- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass

How to Write a Style Analysis Essay
Writing a style analysis essay may seem like a daunting task, but, by understanding the basic components of style analysis, it doesn’t have to be a dreaded chore. Analyzing is an ability that will help you in other aspects of life, too, like work and school. With practice and a discerning eye, you will be able to skillfully master the style analysis essay.
Understand the components of style before you begin an analysis of the work. The style of a literary work is the way in which it is written and how it communicates the author's meaning. Many components come together to form a work’s style, from the diction to the point of view. It’s important to familiarize yourself with these components so that you may better understand how they contribute to the ideas expressed in literature. (See the Resources for a glossary of literary terms.)
Read the work critically. Performing a style analysis requires a discerning reader. You won’t be reading the work as a general audience, but as an analyst. Look at it carefully, noting what the author writes, how it contributes to the work and what effect the style has on the reader. Bookmark examples of consistent style choices in the text, like how a character thinks or talks, and make notes that you may refer back to when writing your essay.
Accumulate sources for your essay. If your style analysis essay asks that you use only the text as a source, you don’t need to collect other written opinions, but many papers will require that you have a secondary reference. The best information will come from articles and critiques that explore the elements of style in the work. Check your library’s literary criticism section for book analysis to reinforce your paper.
Gather your ideas together so that you will have the general direction of the paper clear in your head before you write your essay. You don’t have to conform to a structured outline, but it’s important to know what you will say and how you want to say it. Start with the big picture. What effect does the general style of the work you’re analyzing have on it as a whole and on you as a reader? Outline examples that further your argument about the style of the piece.
Write your essay, examining how the components that you identified contribute to the overall effect of the text on the reader. Use examples that you noted in your reading to reinforce your argument. You don’t have to cite every type, but use specific examples that best showcase your argument. Remember that a style analysis is not a book report–you don’t want to summarize the work, but to analyze it instead. Use literary terms and make sure that your writing and source documentation conforms to MLA standards, unless otherwise instructed.
Rewrite the essay. Your final draft is just as important as the initial one. Look for basic errors. Ensure that the essay flows, is clear and concise, and presents arguments coherently. It's a good idea to have someone else look it over to point out mistakes that you may have missed.
- Western Michigan University: Writing Papers of Literary Analysis
Jessica Rutland lives in Austin, Texas, where she has worked as a copywriter and editor for two years. She received a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Texas.
Literary Focus
Roundtables

—Style Analysis—
When we refer to a writer's style, we mean the way authors or playwrights use various literary techniques to establish tone and convey theme. To make this process as simple as possible for students, we limit our discussion to what we call the "four pillars" of style analysis: diction, imagery, language, and syntax. We'll look at each of these pillars individually in the sections below.
I. Diction
To understand the significance of diction, or word choice, students first must differentiate between the denotation of a word and its connotation. By denotation we mean the definition found in the dictionary; by connotation we mean the attitude or feelings associated with the word. To make this difference clear to students, we provide three pairs of words that have similar denotations but very different connotations:

In the first example, if we refer to a dog as a "mutt," there is an element of disrespect in that designation, implying that the dog is of an inferior type. In the second example, two groups could be engaged in the exact same behavior that shows they find something funny, but the group described as "giggling" seems young and immature compared to a group that is "laughing." Boys and girls "giggle," whereas men and women "laugh." In the final example, if a teacher is described as "strict," it implies that she maintains order and discipline in the classroom. Even though a "strict" teacher may not be as much fun for students, the adjective carries an element of respect. If a teacher is described as "rigid," however, she may be so disciplined in her approach that she is seen as closed-minded and inflexible, which are obviously negative attributes.
Once students have been introduced to the concept of diction, we analyze a short passage from a literary work they are reading. For instance, in the opening description of Billy Pilgrim in Kurt Vonnegut's Slaughterhouse-Five , the narrator tells us that "Billy has come unstuck in time." When we ask students if the word "unstuck" has a positive or negative connotation, there is usually a pause. On one hand, being "unstuck" implies liberation and freedom, words that have positive connotations, but to be "unstuck in time" also implies a helplessness and lack of control, which is reinforced by the word "spastic" in the following excerpt.

Similar to our interpretation of AP prompts, we encourage students to look at words as not necessarily positive or negative, but as sometimes positive and negative. For Billy, becoming "unstuck in time" is a coping mechanism that helps him deal with the traumatic experiences in his life. By taking a passive, fatalistic approach to life, Billy protects himself from feeling pain in any particular moment. With that "freedom," however, comes a corresponding lack of control and disconnectedness from the reality of his own experience. Moments are seen as transitory and impermanent, and the result is that Billy suffers from perpetual anxiety, or "stage fright," since he has no idea "what part of his life he is going to have to act in next."
The purpose of identifying tone is to determine a narrator's attitude towards a subject. So how does the narrator feel about Billy's being "spastic in time"? As a temporary coping mechanism, it appears to be a successful strategy; as a way to live one's life, however, it appears to be an abject failure. To be "spastic" is to lack control and agency over one's own life. While we understand why Billy responds to trauma in this particular way, we should recognize that Vonnegut does not want us emulating Billy. Our job over the course of the novel is to determine what we can learn from Billy's experience and find a better way to deal with life's difficulties on our own.
II. Imagery
When we refer to an author or playwright's use of imagery, we mean descriptions that include any of the five senses: sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste. Sensory details not only make the reader experience a scene more vividly, but they also serve to establish the narrator's tone, or attitude, towards the subject.

In Leslie Marmon Silko's Ceremony , we are introduced to Tayo, another character who suffers from traumatic experiences in World War II. Silko uses imagery to immerse us in the opening scene so that we can vicariously see, hear, and feel what is going on inside Tayo's head as he lies sleeplessly on his bed after returning to the Laguna Pueblo reservation:

Visually, we can see the "old iron bed" that Tayo "tossed" restlessly upon, but the more dominant sensory detail is the "coiled springs" underneath the mattress that "kept squeaking even after he lay still again." In many ways Tayo is like those "coiled springs" under constant tension. The incessant squeaking triggers "humid dreams of black night," which combines a visual darkness with a tactile humidity that reminds him of the Pacific jungles that still haunt him. From out of the darkness comes a series of "loud voices" that are figuratively "rollling him over and over again" as if he were "debris caught in a flood." Silko makes us experience Tayo's hellish dreamscape through her use of vivid imagery—a disorienting combination of sight, sound, and touch that makes us intimately aware of Tayo's inner distress. Tayo cannot control the shifts that occur inside his mind that combine his present reality with his traumatic past. We know from Silko's use of imagery in the opening description that Tayo's life is in the balance, for he is currently helpless in confronting the confusion and despair that threaten to engulf him.
III. Language
When the AP refers to language in its prompts, they mean figurative language. To simplify this concept for students, we focus only on the three types of figurative language most often used in literature: metaphors, symbols, and allusions.

When authors or playwrights use metaphoric language, they are comparing one thing in terms of another. Similes are metaphors using "like" or "as" to make the comparison more explicit; personification is giving a non-human entity human characteristics. An element in a literary work may be symbolic if it represents something larger than the element itself. Allusions are indirect references to something outside the literary work for the purpose of comparison. The four most common types of allusions that we discuss with students are literary, mythological, historical, and biblical.
In the final soliloquy of Macbeth , William Shakespeare uses all three types of figurative language to show Macbeth's hopelessness and despair after receiving word that Lady Macbeth has died, most likely by suicide. As Macbeth faces his own imminent death as he prepares to defend Dunsinane against his fellow countrymen who have rebelled against his tyrannous rule, he contemplates the absurdity and meaninglessness of life:

When Macbeth says, "Out, out, brief candle," he seems to welcome the thought of his own death, comparing life to a symbolic candle that burns itself down into nothingness. Shakespeare has Macbeth follow this line by stating, "Life's but a walking shadow," which seems to be an allusion to Psalms 23:4 in the Old Testament:
Yea, though I walk through the valley of the shadow of death, I will fear no evil: for thou art with me; thy rod and thy staff they comfort me.
The irony of this biblical allusion is that instead of being comforted by the presence of God in the face of death, Macbeth finds himself utterly alone and in despair. Macbeth's only solace is that perhaps there is no God nor any purpose in life. Instead of a life of goodness and faith, Macbeth has embraced evil and a belief in "nothing." The final metaphor that Macbeth uses is one of a "poor player," or actor, who "struts and frets his hour upon the stage / And then is heard no more." By having Macbeth equate life to acting upon a stage, Shakespeare seems to imply that we all play roles in life, some that may not reflect who we really are. In this final soliloquy, Shakespeare perhaps wants us to remember that Macbeth was once admired and respected for his courage and virtue. Shakespeare suggests that Macbeth's life is a tragedy because he was once capable of goodness. By seeing himself as an actor upon a stage, we imagine that the real Macbeth could have been someone far different from the villain he portrayed.
IV. Syntax
For most students, the most daunting and least utilized pillar of style analysis is syntax, which refers to the way that words are structured and organized in a text. When we refer to syntax, we think of how sentences and paragraphs are built — which includes everything from word order and arrangement to verb tenses and punctuation.

An examination of a writer's syntax requires a subtle and nuanced reading of the text, so we advise students not to put too much pressure on themselves to include a syntactical analysis in their essays. If they focus only on diction, imagery, and language, they should have plenty to discuss. That being said, if they can include elements of syntax in their analysis, it will be impressive to the reader because it is so rarely done.
The first thing we tell students when analyzing the syntax of a passage is to look for any structural elements that seem unusual or interesting. For instance, in the final chapter of Julie Otsuka's When the Emperor Was Divine , the narration shifts from the third-person limited perspective of the mother and her children that was used in the previous chapters to the first-person narration of the father in the final chapter.

From what we know about the mild-mannered father from the previous chapters, we understand that he is in no way guilty of any of the crimes to which he now confesses. In fact, the seemingly never-ending laundry list of supposed crimes he has committed embodies all the accusations that were made against Japanese-Americans in World War II. By shifting to first-person narration, Otsuka gives us an opportunity to enter into the psyche of the falsely accused. The short, terse sentences reveal the pain and bitterness of being considered disloyal simply because of one's racial identity. Furthermore, by having the first-person narrator address the abstract "you" in this final chapter, Otsuka makes all Americans who failed to intervene on behalf of Japanese-Americans complicit in the crime of their internment. Otsuka's shift in style also represents a shift in tone. The readers being addressed as "you" are now put in a defensive position, feeling attacked for things for which we may not feel personally responsible. Now we know, Otsuka seems to suggest, how it feels to be falsely accused. The father also reveals his anger and frustration when he sarcastically repeats, "You were right. You were always right." Despite his innocence, the father knows that he will always be viewed as suspicious, regardless of what he says or does.
When first introducing the "four pillars" of style analysis to students, we focus on one element at a time so as not to overwhelm them. Once students are comfortable, however, we have them work in small groups to work on all four elements at once, as they do when analyzing the following passage from our unit on Margaret Atwood's The Handmaid's Tale :
Once students understand the fundamentals of style analysis and how diction, imagery, language, and syntax help authors establish tone and convey theme, they are ready to write an AP Passage Analysis essay, which is the ultimate assessment of a student's ability to read a passage closely to determine the author's intent.
We aspire to be an active, engaged professional development community. Please submit your questions, comments, or suggestions to join the conversation!
<< Setting
AP Passage Analysis >>
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Citation Generator
Writing Guides
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Human Editing Service
- Essay Hook Generator
Writing Guides / Mastering the Rhetorical Analysis Essay: A Comprehensive Guide
Mastering the Rhetorical Analysis Essay: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Want to know how to write a rhetorical analysis essay that impresses? You have to understand the power of persuasion. The power of persuasion lies in the ability to influence others’ thoughts, feelings, or actions through effective communication. In everyday life, it plays a crucial role in shaping opinions, making decisions, and driving actions. Whether in personal relationships, professional settings, or public discourse, persuasion helps individuals advocate for their ideas, negotiate solutions, and motivate others toward desired outcomes. Mastering persuasion can enhance leadership, improve negotiation skills, and foster better interpersonal connections.
A rhetorical analysis essay examines how an author or speaker uses language and rhetorical strategies to persuade their audience. The purpose of this type of essay is to analyze the effectiveness of these techniques in achieving the author’s goals. This involves looking at various elements, such as the use of ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical arguments), as well as the author’s style, tone, and structure. By understanding how these elements work together to influence the audience, the essay provides insight into the power and impact of the author’s message.
Understanding rhetorical strategies is valuable for several reasons: critical thinking, effective communication, enhanced persuasion, improved audience awareness, and analytical skills. Rhetoric enhances your ability to analyze and evaluate arguments. By recognizing how persuasive techniques are used, you can better assess the strengths and weaknesses of different viewpoints and arguments.
Knowing rhetorical strategies helps you craft your own arguments more persuasively. Whether writing, speaking, or engaging in debate, you can use these strategies to connect with your audience and convey your message more compellingly.
Understanding these strategies allows you to influence others more effectively. By applying appropriate rhetorical techniques, you can better achieve your goals in personal, professional, and public contexts.
Rhetoric helps you tailor your message to the needs and preferences of your audience. By understanding what appeals to different audiences, you can adjust your communication to be more effective. It also develops your ability to dissect complex texts and speeches, leading to a deeper comprehension of both the content and its delivery. This skill is beneficial in both academic and everyday contexts. Overall, mastering rhetorical strategies equips you with the tools to both critically evaluate and create persuasive messages.
In this article, we will examine the various elements of a rhetorical analysis essay. We will start by understanding the basics of rhetoric, cover the steps to writing a rhetorical essay, provide an example essay, and finish with tips.
Understanding the Basics of Rhetoric
Before you can write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have to start by defining rhetoric. Rhetoric is the art of persuasion through effective communication. It involves using language strategically to influence, convince, or inform an audience. Rhetoric aims to achieve a specific goal, such as persuading an audience to adopt a particular viewpoint, take action, or understand a concept. Effective rhetoric takes into account the audience’s needs, values, and emotions. Understanding your audience helps tailor your message to resonate with them.
Rhetoric uses ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade. Ethos establishes credibility and trustworthiness. It involves demonstrating authority or expertise on the topic. Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions, aiming to connect on an emotional level and create a response. Logos uses logical arguments and evidence to persuade through reason and rationality.
Rhetoric also involves choosing the right style and delivery methods. This includes the use of language, tone, structure, and persuasive techniques to convey the message effectively. The effectiveness of rhetoric often depends on the context in which it is delivered, including cultural, social, and situational factors. Overall, rhetoric is a crucial skill in various fields, including politics, business, and personal communication, as it enables individuals to influence and engage others through their use of language effectively.

The Rhetorical Situation
The rhetorical situation encompasses the various elements that define and shape the act of communication. Understanding these elements helps in crafting compelling messages and analyzing how they work.
The speaker or writer is the individual or entity delivering the message. This can be a person, a group, or an organization. The speaker’s credibility, background, and perspective play a significant role in how the message is received. Understanding the speaker’s ethos, or their character and authority on the subject, is crucial for evaluating their arguments.
The audience is the recipients or target of the message. The audience includes the individuals or groups who will read, listen to, or view the communication. Knowing the audience’s characteristics, such as their interests, values, and prior knowledge, helps tailor the message to effectively reach and engage them. Audience analysis helps predict how the message will be perceived and how to address potential objections or questions.
The purpose is the goal or intention behind the communication. The purpose defines what the speaker or writer aims to achieve with the message. This could be to persuade, inform, entertain, or motivate the audience. Clearly defining the purpose helps in structuring the message and focusing on the key points that need to be communicated. The effectiveness of the communication often hinges on how well the purpose aligns with the audience’s needs and expectations.
The context is the surrounding environment or situation in which the communication occurs. Context includes the time, place, cultural, social, and situational factors that influence the message. It can affect both the content and delivery of the communication. For instance, a message delivered during a political campaign may have different implications than the same message delivered in a casual social setting. Understanding the context helps in addressing relevant issues and ensuring the message is appropriate and effective for the given situation.
By analyzing these elements, you can gain a deeper understanding of how effective communication operates and how to craft messages that are appropriate for specific situations and audiences.

