

Manufacturing Business Plan – Detailed Example & Template

Use this manufacturing business plan as your template to start and grow your manufacturing company. This business plan for a manufacturing company includes market analysis, strategy, and more.
Download this Manufacturing Business Plan free for easy editing in Microsoft Word, Google Docs or Apple Pages to make a PDF:
Also Read: MoreBusiness.com’s Free Starting a Business Guide
Table of Contents
Manufacturing Business Plan
1.0 executive summary, 1.1 company.
Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc. designs prototypes and molds, which are used by production manufacturers to fabricate consumer products. We are a start-up company that developed and patented revolutionary design software called Virtual Design Center. Our initial plan is to create a precision manufacturing facility to produce prototypes and molds for clients. Our goal is to provide our customers with fast turnaround, exceptional quality, unparalleled customer service, and competitive pricing.
1.2 PRODUCTS & SERVICES
We design and manufacture prototypes and molds. By utilizing Virtual Design Center, we will work in real-time with our customers to meet their design needs, which will reduce errors and detect design flaws early in the process. In turn, this will save the customer time and money. We plan to position ourselves as a forward-thinking company that continually invests in new ideas and technologies – unlike our competitors, which are similar mold manufacturing facilities. Because of our unique software, sophisticated technology and efficient processes, we will be in a position to potentially compete on price and quality. As this manufacturing business plan will outline, our unique Virtual Design Center gives us a definitive advantage.
1.3 MARKET ANALYSIS
The U.S. manufacturing industry makes up a substantial portion of the GDP, and the mold-manufacturing sector generates sales of more than $5 billion. Manufacturing drives the U.S. economy more than any other industry. Within that enormous industry, we have identified two strong markets with very high growth potential – automotive parts and medical devices manufacturing. As new car companies respond to shifting consumer demands for more fuel-efficient cars, and as the medical community develops new technologies, the need for new parts, designs and molds grows.
1.4 STRATEGY & IMPLEMENTATION
To achieve our business goals, we will create a high-tech, precision manufacturing facility and will implement highly efficient operations processes. We plan to promote Titus Mold Manufacturing and our proprietary Virtual Design Software with an aggressive, targeted marketing campaign. This will include a media campaign, print and online advertising and a targeted direct-mail campaign. In addition, we will focus heavily on establishing our presence within the industry at relevant trade shows.
1.5 MANAGEMENT
Our leadership team currently consists of Chief Executive Officer John Baker, President Michael Smith, and Vice President Susan Jones. Additional key leaders will include directors of finance, marketing and sales, human resources, information technology and operations. While these positions remain unfilled at this time, we do have several extremely qualified candidates interested in joining with us in this new venture.
1.6 FINANCIAL PLAN
Our Company will earn revenue from the sale of design services and manufactured molds. The attached Income Statement demonstrates that our gross profit margin will exceed 72%, and we will achieve break-even with sales of $XXX,XXX. We expect to reach profitability by the middle of Year 2.
1.7 SOURCES & USE OF FUNDS
Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc. requires $4,450,000 to launch. At present, we have raised $150,000 in venture capital funds. In addition, co-owners John Baker, Michael Smith and Susan Jones have each invested $100,000 into the company. We are currently seeking funds from outside investors and business loans.
The start-up funds will be used to cover the facility, build-out costs, equipment, software and initial operating costs including payroll, taxes, and utilities.
2.0 COMPANY
2.1 company & industry.
Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc. is located in Molder, Missouri. Our company designs and manufactures prototypes and molds for use in casting metals or forming other materials, such as plastics, glass or rubber. Our business operates within the manufacturing industry and is classified under NAICS code 333511 – industrial mold manufacturing.
2.2 LEGAL ENTITY & OWNERSHIP
Titus Mold Manufacturing is an S-Corporation that was formally organized in Missouri. The company’s principal owners are John Baker, Michael Smith and Susan Jones, who hold equal shares of ownership in the company.
2.3 COMPANY HISTORY TO DATE
Our company is a new business that will create prototypes and quality molds, utilizing the latest design software, e-commerce technology, high tech machinery and innovative operations processes. As the company’s founders and owners, we have a combined 40 years of experience in software development and the manufacturing industry. Our experience includes product research and development, engineering and production management. After recognizing the need for and value of creating a more efficient customer experience to secure and retain business, we decided to create Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc.
2.4 FACILITIES
Our company is preparing to lease a manufacturing facility in Molder, Missouri. We are presently operating out of temporary administrative offices at the Barton Business Incubation Center.
We are working with a local realtor and BBIC to identify potential industrial space available for lease. We require a 10-12,000 sq. ft. facility to accommodate product development and engineering, a mold shop, a tool shop, quality assurance area, inventory storage and administrative offices. As the business grows, we intend to add injection-molding capabilities.
2.5 KEY ASSETS
Titus Mold Manufacturing holds a patent for its revolutionary Virtual Design Center (VDC). The VDC combines the best of virtual and in-person presentations and meetings, allowing customers to work in real-time with our design engineers. This allows us to serve clients nationwide.
3.0 PRODUCTS/SERVICES
3.1 description.
Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc. will make prototypes and molds for the manufacturing of consumer products. A mold, which is usually made from aluminum or steel, is a hollow form that gives a particular shape to a product while it is in a liquid state. The molds are used for products made from plastic, glass, metal or other raw materials.
There are three main phases to manufacturing a prototype or mold. First, engineers and product developers create a design. Titus Mold Manufacturing is able to complete a design from start to finish for a customer. If need be, Titus will work with the customer through the design process via our one of a kind Virtual Design Center. Secondly, we make test molds. We then inspect and test the molds for quality assurance. Finally, we manufacture prototypes and molds based on specific design specifications, using precision machinery to form the desired prototype or mold.
3.2 FEATURES & BENEFITS
Virtual Design Center will be the key to distinguishing and drawing attention to our company. Once we have a particular industry or customer’s attention, we will sell them on our fast turnaround, exceptional quality, unparalleled customer service and competitive pricing.
Obviously, speed, quality, service and price are qualities most of our competitors will list in their mission statement. However, Titus Mold Manufacturing will – from the beginning – invest in top quality, highly sophisticated machinery as well as implement innovative operations policies. These steps will ensure our ability to deliver beyond normal industry standard and surpass our customers’ expectations saving them time and money.
3.3 COMPETITION
Our competitors are companies that provide similar types of design and mold-making services. There are far too many competitors to list specifically in this manufacturing business plan. To their advantage, they have an established customer base. Further, many mold-making companies also have injection-molding machinery, which enables them to manufacture actual products.
However, the vast majority of our competitors are not taking full advantage of current technology, nor are they implementing modern operational systems. Their waste is ultimately passed along to the customer via longer turnaround times and higher overhead costs .
3.4 COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE/BARRIERS TO ENTRY
By relying on our technology and an activity-based costing system, rather than a time-based system, we will be able to maintain competitive prices and sustain high profitability. Our technology and systematic efficiencies will allow us to have advantages in cost, speed and design capability. Ultimately, these advantages will quickly come to define Titus Mold Manufacturing as an industry leader.
Our Virtual Design Center technology gives us a significant advantage over our competitors, and our patent prevents others from being able to replicate the services we offer.
3.5 DEVELOPMENT
As our company grows, we plan to expand our facility and create an injection-mold manufacturing plant. At that point, we will be able to control all operations in-house from initial design to mold creation and even mass production of the finished products. In addition, we will stay atop technology trends and upgrade equipment and processes as needed and can be afforded. We will also continue to research and pursue shares of existing markets such as packing, defense, electronics and telecommunications and update portions of this manufacturing business plan accordingly.
4.0 MARKET ANALYSIS
4.1 market size.
The US manufacturing sector includes more than 300,000 companies with combined annual sales of about $4 trillion. Furthermore there are approximately 2,500 mold manufacturers with combined annual sales of more than $5 billion. To capture a portion of those sales, Titus Mold Manufacturing will utilize a targeted industry approach to pursue specific, definable, market segments.
4.2 TARGET CUSTOMER
After extensive research, we decided to initially pursue market segments in the automotive and medical devices industries. These are two very distinct markets with very different needs. While the automotive industry’s purchasing decisions are driven primarily by price, the medical device industry focuses on a fast turnaround time and quality to make purchasing decisions.
The U.S. automobile manufacturing industry includes about 160 companies with combined annual revenue of about $250 billion. While the majority of those sales are swallowed up by a handful of major car manufacturers, there are thousands upon thousands of parts needing to be manufactured for each vehicle. By specializing in manufacturing molds for certain parts, we will establish our niche in the market. Our research indicates this is a perfect time to assimilate into this industry as carmakers make dramatic shifts in design and efficiency to address rising fuel costs.
The medical devices industry is by far one of the most forward-thinking, always-evolving industries. Researchers and product developers are continually striving to improve products and procedures. With this constant change and product evolution comes the constant need for new product molds. Couple the advances in medical technology with an increasingly aging population, and it’s clear the healthcare industry as a whole is a solid market and mold manufacturers will reap the benefits.
4.4 SWOT ANALYSIS
The SWOT analysis for this manufacturing business plan is as follows:
- Propriety software (Virtual Design Center)
- Potential for global customer base
- Manufacturing & production expertise
- Software development expertise
- Understanding of emerging technologies
- Understanding of target markets
- Competitive product pricing
- Exceptional quality and customer service
- Implementation of cost saving processes
- No company history
- Small initial customer base
- Lack of leverage with new relationships
Opportunities
- New products & processes
- Bringing new technology into the industry
- Developing a new reputation
- Hiring new talent
- New innovations and applications of our technology
- Impact of new legislation
- Technologies developed by competitors
- Challenges in building a talented staff
- Retaining key staff members
- Market demand fluctuations
5.0 STRATEGY & IMPLEMENTATION
5.1 philosophy.
Titus Mold Manufacturing’s business philosophy is to make the needs of our customers our main priority. It is our mission to provide our customers with fast turnaround, exceptional quality, unparalleled customer satisfaction and competitive pricing. With the introduction of our patented Virtual Design Center program and the unveiling of our modern design and manufacturing facility, we will position Titus Mold Manufacturing as a superbly innovative company and a future industry leader.
To achieve this position, we will implement our company’s plan to create a state-of-the-art mold-manufacturing facility and invest in the most accurate precision machinery available. We will implement the most comprehensive design software and set the highest standards of operational systems and quality control.
5.2 INTERNET STRATEGY
Our plan is to position Titus Mold Manufacturing as a technology-driven innovative company within the mold-manufacturing sector of the manufacturing industry. To do this, we are putting forth a great amount of time and resources into developing a premiere Web site. We are working with a design firm and have secured a domain name – TitusMolds.com. We have already initiated the process of integrating our Virtual Design Center into the site.
In addition to describing our manufacturing processes and design capabilities, we will feature numerous success stories and images of prototypes and molds we have produced. Our site will also include a simple online form to complete for custom quotes as well as a generic form to submit questions and comments.
Our vision is to create a Web site that will become an integral part of our marketing, sales and daily operations. We will use Wix to set up our site. This tool has all of the features we need, including the ability to create and edit the site very quickly. It also has ecommerce and other capabilities. Using Wix will also enable us to save money since we can create the site ourselves and will not have to hire a web designer.
5.3 MARKETING STRATEGY

