Find anything you save across the site in your account

How Harmful Is Social Media?

In April, the social psychologist Jonathan Haidt published an essay in The Atlantic in which he sought to explain, as the piece’s title had it, “Why the Past 10 Years of American Life Have Been Uniquely Stupid.” Anyone familiar with Haidt’s work in the past half decade could have anticipated his answer: social media. Although Haidt concedes that political polarization and factional enmity long predate the rise of the platforms, and that there are plenty of other factors involved, he believes that the tools of virality—Facebook’s Like and Share buttons, Twitter’s Retweet function—have algorithmically and irrevocably corroded public life. He has determined that a great historical discontinuity can be dated with some precision to the period between 2010 and 2014, when these features became widely available on phones.
“What changed in the 2010s?” Haidt asks, reminding his audience that a former Twitter developer had once compared the Retweet button to the provision of a four-year-old with a loaded weapon. “A mean tweet doesn’t kill anyone; it is an attempt to shame or punish someone publicly while broadcasting one’s own virtue, brilliance, or tribal loyalties. It’s more a dart than a bullet, causing pain but no fatalities. Even so, from 2009 to 2012, Facebook and Twitter passed out roughly a billion dart guns globally. We’ve been shooting one another ever since.” While the right has thrived on conspiracy-mongering and misinformation, the left has turned punitive: “When everyone was issued a dart gun in the early 2010s, many left-leaning institutions began shooting themselves in the brain. And, unfortunately, those were the brains that inform, instruct, and entertain most of the country.” Haidt’s prevailing metaphor of thoroughgoing fragmentation is the story of the Tower of Babel: the rise of social media has “unwittingly dissolved the mortar of trust, belief in institutions, and shared stories that had held a large and diverse secular democracy together.”
These are, needless to say, common concerns. Chief among Haidt’s worries is that use of social media has left us particularly vulnerable to confirmation bias, or the propensity to fix upon evidence that shores up our prior beliefs. Haidt acknowledges that the extant literature on social media’s effects is large and complex, and that there is something in it for everyone. On January 6, 2021, he was on the phone with Chris Bail, a sociologist at Duke and the author of the recent book “ Breaking the Social Media Prism ,” when Bail urged him to turn on the television. Two weeks later, Haidt wrote to Bail, expressing his frustration at the way Facebook officials consistently cited the same handful of studies in their defense. He suggested that the two of them collaborate on a comprehensive literature review that they could share, as a Google Doc, with other researchers. (Haidt had experimented with such a model before.) Bail was cautious. He told me, “What I said to him was, ‘Well, you know, I’m not sure the research is going to bear out your version of the story,’ and he said, ‘Why don’t we see?’ ”
Bail emphasized that he is not a “platform-basher.” He added, “In my book, my main take is, Yes, the platforms play a role, but we are greatly exaggerating what it’s possible for them to do—how much they could change things no matter who’s at the helm at these companies—and we’re profoundly underestimating the human element, the motivation of users.” He found Haidt’s idea of a Google Doc appealing, in the way that it would produce a kind of living document that existed “somewhere between scholarship and public writing.” Haidt was eager for a forum to test his ideas. “I decided that if I was going to be writing about this—what changed in the universe, around 2014, when things got weird on campus and elsewhere—once again, I’d better be confident I’m right,” he said. “I can’t just go off my feelings and my readings of the biased literature. We all suffer from confirmation bias, and the only cure is other people who don’t share your own.”
Haidt and Bail, along with a research assistant, populated the document over the course of several weeks last year, and in November they invited about two dozen scholars to contribute. Haidt told me, of the difficulties of social-scientific methodology, “When you first approach a question, you don’t even know what it is. ‘Is social media destroying democracy, yes or no?’ That’s not a good question. You can’t answer that question. So what can you ask and answer?” As the document took on a life of its own, tractable rubrics emerged—Does social media make people angrier or more affectively polarized? Does it create political echo chambers? Does it increase the probability of violence? Does it enable foreign governments to increase political dysfunction in the United States and other democracies? Haidt continued, “It’s only after you break it up into lots of answerable questions that you see where the complexity lies.”
Haidt came away with the sense, on balance, that social media was in fact pretty bad. He was disappointed, but not surprised, that Facebook’s response to his article relied on the same three studies they’ve been reciting for years. “This is something you see with breakfast cereals,” he said, noting that a cereal company “might say, ‘Did you know we have twenty-five per cent more riboflavin than the leading brand?’ They’ll point to features where the evidence is in their favor, which distracts you from the over-all fact that your cereal tastes worse and is less healthy.”
After Haidt’s piece was published, the Google Doc—“Social Media and Political Dysfunction: A Collaborative Review”—was made available to the public . Comments piled up, and a new section was added, at the end, to include a miscellany of Twitter threads and Substack essays that appeared in response to Haidt’s interpretation of the evidence. Some colleagues and kibbitzers agreed with Haidt. But others, though they might have shared his basic intuition that something in our experience of social media was amiss, drew upon the same data set to reach less definitive conclusions, or even mildly contradictory ones. Even after the initial flurry of responses to Haidt’s article disappeared into social-media memory, the document, insofar as it captured the state of the social-media debate, remained a lively artifact.
Near the end of the collaborative project’s introduction, the authors warn, “We caution readers not to simply add up the number of studies on each side and declare one side the winner.” The document runs to more than a hundred and fifty pages, and for each question there are affirmative and dissenting studies, as well as some that indicate mixed results. According to one paper, “Political expressions on social media and the online forum were found to (a) reinforce the expressers’ partisan thought process and (b) harden their pre-existing political preferences,” but, according to another, which used data collected during the 2016 election, “Over the course of the campaign, we found media use and attitudes remained relatively stable. Our results also showed that Facebook news use was related to modest over-time spiral of depolarization. Furthermore, we found that people who use Facebook for news were more likely to view both pro- and counter-attitudinal news in each wave. Our results indicated that counter-attitudinal exposure increased over time, which resulted in depolarization.” If results like these seem incompatible, a perplexed reader is given recourse to a study that says, “Our findings indicate that political polarization on social media cannot be conceptualized as a unified phenomenon, as there are significant cross-platform differences.”
Interested in echo chambers? “Our results show that the aggregation of users in homophilic clusters dominate online interactions on Facebook and Twitter,” which seems convincing—except that, as another team has it, “We do not find evidence supporting a strong characterization of ‘echo chambers’ in which the majority of people’s sources of news are mutually exclusive and from opposite poles.” By the end of the file, the vaguely patronizing top-line recommendation against simple summation begins to make more sense. A document that originated as a bulwark against confirmation bias could, as it turned out, just as easily function as a kind of generative device to support anybody’s pet conviction. The only sane response, it seemed, was simply to throw one’s hands in the air.
When I spoke to some of the researchers whose work had been included, I found a combination of broad, visceral unease with the current situation—with the banefulness of harassment and trolling; with the opacity of the platforms; with, well, the widespread presentiment that of course social media is in many ways bad—and a contrastive sense that it might not be catastrophically bad in some of the specific ways that many of us have come to take for granted as true. This was not mere contrarianism, and there was no trace of gleeful mythbusting; the issue was important enough to get right. When I told Bail that the upshot seemed to me to be that exactly nothing was unambiguously clear, he suggested that there was at least some firm ground. He sounded a bit less apocalyptic than Haidt.
“A lot of the stories out there are just wrong,” he told me. “The political echo chamber has been massively overstated. Maybe it’s three to five per cent of people who are properly in an echo chamber.” Echo chambers, as hotboxes of confirmation bias, are counterproductive for democracy. But research indicates that most of us are actually exposed to a wider range of views on social media than we are in real life, where our social networks—in the original use of the term—are rarely heterogeneous. (Haidt told me that this was an issue on which the Google Doc changed his mind; he became convinced that echo chambers probably aren’t as widespread a problem as he’d once imagined.) And too much of a focus on our intuitions about social media’s echo-chamber effect could obscure the relevant counterfactual: a conservative might abandon Twitter only to watch more Fox News. “Stepping outside your echo chamber is supposed to make you moderate, but maybe it makes you more extreme,” Bail said. The research is inchoate and ongoing, and it’s difficult to say anything on the topic with absolute certainty. But this was, in part, Bail’s point: we ought to be less sure about the particular impacts of social media.
Bail went on, “The second story is foreign misinformation.” It’s not that misinformation doesn’t exist, or that it hasn’t had indirect effects, especially when it creates perverse incentives for the mainstream media to cover stories circulating online. Haidt also draws convincingly upon the work of Renée DiResta, the research manager at the Stanford Internet Observatory, to sketch out a potential future in which the work of shitposting has been outsourced to artificial intelligence, further polluting the informational environment. But, at least so far, very few Americans seem to suffer from consistent exposure to fake news—“probably less than two per cent of Twitter users, maybe fewer now, and for those who were it didn’t change their opinions,” Bail said. This was probably because the people likeliest to consume such spectacles were the sort of people primed to believe them in the first place. “In fact,” he said, “echo chambers might have done something to quarantine that misinformation.”
The final story that Bail wanted to discuss was the “proverbial rabbit hole, the path to algorithmic radicalization,” by which YouTube might serve a viewer increasingly extreme videos. There is some anecdotal evidence to suggest that this does happen, at least on occasion, and such anecdotes are alarming to hear. But a new working paper led by Brendan Nyhan, a political scientist at Dartmouth, found that almost all extremist content is either consumed by subscribers to the relevant channels—a sign of actual demand rather than manipulation or preference falsification—or encountered via links from external sites. It’s easy to see why we might prefer if this were not the case: algorithmic radicalization is presumably a simpler problem to solve than the fact that there are people who deliberately seek out vile content. “These are the three stories—echo chambers, foreign influence campaigns, and radicalizing recommendation algorithms—but, when you look at the literature, they’ve all been overstated.” He thought that these findings were crucial for us to assimilate, if only to help us understand that our problems may lie beyond technocratic tinkering. He explained, “Part of my interest in getting this research out there is to demonstrate that everybody is waiting for an Elon Musk to ride in and save us with an algorithm”—or, presumably, the reverse—“and it’s just not going to happen.”
When I spoke with Nyhan, he told me much the same thing: “The most credible research is way out of line with the takes.” He noted, of extremist content and misinformation, that reliable research that “measures exposure to these things finds that the people consuming this content are small minorities who have extreme views already.” The problem with the bulk of the earlier research, Nyhan told me, is that it’s almost all correlational. “Many of these studies will find polarization on social media,” he said. “But that might just be the society we live in reflected on social media!” He hastened to add, “Not that this is untroubling, and none of this is to let these companies, which are exercising a lot of power with very little scrutiny, off the hook. But a lot of the criticisms of them are very poorly founded. . . . The expansion of Internet access coincides with fifteen other trends over time, and separating them is very difficult. The lack of good data is a huge problem insofar as it lets people project their own fears into this area.” He told me, “It’s hard to weigh in on the side of ‘We don’t know, the evidence is weak,’ because those points are always going to be drowned out in our discourse. But these arguments are systematically underprovided in the public domain.”
In his Atlantic article, Haidt leans on a working paper by two social scientists, Philipp Lorenz-Spreen and Lisa Oswald, who took on a comprehensive meta-analysis of about five hundred papers and concluded that “the large majority of reported associations between digital media use and trust appear to be detrimental for democracy.” Haidt writes, “The literature is complex—some studies show benefits, particularly in less developed democracies—but the review found that, on balance, social media amplifies political polarization; foments populism, especially right-wing populism; and is associated with the spread of misinformation.” Nyhan was less convinced that the meta-analysis supported such categorical verdicts, especially once you bracketed the kinds of correlational findings that might simply mirror social and political dynamics. He told me, “If you look at their summary of studies that allow for causal inferences—it’s very mixed.”
As for the studies Nyhan considered most methodologically sound, he pointed to a 2020 article called “The Welfare Effects of Social Media,” by Hunt Allcott, Luca Braghieri, Sarah Eichmeyer, and Matthew Gentzkow. For four weeks prior to the 2018 midterm elections, the authors randomly divided a group of volunteers into two cohorts—one that continued to use Facebook as usual, and another that was paid to deactivate their accounts for that period. They found that deactivation “(i) reduced online activity, while increasing offline activities such as watching TV alone and socializing with family and friends; (ii) reduced both factual news knowledge and political polarization; (iii) increased subjective well-being; and (iv) caused a large persistent reduction in post-experiment Facebook use.” But Gentzkow reminded me that his conclusions, including that Facebook may slightly increase polarization, had to be heavily qualified: “From other kinds of evidence, I think there’s reason to think social media is not the main driver of increasing polarization over the long haul in the United States.”
In the book “ Why We’re Polarized ,” for example, Ezra Klein invokes the work of such scholars as Lilliana Mason to argue that the roots of polarization might be found in, among other factors, the political realignment and nationalization that began in the sixties, and were then sacralized, on the right, by the rise of talk radio and cable news. These dynamics have served to flatten our political identities, weakening our ability or inclination to find compromise. Insofar as some forms of social media encourage the hardening of connections between our identities and a narrow set of opinions, we might increasingly self-select into mutually incomprehensible and hostile groups; Haidt plausibly suggests that these processes are accelerated by the coalescence of social-media tribes around figures of fearful online charisma. “Social media might be more of an amplifier of other things going on rather than a major driver independently,” Gentzkow argued. “I think it takes some gymnastics to tell a story where it’s all primarily driven by social media, especially when you’re looking at different countries, and across different groups.”
Another study, led by Nejla Asimovic and Joshua Tucker, replicated Gentzkow’s approach in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and they found almost precisely the opposite results: the people who stayed on Facebook were, by the end of the study, more positively disposed to their historic out-groups. The authors’ interpretation was that ethnic groups have so little contact in Bosnia that, for some people, social media is essentially the only place where they can form positive images of one another. “To have a replication and have the signs flip like that, it’s pretty stunning,” Bail told me. “It’s a different conversation in every part of the world.”
Nyhan argued that, at least in wealthy Western countries, we might be too heavily discounting the degree to which platforms have responded to criticism: “Everyone is still operating under the view that algorithms simply maximize engagement in a short-term way” with minimal attention to potential externalities. “That might’ve been true when Zuckerberg had seven people working for him, but there are a lot of considerations that go into these rankings now.” He added, “There’s some evidence that, with reverse-chronological feeds”—streams of unwashed content, which some critics argue are less manipulative than algorithmic curation—“people get exposed to more low-quality content, so it’s another case where a very simple notion of ‘algorithms are bad’ doesn’t stand up to scrutiny. It doesn’t mean they’re good, it’s just that we don’t know.”
Bail told me that, over all, he was less confident than Haidt that the available evidence lines up clearly against the platforms. “Maybe there’s a slight majority of studies that say that social media is a net negative, at least in the West, and maybe it’s doing some good in the rest of the world.” But, he noted, “Jon will say that science has this expectation of rigor that can’t keep up with the need in the real world—that even if we don’t have the definitive study that creates the historical counterfactual that Facebook is largely responsible for polarization in the U.S., there’s still a lot pointing in that direction, and I think that’s a fair point.” He paused. “It can’t all be randomized control trials.”
Haidt comes across in conversation as searching and sincere, and, during our exchange, he paused several times to suggest that I include a quote from John Stuart Mill on the importance of good-faith debate to moral progress. In that spirit, I asked him what he thought of the argument, elaborated by some of Haidt’s critics, that the problems he described are fundamentally political, social, and economic, and that to blame social media is to search for lost keys under the streetlamp, where the light is better. He agreed that this was the steelman opponent: there were predecessors for cancel culture in de Tocqueville, and anxiety about new media that went back to the time of the printing press. “This is a perfectly reasonable hypothesis, and it’s absolutely up to the prosecution—people like me—to argue that, no, this time it’s different. But it’s a civil case! The evidential standard is not ‘beyond a reasonable doubt,’ as in a criminal case. It’s just a preponderance of the evidence.”
The way scholars weigh the testimony is subject to their disciplinary orientations. Economists and political scientists tend to believe that you can’t even begin to talk about causal dynamics without a randomized controlled trial, whereas sociologists and psychologists are more comfortable drawing inferences on a correlational basis. Haidt believes that conditions are too dire to take the hardheaded, no-reasonable-doubt view. “The preponderance of the evidence is what we use in public health. If there’s an epidemic—when COVID started, suppose all the scientists had said, ‘No, we gotta be so certain before you do anything’? We have to think about what’s actually happening, what’s likeliest to pay off.” He continued, “We have the largest epidemic ever of teen mental health, and there is no other explanation,” he said. “It is a raging public-health epidemic, and the kids themselves say Instagram did it, and we have some evidence, so is it appropriate to say, ‘Nah, you haven’t proven it’?”
This was his attitude across the board. He argued that social media seemed to aggrandize inflammatory posts and to be correlated with a rise in violence; even if only small groups were exposed to fake news, such beliefs might still proliferate in ways that were hard to measure. “In the post-Babel era, what matters is not the average but the dynamics, the contagion, the exponential amplification,” he said. “Small things can grow very quickly, so arguments that Russian disinformation didn’t matter are like COVID arguments that people coming in from China didn’t have contact with a lot of people.” Given the transformative effects of social media, Haidt insisted, it was important to act now, even in the absence of dispositive evidence. “Academic debates play out over decades and are often never resolved, whereas the social-media environment changes year by year,” he said. “We don’t have the luxury of waiting around five or ten years for literature reviews.”
Haidt could be accused of question-begging—of assuming the existence of a crisis that the research might or might not ultimately underwrite. Still, the gap between the two sides in this case might not be quite as wide as Haidt thinks. Skeptics of his strongest claims are not saying that there’s no there there. Just because the average YouTube user is unlikely to be led to Stormfront videos, Nyhan told me, doesn’t mean we shouldn’t worry that some people are watching Stormfront videos; just because echo chambers and foreign misinformation seem to have had effects only at the margins, Gentzkow said, doesn’t mean they’re entirely irrelevant. “There are many questions here where the thing we as researchers are interested in is how social media affects the average person,” Gentzkow told me. “There’s a different set of questions where all you need is a small number of people to change—questions about ethnic violence in Bangladesh or Sri Lanka, people on YouTube mobilized to do mass shootings. Much of the evidence broadly makes me skeptical that the average effects are as big as the public discussion thinks they are, but I also think there are cases where a small number of people with very extreme views are able to find each other and connect and act.” He added, “That’s where many of the things I’d be most concerned about lie.”
The same might be said about any phenomenon where the base rate is very low but the stakes are very high, such as teen suicide. “It’s another case where those rare edge cases in terms of total social harm may be enormous. You don’t need many teen-age kids to decide to kill themselves or have serious mental-health outcomes in order for the social harm to be really big.” He added, “Almost none of this work is able to get at those edge-case effects, and we have to be careful that if we do establish that the average effect of something is zero, or small, that it doesn’t mean we shouldn’t be worried about it—because we might be missing those extremes.” Jaime Settle, a scholar of political behavior at the College of William & Mary and the author of the book “ Frenemies: How Social Media Polarizes America ,” noted that Haidt is “farther along the spectrum of what most academics who study this stuff are going to say we have strong evidence for.” But she understood his impulse: “We do have serious problems, and I’m glad Jon wrote the piece, and down the road I wouldn’t be surprised if we got a fuller handle on the role of social media in all of this—there are definitely ways in which social media has changed our politics for the worse.”
It’s tempting to sidestep the question of diagnosis entirely, and to evaluate Haidt’s essay not on the basis of predictive accuracy—whether social media will lead to the destruction of American democracy—but as a set of proposals for what we might do better. If he is wrong, how much damage are his prescriptions likely to do? Haidt, to his great credit, does not indulge in any wishful thinking, and if his diagnosis is largely technological his prescriptions are sociopolitical. Two of his three major suggestions seem useful and have nothing to do with social media: he thinks that we should end closed primaries and that children should be given wide latitude for unsupervised play. His recommendations for social-media reform are, for the most part, uncontroversial: he believes that preteens shouldn’t be on Instagram and that platforms should share their data with outside researchers—proposals that are both likely to be beneficial and not very costly.
It remains possible, however, that the true costs of social-media anxieties are harder to tabulate. Gentzkow told me that, for the period between 2016 and 2020, the direct effects of misinformation were difficult to discern. “But it might have had a much larger effect because we got so worried about it—a broader impact on trust,” he said. “Even if not that many people were exposed, the narrative that the world is full of fake news, and you can’t trust anything, and other people are being misled about it—well, that might have had a bigger impact than the content itself.” Nyhan had a similar reaction. “There are genuine questions that are really important, but there’s a kind of opportunity cost that is missed here. There’s so much focus on sweeping claims that aren’t actionable, or unfounded claims we can contradict with data, that are crowding out the harms we can demonstrate, and the things we can test, that could make social media better.” He added, “We’re years into this, and we’re still having an uninformed conversation about social media. It’s totally wild.”
New Yorker Favorites
An Oscar-winning filmmaker takes on the Church of Scientology .
Wendy Wasserstein on the baby who arrived too soon .
The young stowaways thrown overboard at sea .
As he rose in politics, Robert Moses discovered that decisions about New York City’s future would not be based on democracy .
The Muslim tamale king of the Old West .
Fiction by Jamaica Kincaid: “ Girl .”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .

Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful? Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
It is important to note that social media is a core element of the internet, and it reshaped how a modern human perceives information, communicates, socializes, and learns about the outside world. It became a primary lens through which one interacts with others, and thus, it is critical to properly evaluate whether or not such a state of affairs is beneficial or harmful to human wellbeing. The given assessment argues that social media, not the internet, is harmful to society and humanity in general because it reshapes the social fabric, causes loss of reason, logic, attentiveness, and memory, violates individual rights of all people as well as proliferates misinformation, which means that social media’s harms heavily outweigh its benefits.
Firstly, in order to fairly and properly assess the benefits or harms of social media, the latter should be distinguished from the internet. For example, it is stated that “the notion that the Internet is bad for you seems premised on the idea that the Internet is one thing—a monolith” (Goldsmith 597). In other words, the internet is not one thing but rather a collection of vastly different forms of communication, presentation, information exchange, entertainment, interactions, and other functions. Therefore, the internet is a source of many positive aspects of modernity because it not only brings more informational democracy but also prevents restriction and control of the free exchange of knowledge. However, the question is not about the internet as a whole but rather social media. Unlike the internet, which brings a number of benefits, which far outweigh the harms, social media does not bring a similar imbalance in favor of good. Social media was designed to simplify socialization and communication online, but the outcome is unchecked control of the flow of conversation in favor of a specific agenda, profit, and violation of individual rights.
Secondly, not all internet elements utilize artificial intelligence as extensively as social media platforms. The use of AI allows such companies to fine-tune one typology of information consumed, which means that it is social media that makes decisions for its users. While the internet is a library of knowledge, where a person makes a clear choice on what to read, watch, listen to, or interact with, social media uses AI and complex algorithms to influence its user. The underlying business model of all social media platforms is to learn about its user as much as possible and profit from them in a targeted manner. Such a design is not an inherent feature of the internet, which is not constrained to be profitable in this manner since many websites operate through subscriptions, direct sales, or other means. When it comes to such dangers, AI itself can also be a problem. It is stated that “there are indeed concerns about the near-term future of AI —algorithmic traders crashing the economy, or sensitive power grids overreacting to fluctuations and shutting down electricity for large swaths of the population” (Littman 314). In other words, social media’s extensive use of AI in combination with its problematic business model creates a host of issues that are not attributable to the internet.
Thirdly, in addition to social media-specific problems, they are also linked to harms associated with both devices and the internet in general. As stated before, the internet has its harms and benefits, but the latter usually outweighs the former. Similarly, devices come with harms as well as benefits, where the balance is tilted towards the positive aspects. However, not only social media has its inherent design flaws, but it also has problems with devices and the internet in general, which makes their harms far more abundant than benefits. For example, it is stated that “while our phones offer convenience and diversion, they also breed anxiety” (Carr 582). In addition, “as the brain grows dependent on the technology, the research suggests, the intellect weakens,” and “the division of attention impedes reasoning and performance” (Carr 583). Therefore, these device-related problems are multiplied a hundredfold by the fact that social media amplifies distraction and attention division through notifications. Social media is not a highly intellect-strengthening medium either, which further complicates the dependence factor.
Fourthly, social media companies are not properly regulated, and the nature of the business heavily favors oligopoly rather than a proper competitive environment because people want to have a unified platform for communication and audience-building. Therefore, the industry generates highly powerful companies with unchecked capabilities, where the national and even international discourse takes place exclusively on such mediums. For example, one cannot deny the influence of Twitter or Facebook as drivers of political or social discourse. Therefore, there is a conflict of interest among such big tech companies in regards to providing an open and fair platform versus making a profit, and the decision is clearly made in favor of the latter. The very structure of the business model of social media is to influence users to buy the advertisers’ products or services, and thus, it cannot be a just and fair place for discussion on important subjects by definition. Such a state of affairs threatens the fabric of society whether or not these companies intend to do so.
Fifthly, the conflict of interest described in the previous section brings its biggest harm when it comes to the First Amendment of the United States Constitution, where private enterprises are not obliged to protect the freedom of speech and expression. Since the national and international discourse and communication are taking the place of social media, where the First Amendment is mandatory to have, these platforms are unable, unwilling, and not obliged to provide it. One can easily observe how such companies can become politically tilted towards one agenda over the other, where accounts of even the most influential individuals can be banned because they violated the terms of service of the company. In other words, a company’s rules override the Constitutional rules. It is important to note that only a better speech can be an answer to a bad speech and not a removal of that voice.
Sixthly, social media platforms are heavily engaged in data collection and privacy violations, which was demonstrated by well-known scandals and criticisms. Once again, the business model of social media companies is structured in such a manner that their primary customers are not users but advertisers. A former group is a form of product or service being sold to advertisers, which means that social media advances surveillance capitalism at its core. In a century where the right to privacy is constantly becoming a problem due to governmental antiterrorism interests, social media further threatens these fundamental rights. The problem is even more dangerous when one considers the ever-increasing cyber threat proliferation, which means a breach of security in a social media company endangers all of its users.
Seventhly, social media does not have a well-structured method of combatting misinformation since its primary incentive is to promote engagement and grab attention. Social media companies are conflicted between ensuring the accuracy of the information on their platform and boosting the interactivity with their users. Such companies want to have interesting pieces of information, which are better provided by misinformation since the truth is always more complex and intricate. Therefore, one can see how social media can become a breeding ground for people with agenda of public deception. In addition, these platforms would not have the capability to ensure the accuracy of information even if they were incentivized somehow. Public panic and political polarization are other phenomena that accompany social networks, and the catalyst for these occurrences is information received both directly by the subject and disseminated using modern social communication technologies.
In conclusion, social media is not the internet, and its harms are far more extensive than the latter because it affects memory, attention, and reason and violates individual rights for privacy, free expression, and fairness in discourse, as well as proliferates misinformation. In addition, social media inherits inherent problems associated with modern devices and the internet in general, which further compounds its harm. Therefore, the effects of social media hurt the social fabric by pretending that it serves its users while its actual customers are advertisers. It also pretends to provide an open and free platform for communication while its very business model implies targeted influence on the user’s preferences. The use of AI also adds to all of the concerns related to artificial intelligence safety.
Works Cited
Carr, Nicholas. “How Smartphones Hijack Our Minds.” They Say/I Say , edited by Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein, W.W. Norton & Norton Company, 2021, pp. 582-596.
Goldsmith, Kenneth. “Go Ahead: Waste Time on the Internet.” They Say/I Say , edited by Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein, W.W. Norton & Norton Company, 2021, pp. 597-602.
Littman, Michael. “Rise of the Machines” Is Not a Likely Future.” They Say/I Say , edited by Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein, W.W. Norton & Norton Company, 2021, pp. 311-314.
- The Concept of Internet Etiquette (Netiquette)
- Multicast Routing and Its Protocols
- Innovation in Textiles: New Fabric
- Navigating AI in Security: Safeguarding Privacy and Society
- The Importance of Trust in AI Adoption
- Online Identity-Creating New Personas and Relations
- IT Network Connectivity
- Interconnection of College Campus Lans to Wan
- Extensible HyperText Markup Language
- Influence of YouTube and Facebook on Business
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, July 2). Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful? https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-beneficial-or-harmful/
"Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful?" IvyPanda , 2 July 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-beneficial-or-harmful/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful'. 2 July.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful?" July 2, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-beneficial-or-harmful/.
1. IvyPanda . "Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful?" July 2, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-beneficial-or-harmful/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Social Media: Beneficial or Harmful?" July 2, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-beneficial-or-harmful/.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News
Social media harms teens’ mental health, mounting evidence shows. what now.
Understanding what is going on in teens’ minds is necessary for targeted policy suggestions

Most teens use social media, often for hours on end. Some social scientists are confident that such use is harming their mental health. Now they want to pinpoint what explains the link.
Carol Yepes/Getty Images
Share this:
By Sujata Gupta
February 20, 2024 at 7:30 am
In January, Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook’s parent company Meta, appeared at a congressional hearing to answer questions about how social media potentially harms children. Zuckerberg opened by saying: “The existing body of scientific work has not shown a causal link between using social media and young people having worse mental health.”
But many social scientists would disagree with that statement. In recent years, studies have started to show a causal link between teen social media use and reduced well-being or mood disorders, chiefly depression and anxiety.
Ironically, one of the most cited studies into this link focused on Facebook.
Researchers delved into whether the platform’s introduction across college campuses in the mid 2000s increased symptoms associated with depression and anxiety. The answer was a clear yes , says MIT economist Alexey Makarin, a coauthor of the study, which appeared in the November 2022 American Economic Review . “There is still a lot to be explored,” Makarin says, but “[to say] there is no causal evidence that social media causes mental health issues, to that I definitely object.”
The concern, and the studies, come from statistics showing that social media use in teens ages 13 to 17 is now almost ubiquitous. Two-thirds of teens report using TikTok, and some 60 percent of teens report using Instagram or Snapchat, a 2022 survey found. (Only 30 percent said they used Facebook.) Another survey showed that girls, on average, allot roughly 3.4 hours per day to TikTok, Instagram and Facebook, compared with roughly 2.1 hours among boys. At the same time, more teens are showing signs of depression than ever, especially girls ( SN: 6/30/23 ).
As more studies show a strong link between these phenomena, some researchers are starting to shift their attention to possible mechanisms. Why does social media use seem to trigger mental health problems? Why are those effects unevenly distributed among different groups, such as girls or young adults? And can the positives of social media be teased out from the negatives to provide more targeted guidance to teens, their caregivers and policymakers?
“You can’t design good public policy if you don’t know why things are happening,” says Scott Cunningham, an economist at Baylor University in Waco, Texas.
Increasing rigor
Concerns over the effects of social media use in children have been circulating for years, resulting in a massive body of scientific literature. But those mostly correlational studies could not show if teen social media use was harming mental health or if teens with mental health problems were using more social media.
Moreover, the findings from such studies were often inconclusive, or the effects on mental health so small as to be inconsequential. In one study that received considerable media attention, psychologists Amy Orben and Andrew Przybylski combined data from three surveys to see if they could find a link between technology use, including social media, and reduced well-being. The duo gauged the well-being of over 355,000 teenagers by focusing on questions around depression, suicidal thinking and self-esteem.
Digital technology use was associated with a slight decrease in adolescent well-being , Orben, now of the University of Cambridge, and Przybylski, of the University of Oxford, reported in 2019 in Nature Human Behaviour . But the duo downplayed that finding, noting that researchers have observed similar drops in adolescent well-being associated with drinking milk, going to the movies or eating potatoes.
Holes have begun to appear in that narrative thanks to newer, more rigorous studies.
In one longitudinal study, researchers — including Orben and Przybylski — used survey data on social media use and well-being from over 17,400 teens and young adults to look at how individuals’ responses to a question gauging life satisfaction changed between 2011 and 2018. And they dug into how the responses varied by gender, age and time spent on social media.
Social media use was associated with a drop in well-being among teens during certain developmental periods, chiefly puberty and young adulthood, the team reported in 2022 in Nature Communications . That translated to lower well-being scores around ages 11 to 13 for girls and ages 14 to 15 for boys. Both groups also reported a drop in well-being around age 19. Moreover, among the older teens, the team found evidence for the Goldilocks Hypothesis: the idea that both too much and too little time spent on social media can harm mental health.
“There’s hardly any effect if you look over everybody. But if you look at specific age groups, at particularly what [Orben] calls ‘windows of sensitivity’ … you see these clear effects,” says L.J. Shrum, a consumer psychologist at HEC Paris who was not involved with this research. His review of studies related to teen social media use and mental health is forthcoming in the Journal of the Association for Consumer Research.
Cause and effect
That longitudinal study hints at causation, researchers say. But one of the clearest ways to pin down cause and effect is through natural or quasi-experiments. For these in-the-wild experiments, researchers must identify situations where the rollout of a societal “treatment” is staggered across space and time. They can then compare outcomes among members of the group who received the treatment to those still in the queue — the control group.
That was the approach Makarin and his team used in their study of Facebook. The researchers homed in on the staggered rollout of Facebook across 775 college campuses from 2004 to 2006. They combined that rollout data with student responses to the National College Health Assessment, a widely used survey of college students’ mental and physical health.
The team then sought to understand if those survey questions captured diagnosable mental health problems. Specifically, they had roughly 500 undergraduate students respond to questions both in the National College Health Assessment and in validated screening tools for depression and anxiety. They found that mental health scores on the assessment predicted scores on the screenings. That suggested that a drop in well-being on the college survey was a good proxy for a corresponding increase in diagnosable mental health disorders.
Compared with campuses that had not yet gained access to Facebook, college campuses with Facebook experienced a 2 percentage point increase in the number of students who met the diagnostic criteria for anxiety or depression, the team found.
When it comes to showing a causal link between social media use in teens and worse mental health, “that study really is the crown jewel right now,” says Cunningham, who was not involved in that research.
A need for nuance
The social media landscape today is vastly different than the landscape of 20 years ago. Facebook is now optimized for maximum addiction, Shrum says, and other newer platforms, such as Snapchat, Instagram and TikTok, have since copied and built on those features. Paired with the ubiquity of social media in general, the negative effects on mental health may well be larger now.
Moreover, social media research tends to focus on young adults — an easier cohort to study than minors. That needs to change, Cunningham says. “Most of us are worried about our high school kids and younger.”
And so, researchers must pivot accordingly. Crucially, simple comparisons of social media users and nonusers no longer make sense. As Orben and Przybylski’s 2022 work suggested, a teen not on social media might well feel worse than one who briefly logs on.
Researchers must also dig into why, and under what circumstances, social media use can harm mental health, Cunningham says. Explanations for this link abound. For instance, social media is thought to crowd out other activities or increase people’s likelihood of comparing themselves unfavorably with others. But big data studies, with their reliance on existing surveys and statistical analyses, cannot address those deeper questions. “These kinds of papers, there’s nothing you can really ask … to find these plausible mechanisms,” Cunningham says.
One ongoing effort to understand social media use from this more nuanced vantage point is the SMART Schools project out of the University of Birmingham in England. Pedagogical expert Victoria Goodyear and her team are comparing mental and physical health outcomes among children who attend schools that have restricted cell phone use to those attending schools without such a policy. The researchers described the protocol of that study of 30 schools and over 1,000 students in the July BMJ Open.
Goodyear and colleagues are also combining that natural experiment with qualitative research. They met with 36 five-person focus groups each consisting of all students, all parents or all educators at six of those schools. The team hopes to learn how students use their phones during the day, how usage practices make students feel, and what the various parties think of restrictions on cell phone use during the school day.
Talking to teens and those in their orbit is the best way to get at the mechanisms by which social media influences well-being — for better or worse, Goodyear says. Moving beyond big data to this more personal approach, however, takes considerable time and effort. “Social media has increased in pace and momentum very, very quickly,” she says. “And research takes a long time to catch up with that process.”
Until that catch-up occurs, though, researchers cannot dole out much advice. “What guidance could we provide to young people, parents and schools to help maintain the positives of social media use?” Goodyear asks. “There’s not concrete evidence yet.”
More Stories from Science News on Science & Society

A fluffy, orange fungus could transform food waste into tasty dishes

‘Turning to Stone’ paints rocks as storytellers and mentors

Old books can have unsafe levels of chromium, but readers’ risk is low

Astronauts actually get stuck in space all the time

Scientists are getting serious about UFOs. Here’s why

‘Then I Am Myself the World’ ponders what it means to be conscious

Twisters asks if you can 'tame' a tornado. We have the answer

The world has water problems. This book has solutions
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
Yes, Social Media Really Is Undermining Democracy
Despite what Meta has to say.

