Search This Blog
The glorious education, previous year question paper bcom (prog) business laws university of delhi, case studies of bst class 11 ch - 1 nature and purpose of business, class -11 business studies , chapter - 1 nature and purpose of business, case study and value-based questions with answers .
Q1. Mr. Bhuvan is a Chartered Accountant in a Multinational Company. He gets rs 85,000 per month as his salary. On weekends, Mr. Bhuvan goes to nearby village and teaches some slum children, he does not charge anything from them, he does it out of sympathy and children. This gives him mental and psychological satisfaction. concern for poor.
(a) Working as CA in a MNC refers to which type of human activity. (b) Teaching students in slum is which type of human activity. (c) Identify the values followed by Bhuvan.
Ans. (a) Economic
(b) Non-Economic
(c) (i) Value of love and care.
(ii) Value of helping poor.
Q. 2. Rajiv wants to start a whole sale business of readymade garments, but he is hesitating as it involves various problems such as customers for moving goods from place of production to market, informing customers about new designs and varieties added every season, threat of risk loss by fire or accident, storing the excess stock of goods, etc. He approaches his friend Sandeep who explained him about some branches of commerce, which can help Rajiv to overcome his hesitation.
(a) State the type of business Rajiv is planning to start.
(b) State which dimension of business can help Rajiv to overcome these hindrances. (c) Specify different types of Auxiliaries to trade which can help Rajiv to overcome his problems. Quote the line for each type from above Para.
Ans. (a) Trade - Whole sale Trade.
(b) Commerce
(c) (i) "Searching for Customer" – Trade (ii) "Moving goods"
(iii) "Informing customers"
(iv) "Threat of Risk" Transportation - Advertisement Insurance -
Q. 3. Indu bought a readymade dress for ₹ 5000. Her friend liked the design of dress very much, so Indu sold the same dress to her friend for 5500 and made a profit of 500. After completing her studies Indu opened a shop of selling readymade dresses for girls.
(a) Can transaction between Indu and her friend be termed as business?
(b)State the features related to 'a'.
(c) Can the sale of dresses on her shop be called as business?
Ans.(a) No.
(b) "Regular Basis".
(c) Yes, as it is done on Regular Basis.
Q. 4. Name the following:
(a) The economic activity showing a risk element and carried on profit.
(b) The trade in which two countries are involved.
(c) The trade in which goods are imported from one country for the purpose of exporting to other country.
(d) The industry which involves breeding and reproduction of plants and animals.
(e) The branch of commerce which remove hindrance of place.
Ans. (a) Business
(b) External Trade
(c) Entrepot
(d) Genetic Industry
(e) Transportation.
Q. 5. An organisation planned to use CFL and LED which consume less electricity to reduce operational cost. They also give preference to labour intensive technique of production. What values company is implementing?
Ans.1. Value of saving electricity.
2. Value of creating employment opportunities.
3. Value of reduction in cost.
Q. 6. An organisation arranges recreational activities for its employees to refresh them and also send them for training to update their knowledge. What values are followed by the company? .
Ans. 1. Value of meeting personal objectives.
2. Value of motivating employees.
3. Values of giving job satisfaction to employees.
Q. 7. A Chartered Accountant advised his elient how to convert black money into white money and he also guided him how to save income tax by hiding his income. Is his act justified.
Ans. No conduct of CA and businessmen are not justified:
(a) CA is violating his code of conduct by acting unethically.
(b) Cheating government by paying less income.
(c) Acting dishonestly.
(d) The act is not even unethical but illegal also.
Q. 8. A Tool and Equipment Manufacturing Company gave bribe to purchase manager of a factory to buy tools of low quality and which are not having safety norms. The purchase manager accepted the offer and gave a big order. What values are violated?
Ans. 1. Value of playing with the health of workers.
2. Not fulfilling safety norms competition. 3. Offering bribe is an unlawful act.
Q.9. A unit set up by Tata in rural area and the company plan to develop roads, parks of that area they also started a school for local children of that area. What values are followed?
Ans. 1. Fulfilling social objectives.
2. Increasing literacy rate.
3. Improving standard of living.

Post a Comment
Recent posts.
- MCQs OF CLASS 11 PHYSICAL EDUCATION ALL CHAPTERS LINKS
- CLASS 11 HINDI ANTRA BOOK ALL CHAPTER MCQs
- CLASS 12 HINDI ANTRA BOOK ALL CHAPTER MCQs
- MCQs OF CLASS 12 PHYSICAL EDUCATION ALL CHAPTERS LINKS
Popular posts from this blog
Mcqs of class 11 physical education chapter 1 changing trends and career in physical education, mcqs class 11 hindi ncert antra chapter 1 idgah mcqs, mcqs dopahar ka bhojan hindi antra class 11, mcqs surdas (सूरदास) class 11 hindi antra, mcqs of टोर्च बेचनेवाला class 11 hindi antra chapter- 3, mcqs रांगेय राघव- गूंगे class 11 hindi antra chapter 4 ncert, संवदिया - फणीश्वर नाथ रेणु mcq | class12th hindi antra mcq i गद्य खंड संवदिया, hindi class 12 ramchandra sukla - prem ghan ke chaya mcqs, mcqs class 11 hindi antra ch- 10 kabir.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.
11th Standard CBSE Subjects

11th Standard CBSE Study Materials

Study Materials for Other CBSE Board Standards

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
myCBSEguide
- Entrance Exam
- Competitive Exams
- ICSE & ISC
- Teacher Exams
- UP Board
- Uttarakhand Board
- Bihar Board
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Haryana Board
- Jharkhand Board
- MP Board
- Rajasthan Board
- Courses
- Test Generator
- Homework Help
- News & Updates

- Dashboard
- Mobile App (Android)
- Browse Courses
- New & Updates
- Join Us
- Login
- Register
No products in the cart.
- Business Studies
Class 11 Business Studies Notes & Model Test Papers
- CBSE Syllabus
CBSE Sample Papers
Cbse last year papers, user submitted papers, mock tests, nature and purpose of business, forms of business organisations, public private and global enterprises, business services, emerging modes of business, social responsibility of business and business ethics, sources of business finance, small business and enterprises, internal trade, international trade.
- CBSE Test Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
CBSE Important Questions
Other useful resourses, online tests, learning videos.
As we know business is something that sustains an economy. We are surrounded by a business world which makes it pertinent to have an operational knowledge of Business Studies. This subject is introduced in the plus-two level as an academic elective of the commerce stream. Students can access all valuable resources related to senior secondary Business Studies on the student’s best app myCBSEguide .
Study Material for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies
Knowledge of Business Studies gives a point of view of the business world and methods of interacting with the business environment. The senior secondary Business Studies curriculum develops an understanding of many social and ethical issues among the students. To prepare for this subject well, students can take the help of myCBSEguide where they can find the study material for Class 11 Business Studies. Right from the CBSE syllabus, NCERT textbook, Textbook Solutions, Revision Notes, Important Questions, online tests, test papers, learning videos, model question papers of class 11 Business Studies, etc. Our premium content has been trusted by millions of teachers and students alike.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Syllabus
The syllabus for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies prepares students to analyze and respond to the changes in the business world. The idea is based on the fact that business influences our social, political, and legal surroundings. Therefore the Business Studies syllabus attempts to keep the students up-to-date with the business market. The table below names the chapters included in the class 11 Business Studies syllabus for the current session. Knowing the syllabus right is the first step in beginning your preparation. To get more details about the topics of the mentioned units click on CBSE Class 11 Business Studies-syllabus 2022-23 .
|
|
|
Class 11 Business Studies NCERT Solutions & Important Questions
As we know NCERT solutions are very important while preparing for the CBSE examination. These questions give an outline of the basic types and formats of questions that are probable. Knowing the NCERT textbook solution is a must for every CBSE student. Sometimes, the final board examination question paper is completely based on the NCERT. You can download the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Business Studies on the myCBSEguide mobile app .
We also get some important questions prepared by experienced teachers from significant sections of each chapter. These questions can be found under the extra questions or important questions section of our student dashboard . To know the important questions for Class 11 Business Studies, check out our course content now.
Class 11 Business Studies Sample Papers
Sample papers are the best tool to prepare for the final examination. The sample papers available on myCBSEguide are the true copy of the latest CBSE sample papers with the same blueprint and Marking Scheme. We have a team of experts who do a detailed analysis of the Business Studies question paper to prepare the model question papers provided by us. It is one of our most valued and marketed products. The best part is, we prefer to abide by the latest CBSE syllabus and guidelines for examination (if any). Therefore, students get huge benefits from our sample papers which are reflected on their mark sheets. You can check the details of Class 11 Business Studies Sample Paper 2023 from the app or website and download the same. At the senior secondary level, students need to be more attentive and serious towards their preparation and so they should not miss out the solving sample papers before writing their final papers.
Class 11 Business Studies Test Papers & Mock Tests
Students can also find chapter-based test papers for class 11 Business Studies on the dashboard. These test papers are a good tool for the formative learning process. The sample papers can be accessed after the CBSE releases its official sample paper. But test papers can be used at any point in time.
We also provide online tests for Class 11 Business Studies. These tests are good for objective types of questions like MCQs or one-word answers. Before the final examination, we also arrange for mock tests and test series for core CBSE subjects. Registered students are notified about these tests.
This year CBSE has already released its practice papers, check them on Practice Paper 2023 Class 11 Business Studies question papers are also available here.
Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions
Being a subject of profession Business Studies have a huge scope of presenting real-life situational questions. Hence, senior secondary Business Studies students need good practice with these types of questions.
According to the new education policy , competency-based education is promoted. With this aim, case-based questions were introduced last year. These types of questions are designed to hone the analytical thinking of the students and apply the knowledge and technique that they have acquired in the due course in solving real-life situation-based questions. It enhances the rational thinking of the learners and they eventually gain a critical and analytical understanding of the subject. We have best case study questions for Class 11 Business Studies. You may find many such questions in publication books, but we have an assortment of Business Studies CBQs which require the application of key business concepts covering all important topics. Check the link for Class 11 Business Studies Case-Studies Questions .
Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Sample Question
OLX and qickr are examples of well-known websites used to conduct business. Tarasha’s sofa set got spoiled in the rain. Her friend suggested that she should change the fabric so that it looks new and put it for sale on Olx. Tarasha followed her friend’s advice and got her sofa repaired so that it looked better and uploaded nicely clicked pictures on the website without disclosing the fact that it was damaged from the inside. She found a buyer and sold it for Rs 10,000. After five days the buyer found the real state of the sofa set and called Tarasha but she did not answer any of the calls.
- identify the type of business highlighted in the above case.
- Identify any two values which are overlooked by Tarasha.
- Explain any two benefits and limitations of e-business.
A well-furnished course plan of preparation is a must if you plan to shine in your exams. We have been assisting students in their learning process through our reliable content for a decade. We are a one-stop platform where you can get literally everything (for Class 11 Business Studies (be its textbook, syllabus, revision notes, or model question papers and mock tests. To get study material in other classes and subjects check our CBSE module . From the google play store download the myCBSEguide app now.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions are available on myCBSEguide App. You can also download them from our student dashboard. For students appearing for grade 11 CBSE exams from the Commerce stream, Business Studies is a fundamental subject. Business Studies is considered to be quite interesting as well …
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Syllabus 2022-23
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Syllabus 2022-23 includes Nature and Purpose of Business, Forms of Business Organisations, Public, Private and Global Enterprises, Emerging Modes of Business etc for the session 2022 – 2023. Here is the detailed syllabus. To download class 11 Business Studies CBSE latest sample question papers for …
CBSE to Conduct Two Term Exams in 2021-22
CBSE has issued a circular on 5th July 2021 regarding the Special Scheme of Assessment for Board Examination Classes X and XII for the Session 2021-22. Here is the complete text of the circular. COVID 19 pandemic caused almost all CBSE schools to function in a virtual mode for the …
CBSE Class-11 New Stream Selection Rules
The New Education Policy-2020 has suggested eliminating rigid stream selection rules. We know that there are three streams in class 11 and the choices to select subjects are limited. Students have to select subjects within the stream only. Thus, if you are taking Science Stream, you have no option to …
CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 Released
The syllabus for the session 2021-22 has been released by CBSE, New Delhi. It is available on the myCBSEguide App and CBSE official Website for free download. Here are some important points to note: The syllabus is almost similar to last year without 30% reduction. There are some minor changes …
CBSE Reduced Syllabus by 30% for Session 2020-21
CBSE, New Delhi has reduced the syllabus for classes 9 to 12 by 30%. The CBSE Revised Syllabus 2020-21 is available in CBSE official website and myCBSEguide mobile app. Here is the complete circular regarding CBSE Revised Syllabus 2020-21: CBSE Reduced the Syllabus The prevailing health emergency in the country …
Create CBSE Question Papers Online
Creating question papers online is easy. You can create question papers online with your name and logo in minutes. So, why to waste time consulting many books and finding suitable questions. Just log in to myCBSEguide Test Generator here and create question papers online. Follow 3 simple steps: Select your …
CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 Business Studies 2019-20
CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 Business Studies 2019-20 contains all the topics of this session. myCBSEguide provides you latest Syllabus for Class 11 Business Studies. The study of business is about how individuals and groups of people organize, plan, and act to create and develop goods and services to satisfy …
CBSE Released Syllabus for 2019-20
CBSE syllabus for 2019-20 is now available for download in CBSE official website and myCBSEguide Mobile App. The new syllabus for 2019 and exams to be held in March 2020. CBSE 2019-20 syllabus for March 2020 examination is released by CBSE, New Delhi. CBSE class 10 Syllabus for 2019 and …
Revision Notes of Class 11 Business Studies
Revision Notes of for Class 11 Business Studies in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides class 11 Notes latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE exams and school-based annual examinations. Class 11 Business Studies notes are …