In addition to conveying to our potential customers the fast turnaround, exceptional quality, unparalleled customer service and competitive pricing offered by Titus Mold Manufacturing, we will also position our company as future-minded and a leader in the integration of innovative technology into the mold manufacturing process.
Our marketing plan will include an initial publicity campaign that introduces our company and patented Virtual Design Center. Further, we will launch a comprehensive advertising campaign in automotive manufacturing and medical devise trade publications and related Web sites. The publicity campaign will be closely followed by a direct-mail campaign to targeted customers.
The other main component of our marketing plan will be to attend trade shows which will require booth construction and maintenance, marketing materials such as brochures, and promotional items such as pens with our logo.
To increase local awareness of our company and to foster a positive public perception, we will participate in and sponsor local charity events such as Walk for the Cure and March of Dimes and youth sports teams. We will also reach out to local high schools and colleges to offer internships and promote careers in manufacturing.
5.4 SALES STRATEGY
Titus Mold Manufacturing will build a sales team focused on securing new business in the short and long term. The sales team will be motivated by commissions and performance-based bonuses.
Under the direction of executive management, we will employ an outside sales staff as well as an inside sales staff, which will be cross-trained to handle general customer service calls. The outside sales staff will focus primarily on trade show attendance, comprehensive follow up, relationship building, closing deals, and securing referrals.
5.5 STRATEGIC ALLIANCES
We plan to develop strategic alliances with local and regional injection-molding manufacturing facilities that do not have mold-making capabilities within their facilities. One such alliance has been developed with Hilden Manufacturing Company located within our region. More are developing.
5.6 OPERATIONS
Our facility’s space will be divided in proportion to our needs and will include product development and engineering labs, mold shop, tool shop, quality control and testing area, inventory storage and administrative offices. Each area will be staffed with trained employees and wherever possible factory-floor technicians will be cross-trained. Our administrative offices will include space for executive, marketing and sales, accounting, information technology, security, maintenance, and human resource departments. To become a fully operational mold-manufacturing facility, we will require the following machinery and software.
- Viper, SLA 7000 & SLA 5000
- Eden260, Eden333 & Eden500V
- Vantage, Titan & Maxum
- RTV Tooling
By utilizing the latest precision machinery and software and superior operational and quality control processes such as LEAN Manufacturing, Rapid Prototyping and Manufacturing, and Six Sigma , Titus Mold Manufacturing will control costs while ensuring quality. Additionally, once we are operational, our company will become ISO 9001-2000 certified. Titus will also follow FDA requirements and comply with Medical Directive standards to further ensure quality control.
Operationally, our strengths lie in our knowledge and expertise within the manufacturing industry. We know what fixed assets we require and what regulations we must adhere to. However, while we cannot know for certain the quality of our managerial team at this point, we expect to hire and implement a top notch team. As previously mentioned, we have several promising prospects and will, of course, strive to recruit top talent.
The following is a list of business goals and milestones we wish to accomplish within the next three years.
- Secure necessary funds.
- Locate and lease suitable manufacturing facility.
- Purchase machinery, equipment and supplies.
- Hire skilled employees to complete our team.
- Set up shop and open for business.
- Successfully penetrate targeted markets.
- Secure contracts to achieve projected sales goals.
- Become a profitable company.
- Establish a solid reputation as an industry leader.
Our first major milestones will be securing funds and setting up our business. This is our primary focus right now. In three years, we hope to have established our company in the community and within our industry.
5.8 EXIT STRATEGY
Should management or our investors seek a business exit, there are several options we would be willing to pursue. Our company could most likely be sold to a manufacturing company that does not already have mold manufacturing capabilities. A management buyout could also be pursued once our business credit is firmly established.
6.0 MANAGEMENT ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
6.1 organizational structure.
Titus Mold Manufacturing understands the importance of a loyal and enthusiastic team to reduce turnover and increase productivity. Our company’s management philosophy will encourage responsibility and mutual respect. While we will present a strong decisive management team, we will also foster an atmosphere of genuine employee appreciation and open communication.
6.2 LEADERSHIP
Our company will be managed and run by our executive staff including Chief Executive Officer John Baker, President Michael Smith, and Vice President Susan Jones, as well as our Board of Directors. Our management staff of directors and supervisors will oversee daily operations. However, as a small manufacturing facility starting out, the CEO, President and VP will be responsible for the majority of purchasing, hiring, training, quality control, and additional day-to-day duties.
Additional key leaders will include directors of finance, marketing and sales, human resources, information technology and operations. While these positions remain unfilled at this time, we do have several extremely qualified candidates interested in joining with us in this new venture.
As we start our mold manufacturing business, we will implement a plan to hire management and production staff first and fill in with mid-level management and administrative staff as our budget and needs change.
6.3 BOARD MEMBERS & ADVISORS
Our Board of Directors is not yet fully formed. CEO John Baker will serve as Chairman. The board will consist of company owners (shareholders), officers and directors.
Duties of the Board of Directors may include:
- Establishing broad company policies and objectives.
- Selecting, appointing, and reviewing the performance of executive staff.
- Insuring the availability of adequate financial resources and approving annual budgets.
- Accounting to the stakeholders for the organization’s performance
We will actively seek individuals to sit on our Board of Directors who will have the ability to add to and advise our organization such as lawyers, accountants, and professionals in the automotive or medical fields.
7.0 FINANCIAL PLAN
7.1 requirements.
Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc. requires $4,450,000 to launch and operate. We are currently seeking funding from outside investors and business loans. We are also looking into additional options including supplier financing, deferred rent, subleasing space, partnerships, vending and client advance payment.
At this time, we have raised $450,000 in working capital and are seeking the additional funds to start our business. We have raised $150,000 in venture capital funds. In addition, co-owners John Baker, Michael Smith and Susan Jones have each invested $100,000 into the company.
7.2 USE OF FUNDS
The start-up funds will be used to cover operating costs including payroll, taxes, and utilities. Start-up funds will also be used to purchase capital expenditures such as leasehold improvements, software and machinery, which will produce future benefits for the company. Approximately forty percent will be spent on assets, while the other sixty percent will be spent on operations until we realize profitability.
7.3 INCOME STATEMENT PROJECTIONS
The accompanying income statement demonstrates our company’s profitability. Our income shows a gross profit margin of seventy-two percent. Our monthly operating expenses average $116,325. Projected net income will average $54,075 per month in our third year.
After completing a comprehensive break-even analysis, we will achieve our break-even point by the middle of year two.
7.4 CASH FLOW PROJECTIONS
The nature of our business requires that our company collect payment after the product is complete. So we have included the accompanying cash flow statement, which projects our monthly flow of cash. While we expect to reach break-even by our eighteenth month, it will take nearly two years to become cash flow positive.
7.5 BALANCE SHEET
Our balance sheet will depend greatly on our sources of capital. We expect to raise approximately $1.5 million through loans and $2.95 million through equity capital.
Our assets will be comprised of cash, leasehold improvements, equipment, software and other tangible assets.
7.6 ASSUMPTIONS
Our projections are based on the assumption that the manufacturing industry, particularly the medical and automotive industries, will continue to follow present trends. Industry regulation and government legislation is always poised to interfere with business projections, but there are no indications at this time to expect any negative influence to our projections. Additionally, we are not relying on new regulations or the passage of new legislation to enable our company to reach our projected numbers.
Get This Manufacturing Business Plan Example
Download this Manufacturing Business Plan free for easy editing in Microsoft Word, Google Docs or Apple Pages:
While you’re here, need a sample marketing plan? Download ours free:
- Marketing Plan Example
Like this? Share it with your network:
I need help with:, popular topics:.
- Learning SEO
- Generating Sales
- Writing a Marketing Plan
- Writing a Business Plan
- Leading My Team
- Free Marketing Webinars
- Starting My First Business
Got a Question?
Get personalized expert answers to your business questions – free.
Affiliate Disclosure : This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we get a commission if you decide to purchase something using one of our links at no extra cost to you.
You Might Also Like...

Should I Give a Discount on My Consulting Fees?

SEO Title Tag Makeover: 4 Powerful Examples

5 Steps to Design an Effective Employee Engagement Action Plan

4 Actionable Steps to Find a Mentor for Your Business

5 Effective Scheduling Tips To Boost Your Productivity

Business Coaching vs Executive Coaching: 10 Examples

7 Employee Satisfaction Secrets: Nurturing a Happy Small Business Team

Secure Your First 10 Investors: Step-by-Step Startup Guide

SEO Coaching and Marketing Courses
Get More Business
Marketing tools.
- SEO Keyword Tool
- MSP Website Content Kit
- Done-for-You Content
- Graphic Design Tool
- Webinar Automation
- Getting Referrals
- Hubspot Marketing Automation
Popular Downloads
- MSP Marketing Plan
- Life Coach Business Plan
- Consulting Business Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan
- Clothing Line Business Plan
- Restaurant Business Plan
- Personal Trainer Business Plan
- Trucking Business Plan
- Pizza Restaurant Business Plan
Free Guides
- B2B SaaS SEO Best Practices
- MSP SEO Marketing Playbook
- Buyer Persona Examples
- How to Increase Google Rankings
- New Client Welcome Package
- How to Create a Happy Customer
- Brand Development Guide
- SaaS Metrics Dashboard
- Marketing and SEO Videos
- Salary Calculator
- Executive Coaching Newsletter
- Contributing Content
- Affiliate Disclosure
Manufacturing Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Manufacturing Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Manufacturing business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Manufacturing companies.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Manufacturing business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Perfect Snacks, located in Lincoln, Nebraska, is a food manufacturing company that specializes in the production of snack foods and packaged goods. We manufacture an extensive line of snack products, including trail mix, gummies, and chocolate. Our company focuses on quality and only uses the best natural ingredients in our products. We will primarily sell our products to grocery stores and other establishments that sell snacks, but will also sell bulk orders to individual customers through our website.
Perfect Snacks was founded by Joe Boseley. Joe has been working on the manufacturing company concept over the past few years and began networking with grocery store clients and locating the land to build his manufacturing and distribution center. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own manufacturing company.
Product Offering
Perfect Snacks will manufacture an extensive list of sweet, salty, and healthy snacks. Some of our initial products will include:
We will primarily sell our products to grocery stores, recreation centers, and other businesses that sell snacks in bulk. Consumers can find our products in stores or buy them in bulk on our website.
Customer Focus
Perfect Snacks will primarily serve the residents of Lincoln, Nebraska. The community has a large population of families and children, who are the primary consumers of snack foods. Therefore, we will market our products to recreational centers, schools, grocery stores, and other establishments that sell snacks to children and their parents.
Management Team
Perfect Snacks is owned by Joe Boseley, a local entrepreneur who has worked in various warehouses and manufacturing companies in Lincoln, Nebraska. Working in the manufacturing industry and in warehouses, Joe is very familiar with the processing and distribution of packaged foods. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own manufacturing company.
Joe will utilize his past experience with developing staff roles and functions. He is also very familiar with the manufacturing equipment and plans to purchase the latest technology that is efficient and cost effective. His contacts have allowed him to gain concrete Letters of Intent from local supermarket chains to have his manufactured goods in their stores.
Success Factors
Perfect Snacks will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Taste: Perfect Snacks’ snack products will be made with the highest quality ingredients and offer quality over quantity.
- Price: Perfect Snacks is able to offer the highest quality snacks at a competitive price point.
- Community Relations: Perfect Snacks will be a pillar in the community and be heavily involved in family-related activities in the area. It will sponsor events, provide snacks for schools and daycares at a discounted price, and donate a portion of its proceeds to area family-related charities and organizations.
- Proprietary Technology: Perfect Snacks will invest heavily on the latest technology to manufacture the snack foods for distribution. It will ensure the food products are made safely and free from any harmful chemicals and ingredients.
Financial Highlights
Perfect Snacks is seeking a total funding of $1,200,000 of debt capital to open its manufacturing company. The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures, salaries, marketing expenses, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Manufacturing facility design/build-out: $400,000
- Equipment and supplies: $375,000
- Initial inventory: $100,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $250,000
- Marketing costs: $50,000
- Working capital: $25,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Perfect Snacks.
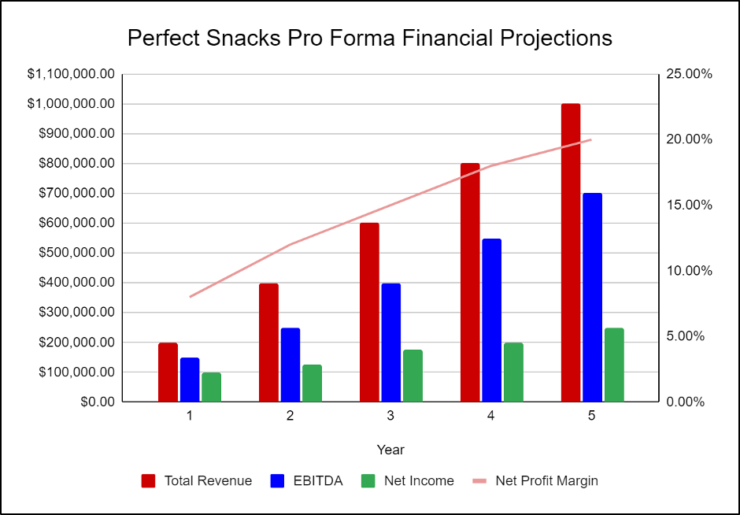
Company Overview
Who is perfect snacks, perfect snacks history.
After conducting a market analysis, Joe Boseley began surveying the local vacant warehouse space and decided on a parcel of land to construct the warehouse and distribution center. Joe incorporated Perfect Snacks as a Limited Liability Corporation on January 1st, 2023.
Once the land is acquired for the warehouse space, construction can begin to build-out the manufacturing facility.
Since incorporation, the Company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located a vacant lot that would be ideal for a manufacturing facility
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Hired a general contractor and architect for the build-out of the warehouse, small office, and distribution area
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Determined beginning inventory
- Attained Letters of Intent from supermarket clients
- Began recruiting key employees
Perfect Snacks Services
Industry analysis.
The Manufacturing sector’s performance is largely attributable to the value of the US dollar, commodity prices, policy decisions and US manufacturing capacity. Food manufacturing has a history of success as it produces a basic human need. According to Grand View Research, the industry is currently valued at $121 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 9.5% from now until 2030.
Commodity prices are currently stabilizing from coronavirus-induced volatility and renewed demand, both in the United States and global economies, which is anticipated to facilitate revenue expansion for manufacturers. Moreover, shifting technological change in the Manufacturing sector is anticipated to benefit large, developed economies, such as the United States. Therefore, now is a great time to start a new food manufacturing company in the U.S.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Perfect Snacks will serve the community residents of Lincoln, Nebraska and its surrounding areas. The community of Lincoln, Nebraska has thousands of households that have children. Statistics show that the main consumers of snack products are children of all ages. They are regularly placed in school lunchboxes, afterschool snacks and programs, and at weekend sporting events. Therefore, we will market to locations where snacks are bought by children or their parents, such as grocery stores, recreational centers, and schools.
The precise demographics Lincoln, Nebraska is as follows:
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,680,988 | 100% |
| Male | 838,675 | 49.9% |
| Female | 842,313 | 50.1% |
| 20 to 24 years | 114,872 | 6.8% |
| 25 to 34 years | 273,588 | 16.3% |
| 35 to 44 years | 235,946 | 14.0% |
| 45 to 54 years | 210,256 | 12.5% |
| 55 to 59 years | 105,057 | 6.2% |
| 60 to 64 years | 87,484 | 5.2% |
| 65 to 74 years | 116,878 | 7.0% |
| 75 to 84 years | 52,524 | 3.1% |
Customer Segmentation
Perfect Snacks will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Grocery stores and recreational centers
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Perfect Snacks will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Snacks N More
Snacks N More is another local manufacturing company that provides snack food to the immediate area. Established over thirty years ago, the company has the knowledge and expertise in food processing, commercialization, and packaging. They are known as a recognized ingredient supplier for the foodservice industry. Their portfolio of products include a variety of nuts, snacks, confections, and dry-blend ingredients. As a private label manufacturer, Snack’s More produces a full line of non-chocolate candy, nuts, and fruit-flavored snacks. The company is known for their fruit flavored snacks, dried raisins, nut mixes, and producing ingredients for local restaurants and establishments. Their line of nuts and dried fruits are often used for baking purposes.
Jaxon’s Candy
Jaxon’s Candy is a manufacturer of all things candy related. As a contract manufacturer, the company works with many companies to create their custom designed confections. Their large 50,000 square foot facility produces over 300,000 pounds of candy every month. All of the products are highly concentrated either in sugar or chocolate, or both. Jaxon’s Candy also designs and manufactures their own custom packaging. The candy produced is also kosher certified, gluten free, peanut free, and non-GMO.
Jaxon’s Candy currently manufactures candy for the following brands – Tommy Candy, Laffy Town, Chocowhoawhoa, Jellylicious, Healthee Candeee, and Sticky Teeth. Jaxon’s Candy can be found in grocery stores and convenient stores along the west coast of the United States.
Gimmy Candy
Gimmy Candy is located in the midwestern portion of the United States and boasts a facility of over 1 million square feet. Their fleet of transportation trucks distributes throughout the continental United States and is considered one of the largest candy manufacturers in the country. Their product portfolio includes assorted chocolates, gummy candy, hard candy, fruit candy, as well as gums and mints. Gimmy Candy was established in 1947 and has grown to be a model of manufacturing companies the industry uses as a model of sustainability and profitability. Their lineup of candy products can be found in every single grocery store and convenient store in the country. Gimmy Candy is considering expanding its distribution globally and start exporting its candy products to Asia, Canada, Europe, and South America. As one of the largest privately held companies in the United States, Gimmy Candy is also considered a top employer in the country and offers its employees a generous benefits package.
Competitive Advantage
Perfect Snacks will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Perfect Snacks will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Fresh and comforting taste
- Community family advocate
- Developed with proprietary technology
- Manufactured with fresh, quality ingredients
- Affordable price
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Perfect Snacks is as follows:
Social Media
Perfect Snacks will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media accounts. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Perfect Snacks will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the snack products. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Major Publications
We will also invest in advertising in selected larger publications until we have achieved significant brand awareness. Advertisements such as billboards and commercials will be shown during peak tv watching time and the billboards will be placed in highly trafficked areas.
Sponsorships
Perfect Snacks will also invest in sponsoring certain athletic and school events so that their banners and collateral material are displayed all over the event where numerous parents and children are at.
Perfect Snacks’s pricing will be moderate so consumers feel they receive great value when purchasing our snack products.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Perfect Snacks.
Operation Functions:
- Joe Boseley will be the CEO of Perfect Snacks. He will oversee the general operations and executive aspects of the business.
- Joe is joined by Candace Smith who will act as the warehouse manager. She will train and manage the staff as well as oversee general production of our products.
- Joe will hire an Administrative Assistant, Marketing Manager, and Accountant, to handle the administrative, marketing, and bookkeeping functions of the company.
- Joe will also hire several employees to manufacture our products and maintain the equipment and machinery.
Milestones:
Perfect Snacks will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
- 02/202X Finalize lease agreement
- 03/202X Design and build out Perfect Snacks
- 04/202X Hire and train initial staff
- 05/202X Kickoff of promotional campaign
- 06/202X Launch Perfect Snacks
- 07/202X Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Perfect Snacks’s revenues will come primarily from its snack food sales. The company will sell the packaged snacks in local grocery stores, convenience stores, and other locations. As the company’s revenues increase, it will look to gain a wider distribution area.
The land purchase, equipment, supplies, opening inventory, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Perfect Snacks. Other cost drivers include taxes, business insurance, and marketing expenditures.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average order value: $250
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Manufacturing Business Plan FAQs
What is a manufacturing business plan.
A manufacturing business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your manufacturing business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Manufacturing business plan using our Manufacturing Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Manufacturing Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of manufacturing businesses , some examples include: Garment manufacturing, Food product manufacturing, Diaper manufacturing, Tile manufacturing, and Toy manufacturing.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Manufacturing Business Plan?
Manufacturing businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Manufacturing Business?
Starting a manufacturing business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Manufacturing Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed manufacturing business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your manufacturing business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your manufacturing business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Manufacturing Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your manufacturing business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your manufacturing business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Manufacturing Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your manufacturing business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your manufacturing business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.

