- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Special Issues
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About Journal of Law and the Biosciences
- About the Duke University School of Law
- About the Harvard Law School
- About Stanford Law School
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic


Article Contents
I. the hope that abortion bans will deter abortion, ii. the hope that abortion bans will send a message, iii. the hope that abortion bans will be competently implemented and enforced, iv. conclusion, acknowledgements, ethics approval statement.
- < Previous
What will and won’t happen when abortion is banned
Katharine & George Alexander Professor of Law, Santa Clara University School of Law.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Michelle Oberman, What will and won’t happen when abortion is banned, Journal of Law and the Biosciences , Volume 9, Issue 1, January-June 2022, lsac011, https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsac011
- Permissions Icon Permissions
For the past 50 years, abortion opponents have fought for the power to ban abortion without little attention to how things might change when they won. The battle to make abortion illegal has been predicated on three nebulous assumptions about how abortion bans work. First, supporters believe banning abortion will deter it. Second, they hope bans will send a message about abortion—specifically, that abortion is immoral. And third, they expect bans to be competently implemented and enforced. Drawing on empirical work from within and outside of the U.S., this Article offers an evidence-based assessment of each of these assumptions. Part One examines the question of deterrence by exploring findings from countries with relatively high and relatively low abortion rates. After explaining why restrictive abortion laws alone do not reduce aggregate abortion rates, I consider the matter of individual deterrence. By identifying those most likely to be deterred by U.S. abortion bans, I illustrate how abortion bans intersect with structural inequalities to disproportionately impact poor women of color and their children. Part Two tests the idea that abortion bans send a message. I consider the bans’ meaning in context with U.S. laws and policies affecting families, exposing the difference between laws discouraging abortion, and those encouraging childbirth. Then, drawing from literature on the expressive function of the law, I assess the limits on the message-sending capacity of abortion bans in a society divided over abortion and over its commitment to children living in poverty. Part Three turns to the expectation that abortion bans will be competently enforced, noting the legitimacy struggles arising from law enforcement patterns, along with the administrative challenges inherent in overseeing the various exceptions to abortion bans. This article concludes by considering why the consequences and limitations of abortion bans should matter to supporters and opponents, alike.
For the past 50 years, abortion opponents have fought for the power to ban abortion without paying much mind to the details of how things might change when they won. The battle to make abortion illegal has been waged over a surprisingly nebulous assumption that banning abortion would, in itself, lead to meaningful changes in the practice of abortion in America. It has been a policy based on hopes and prayers, rather than on actual evidence about how restrictive abortion laws work in practice.
When the law on the ‘books’ changes in the United States, what might the law on the ground look like? Drawing on empirical work from within and outside of the USA, this article offers an evidence-based answer to the question of what will and would not happen where abortion is banned.
In the spirit of full disclosure, like almost everyone who engages with the abortion war, I have a bias: I am an unambivalent supporter of abortion rights. Nonetheless, I strive in this article to maintain a tone that I hope will permit readers who disagree with me to hear my message. I do so because those on all sides of our abortion war should care about it. For 50 years, the USA abortion war has been fought almost exclusively around the issue of legalization. 1 Yet all evidence suggests the changes likely to be wrought by banning abortion should leave even ardent supporters of abortion bans not just disappointed, but profoundly disturbed by their downstream consequences.
The question of how abortion bans work in practice is a live one among abortion-rights advocates, with many, (including myself), working to identify what happens, and to whom, so as to permit advocates and policy makers to mitigate their harsh impact on the vulnerable. 2 By contrast, anti-abortion Americans who have spent decades working to enact such laws have paid relatively little attention to how things actually change when abortion is illegal. Instead, they have rested their support for outlawing abortion on three general assumptions about how abortion bans will work. First, they believe banning abortion will deter it. 3 Second, they hope the bans will send a message about abortion—specifically, that abortion is immoral. 4 And third, they expect the laws will be competently implemented and enforced. 5
This article interrogates each of these expectations. Part One begins its consideration of the question of deterrence by exploring research from countries with relatively high and relatively low abortion rates. This comparison offers powerful evidence that restrictive abortion laws alone do not reduce abortion rates. But while outlawing abortion is unlikely to cause an aggregate decline in abortion rates, bans will cause some to carry to term pregnancies they might otherwise have aborted. 6 This section concludes with an examination of how abortion bans intersect with structural inequalities to disproportionately impact poor women of color and their children–already the most vulnerable and marginalized Americans.
