Undergraduate Research Opportunities Center
Present or publish your research or creative activity, what is research communication.
"The ability to interpret or translate complex research findings into language, format, and context that non experts understand" (IDS 2011).

Research Communication
Research: Discovering new knowledge

Communication: The exchange of information

Research Dissemination vs. Research Communication: What is the difference?
| Research Dissemination | Research Communication |
|---|---|
| Making information accessible | Including all aspects of research dissemination |
| Sharing research products via the internet, journals, and presentations | Tailoring the message for a variety of audiences |
Research communication incorporates the dissemination process but doesn't stop there! The process of tailoring your message for your audience is the hallmark of effective research communication .
Why should Research Communication matter..
Professional development
Improved communication skills
experiencing the real world of researching as well as presenting
To the general public:
Improve the quality of life
Help with miscommunication and misconceptions
Increase interest and participation in the research field especially in the underrepresented social groups
To the research community:
Increase knowledge and further implement research in the future
Strong impacts in the research and science fields
Lead to new collaborations
The 7 C's of Communication
A checklist for communication:
| The C | The Meaning |
|---|---|
| Clear | Making message easy to percieve |
| Concise | Keeping it brief |
| Concrete | Solidifying depiction of what you are communicating |
| Correct | Presenting error free information |
| Coherent | Making information logical |
| Complete | Presenting all the information |
| Courteous | Keeping an open, honest and friendly communication pattern |
Thanks for helping us improve csumb.edu. Spot a broken link, typo, or didn't find something where you expected to? Let us know. We'll use your feedback to improve this page, and the site overall.
- Getting Published
- Open Research
- Communicating Research
- Life in Research
- For Editors
- For Peer Reviewers
- Research Integrity
How to communicate your research more effectively
Author: guest contributor.

by Angie Voyles Askham, Content Marketing Intern
"Scientists need to excite the public about their work in part because the public is paying for it, and in part because science has very important things to say about some of the biggest problems society faces."
Stephen S. Hall has been reporting and writing about science for decades. For the past ten years, he's also been helping researchers at New York University improve their writing skills through the school's unique Science Communication Workshops . In our interview below, he explains why the public deserves good science communication and offers some tips for how researchers can make their writing clear and engaging.
How would you descr ibe your role as a science journalist?
I’ve always made a distinction between "science writer" and a writer who happens to be interested in science. That may sound like wordplay, but I think it captures what we aspire to do. Even as specialists, science journalists wear several hats: we explain, we report, we investigate, we step back and provide historical context to scientific developments to help people understand what’s new, why something is controversial, who drove a major innovation. And like any writer, we look for interesting, provocative, and deeply reported ways to tell these stories.
I know you from the science communication workshop that’s offered to NYU graduate students. One of the most important things that I got out of the workshop, at least initially, was training myself out of the stuffy academic voice that I think a lot researchers fall into when writing academic papers. Why do you think scientists fall into this particular trap, and how do you help them get out of it?
Scientists are trained—and rightly so—to describe their work in neutral, objective terms, qualifying all observations and openly acknowledging experimental limitations. Those qualities play very well in scientific papers and talks, but are terrible for effective communication to the general public. In our Science Communication workshops at NYU, we typically see that scientists tend to communicate in dense, formal and cautious language; they tell their audiences too much; they mimic the scientific literature’s affinity for passive voice; and they slip into jargon and what I call “jargonish,” defensive language. Over ten years of conducting workshops, we’ve learned to attack these problems on two fronts: pattern recognition (training people to recognize bad writing/speaking habits and fixing them) and psychological "deprogramming" (it’s okay to leave some details and qualifications out!). And a key ingredient to successful communication is understanding your audience; there is no such thing as the "general public," but rather a bunch of different potential audiences, with different needs and different levels of expertise. We try to educate scientists to recognize the exact audience they're trying to reach—what they need to know and, just as important, what they don't need to know.
What are some other common mistakes that you see researchers making when they’re trying to communicate about their work, either with each other or with the public?
We see the same tendencies over and over again: vocabulary (not simply jargon, but common expressions—such as gene “expression”—that are second-hand within a field, but not clear to non-experts); abstract, complicated explanations rather than using everyday language; sentences that are too long; and “optics” (paragraphs that are too long and appear monolithic to readers). We’ve found that workshops are the perfect setting to play out the process of using everyday language to explain something without sacrificing scientific accuracy.
Why is it important for researchers to be better communicators?
Scientists need to learn to tell their own stories, first and foremost, because society needs their expertise, their perspective, their evidence-based problem solving skills for the future. But the lay public, especially in an era where every fact seems up for grabs, needs to be reminded of what the scientific method is: using critical thinking and rigorous analysis of facts to reach evidence-based conclusions. Scientists need to excite the public about their work in part because the public is paying for it, and in part because science has very important things to say about some of the biggest problems society faces—climate change, medical care, advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, among many other issues. As climate scientist Michael Mann said in a celebrated 2014 New York Times OpEd, scientists can no longer stay on the sidelines in these important public debates.
As a science journalist, part of your job is to hunt for interesting stories to tell. How can scientists make their work more accessible to people like you—or to other people outside of their specific area of research—so that their stories are told more widely?
The key word in your question is “stories.” Think like a writer. What’s the story behind your discovery? What were the ups and downs on the way to the finding? Where does this fit into a larger history of science narrative? Was there a funny incident or episode in the work (humor is a great way to draw and sustain public interest)? Was there a conflict or competition that makes the work even more interesting? Is there a compelling historical or contemporary figure involved that will help you humanize the science? It's been our-longstanding belief that scientists have a great intuitive feel for good storytelling (we incorporate narrative training in our workshops), but just don’t think about it when it comes to describing their own work. The other key thing is to explain why your research matters.
One of the ways that many researchers try to share their work is through Twitter, but I noticed that on the NYU website it says you’re a Twitter conscientious objector. Why is that? What effect do you think Twitter has had on science communication and journalism in general?
I actually think Twitter can be a great tool for science communication, and many of my colleagues use it deftly. I tend to gravitate toward stories that everyone is not talking about, so Twitter doesn’t help much in that regard. The larger reason I’m a Twitter “refusenik,” as my colleague Dan Fagin sometimes calls me, is that I think the technology has been widely abused to disseminate misinformation, intimidate enemies, and subvert democratic norms; I don’t use it primarily for those reasons.
Are there any other tips that you can offer researchers who want to be better communicators and just aren’t sure where to start?
One first step might be to see if your institution offers any communication training and to take advantage of those programs; if not, think about how you might establish a program. We’ve posted a few of the things we’ve learned at NYU on our website ; we’ve also established a publishing platform for science communicators at NYU called the Cooper Square Review , which is a good way for scientists to get experience publishing their own work and reaching a larger public.
Stephen S. Hall has been reporting and writing about science for nearly 30 years. In addition to numerous cover stories in the New York Times Magazine, where he also served as a Story Editor and Contributing Writer, his work has appeared in The New Yorker, The Atlantic Monthly, and a number of other outlets. He is also the author of six non-fiction books about contemporary science. In addition to teaching the Science Communication Workshops at NYU, he also teaches for NYU's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program (SHERP) and has taught graduate seminars in science writing and explanatory journalism at Columbia University.
Click here to learn how Springer Nature continues to support the needs of Early Career Researchers.
Guest Contributors include Springer Nature staff and authors, industry experts, society partners, and many others. If you are interested in being a Guest Contributor, please contact us via email: [email protected] .
- early career researchers
- research communication
- Open science
- Tools & Services
- Account Development
- Sales and account contacts
- Professional
- Press office
- Locations & Contact
We are a world leading research, educational and professional publisher. Visit our main website for more information.
- © 2024 Springer Nature
- General terms and conditions
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Your Privacy Choices / Manage Cookies
- Accessibility
- Legal notice
- Help us to improve this site, send feedback.
What are research skills?
Last updated
26 April 2023
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Broadly, it includes a range of talents required to:
Find useful information
Perform critical analysis
Form hypotheses
Solve problems
It also includes processes such as time management, communication, and reporting skills to achieve those ends.
Research requires a blend of conceptual and detail-oriented modes of thinking. It tests one's ability to transition between subjective motivations and objective assessments to ensure only correct data fits into a meaningfully useful framework.
As countless fields increasingly rely on data management and analysis, polishing your research skills is an important, near-universal way to improve your potential of getting hired and advancing in your career.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
What are basic research skills?
Almost any research involves some proportion of the following fundamental skills:
Organization
Decision-making
Investigation and analysis
Creative thinking
What are primary research skills?
The following are some of the most universally important research skills that will help you in a wide range of positions:
Time management — From planning and organization to task prioritization and deadline management, time-management skills are highly in-demand workplace skills.
Problem-solving — Identifying issues, their causes, and key solutions are another essential suite of research skills.
Critical thinking — The ability to make connections between data points with clear reasoning is essential to navigate data and extract what's useful towards the original objective.
Communication — In any collaborative environment, team-building and active listening will help researchers convey findings more effectively through data summarizations and report writing.
What are the most important skills in research?
Detail-oriented procedures are essential to research, which allow researchers and their audience to probe deeper into a subject and make connections they otherwise may have missed with generic overviews.
Maintaining priorities is also essential so that details fit within an overarching strategy. Lastly, decision-making is crucial because that's the only way research is translated into meaningful action.
- Why are research skills important?
Good research skills are crucial to learning more about a subject, then using that knowledge to improve an organization's capabilities. Synthesizing that research and conveying it clearly is also important, as employees seek to share useful insights and inspire effective actions.
Effective research skills are essential for those seeking to:
Analyze their target market
Investigate industry trends
Identify customer needs
Detect obstacles
Find solutions to those obstacles
Develop new products or services
Develop new, adaptive ways to meet demands
Discover more efficient ways of acquiring or using resources
Why do we need research skills?
Businesses and individuals alike need research skills to clarify their role in the marketplace, which of course, requires clarity on the market in which they function in. High-quality research helps people stay better prepared for challenges by identifying key factors involved in their day-to-day operations, along with those that might play a significant role in future goals.
- Benefits of having research skills
Research skills increase the effectiveness of any role that's dependent on information. Both individually and organization-wide, good research simplifies what can otherwise be unwieldy amounts of data. It can help maintain order by organizing information and improving efficiency, both of which set the stage for improved revenue growth.
Those with highly effective research skills can help reveal both:
Opportunities for improvement
Brand-new or previously unseen opportunities
Research skills can then help identify how to best take advantage of available opportunities. With today's increasingly data-driven economy, it will also increase your potential of getting hired and help position organizations as thought leaders in their marketplace.
- Research skills examples
Being necessarily broad, research skills encompass many sub-categories of skillsets required to extrapolate meaning and direction from dense informational resources. Identifying, interpreting, and applying research are several such subcategories—but to be specific, workplaces of almost any type have some need of:
Searching for information
Attention to detail
Taking notes
Problem-solving
Communicating results
Time management
- How to improve your research skills
Whether your research goals are to learn more about a subject or enhance workflows, you can improve research skills with this failsafe, four-step strategy:
Make an outline, and set your intention(s)
Know your sources
Learn to use advanced search techniques
Practice, practice, practice (and don't be afraid to adjust your approach)
These steps could manifest themselves in many ways, but what's most important is that it results in measurable progress toward the original goals that compelled you to research a subject.
- Using research skills at work
Different research skills will be emphasized over others, depending on the nature of your trade. To use research most effectively, concentrate on improving research skills most relevant to your position—or, if working solo, the skills most likely have the strongest impact on your goals.
You might divide the necessary research skills into categories for short, medium, and long-term goals or according to each activity your position requires. That way, when a challenge arises in your workflow, it's clearer which specific research skill requires dedicated attention.
How can I learn research skills?
Learning research skills can be done with a simple three-point framework:
Clarify the objective — Before delving into potentially overwhelming amounts of data, take a moment to define the purpose of your research. If at any point you lose sight of the original objective, take another moment to ask how you could adjust your approach to better fit the original objective.
Scrutinize sources — Cross-reference data with other sources, paying close attention to each author's credentials and motivations.
Organize research — Establish and continually refine a data-organization system that works for you. This could be an index of resources or compiling data under different categories designed for easy access.
Which careers require research skills?
Especially in today's world, most careers require some, if not extensive, research. Developers, marketers, and others dealing in primarily digital properties especially require extensive research skills—but it's just as important in building and manufacturing industries, where research is crucial to construct products correctly and safely.
Engineering, legal, medical, and literally any other specialized field will require excellent research skills. Truly, almost any career path will involve some level of research skills; and even those requiring only minimal research skills will at least require research to find and compare open positions in the first place.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Research Skills: What they are and Benefits

Research skills play a vital role in the success of any research project, enabling individuals to navigate the vast sea of information, analyze data critically, and draw meaningful conclusions. Whether conducting academic research, professional investigations, or personal inquiries, strong research skills are essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
By understanding and developing these skills, individuals can embark on their research endeavors with confidence, integrity, and the capability to make meaningful contributions in their chosen fields. This article will explore the importance of research skills and discuss critical competencies necessary for conducting a research project effectively.
Content Index
What are Research Skills?
Important research skills for research project, benefits of research skills.
- Improving your Research Skills
Talk to Experts to Improve Skills
Research skills are the capability a person carries to create new concepts and understand the use of data collection. These skills include techniques, documentation, and interpretation of the collected data. Research is conducted to evaluate hypotheses and share the findings most appropriately. Research skills improve as we gain experience.
To conduct efficient research, specific research skills are essential. These skills are necessary for companies to develop new products and services or enhance existing products. To develop good research skills is important for both the individual as well as the company.
When undertaking a research project, one must possess specific important skills to ensure the project’s success and accuracy. Here are some essential research skills that are crucial for conducting a project effectively:
Time Management Skills:
Time management is an essential research skill; it helps you break down your project into parts and enables you to manage it easier. One can create a dead-line oriented plan for the research project and assign time for each task. Time management skills include setting goals for the project, planning and organizing functions as per their priority, and efficiently delegating these tasks.
Communication Skills:
These skills help you understand and receive important information and also allow you to share your findings with others in an effective manner. Active listening and speaking are critical skills for solid communication. A researcher must have good communication skills.
Problem-Solving:
The ability to handle complex situations and business challenges and come up with solutions for them is termed problem-solving. To problem-solve, you should be able to fully understand the extent of the problem and then break it down into smaller parts. Once segregated into smaller chunks, you can start thinking about each element and analyze it to find a solution.
Information gathering and attention to detail:
Relevant information is the key to good research design . Searching for credible resources and collecting information from there will help you strengthen your research proposal and drive you to solutions faster. Once you have access to information, paying close attention to all the details and drawing conclusions based on the findings is essential.
Research Design and Methodology :
Understanding research design and methodology is essential for planning and conducting a project. Depending on the research question and objectives, researchers must select appropriate research methods, such as surveys, experiments, interviews, or case studies. Proficiency in designing research protocols, data collection instruments, and sampling strategies is crucial for obtaining reliable and valid results.
Data Collection and Analysis :
Researchers should be skilled in collecting and analyzing data accurately. It involves designing data collection instruments, collecting data through various methods, such as surveys or observations, and organizing and analyzing the collected data using appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques. Proficiency in using software tools like SPSS, Excel, or qualitative analysis software can be beneficial.
By developing and strengthening these research skills, researchers can enhance the quality and impact of their research process, contributing to good research skills in their respective fields.
Research skills are invaluable assets that can benefit individuals in various aspects of their lives. Here are some key benefits of developing and honing research skills:
Boosts Curiosity :
Curiosity is a strong desire to know things and a powerful learning driver. Curious researchers will naturally ask questions that demand answers and will stop in the search for answers. Interested people are better listeners and are open to listening to other people’s ideas and perspectives, not just their own.
Cultivates Self-awareness :
As well as being aware of other people’s subjective opinions, one must develop the importance of research skills and be mindful of the benefits of awareness research; we are exposed to many things while researching. Once we start doing research, the benefit from it reflects on the beliefs and attitudes and encourages them to open their minds to other perspectives and ways of looking at things.
Effective Communication:
Research skills contribute to practical communication skills by enhancing one’s ability to articulate ideas, opinions, and findings clearly and coherently. Through research, individuals learn to organize their thoughts, present evidence-based arguments, and effectively convey complex information to different audiences. These skills are crucial in academic research settings, professional environments, and personal interactions.
Personal and Professional Growth :
Developing research skills fosters personal and professional growth by instilling a sense of curiosity, intellectual independence, and a lifelong learning mindset. Research encourages individuals to seek knowledge, challenge assumptions, and embrace intellectual growth. These skills also enhance adaptability as individuals become adept at navigating and assimilating new information, staying updated with the latest developments, and adjusting their perspectives and strategies accordingly.
Academic Success:
Research skills are essential for academic research success. They enable students to conduct thorough literature reviews, gather evidence to support their arguments, and critically evaluate existing research. By honing their research skills, students can produce well-structured, evidence-based essays, projects, and dissertations demonstrating high academic research rigor and analytical thinking.
Professional Advancement:
Research skills are highly valued in the professional world. They are crucial for conducting market research, analyzing trends, identifying opportunities, and making data-driven decisions. Employers appreciate individuals who can effectively gather and analyze information, solve complex problems, and provide evidence-based recommendations. Research skills also enable professionals to stay updated with advancements in their field, positioning themselves as knowledgeable and competent experts.
Developing and nurturing research skills can significantly benefit individuals in numerous aspects of their lives, enabling them to thrive in an increasingly information-driven world.
Improving Your Research Skills
There are many things you can do to improve your research skills and utilize them in your research or day job. Here are some examples:
- Develop Information Literacy: Strengthening your information literacy skills is crucial for conducting thorough research. It involves identifying reliable sources, evaluating the credibility of information, and navigating different research databases.
- Enhance Critical Thinking: Critical thinking is an essential skill for effective research. It involves analyzing information, questioning assumptions, and evaluating arguments. Practice critical analysis by analyzing thoughtfully, identifying biases, and considering alternative perspectives.
- Master Research Methodologies: Familiarize yourself with different research methodologies relevant to your field. Whether it’s qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods research, realizing the strengths and limitations of each approach is crucial.
- Practice Effective Time Management: Research requires dedicated time and effort. Develop good time management skills to ensure that you allocate sufficient time for each stage of the research process, including planning, data collection, analysis, and writing.
- Embrace Collaboration: Collaborating with peers and colleagues can provide a fresh perspective and enrich your research experience. Engage in discussions, share ideas, and seek feedback from others. Collaborative projects allow for exchanging knowledge and skills.
- Continuously Update Your Knowledge: Stay informed about your field’s latest developments and advancements. Regularly read scholarly articles, attend conferences, and follow reputable sources of information to stay up to date with current research trends.
There is plenty of information available on the internet about every topic; hence, learning skills to know which information is relevant and credible is very important. Today most search engines have the feature of advanced search, and you can customize the search as per your preference. Once you learn this skill, it will help you find information.
Experts possess a wealth of knowledge, experience, and insights that can significantly enhance your understanding and abilities in conducting research. Experts have often encountered numerous challenges and hurdles throughout their research journey and have developed effective problem-solving techniques. Engaging with experts is a highly effective approach to improving research skills.
Moreover, experts can provide valuable feedback and constructive criticism on your research work. They can offer fresh perspectives, identify areas for improvement, and help you refine your research questions, methodology, and analysis.
At QuestionPro, we can help you with the necessary tools to carry out your projects, and we have created the following free resources to help you in your professional growth:
- Survey Templates
Research skills are invaluable assets that empower individuals to navigate the ever-expanding realm of information, make informed decisions, and contribute to advancing knowledge. With advanced research tools and technologies like QuestionPro Survey Software, researchers have potent resources to conduct comprehensive surveys, gather data, and analyze results efficiently.
Where data-driven decision-making is crucial, research skills supported by advanced tools like QuestionPro are essential for researchers to stay ahead and make impactful contributions to their fields. By embracing these research skills and leveraging the capabilities of powerful survey software, researchers can unlock new possibilities, gain deeper insights, and pave the way for meaningful discoveries.
Authors : Gargi Ghamandi & Sandeep Kokane
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS
Jotform vs SurveyMonkey: Which Is Best in 2024
Aug 15, 2024

