Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae , and some bacteria use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll. It is the process that converts carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds, especially into glucose , and releases oxygen as a byproduct. This process is vital for life on Earth as it is the primary source of energy for nearly all organisms .

Key Concepts:
- Equation for Photosynthesis: The overall chemical reaction for photosynthesis can be represented as: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + light energy → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2
- Chlorophyll: This is the green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells . It is responsible for absorbing light energy during photosynthesis.
- Light -dependent and Light -independent Reactions: Photosynthesis consists of two main stages: the light -dependent reactions (occur in the thylakoid membranes) and the light -independent reactions (occur in the stroma of the chloroplast).
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis: Light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature can all affect the rate of photosynthesis.
- Importance of Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is crucial for the production of oxygen , the source of food for plants and other organisms , and the basis of the carbon cycle.
Study Guide:
To gain a deeper understanding of photosynthesis, consider focusing on the following key areas for study:
- Memorize the chemical equation for photosynthesis and understand the reactants and products involved.
- Learn about the structure and function of chlorophyll in the process of photosynthesis.
- Understand the difference between the light -dependent and light -independent reactions of photosynthesis, and the substances involved in each stage.
- Explore the factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis and how they impact the process.
- Recognize the importance of photosynthesis to life on Earth and its role in the ecosystem .
By focusing on these key concepts and study guide areas, you can develop a solid understanding of the process of photosynthesis and its significance in the natural world.
Read More...
◂ Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Plant Processes

