
27 Good Study Habits of Straight-A Students

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Study habits refer to the consistent practice and approach to study, on a regular basis, to enhance academic performance.
The good thing about a habit is that once you do it on a regular basis, it becomes easy. So, your job is to get into this habit early. Once you’re into the habit, university becomes easy (well, easier ).
Good study habits that I recommend include getting into the routine of heading to the library (or a similar study space) to study without distractions, chunking your studies by subject, and using spaced repetition for things that require rote memorization .
I also recommend studying with friends – such as by testing one another – whenever possible.
The integration of efficient study habits enhances academic performance and motivation to study . By developing effective study strategies adjusted to your personal learning style, you improve concentration and retention of information – and concentration, more than time spent studying, is found to be a key factor for success (Nonis & Hudson, 2010).
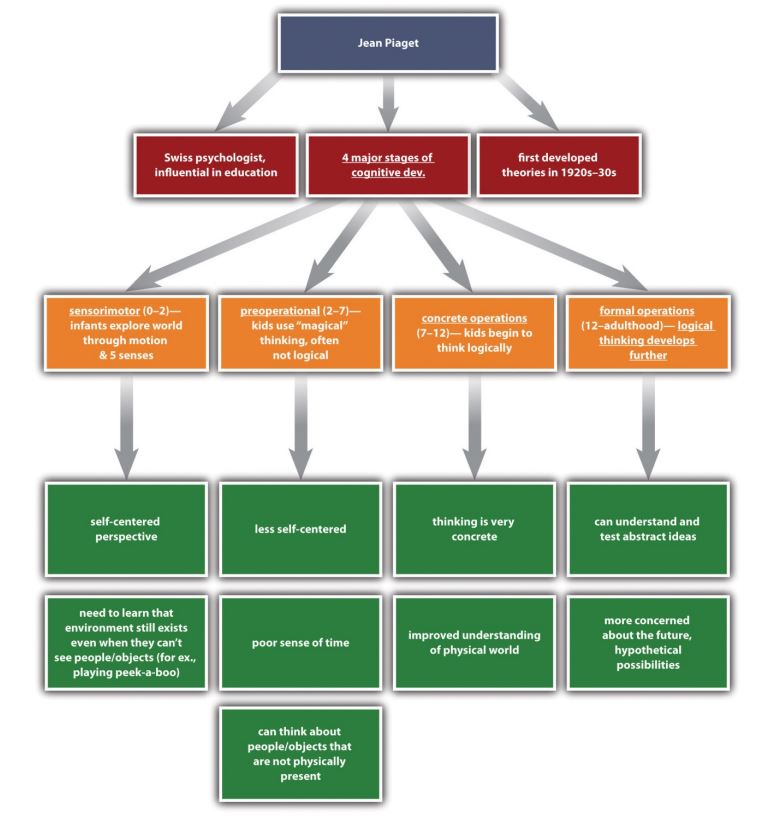
Good Study Habits
1. Time Management Time management refers to being able to efficiently allocate your time so you don’t run out of time, and so you have enough time to allocate to all important tasks. As a basis, you could initiate a dedicated study schedule, specifying the time slots for each subject. For instance, you might want to allot your mornings for theory-heavy subjects like Anatomy, and save the afternoons for practice-oriented subjects like Clinical Skills. Don’t forget to also block time for regular study breaks and social events. This is crucial to prevent burnout and maintain longevity – university is a marathon, not a sprint.
Read Also: 7 Things to do in your First Week of University
2. Using Active Reading Strategies This is the process of engaging with the material by asking questions and drawing connections. Instead of passively reading your texts, you can participate more actively by summarizing the information in your own words, teaching it to someone else, quizzing yourself, or creating visual aids like diagrams and mind maps. As Issa et al. (2012) found, reading relevant information daily is an effective study habit for improving grades.
3. Setting Realistic Goals This strategy involves laying out achievable objectives for each study session or topic. Setting goals not only keeps you focused, but also helps gauge your progress. For example, instead of aiming to read an entire biology textbook in two days, you might target mastering one chapter per day. I recommend setting both short-term study goals and long-term study goals using the SMART Goals method .
4. Prioritization Successful students often prioritize tasks based on their deadlines and degree of importance. You might follow the Eisenhower Box method: divide your tasks into four categories, namely, important and urgent, important but not urgent, not important but urgent, and not important and not urgent. For instance, an upcoming exam translates into an important and urgent task, hence it would be first on your list.
5. Spaced Repetition This strategy involves studying information over incremental intervals instead of cramming it in one sitting. You might review your notes on the day you learn something, then again in a couple of days, then after a week, and so forth. There are even apps like the Anki flashcards app that have a built-in spaced repetition algorithm that can space how often ideas are presented to you.
6. Creating a Suitable Environment Each individual’s ideal study environment may differ based on personal preferences . Some people need complete silence, while others work better with some background noise. If you like silence, the quite section of a library is a good place to start – I recommend making it a habit to go to the library at your university as often as possible. Conversely, if you feel background noise helps you to concentrate, consider studying at a cafe. But the key is to ensure your environment is right for you. As Ogbodo (2010, p. 229) argues: “Where to study is as important as what to study and how to go about studying.”
7. Taking Breaks Integrating regular short breaks into your study pattern can boost your productivity and mental agility because it decreases distractions during focused study time. And this is important. As Walck-Shannon, Rowell and Frey (2021) found, “students reported being distracted about 20% of their study time, and distraction while studying negatively predicted exam performance.” So, let’s avoid that – by splitting our time between strong focus, then rest. Typically, the Pomodoro technique is a popular method for this, where you study for 25 minutes, then take a 5-minute break. After four such cycles, you take a longer break of 15-20 minutes. During your breaks, you can engage in some light activity such as stretching or walking to invigorate yourself.
8. Maintaining Physical Health Eating well, getting regular exercise, and ensuring enough sleep are often overlooked aspects of efficient studying. Research shows that a balanced diet, physical activity, and proper sleep improve cognitive functions , including memory and concentration. You may want to establish a regular sleep schedule, incorporate a balanced diet, and schedule regular exercise sessions each week into your routine.
9. Using Technology Wisely Technology offers a range of tools that can streamline your study process. For instance, you can use apps for time management (e.g., Rescue Time), note-taking (e.g., Evernote), or spaced repetition (e.g., Anki). While these apps can be beneficial, remember to keep checks on screens’ disruptive nature and the habit of digital distraction. As practice, try turning off your phone’s notifications when you study, or set ‘Do Not Disturb’ intervals.
10. Review and Revise Sessions Regular review of study materials aids in long-term retention of information. You can allocate specific time slots each week to revisit old notes, attempt self-test papers or engage in group discussions. For instance, you might dedicate your Sunday mornings to revising everything you’ve covered during the preceding week.
11. Active Writing Transcribing information demands active engagement, thereby reinforcing your understanding and memory of the subject. You might opt to rewrite complex concepts in your own words or diagrammatically represent intricate processes. For example, instead of merely reading about the human circulatory system, consider drawing it out with brief annotations.
12. Seeking Help When Needed Understanding when to seek help is an underrated study habit. If you find yourself struggling with a subject, don’t hesitate to approach your professors, peers, or study groups for clarification. You might also seek online resources such as academic forums or educational websites. Remember, it’s better to clarify doubts initially than to have misconceptions hamper your overall learning.
13. Mindfulness and Focus Mindfulness, or present-moment awareness, can help enhance your comprehension and retention during studying. You could practice mindfulness by removing distractions, concentrating on the task at hand, and making a conscious effort to absorb the material.
14. Integrating Study with Real-Life Scenarios Applying the theoretical knowledge learned during study sessions to real-life instances can facilitate a deeper understanding. You might relate basic principles of economics to household budgeting or chemistry to cooking. This practice can help convert abstract concepts into tangible examples.
15. Regular Self-Assessment Implementing regular exams or quizzes to assess your understanding and memory can be a direct way to monitor progress. You can either use ready-made quizzes available online or design a short assessment yourself. As you answer, mark out the areas you struggled with for further review. This method will help you know where you stand in your preparation and what areas need extra effort.
16. Employing Mnemonics This involves using techniques to retain and retrieve information. The method could be as simple as creating an acronym or conjuring up a relevant mental image. For example, in recalling the taxonomical rank in biology – Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species – you might use the well-known mnemonic phrase: “King Phillip Came Over For Good Soup.” Examples of additional mnemonic techniques include the method of loci and memory linking .
