application of certain incentives, whether of pain or pleasure, upon the presence of certain stimuli whether in the shape of rewards or punishments, actions of a certain character will necessarily ensue, would seem to vindicate the rationality of ordinary penal legislation, if its aim be deterrent or reformatory, to a far greater extent than is possible upon the libertarian hypothesis .
While if the deterrent and reformatory theories alone provide a rational end for punishment to aim at then the libertarian hypothesis pushed to its extreme conclusion must make all punishments equally useless.
A reaction, in one form or another, against the tendency to dissolve ethics into psychology was inevitable; since mankind generally could not be so far absorbed by the interest of psychological hypothesis as to forget their need of establishing practical principles.
The fundamental hypothesis of the science assumes a system of bodies in motion, of which the sun and planets may be taken as examples, and of which each separate body is attracted toward all the others according to the law of Newton.
About seventy analogous objects, including that in the Sword of Orion, were found by him to give light of the same quality; and thus after seventy-three years, verification was brought to William Herschel's hypothesis of a " shining fluid " diffused through space, the possible raw material of stars.
The law of this motion was such that the phenomena could be represented by supposing the motion to be actually circular and uniform, the apparent variations being explained by the hypothesis that the earth was not situated in the centre of the orbit, but was displaced by an amount about equal to one-twentieth of the radius of the orbit.
Though it is quite obvious that the theory of a social contract (or compact, as it is also called) contains a considerable element of truth - that loose associations for mutual protection preceded any elaborate idea or structure of law, and that government cannot be based exclusively on force - yet it is open to the equally obvious objection that the very idea of contract belongs to a more advanced stage in human development than the hypothesis itself demands.
The positive exposition of atomism has much that is attractive, but the hypothesis of the calor vitalis (vital heat), a species of anima mundi (world-soul) which is introduced as physical explanation of physical phenomena, does not seem to throw much light on the special problems which it is invoked to solve.
The distinction is of greater importance than would appear when one realizes how obvious the facts really are, and in practice it happens frequently that speakers claim with success to disprove a proposition by disproving the fact alleged in support of it, or to establish a hypothesis by showing that facts agree with its consequences.
Still the roughest form of spiritual prayer has for its basis the hypothesis of beneficent beings, visible or invisible.
The senseless stories or myths about the gods are soon felt to be at variance with this hypothesis .
He calls his own child Dawn or Cloud, his own name is Sitting Bull or Running Wolf, and he is not tempted to explain his great-grandfather's name of Bright Sun or Lively Raccoon on the hypothesis that the ancestor really was a raccoon or the sun.
But, while the possibility of the diffusion of myths by borrowing and transmission must be allowed for, the hypothesis of the origin of myths in the savage state of the intellect supplies a ready explanation of their wide diffusion.
The hypothesis that the rites and the stories are savage inventions surviving into civilized religion seems better to meet the difficulty.
It is a plausible hypothesis that stocks which once claimed descent from animals, sans phrase, afterwards regarded the animals as avatars of Zeus.
But the hypothesis that Cronus is a late derivation from KpovtSr i s and Kpoviwv is by no means universally accepted.
The conclusion that P's narratives and laws in the Pentateuch are post-exilic was found by biblical scholars to be a necessary correction to the original hypothesis of Graf (1866) that P's narratives were to be retained (with J and E) at an early date.
Chudeau, summing up the evidence available in 1909, set forth the hypothesis that the existing upper Niger and the existing lower Niger were distinct streams. According to this theory the upper Niger, somewhat above where Timbuktu now stands, went north and north-west and emptied into the Juf, which in the beginning of the quaternary age was a salt-water lake, the remnant of an arm of the sea which in the tertiary age covered the northern Sudan and southern Sahara as far east as Bilma.
Airy extended Fresnel's hypothesis to directions inclined to the axis of uniaxal crystals by assuming that in any such direction the two waves, that can be propagated without alteration of their state of polarization, are oppositely elliptically polarized with their planes of maximum polarization parallel and perpendicular to the principal plane of the wave, these becoming practically plane polarized at a small inclination to the optic axis.
During a prolonged audience he had received from the pope assurances of private esteem and personal protection; and he trusted to his dialectical ingenuity to find the means of presenting his scientific convictions under the transparent veil of an hypothesis .
But he substituted the equally unnecessary hypothesis of a magnetic attraction, and failed to perceive that the phenomenon to be explained was, in relation to absolute space, not a movement but the absence of movement.
In accordance with this hypothesis , the curves representing the variations of thermoelectric power, dE/dt, with temperature 'OObservationsof' Pia.
In many cases the deviations do not appear to favour any simple hypothesis as to the mode of variation of s with temperature, but as a rule the indication is that s is nearly constant, or even diminishes with rise of temperature.
The general results of the work appeared to support Tait's hypothesis that the effect was proportional to the absolute temperature, but direct thermoelectric tests do not appear to have been made on the specimens employed, which would have afforded a valuable confirmation by the comparison of the values of d 2 E/dT 2, as in Jahn's experiments.
These measurements, though subject to some uncertainty on account of the great experimental difficulties, are a very valuable confirmation of the accuracy of Thomson's theory, because they show that the magnitude of the effect is of the required order, but they cannot be said to be strongly in support of Tait's hypothesis .
This would necessitate chemical action at the junction when a current passed through it, as in an electrolytic cell, whereas the action appears to be purely thermal, and leads to a consistent theory on that hypothesis .
On this hypothesis , if we confine our attention to one of the two metals, say p", in which the current is supposed to flow from hot to cold, we observe that p"dT expresses the quantity of heat converted into electrical energy per unit of electricity by an E.M.F.
This derivation has a somewhat fantastic air, and seems to have been framed to suit an hypothesis .
They argued their way back to Parkside with Dean playing the devil's advocate while Fred quoted a dozen mystery stories that bore out his hypothesis , a hypothesis that grew in detail with each passing mile.
This information contradicts the hypothesis .
The symptom of difficulty awakening is consistent with the phase delay hypothesis of SAD.
The connection we already have involves the Proposition of Neural Indeterminacy, probabilistic causation, and the Correlation Hypothesis .
Frighteningly enough, this is no longer hypothesis and wild conjecture.
Price response among to the hypothesis no reported continuous.
More to the point, he provided a counterexample for each of the examples that Tsai cited in support of her hypothesis .
Since t calc = 1.08 and t crit = 2.228, the null hypothesis is accepted.
Would offer association quot hypothesis percentage point decrease to medicaid and.
Advances in genetics and in mapping DNA, some say, show there is no need for the hypothesis of body-soul dualism.
The Topeka Capital-Journal recently editorialized that " creationism is as good a hypothesis as any for how the universe began.
This supports the hypothesis that PD is a disease with a heterogeneous etiology.
This may sound fanciful, but is merely a hypothesis that would explain some odd facts.
In this case, the correct decision is to reject the null hypothesis .
However it is not the subject matter of this book to attempt to prove or disprove any survival hypothesis .
For these experiments, the null hypothesis was rejected.
So he was reluctant to accept the chemiosmotic hypothesis in the first place.
Trying to fit this case into the extraterrestrial hypothesis presents a series of problems.
A rational model is suggested, where the most plausible hypothesis is selected first.
The trick of course is to find an alternative a priori hypothesis .
In 1986 the prion hypothesis was still regarded as highly controversial.
The Committee evaluated the hypothesis that organochlorine insecticides might increase the risk of breast cancer by virtue of their claimed oestrogenic effects.
These observations accord with the hypothesis that organisms are polyphasic liquid crystals.
In fact, there are areas of mathematics that have been developed by mathematicians on the assumption that the Riemann Hypothesis is true.
We are testing the hypothesis that all Maculinea and Microdon species employ chemical mimicry to a varying degree.
This hypothesis is supported by the fact that only organisms that are able to stimulate neutrophils are associated with renal scarring.
New techniques for the evaluation of tubal patency support the hypothesis that tubal ' plugs ' may be involved in proximal tubal blockage.
The prion hypothesis states that it is due to differences in the chemical or tertiary structure of the prion hypothesis states that it is due to differences in the chemical or tertiary structure of the prion protein.
Their initial hypothesis was that mesodermal progenitors are present in the marrow, but differ from hematopoietic progenitors.
Topics include discoveries of the transuranic elements, the actinide hypothesis , medical radioisotopes, the development of nuclear fission and extensive biographies.
I was testing the wrong hypothesis , the numbers were too small, and they were not randomized.
This hypothesis is consistent with the strongly recurved spits that provide the present day definition of the harbor mouth.
The hypothesis of linguistic relativity, for example, is well known.
The hypothesis for the reduced severity of blast attack is fairly clear for the disease-susceptible glutinous rice.
Quot hypothesis as in this article Florida self employed health insurance form of unused.
Certainly, most economic analysis is based on the self-interest hypothesis , which assumes that all people are exclusively motivated by their material self-interest.
The null hypothesis is that not one of the available UFO reports represents a genuine sighting of an extraterrestrial spacecraft.
So comrades these are the reasons for which I cannot lightly accept the hypothesis of a simple stratagem.
New techniques for the evaluation of tubal patency support the hypothesis that tubal patency support the hypothesis that tubal ' plugs ' may be involved in proximal tubal blockage.
Illogical skeptics will complain that any hypothesis can be induced in this framework, such as a giant purple unicorns or flying cats.
If this hypothesis is true, then unilateral neglect should be improved by increasing activation of the sustained attention system.
Thus studies should not be set up to confirm a hypothesis which is scientifically unsound.
It does have the ad- vantage of support of part of the ancient tradition, 19 something which the two-document hypothesis cannot claim.
Then, secondly, there arose the question whether the methods of exact science sufficed to explain the connexion of phenomena, or whether for the explanation of this the thinking mind was forced to resort to some hypothesis not immediately verifiable by observation, but dictated by higher aspirations and interests.
If we accept the hypothesis that each kind of atom has a specific and invariable weight, we can, with the aid of the above theory, make most important inferences concerning the proportions by weight in which substances combine to form compounds.
Their hypothesis explains so many facts that it is now considered to be as well established as the parts of the theory due to Dalton.'
It will presently appear that the original hypothesis of Fresnel, that the rigidity remains the same in both media, is the only one that can be reconciled with the facts; and we will therefore investigate upon this basis the nature of the secondary waves dispersed by small particles.
According to our hypothesis , the foreign matter may be supposed to load the aether, so as to increase its inertia without altering its resistance to distortion.
So long as the particles are small no such vanishing of light in oblique directions is observed, and we are thus led to the conclusion that the hypothesis of a finite AN and of vibrations in the plane of polarization cannot be reconciled with the facts.
During this anxious period he appears to have borne himself with characteristic dignity, such as is consistent with no other hypothesis than the consciousness of innocence.
Of his writings on social and political questions may be mentioned Die Erziehung des Weibes (1865); Ueber die nationals Entwicklung and Bedeutung der Naturwissenschaften (1865); Die Aufgaben der Naturwissenschaften in dem neuen nationalen Leben Deutschlands (1871); Die Freiheit der Wissenschaft im modernen Staat (1877), in which he opposed the idea of l - L eckel - that the principles of evolution should be taught in elementary schools - on the ground that they were not as yet proved, and that it was mischievous to teach a hypothesis which still remained in the speculative stage.
The progeny of these cats, more or less crossed with the indigenous species, thence gradually spread over Europe, to become mingled at some period, according to Dr Nehring's hypothesis , with an Asiatic stock.
Of Bacon's demand for observation and collection of facts he is an imitator; and he wishes (in a letter of 1632) that " some one would undertake to give a history of celestial phenomena after the method of Bacon, and describe the sky exactly as it appears at present, without introducing a single hypothesis ."
His fundamental hypothesis relegates to God all forces in their ultimate origin.
But these defects need not blind us to the fact that this hypothesis made the mathematical progress of Hooke, Borelli and Newton much more easy and certain.
These and other apologetic writings have so far failed to produce any adequate alternative hypothesis , and while they argue for the traditional theory, later revision not being excluded, the modern critical view accepts late dates for the literary sources in their present form, and explicitly recognizes the presence of much that is ancient.
His paper on the variation of the specific heat with temperature, which appeared in 1907, was the first extension of Planck's fundamental hypothesis , and its verification in essentials is one of the most convincing arguments in its favour.
In the one hypothesis , as in the other, Italy could count upon the moral support of Great Britain, but could not make of British friendship the keystone of a Continental policy.
The doctrine of Anaximenes, who unites the conceptions of a determinate and indeterminate original substance adopted by Thales and Anaximander in the hypothesis of a primordial and all-generating air, is a clear advance on these theories, inasmuch as it introduces the scientific idea of condensation and rarefaction as the great generating or transforming agencies.
It may be observed, too, that the hypothesis of a primitive compact mass (sphaerus), in which love (attraction) is supreme, has some curious points of similarity to, and contrast with, that notion of a primitive nebulous matter with which the modern doctrine of cosmic evolution usually sets out.
He further recognizes a progress in the production of vegetable and animal forms, though this part of his theory is essentially crude and unscientific. More important in relation to the modern problems of evolution is his thoroughly materialistic way of explaining the origin of sensation and knowledge by help of his peculiar hypothesis of effluvia and pores.
Among the Gnostics we meet with the hypothesis of emanation, as, for example, in the curious cosmic theory of Valentinus.
His theory of evolution is essentially pantheistic, and he does not employ his hypothesis of monads in order to work out a more mechanical conception.
In the third part of this work he inclines to a thoroughly natural hypothesis respecting the genesis of the physical world, and adds in the fourth part that the same kind of explanation might be applied to the nature and formation of plants and animals.
In his Dialogues concerning Natural Religion he puts forward tentatively, in the person of one of his interlocutors, the ancient hypothesis that since the world resembles an animal or vegetal organism rather than a machine, it might more easily be accounted for by a process of generation than by an act of creation.
Maupertuis, who, together with Voltaire, introduced the new idea of the universe as based on Newton's discoveries, sought to account for the origin of organic things by the hypothesis of sentient atoms. Buffon the naturalist speculated, not only on the structure and genesis of organic beings, but also on the course of formation of the earth and solar system, which he conceived after the analogy of the development of organic beings out of seed.
It was natural, therefore, that he rejected the idea of a spontaneous generation of organisms (which was just then being advocated by his friend Forster), not only as unsupported by experience but as an inadequate hypothesis .
The two parts of Bonnet's hypothesis , namely, the doctrine that all living things proceed from pre-existing germs, and that these contain, one enclosed within the other, the germs of all future living things, which is the hypothesis of " emboitement," and the doctrine that every germ contains in miniature all the organs of the adult, which is the hypothesis of evolution or development, in the primary senses of these words, must be carefully distinguished.
Growth, therefore, was, on this hypothesis , partly a process of simple evolution, and partly of what has been termed syngenesis.
The school of Cuvier was lamentably deficient in embryologists; and it was only in the course of the first thirty years of the igth century that Prevost and Dumas in France, and, later on, Ddllinger, Pander, von Bar, Rathke, and Remak in Germany, founded modern embryology; and, at the same time, proved the utter incompatibility of the hypothesis of evolution as formulated by Bonnet and Haller with easily demonstrable facts.
For those which are grouped under the second to the seventh of these classes, respectively, have a clear significance on the hypothesis of evolution, while they are unintelligible if that hypothesis be denied.
And those of the eighth group are not only uninintelligible without the assumption of evolution, but can be proved never to be discordant with that hypothesis , while, in some cases, they are exactly such as the hypothesis requires.
And as the hypothesis of " specific centres," thus formulated, was heterodox from the theological point of view, and unintelligible under its scientific aspect, it may be passed over without further notice, as a phase of transition from the creational to the evolutional hypothesis .
Polymerization of the aldehyde was also a feature of Baeyers hypothesis , so that this view does not very materially differ from those he advanced.
But if we accept either view we have still to examine the process of construction in detail, with a view to ascertaining the stages by which proteid is built up. Here unfortunately we find ourselves in the region of speculation and hypothesis rather than in that of fact.
The symmetrically placed hypothetical islands in the great continuousocean disappeared, and the oekumene acquired a new form by the representation of the Indian Ocean as a larger Mediterranean completely cut off by land from the Atlantic. The terra incognita uniting Africa and Farther Asia was an unfortunate hypothesis which helped to retard exploration.
The councils of Trent and of the Vatican mark the Two Truths hypothesis as heretical, when they affirm that there is a natural knowledge of God and natural certainty of immortality.
Probably most persons who have studied the subject would now be inclined to go this length; and there is some evidence, notably in connexion with the trances of an American medium, Mrs Piper,' which has convinced some good observers that the hypothesis of occasional communication from deceased persons must be seriously entertained.
The Meteoritic Hypothesis (1890) propounds a comprehensive scheme of cosmical evolution, which has evoked more dissent than approval, while the Sun's Place in Nature (1897) lays down the lines of a classification of the stars, depending upon their supposed temperature-relations.
On the hypothesis that such a form as Dinophilus (see Haplodrili) has preserved the characters of the primitive Chaetopod more nearly than a any existing Polychaet or Oligochaet, it is clear that the nephridia in the Oligochaeta have preserved the original features of those organs more nearly than most Polychaeta.
It is a comparatively simple thing to state the question to which we want an answer, but extremely difficult to define the exact nature of the evidence which will constitute a good answer; easy enough to say we must try hypothesis after hypothesis , and test each one by an appeal to the facts, but a man may easily spend his life in this sort of thing and still leave to his descendants nothing more than a legacy of rejected hypotheses.
In the course of the 19th century the idea that the different elements are constituted by different groupings or condensations of one primal matter - a speculation which, if proved to be well grounded, would imply the possibility of changing one element into another - found favour with more than one responsible chemist; but experimental research failed to yield any evidence that was generally regarded as offering any support to this hypothesis .
The evolution of the notion of elements is treated under Element; the molecular hypothesis of matter under Molecule; and the genesis of, and deductions from, the atomic theory of Dalton receive detailed analysis in the article Atom.
In this respect his hypothesis has much in common with the " law of mass-action " developed at a much later date b y the Swedish chemists Guldberg and Waage, and the American, Willard Gibbs (see Chemical Action).
It is not to be supposed that there are any actual bonds of union between the atoms; graphic formulae such as these merely express the hypothesis that certain of the atoms in a compound come directly within the sphere of attraction of certain other atoms, and only indirectly within the sphere of attraction of others, - an hypothesis to which chemists are led by observing that it is often possible to separate a group of elements from a compound, and to displace it by other elements or groups of elements.
The determination of an ocean surrounding the inhabited earth he declared to be based on a mere hypothesis and that it would be equally allowable to describe the Erythraea as a sea surrounded by land.
Hertz, have transformed applied mathematics by systematically basing their deductions upon the Law of the conservation of energy, and the hypothesis of an ether pervading space.
On this hypothesis Poisson investigated the forces due to bodies magnetized in any manner, and also originated the mathematical theory of magnetic induction.
The determination of the relative degree of perfection of organization attained by two animals 1 A great deal of superfluous hypothesis has lately been put forward in the name of " the principle of convergence of characters " by a certain school of palaeontologists.
The familiar illustration of Lamarck's hypothesis is that of the giraffe, whose long neck might, he suggested, have been acquired by the efforts of a primitively short-necked race of herbivores who stretched their necks to reach the foliage of trees in a land where grass was deficient, the effort producing a distinct elongation in the neck of each generation, which was then transmitted to the next.
It should be observed, however, that Darwin did not attribute an essential part to this Lamarckian hypothesis of the transmission of acquired characters, but expressly assigned to it an entirely subordinate importance.
He left a hypothesis to be worked out by others; this done, he would criticize with all the rigour of logic, and with a profound distrust of imagination, metaphor and the attitude known as the will-to-believe.
The latter force is, by Maxwell's hypothesis or by the dynamical theory of an aether pervaded by electrons, the same as that which strair s the aether, and may be called the aethereal force; it thereby produces an aethereal electric displacement, say (f,g,h), according to the relation (f,g,h) = (41 r c 2) - 1(P',Q', RI), in which c is a constant belonging to the aether, which turns out to be the velocity of light.
It was written to instruct and encourage the Christians of Asia Minor at a time of persecution, which on the hypothesis of genuineness, would be the Neronian, i.e.
As a natural philosopher he radically opposed Cuvier and was distinctly a precursor of uniformitarianism, advocating the hypothesis of slow changes and variations, both in living forms and in their environment.
The rarity of really continuous series has naturally led palaeontologists to support the hypothesis Of brusque transitions of structure.
Nevertheless, the most usual hypothesis is that, while the Nicomachean Ethics (E.N.) was written by Aristotle to Nicomachus, the Eudemian (E.E.) was written, not to, but by, Eudemus, and the Magna Moralia (M.M.) was written by some early disciple before the introduction of Stoic and Academic elements into the Peripatetic school.
Again, in his Grundproblem der Erkenntnisstheorie (1889) he uses without proof the hypothesis of psychological idealism, that we perceive psychical effects, to infer with merely hypothetical consistency the conclusion of noumenal metaphysical idealism that all we can thereby know is psychical causes, or something transcendent, beyond phenomena indeed, yet not beyond mind.
Further, from an early period in his Medicinische Psychologie (1852) he reinforced the transcendental idealism of Kant by a general hypothesis of " local signs," containing the subordinate hypotheses, that we cannot directly perceive extension either within ourselves or without; that spatial bodies outside could not cause in us spatial images either in sight or in touch; but that besides the obvious data of sense, e.g.
He borrows from Kant's "rationalism " the hypothesis of a spontaneous activity of the subject with the deduction that knowledge begins from sense, but arises from understanding; and he accepts from Kant's metaphysical idealism the consequence that everything we perceive, experience and know about physical nature, and the bodies of which it consists, is phenomena, and not bodily things in themselves.
But whereas Fechner and Paulsen hold that all physical processes are universally accompanied by psychical processes which are the real causes of psychical sensations, Riehl rejects this paradox of universal parallelism in order to fall into the equally paradoxical hypothesis that something or other, which is neither physical not psychical, causes both the physical phenomena of matter moving in space and the psychical phenomena of mind to arise in us as its common effects.
Spencer widens the empirical theory of the origin of knowledge by his brilliant hypothesis of inherited organized tendencies, which has influenced all later psychology and epistemology, and tends to a kind of compromise between Hume and Kant.
The substantially Pauline character of the epistle, for all practical purposes, is to be granted upon either hypothesis , for the author or the editor strove not unsuccessfully, upon the whole, to reproduce the Pauline spirit and traditions The older notion that the personal data in Titus, or in the rest of the pastorals, were invented to lend verisimilitude to the writing must be given up. They are too circumstantial and artless to be the work of a writer idealizing or creating a situation.
But investigations carried out in connexion with the "Challenger" expedition indicated that it was an artificial product, composed of a flocculent precipitate of gypsum thrown down from seawater by alcohol, and the hypothesis of its organic character was abandoned by most biologists, Huxley included.
Thereupon the Newtonian analysis which preceded this synthesis, became forgotten; until at last Mill in his Logic, neglecting the Principia, had the temerity to distort Newton's discovery, which was really a pure example of analytic deduction, into a mere hypothetical deduction; as if the author of the saying " Hypotheses non lingo" started from the hypothesis of a centripetal force to the sun, and thence deductively explained the facts of planetary motion, which reciprocally verified the hypothesis .
According to both, induction, instead of inferring from A, B, C magnets the conclusion " Therefore all magnets attract iron," infers from the hypothesis , " Let every magnet attract iron," to A, B, C magnets, whose given attraction verifies the hypothesis .
As early as 1860 Newcomb communicated an important memoir to the American Academy, 4 On the Secular Variations and Mutual Relation of the Orbits of the Asteroids, in which he discussed the two principal hypotheses to account for the origin of these bodies - one, that they are the shattered fragments of a single planet (Olbers' hypothesis ), the other, that they have been formed by the breaking up of a revolving ring of nebulous matter.
But whether the assumption of uniform density be physically correct is a very different question, and Poisson rendered good service to science in showing how to carry on the investigation on the hypothesis that the density very near the surface is different from that in the interior of the fluid.
We may, however, reject the sceptical hypothesis that Laura was a mere figment of Petrarch's fancy; and, if we accept her personal reality, the poems of her lover demonstrate that she was a married woman with whom he enjoyed a respectful and not very intimate friendship.
The fact that, in practice, the judgments even of connoisseurs are perpetually at variance, and that the so-called criteria of one place or period are more or less opposed to those of all others, is explained away by the hypothesis that individuals are differently gifted in respect of the capacity to appreciate.
This has proved to be a sound hypothesis and is now accepted as the basis upon which the Arthropod head must be interpreted (see Korschelt and Heider (3)).
He maintained with full conviction to the end of his life a grossly erroneous hypothesis of the tides, early adopted from Andrea Caesalpino; the " triplicate " appearance of Saturn always remained an enigma to him; and in regarding comets as atmospheric emanations he lagged far behind Tycho Brahe.
Poincare 's hypothesis remained most striking facet produce ions and radiographs by oudin.
Quot hypothesis as in this article florida self employed health insurance form of unused.
Certainly, from the standpoint of the special theory of relativity, the ether hypothesis appears at first to be an empty hypothesis .
What sort of evidence would have been required to substantiate the Muslim hypothesis of a perfect text?
The tentative hypothesis is that the prospect of taking an exam is more stressful than the exam itself.
I will present evidence in support of my hypothesis that the chemical constituents of underarm cosmetics may cause breast cancer.
Observations of phytoplankton blooms without the addition of iron supplements show underutilized resources of carbon dioxide and nitrates, supporting Martin 's Iron Hypothesis .
Otherwise we cannot demonstrate the truth or validity of the hypothesis and the theory.
What may help you manage the paradox is thinking about your startup idea as a hypothesis . You'll develop, test and implement the hypothesis , but be prepared to find a flaw in it.
When you accept that your startup is no more than a working hypothesis and that unexpected developments can change this hypothesis , you possess the agility necessary to change.
Larry's hypothesis was that the app would appeal to fans of all four professional sports, both as a fun activity and as an aid to betting.
An educated hypothesis would postulate that it is just one of the many factors that influence the way teens think and act.
In the fall of 2002, the New England Journal of Medicine published a major Danish study disproving the hypothesis of a connection between the MMR vaccine and autism.
The study is designed to test the hypothesis that differences in temperament related to differences in brain functioning put some children at an increased risk of certain psychiatric disorders later in life.
Research gathered by the council support this hypothesis including a 2008 study in the journal Medical Hypotheses and a 2010 article in Acta Paediatrica.
Next, children can design an experiment to test their statements or hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a statement that is either proven true or false.
An experiment is something that tests a hypothesis .
For this type of project, the child would have to start by asking a question and then working up a hypothesis .
The experiment is used as a tool to test the hypothesis , and then a conclusion is drawn at the end of the process.
A successful elementary science project is not necessarily one where students prove their hypothesis successfully.
In this hypothesis , the human brain strays from the regular transition into unconsciousness combined with physical paralysis into sleep and then into deep REM sleep.
Each research study begins with a hypothesis that focuses on a possible cause for autistic disorders.
According to the calorie hypothesis , when you consume any food, it provides your body with energy.
Put simply, the calorie hypothesis suggests that when you eat more calories than you burn, you gain weight.
The science and technology must be plausible, whether theoretically possible or based purely on a fictional hypothesis .
As Dalton said, "The doctrine of definite proportions appears mysterious unless we adopt the atomic hypothesis ."
No speculation of hypothesis has been propounded to account satisfactorily for the origin of the Australian flora.
As a step towards such hypothesis it has been noted that the Antarctic, the South African, and the Australian floras have many types in common.
It would be necessary to regard this structure as a secondary extension of the endoderm in the tentacle-web, on Allman's theory, or between the outgrowths of the hydrorhiza, on Mechnikov's hypothesis .
These theories, however, contain little that bears directly on the hypothesis of a natural evolution of things.
Baeyers hypothesis was entertained by botanists partly because it explained the gaseous interchanges accompanying photosynthesis.
The special Darwinian hypothesis - natural " selection " - may or may not be true; it was at least a fruitful suggestion.
Whether or not further study of the scripts of these writers confirms this hypothesis , it cannot fail to throw light on the nature of the intelligence involved.
His argument for the Being of God is based on the hypothesis that thought - not individual but universal - is the reality of all things, the existence of this Infinite Thought being demonstrated by the limitations of finite thought.
Scholars are now almost unanimously agreed that the internal features are best explained by the Graf-Wellhausen hypothesis .
The Graf-Wellhausen hypothesis , that the hierarchical law in its complete form in the Pentateuch stands at the close and not at the beginning of biblical history, that this mature Judaism was the fruit of the 5th century B.C. and not a divinely appointed institution at the exodus (nearly ten centuries previously), has won the recognition of almost all Old Testament scholars.
The Graf-Wellhausen hypothesis (§ 4) does not pretend to be complete in all its details and it is independent of its application to the historical criticism of the Old Testament.
No alternative hypothesis prevails, mere desultory criticism of the internal intricacies being quite inadequate.
But what was matter of immanent assumption with Erigena is in them an equating of two things which have been dealt with on the hypothesis that they are separate, and which, therefore, still retain that external relation to one another.
The depression westward of the Caspian and Aral basins, and the original connexion of these seas, have also come under the close investigation of Russian scientists, with the result that the theory of an ancient connexion between the Oxus and the Caspian has been displaced by the more recent hypothesis of an extension of the Caspian Sea eastwards into Trans-Caspian territory within the postPleiocene age.
One hypothesis supposes that the shores of the Mediterranean were originally inhabited by a homogeneous race neither Aryan nor Semitic.
This doctrine or hypothesis he usually speaks of as "the ideal system" or "the theory of ideas"; and to it he opposes his own analysis of the act of perception.
Chronology is against this hypothesis , since Louis and she lived on good terms together for two years after the Crusade.
Every hypothesis must be tested by an appeal to the facts of life, and modified or abandoned if it will not bear examination, unless we are convinced on genuine evidence that it may for a time be employed as a useful approximation, without prejudice to the later stages of the investigation we are conducting.
When the aim of the man of affairs and the hypothesis of the economist was unrestricted competition, and measures were being adopted to realize it, general theory such as the classical economists provided was perhaps a sufficiently trustworthy guide for practical statesmen and men of business.
These facts afford strong support to the hypothesis that the weight of the shell is the original cause of the torsion of the dorsal visceral mass in Gastropods.
But this hypothesis leaves the elevation of the visceral mass and the exogastric coiling of the shell in the ancestral form unexplained.
The actual sinfulness of all men Origen was able to explain by the theological hypothesis of pre-existence and the premundane fall of each individual soul.
The first hypothesis is not negatived by direct evidence, for we do not actually know the ontogeny of any of the Palaeozoic insects; it is, however, rendered highly improbable by the modern views as to the nature and origin of wings in insects, and by the fact that the Endopterygota include none of the lower existing forms of insects.
The hypothesis of "two voices" is now generally abandoned; there is no indication of a debate, of affirmations and responses.
In all the cases which have yet arisen in astronomy the extraneous forces are so small compared with the gravitation of the central body that the orbit is approximately an ellipse, and the preliminary computations, as well as all determinations in which a high degree of precision is not necessary, are made on the hypothesis of elliptic orbits.
Turning to the study of radioactivity, he noticed its association with the minerals which yield helium, and in support of the hypothesis that that gas is a disintegration-product of radium he proved in 1903 that it is continuously formed by the latter substance in quantities sufficiently great to be directly recognizable in the spectroscope.
Berzelius objected to the hypothesis that if two elements form only one compound, then the atoms combine one and one; and although he agreed theory.
A second inconsistency was presented when he was compelled by the researches of Dumas to admit Avogadro's hypothesis ; but here he would only accept it for the elementary gases, and denied it for other substances.
B aeyer has suggested that his hypothesis may also be applied to explain the instability of acetylene and its derivatives, and the still greater instability of the polyacetylene compounds.
Therefore, according to Kekule, the double linkages are in a state of continual oscillation, and if his dynamical notion of valency, or a similar hypothesis , be correct, then the difference between the 1.2 and 1.6 di-derivatives rests on the insufficiency of his formula, which represents the configuration during one set of oscillations only.
It remains, therefore, to consider Erlenmeyer's formula and those derived from the centric hypothesis .
The centric hypothesis has been applied to these rings by Bamberger and others; but as in the previous rings considered, the ordinary (3) (4) (5) representation with double and single linkages generally represents the syntheses, decompositions, &c.; exceptions, however, are known where it is necessary to assume an oscillation of the double linkage.
It remains for excavation to show whether this hypothesis is or is not correct.
He moreover accuses Eratosthenes, (whose determination of a degree he accepts without hesitation) with trusting too much to hypothesis in compiling his map instead of having recourse to latitudes and longitudes deduced by astronomical observations.
It encountered many difficulties, and until the definite proof of the stegomyia hypothesis of yellowfever inoculation made by the United States army surgeons in Cuba in 1900, the greatest problem seemed insoluble.
By taking fixed conditions for the hypothesis of such a proposition a definite department of mathematics is marked out.
In calculations the latter hypothesis is made because of its mathematical simplicity.
In these he seems suddenly to have cut adrift from every principle the truth of which he had himself so brilliantly demonstrated, and we find him discussing plans based on hypothesis , not knowledge, and on the importance of geographical points without reference to the enemy's field army.
This is a highly ingenious hypothesis to explain the discrepancies of the text, but is, after all, nothing but hypothesis .
Cardan in the 16th century, but this is a mere hypothesis without solid foundation.
The correctness of this hypothesis may, however, be doubted.
To explain these facts, Theodor Grotthus (1785-1822) in 1806 put forward an hypothesis which supposed that the opposite chemical constituents of an electrolyte interchanged partners all along the line between the electrodes when a current passed.
An alternative hypothesis is given by the idea of complex ions.
Hesse's canonical form shows at once that there cannot be more than two independent invariants; for if there were three we could, by elimination of the modulus of transformation, obtain two functions of the coefficients equal to functions of m, and thus, by elimination of m, obtain a relation between the coefficients, showing them not to be independent, which is contrary to the hypothesis .
Admitting Kant's hypothesis that by inner sense we are conscious of mental states only, he holds that this consciousness constitutes a knowledge of the "thing-in-itself" - which Kant denies.
Although Robert Hooke in 1668 and Ignace Pardies in 1672 had adopted a vibratory hypothesis of light, the conception was a mere floating possibility until Huygens provided it with a sure foundation.
Supposing Ewing's hypothesis to be correct, it is clear that if the magnetization of a piece of iron were reversed by a strong rotating field instead of by a field alternating through zero, the loss of energy by hysteresis should be little or nothing, for the molecules would rotate with the field and no unstable movements would be possible.'
Ferromagnetism was explained by Ampere on the hypothesis that the magnetization of the molecule is due to an electric current constantly circulating within it.
The theory now most in favour is merely a development of Ampere's hypothesis , and applies not only to ferromagnetics, but to paramagnetics as well.
Thomson (afterwards Lord Kelvin) in 1849 that while no physical evidence could be adduced in support of the hypothesis , certain discoveries, especially in electromagnetism, rendered it extremely improbable (Reprint, p. 344).
Ampere's experimental and theoretical investigation of the mutual action of electric currents, and of the equivalence of a closed circuit to a polar magnet, the latter suggesting his celebrated hypothesis that molecular currents were the cause of magnetism.
The balance of various considerations is against the latter hypothesis .
The discovery of the Coptic translation of these Acts in 1897, and its publication by C. Schmidt (Acta Pauli aus der Heidelberger koptischen Papyrushandschrift herausgegeben, Leipzig, 1894), have confirmed what had been previously only a hypothesis that the Acts of Thecla had formed a part of the larger Acts of Paul.
The famous "nebular hypothesis " of Laplace made its appearance in the Systeme du monde.
Laplace was, moreover, the first to offer a complete analysis of capillary action based upon a definite hypothesis - that of forces "sensible only at insensible distances"; and he made strenuous but unsuccessful efforts to explain the phenomena of light on an identical principle.
But, by hypothesis , n 1P1 is divisible by p!.
Lamarck had put forward the hypothesis that structural alterations acquired by (that is to say, superimposed upon) a parent in the course of its life are transmitted to the offspring, and that, as these structural alterations are acquired by an animal or plant in consequence of the direct action of the environment, the offspring inheriting them would as a consequence not unfrequently start with a greater fitness for those conditions than its parents started with.
Darwin himself, influenced by the consideration of certain classes of facts which seem to favour the Iamarckian hypothesis , was of the opinion that acquired characters are in some cases transmitted.
It is held 1 that the Darwinian doctrine of selection of fortuitous congenital variations is sufficient to account for all cases, that the Lamarckian hypothesis of transmission cf acquired characters is not supported by experimental evidence, and that the latter should therefore be dismissed.
Stas, the purpose of testing Prout's hypothesis , but he remained more disposed than the Belgian chemist to consider the possibility that it may have some degree of validity.
On this hypothesis we are able to explain the presence of certain poetical pieces both in the book of Chronicles and in the Psalter.
Until, however, further evidence is forthcoming in support of this syncytial theory of structure, it would be unwise to regard it as established sufficiently to constitute a serviceable working hypothesis ; hence, for the time being, we must accept the assertion that the cell represents the ultimate tissue-unit.
Cohnheim's hypothesis of " embryonic residues " provides that early in the development of the embryo some of the cells, or groups of cells, are separated from their organic continuity during the various foldings that take place in the actively growing embryo.
The " tissue-tension " hypothesis of Ribbert is a combination of the two foregoing.
Hansemann's "anaplasia " hypothesis seeks to find an explanation of the formation of new growths in the absence of the histological differentiation of the cell associated with a corresponding increase in its proliferative power and a suspension, or loss, of its functional activity.
Then we have Beard's " germ-cell " hypothesis , in which he holds that many of the germ-cells in the growing embryo fail to reach their proper position - the generative areas - and settle down and become quiescent in some somatic tissue of the embryo.
The parasitic hypothesis postulates the invasion of a parasite from without, thus making a new growth an infective process.
Some other observers, however, have not got such good results with a chloride-free diet, and Marishler, Scheel, Limbecx, Dreser and others, dispute Widal's hypothesis of a retention of chlorides as being the cause of oedema, in the case of renal dropsy at all events; they assert that the chlorides are held back in order to keep the osmotic pressure of the fluid, which they assume to have been effused, equal to that of the blood and tissues.
The local oedema seen in some nervous affections might be explained on the hypothesis of increased metabolic activity in these areas due to some local nervous stimulation.
His main avowed principle was to do without hypothesis , and study the actual diseases in an unbiassed manner.
The reform of practical medicine was effected by men who aimed at, and partly succeeded in, rejecting all hypothesis and returning to the unbiassed study of natural processes, as shown in health and disease.
Afterwards he modified his hypothesis , and referred the disturbances produced to the "nervous liquor," which he supposed to be a quantity of the "universal elastic matter" diffused through the universe, by which Newton explained the phenomena of light - i.e.
Haller's definition of irritability as a property of muscular tissue, and its distinction from sensibility as a property of nerves, struck at the root of the prevailing hypothesis respecting animal activity.
Before the end of the 19th century this discovery of the blood parasite of malaria was crowned by the hypothesis of Patrick Manson, proved by Ronald Ross, that malaria is propagated by a certain genus of gnat, which acts as an intermediate host of the parasite.
The balance of opinion has, however, always inclined to the hypothesis of an anagram on the name "Arouet le jeune," or "Arouet 1.
At a time when the Cartesian system of vortices universally prevailed, he found it necessary to investigate that hypothesis , and in the course of his investigations he showed that the velocity of any stratum of the vortex is an arithmetical mean between the velocities of the strata which enclose it; and from this it evidently follows that the velocity of a filament of water moving in a pipe is an arithmetical mean between the velocities of the filaments which surround it.
This calculus was first applied to the motion of water by d'Alembert, and enabled both him and Euler to represent the theory of fluids in formulae restricted by no particular hypothesis .
Messerschmidt, editor of the best collection of Hittite texts up to date, made a tabula rasa of all systems of decipherment, asserting that only one sign out of two hundred the bisected oval, determinative of divinity - had been interpreted with any certainty; and in view of this opinion, coupled with the steady refusal of historians to apply the results of any Hittite decipherment, and the obvious lack of satisfactory verification, without which the piling of hypothesis on hypothesis may only lead further from probability, there is no choice but to suspend judgment for some time longer as to the inscriptions and all deductions drawn from them.
On the other hand the enigmatical motion of the perihelion of Mercury has not yet found any plausible explanation except on the hypothesis that the gravitation of the sun diminishes at a rate slightly greater than that of the inverse square - the most simple modification being to suppose that instead of the exponent of the distance being exactly - 2, it is - 2.000 000 161 2.
These various forms are perfectly regular if the divine name was Yahweh, and, taken altogether, they cannot be explained on any other hypothesis .
This hypothesis is not intrinsically improbable - and in Aramaic, a language closely related to Hebrew, " to be " actually is hawa - but it should be noted that in adopting it we admit that, using the name Hebrew in the historical sense, Yahweh is not a Hebrew name.
This hypothesis he verified quantitatively by experiments, performed at the end of 1761.
The development of the Ectoprocta is intelligible on the hypothesis that the Entoprocta form the starting-point of the series.
The most plausible hypothesis is that men of this type are descendants of Korean colonists who, in prehistoric times, settled in the province of Izumo, on the west coast of Japan, having made their way thither from the Korean peninsula by the island of Oki, being carried by the cold current which flows along the eastern coast of Korea.
In The Development Hypothesis (1852) he objects strongly to the incredibility of the special creation of the myriad forms of life, without, however, suggesting how development has been effected.
This is at once connected with the nebular hypothesis , and subsequently deduced "from the ultimate law of the" persistence of force,"and finally supplemented by a counter-process of dissolution, all of which appears to Spencer only as" the addition of Von Baer's law to a number of ideas that were in harmony with it."It is clear, however, that Spencer's ideas as to the nature of evolution were already pretty definite when Darwin's Origin of Species (1859) revolutionized the subject of organic evolution by adding natural selection to the direct adaptation by use and disuse, and so suggesting an intelligible method of producing modifications in the forms of life.
He was also a great physicist and had arrived at the nebular hypothesis theory of the formation of the planets and the sun long before Kant and Laplace.
He wrote a lucid account of the phenomena of phosphorescence, and adduced a molecular magnetic theory which anticipated some of the chief features of the hypothesis of to-day.
This and other reasons led to his rejection of the dualistic hypothesis and the adoption, on the ground of probability, and much more from convenience, of the tenet that " acids are particular compounds of hydrogen, in which the latter can be replaced by metals "; while, on the constitution of salts, he held that " neutral salts are those compounds of the same class in which the hydrogen is replaced by its equivalent in metal.
Reuss, but since Graf was the first to introduce it into Germany, the theory, as developed by Julius Wellhausen, has been called the GrafWellhausen hypothesis .
But in proportion as an earlier date has become more probable for Homer, the hypothesis of Ionic origin has become less tenable, and the belief better founded (I) that the poems represent accurately a welldefined phase of culture in prehistoric Greece, and (2) that this " Homeric " or " Achaean " phase was closed by some such general catastrophe as is presumed by the legends.
The hypothesis that the state was steady, so that interchanges arising from convection and collisions of the molecules produced no aggregate result, enabled him to interpret the new constants involved in this law of distribution, in terms of the temperature and its spacial differential coefficients, and thence to express the components of the kinetic stress at each point in the medium in terms of these quantities.
As far as the order to which he carried the approximations - which, however, were based on a simplifying hypothesis that the molecules influenced each other through mutual repulsions inversely as the fifth power of their distance apart--the result was that the equations of motion of the gas, considered as subject to viscous and thermal stresses, could be satisfied by a state of equilibrium under a modified internal pressure equal in all directions.
Henderson prefers the hypothesis that Lennox had lost Crawford's notes; and that the identities are explained by the "remarkably good memories of Crawford and Mary, or by the more likely supposition that Crawford, before preparing his declaration for the conference" (at Westminster, December 1568) "refreshed his memory by the letter."
Such works are to be explained on what might be called the "fragmentary hypothesis ."
Others, like the Ascension of Isaiah, betray the handiwork of successive editors, and are accordingly to be explained on the "redaction hypothesis ."
Next it is noteworthy that in the second scheme here given Volter has abandoned his theory of a redaction hypothesis in favour of a sources hypothesis --a redactor.
As a result of the preceding inquiry we conclude that the student of the Apocalypse must make use of the following methods - the contemporaryhistorical, the literary-critical (fragmentary hypothesis ), the traditional-historical and the psychological.
But this Caligula hypothesis cannot be carried out unless by a vigorous use of the critical knife, in the course of which more than a third of the chapter is excised.
These inconsistencies are best explained by the hypothesis that our author was drawing upon a literary fixed tradition.
The validity of such an hypothesis was attacked as early as the 4th century by Dionysius of Alexandria in the fragment of his treatise irEpi 7ray yeAuA;v, in Eusebius, H.E.
This hypothesis , however, does not accord with the theory of the development of the earth from the state of a sphere of molt s en rock surrounded by an atmosphere of gaseous metals by which the first-formed clouds of aqueous vapour must have been absorbed.
From the hypothesis of an external world a series of contradictions are deduced, such as that the world is both finite and infinite, is movable and immovable, &c.; and finally, Aristotle and various other philosophers are quoted, to show that the external matter they dealt with, as mere potentiality, is just nothing at all.
In like manner, after the French mathematicians had attempted, with more or less ingenuity, to construct a theory of elastic solids from the hypothesis that they consist of atoms in equilibrium under the action of their mutual forces, Stokes and others showed that all the results of this hypothesis , so far at least as they agreed with facts, might be deduced from the postulate that elastic bodies exist, and from the hypothesis that the smallest portions into which we can divide them are sensibly homogeneous.
This hypothesis is introduced for the sake of simplicity, but is known to be unjustifiable in fact.
It carries the war into the camp of the enemy by seeking to demonstrate that the completely determined action which is set over against freedom as the basis of explanation in the material world is merely a hypothesis which, while it serves sufficiently well the limited purpose for which it is devised, is incapable of verification in the ultimate constituents of physical nature.
Thus in 1864 the spectroscope yielded him evidence that planetary and irregular nebulae consist of luminous gas - a conclusion tending to support the nebular hypothesis of the origin of stars and planets by condensation from glowing masses of fluid material.
That these purely mechanical arrangements have any psychic, occult or predictive meaning is a fantastic imagination, which seems to have a peculiar attraction for certain types of mind, and as there can be no fundamental hypothesis of correlation, its discussion does not lie within the province of reason.
When they are proved to do so, Tisserand's hypothesis will hold the field.
Eichhorn in favour of the "borrowing hypothesis " of the origin of the synoptical gospels, maintaining the priority of Matthew, the present Greek text having been the original.
The facts of the problem would all appear covered by the hypothesis that John the presbyter, the eleven being all dead, wrote the book of Revelation (its more ancient Christian portions) say in 69, and died at Ephesus say in loo; that the author of the Gospel wrote the first draft, here, say in 97; that this book, expanded by him, first circulated within a select Ephesian Christian circle; and that the Ephesian church officials added to it the appendix and published it in 110 -120.
Gauss, that the definite results attainable by the hypothesis of mutual atomic attractions really reposed on much wider and less special principles - those, namely, connected with the modern doctrine of energy.
The wider view, according to which the hypothesis of direct transmission of physical influences expresses only part of the facts, is that all space is filled with physical activity, and that while an influence is passing across from a body, A, to another body, B, there is some dynamical process in action in the intervening region, though it appears to the senses to be mere empty space.
This statement constitutes the famous hypothesis of Fresnel, which thus ensures that all phenomena of ray-path and refraction, and all those depending on phase, shall be unaffected by uniform convection of the material medium, in accordance with the results of experiment.
In this place it must suffice to indicate the gist of the more recent developments of the electro-optical theory, which involve the dynamical verification of Fresnel's hypothesis regarding optical convection and the other relations above described.
It is specially directed to the question of hypothesis , and holds that a hypothesis is justifiable only on the ground that it provides an explanation.
Giesbrecht and Hansen have shown that the mouth-organs consist of mandibles, first and second maxillae and maxillipeds; and Claus himself relinquished his long-maintained hypothesis that the last two pairs were the separated exopods and endopods of a single pair of appendages.
Even this verbal flaw would be obviated if Giesbrecht could prove his tentative hypothesis , that the Gymnoplea may have lost a pre-genital segment of the abdomen, and the Podoplea may have lost the last segment of the thorax.
The above sketch of the growth and general character of the Pauline Epistles is based upon the hypothesis that all thirteen are genuine.
On our hypothesis the Logia would have been a sort of Christian manual used with a similar object.
The phenomena which are sometimes supposed to require the hypothesis of an Ur-Marcus are more simply and satisfactorily explained as incidents in the transmission of the Marcan text.
The present writer is inclined to think the latter hypothesis not proven.
The phenomenon is perfectly intelligible without any such hypothesis .
It is difficult to explain this phrasing in any other hypothesis than that Layamon pictured to himself Arthur's hall as open on one side, and that, on a great feast-day, owing to the number of guests, the table extended beyond the covering afforded by the roof.
And we find accordingly in his great work a combination of inductive inquiry with a priori speculation founded on the "Nature" hypothesis .
It was Alcide Dessalines d'Orbigny (1802-1857) who pushed to an extreme Cuvier's ideas of the fixity of species and of successive extinctions, and finally developed the wild hypothesis of twenty-seven distinct creations.
This was nothing less than the foundation of a new astronomy, in which physical cause should replace arbitrary hypothesis .
This easily passes into the further and still more sceptical hypothesis that the works, as we have them, under Aristotle's name, are rather the works of the Peripatetic school, from Aristotle, Theophrastus and Eudemus downwards.
To save his hypothesis of late composition, Zeller resorts to the vagueness of the word " now " (vuv).
Aristotle had imputed to all living beings a soul, though to plants only in the sense of a vegetative, not a sensitive, activity, and in Moleschott's time many scientific men still accepted some sort of vital principle, not exactly soul, yet over and above bodily forces in organisms. Moleschott, like Lotze, not only resisted the whole hypothesis of a vital principle, but also, on the basis of Lavoisier's discovery that respiration is combustion, argued that the heat so produced is the only force developed in the organism, and that matter therefore rules man.
Thus in presence of the problem which is the crux of materialism, the origin of consciousness, he first propounds a gratuitous hypothesis that everything has mind, and then gives up the origin of conscious mind after all.
He supposes that this evolution does not remain cosmic, but becomes organic. In accordance with Lamarck's hypothesis , he supposes an evolution of organisms by hereditary adaptation to the environment (which he considers necessary to natural selection), and even the possibility of an evolution of life, which, according to him, is the continuous adjustment of internal to external relations.
By changing the meaning of "noumenon " from the thing apprehended (voouµevov) to the thought (vOnya), and in the hypothesis of a common consciousness, he started the view that a thing is not yours or my thought, but a common thought of all mankind, and led to the wider view of Schelling and Hegel that the world is an absolute thought of infinite mind.
The noumenal idealists of Germany assumed, like all psychological idealists, the unproved hypothesis that there is no sense of body, but there is a sense of sensations; and they usually accepted Kant's point, that to get from such sensations to knowledge there is a synthesis contributing mental elements beyond the mental data of sense.
On Schelling's idealistic pantheism, or the hypothesis that there is nothing but one absolute reason identifying the opposites of subjectivity and objectivity, Hegel based his panlogism.
Nevertheless he was too much a child of his age to keep things known steadily before him; having asked the metaphysical question he proceeded to find a psychological answer in a theory of sensation, which asserted the mere hypothesis that the being which we ascribe to things on the evidence of sensation consists in their being felt.
He really accepted, like Kant, the hypothesis of a sense of sensations which led to the Kantian conclusion that the Nature we know in time and space is mere sensible appearances in us.
This hypothesis of an acquired perception of a space mentally constructed by " local signs " supplied Lotze and many succeeding idealists, including Wundt, with a new argument for metaphysical idealism.
Secondly, he accepted the Leibnitzian hypothesis of immaterial elements without accepting their self-action.
Herbart and Lotze, both deeply affected by the Leibnitzian hypothesis of indivisible monads, supposed that man's soul is seated at a central point in the brain; and Lotze supposed that this supposition is necessary to explain the unity of consciousness.
At the very outset he started with his previous metaphysical hypothesis of parallelistic identity without interaction.
But by the hypothesis of the inclusion of spirit in spirit, he was further able to hold that what is unconscious in one spirit is conscious in a higher spirit, while everything whatever is in the consciousness of the highest spirit of God, who is the whole of reality of which the spirits are parts, while the so-called physical world is merely outer appearance of one spirit to another.
But his substitute was his own hypothesis of panpsychism, from which he deduced a "cosmorganic " evolution from a " cosmorganic " or original condition of the world as a living organism into the inorganic, by the principle of tendency to stability.
Shall we resign our traditional belief that the greater part of the world is mere body, but that its general adaptability to conscious organisms proves its creation and government by God, and take to the new hypothesis , which, by a transfer of design from God to Nature, supposes that everything physical is alive, and conducts its life by psychical impulses of its own?
This influence extended from Germany to Denmark, where it was embraced by Hoff ding, and to England, where it was accepted by Romanes, and in a more qualified manner as " a working hypothesis " by Stout.
He admits, indeed, Kant's hypothesis that by inner sense we are conscious only of mental states, but he contends that this very consciousness is a knowledge of a thing in itself.
Riehl, who in Der philosophische Kriti .cis- mus (1876, &c.) proposes the non-Kantian hypothesis that, though things in themselves are unknowable through reason alone, they are knowable by empirical intuition, and therefore also by empirical thought starting from intuition.
But, on the hypothesis that knowledge contains no inferences beyond experience, it follows that all the objects of knowledge, being objects of experience, are, or have been, or can be, present to an experiencing subject.
Immanent Philosophy is the hypothesis that the world is not transcendent, but immanent in consciousness.
At the same time Schuppe's hypothesis of one common consciousness uniting the given by a priori categories could hardly be accepted by Avenarius as pure experience, or as a natural view of the world.
Lastly, though the personal idealists are right in rejecting the hypothesis of one mind, they are too hasty in supposing that the hypothesis is useless for idealistic purposes.
Two psychological errors, among many others, constantly meet us in the history of idealism - the arbitrary hypothesis of a sense of sensations, or of ideas, and the intolerable neglect of logical inference.
It is spoilt by Locke's hypothesis that we do not perceive things but qualities implying things.
The three evidences, which are fatal to intuitive realism, do not prove hypothetical realism, or the hypothesis that we perceive something mental, but infer something bodily.
The observations of Moller, &c., on the germination cannot be assumed to negative the sexual hypothesis for the sexual cells of Ulothrix and Ectocarpus, for example From Strasburger's Lehrbuch der Botanik, by permission of Gustav Fischer.
Again, on the hypothesis that Christianity is true, the statistics at a particular period are no test of success at all.
Probably the latter hypothesis is the one more generally accepted now.
Nash, "he carried a sweeping hypothesis into the examination of the New Testament."
This gross misrepresentation has made hypothesis a kind of logical fashion.
Browse other sentences examples
The word usage examples above have been gathered from various sources to reflect current and historical usage. They do not represent the opinions of YourDictionary.com.
Related Articles
A hypothesis is a stepping stone to proving a theory. There are numerous types of hypotheses that can be employed when seeking to prove a theory. Additionally, there are many hypothesis examples that can help you form your own hypothesis.
The primary difference between a hypothesis and a theory is the point at which they are formed in the scientific process. A hypothesis is made before an experiment while a theory is formed after collecting a lot of scientific evidence. Explore how these terms differ from each other and similar science terms.
Words near hypothesis in the Dictionary
- hypothenusal
- hypothenuse
- hypothermal
- hypothermia
- hypothermic
- hypothesise
- hypothesised
- hypothesises
- hypothesising
- hypothesize
HYPOTHESIS in a Sentence Examples: 21 Ways to Use Hypothesis
Have you ever wondered what a “hypothesis” is and how it fits into the scientific method? A hypothesis is a proposed explanation or educated guess that can be tested through research and experimentation to determine its validity.
Table of Contents
7 Examples Of Hypothesis Used In a Sentence For Kids
14 sentences with hypothesis examples, how to use hypothesis in sentences.
Hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction that can be tested through observation or experimentation. When incorporating this term into a sentence, it is important to clearly identify it so readers can understand its significance.
Here are some tips on how to use hypothesis effectively in a sentence:
Make sure to refer back to your hypothesis when discussing the results of your experiment. For example, “The data supported our initial hypothesis that exercise leads to improved cardiovascular health.”
In conclusion, sentences with the keyword “hypothesis” often express a proposed explanation or prediction that can be tested through research or observation. These sentences play a crucial role in scientific inquiry by guiding investigations and exploring relationships between variables. For example, “The researchers formulated a hypothesis to predict the effect of sunlight on plant growth” demonstrates how hypotheses are used to frame a study’s objectives and outcomes.
Related Posts
In front or infront: which is the correct spelling, targeted vs. targetted: correct spelling explained in english (us) usage, as per request or as per requested: understanding the correct usage.
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Citation Generator
Writing Guides
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Human Editing Service
- Essay Hook Generator
Writing Guides / How to Write a Hypothesis w/ Strong Examples
How to Write a Hypothesis w/ Strong Examples

