How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.

What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
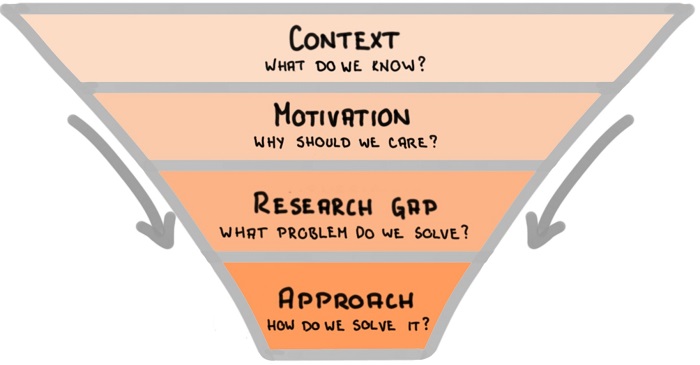
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
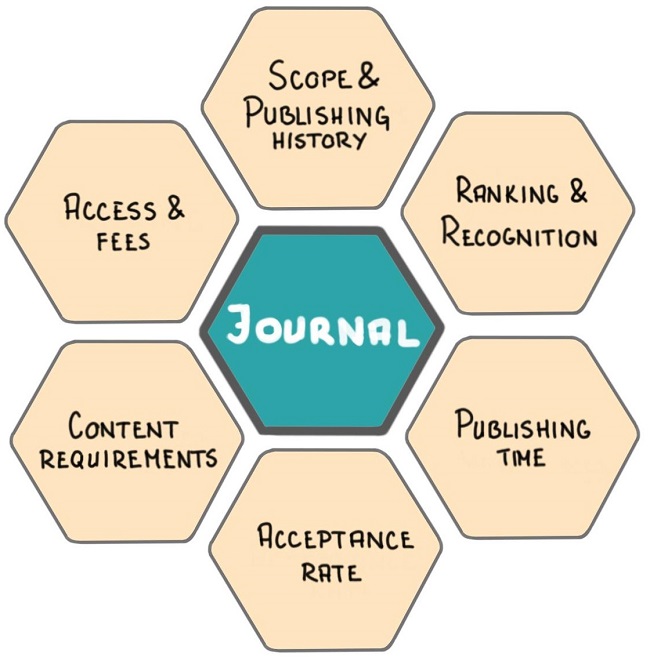
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Download 55 million PDFs for free
Explore our top research interests.

Engineering

Anthropology

- Earth Sciences

- Computer Science

- Mathematics

- Health Sciences

Join 268 million academics and researchers
Track your impact.
Share your work with other academics, grow your audience and track your impact on your field with our robust analytics
Discover new research
Get access to millions of research papers and stay informed with the important topics around the world
Publish your work
Publish your research with fast and rigorous service through Academia.edu Journals. Get instant worldwide dissemination of your work
Unlock the most powerful tools with Academia Premium

Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools
Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts.
- Advanced Search
- PDF Packages of 37 papers
- Summaries and Search Alerts

Share your work, track your impact, and grow your audience
Get notified when other academics mention you or cite your papers. Track your impact with in-depth analytics and network with members of your field.
- Mentions and Citations Tracking
- Advanced Analytics
- Publishing Tools
Real stories from real people

Used by academics at over 15,000 universities

Get started and find the best quality research
- Academia.edu Journals
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Cognitive Science
- Academia ©2024
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

APA Research Paper Format – Example, Sample and...

Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles
Infertility-related stress is associated with quality of life through negative emotions among infertile outpatients
- Li-ping Shi
- Yao-guo Geng
- Jing-jing Gu
Practical preparation of unsaturated very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) and very-long-chain alkene pollinator attractants
- Björn Bohman
- Aylin J. Bersch
- Philipp M. Schlüter

Predictive validity of resource-adjusted Korean Triage and Acuity Scale in pediatric gastrointestinal tract foreign body patients
- Jin Hee Lee
- Jin Hee Jung
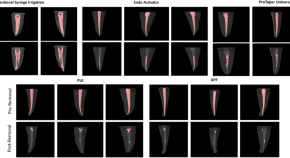
Efficacy of various techniques in calcium silicate-based intracanal medicament removal: a micro-CT analysis
- Rahaf A. Almohareb
- Reem M. Barakat
- Hanan Balto
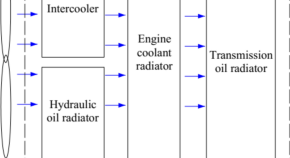
Experimental study of dual-cycle thermal management system for engineering radiator
- Wenbao Zhang
- Huimin Zhao

Performance enhancement of deep learning based solutions for pharyngeal airway space segmentation on MRI scans
- Chattapatr Leeraha
- Worapan Kusakunniran
- Thanongchai Siriapisith
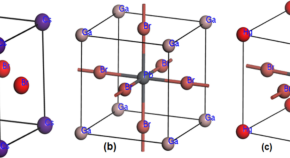
Computational investigation on physical properties of lead based perovskite RPbBr 3 (R = Cs, Hg, and Ga) materials for photovoltaic applications
- Muhammad Khuram Shahzad
- Shoukat Hussain
- Waqar Azeem

Estimation of human age using machine learning on panoramic radiographs for Brazilian patients
- Willian Oliveira
- Mariana Albuquerque Santos
- Cleber Zanchettin
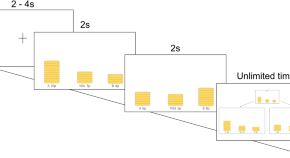
Self-interest overrides rank-reversal aversion in resource distribution
- Minyoung Kim
- Hackjin Kim
Phenolic, amino acids, and fatty acids profiles and the nutritional properties in the fresh and dried fruits of black rosehip ( Rosa pimpinellifolia L.)
- Milad Pashaei
- Hamid Hassanpour

A measurement system for assessing the completeness and deformation of aluminium ladders: case study
- Arkadiusz Kubacki
- Marcin Białek
Predicting social experience from dyadic interaction dynamics: the BallGame, a novel paradigm to study social engagement
- Annika Lübbert
- Malte Sengelmann
- Florian Göschl
Identifying potential repurposable medications for Parkinson’s disease through Mendelian randomization analysis
- Qitong Wang
Analysis of effective area and mass transfer in a structure packing column using machine learning and response surface methodology
- Amirsoheil Foroughi
- Kamyar Naderi
- Mohammad Reza Mosavi
Phytochemical fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles and their antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity
- Hussain Udayagiri
- Siva Sankar Sana
- Rama Rao Karri

The impact of the digital economy on land transfer-out decisions among Chinese farmers: evidence from CHFS micro-data
- Peijiang Zheng
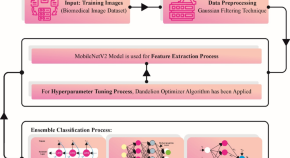
Towards laryngeal cancer diagnosis using Dandelion Optimizer Algorithm with ensemble learning on biomedical throat region images
- Sarah A. Alzakari
- Mashael Maashi
- Ahmed Sayed
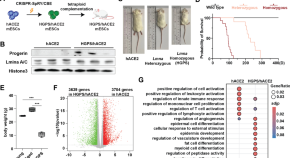
Premature aging effects on COVID-19 pathogenesis: new insights from mouse models
- Wu Guangming
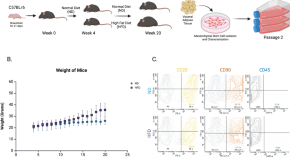
Mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue prone to lose their stemness associated markers in obesity related stress conditions
- Sura Hilal Ahmed Al-Sammarraie
- Şerife Ayaz-Güner
- Servet Özcan
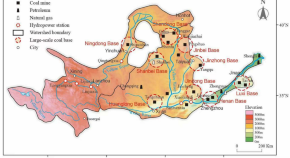
Spatial spillover effect and driving factors of urban carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin using nighttime light data
- Mingjuan Ma
- Yumeng Wang
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.

