- Critical Thinking

Critical thinking: Definition and Structure
- February 2020
- Affiliation: Australian Council for Educational Research

- Australian Council for Educational Research

- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.

Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Educ Inform Tech

- Michael Rasell
- Rouven Seebo

- AL-Shaimaa Abdullah El-Maghraby

- Jeffrey Scheuer

- Richard Paul
- Linda Elder

- Merritt J. Schenk

- Goodwin Watson
- Edward M. Glaser
- Anthony Flew
- John E. McPeck

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

- Programs & Services
- Delphi Center
Ideas to Action (i2a)
- Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
Critical thinking is that mode of thinking – about any subject, content, or problem — in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them. (Paul and Elder, 2001). The Paul-Elder framework has three components:
- The elements of thought (reasoning)
- The intellectual standards that should be applied to the elements of reasoning
- The intellectual traits associated with a cultivated critical thinker that result from the consistent and disciplined application of the intellectual standards to the elements of thought
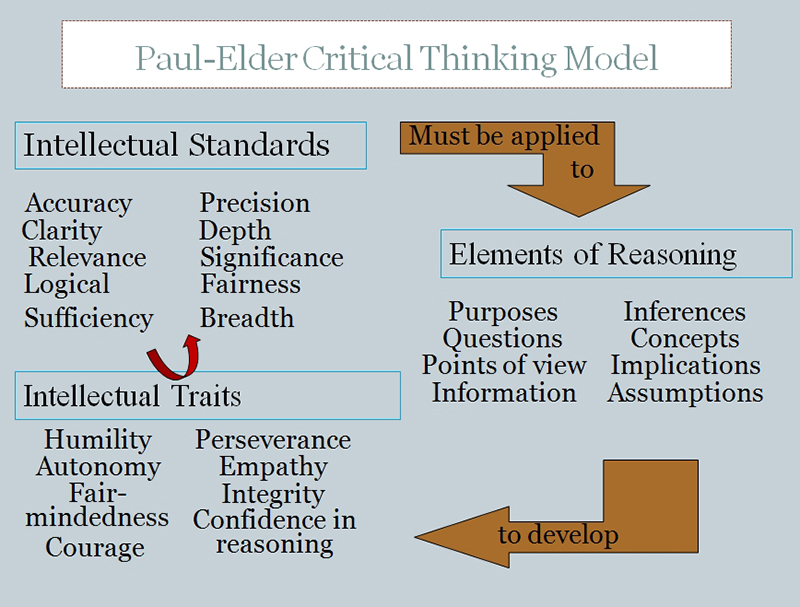
According to Paul and Elder (1997), there are two essential dimensions of thinking that students need to master in order to learn how to upgrade their thinking. They need to be able to identify the "parts" of their thinking, and they need to be able to assess their use of these parts of thinking.
Elements of Thought (reasoning)
The "parts" or elements of thinking are as follows:
- All reasoning has a purpose
- All reasoning is an attempt to figure something out, to settle some question, to solve some problem
- All reasoning is based on assumptions
- All reasoning is done from some point of view
- All reasoning is based on data, information and evidence
- All reasoning is expressed through, and shaped by, concepts and ideas
- All reasoning contains inferences or interpretations by which we draw conclusions and give meaning to data
- All reasoning leads somewhere or has implications and consequences
Universal Intellectual Standards
The intellectual standards that are to these elements are used to determine the quality of reasoning. Good critical thinking requires having a command of these standards. According to Paul and Elder (1997 ,2006), the ultimate goal is for the standards of reasoning to become infused in all thinking so as to become the guide to better and better reasoning. The intellectual standards include:
Intellectual Traits
Consistent application of the standards of thinking to the elements of thinking result in the development of intellectual traits of:
- Intellectual Humility
- Intellectual Courage
- Intellectual Empathy
- Intellectual Autonomy
- Intellectual Integrity
- Intellectual Perseverance
- Confidence in Reason
- Fair-mindedness
Characteristics of a Well-Cultivated Critical Thinker
Habitual utilization of the intellectual traits produce a well-cultivated critical thinker who is able to:
- Raise vital questions and problems, formulating them clearly and precisely
- Gather and assess relevant information, using abstract ideas to interpret it effectively
- Come to well-reasoned conclusions and solutions, testing them against relevant criteria and standards;
- Think open-mindedly within alternative systems of thought, recognizing and assessing, as need be, their assumptions, implications, and practical consequences; and
- Communicate effectively with others in figuring out solutions to complex problems
Paul, R. and Elder, L. (2010). The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools. Dillon Beach: Foundation for Critical Thinking Press.
- SACS & QEP
- Planning and Implementation
- What is Critical Thinking?
- Why Focus on Critical Thinking?
- Culminating Undergraduate Experience
- Community Engagement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is i2a?
Copyright © 2012 - University of Louisville , Delphi Center
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