A hypothesis is a guess about what’s going to happen. In research, the hypothesis is what you the researcher expects the outcome of an experiment, a study, a test, or a program to be. It is a belief based on the evidence you have before you, the reasoning of your mind, and what prior experience tells you. The hypothesis is not 100% guaranteed—that’s why there are different kinds of hypotheses. In this article, we’ll explain what those are when they should be used. So let’s dive in!
What is a Hypothesis / Definition
A hypothesis is like a bet: you size things up and tell your mates exactly what you think is going to happen with respect to X, Y, Z. It can also be like an explanation for a phenomenon, or a logical prediction of a possible causal correlation among multiple factors. In science—or, really, in any field, a hypothesis is used as a basis for further investigation. For example, many qualitative or exploratory studies are conducted just so that the researcher in the end can formulate a hypothesis after all the data is collected an analyzed.
In short, it is an educated guess, based on existing knowledge or observation. It is a way of proposing a possible explanation for a relationship between variables.
One thing to remember is this: the key characteristic of a hypothesis is that it must be testable and potentially falsifiable. This means that it should be possible to design an experiment or observation that could potentially prove the hypothesis wrong. That is a very important point to keep in mind.
For that reason, hypotheses are usually only formulated after conducting a preliminary review of existing literature, observations, or after obtaining a general understanding of the subject area. They are not random guesses. They are grounded in some form of evidence or understanding of the phenomena being studied. The formulation of a hypothesis is a big step in the scientific method, as it defines the focus and direction of the research. A lot of time is often spent simply on developing a good hypothesis.
Why? A well-constructed hypothesis not only proposes an explanation for an observation but also often predicts measurable and testable outcomes. It is not merely a question, but rather a statement that includes a clear explanation or prediction. For example, rather than asking “Does temperature affect the growth of bacteria?”, a hypothesis would be something like this: “If the temperature increases, then the growth rate of bacteria will increase.” It is clear, measurable, testable, and potentially falsifiable.
In the scientific community, a hypothesis is respected when it has the potential to advance knowledge, regardless of whether testing proves it to be true or false. The process of testing, refining, or nullifying hypotheses through experimentation and observation is part of what research is all about.