17. Incorporating Understandable Examples Since abstract concepts can be confusing, associating them with relateable analogies can help you grasp the idea. This technique depends heavily on your creativity and could be as simple as linking a literary theme to a popular movie plot. Ensuring your examples make sense to you is vital.
18. Varying Study Methods It is beneficial to avoid monotony and experiment with multiple learning techniques. This can include oscillating between solitary studying and group study sessions, or alternating between text-based learning and audio-visual aids. For instance, following a hefty reading session, you might want to watch a related documentary or podcast on the topic. Switching up strategies not only prevents burnout but also caters to different facets of your learning style.
19. Note-Taking Strategy Effective note-taking is a skill that helps in better understanding and remembrance of knowledge. You should decide a note-taking strategy which could be outlining, mind mapping, or the Cornell method, and stick to it. For example, you might use the Cornell Method, which divides the paper into notes, cues, and a summary section for enhancing retention and review.
20. Regularity and Consistency Consistency is the cornerstone of strong study habits. Establishing a regular routine that allocates specific periods for study each day leads to better academic performance. For instance, studying for two hours per day consistently is more effective than cramming for fourteen hours once a week.
21. Engage All Senses Engaging multiple senses aids in strengthening your memory of the subject matter. This could involve reading aloud, rewriting notes, creating visual aids, or even using software to convert text to speech. The goal is to consume the information through as many sensory channels as possible to maximize retention. For example, if you’re studying foreign vocabulary, you could listen to the pronunciation, read the definition, write the word several times, and visualize an image related to it.
22. Reflective Learning Reflective learning involves regularly taking a few moments to contemplate what you’ve learned. This process ensures you understand the main concepts and helps you evaluate how effectively the learning material has been understood. For instance, after reading a section on World History, take a moment to think about what questions have been answered and what new questions have arisen in your mind about the topic.
23. Preparing for the Next Class Reviewing the material that will be covered in the next class helps make the class more productive and understandable. By having prior knowledge of the topic, you can better participate in class discussions and raise insightful queries. For example, if tomorrow’s Physics class covers Electromagnetic Waves, you might want to read the corresponding chapter tonight.
24. Constructive Procrastination While complete avoidance of procrastination is the goal, sometimes it’s unavoidable. Constructive procrastination involves doing another task that also needs to be done when you feel like procrastinating. If you find yourself unable to study Civil Law, consider switching to another pending task, such as completing your Mathematics assignment. This way, you remain productive while giving in to the urge to procrastinate.
25. Visualization Techniques Visualization involves picturing the information in your mind, which can significantly improve memory and recall. For instance, when studying Anatomy, envisioning the body parts, systems, and processes can enhance your understanding. If you’d like to explore this strategy more, read my article on the visual peg-word system for memorization .
26. Listen to Music Without Lyrics Listening to music while studying is a controversial topic. Some people think it helps them to achieve a flow state, while most research suggests that “ media multitasking ” is a distraction whether we realize it or not (Xu, Wang, & Woods, 2019). Generally, I recommend that if you do like that background nose, try to listen to music without lyrics, like lo-fi playlists from YouTube, which act as background noise and could potentially prevent your mind from wandering.
27. Study with Friends Thalluri (2016) found that “study buddy support groups” significantly support studying. Friends can keep each other accountable and help motivate one another. And, according to social learning theory , working in groups helps us to reinforce knowledge. For example, if you’re talking about the course content with friends, you’ll hear their unique perspectives, which you can critically compare to your own, which augments, supports, positively alters, and strengthens your own perspectives.
Study habits act as the building blocks of your academic journey. Efficient study habits not only ensure better academic performance but also help in gaining lifelong skills like time management, goal-setting, and self-discipline. By adopting effective study habits, you modulate your academic journey to a more favorable and fruitful path.
If you want to dive deeper into getting good study habits, I’d recommend James Clear’s Atomic Habits book – it’s an amazing book for learning to get more productive and optimize your time as a student.
Issa, A.O., Aliyu, M.B., Akangbe, R.B., and Adedeji, A.F. (2012). Reading interest and habits of the federal polytechnic students. International Journal of Learning & Development, 2 (1): 470-486.
Nonis, S. A., & Hudson, G. I. (2010). Performance of college students: Impact of study time and study habits. Journal of education for Business , 85 (4), 229-238.
Ogbodo, R. O. (2010). Effective Study Habits in Educational Sector: Counselling Implications. Edo Journal of Counselling , 3 (2), 230-242.
Thalluri, J. (2016). Who benefits most from peer support group?–First year student success for Pathology students. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences , 228 , 39-44.
Walck-Shannon, E. M., Rowell, S. F., & Frey, R. F. (2021). To what extent do study habits relate to performance?. CBE—Life Sciences Education , 20 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.20-05-0091
Xu, S., Wang, Z., & Woods, K. (2019). Multitasking and dual motivational systems: A dynamic longitudinal study. Human Communication Research , 45 (4), 371-394. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/hcr/hqz009

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Habits — Study Habits: The Key to Effective Learning and Academic Success
Study Habits: The Key to Effective Learning and Academic Success
- Categories: Habits Learning
About this sample

Words: 652 |
Published: Feb 7, 2024
Words: 652 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Study habits for effective learning, study habits for memory retention, study habits for exam preparation, study habits for online learning.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Life Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1059 words
2 pages / 911 words
3 pages / 1594 words
2 pages / 926 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Habits
Changing a behavior is even more daunting because many habits are learned from an early age. A habit I would like to change, discussed in this essay, is what I refer to as instances of insufficient time management, which result [...]
Habits of mind are the patterns of thought that shape our behaviors and actions. They are the skills and attitudes that we develop over time, and they play a crucial role in determining our personal and professional success. [...]
Listening is a vital skill that is often overlooked and undervalued. As a college student, developing effective listening habits is essential for success in academic endeavors and beyond. This essay aims to explore the habits of [...]
Becoming a peak performer is a journey that requires deliberate effort, a growth mindset, and the cultivation of high-quality habits. It involves embracing challenges, persisting in the face of setbacks, and continually refining [...]
"7 Habits of a Highly Effective Teenager" essay is Stephen Covey’s advice on some habits teens should get used to in order to become a highly effective individual. There are 7 habits, and the first is to be “proactive”. [...]
The key to becoming an effective student is learning how to study smarter, not harder. This becomes truer as you advance in your education. While some students breeze through college with minimal effort, a vast majority of them [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Good study habits are best described as a set of tools that facilitate an increase of the amount of information learned and also make the information to be remembered for a long time. Well, I did not grow up with good study habits, I used to spend most of my free time playing video games, watching movies and listening to music, and hardly doing my homework. Despite my parents’ effort of taking me to a good school, I paid little attention to schoolwork. As a result of these, I registered very poor school grades, which in turn led to frustrations both for me and my parents. It is this experience that made me convict myself to creating a positive change towards studying my school work. I realized that developing good study habits was paramount because through them, I could gain success and satisfaction during the school years and the same could be extended to the working world.
The journey towards attaining this positive change has not been easy though. I am still working on this endeavor. The very first step I am taking is to make sure that, my home is a good place to study. For any positive results to be attained in studying at home, the home environment should be made conducive for thinking. It is now clear to me that, I can only concentrate on one thing at a time; this then means that, the home environment should be free from noise and distraction. In light of the importance of quietness and less distraction, I now design a time chart for one week in which I allocate study time late in the afternoons and early evening because at this time there is minimal activity in my house.
The second step I am taking to make this change happen is to eliminate common distractions such as television, radio, and stereo, just to mention but a few. Well, I was used to studying in a noisy environment. But at the moment, I switch off the television and reduce the volume of the radio while studying. I am optimistic that, within a short time, I will be able to study in absolute silence. Furthermore, I have arranged for phone time when I can make or receive calls to avoid disruptions during study time. In addition, I have informed my friends of the appropriate time they can visit me. Lastly, I keep all the supplies I need in the study area, for instance, pens, papers, clips, calculators, and many others.
The third important step I am taking to make this change happen is providing physical conditions in the study area that are conducive for concentration. To achieve this, I have good lighting, cool temperatures, a comfortable chair, and a table to help me be alert.
For me to have reached where I am now, it took me hard work and patience. When I was starting to cultivate this habit, I felt fatigued and was almost giving up. I even lost some of my friends. Sticking to the goal of developing good study habits in order to make a change for the better, has made me realize the importance of developing a routine and term commitment to each and every decision I make in life. It is through this experience that I also realize, good concentration doesn’t just come but it takes time and patience to shape.