Manufacturing Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Manufacturing Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 7,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their manufacturing businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a manufacturing business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your manufacturing business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Manufacturing Company
If you’re looking to start a new manufacturing business, or grow your existing manufacturing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your manufacturing business in order to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Manufacturing Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a manufacturing business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
Personal savings is the other most common form of funding for a manufacturing business. Venture capitalists will usually not fund a manufacturing business. They might consider funding a manufacturing business with a national presence, but never an individual location. This is because most venture capitalists are looking for millions of dollars in return when they make an investment, and an individual location could never achieve such results. With that said, personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for manufacturing businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a manufacturing company.
If you want to start a manufacturing business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below we detail what you should include in each section of your own business plan:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of manufacturing business you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a manufacturing business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of manufacturing businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the manufacturing industry. Discuss the type of manufacturing business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of business you are operating.
There are many types of manufacturing businesses, such as:
- Clothing manufacturing
- Garment manufacturing
- Food product manufacturing
- Diaper manufacturing
- Tile manufacturing
- Toy manufacturing
- Soap and detergent manufacturing
- Mobile accessories manufacturing
- Mattress manufacturing
- Bicycle manufacturing
- Pillow manufacturing
- Brick manufacturing
- Toilet paper manufacturing
- Furniture manufacturing
- Peanut butter manufacturing
- Cosmetics manufacturing
- Footwear manufacturing
In addition to explaining the type of manufacturing business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of customers served, number of positive reviews, number of wholesale contracts, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the manufacturing industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the manufacturing industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section:
- How big is the manufacturing industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your manufacturing business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of target market segments: wholesalers, other manufacturers, exports, retailers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of manufacturing business you operate. Clearly, retailers would respond to different marketing promotions than export markets, for example.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most manufacturing businesses primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Manufacturing Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other manufacturing businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes manufacturers in other niches, as well as those vertically integrated businesses that make their own product. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other manufacturing businesses with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be house flippers located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of products do they manufacture?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide high quality manufacturing practices?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a manufacturing business, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of manufacturing company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to manufacturing, will you provide R&D, design, prototyping or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your manufacturing company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your manufacturing business located near a distribution hub, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your manufacturing business, including sourcing inputs, designing processes, managing production, coordinating logistics and meeting with potential buyers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to secure your 1,000 th contract, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your manufacturing business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your manufacturing business’ ability to succeed, a strong team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing manufacturing businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in manufacturing or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you offer short-run production, or will you focus strictly on long-run? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your manufacturing business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a manufacturing business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your production facility blueprint, or capabilities specifications.
Putting together a business plan for your manufacturing business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the manufacturing industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful manufacturing business.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Manufacturing business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Manufacturing Business Plan PDF Example
- May 7, 2024
- Business Plan

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful manufacturing business. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your manufacturing business’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a manufacturing business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the manufacturing industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your manufacturing business concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
Our manufacturing business plan covers all essential aspects necessary for a comprehensive strategy. It details operations, marketing strategy , market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts.
- Executive Summary : Provides an overview of the manufacturing company’s business concept, market analysis , management, and financial strategy.
- Facilities & Equipment: Describes the facility’s capabilities, machinery, and technological advancements.
- Operations & Supply: Outlines the production processes, supply chain logistics, and inventory management.
- Key Stats: Offers data on industry size , growth trends, and market positioning.
- Key Trends: Highlights significant trends impacting the industry, such as automation and localization.
- Key Competitors : Analyzes primary competitors and differentiates the company from these rivals.
- SWOT: Analyzes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Marketing Plan : Outlines tactics for attracting new contracts and maintaining client relationships.
- Timeline : Sets out key milestones from inception through the first year of operations.
- Management: Information on the management team and their roles within the company.
- Financial Plan: Projects the company’s financial performance over the next five years, detailing revenue, profits, and anticipated expenses.
{{product_image|large}}
Manufacturing Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
{{product_image|medium}}
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary introduces your manufacturing business plan, offering a concise overview of your manufacturing facility and its products. It should detail your market positioning, the range of products manufactured, the production process, its location, size, and an outline of day-to-day operations.
This section should also explore how your manufacturing business will integrate into the local and broader markets, including the number of direct competitors within the area, identifying who they are, along with your business’s unique selling points that differentiate it from these competitors.
Furthermore, you should include information about the management and co-founding team, detailing their roles and contributions to the business’s success. Additionally, a summary of your financial projections, including revenue and profits over the next five years, should be presented here to provide a clear picture of your business’s financial plan.
Make sure to cover here _ Business Overview _ Market Overview _ Management Team _ Financial Plan
Dive deeper into Executive Summary
Business Overview
Facilities & equipment.
Describe your manufacturing facility. Highlight its design, capacity, and technology. Mention the location, emphasizing accessibility to transport routes. Discuss advantages for efficiency and cost management. Detail essential equipment and its capabilities.
Operations & Supply Chain
Detail product range. Outline your operations strategy for efficiency and scalability. Discuss supply chain management. Highlight sourcing of materials, inventory control, and logistics. Emphasize strong partnerships with suppliers and distributors.
Make sure to cover here _ Facilities & Equipment _ Operations & Supplies

Market Overview
Industry size & growth.
Start by examining the size of the manufacturing industry relevant to your products and its growth potential. This analysis is crucial for understanding the market’s scope and identifying expansion opportunities.
Key Market Trends
Proceed to discuss recent market trends , such as the increasing demand for sustainable manufacturing processes, automation, and advanced materials. For example, highlight the demand for products that utilize eco-friendly materials or energy-efficient production techniques, alongside the rising popularity of smart manufacturing.
Key Competitors
Then, consider the competitive landscape, which includes a range of manufacturers from large-scale enterprises to niche firms. For example, emphasize what makes your business distinctive, whether it’s through advanced technology, superior product quality, or specialization in certain manufacturing niches. This section will help articulate the demand for your products, the competitive environment, and how your business is positioned to thrive within this dynamic market.
Make sure to cover here _ Industry size & growth _ Key competitors _ Key market trends

Dive deeper into Key competitors
First, conduct a SWOT analysis for your manufacturing business. Highlight Strengths such as advanced production technology and a skilled workforce. Address Weaknesses, including potential supply chain vulnerabilities or high production costs. Identify Opportunities like emerging markets for your products or potential for innovation in production processes. Consider Threats such as global competition or economic downturns that may impact demand for your products.
Marketing Plan
Next, develop a marketing strategy that outlines how to attract and retain customers through targeted advertising, trade shows, digital marketing, and strategic partnerships. Emphasize the importance of showcasing product quality and technological advantages to differentiate your business in the market.
Finally, create a detailed timeline that outlines critical milestones for your manufacturing business’s launch, marketing initiatives, customer acquisition, and expansion goals. Ensure the business progresses with clear direction and purpose, setting specific dates for achieving key operational and sales targets.
Make sure to cover here _ SWOT _ Marketing Plan _ Timeline

Dive deeper into SWOT
Dive deeper into Marketing Plan
The Management section focuses on the manufacturing business’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the manufacturing business toward its financial and operational goals.
For your manufacturing business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.

Financial Plan
The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your manufacturing business’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your manufacturing business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here _ Profit and Loss _ Cash Flow Statement _ Balance Sheet _ Use of Funds

Related Posts

Pro One Janitorial Franchise Costs $9K – $76K (2024 Fees & Profits)
- July 5, 2024

Dance Studio Business Plan PDF Example
- June 17, 2024

Carpet and Upholstery Cleaning Business Plan PDF Example
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
Getting started: A guide to creating a manufacturing business plan
What is a manufacturing business plan.

A manufacturing business plan is a formal document that outlines the goals and objectives of your business. It includes detailed information about your:
- Products or services
- Target market
- Marketing strategy
- Financial projections
- Operational details
The purpose of a business plan is to give you a roadmap to follow as you build and grow your business. It forces you to think through every aspect of your venture and identify potential problems or roadblocks before they happen.
Manufacturing business plans can also be used to attract investors or secure funding from lenders. If you are looking for outside financing, your business plan needs to be even more detailed and include information on your management team, financial history, and expected growth.
Ideally, you should update your business plan yearly to ensure that it remains relevant and accurate. As your business grows and changes, so too should your plan.
Why does a manufacturing company need a business plan?

No matter how simple or complex your ideas may be, you need a plan, or they will never become a reality. A business plan will clearly understand your costs, competition, and target market. It will also help you to set realistic goals and track your progress over time.
Let’s look at a manufacturing strategy example. You have a great idea that you think will revolutionize the automotive industry . Your new safety harness will be made from a lightweight, yet incredibly strong, material that cannot be cut or torn. You are confident that your product will be in high demand and generate a lot of revenue.
But before you walk into Ford or Toyota to try and get a purchase order , you need to have a plan. You must know:
- How much will it cost to produce your product
- How many units do you need to sell to break even
- Who is your target market is
- What is your competition selling
- How will you reach your target market
You also need to clearly understand the regulatory landscape and what it takes to bring a new product to market. All of this information (and more) should be included in your business plan.
This is not just a document that you create and forget about. It is a living, breathing tool that should be used to guide your actions as you build and grow your business.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Every manufacturing business plan will be different, but almost always, they will include the same five components:
Executive summary
Company description, products and services, market analysis.
- Financial plan
Let’s take a closer look.
The executive summary is the first section of your business plan, but it is typically written last. This is because it should be a concise overview of everything that follows, and you can only do that once you have completed the rest of your plan.
Include the following in your executive summary:
- The problem that your product or service solves
- Your target market
- Your unique selling proposition (what makes you different from your competitors?)
- Your manufacturing business model (how will you make money?)
- Your sales and marketing strategy
- A brief overview of your financial projections
Someone should be able to quickly scan through your executive summary and have a pretty good understanding of what your business is and how it plans to be successful.
This is where you can get a bit more creative, explaining your company’s history, mission, and values. You will also include information on your team or management structure.
It can be simple but should inspire faith in your ability to execute your business plan.
You will need to provide a detailed description of your product or service, as well as any unique features or benefits that it offers. You should also include information on your manufacturing process and quality control procedures.
If you have any patents or proprietary technology, they should be listed here as significant assets for your business.
For example, let’s say you are planning on creating a brand-new line of disposable coffee cups. The dimensions, materials, and other specifications would be listed here, along with any unique benefits (such as being made from recycled materials).
You might also include information on your manufacturing process, such as the fact that the cups will be produced in a certified clean room or that you will employ workers local to where the product is sold.
Chances are, you started down this path because you realized that there was a market opportunity for your product or service. In this section, you will need to provide detailed information on the opening, as well as the analysis that convinced you to pursue it.
This should include:
- Market size (current and projected)
- Key market segments
- Customer needs and wants
- Competitive landscape
This is where you will need to do your homework, as you will be justifying your business decision to enter this particular market. The more data and analysis you can provide, the better.
For our coffee cup example, the market analysis might include:
- Information on how many cups are used every day
- Projected growth
- Key segments (such as office workers or on-the-go consumers)
- Customer needs (such as convenience or sustainability)
It would also examine the competitive landscape, including both direct and indirect competitors.
Financial plan
You’re in this to make money, and so are your potential investors. In this section, you will need to provide detailed information on your manufacturing business model and how it will generate revenue. This should include:
- Initial investment
- Sales forecast
- Carrying costs
- Pricing strategy
- Expense budget
You will also need to provide information on your long-term financial goals, such as profitability or break-even point. Discuss production line details, inventory management strategies , and other factors impacting your bottom line.
How to write a business plan for a manufacturing company

The process of creating a business plan for a manufacturing company is similar to any other type of business. However, there are some key considerations to keep in mind.
First, you need to understand your industry and what it will take to be successful in it. This includes understanding the competitive landscape, the costs of goods sold , and the margins you can expect to achieve.
You also need to have a clear understanding of your target market and what needs or wants your product or service will address. This market analysis should include information on your target customer’s demographics, psychographics, and buying habits.
While there will be many things specific to your company, here are five questions to answer for each of the sections listed above.
Executive summary:
- What is the problem that your company will solve?
- How will your company solve that problem?
- Who are your target customers?
- What are your key competitive advantages?
- What is your business model?
Company description:
- What is the legal structure of your company?
- What are your company’s core values?
- What is your company’s history?
- Who are the key members of your management team?
- Where is your manufacturing facility located?
Products and services:
- What product or service does your company offer?
- How does your product or service solve the problem that your target market has?
- What are the key features and benefits of your product or service?
- How is your product or service unique from your competitors?
- What is the production process for your product or service?
Market analysis:
- Who is your target market?
- What needs or wants does your target market have that your product or service will address?
- What is the size of your target market?
- How do you expect the needs of your target market to change in the future?
- Who are your key competitors, and how do they serve the needs of your target market?
Financial plan:
- What are the start-up costs for your company?
- How will you finance your start-up costs?
- What are your monthly operating expenses?
- What is your sales forecast for the first year, and how does that compare to your industry’s average sales growth rate?
- What are your gross margin and profit targets?
Even if you do nothing but answer these questions, you’ll be well on your way to creating a thorough manufacturing business plan.
How to stabilize your growth
When getting started, managing your business with spreadsheets might be okay. But, once sales and manufacturing orders start to increase, the inefficiencies of manually managing your business come to light. That’s why many turn to automation to keep their manufacturing on track.
Common mistakes to avoid
However, new manufacturing entrepreneurs often fall into a handful of traps when creating their business plans.
- Not doing enough research – You can’t know everything about your industry, but you should do your best to understand as much as you can before writing your business plan. This means talking to experts, reading trade publications, and studying the competition
- Not being realistic – It’s important to be optimistic when starting a new business, but you also need to be realistic. This is especially true when it comes to financial projections. Don’t overestimate the amount of revenue you will generate or underestimate the costs of goods sold
- Not having a clear understanding of your target market – You need to know who you are selling to and what needs or wants your product or service will address. This market analysis should include information on your target customer’s demographics, psychographics, and buying habits
- Failing to understand your competition – You need to know who your competitors are, what they are offering, and how you can differentiate yourself. This information will be critical in developing your marketing strategy
- Not having a clear vision for the future – Your manufacturing business plan should include a section on your long-term goals and objectives. What does your company hope to achieve in the next five years? Ten years? Twenty years?
Creating a business plan for manufacturing can be simple. It can be quite simple if you break it down into smaller pieces.
Once you have it in place, staying on track can be quite a bit more difficult. By using ERP software like Katana , you can track all of your key metrics in real time, avoid any potential issues, and make course corrections as needed.
To start following your plan and creating a successful manufacturing company, get a Katana demo today.
Table of contents
Manufacturing guide.
1. What is manufacturing
1. 1. Production vs. manufacturing
1.2. Production scheduling software
1.3. Production tracking software
2. How to start a manufacturing business
2.1.How to manufacture a product
2.2. Manufacturing best practice
2.3. A guide to creating a manufacturing business plan
2.4. Manufacturer ecommerce
2.5. Marketing for manufacturers
2.6. Manufacturing business processes
2.7. Food manufacturing
2.8. Small business manufacturing software
3. Manufacturing processes
3.1. Job shop manufacturing
3.2. Production quality control checklist
4. Lean manufacturing principles
4.1. Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing
4.2. Tips to reduce manufacturing waste
4.3. Manufacturing KPIs
5. Light manufacturing
6. Advanced manufacturing
7. IoT in manufacturing
8. Manufacturing challenges
9. Total manufacturing cost
9.1. Manufacturing overhead formula
9.2. Manufacturing inventory software
10. Good manufacturing practices
11. MRP systems
11.1. MRP in supply chain management
11.2. Best MRP software
12. Manufacturing ERP systems
12.1. Best ERP software for manufacturing
12.2. Manufacturing execution systems (MES)
More guides from Katana

Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control
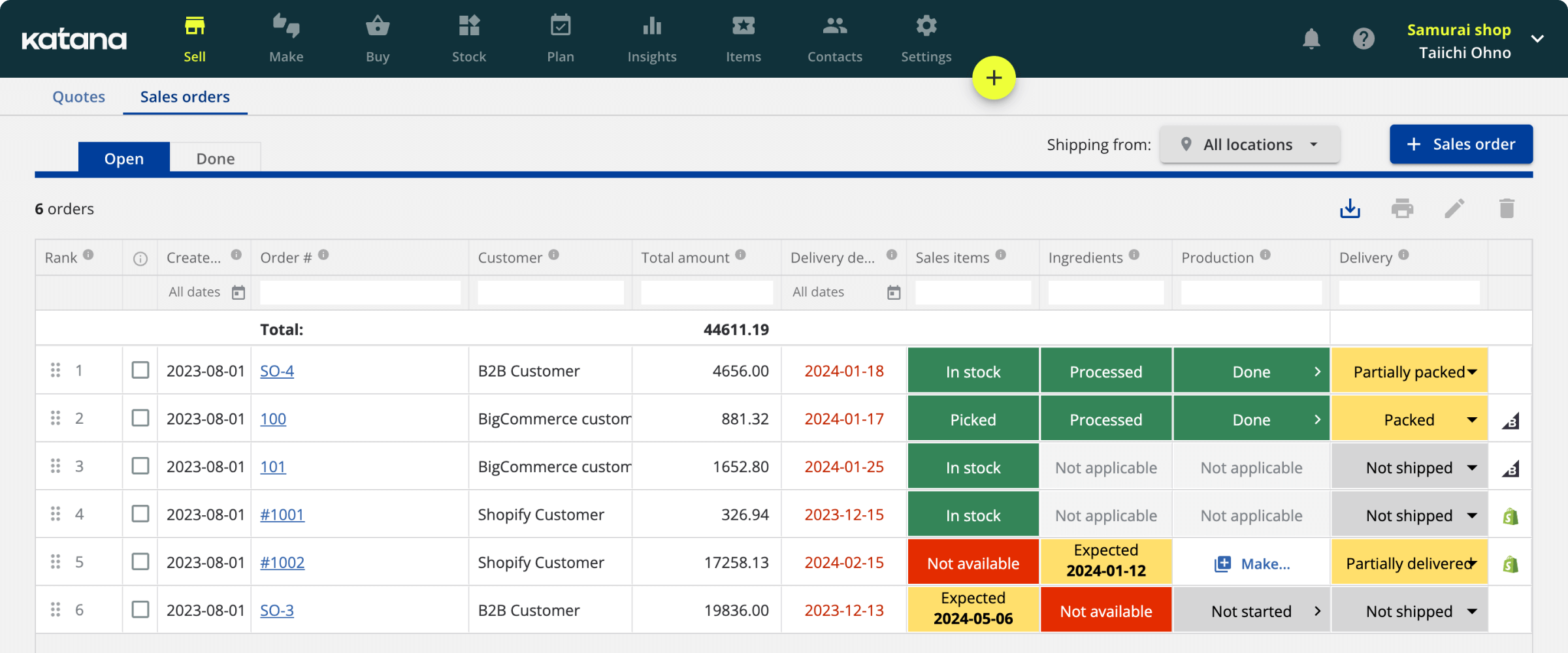
Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a manufacturing company can be an exciting but challenging endeavor. To ensure success, you need a solid business plan that covers all the essential aspects of your operations. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Companies comes in!
Our template provides a comprehensive framework for outlining your company's goals, conducting market analysis, projecting finances, and strategizing your operations. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be able to:
- Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and objectives
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand your target audience and competitors
- Develop financial projections and budgets to secure funding and attract investors
- Create operational strategies to optimize production, logistics, and quality control
Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting out, our Business Plan Template will guide you through the process of building a successful manufacturing company. Don't miss out on the opportunity to turn your vision into reality—get started with ClickUp today!
Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company Benefits
Creating a solid business plan is crucial for success in the manufacturing industry. By using the Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company, you can:
- Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and goals
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to identify target customers and competitors
- Develop a comprehensive financial plan, including revenue projections and cost analysis
- Outline your manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and quality control measures
- Present a professional and well-structured document to potential investors and lenders
- Guide strategic decision-making and ensure alignment with your long-term objectives
- Monitor and track progress towards your business milestones and objectives

Main Elements of Manufacturing Company Business Plan Template
When it comes to creating a comprehensive business plan for your manufacturing company, ClickUp has you covered with its Business Plan Template. Here are the main elements you'll find in this template:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of different sections of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add important details to your business plan using custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section, allowing you to easily organize and categorize information.
- Custom Views: Access different perspectives of your business plan using views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, making it easy to navigate and present your plan effectively.
- Document Collaboration: Collaborate with your team in real-time using ClickUp's Docs feature to work together on your business plan.
- Task Management: Break down your business plan into actionable tasks, assign them to team members, set due dates, and track progress using ClickUp's powerful task management features.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
If you're looking to create a business plan for your manufacturing company, follow these 6 steps using ClickUp's Business Plan Template:
1. Define your company's mission and vision
Start by clearly defining the mission and vision of your manufacturing company. What do you aim to achieve and how do you plan to do it? This will serve as the guiding principles for your business plan.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to outline your company's mission and vision statements.
2. Conduct market research
Thorough market research is essential to understand your target audience, competitors, and industry trends. Identify your niche, analyze customer needs, and assess the competitive landscape. This will help you position your manufacturing company effectively.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to compile and analyze market data, including customer demographics, competitor analysis, and industry trends.
3. Develop your product offerings
Outline the products and services your manufacturing company will offer. Determine the unique selling points of your offerings and how they address customer needs. Consider factors such as pricing, quality, and delivery timelines.
Use tasks in ClickUp to create a product development plan and assign tasks to team members responsible for designing, manufacturing, and testing the products.
4. Create a marketing and sales strategy
Define your marketing and sales strategies to promote your manufacturing company. Identify the channels and tactics you will use to reach your target audience. This may include digital marketing, trade shows, partnerships, or direct sales.
Use Goals in ClickUp to set specific marketing and sales objectives, such as lead generation targets or revenue goals.
5. Establish operational processes
Develop a plan for your manufacturing processes, including procurement, production, quality control, and logistics. Define the roles and responsibilities of your team members and ensure smooth coordination across departments.
Use Automations in ClickUp to streamline your operational processes by automating repetitive tasks and setting up notifications for key milestones.
6. Create financial projections
Project your financials, including revenue, expenses, and cash flow projections for the next few years. Consider factors such as production costs, pricing, sales volume, and market demand. This will help you assess the viability and profitability of your manufacturing company.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to track and visualize your financial projections, allowing you to monitor your company's performance and make informed decisions.
By following these steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be well-equipped to create a comprehensive and effective business plan for your manufacturing company.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
Entrepreneurs and business owners in the manufacturing industry can use the Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company to create a comprehensive plan for their business.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a solid business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize the different sections of your business plan, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Financial Projections, and Operational Strategies.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and visualize the timeline for completing each section of your business plan.
- Use the Business Plan View to have a comprehensive overview of your entire plan, with all the sections and details in one place.
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide you with step-by-step instructions and tips on how to effectively use the template and create a successful business plan.
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional information and track important details.
- Update statuses and custom fields as you make progress and receive feedback from stakeholders.
- Monitor and analyze your business plan to ensure it aligns with your goals and attracts investors.
- Business Plan Template for Distance Learning
- Business Plan Template for Medication Errors
- Business Plan Template for Little Caesars
- Business Plan Template for Technology
- Business Plan Template for Gym Owners
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide

Manufacturing Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Manufacturing Business Plan Template
If you want to start a Manufacturing business or expand your current Manufacturing company, you need a business plan.
The following Manufacturing business plan template gives you the key elements to include in a winning Manufacturing business plan.
You can download our business plan template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Below are links to each of the key sections of a sample manufacturing business plan. Once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors.
I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan
Comments are closed.
Manufacturing Business Plan Home I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan


Manufacturing Business Plan Template

What is a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A manufacturing business plan outlines the objectives, initiatives, and goals of a manufacturing business. It is used to guide the development and execution of a business strategy and to monitor progress towards achieving desired goals. The plan should address all aspects of the business, including marketing, production, personnel, operations, and financials.
What's included in this Manufacturing Business Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Manufacturing Business Plan template for?
This Manufacturing Business Plan template is designed to help manufacturers of all sizes and industries create a plan to launch, run and grow their business. It provides a framework to clearly define and measure the objectives, actions, and measurements that are necessary for success.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is an area of your business that requires extra attention in order to achieve success. Examples of focus areas can include increasing operational efficiency, improving product quality, or strengthening financial management.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
An objective is a goal that you want to achieve within a specific focus area. For example, under the focus area of operational efficiency, the objective could be to reduce shipping wait time.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
KPIs, or key performance indicators, are metrics that help to measure the success of the objectives. For example, to measure the success of the objective to reduce shipping wait time, the KPI would be to decrease the average shipping wait time by 30%.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects, or actions, are the steps necessary to achieve the KPIs. For example, to achieve the KPI of reducing the average shipping wait time, the action would be to analyze the current shipping process.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade is a strategy execution platform that makes it easy to plan, implement, and track progress towards achieving your manufacturing business plan. With Cascade, you can create strategies, assign tasks, track progress, and quickly see the results of your efforts.
manufacturing business plan example
The U.S. manufacturing industry has been a linchpin of the nation’s economic development, tracing its roots back to the Industrial Revolution. From humble artisan workshops, the U.S. manufacturing sector has evolved into sophisticated, technology-driven enterprises, marked by continual growth propelled by innovation, automation, and a steadfast commitment to producing top-quality goods.
Noteworthy among the leaders in this sector are manufacturing giants such as General Electric (GE), boasting diverse manufacturing interests spanning aviation, healthcare, power, and renewable energy. Boeing , a major player in aerospace and defense, is complemented by General Motors and Ford Motor Company, two automotive behemoths. Procter & Gamble (P&G) extends its influence in the consumer goods realm, while Johnson & Johnson takes center stage in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer goods. Caterpillar , IBM , 3M , and Honeywell International further enrich the manufacturing landscape with expertise in construction, technology, and diverse product offerings.
In business planning for manufacturing enterprises, meticulous strategies are imperative. Developing a robust manufacturing business plan involves careful consideration of factors such as production processes, supply chain management, and market positioning. Such plans serve as blueprints for success, encompassing key elements like quality control and financial projections . Recognizing the significance of a comprehensive business plan for manufacturing, companies employ various manufacturing business model and manufacturing plan examples tailored to their specific industry needs.
Business Plan for Manufacturing
A well-crafted manufacture business plan serves as the cornerstone for any manufacturing enterprise, offering a strategic roadmap for navigating the dynamic and competitive terrain of the production and industry landscape. While recognizing that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, using manufacturing business plan example becomes crucial for navigating the process effectively..
Manufacturing business plans take many forms including advanced manufacturing . The manufacturer business model is shifting as new production processes introduce updated deadlines and expectations.
How Technology is Transforming Production Business Plans
Crafting a quality business plan for a manufacturing company requires a strategic approach that integrates technology and business goals. Here are the key components:
Digital Twin Technology
By integrating digital twin technology into a business plan for production company, simulation and prototyping become integral components. This approach enables virtual testing before physical production, accelerating development timelines while ensuring cost-effective and high-quality outcomes.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Real-time monitoring powered by IoT sensors forms a cornerstone in manufacturing plans. This facilitates data-driven decision-making, optimizing performance, predicting maintenance needs, and upholding stringent quality control standards.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML )
The integration of AI and ML algorithms is paramount for predictive analytics and quality control. These technologies analyze production data, predict equipment failures, and guarantee the production of high-quality goods.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation elevate production line efficiency, reducing labor costs and enhancing precision. Making business plan revolves around embracing these technologies to streamline processes.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Through 3D printing, you can achieve intricate designs with precision. Leveraging nanotechnology enhances material properties at a molecular level, allowing your manufacturing business to surpass expectations in strength, weight, and durability.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies play a crucial role in training and maintenance. This can enhance employee skills and troubleshoot issues efficiently, contributing to the overall success of manufacturing operations.
By incorporating these technological advancements into your ultimate business plan for manufacturing business, you are positioned for sustained success in the digital age.
How to Start a Profitable Manufacturing Business [11 Steps]
By Nick Cotter Updated Feb 02, 2024

Business Steps:
1. perform market analysis., 2. draft a manufacturing business plan., 3. develop a manufacturing brand., 4. formalize your business registration., 5. acquire necessary licenses and permits for manufacturing., 6. open a business bank account and secure funding as needed., 7. set pricing for manufacturing services., 8. acquire manufacturing equipment and supplies., 9. obtain business insurance for manufacturing, if required., 10. begin marketing your manufacturing services., 11. expand your manufacturing business..
Performing a market analysis is a crucial step when starting a manufacturing business. It helps you understand the industry landscape, identify your target customers, and evaluate your competition. Here are some key points to consider:
- Industry Overview: Research the size, growth, trends, and outlook of the manufacturing sector relevant to your business.
- Customer Segmentation: Identify and categorize potential customers into segments based on demographics, needs, and purchasing behavior.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze your competitors' strengths and weaknesses, market share, and positioning to find your competitive edge.
- Supply and Demand: Assess the current supply and demand dynamics in your niche to forecast potential sales volumes.
- Regulatory Environment: Understand the regulatory requirements and standards that could impact your manufacturing processes and product compliance.
- Pricing Strategy: Evaluate how pricing works within your niche and what customers are willing to pay for your products.
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to identify internal and external factors that can affect your business.