Part Two tests the assumption that outlawing abortion will send a message that abortion is morally wrong, thereby helping to foster a culture that rejects abortion as an option. This section considers the messages sent by US abortion bans by placing them in context with our laws and policies that inform when and whether people seek abortions. Then, drawing from literature on the expressive function of the law, this section explores the practical and symbolic limits on the message-sending capacity of abortion bans in a society divided over abortion and over its commitments to children living in poverty.
Part Three moves to the expectation that abortion bans will be competently enforced. Here, I examine the legitimacy struggles arising from law enforcement patterns, along with the administrative challenges inherent in overseeing the various exceptions to abortion bans.
This article concludes with a consideration of why the consequences and limitations of abortion bans should matter to supporters and opponents, alike.
Abortion opponents anticipate that banning abortion will deter it. That said, they are not overly sanguine about this hope; anti-abortion advocates acknowledge that abortions will continue to take place, even if illegal. 7 But their support for abortion bans rests firmly on the expectation that there will be fewer of them, once abortion is a crime. 8 In this section, I explore the question of deterrence, first considering the population-wide impact of bans on abortion rates, and then describing the Americans most likely to be deterred by abortion bans.
I.A. Deterrence, in the Aggregate
To think about whether abortion can be deterred by outlawing it, we must begin by reflecting on what leads people to have abortions. Abortion demand is driven by a host of factors—health status, relationship status, job status—but the most commonly cited concern is lack of money. 9 Half of all US abortions go to the 13 per cent of Americans living below the poverty line–which in 2022, means living on less than $13,590. 10 Those living in poverty or near poverty make up a full 76 per cent of abortions every year. 11 These are people whose abortion decisions are motivated, at least in part, because they cannot afford the costs of child rearing. 12
Rather than focusing on reducing abortion demand by offsetting the costs of having children, abortion bans aim to deter abortion solely by reducing access to legal abortion. Even a cursory glance at worldwide abortion rates suggests that strategy might not work. Abortion rates vary dramatically by region. In Latin America, (home to countries with the world’s strictest abortion bans), we find some of the highest abortion rates in the world: 32 abortions for every 1000 women. 13 At the other end of the spectrum, Western Europe, (with relatively liberal abortion laws), has the world’s lowest abortion rates: only 12 abortions per 1000 women. 14
The variation in abortion rates is best understood as an artifact of variation in rates of unintended pregnancy. 15 The single biggest predictor of abortion rates is not the legal status of abortion, but rather, the percentage of pregnancies that occur among those who were not looking to have a baby. In 2014, the most recent year for which data is available, 44 per cent of pregnancies globally were unintended. 53 per cent of those unintended pregnancies ended in abortion. 16 Rates of both unintended pregnancy and abortion vary by a country’s wealth status. In the world’s wealthier nations, over the past quarter century, rates of unintended pregnancies dropped by 30 per cent, triggering a decline in abortion rates from 46 abortions per 1000 women of reproductive age to an average of 27. 17 By contrast, over the same time frame in the developing world, unintended pregnancy rates fell by only 16 per cent, while abortion rates remained static. 18
Like other wealthy countries, U.S. abortion rates have dropped significantly in recent decades. 19 The decline is evident across almost every demographic in the country—younger, older, Northern, Southern. With one exception: abortion rates have remained constant among the poorest Americans. 20 This finding underscores the significance of unintended pregnancy in driving abortion rates: nearly half of all pregnancies in the United States are unintended—a higher rate than in many other developed countries. 21 These rates vary dramatically by class: a poor woman in the USA is more than five times as likely as an affluent woman to have an unintended pregnancy. 22
The single most effective way to help people avoid unwanted pregnancies, thereby deterring abortion, is by increasing contraception rates. When the Affordable Care Act mandated insurance coverage for contraception, the unintended pregnancy rate dropped from 44.7 to 37.9 per cent. 23 And yet, the anti-abortion movement has opted to oppose efforts to increase access to contraception. 24 Indeed, abortion opponents vigorously fought the Affordable Care Act’s birth control mandate, which the Supreme Court ultimately struck down in 2014. 25
If the goal of banning abortions is to deter them, a strategy that fails to focus on reducing unintended pregnancy seems limited, at best. But even if one accepts that abortion opponents are too ambivalent about promoting contraception to center the goal of deterring abortion by reducing unwanted pregnancy, the plan to deter abortion by banning it is flawed for a second reason. Specifically, owing to the ready availability of abortion medicines, abortion bans cannot effectively restrict access to a safe, effective, and affordable means to end a pregnancy.
