

Insurance Agency Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 3,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their insurance agencies. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through an insurance agency business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Insurance Business Plan Template here >
What is an Insurance Agency Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your insurance agency as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for an Insurance Agency
If you’re looking to start an insurance agency or grow your existing insurance agency you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your insurance agency in order to improve your chances of success. Your insurance agency business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your agency grows and changes.
Source of Funding for Insurance Agencies
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for an insurance agency are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable. But they will want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate the business.
The second most common form of funding for an insurance agency is angel investors. Angel investors are wealthy individuals who will write you a check. They will either take equity in return for their funding, or, like a bank, they will give you a loan. Venture capitalists will not fund an insurance agency unless it is based on a unique, scalable technology.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for an insurance agency.
Your insurance agency business plan should include 10 sections as follows:
Executive Summary
- Company Overview
Industry Analysis
Customer analysis, competitive analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team, financial plan.
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of insurance agency you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have an insurance agency that you would like to grow, or are you operating multiple insurance agency locations already.
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the insurance agency industry. Discuss the type of insurance agency you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of insurance business you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types:
- Direct Writer / Captive : this type of insurance agency only sells one insurance company’s products – like Allstate or State Farm
- Independent Insurance Agent : this type of insurance agency is privately-owned, and sells policies with may different insurance companies
In addition to explaining the type of insurance agency you operate, the Company Analysis section of your own business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include sales goals you’ve reached, new location openings, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the insurance business.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the insurance industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy particularly if your research identifies market trends. For example, if there was a trend towards weather-related policy purchases, it would be helpful to ensure your plans call for flood insurance options.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your insurance company business plan:
- How big is the insurance industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key insurance carriers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your insurance agency. You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
The customer analysis section of your insurance agency business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, households, businesses, etc.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of insurance agency you operate. Clearly baby boomers would want different pricing and product options, and would respond to different marketing promotions than recent college graduates.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most insurance businesses primarily serve customers living in their same geographic region, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Insurance Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Insurance Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other insurance agencies.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from you that aren’t direct competitors. This includes self pay and public (Medicare, Medicaid in the case of health insurance) insurance or directly working with an insurance carrier. You need to mention such competition to show you understand that not everyone who purchases insurance does so through an insurance agency.
With regards to direct competition, you want to detail the other insurance agencies with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be insurance agencies located in your geographic region.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What insurance products do they offer?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide superior insurance agency products/services?
- Will you provide insurance agency products that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you make it easier or faster for customers to acquire your products?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an insurance agency, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : in the product section you should reiterate the type of insurance agency that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products/services you will be offering. For example, in addition to P&C insurance, will you also offer life insurance?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the menu items you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your insurance agency. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your insurance agency located next to the Department of Motor Vehicles, or a heavily populated office building, etc. Discuss how your location might provide a steady stream of customers.
Promotions : the final part of your insurance agency marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Making your insurance agency’s front store extra appealing to attract passing customers
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local bloggers and websites
- Partnerships with local organizations (e.g., auto dealerships or car rental stores)
- Local radio advertising
- Banner ads at local venues
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your insurance agency such as serving customers, procuring relationships with insurance carriers, negotiating with repair shops, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to acquire your 500th customer, or when you hope to reach $X in sales. It could also be when you expect to hire your Xth employee or launch a new location.
To demonstrate your insurance agency’s ability to succeed as a business, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in an insurance agency. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in insurance agencies and/or successfully running small businesses.
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you acquire 20 new customers per month or 50? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : While balance sheets include much information, to simplify them to the key items you need to know about, balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. For instance, if you spend $100,000 on building out your insurance agency location and/or website, that will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $100.000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a successful insurance agency:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Marketing expenses
- Website development
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your store design blueprint or location lease.
Free Insurance Business Plan Template
You can download our insurance business plan PDF or sample insurance business plan to help you get started on your own business plan.
If you are looking for the quickest and easiest way to complete your business plan, Growthink’s Ultimate Insurance Business Plan Template has numerous features not available in the free template including its financial projections template which automatically calculates your complete five-year financial projections including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Insurance Business Plan Summary
Putting together a business plan for your insurance business will improve your company’s chances of success. The process of developing your plan will help you better understand the insurance market, your competition, and your customers. You will also gain a marketing plan to better attract and serve customers, an operations plan to focus your efforts, and financial projections that give you goals to strive for and keep your company focused.
Additional Resources for Insurance Agents
- How to Write a Marketing Plan for an Insurance Agency
- How to Start an Insurance Agency
- Association for Independent Agents
- Business License Requirements By State For Insurance Agencies
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Insurance business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to learn about Growthink’s business plan writing services .
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Insurance Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Insurance Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
Insurance Agency Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your own business plan.
We have helped over 100,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their insurance companies.
Essential Components of a Business Plan For an Insurance Agency
Below we describe what should be included in each section of a business plan for a successful insurance agency and links to a sample of each section:
- Executive Summary – In the Executive Summary, you will provide a high-level overview of your business plan. It should include your agency’s mission statement, as well as information on the products or services you offer, your target market, and your insurance agency’s goals and objectives.
- Company Overview – This section provides an in-depth company description, including information on your insurance agency’s history, ownership structure, and management team.
- Industry Analysis – Also called the Market Analysis, in this section, you will provide an overview of the industry in which your insurance agency will operate. You will discuss trends affecting the insurance industry, as well as your target market’s needs and buying habits.
- Customer Analysis – In this section, you will describe your target market and explain how you intend to reach them. You will also provide information on your customers’ needs and buying habits.
- Competitive Analysis – This section will provide an overview of your competition, including their strengths and weaknesses. It will also discuss your competitive advantage and how you intend to differentiate your insurance agency from the competition.
- Marketing Plan – In this section, you will detail your marketing strategy, including your advertising and promotion plans. You will also discuss your pricing strategy and how you intend to position your insurance agency in the market.
- Operations Plan – This section will provide an overview of your agency’s operations, including your office location, hours of operation, and staff. You will also discuss your business processes and procedures.
- Management Team – In this section, you will provide information on your insurance agency’s management team, including their experience and qualifications.
- Financial Plan – This section will detail your insurance agency’s financial statements, including your profit and loss statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It will also include information on your funding requirements and how you intend to use the funds.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Insurance Agency Business Plan FAQs
What is an insurance agency business plan.
An insurance agency business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your insurance business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your insurance agency business plan using our Insurance Agency Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Insurance Companies?
There are a few types of insurance agencies. Most companies provide life and health insurance for individuals and/or households. There are also agencies that specialize strictly in auto and home insurance. Other agencies focus strictly on businesses and provide a variety of liability insurance products to protect their operations.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenue and Expenses for an Insurance Agency Business?
The primary source of revenue for insurance agencies are the fees and commissions paid by the client for the insurance products they choose.
The key expenses for an insurance agency business are the cost of purchasing the insurance, licensing, permitting, and payroll for the office staff. Other expenses are the overhead expenses for the business office, utilities, website maintenance, and any marketing or advertising fees.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Insurance Agency Business Plan?
Insurance agency businesses are most likely to receive funding from banks. Typically you will find a local bank and present your business plan to them. Other options for funding are outside investors, angel investors, and crowdfunding sources. This is true for a business plan for insurance agent or an insurance company business plan.
What are the Steps To Start an Insurance Business?
Starting an insurance business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop An Insurance Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed insurance business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your insurance business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your insurance business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Insurance Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your insurance business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your insurance business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Insurance Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your insurance business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your insurance business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful insurance business:
- How to Start an Insurance Business
Where Can I Get an Insurance Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free insurance business plan template PDF here . This is a sample insurance business plan template you can use in PDF format.

- Financial Analysis
- Budgeting Consultants
- Financial Reporting
- Financial Planning
- Financial Modeling
- Accounting & Bookkeeping
- Market research consultant
- Pakistan Taxation Services
- Company Registration In UAE
- Vat Registration In UAE
- Business Valuation
- Investor Ready Business Plan
- Professional Business Plan Revision
- Investor Ready Pitch Deck Presentation
- Investor Ready Executive Summary
- Investor Ready One Page Project Overview
- Professional Business Plan Review
- Pro Forma Statement of Financial Position/Balance sheet
- Cash Flow Analysis
- Full time CFO
- Special Purpose CFO
- Interim CFO
- Virtual CFO
- Marketing KPI
- Growth Plan KPI
- Financial Metrics KPI
- Break Even Analysis
- Unit Metrics Analysis
- Sales Performance KPI
- Cash Management KPI
- Inventory Management KPI
- Business Plan Packages
- Automotive Industry
- Blockchain Industry Financial Model Template New
- Cosmetics Industry
- Consulting Business
- Education Industry
- Entertainment Industry
- Fintech Industry
- Real Estate
- View All Financial Models
- Healthcare Industry
- Restaurant Business
- View All Business Plan
- Automotive Business
- Blockchain Industry Pitch Deck New
- Education Pitch
- View All Pitch Decks
- Automotive industry
- Testimonials
- Case Studies
- Startup CEOs
- Venture Capital Professionals
Health Insurance Business Plan
- Business Plan , Browse by Categories , Browse by Industry , Healthcare Industry , Healthcare Industry Business Plan

$ 150 Original price was: $150. $ 99 Current price is: $99.
Unveil the power of our Health Insurance Business Plan, a meticulously crafted blueprint designed to cater to both startups and established businesses in the insurance sector. Dive deep into comprehensive market analysis, financial projections, and strategic pathways for sustained growth. With sections dedicated to competitive insights and tailored marketing strategies, our plan promises to be the cornerstone of your venture, guiding you through every step to establish a dominant and thriving insurance enterprise.
Frequently Bought Together
| + | + |
- This Product: Health Insurance Business Plan - $ 150 Original price was: $150. $ 99 Current price is: $99.
- Insurance Agency Excel Financial Model - $ 150 Original price was: $150. $ 95 Current price is: $95.
- Healthcare Pitch Deck Template - $ 30 Original price was: $30. $ 20 Current price is: $20.
Description
- Reviews (0)
- Testimonial
Health Insurance Business Plan
Introduction to our health insurance business plan .
Embarking on the realm of insurance, it’s critical to have a robust roadmap, ensuring the journey from startup to established entity is smooth and strategically sound. This guide offers a comprehensive perspective on formulating a health insurance business plan , blending industry insights with actionable strategies, ensuring success in the intricate world of insurance.
Our Health Insurance Business Plan Template is specifically designed for small businesses seeking to develop comprehensive plans for small business health insurance offerings. This template helps articulate the strategic approach for launching or expanding your insurance products tailored to meet the unique needs of small enterprises. The template includes detailed sections for outlining various insurance products, including group health plans, ensuring that you can offer competitive and comprehensive options to your clients. Designed with insights from experienced insurance agents, this business plan template guides you through analyzing the market and identifying key opportunities for growth and innovation in the health insurance sector.
Keys of Health Insurance Business Plan
The bedrock of any successful venture is its business plan —a compass pointing towards your goals and providing detailed pathways on achieving them. Key components encompass understanding the target audience in the insurance market, gauging competitors, and financial projection of your growth. It’s not just about having an idea; it’s about wrapping that idea in layers of strategies, analysis, and actionable plans to turn it into a reality.
Our Health Insurance Business Plan Template
At the heart of our guide is the actual insurance agency business plan template, catering specifically to the needs and challenges of the insurance market and potential customers and designed keeping in mind both novices and veterans of the insurance industry.
Executive Summary of health Insurance Business Plan
The Executive Summary is the elevator pitch of your health insurance business plan. It’s a snapshot, presenting an overview of what your insurance company is about, its business goals, its mission statement, and the market opportunities it plans to tap into. It defines your business’s essence, its vision, and its mission in the vast expanse of the insurance industry.