MAIN ELEMENTS AND CHARACTERISTICS OF CRITICAL THINKING

Here we cn find the elements and characterisitics of critical think to integrate language skills
Related Papers
Martin Davies
There has been no shortage of definitions of the concept of “critical thinking” over the years and the concept has been subject to much detailed scholarly work. In social and educational terms critical thinking is an important topic. Of late, critical thinking has also been widely discussed in the popular media, and the concept has been regarded as one of the most important graduate outcomes expected of a university education. However, despite this, scholars have yet to arrive at a holistic conception of critical thinking—a model of critical thinking as it were—that might usefully underpin the range of considerations about critical thinking that occur in the higher education literature. This paper: (1) reviews the various definitions and approaches to critical thinking, and (2) incorporates them into a single, coherent model. A number of disagreements in critical thinking scholarship are outlined as ‘axis disputes’ arising from the proposed model.
emolot allan david
At university, critical thinking includes the component skills of analyzing arguments, making inferences using inductive or deductive reasoning, judging or evaluating, and making decisions or solving problems. Critical thinking involves both cognitive skills and dispositions. These dispositions, which can be seen as attitudes or habits of mind, include open- and fairmindedness, inquisitiveness, flexibility, a propensity to seek reason, a desire to be well-informed, and a respect for and willingness to entertain diverse viewpoints. There are both general and domain specific aspects of critical thinking. Empirical research suggests that people begin developing critical thinking competencies at a very young age. Although adults often exhibit deficient reasoning, in theory all people can be taught to think critically. At university, Lecturers should provide explicit instruction in critical thinking, to teach how to transfer to new contexts, and to use cooperative or collaborative learning methods and constructivist approaches that place students at the center of the learning process. In constructing assessments of critical thinking, lecturers should use open-ended tasks, real-world or “authentic” problem contexts, and illstructured problems that require students to go beyond recalling or restating previously learned information. Such tasks should have more than one defensible solution and embed adequate collateral materials to support multiple perspectives. Finally, such assessment tasks should make student reasoning visible by requiring students to provide evidence or logical arguments in support of judgments, choices, claims, or assertions.
patrice chataigner
Peter A Facione
Benjamin Hamby
Critical thinking is an educational ideal with an accumulating canon of scholarship, but conceptualizing it has nevertheless remained contentious. One important issue concerns how critical thinking involves an interplay between cognitive abilities and associated character traits, dispositions, and motivations. I call these and other aspects of the critical thinker “critical thinking virtues”, taking them to be intellectual excellences of character, cultivated by people who tend to aim towards making reasoned judgments about what to do or believe. The central virtue that motivates any critical thinker to engage her skills in critical thinking I call “willingness to inquire”, connecting the character of the person to the skills she must use consistently to be a critical thinker. Willingness to inquire is the virtue that ranges over the application of all critical thinking skills, a basic motivational drive guiding a person towards the educational ideal. Other critical thinking virtues, such as open-mindedness, fairness, and respect for dialectical partners, also facilitate the appropriate application of critical thinking skills in a process of inquiry. Pedagogues should therefore seek not only to instruct for skills, but also to explicitly mention and instruct for the virtues as well. I conclude by offering curricular recommendations in this regard.
Dr. Punam Bansal
