Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.

Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
‘Doughnut economics’: 4 questions for industry leaders
Black bankruptcy filers more likely to be denied debt relief
How assertive communication helped this M&A executive rise to the top
Credit: Mimi Phan
Ideas Made to Matter
Design thinking, explained
Rebecca Linke
Sep 14, 2017
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled “Design Thinking” by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
Since then, the design thinking process has been applied to developing new products and services, and to a whole range of problems, from creating a business model for selling solar panels in Africa to the operation of Airbnb .
At a high level, the steps involved in the design thinking process are simple: first, fully understand the problem; second, explore a wide range of possible solutions; third, iterate extensively through prototyping and testing; and finally, implement through the customary deployment mechanisms.
The skills associated with these steps help people apply creativity to effectively solve real-world problems better than they otherwise would. They can be readily learned, but take effort. For instance, when trying to understand a problem, setting aside your own preconceptions is vital, but it’s hard.
Creative brainstorming is necessary for developing possible solutions, but many people don’t do it particularly well. And throughout the process it is critical to engage in modeling, analysis, prototyping, and testing, and to really learn from these many iterations.
Once you master the skills central to the design thinking approach, they can be applied to solve problems in daily life and any industry.
Here’s what you need to know to get started.

Understand the problem
The first step in design thinking is to understand the problem you are trying to solve before searching for solutions. Sometimes, the problem you need to address is not the one you originally set out to tackle.
“Most people don’t make much of an effort to explore the problem space before exploring the solution space,” said MIT Sloan professor Steve Eppinger. The mistake they make is to try and empathize, connecting the stated problem only to their own experiences. This falsely leads to the belief that you completely understand the situation. But the actual problem is always broader, more nuanced, or different than people originally assume.
Take the example of a meal delivery service in Holstebro, Denmark. When a team first began looking at the problem of poor nutrition and malnourishment among the elderly in the city, many of whom received meals from the service, it thought that simply updating the menu options would be a sufficient solution. But after closer observation, the team realized the scope of the problem was much larger , and that they would need to redesign the entire experience, not only for those receiving the meals, but for those preparing the meals as well. While the company changed almost everything about itself, including rebranding as The Good Kitchen, the most important change the company made when rethinking its business model was shifting how employees viewed themselves and their work. That, in turn, helped them create better meals (which were also drastically changed), yielding happier, better nourished customers.
Involve users
Imagine you are designing a new walker for rehabilitation patients and the elderly, but you have never used one. Could you fully understand what customers need? Certainly not, if you haven’t extensively observed and spoken with real customers. There is a reason that design thinking is often referred to as human-centered design.
“You have to immerse yourself in the problem,” Eppinger said.
How do you start to understand how to build a better walker? When a team from MIT’s Integrated Design and Management program together with the design firm Altitude took on that task, they met with walker users to interview them, observe them, and understand their experiences.
“We center the design process on human beings by understanding their needs at the beginning, and then include them throughout the development and testing process,” Eppinger said.
Central to the design thinking process is prototyping and testing (more on that later) which allows designers to try, to fail, and to learn what works. Testing also involves customers, and that continued involvement provides essential user feedback on potential designs and use cases. If the MIT-Altitude team studying walkers had ended user involvement after its initial interviews, it would likely have ended up with a walker that didn’t work very well for customers.
It is also important to interview and understand other stakeholders, like people selling the product, or those who are supporting the users throughout the product life cycle.
The second phase of design thinking is developing solutions to the problem (which you now fully understand). This begins with what most people know as brainstorming.
Hold nothing back during brainstorming sessions — except criticism. Infeasible ideas can generate useful solutions, but you’d never get there if you shoot down every impractical idea from the start.
“One of the key principles of brainstorming is to suspend judgment,” Eppinger said. “When we're exploring the solution space, we first broaden the search and generate lots of possibilities, including the wild and crazy ideas. Of course, the only way we're going to build on the wild and crazy ideas is if we consider them in the first place.”
That doesn’t mean you never judge the ideas, Eppinger said. That part comes later, in downselection. “But if we want 100 ideas to choose from, we can’t be very critical.”
In the case of The Good Kitchen, the kitchen employees were given new uniforms. Why? Uniforms don’t directly affect the competence of the cooks or the taste of the food.
But during interviews conducted with kitchen employees, designers realized that morale was low, in part because employees were bored preparing the same dishes over and over again, in part because they felt that others had a poor perception of them. The new, chef-style uniforms gave the cooks a greater sense of pride. It was only part of the solution, but if the idea had been rejected outright, or perhaps not even suggested, the company would have missed an important aspect of the solution.
Prototype and test. Repeat.
You’ve defined the problem. You’ve spoken to customers. You’ve brainstormed, come up with all sorts of ideas, and worked with your team to boil those ideas down to the ones you think may actually solve the problem you’ve defined.
“We don’t develop a good solution just by thinking about a list of ideas, bullet points and rough sketches,” Eppinger said. “We explore potential solutions through modeling and prototyping. We design, we build, we test, and repeat — this design iteration process is absolutely critical to effective design thinking.”
Repeating this loop of prototyping, testing, and gathering user feedback is crucial for making sure the design is right — that is, it works for customers, you can build it, and you can support it.
“After several iterations, we might get something that works, we validate it with real customers, and we often find that what we thought was a great solution is actually only just OK. But then we can make it a lot better through even just a few more iterations,” Eppinger said.
Implementation
The goal of all the steps that come before this is to have the best possible solution before you move into implementing the design. Your team will spend most of its time, its money, and its energy on this stage.
“Implementation involves detailed design, training, tooling, and ramping up. It is a huge amount of effort, so get it right before you expend that effort,” said Eppinger.
Design thinking isn’t just for “things.” If you are only applying the approach to physical products, you aren’t getting the most out of it. Design thinking can be applied to any problem that needs a creative solution. When Eppinger ran into a primary school educator who told him design thinking was big in his school, Eppinger thought he meant that they were teaching students the tenets of design thinking.
“It turns out they meant they were using design thinking in running their operations and improving the school programs. It’s being applied everywhere these days,” Eppinger said.
In another example from the education field, Peruvian entrepreneur Carlos Rodriguez-Pastor hired design consulting firm IDEO to redesign every aspect of the learning experience in a network of schools in Peru. The ultimate goal? To elevate Peru’s middle class.
As you’d expect, many large corporations have also adopted design thinking. IBM has adopted it at a company-wide level, training many of its nearly 400,000 employees in design thinking principles .
What can design thinking do for your business?
The impact of all the buzz around design thinking today is that people are realizing that “anybody who has a challenge that needs creative problem solving could benefit from this approach,” Eppinger said. That means that managers can use it, not only to design a new product or service, “but anytime they’ve got a challenge, a problem to solve.”
Applying design thinking techniques to business problems can help executives across industries rethink their product offerings, grow their markets, offer greater value to customers, or innovate and stay relevant. “I don’t know industries that can’t use design thinking,” said Eppinger.
Ready to go deeper?
Read “ The Designful Company ” by Marty Neumeier, a book that focuses on how businesses can benefit from design thinking, and “ Product Design and Development ,” co-authored by Eppinger, to better understand the detailed methods.
Register for an MIT Sloan Executive Education course:
Systematic Innovation of Products, Processes, and Services , a five-day course taught by Eppinger and other MIT professors.
- Leadership by Design: Innovation Process and Culture , a two-day course taught by MIT Integrated Design and Management director Matthew Kressy.
- Managing Complex Technical Projects , a two-day course taught by Eppinger.
- Apply for M astering Design Thinking , a 3-month online certificate course taught by Eppinger and MIT Sloan senior lecturers Renée Richardson Gosline and David Robertson.
Steve Eppinger is a professor of management science and innovation at MIT Sloan. He holds the General Motors Leaders for Global Operations Chair and has a PhD from MIT in engineering. He is the faculty co-director of MIT's System Design and Management program and Integrated Design and Management program, both master’s degrees joint between the MIT Sloan and Engineering schools. His research focuses on product development and technical project management, and has been applied to improving complex engineering processes in many industries.
Read next: 10 agile ideas worth sharing
Related Articles

How to solve problems with design thinking
May 18, 2023 Is it time to throw out the standard playbook when it comes to problem solving? Uniquely challenging times call for unique approaches, write Michael Birshan , Ben Sheppard , and coauthors in a recent article , and design thinking offers a much-needed fresh perspective for leaders navigating volatility. Design thinking is a systemic, intuitive, customer-focused problem-solving approach that can create significant value and boost organizational resilience. The proof is in the pudding: From 2013 to 2018, companies that embraced the business value of design had TSR that were 56 percentage points higher than that of their industry peers. Check out these insights to understand how to use design thinking to unleash the power of creativity in strategy and problem solving.
Designing out of difficult times
What is design thinking?
The power of design thinking
Leading by design
Author Talks: Don Norman designs a better world
Are you asking enough from your design leaders?
Tapping into the business value of design
Redesigning the design department
Author Talks: Design your future
A design-led approach to embracing an ecosystem strategy
More than a feeling: Ten design practices to deliver business value
MORE FROM MCKINSEY
How design helps incumbents build new businesses
A complete guide to the design thinking process

Learn the five stages of the design thinking process, get practical tips to apply them, and get templates to seamlessly run design thinking exercises.
How many projects have you worked on that stalled because your team couldn’t align on the best path forward? How many more got shelved because they didn’t meet user needs or expectations? And how many got delayed in rounds and rounds of never-ending feedback?
Thankfully, you don’t have to keep repeating those experiences month after month. The (not so) secret weapon: design thinking .
Design thinking gives teams a new way to approach their projects and overcome some of those well-known challenges. It can help teams understand their users' needs and challenges, then apply those learnings to solve problems in a creative, innovative way. Understanding design thinking can transform your team’s problem-solving approach — and how you work together.
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an iterative process where teams seek to understand user needs, challenge assumptions, define complex problems to solve, and develop innovative solutions to prototype and test. The goal of design thinking is to come up with user-focused solutions tailored to the particular problem at hand.
While often used in product design, service design, and customer experience, you can use design thinking in virtually any situation, industry, or organization to create user-centric solutions to specific problems.
Design thinking process 101: Definitions and approaches
The design thinking process puts customers’ and users’ needs at the center and aims to solve challenges from their perspective.
Design thinking typically follows five distinct stages:
Empathize stage
The first stage of design thinking lays the foundation for the rest of the process because it focuses on the needs of the real people using your product. At this stage, you want to get familiar with the people experiencing the problems you’re trying to solve, understanding their point of view, and learning about their user experience. You want to understand their challenges and what they need from your product or company to address them.
The goal of this stage is for your team to develop a user-centered vision of the core problem you need to solve. The idea is to challenge any assumptions or biases teams have, instead using their customer perspective as a guiding source. This is important because it aligns the team on what needs to be considered during the rest of the design thinking process.
To help you get a solid understanding of the problems you’re solving, you can ask a lot of questions to build empathy with your users. These will invite people to share their experiences and observations to help your team better understand the problem. Then, you can move on to some specific exercises for the empathy stage of the process.
As you build up your understanding of your users, it's helpful to visualize their experience. A common way to do this is to assemble a customer journey map . This helps identify areas of friction and understand customer preferences.
Learn more: 7 types of questions to build empathy for design thinking
Ideate stage
Your priority here is to think outside the box and source as many ideas as possible from all areas of the business. Bring in people from different departments so you benefit from a wider range of experiences and perspectives during ideation sessions. Don’t worry about coming up with concrete solutions or how to implement each one — you’ll build on that later. The goal is to explore new and creative ideas rather than come up with an actual plan.
Key steps in the ideation phase:
- Define your problem : Creating a problem statement ensures that your team can focus on solving the right problem and staying aligned with your end-user or customer’s problem
- Start ideating : Choose a brainstorming technique to help organize team participation that fits your goal (More on that in the next section.)
- Prioritize your ideas : Once you have several ideas, prioritize them based on how well they take into account the customer’s needs
- Choose the best solution : Choose the best ideas to move forward to either the define stage or the prototype stage
Learn more: The ideation stage of design thinking: What you need to know
Your priority here is to generate as many ideas as possible, without judging or evaluating them. This step encourages designers to think creatively and push the boundaries of what's possible. We’ve put together a list of different brainstorming techniques to help your teams come up with creative new ideas.
Put it into practice: How to facilitate a brainstorming session
Prototyping stage
At this stage, your team’s goal is to remove uncertainty around your proposed solutions. This is where you start thinking about them in more detail, including how you’ll bring them to life. Your prototypes should help the team understand if the design or solution will work as it’s intended to.
Here, the focus is on speed and efficiency — you don’t want to invest a ton of time or resources into these solutions yet because you’re not sure they’re the best ones for the problem you’re trying to solve. You just need a functional, interactive prototype that can prove your concept. These are learning opportunities to help you spot any issues or opportunities before you take it any further.
Learn more: A guide to prototyping: the 4th stage of design thinking
Testing stage
The testing stage is normally one of the last stages of the design thinking process. After you’ve developed a concept or prototype, you need to test it in the real-world to understand its viability and usability. It’s where your product, design, or development teams evaluate the creative solutions they’ve come up with, to see how real users interact with them.
Testing your concepts and observing how people interact with them helps you understand whether or not the prototype solves real problems and meets their needs, before you invest in it fully.
However, design thinking is an iterative process: You may go through the ideation, prototyping, and testing phases multiple times to improve and refine your solutions as you learn more from your users.
Read the guide: Testing: A guide to the 5th stage of design thinking
The relationship between human-centered design and design thinking
These two terms are often used together, because they complement one another. However, they’re two different things, so understanding their differences is important.
Simply put, design thinking is a working process, while human-centered design is a mindset or approach.
The first step in finding success with design thinking is to foster a culture of human-centered design within your team. This is because design thinking focuses so heavily on the users and customers — the people using your product or service.
To inspire your team, we’ve put together four human-centered design examples — and explain why they work so well.
Benefits of design thinking
For organizations who’ve never run a design thinking workshop before, it can feel like a big change in how you approach the design process. But it can offer many benefits for your business.
Foster a true design culture within your organization
Design thinking is an iterative process — it’s not something you do once and call it done. The more you do it, the more you’ll see a design-focused culture emerge within your organization, which is much more effective than going to one-off creative retreats or setting up expensive innovation centers that no one ever uses.
This mindset and cultural shift can help scale design thinking within the business. But it’s important to know how to avoid some of the pitfalls companies can face when trying to create a design culture internally.
Learn more: How to use the LUMA System of Innovation for everyday design thinking
Encourage collaboration across departments
Design thinking isn’t just for the designers on the team. The earlier stages of the process — Empathize, Define, and Ideate — are perfect for bringing in people from across the business. In fact, bringing in varied viewpoints and perspectives can help you come up with more creative or effective solutions.
You can use the design thinking process to get more people involved, and help everyone contribute ideas.
Improve understanding of user needs
So many companies say they’re “customer focused,” but lack a clear understanding of what really matters most to their customers in the context of their product or service. Design thinking puts the user front and center, with the Empathize stage dedicated to understanding and discovering user needs.
Learn more: How to identify user needs and pain points
Skills and behaviors needed for successful design thinking
To get the most out of a design thinking exercise, you’ll need a collaborative and creative mindset within your team. The team needs to be willing to explore new ideas, and laser-focused on customer or user needs.
Here are some specific skills to help your design thinking process run smoothly.
Divergent and convergent thinking
Divergence and convergence is a human-centered design approach to problem-solving. It switches between expansive and focused thinking, giving you a process that balances understanding people’s problems and developing solutions.
It focuses on understanding a user's needs, behaviors, and motivations, to help you develop empathy for their problems. Then, it encourages experimentation and iteration to help you effectively design solutions to meet those needs.
Collaborative working
Design thinking isn’t a solo activity. You’ll bring in people from different teams or business areas. To get the most out of the process, everyone needs to collaborate and communicate effectively. Teams that are good at collaborating drive the best outcomes, while also making it an enjoyable experience working together.
There are several core collaboration skills your team needs to succeed:
- Open-mindedness
- Communication
- Adaptability
- Organization
- Time management
Learn more about why these skills are so important and how you can improve them individually or as a team: 7 collaboration skills your team needs to succeed
Participatory or collaborative design
For many design teams and creative folks, the idea of designing something with other people can be enough to make them shudder. “Design by committee” is their idea of a nightmare. But the design thinking process isn’t about “making the logo 10% bigger” or “using a different shade of blue.” It’s user- and solution-focused.
You’ll get the best outcomes if you bring insights, perspectives, and expertise from multiple stakeholders. That includes at the Prototype and Test stages, as everyone will have ideas to contribute to help you bring solutions to life.
Learn more: What is co-design? A primer on participatory design
Common challenges in design thinking
If your team hasn’t mastered or fully committed to each one of the design thinking steps, you may encounter problems that make it harder to reap the benefits of design thinking.
Here are 4 common challenges that teams face when implementing design thinking practices.
- A company culture that doesn't foster collaboration
- An inability to adjust to non-linear processes
- A lack of in-depth user research
- Getting too invested in a single idea
Learn how to address these in Mural's guide on design thinking challenges .
Design thinking tools and templates to help you get started
Using mural for design thinking.
There are lots of tools you can use to run design thinking workshops — including Mural. We help designers work as effectively as possible, so they can get to better solutions quicker. We’ve incorporated some design thinking shortcuts and “hidden” features into our application, making it perfect for in-person or remote (or even asynchronous) collaborative sessions. These include:
- Use the C-key shortcut to quickly connect ideas with arrows
- Seamlessly import existing information from spreadsheets
- Duplicate elements you already created for faster visualization
- Fit your canvas to your screen and zoom in
- Get even more options using the right-click menu
And to help you get started, we’ve hand-picked some Mural templates relevant to each stage of the design process below.
Templates for the Empathy stage
The empathy map template helps you visualize the thoughts, feelings, and actions of your customersto help you develop a better understanding of the their experiences. The map is divided into four quadrants, where you record the following:
- Thoughts: the customer’s internal dialogue and beliefs
- Feelings: the customer’s emotional responses
- Actions: the customer’s actions and behaviors
- Observations: what the customer is seeing and hearing.
Try Mural’s empathy map template
Templates for the Define stage
This exercise helps you understand a situation or problem by identifying what’s working, what’s not, and areas for improvement. You start by listing out the problem, then identifying the positive aspects (the rose), negatives (thorn), and possible solutions for improvement (the buds).
You can use this template to run the exercise individually or in groups. It gives you a way to gather new ideas and perspectives on the problem you’re solving in real-time.
Try Mural’s Rose, thorn, bud template
Templates for the Ideate stage
The round robin brainstorming exercise is a collaborative session where every person contributes multiple ideas. This is a great way to come up with lots of different ideas and solutions in the ideation stage of design thinking, where you’re focusing on quantity and creativity.
Bringing in ideas from every team member encourages people to share their unique perspectives, and can also help you avoid groupthink.
Try Mural’s Round robin template
Templates for the Prototype stage
This template helps you map out how an idea will work in practice, as a functional system. Schematic diagramming is very flexible, so it can be used in many types of projects to make sure your idea is structurally sound. It can help you map out workflows and identify any decisions you need to make to bring your idea to life.
Try Mural’s Schematic diagramming template
Templates for the Test stage
In think aloud testing, users test out a product or prototype and talk through the relevant tasks as they complete them. You can use this template to record the feedback, insights, and experiences of your testers, and identify the success and failure points in your proposed solution.
Try Mural’s Think aloud testing template
Design thinking examples: What it looks like in practice
Design thinking is a very flexible approach that works for companies of any size, from large enterprises to small startups.
Here are some examples of how companies use design thinking, for many types of creative projects.
IBM uses design thinking to design at scale
IBM was traditionally an engineering-led organization, but now it's shifting its focus onto design, working to spread a design culture throughout the business. One of the main ways of doing that is by launching IBM Design Camps.
These camps are comprehensive educational programs that help people understand the concept of design thinking and how it specifically works at IBM.
Learn more about how IBM runs design thinking workshops with remote or distributed teams .
Somersault Innovation uses design thinking to transform its sales process
Somersault Innovation has used design thinking methods to help their sales team co-create solutions with their customers. It’s helped sellers become more customer-centric.
Now, their sellers can create mutual success plans with their prospects, making it easier for them to find a path forward together.
Mural uses design thinking to drive growth
At Mural, our marketing team is constantly following new trends, evaluating metrics, and working to deliver the best experiences for our customers. Design thinking helps us adopt a customer-centric approach by ensuring that we're focused on the right problems. This helps us have the biggest impact on the company’s long-term growth while creating the most value for our users.
David J. Bland planned a book using the design thinking methodology
It’s not just visual creative projects that can benefit from the design thinking process. Founder, speaker, and author David J. Bland used the methodology to plan out his book and collaborate with other team members in the process. In addition to helping him refine and adjust the structure, Bland also used it to gather feedback from early readers and target audiences, which helped get the final product just right.
Support design thinking with tools that facilitate creative collaboration
While we’ve covered some of the skills and behaviors you need to successfully run design thinking exercises, having the right tools can help a lot, too. A collaborative platform helps teams communicate, share ideas, and turn those ideas into solutions together.
Mural helps teams visualize their ideas in a collaboration platform that unlocks teamwork . This helps everyone stay on the same page, while giving them the ability to add their own ideas freely and easily. Mural facilitates effective collaboration both in person and remotely, making it ideal for design thinking workshops for co-located and distributed teams. Plus, it has tons of ready-to-use templates (like the ones we listed above) to help you get started.
Ready to give it a try? Start your Free Forever account today, and run your next design thinking workshop in Mural.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts

4 common challenges and pitfalls in design thinking
.jpg)
How to encourage thinking outside the box

What Is hybrid work? A primer on the new way of working
Related blog posts.

Leigh-Margaret Stull shares more on the future state of Mural

The best enterprise collaboration tools as of 2024

How to create a meaningful product vision

Design Thinking: How it works [Theory, Practice & Examples]
So you’ve heard of Design Thinking , but it sounds a bit like hocus-pocus? Imagine standing at the entrance of a sleek, futuristic museum, greeted by a door that refuses to budge. Frustration mounts as you struggle to figure out how to open it, but then, a child approaches, effortlessly pushes the door, and you follow suit, feeling a blend of awe and embarrassment. That moment captures the essence of design thinking—a concept that, like that perplexing door, may initially seem locked, yet holds the key to unlocking innovation, creativity, and problem-solving potential in today’s complex world. In a hurry? Skip the theory and get straight to the 5 stages of design thinking .

Design thinking, a term that has surged in popularity, transcends the realm of aesthetics and reaches into the very core of how we tackle challenges , both big and small. It’s a methodology that isn’t confined to designers alone but is a powerful tool for anyone seeking novel solutions, whether in business, education, healthcare, or even personal life. Design thinking isn’t just a buzzword – it’s a dynamic and transformative approach that promises to reshape how we approach problems and create solutions.
Design Thinking: A Definition
Design thinking is a transformative problem-solving approach that puts human needs and experiences at its core. At its essence, it’s a structured methodology that empowers individuals and organizations to tackle complex challenges by fostering empathy, creativity, and innovation. Unlike traditional problem-solving methods, design thinking is not confined to a linear path; instead, it encourages dynamic and iterative thinking to arrive at innovative solutions (see also: Innovation Management ).
Historical Background
To truly grasp the significance of design thinking, it’s essential to delve into its historical roots. The concept finds its origins in the mid-20th century, primarily within the field of industrial design. Visionaries like Herbert A. Simon and L. Bruce Archer were among the early proponents of this methodology, emphasizing the importance of user-centered design . Over the decades, design thinking evolved, incorporating insights from various disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, and business. It gained prominence in the corporate world thanks to influential figures like David Kelley of IDEO and the Stanford d.school, which helped popularize and formalize the design thinking process we know today.
Design Thinking Core Principles
- Empathy : Design thinking starts with deep empathy for the end-user. This means understanding their needs, desires, and pain points on a profound level. Empathy forms the foundation upon which innovative solutions are built.
- Iteration : Design thinking embraces the idea that the first solution is rarely the best one. It encourages continuous refinement and iteration of ideas through prototyping and testing. This iterative process allows for the discovery of unexpected insights and improvements.
- User-Centricity : The user is the focal point of the entire design thinking process. Solutions are not imposed from the top down; they emerge organically from an understanding of the user’s perspective and needs.
- Collaboration : Design thinking thrives on interdisciplinary collaboration . It brings together individuals with diverse skills and perspectives to foster creative problem-solving.
These principles, combined with a structured framework, make design thinking a potent methodology for addressing a wide range of challenges , from designing user-friendly products to solving complex organizational problems.
The Stages of Design Thinking
While Design Thinking is often described as a mindset, at it’s core it is a five step process.

Stage I: Empathize
The journey of design thinking commences with a crucial first step— empathy . In this initial stage, designers and problem-solvers immerse themselves in the world of the end-user, seeking to understand their needs , desires, and challenges on a profound level. This isn’t a casual observation – it’s a deep dive into the user’s experiences. Empathy involves conducting interviews, surveys, and even shadowing users in their daily routines. The goal? To gain insights that go beyond what’s explicitly stated—to uncover the unspoken, the latent, and the emotions that influence user behavior. Empathy is the bedrock upon which the entire design thinking process rests, for it’s from this wellspring of understanding that innovative solutions emerge. If you want to learn more about understanding different personalities, take our DISC-Test.
Stage II: Define
With a wealth of empathetic insights in hand, the next stage is to distill these observations into a clear and concise problem statement . What are the specific challenges and pain points that need to be addressed? Defining the problem is a pivotal moment in the design thinking process because it frames the entire journey. It’s about reframing the issue to focus on what truly matters to the user. This stage requires a delicate balance of precision and creativity—precision in articulating the problem, and creativity in reframing it to inspire fresh ideas.
Stage III: Ideate
Now, armed with a well-defined problem, the design thinking process enters the ideation stage —a veritable playground for creative brainstorming. Here, the emphasis is on quantity rather than quality, as the goal is to generate a broad spectrum of ideas, no matter how wild or unconventional they may seem. Ideation sessions often involve cross-functional teams engaging in free-flowing discussions, sketching, and mind mapping . It’s in this stage that the magic of creativity takes flight, and seemingly impossible solutions begin to take shape.
Stage IV: Prototype
Ideation is a boundless landscape of possibilities, but to transform these concepts into tangible solutions, the process moves to prototyping . Prototypes are simplified representations of the envisioned solutions, ranging from paper sketches to interactive mock-ups. The purpose of prototyping is to bring ideas to life in a tangible form that can be tested and refined. It’s an essential step to bridge the gap between abstract concepts and real-world applicability. Prototypes serve as a canvas for experimentation and iteration, allowing designers to uncover flaws, make improvements, and fine-tune their solutions.
Stage V: Test!
The final stage of design thinking is where ideas are put to the test in the real world . Testing involves presenting prototypes to the end-users and gathering their feedback . This user-centric approach ensures that the proposed solutions align with the users’ needs and expectations. The feedback loop is iterative, often leading back to the ideation and prototyping stages as insights are gained. This process of testing and refinement continues until the most suitable and effective solution emerges, ready to address the defined problem effectively.
In these stages, design thinking transforms from a theoretical concept into a hands-on, user-driven methodology that fosters innovation and creative problem-solving. Each stage plays a vital role in the iterative process that leads to meaningful solutions.
Design Thinking Examples & Benefits
To truly appreciate the transformative power of design thinking, let’s turn to real-world examples where this methodology has reshaped industries and solved complex problems.
Case Studies
One such shining example comes from Airbnb . In its early days, Airbnb faced a significant challenge: how to establish trust between hosts and guests in the sharing economy. By applying design thinking principles, they delved deep into the user experience, empathizing with both hosts and guests. They introduced features like user profiles, reviews, and a secure payment system, all aimed at fostering trust and confidence. This approach not only propelled Airbnb’s growth but also revolutionized the hospitality industry.
Another compelling case is that of the healthcare giant, Mayo Clinic . In an industry fraught with complexities and patient-centric challenges, Mayo Clinic turned to design thinking to improve patient experiences. They revamped waiting areas, redesigned appointment scheduling, and introduced user-friendly mobile apps for patients to access their medical records. These innovations not only improved patient satisfaction but also enhanced the overall quality of care.
Benefits of the Design Thinking Process
Design thinking isn’t just a methodology; it’s a mindset that empowers individuals and organizations to navigate the complexities of our modern world effectively. Its benefits extend far beyond problem-solving and innovation, permeating into the very fabric of how we approach challenges and create solutions:
- Fosters Innovation : Design thinking places the user at the core of problem-solving, encouraging innovative thinking that leads to groundbreaking solutions.
- Promotes Adaptability : In an ever-changing world, design thinking equips organizations with the ability to pivot and evolve in response to shifting market dynamics and customer preferences.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction : Whether in product design or service delivery, design thinking ensures that solutions precisely meet user needs and expectations, resulting in happier and more loyal customers.
- Encourages Collaboration : Design thinking fosters a culture of collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, promoting teamwork and creativity.
Read more about the benefits in this review of educational research: Having good design thinking skills can assist in solving really complex problems.

Challenges and Criticisms

While design thinking has garnered widespread acclaim, it’s not immune to criticism, and one prevalent concern is the risk of over-hyping. In the rush to embrace this transformative approach, there’s a danger of viewing it as a panacea for all organizational challenges. Design thinking, like any methodology, has its limitations. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, and not every problem requires a design thinking approach. Over-hyping can create unrealistic expectations , leading to disappointment when results fall short. It’s essential to strike a balance between recognizing design thinking’s potential and acknowledging its boundaries.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing design thinking within organizations can be a journey fraught with challenges. Resistance to change is a common stumbling block. Employees accustomed to traditional problem-solving methods may find it challenging to adapt to the iterative and user-centric nature of design thinking. Another challenge is the need for time and resources . Design thinking, when done right, demands investment in research, prototyping, and user testing, which can strain budgets and schedules. Additionally, maintaining a consistent commitment to the process throughout the organization can be difficult. Without leadership support and a culture that encourages experimentation and learning from failures, design thinking initiatives may falter. Addressing these challenges requires a thoughtful and strategic approach to ensure that design thinking becomes ingrained in the organizational DNA .
How to Incorporate Design Thinking
Design thinking isn’t reserved for designers alone – it’s a mindset that anyone can cultivate to enhance problem-solving skills and drive innovation in their work and daily lives.
Practical tips for individuals
- Start with Empathy : Whether you’re designing a product or tackling a personal challenge, begin by understanding the needs and perspectives of those involved. Ask questions, actively listen , and put yourself in their shoes.
- Embrace Iteration : Don’t settle for the first solution that comes to mind. Be open to refining and iterating on your ideas. Embrace failure as a learning opportunity.
- Diverse Perspectives : Seek input from people with different backgrounds and viewpoints. Collaborative brainstorming can lead to more creative and effective solutions.
- Prototype and Test : Even in non-design contexts, consider creating prototypes or mock-ups to visualize your ideas. Test them with potential users or stakeholders to gather feedback.
- User-Centric Approach : Always prioritize the end-user or recipient of your work. Your solutions should address their needs and provide value.
Organizational Integration
To foster a design thinking culture within organizations, several steps can be taken:
- Leadership Buy-In : Leaders should champion the adoption of design thinking, setting an example for the rest of the organization. They should communicate its value and allocate resources for its implementation (see also “ Leadership test “)
- Training and Education : Offer design thinking training and workshops to employees at all levels. Equip them with the skills and knowledge to apply design thinking methodologies.
- Cross-Functional Teams : Encourage collaboration across different departments and disciplines. Create teams that bring together diverse skills and perspectives for problem-solving.
- Design Thinking Spaces : Designate physical or virtual spaces where employees can brainstorm, prototype, and test ideas. These spaces should be conducive to creativity and collaboration.
- Reward Innovation : Recognize and reward employees who contribute innovative ideas and solutions through design thinking. Create incentives for innovation and risk-taking.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement : Establish mechanisms for collecting feedback on design thinking initiatives. Use this feedback to refine processes and adapt to evolving needs.
By following these steps, individuals can harness the power of design thinking in their personal and professional lives, while organizations can create an environment where design thinking thrives, leading to innovative solutions and a more agile , customer-centric approach.
It’s worth emphasizing that design thinking holds greater importance than ever before. It equips individuals and organizations with the tools to navigate change effectively , foster innovation, and create solutions that prioritize the needs of users, transcending disciplinary boundaries.
Consider embracing design thinking in your own context . Whether you’re seeking solutions in your daily life or aiming to cultivate a culture of creativity within your organization, the key lies in embracing empathy, collaboration, and a willingness to experiment. These qualities unlock the potential of design thinking.
In the words of the iconic designer and innovator Steve Jobs , “ Design is how it works .” Let design thinking be the guiding light in our intricate world, where innovation and user-centric solutions pave the path forward. Its enduring relevance underscores our innate capacity to create, adapt, and thrive .
You might also be interested in: Pareto Concept – Why it still works!
Additional Resources
For readers eager to dive deeper into the world of design thinking, there is a wealth of resources available to further your understanding and expertise:
- “ Design Thinking for Strategic Innovation ” by Idris Mootee: This book offers a strategic perspective on design thinking and its application in business.
- “ Change by Design ” by Tim Brown: Tim Brown, CEO of IDEO, provides valuable insights into the design thinking process and its potential for innovation.
- “ The Design Thinking Playbook ” by Michael Lewrick, Patrick Link, and Larry Leifer: A comprehensive guide to practical design thinking methods and tools.
- IDEO U ( https://www.ideou.com/ ): IDEO U offers online courses and resources on design thinking, innovation, and leadership.
- Stanford d.school ( https://dschool.stanford.edu/ ): Explore Stanford University’s d.school website for design thinking tools, case studies, and free resources.
- Nielsen Norman Group ( https://www.nngroup.com/ ): The Nielsen Norman Group offers valuable insights and research on user-centered design and usability.
- Coursera Design Thinking Specialization : This series of courses offered by the University of Virginia on Coursera provides a comprehensive understanding of design thinking principles and their application.
- edX Design Thinking MicroMasters Program : This program by Rochester Institute of Technology on edX covers design thinking, innovation, and leadership.
VIDEO: Doreen Lorenzo about Design Thinking (TedTalk)
Teambuilding activities.
- 🤝 Get2Know Games
- 🎄 Christmas Travel Quiz
- 🌎 Team Travel Quiz
- 🚀 Spaceship
- 🎅 Santa’s Online Team Challenge
- 🕵️♂️ Team Memory Hunt
teamazing formats
- Virtual Team Development
- Virtual Teambuilding Events
- Virtual Event Hosting
- Jobs & Careers
- Amazing Teams
- Newsletter (Monthly Digest)
- Team Development in a Nutshell
Trending Blogposts
- Effective Employee Performance Reviews for Managers
- Organizational Structures: Types and Complete Overview
- The best virtual kickoff meeting games to start the new year with your team
- Understanding New Work: What employees really want and why
- Bad Leadership Examples: 9 Ultimate Warning Signs
- Managing Virtual Teams: A guide to Success
- The Ultimate List of Online Team Building Games and Remote Team Activities
- What is Team Building?

- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- How to solve problems using the design ...
How to solve problems using the design thinking process

The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford’s d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions to complex problems.
As humans, we’re approached with problems every single day. But how often do we come up with solutions to everyday problems that put the needs of individual humans first?
This is how the design thinking process started.
What is the design thinking process?
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you tackle complex problems by framing the issue in a human-centric way. The design thinking process works especially well for problems that are not clearly defined or have a more ambiguous goal.
One of the first individuals to write about design thinking was John E. Arnold, a mechanical engineering professor at Stanford. Arnold wrote about four major areas of design thinking in his book, “Creative Engineering” in 1959. His work was later taught at Stanford’s Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (also known as d.school), a design institute that pioneered the design thinking process.
This eventually led Nobel Prize laureate Herbert Simon to outline one of the first iterations of the design thinking process in his 1969 book, “The Sciences of the Artificial.” While there are many different variations of design thinking, “The Sciences of the Artificial” is often credited as the basis.
Anatomy of Work Special Report: How to spot—and overcome—the most crucial enterprise challenges
Learn how enterprises can improve processes and productivity, no matter how complex your organization is. With fewer redundancies, leaders and their teams can hit goals faster.
![problem solving is design thinking [Resource Card] AOW Blog Image](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/fdc408f5-063d-4ea7-8d73-cb3ec61704fc/Global-AOW23-Black-Hole?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A non-linear design thinking approach
Design thinking is not a linear process. It’s important to understand that each stage of the process can (and should) inform the other steps. For example, when you’re going through user testing, you may learn about a new problem that didn’t come up during any of the previous stages. You may learn more about your target personas during the final testing phase, or discover that your initial problem statement can actually help solve even more problems, so you need to redefine the statement to include those as well.
Why use the design thinking process
The design thinking process is not the most intuitive way to solve a problem, but the results that come from it are worth the effort. Here are a few other reasons why implementing the design thinking process for your team is worth it.
Focus on problem solving
As human beings, we often don’t go out of our way to find problems. Since there’s always an abundance of problems to solve, we’re used to solving problems as they occur. The design thinking process forces you to look at problems from many different points of view.
The design thinking process requires focusing on human needs and behaviors, and how to create a solution to match those needs. This focus on problem solving can help your design team come up with creative solutions for complex problems.
Encourages collaboration and teamwork
The design thinking process cannot happen in a silo. It requires many different viewpoints from designers, future customers, and other stakeholders . Brainstorming sessions and collaboration are the backbone of the design thinking process.
Foster innovation
The design thinking process focuses on finding creative solutions that cater to human needs. This means your team is looking to find creative solutions for hyper specific and complex problems. If they’re solving unique problems, then the solutions they’re creating must be equally unique.
The iterative process of the design thinking process means that the innovation doesn’t have to end—your team can continue to update the usability of your product to ensure that your target audience’s problems are effectively solved.
The 5 stages of design thinking
Currently, one of the more popular models of design thinking is the model proposed by the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (or d.school) at Stanford. The main reason for its popularity is because of the success this process had in successful companies like Google, Apple, Toyota, and Nike. Here are the five steps designated by the d.school model that have helped many companies succeed.
1. Empathize stage
The first stage of the design thinking process is to look at the problem you’re trying to solve in an empathetic manner. To get an accurate representation of how the problem affects people, actively look for people who encountered this problem previously. Asking them how they would have liked to have the issue resolved is a good place to start, especially because of the human-centric nature of the design thinking process.
Empathy is an incredibly important aspect of the design thinking process. The design thinking process requires the designers to put aside any assumptions and unconscious biases they may have about the situation and put themselves in someone else’s shoes.
For example, if your team is looking to fix the employee onboarding process at your company, you may interview recent new hires to see how their onboarding experience went. Another option is to have a more tenured team member go through the onboarding process so they can experience exactly what a new hire experiences.
2. Define stage
Sometimes a designer will encounter a situation when there’s a general issue, but not a specific problem that needs to be solved. One way to help designers clearly define and outline a problem is to create human-centric problem statements.
A problem statement helps frame a problem in a way that provides relevant context in an easy to comprehend way. The main goal of a problem statement is to guide designers working on possible solutions for this problem. A problem statement frames the problem in a way that easily highlights the gap between the current state of things and the end goal.
Tip: Problem statements are best framed as a need for a specific individual. The more specific you are with your problem statement, the better designers can create a human-centric solution to the problem.
Examples of good problem statements:
We need to decrease the number of clicks a potential customer takes to go through the sign-up process.
We need to decrease the new subscriber unsubscribe rate by 10%.
We need to increase the Android app adoption rate by 20%.
3. Ideate stage
This is the stage where designers create potential solutions to solve the problem outlined in the problem statement. Use brainstorming techniques with your team to identify the human-centric solution to the problem defined in step two.
Here are a few brainstorming strategies you can use with your team to come up with a solution:
Standard brainstorm session: Your team gathers together and verbally discusses different ideas out loud.
Brainwrite: Everyone writes their ideas down on a piece of paper or a sticky note and each team member puts their ideas up on the whiteboard.
Worst possible idea: The inverse of your end goal. Your team produces the most goofy idea so nobody will look silly. This takes out the rigidity of other brainstorming techniques. This technique also helps you identify areas that you can improve upon in your actual solution by looking at the worst parts of an absurd solution.
It’s important that you don’t discount any ideas during the ideation phase of brainstorming. You want to have as many potential solutions as possible, as new ideas can help trigger even better ideas. Sometimes the most creative solution to a problem is the combination of many different ideas put together.
4. Prototype stage
During the prototype phase, you and your team design a few different variations of inexpensive or scaled down versions of the potential solution to the problem. Having different versions of the prototype gives your team opportunities to test out the solution and make any refinements.
Prototypes are often tested by other designers, team members outside of the initial design department, and trusted customers or members of the target audience. Having multiple versions of the product gives your team the opportunity to tweak and refine the design before testing with real users. During this process, it’s important to document the testers using the end product. This will give you valuable information as to what parts of the solution are good, and which require more changes.
After testing different prototypes out with teasers, your team should have different solutions for how your product can be improved. The testing and prototyping phase is an iterative process—so much so that it’s possible that some design projects never end.
After designers take the time to test, reiterate, and redesign new products, they may find new problems, different solutions, and gain an overall better understanding of the end-user. The design thinking framework is flexible and non-linear, so it’s totally normal for the process itself to influence the end design.
Tips for incorporating the design thinking process into your team
If you want your team to start using the design thinking process, but you’re unsure of how to start, here are a few tips to help you out.
Start small: Similar to how you would test a prototype on a small group of people, you want to test out the design thinking process with a smaller team to see how your team functions. Give this test team some small projects to work on so you can see how this team reacts. If it works out, you can slowly start rolling this process out to other teams.
Incorporate cross-functional team members : The design thinking process works best when your team members collaborate and brainstorm together. Identify who your designer’s key stakeholders are and ensure they’re included in the small test team.
Organize work in a collaborative project management software : Keep important design project documents such as user research, wireframes, and brainstorms in a collaborative tool like Asana . This way, team members will have one central source of truth for anything relating to the project they’re working on.
Foster collaborative design thinking with Asana
The design thinking process works best when your team works collaboratively. You don’t want something as simple as miscommunication to hinder your projects. Instead, compile all of the information your team needs about a design project in one place with Asana.
Related resources

15 creative elevator pitch examples for every scenario

Timesheet templates: How to track team progress

Scaling clinical trial management software with PM solutions

Data-driven decision making: A step-by-step guide
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Design Thinking 101

July 31, 2016 2016-07-31
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
In This Article:
Definition of design thinking, why — the advantage, flexibility — adapt to fit your needs, scalability — think bigger, history of design thinking.
Design thinking is an ideology supported by an accompanying process . A complete definition requires an understanding of both.
Definition: The design thinking ideology asserts that a hands-on, user-centric approach to problem solving can lead to innovation, and innovation can lead to differentiation and a competitive advantage. This hands-on, user-centric approach is defined by the design thinking process and comprises 6 distinct phases, as defined and illustrated below.
The design-thinking framework follows an overall flow of 1) understand, 2) explore, and 3) materialize. Within these larger buckets fall the 6 phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test, and implement.

Conduct research in order to develop knowledge about what your users do, say, think, and feel .
Imagine your goal is to improve an onboarding experience for new users. In this phase, you talk to a range of actual users. Directly observe what they do, how they think, and what they want, asking yourself things like ‘what motivates or discourages users?’ or ‘where do they experience frustration?’ The goal is to gather enough observations that you can truly begin to empathize with your users and their perspectives.
Combine all your research and observe where your users’ problems exist. While pinpointing your users’ needs , begin to highlight opportunities for innovation.
Consider the onboarding example again. In the define phase, use the data gathered in the empathize phase to glean insights. Organize all your observations and draw parallels across your users’ current experiences. Is there a common pain point across many different users? Identify unmet user needs.
Brainstorm a range of crazy, creative ideas that address the unmet user needs identified in the define phase. Give yourself and your team total freedom; no idea is too farfetched and quantity supersedes quality.
At this phase, bring your team members together and sketch out many different ideas. Then, have them share ideas with one another, mixing and remixing, building on others' ideas.
Build real, tactile representations for a subset of your ideas. The goal of this phase is to understand what components of your ideas work, and which do not. In this phase you begin to weigh the impact vs. feasibility of your ideas through feedback on your prototypes.
Make your ideas tactile. If it is a new landing page, draw out a wireframe and get feedback internally. Change it based on feedback, then prototype it again in quick and dirty code. Then, share it with another group of people.
Return to your users for feedback. Ask yourself ‘Does this solution meet users’ needs?’ and ‘Has it improved how they feel, think, or do their tasks?’
Put your prototype in front of real customers and verify that it achieves your goals. Has the users’ perspective during onboarding improved? Does the new landing page increase time or money spent on your site? As you are executing your vision, continue to test along the way.
Put the vision into effect. Ensure that your solution is materialized and touches the lives of your end users.
This is the most important part of design thinking, but it is the one most often forgotten. As Don Norman preaches, “we need more design doing.” Design thinking does not free you from the actual design doing. It’s not magic.
“There’s no such thing as a creative type. As if creativity is a verb, a very time-consuming verb. It’s about taking an idea in your head, and transforming that idea into something real. And that’s always going to be a long and difficult process. If you’re doing it right, it’s going to feel like work.” - Milton Glaser
As impactful as design thinking can be for an organization, it only leads to true innovation if the vision is executed. The success of design thinking lies in its ability to transform an aspect of the end user’s life. This sixth step — implement — is crucial.
Why should we introduce a new way to think about product development? There are numerous reasons to engage in design thinking, enough to merit a standalone article, but in summary, design thinking achieves all these advantages at the same time.
Design thinking:
- Is a user-centered process that starts with user data, creates design artifacts that address real and not imaginary user needs, and then tests those artifacts with real users
- Leverages collective expertise and establishes a shared language, as well as buy-in amongst your team
- Encourages innovation by exploring multiple avenues for the same problem
Jakob Nielsen says “ a wonderful interface solving the wrong problem will fail ." Design thinking unfetters creative energies and focuses them on the right problem.
The above process will feel abstruse at first. Don’t think of it as if it were a prescribed step-by-step recipe for success. Instead, use it as scaffolding to support you when and where you need it. Be a master chef, not a line cook: take the recipe as a framework, then tweak as needed.
Each phase is meant to be iterative and cyclical as opposed to a strictly linear process, as depicted below. It is common to return to the two understanding phases, empathize and define, after an initial prototype is built and tested. This is because it is not until wireframes are prototyped and your ideas come to life that you are able to get a true representation of your design. For the first time, you can accurately assess if your solution really works. At this point, looping back to your user research is immensely helpful. What else do you need to know about the user in order to make decisions or to prioritize development order? What new use cases have arisen from the prototype that you didn’t previously research?
You can also repeat phases. It’s often necessary to do an exercise within a phase multiple times in order to arrive at the outcome needed to move forward. For example, in the define phase, different team members will have different backgrounds and expertise, and thus different approaches to problem identification. It’s common to spend an extended amount of time in the define phase, aligning a team to the same focus. Repetition is necessary if there are obstacles in establishing buy-in. The outcome of each phase should be sound enough to serve as a guiding principle throughout the rest of the process and to ensure that you never stray too far from your focus.

The packaged and accessible nature of design thinking makes it scalable. Organizations previously unable to shift their way of thinking now have a guide that can be comprehended regardless of expertise, mitigating the range of design talent while increasing the probability of success. This doesn’t just apply to traditional “designery” topics such as product design, but to a variety of societal, environmental, and economical issues. Design thinking is simple enough to be practiced at a range of scopes; even tough, undefined problems that might otherwise be overwhelming. While it can be applied over time to improve small functions like search, it can also be applied to design disruptive and transformative solutions, such as restructuring the career ladder for teachers in order to retain more talent.
It is a common misconception that design thinking is new. Design has been practiced for ages : monuments, bridges, automobiles, subway systems are all end-products of design processes. Throughout history, good designers have applied a human-centric creative process to build meaningful and effective solutions.
In the early 1900's husband and wife designers Charles and Ray Eames practiced “learning by doing,” exploring a range of needs and constraints before designing their Eames chairs, which continue to be in production even now, seventy years later. 1960's dressmaker Jean Muir was well known for her “common sense” approach to clothing design, placing as much emphasis on how her clothes felt to wear as they looked to others. These designers were innovators of their time. Their approaches can be viewed as early examples of design thinking — as they each developed a deep understanding of their users’ lives and unmet needs. Milton Glaser, the designer behind the famous I ♥ NY logo, describes this notion well: “We’re always looking, but we never really see…it’s the act of attention that allows you to really grasp something, to become fully conscious of it.”
Despite these (and other) early examples of human-centric products, design has historically been an afterthought in the business world, applied only to touch up a product’s aesthetics. This topical design application has resulted in corporations creating solutions which fail to meet their customers’ real needs. Consequently, some of these companies moved their designers from the end of the product-development process, where their contribution is limited, to the beginning. Their human-centric design approach proved to be a differentiator: those companies that used it have reaped the financial benefits of creating products shaped by human needs.
In order for this approach to be adopted across large organizations, it needed to be standardized. Cue design thinking, a formalized framework of applying the creative design process to traditional business problems.
The specific term "design thinking" was coined in the 1990's by David Kelley and Tim Brown of IDEO, with Roger Martin, and encapsulated methods and ideas that have been brewing for years into a single unified concept.
We live in an era of experiences , be they services or products, and we’ve come to have high expectations for these experiences. They are becoming more complex in nature as information and technology continues to evolve. With each evolution comes a new set of unmet needs. While design thinking is simply an approach to problem solving, it increases the probability of success and breakthrough innovation.
Learn more about design thinking in the full-day course Generating Big Ideas with Design Thinking .
Free Downloads
Related courses, generating big ideas with design thinking.
Unearthing user pain points to drive breakthrough design concepts
Interaction
Service Blueprinting
Orchestrate people, props, and processes that are core to your digital experience
Discovery: Building the Right Thing
Conduct successful discovery phases to ensure you build the best solution
Related Topics
- Design Process Design Process
- Managing UX Teams
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6lmvCqvmjfE

The Role of Design
Don Norman · 5 min

Design Thinking Activities
Sarah Gibbons · 5 min

Design Thinking: Top 3 Challenges and Solutions
Related Articles:
Design Thinking: Study Guide
Kate Moran and Megan Brown · 4 min
Service Blueprinting in Practice: Who, When, What
Alita Joyce and Sarah Gibbons · 7 min
Design Thinking Builds Strong Teams
User-Centered Intranet Redesign: Set Up for Success in 11 Steps
Kara Pernice · 10 min
UX Responsibilities in Scrum Events
Anna Kaley · 13 min
Journey Mapping: 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Alita Joyce and Kate Kaplan · 7 min
Design Thinking: A Guide to Creative Problem-Solving (2024)
Updated: Jan 02, 2024 By: Dessign Team

Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that focuses on human needs. It is a human-centered approach to innovation that aims to create innovative solutions to complex problems. The process begins with empathy, where designers seek to understand the needs, behaviors, and pain points of the users.
This is followed by defining the problem, ideating, prototyping, and testing. The iterative process allows designers to refine their ideas and create solutions that are not only innovative but also meet the needs of the users.
Design thinking is a methodology that can be applied to a wide range of problems. It is used by designers , businesses, and organizations to develop new products, services, and processes. The methodology is based on the idea that the best solutions are created when designers work collaboratively with users and stakeholders.
By involving users in the design process, designers can create solutions that are more effective and meet the needs of the users. Design thinking can also be used to identify new opportunities for growth and innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that focuses on the needs of the users.
- The process involves empathy, defining the problem, ideating, prototyping, and testing.
- Design thinking can be applied to a wide range of problems and is used by designers, businesses, and organizations to develop new products, services, and processes.
Fundamentals of Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that involves building innovative solutions by understanding human needs and constraints. It is a collaborative and iterative process that can help designers and developers create products and services that are both user-centric and profitable.
Understanding the Process
The design thinking process is a non-linear process that involves five stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. The process starts with empathizing with the user and understanding their needs. The next stage is defining the problem statement and organizing the observations. Then, ideation techniques are used to brainstorm solutions, followed by the experimental phase of prototyping. The final stage is testing and iterating on the prototype until the solution meets the user's needs and constraints.
Role of Empathy
Empathy is a critical component of design thinking. It involves putting oneself in the user's shoes and understanding their pain points, emotional needs, and visions. Through empathy, designers can gain insights into the user's behavior and develop innovative solutions that meet their needs.
Importance of Ideation
Ideation is the process of generating creative solutions to the problem statement. Designers use ideation techniques such as the worst possible idea and scampering to come up with innovative solutions. Ideation is an essential stage in the design thinking process because it helps designers generate a range of ideas and select the best solution.
Prototype Development
Prototyping is the process of building a physical or digital representation of the solution. Prototyping allows designers to test the solution and get feedback from users. It is an iterative process that involves building, testing, and refining the prototype until it meets the user's needs and constraints.
Testing and Iteration
Testing is the process of evaluating the prototype and getting feedback from users. It involves observing how users interact with the prototype and collecting data on their behavior. Based on the feedback, designers can iterate on the prototype and refine the solution until it meets the user's needs and constraints.
Design thinking is a powerful methodology that can help designers and developers create innovative solutions to complex problems. By focusing on human needs and constraints, designers can create products and services that provide value to customers and give organizations a competitive advantage.
Applications of Design Thinking
Design thinking has proven to be a valuable methodology for solving complex problems and creating innovative solutions. Its human-centered approach to problem-solving has made it a popular choice in various industries, including business, product development, service design, and organizational culture.
In Business and Strategy
Design thinking is becoming increasingly popular in the business world as it helps organizations to develop innovative solutions that meet the needs of their customers. By using design thinking, businesses can define their problem statement, understand their audience, and create solutions that have a competitive advantage.
Design thinking can also be used in strategy development. It helps businesses to identify and prioritize opportunities, create a vision for growth, and develop a plan to achieve their goals. By using design thinking, businesses can create a strategy that is grounded in human needs and insights.
In Product Development
Design thinking is a valuable methodology for product development as it helps designers to understand the needs of their users and develop products that meet those needs. The process involves empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing.
By using design thinking, designers can create products that provide value to their users and differentiate themselves from their competitors. It also helps them to iterate and improve their products based on feedback from their users.
In Service Design
Design thinking is widely used in service design as it helps designers to create services that are user-centric and meet the needs of their users. The process involves empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing.
By using design thinking, designers can create services that provide value to their users and differentiate themselves from their competitors. It also helps them to iterate and improve their services based on feedback from their users.
In Organizational Culture
Design thinking is not just a methodology for problem-solving but also a way of thinking that can transform organizational culture. By using design thinking, organizations can create a culture that is focused on human needs, collaboration, and innovation.
Design thinking can also be used to develop skills in employees, such as empathy, problem-solving, and collaboration. It helps organizations to create a culture of innovation and change that can drive growth and success.
In conclusion, design thinking is a powerful methodology that can be applied in various industries to create innovative solutions that meet the needs of their users. It is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that can transform organizational culture and drive growth and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 stages of design thinking.
Design thinking involves five stages: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. Each stage is essential to the process and helps to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the user.
What are the key skills required for design thinking?
Design thinking requires a wide range of skills, including empathy, creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication. These skills are necessary to effectively understand the needs of the user and create a product that meets those needs.
What are the steps involved in design thinking?
The steps involved in design thinking include understanding the problem, researching the user, brainstorming ideas, prototyping, and testing. These steps are iterative and require constant feedback to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the user.
How can design thinking benefit individuals and organizations?
Design thinking can benefit individuals and organizations in many ways. By focusing on the needs of the user, design thinking can lead to more effective and innovative solutions. It can also help to improve communication and collaboration within teams and organizations.
What are some examples of design thinking frameworks?
Some examples of design thinking frameworks include the Stanford d.school Design Thinking Process, the IDEO Design Thinking Process, and the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design Thinking at Stanford. Each framework has its own unique approach, but all share a focus on the needs of the user.
Who can benefit from using design thinking?
Design thinking can benefit anyone who is involved in the creation of products or services, from designers and engineers to business leaders and entrepreneurs. By focusing on the needs of the user, design thinking can help to create more effective and innovative solutions.
5+ Best AI Code Generators: (Most Popular in 2024)

5 Best AI Content Detection Tools

500+ Mood Captions for Instagram

Mastering Cold Emails: A Guide to Writing Emails That Get Replies


- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
What is design thinking and why is it important?
Here’s what you need to know about this creative problem-solving technique, including a definition and why it’s taking the business world by storm.