360 Degree Feedback Spider Chart is Back!
Aug 14, 2024

Jotform vs Wufoo: Comparison of Features and Prices
Aug 13, 2024

Product or Service: Which is More Important? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Home › Study Tips › Research Skills: What They Are and How They Benefit You
Research Skills: What They Are and How They Benefit You
- Published May 23, 2024

Research skills give you the ability to gather relevant information from different sources and analyse it critically in order to develop a comprehensive understanding of a subject. Thus, research skills are fundamental to academic success.
Developing these skills will improve your studies, helping you understand subjects better and positioning you for academic success.
That said, how can you develop important research skills? This will explore what research skills are, identify the core ones, and explain how you can develop them.
What Are Research Skills?
Research skills are a set of abilities that allow individuals to find and gather reliable information and then evaluate the information to find answers to questions.
Good research skills are important in academic settings, as finding and critically evaluating relevant information can help you gain a deeper understanding of a subject.
These skills are also important in professional and personal settings. When you graduate and are working in a professional capacity, you’ll often need to analyse sets of data to identify issues and determine how to solve them.
In personal contexts, you’ll always need to assess relevant information to make an informed decision. Whether you’re deciding on a major purchase, choosing a healthcare provider, or planning to make an investment, you’ll need to evaluate options to ensure better decision outcomes.
Different Types of Research Skills
Research skills are categorised into different sub-skills. The most common types are:
Quantitative Skills
Quantitative skills refer to the ability to work with numerical data and perform mathematical and statistical analyses to extract meaningful insights and draw conclusions.
When you have quantitative skills, you’ll be able to apply mathematical concepts and operations in research design and data analysis.
You’ll also be proficient in using statistical methods to analyse data and interpreting numerical data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills refer to the ability to gather data, evaluate it, and draw sound conclusions. When you have analytical skills, you’ll be able to systematically analyse information to reach a reasonable conclusion.
Analytical skills are important in problem-solving. They help you to break down complex problems into more manageable components, think critically about the information at hand, analyse root causes, and develop effective solutions.
Qualitative Skills
Qualitative skills refer to the ability to collect, analyse, and interpret non-numerical data. When you have qualitative skills, you’ll be proficient in observation, interviewing, and other methods for collecting qualitative research data.
You’ll also be able to analyse non-numerical data, such as documents and images, to identify themes, patterns, and meanings.
Research Skills Examples
The core research skills you need for success in academic, professional, and personal contexts include:
Data Collection
Data is at the centre of every research, as data is what you assess to find the answers you seek. Thus, research starts with collecting relevant data.
Depending on the research, there are two broad categories of data you can collect: primary and secondary.
Primary data is generated by the researcher, like data from interviews, observations, or experiments. Secondary data is pre-existing data obtained from different existing databases, like published literature, government reports, etc.
Thus, data collection is more than gathering information from the Internet. Depending on the research, it can require more advanced skills for conducting experiments to generate your own data.
Source Evaluation
When doing research on any subject (especially when using the Internet), you’ll be amazed at the volume of information you’ll find. And a lot is pure garbage that can compromise your research work.
Thus, an important research skill is being able to dig through the garbage to get to the real facts. This is where source evaluation comes in!
Good research skills call for being able to identify biases, assess the authority of the author, and determine the accuracy of information before using it.
Time Management Skills

Have you ever felt that there is not enough time in a day for all that you need to do? When you already have so much to do, adding research can be overwhelming.
Good time management skills can help you find the time to do all you need to do, including relevant research work, making it an essential research skill.
Time management allows you to plan and manage your research project effectively. It includes breaking down research tasks into more manageable parts, setting priorities, and allocating time to the different stages of the research.
Communication Skills

Communication is an important aspect of every research, as it aids in data collection and sharing research findings.
Important communication skills needed in research include active listening, active speaking, interviewing, report writing, data visualisation, and presentation, etc.
For example, when research involves collecting primary data via interviews, you must have sound speaking and listening skills.
When you conclude the research and need to share findings, you’ll need to write a research report and present key findings in easy-to-understand formats like charts.
Attention to Detail
Attention to detail is the ability to achieve thoroughness and accuracy when doing something. It requires focusing on every aspect of the tasks, even small ones.
Anything you miss during your research will affect the quality of your research findings. Thus, the ability to pay close attention to details is an important research skill.
You need attention to detail at every stage of the research process. During data collection, it helps you ensure reliable data.
During analysis, it reduces the risk of error to ensure your results are trustworthy. It also helps you express findings precisely to minimise ambiguity and facilitate understanding.
Note-Taking

Note-taking is exactly what it sounds like—writing down key information during the research process.
Remember that research involves sifting through and taking in a lot of information. It’s impossible to take in all the information and recall it from memory. This is where note-taking comes in!
Note-taking helps you capture key information, making it easier to remember and utilise for the research later. It also involves writing down where to look for important information.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the ability to think rationally and synthesise information in a thoughtful way. It is an important skill needed in virtually all stages of the research process.
For example, when collecting data, you need critical thinking to assess the quality and relevance of data. It can help you identify gaps in data to formulate your research question and hypothesis.
It can also help you to identify patterns and make reasonable connections when interpreting research findings.
Data Analysis
Data may not mean anything until you analyse it qualitatively or quantitatively (using techniques like Excel or SPSS). For this reason, data analysis analysis is an important research skill.
Researchers need to be able to build hypotheses and test these using appropriate research techniques. This helps to draw meaningful conclusions and gain a comprehensive understanding of research data.
Problem-Solving Skills
Research often involves addressing specific questions and solving problems. For this reason, problem-solving skills are important skills when conducting research.
Problem-solving skills refer to the ability to identify, analyse, and solve problems effectively.
With problem-solving skills, you’ll be able to assess a situation, consider various solutions, and choose the most appropriate course of action toward finding a solution.
Benefits of Research Skills
Research skills have many benefits, including:
Enhances Critical Thinking
Research skills and critical thinking are intertwined such that developing one enhances the other.
Research requires people to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, analyse information, and draw conclusions. These activities require you to think critically about the information at hand. Hence, engaging in research enhances critical thinking.
Develops Problem-Solving Skills
Research helps you acquire a set of critical skills that are directly transferable to problem-solving.
For example, research fosters creative thinking, as it often requires synthesising data from different sources and connecting different concepts. After developing creative thinking via research, you can apply the skill to generate innovative solutions in problem-solving situations.
Helps in Knowledge Acquisition
Engaging in research is a powerful way to acquire knowledge. Research involves exploring new ideas, and this helps you expand your breadth of knowledge.
It also involves applying research methods and methodologies. So, you’ll acquire knowledge about research methods, enhancing your ability to design and conduct studies in your higher education or professional life.
Why Are Research Skills Important?
Strong research skills offer numerous benefits, especially for students’ academic learning and development.
When you develop good research skills, you’ll reap great academic rewards that include:
In-Depth Understanding
Conducting research allows you to delve deep into specific topics, helping you gain a thorough understanding of the subject matter beyond what is covered in standard coursework.
Critical Thinking Development
Research involves critical evaluation of information and making informed decisions. This builds your ability to think critically.
This skill will not only help you solve academic problems better, but it’s also crucial to your personal and professional growth.
Encouragement of Independent Learning
Research encourages independent learning. When you engage in research, you seek answers independently. You take the initiative to find, retrieve, and evaluate information relevant to your research.
That helps you develop self-directed study habits. You’ll be able to take ownership of your education and actively seek out information for a better understanding of the subject matter.
Intellectual Curiosity Development
Research skills encourage intellectual curiosity and a love of learning, as they’ll make you explore topics you find intriguing or important. Thus, you’ll be more motivated to explore topics beyond the scope of your coursework.
Enhanced Communication Skills
Research helps you build better interpersonal skills as well as report-writing skills.
Research helps you sharpen your communication skills when you interact with research subjects during data collection. Communicating research findings to an audience also helps sharpen your presentation skills or report writing skills.
Assistance in Career Preparation
Many professions find people with good research skills. Whether you’ll pursue a career in academia, business, healthcare, or IT, being able to conduct research will make you a valuable asset.
So, researching skills for students prepares you for a successful career when you graduate.
Contribution to Personal Growth
Research also contributes to your personal growth. Know that research projects often come with setbacks, unexpected challenges, and moments of uncertainty. Navigating these difficulties helps you build resilience and confidence.
Acquisition of Time Management Skills
Research projects often come with deadlines. Such research projects force you to set goals, prioritise tasks, and manage your time effectively.
That helps you acquire important time management skills that you can use in other areas of academic life and your professional life when you graduate.
Ways to Improve Research Skills
The ways to improve your research skills involve a combination of learning and practice.
You should consider enrolling in research-related programmes, learning to use data analysis tools, practising summarising and synthesising information from multiple sources, collaborating with more experienced researchers, and more.
Looking to improve your research skills? Read our 11 ways to improve research skills article.
How Can I Learn Research Skills?
You can learn research skills using these simple three-point framework:
Clarifying the Objective
Start by articulating the purpose of your research. Identify the specific question you are trying to answer or the problem you are aiming to solve.
Then, determine the scope of your research to help you stay focused and avoid going after irrelevant information.
Cross-Referencing Sources
The next step is to search for existing research on the topic. Use academic databases, journals, books, and reputable online sources.
It’s important to compare information from multiple sources, taking note of consensus among studies and any conflicting findings.
Also, check the credibility of each source by looking at the author’s expertise, information recency, and reputation of the publication’s outlet.
Organise the Research
Develop a note-taking system to document key findings as you search for existing research. Create a research outline, then arrange your ideas logically, ensuring that each section aligns with your research objective.
As you progress, be adaptable. Be open to refining your research plan as new understanding evolves.
Enrolling in online research programmes can also help you build strong research skills. These programmes combine subject study with academic research project development to help you hone the skills you need to succeed in higher education.
Immerse Education is a foremost provider of online research programmes.
Acquire Research Skills with Immerse Education
Research skills are essential to academic success. They help you gain an in-depth understanding of subjects, enhance your critical thinking and problem-solving skills, improve your time management skills, and more.
In addition to boosting you academically, they contribute to your personal growth and prepare you for a successful professional career.
Thankfully, you can learn research skills and reap these benefits. There are different ways to improve research skills, including enrolling in research-based programmes. This is why you need Immerse Education!
Immerse Education provides participants aged 13-18 with unparalleled educational experience. All our programmes are designed by tutors from top global universities and help prepare participants for future success.
Our online research programme expertly combines subject study with academic research projects to help you gain subject matter knowledge and the important research skills you need to succeed in higher education. With one-on-one tutoring or group sessions from an expert academic from Oxford or Cambridge University and a flexible delivery mode, the programme is designed for you to succeed. Subsequently, enrolling in our accredited Online Research Programme will award students with 8 UCAS points upon completion.
- I'm a Parent
- I'm a Student
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Which subjects interest you? (Optional) Architecture Artificial Intelligence Banking and Finance Biology Biotechnology Business Management Chemistry Coding Computer Science Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Creative Writing Creative Writing and Film Criminology Data Science and Analytics Earth Science Economics Encryption and Cybersecurity Engineering English Literature Entrepreneurship Fashion and Design Female Future Leaders Film Studies Fine Arts Global Society and Sustainability Health and Biotechnology History International Relations Law Marketing and Entertainment Mathematics Medicine Medicine and Health Sciences Nanotechnology Natural Sciences Philosophy Philosophy Politics and Economics Physics Psychology Software Development and AI Software Development and Gaming Veterinary Studies Online Research Programme
Secure priority enrolment for our new summer school location with a small refundable deposit.
" * " indicates required fields
Receive priority enrolment for new summer school locations by registering your interest below.
Our programme consultant will contact you to talk about your options.
- Family Name *
- Phone Number
- Yes. See Privacy Policy.
Subject is unavailable at location
You have selected a subject that is not available at the location that you have previously chosen.
The location filter has been reset, and you are now able to search for all the courses where we offer the subject.