In conclusion, good study habits are acquired and developed by an individual. In order to achieve this, it is equally important to set a study time for work at home, allocate a comfortable amount of work every day without being too pushy, provide a conducive studying environment free from destructions and noise, and above all have a positive attitude, commitment, and patience.
- “From Teacher-Centered to Learner-Centered Curriculum: Improving Learning in Diverse Classrooms” by Brown
- Oral Presentation as a Way of Measuring Learning
- Noise and Sound Pollution
- XYZ Company: Conducive Business Proposal
- The Effects of Noise Pollution
- Homework Management and Its Benefits
- Brain-Based Learning and Its Key Principles
- Personal Learning Styles and Management Skills
- Strategies for Teaching Spelling
- “No Significant Difference” Phenomenon
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, December 3). Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits. https://ivypanda.com/essays/creating-positive-change-good-study-habits/
"Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits." IvyPanda , 3 Dec. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/creating-positive-change-good-study-habits/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits'. 3 December.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits." December 3, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/creating-positive-change-good-study-habits/.
1. IvyPanda . "Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits." December 3, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/creating-positive-change-good-study-habits/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits." December 3, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/creating-positive-change-good-study-habits/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .

Essay on Study Habits
Students are often asked to write an essay on Study Habits in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Study Habits
What are study habits.
Study habits are the ways that you choose to study. They can include when you study, where you study, and how you organize your study materials. Good study habits help you learn better and faster.
Importance of Planning
Planning your study time is very important. Decide what you will study and when. This helps you use your time wisely and not waste it. A plan makes studying less stressful.
Creating a Good Study Environment
Your study place should be quiet and have good light. It should have all the things you need so you don’t have to stop and look for them.
Staying Focused
When you study, pay full attention. If you get distracted easily, try to find ways to keep your mind on your work. Taking short breaks can also help keep your mind fresh.
Reviewing Your Work
250 words essay on study habits.
Study habits are the ways that you choose to learn and remember information. They include when, where, and how you sit down to study. Good study habits can help you do well in school, while bad ones can make learning much harder.
Importance of a Quiet Place
Finding a quiet place is key to good studying. This means a spot where distractions are few, so you can focus on your work. It could be a corner of your room, a library, or even a quiet cafe. The important thing is that it’s a place where you can concentrate.
Creating a Study Schedule
Making a schedule helps you manage your time. Decide on what days and times you will study and for how long. Stick to this plan as closely as you can. This helps your brain get into a routine, making studying a regular part of your day.
Take Short Breaks
It’s important not to study for too long at a stretch. After about 45 minutes to an hour, take a short break. This can be a quick walk, some stretches, or just resting your eyes. Breaks help your brain absorb information better and keep you from getting too tired.
Good study habits are about finding the right place, making a plan, and not forgetting to take breaks. By following these simple steps, you can make learning easier and more effective.
500 Words Essay on Study Habits
What are study habits, why are study habits important.
Effective study habits can help students succeed in school. They can help students to:
How to Improve Study Habits
There are many things that students can do to improve their study habits. Such as:
Active Learning
Active learning is a study technique that involves actively engaging with the material. This can be done by:
Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition is a study technique that involves reviewing the material at spaced intervals. This helps to move the information from short-term memory to long-term memory.
Spaced repetition can be done using flashcards, online tools, or simply by setting aside time to review the material at regular intervals.
Get Help When You Need It
If you are struggling with your studies, don’t be afraid to ask for help. There are many resources available to help students, such as:
Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you need it. There are many people who are willing to help you succeed.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
All Subjects
study guides for every class
That actually explain what's on your next test, study habits, from class:, ap psychology.
Study habits refer to the behaviors and routines that students adopt when studying, such as time management, note-taking methods, and concentration strategies. These habits greatly influence academic performance.
Related terms
Motivation : Motivation refers to the internal or external factors that drive individuals to engage in certain behaviors. In the context of study habits, motivation plays a crucial role in sustaining focus and effort during studying.
Reinforcement : Reinforcement involves providing rewards or consequences to strengthen or weaken certain behaviors. In improving study habits, psychologists may use positive reinforcement (such as praise or small rewards) to encourage desirable study behaviors.
Self-regulation : Self-regulation refers to one's ability to control their own thoughts, emotions, and actions. Helping students develop self-regulation skills can assist them in creating consistent and effective study habits.
" Study Habits " also found in:
Subjects ( 2 ).
- Intro to Business
Practice Questions ( 1 )
- How would a psychologist use operant conditioning to help a student improve their study habits?
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
Ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 4: Effective Study Habits
Work smarter, not harder: effective studying techniques, developing smart study skills.
At the beginning of the semester, your workload is relatively light. This is the perfect time to brush up on your study skills and establish good habits. When the demands on your time and energy become more intense, you will have a system in place for handling them. The goal of this section is to help you develop your own method for studying and learning efficiently.
As you work through this section, remember that every student is different. The strategies presented here are techniques that work well for many people; however, you may need to adapt them to develop a system that works well for you personally. If your friend swears by her smartphone, but you hate having to carry extra electronic gadgets around, then using a smartphone will not be the best organizational strategy for you.
Take a moment to consider what techniques have been effective (or ineffective) for you in the past. Which habits from your high school years or your work life could help you succeed now? Which habits might get in your way? What changes might you need to make?
Understanding Your Learning Preferences
To succeed in your post-secondary education—or any situation where you must master new concepts and skills—it helps to know what makes you tick. For decades, educational researchers and organizational psychologists have examined how people take in and assimilate new information, how some people learn differently than others, and what conditions make students and workers most productive. Here are just a few questions to think about:
- What times of day are you most productive? If your energy peaks early, you might benefit from blocking out early morning time for studying or writing. If you are a night owl, set aside a few evenings a week for schoolwork.
- How much clutter can you handle in your workspace? Some people work fine at a messy desk and know exactly where to find what they need in their stack of papers; however, most people benefit from maintaining a neat, organized space.
- How well do you juggle potential distractions in your environment? If you can study at home without being tempted to turn on the television, check your email, fix yourself a snack, and so on, you may make home your workspace. However, if you need a less distracting environment to stay focused, you may be able to find one on campus or in your community.
- Does a little background noise help or hinder your productivity? Some people work better when listening to background music or the low hum of conversation in a coffee shop. Others need total silence.
- When you work with a partner or group, do you stay on task? A study partner or group can sometimes be invaluable. However, working this way takes extra planning and effort, so be sure to use the time productively. If you find that group study sessions turn into social occasions, you may study better on your own.
- How do you manage stress? Accept that at certain points in the semester, you will feel stressed out. In your day-to-day routine, make time for activities that help you reduce stress, such as exercising, spending time with friends, or just scheduling downtime to relax
Video source: https://youtu.be/Bxv9lf5HjZM

Understanding your Learning Style
For the purposes of this chapter, learning style refers to the way you prefer to take in new information, by seeing, by listening, or through some other channel. (For more information, see the section on learning styles.)
Most people have one channel that works best for them when it comes to taking in new information. Knowing yours can help you develop strategies for studying, time management, and note taking that work especially well for you.
To begin identifying your learning style, think about how you would go about the process of assembling a piece of furniture. Which of these options sounds most like you?
- You would carefully look over the diagrams in the assembly manual first so you could picture each step in the process.
- You would silently read the directions through, step by step, and then look at the diagrams afterward.
- You would read the directions aloud under your breath. Having someone explain the steps to you would also help.
- You would start putting the pieces together and figure out the process through trial and error, consulting the directions as you worked.
Now read the following explanations of each option in the list above. Again, think about whether each description sounds like you.
- If you chose 1, you may be a visual learner . You understand ideas best when they are presented in a visual format, such as a flow chart, a diagram, or text with clear headings and many photos or illustrations.
- If you chose 2, you may be a verbal learner . You understand ideas best through reading and writing about them and taking detailed notes.
- If you chose 3, you may be an auditory learner . You understand ideas best through listening. You learn well from spoken lectures or books on tape.
- If you chose 4, you may be a kinesthetic learner . You learn best through doing and prefer hands-on activities. In long lectures, fidgeting may help you focus.