The Rhetorical Triangle (Ethos, Pathos, Logos)
The rhetorical triangle consists of three key elements—ethos, pathos, and logos—that work together to create persuasive and effective communication.
Ethos refers to the credibility and ethical appeal of the speaker or writer. Establishing ethos involves demonstrating expertise, reliability, and trustworthiness. It’s about convincing the audience that the speaker or writer is knowledgeable and has a good character, making them credible sources on the topic. Ethos can be established through:
- Professional Experience : Showcasing relevant qualifications or experience.
- Reputation : Leveraging a solid reputation or previous successes.
- Tone and Presentation : Using a respectful and professional tone and presenting information clearly and accurately.
- Alignment with Values : Connecting with the audience’s values and beliefs to build trust.
Pathos refers to the emotional appeal used to persuade the audience. Pathos involves tapping into the audience’s emotions to create a connection and influence their attitudes or decisions. By evoking feelings such as sympathy, anger, joy, or fear, the communicator can make the message more compelling and memorable. Techniques for using pathos include:
- Anecdotes : Sharing personal stories or testimonials that resonate emotionally.
- Imagery : Using vivid language and imagery to evoke specific feelings.
- Emotional Language : Employing words and phrases that elicit emotional responses.
Logos refers to the logical appeal based on reason and evidence. Logos involves using logical arguments, facts, statistics, and reasoning to persuade the audience. It’s about presenting a well-structured argument supported by evidence that appeals to the audience’s rationality. Effective use of logos includes:
- Evidence : Providing concrete data, examples, and facts.
- Reasoning : Using clear, rational arguments and logical connections.
- Clarity : Presenting information in a coherent and organized manner to facilitate understanding.
The rhetorical triangle demonstrates how ethos, pathos, and logos interact to create persuasive messages. Ethos builds credibility, pathos appeals to emotions, and logos relies on logic and evidence. Effective communication often involves balancing all three elements to engage the audience and achieve the desired outcome.
Rhetorical Devices and Strategies
Writers use various rhetorical devices in essays and strategies to help persuade their audience. Understanding these devices is critical when you want to write an effective rhetorical analysis essay because you need to be able to recognize them and analyze them in your source material.
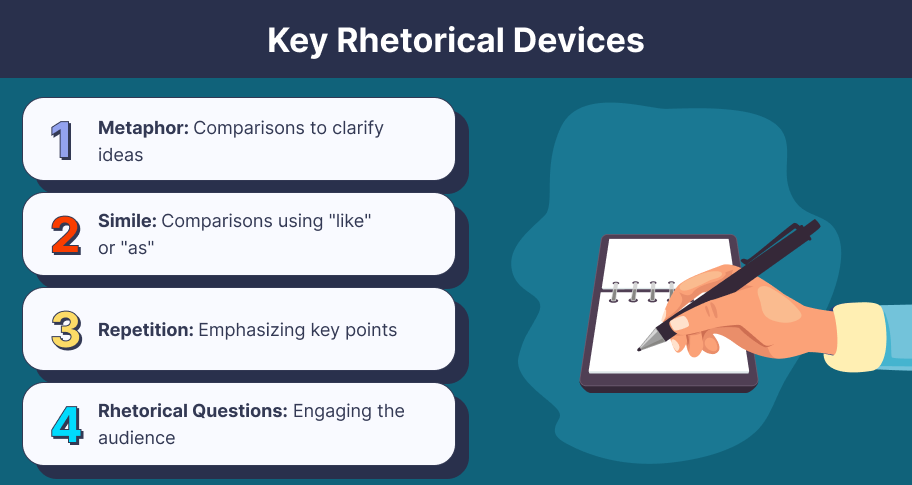
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two unlike things by stating one is the other, suggesting a similarity between them. “Time is a thief” is an example of a metaphor. Metaphors help make abstract concepts more concrete and relatable, enhancing understanding and emotional impact.
A simile is a figure of speech that compares two unlike things using “like” or “as.” “Her smile was like sunshine” is an example of a simile. Similes clarify ideas and evoke imagery, making arguments more vivid and engaging.
Repetition refers to the intentional repetition of words or phrases to emphasize a point or theme. One of the most famous examples of repetition is in Dr. King’s I Have a Dream speech. Repetition reinforces vital messages, making them more memorable and persuasive.
Alliteration is the repetition of the same initial consonant sound in words that are closely positioned. Many tongue-twisters feature repetition, like “Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.” Alliteration adds rhythm and emphasis, making phrases catchier and more engaging.
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that is not meant to be taken literally; it is used for emphasis. “I’ve told you a million times” is a hyperbole parents often use with their children. Hyperbole draws attention to critical points and conveys strong emotions or urgency.
The opposite of hyperbole is an understatement, which is deliberately downplaying the significance of something. “It’s just a small scratch” (when referring to a significant dent) is an example. Understatement can draw attention to the magnitude of an issue by minimizing it, often adding a layer of irony or emphasis.
An analogy is a comparison between two things that are alike in some respects, often used to explain or clarify. An example of an analogy is, “Just as a sword is the weapon of a warrior, a pen is the weapon of a writer.” Analogies help clarify complex ideas by relating them to familiar concepts, making arguments more understandable and persuasive.
Many writers use rhetorical questions, which are questions that they ask to make a point rather than to seek an answer. A politician asking, “Isn’t it time for a change?” is not seeking an answer but trying to encourage people to vote for them. Rhetorical questions engage the audience and prompt them to think about the issue, reinforcing the speaker’s position.
Irony is one of this writer’s favorite rhetorical tools. It refers to a contrast between expectation and reality, often used to highlight discrepancies. A fire station burning down is an example of irony. O’Henry’s short stories are some of the best examples of irony available. Irony can highlight contradictions or absurdities, adding humor or emphasizing a point.
It is essential not to overlook the role that pathos plays as a rhetorical tool. An emotional appeal uses emotions to persuade. Pathos creates an emotional connection, influencing the audience’s feelings and responses.
Devices like metaphors and similes clarify complex ideas by drawing comparisons to familiar concepts. Repetition, alliteration, and rhetorical questions make messages more engaging and memorable. Hyperbole, pathos, and irony tap into emotions, making the argument more compelling and relatable. Analogies and rhetorical questions encourage deeper thinking and reinforce the speaker’s position. By incorporating these rhetorical devices, communicators can effectively persuade their audience, making their arguments more impactful and engaging.
Steps to Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
1. choose a suitable text.
Selecting a text rich in rhetorical devices is crucial when writing a rhetorical analysis essay. It offers substantial material for analysis, lets you highlight the author’s skill, provides clear examples of various rhetorical strategies, enhances critical thinking, engages the reader, and strengthens argumentation.
A text with numerous rhetorical devices offers a wealth of material for analysis. This variety allows for a more comprehensive examination of how different strategies contribute to the effectiveness of the text. It enables you to explore how various devices interplay to persuade or engage the audience.
Analyzing a text rich in rhetorical devices highlights the author’s skill in crafting their message. It provides insight into how deliberate choices in language and structure enhance the overall persuasive impact. This can reveal the author’s intent and the nuances of their argument.
A text rich in rhetorical devices allows you to clearly demonstrate how specific strategies—such as ethos, pathos, and logos—are employed. It shows how the author builds credibility, appeals to emotions, and uses logical arguments to persuade their audience.
With a variety of rhetorical devices, you can offer concrete examples to support your analysis. This strengthens your argument by showing how the author’s use of devices directly impacts the effectiveness of the text.
Analyzing a text with rich rhetorical devices challenges you to think critically about the author’s techniques. It encourages a deeper understanding of how language influences perception and how different strategies can be used to achieve specific effects.
A text with engaging rhetorical devices is more likely to captivate your interest and that of your readers. This engagement can make your analysis more compelling and insightful as you are more invested in examining how the text works.
When a text is rich in rhetorical devices, it provides multiple angles for discussing how the author’s choices contribute to their argument. This can help you build a more nuanced and robust analysis, making your essay more effective.
Selecting a text rich in rhetorical devices is essential for writing a thorough and insightful rhetorical analysis essay. It offers diverse examples and strategies to explore, enhances your ability to demonstrate how the text persuades its audience and enriches your analysis by revealing the intricacies of rhetorical craftsmanship.
Here are some examples of suitable texts for rhetorical analysis essays across various genres:
- “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King Jr. : A powerful speech addressing racial injustice and promoting equality, rich in rhetorical devices like metaphors, repetition, and pathos.
- “The Gettysburg Address” by Abraham Lincoln : Known for its use of ethos, logos, and pathos to unify and inspire a nation during the Civil War.
Advertisements
- Apple’s “Think Different” Campaign : Features persuasive techniques such as ethos and pathos to position Apple as innovative and revolutionary.
- Nike’s “Just Do It” Campaign : Uses ethos and pathos to create a motivational and empowering brand image.
- “Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King Jr. : A compelling essay that uses logos, ethos, and pathos to argue against racial segregation and injustice.
- “A Modest Proposal” by Jonathan Swift employs satire and irony to critique British policy towards the Irish, which is rich in rhetorical devices.
- Op-eds from The New York Times or The Guardian : These pieces often use rhetorical strategies to argue for or against specific policies or issues, providing ample material for analysis.
- “The Case for Reparations” by Ta-Nehisi Coates : Uses historical examples and emotional appeals to argue for reparations for African Americans.
Political Cartoons
- Political cartoons by artists like Gary Trudeau or Thomas Nast : Utilize visual rhetoric and satire to comment on political and social issues.
Literary Works
- “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald : Rich in metaphor, symbolism, and rhetorical style, particularly in the character of Gatsby and the narrative’s social commentary.
- “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen Offers examples of irony and social critique through its characters and plot.
Media Clips
- TED Talks : Various TED Talks feature robust rhetorical strategies in addressing diverse topics, such as Simon Sinek’s “How Great Leaders Inspire Action.”
- Political Campaign Ads : Political campaign ads often use rhetoric to persuade voters, making them suitable for analysis.
Public Service Announcements (PSAs)
- “This Is Your Brain on Drugs” Campaign : Uses emotional appeals and stark imagery to discourage drug use.
- “Dove Real Beauty” Campaign : Employs pathos and ethos to promote body positivity and self-esteem.
These texts are ideal for rhetorical analysis as they provide rich examples of how language, imagery, and structure can be used to persuade, inform, or entertain. They each offer different angles for examining rhetorical strategies and their effectiveness.
2. Carefully Read and Analyze the Text
- Active Reading
It is essential to start with active reading. While reading the text, you want to be able to answer the following questions:
- What is the author’s main argument or message?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What rhetorical appeals are used?
- What rhetorical devices are employed?
- How effective is the author’s use of rhetoric?
You can use active reading to answer those questions. Active reading is an engaged and purposeful approach to reading that involves interacting with the text to enhance understanding and retention. Unlike passive reading, where one merely reads through the material, active reading requires the reader to engage with the content actively.
Skim the headings, subheadings, and introductory paragraphs to get an overview of the main ideas and structure. This will help you identify key terms and concepts that might be important.
Ask questions about the text before, during, and after reading to clarify understanding and maintain focus. Formulate questions such as “What is the author’s purpose?” or “What evidence supports this argument?”
Annotate in order to answer those questions. Highlight or underline important points and key details. Make notes in the margins to summarize information, jot down questions, or highlight significant points. After you finish a section, summarize it—paraphrase sections of the text in your own words to ensure comprehension. Write summaries of paragraphs or sections to capture the main ideas.
Once you have finished reading, think critically about the text’s arguments, biases, and implications. Consider the author’s purpose and whether the evidence supports their claims. Was the author effective at accomplishing their goals?
Active reading is particularly useful for academic study, professional development, and any context where deep comprehension and critical analysis are essential.
3. Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of a paper. It is typically one to two sentences long and clearly articulates the central argument or interpretation that the writer intends to support throughout the essay. In a rhetorical analysis essay, the thesis statement plays a crucial role in guiding the direction and focus of the analysis.
The rhetorical analysis essay thesis statement outlines the specific rhetorical strategies or elements of the text that will be analyzed. For example, it might focus on how the author uses ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade the audience.
It also guides the argument and sets the direction. It presents the central argument or interpretation regarding how effectively the author uses rhetorical techniques to achieve their purpose. The thesis statement helps organize the analysis by indicating which aspects of the rhetorical situation (such as the speaker’s credibility, emotional appeals, or logical arguments) will be examined.
The thesis provides a roadmap to your essay and frames the discussion. It often hints at the main points or sections of the essay, guiding readers on what to expect in the analysis. For instance, a thesis might indicate that the essay will explore how the speaker’s credibility (ethos), emotional appeals (pathos), and logical arguments (logos) contribute to the overall persuasiveness of the text. It serves as the foundation for the analysis, helping to ensure that each section of the essay supports and develops the central argument or claim made in the thesis.
Your thesis statement also needs to engage the reader so that they keep reading. A strong thesis statement presents a clear and intriguing argument that captures the reader’s attention and encourages them to read further.
Looking at an example of a thesis statement of a rhetorical analysis essay, we can break down its elements:
“In his speech, Martin Luther King Jr. effectively uses emotional appeals (pathos), ethical arguments (ethos), and logical reasoning (logos) to persuade his audience of the necessity of civil rights reform, demonstrating how a powerful rhetorical strategy can mobilize public support and drive social change.”
In this example, the thesis specifies that the essay will analyze how King uses emotional appeals, credibility, and logical arguments. It outlines the main areas of focus for the analysis. It provides a preview of what the reader can expect in the essay.
Overall, the thesis statement is a critical component of a rhetorical analysis essay. It provides a clear and focused argument that guides the analysis of how the author’s rhetorical choices influence their audience.
“In Apple’s ‘Think Different’ advertising campaign, the use of minimalist design and inspirational messaging (ethos and pathos) combined with the logical positioning of Apple as a symbol of innovation (logos) effectively rebrands the company as a leader in creativity and individuality, showcasing how branding strategies can influence consumer perception and loyalty.”
This thesis examines the use of design and messaging in advertising, focusing on how these elements create credibility, evoke emotions, and present logical arguments to enhance brand identity.
“In his editorial ‘The Case for Climate Action,’ Bill McKibben utilizes compelling statistics and scientific evidence (logos), personal anecdotes about environmental impact (pathos), and his established expertise in environmental issues (ethos) to persuade readers of the urgent need for climate change intervention, illustrating the power of combining empirical data with emotional and ethical appeals to drive public action.”
The thesis statement addresses McKibben’s use of data, personal stories, and credibility, aiming to analyze how these rhetorical strategies contribute to his persuasive argument about climate action.
4. Create a Detailed Outline
Organization is crucial in a rhetorical analysis essay outline because it ensures a clear, logical, and coherent presentation of your analysis. Effective organization matters. A well-organized essay outline helps you present your thesis and main points clearly, guiding readers through your analysis. It ensures that each part of your essay builds upon the previous one, reinforcing your argument.
Organizing your essay into distinct sections—such as introduction, analysis of rhetorical strategies, and conclusion—helps maintain a logical flow. It allows you to systematically examine how the author’s rhetorical choices contribute to their argument or purpose. An outline helps you stay focused on the specific rhetorical devices and strategies you plan to analyze. By breaking down your essay into sections, you can ensure that each rhetorical element is addressed in detail without deviating from your main argument.
With a structured outline, you can write more efficiently, as you have a clear roadmap to follow. It reduces the likelihood of writer’s block and helps you organize your thoughts before drafting. A well-organized outline contributes to the overall coherence and unity of your essay. It ensures that your analysis is consistent and that all points are relevant to your thesis, creating a more persuasive and compelling argument.
Finally, an outline allows for easier revision, as you can adjust the structure and flow of your argument before committing to the entire draft. This makes it simpler to identify and address any gaps or weaknesses in your analysis.
Effective organization in an outline is essential for crafting a clear, logical, and focused rhetorical analysis essay. It ensures that your argument is presented coherently and that each part of your analysis contributes to your overall thesis.
Here’s a sample outline form for a rhetorical analysis essay, which you can adapt to fit the specific text and rhetorical strategies you’re analyzing:
I. Introduction
A. Hook : Engage the reader with an exciting opening statement related to the text or its rhetorical elements.
B. Background Information : Provide brief context about the text, including its author, title, and purpose.
C. Thesis Statement : State the central argument of your analysis, outlining how the author’s rhetorical strategies achieve their purpose.
II. Summary of the Text
A. Overview : Summarize the main points or arguments of the text.
B. Purpose : Describe the primary goal or purpose of the text.
III. Analysis of Rhetorical Strategies
A. Ethos (Credibility)
1. Explanation : Define how the author establishes credibility or authority.
2. Evidence : Provide examples from the text that demonstrate the use of ethos.
3. Analysis : Discuss the effectiveness of these strategies in persuading the audience.
B. Pathos (Emotional Appeal)
1. Explanation : Define how the author appeals to the emotions of the audience.
2. Evidence : Provide examples from the text that demonstrate the use of pathos.
3. Analysis : Discuss the impact of these emotional appeals on the audience’s response.
C. Logos (Logical Appeal)
1. Explanation : Define how the author uses logic and reasoning to persuade the audience.
2. Evidence : Provide examples from the text that demonstrate the use of logos.
3. Analysis : Evaluate the effectiveness of these logical arguments in supporting the author’s purpose.
D. Additional Rhetorical Devices
1. Device 1 (e.g., Metaphor) – Explanation : Define the rhetorical device. – Evidence : Provide examples from the text. – Analysis : Assess the role and effectiveness of the device in the text.
2. Device 2 (e.g., Repetition) – Explanation : Define the rhetorical device. – Evidence : Provide examples from the text. – Analysis : Evaluate the impact of this device on the overall argument.
IV. Evaluation of Overall Effectiveness
A. Integration of Strategies : Discuss how the author’s use of ethos, pathos, logos, and other rhetorical devices work together to achieve their purpose.
B. Audience Impact : Analyze how these strategies affect the intended audience and contribute to the text’s overall effectiveness.
V. Conclusion
A. Restate Thesis : Summarize how the rhetorical strategies analyzed support the thesis.
B. Summary of Main Points : Recap the key findings from your analysis.
C. Significance : Discuss the importance of understanding these rhetorical strategies in the context of the text and its broader implications.
This outline provides a structured approach to analyzing the rhetorical elements of a text, ensuring that your essay is clear, focused, and well-organized. Adjust the sections as needed based on the specific text and your analysis.
5. Write the Essay
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay introduction involves setting up the context for your analysis, introducing the text, and presenting your thesis statement. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to craft a practical introduction. Start with a hook to capture the reader’s interest and set the stage for your analysis. Provide context by giving the reader background information on the text you will analyze. Include the full title of the text. Mention the author’s name and any relevant background that enhances understanding. Briefly note when and where the text was published, if relevant. Explain the circumstances under which the text was created (e.g., historical context, intended audience).
You want to summarize the text. Remember, a summary is a concise overview of the main argument or message of the text. Highlight the key arguments or themes of the text and describe what the author aims to achieve with the text (e.g., to persuade, inform, entertain). You do not need to go into detail in the summary because you will go into detail in the body of your essay.
Your summary needs to introduce the rhetorical analysis. Then, it leads to the specific aspects of the text that will be analyzed. Mention the main rhetorical strategies or devices that will be discussed (e.g., ethos, pathos, logos). The essay will analyze how these strategies contribute to the text’s effectiveness.
Finally, present your thesis statement. This should be the last sentence of two of your introduction. Clearly state the central argument of your essay. Summarize how the rhetorical strategies are used to achieve the author’s purpose. Briefly mention the critical points of your analysis (e.g., how ethos, pathos, and logos are employed).
Body Paragraphs
In a standard five-paragraph essay, you will have three body paragraphs. Each of those paragraphs should focus on one of the three points in the triangle—ethos, pathos, and logos. It does not matter which order you address them, but you need to address all three of them.
One body paragraph should focus on ethos or credibility. Define how the author establishes credibility or authority. Provide examples from the text that demonstrate the use of ethos. Discuss the effectiveness of these strategies in persuading the audience.
One body paragraph should focus on pathos or emotional appeal. Define how the author appeals to the emotions of the audience. Provide examples from the text that demonstrate the use of pathos. Discuss the impact of these emotional appeals on the audience’s response.
One body paragraph should focus on logos or logical appeal. Define how the author uses logic and reasoning to persuade the audience. Provide examples from the text that demonstrate the use of logos. Evaluate the effectiveness of these logical arguments in supporting the author’s purpose.
Writing a rhetorical analysis essay conclusion involves summarizing your analysis, reflecting on its significance, and reinforcing your thesis. Start with restating your thesis. Remind the reader of your main argument and how the rhetorical strategies support it. Paraphrase your thesis statement, summarizing the key points of your analysis.
Next, summarize the key points of the essay. Briefly review the main rhetorical strategies and their effects, reinforcing how they contribute to the effectiveness of the text. Highlight the significant rhetorical devices and strategies discussed in your essay and how they functioned to achieve the author’s purpose.
It is not enough to summarize; you also need to reflect on the significance of those points. Explain the broader implications of your analysis and the text’s impact on its audience. Discuss how the rhetorical strategies enhanced or diminished the overall effectiveness of the text. Reflect on how the text’s rhetorical choices affected its intended audience or contributed to its persuasive power.
Ideally, you want to use your conclusion to go beyond the text of your essay. Connect your analysis to more prominent themes or contemporary relevance. Discuss how the rhetorical strategies used in the text can be applied to other contexts or texts. If relevant, mention how understanding these strategies can be helpful in today’s media and communication landscape.
Finally, you want to close with a solid final thought. Leave the reader with a memorable insight or reflection related to the text and your analysis. Offer a final observation that ties back to your analysis. Encourage further thought or action based on the insights from your essay.
Revise and Edit
Proofreading and revising are crucial steps in the writing process because they ensure that your work is clear, accurate, and effective.
Proofreading helps identify and correct typographical, grammatical, and spelling errors that could undermine your credibility or confuse your readers. It ensures consistency in style, formatting, and terminology throughout the document, which is essential for professionalism and readability. By reviewing your work, you can spot and fix awkward phrasing or unclear sentences, improving overall clarity and comprehension.
There is no reason you should ever turn in a document with clarity, grammar, or punctuation errors. You can use tools online to check for these errors, and turning in an unchecked paper looks lazy.
Revising allows you to refine your arguments, enhance your ideas, and ensure that your writing effectively communicates your intended message. It helps you to structure your content logically and coherently. It gives you the opportunity to incorporate feedback from others, whether they are peers, editors, or instructors, leading to a more polished and persuasive piece. Revising provides the chance to add depth to your analysis or argument, strengthen your evidence, and ensure that all aspects of the assignment are fully addressed.
Overall, both proofreading and revising contribute to producing a high-quality, effective piece of writing that meets its purpose and engages its audience.

Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Title: The Persuasive Power of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” Speech
Introduction: Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech, delivered during the 1963 March on Washington, is a seminal text in American history. King’s masterful use of rhetorical strategies has cemented this speech as a powerful tool in the civil rights movement. This essay analyzes how King employs ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade his audience of the necessity for racial equality and justice.
Ethos: King establishes credibility through his role as a prominent civil rights leader and his deep moral authority. His reputation and commitment to nonviolent protest lend weight to his message. By referencing the founding documents of the United States, King aligns himself with the nation’s values, enhancing his ethical appeal. His position as a minister also adds to his moral credibility, allowing him to speak with conviction and integrity.
Pathos: King effectively uses emotional appeals to connect with his audience. His vivid imagery and evocative language, such as “a dream deeply rooted in the American dream,” evoke strong feelings of hope and urgency. By sharing personal stories and invoking the suffering of African Americans, he generates empathy and mobilizes his audience to support the cause of racial justice.
Logos: King’s logical arguments are grounded in historical and legal references. He cites the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution to demonstrate that racial inequality is contrary to American principles. His structured arguments and clear examples of injustices provide a rational basis for his call for change, reinforcing his credibility and appealing to the audience’s sense of justice.
Conclusion: Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech exemplifies the effective use of rhetorical strategies to inspire and persuade. Through his establishment of credibility, emotional appeals, and logical arguments, King crafts a compelling message that resonates with his audience and galvanizes support for the civil rights movement. His use of ethos, pathos, and logos ensures the speech’s enduring impact and relevance.
Analysis of Key Elements
- Establishment of Credibility: The essay highlights King’s role and reputation, showing how his credibility as a leader enhances his persuasive power.
- Moral Authority: Mentioning King’s background as a minister adds to his ethical appeal, making his arguments more persuasive.
- Emotional Appeals: The analysis identifies how King uses evocative language and imagery to stir emotions and build a connection with the audience.
- Personal Stories: By pointing out King’s use of personal and historical suffering, the essay demonstrates how pathos can engage the audience’s empathy and support.
- Logical Arguments: The essay notes King’s use of historical and legal references to build a rational case for civil rights.
- Structured Arguments: It highlights how clear, reasoned arguments support King’s call for change, appealing to the audience’s sense of justice and rationality.
4. Overall Analysis:
- Integration of Rhetorical Strategies: The essay effectively integrates the analysis of ethos, pathos, and logos, showing how each element contributes to the speech’s persuasive power.
- Impact and Relevance: By discussing the speech’s enduring impact, the analysis reinforces the effectiveness of King’s rhetorical strategies in achieving his goals.
This example illustrates how a rhetorical analysis essay can dissect a text’s components to understand and explain its effectiveness in persuasion.
Tips for Writing an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- Avoid summarizing the text; focus on analyzing its rhetorical elements.
- Use clear and concise language.
- Support your analysis with evidence from the text.
- Be objective and avoid personal bias.
- Proofread carefully before submitting.
In this article, we have covered the basics of rhetoric, covered the steps to writing a rhetorical essay, provided the form of an outline, provided an example essay, and provided tips to writers. However, nothing teaches someone how to analyze rhetoric like actually doing it. If you are working on rhetorical analysis, practice with different texts. You can find examples online or use our tools to see if your analysis matches what other readers and writers have noted.
Ready to start your essay? Download our Rhetorical Analysis Essay Worksheet for free.
If you found this article insightful and valuable, why not share it with your friends and followers on social media? Your support helps spread important information and spark meaningful discussions. We’d also love to hear from you! Leave a comment below or ask any questions you might have—we’re here to engage and provide answers. Let’s continue the conversation and connect with others who might benefit from this content!
Here are some resources that can help with writing rhetorical analysis essays:
“Everything’s an Argument” by Andrea A. Lunsford, John J. Ruszkiewicz, and Keith Walters
Offers an introduction to rhetorical analysis and the elements of effective argumentation.
“The Rhetorical Situation” by Lloyd Bitzer
Explores the concept of the rhetorical situation and its components.
“Rhetorical Analysis: A Brief Guide for Writers” by Philip K. Jason
Provides an overview of how to analyze rhetorical texts and write about them effectively.
Online Resources
Purdue OWL: Rhetorical Analysis
The Purdue Online Writing Lab offers comprehensive guidelines on writing rhetorical analysis essays, including strategies for analyzing texts and constructing arguments.
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Writing Center: Rhetorical Analysis
Provides practical advice on conducting a rhetorical analysis and includes examples and tips for structuring the essay.
Harvard College Writing Center: Rhetorical Strategies
This resource offers insights into different rhetorical strategies and how they can be used in analysis.
Academic Journals and Articles
“Rhetoric Review”
A journal that features scholarly articles on various aspects of rhetorical theory and practice, including rhetorical analysis.
“The Quarterly Journal of Speech”
Offers articles and research on rhetorical theory and practice, providing insights into rhetorical analysis techniques.
Google Scholar
Search for academic articles and papers on rhetorical analysis to find studies and examples relevant to writing your essays.
These resources should provide a solid foundation for understanding and writing rhetorical analysis essays, offering guidance on everything from basic concepts to advanced analytical techniques.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

Unlock Your Writing Potential with Our AI Essay Writing Assistant

The Negative Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Tactile Learning

Overcome Your Writer’s Block: Essay Writing Tips for Students

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Tips and Techniques
How to Write an Analytical Essay in 6 Steps
An analytical essay is an essay that meticulously and methodically examines a single topic to draw conclusions or prove theories. Although they are used in many fields, analytical essays are often used with art and literature to break down works’ creative themes and explore their deeper meanings and symbolism .
Analytical essays are a staple in academics, so if you’re a student, chances are you’ll write one sooner or later. This guide addresses all the major concerns about how to write an analytical essay, such as the preferred structure and what to put in the outline. Let’s start with an in-depth answer to the question, what is an analytical essay? Give your writing extra polish Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly
What is an analytical essay?
One of the seven main types of essay , analytical essays intricately examine a single topic to explain specific arguments or prove the author’s theories. They commonly deal with creative works like art, literature, film, or music, dissecting the creator’s artistic themes and revealing hidden meanings. However, they can also address other issues in realms like science, politics, and society.
Analytical essays are a type of expository essay , so they’re not supposed to express bias, opinions , or persuasions . Even when the author is trying to prove their own theory (or disprove an opposing theory), their argument should stick solely to facts and logic and keep the author’s personal feelings to a minimum.
An analytical essay example could be a deep dive into the character of Hamlet, but this topic itself could have multiple interpretations. Your essay could focus on whether or not Hamlet truly loved Ophelia, question the motives for his constant hesitation, or even attempt to prove the theory that he was mentally ill—after all, he did see apparitions!
How to structure an analytical essay
Although analytical essays tend to be more detailed, specific, or technical than other essays, they still follow the same loose essay structure as the rest:
1 Introduction
3 Conclusion
The introduction is where you present your thesis statement and prepare your reader for what follows. Because analytical essays focus on a single topic, the introduction should give all the background information and context necessary for the reader to understand the writer’s argument. Save the actual analysis of your topic for the body.
The body is the nucleus of your essay. Here you explain each separate point and offer evidence to support the thesis, breaking up your argument into paragraphs. While the introduction and conclusion are each usually just a single paragraph, the body is composed of many different paragraphs and often stretches out over pages, thereby making up most of the essay.
Every paragraph in the body still relates to your chosen topic and your thesis, but each paragraph should make a different point or focus on a different piece of evidence. For example, if your topic is about how Edgar Allan Poe uses the theme of death in his writing, one paragraph could explore the use of death in “The Tell-Tale Heart,” while a different paragraph could explore death in “The Raven,” and so on.
Finally, the conclusion wraps everything up. Conclusions usually don’t introduce new evidence or supporting details but instead reiterate the previous points and bring them all together to strengthen your original thesis. At this point your reader has sufficient background to understand the topic. With your evidential examples in mind, they’ll be more receptive to your main argument when you present it one last time.
How to write an analytical essay in 6 steps
The process of writing an analytical essay largely follows the same guidelines as all essay writing . Here we break down each individual step from start to finish.
1 Choose your topic
This step may be optional if your topic has been given to you as an assignment. If not, though, you should choose your topic with care.
Your topic should be specific enough that you’re able to discuss it thoroughly. If you choose a broad topic like “love in novels from Victorian England,” it’s unlikely you’ll be able to cover all Victorian novels in a single analytical essay (or even ten analytical essays!). However, narrowing the topic down to something such as “love in Jane Austen novels” makes your task more achievable.
That said, don’t be too specific, or you won’t have enough material to cover. Try to find a good middle ground: specific enough that you can discuss everything but general enough that you’ll be able to find enough research and supporting evidence.
2 Research your topic
Once you know your topic, you can begin collecting data and evidence to discuss it. If your analytical essay is about a creative work, you may want to spend time reviewing or evaluating that work, such as watching a film closely or studying the details of a painting. It’s also useful to review other people’s critiques of that work to inspire new ideas or reveal details you hadn’t noticed before.
Don’t forget to write down where you get your information, including page numbers for books or time codes if you’re watching visual media. You may need to reference these in your essay, so making a quick note about where you find your information while researching saves time later when you’re citing your sources .
It helps to know your thesis from the onset. However, you may realize during your research that your original thesis is not as strong as you thought. If this happens, don’t be afraid to modify it or choose a new one. In any case, by the time your research is finished, you should know what your thesis will be.
3 Create an outline
An essay outline gives you the opportunity to organize all your thoughts and research so you can put them in the optimal order. Ideally, you’ll have finished your research by now and made notes of everything you want to say in your analytical essay. The outline is your chance to decide when to talk about each point.
Outlines are typically broken up by paragraph. Each paragraph should explore an individual point you’re making and include your evidence or statistical data to back up that particular point. Be careful about trying to squeeze too much information into a single paragraph; if it looks excessive, try to break up the information into two or more paragraphs.
Feel free to move around or rearrange the order of paragraphs while outlining—that’s what this step is for! It’s much easier to fix structural problems now in the outline phase than later when writing.
4 Write your first draft
Now is the time you sit down and actually write the rough draft of your analytical essay. This step is by far the longest, so be sure to set aside ample time.
If you wrote your outline thoroughly, all you have to do is follow it paragraph by paragraph. Be sure to include each piece of evidence and data you had planned to include. Don’t worry about details like choosing the perfect wording or fixing every grammar mistake—you can do those later in the revisions phase. For now, focus solely on getting everything down.
Pay particular attention to how you start an essay. The introduction serves different purposes, such as telling the reader what to expect, providing background information, and above all presenting your thesis statement. Make sure your introduction checks all those boxes.
Likewise, be extra careful with your conclusion. There are special techniques for how to write a conclusion, such as using a powerful clincher and avoiding certain cliches like “in summary.” Conclusions usually hold more weight than the other paragraphs because they’re the last thing a person reads and can leave a lasting impression on them.
Finally, don’t forget to include transition sentences in between your body paragraphs when needed. Moving abruptly from one topic to the next can be jarring for the reader; transition sentences improve the essay’s flow and remove distractions.
5 Revise your draft
Your first draft is never meant to be perfect. Once you have all your ideas down on paper, it’s much easier to go back and revise . Now is the perfect time to improve your phrasing and word choice and edit out any unnecessary or tangential parts.
When you revise, pay particular attention to details. Try to find areas that you can remove to make your essay more succinct or passages that aren’t clear that need more explanation. Put yourself in the reader’s shoes: Will someone with no background knowledge still understand your points?
6 Proofread your essay
Last, it’s time to fix any grammar and spelling mistakes by proofreading . While it’s tempting to do this at the same time as your revisions, it’s best to do them separately so you don’t split your attention. This allows you to focus only on word choice, phrasing, and adding/removing content while revising and to concentrate solely on language mistakes during proofreading.
If you’re not confident in your grammar or spelling expertise, you can always use an app like Grammarly . Our app highlights any spelling or grammar mistakes directly in your text and gives proper suggestions on how to fix them. There are even features that help you choose the perfect word or adjust your writing to fit a certain tone. You can also copy and paste your writing to check your grammar and get instant feedback on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and other mistakes you might have missed.
Analytical essay outline example
If you’re having trouble, here’s an analytical essay example that shows how a proper outline or structure should look. The format here uses a five-paragraph essay structure, but for more complicated topics, you can add as many body paragraphs as you need.
Topic: Who is the real villain: Macbeth or Lady Macbeth?
Introduction
- Briefly describe the plot of Macbeth for those who aren’t familiar with it
- Thesis statement : Lady Macbeth is the real villain of Macbeth because she manipulates her husband into committing an atrocious crime
Body Paragraph 1
- Murdering the king is all Lady Macbeth’s idea
- Macbeth is initially against it until Lady Macbeth convinces him
Body Paragraph 2
- Lady Macbeth has her own individual character arc where she is driven mad by her guilt
- Her guilt insinuates she knows her actions are villainous, with appropriate consequences
- Cite quotations from her “Out, damned spot!” speech
Body Paragraph 3
- Macbeth decides to listen to Lady Macbeth, so he is still guilty
- Speculate that he still would not have murdered the king if not for Lady Macbeth
- Macbeth remains the main character because most scenes revolve around him, but the person acting against him most is Lady Macbeth
- Remind reader that Macbeth didn’t want to murder the king until Lady Macbeth convinced him
- Clincher : Macbeth is still the hero albeit a tragic one. But his main antagonist is not Macduff or the king or even the prophecy itself; it’s his wife.
Analytical essay FAQs
An analytical essay is an essay that deeply examines a single topic, often a creative work, to reveal certain conclusions or prove theories held by the essay’s author.
How is an analytical essay structured?
Analytical essays are structured like most other essays: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. However, the body paragraphs have a stricter emphasis on facts, logic, and empirical evidence compared to other essays.
What are the steps to writing an analytical essay?
As with all essays, you first research and then organize all your points into a working outline. Next, you write the rough draft with all the data and evidence collected during your research. Revise the rough draft when it’s finished to improve the phrasing and add/remove certain parts. Last, proofread the essay for any grammar or spelling mistakes.

How to Write a Literary Analysis: 6 Tips for the Perfect Essay
by Kaelyn Barron | 2 comments

Sometimes, you’ll want to read a book just for the pleasure of being entertained and taken to a different time or place, and see the world through the eyes of another.
Other times, however, like when you’re in your English Literature class or reading a classic, you’ll have to dig past the surface and look beyond the words on the page to understand the author’s message.
To do this, you can conduct your own literary analysis, and examine how the author uses various literary devices and techniques to artfully tell their story while delivering a larger message.
What Is a Literary Analysis?
The purpose of a literary analysis is to examine and deconstruct a work of literature to evaluate how the writer uses literary components to convey ideas.
A literary analysis is not a summary; it reaches past basic comprehension and facts. Often, this type of analysis will argue the theme, message, or purpose of a work by analyzing the writer’s use of literary devices and narrative techniques.
How to Write a Literary Analysis
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics.
1. Read the text and identify literary devices.
As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
The following is a checklist of the literary and narrative devices you should take note of while reading. (If possible, marking the text with a pencil can be very helpful.)
- Point of view: First, examine the point of view from which the story is told. Who is the narrator? Is it a character from the story, or an unknown, all-knowing figure? Do they have something at stake? Do you find them to be a reliable narrator? The answers to these questions can help shape your argument.
- Recurring symbols : Things like colors, rivers, and seasons may not seem significant at first glance, but together, and especially if they appear more than once, they can signify a deeper message. (Just look at this analysis of Hemingway’s “Hills Like White Elephants” as an example.) Our guide to symbolism explains some of the most common symbols in literature. If you come across these in a text, highlight or circle them. These symbols can also be part of an extended metaphors, so it’s helpful to keep track of them and look for any possible connections.
- Character motivation : The main character’s motivation is extremely important when it comes to advancing the plot. Ask yourself what the character wants, and what’s keeping them from getting it. Why is that thing important to them? Could it carry any deeper significance that its face value?
- Tone : Evaluate the writer’s tone . Do the words convey an anxious, ominous, or hopeful tone? Is it sad, witty, or whimsical? There are lots of ways to describe tone, and your assessment of this literary device can add important insight to your overall analysis.
- Diction : The author’s word choice, or diction , can also influence the piece’s tone. Do any words seem peculiar? Do you think the author chose that word over other synonyms for a reason? When a word stands out to you, ask yourself why it matters that this particular word was chosen over others.
- Imagery: What types of images does the author paint? This can be done explicitly through vivid descriptions, or implicitly through sensory details, or words that evoke the feelings of a place, emotion, or idea.
- Story structure : How is the story structured, and what impact does this have on the story? Is it told in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? What about the characters, setting, and their relation to the narrative?
- Themes : As you’re taking note of the literary elements outlined above, you’ll likely see certain patterns start to emerge. These patterns represent underlying themes . For example, in The Great Gatsby , recurring images, symbols, and even character motivations point to themes of excess, material wealth, and lost values.
- Characters : Your entire essay might actually be a character analysis, depending on your topic. However, you can also cite characterization as a supporting element to your main argument. For example, a specific character, major or minor, might embody an ideal, which contributes to a larger theme.
2. Develop your thesis.
If you’re writing an essay for your literature class, you’ll likely be given a prompt or question to answer with your essay.
If you’re not assigned a topic, you’ll have to think of one yourself. You may find it helpful to develop questions in order to get started.
The answer to this question is known as your thesis . In order to serve as the foundation for your analysis, your thesis needs to meet several conditions. It must be:
- Arguable : Your thesis should reflect your opinion or interpretation, not a fact. For example, “ The Grapes of Wrath is about a family’s migration from the Oklahoma Dust Bowl to California” is not a good thesis, because that’s a simple fact. However, “ Frankenstein is actually a feminist novel that rejects patriarchy” is an arguable interpretation, and we can argue for or against that statement with supporting evidence.
- Supported through textual evidence : While your thesis shouldn’t be an objective fact, you should still be able to support it with textual evidence and details.
3. Create an outline.
Once you have your thesis, it’s time to make a plan for how you’ll prove your argument. Look back at your notes about the literary and narrative devices above. These will serve as your supporting evidence.
Which elements will help you make the most compelling argument for your thesis? You might choose, for example, to build your argument around imagery, symbolism, and diction.
You can dedicate a section to each of these elements and cite evidence directly from the text to explain why and how they support your thesis.
Create an outline to organize your thoughts, so when it’s time to start writing, you won’t forget where you were going with those points.
4. Cite the evidence.
When you’re making your argument, it’s important that you have concrete evidence from the text to support your claims.
When you can, provide direct quotes and other concrete details. For example, if you’re using symbolism as supporting evidence for why Frankenstein is a feminist text, you should be able to cite passages that illustrate the claim.
5. Write your body paragraphs.
Using your outline and notes from the text, you can now start writing your literary analysis. However, may find it helpful to leave room for your introduction and start by writing the body paragraphs, which contain your main arguments.
You’ll already have all the points and supporting details you need in your outline, so you can jump right in, rather than trying to think of the perfect opening line to your essay.
This strategy can also be beneficial because as you develop your arguments, you may generate new ideas or slightly adjust your thesis.
6. Write your introduction and conclusion.
Once you’ve fleshed out your body paragraphs and written a compelling argument, you can write your introductory paragraph (using the thesis statement you developed earlier), as well as your conclusion, which should neatly tie up your argument and leave your readers with some final insights.
Types of Literary Criticism
When you’re analyzing literature, there are numerous lenses through which you can examine the work. For example, common types of literary criticism include ethical, feminist, historic, and social criticism.
This means that your analysis, interpretation, and evaluation of the work will be through one of those lenses.
Analyzing Literature
The best works of literature are filled with hints that will lead you to a bigger picture, and discovering those clues and how they fit together is what makes reading so fun.
Whether you want to ace your next English essay or refine your critical thinking skills, understanding how to analyze literature will lead you to a more fulfilling reading experience.
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- Symbolism: Common Examples in Life and Literature
- The Last Line of The Great Gatsby, Explained
- Extended Metaphors Explained: Definition, Purpose, and Examples from Literature
- 17 of the Most Common Literary Devices Every Reader and Writer Should Know
As a blog writer for TCK Publishing, Kaelyn loves crafting fun and helpful content for writers, readers, and creative minds alike. She has a degree in International Affairs with a minor in Italian Studies, but her true passion has always been writing. Working remotely allows her to do even more of the things she loves, like traveling, cooking, and spending time with her family.
We read a critic generously when they tackle a difficult topic, so one doesn’t judge Barron overly harshly for a seemingly shallow understanding of the subject. The article is useful as a starting point, giving us a chance to consider why so much of the content is ultimately indefensible. This blog has proven a genuinely valuable teaching resource. My students learn a great deal by exploring how this article manages to fall so far short of the promise in its title. Were her approach more thoughtful and erudite, such a rich opportunity to critically engage with literary theory would be denied Barron’s audience.
Hi Gregory, I’m sorry you found the article shallow. I intended it to be an overview for students, to walk them through the process of writing a solid literary analysis essay. What about the content do you find indefensible?