- Advisers & Contacts
- Bachelor of Arts & Bachelor of Science in Engineering
- Prerequisites
- Declaring Computer Science for AB Students
- Declaring Computer Science for BSE Students
- Class of '25, '26 & '27 - Departmental Requirements
- Class of 2024 - Departmental Requirements
- COS126 Information
- Important Steps and Deadlines
- Independent Work Seminars
- Guidelines and Useful Information
- Undergraduate Research Topics
- AB Junior Research Workshops
- Undergraduate Program FAQ
- Minor Program
- Funding for Student Group Activities
- Mailing Lists and Policies
- Study Abroad
- Jobs & Careers
- Admissions Requirements
- Breadth Requirements
- Pre-FPO Checklist
- FPO Checklist
- M.S.E. Track
- M.Eng. Track
- Departmental Internship Policy (for Master's students)
- General Examination
- Fellowship Opportunities
- Travel Reimbursement Policy
- Communication Skills
- Course Schedule
- Course Catalog
- Research Areas
- Interdisciplinary Programs
- Technical Reports
- Computing Facilities
- Researchers
- Technical Staff
- Administrative Staff
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Alumni
- Climate and Inclusion Committee
- Resources for Undergraduate & Graduate Students
- Outreach Initiatives
- Resources for Faculty & Staff
- Spotlight Stories
- Job Openings
- Graduate Program
Advice on Research Communications Skills
Great researchers are great communicators. This page provides some resources to help you develop your communication skills.
- How to read a paper . S. Keshav. Note: The general principles here are very useful (read a paper in several iterations of increasing depth depending upon your objectives and interest). However, the amount of time it may take you to read a paper will vary greatly depending on the paper and the area. Assuming you can understand a paper deeply in just a few hours may be unrealistic for some papers in some areas. It may take you days or weeks. Do not get discouraged if it takes you more time than suggested here.
- Go to Princeton colloquia, job talks, area meetings, general exams, pre-FPOs and FPOs. Think about what speakers in each context are doing well (or not so well) to communicate their content effectively and memorably.
- How to give a great research talk . Simon Peyton Jones.
- Presenting a technical talk . Nick Feamster and Alex Gray.
General Advice & Courses
- Read more . Of anything that is well written. Doing so improves your vocabulary and exposes you to varied sentence structures. For instance, subscribe to National Geographic or the Atlantic. Start immediately. Improving communication skills is a long-term project and it pays to start immediately.
- Take one of Princeton's writing seminars for graduate students when you have time.
- Join one of Princeton's dissertation boot camps (which doesn't just have to be for writing your thesis, but could be for writing a paper)
- Take Stanford's free online writing class for the sciences when you have time.
- Read article on Mathematical Writing
Internet Articles
- The science of scientific writing . George Gopen and Judith Swan.
- Writer's block is not a struggle with your writing but with your thinking . Write your way out of it.
- Story-telling 101: Writing tips for academics . Nick Feamster and Alex Gray.
- Dave Patterson's writing advice . Dave Patterson.
- How to write a great research paper . Simon Peyton Jones.
- The curse of knowledge . Benjamin Pierce.
- How to give a bad talk (circa 1983) . Dave Patterson.
- Style: Toward clarity and grace . Joseph Williams.
- How to write a lot: A practical guide to academic writing . Paul Silvia.
- The elements of style . William Strunk and E. B. White.
- Writing for computer science. Justin Zobel.
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
The Most Important Research Skills (With Examples)
- What Are Hard Skills?
- What Are Technical Skills?
- What Are What Are Life Skills?
- What Are Social Media Skills Resume?
- What Are Administrative Skills?
- What Are Analytical Skills?
- What Are Research Skills?
- What Are Transferable Skills?
- What Are Microsoft Office Skills?
- What Are Clerical Skills?
- What Are Computer Skills?
- What Are Core Competencies?
- What Are Collaboration Skills?
- What Are Conflict Resolution Skills?
- What Are Mathematical Skills?
- How To Delegate
Find a Job You Really Want In
Research skills are the ability to find out accurate information on a topic. They include being able to determine the data you need, find and interpret those findings, and then explain that to others. Being able to do effective research is a beneficial skill in any profession, as data and research inform how businesses operate. Whether you’re unsure of your research skills or are looking for ways to further improve them, then this article will cover important research skills and how to become even better at research. Key Takeaways Having strong research skills can help you understand your competitors, develop new processes, and build your professional skills in addition to aiding you in finding new customers and saving your company money. Some of the most valuable research skills you can have include goal setting, data collection, and analyzing information from multiple sources. You can and should put your research skills on your resume and highlight them in your job interviews. In This Article Skip to section What are research skills? Why are research skills important? 12 of the most important research skills How to improve your research skills Highlighting your research skills in a job interview How to include research skills on your resume Resume examples showcasing research skills Research skills FAQs References Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs Show More What are research skills?
Research skills are the necessary tools to be able to find, compile, and interpret information in order to answer a question. Of course, there are several aspects to this. Researchers typically have to decide how to go about researching a problem — which for most people is internet research.
In addition, you need to be able to interpret the reliability of a source, put the information you find together in an organized and logical way, and be able to present your findings to others. That means that they’re comprised of both hard skills — knowing your subject and what’s true and what isn’t — and soft skills. You need to be able to interpret sources and communicate clearly.
Why are research skills important?
Research skills are useful in any industry, and have applications in innovation, product development, competitor research, and many other areas. In addition, the skills used in researching aren’t only useful for research. Being able to interpret information is a necessary skill, as is being able to clearly explain your reasoning.
Research skills are used to:
Do competitor research. Knowing what your biggest competitors are up to is an essential part of any business. Researching what works for your competitors, what they’re doing better than you, and where you can improve your standing with the lowest resource expenditure are all essential if a company wants to remain functional.
Develop new processes and products. You don’t have to be involved in research and development to make improvements in how your team gets things done. Researching new processes that make your job (and those of your team) more efficient will be valued by any sensible employer.
Foster self-improvement. Folks who have a knack and passion for research are never content with doing things the same way they’ve always been done. Organizations need independent thinkers who will seek out their own answers and improve their skills as a matter of course. These employees will also pick up new technologies more easily.
Manage customer relationships. Being able to conduct research on your customer base is positively vital in virtually every industry. It’s hard to move products or sell services if you don’t know what people are interested in. Researching your customer base’s interests, needs, and pain points is a valuable responsibility.
Save money. Whether your company is launching a new product or just looking for ways to scale back its current spending, research is crucial for finding wasted resources and redirecting them to more deserving ends. Anyone who proactively researches ways that the company can save money will be highly appreciated by their employer.
Solve problems. Problem solving is a major part of a lot of careers, and research skills are instrumental in making sure your solution is effective. Finding out the cause of the problem and determining an effective solution both require accurate information, and research is the best way to obtain that — be it via the internet or by observation.
Determine reliable information. Being able to tell whether or not the information you receive seems accurate is a very valuable skill. While research skills won’t always guarantee that you’ll be able to tell the reliability of the information at first glance, it’ll prevent you from being too trusting. And it’ll give the tools to double-check .
12 of the most important research skills
Experienced researchers know that worthwhile investigation involves a variety of skills. Consider which research skills come naturally to you, and which you could work on more.
Data collection . When thinking about the research process, data collection is often the first thing that comes to mind. It is the nuts and bolts of research. How data is collected can be flexible.
For some purposes, simply gathering facts and information on the internet can fulfill your need. Others may require more direct and crowd-sourced research. Having experience in various methods of data collection can make your resume more impressive to recruiters.
Data collection methods include: Observation Interviews Questionnaires Experimentation Conducting focus groups
Analysis of information from different sources. Putting all your eggs in one source basket usually results in error and disappointment. One of the skills that good researchers always incorporate into their process is an abundance of sources. It’s also best practice to consider the reliability of these sources.
Are you reading about U.S. history on a conspiracy theorist’s blog post? Taking facts for a presentation from an anonymous Twitter account?
If you can’t determine the validity of the sources you’re using, it can compromise all of your research. That doesn’t mean just disregard anything on the internet but double-check your findings. In fact, quadruple-check. You can make your research even stronger by turning to references outside of the internet.
Examples of reliable information sources include: Published books Encyclopedias Magazines Databases Scholarly journals Newspapers Library catalogs
Finding information on the internet. While it can be beneficial to consulate alternative sources, strong internet research skills drive modern-day research.
One of the great things about the internet is how much information it contains, however, this comes with digging through a lot of garbage to get to the facts you need. The ability to efficiently use the vast database of knowledge that is on the internet without getting lost in the junk is very valuable to employers.
Internet research skills include: Source checking Searching relevant questions Exploring deeper than the first options Avoiding distraction Giving credit Organizing findings
Interviewing. Some research endeavors may require a more hands-on approach than just consulting internet sources. Being prepared with strong interviewing skills can be very helpful in the research process.
Interviews can be a useful research tactic to gain first-hand information and being able to manage a successful interview can greatly improve your research skills.
Interviewing skills involves: A plan of action Specific, pointed questions Respectfulness Considering the interview setting Actively Listening Taking notes Gratitude for participation
Report writing. Possessing skills in report writing can assist you in job and scholarly research. The overall purpose of a report in any context is to convey particular information to its audience.
Effective report writing is largely dependent on communication. Your boss, professor , or general reader should walk away completely understanding your findings and conclusions.
Report writing skills involve: Proper format Including a summary Focusing on your initial goal Creating an outline Proofreading Directness
Critical thinking. Critical thinking skills can aid you greatly throughout the research process, and as an employee in general. Critical thinking refers to your data analysis skills. When you’re in the throes of research, you need to be able to analyze your results and make logical decisions about your findings.
Critical thinking skills involve: Observation Analysis Assessing issues Problem-solving Creativity Communication
Planning and scheduling. Research is a work project like any other, and that means it requires a little forethought before starting. Creating a detailed outline map for the points you want to touch on in your research produces more organized results.
It also makes it much easier to manage your time. Planning and scheduling skills are important to employers because they indicate a prepared employee.
Planning and scheduling skills include: Setting objectives Identifying tasks Prioritizing Delegating if needed Vision Communication Clarity Time-management
Note-taking. Research involves sifting through and taking in lots of information. Taking exhaustive notes ensures that you will not neglect any findings later and allows you to communicate these results to your co-workers. Being able to take good notes helps summarize research.
Examples of note-taking skills include: Focus Organization Using short-hand Keeping your objective in mind Neatness Highlighting important points Reviewing notes afterward
Communication skills. Effective research requires being able to understand and process the information you receive, either written or spoken. That means that you need strong reading comprehension and writing skills — two major aspects of communication — as well as excellent listening skills.
Most research also involves showcasing your findings. This can be via a presentation. , report, chart, or Q&A. Whatever the case, you need to be able to communicate your findings in a way that educates your audience.
Communication skills include: Reading comprehension Writing Listening skills Presenting to an audience Creating graphs or charts Explaining in layman’s terms
Time management. We’re, unfortunately, only given 24 measly hours in a day. The ability to effectively manage this time is extremely powerful in a professional context. Hiring managers seek candidates who can accomplish goals in a given timeframe.
Strong time management skills mean that you can organize a plan for how to break down larger tasks in a project and complete them by a deadline. Developing your time management skills can greatly improve the productivity of your research.
Time management skills include: Scheduling Creating task outlines Strategic thinking Stress-management Delegation Communication Utilizing resources Setting realistic expectations Meeting deadlines
Using your network. While this doesn’t seem immediately relevant to research skills, remember that there are a lot of experts out there. Knowing what people’s areas of expertise and asking for help can be tremendously beneficial — especially if it’s a subject you’re unfamiliar with.
Your coworkers are going to have different areas of expertise than you do, and your network of people will as well. You may even know someone who knows someone who’s knowledgeable in the area you’re researching. Most people are happy to share their expertise, as it’s usually also an area of interest to them.
Networking involves: Remembering people’s areas of expertise Being willing to ask for help Communication Returning favors Making use of advice Asking for specific assistance
Attention to detail. Research is inherently precise. That means that you need to be attentive to the details, both in terms of the information you’re gathering, but also in where you got it from. Making errors in statistics can have a major impact on the interpretation of the data, not to mention that it’ll reflect poorly on you.
There are proper procedures for citing sources that you should follow. That means that your sources will be properly credited, preventing accusations of plagiarism. In addition, it means that others can make use of your research by returning to the original sources.
Attention to detail includes: Double checking statistics Taking notes Keeping track of your sources Staying organized Making sure graphs are accurate and representative Properly citing sources
How to improve your research skills
As with many professional skills, research skills serve us in our day to day life. Any time you search for information on the internet, you’re doing research. That means that you’re practicing it outside of work as well. If you want to continue improving your research skills, both for professional and personal use, here are some tips to try.
Differentiate between source quality. A researcher is only as good as their worst source. Start paying attention to the quality of the sources you use, and be suspicious of everything your read until you check out the attributions and works cited.
Be critical and ask yourself about the author’s bias, where the author’s research aligns with the larger body of verified research in the field, and what publication sponsored or published the research.
Use multiple resources. When you can verify information from a multitude of sources, it becomes more and more credible. To bolster your faith in one source, see if you can find another source that agrees with it.
Don’t fall victim to confirmation bias. Confirmation bias is when a researcher expects a certain outcome and then goes to find data that supports this hypothesis. It can even go so far as disregarding anything that challenges the researcher’s initial hunch. Be prepared for surprising answers and keep an open mind.
Be open to the idea that you might not find a definitive answer. It’s best to be honest and say that you found no definitive answer instead of just confirming what you think your boss or coworkers expect or want to hear. Experts and good researchers are willing to say that they don’t know.
Stay organized. Being able to cite sources accurately and present all your findings is just as important as conducting the research itself. Start practicing good organizational skills , both on your devices and for any physical products you’re using.
Get specific as you go. There’s nothing wrong with starting your research in a general way. After all, it’s important to become familiar with the terminology and basic gist of the researcher’s findings before you dig down into all the minutia.
Highlighting your research skills in a job interview
A job interview is itself a test of your research skills. You can expect questions on what you know about the company, the role, and your field or industry more generally. In order to give expert answers on all these topics, research is crucial.
Start by researching the company . Look into how they communicate with the public through social media, what their mission statement is, and how they describe their culture.
Pay close attention to the tone of their website. Is it hyper professional or more casual and fun-loving? All of these elements will help decide how best to sell yourself at the interview.
Next, research the role. Go beyond the job description and reach out to current employees working at your desired company and in your potential department. If you can find out what specific problems your future team is or will be facing, you’re sure to impress hiring managers and recruiters with your ability to research all the facts.
Finally, take time to research the job responsibilities you’re not as comfortable with. If you’re applying for a job that represents increased difficulty or entirely new tasks, it helps to come into the interview with at least a basic knowledge of what you’ll need to learn.
How to include research skills on your resume
Research projects require dedication. Being committed is a valuable skill for hiring managers. Whether you’ve had research experience throughout education or a former job, including it properly can boost the success of your resume .
Consider how extensive your research background is. If you’ve worked on multiple, in-depth research projects, it might be best to include it as its own section. If you have less research experience, include it in the skills section .
Focus on your specific role in the research, as opposed to just the research itself. Try to quantify accomplishments to the best of your abilities. If you were put in charge of competitor research, for example, list that as one of the tasks you had in your career.
If it was a particular project, such as tracking the sale of women’s clothing at a tee-shirt company, you can say that you “directed analysis into women’s clothing sales statistics for a market research project.”
Ascertain how directly research skills relate to the job you’re applying for. How strongly you highlight your research skills should depend on the nature of the job the resume is for. If research looks to be a strong component of it, then showcase all of your experience.
If research looks to be tangential, then be sure to mention it — it’s a valuable skill — but don’t put it front and center.
Resume examples showcasing research skills
Example #1: Academic Research
Simon Marks 767 Brighton Blvd. | Brooklyn, NY, 27368 | (683)-262-8883 | [email protected] Diligent and hardworking recent graduate seeking a position to develop professional experience and utilize research skills. B.A. in Biological Sciences from New York University. PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE Lixus Publishing , Brooklyn, NY Office Assistant- September 2018-present Scheduling and updating meetings Managing emails and phone calls Reading entries Worked on a science fiction campaign by researching target demographic Organizing calendars Promoted to office assistant after one year internship Mitch’s Burgers and Fries , Brooklyn, NY Restaurant Manager , June 2014-June 2018 Managed a team of five employees Responsible for coordinating the weekly schedule Hired and trained two employees Kept track of inventory Dealt with vendors Provided customer service Promoted to restaurant manager after two years as a waiter Awarded a $2.00/hr wage increase SKILLS Writing Scientific Research Data analysis Critical thinking Planning Communication RESEARCH Worked on an ecosystem biology project with responsibilities for algae collection and research (2019) Lead a group of freshmen in a research project looking into cell biology (2018) EDUCATION New York University Bachelors in Biological Sciences, September 2016-May 2020
Example #2: Professional Research
Angela Nichols 1111 Keller Dr. | San Francisco, CA | (663)-124-8827 |[email protected] Experienced and enthusiastic marketer with 7 years of professional experience. Seeking a position to apply my marketing and research knowledge. Skills in working on a team and flexibility. EXPERIENCE Apples amp; Oranges Marketing, San Francisco, CA Associate Marketer – April 2017-May 2020 Discuss marketing goals with clients Provide customer service Lead campaigns associated with women’s health Coordinating with a marketing team Quickly solving issues in service and managing conflict Awarded with two raises totaling $10,000 over three years Prestigious Marketing Company, San Francisco, CA Marketer – May 2014-April 2017 Working directly with clients Conducting market research into television streaming preferences Developing marketing campaigns related to television streaming services Report writing Analyzing campaign success statistics Promoted to Marketer from Junior Marketer after the first year Timberlake Public Relations, San Francisco, CA Public Relations Intern – September 2013–May 2014 Working cohesively with a large group of co-workers and supervisors Note-taking during meetings Running errands Managing email accounts Assisting in brainstorming Meeting work deadlines EDUCATION Golden Gate University, San Francisco, CA Bachelor of Arts in Marketing with a minor in Communications – September 2009 – May 2013 SKILLS Marketing Market research Record-keeping Teamwork Presentation. Flexibility
Research skills FAQs
What research skills are important?
Goal-setting and data collection are important research skills. Additional important research skills include:
Using different sources to analyze information.
Finding information on the internet.
Interviewing sources.
Writing reports.
Critical thinking.
Planning and scheduling.
Note-taking.
Managing time.
How do you develop good research skills?
You develop good research skills by learning how to find information from multiple high-quality sources, by being wary of confirmation bias, and by starting broad and getting more specific as you go.
When you learn how to tell a reliable source from an unreliable one and get in the habit of finding multiple sources that back up a claim, you’ll have better quality research.
In addition, when you learn how to keep an open mind about what you’ll find, you’ll avoid falling into the trap of confirmation bias, and by staying organized and narrowing your focus as you go (rather than before you start), you’ll be able to gather quality information more efficiently.
What is the importance of research?
The importance of research is that it informs most decisions and strategies in a business. Whether it’s deciding which products to offer or creating a marketing strategy, research should be used in every part of a company.
Because of this, employers want employees who have strong research skills. They know that you’ll be able to put them to work bettering yourself and the organization as a whole.
Should you put research skills on your resume?
Yes, you should include research skills on your resume as they are an important professional skill. Where you include your research skills on your resume will depend on whether you have a lot of experience in research from a previous job or as part of getting your degree, or if you’ve just cultivated them on your own.
If your research skills are based on experience, you could put them down under the tasks you were expected to perform at the job in question. If not, then you should likely list it in your skills section.
University of the People – The Best Research Skills for Success
Association of Internet Research Specialists — What are Research Skills and Why Are They Important?
MasterClass — How to Improve Your Research Skills: 6 Research Tips
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Sky Ariella is a professional freelance writer, originally from New York. She has been featured on websites and online magazines covering topics in career, travel, and lifestyle. She received her BA in psychology from Hunter College.