How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Trending Articles
- Phase III KEYNOTE-789 Study of Pemetrexed and Platinum With or Without Pembrolizumab for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor‒Resistant, EGFR -Mutant, Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Yang JC, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39173098
- Advances and future directions in ROS1 fusion-positive lung cancer. Boulanger MC, et al. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 39177972
- Restoring hippocampal glucose metabolism rescues cognition across Alzheimer's disease pathologies. Minhas PS, et al. Science. 2024. PMID: 39172838
- Acetate enables metabolic fitness and cognitive performance during sleep disruption. He Q, et al. Cell Metab. 2024. PMID: 39163862
- These labs have prepared for a big earthquake - will it be enough? Ikarashi A. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39155315 No abstract available.

Latest Literature
- Am Heart J (3)
- Cell Metab (2)
- Clin Infect Dis (3)
- J Biol Chem (8)
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab (1)
- J Neurosci (1)
- Nature (13)
- Nucleic Acids Res (11)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
arXiv's Accessibility Forum starts next month!
Help | Advanced Search
arXiv is a free distribution service and an open-access archive for nearly 2.4 million scholarly articles in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, statistics, electrical engineering and systems science, and economics. Materials on this site are not peer-reviewed by arXiv.
arXiv is a free distribution service and an open-access archive for scholarly articles in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, statistics, electrical engineering and systems science, and economics. Materials on this site are not peer-reviewed by arXiv.

arXiv Accessibility Forum
Accessibility means access regardless of disability. Join arXiv and global experts this September at the Forum focused on accessibility of scientific research. Learn more .
- Astrophysics ( astro-ph new , recent , search ) Astrophysics of Galaxies ; Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics ; Earth and Planetary Astrophysics ; High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena ; Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics ; Solar and Stellar Astrophysics
- Condensed Matter ( cond-mat new , recent , search ) Disordered Systems and Neural Networks ; Materials Science ; Mesoscale and Nanoscale Physics ; Other Condensed Matter ; Quantum Gases ; Soft Condensed Matter ; Statistical Mechanics ; Strongly Correlated Electrons ; Superconductivity
- General Relativity and Quantum Cosmology ( gr-qc new , recent , search )
- High Energy Physics - Experiment ( hep-ex new , recent , search )
- High Energy Physics - Lattice ( hep-lat new , recent , search )
- High Energy Physics - Phenomenology ( hep-ph new , recent , search )
- High Energy Physics - Theory ( hep-th new , recent , search )
- Mathematical Physics ( math-ph new , recent , search )
- Nonlinear Sciences ( nlin new , recent , search ) includes: Adaptation and Self-Organizing Systems ; Cellular Automata and Lattice Gases ; Chaotic Dynamics ; Exactly Solvable and Integrable Systems ; Pattern Formation and Solitons
- Nuclear Experiment ( nucl-ex new , recent , search )
- Nuclear Theory ( nucl-th new , recent , search )
- Physics ( physics new , recent , search ) includes: Accelerator Physics ; Applied Physics ; Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics ; Atomic and Molecular Clusters ; Atomic Physics ; Biological Physics ; Chemical Physics ; Classical Physics ; Computational Physics ; Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability ; Fluid Dynamics ; General Physics ; Geophysics ; History and Philosophy of Physics ; Instrumentation and Detectors ; Medical Physics ; Optics ; Physics and Society ; Physics Education ; Plasma Physics ; Popular Physics ; Space Physics
- Quantum Physics ( quant-ph new , recent , search )
Mathematics
- Mathematics ( math new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Algebraic Geometry ; Algebraic Topology ; Analysis of PDEs ; Category Theory ; Classical Analysis and ODEs ; Combinatorics ; Commutative Algebra ; Complex Variables ; Differential Geometry ; Dynamical Systems ; Functional Analysis ; General Mathematics ; General Topology ; Geometric Topology ; Group Theory ; History and Overview ; Information Theory ; K-Theory and Homology ; Logic ; Mathematical Physics ; Metric Geometry ; Number Theory ; Numerical Analysis ; Operator Algebras ; Optimization and Control ; Probability ; Quantum Algebra ; Representation Theory ; Rings and Algebras ; Spectral Theory ; Statistics Theory ; Symplectic Geometry
Computer Science
- Computing Research Repository ( CoRR new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Artificial Intelligence ; Computation and Language ; Computational Complexity ; Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science ; Computational Geometry ; Computer Science and Game Theory ; Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ; Computers and Society ; Cryptography and Security ; Data Structures and Algorithms ; Databases ; Digital Libraries ; Discrete Mathematics ; Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing ; Emerging Technologies ; Formal Languages and Automata Theory ; General Literature ; Graphics ; Hardware Architecture ; Human-Computer Interaction ; Information Retrieval ; Information Theory ; Logic in Computer Science ; Machine Learning ; Mathematical Software ; Multiagent Systems ; Multimedia ; Networking and Internet Architecture ; Neural and Evolutionary Computing ; Numerical Analysis ; Operating Systems ; Other Computer Science ; Performance ; Programming Languages ; Robotics ; Social and Information Networks ; Software Engineering ; Sound ; Symbolic Computation ; Systems and Control
Quantitative Biology
- Quantitative Biology ( q-bio new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Biomolecules ; Cell Behavior ; Genomics ; Molecular Networks ; Neurons and Cognition ; Other Quantitative Biology ; Populations and Evolution ; Quantitative Methods ; Subcellular Processes ; Tissues and Organs
Quantitative Finance
- Quantitative Finance ( q-fin new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Computational Finance ; Economics ; General Finance ; Mathematical Finance ; Portfolio Management ; Pricing of Securities ; Risk Management ; Statistical Finance ; Trading and Market Microstructure
- Statistics ( stat new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Applications ; Computation ; Machine Learning ; Methodology ; Other Statistics ; Statistics Theory
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science
- Electrical Engineering and Systems Science ( eess new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Audio and Speech Processing ; Image and Video Processing ; Signal Processing ; Systems and Control
- Economics ( econ new , recent , search ) includes: (see detailed description ): Econometrics ; General Economics ; Theoretical Economics
About arXiv
- General information
- How to Submit to arXiv
- Membership & Giving
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Writing your research paper
How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
All research papers have pretty much the same structure. If you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Learn the steps to start and complete your research paper in our guide.

How to write a problem statement
What is a problem statement and how do you write one? This guide answers all your questions and includes an example of a problem statement.
How to write a research paper outline
Structuring the outline of your research paper early on is important. Read on to learn how to structure a research paper outline and to see examples, including an outline template.

How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal and what should you use it for? This step-by-step guide teaches you how to structure and write a research proposal.

How to write an abstract
Not sure how to write an abstract for your paper? Clear your doubts with this guide, follow our tips, and start writing your abstract!
What are the different types of research papers?
Learn all you need to know about research papers, what differentiates a research paper from a thesis, and what types of research papers there are.

What is a research paper?
Are you confused about what a research paper actually is and what differentiates it from a thesis? Clarify it once and for all with our guide.
What is an appendix in a paper
Not sure what an appendix in a paper is? This guides defines what an appendix is and how to format one.