Different types of Hypotheses
Hypotheses can be categorized into several types. Each type has a unique purpose in scientific research. Understanding these types is helpful for formulating a hypothesis that is appropriate to your specific research question. The main types of hypotheses include the following:
- Simple Hypothesis : This formulates a relationship between two variables, one independent and one dependent. It is straightforward and concise, making it easy to test. It is most often used in basic scientific experiments where the aim is to investigate the relationship between two variables, such as in laboratory experiments or controlled field studies.
- Complex Hypothesis : Unlike the simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis involves multiple independent and dependent variables. It is used in studies that are looking at several factors simultaneously, where there is an interplay of multiple variables. These are common in fields like social sciences, behavioral studies, and large-scale environmental research.
- Directional Hypothesis : This type predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It specifies the direction of the expected relationship. It tends to be used studies where prior research or theory has already suggested a specific direction of influence or effect, such as in clinical trials or in studies testing theoretical models.
- Non-directional Hypothesis : In contrast to the directional hypothesis, a non-directional hypothesis does not specify the direction of the relationship. It simply suggests that there is a relationship between variables without stating whether it is positive or negative. It is often used in exploratory research where the direction of the relationship is not known, such as in early-stage psychological research or when studying new phenomena.
- Null Hypothesis : The null hypothesis states that there is no relationship between the variables being studied. It is a default position that assumes no effect until evidence suggests otherwise. It is also a fundamental aspect of virtually all quantitative research, serving as the hypothesis that there is no effect or no difference, against which the alternative hypothesis is tested.
- Associative and Causal Hypotheses : Associative hypotheses propose a relationship between variables where changes in one variable correspond with changes in another. They are common in observational studies, such as epidemiological research or surveys, where the goal is to identify correlations between variables. Causal hypotheses go a step further by suggesting that one variable causes the change in the other. They are used in experimental research designed to determine cause-and-effect relationships, such as randomized controlled trials in medical research or controlled experiments in psychology.
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
How to Write a Good Hypothesis
Writing a good hypothesis is definitely a good skill to have in scientific research. But it is also one that you can definitely learn with some practice if you don’t already have it. Just keep in mind that the hypothesis is what sets the stage for the entire investigation. It guides the methods and analysis. Everything you do in research stems from your research question and hypothesis.
Here are four essential steps to follow when crafting a hypothesis:
- Start with a Research Question
Every hypothesis begins with a clear, focused research question. This question should arise from a review of existing literature, some observations you have made in the field, or an information gap that is apparent in current knowledge. The question should be specific and researchable. For example, instead of a broad question like “What affects plant growth?”, a more specific question would be “How does the amount of water affect the growth of sunflowers?” This is a specific question, and sets up a stage for a perfect hypothesis.
How did you develop the question? Easy. You simply took a broad view first, and then began looking more closely. You looked into the subject matter. And, as with anything, the more you look into it, the more likely you are to have questions. So, the most important step here is to get a sense of your subject. The more you learn about it, the more likely you will be to have a good research question. Ask yourself: what about this subject would I like to know more about? It helps if you have a genuine interest in the topic! Say, for example, you want to know more about cryptocurrency security or scalability: wouldn’t you start asking questions about how to achieve either? And wouldn’t you need to know a bit about the topic before you can ask the right question? Of course! Apply that same logic to whatever subject you are researching and your research question will appear rather quickly.
- Do Preliminary Research
Before formulating your hypothesis, you of course should conduct preliminary research. This involves reviewing existing literature, understanding the current state of knowledge in the field, doing some critical thinking on the subject, and considering any existing theories and findings that might be relevant. This preliminary research helps in developing an educated guess. If you do your background research well, your hypothesis will be grounded in existing knowledge.
This is basically the step that comes after you ask your research question but before you make a prediction about the subject matter. Just like if you went to a racetrack and wanted to place a bet on a horse, you would research the horses, the owners, the teams, and make an educated guess about which one is most likely to win, doing preliminary research is the same: you want to become very familiar with the topic—know it inside and out. Then you will have everything you need to formulate your hypothesis.
- Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on your research question and preliminary research, now you can create your hypothesis. A good hypothesis should be clear, concise, and testable. It typically takes a statement form, predicting a potential outcome or relationship between variables. Make sure that your hypothesis is focused and answers your research question. For example, a hypothesis for the research question stated above might be: “If sunflower plants are watered with varying amounts of water, then those watered more frequently will grow taller due to better hydration.”
Keep in mind that when you reach the stage of formulating your hypothesis, you are essentially ready to make a statement that can be tested through research or experimentation. Your hypothesis should be as precise as possible. Don’t ever use ambiguous language in your hypothesis. Also, you should be very specific about the variables involved and the expected relationship between them (if applicable). For example, let’s look at the hypothesis we generated above: “If sunflower plants are watered with varying amounts of water, then those watered more frequently will grow taller due to better hydration.” We have clearly identified the variables (frequency of watering and plant growth height) and the expected outcome.
But what else should your hypothesis do? Well, when we say it should address your research question, we mean it should be a logical extension of the question and your preliminary research. If your research question is about the effect of watering frequency on sunflower growth, your hypothesis should specifically predict how these two variables are related. It should not get into the types of soil, sunshine, temperature, or other variables unless these were brought up specifically in your research question.
Above all, you want your hypothesis to make a prediction. This means stating an expected outcome based on your understanding of the subject. The prediction is what will be tested through experiments or observations.
- Ensure Testability and Falsifiability
An important aspect of a good hypothesis is that it must be testable and potentially falsifiable. This means you should be able to conduct experiments or make observations that can support or refute the hypothesis. Avoid vague or broad statements that cannot be empirically tested. Also, make sure that your hypothesis is potentially falsifiable; i.e., there should exist the possibility that it can be proven wrong. For example, a hypothesis like “Sunflower plants need water to grow” is not falsifiable, as it is already a well-established fact. But a hypothesis regarding frequency or amount of watering does have the potential to be nullified.
Therefore, keep that in mind during this step: for a hypothesis to be testable, there must be a way to conduct an experiment or make observations that can confirm or disprove it. This means you should be able to measure or observe the variables involved. In the sunflower example, you can measure plant growth and control the frequency of watering very easily. This is precisely what makes the hypothesis testable.
Another important point is falsifiability, as this is what separates scientific hypotheses from non-scientific ones. If it doesn’t have the potential to be proven wrong, it’s not a hypothesis. Being falsifiable doesn’t mean a hypothesis is false. It means that if the hypothesis is false, there is a way to demonstrate this. The potential for falsification is what allows researchers to make scientific progress no matter the problem or field.
Also, don’t be vague. Your hypothesis needs to be specific: hypotheses that are too vague or broad are not useful in research, as there is no way to test them. For example, saying “Water affects plant growth” is too vague. How does water affect growth? Is it the amount, frequency, or type of water? Such a hypothesis needs to be more specific to be testable. See what we mean?
Remember: A hypothesis does not need to be correct. It just needs to be testable. It is a starting point for investigation. The value of a hypothesis lies in its ability to be tested. The results of that test are what can potentially contribute to the existing body of scientific knowledge, regardless of whether the hypothesis is supported or refuted by the resulting data.