Related posts

50 Jobs That Use Seo The Most
What Is A Visual Learner?
What Is Figurative Language? (With Examples)
How To Multitask At Work (With Examples)
- Career Advice >
- Hard Skills >
- Research Skills
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Oncol Pract
- v.3(6); 2007 Nov
Developing Effective Communication Skills
A practicing oncologist likely uses just about every medium to communicate. They talk on the phone, send e-mail messages, converse one-on-one, participate in meetings, and give verbal and written orders. And they communicate with many audiences—patients and their families, referring physicians, and office staff.
But are you communicating effectively? How do you handle differing or challenging perspectives? Are you hesitant to disagree with others, especially those in authority? Do you find meetings are a waste of time? What impression does your communication style make on the members of your group?
Be an Active Listener
The starting place for effective communication is effective listening. “Active listening is listening with all of one's senses,” says physician communication expert Kenneth H. Cohn, MD, MBA, FACS. “It's listening with one's eyes as well as one's years. Only 8% of communication is related to content—the rest pertains to body language and tone of voice.” A practicing surgeon as well as a consultant, Cohn is the author of Better Communication for Better Care and Collaborate for Success!

Kenneth H. Cohn, MD, MBA, FACS
Cohn suggests creating a setting in which “listening can be accommodating.” For example, don't have a conversation when one person is standing and one person is sitting—make sure your eyes are at the same level. Eliminate physical barriers, such as a desk, between you and the other party. Acknowledge the speaker with your own body language: lean forward slightly and maintain eye contact. Avoid crossing your arms, which conveys a guarded stance and may suggest arrogance, dislike, or disagreement.
When someone is speaking, put a premium on “being present.” Take a deep breath (or drink some water to keep from speaking) and create a mental and emotional connection between you and the speaker. “This is not a time for multitasking, but to devote all the time to that one person,” Cohn advises. “If you are thinking about the next thing you have to do or, worse, the next thing you plan to say, you aren't actively listening.”
Suspending judgment is also part of active listening, according to Cohn. Encourage the speaker to fully express herself or himself—free of interruption, criticism, or direction. Show your interest by inviting the speaker to say more with expressions such as “Can you tell me more about it?” or “I'd like to hear about that.”
Finally, reflect back to the speaker your understanding of what has been said, and invite elaboration and clarification. Responding is an integral part of active listening and is especially important in situations involving conflict.
In active listening, through both words and nonverbal behavior, you convey these messages to the speaker:
- I understand your problem
- I know how you feel about it
- I am interested in what you are saying
- I am not judging you
Communication Is a Process
Effective communication requires paying attention to an entire process, not just the content of the message. When you are the messenger in this process, you should consider potential barriers at several stages that can keep your intended audience from receiving your message.
Be aware of how your own attitudes, emotions, knowledge, and credibility with the receiver might impede or alter whether and how your message is received. Be aware of your own body language when speaking. Consider the attitudes and knowledge of your intended audience as well. Diversity in age, sex, and ethnicity or race adds to the communication challenges, as do different training backgrounds.
Individuals from different cultures may assign very different meanings to facial expressions, use of space, and, especially, gestures. For example, in some Asian cultures women learn that it is disrespectful to look people in the eye and so they tend to have downcast eyes during a conversation. But in the United States, this body language could be misinterpreted as a lack of interest or a lack of attention.
Choose the right medium for the message you want to communicate. E-mail or phone call? Personal visit? Group discussion at a meeting? Notes in the margin or a typed review? Sometimes more than one medium is appropriate, such as when you give the patient written material to reinforce what you have said, or when you follow-up a telephone conversation with an e-mail beginning, “As we discussed.…”
For one-on-one communication, the setting and timing can be critical to communicating effectively. Is a chat in the corridor OK, or should this be a closed-door discussion? In your office or over lunch? Consider the mindset and milieu of the communication receiver. Defer giving complex information on someone's first day back from vacation or if you are aware of situations that may be anxiety-producing for that individual. Similarly, when calling someone on the phone, ask initially if this is a convenient time to talk. Offer to set a specific time to call back later.
Finally, organize content of the message you want to communicate. Make sure the information you are trying to convey is not too complex or lengthy for either the medium you are using or the audience. Use language appropriate for the audience. With patients, avoid medical jargon.
Be Attuned to Body Language—Your Own and Others
Many nonverbal cues such as laughing, gasping, shoulder shrugging, and scowling have meanings that are well understood in our culture. But the meaning of some of these other more subtle behaviors may not be as well known. 1
Hand movements. Our hands are our most expressive body parts, conveying even more than our faces. In a conversation, moving your hand behind your head usually reflects negative thoughts, feelings, and moods. It may be a sign of uncertainty, conflict, disagreement, frustration, anger, or dislike. Leaning back and clasping both hands behind the neck is often a sign of dominance.
Blank face. Though theoretically expressionless, a blank face sends a strong do not disturb message and is a subtle sign to others to keep a distance. Moreover, many faces have naturally down turned lips and creases of frown lines, making an otherwise blank face appear angry or disapproving.
Smiling. Although a smile may show happiness, it is subject to conscious control. In the United States and other societies, for example, we are taught to smile whether or not we actually feel happy, such as in giving a courteous greeting.
Tilting the head back. Lifting the chin and looking down the nose are used throughout the world as nonverbal signs of superiority, arrogance, and disdain.
Parting the lips. Suddenly parting one's lips signals mild surprise, uncertainty, or unvoiced disagreement.
Lip compression. Pressing the lips together into a thin line may signal the onset of anger, dislike, grief, sadness, or uncertainty.
Build a Team Culture
In oncology, as in most medical practices, much of the work is done by teams. Communication within a team calls for clarifying goals, structuring responsibilities, and giving and receiving credible feedback.
“Physicians in general are at a disadvantage because we haven't been trained in team communication,” says Cohn. He points out that when he was in business school, as much as 30% to 50% of a grade came from team projects. “But how much of my grade in medical school was from team projects? Zero.”
The lack of systematic education about how teams work is the biggest hurdle for physicians in building a team culture, according to Cohn. “We've learned team behaviors from our clinical mentors, who also had no formal team training. The styles we learn most in residency training are ‘command and control’ and the ‘pace setting approach,’ in which the leader doesn't specify what the expectations are, but just expects people to follow his or her example.”
Cohn says that both of those styles limit team cohesion. “Recognizing one's lack of training is the first step [in overcoming the hurdle], then understanding that one can learn these skills. Listening, showing sincere empathy, and being willing to experiment with new leadership styles, such as coaching and developing a shared vision for the future are key.”
Stated goals and team values. An effective team is one in which everyone works toward a common goal. This goal should be clearly articulated. In patient care, of course, the goal is the best patient outcomes. But a team approach is also highly effective in reaching other goals in a physician practice, such as decreasing patient waiting times, recruiting patients for a clinical trial, or developing a community education program. Every member of the team must be committed to the team's goal and objectives.
Effective teams have explicit and appropriate norms, such as when meetings will be held and keeping information confidential. Keep in mind that it takes time for teams to mature and develop a climate of trust and mutual respect. Groups do not progress from forming to performing without going through a storming phase in which team members negotiate assumptions and expectations for behavior. 2
Clear individual expectations. All the team members must be clear about what is expected of them individually and accept their responsibility for achieving the goal. They should also understand the roles of others. Some expectations may relate to their regular job duties; others may be one-time assignments specific to the team goal. Leadership of the team may rotate on the basis of expertise.
Members must have resources available to accomplish their tasks, including time, education and equipment needed to reach the goal. Openly discuss what is required to get the job done and find solutions together as a team.
Empowerment. Everyone on the team should be empowered to work toward the goal in his or her own job, in addition to contributing ideas for the team as a whole. Physicians' instinct and training have geared them to solve problems and give orders—so they often try to have all the answers. But in an effective team, each team member feels ownership in the outcome and has a sense of shared accountability. Cohn notes, “You get a tremendous amount of energy and buy-in when you ask ‘What do you think?’”
Team members must trust each other with important tasks. This requires accepting others for who they are, being creative, and taking prudent risks. Invite team members to indicate areas in which they would like to take initiative. Empower them by giving them the freedom to exercise their own discretion.
Feedback. Providing feedback on performance is a basic tenet of motivation. For some goals, daily or weekly results are wanted, while for others, such as a report of the number of medical records converted to a new system or the average patient waiting times, a monthly report might be appropriate. Decide together as a team what outcomes should be reported and how often.
Positive reinforcement. Team members should encourage one another. Take the lead and set an example by encouraging others when they are down and praising them when they do well. Thank individuals for their contributions, both one on one and with the team as a whole. Celebrate milestones as a way to sustain team communication and cohesion.
Effective E-mail
E-mail has numerous features that make it a wonderful tool for communicating with a team: it is immediate; it is automatically time-stamped; and filing and organizing are easy. (E-mail with patients is a more complex topic and is not addressed herein.)
The e-mail subject line is an especially useful feature that is typically underused. Make it your best friend. Use it like a newspaper headline, to draw the reader in and convey your main point or alert the reader to a deadline. In the examples given below, the person receiving an e-mail headed “HCC” is likely to scroll past it—planning to read it on the weekend. The more helpful subject line alerts the reader to be prepared to discuss the topic at an upcoming meeting:
- Vague Subject Line: HCC
- More Helpful Subject Line: HCC Plan to discuss the SHARP trial this Friday—Your comments due December 5 on attached new policies
As with all written communication, the most important aspect to consider is the audience. Consider the knowledge and biases of the person/people you are e-mailing. Where will the reader be when he or she receives your message? How important is your message to the reader?
The purpose of writing is to engage the reader. You want the reader to do something, to know something, or to feel something. Write it in a way that helps the reader. Put the most important information—the purpose of the email—in the first paragraph.
Except among friends who know you well, stay away from sarcasm in e-mail messages. The receiver does not have the benefit of your tone of voice and body language to help interpret your communication. When delivering comments that are even slightly critical, it's better to communicate in person or in a phone call than to do so in an e-mail. Something you wrote with good intentions and an open mind or even with humor can be interpreted as nitpicky, negative, and destructive, and can be forwarded to others.
Because we use e-mail for its speed, it's easy to get in the habit of dashing off a message and hitting the “send” button. We count on the automatic spell-check (and you should have it turned on as your default option) to catch your errors. But spelling typos are the least of the problems in communicating effectively.
Take the time to read through your message. Is it clear? Is it organized? Is it concise? See if there is anything that could be misinterpreted or raises unanswered questions. The very speed with which we dash off e-mail messages makes e-mail the place in which we are most likely to communicate poorly.
Finally, don't forget to supply appropriate contact information, including phone numbers or alternative e-mail addresses, for responses or questions.
Conflict is inevitable in times of rapid change. Effective communication helps one avoid conflict and minimize its adverse consequences when it does occur. The next issue of Strategies for Career Success will cover conflict management.
What Not to Do When Listening:
- Allow distractions
- Use clichéd phrases such as “I know exactly how you feel,” “It's not that bad,” or “You'll feel better tomorrow”
- Get pulled into responding emotionally
- Change the subject or move in a new direction
- Rehearse in your head what you plan to say next
- Give advice
Make Meetings Work for Your Team
A good meeting is one in which team goals are introduced or reinforced and solutions are generated. The first rule—meet in person only if it's the best format to accomplish what you want. You don't need a meeting just to report information. Here are tips for facilitating an effective meeting:
Don't meet just because it's scheduled. If there are no issues to discuss, don't hold the meeting just because it's Tuesday and that's when you always meet.
Use an agenda. Circulate a timed agenda beforehand and append useful background information. Participants should know what to expect. If it's a short meeting or quickly called, put the agenda on a flipchart or board before people arrive.
Structure input. Promote the team culture by making different individuals responsible for specific agenda items. Follow-up on previous task assignments as the first agenda item to hold group members accountable for the team's success.
Limit the meeting time. Use the timed agenda to stay on track. If the discussion goes off on a tangent, bring the group back to the objective of the topic at hand. If it becomes clear that a topic needs more time, delineate the issues and the involved parties and schedule a separate meeting.
Facilitate discussion. Be sure everyone's ideas are heard and that no one dominates the discussion. If two people seem to talk only to each other and not to the group as a whole, invite others to comment. If only two individuals need to pursue a topic, suggest that they continue to work on that topic outside the meeting.
Set ground rules up front. Keep meetings constructive, not a gripe session. Do not issue reprimands, and make it clear that the meeting is to be positive and intended for updates, analysis, problem solving, and decision making. Create an environment in which disagreement and offering alternative perspectives are acceptable. When individuals do offer opposing opinions, facilitate open discussion that focuses on issues and not personalities.
Circulate a meeting summary before the next meeting. Formal minutes are appropriate for some meetings. But in the very least, a brief summary of actions should be prepared. Include decisions reached and assignments made, with deadlines for follow-up at the next meeting.
Kenneth H. Cohn: Better Communication for Better Care: Mastering Physician-Administrator Collaboration. Chicago, IL, Health Administration Press, 2005, www.ache.org/pubs/redesign/productcatalog.cfm?pc=WWW1-2038
Kenneth H. Cohn: Collaborate for Success! Breakthrough Strategies for Engaging Physicians, Nurses, and Hospital Executives. Chicago, IL, Health Administration Press, 2006, www.ache.org/hap.cfm
Suzette Haden Elgin: Genderspeak: Men, Women, and the Gentle Art of Verbal Self-Defense. Hoboken, NJ, Wiley, 1993
Jon R. Katzenbach, Douglas K. Smith: The Wisdom of Teams: Creating the High Performance Organization. New York, NY, Harper Business, 1994
Sharon Lippincott: Meetings: Do's, Don'ts, and Donuts. Pittsburgh, PA, Lighthouse Point Press, 1994
Kenneth W. Thomas: Intrinsic Motivation at Work: Building Energy and Commitment. San Francisco, CA, Berrett-Koehler Publishers, 2000
More Strategies for Career Success!
Deciding About Practice Options—J Oncol Pract 2:187-190, 2006
The Interview: Make it Work for You—J Oncol Pract 2:252-254, 2006
Employment Contracts: What to Look for—J Oncol Pract 2:308-311, 2006
Principles and Tactics of Negotiation—J Oncol Pract 3:102-105, 2007
Professional Advisors: They're Worth It—J Oncol Pract 3:162-166, 2007
Building and Maintaining a Referral Base—J Oncol Pract 3:227-230, 2007
Malpractice Insurance: What You Need to Know—J Oncol Pract 3:274-277, 2007
Joining a Practice As a Shareholder—J Oncol Pract 3:41-44, 2007.
8 Ways You Can Improve Your Communication Skills
Your guide to establishing better communication habits for success in the workplace.
Mary Sharp Emerson
A leader’s ability to communicate clearly and effectively with employees, within teams, and across the organization is one of the foundations of a successful business.
And in today’s complex and quickly evolving business environment, with hundreds of different communication tools, fully or partially remote teams, and even multicultural teams spanning multiple time zones, effective communication has never been more important — or more challenging.
Thus, the ability to communicate might be a manager’s most critical skill.
The good news is that these skills can be learned and even mastered.
These eight tips can help you maximize your communication skills for the success of your organization and your career.
1. Be clear and concise
Communication is primarily about word choice. And when it comes to word choice, less is more.
The key to powerful and persuasive communication — whether written or spoken — is clarity and, when possible, brevity.
Before engaging in any form of communication, define your goals and your audience.
Outlining carefully and explicitly what you want to convey and why will help ensure that you include all necessary information. It will also help you eliminate irrelevant details.
Avoid unnecessary words and overly flowery language, which can distract from your message.
And while repetition may be necessary in some cases, be sure to use it carefully and sparingly. Repeating your message can ensure that your audience receives it, but too much repetition can cause them to tune you out entirely.
2. Prepare ahead of time
Know what you are going to say and how you are going to say before you begin any type of communication.
However, being prepared means more than just practicing a presentation.
Preparation also involves thinking about the entirety of the communication, from start to finish. Research the information you may need to support your message. Consider how you will respond to questions and criticisms. Try to anticipate the unexpected.
Before a performance review, for instance, prepare a list of concrete examples of your employee’s behavior to support your evaluation.
Before engaging in a salary or promotion negotiation, know exactly what you want. Be ready to discuss ranges and potential compromises; know what you are willing to accept and what you aren’t. And have on hand specific details to support your case, such as relevant salaries for your position and your location (but be sure that your research is based on publicly available information, not company gossip or anecdotal evidence).
Before entering into any conversation, brainstorm potential questions, requests for additional information or clarification, and disagreements so you are ready to address them calmly and clearly.