Learning Style Strategies
|
|
|
| When possible, represent concepts visually—in charts, diagrams, or sketches. Use a visual format for taking notes on reading assignments or lectures. Use different coloured highlighters or pens to colour code information as you read. Use visual organizers, such as maps and flow charts, to help you plan writing assignments. Use coloured pens, highlighters, or the review feature of your word processing program to revise and edit writing. | |
| Use the instructional features in course texts—summaries, chapter review questions, glossaries, and so on—to aid your studying. Take notes on your reading assignments. Rewrite or condense reading notes and lecture notes to study. Summarize important ideas in your own words. Use informal writing techniques, such as brainstorming, freewriting, blogging, or posting on a class discussion forum to generate ideas for writing assignments. Reread and take notes on your writing to help you revise and edit. | |
| Ask your instructor’s permission to tape record lectures to supplement your notes. Read parts of your textbook or notes aloud when you study. If possible, obtain an audiobook version of important course texts. Make use of supplemental audio materials, such as CDs or DVDs. Talk through your ideas with other students when studying or when preparing for a writing assignment. Read your writing aloud to help you draft, revise, and edit. | |
| When you read or study, use techniques that will keep your hands in motion, such as highlighting or taking notes. Use tactile study aids, such as flash cards or study guides you design yourself. Use self-stick notes to record ideas for writing. These notes can be physically reorganized easily to help you determine how to shape your paper. Use a physical activity, such as running or swimming, to help you break through writing blocks. Take breaks during studying to stand, stretch, or move around. |
Time Management
Getting Started: Short- and Long-Term Planning
At the beginning of the semester, establishing a daily/weekly routine for when you will study and write can be extremely beneficial. A general guideline is that for every hour spent in class, you should expect to spend another two to three hours on reading, writing, and studying for tests. Therefore, if you are taking a biology course that meets three times a week for an hour at a time, you can expect to spend six to nine hours per week on it outside of class. You will need to budget time for each class just like an employer schedules shifts at work, and you must make that study time a priority.
That may sound like a lot when taking several classes, but if you plan your time carefully, it is manageable. A typical full-time schedule of 15 credit hours translates into 30 to 45 hours per week spent on schoolwork outside of class. All in all, a full-time student would spend about as much time on school each week as an employee spends on work. Balancing school and a job can be more challenging, but still doable.
In addition to setting aside regular work periods, you will need to plan ahead to handle more intense demands, such as studying for exams and writing major papers. At the beginning of the semester, go through your course syllabi and mark all major due dates and exam dates on a calendar. Use a format that you check regularly, such as your smartphone or the calendar feature in your email. (In Section 1.3 Becoming a Successful Writer , you will learn strategies for planning major writing assignments so you can complete them on time.)
PRO TIP: The two- to three-hour rule may sound intimidating. However, keep in mind that this is only a rule of thumb. Realistically, some courses will be more challenging than others, and the demands will ebb and flow throughout the semester. You may have trouble-free weeks and stressful weeks. When you schedule your classes, try to balance introductory-level classes with more advanced classes so that your work load stays manageable.
Self-Practice Exercise
Now that you have learned some time management basics, it is time to apply those skills. For this exercise, you will develop a weekly schedule and a semester calendar.
- Working with your class schedule, map out a week-‐long schedule of study time. Try to apply the two to three-hour rule. Be sure to include any other nonnegotiable responsibilities, such as a job or child care duties.
- Use your course syllabi to record exam dates and due dates for major assignments in a calendar (paper or electronic). Use a star, highlighting, or other special marking to set off any days or weeks that look especially demanding.
Staying Consistent: Time Management Dos and Do Not’s
Setting up a schedule is easy. Sticking with it, however, may be challenging. A schedule that looked great on paper may prove to be unrealistic. Sometimes, despite students’ best intentions, they end up procrastinating or pulling all-nighters to finish a paper or study for an exam.
Keep in mind, however, that your weekly schedule and semester calendar are time management tools. Like any tool, their effectiveness depends on the user: you. If you leave a tool sitting in the box unused (e.g., you set up your schedule and then forget about it), it will not help you complete the task. And if, for some reason, a particular tool or strategy is not getting the job done, you need to figure out why and maybe try using something else.
With that in mind, read the list of time management dos and don’ts. Keep this list handy as a reference you can use throughout the semester to troubleshoot if you feel like your schoolwork is getting off track.
- Do set aside time to review your schedule and calendar regularly and update or adjust them as needed.
- Do be realistic when you schedule study time. Do not plan to write your paper on Friday night when everyone else is out socializing. When Friday comes, you might end up abandoning your plans and hanging out with your friends instead.
- Do be honest with yourself about where your time goes. Do not fritter away your study time on distractions like email and social networking sites.
- Do accept that occasionally your work may get a little off track. No one is perfect.
- Do accept that sometimes you may not have time for all the fun things you would like to do.
- Do recognize times when you feel overextended. Sometimes you may just need to get through an especially demanding week. However, if you feel exhausted and overworked all the time, you may need to scale back on some of your commitments.
- Do make a plan for handling high-stress periods, such as final exam week. Try to reduce your other commitments during those periods—for instance, by scheduling time off from your job. Build in some time for relaxing activities, too.
- Do be kind to yourself – many students balance school and other important responsibilities (work, family, friends, etc.). There will be times where you will have to prioritize where your time goes, and that’s okay.
Try Not To:
- Procrastinate on challenging assignments. Instead, break them into smaller, manageable tasks that can be accomplished one at a time. An assignment calculator can be a useful tool for helping to get yourself organized.
- Fall into the trap of “all or nothing” thinking. (e.g. “There is no way I can fit in a three-hour study session today, so I will just wait until the weekend.”) Extended periods of free time are hard to come by, so find ways to use small blocks of time productively. For instance, if you have a free half hour between classes, use it to preview a chapter or brainstorm ideas for an essay.
One of the best things you can do for yourself as a student is realize that we all procrastinate at some point. Knowing your procrastination style can help you to recognize and change bad habits. Look at the chart below and see if you can identify your procrastination style (you might use more than one!):
| Reluctant to start work because of fears that it will never be good enough | Leave enough time to do multiple drafts of your work. Put you assignment down for a few days, then come back to it and edit/revise. Remind yourself that you’re in school because you are learning and that no one expect perfection. | |
| Is very productive with work… but they aren’t doing the work that they be doing. (Ex. cleaning the apartment instead of studying) | Ask yourself why you’re focused on other things right now. Maybe you’ve been studying too long and need a break? Maybe you don’t understand the assignment and need clarification? | |
| Finds things to do for other people to put off doing their own work (Ex. helping a friend study for their test) | Let friends/family know that you have an upcoming deadline so that they know you are unavailable. | |
| Puts themself into situations where they know they will be distracted or unsuccessful (Ex. studying in a living room) | Create or find a study space that you reserve just for doing your work. As much as possible, it should be isolated and have all of your study materials at-hand. | |
| Has too many ideas and finds it difficult to settle on just one. | Brainstorm a list of your ideas and then compare it to the assignment. Which idea fits the best with what you’re being asked to do? | |
| Gets overwhelmed with the amount of work/assignments and shuts down (Ex. end up playing video games to avoid the situation entirely) | Create a list of everything that you have to do for each class, then put all of the dates into a calendar so that you can see what needs to be prioritized. Breaking up big tasks can make things more manageable. | |
| Does best under the pressure of doing work at the last minute. (Ex. studies for tests the night before or morning of the exam) | Move your deadlines ahead in your calendar to give yourself a few days as a buffer. Set micro goals with a time limit and see if you can beat the clock. Go back and edit/revise once you’re finished. Have someone quiz you on your material after a timed study session. | |
| Ends up getting distracted by other things (Ex. begins researching vaccines and spends hours reading about conspiracy theories) | Set a timer to “check in” on your progress. Are you finding yourself distracted? Keep a list beside you of things you need or want to do once you’re finished studying. Keep your cellphone out of your study area. Use online tools that lock down your social media sites for certain lengths of time. Use a reward system (Ex. Finish this chapter and then one episode on ). |
The key to managing your time effectively is consistency. Completing the following tasks will help you stay on track throughout the semester.
- Establish regular times to “check in” with yourself to identify and prioritize tasks and plan how to accomplish them. Many people find it is best to set aside a few minutes for this each day and to take some time to plan at the beginning of each week.
- For the next two weeks, focus on consistently using whatever time management system you have set up. Check in with yourself daily and weekly, stick to your schedule, and take note of anything that interferes. At the end of the two weeks, review your schedule and determine whether you need to adjust it.
studying & Note-Taking Methods
Summarizing is one of the most effective means of studying and making sure that you’ve learned the concept/skill. Can you go through the steps mentally? Can you describe or explain it to someone else in your own words? This is the process of summarizing and synthesizing information.
When summarizing material from a source, you zero in on the main points and restate them concisely in your own words. This technique is appropriate when only the major ideas are relevant to your paper or when you need to simplify complex information into a few key points for your readers. To create a summary, consider the following points:
- Review the source material as you summarize it.