Are Manufacturing businesses profitable?
It depends on the type of manufacturing business and a variety of other factors, including the size and scope of the business, the market demand for the products the business produces, the cost of raw materials, the cost of labor, and the cost of operating the business. In some cases, manufacturing businesses can be highly profitable, while in other cases they can be relatively unprofitable.
Creating a comprehensive manufacturing business plan is a critical step in establishing a successful operation. It offers a roadmap for turning your product idea into a tangible commodity and lays out the strategy for production, marketing, and financial management. Here are key elements to include in your manufacturing business plan:
- Executive Summary: Summarize your business goals, product offerings, and market potential, as well as your vision and mission statements.
- Business Description: Provide detailed information about your manufacturing business, including the type of products you plan to manufacture and your target market.
- Market Analysis: Research and describe your industry, market size, expected growth, and position within the context of supply and demand.
- Operational Plan: Outline the production process, the equipment you'll need, the facility requirements, and the supply chain logistics.
- Management Structure: Detail your business's organizational structure, the roles of the management team, and the expertise they bring to the business.
- Product Line: Describe your product(s), their life cycles, and any research and development activities.
- Marketing Strategy: Explain how you plan to attract and retain customers, your pricing strategy, and your sales and distribution channels.
- Financial Projections: Include projected income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets for the next 3-5 years.
- Funding Requirements: If seeking investment, specify the amount of funding needed and how it will be used.
How does a Manufacturing business make money?
A manufacturing business typically makes money by selling products that it produces. The business will usually incur costs associated with material, labor, overhead, and other expenses that contribute to the cost of the product. The business then sells the product for a price that is higher than the cost of production, creating a profit.
Developing a manufacturing brand is crucial for setting your business apart in a competitive market. Your brand is not just your logo or product; it's the entire experience customers have with your company. Here are some steps to help you craft a strong manufacturing brand:
- Define Your Brand Identity: Determine what your brand stands for, including its core values, mission, and unique selling proposition (USP). This will guide all other branding decisions.
- Design Your Brand Elements: Create a memorable logo, choose a color scheme, and develop a consistent visual identity that reflects your brand's personality and appeals to your target audience.
- Consistent Brand Messaging: Develop a brand voice and ensure all your communications, from marketing materials to packaging and customer service, convey your brand's message consistently.
- Build Brand Awareness: Use various marketing channels such as social media, trade shows, and PR to increase visibility and recognition of your brand.
- Foster Brand Loyalty: Deliver on your brand promises with high-quality products and excellent customer service to build trust and loyalty among your customers.
- Protect Your Brand: Register trademarks for your brand name, logo, and any other intellectual property to protect your brand legally.
How to come up with a name for your Manufacturing business?
Coming up with a name for a manufacturing business can be a daunting task. Consider the type of products you will be making and the overall feel of your business. Brainstorm words that sum up the essence of your business and then combine them to create a unique name. Take into consideration the domain name availability as well and make sure it's not already taken. With a bit of creativity, you can come up with a memorable and unique name for your manufacturing business.

Formalizing your business registration is a crucial step in establishing the legal structure of your manufacturing business. It involves several key procedures that vary by location, but typically include registering with state and federal agencies. Here's what you need to do:
- Choose a Business Structure: Decide whether your business will be a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation, or S corp. Each has different legal and tax implications.
- Register Your Business Name: File a DBA (Doing Business As) if your business will operate under a name different from your own. Check with your local government for specific requirements.
- Obtain an EIN: Register for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) with the IRS for tax purposes, unless you're a sole proprietor without employees.
- Register with State Agencies: Depending on your location and business structure, you may need to register with state revenue offices and obtain a state tax ID.
- Get Permits and Licenses: Check with your city or county for necessary manufacturing permits, business licenses, and zoning clearances.
- Understand Employer Responsibilities: If you plan to hire employees, register with your state labor department and learn about workers' compensation, unemployment, and other labor laws.
Resources to help get you started:
Explore crucial resources designed for manufacturing entrepreneurs aiming to gain insights on market trends, enhance operational efficiencies, and receive strategic advice for business expansion:
- Manufacturing.net: Provides the latest manufacturing news, trends, and technology advancements, including operational strategies for manufacturers. https://www.manufacturing.net/
- IndustryWeek: Offers in-depth articles and reports on manufacturing industry insights, growth strategies, and best practices. https://www.industryweek.com/
- ThomasNet News: Delivers up-to-date news and analysis across various manufacturing sectors, helping businesses stay ahead of industry shifts. https://www.thomasnet.com/news/
- The Manufacturer: Provides comprehensive coverage on manufacturing technologies, sustainability, leadership strategies, and market opportunities. https://www.themanufacturer.com/
- Manufacturing Leadership Journal: Offers strategic insights and examples of leadership and innovation within the manufacturing industry. Subscription required. https://www.manufacturingleadershipcouncil.com/leadership-journal/
- Modern Machine Shop: Focuses on the practical application of machining technology and operations best practices for metalworking professionals. https://www.mmsonline.com/
Starting a manufacturing business requires thorough compliance with various regulations. Acquiring the necessary licenses and permits is a critical step to ensure your business operates legally and smoothly. Here are some key actions to consider:
- Research local regulations: Check with your city, county, and state to understand the specific licensing requirements for your type of manufacturing business.
- Obtain a business license: Apply for a general business license, which is typically required to operate any form of business.
- Specialized permits: Depending on what you are manufacturing, you may need specialized permits related to health, safety, and environmental regulations.
- Building and zoning permits: Ensure that your manufacturing facility complies with local zoning laws and obtain any necessary building permits for construction or renovation.
- Fire department permit: You may need a permit from the fire department, especially if your business uses flammable materials.
- Register for taxes: Register with the appropriate state and federal authorities to obtain a tax identification number, and understand your obligations for sales, use, and excise taxes.
What licenses and permits are needed to run a manufacturing business?
The exact licenses and permits required to run a manufacturing business vary by location. Generally, businesses need to obtain a business license, permit, or registration with their local government. Depending on the type of products being manufactured, businesses may need to obtain additional licenses and permits from state and federal agencies. Additionally, businesses might need to obtain permits for wastewater, hazardous materials, and air/noise pollution control, depending on the type of manufacturing being done.
When starting a manufacturing business, it is crucial to keep your finances in order by opening a business bank account and securing the necessary funding. A dedicated business account will help you manage your cash flow and expenses effectively. Here's how to approach these essential steps:
- Choose the right bank: Research banks that offer services tailored to small businesses. Consider fees, accessibility, customer service, and any additional services that may be beneficial to your manufacturing business.
- Prepare the necessary documents: Generally, you'll need your business registration documents, EIN (Employer Identification Number), personal identification, and possibly a business plan when opening your account.
- Explore funding options: Determine how much capital you need to start and operate your business until it becomes profitable. Consider traditional loans, investors, grants, and crowdfunding as potential sources of funding.
- Present a solid business plan: When seeking funding, a detailed business plan is essential. It should outline your business model, market analysis, financial projections, and a clear explanation of how the funds will be used.
- Understand the terms: Before accepting any funding, fully understand the terms and conditions, interest rates, repayment schedules, and any potential impacts on your business's equity and control.
Setting the right pricing for your manufacturing services is a critical step that can determine the financial success of your business. It requires a careful balance between covering costs, offering competitive rates, and ensuring profitability. Here are some key points to consider when establishing your pricing strategy:
- Cost Analysis: Calculate all your manufacturing costs including raw materials, labor, overhead, equipment, and maintenance to determine the minimum price needed to break even.
- Market Research: Research competitors' pricing and understand the market demand to set prices that are competitive yet profitable.
- Value-Based Pricing: Consider the value your services provide to customers and price accordingly. If your services offer unique benefits or superior quality, you can command higher prices.
- Volume Discounts: Implement volume discounts to attract larger orders, but ensure they don't erode your profit margins significantly.
- Dynamic Pricing: Be flexible with your pricing strategy to adapt to changes in market conditions, material costs, and demand.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate how your pricing is structured to customers to build trust and avoid confusion.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure your pricing strategy complies with all relevant laws and regulations, including anti-trust and price discrimination laws.
What does it cost to start a Manufacturing business?
Initiating a manufacturing business can involve substantial financial commitment, the scale of which is significantly influenced by factors such as geographical location, market dynamics, and operational expenses, among others. Nonetheless, our extensive research and hands-on experience have revealed an estimated starting cost of approximately $88500 for launching such an business. Please note, not all of these costs may be necessary to start up your manufacturing business.
Securing the right manufacturing equipment and supplies is a critical step in setting up your manufacturing business. It determines the quality of your products, the efficiency of your production process, and ultimately, your ability to compete in the market. Follow these guidelines to ensure you make informed decisions when acquiring the necessary resources.
- Assess Your Needs: Begin with a thorough analysis of what equipment and supplies are essential for your manufacturing processes. Consider both current and future needs to accommodate growth.
- Research Suppliers: Look for reputable suppliers with quality equipment and reliable after-sales service. Compare prices, warranties, and reviews to find the best fit for your business.
- Consider Second-hand Equipment: To save costs, explore the option of purchasing or leasing certified pre-owned machinery. Ensure it is in good condition and can meet your production demands.
- Calculate ROI: Evaluate the return on investment for each piece of equipment. High-quality, efficient machines may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to greater savings and productivity in the long run.
- Plan for Maintenance: Set up a maintenance schedule to keep your equipment running smoothly, and stock up on essential spare parts to minimize downtime.
- Training: Ensure that your staff is adequately trained to operate the new equipment safely and efficiently. If necessary, arrange for supplier-provided training sessions.
List of Software, Tools and Supplies Needed to Start a Manufacturing Business:
- Accounting Software
- Financial Software
- Inventory Management Software
- Product Design Software
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
- Business Intelligence Software
- Equipment and Machinery
- Raw Materials
- Tools and Supplies
- Packaging Materials
- Labeling Materials
- Safety Gear
Ensuring that your manufacturing business is adequately insured is a crucial step in protecting your investment and mitigating risks. Different types of insurance cover various aspects of your business, from property damage to liability issues. Below are key points to guide you through obtaining the right business insurance for your manufacturing operations.
- Evaluate Risks: Understand the specific risks associated with your manufacturing business, such as equipment malfunctions, employee injuries, or product liability issues.
- Consult with Professionals: Seek advice from insurance agents or brokers who specialize in commercial policies for the manufacturing industry to find the best coverage options.
- Consider Necessary Policies: Common insurance types for manufacturers include general liability, product liability, property insurance, business interruption insurance, and workers' compensation.
- Customize Coverage: Tailor your insurance policy to fit the unique needs of your business, ensuring that all potential risks are addressed.
- Review and Update Regularly: As your manufacturing business grows and changes, regularly review and update your insurance coverage to keep it aligned with your current operations.
Once you have your manufacturing services up and running, it's crucial to let the world know about your capabilities and expertise. Effective marketing strategies will help you reach potential clients and establish your brand in the market. Below are some actionable steps to market your manufacturing services:
- Develop a strong brand identity: Create a memorable logo and consistent branding materials that reflect the quality and professionalism of your services.
- Build a professional website: Ensure that your website showcases your manufacturing capabilities, past projects, client testimonials, and contact information.
- Utilize social media: Engage with your audience on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook to showcase your work and industry expertise.
- Network at industry events: Attend trade shows, expos, and conferences to network with potential clients and partners.
- Create compelling content: Publish blog posts, case studies, and white papers that highlight your knowledge and the benefits of your services.
- Invest in digital marketing: Use SEO, pay-per-click advertising, and email marketing to reach a broader audience online.
- Leverage client referrals: Encourage satisfied customers to refer new clients by offering referral discounts or other incentives.
After laying a strong foundation and achieving a measure of success, it's time to focus on growth strategies for your manufacturing business. Expanding your operation can involve several steps, from scaling up production to exploring new markets. Consider the following points to guide your expansion:
- Invest in technology and automation to increase production efficiency and capacity while reducing labor costs.
- Explore new markets by conducting market research to identify untapped customer segments or geographical areas with demand for your products.
- Develop new products or enhance existing ones to meet changing customer needs and stay ahead of competition.
- Strengthen your supply chain by establishing relationships with additional suppliers or considering vertical integration to ensure a steady flow of materials.
- Consider partnerships or mergers with other businesses to combine resources, share risks, and expand your market presence.
- Seek external financing, if necessary, to fund your expansion. This can include loans, investors, or grants tailored for manufacturing growth.
- Expand your workforce and invest in employee training to maintain high-quality production as you scale up.
- Ensure compliance with all regulatory requirements that may come with expansion, such as environmental regulations and international trade laws.
All Formats
Plan Templates
15+ manufacturing business plan templates.
If you’re striking out on your own to start a business, whatever sort it might be, you will benefit from having a business plan template to work from. Such a tool will aid you in your crucial planning and takeoff stages. But there’s more to a business than getting started, and how you proceed from there will largely grow out of the conditions you’ve set for yourself in your business plan. This becomes especially important when you are getting into commodity production. Nowhere else is your command of production lines, personnel, and funding going to be so hard-pressed as in a simple manufacturing business.