What is the abstract of a paper?
Not sure what the abstract of a paper is? Learn the definition of an abstract and how to format one in this guide with resources.

A new ‘AI scientist’ can write science papers without any human input. Here’s why that’s a problem
Dean, School of Computing Technologies, RMIT University, RMIT University
Disclosure statement
Karin Verspoor receives funding from the Australian Research Council, the Medical Research Future Fund, the National Health and Medical Research Council, and Elsevier BV. She is affiliated with BioGrid Australia and is a co-founder of the Australian Alliance for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare.
RMIT University provides funding as a strategic partner of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Scientific discovery is one of the most sophisticated human activities. First, scientists must understand the existing knowledge and identify a significant gap. Next, they must formulate a research question and design and conduct an experiment in pursuit of an answer. Then, they must analyse and interpret the results of the experiment, which may raise yet another research question.
Can a process this complex be automated? Last week, Sakana AI Labs announced the creation of an “AI scientist” – an artificial intelligence system they claim can make scientific discoveries in the area of machine learning in a fully automated way.
Using generative large language models (LLMs) like those behind ChatGPT and other AI chatbots, the system can brainstorm, select a promising idea, code new algorithms, plot results, and write a paper summarising the experiment and its findings, complete with references. Sakana claims the AI tool can undertake the complete lifecycle of a scientific experiment at a cost of just US$15 per paper – less than the cost of a scientist’s lunch.
These are some big claims. Do they stack up? And even if they do, would an army of AI scientists churning out research papers with inhuman speed really be good news for science?
How a computer can ‘do science’
A lot of science is done in the open, and almost all scientific knowledge has been written down somewhere (or we wouldn’t have a way to “know” it). Millions of scientific papers are freely available online in repositories such as arXiv and PubMed .
LLMs trained with this data capture the language of science and its patterns. It is therefore perhaps not at all surprising that a generative LLM can produce something that looks like a good scientific paper – it has ingested many examples that it can copy.
What is less clear is whether an AI system can produce an interesting scientific paper. Crucially, good science requires novelty.
But is it interesting?
Scientists don’t want to be told about things that are already known. Rather, they want to learn new things, especially new things that are significantly different from what is already known. This requires judgement about the scope and value of a contribution.
The Sakana system tries to address interestingness in two ways. First, it “scores” new paper ideas for similarity to existing research (indexed in the Semantic Scholar repository). Anything too similar is discarded.
Second, Sakana’s system introduces a “peer review” step – using another LLM to judge the quality and novelty of the generated paper. Here again, there are plenty of examples of peer review online on sites such as openreview.net that can guide how to critique a paper. LLMs have ingested these, too.
AI may be a poor judge of AI output
Feedback is mixed on Sakana AI’s output. Some have described it as producing “ endless scientific slop ”.
Even the system’s own review of its outputs judges the papers weak at best. This is likely to improve as the technology evolves, but the question of whether automated scientific papers are valuable remains.
The ability of LLMs to judge the quality of research is also an open question. My own work (soon to be published in Research Synthesis Methods ) shows LLMs are not great at judging the risk of bias in medical research studies, though this too may improve over time.
Sakana’s system automates discoveries in computational research, which is much easier than in other types of science that require physical experiments. Sakana’s experiments are done with code, which is also structured text that LLMs can be trained to generate.
AI tools to support scientists, not replace them
AI researchers have been developing systems to support science for decades. Given the huge volumes of published research, even finding publications relevant to a specific scientific question can be challenging.
Specialised search tools make use of AI to help scientists find and synthesise existing work. These include the above-mentioned Semantic Scholar, but also newer systems such as Elicit , Research Rabbit , scite and Consensus .
Text mining tools such as PubTator dig deeper into papers to identify key points of focus, such as specific genetic mutations and diseases, and their established relationships. This is especially useful for curating and organising scientific information.
Machine learning has also been used to support the synthesis and analysis of medical evidence, in tools such as Robot Reviewer . Summaries that compare and contrast claims in papers from Scholarcy help to perform literature reviews.
All these tools aim to help scientists do their jobs more effectively, not to replace them.
AI research may exacerbate existing problems
While Sakana AI states it doesn’t see the role of human scientists diminishing, the company’s vision of “a fully AI-driven scientific ecosystem” would have major implications for science.
One concern is that, if AI-generated papers flood the scientific literature, future AI systems may be trained on AI output and undergo model collapse . This means they may become increasingly ineffectual at innovating.
However, the implications for science go well beyond impacts on AI science systems themselves.
There are already bad actors in science, including “paper mills” churning out fake papers . This problem will only get worse when a scientific paper can be produced with US$15 and a vague initial prompt.
The need to check for errors in a mountain of automatically generated research could rapidly overwhelm the capacity of actual scientists. The peer review system is arguably already broken , and dumping more research of questionable quality into the system won’t fix it.
Science is fundamentally based on trust. Scientists emphasise the integrity of the scientific process so we can be confident our understanding of the world (and now, the world’s machines) is valid and improving.
A scientific ecosystem where AI systems are key players raises fundamental questions about the meaning and value of this process, and what level of trust we should have in AI scientists. Is this the kind of scientific ecosystem we want?
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Computer science
- Research integrity
- Paper mills

Head of Evidence to Action

Supply Chain - Assistant/Associate Professor (Tenure-Track)

Education Research Fellow

OzGrav Postdoctoral Research Fellow

Casual Facilitator: GERRIC Student Programs - Arts, Design and Architecture
Corporate Debt Maturity Matters for Monetary Policy
Joachim Jungherr
Matthias Meier