W ithin the past 15 years, social media has insinuated itself into American life more deeply than food-delivery apps into our diets and microplastics into our bloodstreams. Look at stories about conflict, and it’s often lurking in the background. Recent articles on the rising dysfunction within progressive organizations point to the role of Twitter, Slack, and other platforms in prompting “endless and sprawling internal microbattles,” as The Intercept ’s Ryan Grim put it, referring to the ACLU. At a far higher level of conflict, the congressional hearings about the January 6 insurrection show us how Donald Trump’s tweets summoned the mob to Washington and aimed it at the vice president. Far-right groups then used a variety of platforms to coordinate and carry out the attack.
Social media has changed life in America in a thousand ways, and nearly two out of three Americans now believe that these changes are for the worse. But academic researchers have not yet reached a consensus that social media is harmful. That’s been a boon to social-media companies such as Meta, which argues, as did tobacco companies, that the science is not “ settled .”
The lack of consensus leaves open the possibility that social media may not be very harmful. Perhaps we’ve fallen prey to yet another moral panic about a new technology and, as with television, we’ll worry about it less after a few decades of conflicting studies. A different possibility is that social media is quite harmful but is changing too quickly for social scientists to capture its effects. The research community is built on a quasi-moral norm of skepticism: We begin by assuming the null hypothesis (in this case, that social media is not harmful), and we require researchers to show strong, statistically significant evidence in order to publish their findings. This takes time—a couple of years, typically, to conduct and publish a study; five or more years before review papers and meta-analyses come out; sometimes decades before scholars reach agreement. Social-media platforms, meanwhile, can change dramatically in just a few years .
So even if social media really did begin to undermine democracy (and institutional trust and teen mental health ) in the early 2010s, we should not expect social science to “settle” the matter until the 2030s. By then, the effects of social media will be radically different, and the harms done in earlier decades may be irreversible.
Let me back up. This spring, The Atlantic published my essay “ Why the Past 10 Years of American Life Have Been Uniquely Stupid ,” in which I argued that the best way to understand the chaos and fragmentation of American society is to see ourselves as citizens of Babel in the days after God rendered them unable to understand one another.
I showed how a few small changes to the architecture of social-media platforms, implemented from 2009 to 2012, increased the virality of posts on those platforms, which then changed the nature of social relationships. People could spread rumors and half-truths more quickly, and they could more readily sort themselves into homogenous tribes. Even more important, in my view, was that social-media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook could now be used more easily by anyone to attack anyone. It was as if the platforms had passed out a billion little dart guns, and although most users didn’t want to shoot anyone, three kinds of people began darting others with abandon: the far right, the far left, and trolls.
Jonathan Haidt and Tobias Rose-Stockwell: The dark psychology of social networks
All of these groups were suddenly given the power to dominate conversations and intimidate dissenters into silence. A fourth group—Russian agents––also got a boost, though they didn’t need to attack people directly. Their long-running project, which ramped up online in 2013, was to fabricate, exaggerate, or simply promote stories that would increase Americans’ hatred of one another and distrust of their institutions.
The essay proved to be surprisingly uncontroversial—or, at least, hardly anyone attacked me on social media. But a few responses were published, including one from Meta (formerly Facebook), which pointed to studies it said contradicted my argument. There was also an essay in The New Yorker by Gideon Lewis-Kraus, who interviewed me and other scholars who study politics and social media. He argued that social media might well be harmful to democracies, but the research literature is too muddy and contradictory to support firm conclusions.
So was my diagnosis correct, or are concerns about social media overblown? It’s a crucial question for the future of our society. As I argued in my essay, critics make us smarter. I’m grateful, therefore, to Meta and the researchers interviewed by Lewis-Kraus for helping me sharpen and extend my argument in three ways.
Are Democracies Becoming More Polarized and Less Healthy?
My essay laid out a wide array of harms that social media has inflicted on society. Political polarization is just one of them, but it is central to the story of rising democratic dysfunction.
Meta questioned whether social media should be blamed for increased polarization. In response to my essay, Meta’s head of research, Pratiti Raychoudhury, pointed to a study by Levi Boxell, Matthew Gentzkow, and Jesse Shapiro that looked at trends in 12 countries and found, she said, “that in some countries polarization was on the rise before Facebook even existed, and in others it has been decreasing while internet and Facebook use increased.” In a recent interview with the podcaster Lex Fridman , Mark Zuckerberg cited this same study in support of a more audacious claim: “Most of the academic studies that I’ve seen actually show that social-media use is correlated with lower polarization.”
Does that study really let social media off the hook? It plotted political polarization based on survey responses in 12 countries, most with data stretching back to the 1970s, and then drew straight lines that best fit the data points over several decades. It’s true that, while some lines sloped upward (meaning that polarization increased across the period as a whole), others sloped downward. But my argument wasn’t about the past 50 years. It was about a phase change that happened in the early 2010s , after Facebook and Twitter changed their architecture to enable hyper-virality.
I emailed Gentzkow to ask whether he could put a “hinge” in the graphs in the early 2010s, to see if the trends in polarization changed direction or accelerated in the past decade. He replied that there was not enough data after 2010 to make such an analysis reliable. He also noted that Meta’s response essay had failed to cite a 2020 article in which he and three colleagues found that randomly assigning participants to deactivate Facebook for the four weeks before the 2018 U.S. midterm elections reduced polarization.
Adrienne LaFrance: ‘History will not judge us kindly’
Meta’s response motivated me to look for additional publications to evaluate what had happened to democracies in the 2010s. I discovered four. One of them found no overall trend in polarization, but like the study by Boxell, Gentzkow, and Shapiro, it had few data points after 2015. The other three had data through 2020, and all three reported substantial increases in polarization and/or declines in the number or quality of democracies around the world.
One of them, a 2022 report from the Varieties of Democracy (V-Dem) Institute, found that “liberal democracies peaked in 2012 with 42 countries and are now down to the lowest levels in over 25 years.” It summarized the transformations of global democracy over the past 10 years in stark terms:
Just ten years ago the world looked very different from today. In 2011, there were more countries improving than declining on every aspect of democracy. By 2021 the world has been turned on its head: there are more countries declining than advancing on nearly all democratic aspects captured by V-Dem measures.
The report also notes that “toxic polarization”—signaled by declining “respect for counter-arguments and associated aspects of the deliberative component of democracy”—grew more severe in at least 32 countries.
A paper published one week after my Atlantic essay, by Yunus E. Orhan, found a global spike in democratic “backsliding” since 2008, and linked it to affective polarization, or animosity toward the other side. When affective polarization is high, partisans tolerate antidemocratic behavior by politicians on their own side––such as the January 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol.
And finally, the Economist Intelligence Unit reported a global decline in various democratic measures starting after 2015, according to its Democracy Index.
These three studies cannot prove that social media caused the global decline, but—contra Meta and Zuckerberg—they show a global trend toward polarization in the previous decade, the one in which the world embraced social media.
Has Social Media Created Harmful Echo Chambers?
So why did democracies weaken in the 2010s? How might social media have made them more fragmented and less stable? One popular argument contends that social media sorts users into echo chambers––closed communities of like-minded people. Lack of contact with people who hold different viewpoints allows a sort of tribal groupthink to take hold, reducing the quality of everyone’s thinking and the prospects for compromise that are essential in a democratic system.
According to Meta, however, “More and more research discredits the idea that social media algorithms create an echo chamber.” It points to two sources to back up that claim, but many studies show evidence that social media does in fact create echo chambers. Because conflicting studies are common in social-science research, I created a “ collaborative review ” document last year with Chris Bail, a sociologist at Duke University who studies social media. It’s a public Google doc in which we organize the abstracts of all the studies we can find about social media’s impact on democracy, and then we invite other experts to add studies, comments, and criticisms. We cover research on seven different questions, including whether social media promotes echo chambers. After spending time in the document, Lewis-Kraus wrote in The New Yorker : “The upshot seemed to me to be that exactly nothing was unambiguously clear.”
He is certainly right that nothing is unambiguous. But as I have learned from curating three such documents , researchers often reach opposing conclusions because they have “operationalized” the question differently. That is, they have chosen different ways to turn an abstract question (about the prevalence of echo chambers, say) into something concrete and measurable. For example, researchers who choose to measure echo chambers by looking at the diversity of people’s news consumption typically find little evidence that they exist at all. Even partisans end up being exposed to news stories and videos from the other side. Both of the sources that Raychoudhury cited in her defense of Meta mention this idea.
Derek Thompson: Social media is attention alcohol
But researchers who measure echo chambers by looking at social relationships and networks usually find evidence of “homophily”—that is, people tend to engage with others who are similar to themselves. One study of politically engaged Twitter users, for example, found that they “are disproportionately exposed to like-minded information and that information reaches like-minded users more quickly.” So should we throw up our hands and say that the findings are irreconcilable? No, we should integrate them, as the sociologist Zeynep Tufekci did in a 2018 essay . Coming across contrary viewpoints on social media, she wrote, is “not like reading them in a newspaper while sitting alone.” Rather, she said, “it’s like hearing them from the opposing team while sitting with our fellow fans in a football stadium … We bond with our team by yelling at the fans of the other one.” Mere exposure to different sources of news doesn’t automatically break open echo chambers; in fact, it can reinforce them.
These closely bonded groupings can have profound political ramifications, as a couple of my critics in the New Yorker article acknowledged. A major feature of the post-Babel world is that the extremes are now far louder and more influential than before. They may also become more violent. Recent research by Morteza Dehghani and his colleagues at the University of Southern California shows that people are more willing to commit violence when they are immersed in a community they perceive to be morally homogeneous.
This finding seems to be borne out by a statement from the 18-year-old man who recently killed 10 Black Americans at a supermarket in Buffalo. In the Q&A portion of the manifesto attributed to him, he wrote:
Where did you get your current beliefs? Mostly from the internet. There was little to no influence on my personal beliefs by people I met in person.
The killer goes on to claim that he had read information “from all ideologies,” but I find it unlikely that he consumed a balanced informational diet, or, more important, that he hung out online with ideologically diverse users. The fact that he livestreamed his shooting tells us he assumed that his community shared his warped worldview. He could not have found such an extreme yet homogeneous group in his small town 200 miles from Buffalo. But thanks to social media, he found an international fellowship of extreme racists who jointly worshipped past mass murderers and from whom he copied sections of his manifesto.
Is Social Media the Primary Villain in This Story?
In her response to my essay, Raychoudhury did not deny that Meta bore any blame. Rather, her defense was two-pronged, arguing that the research is not yet definitive, and that, in any case, we should be focusing on mainstream media as the primary cause of harm.
Raychoudhury pointed to a study on the role of cable TV and mainstream media as major drivers of partisanship. She is correct to do so: The American culture war has roots going back to the turmoil of the 1960s, which activated evangelicals and other conservatives in the ’70s. Social media (which arrived around 2004 and became truly pernicious, I argue, only after 2009) is indeed a more recent player in this phenomenon.
In my essay, I included a paragraph on this backstory, noting the role of Fox News and the radicalizing Republican Party of the ’90s, but I should have said more. The story of polarization is complex, and political scientists cite a variety of contributing factors , including the growing politicization of the urban-rural divide; rising immigration; the increasing power of big and very partisan donors; the loss of a common enemy when the Soviet Union collapsed; and the loss of the “Greatest Generation,” which had an ethos of service forged in the crisis of the Second World War. And although polarization rose rapidly in the 2010s, the rise began in the ’90s, so I cannot pin the majority of the rise on social media.
But my essay wasn’t primarily about ordinary polarization. I was trying to explain a new dynamic that emerged in the 2010s: the fear of one another , even—and perhaps especially––within groups that share political or cultural affinities. This fear has created a whole new set of social and political problems.
The loss of a common enemy and those other trends with roots in the 20th century can help explain America’s ever nastier cross-party relationships, but they can’t explain why so many college students and professors suddenly began to express more fear, and engage in more self-censorship, around 2015. These mostly left-leaning people weren’t worried about the “other side”; they were afraid of a small number of students who were further to the left, and who enthusiastically hunted for verbal transgressions and used social media to publicly shame offenders.
A few years later, that same fearful dynamic spread to newsrooms , companies , nonprofit organizations , and many other parts of society . The culture war had been running for two or three decades by then, but it changed in the mid-2010s when ordinary people with little to no public profile suddenly became the targets of social-media mobs. Consider the famous 2013 case of Justine Sacco , who tweeted an insensitive joke about her trip to South Africa just before boarding her flight in London and became an international villain by the time she landed in Cape Town. She was fired the next day. Or consider the the far right’s penchant for using social media to publicize the names and photographs of largely unknown local election officials, health officials, and school-board members who refuse to bow to political pressure, and who are then subjected to waves of vitriol, including threats of violence to themselves and their children, simply for doing their jobs. These phenomena, now common to the culture, could not have happened before the advent of hyper-viral social media in 2009.
Matthew Hindman, Nathaniel Lubin, and Trevor Davis: Facebook has a superuser-supremacy problem
This fear of getting shamed, reported, doxxed, fired, or physically attacked is responsible for the self-censorship and silencing of dissent that were the main focus of my essay. When dissent within any group or institution is stifled, the group will become less perceptive, nimble, and effective over time.
Social media may not be the primary cause of polarization, but it is an important cause, and one we can do something about. I believe it is also the primary cause of the epidemic of structural stupidity, as I called it, that has recently afflicted many of America’s key institutions.
What Can We Do to Make Things Better?
My essay presented a series of structural solutions that would allow us to repair some of the damage that social media has caused to our key democratic and epistemic institutions. I proposed three imperatives: (1) harden democratic institutions so that they can withstand chronic anger and mistrust, (2) reform social media so that it becomes less socially corrosive, and (3) better prepare the next generation for democratic citizenship in this new age.
I believe that we should begin implementing these reforms now, even if the science is not yet “settled.” Beyond a reasonable doubt is the appropriate standard of evidence for reviewers guarding admission to a scientific journal, or for jurors establishing guilt in a criminal trial. It is too high a bar for questions about public health or threats to the body politic. A more appropriate standard is the one used in civil trials: the preponderance of evidence. Is social media probably damaging American democracy via at least one of the seven pathways analyzed in our collaborative-review document , or probably not ? I urge readers to examine the document themselves. I also urge the social-science community to find quicker ways to study potential threats such as social media, where platforms and their effects change rapidly. Our motto should be “Move fast and test things.” Collaborative-review documents are one way to speed up the process by which scholars find and respond to one another’s work.
Beyond these structural solutions, I considered adding a short section to the article on what each of us can do as individuals, but it sounded a bit too preachy, so I cut it. I now regret that decision. I should have noted that all of us, as individuals, can be part of the solution by choosing to act with courage, moderation, and compassion. It takes a great deal of resolve to speak publicly or stand your ground when a barrage of snide, disparaging, and otherwise hostile comments is coming at you and nobody rises to your defense (out of fear of getting attacked themselves).
Read: How to fix Twitter—and all of social media
Fortunately, social media does not usually reflect real life, something that more people are beginning to understand. A few years ago, I heard an insight from an older business executive. He noted that before social media, if he received a dozen angry letters or emails from customers, they spurred him to action because he assumed that there must be a thousand other disgruntled customers who didn’t bother to write. But now, if a thousand people like an angry tweet or Facebook post about his company, he assumes that there must be a dozen people who are really upset.
Seeing that social-media outrage is transient and performative should make it easier to withstand, whether you are the president of a university or a parent speaking at a school-board meeting. We can all do more to offer honest dissent and support the dissenters within institutions that have become structurally stupid. We can all get better at listening with an open mind and speaking in order to engage another human being rather than impress an audience. Teaching these skills to our children and our students is crucial, because they are the generation who will have to reinvent deliberative democracy and Tocqueville’s “art of association” for the digital age.
We must act with compassion too. The fear and cruelty of the post-Babel era are a result of its tendency to reward public displays of aggression. Social media has put us all in the middle of a Roman coliseum, and many in the audience want to see conflict and blood. But once we realize that we are the gladiators—tricked into combat so that we might generate “content,” “engagement,” and revenue—we can refuse to fight. We can be more understanding toward our fellow citizens, seeing that we are all being driven mad by companies that use largely the same set of psychological tricks. We can forswear public conflict and use social media to serve our own purposes, which for most people will mean more private communication and fewer public performances.
The post-Babel world will not be rebuilt by today’s technology companies. That work will be left to citizens who understand the forces that brought us to the verge of self-destruction, and who develop the new habits, virtues, technologies, and shared narratives that will allow us to reap the benefits of living and working together in peace.
About the Author
More Stories
End the Phone-Based Childhood Now
Get Phones Out of Schools Now
10 Positive and Negative Effects of Social Media on Society
Nowadays, social media is so popular among the young, children, and adults. Each of us uses social media to be updated, to entertain ourselves, to communicate with others, to explore new things, and to connect with the world. Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, YouTube, etc. are examples of social media. Social media is a part of our lives today, and consciously or unconsciously, it is becoming our habit to continuously go through it and check the notifications.

What is social media?
Social media is a platform where we can communicate with a large number of people, make connections, and interact with them. It operates on the internet.A user usually creates an account on such a platform and allows interaction with the millions of other users available on it according to their preferences and choices. Apart from the interaction, it also allows users to share information, chat with other people, share their opinions, create content, and embrace their differences.
In today’s world, social media is an important part of young people’s lives, determining and shaping their perspectives.The youth typically adopt and pursue social media trends; for example, in dressing styles, the youth adopt dresses and styles that are promoted as trends by social media.
Social media not only allows people to share their opinions, but it also shapes the opinions of its users.Social media have an impact on their users as well as society as a whole, both positive and negative.
Here we will now discuss the negative and positive impacts of social media on society.
Positive impact of social media on society, negative impacts of social media on society.
Conclusion-
Yachika Yadav is a sociology post graduate student at Banasthali Vidyapith. She loves to capture moments in nature, apart from drawing and writing poetries. Field of research attracts her the most and in future she want to be a part of that. She is a good listener, learner. And tries to always help others.
Essay on Social Media for School Students and Children
500+ words essay on social media.
Social media is a tool that is becoming quite popular these days because of its user-friendly features. Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and more are giving people a chance to connect with each other across distances. In other words, the whole world is at our fingertips all thanks to social media. The youth is especially one of the most dominant users of social media. All this makes you wonder that something so powerful and with such a massive reach cannot be all good. Like how there are always two sides to a coin, the same goes for social media. Subsequently, different people have different opinions on this debatable topic. So, in this essay on Social Media, we will see the advantages and disadvantages of social media.

Advantages of Social Media
When we look at the positive aspect of social media, we find numerous advantages. The most important being a great device for education . All the information one requires is just a click away. Students can educate themselves on various topics using social media.
Moreover, live lectures are now possible because of social media. You can attend a lecture happening in America while sitting in India.
Furthermore, as more and more people are distancing themselves from newspapers, they are depending on social media for news. You are always updated on the latest happenings of the world through it. A person becomes more socially aware of the issues of the world.
In addition, it strengthens bonds with your loved ones. Distance is not a barrier anymore because of social media. For instance, you can easily communicate with your friends and relatives overseas.
Most importantly, it also provides a great platform for young budding artists to showcase their talent for free. You can get great opportunities for employment through social media too.
Another advantage definitely benefits companies who wish to promote their brands. Social media has become a hub for advertising and offers you great opportunities for connecting with the customer.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Disadvantages of Social Media
Despite having such unique advantages, social media is considered to be one of the most harmful elements of society. If the use of social media is not monitored, it can lead to grave consequences.

Thus, the sharing on social media especially by children must be monitored at all times. Next up is the addition of social media which is quite common amongst the youth.
This addiction hampers with the academic performance of a student as they waste their time on social media instead of studying. Social media also creates communal rifts. Fake news is spread with the use of it, which poisons the mind of peace-loving citizens.
In short, surely social media has both advantages and disadvantages. But, it all depends on the user at the end. The youth must particularly create a balance between their academic performances, physical activities, and social media. Excess use of anything is harmful and the same thing applies to social media. Therefore, we must strive to live a satisfying life with the right balance.

FAQs on Social Media
Q.1 Is social media beneficial? If yes, then how?
A.1 Social media is quite beneficial. Social Media offers information, news, educational material, a platform for talented youth and brands.
Q.2 What is a disadvantage of Social Media?
A.2 Social media invades your privacy. It makes you addicted and causes health problems. It also results in cyberbullying and scams as well as communal hatred.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Skip to content
Read the latest news stories about Mailman faculty, research, and events.
Departments
We integrate an innovative skills-based curriculum, research collaborations, and hands-on field experience to prepare students.
Learn more about our research centers, which focus on critical issues in public health.
Our Faculty
Meet the faculty of the Mailman School of Public Health.
Become a Student
Life and community, how to apply.
Learn how to apply to the Mailman School of Public Health.
- Additional Resources
Just How Harmful Is Social Media? Our Experts Weigh-In.
A recent investigation by the Wall Street Journal revealed that Facebook was aware of mental health risks linked to the use of its Instagram app but kept those findings secret. Internal research by the social media giant found that Instagram worsened body image issues for one in three teenage girls, and all teenage users of the app linked it to experiences of anxiety and depression. It isn’t the first evidence of social media’s harms. Watchdog groups have identified Facebook and Instagram as avenues for cyberbullying , and reports have linked TikTok to dangerous and antisocial behavior, including a recent spate of school vandalism .
As social media has proliferated worldwide—Facebook has 2.85 billion users—so too have concerns over how the platforms are affecting individual and collective wellbeing. Social media is criticized for being addictive by design and for its role in the spread of misinformation on critical issues from vaccine safety to election integrity, as well as the rise of right-wing extremism. Social media companies, and many users, defend the platforms as avenues for promoting creativity and community-building. And some research has pushed back against the idea that social media raises the risk for depression in teens . So just how healthy or unhealthy is social media?
Two experts from Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia Psychiatry share their insights into one crucial aspect of social media’s influence—its effect on the mental health of young people and adults. Deborah Glasofer , associate professor of psychology in psychiatry, conducts psychotherapy development research for adults with eating disorders and teaches about cognitive behavioral therapy. She is the co-author of the book Eating Disorders: What Everyone Needs to Know. Claude Mellins , Professor of medical psychology in the Departments of Psychiatry and Sociomedical Sciences, studies wellbeing among college and graduate students, among other topics, and serves as program director of CopeColumbia, a peer support program for Columbia faculty and staff whose mental health has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. She co-led the SHIFT research study to reduce sexual violence among undergraduates. Both use social media.
What do we know about the mental health risks of social media use?
Mellins : Facebook and Instagram and other social media platforms are important sources of socialization and relationship-building for many young people. Although there are important benefits, social media can also provide platforms for bullying and exclusion, unrealistic expectations about body image and sources of popularity, normalization of risk-taking behaviors, and can be detrimental to mental health. Girls and young people who identify as sexual and gender minorities can be especially vulnerable as targets. Young people’s brains are still developing, and as individuals, young people are developing their own identities. What they see on social media can define what is expected in ways that is not accurate and that can be destructive to identity development and self-image. Adolescence is a time of risk-taking, which is both a strength and a vulnerability. Social media can exacerbate risks, as we have seen played out in the news.
Although there are important benefits, social media can also provide platforms for bullying and exclusion, unrealistic expectations about body image and sources of popularity, normalization of risk-taking behaviors, and can be detrimental to mental health. – Claude Mellins
Glasofer : For those vulnerable to developing an eating disorder, social media may be especially unhelpful because it allows people to easily compare their appearance to their friends, to celebrities, even older images of themselves. Research tells us that how much someone engages with photo-related activities like posting and sharing photos on Facebook or Instagram is associated with less body acceptance and more obsessing about appearance. For adolescent girls in particular, the more time they spend on social media directly relates to how much they absorb the idea that being thin is ideal, are driven to try to become thin, and/or overly scrutinize their own bodies. Also, if someone is vulnerable to an eating disorder, they may be especially attracted to seeking out unhelpful information—which is all too easy to find on social media.
Are there any upsides to social media?
Mellins : For young people, social media provides a platform to help them figure out who they are. For very shy or introverted young people, it can be a way to meet others with similar interests. During the pandemic, social media made it possible for people to connect in ways when in-person socialization was not possible. Social support and socializing are critical influences on coping and resilience. Friends we couldn’t see in person were available online and allowed us important points of connection. On the other hand, fewer opportunities for in-person interactions with friends and family meant less of a real-world check on some of the negative influences of social media.
Whether it’s social media or in person, a good peer group makes the difference. A group of friends that connects over shared interests like art or music, and is balanced in their outlook on eating and appearance, is a positive. – Deborah Glasofer
Glasofer : Whether it’s social media or in person, a good peer group makes the difference. A group of friends that connects over shared interests like art or music, and is balanced in their outlook on eating and appearance, is a positive. In fact, a good peer group online may be protective against negative in-person influences. For those with a history of eating disorders, there are body-positive and recovery groups on social media. Some people find these groups to be supportive; for others, it’s more beneficial to move on and pursue other interests.
Is there a healthy way to be on social media?
Mellins : If you feel social media is a negative experience, you might need a break. Disengaging with social media permanently is more difficult—especially for young people. These platforms are powerful tools for connecting and staying up-to-date with friends and family. Social events, too. If you’re not on social media then you’re reliant on your friends to reach out to you personally, which doesn’t always happen. It’s complicated.
Glasofer : When you find yourself feeling badly about yourself in relation to what other people are posting about themselves, then social media is not doing you any favors. If there is anything on social media that is negatively affecting your actions or your choices—for example, if you’re starting to eat restrictively or exercise excessively—then it’s time to reassess. Parents should check-in with their kids about their lives on social media. In general, I recommend limiting social media— creating boundaries that are reasonable and work for you—so you can be present with people in your life. I also recommend social media vacations. It’s good to take the time to notice the difference between the virtual world and the real world.
June 20, 2022
Why Social Media Makes People Unhappy—And Simple Ways to Fix It
Research suggests platform designs make us lose track of time spent on them and can heighten conflicts, and then we feel upset with ourselves
By Daisy Yuhas