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (47)
- Book Promotion (29)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (54)
- How to Find an Editor (12)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (119)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (75)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (47)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (3)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (18)
- Technology (18)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (65)
- Word Choice (68)
- Writing a Book (72)
- Writing Fiction (196)
- Writing Nonfiction (83)

The Power of Analysis: Tips and Tricks for Writing Analysis Essays: Home
Crystal sosa.

Helpful Links
- Super Search Webpage Where to start your research.
- Scribbr Textual analysis guide.
- Analyzing Texts Prezi Presentation A prezi presentation on analyzing texts.
- Writing Essays Guide A guide to writing essays/
- Why is it important?
- Explanation & Example
- Different Types of Analysis Essays
Text analysis and writing analysis texts are important skills to develop as they allow individuals to critically engage with written material, understand underlying themes and arguments, and communicate their own ideas in a clear and effective manner. These skills are essential in academic and professional settings, as well as in everyday life, as they enable individuals to evaluate information and make informed decisions.
What is Text Analysis?
Text analysis is the process of examining and interpreting a written or spoken text to understand its meaning, structure, and context. It involves breaking down the text into its constituent parts, such as words, phrases, and sentences, and analyzing how they work together to convey a particular message or idea.
Text analysis can be used to explore a wide range of textual material, including literature, poetry, speeches, and news articles, and it is often employed in academic research, literary criticism, and media analysis. By analyzing texts, we can gain deeper insights into their meanings, uncover hidden messages and themes, and better understand the social and cultural contexts in which they were produced.
What is an Analysis Essay?
An analysis essay is a type of essay that requires the writer to analyze and interpret a particular text or topic. The goal of an analysis essay is to break down the text or topic into smaller parts and examine each part carefully. This allows the writer to make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more comprehensive understanding of it.
In “The Yellow Wallpaper,” Charlotte Perkins Gilman uses the first-person point of view and vivid descriptions of the protagonist’s surroundings to convey the protagonist’s psychological deterioration. By limiting the reader’s understanding of the story’s events to the protagonist’s perspective, Gilman creates a sense of claustrophobia and paranoia, mirroring the protagonist’s own feelings. Additionally, the use of sensory language, such as the “smooch of rain,” and descriptions of the “yellow wallpaper” and its “sprawling flamboyant patterns,” further emphasize the protagonist’s sensory and emotional experience. Through these techniques, Gilman effectively communicates the protagonist’s descent into madness and the effects of societal oppression on women’s mental health.
There are several different types of analysis essays, including:
Literary Analysis Essays: These essays examine a work of literature and analyze various literary devices such as character development, plot, theme, and symbolism.
Rhetorical Analysis Essays: These essays examine how authors use language and rhetoric to persuade their audience, focusing on the author's tone, word choice, and use of rhetorical devices.
Film Analysis Essays: These essays analyze a film's themes, characters, and visual elements, such as cinematography and sound.
Visual Analysis Essays: These essays analyze visual art, such as paintings or sculptures, and explore how the artwork's elements work together to create meaning.
Historical Analysis Essays: These essays analyze historical events or documents and examine their causes, effects, and implications.
Comparative Analysis Essays: These essays compare and contrast two or more works, focusing on similarities and differences between them.
Process Analysis Essays: These essays explain how to do something or how something works, providing a step-by-step analysis of a process.
Analyzing Texts
- General Tips
- How to Analyze
- What to Analyze
When writing an essay, it's essential to analyze your topic thoroughly. Here are some suggestions for analyzing your topic:
Read carefully: Start by reading your text or prompt carefully. Make sure you understand the key points and what the text or prompt is asking you to do.
Analyze the text or topic thoroughly: Analyze the text or topic thoroughly by breaking it down into smaller parts and examining each part carefully. This will help you make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more comprehensive understanding of it.
Identify key concepts: Identify the key concepts, themes, and ideas in the text or prompt. This will help you focus your analysis.
Take notes: Take notes on important details and concepts as you read. This will help you remember what you've read and organize your thoughts.
Consider different perspectives: Consider different perspectives and interpretations of the text or prompt. This can help you create a more well-rounded analysis.
Use evidence: Use evidence from the text or outside sources to support your analysis. This can help you make your argument stronger and more convincing.
Formulate your thesis statement: Based on your analysis of the essay, formulate your thesis statement. This should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes your main argument.
Use clear and concise language: Use clear and concise language to communicate your ideas effectively. Avoid using overly complicated language that may confuse your reader.
Revise and edit: Revise and edit your essay carefully to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Understanding the assignment: Make sure you fully understand the assignment and the purpose of the analysis. This will help you focus your analysis and ensure that you are meeting the requirements of the assignment.
Read the essay multiple times: Reading the essay multiple times will help you to identify the author's main argument, key points, and supporting evidence.
Take notes: As you read the essay, take notes on key points, quotes, and examples. This will help you to organize your thoughts and identify patterns in the author's argument.
Take breaks: It's important to take breaks while reading academic essays to avoid burnout. Take a break every 20-30 minutes and do something completely different, like going for a walk or listening to music. This can help you to stay refreshed and engaged.
Highlight or underline key points: As you read, highlight or underline key points, arguments, and evidence that stand out to you. This will help you to remember and analyze important information later.
Ask questions: Ask yourself questions as you read to help you engage critically with the text. What is the author's argument? What evidence do they use to support their claims? What are the strengths and weaknesses of their argument?
Engage in active reading: Instead of passively reading, engage in active reading by asking questions, making connections to other readings or personal experiences, and reflecting on what you've read.
Find a discussion partner: Find someone to discuss the essay with, whether it's a classmate, a friend, or a teacher. Discussing the essay can help you to process and analyze the information more deeply, and can also help you to stay engaged.
- Identify the author's purpose and audience: Consider why the author wrote the essay and who their intended audience is. This will help you to better understand the author's perspective and the purpose of their argument.
Analyze the structure of the essay: Consider how the essay is structured and how this supports the author's argument. Look for patterns in the organization of ideas and the use of transitions.
Evaluate the author's use of evidence: Evaluate the author's use of evidence and how it supports their argument. Consider whether the evidence is credible, relevant, and sufficient to support the author's claims.
Consider the author's tone and style: Consider the author's tone and style and how it contributes to their argument. Look for patterns in the use of language, imagery, and rhetorical devices.
Consider the context : Consider the context in which the essay was written, such as the author's background, the time period, and any societal or cultural factors that may have influenced their perspective.
Evaluate the evidence: Evaluate the evidence presented in the essay and consider whether it is sufficient to support the author's argument. Look for any biases or assumptions that may be present in the evidence.
Consider alternative viewpoints: Consider alternative viewpoints and arguments that may challenge the author's perspective. This can help you to engage critically with the text and develop a more well-rounded understanding of the topic.

- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2023 1:01 PM
- URL: https://odessa.libguides.com/analysis

Analytical Essay
Definition of analytical essay, difference between an analytical essay and a critical essay, types of analytical essay, examples of analytical essay in literature, example #1: liposuction: the key to energy independence (by barbara ehrenreich).
“I say to my fellow humans: It’s time to stop feeding off the dead and grow up! I don’t know about food, but I have a plan for achieving fuel self-sufficiency in less time than it takes to say ‘Arctic National Wildlife Refuge.’ The idea came to me from reports of the growing crime of French fry oil theft: Certain desperate individuals are stealing restaurants’ discarded cooking oil, which can then be used to fuel cars. So the idea is: why not skip the French fry phase and harvest high-energy hydrocarbons right from ourselves?”
Example #2: Freedom (by Joyce M. Jarett)
“On the first day of school, I was escorted by hordes of national guardsmen. Like a funeral procession, the steady stream of official-looking cars followed me to the campus. Some patrolmen were parked near campus gates, while others, with guns strapped to their sides, stood near building entrances. Though many of my escorts had given me smiles of support, still I was not prepared for what I encountered upon entering my new school.”
Example #3: The Ways of Meeting Oppression (by Martin Luther King, Jr.)
“The third way open to oppressed people in their quest for freedom is the way of nonviolent resistance. Like the synthesis in Hegelian philosophy, the principle of nonviolent resistance seeks to reconcile the truths of two opposites—the acquiescence and violence—while avoiding the extremes and immoralities of both. The nonviolent resister agrees with the person who acquiesces that one should not be physically aggressive toward his opponent; but he balances the equation by agreeing with the person of violence that evil must be resisted. He avoids the nonresistance of the former and the violent resistance of the latter. With nonviolent resistance, no individual or group need submit to any wrong, nor need anyone resort to violence in order to right a wrong.”
Function of Analytical Essay
Related posts:, post navigation.
How To Write an Analytical Essay

If you enjoy exploring topics deeply and thinking creatively, analytical essays could be perfect for you. They involve thorough analysis and clever writing techniques to gain fresh perspectives and deepen your understanding of the subject. In this article, our expert research paper writer will explain what an analytical essay is, how to structure it effectively and provide practical examples. This guide covers all the essentials for your writing success!
What Is an Analytical Essay
An analytical essay involves analyzing something, such as a book, movie, or idea. It relies on evidence from the text to logically support arguments, avoiding emotional appeals or personal stories. Unlike persuasive essays, which argue for a specific viewpoint, a good analytical essay explores all aspects of the topic, considering different perspectives, dissecting arguments, and evaluating evidence carefully. Ultimately, you'll need to present your own stance based on your analysis, synthesize findings, and decide whether you agree with the conclusions or have your own interpretation.
Wondering How to Impress Your Professor with Your Essay?
Let our writers craft you a winning essay, no matter the subject, field, type, or length!
How to Structure an Analytical Essay
Crafting an excellent paper starts with clear organization and structuring of arguments. An analytical essay structure follows a simple outline: introduction, body, and conclusion.
| Introduction | |
|---|---|
| Body paragraph 1 | |
| Body paragraph 2 | |
| Body paragraph 3 | |
| Conclusion |
Introduction: Begin by grabbing the reader's attention and stating the topic clearly. Provide background information, state the purpose of the paper, and hint at the arguments you'll make. The opening sentence should be engaging, such as a surprising fact or a thought-provoking question. Then, present your thesis, summarizing your stance in the essay.
Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph starts with a clear topic sentence guiding the reader and presents evidence supporting the thesis. Focus on one issue per paragraph and briefly restate the main point at the end to transition smoothly to the next one. This ensures clarity and coherence in your argument.
Conclusion: Restate the thesis, summarize key points from the body paragraphs, and offer insights on the significance of the analysis. Provide your thoughts on the topic's importance and how your analysis contributes to it, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Meanwhile, you might also be interested in how to write a reflection paper , so check out the article for more information!
How to Write an Analytical Essay in 6 Simple Steps
Once you've got a handle on the structure, you can make writing easier by following some steps. Preparing ahead of time can make the process smoother and improve your essay's flow. Here are some helpful tips from our experts. And if you need it, you can always request our experts to write my essay for me , and we'll handle it promptly.
.webp)
Step 1: Decide on Your Stance
Before diving into writing, it's crucial to establish your stance on the topic. Let's say you're going to write an analytical essay example about the benefits and drawbacks of remote work. Before you start writing, you need to decide what your opinion or viewpoint is on this topic.
- Do you think remote work offers flexibility and improved work-life balance for employees?
- Or maybe you believe it can lead to feelings of isolation and decreased productivity?
Once you've determined your stance on remote work, it's essential to consider the evidence and arguments supporting your position. Are there statistics or studies that back up your viewpoint? For example, if you believe remote work improves productivity, you might cite research showing increased output among remote workers. On the other hand, if you think it leads to isolation, you could reference surveys or testimonials highlighting the challenges of remote collaboration. Your opinion will shape how you write your essay, so take some time to think about what you believe about remote work before you start writing.
Step 2: Write Your Thesis Statement
Once you've figured out what you think about the topic, it's time to write your thesis statement. This statement is like the main idea or argument of your essay.
If you believe that remote work offers significant benefits, your thesis statement might be: 'Remote work presents an opportunity for increased flexibility and work-life balance, benefiting employees and employers alike in today's interconnected world.'
Alternatively, if you believe that remote work has notable drawbacks, your thesis statement might be: 'While remote work offers flexibility, it can also lead to feelings of isolation and challenges in collaboration, necessitating a balanced approach to its implementation.'
Your thesis statement guides the rest of your analytical essay, so make sure it clearly expresses your viewpoint on the benefits and drawbacks of remote work.
Step 3: Write Topic Sentences
After you have your thesis statement about the benefits and drawbacks of remote work, you need to come up with topic sentences for each paragraph while writing an analytical essay. These sentences introduce the main point of each paragraph and help to structure your essay.
Let's say your first paragraph is about the benefits of remote work. Your topic sentence might be: 'Remote work offers employees increased flexibility and autonomy, enabling them to better manage their work-life balance.'
For the next paragraph discussing the drawbacks of remote work, your topic sentence could be: 'However, remote work can also lead to feelings of isolation and difficulties in communication and collaboration with colleagues.'
And for the paragraph about potential solutions to the challenges of remote work, your topic sentence might be: 'To mitigate the drawbacks of remote work, companies can implement strategies such as regular check-ins, virtual team-building activities, and flexible work arrangements.'
Each topic sentence should relate back to your thesis statement about the benefits and drawbacks of remote work and provide a clear focus for the paragraph that follows.
Step 4: Create an Outline
Now that you have your thesis statement and topic sentences, it's time to create an analytical essay outline to ensure your essay flows logically. Here's an outline prepared by our analytical essay writer based on the example of discussing the benefits and drawbacks of remote work:
| Introduction | |
|---|---|
| Benefits of Remote Work | |
| Drawbacks of Remote Work | |
| Solutions to Challenges of Remote Work | |
| Conclusion |
Step 5: Write Your First Draft
Now that you have your outline, it's time to start writing your first draft. Begin by expanding upon each point in your outline, making sure to connect your ideas smoothly and logically. Don't worry too much about perfection at this stage; the goal is to get your ideas down on paper. You can always revise and polish your draft later.
As you write, keep referring back to your thesis statement to ensure that your arguments align with your main argument. Additionally, make sure each paragraph flows naturally into the next, maintaining coherence throughout your essay.
Once you've completed your first draft, take a break and then come back to review and revise it. Look for areas where you can strengthen your arguments, clarify your points, and improve the overall structure and flow of your essay.
Remember, writing is a process, and it's okay to go through multiple drafts before you're satisfied with the final result. Take your time and be patient with yourself as you work towards creating a well-crafted essay on the benefits and drawbacks of remote work.
Step 6: Revise and Proofread
Once you've completed your first draft, it's essential to revise and proofread your essay to ensure clarity, coherence, and correctness. Here's how to approach this step:
- Check if your ideas make sense and if they support your main point.
- Make sure your writing style stays the same and your format follows the rules.
- Double-check your facts and make sure you've covered everything important.
- Cut out any extra words and make your sentences clear and short.
- Look for mistakes in spelling and grammar.
- Ask someone to read your essay and give you feedback.
What is the Purpose of an Analytical Essay?
Analytical essays aim to analyze texts or topics, presenting a clear argument. They deepen understanding by evaluating evidence and uncovering underlying meanings. These essays promote critical thinking, challenging readers to consider different viewpoints.
They're also great for improving critical thinking skills. By breaking down complex ideas and presenting them clearly, they encourage readers to think for themselves and reach their own conclusions.
This type of essay also adds to academic discussions by offering fresh insights. By analyzing existing research and literature, they bring new perspectives or shine a light on overlooked parts of a topic. This keeps academic conversations lively and encourages more exploration in the field.
Analytical Essay Examples
Check out our essay samples to see theory in action. Crafted by our dissertation services , they show how analytical thinking applies to real situations, helping you understand concepts better.
With our tips on how to write an analytical essay, you're ready to boost your writing skills and craft essays that captivate your audience. With practice, you'll become a pro at analytical writing, ready to tackle any topic with confidence. And, if you need help to buy essay online , just drop us a line saying ' do my homework for me ' and we'll jump right in!
Do Analytical Essays Tend to Intimidate You?
Give us your assignment to uncover a deeper understanding of your chosen analytical essay topic!
How to Write an Analytical Essay?
What is an analytical essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
The Ultimate Guide to Analytical Essay Writing: How to Craft an A-Grade Paper?
25 January, 2021
17 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
An analytical essay is often considered the most challenging piece of writing. However, those who have dealt with it at least once are a step closer to calling themselves masters of essay writing. This type of paper requires plenty of analytical skills to carry out an in-depth analysis of the assigned topic. Yet, the main goal of an analytical essay is not only to demonstrate your ability to learn the basics of the theme.

You also need to think critically, analyze facts, express your standpoint, and clearly show a deep understanding of key concepts. In short, your main task as an author is to prove the validity of your views by coming up with strong arguments that do not beg any questions.

The given guide provides a full analytical essay definition, as well as specifies its features and structural aspects. The following information will help you properly start your paper, choose a relevant topic, and come up with compelling conclusions.
What is an Analytical Essay?
An analytical essay is a piece of writing aimed to provide a thorough analysis of a definite phenomenon using persuasive arguments and supporting assertions. Analysis in the analytical essay writing process stands for a method of research that allows one to study specific features of an object. Analytical papers also have to do with analysis of a specific problem; that is consideration of the problem itself and identification of its key patterns. The subject matter of analysis can be a well-known or little-studied scientific phenomenon, artistic work, historical event, social problem, etc.
The content of an analytical essay will totally depend on the object that has been chosen for analysis. Thus, when shedding light on any kind of scientific work, an analytical essay can be devoted to the analysis of research credibility, its relevance, or the adequacy of conclusions. When considering a work of art, an essay writer can focus on the analysis of the author’s artistic techniques or issues raised in the book. For this reason, it is essential to accurately determine the topic and subject matter of your future analytical essay.
Steps to Take Before Writing
The preparational stage of analytical essay writing cannot be omitted. It lays the basis for the A-grade paper and should be carefully completed. If you don’t know how to start an analytical essay, read a few handy tips that will ensure a solid foundation for your paper.
Define a subject matter
You first need to clearly understand the issue you will base your essay on. Since analytical essays imply an in-depth analysis of a specific problem, you need to define its core. Try to split the analysis into several components and provide arguments taken either from a book, a research, a scientific work, or a movie (depending on the subject matter of your analysis), and support your views comprehensively.
Decide on the content of your analytical essay
If you are a student who was given an analytical essay topic, read the task several times before you are 100% sure that you clearly understand the requirements as to the analytical essay format. In case you were lucky to choose the topic of the analytical paper by yourself, make sure the theme you will be dealing with is familiar or at least seems interesting to you.
Remember that different subject matters require a different approach to their analysis. If you examine some literature work, you can prove your opinion based on the deeds of a certain or several characters. But if you have been assigned the task to elaborate on some historic events, analyze their main causes, driving forces that have affected their course, and their global consequences.
Take care of the proper start
Don’t forget to start your analytical essay with a thesis statement. It is a sentence or a couple of sentences that aim to summarize the key statements of your paper. A thesis statement should provide readers with a preliminary idea of what your essay is all about.

