7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:

Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
4. Consumption of Free Time
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
7. issues with homework enforcement, reliability, and temptation to cheat, addressing opposing views on homework practices, 1. improvement of academic performance, 2. reinforcement of learning, 3. development of time management skills, 4. preparation for future academic challenges, 5. parental involvement in education, exploring alternatives to homework and finding a middle ground, alternatives to traditional homework, ideas for minimizing homework, useful resources, leave a comment cancel reply.

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.
It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework
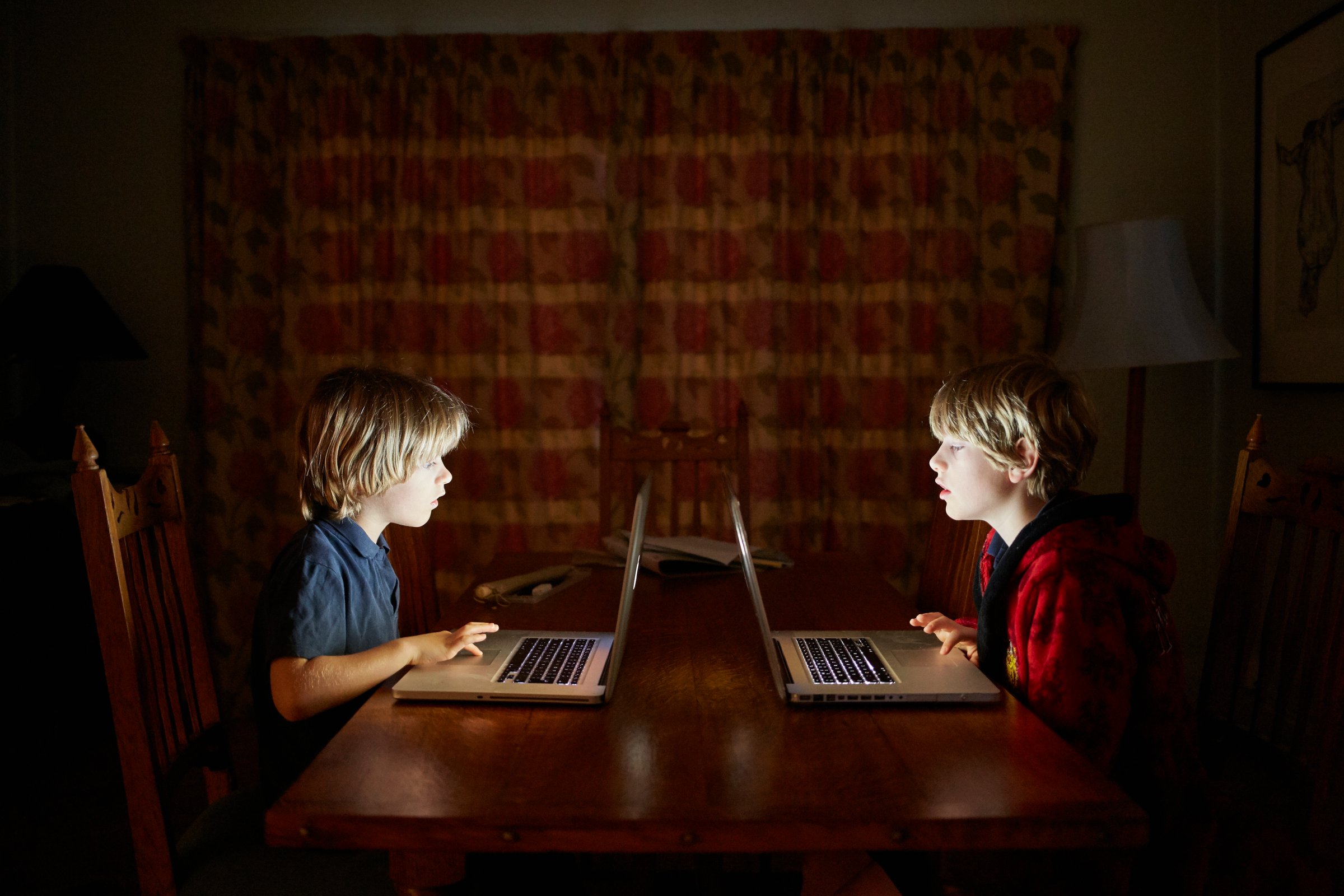

