How to Write a Research Proposal Paper


Table of Contents
What is a research proposal paper, why write a research proposal paper.
- How to Plan a Research Proposal Paper
Components of a Research Proposal Paper
Research proposal examples, help & additional resources, this resource page will help you:.
- Learn what a research proposal paper is.
- Understand the importance of writing a research proposal paper.
- Understand the steps in the planning stages of a research proposal paper.
- Identify the components of a research proposal paper.
A research proposal paper:
- includes sufficient information about a research study that you propose to conduct for your thesis (e.g., in an MT, MA, or Ph.D. program) or that you imagine conducting (e.g., in an MEd program). It should help your readers understand the scope, validity, and significance of your proposed study.
- may be a stand-alone paper or one part of a larger research project, depending on the nature of your assignment.
- typically follows the citation format of your field, which at OISE is APA .
Your instructor will provide you with assignment details that can help you determine how much information to include in your research proposal, so you should carefully check your course outline and assignment instructions.
Writing a research proposal allows you to
- develop skills in designing a comprehensive research study;
learn how to identify a research problem that can contribute to advancing knowledge in your field of interest;
further develop skills in finding foundational and relevant literature related to your topic;
critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem;
see yourself as an active participant in conducting research in your field of study.
Writing a research proposal paper can help clarify questions you may have before designing your research study. It is helpful to get feedback on your research proposal and edit your work to be able to see what you may need to change in your proposal. The more diverse opinions you receive on your proposal, the better prepared you will be to design a comprehensive research study.
How to Plan your Research Proposal
Before starting your research proposal, you should clarify your ideas and make a plan. Ask yourself these questions and take notes:
What do I want to study?
Why is the topic important? Why is it important to me?
How is the topic significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
What problems will it help solve?
How does it build on research already conducted on the topic?
What exactly should I plan to do to conduct a study on the topic?
It may be helpful to write down your answers to these questions and use them to tell a story about your chosen topic to your classmates or instructor. As you tell your story, write down comments or questions from your listeners. This will help you refine your proposal and research questions.
This is an example of how to start planning and thinking about your research proposal assignment. You will find a student’s notes and ideas about their research proposal topic - "Perspectives on Textual Production, Student Collaboration, and Social Networking Sites”. This example is hyperlinked in the following Resource Page:
A research proposal paper typically includes:
- an introduction
- a theoretical framework
- a literature review
- the methodology
- the implications of the proposed study and conclusion
- references
Start your introduction by giving the reader an overview of your study. Include:
- the research context (in what educational settings do you plan to conduct this study?)
- the research problem, purpose (What do you want to achieve by conducting this study?)
- a brief overview of the literature on your topic and the gap your study hopes to fill
- research questions and sub-questions
- a brief mention of your research method (How do you plan to collect and analyze your data?)
- your personal interest in the topic.
Conclude your introduction by giving your reader a roadmap of your proposal.
To learn more about paper introductions, check How to write Introductions .
A theoretical framework refers to the theories that you will use to interpret both your own data and the literature that has come before. Think about theories as lenses that help you look at your data from different perspectives, beyond just your own personal perspective. Think about the theories that you have come across in your courses or readings that could apply to your research topic. When writing the theoretical framework, include
- A description of where the theories come from (original thinkers), their key components, and how they have developed over time.
- How you plan to use the theories in your study / how they apply to your topic.
The literature review section should help you identify topics or issues that will help contextualize what the research has/hasn’t found and discussed on the topic so far and convince your reader that your proposed study is important. This is where you can go into more detail on the gap that your study hopes to fill. Ultimately, a good literature review helps your reader learn more about the topic that you have chosen to study and what still needs to be researched
To learn more about literature reviews check What is a Literature Review .
The methods section should briefly explain how you plan to conduct your study and why you have chosen a particular method. You may also include
- your overall study design (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods) and the proposed stages
- your proposed research instruments (e.g. surveys, interviews)
- your proposed participant recruitment channels / document selection criteria
- a description of your proposed study participants (age, gender, etc.).
- how you plan to analyze the data.
You should cite relevant literature on research methods to support your choices.
The conclusion section should include a short summary about the implications and significance of your proposed study by explaining how the possible findings may change the ways educators and/or stakeholders address the issues identified in your introduction.
Depending on the assignment instructions, the conclusion can also highlight next steps and a timeline for the research process.
To learn more about paper conclusions, check How to write Conclusions .
List all references you used and format them according to APA style. Make sure that everything in your reference list is cited in the paper, and every citation in your paper is in your reference list.
To learn more about writing citations and references, check Citations & APA .
These are detailed guidelines on how to prepare a quantitative research proposal. Adapted from the course APD2293 “Interpretation of Educational Research”. These guidelines are hyperlinked in the following Resource Page:
Related Resource Pages on ASH
- What is a Literature Review?
- How to Prepare a Literature Review
- How to Understand & Plan Assignments
- Citations and APA Style
- How to Integrate Others' Research into your Writing
- How to Write Introductions
- How to Write Conclusions
Additional Resources
- Writing a research proposal– University of Southern California
- Owl Purdue-Graduate-Specific Genres-Purdue University
- 10 Tips for Writing a research proposal – McGill University
On Campus Services
- Book a writing consultation (OSSC)
- Book a Research Consultation (OISE Library)
Resources for Early Career Researchers: Writing a Research Proposal
- Getting Started with Research
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Literature Resources
- Publishing Your Research
- Data Management: Rigor and Reproducibility
- Promoting Your Research
- Promotion and Tenure
- Leadership and Professional Development
Designing Your Research Proposal from SAGE Publications
Writing research proposal resources.
Grant Writing Resources
- Resources for Grantseekers Congressional Research Service
Budgeting for Publication Fees
Good news! Many times you can write the cost of the publication fee into your research grant. The NIH Grants Policy Statement includes a section related to publication and printing costs. The National Science Foundation also outlines publication costs in section 617 of their awards documentation. Be advised that it is best to consider publication costs early on in the research process. A lack of funding for publication fees can limit publishing options.
For more information about how to include Article Processing Charges (APCs) in your funding proposals, watch the short video below. This video includes sample language you can use or adapt for your funding proposals.
Additional Writing Resources
- PLOS Writing Center Free resources for authors looking to build their skills related to scientific writing an publishing.
- Elsevier Author Resources Writing and Publishing Resources from Elsevier.
- Springer Nature Early Career Researchers Resources for early career researchers from Springer Nature.
- Wiley Author Resources Resources for authors from Wiley,
- ECR Community Blog from PLOS Blog for Early Career Researches from PLOS.