The widespread availability of abortion medicines has completely transformed the world of illegal abortion. Unlike the pre-Roe era, medication abortion solves the problem of finding a doctor to perform an illegal abortion, while simultaneously reducing the health risks. 26 The most common and widely available abortion medicine is misoprostol. 27 Although less effective than the FDA-approved combination of mifepristone and misoprostol typically used in medical abortions in the USA, misoprostol alone causes an abortion in approximately 90 per cent of cases. 28 Efforts to restrict access to misoprostol are complicated for two reasons. It is both cheap and easy to manufacture, costing only pennies to make, and it also is an important life-saving medicine. 29 Indeed, the World Health Organization lists misoprostol as an ‘essential medicine,’ owing in part to its vital role in reducing deaths from postpartum hemorrhages, miscarriages, and illegal abortions. 30
There is a robust international market in misoprostol across the world today—particularly in countries where abortion is strictly banned. 31 Even in Central America, which boasts the world’s strictest abortion bans, one in three pregnancies ends in abortion, largely induced by medicines purchased online or on the street. 32 Americans familiar with the black market in opioids should have little trouble imagining how a market in abortion medicines will proliferate, where abortion is banned. As is all too evident from the scope of the opiate problem, it is unrealistic to think the government can prosecute away the expanding market in abortion medicines. 33
Outlawing abortion may lead to a short-term decline in US abortion rates, while people adjust to new market conditions. 34 But as we learn from the experiences of countries throughout the world, this decline is unlikely to be sustained. If anything, given the availability of reliable online information and buying options, it should take far less time for people to adapt to accessing illegal abortion than was true for alcohol access after Prohibition. 35
I.B. Deterrence, in the Specific
Even if abortion bans are unlikely to cause an aggregate decline in abortion rates–at least not independently of other trends 36 –we can predict that they will cause some to carry to term pregnancies they might otherwise have aborted. 37 In fact, we have a surprisingly clear picture of those who the bans are most likely to deter: they will be disproportionately young, poor, Black, and brown women. Abortion bans come as one in a long list of factors that circumscribe the reproductive lives and life options of these Americans. 38 They are more likely to experience unintended pregnancy, and where abortion is outlawed, they are more likely to struggle with accessing abortion, whether by traveling to a legal jurisdiction, or by identifying reliable information about how to safely end an unwanted pregnancy with abortion medications. 39
Those who support abortion bans on deterrence grounds have yet to fully grapple with what happens to those for whom abortion, legal or otherwise, is out of reach. The standard response is to promote the solution of placing newborn babies for adoption. Justice Amy Coney Barrett nodded to this viewpoint at oral argument in the Dobbs case, correcting the assertion that abortion bans amount to ‘forced motherhood’ by noting that safe haven laws permit them to surrender their newborns without legal consequences. 40 Adoption proponents point to the ways in which open adoptions have become the norm, hopeful that the prospect of staying involved in their baby’s life will encourage more people to place them for adoption. 41 Banning abortion, as they see it, can be a ‘win-win-win’ situation, in which the baby survives, the mother gets to go on with her life, and a married couple or family gets to raise the child. 42
Yet all available evidence suggests that banning abortion is unlikely to transform adoption from an outlier into a commonplace response to unwanted pregnancy. Even in the years prior to Roe, when the stigma of unwed motherhood led some facing pregnancy to place their babies, only 9 per cent of women chose adoption. 43 Much of that rate was driven by white women, because the two-parent family norm was less entrenched among Black and brown Americans. Today, the stigma is gone: 40 per cent of all children are born out of wedlock. 44 When faced with an unintended pregnancy, fewer than 5 per cent of people seriously consider adoption, and of those, fewer than 2 per cent ultimately place their children with adoptive families. 45
The best indication of what is likely to happen to those unable to access abortion is found in the Turnaway study, a 10-year longitudinal investigation of the impact of being denied an abortion. 46 That study followed hundreds of women who sought abortions, but were turned away because they were beyond the clinic’s gestational limits. 47 Fully 91 per cent of them opted to raise their child. 48
The Turnaway study also tells us about the consequent intensification of poverty for these families:
[C]hildren of women who are denied an abortion had greater odds (72 vs 55%) of living in poverty compared to children of women who received a wanted abortion. Similarly, existing children were more likely (87 vs 70%) to live in a household in which their mother is not able to afford necessary living expenses such as food, housing, and transportation compared to children of women who received a wanted abortion. 49
As we look to understand what happens when an abortion ban ‘works’ by deterring abortion, the only question is how broad a lens to use. More than one in three single-mother families lived in poverty in 2016. 50 Poverty is not color-blind. Instead, far more women of color live in poverty than do their white counterparts: close to 25 per cent of all American Indian or Alaskan native and 20 per cent of all Black and Hispanic women live in poverty, compared to only 9 per cent of their white counterparts. 51
So severe are the downstream consequences for children born into poverty that the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement decrying the short and long-term consequences of the ‘medicalization of poverty’:
Children who experience poverty, particularly during early life or for an extended period, are at risk of a host of adverse health and developmental outcomes through their life course. Poverty has a profound effect on specific circumstances, such as birth weight, infant mortality, language development, chronic illness, environmental exposure, nutrition, and injury. Child poverty also influences genomic function and brain development…. Children living in poverty are at increased risk of difficulties with self-regulation and executive function, such as inattention, impulsivity, defiance, and poor peer relationships. Poverty can make parenting difficult, especially in the context of concerns about inadequate food, energy, transportation, and housing. Child poverty is associated with lifelong hardship. Poor developmental and psychosocial outcomes are accompanied by a significant financial burden, not just for the children and families who experience them but also for the rest of society…. 52
We should read these statistics as a forecast. To the extent abortion bans deter abortion, we will likely see a disproportionate increase in the number of poor families of color experiencing the devastating consequences of living in poverty. Abortion bans work by leveraging existing inequalities. 53
Abortion opponents are of two minds about how to respond to the poor predicted outcomes for those who opt to raise children after being unable to access abortion. Small numbers of advocates–largely drawn from the volunteer ranks of pregnancy support or ‘crisis pregnancy’ centers–advocate helping women who are in desperate straits by offering housing, counseling, job training, and other support. 54 But the dominant voice of the anti-abortion movement–those advocates engaged in political activism and law reform, rather than direct service–focuses not on supporting poor mothers, but instead, on promoting adoption. 55
The suggestion that adoption is the optimal solution to a poorly timed pregnancy is as convenient as it is naïve. It allows abortion opponents to avoid a reckoning with consequences of having made the Republican party their political home. 56 The GOP’s historical and ongoing objection to family-friendly government policies 57 will make it hard, in the years to come, for abortion opponents to gain much traction for laws aimed at blunting the crushing impact of poverty on those whom the bans deter from having abortions.
Those who support abortion bans do not rest their support solely on the expectation that such laws will deter abortion. Instead, abortion opponents often invoke the belief that changing the law will send a message, thereby promoting culture change. 58 This section first considers the nature of that message, and then turns to whether it will be received.
It is helpful, when considering the message sent by outlawing abortion, to note the difference between an anti-abortion message (one that condemns abortion) and a pro-natal message (one that urges people to have babies). This distinction is easiest to observe when contrasting U.S. laws with those of countries that actively encourage childbearing.
Consider the case of Israel, which makes abortion a crime unless the person can prove to an official ‘pregnancy termination committee’ that they qualify for one of the statute’s exceptions. 59 This law would send a message that, outside of exceptional circumstances, abortion is wrong. 60 But it also exists alongside a host of laws and policies that encourage people to have children. 61 In Israel, there is guaranteed paid maternity leave—you can leave your job for 26 weeks, still get paid, and your employer cannot fire you. 62 Parents enjoy access to local neighborhood, government-subsidized day care. 63 In addition to tax deductions, the Israeli government pays everyone—rich and poor alike—a small monthly allowance for each child under eighteen. 64
In addition to the ways in which these policies help offset some of the most immediate costs associated with having a child, they send a message about how the government feels not just about abortion but also about babies. Israel’s laws send a message that the government wants people to have babies.