Find extra reasoning
Make sure your thesis is supported by compelling arguments. To find enough evidence, you should carry out a thorough analysis of the assigned topic. List the crucial points of your research and ponder over the ways they can be used to prove your final opinion.
Elaborate the outline
A sound outline elaborated at the preparation stage will help you ensure a proper analytical essay structure and make the overall writing process easier. As a rule, an analytical essay consists of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Your outline plan should include the key arguments you want to discuss in each paragraph.
Analytical Essay Thesis
A thesis statement represents the central idea of your paper and must serve as strong proof of your standpoint. While elaborating your thesis statement, it is crucial to include it at the end of the first paragraph and thus set a direction for the overall paper.
Analytical Essay Outline
An outline is not a required element of analytical essays writing and should not be included in the text, but it can greatly facilitate the whole process of paper writing.
The analytical essay structure looks as follows:
Introduction
In the introduction of an analytical essay, you will need to identify your paper’s subject matter. Mention the purpose of your work and specify its scope of research. Don’t forget to include a thesis to let readers know what your work is about.
Body Section
As has already been mentioned, the body section covers three or more main paragraphs, each being supported with arguments and details. Besides, you need to provide a small conclusion to each statement to make your essay sound professional and persuasive.
At this stage, you need to summarize the points elucidated in your paper and make sure there is a smooth and logical transition from the body section to the concluding part of the text. If you don’t know how to conclude an analytical essay, try to restate the thesis statement without copying it word for word.
Analytical Essay Examples
Writing an analytical essay may seem to be a thorny way. If you are still not sure how to properly craft one, try to find some examples that will help you go in the right direction. Below, there are some great examples of analytical essays. Take a look at their structure and try to write something similar based on your views and ideas:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JeR4i4RIZIj448W3KVFyHP-eS3QPN7gW/view
https://stlcc.edu/docs/student-support/academic-support/college-writing-center/rhetorical-analysis-sample-essay.pdf
https://www.germanna.eduhttp://handmadewriting.com/wp-content/uploads/tutoring/handouts/Literary-Analysis-Sample-Paper.pdf
30 Analytical Essay Topics
If you were allowed to choose the theme for your paper by yourself, check on the following analytical essay topics. Each of them can bring you the highest score:
General topics
- The influence of social networks on the life of teens
- Are salaries of football players too high?
- Wearing uniforms in schools should be banned
- A person in society: the problems of loneliness and privacy
- Sociology of corporate relationships
- Does the observation of space need more investments?
- Should the voting age in the UK be decreased?
- Reasons why capital punishment should be brought back in the UK
- A world with no rules: a new human era or a road to the global collapse?
- Life without technologies: will modern people survive?
- Should scientists test drugs on animals to fight cancer?
- The problem of keeping the balance between career and family life
- The importance of listening to your body
- Problems caused by the lack of communication
- Food addiction and the problems it causes
- Problems of vaccination in the XXI century
- Does evil really rule the world?
- How does body size affect life quality?
- Pros and cons of video games
- The role of a family model in the life and career of a person
Analytical Essay Topics on Literature
- “Robinson Crusoe”: fantasy vs reality
- Observation of the artistic uniqueness in the comedy by W. Shakespeare “A Midsummer Night’s Dream”
- Observe the social problems in the novel by John Steinbeck “The Grapes of Wrath”
- Convulsions and death of the “little man” in the networks of impersonal, alienated forces in the novel “The Metamorphosis”
- Observation of the problems of a man on a plagued land in the novel “The Plague”
- Revolt of the protagonist in the novel by J. Salinger “The Catcher in the Rye”
- Observation of friendship and love in the fate of humanity in the XX century
- The triumph of immorality in the novel by F. Sagan “Hello Sadness”
- Observation of the personality of an American student in the novel by J. Salinger “The Catcher in the Rye”
- Eternal tragedies of humanity in the tragedy by W. Shakespeare “The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark”
How to Write a Well-Structured Analytical Essay With a Solid Argument
Writing an analytical essay with a clear structure might be challenging unless you are thoroughly prepared. We decided to help you out and create a detailed guide listing the main things to consider when creating an analytical essay outline. You need to explain your main idea in a concise way to bring your point across. As analytical writing has high requirements, it pays off to find an analytical essay example and analyze how this text was written. It will allow you to understand the analytical essay format better and learn how to provide substantive analysis on various topics. Read on to learn how to write a top-level analytical paper and submit it on time.
Main Tips for Writing an Analytical Essay
An analytical essay should provide a comprehensive analysis of a chosen topic. What makes an analysis essay different from other assignments is that it includes a personal opinion of an author. This is why analytical writing should be persuasive.
Below, we have rounded up the key tips you need to follow when producing an analytical essay outline and the main body of your text. Read on to learn more about the analytical essay format and create a text that will fully meet the requirements.
Select an Analytical Essay Topic
Before creating an analytical essay outline, make sure to pick a topic that you are interested in. It should be provocative enough to engage your readers. A widely-debated topic will help you write an analytical essay that grabs the attention of a wide audience.
Consider your goals and conduct thorough research to see if you have enough sources to support the main thesis of your analysis essay.
Come Up With a Strong Analytical Thesis Statement
When writing an analytical essay, start by formulating a thesis statement that includes the topic and the main goal of your text. It will help you create an analytical essay outline and show your readers what you will discuss in your analysis essay.
Add it to the last paragraph of your analytical essay introduction. Due to this, your analytical essay outline will look better structured. Look at any analytical essay example to see how you can introduce your subject. In most cases, one sentence will suffice to state your analysis essay’s goal. However, a complex analytical essay outline might require you to use two sentences for a thesis statement.
Write an Analytical Essay Body with a Clear Structure
Your analytical essay outline should include 3-4 paragraphs. However, a literary analysis essay usually consists of 5 paragraphs. When it comes to analytical writing, it is important to cover a different point in each section of the main body of an analysis paper.
After writing an analytical essay, check whether each paragraph contains an introduction and the main point. Besides, it should contain evidence. An expertly written analytical essay outline will help you reach out to your target audience more effectively.
Conduct Research Before Writing an Analytical Essay Outline
While this step is preparatory, it is a must for those who want to write a well-grounded analytical paper.
- First, select the best ideas for your essay
- Then, emphasize the problems with works written by other researchers
- Finally, write your analytical essay outline to demonstrate what approach you want to take
Examine the context and find examples to illustrate the scope of the issue. You may draw parallels to emphasize your point and make your topic more relatable.
Analyze the Implications of the Evidence
After listing your pieces of evidence and demonstrating how it is related to your thesis, show why it is important. You need to explore it deeply and use it to support your argument. It will make your analytical essay outline well-grounded facts.
Write an Analytical Essay Conclusion
Whether you write a literary analysis essay or other types of assignments, there is no need to add any new data at the end of your analysis paper. Instead, summarize the arguments you mentioned in your analytical essay outline. The conclusion of your analysis essay should be short and clear. Here, you need to demonstrate that you have achieved your goals.
Analytical Essay Writing Tips
If you want to get the highest grade for your analytical essay, you need to know a little bit more than just the basics of paper writing. Read these handy tips to write a perfect essay you will be proud of:
- Double-check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes. In case your essay contains too many errors, neither an in-depth analysis nor the elaborate writing style will make it look any better. Situations when essays of great value in terms of research and a message they convey are poorly assessed because of the abundance of mistakes are not rare. Make sure you have enough time to proofread your paper before submission. Also, you may consider asking somebody to take a fresh look at your essay and check it for you.
- Reading your analytical essay out loud helps you discover all types of errors or weak phrases. This method might seem a bit uncomfortable, but it has proved to be very effective for many students. Note that silent reading of your paper isn’t even half as helpful as reading it aloud.
- Another great idea to check on the rhythm and flow of your paper is to ask someone to read it for you. While listening to the text, you could perceive it from another perspective and discover even more inconsistencies and mistakes.
- Double-check the facts you use in your analytical essay. The names of people, books, research, publications, as well as dates of historical events are too important to be misspelled. Things like these show your professionalism and the way you treat your readers.
Write an Analytical Essay with HandmadeWriting
Writing an analytical essay requires time, strong writing skills, great attention to detail, and a huge interest in the assigned topic. However, life can be unpredictable sometimes, and students might find themselves at risk of failing their creative assignments. Stress, family issues, poor health, and even unwillingness to work on a certain topic may become significant obstacles on their way to the A-grade work.
If you have similar problems, there is no need to compromise your reputation and grades. You can always refer to HandmadeWriting professionals who are ready to help you with a paper of any type and complexity. They will understand your individual style and totally devote themselv

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
5 Steps to Write a Great Analytical Essay
General Education

Do you need to write an analytical essay for school? What sets this kind of essay apart from other types, and what must you include when you write your own analytical essay? In this guide, we break down the process of writing an analytical essay by explaining the key factors your essay needs to have, providing you with an outline to help you structure your essay, and analyzing a complete analytical essay example so you can see what a finished essay looks like.
What Is an Analytical Essay?
Before you begin writing an analytical essay, you must know what this type of essay is and what it includes. Analytical essays analyze something, often (but not always) a piece of writing or a film.
An analytical essay is more than just a synopsis of the issue though; in this type of essay you need to go beyond surface-level analysis and look at what the key arguments/points of this issue are and why. If you’re writing an analytical essay about a piece of writing, you’ll look into how the text was written and why the author chose to write it that way. Instead of summarizing, an analytical essay typically takes a narrower focus and looks at areas such as major themes in the work, how the author constructed and supported their argument, how the essay used literary devices to enhance its messages, etc.
While you certainly want people to agree with what you’ve written, unlike with persuasive and argumentative essays, your main purpose when writing an analytical essay isn’t to try to convert readers to your side of the issue. Therefore, you won’t be using strong persuasive language like you would in those essay types. Rather, your goal is to have enough analysis and examples that the strength of your argument is clear to readers.
Besides typical essay components like an introduction and conclusion, a good analytical essay will include:
- A thesis that states your main argument
- Analysis that relates back to your thesis and supports it
- Examples to support your analysis and allow a more in-depth look at the issue
In the rest of this article, we’ll explain how to include each of these in your analytical essay.
How to Structure Your Analytical Essay
Analytical essays are structured similarly to many other essays you’ve written, with an introduction (including a thesis), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below is an outline you can follow when structuring your essay, and in the next section we go into more detail on how to write an analytical essay.
Introduction
Your introduction will begin with some sort of attention-grabbing sentence to get your audience interested, then you’ll give a few sentences setting up the topic so that readers have some context, and you’ll end with your thesis statement. Your introduction will include:
- Brief background information explaining the issue/text
- Your thesis
Body Paragraphs
Your analytical essay will typically have three or four body paragraphs, each covering a different point of analysis. Begin each body paragraph with a sentence that sets up the main point you’ll be discussing. Then you’ll give some analysis on that point, backing it up with evidence to support your claim. Continue analyzing and giving evidence for your analysis until you’re out of strong points for the topic. At the end of each body paragraph, you may choose to have a transition sentence that sets up what the next paragraph will be about, but this isn’t required. Body paragraphs will include:
- Introductory sentence explaining what you’ll cover in the paragraph (sort of like a mini-thesis)
- Analysis point
- Evidence (either passages from the text or data/facts) that supports the analysis
- (Repeat analysis and evidence until you run out of examples)
You won’t be making any new points in your conclusion; at this point you’re just reiterating key points you’ve already made and wrapping things up. Begin by rephrasing your thesis and summarizing the main points you made in the essay. Someone who reads just your conclusion should be able to come away with a basic idea of what your essay was about and how it was structured. After this, you may choose to make some final concluding thoughts, potentially by connecting your essay topic to larger issues to show why it’s important. A conclusion will include:
- Paraphrase of thesis
- Summary of key points of analysis
- Final concluding thought(s)

5 Steps for Writing an Analytical Essay
Follow these five tips to break down writing an analytical essay into manageable steps. By the end, you’ll have a fully-crafted analytical essay with both in-depth analysis and enough evidence to support your argument. All of these steps use the completed analytical essay in the next section as an example.
#1: Pick a Topic
You may have already had a topic assigned to you, and if that’s the case, you can skip this step. However, if you haven’t, or if the topic you’ve been assigned is broad enough that you still need to narrow it down, then you’ll need to decide on a topic for yourself. Choosing the right topic can mean the difference between an analytical essay that’s easy to research (and gets you a good grade) and one that takes hours just to find a few decent points to analyze
Before you decide on an analytical essay topic, do a bit of research to make sure you have enough examples to support your analysis. If you choose a topic that’s too narrow, you’ll struggle to find enough to write about.
For example, say your teacher assigns you to write an analytical essay about the theme in John Steinbeck’s The Grapes of Wrath of exposing injustices against migrants. For it to be an analytical essay, you can’t just recount the injustices characters in the book faced; that’s only a summary and doesn’t include analysis. You need to choose a topic that allows you to analyze the theme. One of the best ways to explore a theme is to analyze how the author made his/her argument. One example here is that Steinbeck used literary devices in the intercalary chapters (short chapters that didn’t relate to the plot or contain the main characters of the book) to show what life was like for migrants as a whole during the Dust Bowl.
You could write about how Steinbeck used literary devices throughout the whole book, but, in the essay below, I chose to just focus on the intercalary chapters since they gave me enough examples. Having a narrower focus will nearly always result in a tighter and more convincing essay (and can make compiling examples less overwhelming).
#2: Write a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is the most important sentence of your essay; a reader should be able to read just your thesis and understand what the entire essay is about and what you’ll be analyzing. When you begin writing, remember that each sentence in your analytical essay should relate back to your thesis
In the analytical essay example below, the thesis is the final sentence of the first paragraph (the traditional spot for it). The thesis is: “In The Grapes of Wrath’s intercalary chapters, John Steinbeck employs a variety of literary devices and stylistic choices to better expose the injustices committed against migrants in the 1930s.” So what will this essay analyze? How Steinbeck used literary devices in the intercalary chapters to show how rough migrants could have it. Crystal clear.
#3: Do Research to Find Your Main Points
This is where you determine the bulk of your analysis--the information that makes your essay an analytical essay. My preferred method is to list every idea that I can think of, then research each of those and use the three or four strongest ones for your essay. Weaker points may be those that don’t relate back to the thesis, that you don’t have much analysis to discuss, or that you can’t find good examples for. A good rule of thumb is to have one body paragraph per main point
This essay has four main points, each of which analyzes a different literary device Steinbeck uses to better illustrate how difficult life was for migrants during the Dust Bowl. The four literary devices and their impact on the book are:
- Lack of individual names in intercalary chapters to illustrate the scope of the problem
- Parallels to the Bible to induce sympathy for the migrants
- Non-showy, often grammatically-incorrect language so the migrants are more realistic and relatable to readers
- Nature-related metaphors to affect the mood of the writing and reflect the plight of the migrants
#4: Find Excerpts or Evidence to Support Your Analysis
Now that you have your main points, you need to back them up. If you’re writing a paper about a text or film, use passages/clips from it as your main source of evidence. If you’re writing about something else, your evidence can come from a variety of sources, such as surveys, experiments, quotes from knowledgeable sources etc. Any evidence that would work for a regular research paper works here.
In this example, I quoted multiple passages from The Grapes of Wrath in each paragraph to support my argument. You should be able to back up every claim you make with evidence in order to have a strong essay.
#5: Put It All Together
Now it's time to begin writing your essay, if you haven’t already. Create an introductory paragraph that ends with the thesis, make a body paragraph for each of your main points, including both analysis and evidence to back up your claims, and wrap it all up with a conclusion that recaps your thesis and main points and potentially explains the big picture importance of the topic.

Analytical Essay Example + Analysis
So that you can see for yourself what a completed analytical essay looks like, here’s an essay I wrote back in my high school days. It’s followed by analysis of how I structured my essay, what its strengths are, and how it could be improved.
One way Steinbeck illustrates the connections all migrant people possessed and the struggles they faced is by refraining from using specific titles and names in his intercalary chapters. While The Grapes of Wrath focuses on the Joad family, the intercalary chapters show that all migrants share the same struggles and triumphs as the Joads. No individual names are used in these chapters; instead the people are referred to as part of a group. Steinbeck writes, “Frantic men pounded on the doors of the doctors; and the doctors were busy. And sad men left word at country stores for the coroner to send a car,” (555). By using generic terms, Steinbeck shows how the migrants are all linked because they have gone through the same experiences. The grievances committed against one family were committed against thousands of other families; the abuse extends far beyond what the Joads experienced. The Grapes of Wrath frequently refers to the importance of coming together; how, when people connect with others their power and influence multiplies immensely. Throughout the novel, the goal of the migrants, the key to their triumph, has been to unite. While their plans are repeatedly frustrated by the government and police, Steinbeck’s intercalary chapters provide a way for the migrants to relate to one another because they have encountered the same experiences. Hundreds of thousands of migrants fled to the promised land of California, but Steinbeck was aware that numbers alone were impersonal and lacked the passion he desired to spread. Steinbeck created the intercalary chapters to show the massive numbers of people suffering, and he created the Joad family to evoke compassion from readers. Because readers come to sympathize with the Joads, they become more sensitive to the struggles of migrants in general. However, John Steinbeck frequently made clear that the Joads were not an isolated incident; they were not unique. Their struggles and triumphs were part of something greater. Refraining from specific names in his intercalary chapters allows Steinbeck to show the vastness of the atrocities committed against migrants.
Steinbeck also creates significant parallels to the Bible in his intercalary chapters in order to enhance his writing and characters. By using simple sentences and stylized writing, Steinbeck evokes Biblical passages. The migrants despair, “No work till spring. No work,” (556). Short, direct sentences help to better convey the desperateness of the migrants’ situation. Throughout his novel, John Steinbeck makes connections to the Bible through his characters and storyline. Jim Casy’s allusions to Christ and the cycle of drought and flooding are clear biblical references. By choosing to relate The Grapes of Wrath to the Bible, Steinbeck’s characters become greater than themselves. Starving migrants become more than destitute vagrants; they are now the chosen people escaping to the promised land. When a forgotten man dies alone and unnoticed, it becomes a tragedy. Steinbeck writes, “If [the migrants] were shot at, they did not run, but splashed sullenly away; and if they were hit, they sank tiredly in the mud,” (556). Injustices committed against the migrants become greater because they are seen as children of God through Steinbeck’s choice of language. Referencing the Bible strengthens Steinbeck’s novel and purpose: to create understanding for the dispossessed. It is easy for people to feel disdain for shabby vagabonds, but connecting them to such a fundamental aspect of Christianity induces sympathy from readers who might have otherwise disregarded the migrants as so many other people did.
The simple, uneducated dialogue Steinbeck employs also helps to create a more honest and meaningful representation of the migrants, and it makes the migrants more relatable to readers. Steinbeck chooses to accurately represent the language of the migrants in order to more clearly illustrate their lives and make them seem more like real paper than just characters in a book. The migrants lament, “They ain’t gonna be no kinda work for three months,” (555). There are multiple grammatical errors in that single sentence, but it vividly conveys the despair the migrants felt better than a technically perfect sentence would. The Grapes of Wrath is intended to show the severe difficulties facing the migrants so Steinbeck employs a clear, pragmatic style of writing. Steinbeck shows the harsh, truthful realities of the migrants’ lives and he would be hypocritical if he chose to give the migrants a more refined voice and not portray them with all their shortcomings. The depiction of the migrants as imperfect through their language also makes them easier to relate to. Steinbeck’s primary audience was the middle class, the less affluent of society. Repeatedly in The Grapes of Wrath , the wealthy make it obvious that they scorn the plight of the migrants. The wealthy, not bad luck or natural disasters, were the prominent cause of the suffering of migrant families such as the Joads. Thus, Steinbeck turns to the less prosperous for support in his novel. When referring to the superior living conditions barnyard animals have, the migrants remark, “Them’s horses-we’re men,” (556). The perfect simplicity of this quote expresses the absurdness of the migrants’ situation better than any flowery expression could.
In The Grapes of Wrath , John Steinbeck uses metaphors, particularly about nature, in order to illustrate the mood and the overall plight of migrants. Throughout most of the book, the land is described as dusty, barren, and dead. Towards the end, however; floods come and the landscape begins to change. At the end of chapter twenty-nine, Steinbeck describes a hill after the floods saying, “Tiny points of grass came through the earth, and in a few days the hills were pale green with the beginning year,” (556). This description offers a stark contrast from the earlier passages which were filled with despair and destruction. Steinbeck’s tone from the beginning of the chapter changes drastically. Early in the chapter, Steinbeck had used heavy imagery in order to convey the destruction caused by the rain, “The streams and the little rivers edged up to the bank sides and worked at willows and tree roots, bent the willows deep in the current, cut out the roots of cottonwoods and brought down the trees,” (553). However, at the end of the chapter the rain has caused new life to grow in California. The new grass becomes a metaphor representing hope. When the migrants are at a loss over how they will survive the winter, the grass offers reassurance. The story of the migrants in the intercalary chapters parallels that of the Joads. At the end of the novel, the family is breaking apart and has been forced to flee their home. However, both the book and final intercalary chapter end on a hopeful note after so much suffering has occurred. The grass metaphor strengthens Steinbeck’s message because it offers a tangible example of hope. Through his language Steinbeck’s themes become apparent at the end of the novel. Steinbeck affirms that persistence, even when problems appear insurmountable, leads to success. These metaphors help to strengthen Steinbeck’s themes in The Grapes of Wrath because they provide a more memorable way to recall important messages.
John Steinbeck’s language choices help to intensify his writing in his intercalary chapters and allow him to more clearly show how difficult life for migrants could be. Refraining from using specific names and terms allows Steinbeck to show that many thousands of migrants suffered through the same wrongs. Imitating the style of the Bible strengthens Steinbeck’s characters and connects them to the Bible, perhaps the most famous book in history. When Steinbeck writes in the imperfect dialogue of the migrants, he creates a more accurate portrayal and makes the migrants easier to relate to for a less affluent audience. Metaphors, particularly relating to nature, strengthen the themes in The Grapes of Wrath by enhancing the mood Steinbeck wants readers to feel at different points in the book. Overall, the intercalary chapters that Steinbeck includes improve his novel by making it more memorable and reinforcing the themes Steinbeck embraces throughout the novel. Exemplary stylistic devices further persuade readers of John Steinbeck’s personal beliefs. Steinbeck wrote The Grapes of Wrath to bring to light cruelties against migrants, and by using literary devices effectively, he continuously reminds readers of his purpose. Steinbeck’s impressive language choices in his intercalary chapters advance the entire novel and help to create a classic work of literature that people still are able to relate to today.
This essay sticks pretty closely to the standard analytical essay outline. It starts with an introduction, where I chose to use a quote to start off the essay. (This became my favorite way to start essays in high school because, if I wasn’t sure what to say, I could outsource the work and find a quote that related to what I’d be writing about.) The quote in this essay doesn’t relate to the themes I’m discussing quite as much as it could, but it’s still a slightly different way to start an essay and can intrigue readers. I then give a bit of background on The Grapes of Wrath and its themes before ending the intro paragraph with my thesis: that Steinbeck used literary devices in intercalary chapters to show how rough migrants had it.
Each of my four body paragraphs is formatted in roughly the same way: an intro sentence that explains what I’ll be discussing, analysis of that main point, and at least two quotes from the book as evidence.
My conclusion restates my thesis, summarizes each of four points I discussed in my body paragraphs, and ends the essay by briefly discussing how Steinbeck’s writing helped introduce a world of readers to the injustices migrants experienced during the dust bowl.
What does this analytical essay example do well? For starters, it contains everything that a strong analytical essay should, and it makes that easy to find. The thesis clearly lays out what the essay will be about, the first sentence of each of the body paragraph introduces the topic it’ll cover, and the conclusion neatly recaps all the main points. Within each of the body paragraphs, there’s analysis along with multiple excerpts from the book in order to add legitimacy to my points.
Additionally, the essay does a good job of taking an in-depth look at the issue introduced in the thesis. Four ways Steinbeck used literary devices are discussed, and for each of the examples are given and analysis is provided so readers can understand why Steinbeck included those devices and how they helped shaped how readers viewed migrants and their plight.
Where could this essay be improved? I believe the weakest body paragraph is the third one, the one that discusses how Steinbeck used plain, grammatically incorrect language to both accurately depict the migrants and make them more relatable to readers. The paragraph tries to touch on both of those reasons and ends up being somewhat unfocused as a result. It would have been better for it to focus on just one of those reasons (likely how it made the migrants more relatable) in order to be clearer and more effective. It’s a good example of how adding more ideas to an essay often doesn’t make it better if they don’t work with the rest of what you’re writing. This essay also could explain the excerpts that are included more and how they relate to the points being made. Sometimes they’re just dropped in the essay with the expectation that the readers will make the connection between the example and the analysis. This is perhaps especially true in the second body paragraph, the one that discusses similarities to Biblical passages. Additional analysis of the quotes would have strengthened it.