Plan Template Bundle

- Google Docs
Construction Business Plan Template Bundle

Construction Business Continuity Plan Bundle

Construction Marketing Business Plan Template Bundle

Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Factory Business Plan Template

Business Plan Outline in Word

Printable Business Plan Template in Word

Simple Business Plan Template

Business Continuity Plan Template

Editable Marketing Business Plan Template

Retail Business Plan Template

Food Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Clothing Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Brick Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Manufacturing Business Continuity Plan Template

What Goes into a Manufacturing Business Plan?
- Executive summary . Here is where you condense your business’s intended purposes and goals. What is your mission-vision statement?
- Company description. Define the nature of your intended business, the commodities you are producing, where you will be located, etc.
- Market analysis . Where do you fit in the larger economy and what your relationship will be to existing businesses and competition? Define your target market and your role in fulfilling a real economic need.
- Strategy and implementation. Here you propose your methodology to achieve your goals.
- Management and organization. Assign your founding team and determine its structure and member responsibilities.
- Financial plan and projections. Estimate a budget and forecast your earnings.
- See also Manufacturing Business Marketing Plan to go from production to marketing.
- Also, see Manufacturing Business Continuity Plan above to establish a sustainable company.
Garment Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Furniture Manufacturing Business Plan Template

Manufacturing Business Marketing Plan Template

Manufacturing and Operation Plan Template

How to Use These Plan Templates
- They will give you the outline of an effective, comprehensive, and adequately detailed business plan.
- They will provide key insights into the real considerations you have to take into account per business type.
General FAQs
1. what is the manufacturing business plan, 2. what are the components of a manufacturing business plan.
- Executive Summary
- Business Description
- Products and Services
- Market Research
- Sales & Marketing
- Operations Financials.
3. What is the Purpose of a Manufacturing Business Plan?
4. who should your manufacturing business plan convince, 5 what are the different types of manufacturing businesses.
- Food, Beverage, and Tobacco
- Textiles, Leather, and Apparel
- Wood, Paper, and Printing
- Petroleum and Coal
- Chemicals, Plastics, and Rubber
- Metals and Machinery
- Computer and Electronics.
More in Plan Templates
Sample Swimming Coach & Instructor Resume Template
Sample deaf sign language teacher resume template, fancy cv template, classic cv template, plain cv template, attractive cv template, cfo cv template, nursing cv template, creative cv template, good cv template.
- 7+ Financial Plan Templates
- 10+ Operational Plan Templates
- 9+ Training Plan Templates
- 5+ Shooting Schedule Template
- 11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
- 9+ Interdisciplinary Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Continuity Plan Templates in Google Docs | Ms Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Compensation Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Executive Bonus Plan Templates in PDF
- 8+ Facility Management Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Diversity Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Corrective Action Plan Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
- 9+ Recruitment Agency Marketing Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Recruitment Marketing Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Student Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Templates
Manufacturing Business Plan
Published Jul.06, 2013
Updated Apr.23, 2024
By: Noor Muhammad
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
Do you want to start a Manufacturing business plan?
Have you been thinking about starting a manufacturing business? It’s a great plan if you are. Some of the most profitable businesses happen to be in the manufacturing line. So, you don’t need to worry about market involvement. However, to create a successful business, you will need a manufacture business plan.
Though it is very profitable to start a manufacturing business, you need some money to get it off the ground. If you have enough money, then you’re set. However, if you need capital, you need to apply for a bank loan for business.
Once you’re all set with the financial part of the business, you need to start developing a business plan. You can learn how to write a manufacturing business plan by taking help from this document.
Executive Summary
2.1 the business.
Henry Works will be a startup manufacturing business plan started and owned by Henry Langerman. The business will provide manufacturing services to people in and around Oregon. It will offer services like the development of manufacturing chains in different companies. It will also handle manufacturing for small-scale companies while consulting with medium-level businesses.
2.2 Management of Manufacturing Company
Provided that you have an idea, you will need a manufacturing business plan proposal to make that idea a reality.
For guidance, you can go through manufacturing business plan examples or even a woodworking business plan . You can also take help from an investment group in this business as they can guide you better in the financial aspect of the business.
In this manufacturing business plan pdf, we are providing all the necessary details necessary to make a business successful from the start.
2.3 Customers of Manufacturing Company
The customers of Henry Works will primarily be other businesses who will buy raw manufactured material from Henry Works and develop it the way they want at their end. Our main customer groups, in this case, will be:
- Distributors/Wholesalers
- Production/Merchandising Companies
- Smaller Manufacturing Units
2.4 Business Target
Our primary goal is to become a trustworthy manufacturing business that can cater to the needs of its customers at all times.
The monetary targets we want to achieve within the first five years of starting are as follows:

Company Summary
3.1 company owner.
Henry Works will be owned by Henry Langerman, who completed his MBA four years ago. After graduation, he was attached to a large consulting and manufacturing company for three years, where he learned all the fundamental principles of business in the real world. He then left his job for helping his dream of manufacturing business to start.
3.2 Why the Manufacturing company is being started
During his BA, Henry had noticed that it is costly to come by bulk material in Oregon. And after some research, he understood that it was because of a lack of manufacturing businesses around Oregon. Therefore, he decided to start working on a business continuity plan template for manufacturing.
3.3 How the Manufacturing company will be started
Step1: Plan Everything
Before starting a business, you need to develop a good business plan. Whether it is a business plan for a metal casting shop or a manufacturer business plan, it will guide you in starting up your business.
If you are wondering how to write a business plan pdf manufacturer for your business, you can take help from this business plan. For general guidance, you can also refer to a business plan written for sewing or a small manufacturing business plan. Through these business plans, you will plan out all the major stages of starting your business. And this will help you be prepared for anything that may come up.
Step2: Define the Brand
Recognition is key to a successful business. You need to ensure that your customers pay attention to your products and services. Therefore, you will have to establish a brand for your business that will attract your customers to your business.
Step3: Establish Your Corporate Office
Henry decided to buy a warehouse in the outskirts of Oregon to start his manufacturing business. He will now determine the inventory needed to start the company and the workforce required.
Step4: Establish a Web Presence
Social media and general online presence have become necessary to the existence of a business nowadays. Therefore, Henry will not only have a website developed for his business, but he will also hire a social media manager to keep up a business profile for Henry Works on all Social Media platforms.
Step5: Promote and Market
The final step in starting a business is to promote it through a stellar marketing plan.

| Legal | $301,100 |
| Consultants | $0 |
| Insurance | $23,000 |
| Rent | $45,000 |
| Research and Development | $10,000 |
| Expensed Equipment | $26,000 |
| Signs | $3,400 |
| Start-up Assets | $366,000 |
| Cash Required | $209,000 |
| Start-up Inventory | $39,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $240,000 |
| Long-term Assets | $203,000 |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $408,500 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $1,057,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $1,462,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $167,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $50,000 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $35,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | $18,000 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $58,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | $1,465,500 |
| Investor 1 | $0 |
| Investor 2 | $0 |
| Other | $0 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | $172,500 |
To start a manufacturing business, you need to figure out the services you will provide to your customers. That way, you can plan the steps of developing your startup manufacturing ideas in a better way.
A strong business manufacturing plan will help you map out your business to make it more efficient. There are many types of manufacturing business, and each has its services. Therefore, you can take help from this manufacturing business plan template to develop your plan. Alternatively, you can also take help from other business plans like solid semiconductor business plan etc. for further guidance.
For business ideas manufacturing of Henry Works, the primary services are listed below:
- Production of Raw Materials
We will offer manufacturing services to produce refined raw materials that can be used for developing other products. These raw materials will vary depending on our contracts with customers.
- Specialized End-Product Development
Henry Works will also offer the production of end-products with complete packaging facilities. However, if the product development involves complex or specific-domain processes, the work will be outsourced for retaining the best quality.
We will offer consulting services to manage production and supply chains for medium and large-scale companies so that they can obtain maximum efficiency at each stage.
- Development of Manufacturing Chains
We will offer services to develop and deploy a production chain that they can easily keep track of and stay independent for our small-scale business customers.
Marketing Analysis of Manufacturing Company
When you have decided to open a business, you will need to write a business proposal for manufacturing with a solid marketing analysis. Just like any other business, starting manufacturing business requires you to have an in-depth knowledge of your customers and market positions.
excellent work
excellent work, competent advice. Alex is very friendly, great communication. 100% I recommend CGS capital. Thank you so much for your hard work!
For writing a business continuity plan template manufacturing, you will need to pay attention to not only present market analysis but also information of past and future. If you want, you can take help from logging company business plan or diamond business plan or any other thorough business plan for further guidance.
Your business plan will help you identify your customer base, services, and how to attract the two. Therefore, focus on manufacturing definition business when developing your marketing plan.
Here, we have detailed the marketing plan and its details for Henry Works:
5.1 Market Trends
According to IBISWorld, there are more than 636000 manufacturing businesses, and they are increasing at a steady rate of 3.6% per year. According to NAM, the manufacturing industry also holds a market share of 11.39%. It means that the demand for manufacturing businesses is not going down any time soon. And you will have a good standing in the market for your business which will not decline in the coming years.
5.2 Marketing Segmentation
The potential customers of Henry Works are divided into the following groups:

Business plan for investors
5.2.1 distributors/wholesalers.
Our primary customers will be distributors or wholesalers to provide raw materials or finished products. These companies usually buy and sell in bulk, so they are expected to avail of our services frequently.
5.2.2 Retailers
Our second biggest customers will be retailers. We intend to sell to retailers directly for getting our products to the general public. We will also agree on contracts with retailers to produce products of their choice. Therefore, we expect to receive a fair amount of attention from these stores and companies.
5.2.3 Production/Merchandising Companies
Production and merchandising companies need raw materials to produce their specified merchandise. Therefore, we expect these customers to require our services quite often.
5.2.4 Small Manufacturing Units
Lastly, we will also offer our supplying and consultation services to smaller manufacturing units around Oregon to aid their production.
| Distributors | 31% | 34,500 | 41,400 | 49,680 | 59,616 | 71,539 | 10.00% |
| Retailers | 23% | 22,500 | 27,000 | 32,400 | 38,880 | 46,656 | 10.00% |
| Merch Companies | 24% | 21,700 | 26,040 | 31,248 | 37,498 | 44,997 | 10.00% |
| SMUs | 22% | 19,000 | 22,800 | 27,360 | 32,832 | 39,398 | 11.00% |
| 10% |
5.3 Business Target
- To become the most reliable manufacturing business in Oregon.
- To expand our business and open branches in other states of the US.
- To approach a net profit of $90k/month by the end of the first three years
- To achieve customer satisfaction above 90%.
5.4 Product Pricing
Our prices will be much lower than the imported materials brought into Oregon from other states. However, the quality will be the same or better but not lower. It will be one of the main standout points of Henry Works.
Marketing Strategy
To stand out amongst your competitors, you need to offer several advantages to your customers that the competition cannot. For this, you will need to refer to a business plan for manufacturing company. For general reference, you can also take help from business plan manufacturing and operations plan or business plan coal mining company .
Even If you want to open a small manufacturing business at home, you will still need a strong marketing strategy to make your business a success.
6.1 Competitive Analysis
- We provide the option of contracts to our customers to produce customized materials.
- We have fantastic customer service. We will cater to all the customer’s needs and issues and ask for feedback for further improvement.
- We will use green practices and machines for the production of goods.
- Our customers can book appointments with us through our website or reach out to us on our social media.
6.2 Sales Strategy
- We will advertise our company through Google Ads, billboards, word of mouth, and social media.
- We will offer wholesale prices to our customers with the best quality.
- We will also offer discounts to our first-time customers.
- Our customers can also reach out for a contract entailing the production of customized end-products.
6.3 Sales Monthly

6.4 Sales Yearly

6.5 Sales Forecast

Personnel plan
There are a lot of manufacturing ideas in the USA. But only a few are successful. That is because the value of a business is determined not only by the quality of its products but also by its workforce. Henry knew the importance of good employees. So, he incorporated strict criteria for selecting all company employees within the manufacturing business plan sample pdf.
7.1 Company Staff
- 1 Co-Manager to help in overall operations
- 8 Certified Machinery Operators
- 5 CIMS Certified Commercial Cleaners
- 2 Technicians to maintain the machinery
- 1 Web Developer to manage the online site
- 1 Sales Executives to organize and promote sales
- 1 Accountant
- 1 Receptionist
7.2 Average Salary of Employees
| Co-Manager | $60,000 | $66,000 | $72,600 |
| Machinery Operators | $342,000 | $376,200 | $413,820 |
| Commercial Cleaners | $182,000 | $200,200 | $220,220 |
| Technicians | $54,000 | $59,400 | $65,340 |
| Web Developer Expert | $23,000 | $25,300 | $27,830 |
| Sales Execs | $32,000 | $35,200 | $38,720 |
| Accountant | $26,000 | $28,600 | $31,460 |
| Receptionist | $30,000 | $33,000 | $36,300 |
Financial Plan
When writing a business plan for manufacturing, you also need to focus on the monetary details. There are a lot of low cost manufacturing ideas in the world, but not all of them are beneficial to your business. Therefore, to ensure your company’s efficient and smooth working, you need to develop a detailed financial plan. A financial plan will guide you in managing the available resources in your company, thereby preventing your business from becoming a manufacturing business for sale after significant losses.
Here we’re providing the detailed financial plan made for Pro Cleaning Services so that you can get an idea of the business finances.
8.1 Important Assumptions
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Current Interest Rate | 8.12% | 8.20% | 8.26% |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 8.40% | 8.44% | 8.47% |
| Tax Rate | 24.03% | 24.21% | 24.60% |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 |
8.2 Break-even Analysis

| Monthly Units Break-even | 5340 |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $132,500 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Per-Unit Revenue | $231.00 |
| Average Per-Unit Variable Cost | $0.62 |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $163,800 |
8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| TOTAL COST OF SALES | |||
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $719,000 | $790,900 | $869,990 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $145,000 | $148,000 | $156,000 |
| Depreciation | $2,300 | $2,350 | $2,500 |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Utilities | $2,900 | $3,000 | $3,100 |
| Insurance | $2,100 | $2,100 | $2,100 |
| Rent | $2,900 | $3,000 | $3,200 |
| Payroll Taxes | $24,000 | $25,000 | $27,000 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $339,300 | $631,550 | $1,090,866 |
| EBITDA | $339,300 | $631,550 | $1,090,866 |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Taxes Incurred | $67,860 | $126,310 | $218,173 |
| Net Profit | $271,440 | $505,240 | $872,693 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 10.59% | 16.04% | 22.53% |
8.3.1 Profit Monthly