Timo Reinelt
Immo Schott
Download PDF (4 MB)
2024-30 | August 22, 2024
We provide novel empirical evidence that firms’ investment is more responsive to monetary policy when a higher fraction of their debt matures. In a heterogeneous firm New Keynesian model with financial frictions and endogenous debt maturity, two channels explain this finding: (1.) Firms with more maturing debt have larger roll-over needs and are therefore more exposed to fluctuations in the real interest rate (roll-over risk). (2.) These firms also have higher default risk and therefore react more strongly to changes in the real burden of outstanding nominal debt (debt overhang). Unconventional monetary policy, which operates through long-term interest rates, has larger effects on debt maturity but smaller effects on output and inflation than conventional monetary policy.
Suggested citation:
Jungherr, Joachim, Matthias Meier, Timo Reinelt, and Immo Schott. 2024. “Corporate Debt Maturity Matters for Monetary Policy.” Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Working Paper 2024-30. https://doi.org/10.24148/wp2024-30
New research suggests rainwater could have helped form the first protocell walls
Uchicago-led study casts new light on the origins of life on earth.
One of the major unanswered questions about the origin of life is how droplets of RNA floating around the primordial soup turned into the membrane-protected packets of life we call cells.
A new paper by researchers with the University of Chicago and the University of Houston proposes a solution.
They show how rainwater could have helped create a meshy wall around protocells 3.8 billion years ago, a critical step in the transition from tiny beads of RNA to every bacterium, plant, animal, and human that ever lived.
The paper was published Aug. 21 in Science Advances by UChicago Pritzker Molecular Engineering (PME) postdoctoral researcher Aman Agrawal and his co-authors—including PME Dean Emeritus Matthew Tirrell and Nobel Prize-winning biologist Jack Szostak, director of UChicago’s Chicago Center for the Origins of Life .
“This is a distinctive and novel observation,” said Tirrell.
Droplets and discovery
The research looks at “coacervate droplets”—naturally occurring compartments of complex molecules like proteins, lipids, and RNA. ( In the early 2000s , Szostak started looking at RNA as the first biological material to develop, rather than DNA.)
The droplets, which behave like drops of cooking oil in water, have long been eyed as a candidate for the first protocells. But there was a problem, Szostak found in 2014.
It wasn’t that these droplets couldn’t exchange molecules between each other, a key step in evolution; the problem was that they did it too well, and too fast. Any droplet containing a new, potentially useful pre-life mutation of RNA would exchange this RNA with the other RNA droplets within minutes, meaning they would quickly all be the same.
There would be no differentiation and no competition—meaning no evolution. And that means no life.
“If molecules continually exchange between droplets or between cells, then all the cells after a short while will look alike, and there will be no evolution because you are ending up with identical clones,” Agrawal said.
Agrawal started transferring coacervate droplets into distilled water during his PhD research at the University of Houston with Prof. Alamgir Karim , studying their behavior under an electric field. At this point, the research had nothing to do with the origin of life—just studying the fascinating material from an engineering perspective.
Karim had worked decades earlier at the University of Minnesota under one of the world’s top experts—Tirrell, who later became founding dean of the UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering. During a lunch with Agrawal and Karim, Tirrell brought up how the research into the effects of distilled water on coacervate droplets might relate to the origin of life on Earth. Tirrell asked where distilled water would have existed 3.8 billion years ago.
“I spontaneously said ‘rainwater!’ His eyes lit up and he was very excited at the suggestion,” Karim said. “So, you can say it was a spontaneous combustion of ideas or ideation!”
Tirrell brought Agrawal’s distilled water research to Szostak, who had recently joined the University of Chicago to lead a new push to understand the origins of life on Earth .
Working with RNA samples from Szostak, Agrawal found that transferring coacervate droplets into distilled water increased the time scale of RNA exchange – from mere minutes to several days. This was long enough for mutation, competition, and evolution.
Then, to make sure rain itself could work rather than distilled water, “We simply collected water from rain in Houston and tested the stability of our droplets in it, just to make sure what we are reporting is accurate,” Agrawal said.
In tests with the actual rainwater and with lab water modified to mimic the acidity of rainwater, they found the same results. The meshy walls formed, creating the conditions that could have led to life.
The chemical composition of the rain falling over Houston in the 2020s is not the rain that would have fallen 750 million years after the Earth formed, and the same can be said for the model protocell system Agrawal tested. The new paper proves that this approach of building a meshy wall around protocells is possible and can work together to compartmentalize the molecules of life, putting researchers closer than ever to finding the right set of chemical and environmental conditions that allow protocells to evolve.
“The molecules we used to build these protocells are just models until more suitable molecules can be found as substitutes,” Agrawal said. “While the chemistry would be a little bit different, the physics will remain the same.”
Interdisciplinary findings
Life is by nature interdisciplinary, so Szostak, the director of UChicago’s Chicago Center for the Origins of Life , said it was natural to collaborate with both UChicago PME , UChicago’s interdisciplinary school of molecular engineering, and the chemical engineering department at the University of Houston.
“Engineers have been studying the physical chemistry of these types of complexes—and polymer chemistry more generally—for a long time. It makes sense that there's expertise in the engineering school,” Szostak said. “When we're looking at something like the origin of life, it's so complicated and there are so many parts that we need people to get involved who have any kind of relevant experience.”
Citation: “ Did the exposure of coacervate droplets to rain make them the first stable protocells? ” Agrawal et al, Science Advances , August 21, 2024. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adn9657
Funding: Houston Endowment Fellowship, Welch Foundation, U.S. Department of Energy
— Adapted from an article published by the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering .
Top Stories
- DUNE completes underground excavation in South Dakota for massive neutrino experiment
- How homeownership shaped race in America, with Adrienne Brown (Ep. 141)
- UChicago’s Film Studies Center to preserve groundbreaking work by Black and Filipino filmmakers
Get more with UChicago News delivered to your inbox.
Recommended

The origin of life on Earth, explained

Earth could have supported crust, life earlier than thought
Related Topics
Latest news, big brains podcast: how homeownership shaped race in america.

UChicago political scholars reflect on the DNC, 2024 election

Inside the Lab
Inside the Lab: New ways to grow cells to protect our lungs from disease
Biochemistry

Go 'Inside the Lab' at UChicago
Explore labs through videos and Q&As with UChicago faculty, staff and students

New book explores emergence of touch-based language in DeafBlind communities

Meet a UChicagoan
UChicago biophysicist studies locomotion in creatures from all walks of life
Around uchicago.

Breakthrough by UChicago scientists could ease notoriously difficult chemical reaction
Quantrell and PhD Teaching Awards
UChicago announces 2024 winners of Quantrell and PhD Teaching Awards
Campus News
Project to improve accessibility, sustainability of Main Quadrangles
National Academy of Sciences
Five UChicago faculty elected to National Academy of Sciences in 2024

UChicago’s Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics celebrates 20 years of discovery

University of Chicago Law School
Coase-Sandor Institute for Law and Economics celebrates decade of impact
Biological Sciences Division
“You have to be open minded, planning to reinvent yourself every five to seven years.”

Meet A UChicagoan
Organist pulls out all the stops to bring Bach to UChicago
- All Research Labs
- 3D Deep Learning
- Applied Research
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Deep Imagination
- New and Featured
- AI Art Gallery
- AI & Machine Learning
- Computer Vision
- Academic Collaborations
- Government Collaborations
- Graduate Fellowship
- Internships
- Research Openings
- Research Scientists
- Meet the Team
- Publications
Kilometer-Scale Convection Allowing Model Emulation using Generative Diffusion Modeling