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Breaking Down the 2024 Election Calendar
- Heman Bekele Is TIME’s 2024 Kid of the Year
- The Reintroduction of Kamala Harris
- What a $129 Frying Pan Says About America’s Eating Habits
- A Battle Over Fertility Law in China
- The 1 Heart-Health Habit You Should Start When You’re Young
- Cuddling Might Help You Get Better Sleep
- The 50 Best Romance Novels to Read Right Now
Contact us at [email protected]
Homework – Top 3 Pros and Cons
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
Social Media
- Facebook Facebook Circle Icon
- Twitter Twitter Circle Icon
- Flipboard Flipboard Circle Icon
- RSS RSS Circle Icon
- Culture & Media
- Economy & Labor
- Education & Youth
- Environment & Health
- Human Rights
- Immigration
- LGBTQ Rights
- Politics & Elections
- Prisons & Policing
- Racial Justice
- Reproductive Rights
- War & Peace
- Series & Podcasts
- Federal Reserve
People Caught Up by Criminal Legal System Face More Obstacles to Abortion Access
Mpox vaccine manufacturer is profiting from accelerating global health emergency, republican states are blocking legal gender changes on driver’s licenses, israel launches massive attack on lebanon, pushing region toward all-out war, should us public schools eliminate homework.
Excessive homework is creating stress, not learning, for many U.S. students.