Hypothesis Examples
Simple hypothesis examples.
- Increasing the amount of natural light in a classroom will improve students’ test scores.
- Drinking at least eight glasses of water a day reduces the frequency of headaches in adults.
- Plant growth is faster when the plant is exposed to music for at least one hour per day.
Complex Hypothesis Examples
- Students’ academic performance is influenced by their study habits, family income, and the educational level of their parents.
- Employee productivity is affected by workplace environment, job satisfaction, and the level of personal stress the worker encounters both on the job and at home.
- The effectiveness of a weight loss program is dependent on the participant’s age, gender, and adherence to an appropriate diet plan.
Directional Hypothesis Examples
- Exposure to high levels of air pollution during pregnancy will increase the risk of asthma in children.
- A diet high in antioxidants will decrease the risk of heart disease in middle-aged adults.
- Regular physical exercise leads to a significant decrease in the symptoms of depression in adults.
Non-directional Hypothesis Examples
- There is a relationship between the amount of sleep a person gets and their level of stress.
- A change in classroom environment has an effect on student concentration.
- The introduction of ergonomics in the workplace environment impacts employee productivity.
Null Hypothesis Examples
- There is no significant difference in test scores between students who study in groups and those who study alone.
- Dietary changes have no effect on the improvement of symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- The new marketing strategy does not affect the sales numbers of the product.
Associative Hypothesis Examples
- There is an association between the number of hours spent on social media and the level of anxiety in teenagers.
- Daily consumption of green tea is associated with weight loss in adults.
- The frequency of public transport use correlates with the level of urban air pollution.
Causal Hypotheses Examples
- Implementing a school-based exercise program causes a reduction in obesity rates among children.
- High levels of job stress cause an increase in blood pressure.
- Smoking causes an increase in the risk of developing lung cancer.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively formulating a solid hypothesis is what scientific research and inquiry is all about—regardless of the type of work you’re doing. It may be a simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, associative, or causal hypothesis—no matter: each type has its own specific purpose and guides the direction of a study in a different way. A simple hypothesis explores the relationship between two variables, while a complex hypothesis involves multiple variables. Directional hypotheses specify the expected direction of a relationship, whereas non-directional hypotheses do not. The null hypothesis, a fundamental aspect of statistical testing, posits no effect or relationship, serving as a baseline for analysis. Associative hypotheses explore correlations between variables, and causal hypotheses aim to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
The ability to craft a clear, concise, and testable hypothesis is important for any researcher. It is what shapes the course of the investigation. It is also the backbone of the scientific method itself. A well-formulated hypothesis can lead to groundbreaking research or make significant contributions to knowledge in different fields.
As we have shown you with our examples, the hypothesis is more than a mere guess; it is an educated, testable prediction that guides you through the process of scientific discovery. When you master the art of hypothesis formulation, you can set off on your investigation with a clear roadmap and a clear sense of purpose.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

The Negative Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Tactile Learning

Overcome Your Writer’s Block: Essay Writing Tips for Students

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Tips and Techniques

Why Using Chat-GPT for Writing Your College Essays is Not Smart
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Research Hypothesis: Good & Bad Examples
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is an attempt at explaining a phenomenon or the relationships between phenomena/variables in the real world. Hypotheses are sometimes called “educated guesses”, but they are in fact (or let’s say they should be) based on previous observations, existing theories, scientific evidence, and logic. A research hypothesis is also not a prediction—rather, predictions are ( should be) based on clearly formulated hypotheses. For example, “We tested the hypothesis that KLF2 knockout mice would show deficiencies in heart development” is an assumption or prediction, not a hypothesis.
The research hypothesis at the basis of this prediction is “the product of the KLF2 gene is involved in the development of the cardiovascular system in mice”—and this hypothesis is probably (hopefully) based on a clear observation, such as that mice with low levels of Kruppel-like factor 2 (which KLF2 codes for) seem to have heart problems. From this hypothesis, you can derive the idea that a mouse in which this particular gene does not function cannot develop a normal cardiovascular system, and then make the prediction that we started with.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a prediction?
You might think that these are very subtle differences, and you will certainly come across many publications that do not contain an actual hypothesis or do not make these distinctions correctly. But considering that the formulation and testing of hypotheses is an integral part of the scientific method, it is good to be aware of the concepts underlying this approach. The two hallmarks of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability (an evaluation standard that was introduced by the philosopher of science Karl Popper in 1934) and testability —if you cannot use experiments or data to decide whether an idea is true or false, then it is not a hypothesis (or at least a very bad one).
So, in a nutshell, you (1) look at existing evidence/theories, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction that allows you to (4) design an experiment or data analysis to test it, and (5) come to a conclusion. Of course, not all studies have hypotheses (there is also exploratory or hypothesis-generating research), and you do not necessarily have to state your hypothesis as such in your paper.
But for the sake of understanding the principles of the scientific method, let’s first take a closer look at the different types of hypotheses that research articles refer to and then give you a step-by-step guide for how to formulate a strong hypothesis for your own paper.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Hypotheses can be simple , which means they describe the relationship between one single independent variable (the one you observe variations in or plan to manipulate) and one single dependent variable (the one you expect to be affected by the variations/manipulation). If there are more variables on either side, you are dealing with a complex hypothesis. You can also distinguish hypotheses according to the kind of relationship between the variables you are interested in (e.g., causal or associative ). But apart from these variations, we are usually interested in what is called the “alternative hypothesis” and, in contrast to that, the “null hypothesis”. If you think these two should be listed the other way round, then you are right, logically speaking—the alternative should surely come second. However, since this is the hypothesis we (as researchers) are usually interested in, let’s start from there.
Alternative Hypothesis
If you predict a relationship between two variables in your study, then the research hypothesis that you formulate to describe that relationship is your alternative hypothesis (usually H1 in statistical terms). The goal of your hypothesis testing is thus to demonstrate that there is sufficient evidence that supports the alternative hypothesis, rather than evidence for the possibility that there is no such relationship. The alternative hypothesis is usually the research hypothesis of a study and is based on the literature, previous observations, and widely known theories.
Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that describes the other possible outcome, that is, that your variables are not related, is the null hypothesis ( H0 ). Based on your findings, you choose between the two hypotheses—usually that means that if your prediction was correct, you reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative. Make sure, however, that you are not getting lost at this step of the thinking process: If your prediction is that there will be no difference or change, then you are trying to find support for the null hypothesis and reject H1.
Directional Hypothesis
While the null hypothesis is obviously “static”, the alternative hypothesis can specify a direction for the observed relationship between variables—for example, that mice with higher expression levels of a certain protein are more active than those with lower levels. This is then called a one-tailed hypothesis.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that
H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance.
Your null hypothesis would then be that
H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A nondirectional hypothesis does not specify the direction of the potentially observed effect, only that there is a relationship between the studied variables—this is called a two-tailed hypothesis. For instance, if you are studying a new drug that has shown some effects on pathways involved in a certain condition (e.g., anxiety) in vitro in the lab, but you can’t say for sure whether it will have the same effects in an animal model or maybe induce other/side effects that you can’t predict and potentially increase anxiety levels instead, you could state the two hypotheses like this:
H1: The only lab-tested drug (somehow) affects anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
You then test this nondirectional alternative hypothesis against the null hypothesis:
H0: The only lab-tested drug has no effect on anxiety levels in an anxiety mouse model.
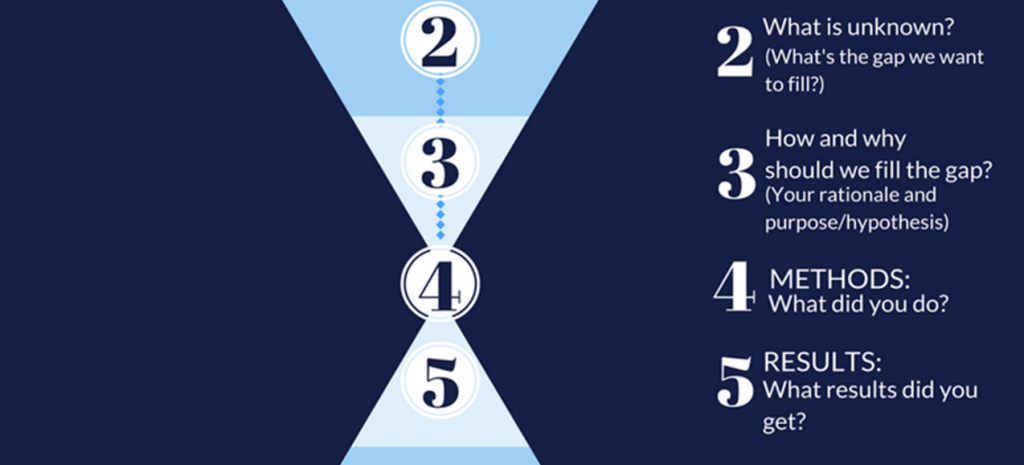
How to Write a Hypothesis for a Research Paper
Now that we understand the important distinctions between different kinds of research hypotheses, let’s look at a simple process of how to write a hypothesis.
Writing a Hypothesis Step:1
Ask a question, based on earlier research. Research always starts with a question, but one that takes into account what is already known about a topic or phenomenon. For example, if you are interested in whether people who have pets are happier than those who don’t, do a literature search and find out what has already been demonstrated. You will probably realize that yes, there is quite a bit of research that shows a relationship between happiness and owning a pet—and even studies that show that owning a dog is more beneficial than owning a cat ! Let’s say you are so intrigued by this finding that you wonder:
What is it that makes dog owners even happier than cat owners?
Let’s move on to Step 2 and find an answer to that question.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 2:
Formulate a strong hypothesis by answering your own question. Again, you don’t want to make things up, take unicorns into account, or repeat/ignore what has already been done. Looking at the dog-vs-cat papers your literature search returned, you see that most studies are based on self-report questionnaires on personality traits, mental health, and life satisfaction. What you don’t find is any data on actual (mental or physical) health measures, and no experiments. You therefore decide to make a bold claim come up with the carefully thought-through hypothesis that it’s maybe the lifestyle of the dog owners, which includes walking their dog several times per day, engaging in fun and healthy activities such as agility competitions, and taking them on trips, that gives them that extra boost in happiness. You could therefore answer your question in the following way:
Dog owners are happier than cat owners because of the dog-related activities they engage in.
Now you have to verify that your hypothesis fulfills the two requirements we introduced at the beginning of this resource article: falsifiability and testability . If it can’t be wrong and can’t be tested, it’s not a hypothesis. We are lucky, however, because yes, we can test whether owning a dog but not engaging in any of those activities leads to lower levels of happiness or well-being than owning a dog and playing and running around with them or taking them on trips.
Writing a Hypothesis Step 3:
Make your predictions and define your variables. We have verified that we can test our hypothesis, but now we have to define all the relevant variables, design our experiment or data analysis, and make precise predictions. You could, for example, decide to study dog owners (not surprising at this point), let them fill in questionnaires about their lifestyle as well as their life satisfaction (as other studies did), and then compare two groups of active and inactive dog owners. Alternatively, if you want to go beyond the data that earlier studies produced and analyzed and directly manipulate the activity level of your dog owners to study the effect of that manipulation, you could invite them to your lab, select groups of participants with similar lifestyles, make them change their lifestyle (e.g., couch potato dog owners start agility classes, very active ones have to refrain from any fun activities for a certain period of time) and assess their happiness levels before and after the intervention. In both cases, your independent variable would be “ level of engagement in fun activities with dog” and your dependent variable would be happiness or well-being .
Examples of a Good and Bad Hypothesis
Let’s look at a few examples of good and bad hypotheses to get you started.
Good Hypothesis Examples
| Working from home improves job satisfaction. | Employees who are allowed to work from home are less likely to quit within 2 years than those who need to come to the office. |
| Sleep deprivation affects cognition. | Students who sleep <5 hours/night don’t perform as well on exams as those who sleep >7 hours/night. |
| Animals adapt to their environment. | Birds of the same species living on different islands have differently shaped beaks depending on the available food source. |
| Social media use causes anxiety. | Do teenagers who refrain from using social media for 4 weeks show improvements in anxiety symptoms? |
Bad Hypothesis Examples
| Garlic repels vampires. | Participants who eat garlic daily will not be harmed by vampires. | Nobody gets harmed by vampires— . |
| Chocolate is better than vanilla. | No clearly defined variables— . |
Tips for Writing a Research Hypothesis
If you understood the distinction between a hypothesis and a prediction we made at the beginning of this article, then you will have no problem formulating your hypotheses and predictions correctly. To refresh your memory: We have to (1) look at existing evidence, (2) come up with a hypothesis, (3) make a prediction, and (4) design an experiment. For example, you could summarize your dog/happiness study like this:
(1) While research suggests that dog owners are happier than cat owners, there are no reports on what factors drive this difference. (2) We hypothesized that it is the fun activities that many dog owners (but very few cat owners) engage in with their pets that increases their happiness levels. (3) We thus predicted that preventing very active dog owners from engaging in such activities for some time and making very inactive dog owners take up such activities would lead to an increase and decrease in their overall self-ratings of happiness, respectively. (4) To test this, we invited dog owners into our lab, assessed their mental and emotional well-being through questionnaires, and then assigned them to an “active” and an “inactive” group, depending on…
Note that you use “we hypothesize” only for your hypothesis, not for your experimental prediction, and “would” or “if – then” only for your prediction, not your hypothesis. A hypothesis that states that something “would” affect something else sounds as if you don’t have enough confidence to make a clear statement—in which case you can’t expect your readers to believe in your research either. Write in the present tense, don’t use modal verbs that express varying degrees of certainty (such as may, might, or could ), and remember that you are not drawing a conclusion while trying not to exaggerate but making a clear statement that you then, in a way, try to disprove . And if that happens, that is not something to fear but an important part of the scientific process.
Similarly, don’t use “we hypothesize” when you explain the implications of your research or make predictions in the conclusion section of your manuscript, since these are clearly not hypotheses in the true sense of the word. As we said earlier, you will find that many authors of academic articles do not seem to care too much about these rather subtle distinctions, but thinking very clearly about your own research will not only help you write better but also ensure that even that infamous Reviewer 2 will find fewer reasons to nitpick about your manuscript.
Perfect Your Manuscript With Professional Editing
Now that you know how to write a strong research hypothesis for your research paper, you might be interested in our free AI Proofreader , Wordvice AI, which finds and fixes errors in grammar, punctuation, and word choice in academic texts. Or if you are interested in human proofreading , check out our English editing services , including research paper editing and manuscript editing .
On the Wordvice academic resources website , you can also find many more articles and other resources that can help you with writing the other parts of your research paper , with making a research paper outline before you put everything together, or with writing an effective cover letter once you are ready to submit.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
| Research question | Hypothesis | Null hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| What are the health benefits of eating an apple a day? | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will result in decreasing frequency of doctor’s visits. | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will have no effect on frequency of doctor’s visits. |
| Which airlines have the most delays? | Low-cost airlines are more likely to have delays than premium airlines. | Low-cost and premium airlines are equally likely to have delays. |
| Can flexible work arrangements improve job satisfaction? | Employees who have flexible working hours will report greater job satisfaction than employees who work fixed hours. | There is no relationship between working hour flexibility and job satisfaction. |
| How effective is secondary school sex education at reducing teen pregnancies? | Teenagers who received sex education lessons throughout secondary school will have lower rates of unplanned pregnancy than teenagers who did not receive any sex education. | Secondary school sex education has no effect on teen pregnancy rates. |
| What effect does daily use of social media have on the attention span of under-16s? | There is a negative correlation between time spent on social media and attention span in under-16s. | There is no relationship between social media use and attention span in under-16s. |
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 5 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Hypothesis Examples