3. Be mindful of nonverbal communication
Our facial expressions, gestures, and body language can, and often do, say more than our words.
Nonverbal cues can have between 65 and 93 percent more impact than the spoken word. And we are more likely to believe the nonverbal signals over spoken words if the two are in disagreement.
Leaders must be especially adept at reading nonverbal cues.
Employees who may be unwilling to voice disagreements or concerns, for instance, may show their discomfort through crossed arms or an unwillingness to make eye contact. If you are aware of others’ body language, you may be able to adjust your communication tactics appropriately.
At the same time, leaders must also be able to control their own nonverbal communications.
Your nonverbal cues must, at all times, support your message. At best, conflicting verbal and nonverbal communication can cause confusion. At worst, it can undermine your message and your team’s confidence in you, your organization, and even in themselves.
4. Watch your tone
How you say something can be just as important as what you say. As with other nonverbal cues, your tone can add power and emphasis to your message, or it can undermine it entirely.
Tone can be an especially important factor in workplace disagreements and conflict. A well-chosen word with a positive connotation creates good will and trust. A poorly chosen word with unclear or negative connotations can quickly lead to misunderstanding.
When speaking, tone includes volume, projection, and intonation as well as word choice. In real time, it can be challenging to control tone to ensure that it matches your intent. But being mindful of your tone will enable you to alter it appropriately if a communication seems to be going in the wrong direction.
Tone can be easier to control when writing. Be sure to read your communication once, even twice, while thinking about tone as well as message. You may even want to read it out loud or ask a trusted colleague to read it over, if doing so does not breach confidentiality.
And when engaging in a heated dialogue over email or other written medium, don’t be too hasty in your replies.
If at all possible, write out your response but then wait for a day or two to send it. In many cases, re-reading your message after your emotions have cooled allows you to moderate your tone in a way that is less likely to escalate the conflict.
Browse our Communication programs.
5. Practice active listening
Communication nearly always involves two or more individuals.
Therefore, listening is just as important as speaking when it comes to communicating successfully. But listening can be more challenging than we realize.
In her blog post Mastering the Basics of Communication , communication expert Marjorie North notes that we only hear about half of what the other person says during any given conversation.
The goal of active listening is to ensure that you hear not just the words the person is saying, but the entire message. Some tips for active listening include:
- Giving the speaker your full and undivided attention
- Clearing your mind of distractions, judgements, and counter-arguments.
- Avoiding the temptation to interrupt with your own thoughts.
- Showing open, positive body language to keep your mind focused and to show the speaker that you are really listening
- Rephrase or paraphrase what you’ve heard when making your reply
- Ask open ended questions designed to elicit additional information
6. Build your emotional intelligence
Communication is built upon a foundation of emotional intelligence. Simply put, you cannot communicate effectively with others until you can assess and understand your own feelings.
“If you’re aware of your own emotions and the behaviors they trigger, you can begin to manage these emotions and behaviors,” says Margaret Andrews in her post, How to Improve Your Emotional Intelligence .
Leaders with a high level of emotional intelligence will naturally find it easier to engage in active listening, maintain appropriate tone, and use positive body language, for example.
Understanding and managing your own emotions is only part of emotional intelligence. The other part — equally important for effective communication — is empathy for others.
Empathizing with an employee can, for example, make a difficult conversation easier.
You may still have to deliver bad news, but (actively) listening to their perspective and showing that you understand their feelings can go a long way toward smoothing hurt feelings or avoiding misunderstandings.
7. Develop a workplace communication strategy
Today’s workplace is a constant flow of information across a wide variety of formats. Every single communication must be understood in the context of that larger flow of information.
Even the most effective communicator may find it difficult to get their message across without a workplace communication strategy.
A communication strategy is the framework within which your business conveys and receives information. It can — and should — outline how and what you communicate to customers and clients, stakeholders, and managers and employees.
Starting most broadly, your strategy should incorporate who gets what message and when. This ensures that everyone receives the correct information at the right time.
It can be as detailed as how you communicate, including defining the type of tools you use for which information. For example, you may define when it’s appropriate to use a group chat for the entire team or organization or when a meeting should have been summarized in an email instead.
Creating basic guidelines like this can streamline the flow of information. It will help ensure that everyone gets the details they need and that important knowledge isn’t overwhelmed by extraneous minutia.
8. Create a positive organizational culture
The corporate culture in which you are communicating also plays a vital role in effective communication.
In a positive work environment — one founded on transparency, trust, empathy, and open dialogue — communication in general will be easier and more effective.
Employees will be more receptive to hearing their manager’s message if they trust that manager. And managers will find it easier to create buy-in and even offer constructive criticism if they encourage their employees to speak up, offer suggestions, and even offer constructive criticisms of their own.
“The most dangerous organization is a silent one,” says Lorne Rubis in a blog post, Six Tips for Building a Better Workplace Culture . Communication, in both directions, can only be effective in a culture that is built on trust and a foundation of psychological safety.
Authoritative managers who refuse to share information, aren’t open to suggestions, and refuse to admit mistakes and accept criticism are likely to find their suggestions and criticisms met with defensiveness or even ignored altogether.
Without that foundation of trust and transparency, even the smallest communication can be misconstrued and lead to misunderstandings and unnecessary conflict.
Communicating with co-workers and employees is always going to present challenges. There will always be misunderstandings and miscommunications that must be resolved and unfortunately, corporate messages aren’t always what we want to hear, especially during difficult times.
But building and mastering effective communication skills will make your job easier as a leader, even during difficult conversations. Taking the time to build these skills will certainly be time well-spent.
Want to build your skills? Find the program that’s right for you.
Browse all Professional & Executive Development programs.
About the Author
Digital Content Producer
Emerson is a Digital Content Producer at Harvard DCE. She is a graduate of Brandeis University and Yale University and started her career as an international affairs analyst. She is an avid triathlete and has completed three Ironman triathlons, as well as the Boston Marathon.
Harvard Professional Development Participant Success Stories
Read about how these skilled professionals used the knowledge and skills they learned in a Harvard PDP to further their career development.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

Foster strong communication skills to enjoy professional success

Jump to section
What are communication skills?
The 5 main types of communication, why should you strengthen your communication skills, the top 7 communication skills for effective communication in the workplace, putting your communication skills to work, understanding yourself.
Humans are communicative animals. From early on, you meet your needs by expressing yourself via audible cries or nonverbal gestures.
Throughout your life, communication affects your fulfillment levels. You can tackle arguments quickly if you’re expressing yourself well and listening actively to the other person. And you’ll enjoy deeper relationships if you can share openly and be vulnerable .
It’s no wonder workplaces prioritize strong communication skills when hiring. Employers want employees who express themselves well to ensure they’re being proactive about having their needs met and can handle workplace conflict tactfully.
When looking for a new job , don’t underestimate the importance of strong communication skills. In a recent survey by GMAC, corporate recruiters ranked oral communication skills in first place on a list of 25 professional skills that included analysis, creativity , and drive.
Listening skills came in second, written communication was fourth, and presentation skills rounded out the top five.
In the same GMAC survey, 81% of recruiters said that interpersonal skills (which include communication skills) were most sought-after, and 57% said the demand for interpersonal skills will grow over the next five years.
It’s clear: developing strong communication skills is a wise investment in your professional future.
Communication skills are the abilities that allow you to effectively share your thoughts and emotions and understand others’. People with excellent communication skills express themselves clearly and effectively interpret what others say.
In the workplace, effective communication is vital . If managers can’t communicate what they want or employees can’t succinctly describe a problem to coworkers, misunderstandings increase, as do mistakes and conflicts.
There are five main types of communication: written, oral (also called “spoken” or “verbal”), nonverbal, visual, and receptive.
1. Oral communication
This involves using spoken words to convey ideas. Politicians giving speeches, parents telling bedtime stories, and workers in Zoom meetings all use oral communication skills to express their thoughts and feelings and understand others’.
2. Nonverbal communication
Nonverbal communication is everything that’s unspoken when someone’s communicating with others, including:
Body language
Hand gestures
Eye contact
Tone of voice
Use of space
Appearance ( like clothing )
While nonverbal communication is most powerful in face-to-face contexts, such as in-person meetings and presentations , it also plays a role in remote work environments. Think about how closely you pay attention to people’s facial expressions (and Zoom backgrounds) in online meetings and webinars.
3. Written communication
Written communication involves using written or typed words (plus punctuation marks and emojis) to convey ideas. Unlike oral communication, written communication is typically asynchronous , meaning that writer and reader aren’t engaging with the message at the same time.
Because written communication is often asynchronous, receivers don’t get as many supporting cues as in oral communication. You can’t see the author’s facial expressions or hear their voice’s tone.
If you’re not extra careful to convey the right emotional tone in written communication, you risk being misinterpreted.

4. Visual communication
Visual communication involves expressing ideas and feelings through illustrations, images, and design. This type often supports other forms of communication. Infographics, for example, are a combination of visual and written communication.
5. Receptive communication
Receptive communication is the ability to decode oral, nonverbal, written, and visual communication. This is the half of the communication equation most people forget, but it’s crucial: what’s the point of writing a story or creating an infographic if nobody can understand it?
Having the right communication skills for a job makes you a more attractive hire. If they’re looking for someone to correspond directly with clients, for example, your written communication skills will stand out .
But even after you get the job, communication challenges will surface in your professional life, like conflicts with a coworker or asking for a raise . To solve them, you’ll need to adapt your techniques and learn new ones constantly.
Strengthening different types of communication skills also helps you build and maintain working relationships , make more intelligent decisions , and motivate and inspire others . It could even increase your chances of getting a promotion since you’ll know how to communicate your value to your manager.
Adding excellent communication skills to your skillset will also make you a better leader. Transformational leaders show exceptional communication skills .
They can explain complex concepts using simple language, use powerful metaphors to make their messages stick, and unite people by sharing the company’s mission.

Here’s a list of the seven most crucial workplace communication skills with examples of communication competency in each and tips for developing them further.
1. Relationship building and maintenance
Human connection is fundamental to experiencing happiness, and genuine workplace connections improve one’s mental health . And the way you connect is by communicating with others: sharing your experiences, giving advice, listening attentively to show you care, etc.
Tips: Small talk is only small if you do it wrong. To enjoy deeper connections, try empathizing with others , asking questions , and using the FORD acronym (family, occupation, recreation, dreams) to brainstorm topics.
And to maintain these relationships, note small details about people (their childrens’ and pets’ names, things they said they were going to do, their food or drink preferences) and bring them up later. To repair relationships, learn how to apologize gracefully and sincerely.
2. Group facilitating
Facilitation is guiding a group of people through a process to achieve a particular goal. Having to chair a meeting , resolve a conflict, or lead a group discussion are all nerve-wracking. But good facilitation is a skill you can learn — and the better you are at it, the less talking you need to do.
Tips: Foster the right emotional environment to help the group reach its goals. When facilitating a brainstorming session, aim to generate positive emotions through praise and enthusiasm, as feeling good makes people more creative .
If you need to solve a problem together, channeling frustration can motivate people to find solutions.
3. Public speaking
Getting comfortable with public speaking will advance your career in leaps and bounds.
Public speaking helps you demonstrate leadership potential within your own company. It also builds your professional reputation, expands your professional network , and exposes you to cutting-edge advances in your industry through attendance at conferences and other professional events.
Tips: Even the best public speakers get nervous. Manage your anxiety before presentations by preparing thoroughly, breathing deeply , and practicing.
Consider asking for feedback on aspects of your nonverbal communication to make sure you radiate a natural confidence , warmth, and professional competence.
Though some people recommend practicing in front of a mirror, this might make you self-conscious. Instead, ask a colleague or coach to listen, or even deliver the talk to your pet.
If it’s an online presentation, check the technology in advance, make sure your background is professional, and look directly into the camera.
4. Storytelling
Storytelling is a popular form of written and verbal communication that’s especially effective for leaders . Research shows that leaders who tell great stories unite their workers under common values and even bring in more investment dollars .
Tips: When telling a story, start with a hook to draw your audience in. Many workplace stories are about solving problems, so your hook could be a brief personal anecdote about a time you found yourself in a sticky situation. Listeners will want to pay attention to learn how you got out of it.
To refine your storytelling skills, develop an elevator pitch: a compelling version of an idea or project that you can communicate in under a minute (i.e., if you’re in an elevator with someone, you have to convince them it’s a great idea before they arrive at their floor).

5. Giving feedback
The best professional environments have a strong feedback culture . To create that culture, you need to be comfortable giving all kinds of feedback: constructive criticism that helps people improve, praise , upward feedback to your boss, and downward feedback to your direct reports.
Tips: When giving constructive feedback, show respect for the other person by listening to them carefully. Make it clear that you empathize with their position before making comments that may be hard to hear.
Consider whether structuring the feedback as a “ feedback sandwich ” (positive feedback, then suggestions for improvement, then more positive feedback) would help the worker assimilate the message.
If you’re a manager, make sure you consistently show appreciation to your team , as this improves morale and performance.
6. Receiving feedback
Receiving feedback can be difficult, even if it’s positive. But knowing how to receive feedback well is just as important as knowing how to give it. Listening carefully to feedback helps you develop self-awareness, improve your performance , and take a more active role in your professional development .
Tips: When you receive difficult feedback, remember that the intent behind the words is to help you improve, even if hearing it makes you feel bad in the moment.
Try to regulate your emotions by finding commonalities between you and the other person or cultivating curiosity about the negative feelings you’re experiencing. If you receive confusing feedback, ask questions to clarify the steps you can take to improve.
7. Active listening
Active listening is an important factor of good communication.
When you listen actively, you’re not just sitting quietly and letting the words wash over you — you’re participating in the conversation by offering supportive verbal and nonverbal responses, asking questions, and paraphrasing what the other person says to show you understand.
Tips: To improve your active listening skills, eliminate all distractions and focus completely on the speaker. Ask open-ended questions to encourage your conversation partner to keep talking.
Avoid interrupting, but do use short verbal and nonverbal responses (“ backchannels ”) like “yeah,” “mm-hm,” and head nodding to show you’re listening.
When applying for jobs, show off your communication skills by incorporating storytelling into cover letters and relevant examples into your resume and LinkedIn summary , as well as using the STAR framework (situation, task, action, result) to tell focused stories in job interviews.
Show recruiters and future team members you’re a good listener by paying close attention to what they’re saying in interviews, rephrasing key points they make, and sending nonverbal signals that you appreciate their point of view.
When you receive a job offer, keep demonstrating your skills by writing a great offer acceptance email . Then enjoy exercising and developing your skills in the new position.