Company Summary
Dive into the depths of your company. Understand its structure, its foundation, and its core management teams. This segment of your health and insurance business plan offers insights into the history, ethos, and operational mechanics of your insurance enterprise, from its inception to its future aspirations.

Service Portfolio
Your services are your offerings to the world. Detail out the insurance policies you plan to offer. Whether it’s life insurance, health, or a combination of various plans, lay them out, ensuring your target audience understands their options and benefits comprehensively.

SWOT Analysis
Every venture has its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This analysis provides a clear picture, allowing for strategic planning around these pillars, ensuring sustained growth and risk mitigation.

Industry Analysis
The insurance industry is vast and dynamic. Delve into its trends, challenges, and market trends and opportunities. Grasp where the industry is heading and position your business to leverage emerging opportunities using a sound business strategy.

Market Analysis
Who is your target audience? Where are they? What do they need? Answer these vital questions, understand your target market, and gauge the growth potential they offer.

Competitive Analysis
You’re not alone in the market. Understand your competitors, their strengths, and their gaps. Position your insurance business to leverage these insights, ensuring a competitive edge in the insurance market.

Marketing Plan
A great product needs visibility. Craft marketing strategies that resonate with your target audience. From digital campaigns to traditional outreach, ensure your insurance offerings are seen and sought after.

Operational Plan
Day-to-day operations are the backbone of your business. Detail out processes, teams, and strategies that will drive your daily business activities, ensuring efficiency and customer satisfaction.

Celebrate achievements, big or small. Define milestones for your insurance business, offering clear markers of growth, achievements, and a roadmap for the future.

Financial Plan
Money is the fuel for your venture. Detail out financial forecast, financial statements, income statements, and cash flow statements. Ensure clarity on expenses, projected revenues, and growth forecasts.

FAQ’s on Health Insurance Business Plan
How do you write an outline for a business plan?
Crafting an outline for a business plan begins with defining the core sections that will embody your enterprise’s essential aspects. For example, the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What is an insurance business plan?
An insurance business plan is a structured document that delineates an insurance company’s or agency’s strategic roadmap. It encapsulates various facets including its service portfolio, target market, marketing and sales strategies, operational outlines, and financial projections, ensuring a systematic approach towards achieving its goals.
How do I write a simple business plan template?
Initiate with a succinct executive summary, following with sections that elaborate your company’s profile, service offerings, target market, competitive and market analyses, organizational structure, marketing, operational and financial plans, making sure each segment coherently reflects your business’s ethos and strategic trajectory.
Conclusion of Health Insurance Business Plan
Crafting a robust health insurance business plan is a blend of strategy, insight, and foresight. With this comprehensive guide, your journey through the complex corridors of the insurance world becomes navigable, ensuring success, growth, and a legacy in the making.
INSTRUCTIONS TO ACCESS YOUR PURCHASE:
- Order Completion : Once your order is finalized, a download link for your files will be available in your dashboard.
- Retrieve Document : Proceed to download your PDF document.
- Engage with Canva : Register for a complimentary Canva account or access your existing account.
- Activate Template : Open the PDF and select the highlighted LINK. This will redirect you to your specific Canva template.
- Personalization : Within Canva, you have the flexibility to adjust colors, fonts, images, and other elements to match your branding specifications.
- Finalize and Share : After customization, download your design and showcase it on your social media platform.
TERMS OF USE :
Oak Business Consultant and our range of products, including this template, are not endorsed by or officially connected to Canva. Your purchase allows you a SINGLE LICENSE FOR PERSONAL USE, which is exclusive to your personal or business needs. Redistribution, resale, or sharing of the files and templates is prohibited. If you appreciate our template and wish to recommend it, please direct others to our shop.
There are no reviews yet.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
The testimonial shows one of our clients who has received our Business Plan Services.

In our pursuit of excellence within the healthcare industry, we had the privilege of partnering with a valued client to address critical challenges. Our article highlights our innovative solutions, we invite you to explore the full article to witness the transformative impact of our work. Click here
Related products

SaaS Customer Services Software Excel Financial Model

Farming Excel Financial Model

Cash Management KPI Dashboard

Online Rental Clothing Business Plan

Online School Business Plan

E-Wallet Excel Financial Model

E-Mail Management Software Excel Financial Model

Unit Metrics Analysis Dashboard

E-Commerce Travel Accessory Business Plan Template

Car Pet Seat Cover Business Plan Template

Voices of Victory: Client Testimonials of Triumph
Dana Todd Founder & CEO
Services: Accounting and Bookkeeping Services
Industry: Fashion Clothing Store
It is my pleasure to recommend Oak’s bookkeeping services to anyone, as I have been using them for many years, and I believe they are genuine and really know their stuff.
Andrina Founder
Services: CFO Services , Market Research
Industry: Beauty Products and Manufacturing
No amount of praise can do justice to the quality of Sadaf’s CFO services. Her dedication to her clients is unparalleled. I have trusted her with two complicated accounts, and she handled everything with a professional attitude and without making any errors.
Denver Maloney CEO
Industry: Healthcare
It is a pleasure to work with the Oak Team, particularly Sadaf. As a result of her partnership with me, I was able to gain a better understanding of financial decisions. For my CFO needs, I fully trust Oak!
Lars Narfeldt COO
Services: Investor-Ready Document Services
Industry: Real Estate
This was our first time working together, but it was so easy to get started and Sadaf quickly understood our targets and accommodated the way we work. She was extremely patient with our continuous change in deliverables, worked hard to meet our expectations and often suggested how we could improve our work and make the project more efficient. Well skilled in her profession and an absolute pleasure to work with.
Emma Sánchez Andrade Smith Co-Founder
Services: Financial Model , Financial Forecasting , Pitch Deck & Market Research
Industry: Fintech
Sadaf was above & beyond what we could’ve asked for! I will certainly hire her again, and will recommend her to anyone I can! Her and her team’s quality of work is excellent, and she gets things done very quickly. She is very engaging, and responsive, there for our every beckon call. She spent nearly an hour on a phone call with us to go over the numbers and helped us brainstorm some new numbers when we needed them. Amazing, incredibly talented professional – you will be doing yourself a big favor if you hire her!! :)
Sufian Chowdhury Founder & CEO
Services: Startup Saas Financial Model , Market Research
Industry: SaaS
Thanks so much for working so hard on this project. Looking forward to working on many more projects with you and your team!
Stephanie Skourti Co-Founder
Industry: Fashion E-store
There is no doubt that Oak is a game-changer. A unique combination of experience and expertise makes them the best in the business. They have helped me relieve a lot of stress and improved the stability of my business. Having a teammate to guide me through big financial decisions is truly a blessing.
Luisa Silva Co- Founder
Industry: Health Care
Sadaf and her team are really helpful and hardworking, would recommend them for any concrete tasks you may need help with in your organization.
Lalit Vidhani Consultant
Services: Financial Model , Business Plan , Pitch Deck & Market Research
Industry: Blockchain
Excellent and professional approach and I am happy with the results. The working with team Oak Consultant was wonderful and all assignments were completed with lot of energy and professionalism by members of the team.
Stacey Powell CEO
Services: Cash Flow Analysis Tool
Industry: Consulting Firm
Sadaf and her team have excellent excel spreadsheet skills. My client provided a rather complicated set of accounting reports that needed to be integrated into a spreadsheet format I had, but I didn’t have time to do it myself. With very limited instructions, Sadaf and her team successfully completed the integration and improved upon my spreadsheet with pivot tables and graphs. Will definitely keep her for future financial analysis and spreadsheet work.
Sabeen Ali Founder
Industry: Information Technology Company
Oak bookkeeping services have been a great help. This company has a high level of professionalism, friendliness, and positivity! The service they provide is excellent, and I highly recommend them.
Ramin Heydari CEO & President
Industry: Telecom
Oak provides exceptional accounting services. You’ll find that they offer a much wider range of knowledge than your average accountant, making them a valuable asset to your company. Highly recommended!!!

Health Insurance Business Plan Template (PDF)
This product ( Health Insurance Business Plan Template ) is a 44-page PDF document, which you can download immediately upon purchase.
| "As a young consulting firm, requests for input from clients vary and it's sometimes impossible to provide expert solutions across a broad spectrum of requirements. That was before I discovered Flevy.com. Through subscription to this invaluable site of a plethora of topics that are key and crucial to consulting, I " |
| "I am extremely grateful for the proactiveness and eagerness to help and I would gladly recommend the Flevy team if you are looking for data and toolkits to help you work through business solutions." |
| "[Flevy] produces some great work that has been/continues to be of immense help not only to myself, but as I seek to provide professional services to my clients, it give me a large "tool box" of resources that are critical to provide them with the quality of service and outcomes they are expecting." |
| "As a consultant requiring up to date and professional material that will be of value and use to my clients, I find Flevy a very reliable resource. The variety and quality of material available through Flevy offers a very useful and commanding source for information. Using Flevy saves me time, enhances my expertise and ends up being a good decision." |
| "If you are looking for great resources to save time with your business presentations, Flevy is truly a value-added resource. Flevy has done all the work for you and we will continue to utilize Flevy as a source to extract up-to-date information and data for our virtual and onsite presentations!" |
| "FlevyPro provides business frameworks from many of the global giants in management consulting that allow you to provide best in class solutions for your clients." |
| "As a consulting firm, we had been creating subject matter training materials for our people and found the excellent materials on Flevy, which saved us 100's of hours of re-creating what already exists on the Flevy materials we purchased." |
| "As a niche strategic consulting firm, Flevy and FlevyPro frameworks and documents are an on-going reference to help us structure our findings and recommendations to our clients as well as improve their clarity, strength, and visual power. For us, it is an invaluable resource to increase our impact and value." |
- Full History
|
|
Download our FREE Strategy & Transformation Framework Templates
Get our free product..

| Strategy & Transformation Digital Transformation Operational Excellence Organization & Change Financial Models Consulting Frameworks PowerPoint Templates / / / Contact Us: | | | | |

Insurance Business Plan

Back in 2018, the Insurance Information Institute (III) reported that the insurance industry’s written premiums reached USD 1.22 trillion worth in the United States alone. In line with this, fifty-one percent consists of car and other property insurance, while the forty-nine percent are covered by health and annuity or life insurance. With that much worth in mind, making your very own insurance agency is surely a good idea. So, what’s stopping you? Don’t waste time and create a business plan that outlines your future business process, market analysis , SWOT analysis , marketing strategies, budget , and other business development coverage! For your convenience in planning your financial protection service provider business, we encourage you to look at our examples below!
10+ Insurance Business Plan Examples
1. insurance business plan template.

- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
2. Insurance Agency Business Plan Template

3. Sample Insurance Agency Business Plan Template

4. Insurance Business Plan Example

Size: 69 KB
5. Insurance Business Plan in PDF

Size: 129 KB
6. Insurance Agency Business Plan

Size: 165 KB
7. Insurance Financial Business Plan

8. Insurance Agency Business Plan in PDF
9. Basic Insurance Business Plan

Size: 390 KB
10. Insurance Company Business Plan

Size: 59 KB
11. Client Insurance Business Plan Template
What Is an Insurance Business Plan?
An insurance business plan is a process document covering how an insurance agency will be developed and maintained. In the blog site Now From Nationwide, such a document is referred to as a roadmap towards a business’s success . The same article shared that it provides entrepreneurs a clear understanding of all aspects of a business right from its operations to the complete description of its products or services. This document is necessary, especially for startup businesses, to acquire much-needed financial assistance from bank loans or investors. It is also a crucial element in the documentation policy or documentation plan of the business.
Types of Insurance Most People Need
There are many types of insurance , with each of them serving a distinct purpose. However, not all of them are necessary for most people. Investing in the wrong insurance policy can obviously do more harm than good. Here are the types of insurance that people must have:
1. Life Insurance – covers your funeral expenses while securing the financial assistance of your beneficiaries 2. Health Insurance – insure people from medical expenses 3. Disability Insurance – provides financial assistance to workers who lost the capability to work due to a certain disability 4. Auto Insurance – indemnifies people during vehicle mishaps
How To Create an Insurance Business Plan
Every element of a business plan is essential for the development and sustainability of a business. Because of that fact, there’s a need for you to be thorough and concise on its content. Not only those, you also have to make it in accordance with the standard documentation procedure . In order for you to achieve the aforementioned qualities, we have made our standardized outline ready for you. Check them out below.
1. Provide the Executive Summary
Even though the executive summary is the first section of a business plan, it is written last. Its role is to make a good first impression to the readers by abiding by the proper executive summary writing practices. This section must give brief details on the overall business, long-term goals , products or services, target market, methodologies, and financial outlook.
2. Present the Business Overview
The business overview section comes right after the executive summary . In this section, you give out the full details of the mission statement , short-term and long-term goals , target market, business structure, competitive advantage, as well as the product and service descriptions. These areas will help readers know what kind of business you have, how you can sustain it, and who your audience will be.
3. Write Down Sales & Marketing Strategy
After presenting the business overview, write down the sales and marketing strategies for your business. With most business activities shifting to digital platforms, both the sales and marketing aspects of a business plan should focus on online engagement. In fact, many insurance companies attract potential policyholders through their respective websites and social media accounts. The same goes in the selling of these policies.

4. Advance the Operations & Management Processes
Once the strategies for both sales and marketing aspects have been laid down, give the full details on how your business will operate and how it will be sustained in the years to come. It is in this section where you have to proffer various insurance workflows and methodologies. The stakeholders for each of your business’s departments are also considered in this part, along with their job descriptions.
5. Summarize Financial Plan
To conclude your business plan, summarize your financial plan. This should thoroughly discuss the money that you’ll be getting to get your business started and how you’ll be getting them. If you’re a startup, the most common way is to reach out to banks to make loans, which pretty much require business plans.
What is an insurance policy?
An insurance policy is a contract that binds the insurer and the insured. It provides complete details of the premium payment, insurance coverage, and more. The most common provision in all insurance policies is the insurer’s rights to withhold coverage if the insured refuses to pay the premiums.
How does an insurance company make money?
An insurance company makes money in two ways. The first one is through underwritings, where the insurer gambles to offer coverage to the insured with high hopes to collect more money than the payouts. The second one is with investments. Whenever the insured pays their premium, the insurer places them down in financial markets to grow.
What happens to the insurance company when policyholders decide to get their cash back?
Insurance companies not just secure the money of the policyholders, but also grow them. Once these policyholders find that out, they will most likely try to withdraw them right away along with the cash value. At the same time, they close their accounts.
When such a circumstance happens, all the liabilities that the insurance company holds will end. Moreover, it keeps the paid premiums but pays the customer with deductions on the interests brought about by investments. These interests and other remaining cash goes directly to the company’s revenue.
If helping out individuals does not always go hand in hand with making profits, then an insurance business is a special case. There’s no denying that such a business is too risky for an entrepreneur. However, we can’t also disagree with the fact that it can be profitable when done carefully. And, an insurance business plan is a perfect document that can help you with being so.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Health Plan Administration Business Plan
Start your own health plan administration business plan
Southeast Health Plans
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. is a service company that will provide health plan administrative services to self-insured employers. The company will concentrate on employers with 50 to 500 employees. Many of these employers have current HMO, PPO, or major national insurance carrier health plans. While the majority of employers with 500 or more employees have at least some element of self-insurance incorporated into their health care programs, our target market is often ignored by the major national insurance companies. While more than 80% of companies with 500 or more employees are self-insured, the management of Southeast Health Plans has identified that less than 25% of Atlanta area companies with 50 to 500 employees have self-insured plans.
The market for self-insured and administrative services consist of those companies that are currently self-insured and companies that have other types of health plans that will be encouraged to shift to self-insurance. One factor in the transition to self-insurance is the availability of quality administrative and consultative services. Southeast Health Plans, Inc. is led by experienced management and has formed a strategic alliance with Blair Mill Administrator, a wholly owned subsidiary of Blue Cross/Blue Shield of Pennsylvania, for the purpose of providing first class benefits management services to its target market.
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. will achieve revenue of more than $5 million in five years with a net profit after tax of $1.6 million. The company will turn profitable in year three with after-tax earnings of $560 thousand. As a marketing organization and service provider, margins will be extremely high with gross margins above 80% (less only sales incentive costs) and approaching 50% after all operating expenses, once market penetration has reached maturity.
The key to success for Southeast Plans, Inc. will be the ability to attract the initial capital in order to successfully market its services in the metro Atlanta area and in northern Georgia. Adequate professional sales staffing is essential. The company must then expand a successful formula throughout Southeastern markets. Cost control, particularly with regard to sales and marketing programs, will enable controlled expansion that is fully funded by internal cash flow.

1.1 Objectives
The objectives for the company are:
- To initiate co-operative marketing utilizing Blair Mill advertising executions with media in the Atlanta metro market.
- To hire sales staff both currently identified and unidentified to implement sales lead follow-up strategy.
- To have at least 4,800 cumulative employees under management by the end of year one.
- To approach break-even by the end of year two holding total loss for the second year under $100 thousand while increasing market share.
- To shift to earnings in year three and to accelerate gross margin contributions by building market maturity on top of infrastructure.
- To expand regionally with both media and sales personnel to penetrate new markets while consolidating service capability.
- To constantly achieve cost benefit through an expanding provider network while not compromising patient care.
- To have more than 98,000 cumulative employees under management by the end of year five.
1.2 Mission
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. is dedicated to providing small and mid-size employers with a comprehensive benefits administration program that will enable employers to control health benefits costs while allowing employees within the plan to have access to quality health care. By combining self-insurance with stop-loss programs and efficient plan administration Southeast will provide to its clientele, both employers and employees, the best of health care with the minimum of restrictions and the broadest individual choice of providers. Southeast will deliver a balance of quality care and freedom of choice at a fair price.
1.3 Keys to Success
The keys to success in this business are:
- Marketing. Southeast Health Plans will have the ability to sell both directly to employers and through independent insurance brokers and agents. It will be necessary to establish name recognition among more established programs. It is essential that media budgets be controlled and that closing ratios of at least 5% of leads per year be maintained.
- Service quality. The services provided by Blair Mill Administrators are already state-of-the art among small-employer providers. The value added experience of the Southeast Health Plans, Inc. management team and their provider networks will ensure customer satisfaction. It is a necessity that clients maintain satisfaction both with service and plan cost to minimize client erosion and to combat competition. Renewals should exceed 85% of established clients.
- Controlled growth. Growth needs to be aggressive with rapid expansion to new geographic markets but also must focus on profitability. Each established market must mature as new markets develop so that growth can be internally funded. Cash flow management is essential. Both market expansion and media effectiveness must be constantly tested, and then reviewed or refined as required.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. is a service company founded by experienced medical insurance industry executives to both serve and capitalize upon the growing number of small and midsize companies that seek to control health benefits costs and manage risk by self-insurance.
The utilization of Blair Mill’s existing services, products and infrastructure enables Southeast to provide necessary service without incurring the costs of establishing proprietary programs. In addition, Blair Mill’s existing provider networks enable Southeast to serve employers with multiple locations or a wide-spread workforce.
Southeast targets those employers who have from 50 to 500 employees. Services include all-encompassing benefit management programs. Blair Mill Administrators will be utilized to provide benefits management services including:
- A full array of managed care services
- Patient care management
- Local, regional, and national provider networks
- Tailored administrative services
- Flexible plan design
- Underwriting and actuarial services
- Thorough stop-loss insurance administration.
2.1 Start-up Summary
The following tables and chart show a summary of our start-up requirements and anticipated funding.

| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $0 |
| Consultants | $12,500 |
| Offering Expenses | $15,000 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $27,500 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $272,500 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 |
| Long-term Assets | $0 |
| Total Assets | $272,500 |
| Total Requirements | $300,000 |
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $27,500 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $272,500 |
| Total Funding Required | $300,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $0 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $272,500 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $272,500 |
| Total Assets | $272,500 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Private Placement ’96 | $300,000 |
| Investor | $0 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $300,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($27,500) |
| Total Capital | $272,500 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $272,500 |
| Total Funding | $300,000 |
2.2 Company Ownership
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. is a privately-held Georgia corporation. It is owned by its founders and managing partners: James J. Peters, Thomas R. Cormier, and L. Richard Schumacher, MD.
The company has been established with the founders’ own capital. The founders have negotiated an exclusive strategic alliance with Blair Mill Administrators for certain markets in the state of Georgia.
The founders are now seeking to extend outside ownership interest for the first time in order to raise the funds required to execute the expansion plans of the business.
2.3 Company Locations and Facilities
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. currently occupies office space at … Atlanta, GA.
The phone number is … and the fax number is … .
The current offices provide sufficient space to launch business in the Atlanta and north Georgia market. More space will be required as the Atlanta market matures and central services are provided to other geographic markets. In addition, local sales offices will be required in other markets.