The resources above cover the following skills:
- Download and Print thousands of standards-based ELA, Social Study, Science and Math Worksheets and Study Guides!
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Membership Benefits
- Completing Worksheets Online
- Share to Google Classroom
- NewPathLearning
We see you're using an old version of Internet Explorer. This will result in performance problems with this website. We suggest that you upgrade Internet Explorer , or switch to Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome instead.
- 1.1 Living things
- 1.2 Non-living things
- 2.1 Structure of plants
- 2.2 Structure of animals
- 3.1 Conditions for growth
- 3.2 Growing new plants
- 4.1 What is a habitat?
- 4.2 Different habitats
- 4.3 Why do animals need a habitat?
- 5.1 Natural and man-made shelters
- 5.2 Structures and materials for animal shelters
- 1.1 Solids, liquids and gases
- 1.2 Change of state
- 1.3 The water cycle
- 2.1 Solid materials all around us
- 2.2 Raw and manufactured materials
- 2.3 Properties of materials
- 2.4 Different materials for the same object
- 3.1 Ways to strengthen materials
- 4.1 Struts and frame structures
- 4.2 Indigenous structures
- 1.1 Energy for life
- 1.2 Energy from the Sun
- 2.2 Input and output energy
- 3.1 Movement and musical instruments
- 3.2 Movement causes sound
- 3.3 Indigenous musical instruments in South Africa
- 4.1 Vibrations and sound
- 4.2 Noise pollution
- 1.1 Features of the Earth
- 1.2 The Earth in Space
- 2.1 The Sun is the closest star
- 3.1 Moving around the Sun
- 3.2 The Earth and other planets
- 3.3 The Sun and life
- 4.1 The Thunderbolt Kids need a rocket
- 4.2 How do rockets work?
- 4.3 Modelling a rocket
- 5.1 Features of the Moon
- 5.2 The phases of the Moon
- 5.3 Moon stories
- 1.1 Many different plants and animals
- 1.2 Interdependence in an ecosystem
- 1.3 Animal types
- 2.1 Skeletons of vertebrates
- 2.2 Movement in vertebrates
- 3.1 Structures
- 4.1 Food and feeding in plants and animals
- 4.2 Food chains
- 5.1 Growth and development
- 5.2 Plant life cycles
- 5.3 Animal life cycles
- 1.1 Properties of metals
- 1.2 Properties of non-metals
- 2.1 Special properties of metals
- 2.2 Uses of metals
- 3.1 Combining material
- 4.1 Properties and uses
- 4.2 Traditional processing
- 1.1 What are fuels?
- 1.2 Burning fuels
- 1.3 Fire safety
- 2.1 Cells and batteries
- 2.2 Mains electricity
- 2.3 Safety and electricity
- 3.1 Elastics and springs
- 4.1 Wheels and axles
- 1.1 The Earth moves
- 2.2 Soil comes from rocks
- 2.3 Soil types
- 3.1 Formation of sedimentary rock
- 3.2 Uses of sedimentary rock
- 4.1 Fossils in rock
- 4.2 Body and trace fossils
- 4.3 Importance of South African fossils
- 1.1 Plants and food
- 1.2 Food from photosynthesis
- 1.3 Plants and air
- 2.1 Food groups
- 3.1 A balanced diet
- 3.2 Diseases caused by an unhealthy diet
- 4.1 Why do we need food processing?
- 4.2 How are foods processed?
- 5.1 Different ecosystems
- 5.2 Living and non-living things in ecosystems
- 5.3 Food webs
- 1.1 Arrangement of particles
- 2.1 Mixtures of materials
- 3.1 Solutions
- 3.2 Soluble substances
- 3.3 Saturated solutions
- 4.1 What is dissolving?
- 4.2 Rates of dissolving
- 5.1 Water pollution
- 5.2 Importance of wetlands
- 6.1 Clean water
- 1.1 A simple circuit
- 1.2 Circuit diagrams
- 2.1 What are conductors and insulators?
- 2.2 Good electrical conductors and insulators
- 3.1 Using electric circuits
- 3.2 Be an electrical engineer or technician
- 4.1 Fossil fuels
- 4.2 Cost of electricity
- 4.3 Illegal connections
- 4.4 Renewable ways to generate electricity
- 1.1 The Sun, planets and asteroids
- 2.1 Rotation (Earth)
- 2.2 Revolution (Earth)
- 3.1 Rotation (Moon)
- 3.2 Revolution (Moon)
- 4.1 Vehicles used on Mars
- 4.2 Vehicles used on the Moon
- 4.3 Design and make a vehicle to collect Moon rocks
- 5.1 Telescopes
- 1.1 Lewende dinge
- 1.2 Nie-lewende dinge
- 2.1 Strukture van plante
- 2.2 Strukture van diere
- 3.1 Voorwaardes vir groei
- 3.2 Groeiende nuwe plante
- 4.1 Wat is 'n habitat?
- 4.2 Verskillende habitatte
- 4.3 Waarom het diere 'n habitat nodig?
- 5.1 Natuurlike en mensgemaakte skuilings
- 5.2 Strukture en materiale vir diereskuilings
- 1.1 Vaste stowwe, vloeistowwe en gasse
- 1.2 Verandering van toestand
- 1.3 Die watersiklus
- 2.1 Vastestowwe is orals om ons
- 2.2 Rou en vervaardigde materiale
- 2.3 Eienskappe van materiale
- 2.4 Verskillende materiale vir dieselfde doel
- 3.1 Maniere om materiale te versterk
- 4.1 Stutte en raam strukture
- 4.2 Inheemse strukture
- 1.1 Energie vir lewe
- 1.2 Energie van die Son
- 2.1 Energie
- 2.2 Inset- en uitset-energie
- 3.1 Beweging en musiekinstrumente
- 3.2 Beweging veroorsaak klank
- 3.3 Inheemse musiekinstrumente in Suid-Afrika
- 4.1 Vibrasies en klank
- 4.2 Geraasbesoedeling
- 1.1 Kenmerke van die maan
- 1.2 Die aarde in die ruimte
- 2.1 Die Son is die naaste ster
- 3.1 Beweeg om die son
- 3.2 Die aarde en ander planete
- 3.3 Die Son en lewe
- 4.1 Die Thunderbolt Kids het 'n vuurpyl nodig
- 4.2 Hoe werk vuurpyle?
- 4.3 'n Model van 'n vuurpyl
- 5.1 Kenmerke van die Maan
- 5.2 Die fases van die Maan
- 5.3 Maanstories
- 1.1 Baie verskillende plante en diere
- 1.2 Interafhanklikheid in 'n ekosisteem
- 1.2 Diersoorte
- 2.1 Geraamtes van gewerwelde
- 2.2 Beweging in werweldiere
- 3.1 Strukture
- 4.1 Voedsel en voeding in plante en diere
- 4.2 Voedselkettings
- 5.1 Groei en ontwikkeling
- 5.2 Plantlewensiklusse
- 5.3 Dierelewensiklusse
- 1.1 Eienskappe van metale
- 1.2 Eienskappe van nie-metale
- 2.1 Spesiale eienskappe van metale
- 2.2 Gebruike van metale
- 3.1 Kombineer stowwe
- 4.1 Eienskappe en gebruike
- 4.2 Tradisionele verwerking
- 1.1 Wat is brandstowwe?
- 1.2 Verbrand brandstowwe
- 1.3 Veiligheid by vure
- 2.1 Selle en batterye
- 2.2 Hooflyn-elektrisiteit
- 2.2 Veiligheid en elektrisiteit
- 3.1 Rekke en springe
- 4.1 Wiele en asse
- 1.1 Die Aarde beweeg
- 2.2 Grond kom van rotse
- 2.3 Grondsoorte
- 3.1 Hoe vorm afsettingsgesteentes
- 3.2 Gebruike van afsettingsgesteentes
- 4.1 Fossiele in rots
- 4.2 Liggaams- en spoorfossiele
- 4.3 Belangrikheid van Suid-Afrika se fossiele
- 1.1 Plante en kos
- 1.2 Voedsel uit fotosintese
- 1.3 Plante en lug
- 2.1 Voedselgroepe
- 3.1 'n Gebalanseerde dieet
- 3.2 Siektes veroorsaak deur 'n ongesonde dieet
- 4.1 Hoekom het ons voedselverwerking nodig?
- 4.2 Hoe word voedsel geprosesseer?
- 5.1 Verskillende ekosisteme
- 5.2 Lewende en nie-lewende dinge in ekosisteme
- 5.3 Voedselwebbe
- 1.1 Rangskikking van deeltjies
- 2.1 Mengsels van materiale
- 3.1 Oplossigs
- 3.2 Oplosbare stowwe
- 3.3 Versadigde oplossings
- 4.1 Wat is oplossing?
- 4.2 Tempo van oplossing
- 5.1 Waterbesoedeling
- 5.2 Belangrikheid van vleilande
- 6.1 Skoon water
- 1.1 'n Eenvoudige stroombaane
- 1.2 Stroombaandiagramme
- 2.1 Wat is geleiers en nie-geleiers?
- 2.2 Goeie elektriese geleiers en isolators
- 3.1 Gebruik van elektriese stroombane
- 3.2 Wees 'n elektriese ingenieur of 'n tegnikus
- 4.1 Fossielbrandstof
- 4.2 Koste van elektrisiteit
- 1.1 Die Son, planete en astroïedes
- 2.1 Rotasie (aarde)
- 2.2 Omwenteling (aarde)
- 3.1 Rotasie / draai (maan)
- 3.2 Omwenteling (maan)
- 4.1 Voertuie wat op mars gebruik word
- 4.2 Voertuie wat op die maan gebruik word
- 4.3 Ontwerp en maak 'n voertuig om rotse op die maan te versamel
- 5.1 Teleskope
Photosynthesis
- Why can a plant make its own food but an animal cannot?
- What is needed for photosynthesis to happen?
- How do plants make food and store food?
- Why do plants need so much water?
- Can plants live in the dark?
- Why are plants mostly green?
Teachers are encouraged to make a large circle on the wall using large arrows that can be cut from blue or even black plastic bags. Then cut out white letters to say "Photosynthesis" in the centre of the circle and stick large posters on the arrows to say:
- Plants absorb carbon dioxide
- Plants release oxygen
- Animals breathe in oxygen
- Animals breathe out carbon dioxide
Perhaps cut out pictures of plants or get learners to make plants and animals in Art and stick them next to the specific labels they illustrate. Create a glossary by placing words relating to the topic around the classroom. Tell the learners that they are going to be plant investigators, and that their job is to find out what the words mean, and how they relate to plants and photosynthesis.
When introducing this topic remind them of the work on interdependence they covered in Gr. 5. Discuss how animals and plants are interdependent upon each other - plants produce food and oxygen for animals, while animals - when they die - decay, replacing nutrients in the soil for plants, and releasing carbon into the air to continue the carbon cycle.
Plants and food
Green plants are just like factories! They make food for themselves and every animal on earth using sunlight energy, water and the gas carbon dioxide. They also recycle the air and make oxygen for us to breathe.
Scientists have found out exactly how plants are able to do all all these things. Let's take a closer look at how scientists did this and see how plants make food for themselves and us.
What happens in a factory? Why do you think we can say plants are like factories?
A factory is a place where goods or products are made/assembled/manufactured and then delivered to other places to be used. Plants are therefore like factories as they use raw products to make new products (food).
Plants make food for themselves and plants are the beginning of the food chain, therefore all other animals, whether herbivores which eat plants directly, or carnivores which eat the herbivores, depend on plants for food.
The process of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to change the energy from sunlight into energy for food. Plants change light energy from the sun into food energy. Photosynthesis happens in all green parts of a plant. Leaves are usually the greenest parts. So plants do this mostly in their leaves.
There are some important requirements for photosynthesis to happen:
1. Chlorophyll : Chlorophyll is a green substance that plants use to capture light energy from the sun. Chlorophyll is very important. Without chlorophyll plants cannot use the sunlight energy to make food. Also, oxygen levels in the air will go down. If that happens plants and animals will suffocate.
As a fun activity, take learners outside to see if there are other colours found in leaves, and not just the green pigment chlorophyll. Although green chlorophyll is predominant, there are also yellow, orange and purple pigments found in leaves, especially in autumn when the leaves change colour. In the body, the pigment melanin, is the main determinant of skin colour and it is also found in hair and the iris in the eye.
2. Sunlight: Sunlight has energy. Plants use this energy to make sugars from water and carbon dioxide.
3. Water : The roots of a plant absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Water is a solvent in all living things. Dissolved substances are moved around the body to where they are needed. Just like you, plants have veins for this movement. They move minerals from the roots upwards. They move sugars from the leaves downwards. Photosynthesis can only happen in a water solution. Water is also important because it provides support to the plant to keep it upright. Like you, plants have skeletons. But unlike you many plants have water skeletons!
In the second term in Matter and Materials, learners will do more on mixtures, solutions and dissolving, and this will therefore make sense. Refer back to this section when you are doing solutions and discussing water as a solvent.
4. Carbon dioxide: The plant absorbs or takes in carbon dioxide from the air through little holes. These holes are found all over the plant, mostly under the leaves.
5. Soil : The soil provides mineral nutrients and water for the plant that are necessary during photosynthesis. Soil also provides anchorage to the plant, otherwise the plant cannot stand up straight.
A really good website on photosynthesis http://www.realtrees4kids.org/sixeight/letseat.htm
How does photosynthesis occur?
Plants use chlorophyll, sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make food. Here is a simple illustration to show how this process occurs:
- Chlorophyll captures the sunlight energy.
- This energy splits the water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The oxygen is released into the air.
- The hydrogen is used with the carbon dioxide to make glucose (sugars).
- The sugars are moved from the leaves to other parts of the plants where they are stored.
- The water in the plant veins carries the sugars. When the sugars reach the storage parts they are changed into starch.
- leaves (cabbage, spinach, lettuce)
- fruit (apples, banana, peaches)
- stem (sugar cane)
- seeds (wheat or mealies)
- flowers (nasturtiums, broccoli and cauliflower)
- roots (carrots or beetroot)
Starch is insoluble in water which is why plants store starch and not glucose, which is soluble in water. Refer back to this section when doing soluble and insoluble substances in the second term.
Dramatise the process of photosynthesis
Prepare beforehand by collecting the different materials needed. The characters need different colours to identify themselves as what they are, possibly some t-shirts that they can pull over their clothes, or else a scarf or ribbon or coloured piece of paper to pin onto their front. You will also need tin foil, glitter and string for the roots. For the animals, you can make masks out of paper plates with the eyes cut out, and tied around the head with a piece of string. Learners can draw animal faces on the front.