Student Subscription
Unlock the exclusive content designed for the toppers, more courses.

Mathematics

Download myCBSEguide App
All courses.
- Entrance Exams
- Competative Exams
- Teachers Exams
- Uttrakand Board
- Bihar Board
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Haryana Board
- Jharkhand Board
- Rajasthan Board
Other Websites
- Examin8.com
CBSE Courses
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 09
- CBSE Class 08
- CBSE Class 07
- CBSE Class 06
- CBSE Class 05
- CBSE Class 04
- CBSE Class 03
- CBSE Class 02
- CBSE Class 01
- CBSE MCQ Tests
- CBSE 10 Year Papers
NCERT Solutions
- Submit Your Papers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 09
- NCERT Solutions for Class 08
- NCERT Solutions for Class 07
- NCERT Solutions for Class 06
- NCERT Solutions for Class 05
- NCERT Solutions for Class 04
- NCERT Solutions for Class 03
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 09 Sample Papers
- CBSE Results | CBSE Datesheet
Please Wait..
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 - Business, Trade and Commerce
- Class 11 Important Question
- Business Studies
- Chapter 1: Business, Trade And Commerce

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-1 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Important questions for class 11 business studies chapter 1 are now available on Vedantu for free download. Students can practice all the questions to get a clear idea about the chapter. The topics covered in this chapter become easier to learn and revise with the help of these important questions and answers prepared by the subject experts at Vedantu. Students can refer to these important questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 online as well as offline for free of cost. By solving these questions, they will get a conceptual understanding of the topics covered in this chapter.
Study Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 – Business, Trade and Commerce
Very short answer questions (1 mark).
1. Give an example of activity which is economic in one side and non-economic on other side.
Ans: Profession requires specialized knowledge and it is economic on one side and non economic on the other side.
State different types of economic activities?
Ans: Economic activities can be categorised as:
Name the economic activity in which specialized knowledge is required.
Ans: Profession requires specialized knowledge.
2. A person sells his domestic furniture at a profit, will it be considered a business? Explain the characteristics of business which is being stressed upon.
Mr Sonu sold his washing machine & refrigerator on Quikr as he was shifting base to London. Is this a business activity?
Ans: No, for an activity to be business it must have ‘regularity’ characteristic of business. This characteristic means that there must be regular dealing of such goods and services.
3. Why is insurance known as a tertiary industry?
Ans: Insurance is known as a tertiary industry because it provides supporting services finance and mitigation of risk to primary and secondary industries.
Which industries provide support services to other industries?
Ans: Tertiary industries provide supporting services to other industries. Such as telecommunication, banking, insurance, advertising etc.
4. What type of industry is fishing?
What type of industry are poultry farms and plant nurseries?
Which one of the broad categories of industries covers oil refinery and sugar mills?
Ans: Primary Industry
5. Categorise the following into business, profession and employment?
(i) A farmer
Ans: Business
(ii) An advocate
Ans: Profession
(iii) A clerk
Ans: Employment
(iv) A hawker selling toys for children
(v) A doctor
(vi) A person working in scooter repair shop on roadside
6. ABC Ltd. inventing new machinery to curb its production problem. Which objective it is trying to achieve?
Ans: Innovation under economic objective.
7. What reward does the businessman get for bearing risks?
Ans: Profit
8. Name the occupation in which people work for others and get remunerated in return.
a. Business
b. Profession
c. Employment
d. None of the above
Ans: (c) Employment
Employment is an occupation in which people work for others as per agreed terms and conditions and receive salary in return.
Short answer Questions (3 or 4 Marks)
1. What are the causes for the possibility of inadequate profits due to uncertainties or unexpected events?
No business is risk free in the light of this statement, explain the concept of business risk and it’s any three causes.
Ans: No business can function without taking risk as there is always a possibility of inadequate profits or even losses. The uncertainty of profits puts business at risk, like change in demand, change in technology, change in government policies etc.
Business risks are the uncertainties or unexpected events which may result in inadequate profits or losses.
The three causes of business risk are:
Natural causes: These are due to natural causes such as floods, earthquakes, etc. Every person has little control or no control over these causes.
Human causes: These causes include unexpected events caused by man, such as negligence of employees, power failure, employee’s or customer’s dishonest practices etc.
Economic causes: The economic causes involve the changes and variations taking place in the economy such as uncertainties due change of technology and method of production,political disturbances, change in prices, tax rates etc.
2. Compare between Business, profession & Employment on the basis of the following:
a) Capital Investment
c) Transfer of interest
Ans: The difference between Business, profession & Employment are:
Basis | Business | Profession | Employment |
Capital Investment | Owner needs to organise investment through personal or other sources depending on the size and nature of the business. | Limited capital needed to establish. | No investment required. |
Risk | Risk arises due to uncertainty of profits. | A professional usually receives a pre-determined or agreed fee thus moderate risk. | Salaries are fixed, they do not depend on the company's performance therefore no risk at all. |
Transfer of interest | Interest can be transferred for consideration or otherwise after following legal formalities. | Not possible | Not possible |
3. What is business risk?
Ans: Business is the possibility of earning inadequate profits or losses due to uncertainties and unexpected changes in the market conditions. Business risk may be due to natural causes, human causes, economic causes and external causes.
Nature of Business Risks
Risk is an essential part of every business. It can only be reduced but not eliminated in full.
It arises due to uncertainties like natural calamities such as earthquakes, floods etc., which are unavoidable.
The extent of risk depends upon the nature and size of business.
’No risk, no gain’ is applicable to every business. Hence, profit is the reward for risk taking.
4. Explain any four objectives of business?
Ans: Objectives are the purpose for which activity is performed. The four objectives of business are as follows:
Profit earning: Profit earning is necessary for successful survival and continuous growth of the organisation. Profits can be maximised by reducing cost and minimum wastage. Profits are the rewards for taking risks.
Productivity: Productivity can be calculated by comparing the value of output and value of input. Productivity can be increased by optimum utilisation of the physical and human resources.
Innovation: For surviving in the market, the business should take opportunities and become the first one to bring a new change in product, technology etc. A business should take first mover advantage against its competitors.
Market Standing: The business must convert its potential customer to actual customer and must maintain its actual customers as permanent customers. This will maintain the position of business in the market.
5. Define commerce, why is it of great importance in modern life?
Ans: Commerce acts as a link between the producer and consumers to enhance efficient distribution of goods and services.
Importance of Commerce:
It helps in free and smooth flow of goods and services between the producer and customer.
It creates employment opportunities.
It helps in the growth of industrial development.
It helps in increasing the standard of living of the society.
6. Distinguish between primary and secondary industry Give examples.
Ans : The difference between primary and secondary industry is given below:
Basis | Primary Industry | Secondary Industry |
Meaning | It involves production and extraction of natural resources. | It processes raw material by primary industry to produce goods for final consumption. |
Scope | It includes extractive and genetic industries. | It includes manufacturing and construction industries. |
Examples | Farming, Fishing, Mining, etc. | Automobile industry, petroleum, kerosene oil, etc. |
7. “Business is an institution organized to provide goods and services under the incentive of private gain.” Discuss.
Define business. Explain the characteristics of business (any three)
Ans: Business is an economic activity which is regularly engaged in production or purchase and sale of goods and services to satisfy human needs and wants with an aim to earn profit.
The characteristics of business are as follows:
Production and/or procurement: Business is related to conversion of raw material into finished goods or sale and purchase of goods and services in the market. As a result, a business either manufactures the goods on its own or purchases them from producers, and then sells them to end customers.
Economic Activity: Business is an economic activity as it is done to earn money for livelihood. It satisfies human needs by providing goods and services for earning profits.
Regular Activity: To constitute a business there should be dealings in goods and services on regular intervals. Doing one single transaction does not constitute business. For example selling your old books, or furniture and purchasing a new one is not termed as business.
Element of Risk: Business is associated with a certain amount of risk as there is possibility of inadequate profits or losses due to change in tastes and preferences of customers, change in technology, fire theft, natural calamities, etc
8. Write differences among industry, commerce and trade on any five bases.
Ans: The difference between Industry, Commerce, and Trade
Basis | Industry | Commerce | Trade |
Meaning | It involves the production and manufacture of goods and services. | It refers to smooth flow of goods and services from producer to consumers. | It refers to exchange of goods and services. |
Scope | It includes primary, secondary and tertiary industry. | It includes trade and auxiliaries to trade. | It includes internal and external trade. |
Utility | It creates form utility | It creates time and place utility. | It creates place utility. |
Capital Requirement | Large amount of capital investment required | Comparatively lesser capital investment required | Less capital requirement |
Risk | Maximum risk involved | Lesser risk involved than industry | Least risk involved |
9. “Commerce comprises trade and all the services that make trade possible.” Discuss.
Ans: Commerce includes all the activities which are required for the exchange of goods and services. Commerce maintains smooth flow of goods and services from producer to customers by removing all the hindrances related to people, place, time, finance and information. It includes two types of activities:
Trade: The buying and selling of goods and services with an aim to earn profit is termed as trade. The people who are involved in trade are referred to as traders
Auxiliaries to trade : Auxiliaries to trade assists the buying and selling of the goods and services by removing the hindrances of place, people, time, finance, risk and information.
Long Answer Questions (5 or 6 Marks)