Design thinking started out as a process for creating sleek new technology and products. But this methodology is now widely used across both the private and public sectors, for business and personal projects, all around the world.
Design-thinking methodology was popularized by design consulting firm IDEO . The methods gained momentum in the larger business world after Tim Brown, the chief executive officer of IDEO, wrote an article in 2008 for the Harvard Business Review about the use of design thinking in business—including at a California hospital, a Japanese bicycle company, and the healthcare industry in India. Today, one of the most popular courses at Stanford University is Designing Your Life , which applies design thinking to building a joyful career and life.
Here’s what design thinking is, how it works, and why it’s important.

What is design thinking?
Design thinking is a process for solving problems by prioritizing the consumer’s needs above all else. It relies on observing, with empathy, how people interact with their environments , and employs an iterative, hands-on approach to creating innovative solutions .
Design thinking is “human-centered,” which means that it uses evidence of how consumers (humans) actually engage with a product or service, rather than how someone else or an organization thinks they will engage with it. To be truly human-centered, designers watch how people use a product or service and continue to refine the product or service in order to improve the consumer’s experience. This is the “iterative” part of design thinking. It favors moving quickly to get prototypes out to test, rather than endless research or rumination.
In contrast to traditional problem-solving, which is a linear process of identifying a problem and then brainstorming solutions , design thinking only works if it is iterative. It is less of a means to get to a single solution, and more of a way to continuously evolve your thinking and respond to consumer needs.
Why is design thinking important?
Design thinking enables organizations to create lasting value for consumers. The process is useful in any complex system ( not just design systems ) because it:
Aims to solve a concrete human need
Using an observational, human-centric approach, teams can uncover pain points from the consumer that they hadn’t previously thought of, ones that the consumer may not even be aware of. Design thinking can provide solutions to those pain points once they’re identified.
Tackles problems that are ambiguous or difficult to define
Consumers often don’t know what problem they have that needs solving or they can’t verbalize it. But upon careful observation, one can identify problems based on what they see from real consumer behavior rather than simply working off of their ideas of the consumer. This helps define ambiguous problems and in turn makes it easier to surface solutions.
Leads to more innovative solutions
Humans are not capable of imagining things that are not believed to be possible, which makes it impossible for them to ask for things that do not yet exist. Design thinking can help surface some of these unknown pain points that would otherwise have never been known. Using an iterative approach to tackle those problems often lead to non-obvious, innovative solutions .
Makes organizations run faster and more efficiently
Rather than researching a problem for a long time without devising an outcome, design thinking favors creating prototypes and then testing to see how effective they are.

The five stages of the design-thinking process
Design thinking follows a five-stage framework.
1. Empathize
In this first stage, the designer observes consumers to gain a deeper understanding of how they interact with or are affected by a product or issue. The observations must happen with empathy, which means withholding judgment and not imparting preconceived notions of what the consumer needs. Observing with empathy is powerful because it can uncover issues the consumer didn’t even know they had or that they could not themselves verbalize. From this point, it’s easier to understand the human need for which you are designing.
In this second stage, you gather your observations from the first stage to define the problem you’re trying to solve. Think about the difficulties your consumers are brushing up against, what they repeatedly struggle with, and what you’ve gleaned from how they’re affected by the issue. Once you synthesize your findings, you are able to define the problem they face.
The next step is to brainstorm ideas about how to solve the problem you’ve identified. These ideation sessions could be in a group, where your team gathers in an office space that encourages creativity and collaboration , an innovation lab , or can be done solo. The important part is to generate a bunch of different ideas. At the end of this process, you’ll come up with a few ideas with which to move forward.
4. Prototype
This is the stage that turns ideas into an actual solution. Prototypes are not meant to be perfect. The point of a prototype is to come out quickly with a concrete version of the idea to see how it is accepted by consumers. Examples of prototypes include a landing page to test consumer desire for a product or a video that demonstrates streamlined logistic processes.
Once you give a prototyped solution to consumers, you must observe how they interact with it. This testing stage is the one in which you collect feedback on your work.
The design-thinking process is an iterative, rather than linear, one. At the end of the fifth stage, you’ll likely have to go back to one or several of the other stages. Perhaps the testing has shown you need to develop another prototype, for which you’d return to the fourth stage. Or perhaps it’s shown that you’ve misdefined the consumer’s needs. If so, you would have to return to an earlier stage of the process.
What industries and roles can benefit from design thinking?
While design thinking originated with designers, it is now widely used by people from all disciplines . Even among design agencies the work is famously cross-functional: IDEO and similar agencies hire non-designers—chefs, engineers, social scientists, biologists—and integrate them into their project teams to add perspective.
Our growth innovation team at WeWork comprises a designer, who focuses on applying this method for the end consumer of a project; a technologist, who uses this technique to deliver value to engineers; and a business strategist, who applies this method to deliver value for business owners and various stakeholders.
Design thinking has been used at Kaiser Permanente to overhaul the system of shift changes among nursing staff. It has helped the Singapore government make the process for securing a work pass in the nation-state easier and more human. Design thinking has been used to solve business problems at companies like Toyota, Intuit, SAP, and IBM .
One reason for the proliferation of design thinking in industries is that it’s useful to break down problems in any complex system, be it business, government, or social organizations. It can be used to explore big questions about how to respond to the growth of technology and globalization, how to pivot in response to rapid change, and how to support individuals while catering to larger organizations.
Design thinking can be used by all departments in a business. It can be fostered by bright, airy physical workspaces that cater to the way employees prefer to work. To employ design thinking in all projects, managers should first define the consumers they’re trying to help and then employ the five stages of design thinking to define and tackle the identified problems. Employing a design-thinking process makes it more likely a business will be innovative, creative, and ultimately more human.
Related articles

This article was originally published on October 18, 2019, and has been updated throughout by the editors.
Graham Tuttle was a director of growth innovation at WeWork. He has more than a decade of experience in design and new product development. Prior to WeWork, Tuttle worked at frog in design strategy, helping global enterprises and startups take a user-centered approach to product development, innovation, and investment strategy. He has an M.B.A. and a masters of design from the Illinois Institute of Technology and contributed to the development of 101 Design Methods: A Structured Approach for Driving Innovation in Your Organization , a step-by-step guidebook for innovation planning.

Every leader wants a thriving culture, but only select leaders know that investing in wellness can make it happen. Companies ahead of the game have already seen positive results, as research shows nine out of 10 companies that track their wellness spending see a positive ROI.

Designed to cultivate a positive and respectful working environment, here are the most common coworking etiquette rules.

“Busyness” doesn’t always equate with progress—learning how to prioritize tasks will help you make the most of your workday
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
25 Design Thinking Questions: What To Ask + Answer Examples

As Walter Isaacson, acclaimed biographer of creative genius Steve Jobs, emphasizes, “Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower.” The pursuit of innovation in business is what sets leaders apart; it’s the driving force behind the transformation of customer experiences. Every innovation, every groundbreaking product, and every revolutionary service begins with a question. That’s where the journey of design thinking questions and the power of asking comes into play.
Design Thinking isn’t just a methodology but a culture, and it’s been the driving force behind many remarkable creations. And what fuels this culture is all about asking the right questions.
Although formalized in the 21st century, design thinking has deep roots in history. In the 1950s, brilliant minds at Stanford University were already exploring new ways to enhance creative thinking. The goal was simple: breaking free from conventional problem-solving strategies. Let’s jump now to the 21st century, where design thinking has become a structured methodology at the heart of many renowned organizations’ strategies, such as Apple, Google, and Amazon.
What Are Design Thinking Questions?
The journey of design thinking is underpinned by a singular philosophy: to understand a problem truly, you must question it thoroughly and empathize with its challenges. This is where design thinking questions come into play.
Design thinking questions are open-ended, thought-provoking inquiries to understand a problem’s depths. These questions don’t just scratch the surface; they delve into the heart of the matter, searching for insights, ideas, and opportunities. The true power of these questions lies in their ability to cultivate empathy , unlock creativity , and catalyze innovative solutions.
We put together a table showcasing the elements of good design thinking questions:
| Element of Good Design Thinking Questions | Description |
|---|---|
| Questions demonstrate a genuine interest in understanding the user’s perspective and experiences. | |
| Questions are non-restrictive, allowing for diverse and extensive responses. | |
| Questions do not lead or prompt users to a particular response; they are neutral. | |
| Questions help generate insights and drive action and solutions. | |
| Questions are easy to understand, with no ambiguity or unnecessary complexity. | |
| Questions revolve around identifying and addressing the core problem or challenge. | |
| Questions involve various stakeholders and perspectives, fostering collaboration. | |
| Questions explore possibilities and future scenarios, encouraging innovative thinking. | |
| Questions are revisited and adjusted as the design process progresses and new insights emerge. | |
| Questions are non-restrictive, allowing for diverse and extensive responses. |
These elements guide the formulation of effective design thinking questions essential for uncovering insights, sparking innovation, and solving complex problems through a human-centered approach.
What Are the Questions of Design Thinking and Their Use?
Behind design thinking, there’s a series of carefully crafted questions, each designed to guide problem-solvers through the journey of creativity and innovation. These questions serve several vital functions like:
- Empathy Building: They encourage the development of empathy for the end-users or the people affected by the problem you’re solving. These questions put you in their shoes to truly understand their needs and desires.
- Problem Definition: The right questions help you accurately define the problem you’re dealing with. You uncover hidden issues and complexities by questioning the situation from different angles.
- Ideation: Design thinking questions stimulate ideation. They fuel creativity, inspire innovative ideas, and help teams think outside the box.
- Solution Validation: Once you’ve generated ideas and developed solutions, questions become tools for validating your concepts. They help you ensure that the proposed solutions indeed address the problem.
- Continuous Improvement: Design thinking questions don’t stop with the first solution. They play a crucial role in ongoing evaluation, helping you continuously refine and enhance your offerings.
What Are the Most Important Points of Design Thinking?
To truly grasp the essence of design thinking questions, consider these vital principles that underpin the whole approach:
- User-Centric Approach: Design thinking fundamentally addresses the end-users’ needs and desires. Your questions should revolve around understanding them, their challenges, and their aspirations.
- Iterative Process: Design thinking isn’t a linear journey; it’s a continuous loop of understanding, ideating, prototyping, and testing. Questions guide you through these iterations.
- Problem Framing: Before diving into solutions, design thinking encourages an in-depth understanding of the problem itself. Your questions should focus on framing the issue from multiple perspectives.
- Collaboration: Design thinking is a collaborative effort. The questions foster teamwork, bringing together diverse skills and perspectives.
- Prototype Testing: Questions are tools for validating prototypes. The process includes creating a basic version of the solution and testing it to gather feedback, which is then incorporated into improvements.
In summary, design thinking is an innovation-driven approach that thrives on customer empathy , problem-solving, and continuous improvement, all facilitated by thought-provoking, open-ended questions.
Design Thinking Question Types
Throughout the design thinking process, specific types of questions serve as guiding stars, illuminating the path to innovation and customer-centric solutions:
- These questions go beyond the surface, delving into the heart of the matter: the people. They invite you to walk in your end-users or stakeholders’ shoes, to see the world through their eyes. When you ask empathizing questions, you’re on a quest to truly understand their needs, desires, challenges, and aspirations. It’s about peeling back the layers and getting to the core of human experiences. With empathizing questions, you unlock the profound insights needed to create solutions that genuinely resonate with people.
- In the realm of design thinking, defining the problem is an art form. These questions are like the skilled strokes of a painter’s brush, meticulously crafting the contours of the challenge at hand. They prompt you to consider the subtle details, the shades of the issue that might have gone unnoticed. With problem definition questions, you frame the challenge with precision, ensuring you’re targeting the right problem—no more, no less. They provide the scaffolding for your entire creative process.
- If empathy questions allow you to understand, ideation questions inspire you to dream to explore the uncharted territories of imagination. They’re your passport to a realm where possibilities are endless, and conventional thinking takes a back seat. These questions aren’t just about generating ideas; they’re about opening the doors to unbridled creativity. Ideation questions are open-ended, enticing you to challenge the status quo and venture into the territory of “thinking outside the box.” In this realm, groundbreaking ideas are born.
- You have ideas—bold, innovative, and possibly game-changing. But how do you know which ones have the potential to revolutionize your industry? That’s where validation questions come into play. They are the litmus test, the rigorous assessment that ensures your solutions are on target. Validation questions are the guardians of practicality, making certain that your ideas are not just impressive on paper but feasible in the real world. They help you confirm that the proposed solutions genuinely address the problem and, most importantly, the needs of your users.
- Once your solution is out in the wild, your journey doesn’t end; it transforms into an ongoing quest for refinement and enhancement. Iterative questions are the driving force behind this evolution. They encourage you to listen, learn, and adapt. With these questions, you delve into the feedback, data, and user experiences. You ask what’s working, what’s not, and most crucially, how you can make it better. Iterative questions are the engines of continuous improvement, enabling you to evolve your solutions harmoniously with the ever-changing landscape of customer needs and market dynamics.
With this arsenal of questions, design thinking becomes a powerful vehicle for innovation and transformation, propelling your organization to new heights of customer satisfaction and competitive success.
Design Thinking Success Examples
The impact of design thinking questions is most evident in the real-world examples of companies and organizations that have successfully employed this approach.
- Apple: One of the pioneers in using design thinking, Apple applies this philosophy from product design to the customer experience. They frequently ask empathizing questions like, “ How can we make the iPhone experience even more intuitive? “
- Google: Google’s work culture revolves around creative problem-solving. Their teams use ideation questions such as, “ What are new ways to simplify complex data access for users? “
- Amazon: Amazon applies design thinking to enhance its customer service and satisfaction. Questions like, “How can we make the customer’s online shopping experience more seamless and enjoyable? ” drive their innovation.
- IDEO: A global design consultancy, IDEO, is renowned for its design thinking expertise. They ask many problem definition questions to deeply understand various challenges before proposing solutions.
Free Template: 25 Design Thinking Questions (with Answer Examples)
Design thinking questions with example hypothetical answers:
| Design Thinking Questions | Hypothetical Example Answers |
|---|---|
| 1. What are the key challenges our customers face? | Example: Our customers struggle with finding time for exercise. |
| 2. How do our users feel about our current product? | Example: Users find our app confusing and overwhelming. |
| 3. What are the most common daily frustrations they have? | Example: Daily traffic congestion is a major frustration. |
| 4. What are their goals, both short-term and long-term? | Example: Short-term goal – Lose weight. Long-term – Stay healthy. |
| 5. What motivates our customers and drives their decisions? | Example: Convenience and saving time motivate purchase decisions. |
| 6. What specific pain points does our product need to address? | Example: Our software needs to simplify complex data analysis. |
| 7. How might we refine the problem to make it more actionable? | Example: Instead of “improve app,” it’s “streamline checkout.” |
| 8. What is the root cause of the issues we aim to solve? | Example: Our website’s slow loading times are due to heavy graphics. |
| 9. What constraints (budget, time, etc.) do we need to consider? | Example: We have a limited budget for redesigning the office. |
| 10. Who are the key stakeholders we should involve in problem-solving? | Example: Customers, product managers, and designers. |
| 11. How might we enhance the user onboarding experience? | Example: By creating interactive tutorials and simplified navigation. |
| 12. What if we could completely rethink our packaging? | Example: We could introduce eco-friendly, reusable packaging. |
| 13. How can we encourage more user engagement with our app? | Example: Incorporating gamification elements into the design. |
| 14. What if we offered subscription-based services? | Example: Customers would have access to premium features. |
| 15. How might we leverage emerging technologies in our industry? | Example: Using AI for personalized recommendations. |
| 16. How do we know our new website design is user-friendly? | Example: Positive feedback and increased user interaction. |
| 17. What data can we collect to assess the success of our changes? | Example: Tracking click-through rates and conversion rates. |
| 18. Have we addressed the core issues identified in the problem? | Example: Yes, our solution simplifies the registration process. |
| 19. What feedback loops can we establish for real-time validation? | Example: Implementing a chat support feature for user questions. |
| 20. How do our improvements align with our user’s needs and expectations? | Example: The redesigned product aligns with user feedback. |
| 21. What are users saying about our latest feature updates? | Example: Users appreciate the improved search functionality. |
| 22. How can we gather ongoing feedback to drive future enhancements? | Example: Conduct regular surveys and feedback forms. |
| 23. What is our process for swiftly addressing user-reported issues? | Example: A dedicated team for bug fixes and updates. |
| 24. How can we continuously adapt to changing market trends? | Example: Regular market research to spot emerging trends. |
| 25. What data-driven insights can help us evolve our product? | Example: Analyzing customer behavior to shape future updates. |
Feel free to adapt these questions to your specific design thinking project and use them as a starting point for your journey into innovative problem-solving and product development.
Design Thinking Questions with QuestionPro
Integrating QuestionPro into your design thinking process can be a game-changer. Our suite of tools and solutions empowers you to formulate the right design thinking questions, collect valuable feedback, and convert insights into actionable strategies.
Whether you’re looking to enhance your product, service, or overall customer experience, our platform offers:
- Survey Design: Create custom surveys tailored to your design thinking needs with our intuitive survey builder.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback and responses effectively from diverse sources, from customers to employees.
- Data Analysis: Utilize advanced analytics to decipher the insights gained from your design thinking questions.
- Actionable Insights: Transform insights into actionable strategies for innovation and continuous improvement.
Design thinking questions are the compass guiding you through the intricate terrain of innovation. They empower you to understand, define, ideate, validate, and improve solutions.
When harnessed effectively, these questions can unlock a world of creativity and set your organization on a path to lasting success. So, embark on this journey with the right questions, and remember, innovation is just a question away.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Types of Organizational Change & Strategies for Business
Aug 2, 2024

Voice of the Customer Programs: What It Is, Implementations
Aug 1, 2024

A Case for Empowerment and Being Bold — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jul 30, 2024
Typeform vs. Google Forms: Which one is best for my needs?
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
We are currently accepting payments through PayPal only. Flexible options such as PayPal Debit, Credit, Pay Later, and split payments may be available (subject to personal circumstances).
Creativity, Problem Solving and Design Thinking
Boost your creative skills and creative confidence with a structured approach to idea generation, exploration and development.