By contrast, US laws reflect little interest in encouraging people to have babies, particularly ones they cannot afford to raise. There is no paid parental leave, and no job security at all beyond the first 12 weeks of unpaid leave. 65 There is no child allowance. The Covid-related child income tax break, which reduced child poverty by 30 per cent, was permitted to lapse after a single year. 66 The goal of providing universal access to quality day care and preschool remains a pipedream. 67 The federal assistance program, Temporary Assistance to Needy Families, is so under-funded that no state’s subsidy amounts to more than 60 per cent of the federal poverty line, with the result that even in states with relatively generous monthly allocations, families cannot afford modest rent. 68
Those who believe abortion bans promote a culture of life might do well to recognize that any message sent by an abortion ban is necessarily entwined with the messages sent by government laws and policies that set the price of having a child. The message of an abortion ban on its own says little about embracing life, and instead merely suggests that abortion is wrong. 69
As to whether that message will be received, the answer is complicated. For all that, it is common to suggest the law can send messages, there is surprisingly little evidence for how it might do so. Professor Richard McAdams, one of the leading authorities on the ‘expressive function’ of the law, posits that an expressive law reveals the lawmakers’ beliefs, which in turn causes individuals to update their beliefs and ultimately to change their behaviors, usually in the direction of compliance. 70 He points to the example of indoor smoking bans by way of illustration. In the face of mounting evidence on the harmfulness of secondhand smoke, lawmakers enacted indoor smoking bans that served, in part, to send the message that tobacco was dangerous. In turn, these bans helped shift the culture away from smoking. 71
According to McAdams, smoking bans succeeded because lawmakers had a clear, credible message. But government credibility is not automatic; rather, it is earned. To send a message, government actors must offer some reason why the public should trust their conclusions. McAdams suggests the government earned credibility by persuading the public they were acting on data showing that the hazards of secondary smoke inhalation required nothing less. 72
Unlike smoking bans, abortion bans address themselves to a question of morality—one that cannot be settled by aggregated data or special expertise. A government hoping to persuade the public that abortion is immoral will struggle simply because it lacks the expertise needed to settle the question. 73
The challenge of sending a message by banning abortion is intensified by the impact of the ongoing battle over abortion’s legality. When it comes to the law’s ability to send a message, Professor McAdams notes, background noise can be fatal:
Individuals are constantly being bombarded by information from sources other than the law: the print media, Internet, social acquaintances, etc. For expression to change beliefs, there must be some factor that makes the legal signal strong enough to stand out against this background. 74
To send a message, abortion bans must compete for air time with a world of counter-messages. After all, the fight over abortion does not end with abortion bans. Together with the likelihood that abortion remains commonplace, even where banned, and remains legal in almost half the country, the message-sending capacity of abortion bans is more akin to that of marijuana bans than to indoor smoking bans. 75
At the end of the day, perhaps the most that can be said for the message-sending capacity of abortion bans is that, where popularly embraced by an anti-abortion electorate, the bans might contribute to a broader cultural message that abortion is wrong. As Katrina Kimport forcefully demonstrates in her book, No Real Choice , the ‘abortion as killing’ narrative can combine with structural constraints like legal barriers and cost to render abortion ‘unchoosable.’ 76
The final set of expectations harbored by those who support outlawing abortion involves tacit baseline assumptions about how the law will work, in practice. Specifically, supporters assume that abortion bans will be competently implemented and enforced—that the laws will have integrity. Competent implementation and enforcement are not abstract ideals, but rather, are necessary preconditions for a law to be considered a legitimate exercise of state authority. The failure to competently implement an abortion ban will undercut its legitimacy, thereby undermining both the law’s capacity to deter abortion and also its ability to send a message.
To understand the practical considerations relevant to enforcing abortion bans, begin by noting what is required in order to implement them. The standard form of US abortion bans includes a general prohibition, accompanied by a small number of exceptions. 77 This structure gives rise to two implementation and enforcement questions, both of which will determine whether the laws are ultimately seen as legitimate exercises of government authority. When and how will prosecutors endeavor to enforce the bans, and by what mechanisms will states evaluate cases involving exceptions to the bans?
Let us examine each of these in turn.
III.A. Enforcing Abortion Bans
Supporters of abortion bans have given relatively little thought to the question of how abortion laws will be enforced. In late 2021, movement leader Marjorie Dannenfelser, President of the Susan B. Anthony List (a nonprofit that supports pro-life politicians) explained how she views the question of enforcement:
[M]y view, and the view of the entire movement—without any exception that I’m aware of—is that the doctor, the one who has been planning to break the law, is the guilty party. The law is enforced against that person, not the woman. 78
But illegal abortion today need not involve a doctor or any third party besides an overseas pharmacy, outside the easy reach of US laws. 79 Given abortion medicines, the reality is that there are no doctors to prosecute.