8.3.2 Profit Yearly

8.3.3 Gross Margin Monthly

8.3.4 Gross Margin Yearly

8.4 Projected Cash Flow

| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $51,000 | $55,080 | $59,486 |
| Cash from Receivables | $22,000 | $23,760 | $25,661 |
| SUBTOTAL CASH FROM OPERATIONS | |||
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| SUBTOTAL CASH RECEIVED | |||
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $42,000 | $42,000 | $45,000 |
| Bill Payments | $27,000 | $28,000 | $31,000 |
| SUBTOTAL SPENT ON OPERATIONS | |||
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| SUBTOTAL CASH SPENT | |||
| Net Cash Flow | $21,000 | $23,000 | $25,000 |
| Cash Balance | $27,000 | $30,000 | $33,000 |
8.5 Projected Balance Sheet
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $275,000 | $308,000 | $338,800 |
| Accounts Receivable | $24,000 | $26,880 | $30,213 |
| Inventory | $4,300 | $4,816 | $4,900 |
| Other Current Assets | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 |
| TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS | |||
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $19,400 | $21,728 | $24,444 |
| TOTAL LONG-TERM ASSETS | |||
| TOTAL ASSETS | |||
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $18,700 | $20,944 | $23,541 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| SUBTOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES | |||
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | |||
| Paid-in Capital | $30,000 | $30,000 | $31,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $53,000 | $57,770 | $63,547 |
| Earnings | $193,400 | $210,806 | $231,887 |
| TOTAL CAPITAL | |||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND CAPITAL | |||
| Net Worth | $293,400 | $319,806 | $351,787 |
8.6 Business Ratios
| Sales Growth | 7.25% | 8.03% | 8.90% | 3.00% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 9.21% | 10.20% | 11.31% | 9.80% |
| Inventory | 5.39% | 5.97% | 6.62% | 9.90% |
| Other Current Assets | 2.11% | 2.34% | 2.59% | 2.40% |
| Total Current Assets | 149.80% | 151.00% | 152.00% | 158.00% |
| Long-term Assets | 11.55% | 11.60% | 11.64% | 12.00% |
| TOTAL ASSETS | ||||
| Current Liabilities | 4.90% | 4.94% | 4.98% | 4.34% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Total Liabilities | 7.59% | 7.65% | 7.72% | 7.38% |
| NET WORTH | ||||
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 94.60% | 97.15% | 99.87% | 99.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 93.56% | 96.09% | 98.78% | 97.80% |
| Advertising Expenses | 1.52% | 1.56% | 1.60% | 1.40% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 41.50% | 42.62% | 43.81% | 33.90% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 34 | 35 | 36 | 32 |
| Quick | 33 | 33.8 | 34.645 | 33 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 0.18% | 0.18% | 0.17% | 0.40% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 74.08% | 74.89% | 75.00% | 75.00% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 96.30% | 101.12% | 106.17% | 111.30% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 33.56% | 34.60% | 35.67% | N.A. |
| Return on Equity | 55.80% | 57.53% | 59.31% | N.A. |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.8 | N.A. |
| Collection Days | 100 | 100 | 100 | N.A. |
| Inventory Turnover | 32.4 | 34.02 | 35 | N.A. |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 15.6 | 16 | 16.3 | N.A. |
| Payment Days | 27 | 27 | 27 | N.A. |
| Total Asset Turnover | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.6 | N.A. |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | -0.04 | -0.03 | -0.04 | N.A. |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 1 | 1 | 1 | N.A. |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $244,000 | $257,664 | $272,093 | N.A. |
| Interest Coverage | 0 | 0 | 0 | N.A. |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.89 | N.A. |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 1% | 0% | 0% | N.A. |
| Acid Test | 29 | 29.12 | 29.16 | N.A. |
| Sales/Net Worth | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.2 | N.A. |
| Dividend Payout | 0 | 0 | 0 | N.A. |
- What are manufacturing plans in a business plan?
Manufacturing plans are just details laid out in a manufacture business plan that tell you how a business will operate.
- How can I start my manufacturing business?
To start manufacturing business plan, you have to figure out all the details of how your business will operate. For this, a business plan is usually drafted. For more information, you can refer to the template above.
- What is an example of a manufacturing business?
There are different kinds of manufacturing businesses. One manufacturing business example is of electronics manufacturing business.
- What are the 3 types of manufacturing businesses?
There are 3 types of manufacturing business:
- Make-to-Stock (MTS)
- Make-to-Order (MTO) 3. Make-to-Assemble (MTA)
Download Manufacturing Business Plan Sample in pdf
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Rabbit Farming Business Plan

Beverages Business Plan

Private Schools Business Plan

Business Plan for a Lounge

Crowdfunding Business Plan

Water Refilling Station Business Plan

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Chinese businesses hoping to expand in the US and bring jobs face uncertainty and suspicion
FILE - U.S. and Chinese flags are set up at the Diaoyutai State Guesthouse in Beijing, on July 8, 2023. Lured by the large U.S. market, Chinese businesses are coming to the U.S. with money, jobs and technology, only to find rising suspicion at a time of an intensifying U.S.-China rivalry that has spread into the business world. (AP Photo/Mark Schiefelbein, Pool, File)
FILE - Gov. Gretchen Whitmer speaks during a news conference in Lansing, Mich., Jan. 25, 2022. Whitmer in 2022 welcomed a Chinese lithium-ion battery company’s plan to build a $2.36 billion factory and bring a couple of thousand of jobs to Big Rapids, Mich. But now the project by Gotion High-Tech is in the crosshairs of some U.S. lawmakers and local residents. Chinese businesses are coming to the U.S. are finding rising suspicion at a time of an intensifying U.S.-China rivalry that has spread into the business world. (AP Photo/Paul Sancya)
FILE - Rep. John Moolenaar, R-Mich., questions witnesses during a hearing on Capitol Hill, Feb. 28, 2023, in Washington. Moolenaar, chairman of the House Select Committee on China, is leading the charge against Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer’s plan to bring a Chinese lithium-ion battery company to Big Rapids, Mich. Chinese businesses are coming to the U.S. with money, jobs and technology, only to find rising suspicion at a time of an intensifying U.S.-China rivalry that has spread into the business world. (AP Photo/Alex Brandon, File)
- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — It was billed as the “biggest ever economic development project” in north Michigan when Gov. Gretchen Whitmer in 2022 welcomed a Chinese lithium-ion battery company’s plan to build a $2.36 billion factory and bring a couple thousand jobs to Big Rapids.
But now the project by Gotion High-Tech is in the crosshairs of some U.S. lawmakers and local residents.
Leading the charge is Republican Rep. John Moolenaar of Michigan, chairman of the House Select Committee on China, who accuses the Chinese company of having ties to forced labor and says he fears it could spy for Beijing and work to extend China’s influence in the U.S. heartland. Gotion rejects the accusations.
“I want to see this area have more jobs and investments, but we must not welcome companies that are controlled by people who see us as the enemy and we should not allow them to build here,” Moolenaar said at a recent roundtable discussion in Michigan.
Lured by the large U.S. market, Chinese businesses are coming to the United States with money, jobs and technology, only to find rising suspicion at a time of an intensifying U.S.-China rivalry that has spread into the business world.
U.S. wariness of China, coupled with Beijing’s desire to protect its technological competitiveness, threatens to rupture ties between the world’s two largest economies. That could hurt businesses, workers and consumers, which some warn could undermine the economic foundation that has helped stabilize relations.
“This is a lose-lose scenario for the two countries,” Zhiqun Zhu, professor of political science and international relations at Bucknell University, said in an email. “The main reason is U.S.-China rivalry, and the U.S. government prioritizes ‘national security’ over economic interests in dealing with China.”
Lizhi Liu, an assistant professor of business at Georgetown University, said the trend, along with the decline of U.S. investments in China, could hurt China-U.S. relations.
“Strong investment ties between the two nations are crucial not only for economic reasons but also for security, as intertwined economic interests reduce the likelihood of major conflicts or even war,” she said.
But U.S. lawmakers believe the stakes are high. Sen. Marco Rubio said at a July hearing that China is not only a military and diplomatic adversary for the U.S. but also a “technological, industrial and commercial” opponent.
“The technological and industrial high ground has always been a precursor of global power,” said Rubio, a Republican from Florida. He argued that U.S. foreign policy should take into account the country’s commercial, trade and technological interests.
The bipartisan House Select Committee on China has warned that widespread adoption in the US. of technologies developed by China could threaten long-term U.S. technological competitiveness.
U.S. public sentiment against Chinese investments began to build up during President Barack Obama’s administration, in a pushback against globalization, and were amplified after President Donald Trump came into office, said Yilang Feng, an assistant professor of business at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, who studies economic nationalism and resistance to foreign direct investments in the U.S.
“The scale has increased, so has the intensity,” Feng said.
As President Joe Biden’s administration seeks to revive American manufacturing and boost U.S. technological capabilities, many politicians believe Chinese companies should be kept out.
“Can you imagine working for an American company working tirelessly to develop battery technology and then you find out that your tax dollars are being used to subsidize a competitor from China?” Moolenaar said as he campaigned against the Gotion project in his congressional district in a state that is critical in the presidential election.
Whitmer’s office has declined to comment on the project. The Michigan Economic Development Corporation told The Associated Press it has received “bipartisan support at all levels” to move forward with the project, which will create up to 2,350 jobs.
Danielle Emerson, spokesperson for MEDC, said the project is “critical to onshore the battery supply chain and create thousands of good-paying local jobs, which reduces our reliance on overseas disruptions and further protects our national security.”
Local residents of Green Charter Township, however, revolted against the project over its Chinese connections last year when they removed five officials who supported it in a recall election.
Also in Michigan, a partnership between Ford and CATL, another Chinese battery manufacturer, has been scaled back, following pushback over CATL’s potential connections to China’s ruling party.
In Worcester, Massachusetts, the Chinese biotech company WuXi Biologics paused construction of a large facility a few weeks after lawmakers introduced a bill that would, over data security concerns, ban U.S. entities receiving federal funds from doing business with a number of China-linked companies, WuXi Biologics included.
John Ling, who has helped South Carolina and Georgia attract Chinese businesses for nearly two decades, said geopolitics have been getting in the way in recent years. Chinese companies are less likely to consider South Carolina after the state senate last year approved a bill banning Chinese citizens from buying property, even though the bill has yet to clear the statehouse, Ling said.
Data by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis show the total investments by China in the U.S. fell to just under $44 billion in 2023, from a high point of $63 billion in 2017, although first-year expenditures rose to $621 million in 2023, up from $531 million in 2022 but drastically down from the high of $27 billion in 2016. The figures include acquisitions, new business establishments and expansions.
Thilo Hanemann, a partner at the research provider Rhodium Group, said there’s been an upswing in new Chinese investments in the U.S. following a major decline, prompted by the end of disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic and the need for Chinese companies to go overseas when margins at home are dwindling.
U.S. policymakers are worried that Chinese companies, beholden to the ruling Chinese Communist Party, could pose national security risks, he said, while Beijing is concerned that overseas investments could lead to Chinese technology leakage.
“Chinese companies are in between a rock and a hard place, dealing with both domestic governments in terms of not letting them go abroad and then the U.S. or host governments that have concerns,” Hanemann said.
Yet, Chinese investors may still find the U.S. market appealing “due to its high consumption levels and judicial independence,” said Liu of Georgetown University.
In 2022, Michigan beat out several other states in luring Gotion, according to the governor’s office. Keen to revive its manufacturing base, the state offered a package of incentives , including $175 million in grants and the approval of a new zone that could save the company $540 million. Local townships approved tax abatements for Gotion to build a factory to make components for electrical vehicle batteries.
In Green Charter Township, the new board dropped support for the project and rescinded an agreement that would extend water to the factory site, only to be rebuked by a U.S. district judge .
The future of the plant remains uncertain, as Moolenaar is rallying support for his bill that would prevent Gotion from receiving federal subsidies. He has accused the company of using forced labor, after congressional staff discovered links between the company and Xinjiang Production Construction Corps., a paramilitary group sanctioned by the U.S. Commerce Department for its involvement in China’s forced labor practice.
Chuck Thelen, vice president of manufacturing of Gotion North America, in recent town hall meetings called the forced labor accusations “categorically false and clearly intended to deceive.”
By allowing the Chinese company to build a plant in Michigan, it would help “onshore a technology that has been vastly leapfrogged” outside of the U.S., he said.
It doesn’t amount to “a Chinese invasion,” Thelen said. “This is a global approach, an energy solution.”
3 reasons why US manufacturing is coming back— and how to invest in a reindustrializing economy
- After decades of decay, manufacturing jobs are finally returning to the US.
- Optimal legislation, reshoring trends, and AI are all spurring reindustrialization.
- Investors should expect increased cyclicality in the coming years as a result. Here's how to invest.

For the last half-century, US manufacturing languished as companies outsourced their operations to cheaper locations overseas, leaving behind swathes of economically decrepit Rust Belt communities.
Politicians on both sides of the aisle have been promising for years to bring back American jobs and revitalize the economy. Now, it looks like that's finally happening.
Manufacturing spending has sharply risen in recent years, increasing over 20% in the last year and over 200% since May 2020. John Osterweis, founder and co-chief investment officer of $7.2 billion Osterwies Capital Management, sees this development as a sign of a revitalizing domestic manufacturing sector.
Rust no more
In the last few years, the US has been moving away from globalization and back toward domestic production.
Favorable legislation is one factor. The passage of the Inflation Reduction Act, the CHIPS Act, and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act boosted the domestic infrastructure, semiconductor, and clean energy sectors through initiatives such as subsidies and tax incentives. In particular, the CHIPS Act poured over $50 billion into American semiconductor research, development, manufacturing, and workforce development.
These pieces of legislation are all indicators of the larger trend of reshoring, the second factor that's reviving manufacturing.
Related stories
Goldman Sachs and Bank of America have identified it as a long-term theme in the world economy. Companies are keen on bringing jobs and supply chains closer to home, especially after the Covid pandemic exposed the downsides of having interlocked and geographically dispersed supply chains. Earlier this year, annual US imports from Mexico surpassed those from China for the first time in 20 years. Reducing international dependency is also a goal of the CHIPS Act, as the US relies primarily on East Asia for semiconductor chip production.
Corporate supply chain restrategizing, combined with government stimulus, has clearly put the wheels of reshoring into motion. Nearly two million reshoring and foreign direct investment jobs have been announced since 2010, according to Bank of America.
The omnipresent shadow of AI is the third factor helping to boost US manufacturing as it transforms the technology industry into a more capital-intensive model. The data centers powering AI require large upfront investments, and the race to develop AI technology has turbocharged the manufacturing-heavy semiconductor industry. This trend isn't stopping anytime soon: Big Tech companies such as Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft are planning to increase their capital expenditures from $120 billion in 2023 to $180 billion in 2024.
All of these factors are pointing toward a reindustrializing US economy.
Investing in reindustrialization
For many investors, a manufacturing-focused market might be unfamiliar territory.
The US manufacturing sector has been declining for much of recent history, with the manufacturing portion of US GDP shrinking from 16% to 11% in the period between 1997 and 2021, the Osterweis note said. Capital-light industries such as technology, media, consulting, and healthcare replaced heavy industry, creating a service economy.
According to Osterweis, investors should expect increased cyclicality going forward.
The earlier shift to a service economy resulted in longer stretches of economic expansion, with three of the four longest economic expansions in the last 150 years occurring after 1982. Economic expansion periods have roughly doubled over the last 40 years, from four to eight years.
Offshoring created more efficient supply chains that allowed companies to better match inventory supply with demand. Osterweis believes this led to longer and smoother economic expansion cycles. The shift to a service economy also reduced the impact of inventory cycles on the overall US economy.
Now, with increased investment in AI and several initiatives to revitalize domestic manufacturing, Osterweis believes the US could see a return to shorter expansion periods.
Investors can buckle up for more frequent economic fluctuations by increasing their concentration in quality growth equities. Osterweis identifies quality growth businesses based on three characteristics: a unique competitive advantage, robust free cash flow to reinvest in the business, and a strong management team. Investing in quality growth businesses not only drives strong returns but also protects against the ups and downs of business cycles.
Osterweis also sees AI as a sustainable trend and recommends investors continue holding semiconductor companies. Specifically, Osterweis implements a defensive strategy by investing in Nvidia competitors that offer similar products at cheaper price points. He also recommends investing in companies further up the semiconductor value chain. Investors with diversified semiconductor holdings can better protect themselves from a potential sector pullback or a cyclical downturn, which Osterweis believes is likely after the current wave of aggressive semiconductor spending dies down.
ETFs such as American Century US Quality Growth ETF ( QGRO ), WisdomTree US Quality Growth ETF ( QGRW ), VanEck Semiconductor ETF ( SMH ), and First Trust Nasdaq Semiconductor ETF ( FTXL ) can give investors exposure to these areas of the equity market.
Watch: Nearly 50,000 tech workers have been laid off — but there's a hack to avoid layoffs
- Main content