INSTRUCTIONS:
- Your teacher will explain to you how to act out the process of photosynthesis.
- Characters needed for this dramatisation:
- Narrator to describe the process. This can be a teacher or a learner. It might be a good idea to make short notes from the information above to remember in what order everything is happening.
- Sun - this learner can dress in yellow and perhaps get some old tin foil or shiny paper to decorate their head or body to show the light and heat energy that the sun produces.
- Plants - a few learners can dress in green and perhaps tie a few strings to their feet to represent roots. They need to hold some rice or shiny glitter in their hands or their pockets to show that the water evaporates after photosynthesis.
- Rain / water - a few learners can dress in blue and perhaps have some rice, shiny glitter, small pieces of tin foil or something similar to represent the rain falling.
- Carbon dioxide - attach signs to the learner's chests that say 'Carbon dioxide' and dress in purple.
- Oxygen - attach signs to the learner's chests that say 'Oxygen' and dress in orange.
- Glucose energy as fruit and vegetables - dress up or make posters from scrap cardboard to show large carrots, apples, potatoes, or something similar.
- Some learners need to be animals who breathe out carbon dioxide and eat the plants. You can make masks out of paper plates with eyes cut out.
The dramatisation: When the dramatisation starts, the glucose and oxygen actors sit quietly in small groups around the plants with their heads down, not looking at the audience.
The narrator introduces the play and explains the different processes as these occur.
The sun shines in the centre of the stage and can turn and/or raise their arms to show the sunlight radiating from it.
The plants stand away from the sun and the rainwater actors can 'water' them by gently throwing the rice or similar little objects over their heads. Then sit down around the plants.
The carbon dioxide actors run from the animals and circle the plants, and then sit down around the plants.
Now the oxygen and glucose actors rise and run around the plants, and then run to the animals to show they are receiving oxygen and food.
You might want to repeat this a few times to show that this cycle continues.
Why do plants die when there is a drought?
There are many processes which shut down without water, photosynthesis being one of them. Plants cannot photosynthesise sunlight without water. If they cannot photosynthesise they cannot create glucose to support life processes within the plant. If the plant cannot support its own life processes it dies. The plant also loses its support from the water in the veins acting as a 'skeleton'.
- Design a poster for your Gr. 4 friends to explain the process of photosynthesis to them. You can use sentences and short paragraphs but make sure you use many illustrations.
Soil was looked at in Gr. 5 Earth and Beyond, especially the particles of soil and which types of soil plants grow best in. However, it would be useful to also emphasise soil in this section and have a discussion on what makes up soil, namely organic and inorganic material, water, air, rocks and sand. Where possible, bring examples of different soil types to class (such as loam soil, clay, beach sand) and get the learners to touch and feel the soil and explore what makes up soil.
Food from photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process inside plants that changes the energy from the sun's light into a form of energy that animals can eat and use to carry out their life processes.
Plants changes the glucose into starch, for example mealies (mealies and maize flour), rice (rice flour and rice) and wheat (flour).
Plants then store this food in different parts of the plant that an animal will eat. They can store it in their leaves, stems or roots, flowers, fruits or seeds.
Look at the images below of different plant products. For each image, identify which part of that plant we eat (for example: When we eat an apple, are we eating the leaf, the stem, the root, the fruit or the seed of the plant?) Use the space below to draw a table for your answers.
|
|
|
| cabbage | flower |
| tomatoes | fruit |
| potatoes | root |
| broccoli | flower |
| celery | stem |
| carrots | root |
| sunflower seeds | seed |
| lettuce | leaf |
| sugar cane | stem |
| hazelnuts | seed |
| mealies | seed |
| bananas | fruit |
We know that plants make glucose (a sugar) but they store starch. Let's now find out what the difference is.
Difference between a starch and a sugar
Prepare beforehand: Prepare at least 10 different plant products in advance of this lesson and mark each item from 1 - 10. Cut up fruit/potato/sweets into bite-sized cubes. Place flour/cooked rice/etc. into bowls. Use teaspoons to taste the flour/cooked rice/etc.
IMPORTANT: Before doing this activity find out if any of the learners have any allergies to these foods and if learners with diabetes are allowed to eat/taste the fruit/sweets.
- mealie flour
- cooked rice, potato, bread
- glucose sweets
- sugar cane, if possible
- fresh fruit
- Work in pairs.
- One partner must be blindfolded.
- On a piece of paper list the numbers 1 - 10.
- The other partner must let the blindfolded partner taste each of the foods marked 1 - 10. If it is a flour, use a teaspoon to spoon the flour into your partner's mouth. If it is a kernel like a rice or mealie kernel, or a cube of fruit, put it in the palm of their hand and let them eat it themselves.
- After each taste your blindfolded partner must guess if it is a sugar or a starch based on the taste.
- Record your partners answers on the piece of paper containing the numbers 1 - 10.
- Swap with your partner and repeat the test.
While learners are swapping with their blindfolded partners, rearrange the foods with the numbers to ensure fairness. The aim of the test is not to establish the exact name of the fruits and foods but to establish that taste is not a suitable method to test for sugar or starch. Generally sugars are sweet and starches are not, but not always.
Was it easy to distinguish between the sugar and the starch each time? Which foods did you find difficult to classify?
What can you say about the difference between a starch and a sugar based on taste?
Sugars are sweet, starches are not.
Using TASTE to check if a food is a sugar or a starch is not very reliable.
There is a special test that scientists use to see if a food product is a starch or not. It is called the iodine starch test .
Iodine solution is a special solution that is normally a brown liquid .
Iodine is what we call an indicator .
When iodine solution is dropped on starch, the iodine and starch combine and produce a blue colour. We use this to test whether there is starch in a food product.
Let's see how this works!
The iodine starch test
Note: There will be NO tasting in this activity.
- the same foods used in the taste test (they should be marked 1 - 10 )
- include some other foods such as cheese and a boiled egg
- Write the food or plant product that you chose in the first column below.
- You are going to test whether this food product is a starch or not. When the iodine solution turns blue-black you will know it is a starch.
Explanation for starch turning blue-black when iodine is placed on it: Starch is composed of polymers of glucose. Long linear chains are amylose. Amylose coils into a structure resembling a tube with a hollow core. Certain molecules, including iodine, can lodge inside the core. The complex of iodine stuck inside the amylose coil produces a characteristic blue-black colour. The starch itself is not altered. NB: This explanation is not necessary for learners, but do say that the iodine reacts with the starch to form a blue-black colour.
- Use a dropper and drop iodine solution onto each food group.
- Put a tick next to the food product that turns blue-black - this is a starch. Put a cross next to the food product that stays brown - this is not a starch.
|
|
| |
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | ||
| 12 |
QUESTI ONS:
Which test do you think is more accurate to test for starch - the taste test or the iodine starch test?
Did the animal products, such as cheese and boiled egg, contain starch? Why do you think so?
Animals do not produce or store starch. Starch is only stored in plant products.
Animals do store carbohydrates, but not in the form of starch. Only plants produce and store starch. Animals store glucose in the form of glycogen.
Plants and air
All animals and plants need oxygen to live and carry out their life processes.
Animals breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide, all through the day and the night. Oxygen is used to release energy from food inside the body, which is used for the life processes.
Do you remember what the seven life processes of living things are? Write them down below.
Movement, reproducing, sensing, feeding, excreting, breathing, growing.
Just like animals, plants also use oxygen throughout the day and the night. Oxygen is necessary for plant growth and the development of new plants, seeds, leaves and shoots for example. Plants, therefore, also produce carbon dioxide as a 'waste product' once the oxygen has been used.
Plants do not photosynthesise through the night because there is no sunlight energy available to do that. This means that plants only need carbon dioxide during the day, for photosynthesis.
This cycle of using and producing both oxygen and carbon dioxide is very important to life on Earth.
The oxygen and carbon dioxide cycle
- Carefully study the following illustration.
- Answer the questions that follow.
Make a list of living organisms that produce both oxygen and carbon dioxide in this picture.
Tree, reeds, water plants, and shrubs on the bank
Identify three living organisms that cannot produce oxygen in this picture.
Fish, duiker (buck), squirrel, dragonfly
Predict what you think would happen if all the animals were removed from this habitat.
Probably not much would change as the leaves that decay would still give off carbon dioxide for the plants to use, as well as the carbon dioxide that the plants produce themselves.
What two life processes are involved in the carbon dioxide/oxygen cycle?
breathing in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide
Complete this cycle by filling in the missing information for the two arrows on the left hand side of the illustration. Supply the labels for arrows 1 and 2.
- Arrow 1: Plants produce oxygen
- Arrow 2: Animals breathe out carbon dioxide
Explain why animals would not survive if all the plants on earth were to suddenly die.
- Animals need oxygen for their cells to work and to carry out life processes.
- If animals do not have oxygen they cannot carry out the life processes and will die.
- Plants also produce food from the sun that animals need to eat for energy to carry out the life processes.
Why do we say the oxygen and carbon dioxide are in a cycle?
For life on Earth to continue, there needs to be an unlimited supply of carbon dioxide and oxygen. It is in a cycle to ensure that similar amounts of both are produced.
- Plants produce their own food (glucose) by a process called photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis takes place mainly in the leaves.
- During photosynthesis the plant uses chlorophyll, sunlight energy, carbon dioxide (from the atmosphere) and water to make glucose.
- Plants change some of the glucose (sugar) into starch which they store in their leaves, stems and roots, flowers, fruits and seeds.
- Animals take in oxygen from the air and produce carbon dioxide when they breathe.
- Plants recycle carbon dioxide and make oxygen during the process of photosynthesis.
List the four things that are vitally important for plants and photosynthesis.
Sunlight energy, water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll
| Word box: |
- The process when the green parts of plants make food is named _____.
- Water and minerals are absorbed by the _____ of plants.
Soil is made up of _____, _____, _____, _____.
- The process when the green parts of plants make food is named photosynthesis.
- Water and minerals are absorbed by the roots of plants.
- Soil is made up of organic and inorganic material, water, air, sand and rocks .
The seedlings that were planted in the newspaper cuttings or cotton wool did not grow very well at all, even though they had sunlight and water. What could they not get from the newspaper or cotton wool that plants normally get from soil?
Nutrients and minerals
Where does photosynthesis usually take place? Explain your answer.
Photosynthesis usually takes place in the leaves. The leaves are green as they contain chlorophyll. Leaves also face the sunlight and are exposed to the most sun to drive the process of photosynthesis.
Do you think photosynthesis takes place at night? Explain your answer.
No, it will not take place. At night there is no sunlight energy to drive the process of photosynthesis.
What is the name given to the sugar that plants produce during photosynthesis?
What do plants store glucose as? List some places where it is stored.
Starch, stored in leaves, stems, roots, flowers, seeds, fruits.
Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Photosynthesis
2nd - 3rd , cell respiration & photosynthesis, professional development , how do plants get their food, kg - 3rd , cycling of matter, 11th - 12th , 14.2k plays, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, 7th - 8th , carbon cycle, 6th - 8th .