When abortion becomes a crime, the question of who is the criminal will require an answer. And rather than being answered by movement leaders, the decision will rest in the hands of locally-elected prosecutors. No county can afford to prosecute every crime–far from it–so local District Attorneys set priorities when enforcing the law. 80 Their choices may be informed by many factors: staff resources, strength of evidence, heinousness of crime, perception of public will, or say, pro-choice or anti-abortion sentiment. As Judge Stephanos Bibas notes, there is no check on ‘idiosyncratic prosecutorial discretion.’ 81
A quick review of abortion prosecutions both historically and today helps us understand what idiosyncratic abortion prosecutions might look like. Historian Leslie Regan’s work documents the episodic nature of abortion prosecutions in the years prior to Roe , showing how they tended to be sporadic—an occasional crackdown, motivated by a zealous prosecutor, rather than a comprehensive effort at enforcement. 82
A similar pattern is seen today in places where abortion is outlawed. For example, consider El Salvador, which bans abortion without exception. In the 10 years from 2000–2010, there were 129 prosecutions. 83 This number suggests enforcement is relatively rare—just over 10 prosecutions per year—when, by the government’s own estimates, the country sees tens of thousands of abortions every year. 84 But there is a pattern to the prosecutions. Those charged with abortion crimes are drawn from the most vulnerable, marginalized sectors of society. 85 Almost half were illiterate; only a quarter had attended high school. 86
In the U.S. we already see a version of this pattern: abortion-related prosecutions are brought by zealous prosecutors 87 , and they disproportionately target Black and brown women. 88 The work of National Advocates for Pregnant Women helps us to understand the scope of abortion-related prosecutions in the years since Roe legalized abortion. They have tracked 1600 USA such cases since 1973. 89 These cases involve a range of allegations, linked by the common thread of alleged harm to a pregnancy. 90 The prosecutions overwhelmingly target poor people, and in particular, poor Black pregnant women. Of 413 cases arising from 1973 to 2005, 71 per cent involved low income women, of whom 59 per cent were women of color, with 52 per cent identifying as Black. 91
These patterns in abortion-related prosecutions tell us two important things. First, we can expect abortion bans to be enforced against those who end their own pregnancies. 92 And second, abortion prosecutions are likely to target the most marginalized, vulnerable members of society—those whom prosecutors view, or at least believe others will be willing to view, not as victims but rather, as villains. 93
Supporters of abortion should stop insisting that bans won’t be enforced against women, and should start figuring out what to do about the fact that, when abortion bans are enforced, the defendants will likely be Black and brown. It is, of course, unfair to make one subset of the population pay the price for acts that go unpunished when committed by others. Furthermore, as we learn from racial disparities in drug law enforcement, such patterns undermine the legitimacy of the law, and have downstream corrosive effects both on the people disproportionately targeted by the law and on society as a whole. 94
III.B. The Return of Conditional Abortion Access
Setting aside the question of prosecution, abortion laws also must be fully implemented in the regulatory sense of the word. A law that limits abortion access to patients with qualifying conditions presupposes an adjudicatory mechanism for determining eligibility. And barring a dramatic evisceration of the right to life for those who are pregnant, every state will have to make at least one exception to their abortion bans, for life-threatening pregnancies. 95
How will a patient establish their right to an abortion when they are experiencing a life-threatening pregnancy?
There are a variety of models by which states might screen such claims, ranging from relatively formal proceedings, such as those seen in cases involving termination of government benefits, to loosely structured processes like school disciplinary hearings. 96 Indeed, we already have a model for abortion-related adjudications in the judicial bypass system, by which minors can seek permission to end a pregnancy without parental involvement. 97
Each model is fraught, when it comes to screening for abortion eligibility. Formal judicial hearings pose challenges in terms of accuracy (there is surprisingly little agreement on what constitutes a life-threatening pregnancy) 98 and efficiency (given the urgent, technical nature of the inquiry). 99 A judge could not conceivably rule on such petitions without expert testimony, which raises numerous questions about process and evidence.
Prior to Roe , rather than ask judges to decide these cases, states delegated the determination to doctors, essentially leaving the medical profession to devise its own ways of complying with the law. 100 For reasons ranging from lack of consensus about qualifying conditions, 101 to concern over the legal implications of their decisions (which might trigger prosecution on the one hand, or a wrongful death suit if the pregnant patient dies, on the other), 102 doctors eschewed this responsibility. By the mid-20th century, hospitals around the country used so-called ‘therapeutic abortion committees’ to establish eligibility. 103 These committees were marked by inconsistent outcomes, stemming from a lack of consensus over what constituted a ‘valid’ reason for terminating a pregnancy, whether legally or morally. 104 Rather than standardizing the application of the law, the committee process facilitated ad hoc decision-making. 105
As states set about banning abortion, it is urgent that they erect a scientifically sound, impartial process by which to evaluate cases involving potentially life-saving abortions. Given that the vast majority of Americans support abortion in cases of life-threatening pregnancy, we can expect an enormous outcry from all quarters in the case of an incompetent oversight process, let alone a highly publicized death. 106
Yet the struggle to define what constitutes a life-threatening pregnancy, (or depending upon the law, a qualifying rape or fetal anomaly), is just the start. Which parties’ interests will be represented at these adjudicatory proceedings; however, they are configured? Will the pregnant patient be entitled to a lawyer? 107 Will the fetus? If unhappy with the outcome, can either side appeal? Will there be an expedited appeals process? By what criteria will adjudicators be chosen? Will these be adversarial proceedings, with experts from the state and from the pregnant patient’s medical team, or will the patient’s doctor’s testimony suffice? How will the government determine whose interests it represents: those of the patient in peril, or those of the fetus?