As health care in the United States has been changing rapidly over the past two decades, so has the way health care has been provided and how it is billed and paid. Large insurance companies and private physicians have given way to HMOs and Managed Care Plans and the TPA (Third Party Administrator) has been prospering. A TPA (like Blair Mill) exists to administer all the health care functions for a company that would have been handled by an insurance company. HMOs primarily contract for services based upon price, then re-sell those services to groups. Often, service and choice are less than satisfactory. But, most importantly, cost-effective concerns predominate. Employers are seeking to provide health care for employees at an affordable cost. A backlash has been the increase in self-insured programs administered by TPAs.
In short, a business now demands much more in the way of service and analysis than traditional support institutions have been providing to their clients. The claims processor is a case in point. Merely processing claims does nothing to help a business analyze and control its health benefits plan and to control the costs associated with the plan. And there has not traditionally been a measure for the “quality” of health care service.
Southeast has compiled, through its own proprietary systems and an alliance of external providers, a service mix that includes Network Administration Services, Network Contracting Services, Policy Formation and Quality Assurance, and Marketing Services.
Health benefits are a fact of life for any business. The small and mid-size business is concerned with cost control and administration, just as in any other department of their business operations, except they are ill-equipped in personnel, know-how, and in systems, to administer health care internally.
Thus a full array of TPA self-insured services would include:
- Claims experience analysis and cost projections
- Plan design consulting
- Comprehensive plan analysis
- Provider network analysis
- Plan documentation
- Stop-loss brokerage and administration
- Prescription drug programs
- Vision benefits administration
- Dental benefits administration
- COBRA administration
- Short-term disability administration
- Worker’s compensation services
- Custom tailored services.
3.1 Competitive Comparison
Health plans for businesses and their employees comprise a multi-billion dollar industry that is highly competitive. Well known national insurance companies like Prudential, Cigna, Aetna/US Healthcare, and the regional Blue Cross and Blue Shield Companies seek the employer’s dollar. A plenitude of HMOs, both regional and national, also compete. Many companies are already self-insured. Some of these companies use TPAs for outside claims processing while others use insurers or attempt to self-administer. Certain claims processors are also gravitating toward benefits management services.
Southeast Health Plans believes that a niche exists that is both too small for concentrated coverage by large national companies and that is not well served with broad enough quality services by other TPAs. Most TPAs are still evolving toward the service mix that small and mid-size companies are demanding. By providing those quality services now, at a fair price, Southeast believes a competitive sales advantage exists that will permit attainment of the market shares sought.
3.2 Sales Literature
Much of the sales materials and literature prepared by Blair Mill will be utilized by Southeast. Advertising executions are included in a supplement to this plan. Direct mail pieces are being developed. A Blair Mill portfolio and video tape provides a professional presentation to prospective clients.
3.3 Fulfillment
The Strategic Alliance with Blair Mill Administrators of Philadelphia, PA., provides the principal source of health plan administrative services. Southeast will earn revenue both from enrollment sales as well as from cost advantages in the delivery of health care services.
From a product perspective, this relationship is analogous to the role of a regional dealer that sells services and brand name products within a licensed and protected geographic area. The dealer brings competence and value-added expertise to the enterprise while the source brings the credibility of brand name recognition and a substantial existing client base. This serves to reduce the risk normally associated with an early stage, unrecognized health services provider.
On the health care provider side, the sourcing of health care services is already in place from a variety of provider organizations. Southeast management has had working relationships with Georgia Baptist Health Care System, Meridian Medical Group, Emory Health System, Columbia/HCA, Northside Hospitals, Scottish Rite Medical Centers and other independent health care organizations.
The management of Southeast Health Plans remains in ongoing negotiations with physician groups and hospitals to obtain the optimum mix of quality service and price for its clients. The health care providers are receptive both from the standpoint of pricing and freedom to control care. Both consumer and provider benefit from a cost/benefit mix that they find preferable to the insured HMO or Managed Care models. It is not anticipated that service sourcing will be a problem for Southeast Health Plans. Rather, the key to success will be marketing to employers coupled with provider cost negotiation. Quality of care will not be compromised.
3.4 Future Services
Future services will include establishing both a geographic network of clients and health care providers throughout the southeast. As Southeast Health Plans grows and expands it will begin to look less like a TPA and more like a Health Plan. As critical mass of clientele and medical providers is achieved cost benefit is attained and administrative functions and services are consolidated in economies of scale. At that point of critical mass when approximately 50,000 cumulative employees are under managed care the option exists for Southeast to develop its own proprietary heath plan. Many administrative services and functions that will be outsourced by Southeast can be developed as internal company centers.
At that point options exist to finance the shift to a Health Plan company. Mezzanine, or Venture funding will be obtainable for a company with $5 million in revenue and $1.6 million in earnings (and no debt). After ramp-up to a $10 to $20 million dollar company an IPO is a potential. Also, the company would be an attractive target for acquisition.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
The initial target market is the Atlanta metro and north Georgia market. The agreement with Blair Mill encompasses the following zip codes:
All three digits beginning with [Proprietary and confidential information removed].
This includes all of metro Atlanta and surrounding counties in north Georgia. At present Southeast Health Plans holds the only strategic marketing alliance with Blair Mill in the entire southeastern United States. Both sides recognize and desire an expanded agreement after phase one goals and objectives are attained.
The critical data to establish potential customer base and market share is to sort employers within the region by number of employees, regardless of whether they are currently with an HMO, an outside insurance carrier, are self-insured, or have no insurance. All are potential clients of Southeast Health Plans. The curve to attainment of critical mass is one of education, media, contact, and sales closure.
The market segment data is presented in the next section.
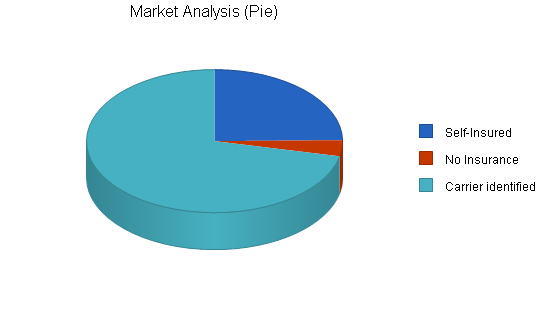
4.1 Market Segmentation
Within the targeted ZIP codes defined by the agreement with Blair Mill, the management of Southeast Health Plans has identified 1,801 employers with 50 to 500 employees. Of these, 1,289 are known to have an identifiable insurance carrier, 446 are known to be self-insured, and 66 are known to have no insurance.
| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Self-Insured | 10% | 446 | 491 | 540 | 594 | 653 | 10.00% |
| No Insurance | 0% | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 0.00% |
| Carrier identified | 0% | 1,289 | 1,289 | 1,289 | 1,289 | 1,289 | 0.00% |
| Total | 2.76% | 1,801 | 1,846 | 1,895 | 1,949 | 2,008 | 2.76% |
4.2 Service Business Analysis
Together the national insurance carriers, HMOs, and PPOs account for 72% of the current market for employer-based health plan services. The majority of HMOs and PPOs have their own marketing and sales programs which include company employed sales forces. National insurance companies may have company sales people or may utilize independent insurance agents. Both have strong media programs.
Neither, however, provide the mix of services that Southeast Health Plans can provide. Nor can they provide the quality/cost ratio or the ancillary consultative and custom services of Southeast combined with Blair Mill. Thus, Southeast feels that this entire employer universe of 1,801 companies is vulnerable to penetration.
4.2.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
Buying patterns vary by the size of the employer and according to his internal organization.
The company with 50 to 100 employers may have health care handled by the owner or a key executive. Often it is the responsibility of the Personnel Administrator as an individual (if that function is internal to the company). Also, Personnel Administration may be outsourced, but benefits may not. Sometimes an independent benefits brokerage firm handles all recommendations.
Larger companies from 200 to 500 employees may have Personnel Departments of several people. They might also employ a broker or a consultant.
Thus, it is imperative that Southeast have flexible programs and sales and marketing efforts that are targeted to a diverse set of potential buying patterns.
It is worthy to note that customer buying patterns for health plan coverage tend to revolve around annual renewal dates. That’s when competition intensifies from traditional providers. Southeast will have an extremely significant marketing advantage since an employer may retain Southeast for its proprietary service mix at any time. Southeast can initiate service for a client by helping him analyze and administer his current plan. Often, such an engagement will progress to full service and to administration of self-insurance.
4.2.2 Business Participants
Insurance carriers provide economic protection only. Such protection is at a high cost. Deductibles are increasing and the employer’s ability to handle the cost burden of medical insurance coverage is diminishing. Compromises must be made in the extent of coverage, the size of the deductible, the medical services included, or often the employee is required to cover an ever-increasing percentage of the cost of his own plan as a payroll deduction. These are all unattractive options both for the employer and the individual client. The spiraling cost of health care is the culprit.
HMOs have gained substantial and significant market share over the past two decades. Their cumulative share of covered insured employees now exceeds the national commercial insurance carriers by a wide margin. However, these plans have been ruled primarily by cost containment strictures. Freedom of choice is severely limited – there is a perception that the quality of care is at an all-time low. Liability issues are beginning to surface based on compromised or neglected care due to cost parameters. Many service costs are not adequately covered under these plans and the provider base of physicians are extremely dissatisfied with compensation allowances. Many physicians complain that the freedom of decision is diminishing constantly from time and cost constraints that are imposed upon them. The ultimate client, the individual patient, is equally dissatisfied. Thus, the employer becomes dissatisfied as well.
The market niche for the quality TPA is ripe for picking. However, services must be of high quality. Many small TPAs are promising high levels of service but often don’t deliver as promised because of the expense of building the internal resources required to compete effectively. Southeast Health Plans, by virtue of its alliance with Blair Mill Administrators, already has the necessary resources in place.
4.2.3 Distributing a Service
HMOs and Managed Care Companies are experienced and effective direct marketers. They employ media marketing and company sales forces to good effect. The primary problem they face is increasing dissatisfaction with their product. They will not be able to provide the multi-regional, customizable services that an increasing number of employers will demand. In addition, self-insurance is contrary to the buy-and-resell philosophy of these providers.
Many national insurance companies market through company sales forces and independent brokers and agents. Herein lies a potential barrier to entry into the small company market for an emerging TPA. Often the company has a pre-existing relationship with an insurance agent that may encompass a broader range of insurance services than health care. The company is, in fact, buying a “package” of varied insurance coverages that are necessary to business operation and also happen to include health care coverage. The task here is one of general education about the potential of self-insurance programs. If the insurance agent doesn’t provide this alternative he stands to eventually lose the health insurance coverage. But his current “franchise” with his client can be a barrier.
It is the intention of Southeast Health Plans both to market directly and to work through independent agents to reach their existing clients. A competitive agent compensation program is in place to accomplish this objective. It is the intention of the company to both work with independent agents who recognize the mutual value of co-operation or to sell in head-to-head competition with those who don’t.
Ultimately, product, service, and price will prevail. All sales forecasts of the company recognize the time line of market penetration, and have realistic, if not conservative, market share goals.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
With provider services already in place, the launching of sales and marketing strategies and implementation is the next task of Southeast Health Plans. Executions include print media in targeted general business publications, direct mail programs, and sales contact follow-up.
In addition contacts and seminars directed at independent agents and benefit brokerage firms will be launched. Additional sales materials will be produced that are targeted specifically toward these intermediary “customers.”
5.1 Marketing Strategy
Print media utilized will be the weekly Atlanta Business Chronicle . An extensive direct mail lead generation campaign will also be employed, targeted at employers, brokers, and consultants. Both will be followed by direct sales contact by Southeast’s professional sales executives.
5.1.1 Pricing Strategy
Pricing for administrative services provided by Blair Mill is billed on a cost-per-employee basis.
Actual medical costs within self-insured programs will vary as a combination function of negotiated provider service costs coupled with the level of stop-loss (deductible) coverage.
Revenues to Southeast Health Plans, Inc. are determined by sales commission formulas and also by cost advantages for medical services negotiated by Southeast contracted care providers. Thus, if Southeast provides medical service to the plan at a cost below the expected cost for the same service, differential revenue accrues to Southeast.
According to the terms of the existing agreement with Blair Mill, Southeast Health Plans will earn 25% of medical facility cost savings (as incurred) in years one and two and 17% in year three.
All services revenues generated by Southeast for new clients produced for Blair Mill will be paid as sales commissions according to the formula contained in the agreement. (A copy of the agreement is available to investors).
The sales commissions are as follows:
- 11.2% of all fees in the first year of the sale.
- 2% of all fees in the second and third years.
- 5% of all fees in the fourth year and in each renewal year thereafter.
- Blair Mill administrative service costs average about $15 per month per employee covered.
- In addition, commissions on new stop-loss policies will average 15% in year one.
5.2 Sales Strategy
The sales strategy for Southeast Health Plans is based upon concentrated targeted direct marketing with sales call follow-up. Closing ratios are estimated at only 5% of prospects to yield cumulative covered plan employees projected in the sales forecasts. Thus, higher closing ratios are potentially possible and would accelerate growth and revenue beyond the forecasts.
All forecasts are based upon per employee estimates. Dollar charges are based upon “A,” “B”, and “C” size markets and the prevailing costs for medical care for those markets respectively. Back-up market data is too extensive to include in this plan.
Note: An “A” market is defined as metro Atlanta. A “B” market is a population center over one million. A “C” market is any market below one million in population.
Annual projected revenues are illustrated in the chart below.
Monthly sales forecasts for the first year are included in the appendix.
Note: A total of 23 employer groups have already become active through Blair Mill as of November 1, 1996. Revenues based upon health care cost savings will show up in the beginning of 1997. Initial monthly revenues are based upon these employer groups, which represent approximately 1,500 employees (already 31% of the first year goal of 4,800 covered employees).
On an average annual basis, the revenue projections for health care savings revenue to Southeast are based upon $7.40 per employee for 1997. This number is for “A” markets. “B” markets are estimated at $5.66, and “C” markets at $3.71 per employee. Rationale: Atlanta is over-bedded and under-utilized, while in smaller markets the reverse is true.
Additional selling and retention fees are added to the above estimates to obtain total revenue numbers. In “A” markets, for example, this is set at $1.75 for new employees and at $0.75 for renewal/retention fees.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The following sales forecasts are based upon the premises previously presented.
Management feels these forecasts are highly attainable.

| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Sales | $288,599 | $1,399,223 | $3,067,966 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $288,599 | $1,399,223 | $3,067,966 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Sales | $57,000 | $201,000 | $427,500 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $57,000 | $201,000 | $427,500 |
5.3 Strategic Alliances
In addition to the primary strategic alliance with Blair Mill, Southeast Health Plans, Inc. has already formed alliances on the health care provider network side which will provide cost advantages and thereby guaranteed revenue via Blair Mill on billed medical services.
The initial agreement with Columbia Health Care Systems will provide coverage to a substantial portion of metro Atlanta. In addition, a second agreement is forthcoming with Independent Health Care Providers, which includes DeKalb Medical Center, Scottish Rite Hospitals, and Northside Hospital System. Comprehensive availability for Atlanta Metro will then be in place. 52% of available hospital beds will then be included. Cost savings are reflected in revenue projections on a per covered employee basis.
5.4 Milestones
Milestones already achieved:
- Founder “seed” funding of $200 K to develop and research plan, secure strategic alliances, and establish initial infrastructure.
- Strategic alliances in place with Blair Mill and with Columbia Health Systems.
- 23 employer groups and 1500 employees already under managed care contracts.
- 52% of Atlanta metro area available hospital beds under contract at acceptable cost discounts.
Upcoming milestones:
- Obtain $300 K capital to staff and launch full sales and marketing executions.
- Present Blair Mill products and services to 50 of the largest employers in our target market by March 1, 1997.
- To reach stated first year goal of 4800 covered plan employees by January 1, 1998.
- To reach first year revenue goal of $288 K by December 31, 1997.
- To attain break-even cash flow by the end of year two.

| Milestones | |||||
| Milestone | Start Date | End Date | Budget | Manager | Department |
| Sample Milestones | 1/4/2008 | 1/4/2008 | $0 | ABC | Department |
| Finish Business Plan | 5/13/2009 | 6/12/2009 | $100 | Dude | LeGrande Fromage |
| Acquire Financing | 5/23/2009 | 7/12/2009 | $200 | Dudette | Legumers |
| Ah HA! Event | 6/2/2009 | 6/7/2009 | $60 | Marianne | Bosses |
| Oooooh Noooooo! Event | 7/2/2009 | 7/7/2009 | $250 | Marionette | Chèvre deBlâme |
| Grande Opening | 7/12/2009 | 7/17/2009 | $500 | Gloworm | Nobs |
| Marketing Program Starts | 6/12/2009 | 7/7/2009 | $1,000 | Glower | Marketeers |
| Plan vs. Actual Review | 11/7/2009 | 11/14/2009 | $0 | Galore | Alles |
| First Break-even Month | 3/11/2010 | 4/10/2010 | $0 | Bouys | Salers |
| Hire Employees | 2/7/2010 | 3/9/2010 | $150 | Gulls | HRM |
| Upgrade Business Plan Pro | 4/28/2010 | 4/30/2010 | $100 | Brass | Bossies |
| Totals | $2,360 | ||||
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
The founding management of Southeast Health Plans has an accumulated 75 plus years of industry related experience. All are well versed in industry fundamentals, educated in the evolution of the health care services industry, and share a vision for the successful positioning of Southeast Health Plans, Inc. within the industry.
6.1 Organizational Structure
The three founders will manage the company’s growth jointly as managing partners.
All staff and sales and marketing personnel will report to them through a sales manager (heavy in industry experience) who has also been identified.
Future branch offices will each have a general manager.
6.2 Management Team
James J. Peters, Managing Partner
Mr. Peters has more than 25 years experience in sales and marketing management in employee benefits, securities, and real estate.
He has managed the marketing and sale of pension investment services for MetLife in their Western region and for CNA and Pacific Mutual nationally.
Mr. Peters joined the MetLife HealthCare Network of Georgia as Regional Director for managed care sales in 1992. He built the marketing, sales, and service organizations for the Georgia network. Under his leadership, the network added 40,000 new, fully insured members over three years.
Mr. Peters holds a BA from the University of Notre Dame and an MA from the University of Oregon.
Thomas R. Cormier, Managing Partner
Mr. Cormier has more than 25 years of experience in the field of Employee Benefits. He began his career with Aetna Life and Casualty as a group insurance underwriter. As Project Team Leader in the Group Actuarial Department he developed procedures for the coordination of operations among departments within the Group Insurance Division.
He then spent 15 years with MetLife in the sale and servicing of large group accounts, support for regional sales staff, and budget administration.
Most recently, he was responsible for integration of capitated services with fee-for-service contracts, and the installation of risk pool arrangements for MetLife networks. He also was responsible for interfacing with corporate MIS.
Mr. Cormier holds a BA from the University of Notre Dame.
L. Richard Schumacher, MD, Managing Partner
Dr. Schumacher is a specialist in internal medicine with 25 years in practice who has been in leadership positions in managed care organizations since 1983. He has more than eight years experience in two major national insurance companies serving as Regional Medical Director and then as Vice President of Medical Affairs for Prudential in the Southeast. He later became CEO of MetLife’s Georgia HMO. He has established himself as a well respected advisor/consultant within the managed care industry.
Dr. Schumacher holds a BA from Amherst College and a Doctor of Medicine from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine.
Jeffrey E. Farmer, Sales Manager
Mr. Farmer is a sales management professional with a consistently outstanding record of production achievement in employee benefits and managed care sales. He worked first for US Healthcare in their Boston office and was subsequently recruited by John Hancock.
He later joined MetLife Group Benefits in their Tampa regional office and graduated from the MetLife Group Benefits Training Program. With MetLife Health Care, Mr. Farmer led all MetLife sales representatives in 1995 with more than $12 million in managed health care sales.
Mr. Farmer has a current extensive and active client base. He has completed all Health Insurance of America (HIAA) courses with honors. He is a member of the National Association of Health Underwriters, and the Atlanta Association of Health Underwriters.
Mr. Farmer holds a BA from Boston College.
6.3 Personnel Plan
The following table illustrates the Personnel Plan for Southeast Health Plans, Inc. Specific needs, compensation, and timing are indicated for each position. Future branch office staffing needs are lumped together as one line item.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| James J. Peters | $60,000 | $60,000 | $66,000 |
| Thomas R. Cormier | $60,000 | $60,000 | $66,000 |
| L. Richard Schumacher | $60,000 | $60,000 | $66,000 |
| Jeffrey Farmer, Sales Mgr. | $64,992 | $66,000 | $66,000 |
| Sales Executive | $42,000 | $45,000 | $48,000 |
| Sales Executive | $42,000 | $45,000 | $48,000 |
| Sales Executive | $10,500 | $45,000 | $48,000 |
| Account Service Executive | $36,000 | $38,000 | $40,000 |
| Administrative Asst. | $30,000 | $30,000 | $32,000 |
| Administrative Asst. | $6,000 | $24,000 | $25,000 |
| VP Corp Dev. | $18,000 | $24,000 | $30,000 |
| CFO | $12,000 | $60,000 | $66,000 |
| Branch Sales | $0 | $200,000 | $380,000 |
| Total People | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Payroll | $441,492 | $757,000 | $981,000 |
6.4 Management Team Gaps
Two current gaps exist within the management team:
- a Chief Financial Officer
- a Business Development (Capitalization) Specialist.
Both functions will be performed on a consultative basis in the first year of operations (1997). The CFO position can later be filled on a full-time basis, and capitalization will be handled by Investment Banking Relationships.
The interim positions will be staffed by:
- Interim CFO *Confidential and Proprietary information omitted.*
- Interim VP Corporate Development Timothy Dineen Mr. Dineen is Principal and Founder of Leprechaun Capital. He is experienced in raising capital for both public and private companies in an advisory capacity. Mr. Dineen holds a BA from the University of Notre Dame.
6.5 Other Management Considerations
An advisory board of prominent managed health care professionals is already being assembled. These individuals are available for consultative assignment as well as Strategic Planning for Southeast Health Plans, Inc. The preliminary advisory board includes:
Dr. Nancy W. Ashbach, MD, MBA
Dr. Ashbach is a former CEO of MetLife of Colorado and Utah with responsibility for HMO, POS, and PPO products. Her areas of expertise include outcomes management, reference standard benefits, and doctor/plan relationships.
Dr. Leslie Moldauer, MD
Dr. Moldauer is a psychiatrist who was formerly the National Director of Mental Health and Chemical Dependency Services at MetLife Health Care Management Corporation. Her special interest is in the integration of mental health and chemical dependency programs into health plans as a whole.
Dr. Tighe E. Shomer, MD
Dr. Schomer has been Medical Director for a national managed care company with more than 200,000 HMO members and 1,250,000 PPO members. He has been a partner and director in a medical software and hardware company. He also advises Fortune 500 clients on issues pertaining to managed care, particularly preventative care and quality improvement.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The financial plan for rapid, but controlled growth for Southeast Health Plans, Inc. is presented in detail in the following sections.
Initial capitalization (after $300 thousand founder’s seed funding) is pegged at $1 million (with cash streaming in from April through September).
The company will be debt free at that point (barring any interim management decisions to accelerate growth further). The company will also have significant IPO potential in the future and/or be an acquisition candidate in an industry that traditionally undergoes consolidation.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The financial assumptions upon which this plan is based are outlined in the following table:
| General Assumptions | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Current Interest Rate | 8.00% | 8.00% | 8.00% |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 8.00% | 8.00% | 8.00% |
| Tax Rate | 33.00% | 33.00% | 33.00% |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 |
7.2 Key Financial Indicators
Key financial indicators are increasing sales volume coupled with maintenance and improvement of margins. On-going cost control is paramount to success.