Grade 6 Photosynthesis
5 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Name of green pigment involved in photosynthesis
Chlorophyll
Chloroplast
Products of photosynthesis includes all except?
Carbon dioxide
Plants use from the sun.
What part of the plant does it use to feed?
What are the small cell structures in the epidermis of the leaves called?
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
- Kindergarten
- Greater Than Less Than
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Place Value
- Subtraction
- Punctuation
- 1st Grade Reading
- 2nd Grade Reading
- 3rd Grade Reading
- Cursive Writing
- Alphabet Coloring
- Animals Coloring
- Birthday Coloring
- Boys Coloring
- Buildings Coloring
- Cartoons Coloring
- Christmas Coloring
- Country Flag Coloring
- Country Map Coloring
- Disney Coloring
- Fantasy Coloring
- Food Coloring
- Girls Coloring
- Holidays Coloring
- Music Coloring
- Nature Coloring
- New Year Coloring
- People Coloring
- Religious Coloring
- Sports Coloring
- Toys Coloring
- Transportation Coloring
- US Sports Team Coloring
- Valentine Day Coloring
Photosynthesis Grade 6
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Photosynthesis Grade 6 .
Some of the worksheets for this concept are A tree is like a hungry kid, Photosynthesis, What is photosynthesis, Name date period photosynthesis making energy, Photosynthesis review work, 1 natural sciences and technology grade 6 term 1, Photosynthesis a survival guide, Photosynthesis.
Found worksheet you are looking for? To download/print, click on pop-out icon or print icon to worksheet to print or download. Worksheet will open in a new window. You can & download or print using the browser document reader options.
1. A Tree is Like a Hungry Kid
2. photosynthesis, 3. what is photosynthesis, 4. name date period photosynthesis: making energy, 5. photosynthesis review worksheet, 6. 1 natural sciences and technology grade 6 term 1, 7. photosynthesis a survival guide, 8. photosynthesis.
6th Grade Science Quiz On Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is how green plants use sunlight to produce foods from carbon dioxide and water. This "6th-grade science quiz on photosynthesis" will help you test your understanding of the concept. Did you know that Photosynthesis is also in charge of balancing oxygen and carbon dioxide amounts in the atmosphere? Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen. If you are keen on discovering more about photosynthesis, you should try this quiz. If you like the quiz, do share it with your friends and family. All the best!
What are the products of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide and Water
Oxygen and Water
Oxygen and Sugars
Only oxygen
Rate this question:
What happens during photosynthesis?
The cell uses oxygen to make food
The cell uses the energy in sunlight to make food
The cell uses glucose to make oxygen
None of the above
How does photosynthesis benefit heterotrophs?
It adds carbon dioxide to the air
It creates food that they can eat
It eliminates harmful sugars
Parenchyma cells
What captures energy from sunlight during photosynthesis?
Solar cells
Chlorophyll and other pigments
Carbon dioxide enter plants through the
Chloroplasts
Plants use energy from the sun to produce carbon dioxide and sugars.
Plants use energy from the sun to produce ________________ and sugars..
Carbon dioxide
A heterotroph is an organism that cannot make its own food.
Photosynthesis and respiration form a cycle that keeps the levels of water and carbon dioxide fairly constant in the atmosphere., photosynthesis and respiration form a cycle that keeps the levels of _____________ and carbon dioxide fairly constant in the atmosphere., small openings called ____________________ allow carbon dioxide to enter a leaf., plants make their own food using energy that comes from the ____________________, almost all the plants depend on the process of _____________________ to supply them with the energy they need..
Photosynthesis
Transpiration
Respiration
Chloroplasts contain a pigment called __________________ that captures the energy in light.
Chlorophyll
Colored chemical compounds that capture light are called_____________
The two raw materials in photosynthesis are ___________________ and ______________.
Carbondioxide, water
Oxygen, carbondioxide
Carbondioxide, oxygen
Water, ammonia