This course equals 48 hours of CPD time
8 hours per week
Tutor guided
Certificate of Achievement
Evidence your learning with a Certificate of Achievement from the University of Cambridge on successful completion.
07 October 2024
18 November 2024
30 September 2024
Discover more about this course from the expert(s) behind it
Course overview
Creative problem solving is increasingly recognised as the most sought-after skill in business. This is true across a wide range of industries, and across both private and public sectors. Entrepreneurs, employees, managers, and leaders are all required to find valuable opportunities, generate and develop new ideas and then trial and implement innovative solutions. These processes can be modelled on design activities, where key stakeholders are identified and designed for through processes of research, ideation and prototyping. This is all equally applicable to the development of strategies, products, processes and a variety of socio-technical systems.
This course will help you to learn about the role of creativity in problem solving, and the application of design thinking to different business tasks. You will discover the characteristics of difficult problems, the thinking skills that are used to address them and the various biases that need to be overcome. Through the course content and activities, you will recognise and develop your creative skills, gaining confidence in them and in your capacity to develop them further. This applies not just to individual work, but also to group work, where diverse perspectives and skills can be leveraged.
The course offers an excellent opportunity for professional development, whether you are looking to advance in your current role or change roles or sectors. Through the course, you will apply a structured process to identifying problems and generating wide-ranging solution ideas before selecting and developing one (or more) for communication and implementation. You will have the opportunity to practice these skills in various course-specific scenarios, and also to a project that is relevant to your own professional context. The course is highly interactive, and you will be encouraged, through individual and collaborative work, to apply and manage a selection of evidence-based creative approaches.
This course is certified by the United Kingdom CPD Certification Service, and may be applicable to individuals who are members of, or are associated with, UK-based professional bodies. The course has an estimated 48 hours of learning.
Note: should you wish to claim CPD activity, the onus is upon you. Cambridge Advance Online accept no responsibility, and cannot be held responsible, for the claiming or validation of hours or points.
What will I learn?
By the end of the course, you will have a broad understanding of the application of creative approaches, processes and tools, including how to:
- articulate the components of creative work, and the skills (and biases) that are involved
- apply creative processes and tools yourself
- manage the application of creative processes and tools by others
- develop confidence in your creative skills, and in your ability to improve those skills
- represent your own creative skills and experiences, and elicit those of others.
Who is this course for?
- Those interested in improving how they think and act creatively, moving past learned behaviour to reach new and effective solutions.
- Professionals working in business development, transformation, or strategy who are seeking a structured and innovative approach to solving problems.
- Individuals facing novel problems in the workplace, who need to challenge conventions to develop original solutions and pitch these to stakeholders.
Course delivery
Our certificated courses reflect the Cambridge experience and values, with low student to tutor ratios and academically rigorous standards. Our learning model is designed to help you advance your skills and specialise in emerging areas that address global challenges. We will help you build your network through an engaging and impactful learning journey that encourages collaboration. Courses are delivered in weekly modules, allowing you to plan your time effectively. The assessment criteria will be presented to you at the start of the course, so you can approach your studies with confidence and motivation, knowing what is expected of you and how to meet those expectations.
Throughout your online learning experience, you will have access to your course tutor, who will help facilitate your learning and provide you with support and guidance during your studies. You can interact with your tutor through a range of media, such as live sessions, discussion forums, email or canvas messaging.
Each course includes a balance of:
- interactive learning and real-world application so you can directly apply what you’re learning to your own context
- diverse teaching methods to enhance learning outcomes which will be delivered via learning activities such as University of Cambridge academic led videos, quizzes and group work
- optional live sessions (1 hour) with University of Cambridge academics and tutors to deepen your understanding of the week's material. These sessions may include an informal Q&A, a short lecture or a breakout activity that builds on the content introduced that week. All sessions are recorded and made available to stream so you can catch up whenever suits you
- guided critical thinking via our reflective workbook so you can collect, structure and summarise information and your thoughts as you progress through the course.
What will I get on completion?
University of cambridge course lead.
Professor Nathan Crilly
Course dates.
07 Oct - 18 Nov
Places available
Enrol by 30 Sep
Requirements
Level of knowledge.
- a level of spoken and written English sufficient to allow you to participate and succeed in the course (we recommend that you have an English Language level equivalent to an IELTS score of 7, as outlined in section 5 of our Terms of Purchase (Opens in a new window) )
Materials & equipment
- sufficient internet speed and stability for video streaming (2 Mbps up/down)
- please see our recommendations on web browsers (Opens in a new window)
A Q&A with the course leader of Creativity, Problem-Solving and Design Thinking

Problem solve like a pro

What our learners are saying
Professor Crilly is truly world-class. His videos were informative and concise, and he was present, warm and engaging for all the live sessions. He made himself exceptionally available for questions and support and I couldn't be more grateful for his instruction.
The delivery of this course has been spectacular in content, presentation and delivery…I have no hesitation recommending it to anyone interested in the subject.
As well as an overall understanding of creative, problem-solving and design thinking processes, the course has provided very well-constructed opportunities to consolidate knowledge and understanding about those processes in practice, alongside other course members.
Let’s keep in touch
Sign up here to receive news and updates about Cambridge Advance Online courses from us and relevant university departments.
Your privacy is important to us. View our Privacy notice (Opens in a new window) for more information. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy (Opens in a new window) and Terms of Service (Opens in a new window) apply.
Design Thinking
What makes design thinking different.
Traditional courses progress the student learning from conceptual understanding towards demonstrations of skill and capacity in a linear, topically focused manner. Setting this scaffolding is set in place, fixes the problems, and the solutions are typically within a known range. But many course problems are research questions that defy simple explanations or right/wrong answers. For these courses, need a more dexterous approach.
In Design Thinking, they are discovering knowledge through exploration. Students help define the problems, identify and develop potential solutions, and determine ways to assess the work. Instructors serve as facilitators and advisors to this learning. Embedded throughout the process is capacity-building through linked-learning experiences, collaborative exercises, and creative problem-solving [iii] . Learning often involves hands-on experiences focused on real-world challenges. By centering course activities around a problem and generating creative solutions, these courses support the development of essential competencies such as critical thinking, reflective learning, adaptability, effective collaboration, and systems thinking.
The Design Thinking Multi-Stage Model
Discovery (empathy, research, and problem definition), ideation (interpret, create, and make), experimentation (prototype, test and evaluate), evolution (re-think, re-make, repeat), deployment (socialize, pilot, and integrate).