- NIH e-Protocol Writing Tool Writing assistance from the National Institutes of Health.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Eliminating Words Resource from the Purdue Online Writing Lab to help you eliminate unnecessary words.
- 5 Ways to Cut the Clutter in Writing Writing tips to help decrease word counts.
- 129 Deadwood Phrases that Kill Good Writing List of phrases that can be consolidated.
- << Previous: Getting Started with Research
- Next: Literature Resources >>

- Last Updated: Jul 1, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/EarlyCareerResearchers

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2962
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal is a type of text which maps out a proposed central research problem or question and a suggested approach to its investigation.
In many universities, including RMIT, the research proposal is a formal requirement. It is central to achieving your first milestone: your Confirmation of Candidature. The research proposal is useful for both you and the University: it gives you the opportunity to get valuable feedback about your intended research aims, objectives and design. It also confirms that your proposed research is worth doing, which puts you on track for a successful candidature supported by your School and the University.
Although there may be specific School or disciplinary requirements that you need to be aware of, all research proposals address the following central themes:
- what you propose to research
- why the topic needs to be researched
- how you plan to research it.
Purpose and audience
Before venturing into writing a research purposal, it is important to think about the purpose and audience of this type of text. Spend a moment or two to reflect on what these might be.
What do you think is the purpose of your research proposal and who is your audience?
The purpose of your research proposal is:
1. To allow experienced researchers (your supervisors and their peers) to assess whether
- the research question or problem is viable (that is, answers or solutions are possible)
- the research is worth doing in terms of its contribution to the field of study and benefits to stakeholders
- the scope is appropriate to the degree (Masters or PhD)
- you’ve understood the relevant key literature and identified the gap for your research
- you’ve chosen an appropriate methodological approach.
2. To help you clarify and focus on what you want to do, why you want to do it, and how you’ll do it. The research proposal helps you position yourself as a researcher in your field. It will also allow you to:
- systematically think through your proposed research, argue for its significance and identify the scope
- show a critical understanding of the scholarly field around your proposed research
- show the gap in the literature that your research will address
- justify your proposed research design
- identify all tasks that need to be done through a realistic timetable
- anticipate potential problems
- hone organisational skills that you will need for your research
- become familiar with relevant search engines and databases
- develop skills in research writing.

The main audience for your research proposal is your reviewers. Universities usually assign a panel of reviewers to which you need to submit your research proposal. Often this is within the first year of study for PhD candidates, and within the first six months for Masters by Research candidates.
Your reviewers may have a strong disciplinary understanding of the area of your proposed research, but depending on your specialisation, they may not. It is therefore important to create a clear context, rationale and framework for your proposed research. Limit jargon and specialist terminology so that non-specialists can comprehend it. You need to convince the reviewers that your proposed research is worth doing and that you will be able to effectively ‘interrogate’ your research questions or address the research problems through your chosen research design.
Your review panel will expect you to demonstrate:
- a clearly defined and feasible research project
- a clearly explained rationale for your research
- evidence that your research will make an original contribution through a critical review of the literature
- written skills appropriate to graduate research study.
Research and Writing Skills for Academic and Graduate Researchers Copyright © 2022 by RMIT University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on September 5, 2024.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2024, September 05). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
- Utility Menu
GA4 tracking code

- All URAF Opportunities
- CARAT (Opportunities Database)
- URAF Application Instructions
- URAF Calendar of Events and Deadlines
Writing Research Proposals
The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…
- You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project;
- You have the necessary background to complete this project;
- You have the proper support system in place;
- You know exactly what you need to complete this project and how to do so; and
- With this funding in hand, you can be on your way to a meaningful research experience and a significant contribution to your field.
Research proposals typically include the following components:
- Why is your project important? How does it contribute to the field or to society? What do you hope to prove?
- This section includes the project design, specific methodology, your specific role and responsibilities, steps you will take to execute the project, etc. Here you will show the committee the way that you think by explaining both how you have conceived the project and how you intend to carry it out.
- Please be specific in the project dates/how much time you need to carry out the proposed project. The scope of the project should clearly match the timeframe in which you propose to complete it!
- Funding agencies like to know how their funding will be used. Including this information will demonstrate that you have thoughtfully designed the project and know of all of the anticipated expenses required to see it through to completion.
- It is important that you have a support system on hand when conducting research, especially as an undergraduate. There are often surprises and challenges when working on a long-term research project and the selection committee wants to be sure that you have the support system you need to both be successful in your project and also have a meaningful research experience.
- Some questions to consider are: How often do you intend to meet with your advisor(s)? (This may vary from project to project based on the needs of the student and the nature of the research.) What will your mode of communication be? Will you be attending (or even presenting at) lab meetings?
Don’t be afraid to also include relevant information about your background and advocate for yourself! Do you have skills developed in a different research experience (or leadership position, job, coursework, etc.) that you could apply to the project in question? Have you already learned about and experimented with a specific method of analysis in class and are now ready to apply it to a different situation? If you already have experience with this professor/lab, please be sure to include those details in your proposal! That will show the selection committee that you are ready to hit the ground running!
Lastly, be sure to know who your readers are so that you can tailor the field-specific language of your proposal accordingly. If the selection committee are specialists in your field, you can feel free to use the jargon of that field; but if your proposal will be evaluated by an interdisciplinary committee (this is common), you might take a bit longer explaining the state of the field, specific concepts, and certainly spelling out any acronyms.