When Finnish students enroll in school at age seven, they can expect to take three or four classes a day. There are frequent breaks, plus a daily 20-minute recess. What’s more, when school is dismissed, there’s rarely any work to be completed at home. Nonetheless, Finnish students consistently rank among the world’s highest achievers in reading, math and science.
Experts attribute this to the country’s low ( 5.8 percent ) poverty rate, extensive social welfare system, 12-to-1 student-teacher ratio, and classes that fully integrate special needs students into general education classrooms. They also note that the Finnish government values teachers and encourages staff to prioritize collaboration, network building and the sharing of best practices.
Contrast this with the United States. Throughout the country, many elementary schools have completely eliminated recess. Eighteen percent of students live in poverty and approximately 1.3 million of the nation’s 50.7 million public school students are homeless.
And then there’s homework, which is increasingly assigned to students as young as five. In fact, by high school, the average time teenagers spend on homework is now 3 hours and 58 minutes a night, up from 2 hours and 38 minutes — an increase of 51 percent — over the past several decades.
The reason for this, say pro-homework teachers and administrators, is to raise the scores of U.S. students on standardized tests.
It hasn’t worked. While progressive educators agree that testing is not the only, or even the best, marker of academic achievement, it is still startling that the U.S. ranks 21st in educational outcome among the 34 Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) competing countries, while Finland comes in third .
For their part, the National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association support assigning 10 minutes of homework per grade. Under this policy, first graders would be given homework taking no more than 10 minutes a day, while 12 th graders would be given up to two hours of daily work.
But many schools have sidestepped these recommendations, with kindergarteners, first and second graders often getting 25-30 minutes of work per night. Among older students, researchers have noted that excessive homework assignments have led to an increase in stress-related headaches, exhaustion, sleep difficulties and stomach ailments. They also suggest that it contributes to alcohol and drug abuse.
Abolishing Homework
It doesn’t have to be this way.
A Duke University study found that homework does little to boost elementary school achievement, a finding that has led a smattering of K-6 schools in California , Florida, Illinois, New Jersey, New York, Massachusetts and Vermont to either eliminate homework completely or eliminate it during school breaks.
“Kids are terribly stressed about school, grades, peers, parental expectations and the known threats and ideation around climate change,” Nancy Romer, a longtime New York City activist and former psychology professor at Brooklyn College, told Truthout . “Many kids live in a state of impending doom.”
Add in other worries — about gun violence, racial bias, police brutality and sexual assault — and it is obvious that students of all ages have good reason to be fearful and anxious.
But can eliminating homework address even a small part of this anxiety-producing equation, increase academic achievement and lift morale?
The Upside to Homework
Jessie Winslow teaches sixth grade social studies at the Ephraim Curtis Middle School in Sudbury, Massachusetts, a wealthy community with a median household income of more than $170,000.
Winslow acknowledges that her students are coming into school with more anxiety and depression than previous academic cohorts. Nonetheless, she says she feels conflicted about the idea of skipping homework because she thinks that by middle school, students should be able to do some independent work at home. “Homework teaches time management and other coping skills,” she continues. “These kids are going to have situations that will cause them stress and they need to figure out how to handle it.”
Virginia Naughton, a grandmother in Brooklyn, New York, says she sees homework as the most direct way to know what’s going on in kids’ daily lives. “Homework is sort of a pulse, a starting point, to talk about classes, school friends and whatever else is going on,” she says.
Sid Kivanoski, a recently retired teacher at one of New York City’s highly competitive specialized high schools, is also a proponent of homework. He explains that because New York students have to pass Regents exams in English, math, science and social studies to earn a diploma, assigning homework ensures coverage of material that might appear on the exam, but that he was unable to address during class.
“I also gave homework to get them thinking about things that we’d talk about the next day, for example, why they thought the U.S. fought a war in Vietnam,” he says.
Barriers to Homework Completion
Still, Kivanoski knows that many of his students faced enormous challenges in completing their assignments. “I had one kid who would wake up at 2:00 a.m. to do homework because that was the only time it was quiet at home. Another went to the library on the way home every afternoon for the same reason. It was the sole place she could concentrate.”
Likewise, Chicago elementary school teacher Mariam Cosey sees the impact of poverty, hunger, and insecure or overcrowded housing in her classroom each and every day. “I always give my students a choice packet where they can choose which homework assignment they want to complete — word finds or word games, worksheets, or special projects — and it’s always due at the end of the week or on Monday, to give them the opportunity to get it done,” she begins. “Furthermore, I always make sure that there is something that every child has the ability to do.”
She does this despite mandates from the Chicago Board of Education dictating what should be taught and how much homework should be assigned for each grade level. In addition, Cosey offers incentives for her students to encourage assignment completion. The incentives help Cosey assess how a particular student is doing in a specific subject, and also give a window into her students’ home situations. “Kids can pick their prizes. When a child chooses gloves over candy, it tells me what’s going on in that child’s life. We love on these students, wash their faces, bring in clothes for them, and are compassionate. As teachers, we know that these kids need extra love and we give it to them.”
Homeless students face even greater hurdles when it comes to finishing their work. “There are so many barriers,” Barbara Duffield, executive director of SchoolHouse Connection , a Washington, D.C.-based advocacy organization that works to improve the educational achievement of homeless youth, told Truthout . Some are related to the living situation, with barriers like not having a quiet place to study or do homework, or no computer or internet access.