The two products of photosynthesis are _______________ and ____________
Sugar, oxygen
Oxygen, carbon di oxide
Oxygen, ammonia
Oxygen, hydrogen
The ______________ powers the process of photosynthesis.
If an organism is a heterotroph, it will get its energy from the sun _______________.
Both directly and indirectly
If an organism is an autotroph, it will get its energy from the sun ______________
Quiz Review Timeline +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
- Current Version
- Aug 19, 2024 Quiz Edited by ProProfs Editorial Team
- Nov 20, 2011 Quiz Created by Tylaha
Related Topics
- 6th Grade World Social Study
- 6th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Vocabulary
Recent Quizzes
Featured Quizzes
Popular Topics
- 6th Grade Earth Science Quizzes
- 6th Grade English Quizzes
- 6th Grade Literature Quizzes
- 6th Grade Social Study Quizzes
- 6th Grade Technology Quizzes
- 6th Grade World History Quizzes

Related Quizzes
Wait! Here's an interesting quiz for you.
- TEACHA! INSPIRE

- Resource Collections
- Snapplify Engage
- Teacha! Inspire

GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES TERM- 1 WORKSHEET ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS
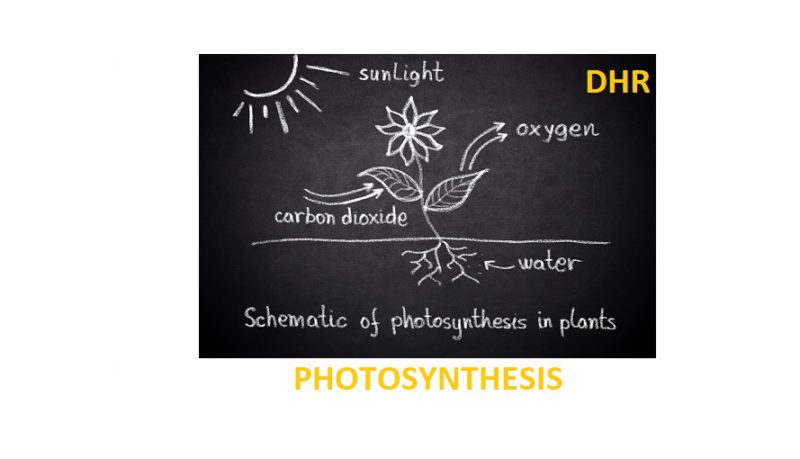
R 14.81
Share this resource
Use, by you or one client, in a single end product which end users are not charged for. The total price includes the item price and a buyer fee.
Resource Description
Resource reviews.
Store reviews: ( 41 ratings )
Related Resources