The first stages are directed towards understanding and defining potential problems for solutions by asking, “What Is It?” The requisite foundation for all other design thinking stages is the ability to generate informed and empathetic work during this stage. How? Through literature reviews and consultations with experts along with the combined observations and engagements with people and physical environments relevant to the topic. Information gathered and documented during this stage can be aligned with course objectives and assessments. Students will gain a deeper understanding of the issues throughout the process.
Upon completing the information gathering, teams organize, interpret, and make sense of the data to define a problem scope. Doing so requires both analysis (i.e., breaking down complex concepts) and synthesis (i.e., creatively piecing information together to form whole ideas). A good problem statement should be human-centered, broad enough for creative freedom, but narrow enough to be manageable. As a general rule, consider using the Stanford d. school “Why-How Ladder” (a variation of the Sakichi Toyoda “5 Whys” technique) to refine the problem statement and to suggest how to move forwards with design problem-solving.
Unlike the traditional project-based learning method, instructors do not define the problem in design thinking. They can, and should, define a scope, but defining the actual problem is part of the student responsibility.
At this stage, students interpret their research into a range of creative ideas and potential solutions. This step starts the “What If?” phase of the work. Instructors should encourage enthusiasm and collaborative participation by incorporating active-learning methods, visualization techniques of “systems-thinking,” and other image-oriented methods to document brainstorming.
Expert guidance is required to maintain enthusiasm in the ideation process by guiding proposals and bringing focus to the expectations. Instructors suggest practices to enhance the solutions and temper expectations (e.g., “your solution won’t solve world hunger as you proposed, but it can make a difference in one stage of food production—let’s use that to refocus the design effort.” Eventually a more narrow range of possible solutions is identified, and the work of making/designing begins.
In this stage, ideas become manifest. Students are deciding how and what to produce is of central importance. Iteration is essential. Align activities with course objectives and professional practice models. As ideation moves into prototyping, the expectation is that student groups produce several scaled-down versions or features of the final solution. Doing so allows students to understand better the constraints and benefits inherent to the solutions they’ve designed. The introduction of new tools and skills can occur during this stage, along with emphasizing collaborative efforts.
Experimentation is only complete when identifying problems by breaking the project down through evaluation.
This process looks for failures and revelations that emerge through testing; profound learning opportunities arise when solutions don’t meet their objectives.
Learning how to define and evaluate the relative value and efficacy of the prototypes follows is an essential skill. Students often return to the Discovery stage to identify the proper standards for evaluating success (Who does it work for? Does it work in the way you intended? How would you know?). At this stage, instructors can show how practical conditions affect evaluation (industry standards, code requirements, etc.) and how exigent forces would affect the solution (e.g., broader economic, sociological, and cultural conditions).
This stage isn’t the end of the process; ultimately, testing is a generative process for redesign as it reveals opportunities for improvement. By trying to determine how and why specific solutions are rejected, improved, or accepted, students develop clarity of how real users would behave, think, and feel when interacting with the solution. At this stage, alterations and refinements are expected to be more mature and technically developed. Collaborations may be extended into communities to expand testing and assessment.
The multi-stage process implies a linear direction of progress, but designing and learning are inherently more unpredictable, so the model is flexible. Information learned from testing helps refine the problem definition and the overall design. There is a perpetual loop of feedback. Ultimately, solutions are evolved and improved through reiteration and repetition, as fewer factors are considered for each iteration.
The challenge of design thinking is often knowing when this evolutionary process of redesigning is “done.” Solving a problem, particularly a vexing one, is unlikely within the constraints of school. Academic calendars and restrictions are quite different from practice, so there are often situations in which a “good enough for now” scenario is the goal.
Ideally, of course, the process can spark an interest in students to continue a life-long engagement in these research projects. This process is ultimately about joining on-going conversations and searching for new knowledge through design solutions. It isn’t about resolution. The passion of the search is what is essential to teach and learn.
Specific projects may have the opportunity to develop into real-world solutions. This stage of deployment focuses on ways that solutions become tangible, actionable, and ready for use. In the socializing phase, the ideas develop to the degree that buy-in occurs and teams built around the solution. This phase relies on the ability to tell compelling stories about the solution. Because these stories have naturally developed through a rigorous Design Thinking process, it is relatively easy to build a narrative around a solution based on the process.
In the piloting phase, the solution is introduced to a predetermined group to gain real-world feedback and reviews. Depending on the solution’s stage and scope, this may occur at a smaller scale during prototyping. In this phase, the focus is on identifying barriers to implementation of use and integration. Depending on the solution, these barriers to production and method may be profound. This work takes in-depth expertise and cross-disciplinary collaborations to understand markets, supply-chains, production, delivery models, and how the solution will enhance or disrupt existing models.
What is the Difference between Project-Based Learning (PBL), Understanding by Design (UbD), and Design Thinking (DT)?
Project-based learning (PBL) is a broader category of educational activities in which curricular activities are all centered around sustained engagement with a problem or project. Using PBL, a potentially important study narrowed down into a series of discrete activities using student-directed learning. A PBL approach can closely align with curricular checkpoints by defining a path of inquiry and production through essential guiding questions and required deliverables.
The Understanding by Design (UbD) model, is similar to PBL in its use of creative problem solving as the central learning activity. It differs mostly in the way of evaluating success. In UbD, educators help define the problem and develop a process of design-learning with the final result. In some courses, particularly those with complex topics, there may not be a readily available answer. The problem itself may not be easily defined, which complicates the PBL and UbD model.
Design Thinking is intentionally more open-ended than these other options. Students help to define the problem based on a generative topic that opens an area of research. Students are encouraged to align what they produce with their broader research questions. Assessment is related to prototyping and rebuilding intended to promote creative risk-taking.
Design Thinking Resources for Educators
- Kelley, T. (2016). The Art Of Innovation . London: Profile Books.
- O’Donnell Wicklund Pigozzi Peterson, Architects Inc, VS Furniture, & Bruce Mau Design. (2010). The third teacher : 79 ways you can use design to transform teaching & learning / OWP/P Architects, VS Furniture, Bruce Mau Design . New York: Abrams.
- Weinschenk, S. (2015). 100 MORE Things Every Designer Needs to Know About People (1st ed.) . New Riders.
Manuals / Toolkits
- IDEO.org. (2015). T he Field Guide to Human-Centered Design (Community Engagement Manual) . Retrieved from https://www.designkit.org/
- Riverdale Country School & IDEO.org. (2019). Design Thinking for Educators Toolkit (2 nd Edition). Retrieved from https://www.ideo.com/post/design-thinking-for-educators/
Organizations
- Institute of Design at Stanford (d.School) website (Hasso-Plattner)
- RED lab: Research in Education and Design website (Stanford School of Education)
- TD4Ed: Teachers Design for Education website (Business Innovation Factory)
- Edutopia, Design Thinking Video Collection
- Design Thinking For Educators” context / profession / practice / mindse
[i] Tim Brown, “Change by Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation,” Harper Business, 2009. https://designthinking.ideo.com
[ii] Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (d.school) at Stanford, “Design Thinking Mix Tapes,” 2018. https://dschool.stanford.edu/resources/chart-a-new-course-put-design-thinking-to-work
[iii] IDEO, “Design Thinking for Educators Toolkit” (2 nd Edition), IDEO + Riverdale Country School, 2019. https://www.ideo.com/post/design-thinking-for-educators
[iv] Herbert Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial (3 rd Ed.), 1996
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
What is Design Thinking and Why Is It So Popular?
Design Thinking is not an exclusive property of designers—all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering, and business have practiced it. So, why call it Design Thinking? What’s special about Design Thinking is that designers’ work processes can help us systematically extract, teach, learn and apply these human-centered techniques to solve problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, in our businesses, in our countries, in our lives.
Some of the world’s leading brands, such as Apple, Google and Samsung, rapidly adopted the design thinking approach, and leading universities around the world teach the related methodology—including Stanford, Harvard, Imperial College London and the Srishti Institute in India. Before you incorporate design thinking into your own workflows, you need to know what it is and why it’s so popular. Here, we’ll cut to the chase and tell you what design thinking is all about and why it’s so in demand.
What is Design Thinking?
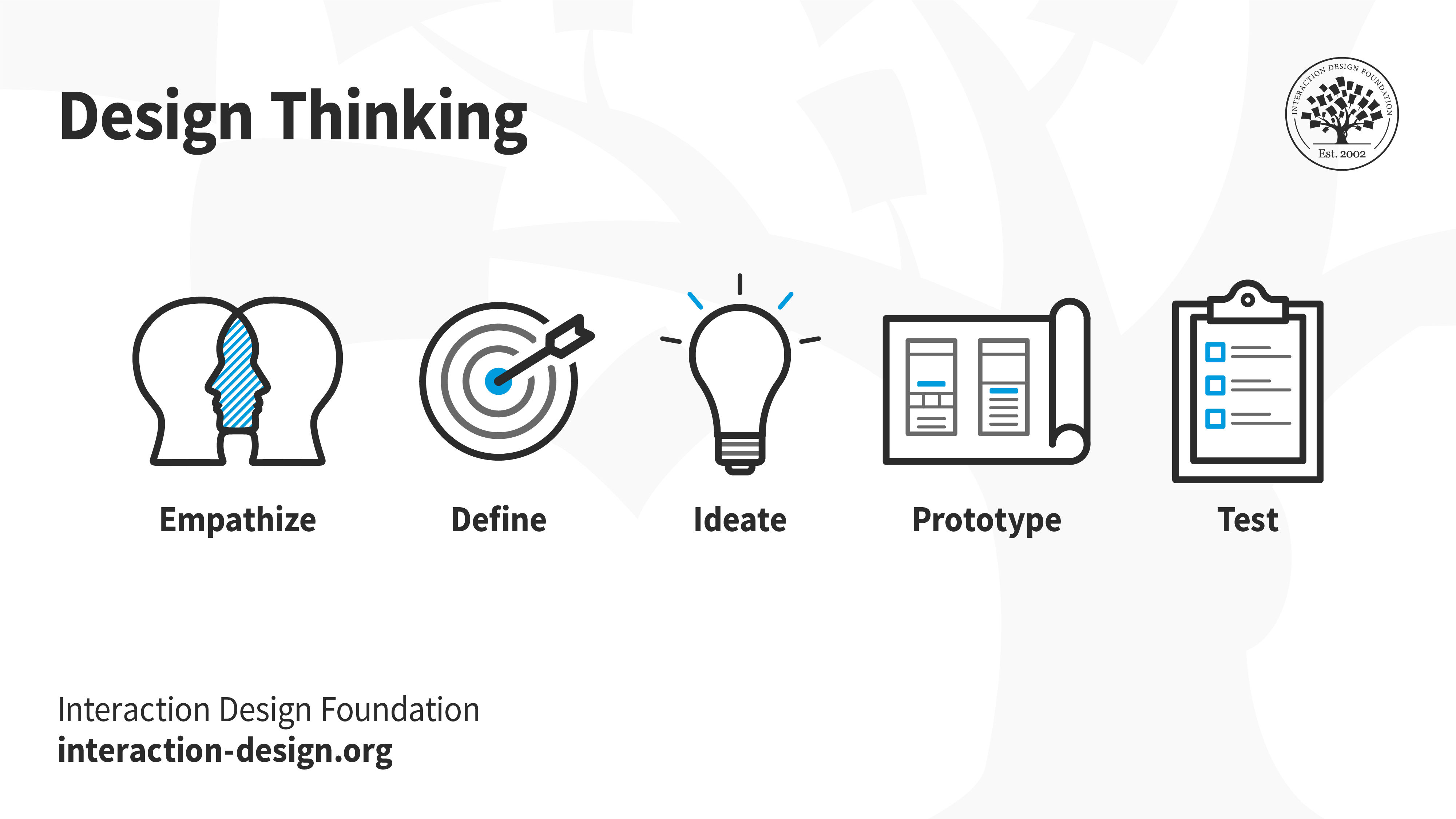
Design thinking is an iterative and non-linear process that contains five phases: 1. Empathize , 2. Define, 3. Ideate, 4. Prototype and 5. Test.
Design thinking is an iterative process in which you seek to understand your users, challenge assumptions , redefine problems and create innovative solutions which you can prototype and test. The overall goal is to identify alternative strategies and solutions that are not instantly apparent with your initial level of understanding.
Design thinking is more than just a process; it opens up an entirely new way to think, and it offers a collection of hands-on methods to help you apply this new mindset.
In essence, design thinking:
Revolves around a deep interest to understand the people for whom we design products and services.
Helps us observe and develop empathy with the target users.
Enhances our ability to question: in design thinking you question the problem, the assumptions and the implications.
Proves extremely useful when you tackle problems that are ill-defined or unknown.
Involves ongoing experimentation through sketches , prototypes, testing and trials of new concepts and ideas.
- Transcript loading…
In this video, Don Norman , the Grandfather of Human-Centered Design , explains how the approach and flexibility of design thinking can help us tackle major global challenges.
What Are the 5 Phases of Design Thinking?
Hasso-Platner Institute Panorama
Ludwig Wilhelm Wall, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Design thinking is an iterative and non-linear process that contains five phases: 1. Empathize, 2. Define, 3. Ideate, 4. Prototype and 5. Test. You can carry these stages out in parallel, repeat them and circle back to a previous stage at any point in the process.
The core purpose of the process is to allow you to work in a dynamic way to develop and launch innovative ideas.
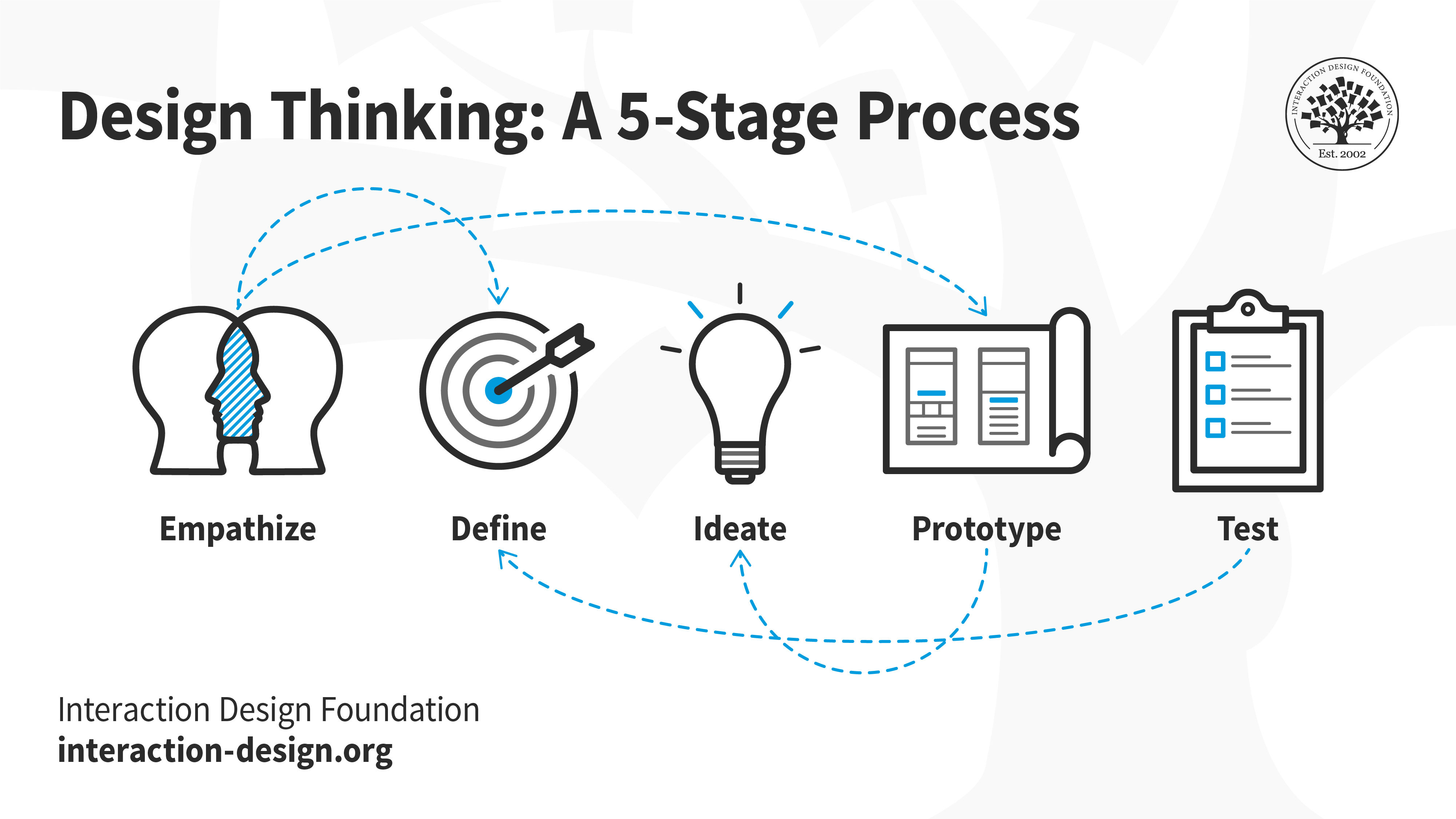
Design thinking is an iterative and non-linear process that contains five phases: 1. Empathize, 2. Define, 3. Ideate, 4. Prototype and 5. Test.
Design Thinking Makes You Think Outside the Box
Design thinking can help people do out-of-the-box or outside-the-box thinking. People who use this methodology:
Attempt to develop new ways of thinking —ways that do not abide by the dominant or more common problem-solving methods.
Have the intention to improve products, services and processes. They seek to analyze and understand how users interact with products to investigate the conditions in which they operate.
Ask significant questions and challenge assumptions. One element of outside-the-box / out-of-the-box thinking is to to make previous assumptions falsifiable—i.e., make it possible to prove whether they’re valid or not.
As you can see, design thinking offers us a means to think outside the box and also dig that bit deeper into problem-solving. It helps us carry out the right kind of research, create prototypes and test our products and services to uncover new ways to meet our users’ needs.
The Grand Old Man of User Experience , Don Norman, who also coined the very term User Experience , explains what Design Thinking is and what’s so special about it:
“…the more I pondered the nature of design and reflected on my recent encounters with engineers, business people and others who blindly solved the problems they thought they were facing without question or further study, I realized that these people could benefit from a good dose of design thinking. Designers have developed a number of techniques to avoid being captured by too facile a solution. They take the original problem as a suggestion, not as a final statement, then think broadly about what the real issues underlying this problem statement might really be (for example by using the " Five Whys " approach to get at root causes). Most important of all, is that the process is iterative and expansive. Designers resist the temptation to jump immediately to a solution to the stated problem. Instead, they first spend time determining what the basic, fundamental (root) issue is that needs to be addressed. They don't try to search for a solution until they have determined the real problem, and even then, instead of solving that problem, they stop to consider a wide range of potential solutions. Only then will they finally converge upon their proposal. This process is called "Design Thinking." — Don Norman, Rethinking Design Thinking
Design Thinking is for Everybody
How many people are involved in the design process when your organization decides to create a new product or service? Teams that build products are often composed of people from a variety of different departments. For this reason, it can be difficult to develop, categorize and organize ideas and solutions for the problems you try to solve. One way you can keep a project on track, and organize the core ideas, is to use a design thinking approach—and everybody can get involved in that!
Tim Brown, CEO of the celebrated innovation and design firm IDEO, emphasizes this in his successful book Change by Design when he says design thinking techniques and strategies belong at every level of a business.
Design thinking is not only for designers but also for creative employees, freelancers and leaders who seek to infuse it into every level of an organization. This widespread adoption of design thinking will drive the creation of alternative products and services for both business and society.
“Design thinking begins with skills designers have learned over many decades in their quest to match human needs with available technical resources within the practical constraints of business. By integrating what is desirable from a human point of view with what is technologically feasible and economically viable, designers have been able to create the products we enjoy today. Design thinking takes the next step, which is to put these tools into the hands of people who may have never thought of themselves as designers and apply them to a vastly greater range of problems.” — Tim Brown, Change by Design, Introduction

Design thinking techniques and strategies belong at every level of a business. You should involve colleagues from a wide range of departments to create a cross-functional team that can utilize knowledge and experience from different specialisms.
Tim Brown also shows how design thinking is not just for everybody—it’s about everybody, too. The process is firmly based on how you can generate a holistic and empathic understanding of the problems people face. Design thinking involves ambiguous, and inherently subjective, concepts such as emotions, needs, motivations and drivers of behavior .
In a solely scientific approach (for example, analyzing data), people are reduced to representative numbers, devoid of emotions. Design thinking, on the other hand, considers both quantitative as well as qualitative dimensions to gain a more complete understanding of user needs . For example, you might observe people performing a task such as shopping for groceries, and you might talk to a few shoppers who feel frustrated with the checkout process at the store (qualitative data). You can also ask them how many times a week they go shopping or feel a certain way at the checkout counter (quantitative data). You can then combine these data points to paint a holistic picture of user pain points, needs and problems.
Tim Brown sums up that design thinking provides a third way to look at problems. It’s essentially a problem-solving approach that has crystallized in the field of design to combine a holistic user-centered perspective with rational and analytical research—all with the goal to create innovative solutions.
“Design thinking taps into capacities we all have but that are overlooked by more conventional problem-solving practices. It is not only human-centered; it is deeply human in and of itself. Design thinking relies on our ability to be intuitive, to recognize patterns, to construct ideas that have emotional meaning as well as functionality, to express ourselves in media other than words or symbols. Nobody wants to run a business based on feeling, intuition, and inspiration, but an overreliance on the rational and the analytical can be just as dangerous. The integrated approach at the core of the design process suggests a ‘third way.’” — Tim Brown, Change by Design, Introduction
Design Thinking Has a Scientific Side
Design thinking is both an art and a science. It combines investigations into ambiguous elements of the problem with rational and analytical research —the scientific side in other words. This magical concoction reveals previously unknown parameters and helps to uncover alternative strategies which lead to truly innovative solutions.
The scientific activities analyze how users interact with products, and investigate the conditions in which they operate. They include tasks which:
Research users’ needs.
Pool experience from previous projects.
Consider present and future conditions specific to the product.
Test the parameters of the problem.
Test the practical application of alternative problem solutions.
Once you arrive at a number of potential solutions, the selection process is then underpinned by rationality. As a designer, you are encouraged to analyze and falsify these solutions to arrive at the best available option for each problem or obstacle identified during phases of the design process.
With this in mind, it may be more correct to say design thinking is not about thinking outside the box, but on its edge, its corner, its flap, and under its bar code—as Clint Runge put it.

Clint Runge is Founder and Managing Director of Archrival, a distinguished youth marketing agency, and adjunct Professor at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Resetting Our Mental Boxes and Developing a Fresh Mindset
Thinking outside of the box can provide an innovative solution to a sticky problem. However, thinking outside of the box can be a real challenge as we naturally develop patterns of thinking that are modeled on the repetitive activities and commonly accessed knowledge we surround ourselves with.
Some years ago, an incident occurred where a truck driver tried to pass under a low bridge. But he failed, and the truck was lodged firmly under the bridge. The driver was unable to continue driving through or reverse out.
The story goes that as the truck became stuck, it caused massive traffic problems, which resulted in emergency personnel, engineers, firefighters and truck drivers gathering to devise and negotiate various solutions for dislodging the trapped vehicle.
Emergency workers were debating whether to dismantle parts of the truck or chip away at parts of the bridge. Each spoke of a solution that fitted within his or her respective level of expertise.
A boy walking by and witnessing the intense debate looked at the truck, at the bridge, then looked at the road and said nonchalantly, “Why not just let the air out of the tires?” to the absolute amazement of all the specialists and experts trying to unpick the problem.
When the solution was tested, the truck was able to drive free with ease, having suffered only the damage caused by its initial attempt to pass underneath the bridge. The story symbolizes the struggles we face where oftentimes the most obvious solutions are the ones hardest to come by because of the self-imposed constraints we work within.

It’s often difficult for us humans to challenge our assumptions and everyday knowledge because we rely on building patterns of thinking in order to not have to learn everything from scratch every time. We rely on doing everyday processes more or less unconsciously—for example, when we get up in the morning, eat, walk, and read—but also when we assess challenges at work and in our private lives. In particular, experts and specialists rely on their solid thought patterns, and it can be very challenging and difficult for experts to start questioning their knowledge.
Stories Have the Power to Inspire
Why did we tell you this story about the truck and the bridge? Well, it’s because stories can help us inspire opportunities, ideas and solutions. Stories are framed around real people and their lives and are important because they’re accounts of specific events, not general statements. They provide us with concrete details which help us imagine solutions to particular problems.
Stories also help you develop the eye of a designer. As you walk around the world, you should try to look for the design stories that are all around you. Say to yourself “that’s an example of great design” or “that's an example of really bad design ” and try to figure out the reasons why.
When you come across something particularly significant, make sure you document it either through photos or video. This will prove beneficial not only to you and your design practice but also to others—your future clients, maybe.
The Take Away
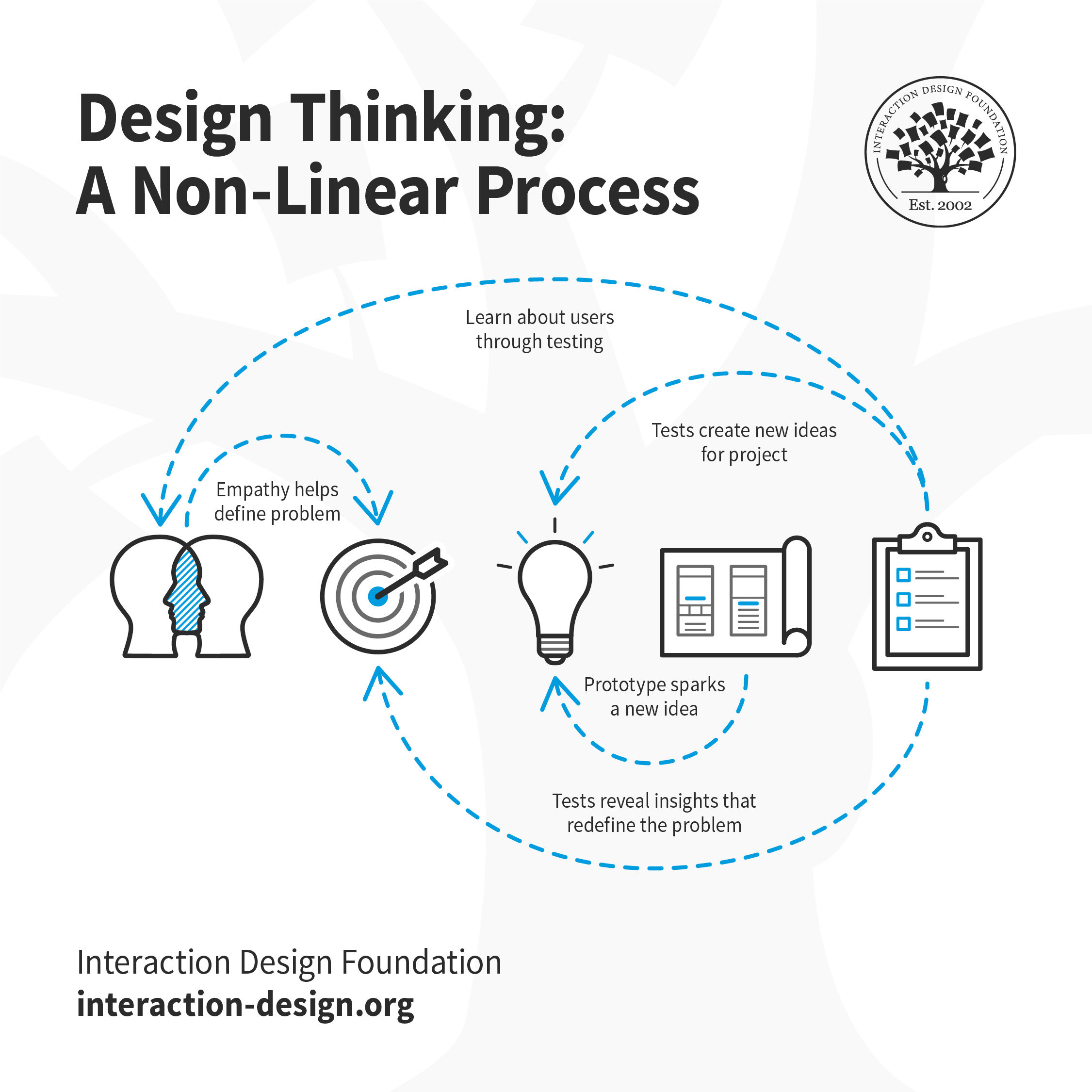
Design Thinking is an iterative and non-linear process. This simply means that the design team continuously uses their results to review, question and improve their initial assumptions, understandings and results. Results from the final stage of the initial work process inform our understanding of the problem, help us determine the parameters of the problem, enable us to redefine the problem, and, perhaps most importantly, provide us with new insights so we can see any alternative solutions that might not have been available with our previous level of understanding.
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that consists of 5 phases: 1. Empathize, 2. Define, 3. Ideate, 4. Prototype and 5. Test. You can carry out the stages in parallel, repeat them and circle back to a previous stage at any point in the process—you don’t have to follow them in order.
It’s a process that digs a bit deeper into problem-solving as you seek to understand your users, challenge assumptions and redefine problems. The design thinking process has both a scientific and artistic side to it, as it asks us to understand and challenge our natural, restrictive patterns of thinking and generate innovative solutions to the problems our users face.
Design thinking is essentially a problem-solving approach that has the intention to improve products. It helps you assess and analyze known aspects of a problem and identify the more ambiguous or peripheral factors that contribute to the conditions of a problem. This contrasts with a more scientific approach where the concrete and known aspects are tested in order to arrive at a solution.
The iterative and ideation -oriented nature of design thinking means we constantly question and acquire knowledge throughout the process. This helps us redefine a problem so we can identify alternative strategies and solutions that aren’t instantly apparent with our initial level of understanding.
Design thinking is often referred to as outside-the-box thinking, as designers attempt to develop new ways of thinking that do not abide by the dominant or more common problem-solving methods—just like artists do.
The design thinking process has become increasingly popular over the last few decades because it was key to the success of many high-profile, global organizations. This outside-the-box thinking is now taught at leading universities across the world and is encouraged at every level of business.
“The ‘Design Thinking’ label is not a myth. It is a description of the application of well-tried design process to new challenges and opportunities, used by people from both design and non-design backgrounds. I welcome the recognition of the term and hope that its use continues to expand and be more universally understood, so that eventually every leader knows how to use design and design thinking for innovation and better results.” — Bill Moggridge, co-founder of IDEO, in Design Thinking: Dear Don
References & Where to Learn More
Enroll in our engaging course, “Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide”
Here are some examples of good and bad designs to inspire you to look for examples in your daily life.
Read this informative article “What Is Design Thinking, and How Can SMBs Accomplish It?” by Jackie Dove.
Read this insightful article “Rethinking Design Thinking” by Don Norman.
Check out Tim Brown’s book “Change by Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation Introduction,” 2009.
Learn more about Design Thinking in the article “Design Thinking: Dear Don” by Bill Moggridge.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide

Get Weekly Design Tips
Topics in this article, what you should read next, the 5 stages in the design thinking process.
- 1.8k shares
Personas – A Simple Introduction

- 1.5k shares
Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results

- 1.3k shares
What is Ideation – and How to Prepare for Ideation Sessions
- 1.2k shares
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights

- 2 years ago
Stage 4 in the Design Thinking Process: Prototype

- 3 years ago
Stage 3 in the Design Thinking Process: Ideate

- 4 years ago
Stage 1 in the Design Thinking Process: Empathise with Your Users
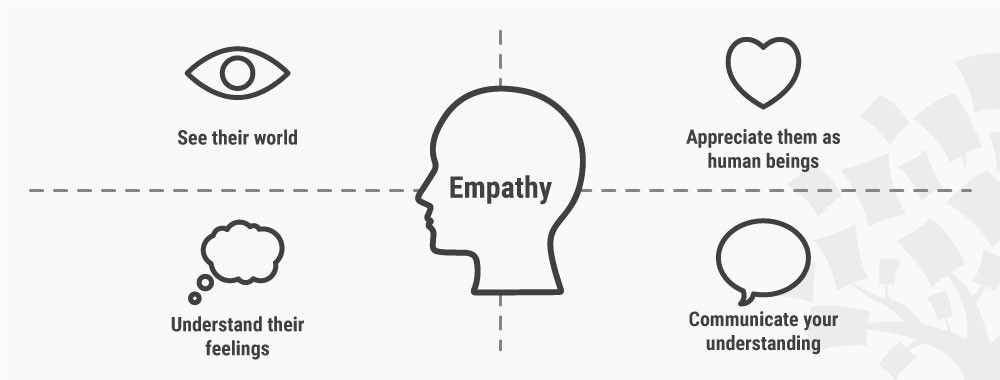
Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It
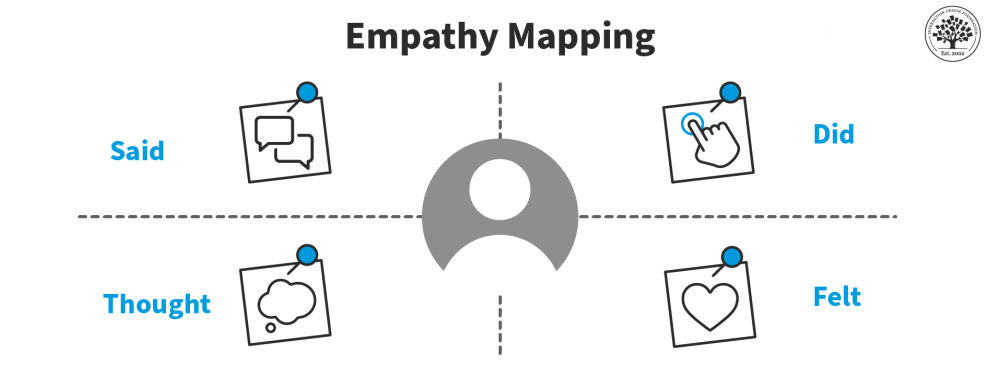
What Is Empathy and Why Is It So Important in Design Thinking?
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
Just added to your cart
Systems thinking vs design thinking, what’s the difference.

JUMP TO SECTION
- Introduction
- What is Systems Thinking?
- What is Design Thinking?
- The Differences Between Systems Thinking vs. Design Thinking
- Advantages and Drawbacks of Systems Thinking
- Advantages and Drawbacks of Design Thinking
- Human-Centered Systems Thinking: Integrating Systems Thinking and Design Thinking
- Frameworks, Tools, and Methodologies for Human-Centered Systems Thinking
1. Introduction
Systems thinking and design thinking are both approaches to problem solving and innovation. Systems thinking starts with understanding entire systems rather than individualized elements to spot opportunities for change, whereas design thinking is focused on understanding people’s real needs to create human-centered products, services, and processes. It’s important to learn the nuances of each when incorporating them into your practice.
2. What is Systems Thinking?
Systems, like healthcare and cities, are big, multifaceted, dynamic things built for a purpose. They span several services and products working together simultaneously. Some systems benefit society, but some can lead to harm too. Donella Meadows, author of Thinking in Systems , describes systems as made up of structures (institutions), relationships (stakeholders and power dynamics), and paradigms (culture and mindsets).
So what is systems thinking ? In his book The Fifth Discipline , Peter Senge gives a systems thinking definition as “A discipline for seeing wholes. It is a framework for seeing interrelationships rather than things, for seeing patterns of change rather than static ‘snapshots.’ And systems thinking is a sensibility—for the subtle interconnectedness that gives living systems their unique character."
Systems thinking has been around for a long time. If you search the history of the field, you will find your way to pioneering systems theorists like Jay W. Forrester, Russell Ackoff, Donella Meadows, Peter Senge, and more. They codified much of our modern thinking on systems theory, dynamics, and modeling. But were they the first systems thinkers? Certainly not. There are roots in Native American cultures and worldviews, early feminism, and many other examples.
The concept of wholeness is integral to a systems thinking approach. A system is more than the sum of its parts—it's defined by the interaction of its parts. To understand how a system works, you have to study not the individual elements but the linkages between them. When you start thinking in systems, you can then spot opportunities for change. By bringing more awareness to the process of designing systems, we can all be more intentional about creating equitable ones and dismantling harmful ones.
“A system is more than the sum of its parts—it's defined by the interaction of its parts.”
3. What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation—anchored in understanding customer’s needs, prototyping, and generating creative ideas—to transform the way you develop products, services, processes, and organizations.
When using design thinking principles, you bring together what is desirable from a human point of view with what is technologically feasible and economically viable.
- Desirability: What makes sense to people and for people?
- Feasibility: What is technically possible within the foreseeable future?
- Viability: What is likely to become part of a sustainable business model?

We teach the phases of design thinking as linear steps, but in practice the process is not always linear. Some of these steps may happen several times, and you may even jump back and forth between them. The phases of the design thinking process include:

Frame a Question —Identify a driving question that inspires others to search for creative solutions.
Gather Inspiration —Inspire new thinking by discovering what people really need.
Generate Ideas —Push past obvious solutions to get to breakthrough ideas.
Make Ideas Tangible —Build rough prototypes to learn how to make ideas better.
Test to Learn —Refine ideas by gathering feedback and experimenting forward.
Share the Story —Craft a human story to inspire others toward action.
If you want to learn more about using a design thinking approach, you can explore design thinking examples, case studies, and activities in our free Design Thinking Resources .
4. The Differences Between Systems Thinking vs. Design Thinking
You might be wondering: when should I use design thinking and when should I use systems thinking? Each approach has its own distinct characteristics and benefits. Here is a comparison of systems thinking and design thinking:

5. Advantages and Drawbacks of Systems Thinking
Systems thinking enables us to overcome stalled decision-making that often occurs when we’re overwhelmed by the scale of a problem and it’s hard to know where to get started. It helps us see the interconnectedness of things, spot patterns, and identify the right areas to focus our efforts. This approach is a good fit for challenges where there's a lot of stakeholders, competing incentives, or no obvious solution.
Other benefits of systems thinking include:
- Deepening understanding of a problem by getting different perspectives from people within the system.
- Expanding the range of choices by framing the problem in new and different ways.
- Making more informed choices by understanding how things are interrelated and how choices may impact other parts of the system.
- Anticipating the impact of trade-offs to reduce the risk of unintended consequences.
- Building buy-in and support for solutions by making sure everyone's viewpoint is included.
The goal of systems thinking is ultimately to come up with solutions that are more holistic and take into account the needs of all stakeholders while also understanding the dynamics of the system. A common drawback or limitation of systems thinking is getting stuck in the ideation and thinking phase without getting tangible. When practicing systems thinking without including the prototyping mindsets of design thinking, it can be more difficult to implement the solutions that you come up with. Additionally, when you use a solely systems thinking approach, you may overlook the individual human needs and behaviors that you uncover with design thinking.
6. Advantages and Drawbacks of Design Thinking
Design thinking is valuable because it puts people at the center of problem solving. It encourages us to ask questions and find out what our customers and clients need, rather than assuming we already know all the answers. Brainstorming ideas , prototyping, and iterating allow us to learn faster and improve products and services before they go out into the real world.
Over time, the methods and mindsets of design thinking lead to something even more important—creative confidence. The subtle techniques of design thinking unlock mindset shifts that lead people (many for the first time in their lives) to see themselves as creative. Creative confidence gives people the ability to fearlessly (or with less fear) tackle complex problems in the world.
Here are some additional benefits of design thinking, and how it can help your team or organization:
- Understanding the unmet needs of the people you’re creating for.
- Reducing the risk associated with launching new ideas, products, and services.
- Generating solutions that are revolutionary, not just incremental.
- Learning and iterating faster.
- Collaborating better and tapping into the creative potential of individuals and teams.
When it comes to drawbacks or limitations of design thinking, some teams may find it difficult to incorporate design thinking because it involves a lot of ambiguity. It’s not a linear path, and sometimes requires looping back to different parts of the process. Additionally, it takes time and practice to practice design thinking at a high level.
Some may also find it difficult to change social norms or behavior on their team. If an organization is used to doing things in a certain way, it might be resistant to a new, more creative way of working. It can be challenging when a team isn’t aligned on applying a design thinking mindset, since it’s such a collaborative approach.
7. Human-Centered Systems Thinking: Integrating Systems Thinking and Design Thinking
Human-centered systems thinking brings together the analytical, holistic tools of systems thinking with the creative human-centered process of design thinking. It’s a mindset and methodology for tackling complex systemic challenges in a human way: staying grounded in the needs of multiple stakeholders while also seeing larger dynamics at play so you can diagnose the real problem, design more effective solutions, and drive real behavior change and positive impact within systems.
Combining systems thinking and design thinking enables you to:
- Zoom in and out, and toggle back and forth between a systems lens and a human lens.
- Gain a deeper, more holistic and human understanding of the system and its stakeholders.
- Develop empathy for both the people and the system itself.
- Understand what drives human behavior and system behavior.
- Redesign the system to produce better outcomes by designing and implementing interventions that drive positive change within the system.
Today, human-centered systems thinking is needed more than ever. We have a greater awareness of the interconnected nature of our world. The challenges we face—as individuals, teams, organizations, communities, and as a society—are myriad and multifaceted. Their scale and complexity can be overwhelming. Where do we begin? How do we start to make sense of things?
So many of our complex systems today are human systems like organizations, which are made up of relationships between people. A human-centered approach to systems thinking starts with people and diagnoses the underlying causes of problems before taking action to solve them, and stays grounded in the needs of many stakeholders while also seeing the larger dynamics at play. When you approach problem solving in this way—deeply human and holistic—you will get to solutions that are more effective, connected, integrated, and ethical.
8. Frameworks, Tools, and Methodologies for Human-Centered Systems Thinking
Human-centered systems thinking isn’t just a theoretical concept—there are practical frameworks and tools that you use to bring it to life. Here are a couple of our favorites:
The Iceberg Model

In a complex system, solving problems requires considering the whole picture and surfacing the root of the problem. The iceberg model is a framework for uncovering the many layers of a system, including behaviors, structures, and mindsets. It helps you:
- Look for patterns over time, starting with what you see
- Uncover deeper structural influences
- Surface underlying mindsets
The Systems Map

A systems map is a tool commonly used by systems designers to lay out all the relationships and interactions between stakeholders in a given system, such as a local high school (shown in the image above). Mapping systems can help you spot opportunities for growth and change.
To create a systems map, follow these steps:
- Write down every stakeholder in your system on a blank piece of paper. Push yourself to think past the obvious.
- Draw arrows between the different parts of your system to identify how they’re connected.
- Reflect on what specific areas you want to examine more closely. What questions come up for you? What gaps do you see?
If you want to dive deeper into systems thinking and learn more tools and frameworks, check out our 5-week online course Human-Centered Systems Thinking.
Expand your design thinking skills and confidence with our Foundations in Design Thinking certificate.
- Design Thinking
- Human-Centered Design
- Systems Thinking
- Combined Shape Copy Created with Sketch. LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn
- Share Share on Facebook
- Combined Shape Created with Sketch. Tweet Tweet on Twitter
- Pin it Pin on Pinterest
- RSS Feed Subscribe on RSS
Want to get up to speed on design thinking?
Starting soon.

- choosing a selection results in a full page refresh
- press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection
Cart Preview
If this box is checked, you will be able to enter name and email of the recipient(s) after your purchase is complete.

You are creative
Get tips on building creative confidence and applying the skills of design thinking.
- Please complete this required field.
Awesome, you're in!
Get the Syllabus
Enter your email to receive the syllabus and email communications from IDEO U.
The syllabus should be in your inbox shortly. Click below to view the syllabus now.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author

- edWebinar Calendar
- edWebinar Recordings
- AI in Education
- Mental Health & Wellness Week 2024
- Amplify Excellence Across the Curriculum Week 2024
- Structured Literacy and Language Diversity Week: Spring 2024
- Elementary Writing Week 2024
- Power of Purposeful Reading Practice Week 2024
- Science of Reading Week 2024
- Emergent Bilingual Week
- Earn Free CE Certificates
- K-12 State Approvals
- Early Childhood
- Professional Associations
- Communities
- Create a Private PLC on edWeb for Your Teachers and Staff
- District and Regional Members
- Best Practices Guide & Framework
- Case Studies: Virtual Professional Learning
- edWeb 2024 Professional Learning Survey
- About edWeb
- Advisory Board
- Press Releases
- Awards & Recognition
- Partners and Sponsors
- Testimonials
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- edWeb Tutorials
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Accessibility Information
- Member Login
Join live or receive a link to the recording and earn a CE certificate
« All Events
Unleash AI Design Innovation in Your Classroom
Monday, august 12, 2024 @ 5:00 pm - 6:00 pm edt.

Presented by Joyce Lourenco Pereira, High School Design and Innovation, Korea International School Moderated by Toni Rose Deanon, Sr. Manager, Community Management, The Modern Classrooms Project
Sponsored by The Modern Classrooms Project
Register Here
Learn more about viewing the live presentation and the recording, earning your CE certificate, and using our new accessibility features.
Spark creativity, promote sustainability, and check for bias. The future of design is here, and it’s powered by AI! This interactive edWebinar equips educators with the knowledge and tools to bring AI design innovation into their classrooms.
Discover how AI can transform your curriculum by helping students:
- Generate groundbreaking ideas: Go beyond traditional brainstorming with AI-powered tools
- Design for a better future: Explore how AI can create sustainable solutions aligned with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Develop critical-thinking skills: Learn to identify and mitigate potential bias in AI-generated designs, fostering a culture of responsible innovation
Whether you teach art, technology, or any subject that involves design thinking, this session provides engaging activities and resources to empower your students to become the next generation of AI-powered design leaders. This edWebinar will be of interest to teachers, librarians, school leaders, district leaders, and education technology leaders of all grade levels. There will be time for questions at the end of the presentation.