7.3 Break-even Analysis
Monthly break-even, based upon fixed initial market overheads, will be attained prior to the end of year two.
Cost control and market maturation will then accelerate profitability which increases disproportionately as market development costs are offset with a critical mass of baseline business in each new market.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $72,637 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 20% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $58,291 |
7.4 Projected Profit and Loss
Southeast Health Plans, Inc. projects over-all profitability in year three.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $288,599 | $1,399,223 | $3,067,966 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $57,000 | $201,000 | $427,500 |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $57,000 | $201,000 | $427,500 |
| Gross Margin | $231,599 | $1,198,223 | $2,640,466 |
| Gross Margin % | 80.25% | 85.63% | 86.07% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $441,492 | $757,000 | $981,000 |
| Marketing/Promotion | $180,000 | $288,000 | $456,000 |
| Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Rent | $30,000 | $90,000 | $120,000 |
| Telephone/Utilities | $12,000 | $24,000 | $30,000 |
| Payroll Taxes | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Contract/Consultants | $36,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $699,492 | $1,159,000 | $1,587,000 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($467,893) | $39,223 | $1,053,466 |
| EBITDA | ($467,893) | $39,223 | $1,053,466 |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Taxes Incurred | $0 | $12,944 | $347,644 |
| Net Profit | ($467,893) | $26,279 | $705,822 |
| Net Profit/Sales | -162.13% | 1.88% | 23.01% |
7.5 Projected Cash Flow
Cash flow is the most critical indicator of business success.
At no point does our business model run out of cash. Significant margin for error is included. Initial and second round investment is procured prior to need and allowing for potential time lag to close.
All future growth is based upon a debt-free internally funded model. Attainment of targeted sales revenues will ensure the accumulation of required cash to execute expansion plans as presented.
Plans can always be curtailed or postponed in the event of future sales shortfalls.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $288,599 | $1,399,223 | $3,067,966 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $288,599 | $1,399,223 | $3,067,966 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $1,000,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $1,288,599 | $1,399,223 | $3,067,966 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $441,492 | $757,000 | $981,000 |
| Bill Payments | $286,967 | $593,351 | $1,318,251 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $728,459 | $1,350,351 | $2,299,251 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $728,459 | $1,350,351 | $2,299,251 |
| Net Cash Flow | $560,140 | $48,872 | $768,715 |
| Cash Balance | $832,640 | $881,512 | $1,650,227 |
7.6 Projected Balance Sheet
Projected Balance Sheet follows.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $832,640 | $881,512 | $1,650,227 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $832,640 | $881,512 | $1,650,227 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $832,640 | $881,512 | $1,650,227 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $28,033 | $50,626 | $113,519 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $28,033 | $50,626 | $113,519 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $28,033 | $50,626 | $113,519 |
| Paid-in Capital | $1,300,000 | $1,300,000 | $1,300,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($27,500) | ($495,393) | ($469,114) |
| Earnings | ($467,893) | $26,279 | $705,822 |
| Total Capital | $804,607 | $830,886 | $1,536,709 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $832,640 | $881,512 | $1,650,227 |
| Net Worth | $804,607 | $830,886 | $1,536,709 |
7.7 Business Ratios
These business ratios are only partially relevant as long as the business is able to remain debt free. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 6411, Insurance Agencies and Brokerages, are shown for comparison.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 384.83% | 119.26% | 3.95% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 93.54% |
| Total Current Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 93.54% |
| Long-term Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 6.46% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 3.37% | 5.74% | 6.88% | 35.88% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 9.61% |
| Total Liabilities | 3.37% | 5.74% | 6.88% | 45.49% |
| Net Worth | 96.63% | 94.26% | 93.12% | 54.51% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 80.25% | 85.63% | 86.07% | 100.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 242.38% | 83.76% | 63.06% | 59.40% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.23% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | -162.13% | 2.80% | 34.34% | 6.74% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 29.70 | 17.41 | 14.54 | 1.91 |
| Quick | 29.70 | 17.41 | 14.54 | 1.64 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 3.37% | 5.74% | 6.88% | 54.69% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | -58.15% | 4.72% | 68.55% | 7.55% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | -56.19% | 4.45% | 63.84% | 16.65% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | -162.13% | 1.88% | 23.01% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | -58.15% | 3.16% | 45.93% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 11.24 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 23 | 22 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 0.35 | 1.59 | 1.86 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $804,607 | $830,886 | $1,536,709 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 2.89 | 0.63 | 0.54 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 3% | 6% | 7% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 29.70 | 17.41 | 14.54 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 0.36 | 1.68 | 2.00 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Sales | 0% | $11,101 | $11,102 | $12,017 | $13,845 | $15,674 | $18,415 | $22,985 | $27,554 | $32,123 | $36,692 | $41,261 | $45,830 |
| Other | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $11,101 | $11,102 | $12,017 | $13,845 | $15,674 | $18,415 | $22,985 | $27,554 | $32,123 | $36,692 | $41,261 | $45,830 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Sales | $0 | $0 | $1,500 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $4,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $1,500 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $4,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| James J. Peters | 0% | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| Thomas R. Cormier | 0% | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| L. Richard Schumacher | 0% | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| Jeffrey Farmer, Sales Mgr. | 0% | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 | $5,416 |
| Sales Executive | 0% | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 |
| Sales Executive | 0% | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 |
| Sales Executive | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 |
| Account Service Executive | 0% | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Administrative Asst. | 0% | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 |
| Administrative Asst. | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| VP Corp Dev. | 0% | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 |
| CFO | 0% | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 |
| Branch Sales | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total Payroll | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $40,916 | $40,916 | $40,916 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $11,101 | $11,102 | $12,017 | $13,845 | $15,674 | $18,415 | $22,985 | $27,554 | $32,123 | $36,692 | $41,261 | $45,830 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $1,500 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $4,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $1,500 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $4,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | |
| Gross Margin | $11,101 | $11,102 | $10,517 | $10,845 | $12,674 | $13,915 | $15,485 | $20,054 | $24,623 | $29,192 | $33,761 | $38,330 | |
| Gross Margin % | 100.00% | 100.00% | 87.52% | 78.33% | 80.86% | 75.56% | 67.37% | 72.78% | 76.65% | 79.56% | 81.82% | 83.64% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $40,916 | $40,916 | $40,916 | |
| Marketing/Promotion | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | |
| Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Rent | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | |
| Telephone/Utilities | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Contract/Consultants | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $56,916 | $62,416 | $62,416 | $62,416 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($45,815) | ($45,814) | ($46,399) | ($46,071) | ($44,242) | ($43,001) | ($41,431) | ($36,862) | ($32,293) | ($33,224) | ($28,655) | ($24,086) | |
| EBITDA | ($45,815) | ($45,814) | ($46,399) | ($46,071) | ($44,242) | ($43,001) | ($41,431) | ($36,862) | ($32,293) | ($33,224) | ($28,655) | ($24,086) | |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxes Incurred | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Profit | ($45,815) | ($45,814) | ($46,399) | ($46,071) | ($44,242) | ($43,001) | ($41,431) | ($36,862) | ($32,293) | ($33,224) | ($28,655) | ($24,086) | |
| Net Profit/Sales | -412.71% | -412.66% | -386.11% | -332.76% | -282.26% | -233.51% | -180.25% | -133.78% | -100.53% | -90.55% | -69.45% | -52.56% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $11,101 | $11,102 | $12,017 | $13,845 | $15,674 | $18,415 | $22,985 | $27,554 | $32,123 | $36,692 | $41,261 | $45,830 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $11,101 | $11,102 | $12,017 | $13,845 | $15,674 | $18,415 | $22,985 | $27,554 | $32,123 | $36,692 | $41,261 | $45,830 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $200,000 | $100,000 | $200,000 | $100,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $11,101 | $11,102 | $12,017 | $213,845 | $115,674 | $218,415 | $122,985 | $227,554 | $232,123 | $36,692 | $41,261 | $45,830 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $35,416 | $40,916 | $40,916 | $40,916 | |
| Bill Payments | $717 | $21,500 | $21,550 | $23,050 | $24,500 | $24,550 | $26,100 | $29,000 | $29,000 | $29,000 | $29,000 | $29,000 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $36,133 | $56,916 | $56,966 | $58,466 | $59,916 | $59,966 | $61,516 | $64,416 | $64,416 | $69,916 | $69,916 | $69,916 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $36,133 | $56,916 | $56,966 | $58,466 | $59,916 | $59,966 | $61,516 | $64,416 | $64,416 | $69,916 | $69,916 | $69,916 | |
| Net Cash Flow | ($25,032) | ($45,814) | ($44,949) | $155,379 | $55,758 | $158,449 | $61,469 | $163,138 | $167,707 | ($33,224) | ($28,655) | ($24,086) | |
| Cash Balance | $247,468 | $201,654 | $156,705 | $312,084 | $367,842 | $526,291 | $587,760 | $750,898 | $918,605 | $885,381 | $856,726 | $832,640 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $272,500 | $247,468 | $201,654 | $156,705 | $312,084 | $367,842 | $526,291 | $587,760 | $750,898 | $918,605 | $885,381 | $856,726 | $832,640 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $272,500 | $247,468 | $201,654 | $156,705 | $312,084 | $367,842 | $526,291 | $587,760 | $750,898 | $918,605 | $885,381 | $856,726 | $832,640 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $272,500 | $247,468 | $201,654 | $156,705 | $312,084 | $367,842 | $526,291 | $587,760 | $750,898 | $918,605 | $885,381 | $856,726 | $832,640 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $20,783 | $20,783 | $22,233 | $23,683 | $23,683 | $25,133 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $20,783 | $20,783 | $22,233 | $23,683 | $23,683 | $25,133 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 | $20,783 | $20,783 | $22,233 | $23,683 | $23,683 | $25,133 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 | $28,033 |
| Paid-in Capital | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $500,000 | $600,000 | $800,000 | $900,000 | $1,100,000 | $1,300,000 | $1,300,000 | $1,300,000 | $1,300,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) | ($27,500) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($45,815) | ($91,629) | ($138,028) | ($184,099) | ($228,341) | ($271,342) | ($312,773) | ($349,635) | ($381,928) | ($415,152) | ($443,807) | ($467,893) |
| Total Capital | $272,500 | $226,685 | $180,871 | $134,472 | $288,401 | $344,159 | $501,158 | $559,727 | $722,865 | $890,572 | $857,348 | $828,693 | $804,607 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $272,500 | $247,468 | $201,654 | $156,705 | $312,084 | $367,842 | $526,291 | $587,760 | $750,898 | $918,605 | $885,381 | $856,726 | $832,640 |
| Net Worth | $272,500 | $226,685 | $180,871 | $134,472 | $288,401 | $344,159 | $501,158 | $559,727 | $722,865 | $890,572 | $857,348 | $828,693 | $804,607 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
(1).jpeg)
Small Business Guide to Health Insurance (2023)
We provide an overview of insurance requirements, costs and considerations, and recommendations for the best health insurance providers for small businesses.
Download Template
Fill the form below to download this template
Thank for you submitting the information.
Click below to download template.
Calculating Stripe fees for customer payments is easy with our calculator. Enter the payment amount to calculate Stripe's transaction fees and what you should charge to receive the full amount.
Our calculations are based on Stripe's per-transaction fees of 2.9% plus $0.30.
Calculate how much you’ll pay in Square fees for online, in-person, and manually-entered payments.
Enter your loan information to get an estimated breakdown of how much you'll pay over the lifetime of your loan.
PayPal fees can be confusing. Our calculator helps you understand how much you’ll pay in fees for common transaction methods.
electing a small business health insurance plan is one of many important decisions you’ll need to make as a small business owner.
To help you choose a health insurance plan that balances your budget and your employees’ healthcare needs, we’ve created this small business guide to health insurance.
Read on to get an overview of insurance requirements, costs and considerations, and recommendations for the best health insurance providers for small businesses.
How does small business health insurance work?
Rules can vary from state to state, but there are four basic rules of thumb when it comes to small business health insurance:
- Coverage cannot be denied based on pre-existing medical conditions. Coverage is almost always guaranteed.
- Typically, a business needs at least one employee to qualify.
- You can sign up any time of year, not just during open enrollment, with premiums usually locked for a year.
- Typically, employers will have to pay at least half of employees’ monthly premiums.
Are you required to provide health insurance?
Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) , you are required to provide health insurance if you have fifty or more full-time employees. You may have to pay penalties if you don’t provide benefits to those employees who qualify. There may be additional criteria depending on where your business is based, so we highly recommend referencing your state laws and regulations.
Why should you offer small business health insurance?
Understandably, you may be worried about whether you can afford to provide health care coverage to your employees. While it will use up a portion of your business expenses, offering health insurance doesn’t need to be completely cost-prohibitive.
For instance, you can utilize health reimbursement arrangements or health savings accounts to help you and your employees afford health benefits. Whatever you choose, it’s a good idea to seek the help of a tax or financial professional who specializes in these sorts of matters to help you determine how it could affect your business financially.
Here are some of the top reasons to consider offering health insurance:
- Attract first-rate talent. A comprehensive benefits package demonstrates to job candidates that your business is competitive and prioritizes employee well-being.
- Improve employee retention. Raises aren’t the only way to keep employees. Glassdoor’s Employment Confidence Survey showed that 40% of employees value health insurance benefits more than a pay raise. Retaining employees means fewer costs associated with onboarding, training new workers, and interrupting business flow.
- Benefit from tax incentives. In most cases, you can deduct 100% of the cost of monthly premiums from federal taxes . You could also benefit from reductions in payroll tax and deductions from HSA contributions.
How much does health insurance for a small business cost?
Small business owners tend to be concerned about costs when offering group health insurance. There are plenty of health insurance options to ensure you stay within budget and increase health insurance coverage as you need to.
According to a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation study , the average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance was $7,911 for single coverage, with the employer contributing $6,581 on average.
Cost to employer
Employers should expect to pay about 50% of insurance premiums for their employees. This is a requirement to qualify for the federal small-business healthcare tax credit. It is also often required by the insurance companies themselves.
Therefore, if the annual average in 2022 for health insurance for an individual was $7,911, you would have to pay about $3,955 a year for a single employee.
Cost to employees
With the introduction of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the maximum out-of-pocket limit for 2023 is:
- $9,100 for individual coverage
- $18,200 for family coverage
The most budget-friendly option for group coverage is a high deductible, low premium plan. That way, your upfront out-of-pocket costs are lower. You might also look at options for low deductible, high premium plans if you or your employees carry different health needs – this will come at a higher cost.
In general, you’ll be able to choose from different tiers to see how much coverage other plans provide. Coverage options might look like this:
- Bronze Tier: 60% coverage, 40% deductible
- Silver Tier: 70% coverage, 30% deductible
- Gold Tier: 80% coverage, 20% deductible
- Platinum Tier: 90% coverage, 10% deductible
There are some insurance companies that offer the following types of tiers:
- No deductible plans: The plan provides all coverage.
- High deductible plans: With these plans, there are a significant amount of out-of-pocket expenses but with lower premiums.
- Low deductible plans: With these plans, there are some out-of-pocket expenses and higher premiums.
Don’t forget to factor in a plan’s total deductible and out-of-pocket limits. The entire plan cost will be the same as the deductible plus the monthly premium. This means that even if your premium seems low, it could end up more expensive compared to other plans once you factor in the total deductible.
It’s also essential to consider copays that your employees will need to pay. Some employees will want to set up a Health Reimbursement Account (HRA) or Health Savings Account (HSA). Make sure to look into where this fits into your group health insurance plans.
Factors that affect the cost of health insurance
In general, five factors will determine the cost of health insurance coverage:
- Choice of provider
- Type of plan selected
- Number of employees
- Demographics of your employees
- Qualifying tax credits
You’ll also find plans that differ by type of network. This will determine how accessible various doctors are to your employees. You’ll usually find the following options:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO). These plans are generally the most restrictive, as they require patients to choose from a list of approved doctors, do not include any out-of-network coverage, and will typically need referrals for specialists. However, HMOs tend to be the cheaper plan when compared to PPOs.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO). PPOs are generally the most flexible, as the patient can choose their own doctor and may not need approval to see specialists. They will also likely cover some out-of-network providers. However, they are usually the more expensive plan option.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO). These plans have similarities to both HMOs and PPOs. With an EPO plan, there is no out-of-network coverage, but patients typically don’t need referrals for specialists.
How to Choose the Right Health Insurance for Your Small Business
In addition to understanding the components of health insurance plans outlined above, reviewing a plan’s eligibility features will help you determine what your employees will appreciate the most.
In most cases, health insurance plans will offer the following benefits:
- Outpatient care
- Inpatient care (including in-hospital stays)
- Pediatric services
- Preventative services
- Prescription drugs
- Emergency room visits
- Treatments for chronic conditions
- Pre- and post-natal care
- Mental health and substance abuse services
Take a careful look at what different plans offer as far as deductibles and coverage costs. There may be limits or caps in place to prevent employees from accessing too much of a particular type of service. Keep in mind that some employees may have dependents they wish to add to their health insurance coverage.
When choosing a health insurance plan, consider your employees’ needs and what they may benefit from the most. You may end up paying more upfront, but retaining your best employees will lead to a significant positive impact on your business's success in the long run.
Now that you know a little more about small business health insurance, let’s look at how to shop for affordable insurance options.
How to find affordable small business health insurance
- Seek out the providers directly. Contacting the insurance companies directly is the most straightforward option, though you may need to work with a broker depending on the provider. You can typically request a quote based on your location and headcount and then compare your options.
- Use SHOP. The Small business Health Options Program (SHOP) is available for employers with 1-50 full-time employees via the ACA. This program helps small businesses provide private health insurance options to their employees without needing to shop around (no pun intended). With SHOP, companies work with a registered broker to help select a plan, determine any tax credits, and assist employees with understanding their benefits.
- Consider PEOs. Professional Employer Organizations (PEOs) are great options for small businesses since they typically include large-business health insurance coverage as part of their offerings. In addition, they usually handle HR and administrative tasks like payroll.
Best health insurance companies for small business owners
These are a few of the top health insurance companies for small businesses, as well as an overview of each:
United Healthcare
Pros: United stands out for providing the largest network of providers. It also offers benefits options for part-time and seasonal employees, virtual therapy, and specialty healthcare, and is a leader in technology in the form of helpful in-app services.
Cons: United has been sued for wrongfully denied claims. It also does not offer a platinum plan.
Blue Cross Blue Shield
Pros: BCBS stands out for its customer service ratings. It operates in all 50 states (and some international locations) and has comprehensive healthcare offerings, including workplace wellness plans.
Cons: This service comes at a cost. BCBS has higher-than-average healthcare premiums and high deductibles.
Pros: Elevance is one of the most affordable insurers in this group. It offers numerous plan types and an extensive network of healthcare providers.
Cons: Elevance is only available in 14 states. It has a high rate of coverage denials which may explain its low customer satisfaction ratings.
Pros: Aetna places a strong emphasis on preventative treatments and encourages participants to make healthy lifestyle choices. It is also known for user-friendly experiences, whether online, in-app, or over the phone, and for its affordable prices.
Cons: Aetna only operates in 16 states and has a history of wrongfully denying claims. This may also explain its higher-than-average complaint rate.
Kaiser Permanente
Pros: Kaiser Permanente is the cheapest insurer in the group providing low prices for equivalent plan options. It has a wide range of available plans and runs a system of private hospitals only available to its plan participants.
Cons: It is only available in eight states and Washington D.C., and because it is a closed group, care options may be limited.
Pros: Humana offers participants the most flexibility to customize their plans, with add-ons like dental, vision, and hearing insurance.
Cons: Their plans are pricey compared to other insurers.
Pros: Cigna stands out because of its live customer service, accessible 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. It also gets excellent customer reviews and has a huge network of 1.5 million providers worldwide.
Cons: It is only available in 12 states, and its monthly premiums are expensive.
Alternatives to health insurance
You can utilize health reimbursement arrangements or offer health savings accounts (typically only available on high deductible health plans) to make benefits more affordable.
Additionally, there may be tax credits or other state services that are available to you depending on the size of your small business.
Affordable health insurance for your small business isn’t impossible to find! Carefully consider your budget and benefit options, as well as your employees’ needs, to choose the best plan.
You may end up paying more upfront, but think of this as the cost to retain key employees.
For more information, visit healthcare.gov to learn more about small business health insurance options, costs, and eligibility.
Novo Platform Inc. strives to provide accurate information but cannot guarantee that this content is correct, complete, or up-to-date. This page is for informational purposes only and is not financial or legal advice nor an endorsement of any third-party products or services. All products and services are presented without warranty. Novo Platform Inc. does not provide any financial or legal advice, and you should consult your own financial, legal, or tax advisors.
All-in-one money management
Take your business to new heights with faster cash flow and clear financial insights —all with a free Novo account. Apply in 10 minutes .
How to Run Payroll for Your Small Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
A small business checklist to hiring your first employee, spend less time managing your finances.
Take your business to new heights with faster cash flow and clear financial insights—all with a free Novo account. Apply online in 10 minutes.
More Articles On
Managing employees, how to hire virtual assistant services for small business, what is a peo pros, cons & considerations, small business guide to employee benefits packages.
- Skip to main content
- SHOP Marketplace
Get health insurance for your small business
Health insurance is a critical factor for small businesses to help retain and recruit employees and sustain productivity and satisfaction. UnitedHealthcare offers a range of group health insurance options designed to help your small business save money and support your employees’ health and well-being.
Request a quote for your small business (2-50 employees)
Simply complete a quick form to get started with a quote for your small business. A UnitedHealthcare representative will get in touch and work with you to help find group health insurance options that best fit your business.