GRADE 6 TERM- 1 NATURAL SCIENCES MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ON FOOD GROUPS (2 WORKSHEETS)
DHR (WORLD OF SUCCESS)

GRADE 6 SOCIAL SCIENCES TERM-1 WORKSHEETS (7 WORKSHEETS)
PTS (PATH TO SUCCESS)

Grade 6 Opposite Operations
Mathematique

Grade 6 English FAL Term 3 Language Worksheet 2
Wize-Up Learning

Assessment: Visual literacy (Red Pandas)
Called to Teach
GRADE 6 TERM 4 MATHEMATICS WORKSHEET 6 (Q&A)
Home School Hero
More from this seller
GRADE 7 NATURAL SCIENCES TERM-2 WORKSHEET ON PERIODIC TABLE

GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM 1 WORKSHEETS ON DATA HANDLING (2 WORKHEETS)

GR 12 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 TERM QUESTIONS AND MEMORANDUM

GR 12 LIFE SCIENCES EVOLUTION SECTION B TYPE QUESTIONS AND MEMORANDUM

GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES TERM-3 TEST 2021 WITH MEMORANDUM

GRADE 4 MATHEMATICS WORKSHEETS ON MONEY PROBLEMS (ADDITION) WITH MEMORANDUM

Delete Confirmation
Always update your resources, rather than deleting and re-uploading a new one: If a resource is deleted from the system, those that have paid for the resource are no longer able to access their bought product.
Download and Print Printable Crossword Puzzles
Download or print printable Crossword Puzzles here for free. Enjoy playing Crossword Puzzles with your friend using our latest printable.
About Crossword Puzzles
Crossword Puzzles have long been a popular game. It’s often a first choice for many online searchers when looking for something to do on the Internet. While some websites offer free crossword puzzles, you need to pay to access more advanced options. If you’re just starting out, you can choose any number of basic crossword puzzle options. There is no question that this is a great way to spend a few minutes and challenge your brain, but did you know there are a number of other benefits to playing crossword puzzles?
The Benefits of Playing Crossword Puzzles
Studies have shown that playing crossword puzzles on a regular basis can have positive effects not only on your cognitive abilities but on your physical health as well. You will begin to see an improvement in your hand eye coordination and quick mental abilities. Studies have even shown that playing crossword puzzles can have positive affects on your mood and general outlook on life. It’s been found that those who regularly play crossword puzzles have improved mathematical ability. While this improvement is not going to dramatically alter your lifestyle or your habits, you will certainly notice an increase in your ability to solve problems and to make quick decisions.
In addition to the positive effects that playing crossword puzzles has on your brain and your health, it’s also a fun activity. Many people find that they actually like it better than other leisure activities. You won’t find yourself bored or irritated by it. You might find yourself starting a new game because of one of your current favorites. When you first start playing, you might even get frustrated at your lack of knowledge and difficulty finding the correct answer. But you’ll soon find that as you become familiar with the different moves and words that you’re using, your mind starts to relax and your concentration improves.
Another of the great things about playing crossword puzzles is the way that they exercise your brain. Because the puzzle is challenging, it requires your cognitive skills to be used at a higher level. This is one of the most effective ways to increase your intellectual capacity. As you learn more of the words, you will begin to see how well you are able to process all of the information that you are being presented. And because you are using your brain to search for the correct answer, you are going to find that you will pick up a lot of new skills as a result.
Finally, another of the positive benefits is that you will begin to find a need for more organized skills. One of the biggest problems that people face is organization. They aren’t able to stay on top of all of the information that is going in and out of their head. With puzzles, you are going to find that you are able to stay on top of all of the information, both in terms of the words and the information that are taking place in your brain. As a result, you will be able to organize your information and you will be able to get it where you need it at a moment’s notice.
As you can see, there are many reasons that playing crossword puzzles can benefit you. These are just a few of the benefits that you can receive when you start playing this type of game. As you work your way through the steps, you will find that you are growing more mentally tough, exercising your brain in more sophisticated ways, developing better organization skills, strengthening your reading skills and much more. Just remember, when you are first starting out, playing crossword puzzles will probably be the easiest way for you to learn how to read. As you progress in your reading, you can slowly work your way up to other forms of reading and learning.
Download or Print Daily Printable Crossword Puzzles for Free
If you want to play crossword puzzles with your friends offline and you need the printable Crossword Puzzles, you can download them down below. We update the puzzles daily so that you can get fresh printables whenever you visit our website.

Download Printable Crossword Puzzles Type 1
Daily Printable Crossword Puzzles Type 2
Crossword Puzzles Printable Type 3
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Grade 6 Natural Sciences and Technology Resources for teachers, Lesson plans, Notes, Worksheets. All CAPS aligned
This file is too large to preview. You can download it using the button below.
Do you have an educational app, video, ebook, course or eResource?
Contribute to the Western Cape Education Department's ePortal to make a difference.

Home Contact us Terms of Use Privacy Policy Western Cape Government © 2024. All rights reserved.