Matthew Holland
Disrupted sleep, lower life satisfaction and poor self-esteem are just a few of the negative mental health consequences that researchers have linked to social media. Somehow the same platforms that can help people feel more connected and knowledgeable also contribute to loneliness and disinformation. What succeeds and fails, scientists say, is a function of how these platforms are designed. Amanda Baughan, a graduate student specializing in human-computer interaction at the University of Washington, studies how social media triggers what psychologists call dissociation, or a state of reduced self-reflection and narrowed attention. She presented results at the 2022 Association for Computing Machinery Computer-Human Interaction Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Baughan spoke with Mind Matters editor Daisy Yuhas to explain how and why apps need to change to give the people who use them greater power.
[ An edited transcript of the interview follows .]
You’ve shown how changing social media cues and presentations could improve well-being, even when people strongly disagree on issues. Can you give an example?
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The design of social media can have a lot of power in how people interact with one another and how they feel about their online experiences. For example, we’ve found that social media design can actually help people feel more supportive and kind in moments of online conflict, provided there’s a little bit of a nudge to behave that way. In one study, we designed an intervention that encouraged people who start talking about something contentious in a comment thread to switch to direct messaging. People really liked it . It helped to resolve their conflict and replicated a solution we use in-person: people having a public argument move to a private space to work things out.
You’ve also tackled a different problem coming out of social media usage called the 30-Minute Ick Factor. What is that?
We very quickly lose ourselves on social media. When people encounter a platform where they can infinitely scroll for more information, it can trigger a similar neurocognitive reward system as in anticipating a winning lottery ticket or getting food. It’s a powerful way that these apps are designed to keep us checking and scrolling.
The 30-Minute Ick Factor is when people mean to check their social media briefly but then find that 30 minutes have passed, and when they realize how much time they have spent, they have this sense of disgust and disappointment in themselves. Research has shown that people are dissatisfied with this habitual social media use. A lot of people frame it as meaningless, unproductive or addictive.
You’ve argued this experience is less a matter of addiction and more an issue of dissociation. Why?
Dissociation is a psychological process that comes in many forms. In the most common, everyday dissociation, your mind is so absorbed that you are disconnected from your actions. You could be doing the dishes, start daydreaming and not pay attention to how you are doing the dishes. Or you might seek immersive experiences—watching a movie, reading a book or playing a game—that pass the time and cause you to forget where you are.
During these activities, your sense of reflective self-consciousness and the passage of time is reduced. People only realize that they dissociated in hindsight. Attention is restored with the sense of “What just happened?” or “My leg fell asleep while we were watching that movie!”
Dissociation can be a positive thing, especially if it’s an absorbing experience, meaningful activity or a needed break. But it can also be harmful in certain cases, as in gambling, or come in conflict with people’s time-management goals, as with social media scrolling.
How do you measure people’s dissociation on social media?
We worked with 43 participants who used a custom mobile app that we created called Chirp to access their Twitter accounts. The app let people interact with Twitter content while allowing us to ask them questions and test interventions. So when people were using Chirp, after a given number of minutes, we would send them a questionnaire based on a psychological scale for measuring dissociation. We asked how much they agreed with the statement “I am currently using Chirp without really paying attention to what I’m doing” on a scale of 1 to 5. We also did interviews with 11 people to learn more. The results showed dissociation occurred in 42 percent of our participants, and they regularly reported losing track of time or feeling “all-consumed.”
You designed four interventions that modified people’s Twitter experience on Chirp to reduce dissociation. What worked?
The most successful were custom lists and reading history labels. In custom lists, we forced users to categorize the content they followed, such as “sports” or “news” or “friends.” Then, instead of interacting with Twitter’s main feed, they engaged only with content on these lists. This approach was coupled with a reading history intervention in which people received a message when they were caught up on the newest tweets. Rather than continuing to scroll, they were alerted to what they had already seen, and so they focused on just the newest content. Those interventions reduced dissociation, and when we did interviews, people said they felt safer checking their social media accounts when these modifications were present.
In another design, people received timed messages letting them know how long they had been on Chirp and suggesting they leave. They also had the option of viewing a usage page that showed them statistics such as how much time they’d spent on Chirp in the past seven days. These two solutions were effective if people opted to use them. Many people ignored them, however. Also, they thought the timed messages were annoying. Those findings are interesting because a lot of the popular time-management tools available to people look like these time-out and usage notifications.
So what could social media companies be doing differently? And is there any incentive for them to change?
Right now there is a lot working against people who use social media. It’s impossible to ever fully catch up on a social media feed, especially when you consider the algorithmically inserted content such as Twitter’s trending tweets or TikTok’s “For You” page. But I think that there is hope that relatively simple tweaks to social media design, such as custom lists, can make a difference. It’s important to note that the custom lists significantly reduced dissociation for people—but they did not significantly affect time spent using the app. To me, that points out that reducing people’s dissociation may not be as antithetical to social media companies’ revenue goals as we might intuitively think.
What’s most important for people using social media now to know?
First, don’t pile a bunch of shame onto your social media habits. Thousands of people are employed to make you swipe your thumb up on that screen and keep you doing what you’re doing. Let’s shift the responsibility of designing safe and fulfilling experiences from users to the companies.
Second, get familiar with the well-being tools that are already offered. TikTok has a feature that, every hour, will tell you that you’ve been scrolling for a while and should consider a break. On Twitter, custom lists are a feature that already exists; it’s just not the default option. If more people start using these tools, it could convince these companies to refine them.
Most important, vote for people who are interested in regulating technology because I think that’s where we’re going to see the biggest changes made.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Sociology Social Media
How Social Networking Can Ruin Your Life: Negative Effects of Social Media

Table of contents
Why is social media bad for mental health, why social media is bad: a conclusion.
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive Medicine Reports, 15, 100928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2019.100928
- Lin, L. Y., Sidani, J. E., Shensa, A., Radovic, A., Miller, E., Colditz, J. B., ... & Primack, B. A. (2016). Association between social media use and depression among US young adults. Depression and Anxiety, 33(4), 323-331. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22466
- Rosen, L. D., Whaling, K., Carrier, L. M., Cheever, N. A., & Rokkum, J. (2013). The media and technology usage and attitudes scale: An empirical investigation. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(6), 2501-2511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.07.009
- Kross, E., Verduyn, P., Demiralp, E., Park, J., Lee, D. S., Lin, N., ... & Ybarra, O. (2013). Facebook use predicts declines in subjective well-being in young adults. PloS one, 8(8), e69841. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069841
- Turel, O., & Qahri-Saremi, H. (2016). Problematic use of social media: Antecedents and consequences. Information Systems Journal, 26(2), 99-118. https://doi.org/10.1111/isj.12082
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Social Inequality
- First Impression
- Self Identity
- American Dream
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.

Essay on Is Social Media Good or Bad
Students are often asked to write an essay on Is Social Media Good or Bad in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Is Social Media Good or Bad
Introduction.
Social media, platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, have become a significant part of our lives. But is social media good or bad?
The Good Side
Social media connects us with people worldwide. It helps us share ideas, learn new things, and even raise awareness about important issues.
The Bad Side
However, social media can also be harmful. It can lead to addiction, cyberbullying, and can sometimes spread false information.
In conclusion, social media can be both good and bad. It depends on how we use it. We should use it responsibly to enjoy its benefits and avoid its drawbacks.
250 Words Essay on Is Social Media Good or Bad
The advent of social media has revolutionized the way we communicate, share information, and perceive the world. However, its impact on society is a topic of intense debate, with proponents highlighting its benefits and critics cautioning about its potential harm.
The Bright Side of Social Media
Social media platforms serve as powerful tools for connection and communication. They have facilitated the democratization of information, allowing anyone to share their perspectives and experiences. Furthermore, they have become crucial for modern businesses, providing cost-effective marketing strategies and customer engagement.
The Dark Side of Social Media
Despite the benefits, social media also has its drawbacks. It can contribute to mental health issues, with studies linking excessive use to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Additionally, it can facilitate the spread of misinformation, with the potential to incite public panic and influence political outcomes.
In conclusion, social media is a double-edged sword. It can connect us, promote free expression, and boost businesses, but it can also harm mental health and spread misinformation. As users, it is essential to navigate this digital landscape responsibly, understanding its potential benefits and pitfalls. As a society, it is crucial to promote digital literacy and regulate social media platforms to mitigate their negative impacts.
500 Words Essay on Is Social Media Good or Bad
Social media, a technological innovation of the 21st century, has become an integral part of our daily lives. It has radically transformed the way we communicate, interact, and share information. However, the debate about whether social media is good or bad is ongoing, with valid arguments on both sides.
The Benefits of Social Media
Arguably, the most significant benefit of social media is its ability to connect people worldwide. It breaks geographical barriers, allowing us to interact with individuals from different cultures, backgrounds, and perspectives. This global interaction fosters a sense of unity and understanding among diverse populations.
Furthermore, social media has created new opportunities for business and marketing. Companies can reach a global audience, gather consumer insights, and engage with customers in a more personalized way. It has also paved the way for influencer marketing, a new-age promotional strategy.
The Detriments of Social Media
Despite its benefits, social media has its pitfalls. One of the most pressing issues is its impact on mental health. Studies have linked excessive social media use to increased levels of anxiety, depression, and loneliness. The pressure to maintain an idealized online persona and the constant comparison with others can lead to low self-esteem and dissatisfaction.
Furthermore, social media can be a breeding ground for cyberbullying and harassment. The anonymity it offers can embolden individuals to engage in harmful behaviors with little fear of repercussions.
In conclusion, social media is neither inherently good nor bad. Its value is determined by how it is used. On one hand, it has the power to connect people, disseminate information, and create business opportunities. On the other hand, it can negatively impact mental health, spread misinformation, and facilitate cyberbullying.
As responsible users, we must strive to maximize the benefits while mitigating the drawbacks. This could involve setting boundaries for usage, critically evaluating the information received, and promoting respectful online interactions. Ultimately, the key lies in mindful and ethical use of social media.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Social Media Seen as Mostly Good for Democracy Across Many Nations, But U.S. is a Major Outlier
- 2. Views of social media and its impacts on society
Table of Contents
- Most do not think they can influence politics in their country
- Widespread smartphone ownership while very few do not own a mobile phone at all
- Most say they use social media sites
- Frequent posting about social or political issues on social media is uncommon
- Acknowledgments
- Appendix A: Classifying democracies
- Appendix B: Negative Impact of the Internet and Social Media Index
- Appendix C: Political categorization
- Classifying parties as populist
- Classifying parties as left, right or center
- Appendix E: Country-specific examples of smartphones
- Appendix F: Country-specific examples of social media sites
- Methodology
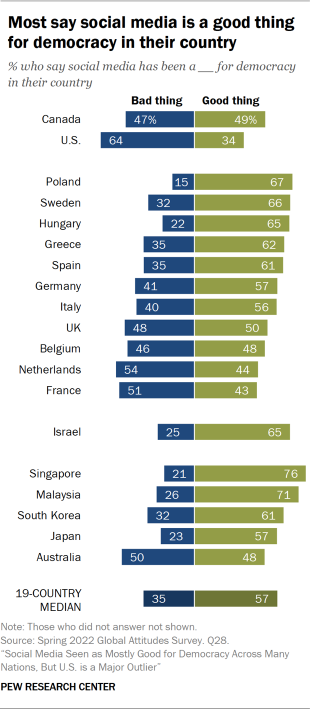
When asked whether social media is a good or bad thing for democracy in their country, a median of 57% across 19 countries say that it is a good thing. In almost every country, close to half or more say this, with the sentiment most common in Singapore, where roughly three-quarters believe social media is a good thing for democracy in their country. However, in the Netherlands and France, about four-in-ten agree. And in the U.S., only around a third think social media is positive for democracy – the smallest share among all 19 countries surveyed.
In eight countries, those who believe that the political system in their country allows them to have an influence on politics are also more likely to say that social media is a good thing for democracy. This gap is most evident in Belgium, where 62% of those who feel their political system allows them to have a say in politics also say that social media is a good thing for democracy in their country, compared with 44% among those who say that their political system does not allow them much influence on politics.
Those who view the spread of false information online as a major threat to their country are less likely to say that social media is a good thing for democracy, compared with those who view the spread of misinformation online as either a minor threat or not a threat at all. This is most clearly observed in the Netherlands, where only four-in-ten (39%) among those who see the spread of false information online as a major threat say that social media has been a good thing for democracy in their country, as opposed to the nearly six-in-ten (57%) among those who do not consider the spread of misinformation online to be a threat who say the same. This pattern is evident in eight other countries as well.
Views also vary by age. Older adults in 12 countries are less likely to say that social media is a good thing for democracy in their country when compared to their younger counterparts. In Japan, France, Israel, Hungary, the UK and Australia, the gap between the youngest and oldest age groups is at least 20 percentage points and ranges as high as 41 points in Poland, where nearly nine-in-ten (87%) younger adults say that social media has been a good thing for democracy in the country and only 46% of adults over 50 say the same.
The perceived impacts of the internet and social media on society
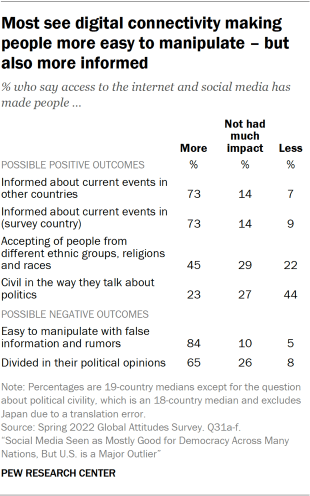
The publics surveyed believe the internet and social media are affecting societies. Across the six issues tested, few tend to say they see no changes due to increased connectivity – instead seeing things changing both positively and negatively – and often both at the same time.
A median of 84% say technological connectivity has made people easier to manipulate with false information and rumors – the most among the six issues tested. Despite this, medians of 73% describe people being more informed about both current events in other countries and about events in their own country. Indeed, in most countries, those who think social media has made it easier to manipulate people with misinformation and rumors are also more likely to think that social media has made people more informed.
When it comes to politics, the internet and social media are generally seen as disruptive, with a median of 65% saying that people are now more divided in their political opinions. Some of this may be due to the sense – shared by a median of 44% across the 19 countries – that access to the internet and social media has led people to be less civil in the way they talk about politics. Despite this, slightly more people (a median of 45%) still say connectivity has made people more accepting of people from different ethnic groups, religions and races than say it has made people less accepting (22%) or had no effect (29%).
There is widespread concern over misinformation – and a sense that people are more susceptible to manipulation
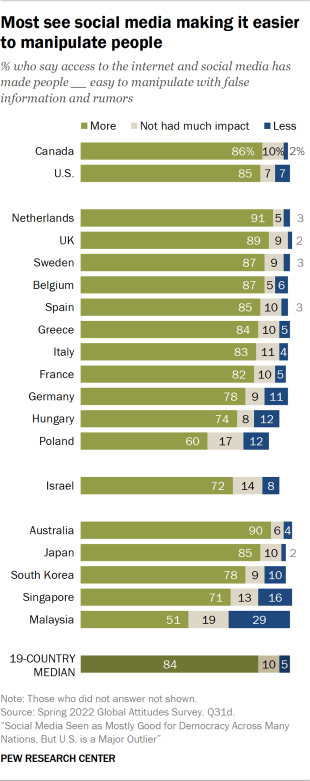
Previously reported results indicate that a median of 70% across the 19 countries surveyed believe that the spread of false information online is a major threat to their country. In places like Canada, Germany and Malaysia, more people name this as a threat than say the same of any of the other issues asked about.
This sense of threat is related to the widespread belief that people today are now easier to manipulate with false information and rumors thanks to the internet and social media. Around half or more in every country surveyed shares this view. And in places like the Netherlands, Australia and the UK, around nine-in-ten see people as more manipulable.
In many places, younger people – who tend to be more likely to use social media (for more on usage, see Chapter 3 ) – are also more likely to say it makes people easier to manipulate with false information and rumors. For example, in South Korea, 90% of those under age 30 say social media makes people easier to manipulate, compared with 65% of those 50 and older. (Interestingly, U.S.-focused research has found older adults are more likely to share misinformation than younger ones.) People with more education are also often more likely than those with less education to say that social media has led to people being easier to manipulate.
In 2018, when Pew Research Center asked a similar question about whether access to mobile phones, the internet and social media has made people easier to manipulate with false information and rumors, the results were largely similar. Across the 11 emerging economies surveyed as part of that project , at least half in every country thought this was the case and in many places, around three-quarters or more saw this as an issue. Large shares in many places were also specifically concerned that people in their country might be manipulated by domestic politicians. For more on how the two surveys compare, see “ In advanced and emerging economies, similar views on how social media affects democracy and society .”
Spotlight on the U.S.: Attitudes and experiences with misinformation
Misinformation has long been seen as a source of concern for Americans. In 2016 , for example, in the wake of the U.S. presidential election, 64% of U.S. adults thought completely made-up news had caused a great deal of confusion about the basic facts of current events. At the time, around a third felt that they often encountered political news online that was completely made up and another half said they often encountered news that was not fully accurate. Moreover, about a quarter (23%) said they had shared such stories – whether knowingly or not.
When asked in 2019 who was the cause of made-up news, Americans largely singled out two groups of people: political leaders (57%) and activists (53%). Fewer placed blame on journalists (36%), foreign actors (35%) or the public (26%). A large majority of Americans that year (82%) also described themselves as either “very” or “somewhat” concerned about the potential impact of made-up news on the 2020 presidential election. People who followed political and election news more closely and those with higher levels of political knowledge also tended to be more concerned.
Among adult American Twitter users in 2021, in particular, there was widespread concern about misinformation: 53% said inaccurate or misleading information is a major problem on the platform and 33% reported seeing a lot of that type of content when using the site.
As of 2021 , around half (48%) of Americans thought the government should take steps to restrict false information, even if it meant losing freedom to access and publish content – a share that had increased somewhat substantially since 2018, when 39% felt the same.