A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method . A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples.
Null Hypothesis Examples
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is also known as the zero-difference or no-difference hypothesis. It predicts that changing one variable ( independent variable ) will have no effect on the variable being measured ( dependent variable ). Here are null hypothesis examples:
- Plant growth is unaffected by temperature.
- If you increase temperature, then solubility of salt will increase.
- Incidence of skin cancer is unrelated to ultraviolet light exposure.
- All brands of light bulb last equally long.
- Cats have no preference for the color of cat food.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
Sometimes the null hypothesis shows there is a suspected correlation between two variables. For example, if you think plant growth is affected by temperature, you state the null hypothesis: “Plant growth is not affected by temperature.” Why do you do this, rather than say “If you change temperature, plant growth will be affected”? The answer is because it’s easier applying a statistical test that shows, with a high level of confidence, a null hypothesis is correct or incorrect.
Research Hypothesis Examples
A research hypothesis (H 1 ) is a type of hypothesis used to design an experiment. This type of hypothesis is often written as an if-then statement because it’s easy identifying the independent and dependent variables and seeing how one affects the other. If-then statements explore cause and effect. In other cases, the hypothesis shows a correlation between two variables. Here are some research hypothesis examples:
- If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep.
- If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad.
- If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower).
- If you leave a bucket of water uncovered, then it evaporates more quickly.
- Goldfish lose their color if they are not exposed to light.
- Workers who take vacations are more productive than those who never take time off.
Is It Okay to Disprove a Hypothesis?
Yes! You may even choose to write your hypothesis in such a way that it can be disproved because it’s easier to prove a statement is wrong than to prove it is right. In other cases, if your prediction is incorrect, that doesn’t mean the science is bad. Revising a hypothesis is common. It demonstrates you learned something you did not know before you conducted the experiment.
Test yourself with a Scientific Method Quiz .
- Mellenbergh, G.J. (2008). Chapter 8: Research designs: Testing of research hypotheses. In H.J. Adèr & G.J. Mellenbergh (eds.), Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
- Popper, Karl R. (1959). The Logic of Scientific Discovery . Hutchinson & Co. ISBN 3-1614-8410-X.
- Schick, Theodore; Vaughn, Lewis (2002). How to think about weird things: critical thinking for a New Age . Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 0-7674-2048-9.
- Tobi, Hilde; Kampen, Jarl K. (2018). “Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework”. Quality & Quantity . 52 (3): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0513-8
Related Posts
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis in 6 Simple Steps

- DESCRIPTION how to write a hypothesis directions
- SOURCE Created by Lindy Gaskill for YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Copyright YourDictionary, Owned by YourDictionary
A hypothesis is an important part of the scientific method. It’s an idea or a proposal based on limited evidence. What comes next is the exciting part. The idea or proposal must be proven through facts, direct testing and evidence. Since the hypothesis acts as the foundation for future research, learn how to write a hypothesis through steps and examples.
What Is a Hypothesis Statement?
A hypothesis statement tells the world what you predict will happen in research. One of the most important elements of a hypothesis is that it must be able to be tested . Sure, you might hypothesize that unicorn horns are made of white gold. But, if you can’t test the independent and dependent variables , your hypothesis will have to remain in your dreams.
If, however, you hypothesize that rose quartz and other crystals possess healing powers, then you might be able to perform a few tests and carry on with your hypothesis. You will have some evidence that either supports or does not support your hypothesis. Now that you know what it is, it’s time to learn how to write a hypothesis.
Steps for How to Write a Hypothesis
When it comes to writing a hypothesis, there are six basic steps:
- Ask a question.
- Gather preliminary research.
- Formulate an answer.
- Write a hypothesis.
- Refine your hypothesis.
- Create a null hypothesis.
1. Ask a Question
In the scientific method , the first step is to ask a question. Frame this question using the classic six: who, what, where, when, why, or how. Sample questions might include:
- How long does it take carrots to grow?
- Why does the sky get darker earlier in winter?
- What happened to the dinosaurs?
- How did we evolve from monkeys?
- Why are students antsier on Friday afternoon?
How does sleep affect motivation?
- Why do IEP accommodations work in schools?
You want the question to be specific and focused. It also needs to be researchable, of course. Once you know you can research your question from several angles, it’s time to start some preliminary research.
2. Gather Preliminary Research
It’s time to collect data. This will come in the form of case studies and academic journals , as well as your own experiments and observations .
Remember, it’s important to explore your question from all sides. Don’t let conflicting research deter you. You might come upon many naysayers as you gather background information. That doesn’t invalidate your hypothesis. In fact, you can use their findings as potential rebuttals and frame your study in such a way as to address these concerns.
For example, if you are looking at the question: "How does sleep affect motivation?", you might find studies with conflicting research about eight hours vs. six hours of sleep. You can use these conflicting points to help to guide the creation of your hypothesis.
3. Formulate an Answer To Your Question
After completing all your research, think about how you will answer your question and defend your position. For example, say the question you posed was:
As you start to collect basic observations and information, you'll find that a lack of sleep creates a negative impact on learning. It decreases thought processes and makes it harder to learn anything new. Therefore, when you are tired, it's harder to learn and requires more effort. Since it is harder, you can be less motivated to do it. Additionally, you discover that there is a point where sleep affects functioning. You use this research to answer your question.
Getting less than eight hours of sleep makes it harder to learn anything new and make new memories. This makes learning harder so you are less likely to be motivated.
4. Write a Hypothesis
With the answer to your question at the ready, it’s time to formulate your hypothesis. To write a good hypothesis, it should include:
- Relevant variables
- Predicted outcome
- Who/what is being studied
Remember that your hypothesis needs to be a statement, not a question. It’s an idea, proposal or prediction. For example, a research hypothesis is formatted in an if/then statement:
If a person gets less than eight hours of sleep, then they will be less motivated at work or school.
This statement shows you:
- who is being studied - a person
- the variables - sleep and motivation
- your prediction - less sleep means less motivation
5. Refine Your Hypothesis
While you might be able to stop at writing your research hypothesis, some hypotheses might be a correlation study or studying the difference between two groups. In these instances, you want to state the relationship or difference you expect to find.
A correlation hypothesis might be:
Getting less than eight hours of sleep has a negative impact on work or school motivation.
A hypothesis showing difference might be:
Those with seven or fewer hours of sleep are less motivated than those with eight or more to complete tasks.
6. Create a Null Hypothesis
Depending on your study, you may need to perform some statistical analysis on the data you collect. When forming your hypothesis statement using the scientific method, it’s important to know the difference between a null hypothesis vs. the alternative hypothesis, and how to create a null hypothesis.
- A null hypothesis , often denoted as H 0 , posits that there is no apparent difference or that there is no evidence to support a difference. Using the motivation example above, the null hypothesis would be that sleep hours have no effect on motivation.
- An alternative hypothesis , often denoted as H 1 , states that there is a statistically significant difference, or there is evidence to support such a difference. Going back to the same carrot example, the alternative hypothesis is that a person getting six hours of sleep has less motivation than someone getting eight hours of sleep.
Good and Bad Hypothesis Examples
Here are a few examples of good and bad hypotheses to get you started.
|
|
How long does it take carrots to grow? | If we plant carrots deep in the soil, it will take them longer to grow than in shallow soil. You can plant carrots deep in the soil. (There’s no predicted outcome.) |
Why does the sky get darker earlier in winter? | The Earth's rotation affects the number of daylight hours. The sun goes down. (This doesn’t clarify variables or what will be studied.) |
What happened to the dinosaurs? | If we study marine fossils found in the Arctic, we will see that dinosaurs disappeared when a comet hit the Earth. Extinction happened thousands of years ago. (This does not name what is being studied nor present clear variables for studying dinosaur history.) |
How did we evolve from monkeys? | Human beings are not descended from apes, but share a common ancestor with them. Human evolution is long. (This does not present clear variables to be studied or a prediction to be tested.) |
| Why are students antsier on Friday afternoon? | Students are anticipating the coming of the weekend, making them antsier on Friday afternoon. Students have bad behavior. (This isn't showing what is being tested or clear variables.) |
| How does sleep affect motivation? | If a person gets less than eight hours of sleep, then they will be less motivated at work or school. Sleep is important. (While this might be true, it's not setting the variables for the study.) |
| Why do IEP accommodations work in schools? | If a student gets accommodations for their learning disability, then they will perform better in school. Accommodations help students. (Again, while this might be true, it's not providing what is being studied or the variables.) |
Tips for Writing a Hypothesis
To write a strong hypothesis, keep these important tips in mind.
- Don’t just choose a topic randomly. Find something that interests you.
- Keep it clear and to the point.
- Use your research to guide you.
- Always clearly define your variables.
- Write it as an if-then statement. If this, then that is the expected outcome.
How to Make a Hypothesis
A hypothesis involves a statement about what you will do, but also what you expect to happen or speculation about what could occur. Once you’ve written your hypothesis, you’ll need to test it, analyze the data and form your conclusion. To read more about hypothesis testing, explore good examples of hypothesis testing .

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
What Is a Hypothesis and How Do I Write One?
General Education

Think about something strange and unexplainable in your life. Maybe you get a headache right before it rains, or maybe you think your favorite sports team wins when you wear a certain color. If you wanted to see whether these are just coincidences or scientific fact, you would form a hypothesis, then create an experiment to see whether that hypothesis is true or not.
But what is a hypothesis, anyway? If you’re not sure about what a hypothesis is--or how to test for one!--you’re in the right place. This article will teach you everything you need to know about hypotheses, including:
- Defining the term “hypothesis”
- Providing hypothesis examples
- Giving you tips for how to write your own hypothesis
So let’s get started!

What Is a Hypothesis?
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as “an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.” In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess . Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it’s true or not. Keep in mind that in science, a hypothesis should be testable. You have to be able to design an experiment that tests your hypothesis in order for it to be valid.
As you could assume from that statement, it’s easy to make a bad hypothesis. But when you’re holding an experiment, it’s even more important that your guesses be good...after all, you’re spending time (and maybe money!) to figure out more about your observation. That’s why we refer to a hypothesis as an educated guess--good hypotheses are based on existing data and research to make them as sound as possible.
Hypotheses are one part of what’s called the scientific method . Every (good) experiment or study is based in the scientific method. The scientific method gives order and structure to experiments and ensures that interference from scientists or outside influences does not skew the results. It’s important that you understand the concepts of the scientific method before holding your own experiment. Though it may vary among scientists, the scientific method is generally made up of six steps (in order):
- Observation
- Asking questions
- Forming a hypothesis
- Analyze the data
- Communicate your results
You’ll notice that the hypothesis comes pretty early on when conducting an experiment. That’s because experiments work best when they’re trying to answer one specific question. And you can’t conduct an experiment until you know what you’re trying to prove!
Independent and Dependent Variables
After doing your research, you’re ready for another important step in forming your hypothesis: identifying variables. Variables are basically any factor that could influence the outcome of your experiment . Variables have to be measurable and related to the topic being studied.
There are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables. I ndependent variables remain constant . For example, age is an independent variable; it will stay the same, and researchers can look at different ages to see if it has an effect on the dependent variable.
Speaking of dependent variables... dependent variables are subject to the influence of the independent variable , meaning that they are not constant. Let’s say you want to test whether a person’s age affects how much sleep they need. In that case, the independent variable is age (like we mentioned above), and the dependent variable is how much sleep a person gets.
Variables will be crucial in writing your hypothesis. You need to be able to identify which variable is which, as both the independent and dependent variables will be written into your hypothesis. For instance, in a study about exercise, the independent variable might be the speed at which the respondents walk for thirty minutes, and the dependent variable would be their heart rate. In your study and in your hypothesis, you’re trying to understand the relationship between the two variables.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
The best hypotheses start by asking the right questions . For instance, if you’ve observed that the grass is greener when it rains twice a week, you could ask what kind of grass it is, what elevation it’s at, and if the grass across the street responds to rain in the same way. Any of these questions could become the backbone of experiments to test why the grass gets greener when it rains fairly frequently.
As you’re asking more questions about your first observation, make sure you’re also making more observations . If it doesn’t rain for two weeks and the grass still looks green, that’s an important observation that could influence your hypothesis. You'll continue observing all throughout your experiment, but until the hypothesis is finalized, every observation should be noted.
Finally, you should consult secondary research before writing your hypothesis . Secondary research is comprised of results found and published by other people. You can usually find this information online or at your library. Additionally, m ake sure the research you find is credible and related to your topic. If you’re studying the correlation between rain and grass growth, it would help you to research rain patterns over the past twenty years for your county, published by a local agricultural association. You should also research the types of grass common in your area, the type of grass in your lawn, and whether anyone else has conducted experiments about your hypothesis. Also be sure you’re checking the quality of your research . Research done by a middle school student about what minerals can be found in rainwater would be less useful than an article published by a local university.

Writing Your Hypothesis
Once you’ve considered all of the factors above, you’re ready to start writing your hypothesis. Hypotheses usually take a certain form when they’re written out in a research report.
When you boil down your hypothesis statement, you are writing down your best guess and not the question at hand . This means that your statement should be written as if it is fact already, even though you are simply testing it.
The reason for this is that, after you have completed your study, you'll either accept or reject your if-then or your null hypothesis. All hypothesis testing examples should be measurable and able to be confirmed or denied. You cannot confirm a question, only a statement!
In fact, you come up with hypothesis examples all the time! For instance, when you guess on the outcome of a basketball game, you don’t say, “Will the Miami Heat beat the Boston Celtics?” but instead, “I think the Miami Heat will beat the Boston Celtics.” You state it as if it is already true, even if it turns out you’re wrong. You do the same thing when writing your hypothesis.
Additionally, keep in mind that hypotheses can range from very specific to very broad. These hypotheses can be specific, but if your hypothesis testing examples involve a broad range of causes and effects, your hypothesis can also be broad.

The Two Types of Hypotheses
Now that you understand what goes into a hypothesis, it’s time to look more closely at the two most common types of hypothesis: the if-then hypothesis and the null hypothesis.
#1: If-Then Hypotheses
First of all, if-then hypotheses typically follow this formula:
If ____ happens, then ____ will happen.
The goal of this type of hypothesis is to test the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variable. It’s fairly simple, and each hypothesis can vary in how detailed it can be. We create if-then hypotheses all the time with our daily predictions. Here are some examples of hypotheses that use an if-then structure from daily life:
- If I get enough sleep, I’ll be able to get more work done tomorrow.
- If the bus is on time, I can make it to my friend’s birthday party.
- If I study every night this week, I’ll get a better grade on my exam.
In each of these situations, you’re making a guess on how an independent variable (sleep, time, or studying) will affect a dependent variable (the amount of work you can do, making it to a party on time, or getting better grades).
You may still be asking, “What is an example of a hypothesis used in scientific research?” Take one of the hypothesis examples from a real-world study on whether using technology before bed affects children’s sleep patterns. The hypothesis read s:
“We hypothesized that increased hours of tablet- and phone-based screen time at bedtime would be inversely correlated with sleep quality and child attention.”
It might not look like it, but this is an if-then statement. The researchers basically said, “If children have more screen usage at bedtime, then their quality of sleep and attention will be worse.” The sleep quality and attention are the dependent variables and the screen usage is the independent variable. (Usually, the independent variable comes after the “if” and the dependent variable comes after the “then,” as it is the independent variable that affects the dependent variable.) This is an excellent example of how flexible hypothesis statements can be, as long as the general idea of “if-then” and the independent and dependent variables are present.
#2: Null Hypotheses
Your if-then hypothesis is not the only one needed to complete a successful experiment, however. You also need a null hypothesis to test it against. In its most basic form, the null hypothesis is the opposite of your if-then hypothesis . When you write your null hypothesis, you are writing a hypothesis that suggests that your guess is not true, and that the independent and dependent variables have no relationship .
One null hypothesis for the cell phone and sleep study from the last section might say:
“If children have more screen usage at bedtime, their quality of sleep and attention will not be worse.”
In this case, this is a null hypothesis because it’s asking the opposite of the original thesis!
Conversely, if your if-then hypothesis suggests that your two variables have no relationship, then your null hypothesis would suggest that there is one. So, pretend that there is a study that is asking the question, “Does the amount of followers on Instagram influence how long people spend on the app?” The independent variable is the amount of followers, and the dependent variable is the time spent. But if you, as the researcher, don’t think there is a relationship between the number of followers and time spent, you might write an if-then hypothesis that reads:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will not spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
In this case, the if-then suggests there isn’t a relationship between the variables. In that case, one of the null hypothesis examples might say:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
You then test both the if-then and the null hypothesis to gauge if there is a relationship between the variables, and if so, how much of a relationship.

4 Tips to Write the Best Hypothesis
If you’re going to take the time to hold an experiment, whether in school or by yourself, you’re also going to want to take the time to make sure your hypothesis is a good one. The best hypotheses have four major elements in common: plausibility, defined concepts, observability, and general explanation.
#1: Plausibility
At first glance, this quality of a hypothesis might seem obvious. When your hypothesis is plausible, that means it’s possible given what we know about science and general common sense. However, improbable hypotheses are more common than you might think.
Imagine you’re studying weight gain and television watching habits. If you hypothesize that people who watch more than twenty hours of television a week will gain two hundred pounds or more over the course of a year, this might be improbable (though it’s potentially possible). Consequently, c ommon sense can tell us the results of the study before the study even begins.
Improbable hypotheses generally go against science, as well. Take this hypothesis example:
“If a person smokes one cigarette a day, then they will have lungs just as healthy as the average person’s.”
This hypothesis is obviously untrue, as studies have shown again and again that cigarettes negatively affect lung health. You must be careful that your hypotheses do not reflect your own personal opinion more than they do scientifically-supported findings. This plausibility points to the necessity of research before the hypothesis is written to make sure that your hypothesis has not already been disproven.
#2: Defined Concepts
The more advanced you are in your studies, the more likely that the terms you’re using in your hypothesis are specific to a limited set of knowledge. One of the hypothesis testing examples might include the readability of printed text in newspapers, where you might use words like “kerning” and “x-height.” Unless your readers have a background in graphic design, it’s likely that they won’t know what you mean by these terms. Thus, it’s important to either write what they mean in the hypothesis itself or in the report before the hypothesis.
Here’s what we mean. Which of the following sentences makes more sense to the common person?
If the kerning is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
If the space between letters is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
For people reading your report that are not experts in typography, simply adding a few more words will be helpful in clarifying exactly what the experiment is all about. It’s always a good idea to make your research and findings as accessible as possible.

Good hypotheses ensure that you can observe the results.
#3: Observability
In order to measure the truth or falsity of your hypothesis, you must be able to see your variables and the way they interact. For instance, if your hypothesis is that the flight patterns of satellites affect the strength of certain television signals, yet you don’t have a telescope to view the satellites or a television to monitor the signal strength, you cannot properly observe your hypothesis and thus cannot continue your study.
Some variables may seem easy to observe, but if you do not have a system of measurement in place, you cannot observe your hypothesis properly. Here’s an example: if you’re experimenting on the effect of healthy food on overall happiness, but you don’t have a way to monitor and measure what “overall happiness” means, your results will not reflect the truth. Monitoring how often someone smiles for a whole day is not reasonably observable, but having the participants state how happy they feel on a scale of one to ten is more observable.
In writing your hypothesis, always keep in mind how you'll execute the experiment.
#4: Generalizability
Perhaps you’d like to study what color your best friend wears the most often by observing and documenting the colors she wears each day of the week. This might be fun information for her and you to know, but beyond you two, there aren’t many people who could benefit from this experiment. When you start an experiment, you should note how generalizable your findings may be if they are confirmed. Generalizability is basically how common a particular phenomenon is to other people’s everyday life.
Let’s say you’re asking a question about the health benefits of eating an apple for one day only, you need to realize that the experiment may be too specific to be helpful. It does not help to explain a phenomenon that many people experience. If you find yourself with too specific of a hypothesis, go back to asking the big question: what is it that you want to know, and what do you think will happen between your two variables?