“But remember,” Duffield explains, “only 14.4 percent of students who are homeless are even staying in a shelter. Most are in hotels or motels, moving from couch to couch, or living on the streets. No matter where they’re staying, they may also be caring for their parents or younger siblings. Most are struggling to stay safe. They may be working 30 hours a week while going to school. The notion that homeless students have the time, space and consistency for good home study is seriously flawed.”
This is something that San Diego State University student Destiny Dickerson, the recipient of a SchoolHouse Connection scholarship (which grants post-secondary scholarships to students who’ve experienced homelessness), understands well. Six years ago, when Dickerson was in her first year of high school, her family was evicted from their three-bedroom home. For a short time, they lived with her grandmother, but severe overcrowding made this situation untenable and the family — four kids and two adults — ended up in a series of motels and hotels in and around Rancho Cucamonga, California.
“I would do as much homework as I could in school because there was no guarantee that we’d have WIFI at the hotel,” she explains. “In addition, all of my textbooks were stolen when someone broke into my mom’s car. My parents had told us to keep our homelessness quiet because it was embarrassing to admit that we’d lost our residence, so no one at school knew that I had no books. Some days I’d go to the library to do my homework and some hotels had a communal computer I could use, but sometimes I forgot about doing assignments because I was so focused on what was going on outside of class. I also missed assignments that were posted online since I did not have reliable access to a computer.”
Still, Dickerson maintained a B average throughout high school and reports that her teachers learned of her situation only after she won the SchoolHouse Connection scholarship. “They were shocked,” she says, “and the school cleared all the fees owed for the stolen textbooks and helped me pay for all the senior year activities.”
Dickerson considers herself lucky — she now has an affordable, stable, off-campus apartment, a laptop computer and consistent internet access — and expects to graduate with a degree in psychology in 2022.
Homework for Parents
Shomari Gallagher, a parent in Brooklyn, New York, says that while she appreciates that homework gives her a window into what her 10-year-old son is learning in school, it also often puts parents in the position of being teachers. “If the homework reinforces what they learned in school, fine,” she says. “But to have students struggle to learn something new without the benefit of a teacher’s instruction seems unfair. I sometimes look at my son’s math homework as if it’s a foreign language and have had to watch YouTube videos in order to help him. Homework is the only thing my son and I fight over. At the end of the school day he’s tired and gets frustrated.”
This set-up, Gallagher continues, also favors richer, better-educated parents who already grasp the subject matter, or have the time, research skills and English language proficiency to assist their kids. Moreover, she believes that homework serves an insidious function: “I think it trains kids to become adults who take work home from their jobs,” she says.
A Different Way
The debate over the efficacy of homework is not new. Nonetheless, the U.S. has a long way to go before consensus is reached.
Gin Langan, a mother and substitute teacher in Hayward, California, who is also an active member of the Bad Ass Teachers Association, is an outspoken critic of excessive homework. Nonetheless, she told Truthout that she is distressed by the lack of organizing on this issue.
“Many people are under the impression that homework is something that has to be done,” she begins. I talk to people about this all the time, and I always stress the social inequities in education. I speak about how inappropriate and ineffective it is for homework to be given in lower grades, and how difficult it is for kids who don’t have a quiet place to work. I discuss why we need to shift away from a white middle-class paradigm. But many parents have bought the line that homework is necessary for their kids to be competitive and get into a good college.”
Even worse, she says, in locales like Fremont, California, the district has mandated that homework be given in every grade, K-12, five nights a week.
Nevertheless, Langan believes that fact-based conversations about reducing or eliminating homework are the best way to chip away at the conventional wisdom.
Thankfully, she has the Duke University study and other research to draw on.
A white paper composed by Challenge Success, a California-based educational advocacy group, is one such resource. The paper, “ Changing the Conversation about Homework from Quantity and Achievement to Quality and Engagement ,” offers concrete recommendations for schools, school administrators and parents.
Teachers, the paper concludes, should assign work that students can do on their own, without adult intervention. Moreover, it argues, this work should be doable — not too easy, not too hard, and not too time-consuming — to give the students a sense of accomplishment. Furthermore, the paper suggests that instructors give students a clear overview of the assignment before they leave for the day, and try to focus as many assignments as possible on tasks that can’t be completed at school.
For example, the paper suggests having students conduct interviews that will later be used to compile oral histories or require them to collect soil samples or other materials for a science experiment. Lastly, they caution against busy work, recommend quarterly “no homework nights” for middle school and high school students, and support the elimination of summer and vacation assignments.
As for parents, the paper reminds them that different kids have different study and learning styles — and that they should not elevate one modality over another. To wit: kids who like to get their work done in one sitting immediately after school ends are not inherently superior to kids who prefer taking breaks, working to music, or completing tasks late at night. They also remind parents not to overschedule their children, hover over them, or do the work for them.
But the gold standard may still be the model developed by Finnish educators. There, 15-year-olds spend an average of 2.8 hours a week outside of class doing homework and typically use their free time to play team sports, read, volunteer or socialize with family and friends.
Join us in defending the truth before it’s too late
The future of journalism is uncertain, and the consequences of losing it are too grave to ignore. To ensure Truthout remains fearless, tough, and 100 percent independent, we still need to raise $11,000. Every dollar raised goes directly toward the costs of producing news you can trust.
Please give what you can — because by supporting us with a tax-deductible donation, you’re not just preserving a source of news, you’re helping to safeguard what’s left of our democracy.
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