- Identify the main idea and restate it as concisely as you can—preferably in one sentence. Depending on your purpose, you may also add another sentence or two condensing any important details or examples.
- Check your summary to make sure it is accurate and complete.
- Make a careful record of where you found the information because you will need to include the reference and citation if you choose to use the information in an essay. It is much easier to do this when you are creating the summary and taking notes than having to go back and hunt for the information later. Guessing where you think you got it from is not good enough.
Summaries and Abstracts
When you read many academic journal articles, you will notice there is an abstract before the article starts: this is a summary of the article’s contents. Be careful when you are summarizing an article to not depend too much on the abstract as it is already a condensed version of the content. The author of the abstract identified the main points from his or her perspective; these may not match your own purpose or your own idea of what is important. What may also happen if you try to summarize the abstract is you will probably end up replacing some words with synonyms and not changing the overall ideas into your own words because the ideas are already summarized, and it is difficult to make them more generalized. You have to read the entire source or section of the source and determine for yourself what the key and supporting ideas are.
PRO TIP: A summary or abstract of a reading passage is one-tenth to one-quarter the length of the original passage, written in your own words. The criteria for a summary are that it:
- Is similar to an outline but in complete sentences and can stand as an independent piece of writing
- Includes only the main points and key details
- Is valuable because it is the surest way to measure your understanding
- Helps you remember because you must attend carefully to what you read, organize your thoughts, and write them out to make it meaningful to you (This is absolutely necessary when you cannot mark a book because it belongs to someone else.)
- Challenges you to be concise in your writing while providing balanced coverage of the main points.
- Challenges you to paraphrase or use your own words and avoid using too many quotations.
- Is important to remain objective because you are giving the author’s views not your own.
Article: Assessing the Efficacy of Low – Carbohydrate Diets
Adrienne Howell, Ph.D. (2010)
Over the past few years, a number of clinical studies have explored whether high-protein, low-carbohydrate diets are more effective for weight loss than other frequently recommended diet plans, such as diets that drastically curtail fat intake (Pritikin) or that emphasize consuming lean meats, grains, vegetables, and a moderate amount of unsaturated fats (the Mediterranean diet). A 2009 study found that obese teenagers who followed a low-carbohydrate diet lost an average of 15.6 kilograms over a six-month period, whereas teenagers following a low-fat diet or a Mediterranean diet lost an average of 11.1 kilograms and 9.3 kilograms respectively. Two 2010 studies that measured weight loss for obese adults following these same three diet plans found similar results. Over three months, subjects on the low-carbohydrate diet plan lost anywhere from four to six kilograms more than subjects who followed other diet plans.
In three recent studies, researchers compared outcomes for obese subjects who followed either a low-carbohydrate diet, a low-fat diet, or a Mediterranean diet and found that subjects following a low-carbohydrate diet lost more weight in the same time (Howell, 2010).
What Is aNNOTATION?
Most students already know how to annotate. When you make notes in the margins and highlight your textbooks, you are annotating that source.
When you take notes in the margins of your readings, highlight key ideas, underline passages, etc, you are annotating a source. Annotations are a valuable research tool because they allow you to capture your first ideas and impressions of a text, as well as enable you to find key information again quickly without having to re-read the entire text.
When annotating, you should be looking for several things:
- Key ideas, terms, and concepts
- Words or concepts that you don’t understand yet
- Points that are being made with which you (dis)agree
- Pieces of evidence that would be useful for your own paper
- Inconsistent information with what you have read elsewhere
- Parts of the text you may wish to return to later in the research process
PRO TIP: LEARN TO USE YOUR HIGHLIGHTER PROPERLY!
Many students – if not most – do not use highlighters effectively. Highlighting is a visual cue that is intended to help you recall or find information quickly. If you are the person who highlights 3/4 of the page or chapter, you are not using the tool effectively.
When studying, you should have multiple colours of highlighter with you and designate certain colours for certain things. For example:
DEFINITIONS MAIN IDEAS UNCLEAR CONCEPTS KEY EVIDENCE OR POINTS
This strategy has a few benefits:
- It forces you to slow down to switch colours, giving you more time to process what you’re reading
- It makes you read actively in order to determine how the information should be classified (for example: is this a definition or a main idea ?)
- It creates a study system for you that is consistent and easier to follow
Video source: https://youtu.be/eVajQPuRmk8
- Read the following passage and use a note-‐taking method to identify the main points.
- Compose a sentence summarizing the paragraph’s main points.
Several factors about the environment influence our behaviour. First, temperature can influence us greatly. We seem to feel best when the temperature is in the high teens to low 20s. If it is too hot or cold, we have trouble concentrating. Lighting also influences how we function. A dark lecture hall may interfere with the lecture, or a bright nightclub might spoil romantic conversation. Finally, our behaviour is affected by colour. Some colours make us feel a peaceful while others are exciting. If you wanted a quiet room in which to study, for example, you would not paint it bright orange or red.
Collaboration: Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Here are possible answers:
Key points:
Environmental factors influence behaviour:
- Temperature: extremes make focus difficult
- Lighting: inappropriate lighting is disorientating
- Colour: colour affects relaxation
Summary sentence: Three environmental influences that impact human behaviour include temperature, as extreme fluctuations make it difficult to focus; lighting, which can affect our ability to engage with different environments; and colour, which affects our mood.
Passage taken from: Ueland, B. (2006). Becoming a Master Student. Boston, MA : Houghton Mifflin College Div., p. 121.
- Read the passage.
- Highlight or underline necessary information (hint: there are five important ideas).
- Write your summary.
Most people drink orange juice and eat oranges because they are said to be rich in vitamin C. There are also other foods that are rich in vitamin C. It is found in citrus fruits and vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, cabbage, cauliflower, and carrots.
Vitamin C is important to our health. Do you really know how essential this nutrient is to our health and well-being? Our body needs to heal itself. Vitamin C can repair and prevent damage to the cells in our body and heal wounds. It also keeps our teeth and gums healthy. That is not all. It protects our body from infections such as colds and flu and also helps us to get better faster when we have these infections. That is why a lot of people drink orange juice and take vitamin C tablets every day. This wonderful vitamin is also good for our heart. It protects the linings of the arteries, which are the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood. In other words, it offers protection against heart disease.
If we do not get enough vitamin C, which means we are not eating enough food that contains this vitamin, it can lead to serious diseases. Lack of vitamin C can lead to scurvy, which causes swollen gums, cheeks, fingers, hands, toes, and feet. In serious conditions, it can lead to bleeding from wounds, loss of teeth, and opening up of wounds. Therefore, make sure you have enough vitamin C in your diet.
Exercise taken from: http://www.scribd.com/doc/98238709/Form-‐Three-‐Summary-‐Writing-‐Exercise
Annotating, note making, or note taking is a matter of personal preference in terms of style. The most important thing is to do something . Again we stress that reading is like a dialogue with an author. The author wrote this material. Pretend you are actually talking to the author.
- Do not let an idea pass without noting it.
- Do not let an ambiguity go by without questioning it.
- Do not let a term slip away if context does not help you understand it; look it up!
- Engage and you will both understand and remember.
PRO TIP: Put small checks in pencil where you would normally underline. When you finish a section, look back and see what you really need to mark. (If you check over 50 percent of the page, you probably are marking to go back and learn later versus thinking about what is really important to learn now!)
Use consistent symbols to visually help you identify what is happening on the page:
- Circle central themes or write at the beginning of the section if it is not directly stated.
- [Bracket] main points.
- Underline key words or phrases for significant details.
- Put numbers 1, 2, 3 for items listed.
- Put square brackets or highlights for key terms when the definition follows.
- Use stars (*), question marks (?), or diagrams in the margins to show relevance.
- Use key word outlines in the margins for highlighting.
- Write questions in the margin that test your memory of what is written right there.
- Use blank spaces indicating the number of ideas to be remembered, forcing you to test yourself versus just rereading.
General Note-Taking Guidelines
- Before class, quickly review your notes from the previous class and the assigned reading. Fixing key terms and concepts in your mind will help you stay focused and pick out the important points during the lecture.
- Come prepared with paper, pens, highlighters, textbooks, and any important handouts.
- Come to class with a positive attitude and a readiness to learn. During class, make a point of concentrating. Ask questions if you need to. Be an active participant.
- During class, capture important ideas as concisely as you can. Use words or phrases instead of full sentences, and abbreviate when possible.