Building strong communication skills makes you a great hire, friend, and family member. But it also means you’ll better understand yourself. You’ll notice when your body language has become defensive and can ease back, or when your voice’s volume is too soft for a large room and can amplify.
In the end, you’re learning more about your behavior to exercise control over unwanted habits and live a more authentic life — and that’s priceless.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Allaya Cooks-Campbell
With over 15 years of content experience, Allaya Cooks Campbell has written for outlets such as ScaryMommy, HRzone, and HuffPost. She holds a B.A. in Psychology and is a certified yoga instructor as well as a certified Integrative Wellness & Life Coach. Allaya is passionate about whole-person wellness, yoga, and mental health.
The 5 business communication skills worth perfecting
The significance of written communication in the workplace, 7-38-55 rule of communication: how to use for negotiation, member story: developing communication skills and owning the spotlight, how to improve your listening skills for better communication, improve your interpersonal communication skills with these 6 tips, 15 human resources skills to help your resume stand out, how to be more persuasive: 6 tips for convincing others, 18 jobs for extroverts to excel professionally, 18 effective strategies to improve your communication skills, relationship-building skills examples to practice at work, 11 communication skills every leader should have, 10 essential workplace skills for success, how to identify and overcome communication barriers at work, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

What are Communication Skills? A Comprehensive Guide
Great Communication Skills act as a pillar in your success story. This comprehensive blog will explain to you what Communication Skills are and how you can improve your Communication Skills. Read till the end to gain insights into how to communicate effectively and why it is important to pay attention to body language.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- English Speaking Course
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Executive Communication Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Your Communcation Skills act as your advocate, they represent who you are and add personality to your voice. And just like in court, you would like to have a good advocate to win your case and set you on the path to success.
This blog will help you understand what Communication Skills are and how you can work on them efficiently. Read till the end to gain insights into the Communication Skills you will need in a job interview. So, grab your briefcase and get ready to build your own advocate.
Table of Contents
1) What are Communication Skills?
2) How to improve your Communication Skills?
3) Why do you require Communication Skills?
4) Examples of Communication Skills
5) Communication Skills in job interviews
6) Conclusion
What are Communication Skills?
Communication Skills involve the methods used in conveying, receiving and processing information through verbal and non-verbal means. It includes speaking and listening effectively, interpreting gestures, body language, and emotions and being able to use the right communication on the right occasion. Communication Skills broadly refers to a person’s ability to establish rapport, work in teams, negotiate, quit and effectively deliver messages.
Effective Communication Skills encompass a variety of methods, such as written text, oral presentations, and digital platforms like email and social media. By enhancing these skills, you can swiftly mobilise your team, facilitating the swift and efficient achievement of your business objectives.
For instance, when discussing a particular issue or a subject, you want to be convincing and create a statement. It is crucial to involve people in the project and keep them informed about everything that goes on to guarantee accountability. It is also good to be able to describe how one feels and do so in a professional manner to maintain satisfactory working conditions.
Points to consider:
a) Business communication isn't limited to face-to-face or phone conversations.
b) Being comfortable with digital tools like Social Media and Email is essential for effective remote collaboration and networking.
c) Good business communication involves active listening, observing, and understanding others. It builds trust, improves teamwork, and leads to successful negotiations.

How to improve your Communication Skills?
The following tips will tell you all about How to Improve Your Communication Skills .
Consider your audience
Effective Communication begins with understanding your audience. Take the time to assess who you are communicating with. Consider their background, expertise, interests, and expectations. Whether you are speaking to a colleague, a client, or a group of employees, tailoring your message to align with their needs and preferences is crucial. By doing so, you can ensure that your message resonates more effectively and is more likely to be well-received.
Think about the most effective way to convey your message
Communication is not one-size-fits-all. One cannot overemphasise the fact that different circumstances require the adoption of different measures. Consider the message which you have to share and the environment where you need to dispatch it. Email, face-to-face meeting, or phone call – which is the best approach to address your conflict situations?
Take into account the subject matter of the message, the level of emergency and the audience’s propensity to read lengthy messages. Picking the right media and tonality improves the likelihood of your message being received and responded to.
Encourage participation
Effective communication is a dialogue, not a monologue. Promote engagement through cultivating an environment that welcomes all members. Encourage them to ask questions and to give us back their feedback and thoughts.
Listen to the things they say with interest, try to understand what they want to explain to you. If more people are willing to get involved into what is being said then they will consider it worthwhile to listen to what you have to say and even participate actively in the process. This participatory approach makes it easier to solve conflicts and early involvement of the workers should be encouraged.
Leverage face-to-face contact
Although instant and efficient, digital communication lacks a certain level of intimacy, especially when it comes to communicating in confidence, negotiating, and sharing sensitive information.
Generally, prefer face to face communication specially when the topic is serious or sensitive. At least, you are there and, in a position, to sense signals such as gestures, intonation, and looks, which may give one vital information or make a big difference.
Make eye contact
Interpersonal eye contact is a significant aspect of the non-verbal communication process. By increasing eye contact to an appropriate level, you make sure that the other person perceives you as interested, attentive, and receptive thereby enhancing interpersonal communication skills . It is affectionate and warm and enables a rapport to be built.
But do not overdo it because staring in a very intense manner or for an extended period of time takes people off guard or makes them feel uneasy. And there we have it; the whole idea is all about striking the perfect balance that will make the end result appealing to a broad range of people.
Recognise non-verbal cues
Communication is not only the use of words but also the meaning and having proper practices. When observing people’s communicative behaviour, focus on kinaesthetic, vocal, and ocular modes of communication. It is the unspoken communication or hidden messages that may help to understand people's feelings and responses.
Noting these cues enables a person to actively modify the conversational pattern in the ongoing interaction. For example, if the employee looks lost, you can help him/her by providing more information; or if they seem stressed, using reassuring and calming language.
Reduce interruptions
It is also important to reduce interferences during communication so that messages get to the intended recipient with ease. Focus entirely on what you are doing while talking to a partner. This not only does show respect of their time and ideas but also helps in focusing the communication and information exchange on a particular track.
If you’re working in front of a computer, minimise all the unnecessary windows, shut the chat programs and apps, make yourself comfortable, and be ready to have a meaningful Communication. In this way, you can make sure that people have an environment that can support idea sharing and no interruption.
Why do you require Communication Skills?
Communication Skills are necessary because they help us effectively share information, understand others, and build connections. Let’s dive deeper to know why Communication Skills are so important :
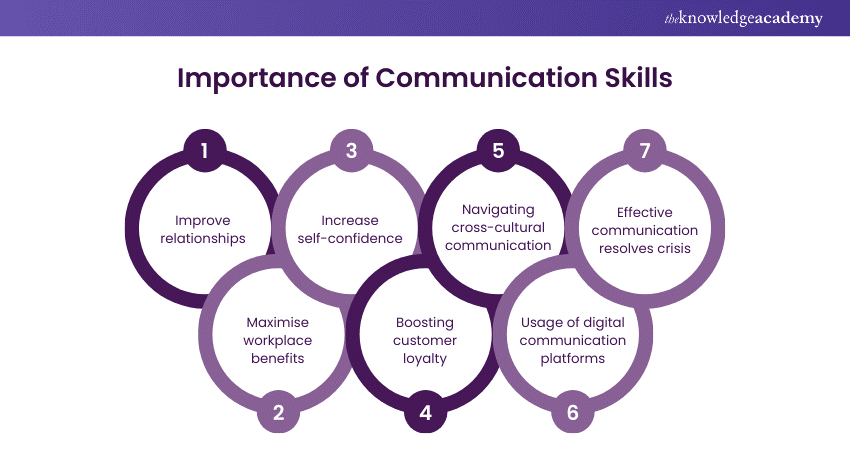
Improve relationships
When you work on your Communication Skills, you can share your ideas, emotions and needs, therefore developing better inter-personal relation. They resolve conflicts, establish trust, and improve relationships Therefore they improve relationships. Similar to Conflict Solving, Effective Communication also leads to better relations, empathy, active listening, and better means of responding.
Effective Communication is essential at all forms of the industry to ensure good working relations with other employees, customers, and investors. It helps to work together, establish rapport and foster, cooperation hence resulting in better performance and results in the organisation.
Level up your assertiveness with our Assertiveness Skills Training - Register now!
Maximise workplace benefits
Interpersonal communication is regarded as an essential component of business organisations. Communication enables the formulation of proper instructions, efficiency of the flow of information, and proper coordination in a particular team or organisation.
It is very effective in preventing misinterpretation and communication gaps that lead to conflict and sometimes costly mistakes. Also, the flow of information encourages a healthy workplace climate and increases the motivation and retention levels of workers.
Increase self-confidence
Practical Communication Skills in business can increase self-confidence by enabling individuals to express themselves, deliver impactful speeches, assert their needs, build professional relationships, and confidently handle challenging situations. Excellent Communication Skills enhance self-confidence, professional networking, and career advancement opportunities. They enable individuals to convey ideas, influence others, and showcase expertise, leading to greater recognition and success.
Boosting customer loyalty
Effective Communication Skills play an essential role in building and maintaining strong customer relationships. Businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by actively listening to customer needs, addressing their concerns promptly, and providing clear and empathetic communication. This improves business relations, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and long-term success.
Navigating cross-cultural communication
In today's global business landscape, cross-cultural Communication Skills are increasingly valuable. Understanding cultural gaps, adapting communication styles, and respecting diverse perspectives are essential for successful international collaborations and negotiations . Businesses prioritising cross-cultural Communication Skills gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Usage of digital communication platforms
Technology is advancing day by day hence a proper understanding and usage of digital media is highly important. Today, Business Communication Skills is not only limited to face-to-face and telephone communication. They also utilise platforms like e-mailing, Facebook, X (formally known as twitter), video conferencing and other virtual collaborating tools.
These channels can be mastered for facilitating, remote communication, virtual teams, and market expansion at a global level. Knowing how to use them effectively can work wonders to boost your business.
Effective communication resolves crisis
In the course of disasters or when the market situation is volatile, it is necessary to disseminate information widely to foster trust and confidence. Crisis management communication refers to the timely release of information. The compassionate approach of addressing stakeholders’ concerns and the active management of the stakeholder concerns during a particular crisis.
Hence, it is possible to sum up that only with appropriate, clear, and empathetic management of crises, companies are able to manage to avoid losses to their reputation and protect the trust of stakeholders with great care.
Master the art of Effective Communication with our Effective Communication Skills Course .Sign up now!
Examples of Communication Skills
When applying for a job, showcasing the Communication Skills that recruiters value in your cover letter and resume is essential. These skills are also crucial to demonstrate during your job interview. Here are some examples of Communication Skills and what they include:
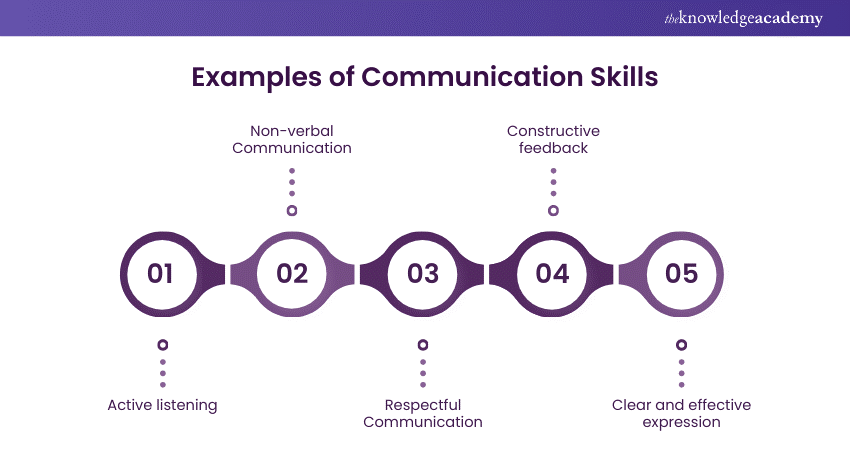
Active listening
Active listening means focusing entirely on and understanding what others say. It involves giving your undivided attention, asking clarifying questions, and providing verbal and non-verbal feedback to show you are engaged. For example, during a team meeting, actively listening would involve maintaining eye contact, nodding in agreement, and paraphrasing what others have said to demonstrate understanding, which are all essential aspects of effective verbal communication .
Non-verbal Communication
Non-verbal Communication refers to the messages conveyed through gestures, facial expressions, and body language. It plays a vital role in how others perceive and interpret your communication. For example, maintaining an open and confident posture, smiling, and using appropriate hand gestures can enhance communication effectiveness.
Respectful Communication
Respectful Communication include s treating others with dignity, courtesy, and consideration. It involves valuing diverse perspectives and opinions, even when they differ from your own. Respecting others' ideas creates a positive and inclusive work environment. During the Communication Skills Interview or in your cover letter, emphasising your ability to actively listen, appreciate differing viewpoints, and provide constructive feedback demonstrates respectful communication.
Learn how to implement effective strategies to improve cross-cultural Communication Skills with our Cross-Cultural Communications Training - Join today!
Constructive feedback
Giving and taking constructive feedback is crucial for personal and professional growth. It involves providing specific and actionable suggestions to help others improve. Being open to feedback and responding positively also showcases your willingness to learn and grow. In an interview, you can highlight instances where you have given or received constructive feedback, emphasising its generated positive outcomes.
Clear and effective expression
Clear communication is essential for accurately conveying ideas and information. It involves articulating thoughts clearly, using appropriate language and tone, and structuring your message concisely and organised. In your cover letter, resume, and interview responses, focus on showcasing your ability to express yourself effectively, using simple and concise language that is easy to understand.
Communication Skills for job interviews
In a job interview, make sure to actively listen to the person speaking to you. Make sure to sit straight and make eye contact with the interviewers whenever you are speaking. Remember to speak confidently, be positive, make eye contact and smile.
Almost everything you do, both in terms of the job interview as well as in life, can be seen as a form of communication. By correctly identifying and assessing your strengths and weaknesses and practising good communication habits, you can enhance your Communication Skills to a great extent.
Conclusion
To sum it up, e ffective Communication Skills are the key to building connections, fostering collaboration, and achieving success. Effective Communication promotes teamwork, collaboration, and problem-solving, improving productivity and positive outcomes. Improving your Communication Skills for personal and professional growth will help you explore better employment prospects and career options.
Learn real-world Communication Skills that can be applied in the organisation by registering for our Communication Skills Training . Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Effective communication is vital for career success as it fosters clarity and reduces the chance of misunderstandings. Good communication helps you create a collaborative environment that helps build teamwork and get work done.
Cultural awareness enhances communication by fostering respect for diverse perspectives, avoiding misunderstandings, and promoting inclusivity. Recognising and adapting to cultural differences strengthens relationships, boosts collaboration, and creates a harmonious environment.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Communication skills Courses including Negotiation skills and Negotiation techniques. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Negotiation methodologies.
Our blogs on Business skills covers a range of topics related to communication skills along with negotiation techniques and examples, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Communication skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

- Relationships
The Most Crucial Skill Sets for Successful Communication
Good communication depends on two skill sets that can be mastered..
Posted August 14, 2024 | Reviewed by Monica Vilhauer
- Why Relationships Matter
- Take our Relationship Satisfaction Test
- Find a therapist to strengthen relationships
- Learn how to speak clearly and listen deeply without being defensive.
- If someone begins to feel they are not being heard, the issue won't get resolved.
- Recognize how your own interaction with someone can rescue an argument.
I have spent more than four decades teaching basic communication skills to relationship partners. Successful communication depends on two sets of skills. The first is the mastery of the basic ABC's: learning how to speak clearly and listen deeply without defensiveness or invalidation of the other. Most relationship partners can practice and master these.
But, as is true for so many couples, these tried-and-true responses don’t always work when arguments become heated. If either partner begins to feel they are not going to be heard or get their needs met, they will be unable to resolve the issue that is causing their relationship distress.
To rescue a deteriorating argument, a couple must be able to activate the second skill, recognizing that something has gone wrong in the way they are interacting with each other. The interpersonal atmosphere is now tense and unsafe. The angry words being exchanged are becoming harsher. Exploration of different points of view is now impossible.
The example below illustrates how and when that second skill must be implemented to save an interaction that's going in the wrong direction.
Ben and Mary are trying to resolve an ongoing issue between them. They begin their interaction by using their basic communication skills. They are both trying hard to listen and understand the other’s point of view.
At some point, their interaction begins to go awry. They are both becoming more distressed and no longer feel heard by the other. Feelings and expressions escalate. Very soon, both of them are talking at each other rather than to each other.
They recognize that they are no longer on the same team. They have gone from two people who truly wanted to solve their dispute to trying to win an argument with an enemy. Both notice that the way in which they are interacting is interfering with their ability to listen objectively to what each is saying. They realize that, unless they feel and support each other’s mounting frustration and discouragement, and heal those reactions, they can no longer resolve the disagreement they are having.
The 2-Part Skill Sequence That Took Ben and Mary From Failing to Success
Ben: (expressing distress with his partner’s behavior)
“I’m really uncomfortable about the way you treated my mother yesterday. You didn’t need to be that harsh, even if she was a little out of line.”
Mary: (responding with good, basic communication skills)
“I really try to understand her need to control you and I try so hard to be patient and wait for you to stop her, but it really distresses me and sometimes I just can’t hold back.”
Ben: (wanting to hear her out but also to get his point across)
“Look, I know it’s hard, but she’s the only mother I have, so I need you to sacrifice for me here so I’m not in the middle.”
Mary: (now feeling unheard, misunderstood, and unsupported, feeling she has to counter-attack)
“So, what you’re telling me is that she comes first no matter what my feelings are.”
Ben: (now seeing Mary as an enemy and insulting her character)
“Don’t go there. We’ve had this discussion so many times. I’m getting really frustrated again. You just aren’t getting it.”
Mary: (now calling Ben someone who would sacrifice her to make himself okay)
“So, I’m just supposed to suck it up, just to make you more comfortable?”
Ben: (accusing Mary of trying to manipulate him)
“Don’t pull this martyr crap on me, just to change my mind.”
Their interaction has now deteriorated into a power struggle with only one possible winner. If it continues in this direction, a resolution will not be possible and the issue will come up again with the same result.
Mary realizes what is happening and switches to the second skill.
Mary: (realizing they are no longer able to resolve the situation because they’ve lost each other’s support and care)
“Hold on. We’re both so upset and we can’t hear each other anymore. We’ve lost each other’s support and understanding because we’re both afraid that we won’t get what we need. Let’s take a few minutes and calm down and get back on the same team. I love you and you love me. Your issues with your mom are yours to work out and I just need your support when they upset me.”