1. What provides the necessary link between producers & consumers with all those activities which are necessary for maintaining a free flow of goods & services? Discuss all those activities.
In business activities, there are some activities that are involved in the removal of hindrances in process of exchange i.e. from the producer to the consumer. Identify them. Also classify the activities which help in removing the following hindrances:
(i)Hindrance of place (ii) Hindrance of risk (iii) Hindrance of time (iv) Hindrance of finance (v) Hindrance of information
Tea is mainly produced in Assam, while cotton in Gujarat & Maharashtra but they are required for consumption in different parts of the country. How can this hindrance of place be removed? Also under what business activity will it be categorised.
Commerce is the sum total of activities that remove hindrances in the free flow of goods from producers to consumers. Explain.
How do traders remove the hindrance of person?
Ans: Commerce maintains smooth flow of goods and services from producer to customers by removing all the hindrances related to people, place, time, finance and information.
Auxiliaries to Trade
Auxiliaries to trade assists the buying and selling of the goods and services by removing the hindrances of place, people, time, finance, risk and information.
Transportation: It facilitates smooth flow of goods and services from the place of production to the place of consumption. Hence, it removes the hindrance of place. Example- Selling of mobile in Lucknow which is manufactured in Bangalore, tea produced in Assam, while cotton in Gujarat & Maharashtra but they are transported for consumption in different parts of the country.
Communication: Effective and timely communication between the supplier, producer and consumers leads to successful trading. Thus, it removes the hindrance of information.
Banking: Banks and financial institutions help producers or traders in providing finance required them in the form of loans, trade credit, overdraft, etc and hence, removing the hindrance of finance.
Warehousing : Producers and traders cannot sell the entire goods produced and thus stock of goods is always maintained by the producers or traders. Warehousing provides the facility to store unsold goods and hence removing the hindrance of time.
Insurance: Insurance removes the hindrance of risk. It facilitates business to reduce the risk of damages due to fire, theft, natural calamities, etc.
Advertising : Advertising acts as a link between producers, traders and consumers. It brings awareness among consumers about the goods and services available. Hence, removing the hindrance of information.
2. Starters of a new business are largely responsible for the success of the business they undertake various functions. Discuss the basic factors which influence the starter functions.
Explain any six factors that are important to be considered while starting a business.
Ans: The factors that are important to be considered while starting a business are as follows:
Size of business: The decision regarding the size of the business largely depends on the demand of the product and services in the market, the amount of risk and investment involved.
Choice of form of ownership: The choice of suitable form of business depends on the factors like legal formalities, line of business, capital requirement, liability of the business, profit etc. The entrepreneur can decide the form of business as:
Sole proprietorship
Partnership
Joint stock company
Cooperative society
Location of business enterprise: Location of a business directly affects the availability of raw material and labour, cost of production, and services like banking, transportation, warehousing etc.
Financing proposition : Finance is required not only to start a business but also for surviving in the market in the long run. Financial planning includes the amount of finance required for the capital and its source.
Physical facilities: While starting a business, the availability of physical facilities like land and building, plant and machinery and others services required for commencing business.
Competent workforce: Human resource is the greatest asset of any business. Competent and skilled workforce helps the business in reaching the height of the success. Thus, every business should wisely do the recruitment of personnel and must have training and development plans to increase the potential level of the workforce.
3. Profit maximization cannot be the sole objective of a business. Explain.
“Overemphasis on objective to earn profit may exploit the business”. What does a business should do to enable itself to bring the balance?
Ans: Business is established for earning livelihood and for this maximisation of profit is the main objective. But it is not the sole objective of business as it operates in the society and uses the resources of the society.
So, it also has some social objectives that could is undertaken to maintain balance, these are as follows:
Social Objectives
Supply of desired goods and services: Business must supply goods and services of proper quality and with all required certifications. It must aim for customer satisfaction.
Social and Fair Trade Practices: Business must not indulge into malpractices like black marketing, hoarding, compromising on quality or safety of products. Business must work for society.
Employment Opportunities: Business must create employment opportunities for the society especially for less advantaged sections of society.
Welfare of Employees: Businesses must work for growth and development of employees like training social and personal skills, and a good working environment. As employees directly contribute to productivity and profitability.
Social Welfare: Businesses must utilize their profits towards society like setting up schools, charitable hospitals, etc that are necessary for the development of society.
“Profit is not an objective but a requirement of business.” Do you agree with the statement? Support your answers with reasons
Ans: I agree that profit is a requirement of a business. The reasons are:
Long term survival: A business can survive in the market in the long run, only when it earns profit. This is because finance is needed by business in all the activities, and in all the areas. From day to day expenses, to expansion of business, finance is needed. Hence if a firm will not earn any profit, it won’t be able to pay expenses, or grow or survive in the market, leading to its closure.
Growth: Profits are needed for the growth, diversification and expansion of business. A business with no or less profit cannot implement such growth policies.
Efficient performance: Profits act as a motivating factor to the owners as well as the employees. Higher profits leads to higher efficiency and productivity on the part of people in the organization, thus leading to quality performance.
Reputation: Decent profit making enables the firm to pay out its expenses on time, in terms of salaries, wages, dividends, rents, etc. Hence all the stakeholders, and shareholders remain happy and content with the firm, thus leading to a high reputation and goodwill of the business in the market.
Fulfil social objectives: All other objectives of the business could be achieved only if the business earns sufficient profit. A business cannot fulfil the societal needs, and contribute towards the society if it does not earn satisfactory profits.
Innovation: Change is the law of nature. Hence, an organisation needs to keep changing and innovating to match with the changing and challenging environment. However, innovation requires skilled manpower, intense research, and high end technology, which is only possible when the business is able to generate suitable profits.
Reward for risk-bearing : A business undertakes multiple risks to keep the operations going, hence profits act as the reward of risk bearing.
4. ‘Kodak Pics’ is an advertisement agency initiated by Rahul, Sushmita & Prema. They have called a meeting to discuss the below given points
(i) Increase the profit margin by 20% in july.
(ii) Aiming bigger share in the market.
(ii) Making use of better lenses & improved techniques.
(iv) Making best use of cameramen, finance etc. employed by the business
(v) Improve efficiency in functioning of business.
(a) Which aspects of business objectives are being referred to here?
Ans: Economic Objectives are reflected here.
(b) Also develop each point to be discussed in the meeting by classifying the objective.
Ans: The objective are:
Increase the profit margin by 20% in july: Profit earning: Profit earning is reflected in this point. Profits can be maximised by reducing cost and minimum wastage. Profits are the rewards for efforts and investment put in by the owner.
Aiming bigger share in the market: Market Standing: Market standing is reflected in this point. The business must convert its potential customers to actual customers and must maintain its actual customers as permanent customers. This will maintain the position of business in the market.
Making use of better lenses & improved techniques: Innovation: Innovation objective is highlighted here. It means developing new products or modification in existing products. Every business in order to survive in a competitive environment should innovate its products or develop new ideas to tackle competition.
Making best use of cameramen, finance etc. employed by the business: Physical and financial resources: This objective is reflected in this point. Business must use its resources according to the requirement and with minimum wastage.
Improve efficiency in functioning of business: Productivity: This objective is reflected in this point. Productivity t is a measure of efficiency. Every business must aim at increasing its productivity through the efficient use of resources. Productivity can be increased by optimum utilisation of the physical and human resources.
5. Jawaharlal prepares ‘Ghujiya’ for customers during Holi season every year. He prepared more ‘Ghujiya’ than he could sell this year. He employed women and children also and paid them less salary manufacturing on the packages. This way he generated profit for himself.
(a) Do you think he is fulfilling all the objectives of business?
Ans: No, he is not fulfilling all the objectives of business.
(b) If not which aspects of this objective is not being fulfilled?
Ans: Social Objectives are not fulfilled as Jawaharlal is paying less salary to the women and children, and keeping all the profits to himself.
(c) Write any two values lacking in Jawaharlal.
Wastage of time and resources by preparing excess ghujia.
Fair and just behaviour by paying less salary to women and childre.
6. Different situations in different business are being elaborated below:
(i) Raghunath Gorkha had a match stick factory in Nepal which got destructed by the recent earthquake.
(ii) Mr Arya, a senior manager in a telecom company shared confidential information about the company with a competitor which led to huge losses for the company.
(iii) Vodafone Co. was charged with evasion of tax and asked to pay fine in cross which would lead to heavy losses for the company.
(iv) Type writers becoming redundant.
(a) Which characteristic of business is being referred to in all the above cases?
Ans: ‘Business Risk’ is reflected in the above cases.
(b) How can you classify the different cases based on this characteristic?
Ans: The classification is given below:
Raghunath Gorkha had a match stick factory in Nepal which got destructed by the recent earthquake.
Natural Causes: These are due to natural causes such as floods, earthquakes, etc. Every person has little control or no control over these causes.
Mr Arya, a senior manager in a telecom company shared confidential information about the company with a competitor which led to huge losses for the company.