- Class 6 Hindi Malhar
- Joyful Mathematics Class 1
- Joyful Mathematics Class 2
- Class 1 Hindi
- Class 2 Hindi Sarangi
- Class 3 Hindi Veena
- Class 5 Hindi
- Class 5 EVS
- Class 5 Maths
NCERT Curiosity Class 6 Science Worksheets with Answers
Are you looking for engaging and effective tools to help your child excel in Science? Our collection of Class 6 Science Worksheets is designed to make learning fun and interactive.
Our worksheets cover a wide range of topics, from the amazing world of plants and animals to the wonders of the human body and the laws of physics. With our carefully crafted worksheets, your child will have the opportunity to practice key concepts, and reinforce their understanding.
Whether you’re a parent looking to supplement your child’s schoolwork or a teacher searching for engaging classroom activities, our Science Worksheets for Class 6 are the perfect resource.
Click to Join Us on WhatsApp Channel for latest updates!
Class 6 Science Worksheets
Don’t miss out on these valuable resources! Download our free Class 6 Science curiosity Worksheets today and unlock a world of fascinating discoveries.
Use our worksheets alongside NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science to enhance your child’s understanding and performance.
Also download: Class 6 Hindi Worksheet with Answers
1: The Wonderful World of Science 2: Diversity in the Living World 3: Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body 4: Exploring Magnets 5: Measurement of Length and Motion 6: Materials Around Us 7: Temperature and its Measurement 8: A Journey through States of Water 9: Methods of Separation in Everyday Life 10: Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics 11: Nature’s Treasures 12: Beyond Earth
NCERT Class 6 Science Book Curiosity
The NCERT board has introduced new textbooks for the academic year 2024-25, incorporating modern teaching methods and updated content. Please visit the official NCERT website to download the NCERT Class 6 science book PDF .
Curiosity: Class 6 Science book is designed to spark a lifelong passion for learning in young minds. Aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, this innovative textbook shifts away from rote memorization towards a competency based approach.
By emphasizing hands-on activities, critical thinking, and real-world applications, Curiosity empowers students to become active participants in their own learning. The Science textbook integrates concepts from biology, chemistry, and physics, helping students to understand the interconnection of the natural world.
With a focus on inquiry-based learning and problem-solving, Curiosity aims to equip students with the latest skills of 21st century. Through engaging experiments, thought-provoking questions, and real-world examples, the textbook fosters a love of learning and a curiosity about the world around us.
Benefits of Our Class 6 Science Worksheets
Our Science Worksheet for Class 6 PDF offer a multitude of benefits for students.
- Reinforced Learning: Our worksheets are designed to reinforce key concepts taught in the classroom, helping students solidify their understanding of scientific principles.
- Engaging Activities: Our worksheets feature a variety of engaging activities, such as diagrams, true or false and experiments, making learning fun and interactive.
- Skill Development: These worksheets help students develop essential skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, and analysis.
- Self-Paced Learning: Students can work through the worksheets at their own pace, allowing them to focus on areas where they need more support.
- Printable and Convenient: Our PDFs are easy to download and print, making them a convenient resource for both home and classroom use.
- Aligned with Curriculum: Our worksheets are carefully aligned with the NCERT Class 6 Science curriculum, ensuring that students are practicing the right concepts.
In conclusion, by downloading and using our free Science Worksheets, you’re providing your child with a valuable tool to enhance their learning and achieve academic success.
- free worksheets
- ncert worksheets
- science worksheets
RELATED ARTICLES
Free ncert solutions for class 6 hindi malhar pdf, free and engaging class 6 hindi worksheets with answer.
Welcome to your one-stop destination for free worksheets, NCERT Solutions, practice tests and high-quality educational resources to help you reach your goals.
Copyright © 2023 onepointlearning.com. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
GR.6C- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Revision 1)

JOHN GALATI LETCHE
Revision for Gr. 6
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF
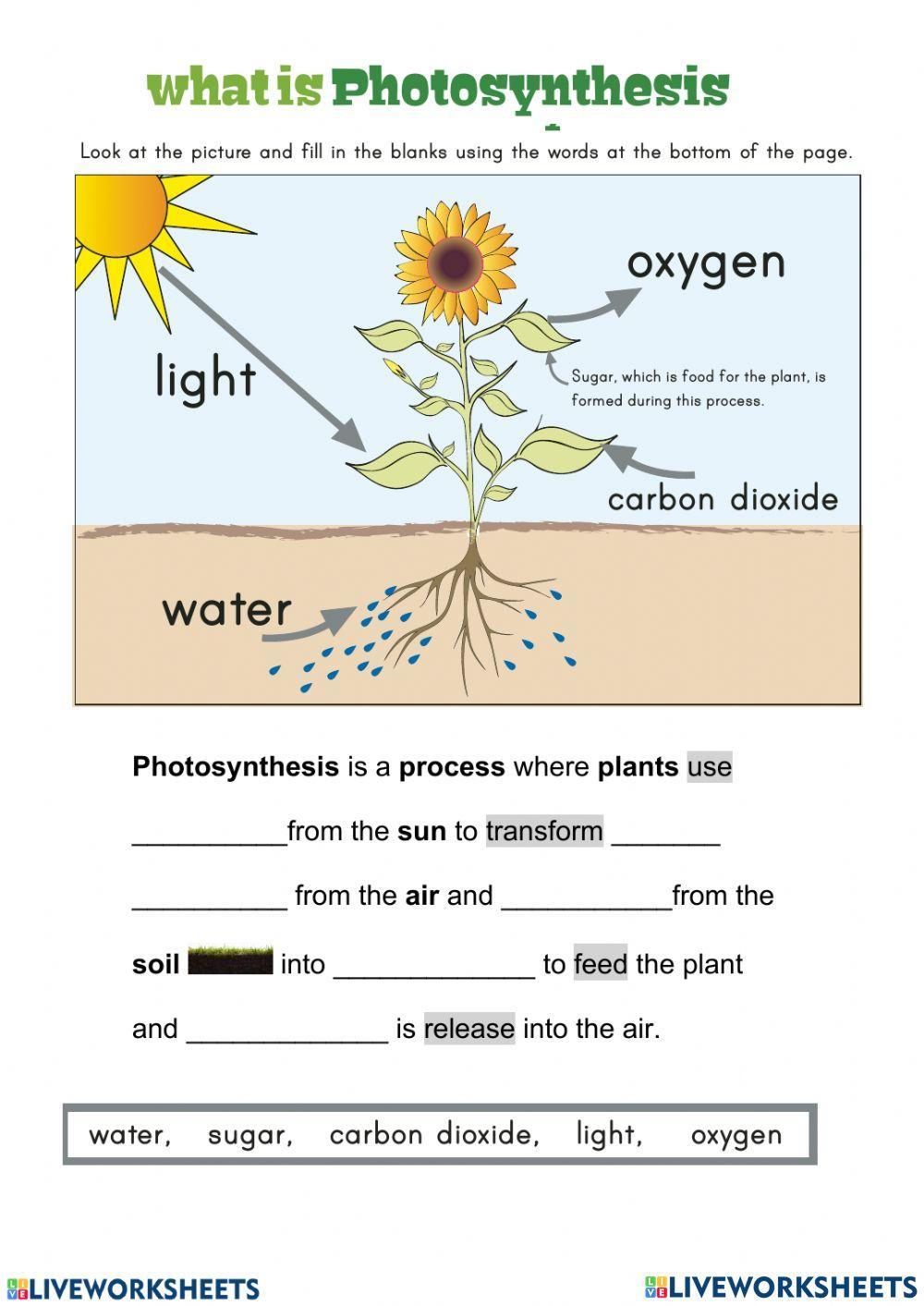