New genetic sensor for DNA methylation discovered
4 minutes ago

Researchers develop high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide glass for smart functional materials
3 hours ago

Mapping the sex life of malaria parasites at single cell resolution reveals genetics underlying transmission

Communicating consensus strengthens beliefs about climate change, finds 27-country study

Matching dinosaur footprints found on opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean
20 hours ago

Heaviest antimatter observation yet will fine-tune numbers for dark matter search
21 hours ago

NASA decides to keep 2 astronauts in space until February, nixes return on troubled Boeing capsule
Aug 25, 2024

Saturday Citations: Tarantulas and their homies; how mosquitoes find you; black holes not mysterious at all
Aug 24, 2024
Test of a prototype quantum internet runs under New York City for half a month
Researchers discover dual epicenters in New Year's Day Noto earthquake
Aug 23, 2024
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Incandescent bulbs in teaching.
Aug 21, 2024
How to explain Bell's theorem to non-scientists
Aug 18, 2024
Free Abstract Algebra curriculum in Urdu and Hindi
Aug 17, 2024
Sources to study basic logic for precocious 10-year old?
Jul 21, 2024
Kumon Math and Similar Programs
Jul 19, 2024
AAPT 2024 Summer Meeting Boston, MA (July 2024) - are you going?
Jul 4, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

More academic freedom leads to more innovation, reports study

Statistical analysis can detect when ChatGPT is used to cheat on multiple-choice chemistry exams
Aug 14, 2024

Larger teams in academic research worsen career prospects, study finds

The 'knowledge curse': More isn't necessarily better
Aug 7, 2024

Visiting an art exhibition can make you think more socially and openly—but for how long?
Aug 6, 2024

Autonomy boosts college student attendance and performance
Jul 31, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- The Highlight
Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
by Jacob Sweet

As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.
There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
- Mental Health
- Social Policy
Most Popular
- The difference between American and UK Love Is Blind
- The massive Social Security number breach is actually a good thing
- Kamala Harris’s speech triggered a vintage Trump meltdown
- A Trump judge ruled there’s a Second Amendment right to own machine guns
- This chart of ocean heat is terrifying
Today, Explained
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
This is the title for the native ad
More in The Highlight

How being labeled “gifted” can rearrange your life — for better and for worse.

Why getting “real” in the age of personal branding feels so hard.

Japan’s early-warning system shows a few extra seconds can save scores of lives.

Being an only child doesn’t mess you up for life. We promise.

Your old friend probably wants to DM you too.

Growing up “gifted,” helping shy kids thrive, the rise of homeschools, what extracurriculars are for, and more!
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Never Mind the Students; Homework Divides Parents

By Kyle Spencer
- April 25, 2017
Last spring, when Public School 11, a prekindergarten through fifth-grade school in Manhattan’s Chelsea neighborhood, banned mandatory traditional homework assignments for children up to fourth grade, you might have expected universal acclaim. Rather than filling out worksheets, students were encouraged to read nightly, and a website offered tips for parents looking for engaging after-school activities.
Instead, war broke out among the parents. Those who wanted to keep homework accused the anti-worksheet group of trying to force through a policy supported by a select few. Some privately called the plan “economically and racially insensitive,” favoring families with time and money to provide their own enrichment. There was a series of contentious PTA meetings and jockeying to get on the school’s leadership team, a board that some schools have had trouble getting parents to join. At least three families left the school.
Robin Broshi, a former education technology consultant, a parent of a third grader and one of the architects of the plan, said the changes gave students time to discover the things they were “really passionate about.” Homework time with her son used to be a “huge battle,” she added, but he now spends hours after school with innovative software programs that enthrall him.
But Ashley Sierra, an executive assistant and a single mother with three children at the school, said the policy had created an unwelcome burden on her and other less affluent families that could not afford extra workbooks, or software programs to supplement the new policy. “I hate it,” Ms. Sierra said.
Researchers who study academic history said they were not surprised that debate over young children and homework had resurfaced now. Education and parenting trends are cyclical, and the nation is coming off a stress-inducing, federally mandated accountability push that has put standardized testing at the center of the national education debate. Further, many parents say that homework has become particularly stressful since the arrival of Common Core, a set of rigorous and often confusing learning goals adopted by many states.
Tom Hatch, a professor of education at Columbia University’s Teachers College and co-director of the National Center for Restructuring Education, Schools and Teaching , said homework wars were really a proxy fight about what constitutes learning. He added that they were intrinsically linked to the debates over standardized testing that have fueled the national “opt-out” movement.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