Ben: (feeling her correct assessment of how they’re losing each other in the way they are interacting)
“I’m sorry. I was feeling cornered and defensive, like I had to choose between the two of you. I hate it when I have to sacrifice you when she needs me but I just can’t abandon her when she is in so much trouble. I really need your help but I don’t want you to feel that you don’t matter because you are everything to me.”
Mary: (softening and feeling like they are connecting again)
“We can make this work. We just need to remember how much we love each other and not lose that when we need to fix something that is broken. I don’t have the connection to your mom the way you do and she does kind of drive me crazy at times, but I don’t want you to feel guilty either. I want to help you. At the same time, I know you have your own issues with her and we just need to find a way to balance things better.”
Ben: (noticeably relaxing, some tears, head in his hands)
“Thank you for caring. I feel more hopeful. You’re not my enemy or trying to hurt me, but sometimes I make you into that when I feel cornered. My mom can be too demanding. And when you care like this, it helps me to figure out how to set boundaries with her. I’ve always needed to do that.”
Mary: (putting her arms around him)
“We can do this together if we remember to stay connected when we’re trying to figure it out.”

Randi Gunther, Ph.D. , is a clinical psychologist and marriage counselor in Southern California.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
A Research on the Relationship Between Health Literacy Level and Health Communication Skills
- Conference: 10th International Conference on Lifelong Education and Leadership for All
- At: Óbuda University- Budapest / Hungary

- Dicle University

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
No full-text available
To read the full-text of this research, you can request a copy directly from the authors.
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
45+ Best Communication Skills for Your Resume (Examples)
Discover the best communication skills for your resume. From verbal to written communication, learn how to list and describe them to make a lasting impression.

When adding communication skills to your resume, focus on tailoring them to the job ad and using specific terms from the job description. Highlight achievements showcasing your communication strengths, whether it's leading a project, resolving conflicts, or using digital tools like Slack and Zoom. This not only aligns you with what employers are seeking, but also boosts your chances with applicant tracking systems. Always back up your skills with examples to show you can deliver results and work well with others.
Soft skills often get a bad rap for being less important. But they hold serious value — these skills are innate and not always teachable. Yet, simply stating “communication skills” in your resume is too vague to show off your strengths to a recruiter.
Solid communication is key to building relationships, expressing needs, and sharing information — it’s everywhere, including the workplace. The trick is to show your communication skills in a way that highlights what you can achieve and the potential you bring to the company.
And you can do this through your resume. This article will tell you:
- All the top communication skills to include.
- How to list your communication skills on a resume.
- The best ways to improve your abilities for future job opportunities.
What Are Communication Skills and Why They Matter on a Resume?
Communication skills are how you share ideas, listen, and respond to others, whether verbal, non-verbal, visual, or written. We use these skills every day, so I’ll spare you the full textbook definition — it’s basically how you get your point across and understand others.
Here’s how the main types of communication can translate into a resume:
- Verbal communication. We all learn to talk early on, but clear and confident communication is a skill that takes practice. On your resume, you can highlight cases where you led a meeting, conducted a presentation, or explained complex ideas to a colleague.
- Non-verbal communication. This includes body language, eye contact, and facial expressions. Ever noticed how a smile can make someone more approachable? That’s non-verbal communication in action. Demonstrate this on your resume by mentioning roles where you engaged with clients face-to-face, showing approachability and confidence.
- Written communication. Writing emails, reports, or even messages in a chat all fall under written communication. If you’ve ever written a LinkedIn post, a persuasive email, or a detailed report, highlight these experiences on your resume. Show your impact with examples of increased engagement or positive feedback.
- Visual communication. Using visuals like graphs, charts, or slides to communicate is a great way to get your message across. On your resume, you can mention creating PowerPoint presentations or designing infographics to convey complex ideas or data.
Many communication skills are considered soft skills because they are personal traits that largely come from everyday experience—think active listening or body language. But many others are hard skills because they require specific knowledge and, usually, on-the-job training—for instance, negotiation techniques or even presentation skills.
With that said, all communication skills are precisely that: skills, not talents . And skills you can learn and improve. Even if you don’t think of yourself as a natural-born communicator, you can take steps to get better at both “hard” and “soft” types of communication skills.
Why do communication skills matter to employers?
Employers want candidates who can clearly express themselves and work well with others — would you really want a Dwight in your office? Good communication can prevent misunderstandings and frustration, making the workplace more productive.
Communication skills are also crucial across many areas of professional life. You can apply them in business meetings, team projects, customer interactions, or those “networking” sessions in the office kitchen. Showing recruiters you’ve mastered the art of communication is showing them your versatility.
Here’s a round-up of the top communication skills to include on your resume:

Top Communication Skills Examples
Once your resume grabs the recruiter’s attention, be prepared to discuss all those impressive skills during the interview. Make sure you genuinely understand each skill you’ve listed and how it relates to your experience.
Here’s a rundown of the top communication skills and how they play out in the workplace:
Verbal communication
Verbal communication skills are basically about how good you are with the words and sounds that come out of your or other people’s mouths — about how well you articulate your thoughts and how well you understand what others say. These skills include expressing your ideas, dealing with customers, or persuading your boss to upgrade the office coffee machine.
Strong verbal communication tells employers you can articulate information, suggestions, and feedback. For roles involving customer interactions or leadership, having solid speaking skills shows you can convey messages clearly and lead with confidence. But remember, verbal communication (like any other form of communication) is a two-way street. Active listening is just as important as speaking clearly.
Most of us can hold a conversation, so be specific on your resume.
Here are some examples of how to list verbal communication on a resume:
- Interpersonal communication
- Listening skills
- Outbound calling
- Body language
- Foreign languages
- Presenting skills
Written communication
Written communication skills are about how well you convey information through messages, emails, reports, and notes. You don’t need to be a literary genius, but you should be clear and concise to avoid misunderstandings.
One key thing to note: even if your job title doesn’t immediately bring “writing” to mind, strong writing skills can still be an asset on your resume.
When you write well, you can inform and persuade through your words, whether drafting reports, creating social media posts, or sending emails. And with so many of us working remotely, knowing how to communicate professionally (without overusing emojis or exclamation marks) is always a plus.
Check out these valuable writing skills for your resume:
- Sending emails
- Proposal and report writing
- Spelling and grammar
- Editing skills
- Paraphrasing
- Translation
Giving and accepting feedback
Giving and accepting feedback helps improve performance and productivity by showing employees and managers what’s working and what needs to change.
Employers want to know you can handle constructive criticism without feeling like you’re under attack. Including this skill on your resume highlights that you’re committed to growth and can push others to do the same, making you a strong collaborator and proactive learner.
Here’s how to frame those skills on a resume to show you’re dedicated to your development:
- Constructive feedback
- Active listening
- Accountability
- Willingness to learn
- Open-mindedness
Team-building and collaboration
Team-building and collaboration involve working well with others to solve problems and achieve common goals. Effective team builders can delegate tasks, communicate clearly, and help team members grow.
Teamwork makes the dream work, so being able to share ideas and listen to others tells employers you can work harmoniously in a group. Highlighting team-building and collaboration on your resume also shows you can motivate and support your team toward success.
Here are some more skills to show you work well in a team:
- Team communication
- Delegation
- Goal setting
- Adaptability
- Taking ownership
- Inclusivity
Leadership skills
Leadership skills involve firing up your team, setting goals, training employees, and running operations. A successful leader can push their team to their full potential while making them feel valued and appreciated.
Trust is key, and people work better for managers they believe in — so your ability to build rapport and guide teams in a positive working environment is a must. Nobody feels inspired by a micromanaging boss breathing down their neck, right?
Here are some phrases that will make your leadership abilities shine on a resume:
- Management abilities
- Employee training
- Motivational feedback
- Planning and organization
- Interviewing skills
- Customer relationship management
Digital communication
Digital communication skills are essential in today’s remote and hybrid work environments. Knowing your way around Zoom, Slack, Asana and Microsoft Teams ensures easy collaboration and interaction.
Nobody wants to be the person who accidentally sends a private message to the entire team. Including this skill on your resume shows your ability to keep up with the times, especially handy for remote workers, or in areas like customer support or social media.
Consider listing these skills on your resume to show your technical communication prowess:
- Online meeting etiquette
- Remote collaboration
- Professional branding
- Customer support
- Digital messaging
- Social media networking
Conflict resolution
Conflict resolution skills help navigate and settle any disputes to maintain a positive workplace. Whether you’re negotiating tough deals, dealing with customer complaints, or deciding on the office AC temperature, you can apply these skills to a range of situations.
But it’s not just about settling disputes. Adding conflict resolution to your resume tells employers you value workplace harmony, which can boost productivity. It shows you have solid listening skills and that you consider others’ perspectives and respond thoughtfully.
Check out these examples of how to frame conflict resolution on a resume:
- Mediation skills
- Trust building
- Employee relations
- Problem-solving
- Emotional intelligence
- Impartiality
Negotiating skills
Negotiating skills are about reaching mutually beneficial agreements through formal contracts or verbal agreements. Skilled negotiators adapt their communication styles to fit the listener’s requests and avoid misunderstandings.
Pulling off a successful negotiation requires problem-solving, persuasive communication, and reading the room — all abilities that will make you an impressive candidate for future employers.
Negotiation skills aren’t limited to the bargaining table, though.
Take a look at some more specific ways to describe them on a resume:
- Strategic thinking
- Persuasive speaking
- Assertive attitude
- Rapport-building
- Contract negotiation
- Business negotiation
How to Find the Best Communication Skills to Put on a Resume?
Googling “communication skills” and copy-pasting the first result won’t cut it. Recruiters have seen “listening skills” way too many times.
To make an impression, you need to be smart with your word choice, understand what the employer is looking for, and show exactly how your skills make a difference.
Check the job description
Tweaking your resume to match the job description might seem like extra effort — but it’s an easy way to get inspiration on what skills and experience the employer wants from you.
Will you be working with a global team? Mention how your remote collaboration skills have helped you build connections. Are they looking for someone with growth potential? Outline your experiences in accepting and acting on feedback.
Using similar terms from the job description shows recruiters you’re the right fit for the role and boosts your chances with applicant tracking systems (ATS) when scanning resumes for keywords.
Check out this job ad for a product manager position:

This company’s looking for someone who can communicate in group discussions, so mention times you led projects or regularly contributed to meetings to show you’re a team player. They also emphasized data visualization, so include your knack for explaining complex ideas to non-technical clients.
You don’t need to quote the job ad word for word — just outline your relevant experiences, and your skills will speak for themselves.
Research skills relevant to your industry
Every industry has its own communication style — whether it’s interviewing in recruitment, content creation in marketing, or interacting with customers in sales. Some working environments require online collaboration, while others have you mingling with your colleagues.
Recruiters look for candidates who understand the core skills of your chosen industry and can show proficiency in those areas. Doing your homework on industry-specific communication tells employers you have the skills to address the unique challenges and needs of that field.
Consider your achievements
If your skills list is still looking pretty thin, think about your accomplishments and how you’ve applied your skills in real-world scenarios.
Look at your past achievements and identify the communication skills that played a key role. Have you successfully led a team project? Emphasize your abilities in team communication, delegation, and even conflict resolution.
If you’re short on work experience, think about your days in education. Did you navigate a year of online learning during the pandemic? Perfect — you can list skills like remote collaboration, online messaging, and a great deal of patience on your resume.
Still stuck on inspiration? Check out our AI Skill Explorer to dig deeper into any key skills you may have missed.
How to Put Communication Skills on a Resume?
You’ve pinpointed your skills, but you can’t just list them on your resume and call it a day. Recruiters only spend a few seconds on each resume, so your skills must stand out and prove you’re a top-notch candidate.
Let’s dig into where you should include your skills and how to use them to show off your accomplishments.
Tailor to the job description
Job postings spell out exactly what they want — so use that to your advantage.
Start by digging into the job ad and highlighting any specific communication skills listed as requirements. But avoid copying and pasting generic terms like “client support.” These phrases are bland and don’t tell the recruiter what you bring to the table.
Focus on real wins — if they need someone to handle customer interactions, highlight your successes in customer service. You can also use action verbs, such as “presented” and “collaborated” to make your resume more dynamic and easier to scan by ATS systems.
You don’t need to overhaul your resume completely for each application. Just tweak your word choice and skill selection to match what each employer is looking for, and show how your skills translate into success.
Mention top skills in the resume summary
Your resume summary is your elevator pitch and how you’re going to grab a recruiter’s attention right off the bat. Make it concise, relevant, and interesting by focusing on the communication skills that make you a standout candidate.
Include the communication skills that are most relevant to the position. If the job requires strong verbal skills, emphasize your expertise in delivering engaging presentations or negotiating with stakeholders. Always aim to link these communication skills to your achievements to show the impact of your abilities.
Here’s an example of an eye-catching summary with a focus on communication skills:
Customer service specialist with a knack for effective verbal communication and problem-solving. Skilled in handling customer inquiries, resolving complaints, and presenting product features. Recognized for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and maintaining positive client relationships.
Showcase skills via your work experience
Listing skills in bullet points is neat for summarizing, but it’s just that — a summary. Recruiters need to see how you put those skills into action and how they benefit the company. Saying you’re great with phone calls doesn’t mean much if you prefer leaving long voice notes (guilty as charged)!
When describing your work experience , pick specific examples that show how you’ve used your communication skills. Think about times when your communication skills were pivotal and delivered real results.
Did you lead a successful project meeting? Or negotiate a deal that brought in significant revenue? These are gold for showcasing your abilities. And you can add more weight to your accomplishments by using real numbers to back up your claims.
Here’s how to show your skills in your work experience section with measurable outcomes:
Administrative Assistant | ABC Company March 2019 — Present • Managed office communications, including emails, phone calls, and scheduling meetings, ensuring smooth day-to-day operations. • Coordinated travel arrangements and itineraries for executives, managing detailed records and expense reports. • Developed and maintained filing systems, boosting data retrieval efficiency by 30%. • Assisted in preparing presentations and translating complex data into clear, concise information for team meetings. • Acted as a liaison between departments, encouraging effective communication and collaboration across the organization. • Organized company events and meetings, ensuring all logistics were handled seamlessly and attendees were well-informed.
Through these experiences, the jobseeker is demonstrating key skills, like conveying complex information, teamwork, and leadership abilities. It's not about cramming “communication” into every sentence, but strategically emphasizing how strong communication skills helped you deliver results.
Summarize with a list of skills
Once you’ve woven your abilities into your work experience, you can summarize them in your skills section. Including a bulleted list lets recruiters and ATS scanners quickly identify your strengths.
Here’s an example of how to outline your skills:
• Presenting data. Excellent at presenting complex information and ideas in meetings and client interactions. • Team Collaboration. Effective in working with cross-functional teams to achieve common goals. • Data Visualization. Adept at explaining data insights to non-technical stakeholders. • Analytical Skills. History of identifying issues and implementing practical solutions. • Project Management. Expertise in planning, executing, and overseeing projects to ensure successful completion. • Technical Knowledge. Proficiency with Microsoft Office Suite and project management software, like Asana and Trello.
But remember, recruiters will only glance over this section — they might even use it to determine if the rest of your resume is worth investigating. So make sure you tailor your skills to match keywords in the job description.
While it’s handy to cover the basics, avoid using too many generic terms. Instead, opt for specific skills and tools, such as “Project Management,” “Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software,” or “Digital Marketing Campaigns.”
Spotlight skills using the right format
Many assume that a functional or combination format is the answer to drawing attention to your skills. However, using a functional or combination resume is a risky departure from the standard, recruiter-approved reverse-chronological resume format, which places your work experience front and center.
Here’s a rundown of the main resume formats:
- Reverse-chronological format . This widely used format highlights your work history, starting with your most recent position and working backward. Recruiters favor this layout because it clearly showcases your career progression and makes it easy to find key information. I highly recommend this structure to boost your chances of getting noticed.
- Functional (skills-based) format . The functional format places your skills front and center, but can often lead recruiters to make the wrong assumptions and wonder what you have to hide. This outdated format also doesn’t perform well with Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), so I wouldn’t recommend going down this route.
- Hybrid (combination) format. Combining these two formats can be effective if you want to highlight your extensive skills upfront with extensive work experience. This format is a good choice if you have plenty of work experience, numerous accomplishments, or a diverse set of technical skills.
My go-to choice would be the reverse chronological format or the hybrid structure, where you place your skills up top with specific examples or achievements that show how you’ve used these skills in real situations.
Here’s an example from a combination resume:
Customer Service:
• Resolved an average of 30 customer inquiries per day, with a 95% satisfaction rate. • Implemented a new customer feedback system that improved response times by 50%. • Improved retention rates by over 25% by designing and implementing customized cancellation surveys. • Trained and onboarded 22 Junior Customer Service Representatives.
Organizing your skills like this shows employers exactly what expertise you bring to the table. But you can demonstrate your skills just as effectively using a reverse chronological format — you just need to make sure that your descriptions of past jobs reflect whatever skills you listed in the skills section.
Focus on positive outcomes
You’ve got the gist by now — whenever you mention your skills or experiences, highlight the positive outcomes. So, you wrote social media posts for your company; did they boost engagement? Did your powers of persuasion close any deals?
Focusing on positive outcomes means you’re not just listing responsibilities — you’re showing employers the real impact of your communication skills and your ability to deliver results. Talk about how your clear communication helped finish a project ahead of schedule, or how your presentation skills secured a new client.
Use numbers and metrics whenever you can. Instead of saying you improved customer satisfaction, say you increased it by 20% through adaptable communication strategies.
If you’ve received awards or recognition tied to your communication skills, flaunt them. Mention specific achievements like winning a speech competition or receiving praise for a successful presentation.
Be clear and concise
You can’t claim to be a master communicator if your resume isn’t clear. Your grammar skills, writing style, and ability to tell your story will be under scrutiny — you don’t want to miss an opportunity because of a few typos.
When crafting your resume, go through it with a fine-tooth comb and remove any unnecessary details or wordy phrases to keep it to the point. Remember, recruiters take less than ten seconds to scan your resume — you want them to focus on the good stuff.
Space on your resume is precious real estate, so make every word count. Highlight your communication skills and other abilities concisely. Use bullet points to list achievements and skills — it’s easier to read and quickly grabs the recruiter’s attention.
Ways to Improve Your Communication Skills
You’re probably itching to send out your resume and land that job, not spend more time tweaking your skills. But trust me, sharpening your communication skills is worth it. These skills are versatile and can open up all kinds of doors in any industry you choose. Plus, those improved skills will eventually shine on your resume.
Improving your communication skills is easy. It just takes a bit of self-reflection, a fresh perspective, and a genuine desire to get better. Simple steps that can lead to big results down the road.
Master active listening
The tech boom has made our attention spans shorter — how many times have you glanced at your phone mid-conversation? Start by putting away your phone, closing your laptop, and giving the person your full attention.
Resist the urge to jump in with questions or solutions prematurely. We’ve all been guilty of planning our response before the other person finishes — and people notice. Let them complete their thoughts to show you’re genuinely listening and understanding their message.
Once they’ve wrapped up, take a moment to summarize what you’ve heard. You might say, “So, what I’m hearing is…” This shows you’re paying attention while clarifying any potential misunderstandings.
Show interest and ask questions
Small talk easily makes it on the list of things I prefer to avoid. You’re not exactly showcasing your communication skills if your go-to topic is the weather.
Try asking open-ended questions in discussions that get people talking more. Skip the yes or no non-starters and go for open-ended questions like, “How did you tackle that problem?” or “What do you think about this plan?” It shows you’re genuinely curious about their perspective and opens the conversation.
Don't be afraid to dig deeper into topics that interest you or where you need more clarity. Asking follow-up questions shows you’re really processing what’s being said and want to learn more, leading to more engaging chats and stronger connections.
Go out of your comfort zone
Fun fact: Back in my early 20s, I moved to a foreign country by myself — no job, no friends, and no grasp of the language. Did it make me a more confident and self-assured person? Absolutely.
There’s a reason people tell you to venture out of your comfort zone — and honestly, it’s never as scary as you imagine.
Challenge yourself with new communication tasks regularly. It could mean stepping up to lead a meeting, speaking up in group discussions, or presenting ideas to a larger audience. Each challenge (whether big or small) adds to your confidence and broadens your skills, making future interactions less daunting.
And you don’t have to dive in headfirst. Let’s say you have a presentation coming up — take some time to outline your points, anticipate questions, and consider how best to get your message across. Practice and preparation are key to making you feel more at ease.
Build relationships
Good communication starts with getting along with the people around you. Take time to connect with your coworkers on a personal level. Ask about their weekend plans or what they do for fun outside of work.
Approach conversations with a friendly and positive attitude. No one wants to talk to someone who looks like they just had a sour glass of milk. Smile, make eye contact, and use a polite tone to create a welcoming atmosphere where communication flows naturally.
As you build deeper relationships, your confidence will grow, giving you more room to improve your communication skills. Who knows? It might even lead to a promotion or an interesting networking opportunity.
Change your mindset
Changing your perspective is easier said than done, right? When I first entered the professional world, I wasn’t great at taking feedback. I’d get frustrated and defensive whenever someone pointed out areas for improvement.
But then I realized, how does getting defensive serve me? It doesn't help me learn or grow; it only holds me back. So, I decided to shift my mindset. I started seeing feedback not as criticism, but as valuable insights to help me get better.
Surprise, surprise — once I started embracing feedback and thinking about how I could use it to improve, things got a lot smoother. Those negative feelings I used to have? They faded away.
Feedback is your golden opportunity to learn and grow. When someone gives you feedback, they are ultimately trying to help, so listen with an open mind. Everyone’s got their perspective, so take the time to understand where they’re coming from. And don’t be afraid to challenge your own beliefs — sometimes, our mindset can hold us back without us even realizing it.
Learn from the experts
We all know someone who can stroll into any room and strike up a conversation with ease. Pay attention to how they talk — their tone, facial expressions, and body language. What makes their communication so smooth and engaging? Reflect on this and apply those techniques to your conversations and presentations.
If your job relies heavily on customer service or client interaction, you can even check out platforms like Coursera and Udemy, which offer a range of courses on communication skills.
Here are some top recommendations:
- Successful Negotiation: Essential Strategies and Skills (edX)
- Finding Your Professional Voice: Confidence & Impact (Coursera)
- The Complete Communication Skills Master Class for Life (Udemy)
- Winning Communication Skills for Telephone & Conference Calls (Udemy)
- Effective Communication: Writing, Design, and Presentation Specialization (Coursera)
Look for courses that align with your interests and career goals. Whether it’s nailing public speaking or polishing your writing chops, structured courses can dish out some great tips and techniques.
But I'd only recommend shelling out for a course if your job hinges on strong communication skills. If not, there are tons of freebies out there, like TED Talks and documentaries on communication styles and tricks. Take notes on how top-notch speakers grip their audience, organize their messages, and use language to get their point across.
Here’s a recap of all the tips and tricks you need to know when adding communication skills to your resume:
- Don’t just say “excellent communication skills.” Instead, mention specific skills like “negotiation,” or “public speaking,” to add clarity and show recruiters what you can offer the company.
- Match your communication skills to those listed in the job description. If they value teamwork, emphasize specific collaborative skills or your experiences working on successful team projects.
- Start bullet points with action verbs like “presented,” “collaborated,” “mediated,” or “negotiated” to show practical application and boost your chances with ATS scanners.
- Include numbers to quantify your positive impact. For example, “increased customer satisfaction by 20% through effective communication strategies.”
- Mention specific situations where your communication skills made a difference, such as closing a deal or delivering a key presentation to clients.
- Focus on positive outcomes of your communication efforts, like “secured a new client” or “resolved conflicts efficiently,” to demonstrate results and achievements.
- If you have many communication skills under your belt, consider a dedicated skills section to list them clearly — just avoid generic statements.
- Be clear and concise in your descriptions to keep your resume easy to read and impactful, ensuring it grabs the recruiter's attention.
How do you describe communication skills on a resume?
First, include your most important skills in the skills section. But don’t stop there. Describe your communication skills by outlining your experiences and any positive outcomes. For example, “Negotiated contracts with vendors, resulting in a 15% cost reduction.” By focusing on your accomplishments, you’re telling the recruiter how your skills have a tangible impact.
What is considered an extensive communication skill?
Extensive communication skills cover a broad spectrum of abilities, including verbal (public speaking, storytelling), written (emails, reports), listening (active listening, empathy), and non-verbal communication (body language, eye contact). Mastery in multiple areas, such as conflict resolution, persuasive communication, and digital communication tools, also falls under this category.
How to say you have good communication skills on a resume?
Simply saying you have “good communication skills” is generic and doesn’t tell recruiters what you can bring to the table. Instead, use specific skills to showcase your achievements. For example, “Authored and edited newsletters that increased readership by 40%.”
What is another word for communication?
“Interaction” or “dialogue” can serve as alternatives for communication. Depending on the context, terms like “correspondence” (for written communication) or “engagement” (for interactive communication) could also be appropriate.
Other synonyms for communication skills include “people skills”, “social intelligence”, and “interpersonal skills”.
What is a good sentence for communication skills?
A good sentence demonstrating your communication skills should focus on specific abilities and how they contributed towards your accomplishments. You could say, “articulated complex ideas clearly, boosting team productivity through improved understanding and collaboration.

Lauren Bedford
Lauren Bedford is a seasoned writer with a track record of helping thousands of readers find practical solutions over the past five years. She's tackled a range of topics, always striving to simplify complex jargon. At Rezi, Lauren aims to craft genuine and actionable content that guides readers in creating standout resumes to land their dream jobs.
Ready to build your resume?
Join over 3 million people who use Rezi to take control of their job search.

- Directories
Project Info
Decentralized environmental monitoring with communication constraints using a swarm of drones, project goals and description:, more information:, primary contacts:, student preparation, qualifications, time commitment (hrs/wk), skills/techniques gained, mentoring plan, preferred student status.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Improved communication skills. experiencing the real world of researching as well as presenting . To the general public: Improve the quality of life. Help with miscommunication and misconceptions. Increase interest and participation in the research field especially in the underrepresented social groups. To the research community: Increase ...
Research skills are the ability to find an answer to a question or a solution to a problem. They include your ability to gather information about a topic, review that information and analyze and interpret the details in a way to support a solution. Having research skills is necessary to advance your career as they directly relate to your ...
Critical thinking. Critical thinking refers to a person's ability to think rationally and analyze and interpret information and make connections. This skill is important in research because it allows individuals to better gather and evaluate data and establish significance. Common critical thinking skills include: Open-mindedness.
The researcher interview guide was designed to understand researchers' perspectives on communicating and disseminating research findings to participants; explore past experiences, if any, of researchers with communication and dissemination of research findings to study participants; document any approaches researchers may have used or intend ...
Whether you're giving a conference talk, writing a grant, or explaining your work to a family member, the ability to effectively communicate about your research is an essential skill for an Early Career Researcher (ECR) to develop.Read on for our interview with science writer Stephen S. Hall to learn how he helps researchers improve their communication skills, and why that matters.
Research skills are practically any skill used to investigate or analyze information relevant to a topic of interest.. Broadly, it includes a range of talents required to: Find useful information. Perform critical analysis. Form hypotheses. Solve problems. It also includes processes such as time management, communication, and reporting skills to achieve those ends.
Research skills are the capability a person carries to create new concepts and understand the use of data collection. These skills include techniques, documentation, and interpretation of the collected data. Research is conducted to evaluate hypotheses and share the findings most appropriately. Research skills improve as we gain experience.
Research skills encourage intellectual curiosity and a love of learning, as they'll make you explore topics you find intriguing or important. Thus, you'll be more motivated to explore topics beyond the scope of your coursework. Enhanced Communication Skills. Research helps you build better interpersonal skills as well as report-writing skills.
Doing so improves your vocabulary and exposes you to varied sentence structures. For instance, subscribe to National Geographic or the Atlantic. Start immediately. Improving communication skills is a long-term project and it pays to start immediately. Take one of Princeton's writing seminars for graduate students when you have time.
Communication skills. Effective research requires being able to understand and process the information you receive, either written or spoken. That means that you need strong reading comprehension and writing skills — two major aspects of communication — as well as excellent listening skills.. Most research also involves showcasing your findings.
Research has shown that people who are confident in their communication skills and problem-solving abilities have greater relationship satisfaction (Eğeci & Gençöz, 2006). If you don't feel confident in your ability to communicate with your partner that might create problems and misunderstandings.
Research skills refer to the ability to find, organise, analyse and present relevant information about a specific subject. Being able to research requires having several soft and hard skills, including the ability to conduct investigations, make observations, draw inferences, perform analysis and derive solutions to a particular issue.
The starting place for effective communication is effective listening. "Active listening is listening with all of one's senses," says physician communication expert Kenneth H. Cohn, MD, MBA, FACS. "It's listening with one's eyes as well as one's years. Only 8% of communication is related to content—the rest pertains to body language and ...
Researcher Connect is a series of short interactive modules for researchers at any stage of their career and from any academic discipline. It focuses on the development of excellent communication skills using English language in international, multi-cultural contexts. It is appropriate for B2 (Upper Intermediate) level learners and above, and ...
Try incorporating their feedback into your next chat, brainstorming session, or video conference. 4. Prioritize interpersonal skills. Improving interpersonal skills —or your ability to work with others—will feed into the way you communicate with your colleagues, managers, and more.
Examples of communication skills. Here are some communication skills you can practice to be more effective in the workplace: active listening. adapting your communication style. friendliness. confidence. giving and receiving feedback. volume and clarity. empathy.
modifying or even changing in behaviour. Specifically, communication is held to. share feelings and thoughts for several purposes that aim to connect with others. such as: inspiring, motivati ng ...
The good news is that these skills can be learned and even mastered. These eight tips can help you maximize your communication skills for the success of your organization and your career. 1. Be clear and concise. Communication is primarily about word choice. And when it comes to word choice, less is more.
Effective communication is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. When we communicate effectively, both the sender and receiver feel satisfied. Communication occurs in many forms, including verbal and non-verbal, written, visual, and ...
Here's a list of the seven most crucial workplace communication skills with examples of communication competency in each and tips for developing them further. 1. Relationship building and maintenance. Human connection is fundamental to experiencing happiness, and genuine workplace connections improve one's mental health.
The definition of communication skills is the ability for an individual to accurately convey a message to another person or group of people. This is an important skillset to have in life because ...
Communication Skills broadly refers to a person's ability to establish rapport, work in teams, negotiate, quit and effectively deliver messages. Effective Communication Skills encompass a variety of methods, such as written text, oral presentations, and digital platforms like email and social media.
Successful communication depends on two sets of skills. The first is the mastery of the basic ABC's: learning how to speak clearly and listen deeply without defensiveness or invalidation of the other.
The discernment of employability skills is enormously based on communication skills. The degree of effectiveness of communication is clearly shown through the behavior of the sender and receiver.
Include the communication skills that are most relevant to the position. If the job requires strong verbal skills, emphasize your expertise in delivering engaging presentations or negotiating with stakeholders. Always aim to link these communication skills to your achievements to show the impact of your abilities.
skills/techniques gained The student will be responsible for implementing a provided algorithm that will allow the swarm of drones to actively explore and monitor an unknown phenomenon. The student will gain experience in probabilistic machine learning methods, distributed networks, and programming a real robot system.