Human Causes: These causes include unexpected events caused by man, such as negligence of employees, power failure, employee’s or customer’s dishonest practices etc.
Vodafone Co. was charged with evasion of tax and asked to pay fine in cross which would lead to heavy losses for the company.
Type writers becoming redundant.
Economic Causes: he economic causes involve the changes and variations taking place in the economy such as uncertainties due change of technology and method of production,political disturbances, change in prices, tax rates etc.
7. Dr. Sanvi is an orthopedic surgeon in AIIMS Hospital and Dr Maruti, her friend is a Pediatrician who has set his own clinic. Dr Maruti’s wife, Ms. Aditi operates her Cosmetic store. Compare & differentiate the nature of tasks undertaken by them.
Ans: Dr. Sanvi is involved in employment, Dr Maruti is involved in Profession and Ms. Aditi is involved in business.
The differences between business, profession and employment are:
Basis | Business | Profession | Employment |
Meaning | Business is an economic activity which is regularly engaged in production or purchase and sale of goods and services with an aim to earn profit. | Any economic activity which is carried out by a person with specialised knowledge and skills in order to serve society is called profession. | Employment is an occupation in which people work for others as per agreed terms and conditions and receive salary in return. |
Mode of establishment | Established after fulfilling some required legal formalities. | A certificate of practice required. | Starts after receiving an appointment letter. |
Nature of work | Selling and buying of goods and services. | Rendering specialized services | Work is as per the contract and the rules of service. |
Qualification | No minimum qualification required. | Formal qualification and training from a professional body is a must. | Qualification requirements differ with job type. |
Reward or return | Profit | Professional fee | Wages or salary earned |
Capital investment | It is dependent upon the type and size of business. | Limited capital needed. | No capital. |
Risk | High uncertainty and risk. | Little or limited risk | No risk |
Transfer of interest | Possible | Not possible | Not possible |
Code of conduct | No code of conduct is prescribed. | Professional code of conduct is there. | Rules set by the employer are to be followed. |
Example | A person having his shop, factory etc. | Chartered Accountants, Lawyers, Doctors are all professionals. | Jobs in banks, companies etc. |
8. Zainab, Shelly & Ravina are friends. They have just completed a fashion designing course. They wish to start a business together. They have Rs.10,00,000 savings put together and are planning to take a bank loan of additional Rs.10 lakhs. They have found a prime location in KarolBagh where they can set their boutique. They decide that they will initially not take very big orders. Based on this information, quote the lines associated with factors affecting the decision to start a business and classify them.
Ans: The Factors are:
Selection of type of business: A person can enter primary, secondary or tertiary industry, based on the possibility of profit, demand, customer preference etc. In the case above they selected the business to be a boutique.
Quotation: “They have just completed a fashion designing course. They wish to start a business together.”
Financing proposition: For every business, availability of capital or funds is an important factor while starting a business. Because capital is needed in each activity and aspect of business, such as in investment in fixed assets, stocks, meeting day to day expenses, etc.
Quotation: “They have Rs.10,00,000 savings put together and are planning to take a bank loan of additional Rs.10 lakhs.”
Location of business enterprise: It's an important factor while starting a business. The location of business is dependent on the easy availability of raw materials and labour, banking services, transportation services nearby etc. Any mistake in this can result in high losses to business.
Quotation: “They have found a prime location in KarolBagh where they can set up their boutique.”
Size of Business : Every person has to decide whether it wants to operate on a large scale or at a medium scale. It depends upon demand for the product and the necessary capital that person has. If a person is optimistic about all the factors, he can open up his business on a large scale, and vice versa.
Quotation: “They decide that they will initially not take very big orders.”
Students who are trying to get ahead in their class and score some good marks in the exams need to ensure that they have all the help that they need. This is where the important questions for class 11 business studies chapter-wise selections might be a great help to the students. These questions are created after careful observation of the syllabus and hence contain all the details which might be essential for passing the exams with proper marks. There is simply not a single speck of doubt about the fact that having some help from these class 11 business studies chapter 1 important questions is going to make things a lot easier for students.
Important Questions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1
Some important questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 are given below.
1. Insurance is a tertiary industry. Give an explanation.
2. How can a trader get rid of the hindrance of a person?
3. Provide a few differences between a primary and secondary industry.
4. Define commerce. What is the significance of commerce in modern times?
5. State the different objectives of a business.
The 1st chapter of the class 11 business studies textbook gives the students an idea about businesses and the other factors that are included in it. When students practice these questions, they will be able to understand the commercial position of our country and other countries in a better way. There are also some mentions about different industries that are considered to be a part of the business. Having class 11 business studies chapter 1 extra questions will also be a great help to the students who want to ensure that they have all the basic knowledge that they need about the business sectors in the best way. Not to mention that with regular practice and thorough reading, they can get more and more understanding of the whole chapter and hence will be able to solve more complicated questions as well.
Why Choose Us To Get Important Questions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter Wise
Class 11 business studies chapter 1 questions, cover, different topics to help students out when they need to ensure that they get good marks in their examination. These questions have been picked by professional experts who have an idea about the subject. Also, these experts are totally aware of all the rules and regulations of CBSE and NCERT related exams. So, downloading the important questions for class 11 business studies chapter 1 will be a good idea for the students. They can read the questions and get the solutions to make sure that all of their doubts are cleared in a single place.
Also, these questions are really free of cost and available at the official site of Vedantu. There is a PDF version available for download or students can also have a look at the questions online.
For a subject like business studies, it is essential for students to gain as much info about the topics as they can. This could be one of the main reasons why students are always on the lookout for important questions for class 11 business studies in the best way. We have so many different types of important questions so that students can actually have some help when it comes to preparing for the topics of business studies.
We hope our crucial questions for Class 11 Business Studies will aid your study. Whether preparing for exams or seeking assignment help, these questions address chapter-specific doubts. Download the PDF on any device for easy access. Practicing these questions enhances knowledge, critical thinking, and analytical skills, covering topics like business objectives, stakeholders, and government's role. With a focused approach, students can prioritize study efforts and allocate time wisely. By practicing these questions, confidence grows, leading to improved exam performance. Start your preparations by downloading the questions and unlock your potential.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 - Business, Trade and Commerce
1. Where do I get one mark questions of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies?
To practice the most relevant and recurring one mark questions of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies, it is best if you practice from the NCERT textbook and NCERT Exemplar. There are plenty of questions to practice from in these two books. While studying the chapter, you must take a special note of the definitions and formulae, as they tend to come as one marker. Also pay attention to the facts and figures given in certain concepts and memorise them thoroughly to leave no scope for error.
2. Where can I get the list of Important Questions of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies?
You can get a list of the Important Questions of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies on Vedantu. These important questions are available at free of cost on Vedantu(vedantu.com) and mobile app. Regardless, you must treat every NCERT question important and practise each one of them thoroughly. The NCERT must be considered of prime importance and all the concepts and questions must be memorised to the best of the student’s abilities. This is where the key questions for Class 11 Business Studies chapter-by-chapter selections might come in handy. These questions are based on a thorough examination of the curriculum, and so include all of the information that may be necessary for passing the examinations with good grades.
3. What are the main concepts of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies?
The first chapter of the Class 11 Business Studies textbook introduces students to businesses and the various variables that influence them. When students practise the NCERT questions, they will have a better understanding of our country's and other nations' commercial positions. There are also mentions of several industries that are regarded to be a component of the business as well. Students who wish to ensure that they have all of the basic knowledge they need about the business sectors will benefit greatly from having additional questions of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies.
4. Is Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies easy?
Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies can come across as a bit difficult because it is the first time the students are introduced through this subject. But to make sure that they don’t have a fall out with business studies, they need to make sure that they pay some extra attention and put in extra effort to understand it. Regular practice and consistent studies will help students get the hang of the chapter and they will set up the right base for the board exams of Class 12.
5. Are NCERT Solutions enough to prepare Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies?
Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 NCERT questions include a variety of subjects to assist students in ensuring that they receive high marks in their exams. These questions were chosen by experienced specialists who are knowledgeable about the issue. Furthermore, these professionals are well familiar with all of the norms and regulations of CBSE and NCERT related exams. As a result, students should obtain the key questions for Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies. They would read the questions and obtain the answers in one spot, ensuring that all of their uncertainties are addressed.