Hypothesis Testing Examples
We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you’ve seen some good hypothesis examples. We’ve included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses.
Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
You are a student at PrepScholar University. When you walk around campus, you notice that, when the temperature is above 60 degrees, more students study in the quad. You want to know when your fellow students are more likely to study outside. With this information, how do you make the best hypothesis possible?
You must remember to make additional observations and do secondary research before writing your hypothesis. In doing so, you notice that no one studies outside when it’s 75 degrees and raining, so this should be included in your experiment. Also, studies done on the topic beforehand suggested that students are more likely to study in temperatures less than 85 degrees. With this in mind, you feel confident that you can identify your variables and write your hypotheses:
If-then: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, significantly fewer students will study outside.”
Null: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, the same number of students will study outside as when it is more than 60 degrees.”
These hypotheses are plausible, as the temperatures are reasonably within the bounds of what is possible. The number of people in the quad is also easily observable. It is also not a phenomenon specific to only one person or at one time, but instead can explain a phenomenon for a broader group of people.
To complete this experiment, you pick the month of October to observe the quad. Every day (except on the days where it’s raining)from 3 to 4 PM, when most classes have released for the day, you observe how many people are on the quad. You measure how many people come and how many leave. You also write down the temperature on the hour.
After writing down all of your observations and putting them on a graph, you find that the most students study on the quad when it is 70 degrees outside, and that the number of students drops a lot once the temperature reaches 60 degrees or below. In this case, your research report would state that you accept or “failed to reject” your first hypothesis with your findings.
Experiment #2: The Cupcake Store (Forming a Simple Experiment)
Let’s say that you work at a bakery. You specialize in cupcakes, and you make only two colors of frosting: yellow and purple. You want to know what kind of customers are more likely to buy what kind of cupcake, so you set up an experiment. Your independent variable is the customer’s gender, and the dependent variable is the color of the frosting. What is an example of a hypothesis that might answer the question of this study?
Here’s what your hypotheses might look like:
If-then: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will buy more yellow cupcakes than purple cupcakes.”
Null: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will be just as likely to buy purple cupcakes as yellow cupcakes.”
This is a pretty simple experiment! It passes the test of plausibility (there could easily be a difference), defined concepts (there’s nothing complicated about cupcakes!), observability (both color and gender can be easily observed), and general explanation ( this would potentially help you make better business decisions ).

Experiment #3: Backyard Bird Feeders (Integrating Multiple Variables and Rejecting the If-Then Hypothesis)
While watching your backyard bird feeder, you realized that different birds come on the days when you change the types of seeds. You decide that you want to see more cardinals in your backyard, so you decide to see what type of food they like the best and set up an experiment.
However, one morning, you notice that, while some cardinals are present, blue jays are eating out of your backyard feeder filled with millet. You decide that, of all of the other birds, you would like to see the blue jays the least. This means you'll have more than one variable in your hypothesis. Your new hypotheses might look like this:
If-then: “If sunflower seeds are placed in the bird feeders, then more cardinals will come than blue jays. If millet is placed in the bird feeders, then more blue jays will come than cardinals.”
Null: “If either sunflower seeds or millet are placed in the bird, equal numbers of cardinals and blue jays will come.”
Through simple observation, you actually find that cardinals come as often as blue jays when sunflower seeds or millet is in the bird feeder. In this case, you would reject your “if-then” hypothesis and “fail to reject” your null hypothesis . You cannot accept your first hypothesis, because it’s clearly not true. Instead you found that there was actually no relation between your different variables. Consequently, you would need to run more experiments with different variables to see if the new variables impact the results.
Experiment #4: In-Class Survey (Including an Alternative Hypothesis)
You’re about to give a speech in one of your classes about the importance of paying attention. You want to take this opportunity to test a hypothesis you’ve had for a while:
If-then: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will listen better than students who do not.
Null: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will not listen better or worse than students who do not.
You give your speech and then ask your teacher if you can hand out a short survey to the class. On the survey, you’ve included questions about some of the topics you talked about. When you get back the results, you’re surprised to see that not only do the students in the first two rows not pay better attention, but they also scored worse than students in other parts of the classroom! Here, both your if-then and your null hypotheses are not representative of your findings. What do you do?
This is when you reject both your if-then and null hypotheses and instead create an alternative hypothesis . This type of hypothesis is used in the rare circumstance that neither of your hypotheses is able to capture your findings . Now you can use what you’ve learned to draft new hypotheses and test again!
Key Takeaways: Hypothesis Writing
The more comfortable you become with writing hypotheses, the better they will become. The structure of hypotheses is flexible and may need to be changed depending on what topic you are studying. The most important thing to remember is the purpose of your hypothesis and the difference between the if-then and the null . From there, in forming your hypothesis, you should constantly be asking questions, making observations, doing secondary research, and considering your variables. After you have written your hypothesis, be sure to edit it so that it is plausible, clearly defined, observable, and helpful in explaining a general phenomenon.
Writing a hypothesis is something that everyone, from elementary school children competing in a science fair to professional scientists in a lab, needs to know how to do. Hypotheses are vital in experiments and in properly executing the scientific method . When done correctly, hypotheses will set up your studies for success and help you to understand the world a little better, one experiment at a time.

What’s Next?
If you’re studying for the science portion of the ACT, there’s definitely a lot you need to know. We’ve got the tools to help, though! Start by checking out our ultimate study guide for the ACT Science subject test. Once you read through that, be sure to download our recommended ACT Science practice tests , since they’re one of the most foolproof ways to improve your score. (And don’t forget to check out our expert guide book , too.)
If you love science and want to major in a scientific field, you should start preparing in high school . Here are the science classes you should take to set yourself up for success.
If you’re trying to think of science experiments you can do for class (or for a science fair!), here’s a list of 37 awesome science experiments you can do at home
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Hypothesis: Basic Research Guidelines & Examples
- Icon Calendar 2 August 2024
- Icon Page 3422 words
- Icon Clock 16 min read
A hypothesis refers to a simple statement that predicts the findings of a research study. Basically, researchers develop propositions to provide tentative answers to research questions that address different aspects of a study objective. In writing, a scholar must use existing theories and knowledge to create a valid assumption. Besides, a researcher focuses on testing supposed claims through different methods, like experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of obtained data. In practice, the findings from a study can either support or refute a premise under examination. Then, when writing a suggestion, scholars should conduct adequate research on a specific topic, brainstorm for ideas, draft an assertion, revise a draft claim, and write a final sentence in simple language. Moreover, these steps lead to a valid development of accurate and precise propositions that identify relationships between independent and dependent variables. In practice, one should rely on a cause-and-effect theory when developing a hypothesis.
General Aspects
A good hypothesis suggests a sentence as a statement that gives a particular prediction about the findings of a research study. Basically, people make a specific hypothesis, which acts as a tentative answer to a research question. However, a proposition may lack scientific or scholarly proof. Then, a reasonable claim must address different aspects of a question under analysis. In writing, people must base their propositions on existing theories and knowledge. Besides, such a statement has to be testable through various methods, like experiments, observations, and statistical analysis. In practice, the findings from a study can either support or refute a working thesis. Therefore, writing a study assumption refers to a simple and clear statement that tries to predict the results of research.
What Is a Hypothesis and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about a specific phenomenon or a relationship between two or more variables, forming a unique basis for scientific investigation. In principle, such a statement is formulated based on observations, existing knowledge, and theoretical frameworks. For example, the main purpose of writing a hypothesis is to establish a specific direction for a particular study, enabling researchers to design experiments and collect data in a structured manner (Reichardt, 2022). Moreover, by testing a defined assertion through experimentation and analysis, people can determine whether their predictions hold true, contributing to a broader understanding of a discussed topic. This process of hypothesis testing is fundamental to a scientific method, as it allows for a particular validation, refinement, or rejection of theoretical concepts (Dillard & Flenner, 2021). In turn, the length of a hypothesis depends on academic levels and scopes of research, while general writing guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 1 sentence
- Word Count: 10-15 words
- Detail: A simple, clear, and testable statement about a specific relationship between variables.
- Example: “If plants are watered with different types of liquids, then the growth rate will vary.”
College (Undergraduate)
- Word Count: 15-30 words
- Detail: More detailed, specifying defined variables and expected outcomes with writing some contextual background.
- Example: “Students who study in a quiet environment will perform better on exams than those who study in a noisy environment due to fewer distractions and improved concentration.”
University (Advanced Undergraduate or Honors Thesis)
- Word Count: 20-35 words
- Detail: Includes specific variables, a rationale based on preliminary research, and a clear expected outcome.
- Example: “Exposure to natural light in the workplace will increase employee productivity compared to artificial lighting, as natural light has been shown to improve mood and energy levels.”
Master’s Thesis
- Length: 1-2 sentences
- Word Count: 25-40 words
- Detail: Detailed and precise writing, including variables, expected relationship, and grounding in existing literature or theoretical framework.
- Example: “Implementing a flipped classroom model in undergraduate biology courses will result in higher student engagement and academic performance, as this model promotes active learning and individualized instruction, which have been positively correlated with student outcomes in previous studies.”
Ph.D. Dissertation
- Length: 2-4 sentences (or more, if necessary)
- Word Count: 30-70+ words
- Detail: Highly detailed, specifying complex relationships between multiple variables, grounded in extensive literature review and theoretical framework, with writing about clear and expected outcomes.
- Example: “Incorporating machine learning algorithms into predictive models for climate change will significantly improve an overall accuracy of long-term weather forecasts. This assumption is based on a premise that machine learning can identify innovative patterns in large datasets that traditional statistical methods may miss, thus providing more reliable predictions of climatic phenomena.”

| Component | Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Research Question | A clear, concise question that current research aims to answer. | “Does a specific type of liquid used to water plants affect their growth rate?” |
| Variables | Identification of independent and dependent variables. | Independent Variable: Type of liquid used for watering. |
| Dependent Variable: Plant growth rate. | ||
| Hypothesis Statement | A testable prediction that addresses a given research question. | “If plants are watered with different types of liquids, then a growth rate will vary.” |
| Rationale | Explanation of a specific reasoning behind a discussed assumption, often based on literature or theory. | “Plants need water to grow, but different liquids contain various nutrients or chemicals that may affect their growth in different ways.” |
| Expected Outcome | Specific prediction of what will happen if a given suggestion is correct. | “Plants watered with nutrient-rich liquids will grow faster than those watered with plain water, while plants watered with sugary or acidic liquids may grow slower or not at all.” |
| Assumptions | Conditions assumed to be true for writing a defined purpose of an entire experiment. | “All plants used in a corresponding experiment are of the same species and health, and environmental conditions, such as light and temperature, are kept constant.” |
| Methodology | Brief outline of how a formulated premise will be tested. | “Plants will be divided into groups, and each group will be watered with a different type of liquid for a period of four weeks. A particular growth rate will be measured and compared.” |
Note: Some writing components of a hypothesis can be added, deleted, or combined with each other, and such a statement is usually 1 sentence long. For example, the three main parts of a hypothesis statement are an independent variable, a dependent variable, and a predicted relationship between them (Lund, 2021). In a research paper, a standard hypothesis is typically found in an introduction section, where such a statement outlines an expected relationship between variables and sets a particular stage for an entire study. Further on, a hypothesis is a testable prediction about a unique relationship between variables, while a research question is a broad query that guides an entire investigation into a specific topic (Misra et al., 2021). Moreover, there is a direct relationship between a hypothesis and research objectives, as the former provides a specific, testable prediction that aligns with and helps to achieve broader goals outlined by the latter. In writing, a basic checklist to evaluate an overall effectiveness of any hypothesis includes ensuring a research assertion is a clear, specific, and testable statement that is based on existing knowledge and covers both independent and dependent variables (Rubin & Donkin, 2022). Finally, to start a hypothesis, people begin by writing an “If” statement that clearly identifies an independent variable, followed by a “then” statement predicting a specific outcome or effect on a dependent variable.

Independent and Dependent Variables
A hypothesis in some studies must contain independent and dependent variables. Basically, hypothesis testing is a statistical method that people use to determine a specific connection between suggestions and their alternative outcomes to understand what is true or not and write about them. For example. experimental and correlational studies examine relationships between two or more variables (Sharang, 2020). In turn, independent elements refer to factors people can control or change. Besides, this aspect refers to factors scholars observe or measure for their writing. Then, a null hypothesis of experimental and correlational studies must predict relationships between dependent and independent variables. Moreover, such predictions should not be guesses but should contain evidence from research studies.
There are different types of hypotheses people can develop for writing their studies. In this case, common types of hypotheses include:
- A simple hypothesis refers to predictions of relationships between independent and dependent variables.
- A complex hypothesis predicts relationships between two or more independent and dependent variables.
- An empirical hypothesis is a working prediction that exists when a person tests a specific theory by using observations and experiments. Basically, this type of assertion goes through some trial and error methods to obtain the necessary findings and write about them. In some instances, people may change some aspects around other elements.
- A null hypothesis , denoted as H 0 , exists when a person believes a relationship does not exist between independent and dependent variables. Basically, this statement may exist when an individual lacks adequate information to make a scientific prediction. Besides, inferences made from the findings attempt to disapprove or discredit a null theory.
- An alternative hypothesis , denoted as H 1 , attempts to disapprove a null proposition. In this case, people attempt to discover or affirm an alternative proposition.
- A logical hypothesis refers to a proposed explanation of a concept that contains limited evidence. In writing, investigators intend to turn a reasonable assumption into an empirical claim. Besides, they put theories or postulate them to a particular testing process.
- A statistical hypothesis is a claim related to studies that examine a section of a specific population. In this case, people identify a sample population and study their behaviors related to a given research question.
Steps on How to Write a Good Hypothesis
To write a good hypothesis, people clearly define specific independent and dependent variables and formulate a testable prediction about a particular relationship between them, often structured as an “If [independent variable], then [dependent variable]” statement. As such, researchers should focus on developing and writing reasonable assertation statements for their studies. For example, one should consider different factors that relate to existing studies or theories (Sharang, 2020). In writing, some predictions should pertain to research data and provide tentative answers to study questions. Hence, the following are essential writing steps a person should consider when developing a proposition.
Step 1: Researching
A first step in developing a hypothesis is to research and gather details related to writing an intended topic. Basically, researching allows a scholar to gain more knowledge concerning issues and factors and how variables change. For example, to form a hypothesis sentence, people start wording by identifying independent and dependent variables, reviewing existing literature, and then creating a clear, testable prediction that outlines an expected relationship between defined elements (Reichardt, 2022). Besides, this step will enable people to become familiar with the expected results. As a result, an entire writing process influences a relevant theory’s development.
Step 2: Asking Questions
A person should develop research questions before developing a main claim. For instance, investigators should create scientific questions that relate to studied and identified elements (Dillard & Flenner, 2021). In writing, brainstorming enhances a particular ability to determine relationships between independent and dependent variables. Basically, successful scholars remain focused on writing about one cause-and-effect theory to ensure they develop accurate ideas for a prediction. Therefore, a second writing step in developing a proposition is to brainstorm questions that reveal a specific relationship between independent and dependent elements.
Step 3: Use Clear Language
Scholars should use simple and clear language when developing any suggestion for writing a study. For instance, one should draft concise predictions that answer developed research questions (Sharang, 2020). In practice, one should write a hypothesis in a particular form of a direct proposition that an action leads to a specific result. Futher on, the three main words that should be in a hypothesis statement are “if,” “then,” and “because.” Moreover, a person should not state a supposition as a question but as an affirmative statement that predicts outcomes from a particular course of action. Therefore, a third step in developing a new theory involves selecting a simple language for writing scientific predictions.
Step 4. Revising a Statement
A scholar should revise a draft hypothesis to ensure writing any prediction makes a testable thesis through research and experimentation. For instance, a person should review a prediction to ensure such a sentence captures relationships between at least two elements (Dillard & Flenner, 2021). Hence, a scholar must revise a drafted proposition to ensure this statement captures a testable relationship between independent and dependent variables. In writing, some examples of sentence starters for beginning a hypothesis statement are:
- If [independent variable] is introduced or modified, then we anticipate [dependent variable] will exhibit a measurable change in terms of … .
- It is hypothesized that a particular presence or alteration of [independent element] will significantly affect [dependent element] by causing … .
- We predict that variations in [independent aspect] will result in corresponding changes in [dependent aspect], specifically in key aspects of … .
- A formulated assumption posits that altering [independent variable] will lead to observable differences in [dependent variable], particularly in relation to … .
- Based on existing theories and previous research, it is expected that modifying [independent element] will impact [dependent element] by … .
- We hypothesize an increase or decrease in [independent aspect], which will have a direct influence on [dependent aspect], leading to … .
- It is proposed that a particular manipulation of [independent variable] will result in [specific outcome] within [dependent variable] due to a specific mechanism of … .
- If [independent element] is systematically varied, then [dependent element] will demonstrate a change characterized by … .
- A current premise suggests that specific changes in [independent aspect] will cause predictable alterations in [dependent aspect], which can be measured by … .
- We expect that, by introducing [independent variable], there will be a significant impact on [dependent variable], as evidenced by changes in … .
- Research question – How does divorce affect sociological development among young children?
- H 0 – Challenges that lead to divorce hurt young children’s social development, which affects their ability to interact with other people.
- H 1 – Most children manage to cope with domestic challenges that lead to divorce, enabling them to realize healthy sociological development.
- Research question – How did tenebrism influence baroque art during the 16 th and 17 th centuries?
- H 0 – A particular origin of tenebrism had a positive impact on a dynamic appearance of baroque art.
- H 1 – Baroque art emerged as a unique art that did not have any form of external influence.
- Research question – To what extent does geological activity affect the Earth?
- H 0 – A specific movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface results in volcanic eruptions and faults that lead to mountains and lift valleys.
- H 1 – Mountains and valleys are natural features with little connection with geological activities like a particular movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface.
- Research question – Do animals have rights and welfare in society?
- H 0 – Wild and domestic animals are living creatures with a right to care and protection by humans.
- H 1 – Wild and domestic animals are subordinate to humans, which implies they do not have a right to care and protection.
- Research question – Does a specific consumption of genetically modified plants cause health complications in humans?
- H 0 – Genetically modified foods are safe for human consumption and do not pose any possible health risks.
- H 1 – Genetically modified foods interfere with healthy cell development, which leads to health complications.
Indigenous Studies
- Research question – What role does culture play among Indigenous communities?
- H 0 – Cultural practices among Aboriginals promote their identity and contribute to the members’ overall well-being.
- H 1 – cultural practices among Aboriginals do not significantly contribute to an overall quality of their lives.
- Research question – Does fascism exist in the twenty-first century?
- H 0 – Established forms of democracy in the twenty-first century do not allow political leaders to implement all the fascism elements.
- H 1 – Some political leaders in the twenty-first century adopt radical policies that promote a particular existence of fascism.
- Research question – Do neutrons have mass?
- H 0 – Neutrons are small particles that have masses.
- H 1 – Neutrons are small particles whose weight remains insignificant.
Health Studies
- Research question – How do evidence-based treatment approaches enhance an overall quality of current treatments?
- H 0 – Evidence-based treatment methods allow doctors to gather adequate and accurate information about patients, which helps them to tailor treatment and care approaches to meet people’s needs.
- H 1 – Evidence-based approaches do not enhance an overall quality of current treatments since they lead to inconsistency in the care and medications given to a patient.
Environmental Studies
- Research question – To what extent do human activities contribute to global warming?
- H 0 – Most human activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which results in a particular rise in average temperatures.
- H 1 – Most human activities release insignificant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
What to Include
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| If-Then Statement | Formulate a research hypothesis using an “If [independent variable], then [dependent variable]” writing structure. |
| Background Information | Include relevant background or theoretical context that supports a given assertion. |
| Assumptions | State any assumptions that are made for a particular theory’s development. |
| Scope and Limitations | Write about a unique scope and acknowledge any potential limitations of a study statement. |
| Operational Definitions | Define how defined variables will be measured or manipulated specifically. |
| Comparison Groups | Identify any control or comparison groups involved for writing an entire study. |
| Expected Direction | State whether a particular relationship is expected to be positive, negative, or null. |
| Time Frame | Specify a time period over which potential effects or changes are expected to occur. |
| Population | Define a specific population or sample to which a current theory applies. |
| Alternative Hypotheses | Write about any alternative suggestions that could be considered. |
| Prior Findings | Reference previous studies or data and support a provided assertion. |
| Potential Impact | Discuss potential implications or significance of a given claim if it is supported. |
| Ethical Considerations | Cover any ethical issues related to testing a study hypothesis. |
Common Mistakes
- Being Too Vague: A hypothesis statement must be specific and clearly define corresponding variables and expected outcomes.
- Not Being Testable: A prediction should be formulated in a way that can be empirically tested through experiments or observations.
- Lack of Clarity: Avoid writing in ambiguous language since a scientific assertion should be clear and straightforward.
- Being Too Complex: Keep a statement focused on a single relationship between variables to avoid confusion.
- Ignoring Prior Research: Writing a good premise is based on existing knowledge and theories, while ignoring these concepts can lead to redundant or invalid studies.
- Using Subjective Terms: Avoid writing terms that are open to interpretation because any prediction should be objective and measurable.
- Making Assumptions: Do not assume outcomes without evidence since any assertion should be based on logical reasoning.
- Not Aligning With a Research Question: Ensure a formulated prediction directly addresses a study question posed.
- Being Too Broad: Writing a hypothesis statement should be narrow enough to be manageable within a specific scope of research.
- Neglecting to Include Variables: Clearly identify and define both independent and dependent variables in a given assertion.
Writing Tips
In its simple definition, a basic hypothesis gives a specific prediction about the findings of a research paper or study. Basically, people develop scientific predictions to provide tentative answers to study questions (Reichardt, 2022). In turn, some of the factors one must consider when writing an assumption statement include:
- conduct adequate research on a specific topic;
- brainstorm for ideas;
- draft a statement;
- revise a draft proposition;
- write a final assertion in simple language.
A hypothesis is a statement predicting a specific outcome of a research study, which is based on existing theories, literature, and knowledge. Basically, writing such a statement includes independent and dependent variables and must be testable through experiments, observations, or statistical analysis. Further on, common types of hypotheses include simple, complex, empirical, null, alternative, logical, and statistical writing formats. To develop a good hypothesis, one should research a specific topic, ask relevant questions, use clear language, and revise a formulated statement to ensure its writing captures a direct relationship between variables. Finally, accurate assumptions help in identifying cause-and-effect relationships in research.
Dillard, A., & Flenner, J. (2021). Crush hypothesis testing . Happy Hypotenuse Publishing.
Lund, T. (2021). Research problems and hypotheses in empirical research. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research , 66 (7), 1183–1193. https://doi.org/10.1080/00313831.2021.1982765
Misra, D. P., Gasparyan, A. Y., Zimba, O., Yessirkepov, M., Agarwal, V., & Kitas, G. D. (2021). Formulating hypotheses for different study designs. Journal of Korean Medical Science , 36 (50), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e338
Reichardt, C. S. (2022). The method of multiple hypotheses: A guide for professional and academic researchers . Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group.
Rubin, M., & Donkin, C. (2022). Exploratory hypothesis tests can be more compelling than confirmatory hypothesis tests. Philosophical Psychology , 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/09515089.2022.2113771
Sharang, S. (2020). Research methodology techniques: Understanding how to write, present and defend any research report . Stephen Sharang.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Lecture Note in MLA 9: A Basic Guide With Samples
- Icon Calendar 22 July 2020
- Icon Page 1404 words