Most say people are more informed about current events – foreign and domestic – thanks to social media and the internet
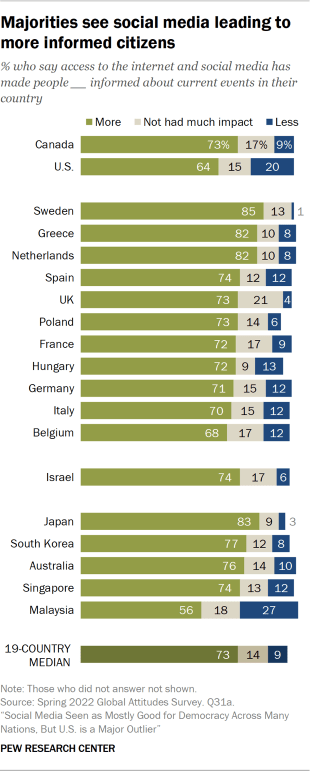
A majority in every country surveyed thinks that access to the internet and social media has made people in their country more informed about domestic current events. In Sweden, Japan, Greece and the Netherlands, around eight-in-ten or more share this view, while in Malaysia, a smaller majority (56%) says the same.
Younger adults tend to see social media making people more informed than older adults do. Older adults, for their part, don’t necessarily see the internet and social media making people less informed about what’s happening in their country; rather, they’re somewhat more likely to describe these platforms as having little effect on people’s information levels. In the case of the U.S., for example, 71% of adults under 30 say social media has made people more informed about current events in the U.S., compared with 60% of those ages 50 and older. But those ages 50 and older are about twice as likely to say social media has not had much impact on how informed people are compared with those under 30: 19% vs. 11%, respectively.
In seven of the surveyed countries, people with higher levels of education are more likely than those with lower levels to see social media informing the public on current events in their own country.
Majorities in every country also agree that the internet and social media are making people more informed about current events happening in other countries. The two questions are extremely highly correlated ( r = 0.94), meaning that in most places where people say social media is making people more informed about domestic events, they also say the same of international events. (See the topline for detailed results for both questions, by country.)
In the 2018 survey of emerging economies , results of a slightly different question also found that a majority in every country – and around seven-in-ten or more in most places – said people were more informed thanks to social media, the internet and smartphones, rather than less.
In some countries, those who think social media has made it easier to manipulate people with misinformation and rumors are also more likely to think that social media has made people more informed. This finding, too, was similar in the 2018 11-country study of emerging economies: Generally speaking, individuals who are most attuned to the potential benefits technology can bring to the political domain are also the ones most anxious about the possible harms.
Spotlight on the U.S.: Social media use and news consumption
In the U.S. , around half of adults say they either get news often (17%) or sometimes (33%) from social media. When it comes to where Americans regularly get news on social media, Facebook outpaces all other social media sites. Roughly a third of U.S. adults (31%) say they regularly get news from Facebook. While Twitter is only used by about three-in-ten U.S. adults (27%), about half of its users (53%) turn to the site to regularly get news there. And a quarter of U.S. adults regularly get news from YouTube, while smaller shares get news from Instagram (13%), TikTok (10%) or Reddit (8%). Notably, TikTok has seen rapid growth as a source of news among younger Americans in recent years.
On several social media sites asked about, adults under 30 make up the largest share of those who regularly get news on the site. For example, half or more of regular news consumers on Snapchat (67%), TikTok (52%) or Reddit (50%) are ages 18 to 29.
While this survey finds that 64% of Americans think the public has become more informed thanks to social media, results of Center analyses do show that Americans who mainly got election and political information on social media during the 2020 election were less knowledgeable and less engaged than those who primarily got their news through other methods (like cable TV, print, etc.).
Majorities or pluralities tend to see social media leading to more political divisions
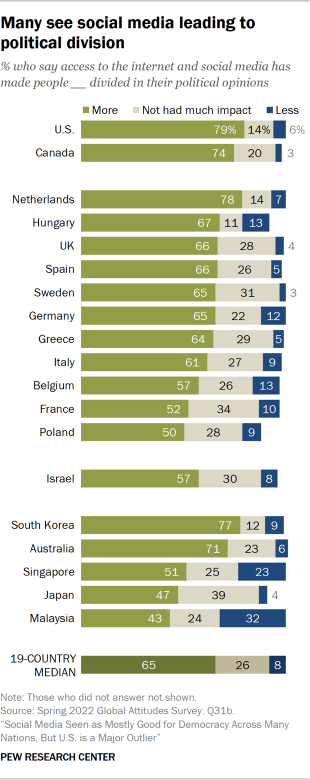
Around half or more in almost every country surveyed think social media has made people more divided in their political opinions. The U.S., South Korea and the Netherlands are particularly likely to hold this view. As a separate analysis shows, the former two also stand out for being the countries where people are most likely to report conflicts between people who support different political parties . While perceived political division in the Netherlands is somewhat lower, it, too, stands apart: Between 2021 and 2022, the share who said there were conflicts increased by 23 percentage points – among the highest year-on-year shifts evident in the survey.
More broadly, across each of the countries surveyed, people who see social division between people who support different political parties, are, in general, more likely to see social media leading people to be more divided in their political opinions.
In a number of countries, younger people are somewhat more likely to see social media enlarging political differences than older people. More educated people, too, often see social media exacerbating political divisions more than those with less education.
Similarly, in the survey of 11 emerging economies conducted in 2018, results of a slightly different question indicated that around four-in-ten or more in every country – and a majority in most places – thought social media had made people more divided.
Publics diverge over whether social media has made people more accepting of differences
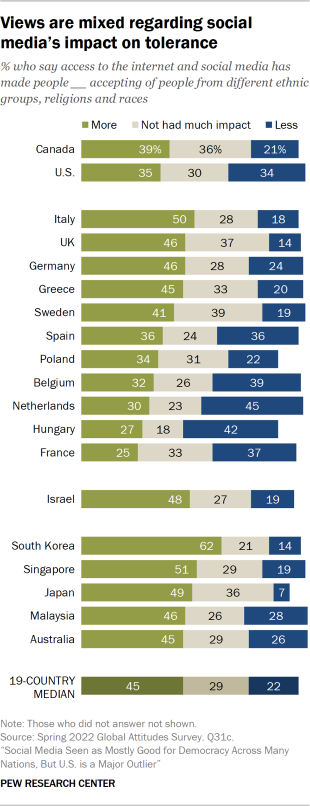
There is less consensus over what role social media has played when it comes to tolerance: A 19-country median of 45% say it has made people more accepting of people from different ethnic backgrounds, religions and races, while a median of 22% say it has made them less so, and 29% say that it has not had much impact either way.
South Korea, Singapore, Italy and Japan are the most likely to see social media making people more tolerant. On the flip side, the Netherlands and Hungary stand out as the two countries where a plurality says the internet and social media have made people less accepting of people with racial or religious differences. Most other societies are somewhat divided, as in the case of the U.S., where around a third of the public falls into each of the three groups.
Younger people are more likely than older ones in most countries to say that social media has increased tolerance. This is the case, for example, in Canada, where 54% of adults under 30 say social media has contributed to people being more accepting of people from different ethnic groups, religions and races, compared with a third of those ages 50 and older. In some places – and in Canada – older people are more likely to see social media leading to less tolerance, though in other places, older people are simply less likely to see much impact from the technology.
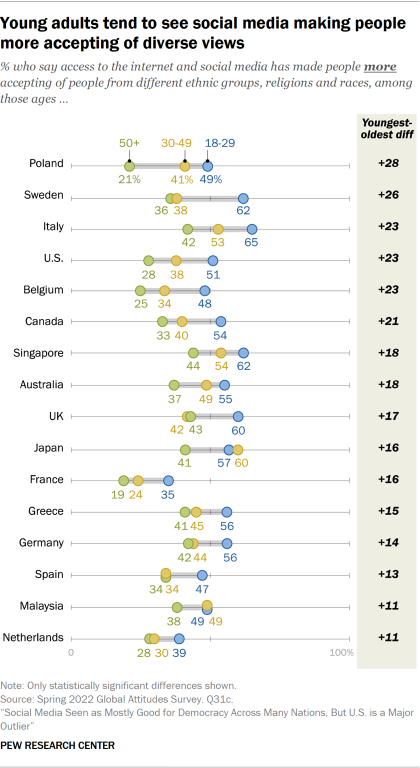
In most countries, people who see social media leading to more divisions between people with different political opinions are more likely to say social media has made people less accepting of those racially and religiously different from them than those who say social media is having no effect on political division. People who see more conflicts between partisans in their society are also more likely than those who see fewer divisions to place some of the blame on social media, describing it as making people less accepting of differences.
Results of an analysis of the 11-country poll did find that people who used smartphones and social media were more likely to regularly interact with people from diverse backgrounds – though the question did not ask about acceptance , just about interactions. The publics in these emerging economies were also somewhat divided when it came to their opinions on how social media has led to people being more or less accepting of those with different viewpoints.
Mixed views on whether social media has made people discuss politics civilly
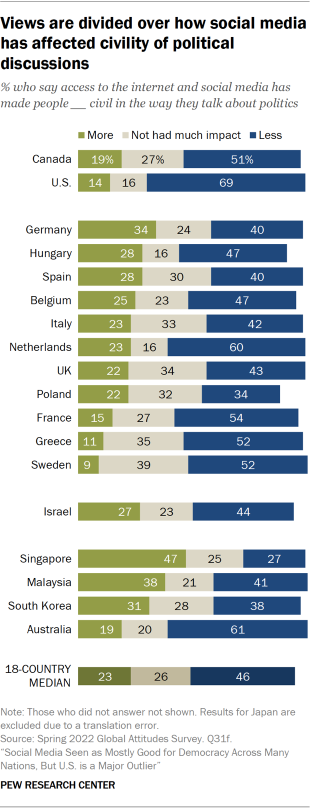
Across the countries surveyed, a median of 46% say access to the internet and social media has made people less civil when they talk about politics. This is more than the 23% who say it has made them more civil – though a median of 26% see little impact either way.
In the U.S., the Netherlands and Australia, a majority sees the internet and social media making people less civil. Roughly seven-in-ten Americans say this. Singapore stands out as the only country where around half see these technologies increasing civility. All other countries surveyed are somewhat divided.
People with higher levels of education tend to see less civility thanks to social media relative to those with lower levels of education.
In most places surveyed, those who think social media has made people more divided politically, compared with those who say it has had no impact on divisions, are also more likely to say social media has made people less civil in how they talk about politics.
Majorities view social media as a way to raise awareness among the public and elected officials
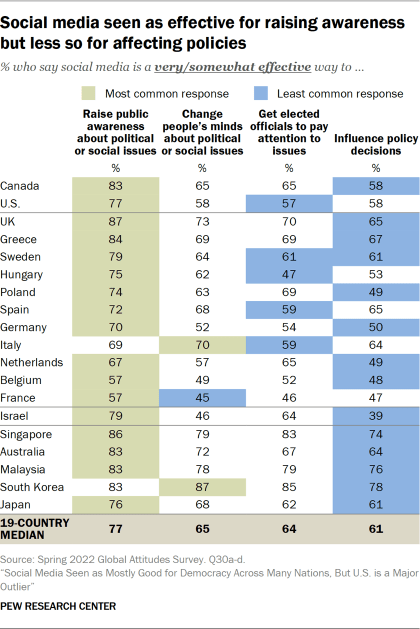
Across advanced economies, people generally recognize social media as useful for bringing the public’s and elected officials’ attention to certain issues, for changing people’s minds and for influencing policy choices. A median of 77% across the 19 countries surveyed say social media is an effective way to raise public awareness about sociopolitical issues. Those in the UK are particularly optimistic about social media as a way of bringing public attention to a topic, with about nine-in-ten holding this belief. People in France and Belgium are the least convinced about social media’s role in raising public awareness, but majorities in both countries still say it’s effective for highlighting certain issues among the public.
Many also consider social media effective for changing people’s minds on social or political issues (65% median). Confidence in social media’s effect on changing people’s minds is strongest in South Korea, Singapore and Malaysia. Germans, Belgians, Israelis and French adults are more skeptical, with no more than about half seeing social media as effective for changing people’s minds on sociopolitical issues.
Views on social media as a way to bring the attention of elected officials to certain issues are similar. A median of 64% consider social media effective for directing elected officials’ attention to issues, and this view is especially prevalent in South Korea, Singapore and Malaysia. People in Belgium, Hungary and France are less convinced.
Somewhat fewer consider social media effective for influencing policy decisions (61% median). Israelis are particularly doubtful of social media as a way for affecting policy change: A majority of Israelis say social media is an ineffective way of influencing policy decisions, and about half in France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany agree. About a fifth in Poland also did not provide an answer.
An additional question was asked in the U.S. about social media’s role in creating sustained social movements; roughly seven-in-ten Americans say social media is effective for this. Younger Americans, as well as those with more education or higher incomes, are more likely than others to hold this view. Social media users and those who say social media has been generally good for U.S. democracy are also more likely to believe social media is effective at creating sustained social movements.
Age plays a role in how people in many of the 19 nations surveyed view social media’s role in public discourse. Those ages 18 to 29 are especially likely to see social media as effective for raising public awareness. For example, in France, 70% of those ages 18 to 29 see social media as an effective way of raising public awareness. Only 48% of those 50 and older share this view, a difference of 22 percentage points.
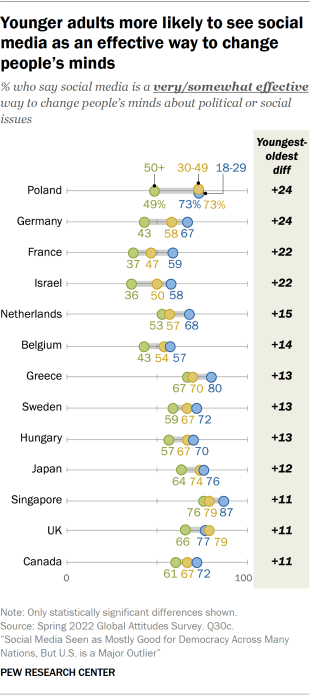
Similarly, younger adults are also more likely to consider social media an effective way for changing people’s minds on issues. The difference is greatest in Poland and Germany, where younger adults are 24 points more likely than their older counterparts to see social media this way. There are fewer differences between younger and older adults when it comes to social media’s effectiveness for directing elected officials’ attention and influencing policy decisions. Younger adults are also generally more likely to be social media users and provide answers to these questions.
Education and income are other demographic characteristics related to people’s view of social media as a way to influence public discourse. In 11 countries, those with incomes higher than the median income are more likely than those with lower incomes to consider social media effective for raising public awareness about sociopolitical issues. Those with more education are similarly more likely to consider social media effective for elevating sociopolitical issues in the public consciousness in eight countries. People with lower levels of education and income are somewhat less likely than others to provide answers to questions about social media’s effectiveness for influencing policies, changing minds and bringing attention to issues.
Social media usage is also connected to how people evaluate these platforms as a way to affect public discourse and policy choices. In nearly all countries, social media users are more likely than those who are not on social media to say social media is effective for raising public awareness, and social media users are also more likely to consider social media useful for changing people’s minds in 11 of 19 countries. The differences are greatest in Israel in both cases. Israeli social media users are 47 points more likely than non-users to say social media is effective for raising awareness and 38 points more likely to consider it effective for changing people’s minds on sociopolitical issues. Different views between social media users and non-users are less common when it comes to social media as an effective way for bringing elected officials’ attention to issues or influencing policy decisions. Social media users are also more likely than non-users to answer these questions.
Among social media users, those who are more active are more likely to consider social media an effective avenue for shaping people’s views and attention. Those who post about political or social issues at least sometimes on social media have a greater chance of seeing social media as effective for raising awareness for sociopolitical issues than those who post rarely or never in 16 countries. For example, in Spain, 84% of social media users who post sometimes or often see social media as an effective way to bring awareness to issues, compared to 71% of users who never or rarely post. Similarly, social media users who post more frequently are more likely to see social media as effective for changing minds in 13 countries, for influencing policy decisions in 15 countries, and bringing elected officials’ attention to issues in 12 nations.
People’s views of social media as a way to spread awareness or affect change are additionally related to how they see democracy. The beliefs that social media is effective for influencing policy decisions and for bringing issues to the attention of elected officials or the public are especially common among people who also believe they have a say in politics. For example, in Germany, 60% of people who say people like them have at least a fair amount of influence on politics also say social media is effective for affecting policy choices. In comparison, 43% of Germans who do not think they have a say in politics also think social media can influence policy decisions.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Global Tech & Cybersecurity
- International Political Values
- Internet Connectivity
- Misinformation
- Political Discourse
- Politics & Media
- Politics Online
- Smartphones
- Social Media
- Social Media & the News
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
- U.S. Democracy
72% of Americans say the U.S. used to be a good example of democracy, but isn’t anymore
Satisfaction with democracy has declined in recent years in high-income nations, more than 80% of americans believe elected officials don’t care what people like them think, support for democracy is strong in hong kong and taiwan, how people in 24 countries think democracy can improve, most popular, report materials.
- Detailed tables: Internet, smartphone and social media use in advanced economies (2022)
- American Trends Panel Wave 105
- Spring 2022 Survey Data
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Support the nation's leading Black news publishers
Invest in Word In Black’s mission to confront inequities, elevate solutions, and amplify the Black experience.
Black stories matter
Stay up-to-date on reporting that amplifies the stories, voices, and perspectives of Black America.
- Word In Black Weekly
- Climate Justice

Word In Black
A groundbreaking collaboration of 10 legendary Black news publishers.

Teens and Social Media: How to Balance the Good and the Bad
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
This post was originally published on Atlanta Voice
By Clayton Gutzmore
The time teenagers spend on their devices and what material they engage in can cause adults to worry. Three university professors gathered virtually to discuss this subject’s bad and good aspects. They explain social media’s physical and mental impact on teenagers’ health. The group also discusses how everyone is bundling issues surrounding this matter, causing more concern than necessary. One point that all three experts agreed upon is that social media is not all good or bad.
“One of the themes we see in our work is that social media is not a monolith. The story of teens on social media is neither all good nor all bad. We’ve found that teens are more likely to say social media’s impact on them personally has been mostly positive than mostly negative,” said Colleen McClain, research associate at the Pew Research Center.
The media briefing on Teens and social media took place in June. McClain was joined by Dr. Linda Charmaraman of Wellesley College and Dr. Jason Nagata of the University of California, San Francisco. Each expert tackled a specific topic and explained how parents and adults can apply what is shared. McClain revealed that most teens use YouTube, TikTok, Snapchat, and Instagram today. Her data showed that teen girls use TikTok the most out of the four, and connection and socialization are the reason for it. McClain’s material also uncovered that social media overwhelms teen girls with drama, fear of missing out (FOMO), or pressure to post for content or likes.
Dr. Charmaran’s research dives into how to prepare teens for social media. Her information deals with identifying risk and resilience in adolescent media use to empower them for greater well-being. Dr. Charmaraman explains that social media is not inherently good or bad. It depends on what the teens see and do. She further elaborates that parents should discuss with their teenagers what to do rather than what not to do. Dr Charmaran talks about pre-arming teens with self-awareness for the good and bad on social media. She encourages teens who seek out connections online only to keep the ones that make them feel good and eliminate the connections that make them feel bad. Dr. Charmaran advises parents to enlist aunts, uncles, coaches, school counselors, or whoever is in the teenager’s village to help guide them on online interactions.
“Our last study about parental monitoring of middle school and early adolescent youth showed that the dialect that you have to pre-warn young people with everything that could be happening on social media is a lot more positive and powerful predictor of if it’s going to go well or not if they’re going to have problematic internet use,” said Dr. Charmaran.
“If you wait until something happens, you must start clamping down on their use. It’s hard to treat it after it’s already happened rather than prevent it,” said Dr. Charmaran.
Dr. Jason Nagata discussed the toll social media and screen time take on teenagers’ health-related behaviors. He discussed how increased screen time leads to overeating. Teenagers online are exposed to food advertisements and usually sit down when scrolling online, which increases their time being sedentary when they could be active.
The data in his presentation expounded on this. Every hour a nine or ten-year-old child stays on social media, there is a 62 percent chance they develop an eating disorder the following year. Dr. Nagata elaborated on the connection between social media and eating disorders when he mentioned the constant comparison to unattainable body ideals, the pressure to display the body for likes, and exposure to eating disorder content.
Dr. Nagata shared some methods for reducing screen use in teenagers, such as restricting devices in the bedroom and at mealtimes. Parents can also present model behavior to teenagers by limiting their screen time.
“One of the biggest predictors of adolescent screen use was parent screen use. I think it’s imperative to practice what you preach and model good behavior. Family meal time and bedroom screen use could be times to limit screen use. This can affect eating and sleeping issues,” said Dr. Nagata.
Social media is a tool that, if misused, can create more problems than solve them. Material from all three experts illustrates that teenagers will use social media and screens no matter what, but parents can equip them with the proper knowledge and present the correct behaviors to prevent this tool from overrunning their lives.
The post Teens and social media: How to balance the good and the bad appeared first on The Atlanta Voice .
Dealing with Revenge Porn and “Sextortion”
Smartphone and internet addiction.
- Cyberbullying: Dealing with Online Bullies
- Self-Care Tips to Prioritize Your Mental Health
- Self-Esteem: How to Feel Good About Yourself
- How to Break Bad Habits and Change Negative Behaviors
- Imposter Syndrome: Causes, Types, and Coping Tips
Personality Types, Traits, and How it Affects Mental Health
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
How does social media affect mental health?
The pros of social media, the cons of social media, what’s driving your social media use, signs that social media is impacting your mental health, how to change your social media use, step 1: reduce time online, step 2: change your focus, step 3: spend more time with offline friends, step 4: express gratitude, helping a child or teen with unhealthy social media use, social media and mental health are you addicted to social media.
While many of us enjoy staying connected on social media, excessive use can fuel feelings of addiction, anxiety, depression, isolation, and FOMO. Here’s how to modify your habits and improve your mood.