These are serious questions, made all the more so because they implicate vital interests and therefore trigger Constitutional due process rights. 108 Surely, there will be litigation over the answers in the years to come. But what is interesting about these questions is not so much their answers, but instead, the reality that they demand answers now. We are past the time when those who support banning abortion can respond to such questions about how the laws will be implemented with vague references to ‘traditional means of enforcement.’ 109 And the quality of those answers matters because inconsistent, incompetent or otherwise corrupt law enforcement cannot help but undermine the legitimacy of abortion bans.
We have spent half a century reckoning with abortion largely in abstractions, fighting over rights rather than focusing on the people whose lives are affected by those rights. If nothing else, the impact of abortion bans seems likely to put human faces on the abortion war. And if we stay true to the patterns laid out in this essay, those faces will be disproportionately poor, Black and brown women and children.
Abortion bans are not color blind.
It has become common for abortion opponents to invoke allegations of eugenics and racism when talking about abortion rates among Black Americans. 110 That rhetoric–already contested 111 –will become strained as the country witnesses the actual racist impact of abortion bans: their disparate impact on poor Black families, coupled with the disparate rates of prosecution of Black women for acts that go largely unpunished when committed by whites. 112
By bringing into focus the struggles facing the most vulnerable among us, abortion bans have the potential to transform the abortion war by forcing a direct engagement with the structural forces driving abortion, poverty, and racism. We are approaching a moment of truth for advocates on all sides of the abortion war.
For advocates of abortion rights, there will be a reckoning with the question of whether being pro-choice simply means supporting the right to abortion, rather than a commitment to working to offset the forces that constrain all reproductive options–including having a child. As Sister Song, a leading voice of the reproductive justice movement puts it, the commitment is to support, ‘the human right to maintain personal bodily autonomy, have children, not have children, and parent the children we have in safe and sustainable communities.’ 113 As the impact of abortion bans brings structural inequality into sharp focus, will pro-choice movement leaders stay focused on legalizing abortion, or will the movement commit to this more robust understanding of reproductive autonomy?
For abortion opponents, the question is whether the term ‘pro-life’ has come to mean anything beyond one’s support for abortion bans. The years ahead likely will pose an existential challenge for people who have supported abortion bans, but who cannot help but be disturbed by the ways in which they fall short of expectations. Perhaps this result will embolden those who care deeply about deterring abortion, and find them laboring to craft policies that might actually help those contemplating abortion to continue their pregnancies. 114
Certainly, anti-abortion movement leaders are aware of the need to do something proactive in response to the impact of abortion bans on the poor. As Marjorie Dannenfelser, of the Susan B. Anthony Fund, put it: ‘Speaking for the pro-life movement, which is obviously attempting to lead Republicans, we absolutely, without question, have a responsibility to serve the needs of women and children as we pass ambitious laws. There’s no question about it.’ At the same time, Dannenfelser is aware that such policies are unlikely to fly, at least not in states dominated by a Republican party that has long opposed family-friendly government programs. 115
There’s a quote I keep on my desk these days: “How will we go when we’re faced with this? I don’t think it’s predetermined, and a great human moral drama is being played out in front of us.” 116 It is from a historian of pandemics, written in the early days of Covid-19. I keep it there because it speaks to me as we navigate the era of abortion bans. There is comfort in the invitation to step back and notice that we are in a time of high moral drama, in which things are in flux. But there is also, within it, a call to action. “How will we go when we’re faced with this?”
For helpful suggestions and conversation, I’m grateful to Diana Greene Foster, Julia Hejduk, Carole Joffe, Katrina Kimport, Larry Marshall, and my anonymous reviewers. I was particularly lucky to work with Jenai Howard (SCU Law, 2022), who provided outstanding research assistance. All errors are my own.
Human Subjects Research for this article was approved by Santa Clara University’s IRB, Protocol 17-03-950.
Research was funded in part by a Hackworth Grant (Santa Clara University, Markkula Ethics Center).
See Mary Ziegler, After Roe: The Lost History Of The Abortion Debate (2015), for a rich history of the anti-abortion movement in the early years after Roe v. Wade, illustrating among other things the way the anti-abortion movement shifted its focus from efforts to support pregnant women to the narrow issue of criminalization.