- Getting Started
- Application Components
- Interviews and Offers
- Building On Your Experiences
- Applying FAQs
Writing a Research Proposal
- First Online: 10 April 2022
Cite this chapter

- Fahimeh Tabatabaei 3 &
- Lobat Tayebi 3
1133 Accesses
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform your research in a well-organized and timely manner. In other words, by writing a research proposal, you get a map that shows the direction to the destination (answering the research question). If the proposal is poorly prepared, after spending a lot of energy and money, you may realize that the result of the research has nothing to do with the initial objective, and the study may end up nowhere. Therefore, writing the proposal shows that the researcher is aware of the proper research and can justify the significance of his/her idea.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
A. Gholipour, E.Y. Lee, S.K. Warfield, The anatomy and art of writing a successful grant application: A practical step-by-step approach. Pediatr. Radiol. 44 (12), 1512–1517 (2014)
Article Google Scholar
L.S. Marshall, Research commentary: Grant writing: Part I first things first …. J. Radiol. Nurs. 31 (4), 154–155 (2012)
E.K. Proctor, B.J. Powell, A.A. Baumann, A.M. Hamilton, R.L. Santens, Writing implementation research grant proposals: Ten key ingredients. Implement. Sci. 7 (1), 96 (2012)
K.C. Chung, M.J. Shauver, Fundamental principles of writing a successful grant proposal. J. Hand Surg. Am. 33 (4), 566–572 (2008)
A.A. Monte, A.M. Libby, Introduction to the specific aims page of a grant proposal. Kline JA, editor. Acad. Emerg. Med. 25 (9), 1042–1047 (2018)
P. Kan, M.R. Levitt, W.J. Mack, R.M. Starke, K.N. Sheth, F.C. Albuquerque, et al., National Institutes of Health grant opportunities for the neurointerventionalist: Preparation and choosing the right mechanism. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 13 (3), 287–289 (2021)
A.M. Goldstein, S. Balaji, A.A. Ghaferi, A. Gosain, M. Maggard-Gibbons, B. Zuckerbraun, et al., An algorithmic approach to an impactful specific aims page. Surgery 169 (4), 816–820 (2021)
S. Engberg, D.Z. Bliss, Writing a grant proposal—Part 1. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (3), 157–162 (2005)
D.Z. Bliss, K. Savik, Writing a grant proposal—Part 2. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (4), 226–229 (2005)
D.Z. Bliss, Writing a grant proposal—Part 6. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (6), 365–367 (2005)
J.C. Liu, M.A. Pynnonen, M. St John, E.L. Rosenthal, M.E. Couch, C.E. Schmalbach, Grant-writing pearls and pitfalls. Otolaryngol. Neck. Surg. 154 (2), 226–232 (2016)
R.J. Santen, E.J. Barrett, H.M. Siragy, L.S. Farhi, L. Fishbein, R.M. Carey, The jewel in the crown: Specific aims section of investigator-initiated grant proposals. J. Endocr. Soc. 1 (9), 1194–1202 (2017)
O.J. Arthurs, Think it through first: Questions to consider in writing a successful grant application. Pediatr. Radiol. 44 (12), 1507–1511 (2014)
M. Monavarian, Basics of scientific and technical writing. MRS Bull. 46 (3), 284–286 (2021)
Additional Resources
https://grants.nih.gov
https://grants.nih.gov/grants/oer.htm
https://www.ninr.nih.gov
https://www.niaid.nih.gov
http://www.grantcentral.com
http://www.saem.org/research
http://www.cfda.gov
http://www.ahrq.gov
http://www.nsf/gov
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Dentistry, Marquette University, Milwaukee, WI, USA
Fahimeh Tabatabaei & Lobat Tayebi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Tabatabaei, F., Tayebi, L. (2022). Writing a Research Proposal. In: Research Methods in Dentistry. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98028-3_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98028-3_4
Published : 10 April 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-98027-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-98028-3
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Leedy And Ormrod Research Book Quiz!

According to Leedy and Ormrod (2010), the most effective research proposals:
Are a brief outline of the study you intend to conduct without an excess of detail.
Justify the study to be conducted by explaining how it will contribute to the professional literature.
Are detailed and straightforward explanations of the research problem and methodology.
Include an autobiographical section that explains how the researcher became interested in the research topic.
Rate this question:
A proposal for a quantitative study typically includes these elements in this order:
A statement of the problem, a review of the literature, an explanation of the means for collecting data, a description of how the study will be conducted.
A review of the literature, a statement of the problem, an explanation of the means for collecting data, a description of how the study will be conducted.
A review of the literature, a statement of the problem, a description of how the study will be conducted, an explanation of the means for collecting data.
A statement of the problem, an explanation of the means for collecting data, a review of the literature, a description of how the study will be conducted.
A proposal for a qualitative study typically includes these elements in this order:
An explanation of how the findings will fit with the larger literature, a statement of the purpose of the study and its guiding questions, a management plan, an explanation of theoretical and methodological grounding.
A statement of the purpose of the study and its guiding questions, an explanation of how the findings will fit with the larger literature, an explanation of theoretical and methodological grounding, a management plan.
A statement of the purpose of the study and its guiding questions, an explanation of theoretical and methodological grounding, an explanation of how the findings will fit with the larger literature, a management plan.
A statement of the purpose of the study and its guiding questions, an explanation of theoretical and methodological grounding, a management plan, an explanation of how the findings will fit with the larger literature.
Proposals for ______ studies include a methodology section.
Qualitative
Quantitative
Both quantitative and qualitative
Neither quantitative or qualitative
In ______ research proposal(s), the review of literature comes late in the document in conjunction with the interpretation of data.
A quantitative
A qualitative
In ______ research proposal(s), a specific research problem is clearly stated at the outset of the proposal.
In ______ research proposal(s), a specific plan for how the data will be handled is clearly laid out in the document., in ______ research proposal(s), specific hypotheses regarding findings are often stated., in regard to the style you will use for headings and subheadings in the research proposal:.
There are no special formatting requirements unless the document is a thesis or dissertation.
All disciplines recognize the major formal styles, so it is a matter of personal choice.
The writer is free to show creativity as long as s/he is consistent throughout the document.
Disciplines often dictate the use of specific formal styles, so you must find out what the expectations are.
Experienced writers of research proposals typically:
Plan to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal.
Do not need to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal.
Make revisions to the first draft of the proposal only if they are requested by a reviewer.
May need to edit the first draft of the proposal for typos, but not content.
When writing the proposal, you should assume that the reader:
Will know which data analytic techniques are appropriate for your study without a detailed explanation.
Is an expert in the area you are addressing and will be familiar with common issues, variables, instruments, etc.
Can discern for him/herself what the importance of the study is.
Knows nothing about the proposed project, so all the details must be thoroughly explained.
When explaining how the data are to be analyzed and interpreted:
It is best to provide only a general plan as things will probably change over the course of the study anyway.
It is best to be as detailed as possible so all contingencies related to analysis and interpretation can be anticipated.
It is impossible to be highly detailed until one has the actual data in hand.
An overly specific plan may bias the analyses or interpretation, impairing the validity of the study.
Research proposals that ______ are commonly judged to be of higher quality than proposals that do not.
Favor straightforward vocabulary
Employ complex sentence structure
Favor a highly esoteric vocabulary
Rely on the reader to draw inferences
Three of the following are elements in the proposal revision process. Which one is NOT?
Reconsider the feasibility of what you are proposing to do.
Carefully assess the logic and organization of the information in the document.
Avoid breaks of 24 hours or more as the material will get too “cold” in your mind.
Seek feedback from knowledgeable others.
The research proposal is best thought of as:
A general and flexible outline of how the research problem is to be investigated.