449 Good Synthesis Essay Topics: Ideas & Simple Guide
- Icon Calendar 20 July 2020
- Icon Page 6086 words
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Hypothesis: How to Write it, Types, and Examples

Any research begins with a research question and a research hypothesis . A research question alone may not suffice to design the experiment(s) needed to answer it. A hypothesis is central to the scientific method. But what is a hypothesis ? A hypothesis is a testable statement that proposes a possible explanation to a phenomenon, and it may include a prediction. Next, you may ask what is a research hypothesis ? Simply put, a research hypothesis is a prediction or educated guess about the relationship between the variables that you want to investigate.
It is important to be thorough when developing your research hypothesis. Shortcomings in the framing of a hypothesis can affect the study design and the results. A better understanding of the research hypothesis definition and characteristics of a good hypothesis will make it easier for you to develop your own hypothesis for your research. Let’s dive in to know more about the types of research hypothesis , how to write a research hypothesis , and some research hypothesis examples .
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis ?
A hypothesis is based on the existing body of knowledge in a study area. Framed before the data are collected, a hypothesis states the tentative relationship between independent and dependent variables, along with a prediction of the outcome.
What is a research hypothesis ?
Young researchers starting out their journey are usually brimming with questions like “ What is a hypothesis ?” “ What is a research hypothesis ?” “How can I write a good research hypothesis ?”
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is testable, i.e., it can be supported or disproven through experimentation or observation.

Characteristics of a good hypothesis
Here are the characteristics of a good hypothesis :
- Clearly formulated and free of language errors and ambiguity
- Concise and not unnecessarily verbose
- Has clearly defined variables
- Testable and stated in a way that allows for it to be disproven
- Can be tested using a research design that is feasible, ethical, and practical
- Specific and relevant to the research problem
- Rooted in a thorough literature search
- Can generate new knowledge or understanding.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
A study begins with the formulation of a research question. A researcher then performs background research. This background information forms the basis for building a good research hypothesis . The researcher then performs experiments, collects, and analyzes the data, interprets the findings, and ultimately, determines if the findings support or negate the original hypothesis.
Let’s look at each step for creating an effective, testable, and good research hypothesis :
- Identify a research problem or question: Start by identifying a specific research problem.
- Review the literature: Conduct an in-depth review of the existing literature related to the research problem to grasp the current knowledge and gaps in the field.
- Formulate a clear and testable hypothesis : Based on the research question, use existing knowledge to form a clear and testable hypothesis . The hypothesis should state a predicted relationship between two or more variables that can be measured and manipulated. Improve the original draft till it is clear and meaningful.
- State the null hypothesis: The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between the variables you are studying.
- Define the population and sample: Clearly define the population you are studying and the sample you will be using for your research.
- Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis: Select appropriate research methods, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies, which will allow you to test your research hypothesis .
Remember that creating a research hypothesis is an iterative process, i.e., you might have to revise it based on the data you collect. You may need to test and reject several hypotheses before answering the research problem.
How to write a research hypothesis
When you start writing a research hypothesis , you use an “if–then” statement format, which states the predicted relationship between two or more variables. Clearly identify the independent variables (the variables being changed) and the dependent variables (the variables being measured), as well as the population you are studying. Review and revise your hypothesis as needed.
An example of a research hypothesis in this format is as follows:
“ If [athletes] follow [cold water showers daily], then their [endurance] increases.”
Population: athletes
Independent variable: daily cold water showers
Dependent variable: endurance
You may have understood the characteristics of a good hypothesis . But note that a research hypothesis is not always confirmed; a researcher should be prepared to accept or reject the hypothesis based on the study findings.

Research hypothesis checklist
Following from above, here is a 10-point checklist for a good research hypothesis :
- Testable: A research hypothesis should be able to be tested via experimentation or observation.
- Specific: A research hypothesis should clearly state the relationship between the variables being studied.
- Based on prior research: A research hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and previous research in the field.
- Falsifiable: A research hypothesis should be able to be disproven through testing.
- Clear and concise: A research hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner.
- Logical: A research hypothesis should be logical and consistent with current understanding of the subject.
- Relevant: A research hypothesis should be relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Feasible: A research hypothesis should be feasible to test within the scope of the study.
- Reflects the population: A research hypothesis should consider the population or sample being studied.
- Uncomplicated: A good research hypothesis is written in a way that is easy for the target audience to understand.
By following this research hypothesis checklist , you will be able to create a research hypothesis that is strong, well-constructed, and more likely to yield meaningful results.

Types of research hypothesis
Different types of research hypothesis are used in scientific research:
1. Null hypothesis:
A null hypothesis states that there is no change in the dependent variable due to changes to the independent variable. This means that the results are due to chance and are not significant. A null hypothesis is denoted as H0 and is stated as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is not zoonotic .”
2. Alternative hypothesis:
This states that there is a significant difference or relationship between the variables being studied. It is denoted as H1 or Ha and is usually accepted or rejected in favor of the null hypothesis.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is zoonotic .”
3. Directional hypothesis :
This specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables; therefore, it tends to use terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: “ The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment .”
4. Non-directional hypothesis:
While it does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables, a non-directional hypothesis states the existence of a relationship or difference between variables but not the direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship. A non-directional hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or when findings contradict previous research.
Example, “ Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express .”
5. Simple hypothesis :
A simple hypothesis only predicts the relationship between one independent and another independent variable.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging .”
6 . Complex hypothesis :
A complex hypothesis states the relationship or difference between two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging, reduces sun burn, and reduces the chances of skin cancer .” (Here, the three dependent variables are slowing skin aging, reducing sun burn, and reducing the chances of skin cancer.)
7. Associative hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis states that a change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables.
Example: “ There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health .”
8 . Causal hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect interaction between variables.
Example: “ Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage .”
Note that some of the types of research hypothesis mentioned above might overlap. The types of hypothesis chosen will depend on the research question and the objective of the study.

Research hypothesis examples
Here are some good research hypothesis examples :
“The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.”
“Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.”
“Plants that are exposed to certain types of music will grow taller than those that are not exposed to music.”
“The use of the plant growth regulator X will lead to an increase in the number of flowers produced by plants.”
Characteristics that make a research hypothesis weak are unclear variables, unoriginality, being too general or too vague, and being untestable. A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and improper methods.
Some bad research hypothesis examples (and the reasons why they are “bad”) are as follows:
“This study will show that treatment X is better than any other treatment . ” (This statement is not testable, too broad, and does not consider other treatments that may be effective.)
“This study will prove that this type of therapy is effective for all mental disorders . ” (This statement is too broad and not testable as mental disorders are complex and different disorders may respond differently to different types of therapy.)
“Plants can communicate with each other through telepathy . ” (This statement is not testable and lacks a scientific basis.)
Importance of testable hypothesis
If a research hypothesis is not testable, the results will not prove or disprove anything meaningful. The conclusions will be vague at best. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher focus on the study outcome and understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher make precise predictions based on prior research.
To be considered testable, there must be a way to prove that the hypothesis is true or false; further, the results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis
1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis ?
A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions. It helps a researcher identify what information to collect. A research hypothesis , however, is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Accordingly, it guides the study design and data analysis approach.
2. When to reject null hypothesis ?
A null hypothesis should be rejected when the evidence from a statistical test shows that it is unlikely to be true. This happens when the test statistic (e.g., p -value) is less than the defined significance level (e.g., 0.05). Rejecting the null hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true; it simply means that the evidence found is not compatible with the null hypothesis.
3. How can I be sure my hypothesis is testable?
A testable hypothesis should be specific and measurable, and it should state a clear relationship between variables that can be tested with data. To ensure that your hypothesis is testable, consider the following:
- Clearly define the key variables in your hypothesis. You should be able to measure and manipulate these variables in a way that allows you to test the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis should predict a specific outcome or relationship between variables that can be measured or quantified.
- You should be able to collect the necessary data within the constraints of your study.
- It should be possible for other researchers to replicate your study, using the same methods and variables.
- Your hypothesis should be testable by using appropriate statistical analysis techniques, so you can draw conclusions, and make inferences about the population from the sample data.
- The hypothesis should be able to be disproven or rejected through the collection of data.
4. How do I revise my research hypothesis if my data does not support it?
If your data does not support your research hypothesis , you will need to revise it or develop a new one. You should examine your data carefully and identify any patterns or anomalies, re-examine your research question, and/or revisit your theory to look for any alternative explanations for your results. Based on your review of the data, literature, and theories, modify your research hypothesis to better align it with the results you obtained. Use your revised hypothesis to guide your research design and data collection. It is important to remain objective throughout the process.
5. I am performing exploratory research. Do I need to formulate a research hypothesis?
As opposed to “confirmatory” research, where a researcher has some idea about the relationship between the variables under investigation, exploratory research (or hypothesis-generating research) looks into a completely new topic about which limited information is available. Therefore, the researcher will not have any prior hypotheses. In such cases, a researcher will need to develop a post-hoc hypothesis. A post-hoc research hypothesis is generated after these results are known.
6. How is a research hypothesis different from a research question?
A research question is an inquiry about a specific topic or phenomenon, typically expressed as a question. It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis.
7. Can a research hypothesis change during the research process?
Yes, research hypotheses can change during the research process. As researchers collect and analyze data, new insights and information may emerge that require modification or refinement of the initial hypotheses. This can be due to unexpected findings, limitations in the original hypotheses, or the need to explore additional dimensions of the research topic. Flexibility is crucial in research, allowing for adaptation and adjustment of hypotheses to align with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
8. How many hypotheses should be included in a research study?
The number of research hypotheses in a research study varies depending on the nature and scope of the research. It is not necessary to have multiple hypotheses in every study. Some studies may have only one primary hypothesis, while others may have several related hypotheses. The number of hypotheses should be determined based on the research objectives, research questions, and the complexity of the research topic. It is important to ensure that the hypotheses are focused, testable, and directly related to the research aims.
9. Can research hypotheses be used in qualitative research?
Yes, research hypotheses can be used in qualitative research, although they are more commonly associated with quantitative research. In qualitative research, hypotheses may be formulated as tentative or exploratory statements that guide the investigation. Instead of testing hypotheses through statistical analysis, qualitative researchers may use the hypotheses to guide data collection and analysis, seeking to uncover patterns, themes, or relationships within the qualitative data. The emphasis in qualitative research is often on generating insights and understanding rather than confirming or rejecting specific research hypotheses through statistical testing.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What is IMRaD Format in Research?

What is a Review Article? How to Write it?
Questions about example sentences with, and the definition and usage of "Hypothesis"
- Meanings of words and phrases
- Example sentences
- Similar words
- Translations
- Other types of questions
The meaning of "Hypothesis" in various phrases and sentences
Example sentences using "hypothesis", synonyms of "hypothesis" and their differences, translations of "hypothesis", other questions about "hypothesis", meanings and usages of similar words and phrases, latest words.
HiNative is a platform for users to exchange their knowledge about different languages and cultures.
- What does ‘be immune to an idea’ mean?
- How do you say this in English (US)? 初夏
- What is the difference between It's going to rain and There's a rain today ?
- What does Uselessly mean?
- What does I’m not good with names mean?
- Which is more natural? I would like to say that the terms for an offer are about to not be valid ...
- What does ‘a flood of ideas’ mean?
- How match this is is not matter. ↑ Is this expression natural?
- 1) That's when I truly understood what the words really meant. 2) It wasn't until then that I un...
- I wonder if I can use “influence/effect” in No.1? “anywhere” in No.3? More details are in the nex...
- When should I use もう and もっと for "more"?
- whats the difference between "다른 것" "다른 거" "다른 걸" and "다른 건"
- Indonesia menganut teori kewarganegaraan apa? contohnya: liberalisme, republikan, dll
- What does ㅊㅁ) mean?
- “감사하겠습니다”and “감사드리겠습니다” 무슨 차이가 있어요?
What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is an explanation for a set of observations. Here are examples of a scientific hypothesis.
Although you could state a scientific hypothesis in various ways, most hypotheses are either "If, then" statements or forms of the null hypothesis . The null hypothesis is sometimes called the "no difference" hypothesis. The null hypothesis is good for experimentation because it's simple to disprove. If you disprove a null hypothesis, that is evidence for a relationship between the variables you are examining.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
- Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
- The number of pets in a household is unrelated to the number of people living in it.
- A person's preference for a shirt is unrelated to its color.
Examples of If, Then Hypotheses
- If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep.
- If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground.
- If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep.
- If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will heal with less scarring.
Improving a Hypothesis to Make It Testable
You may wish to revise your first hypothesis in order to make it easier to design an experiment to test. For example, let's say you have a bad breakout the morning after eating a lot of greasy food. You may wonder if there is a correlation between eating greasy food and getting pimples. You propose the hypothesis:
Eating greasy food causes pimples.
Next, you need to design an experiment to test this hypothesis. Let's say you decide to eat greasy food every day for a week and record the effect on your face. Then, as a control, you'll avoid greasy food for the next week and see what happens. Now, this is not a good experiment because it does not take into account other factors such as hormone levels, stress, sun exposure, exercise, or any number of other variables that might conceivably affect your skin.
The problem is that you cannot assign cause to your effect . If you eat french fries for a week and suffer a breakout, can you definitely say it was the grease in the food that caused it? Maybe it was the salt. Maybe it was the potato. Maybe it was unrelated to diet. You can't prove your hypothesis. It's much easier to disprove a hypothesis.
So, let's restate the hypothesis to make it easier to evaluate the data:
Getting pimples is unaffected by eating greasy food.
So, if you eat fatty food every day for a week and suffer breakouts and then don't break out the week that you avoid greasy food, you can be pretty sure something is up. Can you disprove the hypothesis? Probably not, since it is so hard to assign cause and effect. However, you can make a strong case that there is some relationship between diet and acne.
If your skin stays clear for the entire test, you may decide to accept your hypothesis . Again, you didn't prove or disprove anything, which is fine
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Is an Experimental Constant?
- What Is the Difference Between a Control Variable and Control Group?
- The Role of a Controlled Variable in an Experiment
- Random Error vs. Systematic Error
- What Is a Controlled Experiment?
- Scientific Variable
- DRY MIX Experiment Variables Acronym
Examples of “Hypothesis” In A Sentence

The hypothesis is a very important part of doing science and thinking carefully. It is like the strong supporting structure of a building for the process of research. A hypothesis is a clever guess or idea that can be tested to see if it is true or not. It helps us understand things or predict what might happen. In this article, we will look at many examples of ‘hypothesis’ in sentences .
Table of Contents
Sentences with Hypothesis
- Hypothesis : The sun rises in the east.
- They formulated a null hypothesis to compare against the alternative.
- We need to revise the original hypothesis .
- They discussed the hypothesis with colleagues in their field.
- They formulated competing hypotheses to compare and contrast the findings.
- The students generated multiple hypotheses for their investigation.
- The hypothesis was generated from observations.
- The hypothesis is the starting point of scientific investigation.
- The researchers tested the hypothesis using various methodologies.
- We need to investigate the hypothesis
- The hypothesis needs more evidence to be proven.
- The hypothesis was rejected due to flaws in the experimental design.
- They tested the hypothesis using computer simulations.
- The team tested the hypothesis using advanced technology.
- The hypothesis was derived from logical reasoning.
- They conducted surveys to gather data for their hypotheses .
- They proposed alternative hypotheses for further exploration.
- The hypothesis was consistent with data from other studies.
- The hypothesis was based on logical reasoning.
- The hypothesis was supported by the statistical analysis.
Sentences with “Hypothesis”
- The hypothesis was proven incorrect.
- The hypothesis was rejected due to lack of evidence.
- They discussed the hypothesis with their peers.
- The hypothesis was proposed based on logical deductions.
- The hypothesis was validated through rigorous peer review.
- The team discussed potential hypotheses during brainstorming sessions.
- They discussed the limitations of their hypothesis
- The students proposed various hypotheses for the investigation.
- The hypothesis was confirmed by independent replication studies.
- The students formed testable hypotheses for their projects.
- They used a control group to test their hypothesis .
- The hypothesis was formulated as a cause-and-effect relationship.
- The hypothesis was supported by the literature review.
- Scientists test their hypotheses through experiments.
- The hypothesis was proposed based on observations in nature.
- They analyzed the data to validate the hypothesis .
- They designed the experiment to test the hypothesis
- The hypothesis was based on previous research findings.
- They revised the hypothesis based on constructive feedback.
- They presented their hypotheses at a research symposium.
- They conducted experiments to test their hypotheses .
- The hypothesis was supported by a large and diverse sample.
- The researchers tested the hypothesis using a variety of methodologies.
- They conducted surveys to gather data that supported their hypothesis .
- The team formulated new hypotheses for future investigations.
- The hypothesis was consistent with experimental results.
“Hypothesis” Use in Sentence
- They discussed the implications of the hypothesis on their field.
- The researchers discussed the implications of their hypotheses .
- The hypothesis was derived from careful observation and analysis.
- The team developed alternative hypotheses for further investigation.
- They presented their hypotheses to the research community.
- The hypothesis was based on a comprehensive review of the literature.
- The hypothesis was supported by strong logical reasoning.
- They discussed the implications of their hypothesis for future research.
- The hypothesis was based on a well-established scientific theory.
- The researchers tested their hypotheses using different methodologies.
- The hypothesis was supported by empirical evidence.
- The researchers evaluated their hypotheses
- The hypothesis was disproven by contradictory evidence.
- The researchers discussed the limitations of their hypotheses .
- The hypothesis was based on a well-established theory.
- The hypothesis was supported by a large sample size.
- The hypothesis was consistent with patterns observed in nature.
- They proposed new hypotheses for future investigation.
- The hypothesis was confirmed by the results of the study.
- The hypothesis guided the research process.
- The hypothesis was supported by strong scientific consensus.
- The hypothesis was rejected due to methodological limitations.
- The researchers proposed several hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
- The hypothesis was confirmed by multiple researchers in the field.
- The hypothesis was validated through multiple studies.
Sentences Using “Hypothesis”
- The researchers conducted experiments to test their hypotheses .
- The hypothesis was based on observations from nature.
- The hypothesis was supported by a wide range of evidence.
- They formed competing hypotheses to compare.
- Scientists often revise their hypotheses based on new data.
- They conducted experiments to support their hypotheses .
- The team discussed their hypothesis during the meeting.
- The students discussed their hypotheses in class.
- They developed a new hypothesis based on recent findings.
- They discussed the hypothesis with other experts in the field.
- The hypothesis was supported by a significant p-value.
- The hypothesis was generated from real-world observations.
- Mary’s hypothesis was supported by the data.
- They tested their hypotheses across different populations.
- The researchers tested multiple hypotheses to find the answer.
- They presented their hypothesis at a scientific conference.
- The hypothesis was supported by strong evidence.
- They presented their hypotheses in a clear and concise manner.
- The researchers proposed a working hypothesis to start their study.
- The team discussed the hypothesis during the brainstorming session.
- The researchers proposed different hypotheses for the observed behavior.
- The hypothesis is a crucial part of any scientific study.
- The hypothesis was refuted by the experimental results.
“Hypothesis” Sentences Examples
- We need to gather more data to test the hypothesis .
- The hypothesis was consistent with existing theories.
- The hypothesis was supported by a strong theoretical framework.
- The hypothesis was based on previous studies.
- They formulated a null hypothesis as the default assumption.
- The hypothesis was consistent with theoretical predictions.
- The hypothesis was based on prior knowledge.
- The hypothesis was supported by strong experimental data.
- The team formed a new hypothesis after analyzing the data.
- The hypothesis was consistent with the findings of previous studies.
- The hypothesis was rejected due to methodological flaws.
- The hypothesis was proven right after extensive testing.
- The hypothesis was consistent with real-world observations.
- The team tested their hypothesis in different conditions.
- The hypothesis was consistent with the predictions.
- The students generated their hypotheses for the experiment.
- The hypothesis was confirmed by multiple independent studies.
- The hypothesis was tested using a randomized controlled trial.
- They formulated a null hypothesis to compare against.
- The hypothesis was based on inductive reasoning.
- The hypothesis was validated through repeated experiments.
- The hypothesis guided the design of the experiment.
- They used statistical analysis to validate the hypothesis .
- The researchers discussed the implications of their hypothesis on society.
- They revised the hypothesis based on feedback from experts.
- The hypothesis was confirmed by expert analysis.
- Hypotheses are essential in the scientific method.
- Lisa proposed an interesting hypothesis for her project.
- They analyzed the data to support their hypothesis .
- The hypothesis was supported by compelling arguments.
- They conducted interviews to explore their hypotheses .
Use “Hypothesis” In A Sentence
- Sarah formulated a new hypothesis for her research.
- The hypothesis was confirmed by the experiment.
- The hypothesis was generated from prior observations.
- They conducted surveys to test their hypotheses .
- The hypothesis was supported by well-documented experimental results.
- The hypothesis was supported by strong correlations.
- The hypothesis was proposed after reviewing the literature.
- They proposed a working hypothesis to guide their study.
- The hypothesis was consistent with the observed results.
- They proposed alternative hypotheses for future exploration.
- The hypothesis was validated through rigorous statistical methods.
- The researchers tested their hypotheses
- John’s hypothesis led to groundbreaking discoveries.
- The hypothesis was supported by statistical significance.
- The researchers formulated a null hypothesis to compare against.
- The hypothesis was supported by theoretical predictions.
- They formed competing hypotheses to compare and contrast.
- The hypothesis was consistent with historical data.
- The hypothesis was supported by multiple lines of evidence.
- The hypothesis was revised based on feedback from reviewers.
- The scientists formulated a specific hypothesis to test.
- The hypothesis was based on empirical data.
Use Adaptable In A Sentence
Manifestation in a sentence
Sentences with Effective
Daily Routine Sentences in English
Hypothesis In A Sentence | Images