Summary: How to Write an Analytical Essay
What is an analytical essay? A critical analytical essay analyzes a topic, often a text or film. The analysis paper uses evidence to support the argument, such as excerpts from the piece of writing. All analytical papers include a thesis, analysis of the topic, and evidence to support that analysis.
When developing an analytical essay outline and writing your essay, follow these five steps:
Reading analytical essay examples can also give you a better sense of how to structure your essay and what to include in it.
What's Next?
Learning about different writing styles in school? There are four main writing styles, and it's important to understand each of them. Learn about them in our guide to writing styles , complete with examples.
Writing a research paper for school but not sure what to write about? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Literary devices can both be used to enhance your writing and communication. Check out this list of 31 literary devices to learn more !
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

Guide to Writing an Analytical Essay
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing in which a complicated topic or idea is broken down into smaller parts, analyzed and looked at, and a well-structured argument or evaluation is given. The main purpose of an analytical essay is to show that the writer has a deep understanding of the topic and can also think critically about it. Analytical essays are important in many fields, such as literature, history, science, and sociology. They require a deep knowledge of the topic and the ability to think critically and objectively about the information given. Analytical essays include things like a literary analysis, a research paper , or an analysis of a piece of rhetoric. Writing an analytical essay is useful because it helps the writer improve their analytical and critical thinking skills. In analytical essays, students must look at and evaluate different sources, find patterns and relationships, and come to meaningful conclusions. When students write analytical essays, they also improve their research skills because they have to find relevant information from multiple sources and put it all together in a logical argument.
Also, analytical essays are important in academic writing because they help students understand ideas, theories, and concepts that are hard to understand. By breaking a topic down into smaller parts, students can better understand it and figure out what the main ideas and themes are. Analytical essays help students get better at writing by making them present their arguments in a way that is clear, concise, and well-organized. Writing an analytical essay is a skill that students need to learn if they want to do well in school and in their careers. For analytical essays, you need to be able to think critically , do research, and write well, all of which are important for success in many fields. By getting better at these skills, students can become better writers and thinkers, which will help them reach their academic and career goals.
What You'll Learn
Understanding the Basics of Analytical Essays
There are a few main things that set an analytical essay apart from other types of essays. One of the most important things about it is that it requires a thorough look at the subject. An analytical essay isn’t just a description of a topic or a point of view. Instead, it calls for a thorough look at the subject, breaking it down into its different parts and evaluating each one carefully.
Argumentative essays try to convince the reader to agree with a certain point of view. Descriptive essays, on the other hand, try to give a detailed description of a topic. Analytical essays, on the other hand, require the writer to look at the topic objectively and judge it, as well as use evidence from different sources to back up their claims. In an analytical essay, you can’t say enough about how important analysis is. Analysis is the process of breaking down big ideas or thoughts into smaller, more manageable pieces. By analyzing the topic, the writer can find the main ideas, patterns, and connections, which can then be used to back up their arguments.
Also, analysis lets the author draw conclusions that make sense based on the evidence given. If there wasn’t any analysis in an analytical essay, it would just be a list of facts and opinions. Analysis is what gives depth and substance to an analytical essay and lets the writer make a well-reasoned, evidence-based argument.
Analytical essays are different from other types of essays because they focus on analysis and evaluation. They require a thorough look at a subject, breaking it down into its different parts and judging each one objectively. Students can get the skills they need to do well in school and in the workplace by learning what makes an analytical essay unique and what role analysis plays in this type of writing.
Choosing a Topic for Your Analytical Essay
It can be hard to decide what to write about in an analytical essay, but there are several ways to come up with ideas. One way to do this is to make a list of possible topics based on your interests, your schoolwork, or what’s going on in the world right now. You can also find possible topics by reading articles, books, or other materials in your field of study. When choosing a topic for your analytical essay, you should think about a few things. First and foremost, the topic must fit with the needs of the course or assignment. It should also be narrow enough to allow for a detailed analysis while still having enough information for research . Also, the topic should be something you’re interested in as a writer. This will make the writing process more interesting and fun.
To help you get started, here are some examples of potential analytical essay topics:
1. The impact of social media on mental health
2. Analyzing the themes of race and identity in Toni Morrison’s “Beloved”
3. The role of technology in modern education
4. An analysis of the effectiveness of the Affordable Care Act
5. Examining the causes and consequences of income inequality in the United States
6. The portrayal of gender roles in Shakespeare’s plays
7. Analyzing the impact of climate change on global food production
8. A critical analysis of the role of the media in shaping public opinion
9. A comparison of different political ideologies and their impact on society
10. An analysis of the ethical implications of gene editing technology.
A topic for an analytical essay must be chosen with care, taking into account several factors such as relevance, scope, and personal interest. By brainstorming ideas, researching different sources, and applying these criteria, you can choose a topic that is both interesting and informative, allowing you to write a well-researched and well-argued analytical essay.
Conducting Research for Your Analytical Essay
In order to write an analytical essay, you need to do research. It lets the writer gather relevant information, find patterns and relationships, and come to conclusions that make sense. If you didn’t do research for your analytical essay, it wouldn’t have much substance or credibility, and the arguments you made would be weak and not backed up. You can gather information for your analytical essay from a number of different places. There are many examples, such as books, academic journals, online databases, government reports, and reputable news sources. When choosing sources, think about how relevant, reliable, and trustworthy they are. Academic sources like peer-reviewed journals and scholarly books are more reliable and credible than popular sources like blogs and social media posts.
To conduct effective research for your analytical essay, here are some tips to keep in mind:
1. Start early: Give yourself plenty of time to conduct research, as it can be a time-consuming process.
2. Use multiple sources: Gather information from a variety of sources to ensure you have a well-rounded understanding of the topic.
3. Take notes: Keep detailed notes on the information you gather, including the source and page number, to make it easier to cite your sources later.
4. Evaluate your sources: Assess the reliability and credibility of your sources, looking for biases or conflicts of interest that may affect the information presented.
5. Organize your research: Create a system for organizing your research, such as using annotated bibliographies or note-taking apps, to keep track of your sources and ideas.
You can conduct effective research for your analytical essay by following these tips, gathering reliable and credible information that supports your arguments and improves the overall quality of your writing.
Developing a Thesis Statement for Your Analytical Essay
A thesis statement is a short sentence that sums up the main argument or point of an essay. It gives the reader a clear idea of where the author stands on the subject and acts as a road map. In an analytical essay, the thesis statement is very important because it sets the tone for the whole essay and shows the writer how to analyze and evaluate the subject . In an analytical essay, you can’t say enough about how important a strong thesis statement is. A well-written thesis statement states the writer’s main point in a clear and concise way, making it easier for the reader to follow the writer’s thought process and understand the purpose of the essay. A strong thesis statement also helps the writer focus their analysis and evaluation, making sure that each paragraph supports the main point and builds on it.
To develop a strong thesis statement for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Start with a question: Ask yourself a question related to your topic and use the answer to develop your thesis statement.
2. Be specific: Your thesis statement should be specific and focused on the main argument of your essay .
3. Use evidence: Support your thesis statement with evidence from your research, such as quotes or statistics, to give it more credibility and strength.
4. Be original: Your thesis statement should be unique and original, providing a fresh perspective on the topic.
5. Revise as needed: As you write your essay , revisit your thesis statement and revise it if necessary to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
By following these tips, you can develop a strong thesis statement for your analytical essay, providing a clear and concise statement of your main argument and guiding the reader through your analysis and evaluation of the topic.
Analytical Essay Structure
An analytical essay is made up of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, just like a regular essay. The purpose of the introduction is to give background on the topic, introduce the thesis statement, and get the reader interested. Through analysis and evaluation of the topic, the body paragraphs should support the thesis statement with evidence and examples . The conclusion should sum up the main points of the essay and restate the thesis statement in a new way that makes sense.
Here is a more detailed breakdown of the structure of an analytical essay:
1. Introduction: The introduction should set the tone for the essay by providing background information on the subject as well as a clear thesis statement. It should also engage the reader and convey the writer’s point of view on the subject.
2. Body paragraphs: The body of the essay should be divided into several paragraphs, each focusing on a different aspect of the topic. Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence that supports the thesis statement and then proceed to an analysis and evaluation of the subject matter, using evidence and examples to support the writer’s argument.
3. Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the essay’s main points and restate the thesis statement in a new and meaningful way. It should also provide the reader with a sense of closure, leaving them with a clear understanding of the writer’s point of view on the subject.
To organize your ideas in an analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Create an outline: Before you start writing your essay , create an outline that organizes your ideas and supports your thesis statement. This will help you to organize your thoughts and ensure that each paragraph supports the main argument.
2. Use topic sentences: Each paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that supports the thesis statement and provides a roadmap for the reader.
3. Use evidence: Use evidence and examples to support each point you make in your essay , ensuring that each paragraph reinforces the main argument.
4. Use transitions: Use transitional phrases and sentences to connect your ideas and ensure that your essay flows smoothly from one paragraph to the next.
By following these tips, you can organize your ideas effectively in an analytical essay, producing a well-structured and well-supported piece of writing.
Writing the Introduction Paragraph
An analytical essay’s introduction paragraph serves as a road map for the reader, providing background information on the topic, introducing the thesis statement, and engaging the reader. The introduction’s purpose is to set the tone for the essay , grab the reader’s attention, and provide a clear understanding of the writer’s viewpoint on the topic.
To write an engaging introduction paragraph for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Start with a hook: Begin your introduction with a hook that captures the reader’s attention and makes them want to keep reading. This could be a surprising statistic, a provocative question, or a striking image.
2. Provide background information: Provide some context for the topic by providing background information and explaining why it is important.
3. Introduce the thesis statement: Clearly state your thesis statement in the introduction, providing a roadmap for the reader and guiding the rest of your essay.
4. Be concise: Keep your introduction concise and to the point, avoiding unnecessary information or tangents.
5. Revise as needed: As you write your essay, revisit your introduction and revise it as needed to ensure that it remains relevant and engaging.
Here are some examples of effective introduction paragraphs for an analytical essay:
1. “Throughout history, the concept of justice has been a subject of debate and controversy. From the ancient Greeks to modern-day philosophers, the definition and application of justice have been explored in depth. In this essay, I will examine the concept of justice in the context of criminal justice reform and argue that a more restorative approach is needed to address the root causes of crime and reduce recidivism.
2. The rise of social media has had a profound impact on our society, transforming the way we communicate, share information, and interact with the world around us. However, this transformation has not been without its challenges. In this essay, I will explore the impact of social media on mental health and argue that we need to take a more proactive approach to addressing the negative effects of social media on our well-being.
3. “Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, affecting everything from the environment to the economy. Despite the overwhelming scientific evidence, there are still those who deny the reality of climate change or refuse to take action. In this essay, I will analyze the reasons for this denial and argue that we need to take urgent action to address the threat of climate change before it’s too late.”
Writing the Body Paragraphs
An analytical essay’s body paragraphs are where the writer presents their analysis and evaluation of the topic. The purpose of the body paragraphs is to provide evidence and examples to support the thesis statement, while using clear and concise language to make the argument as persuasive as possible.
To write clear and concise body paragraphs for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Use topic sentences: Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that supports the thesis statement and provides a roadmap for the reader.
2. Provide evidence: Use evidence and examples to support each point you make in your essay , ensuring that each paragraph reinforces the main argument. The evidence should be relevant, reliable, and credible.
3. Use analysis and evaluation: Analyze and evaluate the evidence you present to demonstrate how it supports your argument. This shows the reader that you have thought deeply about the topic and considered multiple perspectives.
4. Be clear and concise: Use clear and concise language to make your argument as persuasive as possible. Avoid using jargon, complex sentences, or overly technical language that may confuse the reader.
5. Use transitions: Use transitional phrases and sentences to connect your ideas smoothly and ensure that your essay flows from one paragraph to the next.
Here are some examples of effective body paragraphs for an analytical essay:
1. The first reason why a restorative approach to criminal justice reform is necessary is that it addresses the root causes of crime. Rather than simply punishing offenders, restorative justice encourages dialogue between the offender and the victim, allowing both parties to understand the harm that has been caused and work together to find a solution. This approach has been shown to reduce recidivism rates and promote healing within communities.”
2. One of the most significant negative effects of social media on mental health is the increase in anxiety and depression. Studies have shown that social media use is associated with feelings of isolation, comparison, and low self-esteem, all of which contribute to poor mental health . In order to address this issue, we need to take a more proactive approach to promoting mental health and well-being, such as limiting social media use, encouraging face-to-face interactions, and providing mental health resources for those in need.
3. One of the main reasons why climate change denial persists is due to the influence of special interest groups and political ideology . These groups use their resources to spread misinformation and discredit the overwhelming scientific consensus on climate change. In order to combat this, we need to prioritize education and awareness, promote scientific literacy, and hold those who spread misinformation accountable for their actions.”
Writing the Conclusion Paragraph
The conclusion paragraph of an analytical essay summarizes the author’s main points and emphasizes the significance of the thesis statement. The conclusion’s goal is to leave a lasting impression on the reader by bringing the essay to a close and reinforcing the main argument .
To write a strong conclusion for your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Restate the thesis statement: The conclusion should restate the thesis statement in a new and meaningful way, emphasizing its importance and relevance to the topic.
2. Summarize the main points: Summarize the main points of the essay, highlighting the evidence and examples that support the thesis statement .
3. Provide a final thought: End the essay with a final thought or reflection on the topic, leaving the reader with something to think about or consider.
4. Be concise: Keep the conclusion concise and to the point, avoiding any new information or arguments.
5. Make it memorable: Use language and phrasing that is memorable and impactful, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Here are some examples of effective conclusion paragraphs for an analytical essay:
1. “In conclusion, a restorative approach to criminal justice reform is not only necessary but essential. By addressing the root causes of crime, promoting dialogue and understanding, and fostering healing within communities, we can create a more just and equitable society for all.”
2. In order to address the negative effects of social media on mental health , we need to take a more proactive approach to promoting well-being. By limiting social media use, encouraging face-to-face interactions, and providing mental health resources, we can create a healthier and more connected society.
3. “Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and we must take urgent action to address it. By promoting education and awareness, prioritizing scientific literacy, and holding those who spread misinformation accountable, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future for generations to come.”
Editing and Proofreading Your Analytical Essay
The editing and proofreading stages of the essay writing process are critical. It ensures that the essay is clear, concise, and error-free, improving overall writing quality and the credibility of the arguments presented.
To edit and proofread your analytical essay, here are some tips to consider:
1. Take a break: After completing your essay, take a break before editing and proofreading it. This will allow you to approach the essay with fresh eyes and a clear mind.
2. Read it out loud: Reading the essay out loud can help you to identify awkward phrasing, grammatical errors, and other issues.
3. Be consistent: Ensure that you are consistent in your use of language, formatting, and citation styles throughout the essay.
4. Use a checklist: Use a checklist to ensure that you have addressed all the necessary components of the essay, such as the thesis statement, evidence, and analysis.
5. Get feedback: Ask a friend or colleague to read your essay and provide feedback on areas that need improvement.
Common mistakes to avoid in analytical essays include:
1. Using overly complicated language or jargon that may confuse the reader.
2. Failing to provide evidence or examples to support the thesis statement.
3. Neglecting to address counterarguments or alternative perspectives on the topic.
4. Making unsupported claims or presenting opinions as facts.
5. Failing to proofread and edit the essay thoroughly, leading to grammatical errors and typos.
By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can edit and proofread your analytical essay effectively, producing a well-written and error-free piece of writing.
Analytical Essay Examples
Here are some examples of successful analytical essays:
1. “The Symbolism of the Green Light in The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald: This essay analyzes the symbolism of the green light in the novel, arguing that it represents Gatsby’s hopes and dreams and his ultimate failure to achieve them.
2. “The Rhetoric of Malcolm X” by Malcolm X: In this essay, Malcolm X analyzes his own rhetorical strategies, explaining how he uses language and persuasion to achieve his goals.
3. “The Role of Women in Shakespeare’s Macbeth” by William Shakespeare: This essay analyzes the role of women in the play, arguing that they are often marginalized and oppressed by the male characters.
Each of these essays follows a clear and well-structured format, with a strong thesis statement, supporting evidence, and a clear conclusion. The writers use analysis and evaluation to present their arguments, using evidence and examples to support their claims.
When using analytical essay examples to improve your writing, here are some tips to consider:
1. Choose examples that are relevant to your topic or subject matter.
2. Read the example essays carefully, paying attention to the structure, language, and evidence used.
3. Identify the thesis statement and main arguments of the essay.
4. Analyze the evidence used to support the arguments, evaluating its relevance and credibility.
5. Consider how the writer uses language and rhetoric to persuade the reader.
6. Use The examples as a guide for structuring your own essay, but be sure to use your own unique ideas and perspective.
7. Practice writing your own analytical essays and seek feedback from others to improve your writing skills.
8. Avoid copying or plagiarizing the example essays, as this can lead to serious academic consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is an analytical essay.
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing that requires the writer to analyze and evaluate a specific topic or subject matter. The writer presents an argument or thesis statement and supports it with evidence and examples, using analysis and evaluation to persuade the reader.
2. What are the main characteristics of an analytical essay?
The main characteristics of an analytical essay include:
– A clear and concise thesis statement that presents the writer’s argument
– Use of evidence and examples to support the argument
– Analysis and evaluation of the evidence presented
– Clear and logical structure, with well-developed paragraphs and transitions between them
– Use of formal and academic language
– Objective and impartial tone
3. What are some tips for writing an analytical essay?
Here are some tips for writing an analytical essay:
– Choose a topic that interests you and that you can analyze in depth
– Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that presents your argument
– Use evidence and examples to support your argument, ensuring that they are relevant, reliable, and credible
– Analyze and evaluate the evidence presented, demonstrating your critical thinking skills
– Use a clear and logical structure, with well-developed paragraphs and transitions between them
– Use formal and academic language, avoiding slang and colloquialisms
– Edit and proofread your essay thoroughly, ensuring that it is error-free and well-written.
To summarize, writing an effective analytical essay necessitates a thorough understanding of the subject matter, a well-developed thesis statement, strong evidence and analysis, and a clear and logical structure. To summarize the main points covered in this guide:
– The writer of an analytical essay must analyze and evaluate a specific topic or subject matter.
– A clear thesis statement, evidence and examples to support the argument, analysis and evaluation of the evidence, a clear and logical structure, formal and academic language, and an objective tone are the main characteristics of an analytical essay.
– Choosing a relevant topic, developing a clear thesis statement, using credible evidence and examples, analyzing and evaluating the evidence, using a clear and logical structure, using formal and academic language, and thoroughly editing and proofreading the essay are all tips for writing a successful analytical essay.
An effective analytical essay demonstrates critical thinking skills as well as the ability to analyze and evaluate complex issues. It is an important skill for both academic and professional success.
Finally, practicing writing on a regular basis, seeking feedback from others, and reading and analyzing examples of successful analytical essays can all help you improve your own writing skills.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples
Published on August 28, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Key concepts in rhetoric, analyzing the text, introducing your rhetorical analysis, the body: doing the analysis, concluding a rhetorical analysis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about rhetorical analysis.
Rhetoric, the art of effective speaking and writing, is a subject that trains you to look at texts, arguments and speeches in terms of how they are designed to persuade the audience. This section introduces a few of the key concepts of this field.
Appeals: Logos, ethos, pathos
Appeals are how the author convinces their audience. Three central appeals are discussed in rhetoric, established by the philosopher Aristotle and sometimes called the rhetorical triangle: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos , or the logical appeal, refers to the use of reasoned argument to persuade. This is the dominant approach in academic writing , where arguments are built up using reasoning and evidence.
Ethos , or the ethical appeal, involves the author presenting themselves as an authority on their subject. For example, someone making a moral argument might highlight their own morally admirable behavior; someone speaking about a technical subject might present themselves as an expert by mentioning their qualifications.
Pathos , or the pathetic appeal, evokes the audience’s emotions. This might involve speaking in a passionate way, employing vivid imagery, or trying to provoke anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response in the audience.
These three appeals are all treated as integral parts of rhetoric, and a given author may combine all three of them to convince their audience.
Text and context
In rhetoric, a text is not necessarily a piece of writing (though it may be this). A text is whatever piece of communication you are analyzing. This could be, for example, a speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image.
In these cases, your analysis would focus on more than just language—you might look at visual or sonic elements of the text too.
The context is everything surrounding the text: Who is the author (or speaker, designer, etc.)? Who is their (intended or actual) audience? When and where was the text produced, and for what purpose?
Looking at the context can help to inform your rhetorical analysis. For example, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech has universal power, but the context of the civil rights movement is an important part of understanding why.
Claims, supports, and warrants
A piece of rhetoric is always making some sort of argument, whether it’s a very clearly defined and logical one (e.g. in a philosophy essay) or one that the reader has to infer (e.g. in a satirical article). These arguments are built up with claims, supports, and warrants.
A claim is the fact or idea the author wants to convince the reader of. An argument might center on a single claim, or be built up out of many. Claims are usually explicitly stated, but they may also just be implied in some kinds of text.
The author uses supports to back up each claim they make. These might range from hard evidence to emotional appeals—anything that is used to convince the reader to accept a claim.
The warrant is the logic or assumption that connects a support with a claim. Outside of quite formal argumentation, the warrant is often unstated—the author assumes their audience will understand the connection without it. But that doesn’t mean you can’t still explore the implicit warrant in these cases.
For example, look at the following statement:
We can see a claim and a support here, but the warrant is implicit. Here, the warrant is the assumption that more likeable candidates would have inspired greater turnout. We might be more or less convinced by the argument depending on whether we think this is a fair assumption.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Rhetorical analysis isn’t a matter of choosing concepts in advance and applying them to a text. Instead, it starts with looking at the text in detail and asking the appropriate questions about how it works:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Do they focus closely on their key claims, or do they discuss various topics?
- What tone do they take—angry or sympathetic? Personal or authoritative? Formal or informal?
- Who seems to be the intended audience? Is this audience likely to be successfully reached and convinced?
- What kinds of evidence are presented?
By asking these questions, you’ll discover the various rhetorical devices the text uses. Don’t feel that you have to cram in every rhetorical term you know—focus on those that are most important to the text.
The following sections show how to write the different parts of a rhetorical analysis.
Like all essays, a rhetorical analysis begins with an introduction . The introduction tells readers what text you’ll be discussing, provides relevant background information, and presents your thesis statement .
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how an introduction works.
Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is widely regarded as one of the most important pieces of oratory in American history. Delivered in 1963 to thousands of civil rights activists outside the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the speech has come to symbolize the spirit of the civil rights movement and even to function as a major part of the American national myth. This rhetorical analysis argues that King’s assumption of the prophetic voice, amplified by the historic size of his audience, creates a powerful sense of ethos that has retained its inspirational power over the years.
The body of your rhetorical analysis is where you’ll tackle the text directly. It’s often divided into three paragraphs, although it may be more in a longer essay.
Each paragraph should focus on a different element of the text, and they should all contribute to your overall argument for your thesis statement.
Hover over the example to explore how a typical body paragraph is constructed.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis wraps up the essay by restating the main argument and showing how it has been developed by your analysis. It may also try to link the text, and your analysis of it, with broader concerns.
Explore the example below to get a sense of the conclusion.
It is clear from this analysis that the effectiveness of King’s rhetoric stems less from the pathetic appeal of his utopian “dream” than it does from the ethos he carefully constructs to give force to his statements. By framing contemporary upheavals as part of a prophecy whose fulfillment will result in the better future he imagines, King ensures not only the effectiveness of his words in the moment but their continuing resonance today. Even if we have not yet achieved King’s dream, we cannot deny the role his words played in setting us on the path toward it.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/rhetorical-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write a literary analysis essay | a step-by-step guide, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Organizing Your Analysis