View plans or request a quote (2-50 employees)
To get more details on health insurance options for your small business, click on your state below. In markets where the Small Business Store is available, 1 you will be directed there. In markets where the Small Business Store is not available, you can request a quote from UnitedHealthcare.
- Connecticut
- District of Columbia
- Florida (North)
- Florida (South)
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- New York (upstate)
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- U.S. Virgin Islands
- West Virginia
- Back to top
For companies with 51 or more employees
Find the right medical plans for your employees and your business, plus supplemental plans for dental, vision, disability and more.
Explore products and solutions for small businesses
There's not just one way we work to help small businesses like yours. By offering benefits packages designed to improve employee experience and help employers manage cost, there's a number of products and solutions that may be right for your business.
Explore a range of group health plans and network options.
Discover how integrated pharmacy benefits from OptumRx may help lower costs for you and your employees.
Enhance your employees’ specialty benefits package with vision, dental, financial protection plans and more.
See how we are guiding employees to the behavioral care they need.
Get more health plan resources
Find information to help you and your employees get the most from their health benefits.
Did you know?
UnitedHealthcare’s employer-sponsored insurance plans serve groups that fall into three categories: Small Group plans refer to employers with up to 100 employees; Key Accounts is for employers with 101 to 5,000 employees; and National Accounts serves employers with more than 5,000 employees.
Building healthier businesses together with Rubber & Accessories
The owner and co-founder of a small industrial rubber products distributor shares how critical providing quality, cost-effective benefits is to his company and his 40 employees, plus how working with UnitedHealthcare has enabled him to do that.