“Plan A,” with the expectation that “Plan B” or even “Plan C” will become necessary as the study unfolds.
A detailed and firm contract between the researcher and others who are involved in the research project (participants, supervisors, funding agencies, etc.)
A document that is written for others (internal review boards, funding agencies) and is of little value to the researcher.
Quiz Review Timeline +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
- Current Version
- Mar 22, 2023 Quiz Edited by ProProfs Editorial Team
- Aug 16, 2012 Quiz Created by Kaconrad
Related Topics
- The Book Thief
Recent Quizzes
Featured Quizzes

Related Quizzes
Wait! Here's an interesting quiz for you.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide
Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Proposal is a formal document or presentation that outlines a plan, idea, or project and seeks to persuade others to support or adopt it. Proposals are commonly used in business, academia, and various other fields to propose new initiatives, solutions to problems, research studies, or business ventures.
Proposal Layout
While the specific layout of a proposal may vary depending on the requirements or guidelines provided by the recipient, there are some common sections that are typically included in a standard proposal. Here’s a typical layout for a proposal:
- The title of the proposal.
- Your name or the name of your organization.
- Date of submission.
- A list of sections or headings with corresponding page numbers for easy navigation.
- An overview of the proposal, highlighting its key points and benefits.
- Summarize the problem or opportunity.
- Outline the proposed solution or project.
- Mention the expected outcomes or deliverables.
- Keep it concise and compelling.
- Provide background information about the issue or context.
- Explain the purpose and objectives of the proposal.
- Clarify the problem statement or opportunity that the proposal aims to address.
- Describe in detail the methodology , approach , or plan to achieve the objectives.
- Outline the steps or tasks involved in implementing the proposal.
- Explain how the proposed solution or project will be executed.
- Include a timeline or schedule to demonstrate the project’s timeline.
- Define the specific activities, tasks, or services to be provided.
- Clarify the deliverables and expected outcomes.
- Mention any limitations or exclusions, if applicable.
- Provide a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with the proposal.
- Include itemized expenses such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other relevant costs.
- If applicable, include a justification for each cost.
- Introduce the individuals or team members involved in the proposal.
- Highlight their qualifications, expertise, and experience relevant to the project.
- Include their roles and responsibilities.
- Specify how the success of the proposal will be measured.
- Define evaluation criteria and metrics to assess the outcomes.
- Explain how progress will be tracked and reported.
- Recap the main points of the proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and advantages of the proposed solution.
- Emphasize the value and importance of supporting or adopting the proposal.
- Include any additional documents, references, charts, graphs, or data that support your proposal.
- These can include resumes, letters of support, financial projections, or relevant research materials.
Types of Types of Proposals
When it comes to proposals, there are various types depending on the context and purpose. Here are some common types of proposals:
Business Proposal
This type of proposal is used in the business world to present a plan, idea, or project to potential clients, investors, or partners. It typically includes an executive summary, problem statement, proposed solution, timeline, budget, and anticipated outcomes.
Project Proposal
A project proposal is a detailed document that outlines the objectives, scope, methodology, deliverables, and budget of a specific project. It is used to seek approval and funding from stakeholders or clients.
Research Proposal
Research proposals are commonly used in academic or scientific settings. They outline the research objectives, methodology, timeline, expected outcomes, and potential significance of a research study. These proposals are submitted to funding agencies, universities, or research institutions.
Grant Proposal
Non-profit organizations, researchers, or individuals seeking funding for a project or program often write grant proposals. These proposals provide a detailed plan of the project, including goals, methods, budget, and expected outcomes, to convince grant-making bodies to provide financial support.
Sales Proposal
Sales proposals are used by businesses to pitch their products or services to potential customers. They typically include information about the product/service, pricing, features, benefits, and a persuasive argument to encourage the recipient to make a purchase.
Sponsorship Proposal
When seeking sponsorship for an event, sports team, or individual, a sponsorship proposal is created. It outlines the benefits for the sponsor, the exposure they will receive, and the financial or in-kind support required.
Marketing Proposal
A marketing proposal is developed by marketing agencies or professionals to present their strategies and tactics to potential clients. It includes an analysis of the target market, proposed marketing activities, budget, and expected results.
Policy Proposal
In the realm of government or public policy, individuals or organizations may create policy proposals to suggest new laws, regulations, or changes to existing policies. These proposals typically provide an overview of the issue, the proposed solution, supporting evidence, and potential impacts.
Training Proposal
Organizations often create training proposals to propose a training program for their employees. These proposals outline the training objectives, topics to be covered, training methods, resources required, and anticipated outcomes.
Partnership Proposal
When two or more organizations or individuals wish to collaborate or form a partnership, a partnership proposal is used to present the benefits, shared goals, responsibilities, and terms of the proposed partnership.
Event Proposal
Event planners or individuals organizing an event, such as a conference, concert, or wedding, may create an event proposal. It includes details about the event concept, venue, logistics, budget, marketing plan, and anticipated attendee experience.
Technology Proposal
Technology proposals are used to present new technological solutions, system upgrades, or IT projects to stakeholders or decision-makers. These proposals outline the technology requirements, implementation plan, costs, and anticipated benefits.
Construction Proposal
Contractors or construction companies create construction proposals to bid on construction projects. These proposals include project specifications, cost estimates, timelines, materials, and construction methodologies.
Book Proposal
Authors or aspiring authors create book proposals to pitch their book ideas to literary agents or publishers. These proposals include a synopsis of the book, target audience, marketing plan, author’s credentials, and sample chapters.
Social Media Proposal
Social media professionals or agencies create social media proposals to present their strategies for managing social media accounts, creating content, and growing online presence. These proposals include an analysis of the current social media presence, proposed tactics, metrics for success, and pricing.

Training and Development Proposal
Similar to training proposals, these proposals focus on the overall development and growth of employees within an organization. They may include plans for leadership development, skill enhancement, or professional certification programs.
Consulting Proposal
Consultants create consulting proposals to present their services and expertise to potential clients. These proposals outline the problem statement, proposed approach, scope of work, timeline, deliverables, and fees.
Policy Advocacy Proposal
Organizations or individuals seeking to influence public policy or advocate for a particular cause create policy advocacy proposals. These proposals present research, evidence, and arguments to support a specific policy change or reform.
Website Design Proposal
Web designers or agencies create website design proposals to pitch their services to clients. These proposals outline the project scope, design concepts, development process, timeline, and pricing.
Environmental Proposal
Environmental proposals are created to address environmental issues or propose conservation initiatives. These proposals may include strategies for renewable energy, waste management, biodiversity preservation, or sustainable practices.