Storm-scale convection-allowing models (CAMs) are an important tool for predicting the evolution of thunderstorms and mesoscale convective systems that result in damaging extreme weather. By explicitly resolving convective dynamics within the atmosphere they afford meteorologists the nuance needed to provide outlook on hazard. Deep learning models have thus far not proven skilful at km-scale atmospheric simulation, despite being competitive at coarser resolution with state-of-the-art global, medium-range weather forecasting. We present a generative diffusion model called StormCast, which emulates the high-resolution rapid refresh (HRRR) model—NOAA’s state-of-the-art 3km operational CAM. StormCast autoregressively predicts 99 state variables at km scale using a 1-hour time step, with dense vertical resolution in the atmospheric boundary layer, conditioned on 26 synoptic variables. We present evidence of successfully learnt km-scale dynamics including competitive 1-6 hour forecast skill for composite radar reflectivity alongside physically realistic convective cluster evolution, moist updrafts, and cold pool morphology. StormCast predictions maintain realistic power spectra for multiple predicted variables across multi-hour forecasts. Together, these results establish the potential for autoregressive ML to emulate CAMs – opening up new km-scale frontiers for regional ML weather prediction and future climate hazard dynamical downscaling.
Publication Date
Research area, uploaded files.
Notification: View the latest site access restrictions, updates, and resources related to the coronavirus (COVID-19) »
NREL Research Synthesizes Molecular Aggregates for Solar Energy Applications
No molecule stands alone—they need others, at least when it comes to being able to display useful photophysical, electronic, and chemical properties. When individual molecules combine into an aggregate, or a complex of two or more molecules, they become much more than the sum of their individual parts.
Photoactive molecular aggregates, though—complexes of two or more chromophores, which are molecules that absorb light at certain wavelengths, thereby displaying color—go where isolated molecules do not. Due to the favorable interactions between molecules, these aggregates are of interest for biomedical, solar-energy-harvesting, and light-generating technologies. That is because—in natural photosynthesis and in bioinspired technological applications—photoactive aggregates are efficient at energy transfer, the transport of solar energy from one place to another. For instance, in natural photosynthesis, the most widespread energy conversion system on our planet, aggregates efficiently transfer the energy from where the light is absorbed to where it is converted into charges for electricity or chemicals for fuel production.
National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) researchers have synthesized two new compounds and studied how the properties of the individual molecules contribute to the—often unexpected—properties of the larger aggregates. The team synthesized tetracene diacid (Tc-DA) and a dimethyl ester analogue (Tc-DE) designed to prevent intermolecular hydrogen bonding while preserving Tc-DA's core electronics. The results are described in a Journal of the American Chemical Society paper , " Tetracene Diacid Aggregates for Directing Energy Flow toward Triplet Pairs ."
"The goal of this fundamental study was to decipher which molecular properties dictate the eventual emergent properties of the collective ensemble where the whole is greater than the sum of the individual parts, similar to putting seemingly unrelated puzzle pieces together and an unexpected image emerges," said NREL's Justin Johnson, senior scientist. "For molecular-based light harvesting architectures that aim to use unconventional mechanisms to more efficiently use the solar spectrum than typical solar cells, it's the collective properties that determine efficiency."
"Tc-DA was created to exploit intermolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions at semiconductor surfaces to well-ordered monolayers," said NREL's Nicholas Pompetti, postdoctoral researcher. "However, we found that we could control the aggregation of Tc-DA as it approached the surface through solvent and concentration choices. This opened up insights about tetracene-based aggregates and how their size and structure provide promising pathways for their use in light-harvesting applications."
In a given solvent environment, strong intermolecular interactions direct stable and deterministic aggregation. However, strong but uncontrolled interactions might lead to the formation of large aggregates that may weaken solubility. On the other hand, weak interactions spur dissociation with molecules acting as monomers. Fortunately for Tc-DA, the degree of aggregation can be finely controlled, ranging from monomers to stable larger order aggregates by changing concentration or solvent system.
Tetracene and its derivatives are prime candidates for singlet fission (SF), a process that may improve photoconversion efficiency by reducing wasteful heat production and relies on specific molecular dispositions that aggregates can achieve. Researchers used 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, computational modeling, and concentration-dependent optical behavior to investigate the likely aggregate structure of Tc-DA and Tc-DE. Steady-state spectroscopy analysis allowed them to observe absorption behavior and emission profiles of the aggregates. Computational modeling using density functional theory (performed by Kori Smyser and Sandeep Sharma at the University of Colorado Boulder), in combination with the NMR results, informed the researchers of the likely orientation of molecules within an aggregate structure. Researchers then examined the impacts of aggregation on Tc-DA's excited-state dynamics using transient absorption spectroscopy.
"The excited-state dynamics were surprisingly sensitive to crossing a well-defined threshold of concentration, almost like going through a phase transition for a pure material," Johnson said.
As the size and structure of the aggregates are important to light harvesting, researchers systematically varied solvent polarity and concentration in solution to analyze the well-defined tetracene aggregates and their behaviors, including the potentially important singlet fission. The researchers found that noncovalent tetracene-based aggregates beyond a dimer were stabilized at certain solvent polarities and concentrations, rapidly forming charge transfer and multiexcitonic states, which are desirable species for delivering charges (sometimes multiple units) to an electrode or catalyst.
The combination of NMR, computational studies, and spectroscopic results allowed the researchers to describe aggregate structures not often seen in solution-phase polyacenes.
"Controlling the landscape through molecular design and the associated solvent clearly allows us to dictate what the electrons do when they are photoexcited," Johnson said. "Nature uses hydrogen bonds in many types of aggregated architectures to tune energy landscapes in a similar fashion, like funneling water to a reservoir. Bringing such principles to artificial light-harvesting systems with the potential for controlling multiexcitons is a logical pursuit that is leading to interesting consequences."
Learn more about Basic Energy Sciences at NREL and about the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science Basic Energy Sciences program . Read " Tetracene Diacid Aggregates for Directing Energy Flow toward Triplet Pairs " in the Journal of the American Chemical Society .
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Sustainability
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
MIT engineers’ new theory could improve the design and operation of wind farms
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
The blades of propellers and wind turbines are designed based on aerodynamics principles that were first described mathematically more than a century ago. But engineers have long realized that these formulas don’t work in every situation. To compensate, they have added ad hoc “correction factors” based on empirical observations.