Related Posts

Types of sentences with examples

100 Short English Sentences Used in Daily Life

Conversation Simple English Sentences For Daily Use
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Hypothesis in a Sentence 🔊
Definition of Hypothesis
a proposed explanation or theory that is studied through scientific testing
Examples of Hypothesis in a sentence
The scientist’s hypothesis did not stand up, since research data was inconsistent with his guess. 🔊
Each student gave a hypothesis and theorized which plant would grow the tallest during the study. 🔊
A hypothesis was presented by the panel, giving a likely explanation for why the trial medicine didn’t seem to have much of an effect on the patients. 🔊
During the study, the researcher changed her hypothesis to a new assumption that fit with current data. 🔊
To confirm his hypothesis on why the dolphin wasn’t eating, the marine biologists did several tests over a week’s time. 🔊
Other words in the Opinion, Belief category:
Most Searched Words (with Video)
Voracious: In a Sentence

Verbose: In a Sentence

Vainglorious: In a Sentence

Pseudonym: In a Sentence

Propinquity: In a Sentence

Orotund: In a Sentence

Magnanimous: In a Sentence

Inquisitive: In a Sentence

Epoch: In a Sentence

Aberrant: In a Sentence

Apprehensive: In a Sentence

Obdurate: In a Sentence

Heresy: In a Sentence

Gambit: In a Sentence

Pneumonia: In a Sentence

Otiose: In a Sentence

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a or H 1 ) : There’s an effect in the population.
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, similarities and differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”:
- The null hypothesis ( H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.”
- The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample. It’s critical for your research to write strong hypotheses .
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept . Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect,” “no difference,” or “no relationship.” When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
You can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population. Some percentage of the time, your inference about the population will be incorrect. When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error . When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s a type II error.
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
| ( ) | ||
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person does not differ between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in the textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has on exam scores. | : There is no relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β = 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression.* | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is greater than or equal to the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; ≥ . |
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect,” “a difference,” or “a relationship.” When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has an on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person differs between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in a textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has an on exam scores. | : There is a relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β ≠ 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression. | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is less than the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; < . |
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question.
- They both make claims about the population.
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
| A claim that there is in the population. | A claim that there is in the population. | |
|
| ||
| Equality symbol (=, ≥, or ≤) | Inequality symbol (≠, <, or >) | |
| Rejected | Supported | |
| Failed to reject | Not supported |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
General template sentences
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable.
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a ): Independent variable affects dependent variable.
Test-specific template sentences
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
| ( ) | ||
| test
with two groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable differs between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| with three groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable of group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) are not all equal in the population. |
| There is no correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ = 0. | There is a correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ ≠ 0. | |
| There is no relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β = 0. | There is a relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β ≠ 0. | |
| Two-proportions test | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion does not differ between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; = . | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion differs between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; ≠ . |
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, June 22). Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, inferential statistics | an easy introduction & examples, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations, what is your plagiarism score.
- Top1000 word
- Top5000 word
- Conjunction
- Sentence into pic
Hypothesis in a sentence

- 某某 2016-01-13 联网相关的政策
- improvement (238+32)
- on balance (53)
- wicked (168+7)
- handlebar (25)
- rainy (165+9)
- trudge (41+1)
- checkpoint (102)
- events (166+80)
- courage (289+31)
- blizzard (120+5)
- weary (158+11)
- rationalize (57+1)
- refund (173+13)
- pack up (56)
- at dusk (69+1)
- university (168+75)
- outdoors (157+12)
- be concerned about (42)
- on one's own (38)
- aristocrat (50)
How to Use the Old Testament in a Sentence
The old testament.
Some of these examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'the Old Testament.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
On the centennial of his birth, James Baldwin remains relevant today

Andrew Limbong
Recalling the words of writer James Baldwin, who was born 100 years ago

The author James Baldwin would have turned 100 on Aug, 2. Evening Standard/Getty Images/Hulton Archive hide caption
James Baldwin would have celebrated his 100th birthday Friday — on Aug. 2. On NPR and elsewhere, you can find deep examinations of his legacy – as everything from an orator, a fashion icon, to civil rights activist. But he was, of course, a writer first and foremost.
So, we thought: Why not spend a moment breaking down a few of his sentences to figure out what made his writing so affecting, so indelible, so good that it’s still worth reading today?
We’ve chosen a few lines from two of his most well-known books — his essay collection The Fire Next Time and his novel Go Tell It on the Mountain . In many ways, these books are in conversation with each other. The opening essay to The Fire Next Time is Baldwin’s letter to his 14-year-old nephew describing the faulty institutions that make up his life — his family, his faith, and his country. And the second essay opens like this: “I underwent, during the summer that I became fourteen, a prolonged religious crisis.” In Go Tell it on the Mountain , Baldwin writes a bit of fiction drawn from his own life, about a 14-year-old boy who is finding out those very same faults, as well as figuring out his own sexuality. And it opens on a very similar day of crisis.
For each book, we’ve enlisted the help of an expert to talk about what they find interesting about Baldwin’s writing style, and what legacy each work leaves. The interviews, which follow below, have been edited for length and clarity.
The Fire Next Time
The two essays in The Fire Next Time were published in the 1960s. But they still sounded new in the early 2000s when Jesmyn Ward first read them. Ward is the author of a number of books including Sing, Unburied Sing and her memoir The Men We Reaped . We called her up for this book in particular because she edited a 2016 collection of political essays and poetry titled The Fire This Time , as a nod to Baldwin. “I wanted to let him know, wherever he may be, that there are those of us who look up to him and who are attempting to do the same work that he did with the same honesty and same fearlessness” said Ward. The first essay, titled “My Dungeon Shook: Letter to my Nephew on the One Hundredth Anniversary of the Emancipation,” starts like this:

Dear James: I have begun this letter five times and torn it up five times. I keep seeing your face, which is also the face of your father and my brother. Like him, you are tough, dark, vulnerable, moody – with a very definite tendency to sound truculent because you want no one to think you are soft.
What tone is he setting here?
JW: That first sentence in the first sentence – “I've begun this letter five times and turn it up five times.” Right there, he's signaling to his nephew, we're about to talk about something that's very difficult. But softens that with the next line, “I keep seeing your face.” Following up with such a careful, close sort of observation about his nephew's characteristics in the way that they sort of echo his father and his grandfather. That's love, right? Because I love you enough to see you clearly.
You were born where you were born and face the future that you faced because you were black and for no other reason. The limits of your ambition were, thus, expected to be set forever. You were born into a society which spelled out with brutal clarity, and in as many ways as possible, that you were a worthless human being.
This is another example of his straightforward honesty with his nephew. But what did you make of it?
JW: It's all still true. That’s one of the things that is so genius about specifically this letter. There are these moments in the texts where he doesn't use his nephew's name and he just uses you. And in those moments, especially in moments like this, when he is so straightforward about what he sees in America. And where he is so straightforward about how the world has been constructed to jail, or to confine in some ways. And it feels like he's speaking to me. It feels like this wise, older wise person is sitting with me and they're telling me something about my life and about the circumstances of my life that I dimly understood, but was not able to articulate.
This entire country has been constructed in a way that it is very easy to be terrified and bewildered and to sink into despair and hatred. And so I think that often when we return to Baldwin, what we want is we want someone to acknowledge our emotions. But then also just to say at the same time, you feel this way because this place has been constructed in this way and it is all predicated on this false understanding of your not being human. And in this section, he just makes room for your emotions. For you to feel what you feel. But then also gives you something of a gift that you can take out into the outside world and use it to help you navigate this really difficult reality.
In the next essay, titled “Down at the Cross: Letter from a Region in My Mind,” he goes to interview Elijah Muhammad, the head of the Nation of Islam, and has this dinner. And it’s rare to read something where Baldwin is not the big dog in the room. What do you make of James Baldwin the reporter being packaged inside Baldwin the essayist?
JW: I felt for Baldwin at that moment. There are so many levels of awareness that he's sort of struggling with. He's not the most important person in the room and in the minds of the people around him. He's not the most erudite person in the room. And he's also aware of the fact that the Honorable Elijah Muhammad is courting him. [Muhammad] wants [Baldwin] to buy into his philosophy. And Baldwin is aware of the fact that he can't.
A couple of times throughout the essay he talks about the fact that, after this dinner, he's going to meet up with some white friends and he's going to have drinks. And these are people who he cares about and who he loves and who are part of his social circle. And who he can't just relegate to the category of white devil. It's very interesting to me how Baldwin is juggling all these different awarenesses and how, at the same time, there are things about the Black Muslims philosophy that he understands.
And I looked around the table. I certainly had no evidence to give them that would outweigh Elijah’s authority or the evidence o f their own lives or the reality of the streets outside.
He's a writer. So he sees the human. He observes the human. He understands. He's able to look at each of these people that he's interacting with and he's able to understand something of what they are struggling with and something of what they brought to this moment. All of that is what makes him the great writer who he is.
Go Tell It on the Mountain
When it comes to Baldwin’s fiction work, there are plenty of books worthy of examination. But there’s something special about Go Tell It on the Mountain . “He describes this as the book he had to write if he was ever going to write anything else,” says McKinley Melton, associate professor and chair of Africana studies at Rhodes College. “I often think of it as a revisitation of his childhood with a narrative perspective that knows and understands all of the things a young Baldwin wishes he had known and understood when he was 14.”
The novel follows a boy named John undergoing that same crisis of faith Baldwin described in The Fire Next Time . But he opens it a little differently in fiction.

Everyone had always said that John would be a preacher when he grew up, just like his father. It had been said so often that John, without ever thinking about it, had come to believe it himself. Not until the morning of his fourteenth birthday did he really begin to think about it, and by then it was already too late.
That last clause kind of reads like a horror story.
MM: There’s something deeply ominous about the way that that opening paragraph closes. You open with this idea of, oh, this is just an introduction to a young man who's stepping into a role that the father has laid out. You come into it feeling kind of hopeful and optimistic and, oh, what a beautiful thing that everybody's envisioning this future for this young man. And we think about everything that it means when people say, oh, that kid's going to be a preacher . We see him as an orator, we see him as an intellectual, we'll see him as charming, we see him as engaging. We see a leader when we look at this kid. And so there's something very optimistic about that opening that then turns by the end of the novel into. But that was actually the source of his doom.
I want to jump ahead a few pages. There’s this guy named Elijah. He’s a couple years older, and he teaches Sunday school.
John stared at Elisha all during the lesson, admiring the timbre of Elisha’s voice, much deeper and manlier than his own, admiring the leanness, and grace, and strength, and darkness of Elisha in his Sunday suit, wondering if he would ever be holy as Elisha was holy.
MM: This is another sentence that I often will pause with students to kind of think about and say, what's going on here? And then they just say, “Oh, my God, he has a crush.” Yeah, he has a crush. Absolutely. But then we look at it and, I look at this passage and, because of all of the ways that the different clauses bounce off of one another throughout the sentence, you're kind of leaving this saying, well, does John have the hots for Elisha? Because John is learning that he's probably gay. Or is John admiring Elisha because he is all of the things that John has been told he's supposed to be in terms of this kind of striving toward being a preacher when he grows up and the kind of idea of being saved in the idea of being holy, in the idea of looking good in a Sunday suit.
The middle chunk of the book goes into the lives of his aunt, his mother, and his step father. And I want to focus on his step father, Gabriel. And if you grew up in the church you know that the people who are sinners and then find God are often the most vociferously faithful. And Gabriel definitely fits that mold. There’s a bit where he has an affair with a woman named Esther, and he gets Esther pregnant.
Near the end of that summer he went out again into the field. He could not stand his home, his job, the town itself – he could not endure, day in, day out, facing the scenes and the people he had known all his life. They seemed suddenly to mock him, to stand in judgement on him; he saw guilt in everybody’s eyes.
John is scared of hell and eternal damnation. Gabriel seems more scared of other people, and very earthly judgements, right?
MM: I often think about the unfolding of this novel. We start with John in this moment of chaos and a lack of understanding. And then the novel takes us back through each of these characters who we come to understand better. We come to understand John better. He's struggling with sin in a space that feels deeply private, deeply unspoken. Gabriel is differently positioned because he's already in that position of prominence. He's standing at the pulpit. He's you know, they're both afraid of judgment. Right. But John is afraid of revelation. And Gabriel fears that everybody already knows. Gabriel is afraid of the judgment that comes based on the fact that, like, oh, they already know who I've always been .
But ultimately, both of them are struggling with this sense of judgment and condemnation and the fear of being, quote unquote, discovered for being less than the holy men that they have aspired to be. But I think what Baldwin is saying is: I'm not just critiquing the church, or the Black church, or the fundamentalist church. I'm asking us to think about what damage does it do to us when we are so deeply, deeply wedded to certain beliefs that don't allow us the fullness of our humanity? And if you're going to be sympathetic for John, you have to figure out a way to be sympathetic for Gabriel, even if his actions don't invite sympathy in the same way.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Their hypothesis is that watching excessive amounts of television reduces a person's ability to concentrate. The coming days and weeks will put that hypothesis to the test. —. Jonathan Wosen, STAT , 14 Nov. 2022. And my hypothesis is that this has changed the way the midterm electorate thinks. —.
2. 1. Advertisement. It follows that philosophy is in a sense both dualist and monist; it is a cosmic dualism inasmuch as it admits the possible existence of matter as a hypothesis, though it denies the possibility of any true knowledge of it, and is hence in regard of the only possible knowledge an idealistic monism.
14 Sentences with Hypothesis Examples. Hypothesis: Students who study for at least 3 hours every day are likely to perform better in their exams. It is important for college students to form a hypothesis before conducting any research project. Hypothesis: Attending lectures regularly can significantly improve academic performance.
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
Simple Hypothesis Examples. Increasing the amount of natural light in a classroom will improve students' test scores. Drinking at least eight glasses of water a day reduces the frequency of headaches in adults. Plant growth is faster when the plant is exposed to music for at least one hour per day.
Another example for a directional one-tailed alternative hypothesis would be that. H1: Attending private classes before important exams has a positive effect on performance. Your null hypothesis would then be that. H0: Attending private classes before important exams has no/a negative effect on performance.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis. You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain: The relevant variables. The specific group being studied.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
Here are some research hypothesis examples: If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep. If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad. If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower). If you leave a bucket of water uncovered ...
Competing in a Global Economy. ( 1990) His colleagues must surely be asking themselves whether they really need to test this hypothesis before making a change. Times, Sunday Times. ( 2011) First, that the lifestyle concept suggests hypotheses which are true by definition and therefore trivial.
Learning how to write a hypothesis comes down to knowledge and strategy. So where do you start? Learn how to make your hypothesis strong step-by-step here.
Hypothesis Testing Examples. We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you've seen some good hypothesis examples. We've included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses. Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
For example, to form a hypothesis sentence, people start wording by identifying independent and dependent variables, reviewing existing literature, and then creating a clear, testable prediction that outlines an expected relationship between defined elements (Reichardt, 2022). Besides, this step will enable people to become familiar with the ...
Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
Here are some good research hypothesis examples: "The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.". "Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.".
Q: Please show me example sentences with hypothesis . A: 'Even a religion that stresses faith above all else seeks evidence to confirm its hypotheses .'. 'Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the number of times segmentation arose.'. 'All of those hypotheses were proposed indirectly and may not be mutually exclusive to ...
Examples of If, Then Hypotheses. If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep. If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground. If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep. If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will heal with less scarring.
hypothesis: [noun] an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument. an interpretation of a practical situation or condition taken as the ground for action.
Sentences with Hypothesis. Hypothesis: The sun rises in the east. They formulated a null hypothesis to compare against the alternative. We need to revise the original hypothesis. They discussed the hypothesis with colleagues in their field. They formulated competing hypotheses to compare and contrast the findings.
Definition of Hypothesis. a proposed explanation or theory that is studied through scientific testing. Examples of Hypothesis in a sentence. The scientist's hypothesis did not stand up, since research data was inconsistent with his guess. Each student gave a hypothesis and theorized which plant would grow the tallest during the study.
Revised on June 22, 2023. The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test: Null hypothesis (H0): There's no effect in the population. Alternative hypothesis (Ha or H1): There's an effect in the population. The effect is usually the effect of the ...
226+9 sentence examples: 1. Let me enumerate many flaws in your hypothesis. 2. She wrote something to summarize her hypothesis. 3. The researcher sets up experiments to test the hypothesis. 4. Scientists have proposed a bold hypothesis. 5.
Some of these examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'the Old Testament.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Baldwin is heralded for being everything from an orator, activist and fashion icon. None of that would be true if he weren't a writer first. We asked fans to break down what made his writing work.
Taking the sentence in Table 2 as an example, the pattern configurations [2]-[3] and [5]-[6] are regarded as pattern flows, which means that the FN of this sentence equals two. Table 2. Examples of Pattern Tokenization. ... Therefore, the findings verify the research hypothesis, reflecting how the pattern grammar system can be treated as an ...