Health and Wellness Proposal
Proposals related to health and wellness can cover a range of topics, such as wellness programs, community health initiatives, healthcare system improvements, or health education campaigns.
Human Resources (HR) Proposal
HR professionals may create HR proposals to introduce new policies, employee benefits programs, performance evaluation systems, or employee training initiatives within an organization.
Nonprofit Program Proposal
Nonprofit organizations seeking funding or support for a specific program or project create nonprofit program proposals. These proposals outline the program’s objectives, activities, target beneficiaries, budget, and expected outcomes.
Government Contract Proposal
When bidding for government contracts, businesses or contractors create government contract proposals. These proposals include details about the project, compliance with regulations, cost estimates, and qualifications.
Product Development Proposal
Businesses or individuals seeking to develop and launch a new product present product development proposals. These proposals outline the product concept, market analysis, development process, production costs, and marketing strategies.
Feasibility Study Proposal
Feasibility study proposals are used to assess the viability and potential success of a project or business idea. These proposals include market research, financial analysis, risk assessment, and recommendations for implementation.
Educational Program Proposal
Educational institutions or organizations create educational program proposals to introduce new courses, curricula, or educational initiatives. These proposals outline the program objectives, learning outcomes, curriculum design, and resource requirements.
Social Service Proposal
Organizations involved in social services, such as healthcare, community development, or social welfare, create social service proposals to seek funding, support, or partnerships. These proposals outline the social issue, proposed interventions, anticipated impacts, and sustainability plans.
Proposal Writing Guide
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with proposal writing:
- Understand the Requirements: Before you begin writing your proposal, carefully review any guidelines, instructions, or requirements provided by the recipient or organization. This will ensure that you meet their expectations and include all necessary information.
- Research and Gather Information: Conduct thorough research on the topic or project you are proposing. Collect relevant data, statistics, case studies, and any supporting evidence that strengthens your proposal. This will demonstrate your knowledge and credibility.
- Define the Problem or Opportunity: Clearly identify and articulate the problem or opportunity that your proposal aims to address. Provide a concise and compelling explanation of why it is important and relevant.
- State Your Objectives: Outline the specific objectives or goals of your proposal. What do you hope to achieve? Make sure your objectives are clear, measurable, and aligned with the needs of the recipient.
- Present Your Solution: Propose your solution or approach to the problem. Describe how your solution is unique, innovative, and effective. Provide a step-by-step plan or methodology, highlighting key activities, deliverables, and timelines.
- Demonstrate Benefits and Impact: Clearly outline the benefits and impact of your proposal. Explain how it will add value, solve the problem, or create positive change. Use evidence and examples to support your claims.
- Develop a Budget: If applicable, include a detailed budget that outlines the costs associated with implementing your proposal. Be transparent and realistic about expenses, and clearly explain how the funding will be allocated.
- Address Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies: Identify any potential risks, challenges, or obstacles that may arise during the implementation of your proposal. Offer strategies or contingency plans to mitigate these risks and ensure the success of your project.
- Provide Supporting Documentation: Include any supporting documents that add credibility to your proposal. This may include resumes or bios of key team members, letters of support or partnership, relevant certifications, or past success stories.
- Write Clearly and Concisely: Use clear and concise language to communicate your ideas effectively. Avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse or alienate the reader. Structure your proposal with headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance readability.
- Proofread and Edit: Carefully review your proposal for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors. Ensure that it is well-organized, coherent, and flows logically. Consider asking someone else to review it for feedback and suggestions.
- Include a Professional Cover Letter: If appropriate, attach a cover letter introducing your proposal. This letter should summarize the key points, express your enthusiasm, and provide contact information for further discussion.
- Follow Submission Instructions: Follow the specific instructions for submitting your proposal. This may include submitting it electronically, mailing it, or delivering it in person. Pay attention to submission deadlines and any additional requirements.
- Follow Up: After submitting your proposal, consider following up with the recipient to ensure they received it and address any questions or concerns they may have. This shows your commitment and professionalism.
Purpose of Proposal
The purpose of a proposal is to present a plan, idea, project, or solution to a specific audience in a persuasive and compelling manner. Proposals are typically written documents that aim to:
- Convince and Persuade: The primary purpose of a proposal is to convince the recipient or decision-makers to accept and support the proposed plan or idea. It is important to present a strong case, providing evidence, logical reasoning, and clear benefits to demonstrate why the proposal should be approved.
- Seek Approval or Funding: Proposals often seek approval or funding for a project, program, research study, business venture, or initiative. The purpose is to secure the necessary resources, whether financial, human, or technical, to implement the proposed endeavor.
- Solve Problems or Address Opportunities: Proposals are often developed in response to a problem, challenge, or opportunity. The purpose is to provide a well-thought-out solution or approach that effectively addresses the issue or leverages the opportunity for positive outcomes.
- Present a Comprehensive Plan : Proposals outline a comprehensive plan, including objectives, strategies, methodologies, timelines, budgets, and anticipated outcomes. The purpose is to demonstrate the feasibility, practicality, and potential success of the proposed plan.
- Inform and Educate: Proposals provide detailed information and analysis to educate the audience about the subject matter. They offer a thorough understanding of the problem or opportunity, the proposed solution, and the potential impact.
- Establish Credibility: Proposals aim to establish the credibility and expertise of the individual or organization presenting the proposal. They demonstrate the knowledge, experience, qualifications, and track record that make the proposer capable of successfully executing the proposed plan.
- I nitiate Collaboration or Partnerships: Proposals may serve as a means to initiate collaboration, partnerships, or contractual agreements. They present an opportunity for individuals, organizations, or entities to work together towards a common goal or project.
- Provide a Basis for Decision-Making: Proposals offer the information and analysis necessary for decision-makers to evaluate the merits and feasibility of the proposed plan. They provide a framework for informed decision-making, allowing stakeholders to assess the risks, benefits, and potential outcomes.
When to write a Proposal
Proposals are typically written in various situations when you need to present a plan, idea, or project to a specific audience. Here are some common scenarios when you may need to write a proposal:
- Business Opportunities: When you identify a business opportunity, such as a potential client or partnership, you may write a proposal to pitch your products, services, or collaboration ideas.
- Funding or Grants: If you require financial support for a project, research study, non-profit program, or any initiative, you may need to write a proposal to seek funding from government agencies, foundations, or philanthropic organizations.
- Project Planning: When you plan to undertake a project, whether it’s a construction project, software development, event organization, or any other endeavor, writing a project proposal helps outline the objectives, deliverables, timelines, and resource requirements.