Now, for the first time, engineers at MIT have developed a comprehensive, physics-based model that accurately represents the airflow around rotors even under extreme conditions, such as when the blades are operating at high forces and speeds, or are angled in certain directions. The model could improve the way rotors themselves are designed, but also the way wind farms are laid out and operated. The new findings are described today in the journal Nature Communications , in an open-access paper by MIT postdoc Jaime Liew, doctoral student Kirby Heck, and Michael Howland, the Esther and Harold E. Edgerton Assistant Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering.
“We’ve developed a new theory for the aerodynamics of rotors,” Howland says. This theory can be used to determine the forces, flow velocities, and power of a rotor, whether that rotor is extracting energy from the airflow, as in a wind turbine, or applying energy to the flow, as in a ship or airplane propeller. “The theory works in both directions,” he says.
Because the new understanding is a fundamental mathematical model, some of its implications could potentially be applied right away. For example, operators of wind farms must constantly adjust a variety of parameters, including the orientation of each turbine as well as its rotation speed and the angle of its blades, in order to maximize power output while maintaining safety margins. The new model can provide a simple, speedy way of optimizing those factors in real time.
“This is what we’re so excited about, is that it has immediate and direct potential for impact across the value chain of wind power,” Howland says.
Modeling the momentum
Known as momentum theory, the previous model of how rotors interact with their fluid environment — air, water, or otherwise — was initially developed late in the 19th century. With this theory, engineers can start with a given rotor design and configuration, and determine the maximum amount of power that can be derived from that rotor — or, conversely, if it’s a propeller, how much power is needed to generate a given amount of propulsive force.
Momentum theory equations “are the first thing you would read about in a wind energy textbook, and are the first thing that I talk about in my classes when I teach about wind power,” Howland says. From that theory, physicist Albert Betz calculated in 1920 the maximum amount of energy that could theoretically be extracted from wind. Known as the Betz limit, this amount is 59.3 percent of the kinetic energy of the incoming wind.
But just a few years later, others found that the momentum theory broke down “in a pretty dramatic way” at higher forces that correspond to faster blade rotation speeds or different blade angles, Howland says. It fails to predict not only the amount, but even the direction of changes in thrust force at higher rotation speeds or different blade angles: Whereas the theory said the force should start going down above a certain rotation speed or blade angle, experiments show the opposite — that the force continues to increase. “So, it’s not just quantitatively wrong, it’s qualitatively wrong,” Howland says.
The theory also breaks down when there is any misalignment between the rotor and the airflow, which Howland says is “ubiquitous” on wind farms, where turbines are constantly adjusting to changes in wind directions. In fact, in an earlier paper in 2022, Howland and his team found that deliberately misaligning some turbines slightly relative to the incoming airflow within a wind farm significantly improves the overall power output of the wind farm by reducing wake disturbances to the downstream turbines.
In the past, when designing the profile of rotor blades, the layout of wind turbines in a farm, or the day-to-day operation of wind turbines, engineers have relied on ad hoc adjustments added to the original mathematical formulas, based on some wind tunnel tests and experience with operating wind farms, but with no theoretical underpinnings.
Instead, to arrive at the new model, the team analyzed the interaction of airflow and turbines using detailed computational modeling of the aerodynamics. They found that, for example, the original model had assumed that a drop in air pressure immediately behind the rotor would rapidly return to normal ambient pressure just a short way downstream. But it turns out, Howland says, that as the thrust force keeps increasing, “that assumption is increasingly inaccurate.”
And the inaccuracy occurs very close to the point of the Betz limit that theoretically predicts the maximum performance of a turbine — and therefore is just the desired operating regime for the turbines. “So, we have Betz’s prediction of where we should operate turbines, and within 10 percent of that operational set point that we think maximizes power, the theory completely deteriorates and doesn’t work,” Howland says.
Through their modeling, the researchers also found a way to compensate for the original formula’s reliance on a one-dimensional modeling that assumed the rotor was always precisely aligned with the airflow. To do so, they used fundamental equations that were developed to predict the lift of three-dimensional wings for aerospace applications.
The researchers derived their new model, which they call a unified momentum model, based on theoretical analysis, and then validated it using computational fluid dynamics modeling. In followup work not yet published, they are doing further validation using wind tunnel and field tests.
Fundamental understanding
One interesting outcome of the new formula is that it changes the calculation of the Betz limit, showing that it’s possible to extract a bit more power than the original formula predicted. Although it’s not a significant change — on the order of a few percent — “it’s interesting that now we have a new theory, and the Betz limit that’s been the rule of thumb for a hundred years is actually modified because of the new theory,” Howland says. “And that’s immediately useful.” The new model shows how to maximize power from turbines that are misaligned with the airflow, which the Betz limit cannot account for.
The aspects related to controlling both individual turbines and arrays of turbines can be implemented without requiring any modifications to existing hardware in place within wind farms. In fact, this has already happened, based on earlier work from Howland and his collaborators two years ago that dealt with the wake interactions between turbines in a wind farm, and was based on the existing, empirically based formulas.
“This breakthrough is a natural extension of our previous work on optimizing utility-scale wind farms,” he says, because in doing that analysis, they saw the shortcomings of the existing methods for analyzing the forces at work and predicting power produced by wind turbines. “Existing modeling using empiricism just wasn’t getting the job done,” he says.
In a wind farm, individual turbines will sap some of the energy available to neighboring turbines, because of wake effects. Accurate wake modeling is important both for designing the layout of turbines in a wind farm, and also for the operation of that farm, determining moment to moment how to set the angles and speeds of each turbine in the array.
Until now, Howland says, even the operators of wind farms, the manufacturers, and the designers of the turbine blades had no way to predict how much the power output of a turbine would be affected by a given change such as its angle to the wind without using empirical corrections. “That’s because there was no theory for it. So, that’s what we worked on here. Our theory can directly tell you, without any empirical corrections, for the first time, how you should actually operate a wind turbine to maximize its power,” he says.
Because the fluid flow regimes are similar, the model also applies to propellers, whether for aircraft or ships, and also for hydrokinetic turbines such as tidal or river turbines. Although they didn’t focus on that aspect in this research, “it’s in the theoretical modeling naturally,” he says.
The new theory exists in the form of a set of mathematical formulas that a user could incorporate in their own software, or as an open-source software package that can be freely downloaded from GitHub . “It’s an engineering model developed for fast-running tools for rapid prototyping and control and optimization,” Howland says. “The goal of our modeling is to position the field of wind energy research to move more aggressively in the development of the wind capacity and reliability necessary to respond to climate change.”
The work was supported by the National Science Foundation and Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Unified momentum model software
- Howland Lab
- Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Related Topics
- Civil and environmental engineering
- Renewable energy
- Climate change
Related Articles