- Featured Articles
- Report Card Comments
- Needs Improvement Comments
- Teacher's Lounge
- New Teachers
- Our Bloggers
- Article Library
- Featured Lessons
- Every-Day Edits
- Lesson Library
- Emergency Sub Plans
- Character Education
- Lesson of the Day
- 5-Minute Lessons
- Learning Games
- Lesson Planning
- Subjects Center
- Teaching Grammar
- Leadership Resources
- Parent Newsletter Resources
- Advice from School Leaders
- Programs, Strategies and Events
- Principal Toolbox
- Administrator's Desk
- Interview Questions
- Professional Learning Communities
- Teachers Observing Teachers
- Tech Lesson Plans
- Science, Math & Reading Games
- Tech in the Classroom
- Web Site Reviews
- Creating a WebQuest
- Digital Citizenship
- All Online PD Courses
- Child Development Courses
- Reading and Writing Courses
- Math & Science Courses
- Classroom Technology Courses
- A to Z Grant Writing Courses
- Spanish in the Classroom Course
- Classroom Management
- Responsive Classroom
- Dr. Ken Shore: Classroom Problem Solver
- Worksheet Library
- Highlights for Children
- Venn Diagram Templates
- Reading Games
- Word Search Puzzles
- Math Crossword Puzzles
- Geography A to Z
- Holidays & Special Days
- Internet Scavenger Hunts
- Student Certificates
Newsletter Sign Up
Search form
Schools doing away with homework brings up the age-old debate on its pros and cons.
Ask just about any student if homework should be eliminated and you’re likely to get a resounding “yes!” Ask a teacher or parent though, and the results are going to vary -- often significantly. With the summer winding down and the “back-to-school” mindset beginning to seep back into the consciousness of parents, teachers, and students alike, the debate over homework has risen again.
In 2016, Brandy Young, a second-grade teacher in Texas, earned praise from parents (and of course students) around the nation when she banned homework , instead encouraging her students to engage in family time or go to bed early.
Young isn’t the only educator who has decided to have her students leave their studies in the school classroom, either. Mark Trifilio, a principal at Orchard Elementary in Vermont proposed a no-homework policy to his teaching staff and all 40 wanted to try it out. Students were encouraged to read book recommendations or have their parents read to them, but that was it. Six-months in, Trifilio reported that his students hadn’t fallen behind in their academics.
“My son declared on Monday that he can read now and that he doesn’t need any help,” said James Conway, whose son Sean is a kindergartner at Orchard. Not all parents shared Conway’s enthusiasm though over the new policy. "My kids would be thrilled if I let them eat brownies everyday. But as a parent, I can't let them," Tara Chitko, the mother of a third-grader told the Burlington Free Press .
The long-standing recommendation for homework by the PTA has been 10 minutes of homework per grade level, meaning by the time students are high school seniors they’re taking home around two hours of homework every night.
Advocates against homework argue that its absence frees kids up to discover things they’re passionate about it and say it can discourage students eagerness to learn. However, there are still educators who tote the benefits of sending students home with a manageable amount of homework.
Harris M. Cooper, a neuroscience and psychology professor at Duke University is known for being a homework advocate saying that it has clear benefits, such as organization, time management, and discipline. A 2006 data analysis he conducted of 60 studies on the topic revealed homework had somewhat of a benefit for older children, but didn’t have a significant impact on the grades or test scores of elementary school children. He fully endorses the PTA’s 10-minute per year homework recommendation.
The issue of homework is often one of frustration for parents who feel that it places unnecessary stress on their children. For Jenney Sims, a parent of twins in the second-grade, one of whom is dyslexic, homework equaled hours of daily frustration. “What should take 20 minutes would take hours and there were a lot of tears,” Sims told the Ocala Star Banner.
Cooper told Time that the debate over homework comes and goes in cycles and now the popular view is that it’s too much and should be done away with. "You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness," he added.
The debate isn’t likely to go away anytime soon and but for Lisa Fontaine-Dorsey, a third-grade math teacher in Florida at Wyomina Park Elementary, the school’s new no-homework policy is a healthy thing for her students. “All day at school they are pressured with the test, test, test environment,” Fontaine-Dorsey said. “They need to go home and get away from that.”
Article by Joel Stice, Education World Contributor