Video transcript
Instrumental music plays throughout. Three white lines curl across a blue background. Blue text centers a white screen.
ONSCREEN TEXT: Building healthier
businesses together
A closer look
A sunlit sign outside a warehouse facility reads, "Rubber & Accessories, Inc." Buzz Hooper speaks as employees work with rubber inside the sprawling warehouse.
BUZZ: We are a distributor of industrial products. Rubber products. We're a family business. We're a small business, by any comparison. That family, small business atmosphere, I think, is very important.
Buzz works at his desk in his office, then interviews before a white background. A blue bar slides into the bottom left of the screen, containing white text.
ONSCREEN TEXT: Buzz Hoooper
President &Founder, Rubber & Accessories.
BUZZ: My name is Buzz. Company name is Rubber & Accessories, and we've been in business over 50 years. We founded the company in 1972.
A sign on the building reads, "Rubber & Accessories, Lakeland, Florida. Founded 1972. H. Hooper, H.Ross." An old photo shows Buzz stands beside his business partner at the future site of the warehouse.
BUZZ: My partner and I loved each other like brothers. We made a profit the first year that we were in business. There's always a fear of losing what you've created. But I love that challenge.
Employees work on a heavy-duty machine inside the warehouse. Keith Johnson interviews before a white background. A blue bar slides into the bottom left of the screen, containing white text.
ONSCREEN TEXT: Keith Johnson
KEITH: As I graduated college, I'd always heard about Rubber & Accessories as a quality company. I started with a sales position at age 22.
BUZZ: Early on, health benefits were a very important part of what we wanted to establish as a culture of the company.
KEITH: It's not just about the pay, it's about the health benefits that are afforded to you. They have your back. It makes you want to keep showing up.
A montage shows Buzz smiling and talking with several employees around the office.
BUZZ: Switching to the UnitedHealthcare level funded plan has permitted us to have to charge less of the premium cost to our employees.
KEITH: We're treated pretty well here at Rubber & Accessories with our UnitedHealthcare plan. It makes you feel better when you go home at night.
Ronnie Barker interviews before a white background. A blue bar slides into the bottom left of the screen, containing white text .
ONSCREEN TEXT: Ronnie Barker
RONNIE: My name's Ronnie. I work at Rubber & Accessories. I've been here 23 years. It makes me feel safer. If something happens to me, I can go somewhere without breaking the bank.
BUZZ: The reputation of UnitedHealthcare is unmatched as far as I'm concerned. We feel that it's very important that we supply health benefits to our employees at a minimum cost to them. Our employees are like family and we want to treat them like we would treat a member of our family.
An American flag blows in the wind outside the Rubber & Accessories office. The warehouse is seen from above on a sunny day. Blue text flashes quickly on screen, centering a white background.
ONSCREEN TEXT: There
ONSCREEN TEXT: for
ONSCREEN TEXT: what
ONSCREEN TEXT: matters
A blue u-shaped logo appears against a white background, followed by text.
ONSCREEN TEXT: United
Healthcare
Small black text runs along the bottom of the screen.
ONSCREEN TEXT: This case study is true and based on client’s own opinions. Results are not guaranteed and will vary based on client specific demographics, funding type and plan design. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
ONSCREEN TEXT: Administrative services provided by United HealthCare Services, Inc. or their affiliates, and UnitedHealthcare Service LLC in NY. Stop-loss insurance is underwritten by UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company or their affiliates, including UnitedHealthcare Life Insurance Company in NJ, and UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company of New York in NY.
ONSCREEN TEXT: © 2023 United HealthCare Services, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 23-2301519
ONSCREEN TEXT: EI232389000 7/23
The music fades.

COMMENTS
1) Create Insurance Business Plan. 2) Download And Print - 100% Free 'Til 2/15!
Growthink's insurance business plan template is a comprehensive guide to help entrepreneurs and business owners create a professional and effective plan for their insurance agencies.
Learn how to start a profitable insurance agency with this sample business plan. Download a free insurance company business plan pdf or doc file and customize it with Upmetrics software.
Writing a business plan is a crucial step in starting an insurance company. Not only does it provide structure and guidance for the future, but it also helps to create funding opportunities and attract potential investors. For aspiring insurance company owners, having access to a sample insurance business plan can be especially helpful in providing direction and gaining insight into how to ...
A thoughtful business plan provides a roadmap for building a successful insurance agency. Here's what to include in yours, from objectives and product offerings to your target market and financial projections. A great business plan can guide you through every critical early step of building your company. As you start your insurance company ...
Learn how to start your own insurance company with this sample business plan. Find out the key factors, goals, and strategies for success in the insurance industry.
A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your insurance agency in order to improve your chances of success. Your insurance agency business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your agency grows and changes.
PlanBuildr's insurance business plan template will help you to quickly & easily complete your plan & level up your insurance agency.
Our Health Insurance Business Plan Template is specifically designed for small businesses seeking to develop comprehensive plans for small business health insurance offerings. This template helps articulate the strategic approach for launching or expanding your insurance products tailored to meet the unique needs of small enterprises.
The most important component of an effective Insurance agent business plan is its accurate marketing analysis. If you are starting on a smaller scale, you can do the market analysis yourself by taking help from this Insurance agent business plan sample or other sample Insurance agent business plans available online.
An insurance business plan is a structured document that delineates an insurance company's or agency's strategic roadmap. It encapsulates various facets including its service portfolio, target market, marketing and sales strategies, operational outlines, and financial projections, ensuring a systematic approach towards achieving its goals.
Group Health Insurance: A health insurance plan that provides benefits for employees of a business or members of an organization, as opposed to individual and family health insurance.
Position agency as advisor. Identify gaps & recommend solutions. Increase limits and values. Create EB & business continuation opportunities for producers. xit strategy for unprofitable accountsIncrease retention to. LARGE COMMERCIAL SALES & MARKETING PLAN FOR 2012. Objective: New business revenue goal $700,000.
Commercial health insurance, also referred to as private insurance, is the most common form of health insurance in the United States, covering nearly two-thirds of Americans, most of whom receive coverage through their employer.1 This paper provides an overview of commercial health insurance, including a description of comprehensive health ...
Exploring coverage options for small businesses The ACA established the Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) for businesses and non-profits with 1-50 employees.
Introduction Getting health insurance for your company is an important decision for your company, both for yourself as a business owner and for your employees who will be covering themselves and their families. Making sure that you offer the most appropriate health insurance plan will ensure that your employees are properly covered without overspending on insurance premiums.
Insurance Business Plan Back in 2018, the Insurance Information Institute (III) reported that the insurance industry's written premiums reached USD 1.22 trillion worth in the United States alone. In line with this, fifty-one percent consists of car and other property insurance, while the forty-nine percent are covered by health and annuity or life insurance. With that much worth in mind ...
Explore a real-world health plan administration business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan.
Learn how to get health insurance for employees. Marketplace for Small Business, 50 employees or fewer. Small Business Health Options Program details
Health insurance is a legal entitlement to payment or reimbursement for your health care costs, generally under a contract with a health insurance company. Health insurance provides important financial protection in case you have an accident or sickness. For example, health insurance may help to pay for doctors' services, medications, hospital care, and special equipment when someone is sick ...
To help you choose a health insurance plan that balances your budget and your employees' healthcare needs, we've created this small business guide to health insurance. Read on to get an overview of insurance requirements, costs and considerations, and recommendations for the best health insurance providers for small businesses.
Compare the best small business health insurance providers & plan options. Learn more & get free quotes with eHealth.
Health insurance is a critical factor for small businesses to help retain and recruit employees and sustain productivity and satisfaction. UnitedHealthcare offers a range of group health insurance options designed to help your small business save money and support your employees' health and well-being.
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE FOR CHOOSING A HEALTH PLAN Choosing the right insurance plan is a judgement call based on what is covered, how much flexibility you want and how you prefer to spread health care costs throughout the year. Your decision can impact your health and finances for the year.