Human beings are social creatures. We need the companionship of others to thrive in life, and the strength of our connections has a huge impact on our mental health and happiness. Being socially connected to others can ease stress, anxiety, and depression, boost self-worth, provide comfort and joy, prevent loneliness, and even add years to your life. On the flip side, lacking strong social connections can pose a serious risk to your mental and emotional health.
In today’s world, many of us rely on social media platforms such as Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), Snapchat, YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram to find and connect with each other. While each has its benefits, it’s important to remember that social media can never be a replacement for real-world human connection. It requires in-person contact with others to trigger the hormones that alleviate stress and make you feel happier, healthier, and more positive. Ironically for a technology that’s designed to bring people closer together, spending too much time engaging with social media can actually make you feel more lonely and isolated—and exacerbate mental health problems such as anxiety and depression.
If you’re spending an excessive amount of time on social media and feelings of sadness, dissatisfaction, frustration, or loneliness are impacting your life, it may be time to re-examine your online habits and find a healthier balance.
Speak to a Licensed Therapist
BetterHelp is an online therapy service that matches you to licensed, accredited therapists who can help with depression, anxiety, relationships, and more. Take the assessment and get matched with a therapist in as little as 48 hours.
While virtual interaction on social media doesn’t have the same psychological benefits as face-to-face contact, there are still many positive ways in which it can help you stay connected and support your wellbeing.
Social media enables you to:
- Communicate and stay up to date with family and friends around the world.
- Find new friends and communities; network with other people who share similar interests or ambitions.
- Join or promote worthwhile causes; raise awareness on important issues.
- Seek or offer emotional support during tough times.
- Find vital social and professional connections (such as online therapy ) if you live in a remote area, for example, or have limited independence, social anxiety, or are part of a marginalized group.
- Find an outlet for your creativity and self-expression.
- Discover (with care) sources of valuable information and learning.
Since it’s a relatively new technology, there’s little research to establish the long-term consequences, good or bad, of social media use. However, multiple studies have found a strong link between heavy social media and an increased risk for depression, anxiety, loneliness, self-harm , and even suicidal thoughts .
Social media may promote negative experiences such as:
Inadequacy about your life or appearance . Even if you know that images you’re viewing on social media are manipulated, they can still make you feel insecure about how you look or what’s going on in your own life. Similarly, we’re all aware that other people tend to share just the highlights of their lives, rarely the low points that everyone experiences. But that doesn’t lessen those feelings of envy and dissatisfaction when you’re scrolling through a friend’s airbrushed photos of their tropical beach holiday or reading about their exciting new promotion at work.
Fear of missing out (FOMO) and social media addiction . While FOMO has been around far longer than social media, sites such as Facebook and Instagram seem to exacerbate feelings that others are having more fun or living better lives than you are. The idea that you’re missing out on certain things can impact your self-esteem, trigger anxiety, and fuel even greater social media use, much like an addiction. FOMO can compel you to pick up your phone every few minutes to check for updates, or compulsively respond to each and every alert—even if that means taking risks while you’re driving, missing out on sleep at night, or prioritizing social media interaction over real world relationships.
Isolation . A study at the University of Pennsylvania found that high usage of Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram increases rather decreases feelings of loneliness . Conversely, the study found that reducing social media usage can actually make you feel less lonely and isolated and improve your overall wellbeing.
Depression and anxiety . Human beings need face-to-face contact to be mentally healthy. Nothing reduces stress and boosts your mood faster or more effectively than eye-to-eye contact with someone who cares about you. The more you prioritize social media interaction over in-person relationships, the more you’re at risk for developing or exacerbating mood disorders such as anxiety and depression .
Cyberbullying. About 10 percent of teens report being bullied on social media and many other users are subjected to offensive comments. Social media platforms such as Twitter can be hotspots for spreading hurtful rumors, lies, and abuse that can leave lasting emotional scars.
Self-absorption. Sharing endless selfies and all your innermost thoughts on social media can create an unhealthy self-centeredness and distance you from real-life connections.
These days, most of us access social media via our smartphones or tablets. While this makes it very convenient to keep in touch, it also means that social media is always accessible. This round-the-clock, hyper connectivity can trigger impulse control problems, the constant alerts and notifications affecting your concentration and focus, disturbing your sleep, and making you a slave to your phone .
Social media platforms are designed to snare your attention, keep you online, and have you repeatedly checking your screen for updates. It’s how the companies make money. But, much like a gambling compulsion or an addiction to nicotine, alcohol, or drugs, social media use can create psychological cravings. When you receive a like, a share, or a favorable reaction to a post, it can trigger the release of dopamine in the brain, the same “reward” chemical that follows winning on a slot machine, taking a bite of chocolate, or lighting up a cigarette, for example. The more you’re rewarded, the more time you want to spend on social media, even if it becomes detrimental to other aspects of your life.
Other causes of unhealthy social media use
A fear of missing out (FOMO) can keep you returning to social media over and over again. Even though there are very few things that can’t wait or need an immediate response, FOMO will have you believing otherwise. Perhaps you’re worried that you’ll be left out of the conversation at school or work if you miss the latest news or gossip on social media? Or maybe you feel that your relationships will suffer if you don’t immediately like, share, or respond to other people’s posts? Or you could be worried you’ll miss out on an invitation or that other people are having a better time than you.
Many of us use social media as a “security blanket”. Whenever we’re in a social situation and feel anxious, awkward, or lonely, we turn to our phones and log on to social media. Of course, interacting with social media only denies you the face-to-face interaction that can help to ease anxiety .
Your heavy social media use could be masking other underlying problems , such as stress, depression, or boredom. If you spend more time on social media when you’re feeling down, lonely, or bored, you may be using it as a way to distract yourself from unpleasant feelings or self-soothe your moods. While it can be difficult at first, allowing yourself to feel can open you up to finding healthier ways to manage your moods .
The vicious cycle of unhealthy social media use
Excessive social media use can create a negative, self-perpetuating cycle:
- When you feel lonely, depressed, anxious, or stressed, you use social media more often—as a way to relieve boredom or feel connected to others.
- Using social media more often, though, increases FOMO and feelings of inadequacy, dissatisfaction, and isolation.
- In turn, these feelings negatively affect your mood and worsen symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress.
- These worsening symptoms cause you to use social media even more, and so the downward spiral continues.
Everyone is different and there is no specific amount of time spent on social media, or the frequency you check for updates, or the number of posts you make that indicates your use is becoming unhealthy. Rather, it has to do with the impact time spent on social media has on your mood and other aspects of your life, along with your motivations for using it.
For example, your social media use may be problematic if it causes you to neglect face-to-face relationships, distracts you from work or school, or leaves you feeling envious, angry, or depressed. Similarly, if you’re motivated to use social media just because you’re bored or lonely, or want to post something to make others jealous or upset, it may be time to reassess your social media habits.
Indicators that social media may be adversely affecting your mental health include:
Spending more time on social media than with real world friends . Using social media has become a substitute for a lot of your offline social interaction. Even if you’re out with friends, you still feel the need to constantly check social media, often driven by feelings that others may be having more fun than you.
Comparing yourself unfavorably with others on social media . You have low self-esteem or negative body image. You may even have patterns of disordered eating.
Experiencing cyberbullying . Or you worry that you have no control over the things people post about you.
Being distracted at school or work . You feel pressure to post regular content about yourself, get comments or likes on your posts, or respond quickly and enthusiastically to friends’ posts.
Having no time for self-reflection . Every spare moment is filled by engaging with social media, leaving you little or no time for reflecting on who you are, what you think, or why you act the way that you do—the things that allow you to grow as a person.
Engaging in risky behavior in order to gain likes , shares, or positive reactions on social media. You play dangerous pranks, post embarrassing material, cyberbully others, or access your phone while driving or in other unsafe situations.
[ Read: Dealing with Revenge Porn and “Sextortion” ]
Suffering from sleep problems . Do you check social media last thing at night, first thing in the morning, or even when you wake up in the night? The light from phones and other devices can disrupt your sleep , which in turn can have a serious impact on your mental health.
Worsening symptoms of anxiety or depression . Rather than helping to alleviate negative feelings and boost your mood, you feel more anxious, depressed, or lonely after using social media.
If you feel that your social media use has become an addiction, or it’s fueling your levels of anxiety, depression, FOMO, or sense of isolation, the following steps can help you modify your habits :
A 2018 University of Pennsylvania study found that reducing social media use to 30 minutes a day resulted in a significant reduction in levels of anxiety, depression, loneliness, sleep problems, and FOMO. But you don’t need to cut back on your social media use that drastically to improve your mental health. The same study concluded that just being more mindful of your social media use can have beneficial results on your mood and focus.
While 30 minutes a day may not be a realistic target for many of us—let alone a full “social media detox”— we can still benefit from reducing the amount of time we spend on social media. For most of us, that means reducing how much we use our smartphones. The following tips can help:
- Use an app to track how much time you spend on social media each day. Then set a goal for how much you want to reduce it by.
- Turn off your phone at certain times of the day, such as when you’re driving, in a meeting, at the gym, having dinner, spending time with offline friends, or playing with your kids. Don’t take your phone with you to the bathroom.
- Don’t bring your phone or tablet to bed . Turn devices off and leave them in another room overnight to charge.
- Disable social media notifications. It’s hard to resist the constant buzzing, beeping, and dinging of your phone alerting you to new messages. Turning off notifications can help you regain control of your time and focus.
- Limit checks. If you compulsively check your phone every few minutes, wean yourself off by limiting your checks to once every 15 minutes. Then once every 30 minutes, then once an hour. There are apps that can automatically limit when you’re able to access your phone.
- Try removing social media apps from your phone so you can only check Facebook, Twitter and the like from your tablet or computer. If this sounds like too drastic a step, try removing one social media app at a time to see how much you really miss it.
For more tips on reducing your overall phone use, read Smartphone Addiction .
Many of us access social media purely out of habit or to mindlessly kill moments of downtime. But by focusing on your motivation for logging on, you can not only reduce the time you spend on social media, you can also improve your experience and avoid many of the negative aspects.
If you’re accessing social media to find specific information, check on a friend who’s been ill, or share new photos of your kids with family, for example, your experience is likely to be very different than if you’re logging on simply because you’re bored, you want to see how many likes you got from a previous post, or to check if you’re missing out on something.
Next time you go to access social media, pause for a moment and clarify your motivation for doing so.
Are you using social media as a substitute for real life? Is there a healthier substitute for your social media use? If you’re lonely, for example, invite a friend out for coffee instead. Feeling depressed? Take a walk or go to the gym. Bored? Take up a new hobby. Social media may be quick and convenient, but there are often healthier, more effective ways to satisfy a craving.
Are you an active or a passive user on social media? Passively scrolling through posts or anonymously following the interaction of others on social media doesn’t provide any meaningful sense of connection. It may even increase feelings of isolation. Being an active participant, though, will offer you more engagement with others.
Does social media leave you feeling inadequate or disappointed about your life? You can counter symptoms of FOMO by focusing on what you have, rather than what you lack. Make a list of all the positive aspects of your life and read it back when you feel you’re missing out on something better. And remember: no one’s life is ever as perfect as it seems on social media. We all deal with heartache, self-doubt, and disappointment, even if we choose not to share it online.
We all need the face-to-face company of others to be happy and healthy. At its best, social media is a great tool for facilitating real-life connections. But if you’ve allowed virtual connections to replace real-life friendships in your life, there are plenty of ways to build meaningful connections without relying on social media.
Set aside time each week to interact offline with friends and family. Try to make it a regular get-together where you always keep your phones off.
If you’ve neglected face-to-face friendships, reach out to an old friend (or an online friend) and arrange to meet up. If you both lead busy lives, offer to run errands or exercise together .
Join a club . Find a hobby, creative endeavor, or fitness activity you enjoy and join a group of like-minded individuals that meet on a regular basis.
Don’t let social awkwardness stand in the way . Even if you’re shy, there are proven techniques to overcome insecurity and build friendships .
If you don’t feel that you have anyone to spend time with, reach out to acquaintances . Lots of other people feel just as uncomfortable about making new friends as you do—so be the one to break the ice. Invite a coworker out for lunch or ask a neighbor or classmate to join you for coffee.
Interact with strangers . Look up from your screen and connect with people you cross paths with on public transport, at the coffee shop, or in the grocery store. Simply smiling or saying hello will improve how you feel—and you never know where it may lead.
Feeling and expressing gratitude about the important things in your life can be a welcome relief to the resentment, animosity, and discontent sometimes generated by social media.
Take time for reflection . Try keeping a gratitude journal or using a gratitude app. Keep track of all the great memories and positives in your life—as well as those things and people you’d miss if they were suddenly absent from your life. If you’re more prone to venting or negative posts, you can even express your gratitude on social media—although you may benefit more from private reflection that isn’t subject to the scrutiny of others.
[Read: Gratitude: The Benefits and How to Practice It]
Practice mindfulness . Experiencing FOMO and comparing yourself unfavorably to others keeps you dwelling on life’s disappointments and frustrations. Instead of being fully engaged in the present, you’re focused on the “what ifs” and the “if onlys” that prevent you from having a life that matches those you see on social media. By practicing mindfulness , you can learn to live more in the present moment, lessen the impact of FOMO, and improve your overall mental wellbeing.
Volunteer . Just as human beings are hard-wired to seek social connection, we’re also hard-wired to give to others. Helping other people or animals not only enriches your community and benefits a cause that’s important to you, but it also makes you feel happier and more grateful.
Childhood and the teenage years can be filled with developmental challenges and social pressures. For some kids, social media has a way of exacerbating those problems and fueling anxiety, bullying , depression , and issues with self-esteem.
If you’re worried about your child’s social media use, it can be tempting to simply confiscate their phone or other device. But that can create further problems, separating your child from their friends and the positive aspects of social media. Instead, there are other ways to help your child use TikTok, Facebook, Instagram, and other platforms in a more responsible way.
Monitor and limit your child’s social media use. The more you know about how your child is interacting on social media, the better you’ll be able to address any problems. Parental control apps can help limit your child’s data usage or restrict their phone use to certain times of the day. You can also adjust privacy settings on the different platforms to limit their potential exposure to bullies or predators.
Talk to your child about underlying issues. Problems with social media use can often mask deeper issues. Is your child having problems fitting in at school? Are they suffering from shyness or social anxiety? Are problems at home causing them stress?
Enforce “social media” breaks. For example, you could ban social media until your child has completed their homework in the evening, not allow phones at the dinner table or in their bedroom, and plan family activities that preclude the use of phones or other devices. To prevent sleep problems, always insist phones are turned off at least one hour before bed.
Teach your child how social media is not an accurate reflection of people’s lives. They shouldn’t compare themselves or their lives negatively to others on social media. People only post what they want others to see. Images are manipulated or carefully posed and selected. And having fewer friends on social media doesn’t make your child less popular or less worthy.
Encourage exercise and offline interests. Get your child away from social media by encouraging them to pursue physical activities and hobbies that involve real-world interaction. Exercise is great for relieving anxiety and stress , boosting self-esteem, and improving mood—and is something you can do as a family. The more engaged your child is offline, the less their mood and sense of self-worth will be dependent on how many friends, likes, or shares they have on social media.
More Information
- Study into wellbeing and social media - Details study linking time spent on social media with decreased wellbeing. (Penn Today, University of Pennsylvania)
- Impact on the mental health of young people - Briefing paper analyzing the impact of social media. (Centre for Mental Health)
- Linking child depression - How heavy Instagram and Facebook use may be affecting kids negatively. (Child Mind Institute)
- Hunt, Melissa G., Rachel Marx, Courtney Lipson, and Jordyn Young. “No More FOMO: Limiting Social Media Decreases Loneliness and Depression.” Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology 37, no. 10 (December 2018): 751–68. Link
- Riehm, Kira E., Kenneth A. Feder, Kayla N. Tormohlen, Rosa M. Crum, Andrea S. Young, Kerry M. Green, Lauren R. Pacek, Lareina N. La Flair, and Ramin Mojtabai. “Associations Between Time Spent Using Social Media and Internalizing and Externalizing Problems Among US Youth.” JAMA Psychiatry 76, no. 12 (December 1, 2019): 1266. Link
- Anderson, Monica. (2018, September 27). A majority of teens have been the target of cyberbullying, with name-calling and rumor-spreading being the most common forms of harassment. Pew Research Center: Internet, Science & Tech. Link
- Kross, Ethan, Philippe Verduyn, Emre Demiralp, Jiyoung Park, David Seungjae Lee, Natalie Lin, Holly Shablack, John Jonides, and Oscar Ybarra. “Facebook Use Predicts Declines in Subjective Well-Being in Young Adults.” PLOS ONE 8, no. 8 (August 14, 2013): e69841. Link
- Twenge, Jean M., Thomas E. Joiner, Megan L. Rogers, and Gabrielle N. Martin. “Increases in Depressive Symptoms, Suicide-Related Outcomes, and Suicide Rates Among U.S. Adolescents After 2010 and Links to Increased New Media Screen Time.” Clinical Psychological Science 6, no. 1 (January 1, 2018): 3–17. Link
- Ilakkuvan, Vinu, Amanda Johnson, Andrea C. Villanti, W. Douglas Evans, and Monique Turner. “Patterns of Social Media Use and Their Relationship to Health Risks Among Young Adults.” Journal of Adolescent Health 64, no. 2 (February 2019): 158–64. Link
- Primack, Brian A., Ariel Shensa, Jaime E. Sidani, Erin O. Whaite, Liu Yi Lin, Daniel Rosen, Jason B. Colditz, Ana Radovic, and Elizabeth Miller. “Social Media Use and Perceived Social Isolation Among Young Adults in the U.S.” American Journal of Preventive Medicine 53, no. 1 (July 2017): 1–8. Link
More in Well-being & Happiness
Coping with online abuse and practicing safe sexting

Tips for breaking free of compulsive smartphone use

Cyberbullying
Protect yourself or your child online

Self-Care Tips
Strategies to improve your mental health

Self-Esteem
How to feel good about yourself

How to Break Bad Habits
Tips for changing negative behaviors

Imposter Syndrome
What to do when you feel like a fraud at work, school, or in relationships

Your personality impacts your health, mood, and relationships. Here’s what you need to know.
Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Surgeon General: Parents Are at Their Wits’ End. We Can Do Better.

By Vivek H. Murthy
Dr. Murthy is the surgeon general.
One day when my daughter was a year old, she stopped moving her right leg. Tests found that she had a deep infection in her thigh that was dangerously close to her bone. She was rushed off to surgery. Thankfully, she’s now a healthy, spirited young girl, but the excruciating days we spent in the hospital were some of the hardest of my life. My wife, Alice, and I felt helpless and heartbroken. We got through it because of excellent medical care, understanding workplaces and loved ones who showed up and reminded us that we were not alone.
When I became a parent, a friend told me I was signing up for a lifetime of joy and worry. The joys are indeed abundant, but as fulfilling as parenting has been, the truth is it has also been more stressful than any job I’ve had. I’ve had many moments of feeling lost and exhausted. So many parents I encounter as I travel across America tell me they have the same experience: They feel lucky to be raising kids, but they are struggling, often in silence and alone.
The stress and mental health challenges faced by parents — just like loneliness , workplace well-being and the impact of social media on youth mental health — aren’t always visible, but they can take a steep toll. It’s time to recognize they constitute a serious public health concern for our country. Parents who feel pushed to the brink deserve more than platitudes. They need tangible support. That’s why I am issuing a surgeon general’s advisory to call attention to the stress and mental health concerns facing parents and caregivers and to lay out what we can do to address them.
A recent study by the American Psychological Association revealed that 48 percent of parents say most days their stress is completely overwhelming, compared with 26 percent of other adults who reported the same. They are navigating traditional hardships of parenting — worrying about money and safety, struggling to get enough sleep — as well as new stressors, including omnipresent screens, a youth mental health crisis and widespread fear about the future.
Stress is tougher to manage when you feel you’re on your own, which is why it’s particularly concerning that so many parents, single parents most of all, report feeling lonelier than other adults . Additionally, parents are stretched for time. Compared with just a few decades ago, mothers and fathers spend more time working and more time caring for their children , leaving them less time for rest, leisure and relationships. Stress, loneliness and exhaustion can easily affect people’s mental health and well-being. And we know that the mental health of parents has a direct impact on the mental health of children.
All of this is compounded by an intensifying culture of comparison, often amplified online, that promotes unrealistic expectations of what parents must do. Chasing these expectations while trying to wade through an endless stream of parenting advice has left many families feeling exhausted, burned out and perpetually behind.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission.
How the Diploma Divide Is Remaking American Politics
Education is at the heart of this country’s many divisions..