ABSTRACT In today’s complex world, where human beings need to solve problems, make decisions, or decide in a reasonable and reflective way what to believe or what to do, critical thinking is found to be useful. Critical thinking is that mode of thinking - about any subject, content, or problem - in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them. It entails effective communication and problem solving abilities that can help citizens make sense of their world and participate in a democratic dialogue. To prepare such citizens with higher order thinking skills should be foremost priority of any education system. Therefore ,it is the responsibility of teachers to foster critical thinking skills of their students and switch over to constructivist methods so that students can construct their knowledge and apply it to solve real life problems. This paper is a modest attempt by author to suggest some useful practices in classroom to develop critical thinking skills.
Metacognition and Learning
Carlo Magno
The landmark 1990 APA Delphi Report presents the findings of the two year project to articulate an international expert consensus definition of “critical thinking. Over the past 25 years this report has been adopted by educators at every level and in every discipline, as well as by business, military, healthcare, and technology professionals seeking to make the idea of “critical thinking” practical, positive, and applicable. Today the Delphi conceptualization grounds is used throughout the world. It grounds academic requirements, courses, textbooks, peer-reviewed research, dissertations, competitively funded grants, institutional accreditation projects, and numerous assessment tools used for educational and employment purposes when evaluating an individual’s or a group’s reasoning skills and mindset attributes are important. The international panel of experts who participated in the APA Delphi research project come to the consensus that critical thinking is best understood, taught, and modeled for students as the process of purposeful and reflective judgment. When engaging in critical thinking we solve problems and make decisions by considering the questions, evidence, conceptualizations, context, and standards to apply to the problem or issue at hand. The process is non-linear and the application of our specific critical thinking skills can be recursive, for we can analyze our interpretations, evaluate our inferences, or explain our analyses. The key, of course, is that we are being reflective and fair-minded and truth-seeking throughout the process of determining what to believe or what to do in any given context. Defined in this way, critical thinking is a powerful tool for learning as well as for our professional and civic lives. We all may have different beliefs, values, perspectives, and experiences influencing our problem solving and decision making. But we share the human capacity to be reflective, analytical, open-minded, and systematic about thinking through our problems and choices, so that we can make the best judgments possible about what to believe or what to do. That human process of well-reasoned, reflective judgment is critical thinking. In the Delphi Report the international panel of experts identify the attributes of ideal critical thinker as well as the specific skills that are engaged in the process of purposeful, reflective judgment. The report includes detailed pedagogically focused tables and specific recommendations relating to critical thinking instruction and assessment.
Andrews Daklo Kwame
Seyed Ehsan Afsahi , Akbar Afghari
Critical thinking is an intellectually disciplined process of actively and skilfully conceptualising, applying, analysing and evaluating information gathered from or generated by observation, experience, reflection, reasoning or communication, as a guide to belief and action. To accomplish these critical thinking actions good language ability is crucial. Vygotsky revise great importance to the link between the development of language and critical thinking. This is a correlational research in which 30 MA Students of Azad University of Shiraz branch were selected as participants. California Critical thinking skills questionnaire was used to collect the data in this research. Results indicated that there is significant relationship between mother tongue and critical thinking level, but there is no significant relationship between age, gender and critical thinking level.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
mehebub sahana
Intelligent Systems Reference Library
Michael Hogan , Owen Harney
Nursing Outlook
International Education Studies
Mohammad H Yarmohammadian
Liliana Ciascai
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.