- Visually organize your notes into main topics, subtopics, and supporting points, and show the relationships between ideas. Leave space if necessary so you can add more details under important topics or subtopics.
- If your professor gives you permission to do so, you could consider taking pictures of the notes on the board with a mobile device or audio recording the lecture.
- Ideas that the instructor repeats frequently or points out as key ideas
- Ideas the instructor lists on a whiteboard or transparency
- Details, facts, explanations, and lists that develop main points
- Review your notes regularly throughout the semester, not just before exams.
Organizing Ideas in Your Notes
A good note-taking system needs to help you differentiate among major points, related subtopics, and supporting details. It visually represents the connections between ideas. Finally, to be effective, your note-taking system must allow you to record and organize information fairly quickly. Although some students like to create detailed, formal outlines or concept maps when they read, these may not be good strategies for class notes because spoken lectures may not allow time for to create them.
Instead, focus on recording content simply and quickly to create organized, legible notes. Try one of the following techniques.
Modified Outline Format
A modified outline format uses indented spacing to show the hierarchy of ideas without including roman numerals, lettering, and so forth. Just use a dash or bullet to signify each new point unless your instructor specifically presents a numbered list of items.
The first example shows Crystal’s notes from a developmental psychology class about an important theorist in this field. Notice how the line for the main topic is all the way to the left. Subtopics are indented, and supporting details are indented one level further. Crystal also used abbreviations for terms like development and example .

If you are a visual learner, you may prefer to use a more graphic format for notes, such as a mind map. The next example shows how Crystal’s lecture notes could be set up differently. Although the format is different, the content and organization are the same.
If the content of a lecture falls into a predictable, well organized pattern, you might choose to use a chart or table to record your notes. This system works best when you already know, either before class or at the beginning of class, which categories you should include. The next figure shows how this system might be used.
The Cornell Note-Taking System
In addition to the general techniques already described, you might find it useful to practise a specific strategy known as the Cornell note-taking system. This popular format makes it easy not only to organize information clearly but also to note key terms and summarize content.
To use the Cornell system, begin by setting up the page with these components:
- The course name and lecture date at the top of the page
- A narrow column (about two inches) at the left side of the page
- A wide column (about five to six inches) on the right side of the page
- A space of a few lines marked off at the bottom of the page
During the lecture, you record notes in the wide column. You can do so using the traditional modified outline format or a more visual format if you prefer.
Then, as soon as possible after the lecture, review your notes and identify key terms. Jot these down in the narrow left-hand column. You can use this column as a study aid by covering the notes on the right-hand side, reviewing the key terms, and trying to recall as much as you can about them so that you can mentally restate the main points of the lecture. Uncover the notes on the right to check your understanding. Finally, use the space at the bottom of the page to summarize each page of notes in a few sentences.
Over the next few weeks, establish a note-‐taking system that works for you.
- If you are not already doing so, try using one of the aforementioned techniques. (Remember that the Cornell system can be combined with other note-‐taking formats.)
- It can take some trial and error to find a note-‐taking system that works for you. If you find that you are struggling to keep up with lectures, consider whether you need to switch to a different format or be more careful about distinguishing key concepts from unimportant details.
- If you find that you are having trouble taking notes effectively, set up an appointment with your school’s academic resource centre.
Using Online Study Tools
1. guided study session videos.
One excellent tool to help with accountability is guided study session videos. Much like guided meditation, these videos can help you stay on track and give you some accountability. It’s like a study partner that can’t distract you!
Video source: https://youtu.be/reRYtjr1BNo
2. The Pomodoro Technique
Much like a Guided Study Session, the Pomodoro Study Session plays ambient noise and displays a timer. Every 25 minutes, you take a break from whatever you’re doing. During this time you can stretch, check your phone, etc. Here’s a neat Harry Potter themed one!
Video source: https://youtu.be/SkmH9CsMqOo
3. Browser Lockdown Tools
Are you the person who is always getting distracted while studying? You might consider a website blocker (list of some available here) that will prohibit you from accessing certain sites for a certain length of time. You tell it your guilty procrastination sites (Reddit? Instagram? Discord?) and how long you want them locked.
And maybe leave your phone/tablet in another room… 😏
4. Find a Notetaking Program/System
There are a variety of free notetaking systems and programs available. Many students prefer the ease of a program like Google Docs , but there are others such as Evernote , and OneNote .
5. Looking into Assistive Technology
Assistive technology has been used by students with disabilities for a long time; however, these tools are equally valuable for all students! Not all of them are free, but they can be a game changer for some people:
Digital Highlighters: these cool gadgets allow you to scan hardcopy texts with a pen and it will transfer the text into a digital format on your computer/tablet. Some popular options are Scanmarker and IrisPen
Text-to-Speech Pens/Reader Pens: Similar to digital highlighters, these pens also have the ability to read the text that you scan out loud. Some of them also feature dictionaries built into the pen. They are often a tool of choice for students who are learning English as an additional language and for those with dyslexia, AD(H)D, etc. The most popular option is the C-Pen
Digital Notebooks and Smart Pens: Digital notebooks are an excellent hybrid of physical note taking with technological storage. One of the more popular options is the Rocektbook , which is reusable and allows you to write notes and scan them to a notetaking program using a phone app. Smart Pens, like the LiveScribe Pen allow you to record audio, take pictures, and transfer handwritten notes to a note taking program.
Text-to-Speech Readers: this type of technology has become more popular in recent years. These programs read digital texts aloud to you, and many are available online for free, but you may wish to start with one like NaturalReader to see if it’s helpful.
Speech-to-Text Programs: the opposite of a text-to-speech reader and exactly what it sounds like, Speech-to-Text programs allow you to dictate to the computer using a microphone and what you say will be converted into text. This website has a list of popular free programs, broken down by OS.
Using Available ACADEMIC Support Resources
One reason students sometimes find post-secondary courses overwhelming is that they do not know about, or are reluctant to use, the resources available to them. There is help available; your student fees help pay for resources that can help in many ways, such as a health centre or tutoring service. If you need help, consider asking for help from any of the following:
- Your instructor: If you are making an honest effort but still struggling with a particular course, set a time to meet with your instructor and discuss what you can do to improve. He or she may be able to shed light on a confusing concept or give you strategies to catch up.
- Your academic advisor or program coordinator: Many institutions assign students an academic advisor or program coordinator who can help you choose courses and ensure that you fulfill degree and major requirements.
- The academic resource centre: These centres offer a variety of services, which may range from general coaching in study skills to tutoring for specific courses. Find out what is offered at your school and use the services that you need.
- The writing centre ( Sheridan Tutoring Services ): These centres employ tutors to help you manage your writing assignments. They will not write or edit your paper for you, but they can help you through the stages of the writing process. (In some schools, the writing centre is part of the academic resource centre.)
- The career resource centre: Visit the career resource centre for guidance in choosing a career path, developing a resumé, and finding and applying for jobs.
- Sheridan Counselling services : Sheridan offers counselling services on campus for free. Use these services if you need help coping with a difficult personal situation or managing depression, anxiety, or other problems.
Students sometimes neglect to use available resources due to limited time, unwillingness to admit there is a problem, or embarrassment about needing to ask for help. Unfortunately, ignoring a problem usually makes it harder to cope with later on. Waiting until the end of the semester may also mean fewer resources are available, since many other students are also seeking last minute help.
Writing for Academic and Professional Contexts: An Introduction Copyright © 2023 by Sheridan College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- [email protected]
- (800) 428-8378
Study Habits: How and Why to Practice Effective Studying
Whether in public or private school, most students encounter the same basic curriculum. Granted, the curriculum has changed over the years , but the fundamentals still apply. Math, language arts, history, geography, and sciences are core subjects. Some students will achieve advanced levels in these topics but all will need to develop effective study habits to achieve their best.
Schools cover core and niche subjects well but don’t always address how to study them. Let’s look at what good study habits are, and how to practice them.
Why are study habits important?
Good study habits help don’t just help in school; they help in professional settings and life in general. Practicing good habits regularly allows you to be your most productive and efficient. Successful students tend to become successful professionals, and this success is often built on well-established habits. The best study habits turn into good habits for any time.
Unfortunately, students do not generally learn study skills in school. With rare exceptions, there are few classes in either public or private schools focused on them. Students are expected to develop these skills on their own. All students develop habits, but many of these habits can be counterproductive. For example, countless parents complain about their students doing homework while watching television. That is a study habit, just not a good one.
Developing good study habits early usually leads to retaining and using these habits throughout life. Middle school and college chemistry students are at different levels, but both can use the same habits to learn the material. A CEO and a high school civics students have different needs, but both need to be organized and focused to reach their goals.