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies
NCERT Solutions for Business Studies Subject for Class 11 Students are given here. The 11th grade is an important milestone because it lays the foundation for your final board exams the next year. For students who plan to study commerce, Business Studies is an integral part of your syllabus.
Business studies require you to memorise a lot of business laws and trade sanctions. At LearnCBSE.in, we provide the Class 11 Business Studies NCERT Solutions. You can easily download the solutions and start solving questions to make it easier for yourself!
- Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Business
- Chapter 2 Forms of Business Organisation
- Chapter 3 Private, Public and Global Enterprises
- Chapter 4 Business Services
- Chapter 5 Emerging Modes of Business
- Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
- Chapter 7 Formation of a Company
- Chapter 8 Sources of Business Finance
- Chapter 9 Small Business
- Chapter 10 Internal Trade
- Chapter 11 International Business-I
- Chapter 12 International Business-II

NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies PDF
NCERT Solutions Accountancy Business Studies Indian Economic Development Commerce
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

- Latest Resources
- Quick Links
Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
2023 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
Explore the latest Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos for 2023. These resources are ideal for exam preparation and understanding the current trends in question formats.
- Download GP Business Studies Grade 11 Project 2023 TERM 3 QP and Memo
- Download Limpopo Business Studies Grade 11 September 2023 QP and Memo
2022 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
Access the 2022 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos . A valuable resource for revising and practicing problem-solving techniques.
- Download Business Studies Grade 11 SEPT 2022 QP and Memo
2021 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
Prepare thoroughly with the 2021 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos . These documents are crucial for understanding key concepts and exam expectations.
- Download KZN Business Studies Grade 11 September 2021 QP and Memo
2016 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
Explore the 2016 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos to help you prepare for exams and understand key concepts in Business Studies.
- Download 2016 BUS ST SEPT QPMEMO
2015 Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
For more comprehensive practice, explore additional past papers and memos for Business Studies from 2015.
- Download 2015 SEPT BUS ST QP MEMO
Additional Resources for Grade 11 Business Studies
For a broad range of practice questions and answers, these additional papers and memos cover various aspects of the Business Studies curriculum.
- Download SEPT BUS ST QPMEMO
- Download SEPT BUS QPMEMO
- Download BUS SEPT QPMEMO
Looking for something specific?
Related posts.

Creative Thinking and Problem-solving Grade 11 Business Studies
Creative Thinking and Problem-solving Grade 11 Business Studies: Notes, with Activities Questions and Answers. Welcome to Term 2 of Grade 11 Business Studies, where...
Previous Story
Grade 11 Geography September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos
Grade 11 afrikaans september term 3 past papers and memos.
STANMORE SECONDARY
Exam Papers and Study Notes for grade 10 ,11 and 12
Business Studies(Grade 11)
Study notes , past year exam papers.
(updated 2024/07/04)
advertisement
KZN March QP and Memo
LP June P2 only
EC June P2 and Memo
KZN June P1 and Memo
KZN June P2 and Memo
LP SEPT QP and Memo
LP CSD SEPT QP only
GP Project TERM 3 & Memo
KZN NOV P1 only
KZN NOV P2 only
EC NOV P1 and Memo
EC NOV P2 and Memo
KZN SEPT QP and Memo
KZN April QP and Memo
KZN June QP only
KZN SEPT QP and Memo
March QP only
MARCH QP+ Memo
JUNE P1 QP+ Memo
JUNE P2 QP+ Memo
SEPT QP+ Memo
NOV P1 QP+ Memo
Nov P2 QP+ Memo
MARCH QP+MEMO
SEPT QP+MEMO
NOV QP+MEMO
MARCH QP+MEMO
JUNE QP + MEMO
SEPT QP+MEMO
MARCH QP + MEMO
JUNE QP+MEMO
NOV QP+MEMO
JUNE QP + MEMO
SEPT QP + MEMO
NOV QP + MEMO
STUDY NOTES

Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/08/20/gcse-results-day-2024-number-grading-system/
GCSE results day 2024: Everything you need to know including the number grading system

Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.
Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren’t what you’re expecting.
When is GCSE results day 2024?
GCSE results day will be taking place on Thursday the 22 August.
The results will be made available to schools on Wednesday and available to pick up from your school by 8am on Thursday morning.
Schools will issue their own instructions on how and when to collect your results.
When did we change to a number grading scale?
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths.
By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
The numerical grading system was to signal more challenging GCSEs and to better differentiate between students’ abilities - particularly at higher grades between the A *-C grades. There only used to be 4 grades between A* and C, now with the numerical grading scale there are 6.
What do the number grades mean?
The grades are ranked from 1, the lowest, to 9, the highest.
The grades don’t exactly translate, but the two grading scales meet at three points as illustrated below.
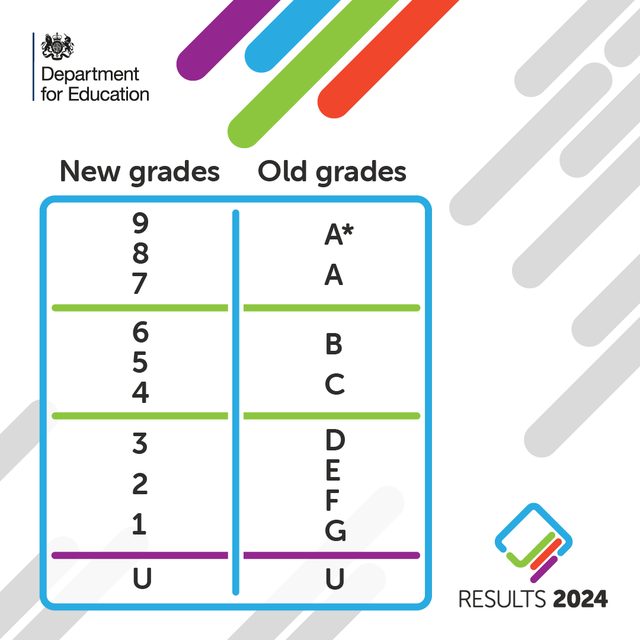
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, while the bottom of grade 4 is aligned to the bottom of grade C.
Meanwhile, the bottom of grade 1 is aligned to the bottom of grade G.
What to do if your results weren’t what you were expecting?
If your results weren’t what you were expecting, firstly don’t panic. You have options.
First things first, speak to your school or college – they could be flexible on entry requirements if you’ve just missed your grades.
They’ll also be able to give you the best tailored advice on whether re-sitting while studying for your next qualifications is a possibility.
If you’re really unhappy with your results you can enter to resit all GCSE subjects in summer 2025. You can also take autumn exams in GCSE English language and maths.
Speak to your sixth form or college to decide when it’s the best time for you to resit a GCSE exam.
Look for other courses with different grade requirements
Entry requirements vary depending on the college and course. Ask your school for advice, and call your college or another one in your area to see if there’s a space on a course you’re interested in.
Consider an apprenticeship
Apprenticeships combine a practical training job with study too. They’re open to you if you’re 16 or over, living in England, and not in full time education.
As an apprentice you’ll be a paid employee, have the opportunity to work alongside experienced staff, gain job-specific skills, and get time set aside for training and study related to your role.
You can find out more about how to apply here .
Talk to a National Careers Service (NCS) adviser
The National Career Service is a free resource that can help you with your career planning. Give them a call to discuss potential routes into higher education, further education, or the workplace.
Whatever your results, if you want to find out more about all your education and training options, as well as get practical advice about your exam results, visit the National Careers Service page and Skills for Careers to explore your study and work choices.
You may also be interested in:
- Results day 2024: What's next after picking up your A level, T level and VTQ results?
- When is results day 2024? GCSEs, A levels, T Levels and VTQs
Tags: GCSE grade equivalent , gcse number grades , GCSE results , gcse results day 2024 , gsce grades old and new , new gcse grades
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | ||
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
Comments and moderation policy
BUSINESS STUDIES FOR CLASS 11 CHAPTER 1 NATURE AND PURPOSE OF BUSINESS MCQS ALONG WITH ANSWERS
Free CBSE Business Studies Multiple Choice Questions for Class 11 along with answers, Chapter 1: Nature and Purpose of Business. Business Studies MCQs for Class 11 chapter-wise with answers are prepared based on the current exam pattern. Students can tackle MCQs with answers to realise their spadework level.
1. The possibilities of inadequate profits or even losses due to uncertainties are known as ____________.
(a) Business contingencies
(b) Business risks
(c) Business ventures
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Business risks
2. Business risk is not likely to arise due to _____.
(a) Changes in government policy
(b) Good management
(c) Employee dishonesty
(d) Power failure
Answer: (b) Good management
3. Name the two broad categories of business activities.
(a) Trade and Commerce
(b) Trade and Industry
(c) Industry and Commerce
Answer: (c) Industry and Commerce
4. The industries which provide support services to other industries are known as _____.
(a) Primary industries
(b) Secondary industries
(c) Commercial industries
(d) Tertiary industries
Answer: (d) Tertiary industries
5. ‘Earning of profit is considered to be the subsidiary objective of the business.’ The given statement is _____.
(c) Cannot say
Answer: (b) False
6. The occupation in which people work for others and get remunerated in return is known as _____.
(a) Business
(b) Profession
(c) Employment
Answer: (c) Employment
7. Transfer of interest exists in the case of _____.
(a) Profession
(b) Employment
(c) Business
Answer: (c) Business
8. Which of the following does not characterise business activity?
(a) Production of goods and services
(b) Presence of risk
(c) Sale or exchange of goods and services
(d) Salary and wages
Answer: (d) Salary and wages
9. Which of the following is not an example of non-economic activity?
(a) Patriotism
(b) Teaching
(c) Sentiment
(d) Sympathy
Answer: (b) Teaching
10. Economic activities may be classified into business, ___________ and employment.
(b) Occupation
(c) Vocation
Answer: (a) Profession
11. Which of the broad categories of industries covers oil refineries and sugar mills?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
Answer: (b) Secondary
12. Following are the characteristics of business risks. One of them is not correct. Please identify it.
(a) Loss is the reward for risk-bearing
(b) Business risks are due to uncertainties
(c) Risk is an essential component of every business
(d) Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business
Answer: (a) Loss is the reward for risk-bearing
13. Which one of the following may not be a factor behind starting a business?
(a) Routine workload
(b) Size of the firm
(c) Finance
(d) Location of the business
Answer: (a) Routine workload
14. Commerce includes activities relating to trade and ___________ to trade.
(a) Supporting
(b) Subsidiaries
(c) Auxiliaries
Answer: (c) Auxiliaries
15. Which of the following cannot be classified as an objective of a business?
(a) Investment
(b) Productivity
(c) Innovation
(d) Profit earning
Answer: (a) Investment
We trust that the offered Business Studies MCQs for Class 11 with respect to Chapter 1: Nature and Purpose of Business will help you. Assuming you have any questions with respect to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies, Nature and Purpose of Business MCQs, drop a remark underneath, and we will hit you up at the most punctual.
| COMMERCE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 – Private, Public and Global Enterprises
Home » CBSE » Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 – Private, Public and Global Enterprises