EW Lesson Plans

EW Professional Development
Ew worksheets.









































































IMAGES
COMMENTS
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can't ...
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7]
In fact, by high school, the average time teenagers spend on homework is now 3 hours and 58 minutes a night, up from 2 hours and 38 minutes — an increase of 51 percent — over the past several decades. The reason for this, say pro-homework teachers and administrators, is to raise the scores of U.S. students on standardized tests.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
Updated Feb 23, 2023, 3:04 AM PST. Jiayue Li for Vox. As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not ...
A 2006 meta-analysis he conducted of more than 60 studies of homework's efficacy showed that doing homework did not necessarily increase an elementary school student's test scores or grades. Dr.
With the summer winding down and the "back-to-school" mindset beginning to seep back into the consciousness of parents, teachers, and students alike, the debate over homework has risen again. In 2016, Brandy Young, a second-grade teacher in Texas, earned praise from parents (and of course students) around the nation when she banned homework ...
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.)
College de Saint-Ambroise, an elementary school in Quebec, is the latest school to ban homework, announcing this week that it would try the new policy for a year. The decision came after officials ...
Consider the Mental Separation, and Leisure Time. Homework elimination, adds Ricks, gives young children plenty of free time after school in which to pursue music, art, sports, and leisure; provides adequate time for family meals, reading (independent and/or with a parent), and rest, and ensures ongoing enthusiasm for learning by allowing ...
Homework is a controversial topic in education, but what does the science say? Explore the pros and cons of homework and its impact on students' well-being in this article from BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Our belief in the value of homework is akin to faith. We assume that it fosters a love of learning, better study habits, improved attitudes toward school, and greater self-discipline; we believe that better teachers assign more homework and that one sign of a good school is a good, enforced homework policy.
Completing homework teaches a student organization and planning; it also improves academic skills and reinforces knowledge. Kathleen McCarthy, Torrance. .. To the editor: After raising a family of ...
Too much homework might have the opposite effect on young students and can negatively impact their lives outside the classroom. But the momentum to get rid of homework is being met by others who ...
Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. The researchers asked students whether they experienced physical symptoms of stress, such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep ...
"Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school," said Alfie Kohn, author of "The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get ...
Excessive workload. The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
On every "normal" day of the school year, those sixth graders left class with their teachers in the late morning, marched down to the lunchroom in lines, cued up to get their lunches on Styrofoam trays, and then sat at crowded lunch tables with built-in plastic seats, beneath harsh fluorescent lights, until it was time to march back to class.
Homework negatively affects students' health. Download Article. Homework takes a toll physically. Recent studies have demonstrated that too much homework can disrupt a student's sleep cycle, and cause stress headaches, stomach problems, and depression. [3] 3.
September 7, 2012 by Bill Blankschaen. I hate homework. Not as much as I hate yellow-jackets, but that's another story. As a successful K-12 school leader and principal for a dozen years, I ...