What are the Best Study Habits?
The best study habits include:
- Organization
- Time management
- Developing a personal learning style
- Clear note-taking
- Studying efficiently
- Working effectively with teachers tutors
Success in every part of life requires good organization . Getting and staying organized allows students and adults alike to accomplish tasks efficiently. It’s more than having a tidy desk; it involves tasks like managing multiple work spaces at school, effective record keeping, and clear labeling.
Time Management is also an excellent habit for both students and professionals. It minimizes stress, errors, and time waste. Time management begins with tools as simple as a calendar or egg timer. Practicing macro (weeks, months) and micro (days, hours, tasks, projects) time management helps students complete tests within the time limit, and project managers track progress on year-long projects.
Developing a personal learning style is important because everyone learns differently. Some students do best with visual examples. Others prefer dialogue with teachers. Some learn everything they need from reading books straight through. Flashcards, mnemonics, and memory tricks can all help different kinds of learners. Find what works for you, and build your study plan around that.
C lear note-taking is essential. Remember, you’re taking notes so you can reference them while you study later. Make sure you can easily read and understand them. There are different ways to do this , so play around.
Studying efficiently means you can retain, repeat, apply, and synthesize information. Studying efficiently tends to happen when your other good habits are in play. Are you organized and managing your time well? Do you know how you best learn and retain information? Are your notes clear and easy for you to understand?
Finally, working effectively with teachers and tutors is key to getting the most out of your education. Trust your educators, and trust the process.
How Can I Improve My Study Habits?
It’s never too late to start improving your habits. It takes a conscious effort, self-discipline, and hard work. Most people, adults included, have a difficult time doing this on their own. It’s hard to be constructive and self-critical, and it’s easy to be complacent. Regardless, every person reaches a point in life where it is too challenging to keep track of accomplish your goals without a plan for doing so. We need to keep changing and growing, and good habits help this.
Start by getting familiar with the habits discussed here. Ask yourself: am I already practicing these? How can I be more effective? Take inventory of your answers. Then, think of simple steps and begin practicing them, one at a time. For example, if you need to work on organization, buy or repurpose folders to organize your notes and resources by subject. If you need to improve time management, get a weekly planner that works for you and fill it out at the start of every week. Regular practice is key.
Parents can help too. Parents should collaborate with students, learning about effective study habits, and working to integrate them into daily life. Practicing these habits together helps parents stay involved and informed about student needs and goals. One simple strategy is to have weekly planning sessions, where students and parents discuss their goals, schedule, and what they’re anticipating for the week.
Finally, consider seeing a tutor. Tutors specialize in maximizing study efficiency, and focus on an individual student’s learning needs to develop a personalized study plan. A fundamental part of any good plan comes down to practicing good habits.
To learn more, visit our academic tutoring page.
Practice Makes Permanent
Developing and practicing these habits makes them permanent. The school year often gets interrupted, through scheduled breaks, through the summer, and through snow days. Sometimes, extenuating circumstances shut schools down and require students to study from home. In these gaps, it’s easy for students to fall off their studies and lose the knowledge they gained in school. However, if you practice these skills regularly, it’s much easier to stay on top of your studies, even when school isn’t in session.
These steps will help you develop positive study habits. Think of it as investing in yourself. Each skill takes time to learn but ultimately saves time and energy in the long run. That is what it’s all about: building an efficient and effective process that allows you to accomplish all of your work while opening up time for the fun things in life.
Sample details
- Social Issues,
- Academic achievement,
- Words: 1217
- Views: 1,335
Related Topics
- Restorative justice
- Eyewitness testimony
- Juvenile Justice
- Social injustice

Study Habits and Academic Achievement
Education is commonly referred to as the process of learning and obtaining knowledge at school, in a form of formal education. Generally, at the start of a very young age, children learn to develop and use their mental, moral and physical powers, which they acquire through various types of education. The process of education does not only start when a child first attend school. Education begins at home when the parent started to give knowledge to the child. This will be followed up by the education given by the teachers. In almost all societies, receiving an education in school is extremely vital and necessary if a person wants to achieve success in life. Thus, education is the key that allows people to move up in the world, seeks better jobs and ultimately succeed fully in life. In education, it involves study habits and this is the ways that you study; the habits that you formed during school years. Study habits can be good ones or bad ones. Good study habits include being organized, keeping good notes, reading your textbook, listening in class, and w2orking everyday. (Mercado, 1999).
Learning can be immensely gratifying, but studying usually involves hard work. The first step towards effective study habits is to face up to this reality. One need not feel guilty if one doesn’t look forward to studying. Once an individual accepts the premise that studying doesn’t come naturally, it should be apparent that one needs to set up an organized programmed to promote adequate study.
ready to help you now
Without paying upfront
One way to increase the likelihood of success in your educational pursuits is to consciously maintain productive and intentional learning habits. While it is debatable how long it takes to break a bad habit or instill a healthy one; one thing is for certain cultivating positive study habits is essential to pursuing a degree in counseling, therapy, social work and psychology. (Dr. Allison A. Buskirk-Cohen, Ph. D).
In fact, many of the Filipino school have also encountered this kind of problem. It has always been the presumption of many educators that students will eventually develop good study habit as they grow and become more experienced in school. But this is only partly true. It has been observed that not all students develop effective study habits and learning strategies unless there is someone who will help them to make them achieve in their academic. However, behind this so-called “study habits” either good or bad there are factors or reasons behind of what kind of study habit the student produce. Golden Heritage Polytechnic College, the School of Discipline support the concern that a 3rd year college students must have a study habits in order for them to increase their academic performance.
Ashish (2003) opines that if students must ensure academic success throughout the entire year, it is important to ditch bad study habits and establish good ones. A students who will practice study habits will surely increase its academic performance.
The primary aim of this study was to examine the effect of study habit on students academic performance. Study habits are importance as they influence the academic performance of students so parents and teachers must help in improving the study habits of students. The topic was chosen based on the concern raised by the school regarding on the study habits in Golden Heritage Polytechnic College. The researchers had chosen the 3rd year college students as the respondents for the reason that they are ahead, mature, and responsible students among others.
In order to improve the quality of education we must develop certain innovative strategies, which will enhance the educational standards. In addition to that from the student’s side there must be some important steps, which form the basis for their academic achievement. Students’ needs, requirements, abilities, capabilities, their pattern of studying etc. have been neglected for a long time and they were forced to learn the same thing, by the same method, by the same person in the same environment. Not only is it important that teachers recognize these diversities in their students, but also it is desirable that they value their study habits. Otherwise, even if appropriate strategies are developed and made available to teachers, there may be little proof of gain in the students. Our educational institutions should take into account basic human differences in their studying, thinking etc., to seek better means of individualized instruction for more effective studying (Arul Lawrence, 2013).
Conceptual Framework
Various researchers proved that there is a significant between study habits towards their academic performance. Whether the study habits is systematic or unsystematic, efficient or otherwise there could always be an impact to students academic performance. In education, there were many different kinds of learning that will required for later interaction in the world. Such aspect includes this behind so-called study habits either good or bad there are factors or reasons behind what kind of of the study habits the student produce.
The theoretical/conceptual framework of this study is anchored on the self determination theory by Edward L. Deci and Richard M. Ryan because the learner himself and the independent variables have a great role in shaping the learners study habit. This will focused on motivation of the learner. Maslow’s theory which is propounded in 1943 in his work entitled “motivation and production”. This theory is simple concerned with the identification of factors and processes to which paid attention must be paid. That whatever we want to do ,whether typing, teaching and learning we must sufficiently motivated before we can put up the necessary action which lead their academic achievement and realization.
Motivation is important in an individual to do once task and if one is not motivated it is impossible to come up a good result. In connection with self motivation theory, Gestalt theory indicates the need for considering the whole but also the details with environment. This implies that in understanding the academic performance of students, the environment which stimulates certain study skills, study techniques, use of instructional materials and teaching method should be considered to know the perception and understanding of a lesson by student. These variables are considered as the nurturing social environment and in one way or other these may influence the study habits of the students. It is important to consider the study habits of the students on how they manage their time efficiently and how to have effective varied study techniques to keep them float.
This study aimed to look into the study habits and its impact to their academic performance of 3rd year college students in Golden Heritage Polytechnic College , School year 2018-2019. Academic achievements used measured by the examination results, was one of the major goals of a school.