Blue America is an increasingly wealthy and well-educated place.
Throughout the second half of the 20th century, Americans without college degrees were more likely than university graduates to vote Democratic. But that gap began narrowing in the late 1960s before finally flipping in 2004 .
John F. Kennedy lost college-educated voters by a two-to-one margin yet won the presidency thanks to overwhelming support among white voters without a degree. Sixty years later, our second Catholic president charted a much different path to the White House, losing non-college-educated whites by a two-to-one margin while securing 60 percent of the college-educated vote. The latest New York Times /Siena poll of the 2022 midterms showed this pattern holding firm, with Democrats winning 55 percent of voters with bachelor’s degrees but only 39 percent of those without.
A more educated Democratic coalition is, naturally, a more affluent one. In every presidential election from 1948 to 2012, white voters in the top 5 percent of America’s income distribution were more Republican than those in the bottom 95 percent. Now, the opposite is true: Among America’s white majority, the rich voted to the left of the middle class and the poor in 2016 and 2020, while the poor voted to the right of the middle class and the rich.
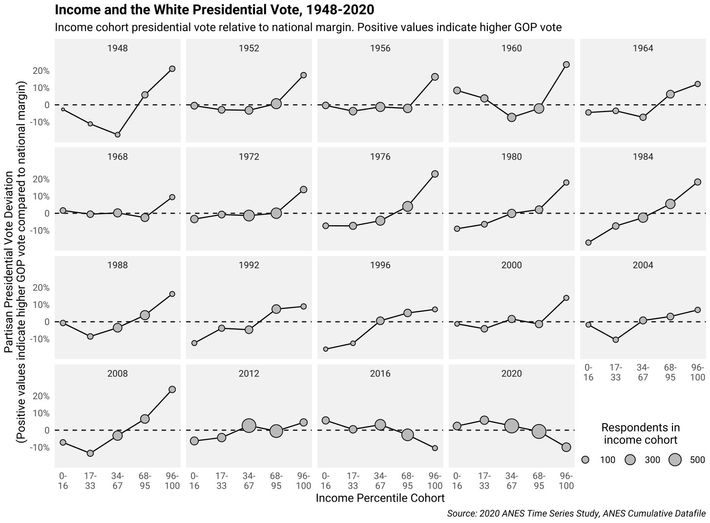
In political-science parlance, the collapse of the New Deal–era alignment — in which voters’ income levels strongly predicted their partisan preference — is often referred to as “class dealignment.” The increasing tendency for politics to divide voters along educational lines, meanwhile, is known as “education polarization.”
There are worse things for a political coalition to be than affluent or educated. Professionals vote and donate at higher rates than blue-collar workers. But college graduates also comprise a minority of the electorate — and an underrepresented minority at that. America’s electoral institutions all give disproportionate influence to parts of the country with low levels of educational attainment. And this is especially true of the Senate . Therefore, if the coalitional trends of the past half-century continue unabated — and Democrats keep gaining college-educated votes at the expense of working-class ones — the party will find itself locked out of federal power. Put differently, such a development would put an increasingly authoritarian GOP on the glide path to political dominance.
And unless education polarization is substantially reversed , progressives are likely to continue seeing their reform ambitions pared back sharply by Congress’s upper chamber, even when Democrats manage to control it.
These realities have generated a lively intra-Democratic debate over the causes and implications of class dealignment. To some pundits , consultants, and data journalists , the phenomenon’s fundamental cause is the cultural divide between educated professionals and the working class. In their telling, college graduates in general — and Democratic college graduates in particular — tend to have different social values, cultural sensibilities, and issue priorities than the median non-college-educated voter. As the New York Times ’s Nate Cohn puts the point, college graduates tend to be more cosmopolitan and culturally liberal, report higher levels of social trust, and are more likely to “attribute racial inequality, crime, and poverty to complex structural and systemic problems” rather than “individualist and parochial explanations.”
What’s more, since blue America’s journalists, politicians, and activists are overwhelmingly college graduates, highly educated liberals exert disproportionate influence over their party’s actions and identity. Therefore, as the Democrats’ well-credentialed wing has swelled, the party’s image and ideological positioning have grown more reflective of the professional class’s distinct tastes — and thus less appealing to the electorate’s working-class majority.
This theory does not sit well with all Democratic journalists, politicians, and activists. Some deny the existence of a diploma divide on cultural values, while others insist on its limited political salience. Many progressives attribute class dealignment to America’s pathological racial politics and/or the Democrats’ failures of economic governance . In this account, the New Deal coalition was unmade by a combination of a backlash to Black Americans’ growing prominence in Democratic politics and the Democratic Party’s failures to prevent its former working-class base from suffering decades of stagnant living standards and declining life expectancy .
An appreciation of these developments is surely indispensable for understanding class dealignment in the United States. But they don’t tell the whole story. Education polarization is not merely an American phenomenon; it is a defining feature of contemporary politics in nearly every western democracy . It is therefore unlikely that our nation’s white-supremacist history can fully explain the development. And though center-left parties throughout the West have shared some common failings, these inadequacies cannot tell us why many working-class voters have not merely dropped out of politics but rather begun voting for parties even more indifferent to their material interests.
In my view, education polarization cannot be understood without a recognition of the values divide between educated professionals and working people in the aggregate. That divide is rooted in each class’s disparate ways of life, economic imperatives, socialization experiences, and levels of material security. By itself, the emergence of this gap might not have been sufficient to trigger class dealignment, but its adverse political implications have been greatly exacerbated by the past half-century of inequitable growth, civic decline, and media fragmentation.
The college-educated population has distinct ideological tendencies and psychological sensibilities.
Educated professionals tend to be more socially liberal than the general public. In fact, the correlation between high levels of educational attainment and social liberalism is among the most robust in political science. As early as the 1950s, researchers documented the tendency of college graduates to espouse more progressive views than the general public on civil liberties and gender roles. In the decades since, as the political scientist Elizabeth Simon writes , this correlation has held up with “remarkable geographical and temporal consistency.” Across national boundaries and generations, voters with college degrees have been more likely than those without to support legal abortion, LGBTQ+ causes, the rights of racial minorities, and expansive immigration. They are also more likely to hold “post-material” policy priorities — which is to say, to prioritize issues concerning individual autonomy, cultural values, and big-picture social goals above those concerning one’s immediate material and physical security. This penchant is perhaps best illustrated by the highly educated’s distinctively strong support for environmental causes, even in cases when ecological preservation comes at a cost to economic growth.
Underlying these disparate policy preferences are distinct psychological profiles. The college educated are more likely to espouse moral values and attitudes associated with the personality trait “ openness to experience .” High “openness” individuals are attracted to novelty, skeptical of traditional authority, and prize personal freedom and cultural diversity. “Closed” individuals, by contrast, have an aversion to the unfamiliar and are therefore attracted to moral principles that promote certainty, order, and security. Virtually all human beings fall somewhere between these two ideal types. But the college educated as a whole are closer to the “open” end of the continuum than the general public is.
All of these distinctions between more- and less-educated voters are probabilistic, not absolute. There are Catholic theocrats with Harvard Ph.D.’s and anarchists who dropped out of high school. A nation the size of the U.S. is surely home to many millions of working-class social liberals and well-educated reactionaries. Political attitudes do not proceed automatically from any demographic characteristic, class position, or psychological trait. At the individual level, ideology is shaped by myriad historical inheritances and social experiences.
And yet, if people can come by socially liberal, “high openness” politics from any walk of life, they are much more likely to do so if that walk cuts across a college campus. (And, of course, they are even more likely to harbor this distinct psychological and ideological profile if they graduate from college and then choose to become professionally involved in Democratic politics.)
The path to the professional class veers left.
There are a few theoretical explanations for this. One holds that spending your late adolescence on a college campus tends to socialize you into cultural liberalism: Through some combination of increased exposure to people from a variety of geographic backgrounds, or the iconoclastic ethos of a liberal-arts education, or the predominantly left-of-center university faculty , or the substantive content of curricula, people tend to leave college with a more cosmopolitan and “open” worldview than they had upon entering.
Proving this theory is difficult since doing so requires controlling for selection effects. Who goes to college is not determined by random chance. The subset of young people who have the interests, aptitudes, and opportunities necessary for pursuing higher education have distinct characteristics long before they show up on campus. Some social scientists contend that such “selection effects” entirely explain the distinct political tendencies of college graduates. After all, the “high openness” personality trait is associated with higher IQs and more interest in academics. So perhaps attending college doesn’t lead people to develop culturally liberal sensibilities so much as developing culturally liberal sensibilities leads people to go to college.
Some research has tried to account for this possibility. Political scientists in the United Kingdom have managed to control for the preadult views and backgrounds of college graduates by exploiting surveys that tracked the same respondents through adolescence and into adulthood. Two recent analyses of such data have found that the college experience does seem to directly increase a person’s likelihood of becoming more socially liberal in their 20s than they were in their teens.
A separate study from the U.S. sought to control for the effects of familial background and childhood experiences by examining the disparate “sociopolitical” attitudes of sibling pairs in which one went to college while the other did not. It found that attending college was associated with greater “support for civil liberties and egalitarian gender-role beliefs.”
Other recent research , however, suggests that even these study designs may fail to control for all of the background factors that bias college attendees toward liberal views before they arrive on campus. So we have some good evidence that attending college directly makes people more culturally liberal, but that evidence is not entirely conclusive.
Yet if one posits that higher education does not produce social liberals but merely attracts them, a big theoretical problem remains: Why has the population of social liberals increased in tandem with that of college graduates?
The proportion of millennials who endorse left-wing views on issues of race, gender, immigration , and the environment is higher than the proportion of boomers who do so. And such views are more prevalent within the baby-boom generation than they were among the Silent Generation. This cannot be explained merely as a consequence of America’s burgeoning racial diversity, since similar generational patterns have been observed in European nations with lower rates of ethnic change. But the trend is consistent with another component of demographic drift: Each successive generation has had a higher proportion of college graduates than its predecessor. Between 1950 and 2019, the percentage of U.S. adults with bachelor’s degrees increased from 4 percent to 33 percent.
Perhaps rising college attendance did not directly cause the “high-openness,” post-material, culturally progressive proportion of the population to swell. But then, what did?
One possibility is that, even if mass college attendance does not directly promote the development of “high openness” values, the mass white-collar economy does. If socially liberal values are well suited to the demands and lifeways inherent to professional employment in a globally integrated economy, then, as such employment expands, we would expect a larger share of the population to adopt socially liberal values. And there is indeed reason to think the professional vocation lends itself to social liberalism.
Entering the professional class often requires not only a four-year degree, but also, a stint in graduate school or a protracted period of overwork and undercompensation at the lowest ranks of one’s field. This gives the class’s aspirants a greater incentive to postpone procreation until later in life than the median worker. That in turn may give them a heightened incentive to favor abortion rights and liberal sexual mores.
The demands of the professional career may influence value formation in other ways. As a team of political scientists from Harvard and the University of Bonn argued in a 2020 paper , underlying the ideological divide between social liberals and conservatives may be a divergence in degrees of “moral universalism,” i.e., “the extent to which people’s altruism and trust remain constant as social distance increases.” Conservatives tend to feel stronger obligations than liberals to their own kin and neighbors and their religious, ethnic, and racial groups. Liberals, by contrast, tend to spread their altruism and trust thinner across a wider sphere of humanity; they are less compelled by the particularist obligations of inherited group loyalties and more apt to espouse a universalist ethos in which all individuals are of equal moral concern, irrespective of their group attachments.
Given that pursuing a professional career often requires leaving one’s native community and entering meritocratic institutions that are ideologically and legally committed to the principle that group identities matter less than individual aptitudes, the professional vocation may favor the development of a morally universalistic outlook — and thus more progressive views on questions of anti-discrimination and weaker identification with inherited group identities.
Further, in a globalized era, white-collar workers will often need to work with colleagues on other continents and contemplate social and economic developments in far-flung places. This may encourage both existing and aspiring professionals to develop more cosmopolitan outlooks.
Critically, parents who are themselves professionals — or who aspire for their children to secure a place in the educated, white-collar labor force — may seek to inculcate these values in their kids from a young age. For example, my own parents sent me to a magnet elementary school where students were taught Japanese starting in kindergarten. This curriculum was designed to appeal to parents concerned with their children’s capacity to thrive in the increasingly interconnected (and, in the early 1990s American imagination, increasingly Japanese-dominated) economy of tomorrow.
In this way, the expansion of the white-collar sector may increase the prevalence of “high-openness” cosmopolitan traits and values among rising generations long before they arrive on campus.
More material security, more social liberalism.
Ronald Inglehart’s theory of “ cultural evolution ” provides a third, complementary explanation for both the growing prevalence of social liberalism over the past half-century and for that ideology’s disproportionate popularity among the college educated.
In Inglehart’s account, people who experience material security in youth tend to develop distinctive values and preferences from those who do not: If childhood teaches you to take your basic material needs for granted, you’re more likely to develop culturally progressive values and post-material policy priorities.
Inglehart first formulated this theory in 1971 to explain the emerging cultural gap between the baby boomers and their parents. He noted that among western generations born before World War II, very large percentages had known hunger at some point in their formative years. The Silent Generation, for its part, had come of age in an era of economic depression and world wars. Inglehart argued that such pervasive material and physical insecurity was unfavorable soil for social liberalism: Under conditions of scarcity, human beings have a strong inclination to defer to established authority and tradition, to distrust out-groups, and to prize order and material security above self-expression and individual autonomy.
But westerners born into the postwar boom encountered a very different world from the Depression-wracked, war-torn one of their parents, let alone the cruel and unforgiving one encountered by common agriculturalists since time immemorial. Their world was one of rapid and widespread income growth. And these unprecedentedly prosperous conditions engendered a shift in the postwar generation’s values: When the boomers reached maturity, an exceptionally large share of the cohort evinced post-material priorities and espoused tolerance for out-groups, support for gender equality, concern for the environment, and antipathy for social hierarchies.
Since this transformation in values wasn’t rooted merely in the passage of time — but rather in the experience of abundance — it did not impact all social classes equally. Educated professionals are disproportionately likely to have had stable, middle-class childhoods. Thus, across the West, the post-material minority was disproportionately composed of college graduates in general and elite ones in particular. As Inglehart reported in 1981 , “among those less than 35 years old with jobs that lead to top management and top civil-service posts, Post-Materialists outnumber Materialists decisively: their numerical preponderance here is even greater than it is among students.”
As with most big-picture models of political development, Inglehart’s theory is reductive and vulnerable to myriad objections. But his core premise — that, all else being equal, material abundance favors social liberalism while scarcity favors the opposite — has much to recommend it. As the World Values Survey has demonstrated, a nation’s degree of social liberalism (a.k.a. “self-expression values”) tightly correlates with its per-capita income. Meanwhile, as nations become wealthier, each successive generation tends to become more socially liberal than the previous one.
Critically, the World Values Survey data does not show an ineluctable movement toward ever-greater levels of social liberalism. Rather, when nations backslide economically, their populations’ progressivism declines. In the West, recessions have tended to reduce the prevalence of post-material values and increase support for xenophobic parties. But the relationship between material security and cultural liberalism is demonstrated most starkly by the experience of ex-communist states, many of which suffered a devastating collapse in living standards following the Soviet Union’s fall. In Russia and much of Eastern Europe, popular support for culturally progressive values plummeted around 1990 and has remained depressed ever since.
Inglehart’s theory offers real insights. As an account of education polarization, however, it presents a bit of a puzzle: If material security is the key driver of social liberalism, why have culture wars bifurcated electorates along lines of education instead of income? Put differently: Despite the material security provided by a high salary, when one controls for educational attainment, having a high income remains strongly associated with voting for conservatives.
One way to resolve this tension is to stipulate that the first two theories of education polarization we examined are also right: While material security is conducive to social liberalism, the college experience and demands of professional-class vocations are perhaps even more so. Thus, high-income voters who did not go to college will tend to be less socially liberal than those who did.
Separately, earning a high income is strongly associated with holding conservative views on fiscal policy. Therefore, even if the experience of material security biases high-income voters toward left-of-center views on cultural issues, their interest in low taxes may nevertheless compel them to vote for right-wing parties.
Voters with high levels of education but low incomes, meanwhile, are very often children of the middle class who made dumb career choices like, say, going into journalism. Such voters’ class backgrounds would theoretically bias them toward a socially liberal orientation, while their meager earnings would give them little reason to value conservative fiscal policy. Perhaps for this reason, “ high-education low-income voters ” are among the most reliably left-wing throughout the western world.
In any case, whatever qualifications and revisions we would wish to make to Inglehart’s theory, one can’t deny its prescience. In 1971, Inglehart forecast that intergenerational value change would redraw the lines of political conflict throughout the West. In his telling, the emergence of a novel value orientation that was disproportionately popular with influential elites would naturally shift the terrain of political conflict. And it would do so in a manner that undermined materialist, class-based voting: If conventional debates over income distribution pulled at the affluent right and the working-class left, the emerging cultural disputes pulled each in the opposite direction.
This proved to be, in the words of Gabriel Almond, “one of the few examples of successful prediction in political science.”
When the culture wars moved to the center of politics, the college educated moved left.
Whether we attribute the social liberalism of college graduates to their experiences on campus, their class’s incentive structures, their relative material security, or a combination of all three, a common set of predictions about western political development follows.
First, we would expect to see the political salience of cultural conflicts start to increase in the 1960s and ’70s as educated professionals became a mass force in western politics. Second, relatedly, we would expect that the historic correlation between having a college degree and voting for the right would start gradually eroding around the same time, owing to the heightened prominence of social issues.
Finally, we would expect education polarization to be most pronounced in countries where (1) economic development is most advanced (and thus the professional sector is most expansive) and (2) left-wing and right-wing parties are most sharply divided on cultural questions.
In their paper “Changing Political Cleavages in 21 Western Democracies, 1948–2020,” Amory Gethin, Clara Martínez-Toledano, and Thomas Piketty confirm all of these expectations.
The paper analyzes nearly every manifesto (a.k.a. “platform”) put forward by left-wing and right-wing parties in the past 300 elections. As anticipated by Inglehart, the researchers found that right-wing and left-wing parties began to develop distinct positions on “sociocultural” issues in the 1970s and that these distinctions grew steadily more profound over the ensuing 50 years. Thus, the salience of cultural issues did indeed increase just as college graduates became an electorally significant demographic.
As cultural conflict became more prominent, educated professionals became more left-wing. Controlling for other variables, in the mid-20th century, having a college diploma made one more likely to vote for parties of the right. By 2020, in virtually all of the western democracies, this relationship had inverted.
Some popular narratives attribute this realignment to discrete historical events, such as the Cold War’s end, China’s entry into the WTO, or the 2008 crash. But the data show no sudden reversal in education’s political significance. Instead, the authors write, the West saw “a very progressive, continuous reversal of educational divides, which unfolded decades before any of these events took place and has carried on uninterruptedly until today.” This finding is consistent with the notion that class dealignment is driven by gradual changes in western societies’ demographic and economic characteristics, such as the steady expansion of the professional class.
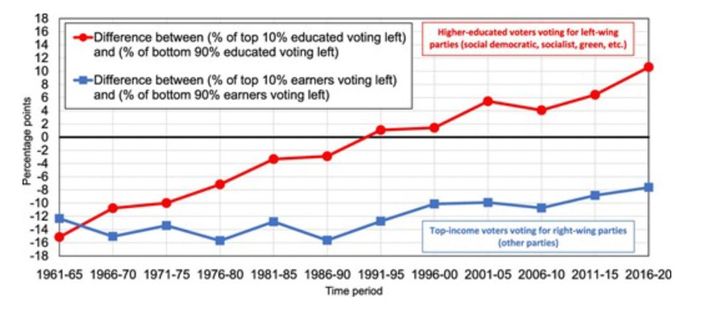
The paper provides further support for the notion that education polarization is a by-product of economic development: The three democracies where college-educated voters have not moved sharply to the left in recent decades — Ireland, Portugal, and Spain — are all relative latecomers to industrialization.
Finally, and perhaps most important, the authors established a strong correlation between “sociocultural polarization” — the degree to which right-wing and left-wing parties emphasize sharply divergent cultural positions — and education polarization. In other words: Countries where parties are highly polarized on social issues tend to have electorates that are highly polarized along educational lines.
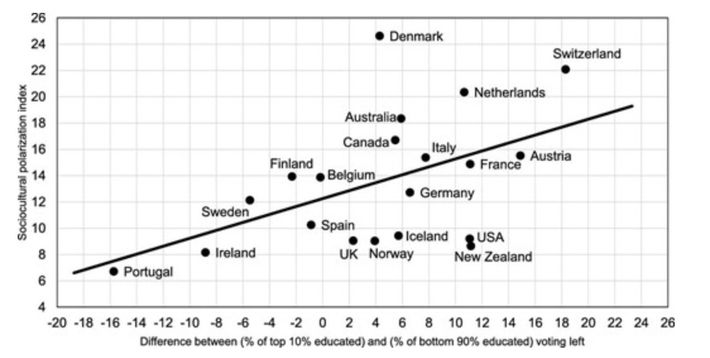
It seems reasonable then to conclude (1) that there really is a cultural divide between educated professionals and the working class in the aggregate and (2) that this gap has been a key driver of class dealignment. Indeed, if we accept the reality of the diploma divide, then an increase of education-based voting over the past 50 years would seem almost inevitable: If you have two social groups with distinct cultural values and one group goes from being 4 percent of the electorate to 35 percent of it, debates about those values will probably become more politically prominent.
And of course, mass higher education wasn’t the only force increasing the salience of social conflict in the West over the past half-century. If economic development increased the popularity of “post-material” values, it also made it easier for marginalized groups to contest traditional hierarchies. As job opportunities for women expanded, they became less dependent on the patriarchal family for material security and thus were more liable to challenge it. As racial minorities secured a foothold in the middle class, they had more resources with which to fight discrimination.
And yet, if an increase in sociocultural polarization — and thus in education polarization — is a foregone conclusion, the magnitude of these shifts can’t be attributed to the existence of cultural divides alone.
Rather, transformations in the economic, civic, and media landscapes of western society since the 1970s have increased the salience and severity of the diploma divide.
When the postwar bargain collapsed, the center-left failed to secure workers a new deal.
To polarize an electorate around cultural conflicts rooted in education, you don’t just need to increase the salience of social issues. You also need to reduce the salience of material disputes rooted in class. Alas, the economic developments of the past 50 years managed to do both.
The class-based alignment that defined western politics in the mid-20th century emerged from a particular set of economic conditions. In the early stages of industrialization, various factors had heightened the class consciousness of wage laborers. Such workers frequently lived in densely settled, class-segregated neighborhoods in the immediate vicinity of large labor-intensive plants. This close proximity cultivated solidarity, as divisions between the laborer’s working and social worlds were few. And the vast scale of industrial enterprises abetted organizing drives, as trade unions could rapidly gain scale by winning over a single shop.
By encouraging their members to view politics through the lens of class and forcing political elites to reckon with workers’ demands, strong trade unions helped to keep questions of income distribution and workers’ rights at the center of political debate and the forefront of voters’ minds. In so doing, they also helped to win western workers in general — and white male ones in particular — unprecedented shares of national income.
But this bargain between business and labor had always been contingent on robust growth. In the postwar era of rising productivity, it was possible for profits and wages to increase in tandem. But in the 1970s, western economies came under stress. Rising energy costs and global competition thinned profit margins, rendering business owners more hostile to labor’s demands both within the shop and in politics. Stagflation — the simultaneous appearance of high unemployment and high inflation — gave an opening to right-wing critics of the postwar order, who argued that the welfare state and pro-labor macroeconomic policies had sapped productivity.
Meanwhile, various long-term economic trends began undermining industrial unionism. Automation inevitably reduced the labor intensity of factories in the West. The advent of the shipping container eased the logistical burdens of globalizing production, while the industrialization of low-wage developing countries increased the incentives for doing so. Separately, as western consumers grew more affluent, they began spending less of their income on durable goods and more on services like health care (one needs only so many toasters, but the human desire for greater longevity and physical well-being is nigh-insatiable). These developments reduced both the economic leverage and the political weight of industrial workers. And since western service sectors had lower rates of unionization, deindustrialization weakened organized labor.
All this presented center-left parties with a difficult challenge. In the face of deindustrialization, an increasingly anti-labor corporate sector, an increasingly conservative economic discourse, an embattled union movement, and a globalizing economy, such parties needed to formulate new models for achieving shared prosperity. And they had to do so while managing rising cultural tensions within their coalitions.
They largely failed.
Countering the postindustrial economy’s tendencies toward inequality would have required radical reforms. Absent policies promoting the unionization of the service sector, deindustrialization inevitably weakened labor. Absent drastic changes in the allocation of posttax income, automation and globalization redistributed economic gains away from “low skill” workers and toward the most productive — or well-situated — professionals, executives, and entrepreneurs.
The United States had more power than any western nation to standardize such reforms and establish a relatively egalitarian postindustrial model. Yet the Democratic Party could muster neither the political will nor the imagination to do so. Instead, under Jimmy Carter, it acquiesced to various policies that reinforced the postindustrial economy’s tendencies toward inequality, while outsourcing key questions of economic management to financial markets and the Federal Reserve. The Reagan administration took this inegalitarian and depoliticized model of economic governance to new extremes. And to highly varying degrees, its inequitable and market-fundamentalist creed influenced the policies of future U.S. administrations and other western governments.
As a result, the past five decades witnessed a great divergence in the economic fortunes of workers with and without college diplomas, while the western working class (a.k.a. the “lower middle class”) became the primary “losers” of globalization .
The center-left parties’ failures to avert a decline in the economic security and status of ordinary workers discredited them with much of their traditional base. And their failure to reinvigorate organized labor undermined the primary institutions that politicize workers into a progressive worldview. These shortcomings, combined with the market’s increasingly dominant role in economic management, reduced the political salience of left-right divides on economic policy. This in turn gave socially conservative working-class voters fewer reasons to vote for center-left parties and gave affluent social liberals fewer reasons to oppose them. In western nations where organized labor remains relatively strong (such as Norway, Sweden, and Finland), education polarization has been relatively mild, while in those countries where it is exceptionally weak (such as the United States), the phenomenon has been especially pronounced.
Finally, the divergent economic fortunes of workers and professionals might have abetted education polarization in one other way: Given that experiencing abundance encourages social liberalism — while experiencing scarcity discourages it — the past half-century of inequitable growth might have deepened cultural divisions between workers with degrees and those without.
The professionalization of civil society estranged the left from its working-class base.
While the evolution of western economies increased the class distance between college graduates and other workers, the evolution of western civil societies increased the social distance between each group.
Back in the mid-20th century, the college educated still constituted a tiny minority of western populations, while mass-membership institutions — from trade unions to fraternal organizations to political parties — still dominated civic life. In that context, an educated professional who wished to exercise political influence often needed to join a local chapter of a cross-class civic association or political party and win election to a leadership position within that organization by securing the confidence of its membership.
That changed once educated professionals became a mass constituency in their own right. As the college-educated population ballooned and concentrated itself within urban centers, it became easier for interest groups to swing elections and pressure lawmakers without securing working-class support. At the same time, the proliferation of “knowledge workers” set off an arms race between interest and advocacy groups looking to influence national legislation and election outcomes. Job opportunities for civic-minded professionals in think tanks, nonprofits, and foundations proliferated. And thanks to growing pools of philanthropic money and the advent of direct-mail fundraising, these organizations could sustain themselves without recruiting an active mass membership.
Thus, the professional’s path to political influence dramatically changed. Instead of working one’s way up through close-knit local groups — and bending them toward one’s political goals through persuasion — professionals could join (or donate to) nationally oriented advocacy groups already aligned with their preferences, which could then advance their policy aims by providing legislators with expert guidance and influencing public opinion through media debates.
As the political scientist Theda Skocpol demonstrates in her book Diminished Democracy , college graduates began defecting from mass-membership civic organizations in the 1970s, in an exodus that helped precipitate their broader decline.
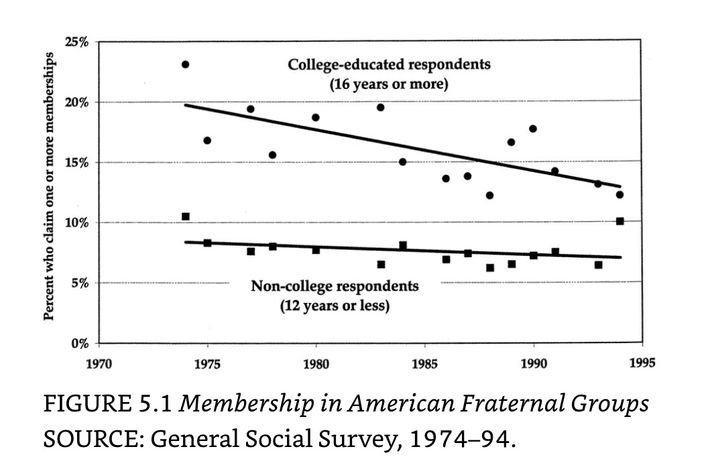
Combined with the descent of organized labor, the collapse of mass participation in civic groups and political parties untethered the broad left from working-class constituencies. As foundation-funded NGOs displaced trade unions in the progressive firmament, left-wing parties became less directly accountable to their less-educated supporters. This made such parties more liable to embrace the preferences and priorities of educated professionals over those of the median working-class voter.
Meanwhile, in the absence of a thriving civic culture, voters became increasingly reliant on the mass media for their political information.
Today’s media landscape is fertile terrain for right-wing populism.
The dominant media technology of the mid-20th century — broadcast television — favored oligopoly. Given the exorbitant costs of mounting a national television network in that era, the medium was dominated by a small number of networks, each with an incentive to appeal to a broad audience. This discouraged news networks from cultivating cultural controversy while empowering them to establish a broadly shared information environment.
Cable and the internet have molded a radically different media landscape. Today, news outlets compete in a hypersaturated attentional market that encourages both audience specialization and sensationalism. In a world where consumers have abundant infotainment options, voters who read at a graduate-school level and those who read at an eighth-grade level are unlikely to favor the same content. And the same is true of voters with liberal and conservative sensibilities — especially since the collapse of a common media ecosystem leads ideologues to occupy disparate factual universes. The extraordinary nature of today’s media ecology is well illustrated by this chart from Martin Gurri’s book, The Revolt of the Public :
This information explosion abets education polarization for straightforward reasons: Since the college educated and non-college educated have distinct tastes in media, in a highly competitive attentional market, they will patronize different outlets and accept divergent facts.
Further, in the specific economic and social context we’ve been examining, the modern media environment is fertile terrain for reactionary entrepreneurs who wish to cultivate grievance against the professional elite. After all, as we’ve seen, that elite (1) subscribes to some values that most working-class people reject, (2) commandeers a wildly disproportionate share of national income and economic status, and (3) dominates the leadership of major political parties and civic groups to an unprecedented degree.
The political efficacy of such right-wing “populist” programming has been repeatedly demonstrated. Studies have found that exposure to Fox News increases Republican vote share and that the expansion of broadband internet into rural areas leads to higher levels of partisan hostility and lower levels of ticket splitting (i.e., more ideologically consistent voting) as culturally conservative voters gain access to more ideologically oriented national news reporting, commentary, and forums.
What is to be done?
The idea that education polarization arises from deep structural tendencies in western society may inspire a sense of powerlessness. And the notion that it emerges in part from a cultural divide between professionals and working people may invite ideological discomfort, at least among well-educated liberals.
But the fact that some center-left parties have managed to retain more working-class support than others suggests that the Democrats have the capacity to broaden (or narrow) their coalition. Separately, the fact that college-educated liberals have distinct social values does not require us to forfeit them.
The commentators most keen to acknowledge the class dimensions of the culture wars typically aim to discredit the left by doing so. Right-wing polemicists often suggest that progressives’ supposedly compassionate social preferences are mere alibis for advancing the professional class’s material interests. But such arguments are almost invariably weak. Progressive social views may be consonant with professional-class interests, but they typically represent attempts to universalize widely held ideals of freedom and equality. The college educated’s cosmopolitan inclinations are also adaptive for a world that is unprecedentedly interconnected and interdependent and in which population asymmetries between the rich and developing worlds create opportunities for mutual gain through migration , if only xenophobia can be overcome. And of course, in an era of climate change, the professional class’s strong concern for the environment is more than justified.
Nevertheless, professional-class progressives must recognize that our social values are not entirely unrelated to our class position. They are not an automatic by-product of affluence and erudition, nor the exclusive property of the privileged. But humans living in rich, industrialized nations are considerably more likely to harbor these values than those in poor, agrarian ones. And Americans who had the privilege of spending their late adolescence at institutions of higher learning are more likely to embrace social liberalism than those who did not.
The practical implications of this insight are debatable. It is plausible that Democrats may be able to gain working-class vote share by moderating on some social issues. But the precise electoral payoff of any single concession to popular opinion is deeply uncertain. Voters’ conceptions of each party’s ideological positioning are often informed less by policy details than by partisan stereotypes. And the substantive costs of moderation — both for the welfare of vulnerable constituencies and the long-term health of the progressive project — can be profound. At various points in the past half-century, it might have been tactically wise for Democrats to distance themselves from the demands of organized labor. But strategically, sacrificing the health of a key partisan institution to the exigencies of a single election cycle is deeply unwise. Meanwhile, in the U.S. context, the “mainstream” right has staked out some cultural positions that are profoundly unpopular with all social classes . In 2022, it is very much in the Democratic Party’s interest to increase the political salience of abortion rights.
In any case, exactly how Democrats should balance the necessity of keeping the GOP out of power with the imperative to advocate for progressive issue positions is something on which earnest liberals can disagree.
The case for progressives to be more cognizant of the diploma divide when formulating our messaging and policy priorities, however, seems clearer.
Education polarization can be self-reinforcing. As left-wing civic life has drifted away from mass-membership institutions and toward the ideologically self-selecting circles of academia, nonprofits, and the media, the left’s sensitivity to the imperatives of majoritarian politics has dulled. In some respects, the incentives for gaining status and esteem within left-wing subcultures are diametrically opposed to the requirements of coalition building. In the realm of social media, it can be advantageous to make one’s policy ideas sound more radical and/or threatening to popular values than they actually are. Thus, proposals for drastically reforming flawed yet popular institutions are marketed as plans for their “abolition,” while some advocates for reproductive rights insist that they are not merely “pro-choice” but “ pro-abortion ” (as though their objective were not to maximize bodily autonomy but rather the incidence of abortion itself, a cause that would seemingly require limiting access to contraception).
Meanwhile, the rhetoric necessary for cogently theorizing social problems within academia — and that fit for effectively selling policy reforms to a mass audience — is quite different. Political-science research indicates that theoretical abstractions tend to leave most voters cold. Even an abstraction as accessible as “inequality” resonates less with ordinary people than simply saying that the rich have too much money . Yet Democratic politicians have nevertheless taken to peppering their speeches with abstract academic terms such as structural racism .
Relatedly, in the world of nonprofits, policy wonks are often encouraged to foreground the racial implications of race-neutral redistributive policies that disproportionately benefit nonwhite constituencies. Although it is important for policy design to account for any latent racial biases in universal programs, there is reason to believe that, in a democracy with a 70 percent white electorate and widespread racial resentment, it is unwise for Democratic politicians to suggest that broadly beneficial programs primarily aid minority groups.
On the level of priority setting, it seems important for college-educated liberals to be conscious of the fact that “post-material” concerns resonate more with us than with the general public. This is especially relevant for climate strategy. Poll results and election outcomes both indicate that working-class voters are far more sensitive to the threat of rising energy prices than to that of climate change. Given that reality, the most politically viable approach to reducing emissions is likely to expedite the development and deployment of clean-energy technologies rather than deterring energy consumption through higher prices. In practice, this means prioritizing the build-out of green infrastructure over the obstruction of fossil-fuel extraction.
Of course, narrowing the social distance between college-educated liberals and working people would be even better than merely finessing it. The burgeoning unionization of white-collar professions and the growing prominence of downwardly mobile college graduates in working-class labor struggles are both encouraging developments on this front. Whatever Democrats can do to facilitate labor organizing and increase access to higher education will simultaneously advance social justice and improve the party’s long-term electoral prospects.
Finally, the correlation between material security and social liberalism underscores the urgency of progressive economic reform. Shared prosperity can be restored only by increasing the social wage of ordinary workers through some combination of unionization, sectoral bargaining, wage subsidies, and social-welfare expansion. To some extent, this represents a chicken-and-egg problem: Radical economic reforms may be a necessary precondition for the emergence of a broad progressive majority, yet a broad progressive majority is itself a precondition for radical reform.
Nevertheless, in wealthy, deep-blue states such as New York and California, Democrats have the majorities necessary for establishing a progressive economic model. At the moment, artificial constraints on the housing supply , clean-energy production, and other forms of development are sapping blue states’ economic potential . If such constraints could be overcome, the resulting economic gains would simultaneously increase working people’s living standards and render state-level social-welfare programs easier to finance. Perhaps the starting point for such a political revolution is for more-affluent social liberals to recognize that their affinity for exclusionary housing policies and aversion to taxation undermines their cultural values.
Our understanding of education polarization remains provisional. And all proposals for addressing it remain open to debate. The laws of political science are more conjectural than those of physics, and even perfect insight into political reality cannot settle disputes rooted in ideology.
But effective political engagement requires unblinkered vision. The Democratic Party’s declining support among working-class voters is a serious problem. If Democrats consider only ideologically convenient explanations for that problem, our intellectual comfort may come at the price of political power.
- political science
- higher education
- the democratic party
- the big picture
Most Viewed Stories
- J.D. Vance Blames Staff for Disastrous Doughnut-Shop Visit
- What Trump Said in His Vulgar and Unhinged Truth Social Spree
- What We Know About the Trump Campaign’s Arlington National Cemetery Incident
- The Bitter Feud at the Heart of the Paleontology World
- The Right-Wing Crusade Against DEI Isn’t Actually Working
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
- J.D. Vance Blames Staff for Disastrous Doughnut-Shop Visit By Margaret Hartmann
- What Trump Said in His Vulgar and Unhinged Truth Social Spree By Margaret Hartmann
- What We Know About the Trump Campaign’s Arlington National Cemetery Incident By Nia Prater
- The Bitter Feud at the Heart of the Paleontology World By Kerry Howley
- The Right-Wing Crusade Against DEI Isn’t Actually Working By Kevin T. Dugan