- Current Issue
- Health Kentucky
- Advertise in The Lane Report
- Ad Dimensions
- Construction
- Economic Development
- Hospitality
- State Government
- National Government
- Manufacturing
- Real Estate
- Transportation
- Philanthropy
- Wealth Management
- Workforce Development
- Big Moves Submissions
- Executive Profile Submission
- Sponsored E Blast Submission
- Seeking Employment
- Submit Your Upcoming Event
- Lane Report
- General Questions
- Writer’s Guidelines
- Privacy Policy
- Google Plus
- Ohio firm will help design Louisville Comprehensive Cultural Plan

LOUISVILLE – Louisville Metro Government is teaming up with Designing Local, a Columbus, Ohio-based consulting firm, to draft a Comprehensive Cultural Plan for Louisville.
This will include an audit of Louisville’s creative economy and an update to the Public Art Master Plan. The Office of Arts + Creative Industries will be working closely with Designing Local over the next year to engage the Louisville community in devising a strategic roadmap arts and culture initiatives across the city. “The Office of Arts + Creative Industries is excited to undertake this important work on behalf of the city. It is essential that it be done in collaboration with residents, artists, and cultural practitioners, which is why it was critical to find the right consultant to partner with us in facilitating this process,” said Jessica Bennett Kincaid, Arts + Creative Industries director. Designing Local is an award-winning firm who has worked with communities across the country, and members of the team are in town this week to get further acquainted with Louisville’s art scene and begin identifying stakeholders. The firm’s design for the future Cultural Plan will be informed by local research, community input, and national benchmarks. The planning process will take a closer look at the role the creative sector plays in our city’s overall economy, which includes non-profit data and private sector jobs, salaries, and sales and tax revenue impact.
The strategic planning process will also update Metro’s initial Public Art Master Plan from 2009 and catalog Louisville’s cultural assets. This includes our anchor arts and culture institutions, artist-run spaces, creative start-ups, as well as social groups and networks that are critical parts of people’s lives but may not be formally organized.
This asset mapping process will identify missing or underdeveloped framework where we need to focus our efforts in strengthening or building certain types of organizational infrastructure.
At certain phases of this process, Designing Local will also collaborate with Artful Places founder, Todd Bressi, and economic strategists Jon Stover & Associates.
Members of the team are in town this week to begin familiarizing themselves with the community and start the process of identifying stakeholders.
We anticipate the entire planning process will take about a year. The product will be a 10-year roadmap that identifies both short and long-term goals, implementation strategies, and metrics for success in collectively strengthening and growing Louisville’s arts and culture ecosystem. These goals and metrics will be informed by regional and national benchmarks and best-practices but adapted to Louisville’s individual context.
To encourage vibrant dialogue around arts and culture, there is a form you can fill out to make sure your voice is heard. The firm will facilitate at least two major community meetings to guide the crafting of a plan that reflects Louisville’s voice and values. We will announce when the first meeting is scheduled.
This morning, the Office of Arts + Creative Industries also noted that Louisville Metro has made positive changes to the External Agency Fund grant program which will provide more support for the arts and culture community. Bennett Kincaid announced that one such funding opportunity is being released this morning that will make more than $125,000 in grant funds available to our arts and culture non-profits.
The Office of Arts + Creative Industries will host a virtual information session for interested applicant organizations this Friday, August 9, at 3 p.m.
For more information about eligibility, the application, and award process, you can visit the Arts + Creative Industries page.
If you would like to give input to Designing Local regarding the cultural plan, you can fill out this online form.
You may also like

WKU Regents expand budget for Cherry Hall, Ford College of Business projects

Lessons learned from a decade of regionalism, with more ground to cover

- Pulaski educators learn manufacturing opportunities, community’s workforce needs through Bus to Biz

Popular Stories
Norton children’s names new pediatric cancer chief, uk extension releases ky data on community needs for future programs.
- Humana Foundation announces 2024 scholarship awards
- Governor appoints Ky leaders to boards and commissions

The Lane Report
- Kentucky Distillers’ Association Joins World Spirits Alliance
- Stoll Keenon Ogden PLLC (SKO) welcomes attorney Alex D. Gaddis as Counsel to the Firm
- Stoll Keenon Ogden PLLC (SKO) welcomes attorney Alan M. Applegate as a Senior Member
- Stoll Keenon Ogden PLLC (SKO) welcomes attorney D. Keith Pulliam as a Member
- Stoll Keenon Ogden PLLC (SKO) welcomes attorney Abigail Fargen Riley
- 6 Ky companies get $650,000 in SBIR/STTR grants
Advertisement
Supported by
Intel Will Cut Over 15,000 Jobs Amid Struggles to Turn Itself Around
The Silicon Valley chip maker also reported a net loss and declining revenue in the latest quarter.
- Share full article

By Don Clark
Reporting from San Francisco
Intel, the Silicon Valley chip maker, said on Thursday that it would slash more than 15,000 jobs to aid a turnaround plan, as the company tries to recover after a series of stumbles.
The job cuts amount to 15 percent of Intel’s work force . The company also announced other restructuring moves and a reduction in capital spending, which are expected to cut costs by $10 billion in 2025. To conserve cash, Intel said, it will suspend its quarterly dividend in the fourth quarter.
“This is painful news for me to share,” Patrick Gelsinger , Intel’s chief executive, said in a letter to employees. “I know it will be even more difficult for you to read. This is an incredibly hard day for Intel as we are making some of the most consequential changes in our company’s history.”
The company’s stock fell more than 20 percent in after-hours trading.
Intel, which produces microprocessor chips that serve as electronic brains in most computers, has battled a slump amid stiff competition in chips used for artificial intelligence. Its last major restructuring was in 2016, when the company said it would cut up to 12,000 jobs, or 11 percent of its work force.
Mr. Gelsinger has worked to reinvigorate the company after being named its top leader in early 2021. Among other actions, he quickly moved to become a top industry lobbyist for federal subsidies to encourage more U.S. production of the foundational components.
He has also tried to fix Intel’s manufacturing issues. Unlike most of its peers, Intel makes chips as well as designs them. Others rely on outside production services called foundries, with most turning to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Boeing to redesign 737 Max door plug that sparked latest crisis

Boeing is redesigning the fuselage component that blew out of a nearly new 737 Max 9 aircraft mid-flight in January, as the planemaker seeks to draw lessons from the accident that has thrown it into crisis.
The company revealed the plan during a daylong hearing with the US National Transportation Safety Board, which grilled executives from Boeing and supplier Spirit AeroSystems Inc. about their safety and manufacturing culture. Boeing said engineers are working on design changes that would prevent the so-called door plug from being closed until it’s firmly secured, after the NTSB found the element hadn’t been properly reinserted and was missing bolts to hold it down.
Boeing has undergone a comprehensive overhaul since the Jan. 5 accident, switching out senior managers, announcing the repurchase of Spirit, and slowing production to improve build quality. NTSB Chair Jennifer Homendy said shortcomings that contributed to the panel mishap had been known for years inside Boeing. At one point in the hearing she reprimanded managers for what she said sounded like an effort to turn the session into a “PR campaign” about Boeing’s resurrection from crisis.
“Why does it take a serious tragedy, which could have been so much more serious, for change to occur?” Homendy said, adding that Boeing has “a long way to go — just based on what I’ve looked at — on safety culture.”
Advertisement
The NTSB released thousands of pages of information at the start of the hearing about the accident, which involved a jet flown by Alaska Airlines. Interviews with Boeing employees show an at-times overstressed workforce that was well aware of 737 Max fuselages arriving from Spirit with defects.
One employee told investigators that “the planes come in jacked up every day” while another said the aircraft have issues “with structures, skins, open holes.”
Boeing is still struggling to leave the accident behind. It announced a new chief executive officer last week, and the company is only now starting to step up its rate of aircraft production again, which had fallen precipitously after the accident, according to Elizabeth Lund, a Boeing senior vice president of quality testifying at the hearing.
Despite the lack of serious injuries, the accident has attracted huge public interest. The panel was found in a yard shortly afterward, and investigators quickly identified it had been missing bolts to keep it in place.
A preliminary NTSB report found evidence suggesting the door plug was removed prior to leaving the facility to fix damaged rivets and then reinstalled without being properly attached. While the rivet work was entered into Boeing’s formal record system, there was no mention of the door removal.
Boeing has said it’s missing formal documentation on the panel’s removal, a serious violation of its manufacturing protocols. At the hearing, Lund said workers believe they only temporarily pushed the door plug in place to prepare the aircraft to move outside.
Boeing did identify two employees who were likely involved in opening the door plug and moved them into a “lateral position” at the company, Lund said, adding that they were now on paid administrative leave at their own request. The NTSB said it hasn’t had a chance to interview the door crew manager, who is on medical leave.
Homendy expressed concern about written statements the NTSB has received from Boeing employees who may have played a role in the door plug’s removal, noting they all seem to end with a comment about having zero knowledge of what happened.
Since the accident, the planemaker has retrained mechanics and managers. It stepped up inspections, including at Spirit, in an effort to tackle defects and missing parts that lead to so-called “traveled work,” where tasks are completed out of the normal sequence.
Boeing has also encouraged employees to submit safety concerns through an internal program called “Speak Up.”
But Lloyd Catlin, a business representative for the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers, said at the hearing that the union — which represents thousands of Boeing workers — still doesn’t have confidence in that program.
“It’s in its early phases,” he said. “It needs help.”

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Download a free manufacturing business plan template and example to start and grow your own company. Learn how to conduct market analysis, develop strategy, create financial projections, and more.
Download a customizable template to create your own manufacturing business plan, including a financial model. Learn how to start a food manufacturing company in Lincoln, Nebraska, with examples and tips.
Learn how to write a manufacturing business plan with this step-by-step guide and sample plan. Download a template and customize it for your own business idea.
If you're planning to start a manufacturing, fabrication, or production business you'll need a business plan to do it. To help you get started, check out our library of sample plans to be sure you're covering everything from sourcing your raw materials to budgeting for plant and equipment.
Manufacturing Business Plan . Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 7,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their manufacturing businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a manufacturing ...
Learn how to create a comprehensive manufacturing business plan with this guide and example. It covers all essential aspects, such as operations, marketing, strategy, management, and financial plan.
A manufacturing business plan is a formal document that outlines the goals and objectives of your business. It includes detailed information about your: The purpose of a business plan is to give you a roadmap to follow as you build and grow your business. It forces you to think through every aspect of your venture and identify potential ...
Our template provides a comprehensive framework for outlining your company's goals, conducting market analysis, projecting finances, and strategizing your operations. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be able to: Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and objectives. Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand your ...
Below are links to each of the key sections of a sample manufacturing business plan. Once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors. I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team
This Manufacturing Business Plan template is designed to help manufacturers of all sizes and industries create a plan to launch, run and grow their business. It provides a framework to clearly define and measure the objectives, actions, and measurements that are necessary for success. 1. Define clear examples of your focus areas.
Fortunately, the #1 Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook provides entrepreneurs and businesses with a detailed roadmap for success. With this template and guidebook, you will have the guidance you need to plan for success and develop a comprehensive business plan that outlines your vision and strategy. Written by:
Get access to Upmetrics software, invite your team members and start writing your business plan. 1. Get tried and tested tips. Upmetrics business plan builder gives you everything you need to stay in sync and guides you on every step of your business plan writing. 3. Stunning business plan cover pages.
A well-crafted manufacture business plan serves as the cornerstone for any manufacturing enterprise, offering a strategic roadmap for navigating the dynamic and competitive terrain of the production and industry landscape. While recognizing that there's no one-size-fits-all approach, using manufacturing business plan example becomes crucial ...
A manufacturing business plan is a strategic blueprint that outlines the objectives, processes, and resources required to initiate and sustain a manufacturing enterprise. It serves as a roadmap ...
2. Draft a manufacturing business plan. 3. Develop a manufacturing brand. 4. Formalize your business registration. 5. Acquire necessary licenses and permits for manufacturing. 6. Open a business bank account and secure funding as needed. 7. Set pricing for manufacturing services. 8. Acquire manufacturing equipment and supplies. 9.
This library of manufacturing and wholesale business plan examples here can inspire and guide you as you begin to plan your business. So, don't worry; we got you covered on that part. Let's learn more about these manufacturing business plan samples, starting with their benefits. Benefits of using an industry-specific business plan example
A manufacturing business plan is a written document that contains the business goals of a manufacturing company. It lays out plans to achieve these goals within a specified time frame and also includes market analysis, strategy, and much more. 2. What are the Components of a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A manufacturing business plan normally follows a standard business plan outline:. Executive summary: provides a concise overview of the business plan, highlighting the key points, financials and objectives of your manufacturing business. Company description: delivers a comprehensive overview of your manufacturing business, covering its vision, legal structure, history, location, and the ...
Take a look at Upmetrics' manufacturing business plan template to formulate a foolproof plan. 7. Budget and Finances. Planning your finances and setting a budget is relevant before you can allocate resources or hire a team for your business. Often business owners gauge their requirements and expand their budget way beyond the expected profit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
2.1 The Business. Henry Works will be a startup manufacturing business plan started and owned by Henry Langerman. The business will provide manufacturing services to people in and around Oregon. It will offer services like the development of manufacturing chains in different companies. It will also handle manufacturing for small-scale companies ...
3. Pick a name and create a logo. Now it's time to start legitimizing your business. When it comes to manufacturer branding, your name and your logo are going to be part of what defines you. In the world of business, together, your name and logo make your dream venture into a "real business" — it authenticates you.
A traditional business plan should include an executive summary, a business description, market research, a business structure, a products and services overview, a marketing plan, your financial ...
3 of 3 | . FILE - Rep. John Moolenaar, R-Mich., questions witnesses during a hearing on Capitol Hill, Feb. 28, 2023, in Washington. Moolenaar, chairman of the House Select Committee on China, is leading the charge against Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer's plan to bring a Chinese lithium-ion battery company to Big Rapids, Mich. Chinese businesses are coming to the U.S. with money, jobs and ...
The US manufacturing sector has been declining for much of recent history, with the manufacturing portion of US GDP shrinking from 16% to 11% in the period between 1997 and 2021, the Osterweis ...
Pulaski educators learn manufacturing opportunities, community's workforce needs through Bus to Biz 6 Ky companies get $650,000 in SBIR/STTR grants Humana Foundation announces 2024 scholarship ...
In contrast, AMD on Tuesday reported a 115 percent jump for its data center business. Overall, Intel swung to a loss of $1.6 billion in the second quarter, while revenue fell 1 percent to $12.8 ...
1. Walz was born in West Point, a Nebraska town of just 3,500 people. But he was raised in an even smaller town called Butte. 2. Walz graduated from Butte High School in 1982. "I come from a ...
The company revealed the plan during a daylong hearing with the US National Transportation Safety Board, which grilled executives from Boeing and supplier Spirit AeroSystems Inc. about their ...