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 – Private, Public, and Global Enterprises
Business studies teaches people how to work together to achieve specific creative and productive goals, generally to make money. Business studies is a vast field that may lead to various job opportunities. The third chapter in the Class 11 Business studies book is Private, Public and Global Enterprises. It teaches about different enterprises. This chapter covers concepts such as business characteristics, different types of businesses, the changing role of the public sector, features of global enterprises, benefits of joint ventures and more. It carries significant weightage in the Business Studies syllabus. Students can easily access all this and more on the Extramarks website.
Quick Links
Business Studies is one such subject that requires a lot of reading and revising. At Extramarks, we understand the importance of solving questions. Hence, Extramarks experts have gathered them from various sources, such as the NCERT Textbook, NCERT Exemplar, other reference books, past years’ exam papers and so on. Our Business Studies academicians have developed stepwise solutions to help students comprehend each chapter in a better way. Students can register today with Extramarks and access Important Questions of Chapter 3 Business Studies Class 11 .
Apart from Chapter 3 Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions, materials like NCERT Solutions, CBSE revision note s, past years’ question papers, and NCERT books can be easily found on the Extramarks’ website.
Get Access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions 2022-23 with Solutions
Sign Up and get complete access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions for other chapters too:
| 1 | Chapter 1 | |
| 2 | Chapter 2 | |
| 3 | Chapter 3 | Private, Public and Global Enterprises |
| 4 | Chapter 4 | |
| 5 | Chapter 5 | |
| 6 | Chapter 6 | |
| 7 | Chapter 7 | |
| 8 | Chapter 8 | |
| 9 | Chapter 9 | |
| 10 | Chapter 10 | |
| 11 | Chapter 11 | |
Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 3 Important Questions and Answers
Extramarks’ subject experts have developed an entire list of Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 3 Important Questions from various sources. The questions comprise a wide variety of topics including characteristics of the business, features of different types of business, the changing role of the public sector, features of global enterprises, benefits of joint ventures and more. These questions and solutions help students to comprehend private, public and global Enterprises easily.
Mentioned below are a few Important Questions from Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 and their solutions:
Q1. Why is the government company form of organisation preferred to other types in the public sector?
Answer. A federal or state government must possess at least 51 per cent of a government enterprise. This business form was created under the Indian Companies Act of 1956.
The arguments for choosing the government-company form over other public-sector models are as follows:
- A government corporation has total autonomy in all organisational operations and decision-making procedures.
- It is not exposed to undue intrusion by the appropriate department in its operations.
- It is distinct from the government in that a government corporation is not the same as the government.
- It provides economic goods and services while also adhering to ethical marketing practices.
Q2. Explain the concept of the public sector and private sector.
Answer. The Private sector: Businesses owned by one person or a group make up the private sector. A private sector business exists solely to make a profit. The private sector includes a wide range of organisations, including:
- Company (LLP, LLC)
- Sole proprietorship
- Cooperative societies
- Partnership
- Joint Hindu family
Public sector: The public sector comprises businesses that the government partially or entirely controls. The government may own a 51 per cent controlling interest in the company. These organisations might have been created due to a particular act of the Parliament. The government contributes to the country’s economic activity through working in the public sector.
Q3. Mention the many types of businesses that operate in multiple nations.
Answer. Multinational corporations (MNCs) do business in more than one country . On the other hand, such firms have their headquarters in a single nation, where they conduct all of their principal commercial operations—for example, Capgemini, Amazon and others.
Q4. What was the role of the public sector before 1991?
Answer. Before 1991, the public sector played the following roles:
- Maintaining the regional balance: During the 1960s and 1970s, India’s regional development disparities were severe. Some regions of the nation were far more developed than others. Regional disparities inhibited the country’s growth and development. Public sector enterprises (PSEs) were founded in backward and rural areas to promote regional balance. These PSEs not only provided jobs but also helped the expansion of supporting industries like banking and transportation in these areas.
- Import substitutions and exports: Self-sufficiency was one of the primary goals of India’s economic strategy. The idea was to minimise imports while simultaneously growing exports. PSEs was founded as a result to produce heavy machinery and engineering products in the nation, restricting imports. PSEs like the Metals and Minerals Trading Corporation of India (MMITC) and the State Trading Corporation (STC) were established simultaneously to promote exports.
- Infrastructural development: For industrial development, communication, transportation, energy supply and financial infrastructure are all required. Because they lacked the skilled personnel and financial means to establish heavy industries fast, as the economy expected, the private sector showed little interest in investing in or growing them in any way. As a result, only the government could raise the money required. As a result, this industry has been responsible for building infrastructure.
- Economies of scale: Economies of scale benefit the natural gas and petroleum industries, for example (benefits derived from them are more significant when operated on a large scale). Because these large-scale industries needed significant capital expenditures, the private sector was not large enough to operate in the years after independence. The functioning of these enterprises on a smaller scale was not an option since it would have resulted in losses. Due to this, people compelled the government to establish and operate these firms.
- Keep an eye on the concentration of economic power: The public sector regulates the private sector. Only a few industrial businesses were willing to invest in heavy industries due to the concentration of wealth in a few hands in the private sector. As a result, there are income disparities. As a result, the government can develop enormous firms that need significant investments, and the money and benefits generated are distributed to many employees and workers.
Q5. What exactly do you mean by “Disinvestment of Shares”?
Answer. The disinvestment of government shareholdings in a small number of public firms has been a significant element of India’s privatisation drive. This initiative aims to provide a non-inflationary source of funding for the government.
The programme began in 1991-92 and lasted until 1995-96, when the government disinvested a portion of its stock in 40 public sector firms, raising Rs. 10,915 crore via several rounds of disinvestment. Financial institutions, mutual funds, private sector firms and the general public offered shares.
In August 1996, the Union Government established the Disinvestment Commission to advise it on the disinvestment policy for public sector firms. For disinvestment recommendations, the government submitted 40 public sector companies to the Commission. The government is now making efforts to implement the Disinvestment Commission’s findings.
Bids are requested for the sale of shares in selected state firms to guarantee openness in the Disinvestment programme and the shares are sold to the highest bidder. The government raised Rs. 1,869 crores from public-sector disinvestment in 2000-01, compared to Rs. 1,829 crores in 1999-2000 and Rs. 5,371 crores in 1998-99. The disinvestment objective was set at Rs for 2002-03. 0 crores.
Q6. State the various types of organisations in the private sector?
Answer. The private sector comprises businesses owned by one person or a group. The private sector’s principal purpose is profitability. Individual investments or shareholder contributions raise funds.
The majority of it is made up of:
- Company: A company is a legal entity with its legal entity and common seal that exists exclusively in the eyes of the law. It has perpetual succession and its legal entity, and a common seal. There are two types of companies: private and public.
- Multinational corporations: Multinational firms operate in one or more nations in addition to their home country. For example, Google..
- Sole proprietorship: A single individual owns the whole firm in this form of business. S/He manages, controls and carries out all the company’s functions and risks.
- Joint Hindu family: A Hindu joint Family owns and operates this firm, governed by Hindu Law.
- Partnership: A partnership is a group of two or more individuals who agree to work together to manage a business, share earnings, and share risks.
Q7. What is a Departmental Undertaking and what does it imply? Mention the benefits and drawbacks.
Answer: It functions as a government ministry or department. The budgets of these departments are presented to the Parliament in the same way as other ministries. It may be seen in the Indian Railways and Post and Telegraph departments. Either the federal government or a state government owns and controls departmental entities.
Benefits of Departmental undertaking are:
- Proper management: Qualified government employees oversee these businesses. Their job is very methodical and these businesses are appropriately overseen and handled. Such a detailed and methodical process of management and supervision keeps all super government officials very alert to their job.
- Service Motive: These businesses were created to provide a service. They prioritise the public good and social welfare. These initiatives also assist in lowering the tax burden on the general populace.
- National Importance: These departmental organisations carry out activities of national significance. Due to stringent budgeting, accounting and auditing, the potential of misusing public funds has been reduced.
- Secrecy: These groups can keep their identities hidden. Since they are under the government’s jurisdiction, based on public interest, the government can avoid disclosing facts.
Drawbacks of Departmental undertaking are:
- Political evils: Every major decision in the departmental organisation is motivated by political considerations. It is handled and overseen by the minister, a political party representative. The minister is responsible for his party’s interests.
- Lack of competition: Departmental organisations often have monopolistic status. They are inept due to a lack of competition. There is no motivation for hard labour and efficiency when there is no rivalry or monetary motive. There isn’t much of a correlation between pay and performance.
- Least profit-making business: The government owns and controls departmental organisations, making them the least profitable venture. It was formed to provide a service. Hence, it is not a high-profit venture.
- Red tape: Employees follow the trodden path due to red tape. They are uninterested in the project. They are irresponsible and just concerned about their pay. Officers are concerned about their reputation and respect. Due to bureaucratic procedures and political factors, decisions are frequently delayed.
- Shortage of competent workers: Government personnel are inefficient in commercial matters due to a lack of skilled professionals. They have considerable administrative experience but not enough to supervise the activities of the enterprise. Competent personnel are not hired since promotion to a higher level is predicated on seniority.
Q8. Describe the Industrial policy of 1991 for the public sector.
Answer. The Industrial Policy of 1991 resulted in a series of reforms for the public sector:
- Public Sector Disinvestment: This procedure entailed selling a portion of a company’s equity or controlling shares to the general public and private sectors. The goal of such a move was to encourage private businesses and the general public to participate in public enterprise ownership.
- Dereservation: In 1991, just eight industries were reserved for the public sector, including guns and ammunition, defence, atomic energy, mining and railroads. The private sector was allowed to indulge in all other areas.
- Policy dealing with sick units: This policy primarily dealt with reorganising or closing sick public sector units. The Board of Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (BIFR) was tasked with determining the units that the government should focus on restructuring and those that should be closed. The government established the National Renewal Fund (NRF) to assist in retraining or redeploying the workforce retrenched from a sick unit and providing compensation to employees seeking voluntary retirement.
- Memorandum of Understanding: This procedure gave public sector units more autonomy while also holding them accountable for their results. The public sector unit and the linked ministries signed a Memorandum of Understanding. The public sector units were given explicit objectives and complete operational autonomy to meet those objectives.
Q9. Briefly define the word “foreign collaboration.”
Answer. Foreign cooperation refers to businesses that have foreign units as equity partners. It is a joint venture between Indians and foreigners owned, managed and controlled together. These businesses benefit from the country’s and the world’s tremendous resources. These businesses bring together two or more countries’ financial, administrative and technical resources.
The profit is split (among the Indian owner and the foreign partner). The government has recently liberalised its policies on foreign investment in Indian businesses. According to the New Industrial Policy, direct foreign investment up to 51 per cent ownership in high priority sectors would be approved in 1999, and foreign technology agreements in recognised high priority industries will be granted automatic authorisation.
Q10. How does the government maintain a regional balance in the country?
Answer. The government maintains regional balance in the country in the following ways:
- The Indian government has built huge steel mills in rural regions to develop these areas and provide jobs for those living there.
- Many other sectors like steel factories have been established to give work possibilities.
- The growth of industries resulted in the development of other related sectors, all of which contributed to the country’s wealth.
- Setting up industries directly influenced the region’s growth, which resulted in better roads, infrastructure development, bridges and rail connectivity, linking all regions of India.
Q11. Define multinational corporations and their impact on a country’s economic growth.
Answer. A multinational corporation is a company with its headquarters in one country and its activities in many others. This suggests that this sort of company will do business in various nations. An MNC has its registered office in one nation (referred to as the “home country”) and conducts business in several other countries (called host countries).