COMMENTS
Glaser defined critical thinking as: (1) an attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that come within the range of one's experience; (2) knowledge of the methods of logical enquiry and reasoning; and (3) some skill in applying those methods. Critical thinking calls for a persistent effort to examine ...
e willing to act yourself. Consider the feelings of others in the same way you want your own. feelings to be considered. Because you don't want others to be rude to you, void being rude to others. Because you don't want to be harmed by others, be. Intellectual Indepen. enceDo your own thinking. Figu.
Here are three definitions of critical thinking by leading researchers. First, Robert Ennis's classic definition:1. Critical thinking is reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on decid-ing what to believe or do. 1. Even before you start reading this text, begin by examining your own con-cept of critical thinking.
The essence of critical thinking concepts and tools distilled into a 20-page pocket-size guide. It is a critical thinking supplement to any textbook or course. It is best used in conjunction with the Analytic Thinking Guide. Keywords: critical thinking concepts; critical thinking tools; analytic thinking; thinker's guide Created Date
Provides grading rubrics and outlines five levels of close reading and substantive writing. #563m. "Aspiring Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking" Mini-Guide Price List: (+ shipping and handling) Item #554m. 1-24 copies $6.00 each 25-199 copies $5.00 each 200-499 copies $4.00 each 500+ copies $3.50 each.
ical thinking both in the classroom and beyond. Teaching and practicing critical thinking provides adults with the opportuni. to embrace and take charge of their learning. Adults engaged in critical thinki. g approach the classroom experience diferently. Typically, students who implement critical thinking skills approach the courseware in a ...
Critical Thinking: Components, Skills, a nd Strategies. Abdullah Bin Mohamed Al-Ghadouni. ABSTRACT. The research paper aimed at un covering the components of critica l thinking and. identifying ...
Emeritus Professor, University of Illinois Last Revised, May, 2011. Critical thinking is reasonable and reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do. This definition I believe captures the core of the way the term is used in the critical thinking movement. In deciding what to believe or do, one is helped by the employment of a ...
The Thinker's Guide Library presents the framework of critical thinking across subject areas and audience levels to foster integration of critical reasoning throughout our world. 1. The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools, Eighth Edition. 2. The Thinker's Guide to Analytic Thinking. 3.
1 The Nature and Value of Critical Thinking . 1.1 The Nature of Critical Thinking, 2 Exercise 1.1, 6 1.2 Critical Thinking and Knowledge, 6 Exercise 1.2, 7 1.2.1 Truth, 7 1.2.1.1 Realism, Relativism, and Nihilism, 8 1.2.1.2 Relativism and the Argument from Disagreement, 10 1.2.2 Belief 13 , 1.2.3 Justification, 15
Angelo, 1995, p.6. 8. "Most formal definitions characterize critical thinking as the intentional application of rational, higher order thinking skills, such as analysis, synthesis, problem recognition and problem solving, inference and evaluation. "Critical thinking is thinking that asses itself". (Center for Critical thinking, 1996b).
The Power of Critical Thinking . Williams and Worth (2002) found that critical thinking skills, measured at the beginning of a college, were a . better. predictor of multiple-choice exam performance than course attendance or note-taking . Characteristics of Critical Thinkers • Flexibility/Open to new ideas - Honest with themselves. When hear ...
Accordingly, critical thinking is purposively put into action and driven by. As a result of this top-down influence, critical thinking is an attitude which does not occur spontaneously. Critical thinking also involves the knowledge, acquisition, and improvement of a spectrum of intellectual resources such as: - methods of logical inquiry;
Summary outline of general critical thinking abilities (or skills): Ideal critical thinkers have the ability to: (Basic Clarification) Focus on a question. Analyze arguments. Ask and answer clarification questions. Understand and use elementary graphs and maths (Bases for a Decision) Judge the credibility of a source.
Wade and Tavris (2005) define Critical Thinking (CT) as "the ability and willingness to assess claims and make objective judgments on the basis of well-supported reasons and evidence rather than emotion or anecdote" (p. 12). Critical thinking has eight tenets, eight premises, and those premis es have been clearly detailed: 1.
Critical thinking is the process of analyzing and assessing thinking with a view to improving it. Critical thinking presupposes knowledge of the most basic structures in thinking (the elements of thought) and the most basic intellectual standards for think-ing (universal intellectual standards). The key to the creative side of critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the thinking abilities that must be given in 21 st -century education, because by having it, the student can think reasonably, reflectively and systematically that ...
The intellectual traits associated with a cultivated critical thinker that result from the consistent and disciplined application of the intellectual standards to the elements of thought According to Paul and Elder (1997), there are two essential dimensions of thinking that students need to master in order to learn how to upgrade their thinking.
openmindedly embrace other opinions and views that challenge their own. reconsider and revise their opinions in the wake of new evidence. listen actively rather than simply wait for their turn to talk. There's no question that effective critical thinkers are also largely creative thinkers.
Critical thinking is an educational ideal with an accumulating canon of scholarship, but conceptualizing it has nevertheless remained contentious. One important issue concerns how critical thinking involves an interplay between cognitive abilities and associated character traits, dispositions, and motivations.
Characteristics of Critical and Uncritical Thinkers. Critical Thinkers... Uncritical Thinkers... Are honest with themselves, acknowledging what they don't know, recognizing their limitations, and being watchful of their own errors. Regard problems and controversial issues as exciting challenges. Strive for understanding, keep curiosity alive ...
critical thinking skills for Army officers, and developed and evaluated the training course. This volume describes the results of a literature review on critical thinking, a model of critical thinking that forms the theoretical basis for the training, and investigations that were conducted to validate the model.
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...