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
There is no one perfect way to organize a rhetorical analysis essay. In fact, writers should always be a bit leery of plug-in formulas that offer a perfect essay format. Remember, organization itself is not the enemy, only organization without considering the specific demands of your particular writing task. That said, here are some general tips for plotting out the overall form of your essay.
Introduction
Like any rhetorical analysis essay, an essay analyzing a visual document should quickly set the stage for what you’re doing. Try to cover the following concerns in the initial paragraphs:
- Make sure to let the reader know you’re performing a rhetorical analysis. Otherwise, they may expect you to take positions or make an evaluative argument that may not be coming.
- Clearly state what the document under consideration is and possibly give some pertinent background information about its history or development. The intro can be a good place for a quick, narrative summary of the document. The key word here is “quick, for you may be dealing with something large (for example, an entire episode of a cartoon like the Simpsons). Save more in-depth descriptions for your body paragraph analysis.
- If you’re dealing with a smaller document (like a photograph or an advertisement), and copyright allows, the introduction or first page is a good place to integrate it into your page.
- Give a basic run down of the rhetorical situation surrounding the document: the author, the audience, the purpose, the context, etc.
Thesis Statements and Focus
Many authors struggle with thesis statements or controlling ideas in regards to rhetorical analysis essays. There may be a temptation to think that merely announcing the text as a rhetorical analysis is purpose enough. However, especially depending on your essay’s length, your reader may need a more direct and clear statement of your intentions. Below are a few examples.
1. Clearly narrow the focus of what your essay will cover. Ask yourself if one or two design aspects of the document is interesting and complex enough to warrant a full analytical treatment.
The website for Amazon.com provides an excellent example of alignment and proximity to assist its visitors in navigating a potentially large and confusing amount of information.
2. Since visual documents often seek to move people towards a certain action (buying a product, attending an event, expressing a sentiment), an essay may analyze the rhetorical techniques used to accomplish this purpose. The thesis statement should reflect this goal.
The call-out flyer for the Purdue Rowing Team uses a mixture of dynamic imagery and tantalizing promises to create interest in potential, new members.
3. Rhetorical analysis can also easily lead to making original arguments. Performing the analysis may lead you to an argument; or vice versa, you may start with an argument and search for proof that supports it.
A close analysis of the female body images in the July 2007 issue of Cosmopolitan magazine reveals contradictions between the articles’ calls for self-esteem and the advertisements’ unrealistic, beauty demands.
These are merely suggestions. The best measure for what your focus and thesis statement should be the document itself and the demands of your writing situation. Remember that the main thrust of your thesis statement should be on how the document creates meaning and accomplishes its purposes. The OWl has additional information on writing thesis statements.
Analysis Order (Body Paragraphs)
Depending on the genre and size of the document under analysis, there are a number of logical ways to organize your body paragraphs. Below are a few possible options. Which ever you choose, the goal of your body paragraphs is to present parts of the document, give an extended analysis of how that part functions, and suggest how the part ties into a larger point (your thesis statement or goal).
Chronological
This is the most straight-forward approach, but it can also be effective if done for a reason (as opposed to not being able to think of another way). For example, if you are analyzing a photo essay on the web or in a booklet, a chronological treatment allows you to present your insights in the same order that a viewer of the document experiences those images. It is likely that the images have been put in that order and juxtaposed for a reason, so this line of analysis can be easily integrated into the essay.
Be careful using chronological ordering when dealing with a document that contains a narrative (i.e. a television show or music video). Focusing on the chronological could easily lead you to plot summary which is not the point of a rhetorical analysis.
A spatial ordering covers the parts of a document in the order the eye is likely to scan them. This is different than chronological order, for that is dictated by pages or screens where spatial order concerns order amongst a single page or plane. There are no unwavering guidelines for this, but you can use the following general guidelines.
- Left to right and top to down is still the normal reading and scanning pattern for English-speaking countries.
- The eye will naturally look for centers. This may be the technical center of the page or the center of the largest item on the page.
- Lines are often used to provide directions and paths for the eye to follow.
- Research has shown that on web pages, the eye tends to linger in the top left quadrant before moving left to right. Only after spending a considerable amount of time on the top, visible portion of the page will they then scroll down.
Persuasive Appeals
The classic, rhetorical appeals are logos, pathos, and ethos. These concepts roughly correspond to the logic, emotion, and character of the document’s attempt to persuade. You can find more information on these concepts elsewhere on the OWL. Once you understand these devices, you could potentially order your essay by analyzing the document’s use of logos, ethos, and pathos in different sections.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis essay may not operate too differently from the conclusion of any other kind of essay. Still, many writers struggle with what a conclusion should or should not do. You can find tips elsewhere on the OWL on writing conclusions. In short, however, you should restate your main ideas and explain why they are important; restate your thesis; and outline further research or work you believe should be completed to further your efforts.
Essay Papers Writing Online
Tips and techniques for writing effective and powerful analytical essays.

Are you struggling to craft an effective analytical essay? Do you find yourself getting lost in a sea of information or unsure of how to present your analysis in a clear and concise manner? Look no further – this step-by-step guide will provide you with valuable tips and strategies to elevate your analytical essay writing skills to the next level.
Writing an analytical essay involves carefully examining a subject or topic and providing a thorough analysis and interpretation of the information gathered. It requires critical thinking, attention to detail, and the ability to express ideas and arguments coherently. In this guide, we will explore various techniques and approaches to help you develop and refine your analytical writing skills, allowing you to tackle any analytical essay with confidence and precision.
One crucial aspect of writing an analytical essay is conducting thorough research. To ensure your essay is well-informed and robust, it’s important to delve into reputable sources, such as academic journals, books, and reliable websites. By gathering a wide range of sources related to your topic, you will acquire a solid understanding of the subject matter, which will enable you to provide a comprehensive analysis in your essay.
Another essential element of analytical essay writing is the development of a strong thesis statement. Your thesis should present a clear and concise argument or claim that you will support throughout your essay. It should be specific, debatable, and relevant to the topic at hand. By crafting a well-defined thesis statement, you provide the backbone for your entire essay, guiding your analysis and helping you maintain a focused approach.
Furthermore, an effective analytical essay requires careful organization and structure. Divide your essay into logical paragraphs, each addressing a specific point or aspect of your analysis. Use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph, guiding your reader and providing a clear roadmap of your essay’s progression. Additionally, utilize transitional phrases and words to create smooth transitions between paragraphs, ensuring a cohesive and coherent flow.
Finding a Strong Topic for Your Essay

Choosing the right topic is a crucial first step in writing an analytical essay. The topic sets the tone for the entire essay and determines its scope and focus. It is important to select a topic that is engaging, relevant, and allows for in-depth analysis. This section will provide you with helpful strategies for finding a strong topic that will captivate your readers.
Gathering and Evaluating Reliable Sources

One of the key aspects of writing an analytical essay is gathering and evaluating reliable sources. The quality of your sources can greatly impact the strength and credibility of your arguments. In this section, we will explore the importance of finding trustworthy sources and discuss strategies for evaluating their reliability.
When conducting research for your essay, it is crucial to seek out sources that are authoritative and trustworthy. Reliable sources are those that have been written by experts in the field or have been published in reputable academic journals. These sources are often backed by extensive research and provide accurate and unbiased information.
When evaluating the reliability of a source, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, check the author’s credentials and expertise in the subject matter. Look for individuals who have relevant qualifications or experience in the field. This will help establish their credibility and ensure that they are knowledgeable on the topic.
In addition to the author’s credentials, consider the publication or website where the source is found. Reputable academic journals, books from respected publishers, and reputable websites such as government or educational institutions are generally more reliable sources of information. Be cautious of sources from unknown or biased sources, as they may not provide accurate or unbiased information.
Furthermore, it is important to analyze the content of the source itself. Look for evidence-based arguments, logical reasoning, and a balanced presentation of different perspectives. A reliable source should provide well-supported claims and back them up with relevant evidence and examples.
Finally, consider the date of publication. While older sources can still provide valuable insights, it is important to have up-to-date information, especially in fields that are rapidly evolving or undergoing significant changes. Check for recent studies and publications to ensure that your information is current.
In conclusion, gathering and evaluating reliable sources is a critical step in writing an analytical essay. By seeking out trustworthy sources and analyzing their credibility, you can strengthen your arguments and provide a solid foundation for your essay. Keep in mind the importance of author expertise, publication credibility, content analysis, and the recency of the information. Through careful evaluation, you can ensure that your essay is well-informed and persuasive.
Creating an Outline for Your Essay
One of the most important steps in the essay writing process is creating an outline. An outline serves as a roadmap for your essay, helping you to organize your thoughts and ideas in a logical and coherent manner.
When creating an outline for your essay, it’s important to start by identifying the main points or arguments that you want to make. These main points will serve as the foundation of your essay and should be presented in a clear and concise manner. You can think of these main points as the “backbone” of your essay.
Once you have identified the main points, you can then begin to develop subpoints that support and expand upon each main point. These subpoints should provide specific examples, evidence, or analysis to strengthen your main arguments. In essence, they help to fill in the details and provide a deeper understanding of your main points.
Organizing your main points and subpoints can be done in various ways. One common method is to use a hierarchical structure, such as an outline with Roman numerals, capital letters, and Arabic numerals. Another method is to use bullet points or a numbered list. You can choose the method that works best for you, based on the complexity of your essay and the level of detail you want to include in your outline.
As you create your outline, it’s important to keep in mind the overall structure of your essay. Your introduction should provide a brief overview of the topic and present your thesis statement. The body paragraphs should present and develop your main points and subpoints, providing evidence and analysis to support your arguments. Finally, your conclusion should summarize your main points and restate your thesis in a concise and compelling manner.
Remember that your outline is a flexible tool that can be revised and adjusted as you work on your essay. It’s not set in stone and can be modified as needed to better reflect your evolving ideas and arguments. Don’t be afraid to make changes and reorganize your outline as you go along.
In conclusion, creating an outline for your essay is an essential step in the writing process. It helps you to organize your thoughts, develop your arguments, and maintain a logical flow throughout your essay. By investing time and effort into creating a strong outline, you’ll set yourself up for success and make the writing process much smoother.
Developing a Clear and Coherent Argument
When it comes to writing analytical essays, one of the most important aspects is developing a clear and coherent argument. It is essential to have a well-structured and logical argument in order to effectively convey your ideas and convince your readers.
First and foremost, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the topic you are writing about. Take the time to thoroughly research and gather relevant information, as this will provide you with the necessary knowledge to build a strong argument. Additionally, make sure to identify any key terms or concepts that are essential to your argument, as this will help you stay focused and ensure coherence throughout your essay.
Once you have a solid foundation of knowledge, it is important to organize your argument in a logical manner. Start by outlining the main points or claims you want to make, and then provide supporting evidence or examples for each of these points. Be sure to clearly state your thesis statement, which should summarize the main argument you are making in your essay.
In order to maintain coherence in your argument, it is important to use logical transitions between your ideas. This can be done through the use of transitional words and phrases, such as “however,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand.” These transitions will help guide your reader through your argument and ensure that your ideas flow smoothly from one point to the next.
Lastly, it is crucial to anticipate and address counterarguments in your essay. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and effectively refuting them, you can further strengthen your overall argument. This demonstrates that you have considered multiple perspectives and have arrived at your own well-supported conclusion.
In conclusion, developing a clear and coherent argument is essential when writing analytical essays. By thoroughly researching your topic, organizing your ideas in a logical manner, using transitions effectively, and addressing counterarguments, you can effectively convey your ideas and make a convincing argument to your readers.
Strengthening Your Essay with Relevant Evidence
In order to create a compelling and persuasive analytical essay, it is essential to back up your arguments with relevant evidence. This evidence serves to support your claims and gives your essay credibility and authority.
When selecting evidence for your essay, it is important to choose examples and facts that are directly related to your topic. This will help to establish a strong connection between your argument and the evidence you present. Additionally, using relevant evidence allows you to make a more convincing case and gives your readers confidence in the validity of your assertions.
Relevant evidence can come in various forms, such as statistics, research studies, expert opinions, and real-life examples. By incorporating a mix of different types of evidence, you can strengthen the overall impact of your essay and appeal to a wider range of readers.
To ensure that the evidence you include in your essay is relevant, it is necessary to thoroughly research your topic and gather information from reliable sources. This will help you to find the most up-to-date and accurate evidence to support your arguments.
In addition to choosing relevant evidence, it is also crucial to properly integrate it into your essay. Make sure to clearly introduce each piece of evidence and explain how it supports your main points. Use strong and persuasive language to highlight the significance of the evidence and its connection to your argument.
Remember that the purpose of using relevant evidence is not only to support your argument but also to engage your readers and help them understand your perspective. By presenting well-chosen and compelling evidence, you can make your essay more persuasive and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
The Shapes of Grief
Witnessing the unbearable.