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Natural Sciences & Technology Grade 6 Term 1 . Strand 1 Natural Sciences: Life and Living Technology: Processing . Plants make food that we eat and put oxygen into the air that we breathe. We would not be able to live without plants and the same for animals. Plants and . Photosynthesis Nutrients in Plants and food air food Food groups Nutrition
Photosynthesis Reading Of all the living things in our natural world, green plants are the only things that can make their own food. This process is called photosynthesis. Synthesis means "putting together or making something." The prefix "photo" means light. Therefore, the word photosynthesis means "to make something with light."
Gr 6 Natural Sciences and Technology - Term 1, Topic 1 WORKSHEET A The Process of Photosynthesis Look at the picture below and fill in the missing words in the sentences that follow. 1. The sunlight energy is captured by the _____in the leaves of the plant. (1) 2. This energy splits the water into _____ and _____. (2)
Home > Science Worksheets > Photosynthesis. Approximately 85% of the world's oxygen is due to this process. That is why if the sun were to suddenly stop producing light, not only would it be dark; we would not be able to breathe much longer. These worksheets explore all aspects of the process of photosynthesis.
Plant Processes. 6th Grade Science Worksheets and Answer key, Study Guides. Covers the following skills: Provide evidence that green plants make food and explain the significance of this process to other organisms. Recognize that producers (plants that contain chlorophyll) use the energy from sunlight to make sugars from carbon dioxide and water through a process called photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process inside plants that changes the energy from the sun's light into a form of energy that animals can eat and use to carry out their life processes. Plants changes the glucose into starch, for example mealies (mealies and maize flour), rice (rice flour and rice) and wheat (flour).
Photosynthesis worksheets by sandhya pallath .Photosynthesis online worksheet for grade 6 Live Worksheets. ... School subject: Science (1061951) Main content: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (2000248) From worksheet author: analyze the equations. Other contents: biology ...
Country: Colombia. School subject: Natural Science (1061921) Main content: Photosynthesis (2008272) From worksheet author: Plants need, photosynthesis and key words. Other contents: The way plants feed. Worksheet description: Objective Explanation: This worksheet aims to enhance students' understanding of photosynthesis, a v...
We've created this lovely What is Photosynthesis? resource, especially for your Grade 6 Natural Science lessons. It covers a wide range of information about Photosynthesis. This resource includes a page packed with information and beautiful illustrations from our in-house team. There are also questions testing learners' knowledge of what they have read. We've included a handy memo, too, that ...
Lesson Plan Gr. 6 Natural Sciences and Technology T1 W1 & W2. Free. Download. Type: pdf. Size: 0.74MB. Share this content. Grade 6 Lesson Plan on Life and Living & Processing with focus on the CAPS Topics: Photosynthesis, addressing the Concepts: Plants and food & Plants and air.
Grade 6 Photosynthesis quiz for 6th grade students. Find other quizzes for Science and more on Quizizz for free!
Photosynthesis Grade 6. Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Photosynthesis Grade 6. Some of the worksheets for this concept are A tree is like a hungry kid, Photosynthesis, What is photosynthesis, Name date period photosynthesis making energy, Photosynthesis review work, 1 natural sciences and technology grade 6 term 1, Photosynthesis a ...
Grade 6 On Photosynthesis. Displaying all worksheets related to - Grade 6 On Photosynthesis. Worksheets are Photosynthesis grade 6 work, Photosynthesis respiration, Grade 6 plant processes, Photosynthesis quiz, Photosynthesis review work, Grade 6 subject natural sciences and, Chapter 4 photosynthesis and cellular respiration work, Lesson plan ...
Summarized class work and worksheets for Natural Science and Technology grade 6 Pictures to keep learning interesting. Perfect for printing in black and white Topics: Photosynthesis Plants & air (the carbon-oxygen exchange) Testing for starch.
In this Grade 6 Natural Sciences video lesson we will be teaching you about Photosynthesis.We've sourced highly-qualified and experienced South African teach...
This wonderful Photosynthesis Experiment allows your Year 6 pupils to investigate if light is needed for photosynthesis. The experiment challenges children to conduct their own experiment using safety, accuracy and independence. This downloadable resource includes everything you need to conduct a Photosynthesis Experiment. Well, except the materials! But don't worry, there are instructions ...
Photosynthesis worksheets by Maureen Acuna A .Photosynthesis online worksheet Live Worksheets. ... Grade 6. Language: English (en) ID: 67141. 24/03/2020. Country code: CR. Country: Costa Rica. School subject: Science (1061951) Main content: What affects photosynthesis (1065234) From worksheet author:
17. During the process of photosynthesis, plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as a source of energy for the plant, while oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct. Therefore, the correct answer is "sugar, oxygen".
Sold By DHR (WORLD OF SUCCESS) Grade / Level Grade 6. Age 11. Year 7. Type Worksheets, Tasks. Language English. School Term Term 1. Curriculum Kenya - CBC, Mauritius Primary Curriculum Framework, Nigeria - Universal Basic Education (UBE), South Africa - CAPS. Subjects Natural Science.
Grade 6 Natural Science Worksheets Photosynthesis - Grade Science Worksheets can be used to teach students about the natural world. These worksheets cover many topics such as climate change, five senses and parts of animals and plants.
Grade 6 Natural Sciences and Technology Resources for teachers, Lesson plans, Notes, Worksheets. All CAPS aligned. Grade 6 Natural Sciences and Technology Resources for teachers, Lesson plans, Notes, Worksheets. All CAPS aligned ... Cape Town Science Centre Maths Curriculum Online Teachers More. ASSESSMENT ...
Photosynthesis worksheets by Asma Begum .Photosynthesis worksheet for grade 6 Live Worksheets. ... School subject: alreeyada international school (974535) Main content: Science (1486320) From worksheet author: photosynthesis. Loading ad... Share / Print Worksheet ...
Our collection of Class 6 Science Worksheets is designed to make learning fun and interactive. ... chemistry, and physics, helping students to understand the interconnection of the natural world. With a focus on inquiry-based learning and problem-solving, Curiosity aims to equip students with the latest skills of 21st century. Through engaging ...
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher. ... GR.6C- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Revision 1) GR.6C- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Revision 1) ... ID: 1318352. 28/08/2021. Country code: PH. Country: Philippines. School subject: Science (1061951) Main ...