Michael Howland gives wind energy a lift
A new method boosts wind farms’ energy output, without new equipment

The answer may be blowing in the wind
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Pursuing the secrets of a stealthy parasite
Read full story →

Study of disordered rock salts leads to battery breakthrough
Toward a code-breaking quantum computer

Uphill battles: Across the country in 75 days

3 Questions: From the bench to the battlefield

Duane Boning named vice provost for international activities
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Research shows our bodies go through rapid changes in our 40s and our 60s
For many people, reaching their mid-40s may bring unpleasant signs the body isn’t working as well as it once did. Injuries seem to happen more frequently. Muscles may feel weaker.
A new study, published Wednesday in Nature Aging , shows what may be causing the physical decline. Researchers have found that molecules and microorganisms both inside and outside our bodies are going through dramatic changes, first at about age 44 and then again when we hit 60. Those alterations may be causing significant differences in cardiovascular health and immune function.
The findings come from Stanford scientists who analyzed blood and other biological samples of 108 volunteers ages 25 to 75, who continued to donate samples for several years.
“While it’s obvious that you’re aging throughout your entire life, there are two big periods where things really shift,” said the study’s senior author, Michael Snyder, a professor of genetics and director of the Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine at Stanford Medicine. For example, “there’s a big shift in the metabolism of lipids when people are in their 40s and in the metabolism of carbohydrates when people are in their 60s.”
Lipids are fatty substances, including LDL, HDL and triglycerides, that perform a host of functions in the body, but they can be harmful if they build up in the blood.
The scientists tracked many kinds of molecules in the samples, including RNA and proteins, as well as the participants’ microbiomes.
The metabolic changes the researchers discovered indicate not that people in their 40s are burning calories more slowly but rather that the body is breaking food down differently. The scientists aren’t sure exactly what impact those changes have on health.
Previous research showed that resting energy use, or metabolic rate , didn’t change from ages 20 to 60. The new study’s findings don't contradict that.
The changes in metabolism affect how the body reacts to alcohol or caffeine, although the health consequences aren’t yet clear. In the case of caffeine, it may result in higher sensitivity.
It’s also not known yet whether the shifts could be linked to lifestyle or behavioral factors. For example, the changes in alcohol metabolism might be because people are drinking more in their mid-40s, Snyder said.
For now, Snyder suggests people in their 40s keep a close eye on their lipids, especially LDL cholesterol.
“If they start going up, people might want to think about taking statins if that’s what their doctor recommends,” he said. Moreover, “knowing there’s a shift in the molecules that affect muscles and skin, you might want to warm up more before exercising so you don’t hurt yourself.”
Until we know better what those changes mean, the best way to deal with them would be to eat healthy foods and to exercise regularly, Snyder said.Dr. Josef Coresh, founding director of the Optimal Aging Institute at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, compared the new findings to the invention of the microscope.
“The beauty of this type of paper is the level of detail we can see in molecular changes,” said Coresh, a professor of medicine at the school. “But it will take time to sort out what individual changes mean and how we can tailor medications to those changes. We do know that the origins of many diseases happen in midlife when people are in their 40s, though the disease may occur decades later.”
The new study “is an important step forward,” said Dr. Lori Zeltser, a professor of pathology and cell biology at the Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons. While we don’t know what the consequences of those metabolic changes are yet, “right now, we have to acknowledge that we metabolize food differently in our 40s, and that is something really new.”
The shifts the researchers found might help explain numerous age-related health changes, such as muscle loss, because “your body is breaking down food differently,” Zeltser said.
Linda Carroll is a regular health contributor to NBC News. She is coauthor of "The Concussion Crisis: Anatomy of a Silent Epidemic" and "Out of the Clouds: The Unlikely Horseman and the Unwanted Colt Who Conquered the Sport of Kings."
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
What Is Academic Writing? | Dos and Don’ts for Students
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You’ll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you’ll be expected to write your essays , research papers , and dissertation in academic style.
Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but it has specific conventions in terms of content, structure and style.
| Academic writing is… | Academic writing is not… |
|---|---|
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Types of academic writing, academic writing is…, academic writing is not…, useful tools for academic writing, academic writing checklist.
Academics mostly write texts intended for publication, such as journal articles, reports, books, and chapters in edited collections. For students, the most common types of academic writing assignments are listed below.
| Type of academic text | Definition |
|---|---|
| A fairly short, self-contained argument, often using sources from a class in response to a question provided by an instructor. | |
| A more in-depth investigation based on independent research, often in response to a question chosen by the student. | |
| The large final research project undertaken at the end of a degree, usually on a of the student’s choice. | |
| An outline of a potential topic and plan for a future dissertation or research project. | |
| A critical synthesis of existing research on a topic, usually written in order to inform the approach of a new piece of research. | |
| A write-up of the aims, methods, results, and conclusions of a lab experiment. | |
| A list of source references with a short description or evaluation of each source. |
Different fields of study have different priorities in terms of the writing they produce. For example, in scientific writing it’s crucial to clearly and accurately report methods and results; in the humanities, the focus is on constructing convincing arguments through the use of textual evidence. However, most academic writing shares certain key principles intended to help convey information as effectively as possible.
Whether your goal is to pass your degree, apply to graduate school , or build an academic career, effective writing is an essential skill.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Formal and unbiased
Academic writing aims to convey information in an impartial way. The goal is to base arguments on the evidence under consideration, not the author’s preconceptions. All claims should be supported with relevant evidence, not just asserted.
To avoid bias, it’s important to represent the work of other researchers and the results of your own research fairly and accurately. This means clearly outlining your methodology and being honest about the limitations of your research.
The formal style used in academic writing ensures that research is presented consistently across different texts, so that studies can be objectively assessed and compared with other research.
Because of this, it’s important to strike the right tone with your language choices. Avoid informal language , including slang, contractions , clichés, and conversational phrases:
- Also , a lot of the findings are a little unreliable.
- Moreover , many of the findings are somewhat unreliable.
Clear and precise
It’s important to use clear and precise language to ensure that your reader knows exactly what you mean. This means being as specific as possible and avoiding vague language :
- People have been interested in this thing for a long time .
- Researchers have been interested in this phenomenon for at least 10 years .
Avoid hedging your claims with words like “perhaps,” as this can give the impression that you lack confidence in your arguments. Reflect on your word choice to ensure it accurately and directly conveys your meaning:
- This could perhaps suggest that…
- This suggests that…
Specialist language or jargon is common and often necessary in academic writing, which generally targets an audience of other academics in related fields.
However, jargon should be used to make your writing more concise and accurate, not to make it more complicated. A specialist term should be used when:
- It conveys information more precisely than a comparable non-specialist term.
- Your reader is likely to be familiar with the term.
- The term is commonly used by other researchers in your field.
The best way to familiarize yourself with the kind of jargon used in your field is to read papers by other researchers and pay attention to their language.
Focused and well structured
An academic text is not just a collection of ideas about a topic—it needs to have a clear purpose. Start with a relevant research question or thesis statement , and use it to develop a focused argument. Only include information that is relevant to your overall purpose.
A coherent structure is crucial to organize your ideas. Pay attention to structure at three levels: the structure of the whole text, paragraph structure, and sentence structure.
| Overall structure | and a . . |
|---|---|
| Paragraph structure | when you move onto a new idea. at the start of each paragraph to indicate what it’s about, and make clear between paragraphs. |
| Sentence structure | to express the connections between different ideas within and between sentences. to avoid . |
Well sourced
Academic writing uses sources to support its claims. Sources are other texts (or media objects like photographs or films) that the author analyzes or uses as evidence. Many of your sources will be written by other academics; academic writing is collaborative and builds on previous research.
It’s important to consider which sources are credible and appropriate to use in academic writing. For example, citing Wikipedia is typically discouraged. Don’t rely on websites for information; instead, use academic databases and your university library to find credible sources.
You must always cite your sources in academic writing. This means acknowledging whenever you quote or paraphrase someone else’s work by including a citation in the text and a reference list at the end.
| In-text citation | Elsewhere, it has been argued that the method is “the best currently available” (Smith, 2019, p. 25). |
| Reference list | Smith, J. (2019). (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Norton. |
There are many different citation styles with different rules. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago . Make sure to consistently follow whatever style your institution requires. If you don’t cite correctly, you may get in trouble for plagiarism . A good plagiarism checker can help you catch any issues before it’s too late.
You can easily create accurate citations in APA or MLA style using our Citation Generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Correct and consistent
As well as following the rules of grammar, punctuation, and citation, it’s important to consistently apply stylistic conventions regarding:
- How to write numbers
- Introducing abbreviations
- Using verb tenses in different sections
- Capitalization of terms and headings
- Spelling and punctuation differences between UK and US English
In some cases there are several acceptable approaches that you can choose between—the most important thing is to apply the same rules consistently and to carefully proofread your text before you submit. If you don’t feel confident in your own proofreading abilities, you can get help from Scribbr’s professional proofreading services or Grammar Checker .
Academic writing generally tries to avoid being too personal. Information about the author may come in at some points—for example in the acknowledgements or in a personal reflection—but for the most part the text should focus on the research itself.
Always avoid addressing the reader directly with the second-person pronoun “you.” Use the impersonal pronoun “one” or an alternate phrasing instead for generalizations:
- As a teacher, you must treat your students fairly.
- As a teacher, one must treat one’s students fairly.
- Teachers must treat their students fairly.
The use of the first-person pronoun “I” used to be similarly discouraged in academic writing, but it is increasingly accepted in many fields. If you’re unsure whether to use the first person, pay attention to conventions in your field or ask your instructor.
When you refer to yourself, it should be for good reason. You can position yourself and describe what you did during the research, but avoid arbitrarily inserting your personal thoughts and feelings:
- In my opinion…
- I think that…
- I like/dislike…
- I conducted interviews with…
- I argue that…
- I hope to achieve…
Long-winded
Many students think their writing isn’t academic unless it’s over-complicated and long-winded. This isn’t a good approach—instead, aim to be as concise and direct as possible.
If a term can be cut or replaced with a more straightforward one without affecting your meaning, it should be. Avoid redundant phrasings in your text, and try replacing phrasal verbs with their one-word equivalents where possible:
- Interest in this phenomenon carried on in the year 2018 .
- Interest in this phenomenon continued in 2018 .
Repetition is a part of academic writing—for example, summarizing earlier information in the conclusion—but it’s important to avoid unnecessary repetition. Make sure that none of your sentences are repeating a point you’ve already made in different words.
Emotive and grandiose
An academic text is not the same thing as a literary, journalistic, or marketing text. Though you’re still trying to be persuasive, a lot of techniques from these styles are not appropriate in an academic context. Specifically, you should avoid appeals to emotion and inflated claims.
Though you may be writing about a topic that’s sensitive or important to you, the point of academic writing is to clearly communicate ideas, information, and arguments, not to inspire an emotional response. Avoid using emotive or subjective language :
- This horrible tragedy was obviously one of the worst catastrophes in construction history.
- The injury and mortality rates of this accident were among the highest in construction history.
Students are sometimes tempted to make the case for their topic with exaggerated , unsupported claims and flowery language. Stick to specific, grounded arguments that you can support with evidence, and don’t overstate your point:
- Charles Dickens is the greatest writer of the Victorian period, and his influence on all subsequent literature is enormous.
- Charles Dickens is one of the best-known writers of the Victorian period and has had a significant influence on the development of the English novel.
There are a a lot of writing tools that will make your writing process faster and easier. We’ll highlight three of them below.
Paraphrasing tool
AI writing tools like ChatGPT and a paraphrasing tool can help you rewrite text so that your ideas are clearer, you don’t repeat yourself, and your writing has a consistent tone.
They can also help you write more clearly about sources without having to quote them directly. Be warned, though: it’s still crucial to give credit to all sources in the right way to prevent plagiarism .
Grammar checker
Writing tools that scan your text for punctuation, spelling, and grammar mistakes. When it detects a mistake the grammar checke r will give instant feedback and suggest corrections. Helping you write clearly and avoid common mistakes .
You can use a summarizer if you want to condense text into its most important and useful ideas. With a summarizer tool, you can make it easier to understand complicated sources. You can also use the tool to make your research question clearer and summarize your main argument.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Use the checklist below to assess whether you have followed the rules of effective academic writing.
- Checklist: Academic writing
I avoid informal terms and contractions .
I avoid second-person pronouns (“you”).
I avoid emotive or exaggerated language.
I avoid redundant words and phrases.
I avoid unnecessary jargon and define terms where needed.
I present information as precisely and accurately as possible.
I use appropriate transitions to show the connections between my ideas.
My text is logically organized using paragraphs .
Each paragraph is focused on a single idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Every part of the text relates to my central thesis or research question .
I support my claims with evidence.
I use the appropriate verb tenses in each section.
I consistently use either UK or US English .
I format numbers consistently.
I cite my sources using a consistent citation style .
Your text follows the most important rules of academic style. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Taboo words in academic writing
- How to write more concisely
- Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples
More interesting articles
- A step-by-step guide to the writing process
- Active vs. Passive Constructions | When to Use the Passive Voice
- Avoid informal writing
- Avoid rhetorical questions
- Be conscious of your adverb placement
- Capitalization in titles and headings
- Exclamation points (!)
- First-Person Pronouns | List, Examples & Explanation
- Forging good titles in academic writing
- Free, Downloadable Educational Templates for Students
- Free, Downloadable Lecture Slides for Educators and Students
- How to avoid repetition and redundancy
- How to write a lab report
- How to write effective headings
- Language mistakes in quotes
- List of 47 Phrasal Verbs and Their One-Word Substitutions
- Myth: It’s incorrect to start a sentence with “because”
- Myth: It’s an error to split infinitives
- Myth: It’s incorrect to start a sentence with a coordinating conjunction (and, but, or, for, nor, yet, so)
- Myth: Paragraph transitions should be placed at the ends of paragraphs
- Tense tendencies in academic texts
- Using abbreviations and acronyms
- What Is Anthropomorphism? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Sentence Case? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Title Case? | Explanation & Worksheet
- Writing myths: The reasons we get bad advice
- Writing numbers: words and numerals
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Learn the steps to write a research paper, from choosing a topic to proofreading your draft. Scribbr offers tips, examples, and a citation checker to help you with your academic writing.
Reading Time: 14 minutes In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper.. The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within ...
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools. Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts. Advanced Search. PDF Packages of 37 papers.
Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the ...
Learn how to write an effective introduction for your research paper, whether it's argumentative or empirical. Follow five steps to introduce your topic, provide background, establish your problem, specify your objective, and map out your paper.
Learn how to write a research paper with this comprehensive guide that covers the definition, structure, examples, and writing process. Find out how to choose a topic, conduct a literature review, develop a thesis, collect and analyze data, organize your paper, and cite your sources.
Learn how to write a research paper properly with this concise guide that covers topics like choosing a topic, gathering sources, writing a thesis, and citing evidence. Find out the difference between research papers and proposals, the length requirements, and the formatting tips.
research articles. Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Article (207738) Conference Proceeding (56) Matters Arising (55) ... Calls for Papers Editor's Choice ...
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Take your research further with Artstor's 3+ million images. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and ...
Learn the three-step process of finding a research topic, reviewing the literature, and writing up your paper with examples and a free template. Grad Coach is an online platform that helps students with academic writing and research skills.
Learn how to format a research paper in APA, MLA, or Chicago style with free templates and guides. Find out the main guidelines for font, margins, spacing, headings, citations, and more.
PubMed® comprises more than 37 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.
Find and access millions of research papers from various sources with these free academic search engines. Learn how to use Google Scholar, BASE, CORE, Science.gov, Semantic Scholar, Baidu Scholar and RefSeek effectively.
A research paper provides an excellent opportunity to contribute to your area of study or profession by exploring a topic in depth.. With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience. Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
arXiv.org is a free online repository of preprints and e-prints covering various topics in physics, mathematics, computer science, and more. Browse the latest papers by subject, search for specific keywords, or subscribe to the blog for updates.
All research papers have pretty much the same structure. If you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Learn the steps to start and complete your research paper in our guide. How to write a problem statement. What is a problem statement and how do you write one? This guide answers all your questions and includes an example ...
Explore various aspects of research paper writing, editing, and publishing in computer science and other disciplines. Find chapters and articles on topics such as R&D project management, library research, parametric tests, copy-editing, and more.
Get a visual overview of a new academic field. Enter a typical paper and we'll build you a graph of similar papers in the field. Explore and build more graphs for interesting papers that you find - soon you'll have a real, visual understanding of the trends, popular works and dynamics of the field you're interested in.
Research integrity; Paper mills; Want to write? Write an article and join a growing community of more than 188,700 academics and researchers from 5,030 institutions. Register now.
Learn how to choose a topic, identify a problem, formulate research questions, create a research design, and write a research proposal for your thesis or dissertation. This guide covers the first steps of the research process with examples and tips.
We provide novel empirical evidence that firms' investment is more responsive to monetary policy when a higher fraction of their debt matures. In a heterogeneous firm New Keynesian model with financial frictions and endogenous debt maturity, two channels explain this finding: (1.) Firms with more maturing debt have larger roll-over needs and are therefore more exposed to fluctuations in the ...
A new paper by researchers with the University of Chicago and the University of Houston proposes a solution. They show how rainwater could have helped create a meshy wall around protocells 3.8 billion years ago, a critical step in the transition from tiny beads of RNA to every bacterium, plant, animal, and human that ever lived.
Storm-scale convection-allowing models (CAMs) are an important tool for predicting the evolution of thunderstorms and mesoscale convective systems that result in damaging extreme weather. By explicitly resolving convective dynamics within the atmosphere they afford meteorologists the nuance needed to provide outlook on hazard. Deep learning models have thus far not proven skilful at km-scale ...
NREL Research Synthesizes Molecular Aggregates for Solar Energy Applications. Aug. 22, 2024 | By Justin Daugherty ... The results are described in a Journal of the American Chemical Society paper, "Tetracene Diacid Aggregates for Directing Energy Flow toward Triplet Pairs." ...
The new findings are described today in the journal Nature Communications, in an open-access paper by MIT postdoc Jaime Liew, doctoral student Kirby Heck, and Michael Howland, the Esther and Harold E. Edgerton Assistant Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering. "We've developed a new theory for the aerodynamics of rotors," Howland ...
Research shows our bodies go through rapid changes in our 40s and our 60s. ... "The beauty of this type of paper is the level of detail we can see in molecular changes," said Coresh, a ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...