A global firm controls manufacturing and marketing operations in many countries. Coca-Cola, for example, is a firm based in the United States with manufacturing and marketing activities in several nations worldwide.
Multinational corporations can benefit the host country in the following ways:
- MNCs establish facilities for the manufacture and distribution of commodities, resulting in the creation of jobs in the host nation. Excess loan pay ranges and career growth options are available to managers, technical, and other employees at multinational.
- The technology in emerging nations is outdated and outmoded. MNCs can serve as conduits for transferring advanced technologies to underdeveloped countries. Developing countries benefit from advanced technical know-how, better skills, and consulting to enhance product quality and save costs.
- MNCs can help emerging economies obtain money from industrialised nations, as they face a capital shortfall necessary for fast industrialisation. They make it easier to move money from places where it is plentiful to those where it is rare. As a result, MNCs can aid in increasing investment, and as a result, the host country’s growth rate. Since its liberalisation, India has drawn billions of dollars in global investment.
- Multinational corporations (MNCs) boost competition and break up domestic monopolies. Inefficient businesses are pushed to either improve or exit the market. Following liberalisation and increased technology, many Indian enterprises now compete with multinationals.
- MNCs assist in the exploitation of idle resources of the host nation, resulting in revenue generation.
- MNCs use professional management and cutting-edge management practices to spark a managerial revolution in the host nations. As a result, the host nations can foster a professional management culture. Management approaches such as MBO and corporate planning help multinationals establish a knowledge base.
- MNCs make it easier for the host country’s economy to integrate with the global market. In the host country, they promote international brotherhood and cultural interactions.
- MNCs can assist domestic enterprises in growing by supplying them with materials, components, and other items. Several auxiliary entities have evolved to give support to MNCs throughout time.
- MNCs deliver high-quality items to the host nation’s people due to their superior technology. This contributes to a higher level of living for them.
Q12. Can the public sector companies compete with the private sector in terms of profits and efficiency? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer. It is challenging for public sector enterprises to compete with the private sector in terms of earnings and efficiency due to the following factors:
- Differences in Ownership: The government is the sole or principal stakeholder in public-sector companies. As a result, the government controls the management and administration of these businesses, which may or may not execute economically sound policies due to political considerations.
- The Difference in Objective: A private company’s primary purpose is to generate profit, but a public company’s primary goal is to offer social welfare. Hence, they can’t be entirely profit-driven.
- Operational Differences: The private sector works in all areas with a decent return on investment, whereas the public sector is mainly involved in the low-returning primary and public utility sectors.
- Differences in Management: Public-sector businesses are run and managed by government officials who may or may not have had professional training, whereas private-sector businesses are managed and run by professionals. This leads to better efficiency in the private sector.
Q13. Mention the principal features/characteristics of global corporations briefly.
Answer. Global Corporation’s Characteristics: The following are the key characteristics of most global corporations:
- MNCs are massive, with billions of dollars in assets and sales, creating significant profits from their activities. IBM’s physical assets, for example, are valued at roughly $8 billion. The sales turnover of some international firms exceeds the gross domestic product of numerous developing nations.
- An MNC’s headquarters are located in the home nation to maintain control over its subsidiaries and affiliates. The parent corporation’s policy framework governs the local administration of branches and subsidiaries. Because the parent firm owns 40 per cent to 100 percent of the ownership in the subsidiary company, this is conceivable.
- An MNC’s international operations are managed by a parent business based in the home country. It operates through a network of branches, subsidiaries, and affiliates throughout the nations where it operates. Production, marketing and other operations are dispersed over many nations to get the economies of local operations.
- A global firm promotes a multilateral resource transfer. Technical know-how, machinery, equipment, raw materials, management knowledge and other items are transferred as a “package.”
- Many multinational firms enjoy oligopolistic power. They have a monopolistic position in the market. An MNC may amass enormous economic power by merging with and acquiring other businesses. Because of this, it has an oligopolistic nature and a strong position in the market. Hindustan Lever Limited, for example bought Tata Oil Mills to expand its market share.
- Because of their significant resources and better marketing skills, MNCs have access to international markets. As a result, multinational corporations (MNCs) can market their products in a variety of nations throughout the world.
- Professional talents, specialised knowledge, and training are used in these businesses. These executives have specific knowledge and experience in finance, marketing and human resources.
Q14. Why are global enterprises considered superior to other business organisations?
Answer. Multinational Companies are thought to be superior to other businesses since they have:
- Product innovation: Multinational corporations have fine-tuned their research and development centres for new product development. This allows them to maintain their competitive edge and large consumer base.
- Massive Financial Resources: MNCs have massive capital resources since they can raise funds from all around the world. They may borrow money from international banks, and many investors are willing to put their money into them in exchange for huge returns due to their goodwill.
- International Collaborations: Multinational corporations (MNCs) usually enter the market with the help of local private companies. This is primarily due to legislative restrictions and a desire to capitalise on the Indian firm’s brand reputation.
- Market Expansion: Their business and activities expand beyond their nations’ borders. They boost their global image and expand their market region, helping them position themselves as global brands.
- Centralised control: MNCs have a headquarters in their home country that oversees the company’s branches and subsidiaries. However, this influence is limited to the parent company’s broad policy framework. Regular operations are not affected by any delays or disruptions.
- Marketing Tactics: The marketing strategies of multinational corporations are far more successful than those of other businesses. They use aggressive marketing strategies to increase sales in a short period. They have a more reliable and current market intelligence system and more effective advertising and sales promotion strategies.
The above-stated section of Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 Important Questions is a list of Important Questions covering the entire chapter.
Benefits of Solving Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 Important Questions
A subject such as Business Studies requires a lot of reading and revising. The basics of this subject are introduced in Class 11 to pave the way for more in-depth study in Class 12. Students are advised to access Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3. Students will gain confidence by solving important questions from all the chapters and going through their solutions.
Mentioning below are some benefits of solving Important Questions of private-public andGlobal Enterprises :
- The questions covered in Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 are based entirely on the chapter- Private, Public and Global Enterprises.
- As mentioned earlier, these questions instil students with a sense of confidence and time management.
- These important questions are prepared by following the actual exam pattern. Going through these will help students prepare for exams too.
Extramarks provides comprehensive learning solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. We have abundant resources available on our website, along with essential questions and solutions. Students can click on the links given below to access some of these resources:
- NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE previous year’s question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Marks: 4 Ans
‘Public Private Partnerships’ refer to partnerships between public sector and private sector in financing, designing and developing infrastructural facilities. The private sector participates in government projects by contributing finance, technical knowhow and managerial expertise. It is primarily used for capital intensive government projects of high priority, meant for public benefits.
Following points describes its features: i. Facilitates Partnership between public and private sector – It is an arrangement between public sector authority and private sector enterprise, in which the private party offers a public service or project and assumes substantial, technical and operational risk in the project.
ii. Pertain to high priority projects It pertains to high priority projects generally in the infrastructure sector.
iii. Suitable for big projects It is suitable for big projects having long gestation period, as capital subsidy may be provided by the government in the form of one time grant.
iv. Public welfare It is used in the government projects mainly aimed at public welfare.
Q.2 Google has worked with NASA on many projects in the past with some wonderful results. To develop the google earth, these two have joined the hands together.
Answer the following based on the above text:
1. Choose from the following, kind of business they are into.
a. MNC b. Joint Venture c. Sole Proprietorship d. Cooperative organisation
2. Google has worked with NASA on many projects in the past with some wonderful results. To develop the google earth, these two have joined the hands together. Into how many kinds such ventures be formed
a. Two b. Three c. Six d. Seven
3. What is/ are the reason/s for forming such ventures
a. Increase costs b. Increase resources c. Increase risks d. Sharing of profits
Marks: 3 Ans
1. b. Joint venture
A joint venture refers to an entity that comes into existence when two or more companies join hands for mutual benefits. It involves combining resources and expertise of two or more business firms together so as to achieve the common objective, for which the venture is formed.
Joint ventures can be Equity based or contractual also. Equity based joint venture is formed through an agreement where two or more business firms parties jointly form a new separate business firm as per the mutual agreement between the parties. Under contractual type of joint venture, an agreement to work together is created.
3. b. Increase resources
JV can be formed between a foreign country and domestic country, which opens new markets for both partners. Products which have reached saturation point in domestic market can be sold in new markets.
Q.3 In India, many public sector enterprises work and act through the officers of the government and employees of such enterprises are also the employees of government.
(i) Which public sector enterprise is being referred here
(ii) What features are used to describe such enterprises specified in (i) above.
Marks: 5 Ans
(i) The public enterprise being referred above is Departmental Undertaking
It is the oldest form of public enterprise and is established as department under the respective ministry. These are managed by government officials under the supervision of the departmental head. These act through government officers and its employees are government employees.
(ii) Features of Departmental undertaking:
- It involves centralized control by the ministry as it is a major division of the government department.
- It involves administrative formalities and excessive paper work.
- The decisions taken by the enterprise requires the approval of concerned ministry.
- There is strict accounting and audit control helps in effective utilisation of money.
- The revenue is deposited into the treasury which is a source of income for such enterprises.
- These are suitable for government activities concerned with national security.
Q.4 Name the organisation formed by passing a special act of Parliament or state legislature. State the features of such an enterprise.
Statutory corporation is an organisation formed by passing a special act of Parliament or state legislature.
The features of statutory corporation are : i. It is governed by the rules and regulations of this act. The act also defines its power and privileges. ii. It is owned by the State. The government has financial responsibility and power to appropriate its profit. iii. A statutory corporation is a body corporate. It can sue and be sued, can enter into contract and acquire property in its own name. iv. It is independently financed and can obtain funds by borrowing from the government or from public through sale of goods and services.
Public sector enterprises are organised as:
i. Departmental Undertaking – It is organised, financed and controlled by the government and is established as department of the concerned Ministry.
ii. Public Corporation It is an autonomous corporate body set up under a special act of the Parliament or of State Assembly.
iii. Government Company It is company in which at least 51 per cent of the paid up share capital is held by the Central or State Government or partly by central Government and partly by one or more State Governments.
Q.6 Kolkata Municipal Corporation decided to start project of an underground parking system to ease parking problems. It was started back in 2007. The project was successful as it has reduced traffic jams, haphazard parkings, etc.
Answer the following questions based on the above case study:
1. State the type of enterprise that is being referred to here.
a. Statutory Corporation b. Departmental enterprise c. MNCs d. Transnational corporation
2. Kind of enterprises as identified in (i) can sue and can be sued. What feature of such enterprises are we talking about
a. Flexibility b. Autonomy c. Separate Legal entity d. Monopoly
3. Funds do not come from central budget for such kind of enterprises. What does this signify
a. Flexibility b. Autonomy c. Monopoly d. Freedom to use money
1. a. Statutory Corporation This is a Statutory Corporation. It refers to an autonomous corporate body set up under a special Act of the Parliament or State Legislature. These have the power of the government as well as flexibility of private enterprises.
2. c. Separate Legal entity This means that Statutory Coporation is the separate legal entity that allows it to enter into contracts and acquire property in its own name. It can sue and can be sued.
3. b. Autonomy This signifies autonomy in finance. Statutory organisations are not financially dependent on the Government as the funds do not come from central budget.
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 11 business studies important questions, chapter 1 - business, trade and commerce.

Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Organisation
Chapter 4 - business services, chapter 5 - emerging modes of business, chapter 6 - social responsibilities of business and business ethics, chapter 7 - formation of a company, chapter 8 - sources of business finance, chapter 9 - small business, chapter 10 - internal trade, chapter 11 - international business, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. where can a student find important questions class 11 business studies chapter 3 in simple language.
Extramarks’ study material is the most excellent source of Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies, Chapter 3. These can be found on the Extramarks’ website. Each question in this chapter is explained in detail and in simple terms to enhance understanding. You will be able to grasp the chapter better and acquire exceptional answer writing abilities to achieve the best marks in the Business Studies exam if you prepare this chapter with the help of Extramarks’ important questions.
2. Why are Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 important?
Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 important increases the basic conceptual knowledge of the students. This chapter can be referred to as a point of reference for the students preparing for competitive exams like VITEEE, BITSAT, NRRT and JEE Main/advanced, etc. These questions provide a stepwise explanation of the chapter.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Business Studies Case Study 1. Read the hypothetical text given and answer the following questions: Manish, Rahul and Madhav live in the same locality. They used to meet and discuss their ideas. After discussing the recent fire breakout in their area, they decided to take fire insurance for their house or work area.
Ans. 1. Value of playing with the health of workers. 2. Not fulfilling safety norms competition. 3. Offering bribe is an unlawful act. Q.9. A unit set up by Tata in rural area and the company plan to develop roads, parks of that area they also started a school for local children of that area.
CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies English medium question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships ...
Class 11 - Business Studies Sample Paper (2023-24) Maximum Marks: 80. Time Allowed: : 3 hours. General Instructions: This question paper contains 34 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. Answers should be brief and to the point. Answers to the questions carrying 3 marks may be from 50 to 75 words.
Business Studies Sample Paper Class 11 Question Paper Design 2023-24. 1. Remembering and Understanding: Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas.
These questions and their solutions help students better comprehend Business, Trade and Commerce. Mentioned below are a few Chapters 1 Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions and their Solutions: Q1. State the meaning of business. Answer: The term 'Business' is derived from the term 'busy.'.
Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies are outlined by the subject matter experts from the latest edition of CBSE books. It is recommended for the students to practise the given Class 11 Business Studies chapter wise important questions with the answers. Learning these would definitely help the students in scoring good marks in the board examinations.
To assess their preparation level, they can download and solve the Class 11 Business Studies term 2 Important Questions with Solutions developed by the subject experts of Vedantu. Find the solutions to these questions and take a step ahead in your preparation. CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-wise Important Questions 2024-25.
technology of an organisation so that improves the profitability of the business.Businesses need to be flexible in their. ganisational design and strategies so that they can compete in a changing marke. ic challenge.4.5 Direct influence on the environment and social responsibility Direct influences on busi.
Conclusion. With the help of these important questions and answers from CBSE Class, 11 Business Studies Chapter 5 - Emerging Modes of Business will help the CBSE Class 11 students to prepare for their exam in a full-fledged manner. Students are advised to download the free-to-download pdf and enjoy free learning from this content.
Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions. Being a subject of profession Business Studies have a huge scope of presenting real-life situational questions. Hence, senior secondary Business Studies students need good practice with these types of questions. ... For students appearing for grade 11 CBSE exams from the Commerce stream, Business ...
Study Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 - Business, Trade and Commerce. Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark) 1. Give an example of activity which is economic in one side and non-economic on other side. Ans: Profession requires specialized knowledge and it is economic on one side and non economic on the other side.
Case Studies Class 11 Chapter 2 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Rani acted as a partner of Simplex Solutions by participating in business negotiations and giving the impression that she was a partner, even though she did not contribute capital or take part in management. As a result, she would be liable as a partner by estoppel if Seema does not ...
11th Cbse Bst Bull's Eye Case Study Final - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 1) The document discusses several case studies related to different types of business activities and economic transactions. 2) Key topics covered include identifying primary, secondary and tertiary industries; causes of business risks like economic changes and human errors ...
NCERT Solutions for Business Studies Subject for Class 11 Students are given here. The 11th grade is an important milestone because it lays the foundation for your final board exams the next year. For students who plan to study commerce, Business Studies is an integral part of your syllabus. Business studies require you to memorise a lot of ...
Explore the latest Grade 11 Business Studies September Term 3 Past Papers and Memos for 2023. These resources are ideal for exam preparation and understanding the current trends in question formats. Download GP Business Studies Grade 11 Project 2023 TERM 3 QP and Memo. Download Limpopo Business Studies Grade 11 September 2023 QP and Memo.
Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 7 Questions and Answers. A team of Extramarks Business Studies experts has developed an entire list of Important Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 7, taking references from numerous primary and secondary sources.These questions include a wide variety of topics, such as essential stages in the formation of a company, steps involved in each stage of ...
Benefits of Solving Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2 Important Questions. Business Studies is one subject that requires a lot of reading and revisions. This subject is introduced in Class 11, and it prepares the base for Class 12 board examinations. Therefore, students are advised to access Important Questions of Business Studies Class 11 ...
STUDY NOTES. Exam papers and Study notes for Business Studies. Grade 11. Download free question papers and memos. Study notes are available as well.
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, ... and get time set aside for training and study related to your role. ... interviews, case studies, and more. Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside ...
Please identify it. (a) Loss is the reward for risk-bearing. (b) Business risks are due to uncertainties. (c) Risk is an essential component of every business. (d) Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business. Answer: (a) Loss is the reward for risk-bearing. 13.
The questions covered in Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3 are based entirely on the chapter- Private, Public and Global Enterprises. As mentioned earlier, these questions instil students with a sense of confidence and time management. These important questions are prepared by following the actual exam pattern.
On 9 August 2024, Moumita Debnath, a trainee doctor at R. G. Kar Medical College in Kolkata, West Bengal, India, was raped and murdered in a college building.Her body was found in a seminar room on campus. The incident has amplified debate about the safety of women and doctors in India, and has sparked significant outrage, nationwide protests, and demands for a thorough investigation.