- Research Studies: In academic or scientific settings, researchers write research proposals to present their study objectives, research questions, methodology, anticipated outcomes, and potential significance to funding bodies, universities, or research institutions.
- Business Development: If you’re expanding your business, launching a new product or service, or entering a new market, writing a business proposal helps outline your plans, strategies, market analysis, and financial projections to potential investors or partners.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: When seeking partnerships, collaborations, or joint ventures with other organizations or individuals, writing a partnership proposal helps communicate the benefits, shared goals, responsibilities, and terms of the proposed partnership.
- Policy or Advocacy Initiatives: When advocating for a particular cause, addressing public policy issues, or proposing policy changes, writing a policy proposal helps outline the problem, proposed solutions, supporting evidence, and potential impacts.
- Contract Bidding: If you’re bidding for contracts, whether in government or private sectors, writing a proposal is necessary to present your capabilities, expertise, resources, and pricing to potential clients or procurement departments.
- Consulting or Service Contracts: If you offer consulting services, professional expertise, or specialized services, writing a proposal helps outline your approach, deliverables, fees, and timeline to potential clients.
Importance of Proposal
Proposals play a significant role in numerous areas and have several important benefits. Here are some key reasons why proposals are important:
- Communication and Clarity: Proposals serve as a formal means of communication, allowing you to clearly articulate your plan, idea, or project to others. By presenting your proposal in a structured format, you ensure that your message is conveyed effectively, minimizing misunderstandings and confusion.
- Decision-Making Tool: Proposals provide decision-makers with the necessary information and analysis to make informed choices. They offer a comprehensive overview of the proposal, including objectives, strategies, timelines, budgets, and anticipated outcomes. This enables stakeholders to evaluate the proposal’s feasibility, alignment with goals, and potential return on investment.
- Accountability and Documentation: Proposals serve as a written record of commitments, responsibilities, and expectations. Once a proposal is approved, it becomes a reference point for all parties involved, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and accountable for their roles and obligations.
- Planning and Organization: Writing a proposal requires thorough planning and organization. It compels you to define objectives, outline strategies, consider potential risks, and create a timeline. This process helps you think critically about the proposal, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas that require further refinement.
- Persuasion and Influence: Proposals are persuasive documents that aim to convince others to support or approve your plan. By presenting a well-constructed proposal, supported by evidence, logical reasoning, and benefits, you enhance your ability to influence decision-makers and stakeholders.
- Resource Allocation and Funding: Many proposals are written to secure resources, whether financial, human, or technical. A compelling proposal can increase the likelihood of obtaining funding, grants, or other resources needed to execute a project or initiative successfully.
- Partnership and Collaboration Opportunities: Proposals enable you to seek partnerships, collaborations, or joint ventures with other organizations or individuals. By presenting a clear proposal that outlines the benefits, shared goals, responsibilities, and terms, you increase the likelihood of forming mutually beneficial relationships.
- Professionalism and Credibility: A well-written proposal demonstrates professionalism, expertise, and credibility. It showcases your ability to analyze complex issues, develop effective strategies, and present ideas in a concise and persuasive manner. This can enhance your reputation and increase trust among stakeholders.
- Continual Improvement: The process of writing proposals encourages you to refine your ideas, explore alternatives, and seek feedback. It provides an opportunity for reflection and refinement, ultimately leading to continuous improvement in your plans and approaches.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
- Referencing and research
Research proposals
How to write an effective proposal.
What's it for?
A research proposal explains the nature and extent of your planned or future research. It is written for an academic reader e.g. for your supervisor or an academic with a similar disciplinary background. By thinking through your entire research project from beginning to end, it may also highlight core issues with the feasibility of the project.
W hat's in it ?
There are some disciplinary differences regarding exactly what is included in the proposal. For example, disciplines such as Psychology may include a prominent hypothesis statement, others in the Social Sciences including Education, may expect a set of research questions that the study will answer. However, all research proposals should cover the four basic elements below.
- The research topic addresses a significant problem and, therefore, advances the state of knowledge in that field.
- Identification of an appropriate methodology and underlying theory to address the problem, including data collection methods and equipment (if required).
- Details of how the collected data will be analysed in such a way that useful conclusions can be drawn.
- An organised plan for any proposed work, including a timeframe.
Possible macro-structures
The structure of your research proposal will vary depending on the requirements of your discipline. Nevertheless, certain structural elements will be expected by your reader and these may be presented in the following order. Check with the Research Coordinator in your area for specific requirements.
Identifies the title of the project, your full name, the institution, department, and supervisor details. The title should be brief and descriptive and may use a colon (:) to separate the topic from the focus (i.e. Stormwater Harvesting: Managing the hazards of surface water pollution by run-off ).
Lists the sections of the Research Proposal (headings and indented sub-headings) and corresponding page numbers.
Outlines the essence of the research project. It describes the purpose and motivation for the study, the problem, the data collection methodology and analysis, significant results and implications of the research.
Provides background information for the research (i.e. the problem being addressed) and is typically structured from general information to narrow or focused ideas with your research question/s or hypotheses at the narrow end.
The Introduction should be about 10% of your proposal.
Imagine you are writing for a general reader rather than an expert audience. The Introduction includes a brief review of relevant literature or knowledge in the field, so that you are able to present a gap in existing knowledge and, therefore, the significance and originality of your research.
Finally, articulate the scope of your research (or what you will not be doing) to limit your task. Your research question/s should encapsulate the primary question/s you aim to solve.
Synthesises the literature in your field. Some disciplines will expect to see this in the Introduction but others will want it placed in this ‘stand-alone’ section (especially in more Humanities-based fields). Again, it could be structured from broad to narrow, so literature on the more general aspects of your topic could come first, narrowing down to published work on your particular area of interest. You might end this section by including a short summary of the main themes you have identified from the literature.
Includes a description and rationale for the methods of data collection and analysis, and the materials you will use in your research. Use subheadings if possible ( i.e. Data Collection, Data Analysis, Ethical Considerations etc.) and write with a future aspect, ( i.e. The research will initially examine water treatment processes in... )
Details any results that you may already have resulting from previous Honours or Masters’ research work, or perhaps from a pilot study. It is important to relate these results to the critical framework of your intended new research project.
Lists the stages of the research project in timeline, spreadsheet or tabular format, and the deadlines for completion of these stages or tasks. You should include any anticipated challenges to completion.
Outlines the proposed chapters of the thesis and the content of each chapter in several lines or a paragraph, including a Table of Contents.
Relates the expected outcomes of your research to the aims expressed in the Introduction so that the need for the study and the contribution to knowledge is clear.