Joumana Medlej, Still from WAKE . Via X
. . . but how, what would the world be with us fully in it . . .
— dionne brand , The Blue Clerk
On May 14, 2022, Roberta A. Drury, Margus D. Morrison, Andre Mackniel, Aaron Salter Jr., Geraldine Talley, Celestine Chaney, Heyward Patterson, Katherine “Kat” Massey, Pearl Young, and Ruth Whitfield were murdered at a Tops Friendly Market in the East Side of Buffalo, New York.
Before and After Again , an exhibition currently on view at the Buffalo AKG Art Museum, presents those women, men, mothers, fathers, grandmothers, friends, children, aunts, cousins, uncles, daughters, sons, a deacon, a community activist, gardeners, people working, meeting, out buying groceries, and those who survive them, as people in their lives. Before and After Again shows people in relation and in community. Living. People loved and mourned. The artists and writers who curated the exhibition—Julia Bottoms, Tiffany Gaines, and Jillian Hanesworth—say that part of their challenge in presenting it was to “celebrate the vibrancy of extraordinary lives in the presence of a wound that will never heal.” The curators are clear that this exhibition is meant to function as a gathering place and not as a memorial.
At the annual literary festival NGC Bocas Lit Fest in April 2024 in Port of Spain, Trinidad, the writer Edwidge Danticat is in conversation with Elizabeth Walcott-Hackshaw. Someone in the audience asks a question about grief, which is really a question about life and more specifically a question about a writing life during grief.
In Danticat’s memoir, Brother, I’m Dying (2007), which is about the deaths and lives of her father and her uncle while she was pregnant with her first child, she reflects,
I write these things now, some as I witnessed them and today remember them, others from official documents as well as the borrowed recollections of family members. But the gist of them was told to me over the years, in part by my uncle Joseph, in part by my father. Some were told offhand, quickly. Others, in greater detail. What I learned from my father and uncle, I learned out of sequence and in fragments. This is an attempt at cohesiveness, and at re-creating a few wondrous and terrible months when their lives and mine intersected in startling ways, forcing me to look forward and back at the same time.
“I am writing this,” she continues, “only because they can’t.”
Danticat writes with such precision and clarity about death and grief. The work is moving, and it is scrubbed of the sentimental and the maudlin.
I am always rereading Brother, I’m Dying when I’m on an airplane.
There is something about the plane, its untethering space, between times and places, that allows me to meet so readily the many gifts of the book—among them language and memory.
In the exhibition materials for Before and After Again, Jillian Hanesworth says, “Once we stop thinking about art as something that we’re infusing into the situation to help us and instead we think about art as a living, breathing part of us, we understand that we’re just being given this water, this air.”
Danticat writes in her New Yorker essay “ The Haiti that Still Dreams ,” “Art is how we dream.”
It is my sighs that give it away to myself. When I catch myself sighing, I remember that after my mother died, I sighed for years—it was a part of mourning that I had not known to anticipate. What I am experiencing now, what I think many of us are experiencing, is a kind of distributed mourning. R. calls it ambient genocide.
I know that some call this feeling around climate catastrophe “climate grief.” Kate Zambreno writes about grief as ecological, as “concerning both the individual and the collective, the human and the nonhuman.”
Craft tells us to modulate our words. Craft tells us that if “we” do it well enough, “they” will listen. Craft tells us to be silent about genocide.
When the climate is everything and the catastrophe everywhere and also somewhere(s) very specific, there is also climate rage.
At Bocas, Danticat tells us that when she was writing Brother, I’m Dying , she looked forward to returning to it each day because in the pages of that book she got to visit with her father and her uncle. To spend time with them.
I know that grief is a vessel, a conduit for relation, but I am nevertheless startled into a new understanding when I hear that. Danticat expands what I understand grief to be and to make. She enlarges its shapes. Names it as connective tissue.
I feel, now, that I know differently the pain but also the possible joys of staying in the company of a loved and missed one through the work of remembering on the page, in the mind, in the world.
Language is one way we make and sustain relation. Words are one way we begin the work of unmaking and changing the shape of the world.
“Words are to be taken seriously,” Toni Cade Bambara insists. “Words set things in motion.”
That is the power of the iterative.
In December, Protean published “ Notes on Craft: Writing in the Hour of Genocide ” by the Palestinian American writer Fargo Nissim Tbakhi. Tbakhi names “Craft” as “the network of sanitizing influences exerted on writing in the English language” by the professional contexts through which it circulates and acquires prestige, including universities and publishing houses: “the influences of neoliberalism, of complicit institutions, and of the linguistic priorities of the state and of empire.” He continues:
Above all, Craft is the result of market forces; it is therefore the result of imperial forces, as the two are so inextricably bound up together as to be one and the same. The Craft which is taught in Western institutions, taken up and reproduced by Western publishers, literary institutions, and awards bodies, is a set of regulatory ideas which curtail forms of speech that might enact real danger to the constellation of economic and social values which are, as I write this, facilitating genocide in Palestine and elsewhere across the globe. If, as Audre Lorde taught us, the master’s tools cannot dismantle the master’s house, then Craft is the process by which our own real liberatory tools are dulled, confiscated, and replaced.
Craft tells us that the market matters. Craft tells us to modulate our words. Craft tells us that if “we” do it well enough, “they” will listen. Craft tells us to be silent about genocide. To be silent about genocides, about antiblackness and white supremacy. “Craft,” Tbakhi continues, “is a machine for regulation, estrangement, sanitization.”
But Tbakhi also notes, “Anticolonial writers in the U.S. and across the globe have long modeled alternative crafts which reject these priorities and continue to do so in this present moment.” Instead of Craft, I think about work. The work that we, writers, are doing now as we try to attend to the violent world and also to what might be in excess of it.
What are the words and the forms with which to do and say and make what we need to live in, now? Not only in some future time but now. What is our work to be? isn’t a grand question. It is a simple question. The question at the base of our writing.
Writers who try to do this work are told that our words don’t matter. When we demand a ceasefire and an end to occupation, we are told that those words are meaningless, that they do not prompt action, and that they cause tremendous injury (as in, to demand a ceasefire or to demand that the genocide in Gaza end is to cause injury and not to demand the cessation of injury). To name a person, institution, state, or a set of acts as racist or anti-Palestinian or antiblack is to cause injury. It is not the racism that injures, it is not the bullets and bombs that injure, it is the words that seek to name the injury—that name a murderous structure like apartheid or settler colonialism—that cause injury.
Meaning is in crisis. And we are embroiled, everywhere, in contests over meaning—which are also contests of power, contests over living. And dying.
When Anne Boyer resigned as poetry editor of The New York Times Magazine in November 2023, she wrote on her Substack,
Because our status quo is self-expression, sometimes the most effective mode of protest for artists is to refuse.
I can’t write about poetry amidst the “reasonable” tones of those who aim to acclimatize us to this unreasonable suffering. No more ghoulish euphemisms. No more verbally sanitized hellscapes. No more warmongering lies.
If this resignation leaves a hole in the news the size of poetry, then that is the true shape of the present.
This past academic year, as I prepared for class, I kept wondering how we were supposed to do our work and what that work should be. I wondered how the students in the class were supposed to do their work, even when the work that we were doing was relevant to what we are living through and trying to witness and to interrupt. We adjusted. We talked. We held space. We read. They were present. They showed up, and together we did our work.
In a three-hour seminar that I led at another university, I asked a group of students and faculty to read Steffani Jemison’s “ On the Stroke, the Glyph, and the Mark .” It’s a piece of writing that I both like and admire—her objects of inquiry, her sense making, and how she builds the essay through thinking and wondering.
Jemison’s first sentence is: “I have made a mark, and I do not know whether I am drawing or writing.”
Jemison is not talking about Craft.
She is talking about work. She is writing about writing/drawing/thinking/escape.
What is the work of composition, of mark making? What should our marks mark? Hold? Move toward?
What I'm working on…🧵 •WAKE• Indigo on washi. 25x??cm With 31,500 killed you-know-where so far, I was struggling with number blindness. When numbers become so large they lose all meaning, how do you remain awake to the scale of the slaughter & the personhood of the victims? pic.twitter.com/qwgN9PxQ58 — Joumana Medlej 🦋 (@joumajnouna) March 17, 2024
The artist Joumana Medlej likewise moves between writing and drawing, perhaps also thinking of escape. She is making a mark in lieu of a name, in lieu of many proper names. She is making a mark for every murdered Palestinian. On March 17, 2024, she posted on X: “With 31,500 killed you-know-where so far, I was struggling with number blindness. When numbers become so large they lose all meaning, how do you remain awake to the scale of the slaughter & the personhood of the victims?”
From the artist Torkwase Dyson, I have learned (again and again) that the practice of mark making is a practice of navigation.
We should rid our writing of the domestication of atrocity, rid our writing of the tense that insists on the innocence of its perpetrators, the exonerative tense of phrases like “lives were lost” and “a stray bullet found its way into the van” and “children died.” We should rid our writing of this dreadful innocence. We should refuse the logic that produces a phrase like “human animals” and a “four-year-old young lady.”
Driving through the neighborhood where we are staying in Salvador in the state of Bahia in Brazil, we keep encountering a particularly long and steep hill. Our friend tells us that it is called Ladeira da Preguiça —the Steep Hill of Laziness.
Slave owners, those who claimed to own other people, named it that. This hill that they did not walk and that they made enslaved people walk up and down carrying heavy goods that they themselves would not carry.
The slaveowners in Brazil, like everywhere black (and blackened) people were enslaved (in Brazil that was until 1888), maintained that the people they literally worked to death were lazy.
And that steep hill that they were forced to ascend and descend, hour after hour and day after day, was named Lazy Hill. They were named lazy. This is devastating language, brutal language.
This is language that undoes.
The descriptions of a prison in El Salvador. The description of a small boat that drifted across the Atlantic to Tobago. The plans to recolonize Haiti. The warnings that twenty-five million people in Sudan are at imminent risk of famine. The descriptions of massacres that Israel has carried out against Palestinians. The wide-open, shocked eyes of the Palestinian man abducted by the IDF. The descriptions of the Greek coast guard throwing people into the sea.
What must we, as writers, animate and set into motion in place of such language?
In “The Sentence as a Space for Living: Prose Architecture,” Renee Gladman writes,
For all my writing life I have been fascinated with notions of origin and passage, though rarely in terms of ancestry—since I don’t know where I’m from. I don’t know the languages or landscapes that preceded the incursion of English and what is now the United States into my lineage. Yet, the violence of that erasure—all the inheritances interrupted—is as foundational to my relationship to language and subjectivity as is grammar. . . . I open my mouth in my own life and I want to distort, rearrange, mispronounce the available vocabulary.
Mispronouncing can rearrange language and open it up; distortion might be a way-making tool that undoes available vocabularies.
And a sentence can also be a space for living through an occupation or preoccupation with the line, with grammars and imagination.
“Encampments are not only zones of demands & refusals, but also processes of communing, making decisions together, enacting solidarity as a verb, embodying autonomous & collective liberation. They are themselves zones of imagination, of connection, of prefiguring life & new worlds.”
This is Harsha Walia writing about the student encampments on campuses in the United States and Canada and France and the United Kingdom and elsewhere.
This is a vocabulary and a practice of our possible living.
As I write this, the university where I teach has sent in riot police to disband an encampment that has been established for less than twenty-four hours. All the universities calling in riot police think that they know the future. They don’t really know what they are making. They know what they want, but they do not know what they are incubating.
Alexis Pauline Gumbs’s “ In the Middle of Fighting for Freedom We Found Ourselves Free ” is a preface to June Jordan’s remembrance of Audre Lorde, her sister in struggle. Gumbs is channeling Jordan’s clarity about her and our perilous times. She writes, “The students are teaching us that, though we cannot undo the incalculable loss of genocidal violence, it is not too late. It is exactly the time to be braver together in service of a livable future. It is time for what June Jordan calls . . . ‘words that death cannot spell or delete.’”
After the Israeli bombing of Rafah on May 26, 2024, the hundredth or thousandth massacre in Palestine in seventy-six years, Jennine K writes on X, “The flour massacre, the tents massacre, the hospital massacre, the refugee camp massacre, the ‘safe corridor’ massacre, the endless massacres, in homes, on the streets, in tents, on foot—eight months of massacre after massacre after massacre.” The poet Ladan Osman writes , “Who or what will cool the eyes of those who witnessed and recorded this carnage, saying: People of the world, look at this?”
Terrible acts. Unbearable. Who is called on to be a continual witness to the unbearable, to survive and carry it?
What survives of those who survive this, eight months and counting of constant terror?
Each time I write that the genocide being carried out by Israel against Palestinians is unbearable, I name a position or positions. I name distance, because the Palestinians who are living this, those who are somehow surviving this, are bearing the unbearable, are being made to bear the unbearable over and over and over again. Their witnessing is a refusal to be silent in the face of genocide. More than that—they are necessary utterances in the midst of devastation.
In April 2024, I read that since October 2023, Israel has dropped over seventy thousand tons of bombs on Gaza.
Who can survive this? What survives of those who survive this, eight months and counting of constant terror? Those who move to what they are told is a “safe zone,” only for that zone to be bombed?
Thousands of people, likely tens of thousands of people buried, alive and dead, under the rubble. I read in The Guardian that people report walking though the destroyed streets and having to bear hearing people calling for help and being unable to help them.
Selma Dabbagh writes in the London Review of Book s, “According to the UN, it could take up to three years to remove the bodies from the 37 million tonnes of rubble in Gaza, which is also contaminated by unexploded ordnance, up to ten per cent of which, they estimate, ‘doesn’t function as designed.’”
Unbearable.
Unbearable, and entire populations are being forced to bear it anyway.
At the end of May 2024, as we are on our way to the airport in Salvador, L. tells us that there are more than three million people living in the favelas of Salvador. He says that a majority of the black people in Salvador live in one of the many favelas and that it is less expensive to live there than in other neighborhoods or in social housing.
L. also tells us that 260,000 people disappeared during the most intense period of Covid. L. does not know where they went.
How do more than a quarter of a million people go missing?
These are economies of scale. Economies of value.
During the same trip to Salvador and on our drive from Salvador to Cachoeira, another friend, G., an architect and professor, tells us that the government moved many people to social housing, but they did so with little thought to how people were assigned to a place. They gave little consideration to the distances that people were being moved or to the infrastructure or lack of it. G. tells us that these moves broke up communities and families. She also tells us that, except for the people on the ground floor, no one in social housing had access to back gardens.
No possibility of extending space horizontally or vertically. That possibility to move up or out is one of the infrastructures of life in Brazil.
G. tells us about the laje, “a flat concrete roof.” These kinds of roofs are considered by some to be incomplete. In the vocabulary of city officials, these structures are unfinished, an eyesore. But in another vocabulary of those who live in them, the laje is the space of the possible.
They are not incomplete; they are a future promise. It is an architecture that reaches upwards, that gestures toward plans. It is an architecture against the foreclosure of possibility.
On June 5, 2024, Omar Hamad, a pharmacist, writer, and film critic from Gaza, writes the following on X: “Describing last night as a harsh night is inaccurate. Out of sheer fear, our hearts reached our throats, as if we wanted to vomit them out. The bombing didn’t cease for a single moment. I don’t know how the sun rose upon us again.”
Not harsh. Something else. Some other word. Some other force of terror.
Each day I come to know even more clearly and urgently that we must commit to the fight for meaning. Not to concede the words, concepts, terms that we need to think and imagine and make livable lives.
This is some of what is required of our writing, some of what our writing can do, some of what our writing is for, in the face of all of this.
Writing in Pictures
Garth greenwell, louise glück’s late style, you might also like, palestinian solidarity, then and now, fady joudah, new perspectives, enduring writing.
Subscribe to The Yale Review and support our commitment to print.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Style Analysis Essay. Writing a style analysis essay may seem like a daunting task, but, by understanding the basic components of style analysis, it doesn't have to be a dreaded chore. Analyzing is an ability that will help you in other aspects of life, too, like work and school. With practice and a ...
Once students understand the fundamentals of style analysis and how diction, imagery, language, and syntax help authors establish tone and convey theme, they are ready to write an AP Passage Analysis essay, which is the ultimate assessment of a student's ability to read a passage closely to determine the author's intent.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Adjust the sections as needed based on the specific text and your analysis. 5. Write the Essay Introduction. Writing a rhetorical analysis essay introduction involves setting up the context for your analysis, introducing the text, and presenting your thesis statement. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to craft a practical introduction.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
provide when you are writing a paper. Here are some useful guidelines: o If you're writing a research paper, do not assume that your reader has read all the sources that you are writing about. You'll need to offer context about what those sources say so that your reader can understand why you have brought them into the conversation.
2 Research your topic. Once you know your topic, you can begin collecting data and evidence to discuss it. If your analytical essay is about a creative work, you may want to spend time reviewing or evaluating that work, such as watching a film closely or studying the details of a painting.
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
There are several different types of analysis essays, including: Literary Analysis Essays: These essays examine a work of literature and analyze various literary devices such as character development, plot, theme, and symbolism. Rhetorical Analysis Essays: These essays examine how authors use language and rhetoric to persuade their audience, focusing on the author's tone, word choice, and use ...
Read about analytical writing. Learn what an analysis essay is, the purpose and characteristics of an analytical essay, and the types of analysis essays. ... Depending on the topic, writing style ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
An analytical essay is just an analysis of a literary text. By contrast, a critical essay involves, not only an analysis of the text in question, but also dissection of the literary terms and devices used by the author to make his meanings clear. The critical essay also explains the functions of the literary terms used, and evaluates their usage, and whether they have achieved the intended ...
Step 4: Create an Outline. Now that you have your thesis statement and topic sentences, it's time to create an analytical essay outline to ensure your essay flows logically. Here's an outline prepared by our analytical essay writer based on the example of discussing the benefits and drawbacks of remote work: Introduction.
Whether you write a literary analysis essay or other types of assignments, there is no need to add any new data at the end of your analysis paper. Instead, summarize the arguments you mentioned in your analytical essay outline. ... They will understand your individual style and totally devote themselv. 17 November, 2022 10 minutes read Examples.
The analysis paper uses evidence to support the argument, such as excerpts from the piece of writing. All analytical papers include a thesis, analysis of the topic, and evidence to support that analysis. When developing an analytical essay outline and writing your essay, follow these five steps: #1: Choose a topic. #2: Write your thesis.
1. Restate the thesis statement: The conclusion should restate the thesis statement in a new and meaningful way, emphasizing its importance and relevance to the topic. 2. Summarize the main points: Summarize the main points of the essay, highlighting the evidence and examples that support the thesis statement. 3.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
There may be a temptation to think that merely announcing the text as a rhetorical analysis is purpose enough. However, especially depending on your essay's length, your reader may need a more direct and clear statement of your intentions. Below are a few examples. 1. Clearly narrow the focus of what your essay will cover.
Finding a Strong Topic for Your Essay. Choosing the right topic is a crucial first step in writing an analytical essay. The topic sets the tone for the entire essay and determines its scope and focus. It is important to select a topic that is engaging, relevant, and allows for in-depth analysis. This section will provide you with helpful ...
This is some of what is required of our writing, some of what our writing can do, some of what our writing is for, in the face of all of this. Christina Sharpe is a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Black Studies in the Humanities at York University in Toronto and the author of Monstrous Intimacies: Making Post-Slavery Subjects , In the Wake: On ...