This study was limited only to the 3rd year college students in Golden Heritage Polytechnic College (GHPC). It involved responses on the surveyed pupils from the mention institution and the study was limited for the school year 2018-2019. As part of the study, researcher gave an emphasis on the study habits and academic achievement of the said students.
Definition of Terms
There are terms that were used throughout the literature review that need to be defined for clarity of understanding. The following are as follows: Academic. This variable refers to practice or habit of being absent from work or school.
Cite this page
https://graduateway.com/study-habits-and-academic-achievement/
You can get a custom paper by one of our expert writers
Check more samples on your topics
The effects of study habits on academic performance sample.
This survey identifies whether survey wonts bring positive or negative effects to the academic public presentation of pupils. This survey gives sufficient information on which survey wonts bring high General Percentage Average of pupils. Introduction The extent of student’s acquisition in faculty members may be determined by the classs a pupil earns for a period of larning.
Effects of Divorce on the Academic Achievement of a Child
Academic achievement
Divorce is one of the many problems facing the family unit today. People have different views on the effect of divorce on children but not a few analysts opine that when a couple opt for divorce, the resultant effects on them and their children are most times negative. The term 'divorce' came from the Latin
Intrinsic Motivation and Its Effects Upon Academic Achievement in Middle
The foundation of academic success is based on several factors and motivation is ahead of all. Some students show high motivations when they come to school where as other students do not show such degree of motivation and are found to be reluctant during their classroom lessons. Teachers put heavy emphasis on making such reluctant
Low Socioeconomic Status and Academic Achievement
Low Socioeconomic Status and Academic Achievement Introduction According to the United States Bureau of Census, the most recent poverty rates of children are higher than they ever were. A large percentage of children in the classroom are coming from low socioeconomic households. And, a huge amount of research has shown that a child’s socioeconomic status affects his
Parenting Styles influence Academic Achievement
Parenting styles
Parents are the primary persons who are responsible to teach good values and behavior in children. Parents have different methods on how to transmit their values, skills, behavior, and attitudes to their children. Most parents want their children to do well in school however not all parents are successful in this. When parents have a
The Importance of Sleep to Health, Behavior, and Academic Performance and the Sleeping Habits of American Teenagers
Importance Of Sleep
American teenagers are getting far less sleep than needed for them in order to function properly. The health, behavior, and academic performance of teenagers are suffering as a result of their sleep deprivation. According to parents reports in the 1999 nationwide survey, Sleep in America, sixty percent of children under the age of eighteen complained
Academic Plagiarism and Why is Academic Integrity
What Is Plagiarism? “Plagiarism is derived from the Latin word “plagiarus” which means “kidnapper,” who abducts the child” (Merriam Webster,). Plagiarism is a widespread problem around the world. There are many types of plagiarism. People don’t acknowledging its author and representing the paper as their own or purchase the assignment from ghost-writers and showing them as
Academic Plagiarism vs. Non-Academic Plagiarism
What is the easiest way to get the best grade on an essay? What is the easiest way to design new clothes in the most fashionable way? What is the fastest way to create the most popular game? I believe the answer would be plagiarizing. According to the article “Understanding Plagiarism and Its Dangers” plagiarizing
Academic Integrity and Academic Misconduct Essay
Academic integrity is the commitment to and demonstration of honest and moral behavior in an academic setting (writingcenter.unc.edu). Therefore, individuals practicing academic integrity is crucial because it displays high standards that protect and uphold your reputation, reflects well in different environments (i.e. professional programs, colleges/universities, potential work settings, etc.) and being major contributors to the

Hi, my name is Amy 👋
In case you can't find a relevant example, our professional writers are ready to help you write a unique paper. Just talk to our smart assistant Amy and she'll connect you with the best match.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Good Study Habits. 1. Time Management. Time management refers to being able to efficiently allocate your time so you don't run out of time, and so you have enough time to allocate to all important tasks. As a basis, you could initiate a dedicated study schedule, specifying the time slots for each subject.
Conclusion. In conclusion, good study habits are essential for academic success. Various study habits such as time management, active learning, note-taking, repetition and practice, mnemonics, visualization, test-taking strategies, reviewing material, time management during exams, time management during online learning, active learning during online learning, and self-motivation during online ...
Essay On Study Habits. 2311 Words10 Pages. INTRODUCTION. Education is the most important invention of mankind, it has a very wide meaning and it is not possible to give it a precise meaning. Different philosophers and scholars have defined education according to their own ideas and philosophies. Education helps an individual to give his/her ...
8 general effective study habits to boost your grades. Adopt the right study mindset. Know the class expectations. Choose an effective study location. Have the right study materials. Use helpful ...
Creating Positive Change: Good Study Habits Essay. Good study habits are best described as a set of tools that facilitate an increase of the amount of information learned and also make the information to be remembered for a long time. Well, I did not grow up with good study habits, I used to spend most of my free time playing video games ...
Good sleep and eating healthy are part of studying well. Your brain needs rest to work at its best. Try to sleep enough and choose healthy snacks when you're studying. Remember, good study habits are about being regular, organized, and taking care of yourself. Stick to these simple rules, and you'll be able to learn better and remember more.
There are many things that students can do to improve their study habits. Such as: Set a regular study schedule and stick to it. Choose a quiet and comfortable place to study. Break down large tasks into smaller, more manageable ones. Take breaks to avoid burnout. Use effective study techniques, such as spaced repetition and active recall.
Definition. Study habits refer to the consistent practices and methods that students develop to facilitate their learning and retention of information. These habits encompass a range of activities, including time management, note-taking, and self-testing, which collectively enhance understanding and performance in reading and writing tasks.
Motivation: Motivation refers to the internal or external factors that drive individuals to engage in certain behaviors. In the context of study habits, motivation plays a crucial role in sustaining focus and effort during studying. Reinforcement: Reinforcement involves providing rewards or consequences to strengthen or weaken certain behaviors.
Use tactile study aids, such as flash cards or study guides you design yourself. Use self-stick notes to record ideas for writing. These notes can be physically reorganized easily to help you determine how to shape your paper. Use a physical activity, such as running or swimming, to help you break through writing blocks.
Abstract and Figures. Study habits are at the core of a learner's academic success. It is an action like reading, taking notes, conducting study groups that students perform frequently, and ...
Introduction. Study habits are commonly known as the usual behavior or habitual practices by a person in order to study and learn effectively. Study habits help students make their studies easier to understand and make their learning experience comfortable and enjoyable. Having good study habits are important for a student because it will help ...
As predicted, structural equation modeling (SEM) indicated that study self-efficacy mediated the study habits—procrastination relation. The mediation effects were medium to large. We conclude that training of, and advice on, study skills and habits should be accompanied by measures that build study self-efficacy.
the academic achievement and study habit of the student to a large extent culminates into shaping an individual destiny. The general belief is that students who exercise good study habits are likely to excel than those with poor study habits. According to Sharma (2005, p.67)" academic
student's success or failure is determined by one's own study habits. Study. abits act as the building blocks for learning and success among students. Tea. hers should guide and inspire students in developing better study habits. With appropriate guidance and motivation from teachers' time to time, students devel.
The best study habits turn into good habits for any time. Unfortunately, students do not generally learn study skills in school. With rare exceptions, there are few classes in either public or private schools focused on them. Students are expected to develop these skills on their own. All students develop habits, but many of these habits can be ...
Study habits, as defined by Uju and Paul (2017), encompass how an individual approaches their studies, emphasizing the importance of good study habits for academic success.
with proper study habits and improving one's study habits is the key to better studying. Being organized and having homework routines are the most important things in helping a child/student develop good study habits for life. Developing good study habits help spell success and a student will find himself working more efficiently and
A standardized tool "Rao's Study Habits Inventory" was used. This inventory consists of 40 items covering the six dimensions of study habits. a) Planning; b) Effective reading habits; c) Note taking preparation and revision; d) Motivation & interest; e) Concentration & clarity; f) Academic neuroticism.
and b y cumulative and interactive effects in the society. The stud y habits comprise of nine different. kinds of study behaviors. These are Compre hension, Concentration, Task orientation, Study ...
In this study, students in a large introductory psychology class completed a "learning how to learn" assignment in which they read one of four randomly assigned empirical articles about the utility of a learning strategy (i.e., distributed practice, rereading, practice testing, or forming mental images) and wrote a paper summarizing ...
Good study habits include being organized, keeping good notes, reading your textbook, listening in class, and w2orking everyday. (Mercado, 1999). Learning can be immensely gratifying, but studying usually involves hard work. The first step towards effective study habits is to face up to this reality. One need not feel guilty if one doesn't ...