Provides all the resources cited in your resource proposal using a referencing format favoured by your faculty or discipline. Do not list resources that are not directly referred to in your Proposal.
Writing the Research Proposal
How much should i write.
A research proposal is usually quite a bit longer than other written academic genres. In the Humanities, it could be around 10,000 words or even longer (excluding the Reference List); whereas those from more Science-oriented disciplines may be shorter.
What should I begin with?
Similar to other academic genres, writing the research proposal is a process. If you are proposing a ‘recycled’ topic that builds on previous assignments already written on the same topic, you might spend some time re-reading these. However, if you are starting a ‘fresh’ project you might consider two key questions:
- What am I really interested in finding out about my research topic?
- How am I going to do this in practice? Brainstorm responses to these questions under a strict time limit – say 30 minutes.
Then leave this ‘free-writing’ for at least 24 hours before reviewing it for a possible more polished second draft.
How should I approach the literature?
Reviewing the academic literature on your topic is one of the most critical stages of your research proposal. This section goes beyond a simple summary of everything written on a subject. Instead, it is a critical synthesis of materials that illuminates selected academic literature on your topic. Your coverage of the literature should reflect the argument or perspective that you have set out in your research question/s.
Try the following techniques for dealing with the literature:
- Develop a theme or series of themes from your broad reading, referencing the work of relevant authors who support your position or who provide counter-arguments against your point/s.
- Limit excessive quoting. Too many direct quotations will dilute your authority over the topic.
- Avoid beginning paragraphs with “Jones argues …”; “Smith states …” This approach risks losing a sense of your writer’s authority to the work of others. Instead, provide an overview of the paragraph in a topic sentence written in your own writer’s voice.
Adapted from Rudestam and Newton (2015) as cited in Paltridge and Starfield (2020). Thesis and dissertation writing in a second language: A handbook for students and their advisers. Routledge.
Tips for writing
- Avoid language that is overly hesitant or tentative (i.e. ‘It seems that…’, ‘It is hoped that …’). Instead, use confident language when you feel able to (i.e. ‘It is clear that…’, ‘I assert that …’).
- Break up large blocks of text into smaller sections using sub-headings and bullet-points.
- Anticipate possible problems with, or limitations of, your research. Address these issues directly for your own benefit as well as to improve the entire proposal.
- Make your proposal is easy for readers to skim read. Never assume your readers will read your work in a ‘logical’ order. Use sub-headings and restate key ideas to guide the reader through your writing.
- Find copies of other Research Proposals in your field and study the way they:
- devise titles.
- structure their proposal.
- use discipline-specific language.
- Take a note of anything else you notice. You might ask your potential supervisor/s for models of previously submitted proposals or search for relevant examples online (look for examples from reputable .edu or .org. web addresses)
Remember, your research proposal should demonstrate:
- the feasibility and logical foundations of your project
- a well-focussed research question, set of research objectives, or hypothesis
- the width and depth of the academic literature on your topic
- understanding of current issues or debates on your topic
- justification of your project through the literature
- a match between the methodology and / or methods and your research question/s
Adapted from Cadman (2002) as cited in Paltridge, B. and Starfield, S. (2020). Thesis and dissertation writing in a second language: A handbook for students and their advisers. Routledge.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
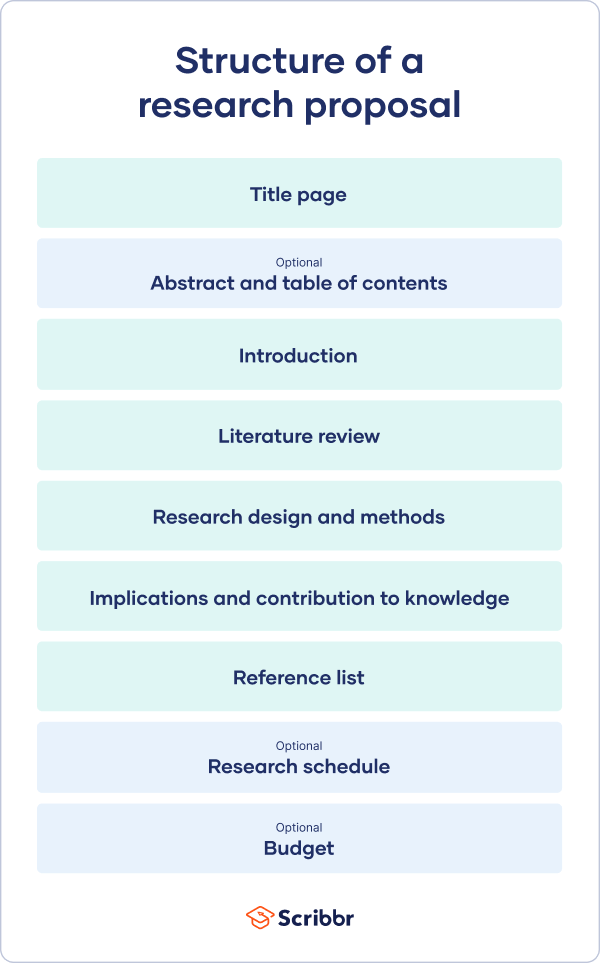
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Encyclopedia for Writers
Writing with artificial intelligence, research proposal.
Research Proposals may be as brief as a page or two or as long as a hundred pages. For instance, if you are pitching an entrepreneurial idea to Y Combinator, they will give you a couple of pages and require a video where you pitch your idea. In contrast, if you are pitching an entrepreneurial idea to NSF SBIR or IES SBIR, your proposal may run 15 pages single spaced and then have another hundred pages of attachments, letters of support, budget projects, and resumes.
Regardless of length, though, research proposals share some common characteristics: First, proposals are arguments, persuasive documents.