About the Presenter
As a woman in the field of computer science, Joyce Lourenco Pereira creatively transforms the perceived chaos and complexity of this subject into order and beauty in ways that bring joy and benefit to herself and others within her circles of influence. As a patterns thinker, Joyce uncovers timeless throughlines in an ever-changing technological world by observing how humans (past and present) look to meet needs and enhance experiences using available resources in innovative ways. As a visual storyteller, Joyce crafts interdisciplinary learning experiences that inspire learners (young and adult) to take action for impact with empathy to connect with others and meet human needs efficiently. She teaches high school design and innovation at Korea International School in South Korea.

About the Moderator
Toni Rose Deanon, Senior Manager, Community Engagement for The Modern Classrooms Project, has been an educator since 2010, with experiences ranging from MS English teacher, adult ESL teacher, and instructional coach for technology. Toni Rose strives to be the educator they never had growing up, so they focus on anti-bias, anti-racist work and aspire to create a brave space for everyone around them. As a queer Filipinx, they understand the importance of being represented and valued and feeling a sense of belonging. To stay grounded and at peace, they practice yoga, write, get lost in stories, and go on two-mile walks with their dogs. Roller skating and bowling bring them so much joy.
Join the Artificial Intelligence in Education community to network with educators, participate in online discussions, receive invitations to upcoming edWebinars, and view recordings of previous programs to earn CE certificates.

- Google Calendar
- Outlook 365
- Outlook Live
Related Events

4:00 pm - 5:00 pm
Computational Thinking for PreK-5: Coding Solutions That Enhance Creativity and Problem-Solving Skills

2:00 pm - 3:00 pm
Digital Days, Positive Ways: Back-to-School Checklist for Digital Well-Being

A PBL Approach to Animation Storytelling to Foster Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging
- Faculty/Staff
- MyMichiganTech
- Safety Data Sheets
- Website Settings
- Engineering
- What is Mechanical Engineering?

The essence of mechanical engineering is problem solving. MEs combine creativity, knowledge and analytical tools to complete the difficult task of shaping an idea into reality.
Mechanical engineering is one of the broadest engineering disciplines—offering opportunities to specialize in areas such as robotics, aerospace, automotive engineering, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), biomechanics, and more. Mechanical engineers design, develop, build, and test. They deal with anything that moves, from components to machines to the human body. The work of mechanical engineers plays a crucial role in shaping the technology and infrastructure that drive our modern world.
What Is Mechanical Engineering?
Technically, mechanical engineering is the application of the principles and problem-solving techniques of engineering from design to manufacturing to the marketplace for any object. Mechanical engineers analyze their work using the principles of motion, energy, and force—ensuring that designs function safely, efficiently, and reliably, all at a competitive cost.
Mechanical engineers make a difference. That's because mechanical engineering careers center on creating technologies to meet human needs. Virtually every product or service in modern life has probably been touched in some way by a mechanical engineer to help humankind.
This includes solving today's problems and creating future solutions in health care, energy, transportation, world hunger, space exploration, climate change, and more.
Being ingrained in many challenges and innovations across many fields means a mechanical engineering education is versatile. To meet this broad demand, mechanical engineers may design a component, a machine, a system, or a process. This ranges from the macro to the micro, from the largest systems like cars and satellites to the smallest components like sensors and switches. Anything that needs to be manufactured—indeed, anything with moving parts—needs the expertise of a mechanical engineer .

What do mechanical engineers do?
Mechanical engineering combines creativity, knowledge and analytical tools to complete the difficult task of shaping an idea into reality.
This transformation happens at the personal scale, affecting human lives on a level we can reach out and touch like robotic prostheses. It happens on the local scale, affecting people in community-level spaces, like with agile interconnected microgrids . And it happens on bigger scales, like with advanced power systems , through engineering that operates nationwide or across the globe.
Mechanical engineers have an enormous range of opportunity and their education mirrors this breadth of subjects. Students concentrate on one area while strengthening analytical and problem-solving skills applicable to any engineering situation. Mechanical engineers work on a wide range of projects, from designing engines, power plants, and robots to developing heating and cooling systems, manufacturing processes, and even nanotechnology.
Mechanical Engineering Disciplines
Disciplines within the mechanical engineering field include but are not limited to:
- Autonomous Systems
- Biotechnology
- Computer Aided Design (CAD)
- Control Systems
- Cyber security
- Human health
- Manufacturing and additive manufacturing
- materials science
- Nanotechnology
- Production planning
- Structural analysis
Technology itself has also shaped how mechanical engineers work and the suite of tools has grown quite powerful in recent decades. Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is an umbrella term that covers everything from typical CAD techniques to computer-aided manufacturing to computer-aided engineering, involving finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD). These tools and others have further broadened the horizons of mechanical engineering.

What careers are there in mechanical engineering?
Society depends on mechanical engineering. The need for this expertise is great in so many fields, and as such, there is no real limit for the freshly minted mechanical engineer. Jobs are always in demand, particularly in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, biotechnology, and energy industries.
Mechanical Engineering Job Types
Here are a handful of mechanical engineering fields .
Mechanical engineers play vital roles in the aerospace industry, contributing to various aspects of aircraft and spacecraft design, development, and maintenance.
In statics , research focuses on how forces are transmitted to and throughout a structure. Once a system is in motion, mechanical engineers look at dynamics , or what velocities, accelerations and resulting forces come into play. Kinematics then examines how a mechanism behaves as it moves through its range of motion.
Materials science delves into determining the best materials for different applications. A part of that is materials strength —testing support loads, stiffness, brittleness and other properties—which is essential for many construction, automobile, and medical materials.
How energy gets converted into useful power is the heart of thermodynamics , as well as determining what energy is lost in the process. One specific kind of energy, heat transfer , is crucial in many applications and requires gathering and analyzing temperature data and distributions.
Fluid mechanics , which also has a variety of applications, looks at many properties including pressure drops from fluid flow and aerodynamic drag forces.
Manufacturing is an important step in mechanical engineering. Within the field, researchers investigate the best processes to make manufacturing more efficient. Laboratory methods focus on improving how to measure both thermal and mechanical engineering products and processes. Likewise, machine design develops equipment-scale processes while electrical engineering focuses on circuitry. All this equipment produces vibrations , another field of mechanical engineering, in which researchers study how to predict and control vibrations.
Engineering economics makes mechanical designs relevant and usable in the real world by estimating manufacturing and life cycle costs of materials, designs, and other engineered products.

What skills do mechanical engineers need?
The essence of engineering is problem solving. With this at its core, mechanical engineering also requires applied creativity—a hands on understanding of the work involved—along with strong interpersonal skills like networking, leadership, and conflict management. Creating a product is only part of the equation; knowing how to work with people, ideas, data, and economics fully makes a mechanical engineer.
Here are ten essential skills for mechanical engineers to possess:
Technical Knowledge: A strong foundation in physics, mathematics, and mechanics is crucial. Understanding principles like thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, materials science, and structural analysis forms the backbone of mechanical engineering.
Problem-Solving: Mechanical engineers often encounter complex problems that require analytical thinking and creative solutions. The ability to break down problems and develop innovative solutions is highly valuable.
Design and CAD: Proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software is essential for creating, analyzing, and optimizing designs. Knowledge of software like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or similar programs is valuable.
Critical Thinking: Assessing risks, evaluating different design options, and making decisions based on data and analysis are critical skills for mechanical engineers.
Communication: Being able to communicate technical information clearly, whether in written reports, presentations, or discussions with team members or clients, is vital for success in this field.
Project Management: Managing projects, including budgeting, scheduling, and coordinating with teams, suppliers, and clients, is often part of a mechanical engineer's role.
Hands-on Application: Practical skills in building prototypes, conducting experiments, and testing designs are valuable. Having a good understanding of manufacturing processes and techniques is beneficial.
Continuous Learning/Improvement: Given the rapid advancements in technology and techniques, a willingness to learn and adapt to new tools, methodologies, and industry trends is crucial for staying competitive.
Teamwork: Mechanical engineers often work in multidisciplinary teams. The ability to collaborate effectively with professionals from various backgrounds is essential.
Ethical Standards: Upholding ethical standards and understanding the broader impact of engineering solutions on society and the environment is increasingly important for modern mechanical engineers.
Developing a balance of technical expertise, problem-solving capabilities, and soft skills is key to becoming a successful mechanical engineer.
What tasks do mechanical engineers do?
Careers in mechanical engineering call for a variety of tasks.
- Conceptual design
- Presentations and report writing
- Multidisciplinary teamwork
- Concurrent engineering
- Benchmarking the competition
- Project management
- Prototyping
- Measurements
- Data Interpretation
- Developmental design
- Analysis (FEA and CFD)
- Working with suppliers
- Customer service

How much do mechanical engineers earn?
Like careers in many other engineering fields, mechanical engineers are well paid. Compared to other fields, mechanical engineers earn well above average throughout each stage of their careers. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the mean salary for a mechanical engineer is $105,220 , with the top ten percent earning close to $157,470 .
| Mean Entry-Level Salary (Payscale) | Mean Annual Salary (BLS) | Top 10 Percent (BLS) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
See additional engineering salary information .
The future of mechanical engineering
Breakthroughs in materials and analytical tools have opened new frontiers for mechanical engineers. Nanotechnology, biotechnology, composites, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and acoustical engineering have all expanded the mechanical engineering toolbox.
Nanotechnology allows for the engineering of materials on the smallest of scales. With the ability to design and manufacture down to the elemental level, the possibilities for objects grows immensely. Composites are another area where the manipulation of materials allows for new manufacturing opportunities. By combining materials with different characteristics in innovative ways, the best of each material can be employed and new solutions found. CFD gives mechanical engineers the opportunity to study complex fluid flows analyzed with algorithms. This allows for the modeling of situations that would previously have been impossible. Acoustical engineering examines vibration and sound, providing the opportunity to reduce noise in devices and increase efficiency in everything from biotechnology to architecture.
How do I become a mechanical engineer?
There are several paths you can take to a career in mechanical engineering . Tomorrow needs MEs who are prepared to make a difference in the world to solve challenges in healthcare, energy, transportation, space exploration, climate change, and more.
Most entry-level mechanical engineering positions require at least a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering or mechanical engineering technology. Positions that are related to national defense may need a security clearance and a US citizenship may be required for certain types and levels of clearances.
In high school, focus on classes in math and physics. Other science courses can also be helpful. Research colleges and universities offering an accredited mechanical engineering degree program. Visit the schools you are interested in and apply early. Become a mechanical engineer.
Mechanical Engineering at Michigan Tech
We are committed to our mission of hands-on education of our mechanical engineering students, by world-class faculty, through innovative teaching, mentoring, and knowledge creation.
Mechanical Engineering Degrees
The bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering at Michigan Tech offers undergraduate students many unique, hands-on learning opportunities:
Undergraduate Research Opportunities
Undergraduate research opportunities are plentiful. Our department offers undergraduate students numerous opportunities in research, hands-on experience, and real-world client work. Research projects often require help from students for running simulations, taking data, analyzing results, etc. These opportunities may even be paid, depending on the availability of funds on the particular project. Take advantage of over 50,000 square feet of labs and computer centers, in the 13-story R. L. Smith Mechanical Engineering-Engineering Mechanics Building.
Real-World Experience
Get ready to contribute on the job from day one. Our students benefit from hands-on experiences ranging from our senior capstone design program to our enterprise teams to internships/co-ops . As a mechanical engineer, you can make a difference in the world by using the latest technologies to help solve today's grand challenges.
ABET Accreditation
Our undergraduate mechanical engineering program is ABET Accredited . ABET accreditation is a significant achievement. We have worked hard to ensure that our program meets the quality standards set by the profession. And, because it requires comprehensive, periodic evaluations, ABET accreditation demonstrates our continuing commitment to the quality of our program—both now and in the future.
Prepare for Graduate Study
Our undergraduate program in mechanical engineering prepares you for advanced study in the field. Earn an MS degree in mechanical engineering , an MS degree in engineering mechanics , or a PhD degree in mechanical Engineering–engineering mechanics .

COMMENTS
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled "Design Thinking" by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
The term "Design Thinking" dates back to the 1987 book by Peter Rowe; "Design Thinking." In that book he describes the way that architects and urban planners would approach design problems. However, the idea that there was a specific pattern of problem solving in "design thought" came much earlier in Herbert A Simon's book, "The Science of the Artificial" which was published ...
Design thinking is a mindset and approach to problem-solving and innovation anchored around human-centered design. While it can be traced back centuries—and perhaps even longer—it gained traction in the modern business world after Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO, published an article about it in the Harvard Business Review .
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams better identify, understand, and solve business and customer problems. When businesses prioritize and empathize with customers, they can create solutions catering to their needs. Happier customers are more likely to be loyal and organically advocate for the product.
Design thinking is a systemic, intuitive, customer-focused problem-solving approach that organizations can use to respond to rapidly changing environments and to create maximum impact. (6 pages) Design and conquer: in years past, the word "design" might have conjured images of expensive handbags or glossy coffee table books.
The proof is in the pudding: From 2013 to 2018, companies that embraced the business value of design had TSR that were 56 percentage points higher than that of their industry peers. Check out these insights to understand how to use design thinking to unleash the power of creativity in strategy and problem solving. Designing out of difficult times.
Design Thinking is defined as a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that prioritizes understanding the needs of users, generating creative solutions, and iterating through rapid prototyping and testing. ... Problem-Solving Approach: Design Thinking offers a systematic approach to problem-solving that can be applied to a ...
Understanding design thinking can transform your team's problem-solving approach — and how you work together. What is design thinking? Design thinking is an iterative process where teams seek to understand user needs, challenge assumptions, define complex problems to solve, and develop innovative solutions to prototype and test.
Design thinking is a transformative problem-solving approach that puts human needs and experiences at its core. At its essence, it's a structured methodology that empowers individuals and organizations to tackle complex challenges by fostering empathy, creativity, and innovation. Unlike traditional problem-solving methods, design thinking is not confined to a linear path; instead, it ...
Design thinking is a methodology which provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It's extremely useful when used to tackle complex problems that are ill-defined or unknown—because it serves to understand the human needs involved, reframe the problem in human-centric ways, create numerous ideas in brainstorming sessions and adopt a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing.
Design thinking is an approach to problem-solving and innovation that's both user-centric and solutions-based—that is, it focuses on finding solutions instead of problems. For example, if a business is struggling with bad reviews, design thinking would advise it to focus on improving how it treats customer-facing employees (a solution ...
Design thinking centers the user in the creative process. Design thinking is a type of creative problem solving. "It's a way of thinking and making that keeps the user at the center of everything," explains experience designer Meg Dryer. "It's a human-centered approach to developing products, services, and experiences.".
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford's d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions ...
Design thinking is an ideology supported by an accompanying process. A complete definition requires an understanding of both. Definition: The design thinking ideology asserts that a hands-on, user-centric approach to problem solving can lead to innovation, and innovation can lead to differentiation and a competitive advantage. This hands-on ...
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that focuses on the needs of the users. The process involves empathy, defining the problem, ideating, prototyping, and testing. Design thinking can be applied to a wide range of problems and is used by designers, businesses, and organizations to develop new products, services, and ...
Design thinking is a user-centric, solutions-based approach to problem-solving that can be described in four stages: Clarify: This phase involves observing a situation without bias. It leans into design thinking's user-centric element and requires empathizing with those affected by a problem, asking them questions about their pain points, and ...
Abstract. Design thinking—understanding the human needs related to a problem, reframing the problem in human-centric ways, creating many ideas in brainstorming sessions, and adopting a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing—offers a complementary approach to the rational problem-solving methods typically emphasized in business schools.
In contrast to traditional problem-solving, which is a linear process of identifying a problem and then brainstorming solutions, design thinking only works if it is iterative. It is less of a means to get to a single solution, and more of a way to continuously evolve your thinking and respond to consumer needs.
The goal was simple: breaking free from conventional problem-solving strategies. Let's jump now to the 21st century, where design thinking has become a structured methodology at the heart of many renowned organizations' strategies, such as Apple, Google, and Amazon. ... In the realm of design thinking, defining the problem is an art form ...
This is all equally applicable to the development of strategies, products, processes and a variety of socio-technical systems. This course will help you to learn about the role of creativity in problem solving, and the application of design thinking to different business tasks. You will discover the characteristics of difficult problems, the ...
Design Thinking can be applied to nearly any course where innovation and creative problem solving is required. Design Thinking fits within the real-world of complicated problems because it promotes the search for many possible options, not a single right answer. Design Thinking is used widely in various entrepreneurial-minded organizations (e.g ...
Design thinking can help people do out-of-the-box or outside-the-box thinking. People who use this methodology: Attempt to develop new ways of thinking —ways that do not abide by the dominant or more common problem-solving methods. Have the intention to improve products, services and processes.
Systems thinking and design thinking are both approaches to problem solving and innovation. Systems thinking starts with understanding entire systems rather than individualized elements to spot opportunities for change, whereas design thinking is focused on understanding people's real needs to create human-centered products, services, and ...
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Willingness to try new things: When problem-solving skills and critical thinking are encouraged by teachers, they set a robust foundation for young learners to experiment, think out of the box ...
AI-powered tools, Artificial Intelligence (AI), critical thinking skills, Design Innovation. Related Events. Tue 06 Aug. 4:00 pm - 5:00 pm. Computational Thinking for PreK-5: Coding Solutions That Enhance Creativity and Problem-Solving Skills. Thu 08 Aug. 2:00 pm - 3:00 pm. Digital Days, Positive Ways: Back-to-School Checklist for Digital Well ...
Technically, mechanical engineering is the application of the principles and problem-solving techniques of engineering from design to manufacturing to the marketplace for any object. Mechanical engineers analyze their work using the principles of motion, energy, and force—ensuring that designs function safely, efficiently, and reliably, all at a competitive cost.
Certainly! Here are some interesting facts about the gaming industry: 1. **Massive Market Size:** The global video game industry is worth over $200...