What is your email?
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.
Home — Essay Samples — Business — Media — Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media for Society
Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media for Society
- Categories: Media Social Media Society
About this sample

Words: 717 |
Published: Feb 12, 2019
Words: 717 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Business Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1651 words
2 pages / 862 words
2 pages / 777 words
2 pages / 1108 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
In Chapter 8 of Thirteen American Arguments, the author Howard Fineman delves into the pervasive influence of television in shaping public opinion and its impact on democracy. Through a blend of , cultural analysis, and critical [...]
In recent years, the intersection of social media and mental health has emerged as a significant area of concern, particularly with regards to the alarming rates of teen suicide. Adolescence is a critical period marked by [...]
Advertising is an omnipresent force in modern American culture, shaping consumer behavior, societal norms, and even personal identities. From the billboards lining urban streets to the subtle product placements in television [...]
"The Merchants of Cool," a documentary produced by the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) in 2001, provides a critical exploration into the symbiotic relationship between teenage consumer culture and the media industry. The [...]
Primarily internet or cellular phone based applications and tools to share information among people. Social media includes popular networking websites, like Facebook and Twitter; as well as bookmarking sites like Reddit. It [...]
In my assignment I will tell you about the “uses and gratification theory”. This theory is different and not like other theories of mass media. The other theories mostly focuses on the effects that media has on the audience. [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Internet ›
- Social Media & User-Generated Content
Industry-specific and extensively researched technical data (partially from exclusive partnerships). A paid subscription is required for full access.
- Share of negative experiences purchasing on social media APAC 2024
In a survey conducted among Asia-Pacific consumers in the first half of 2024, 54 percent of the respondents agreed that they had negative experiences purchasing something via social media. In contrast, 18 percent of the respondents did not have negative social commerce experiences.
Share of negative experiences when purchasing on social media among consumers in the Asia-Pacific region as of June 2024
| Characteristic | Share of respondents |
|---|---|
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
To access all Premium Statistics, you need a paid Statista Account
- Immediate access to all statistics
- Incl. source references
- Download as PDF, XLS, PNG and PPT
Additional Information
Show sources information Show publisher information Use Ask Statista Research Service
7,279 respondents
among respondents across 11 APAC countries and territories
Face-to-face interview, online survey
Original question: To what extent do you agree or disagree with the following statements about social media? Statement: I have had bad experiences purchasing something via social media.
Other statistics on the topic Digital advertising in the Asia-Pacific region
Advertising
- Ad media owners' revenue worldwide from 2023-2025
- Distribution of ad spend worldwide 2022-2026, by medium
- Advertising spending worldwide 2024, by region
Advertising & Marketing
- Advertising spending APAC 2014-2023
To download this statistic in XLS format you need a Statista Account
To download this statistic in PNG format you need a Statista Account
To download this statistic in PDF format you need a Statista Account
To download this statistic in PPT format you need a Statista Account
As a Premium user you get access to the detailed source references and background information about this statistic.
As a Premium user you get access to background information and details about the release of this statistic.
As soon as this statistic is updated, you will immediately be notified via e-mail.
… to incorporate the statistic into your presentation at any time.
You need at least a Starter Account to use this feature.
- Immediate access to statistics, forecasts & reports
- Usage and publication rights
- Download in various formats
* For commercial use only
Basic Account
- Free Statistics
Starter Account
- Premium Statistics
The statistic on this page is a Premium Statistic and is included in this account.
Professional Account
- Free + Premium Statistics
- Market Insights
1 All prices do not include sales tax. The account requires an annual contract and will renew after one year to the regular list price.
Statistics on " Digital advertising in the Asia-Pacific region "
- Ad spending in selected markets worldwide 2024
- Revenue of the digital advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Revenue of the social media advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Revenue of the search advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Revenue of the video advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Revenue of the banner advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Revenue of the digital classifieds market APAC 2022, by country
- Digital ad spending Asia 2019-2028
- Ad spend wasted due to invalid traffic worldwide 2022-2024
- Share of global ad spend lost to fraud APAC 2028, by subregion
- Facebook Messenger ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Instagram ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- YouTube ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- TikTok ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Snapchat ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- LinkedIn ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Most influential types of personalized digital ads among consumers APAC 2024
- Most frequently used shopping channels APAC 2024, by country
- Discomfort level with purchasing via social media APAC 2024
Other statistics that may interest you Digital advertising in the Asia-Pacific region
- Premium Statistic Ad media owners' revenue worldwide from 2023-2025
- Premium Statistic Distribution of ad spend worldwide 2022-2026, by medium
- Premium Statistic Ad spending in selected markets worldwide 2024
- Premium Statistic Advertising spending worldwide 2024, by region
- Premium Statistic Advertising spending APAC 2014-2023
Market segments
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the digital advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the social media advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the search advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the video advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the banner advertising market APAC 2022, by country
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the digital classifieds market APAC 2022, by country
Ad spend and ad spend waste
- Premium Statistic Digital ad spending Asia 2019-2028
- Premium Statistic Ad spend wasted due to invalid traffic worldwide 2022-2024
- Premium Statistic Share of global ad spend lost to fraud APAC 2028, by subregion
- Premium Statistic Facebook Messenger ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Premium Statistic Instagram ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Premium Statistic YouTube ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Premium Statistic TikTok ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Premium Statistic Snapchat ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
- Premium Statistic LinkedIn ad reach rate APAC 2024, by country
Consumer preferences
- Premium Statistic Most influential types of personalized digital ads among consumers APAC 2024
- Premium Statistic Most frequently used shopping channels APAC 2024, by country
- Premium Statistic Discomfort level with purchasing via social media APAC 2024
- Premium Statistic Share of negative experiences purchasing on social media APAC 2024
Further Content: You might find this interesting as well

Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.


COMMENTS
Social Media Impact on Society. Social media has become an integral part of our society, influencing how we communicate, interact, and consume information. The rise of platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok has transformed the way we connect with others, share our thoughts and experiences, and access news and entertainment.
A study published in the journal Computers and Human Behaviour found that people who report using seven or more social media platforms were more than three times as likely as people using 0-2 ...
Mental Health. One of the most significant ways in which social media is harmful to society is through its negative impact on mental health. Research has shown that excessive use of social media is linked to increased rates of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. The constant exposure to curated and often unrealistic ...
The Effects of Social Media on Society Essay. The social networks broke into the everyday life of the majority of common people in the middle of 00s, first giving neglectful and suspicious attitude, as a tracking instrument of the government. Nevertheless, shortly, almost every individual including teenagers and elderly people, created a page ...
Chief among Haidt's worries is that use of social media has left us particularly vulnerable to confirmation bias, or the propensity to fix upon evidence that shores up our prior beliefs. Haidt ...
Firstly, in order to fairly and properly assess the benefits or harms of social media, the latter should be distinguished from the internet. For example, it is stated that "the notion that the Internet is bad for you seems premised on the idea that the Internet is one thing—a monolith" (Goldsmith 597). In other words, the internet is not ...
The concern, and the studies, come from statistics showing that social media use in teens ages 13 to 17 is now almost ubiquitous. Two-thirds of teens report using TikTok, and some 60 percent of ...
About two-thirds of Americans (64%) say social media have a mostly negative effect on the way things are going in the country today, according to a Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted July 13-19, 2020. Just one-in-ten Americans say social media sites have a mostly positive effect on the way things are going, and one-quarter say ...
Social Media Argumentative Essay Topics. This is a comprehensive resource to help you find the perfect social media essay topic. Whether you're navigating the complexities of digital communication, exploring the impact of social media on society, or examining its effects on personal identity, the right topic can transform your essay into a captivating and insightful exploration.
A growing number of studies have examined the psychological corollaries of using social networking sites (SNSs) such as Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter (often called social media). The interdisciplinary research area and conflicting evidence from primary studies complicate the assessment of current scholarly knowledge in this field of high ...
My essay laid out a wide array of harms that social media has inflicted on society. Political polarization is just one of them, but it is central to the story of rising democratic dysfunction.
Sometimes, it leads to violent situations in society. Social media affects the mental health of individuals: The stalking, cybercrimes, frauds, and hate comments adversely affect people; problems of depression, anxiety, severe tension, and fear are emerging. Sometimes, the conditions get worse, leading to suicide as well.
Advantages of Social Media. When we look at the positive aspect of social media, we find numerous advantages. The most important being a great device for education. All the information one requires is just a click away. Students can educate themselves on various topics using social media. Moreover, live lectures are now possible because of ...
As social media has proliferated worldwide—Facebook has 2.85 billion users—so too have concerns over how the platforms are affecting individual and collective wellbeing. Social media is criticized for being addictive by design and for its role in the spread of misinformation on critical issues from vaccine safety to election integrity, as ...
Disrupted sleep, lower life satisfaction and poor self-esteem are just a few of the negative mental health consequences that researchers have linked to social media. Somehow the same platforms ...
Increased sleep issues. Lack of self-esteem. Lack of focus and concentration. Advertisement. "If kids are being asked to get off social media and do their homework, or any unpreferred task, then ...
Why is social media bad for mental health? One of the numerous reasons why social media is bad for mental health is that it can make people sad, anxious, and stressed. Constant exposure to stressful internet content can have negative effects on people physically, emotionally, and mentally.
Facebook said on Monday that it had paused development of an Instagram Kids service that would be tailored for children 13 years old or younger, as the social network increasingly faces questions ...
As a society, it is crucial to promote digital literacy and regulate social media platforms to mitigate their negative impacts. 500 Words Essay on Is Social Media Good or Bad Introduction. Social media, a technological innovation of the 21st century, has become an integral part of our daily lives. It has radically transformed the way we ...
Instead of talking to someone face-to-face and hanging out, people prefer just texting or going on a social network. For some people understanding a life without social media is near impossible. Using social media can have some adverse effects such as: it causes cyberbullying, it can compromise education, and it could have an effect on social ...
Views of social media and its impacts on society. When asked whether social media is a good or bad thing for democracy in their country, a median of 57% across 19 countries say that it is a good thing. In almost every country, close to half or more say this, with the sentiment most common in Singapore, where roughly three-quarters believe ...
Every hour a nine or ten-year-old child stays on social media, there is a 62 percent chance they develop an eating disorder the following year. Dr. Nagata elaborated on the connection between social media and eating disorders when he mentioned the constant comparison to unattainable body ideals, the pressure to display the body for likes, and ...
Since it's a relatively new technology, there's little research to establish the long-term consequences, good or bad, of social media use. However, multiple studies have found a strong link between heavy social media and an increased risk for depression, anxiety, loneliness, self-harm , and even suicidal thoughts .
The stress and mental health challenges faced by parents — just like loneliness, workplace well-being and the impact of social media on youth mental health — aren't always visible, but they ...
This essay argues that "locality" can be the scaffolding to understand the social implications of internet-based new media on the vast local society in China. This focus on "locality" is rooted in academic discussions around spatial differences in social theory ( Giddens, 1984 ; Urry, 1985 ) and around "locality" in human geography ...
This essay introduces a special issue on automation and communication in the digital society. It aims to study how subjectivity, agency, and empowerment become defined and reconfigured in novel human-machine encounters and, more broadly, in societies which in large parts are kept going and sustained by complex digital infrastructures.
Educated professionals and working-class voters have distinct cultural values. Over the past half-century, changes in America's economy, civil society, and media have made that diploma divide ...
Social media makes us more interwoven in each other's lives. Businesses have noticed the value of social networks in our lives, and they are using different techniques to promote their products. Many companies use social media for their awareness campaigns. They can use it to spread their ideas, knowledge and information about their products.
In a survey conducted among Asia-Pacific consumers in the first half of 2024, 54 percent of the respondents agreed that they had negative experiences purchasing something via social media.
"When you read (Project 2025)," Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, "you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare." The Project 2025 document does not call ...