Note: The Research Proposal, at a minimum, should have the following sections: Purpose; Summary; Introduction; Visual Representation of the Problem/Stakeholders/Potential Solutions; Proposed Plan of Work (with Gantt Chart); Qualifications, Budget, Bibliography. Other common parts of Research Proposals are not required but welcome:
| What is the purpose of the proposed research? | Typically proposal writers define the question they seek to answer, its significance, and past scholarly conversations on the matter. Hoping to be persuasive, writers make appeals to , , , and . | |
| What content is included in the document? | This functions as a short-form version of the proposal. Briefly cover the major elements of the document for readers who might not read anything but the summary | |
| What problem(s) does the proposed research project address? | Clear, concise statement of problem; 1-3 sentences (move other detail to Background) : Concise statement of the problem definition and needed textual and empirical research Explain how, why, and for whom the problem exists. What circumstances led to its discovery, relationships or events that affect the problem/solutions, etc. Draw on your preliminary research to describe relevant literature/research related to this problem/research initiative. Describe potential benefits expected from the research in concrete, specific language. Describe what you are going to research and what you are not going to research Describe the organizational pattern the proposal uses Define any specialized terms you will use in the report | |
| Provide a Visual Representation of Problem, Solutions, Stakeholders | ||
| What work will be done? How will it be done? | Organize by tasks to show your boss what research you will doing. Be specific and detailed. (i.e. if you’re doing interviews, say specifically who you’ll be interviewing, why you are interviewing them, and what you want to find out.) Convince the reader that you know what you’re doing by presenting clear, specific plans with a rationale for each. | |
| How are you qualified to lead this project? | Provide biographical profiles of the members of your team who will be doing the work. | |
| How much will it cost to do this research and deliver our final product? | This is the budget for doing this research project (not a budget for implementing the solution.) For this project, provide one clear sentence describing your budget requirements. In the real world, this section can be very lengthy and detailed, but for our purposes, the budget should be very close to zero. | |
| How long is this going to take? | Include a short summary/overview of the task schedule here. Make note of deadlines for major milestones. Provide a Gantt Chart for proposed Textual and Empirical Research | |
| What sources did we cite in the literature review? | Include a bibliography of the sources you addressed in the literature review formatted in a style appropriate for your field: APA, Chicago, MLA, IEEE |

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority & Credibility – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Experienced Writers of Research Proposals Typically
Experienced writers of research proposals typically:
A) plan to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. B) do not need to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. C) make revisions to the first draft of the proposal only if they are requested by a reviewer. D) may need to edit the first draft of the proposal for typos,but not content.
Correct Answer:
Unlock this answer now Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q1: Farhat is interested in the reading practices
Q2: A research proposal should be a _
Q3: A proposal for a quantitative study typically
Q4: After introducing a qualitative study,a well-organized research
Q5: When explaining how the data are to
Q7: Amida recognizes that there are limitations to
Q8: Three of the following are elements in
Q9: When writing the proposal,you should assume that
Q10: In a research proposal,informed consent letters,specific assessment
Q11: In APA style,what level heading consists of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
According to the authors, the most effective research proposals are. Detailed and straightforward explanations of the research problem and methodology. A proposal for a quantitative study typically begins with a. statement of the problem and its setting. List components that should be included in a research proposal-quantitative and qualitative.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Research is a systematic process of _____, _____, and _____ information in order to increase understanding of a phenomenon., Research is considered cyclical because_____., Cameron is conducting a study that addresses the differences in achievement scores between schools that use block scheduling and schools that use a traditional ...
Research Proposal (student's preliminary notes) (91.11 KB, PDF) This is an example of how to start planning and thinking about your research proposal assignment. You will find a student's notes and ideas about their research proposal topic - "Perspectives on Textual Production, Student Collaboration, and Social Networking Sites".
How to Write a Research Proposal in 2024: Structure ...
Good news! Many times you can write the cost of the publication fee into your research grant. The NIH Grants Policy Statement includes a section related to publication and printing costs. The National Science Foundation also outlines publication costs in section 617 of their awards documentation. Be advised that it is best to consider publication costs early on in the research process.
Overview. A research proposal is a type of text which maps out a proposed central research problem or question and a suggested approach to its investigation. In many universities, including RMIT, the research proposal is a formal requirement. It is central to achieving your first milestone: your Confirmation of Candidature.
Proposal Writers Guide Research Proposals - Research Proposals Research Proposals - Cover Letter This (usually optional) letter may be used to convey information that is pertinent to the review of the proposal. Make sure you identify your name, the University of Michigan, project title, RFP or and specific funding mechanism if any.
The key to good writing is linking the text. into a logical project flow. Therefore, in the early stage of writing an RTD proposal, developing the chain of reasoning and creating a flow chart is. recommended to get a clear overview of the entire project and to visualise how the many work packages are connected.
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & ...
Writing Research Proposals
The research journey commences with the selection of a research topic and the preparation of a proposal on the selected topic. Experience has shown that students tend to encounter difficulties in writing research proposals for their supervisors because they do not fully comprehend what constitutes a research proposal.
Abstract. A research proposal is a formal document that outlines a plan for a research project. It serves as a blueprint or roadmap for conducting a research study and is typically submitted to funding agencies, academic institutions, or research review committees for approval and financial support. Proposals are in different formats depending ...
Therefore this book is intended to help those who are unfamiliar with the process of proposal writing or who want to improve their chances of success in a complex and demanding field. Indeed, some of the skills and abilities required can be trans-ferred directly from other pursuits once their relevance and importance is understood; others may ...
1.2 PURPOSE OF WRITING A RESEARCH PROPOSAL The purpose of writing this researchproposal is learning to explain the need and feasibility of your ideas and to sell them to an audience of peers. Writing a research proposal will help you to reach the following learning outcomes as formulated in the Education and Examination Regulation. You will be:
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform ...
In contrast, quantitative research typically follows a more structured and systematic approach, where the review of literature is usually conducted earlier in the research process to inform the development of research questions and hypotheses. ... Experienced writers of research proposals typically plan to make revisions to the first draft of ...
Proposal. Definition: Proposal is a formal document or presentation that outlines a plan, idea, or project and seeks to persuade others to support or adopt it. Proposals are commonly used in business, academia, and various other fields to propose new initiatives, solutions to problems, research studies, or business ventures.
A research proposal is usually quite a bit longer than other written academic genres. In the Humanities, it could be around 10,000 words or even longer (excluding the Reference List); whereas those from more Science-oriented disciplines may be shorter. What should I begin with? Similar to other academic genres, writing the research proposal is ...
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Scope: Describe what you are going to research and what you are not going to research. Organization: Describe the organizational pattern the proposal uses. Key terms: Define any specialized terms you will use in the report. Visual Representation of Rhetorical Situation. Provide a Visual Representation of Problem, Solutions, Stakeholders.
Experienced writers of research proposals typically: may need to edit the first draft of the proposal for typos, but not content. do not need to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. plan to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. make revisions to the first draft of the proposal only if they are requested by a reviewer.
Experienced writers of research proposals typically: A)plan to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. B)do not need to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. C)make revisions to the first draft of the proposal only if they are requested by a reviewer. D)may need to edit the first draft of the proposal for typos,but not content.
True False Question 52 Only in a quantitative research proposal(s), a specific plan for how the data will ... Experienced writers of research proposals typically do not need to make revisions to the first draft of the proposal. ... Question 56. When writing the proposal, you should assume that the reader knows nothing about the proposed project ...