See generally Michelle Oberman, How Abortion Laws Do and Don’t Work , 36 Wis. J. L. Gender & Soc’y 163 (2022); see also Michelle Oberman, Her Body, Our Laws: On The Front Lines Of The Abortion War, From El Salvador To Oklahoma (2018); Diana Greene Foster, The Turnaway Study: Ten Years, A Thousand Women, And The Consequences Of Having Or Being Denied An Abortion (2020) [hereinafter, greene foster, the turnaway study]; Ushma Upadhyay, Alice F. Cartwright, and Daniel Grossman, Barriers to Abortion Care and Incidence of Attempted Self-Managed Abortion Among Individuals Searching Google for Abortion Care: A National Prospective Study , 106 Contraception 49 (2021); Lizzie Widdecombe, What Does an At-Home Abortion Look Like in 2021 , The New Yorker (Nov. 11, 2021), https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/what-does-an-at-home-abortion-look-like-in-2021 (profiling self-managed abortion researcher, Abigail Aiken).
For example, see Ross Douthat, The Case Against Abortion , N.Y. Times (Nov. 30, 2021), https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/30/opinion/abortion-dobbs-supreme-court.html (celebrating the impact of Texas’ S.B. 8, credited with causing a 93 per cent drop in the number of abortions taking place in the state).
See eg Richard Garnett, One Untrue Thing , Nat’l Rev. (Aug. 1, 2007), ( https://www.nationalreview.com/2007/08/one-untrue-thing-nro-symposium/ (‘The point of criminalization, after all, is not merely to put people in prison, or deter people from engaging in harmful behavior. It is, instead, to make a statement—a public statement, in the community’s voice—that certain actions, or certain harms caused, are morally blameworthy.’). See also Oberman, supra note 2, at 85–86 (quoting an anonymous Oklahoma state senator):
The purpose of the law is to stop abortion. To send a moral message. To get the message out via the law, to spark a debate in the population. The government’s responsibility is to give people education. It is up to the government to tell them that abortion is wrong. It’s not an acceptable solution.
This assumption is largely a tacit one, inherent in assertions about how abortion bans will be received by the public, and how they are likely to inspire others states to follow suit. See eg Issac Chotiner, The Pro-Life Movement Plans for a Future Without Roe , The New Yorker (Dec. 7, 2021), https://www.newyorker.com/news/q-and-a/the-pro-life-movement-plans-for-a-future-without-roe (interviewing Marjorie Dannenfelser, president of the Susan B. Anthony List, on her expectations for passing abortion bans in 30 states).
See Diane Greene Foster, Stop Saying That Making Abortion Illegal Won’t Stop People From Having Them , Rewire News Group (Oct. 4, 2018) [hereinafter Green Foster, Stop Saying ], https://rewirenewsgroup.com/article/2018/10/04/stop-saying-that-making-abortion-illegal-doesnt-stop-them/ ; see generally Greene Foster, The Turnaway Study, supra note 2.
See eg Stephanie Ranade Krider, Pro-life Advocates Focused on Legal Battles. They’re Not Enough to End Abortion , Wash. Post (Oct. 15, 2021), https://www.washingtonpost.com/outlook/pro-life-after-roe/2021/10/15/7e2a059e-2cf8-11ec-985d-3150f7e106b2_story.html (Krider, an abortion opponent, acknowledges that while ‘the end of Roe would be a victory and a cause for celebration for those…who oppose abortion, [it] would not end the practice nationwide.’).
See Douthat, supra note 3.
See Biggs, M. Antonia, Heather Gould & Diana Greene Foster, Understanding why Women Seek Abortions in the US , 13 BMC Women’s Health 1–13 (2013); see also Sophia Chae et al., Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: A Synthesis of Findings From 14 Countries , 96 Contraception 233–41 (2017). (Analyzing data from 14 countries to identify the primary reasons given for seeking abortion, and finding that, although people often listed several reasons, the dominant reason involved socioeconomic concerns).
See Annual Update of the HHS Poverty Guideline, 87 Fed. Reg. 3315, 3316 (Jan. 21, 2021).
See Rachel K. Jones & Jenna Jerman, Population Group Abortion Rates and Lifetime Incidence of Abortion: United States, 2008–2014, 107 Am. J. Publ. Health 1904–909 (2017), https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/10.2105/AJPH.2017.304042 ; see also Abortion Rates by Income Level , Infographic , Guttmacher Inst. (Oct. 19, 2017), https://www.guttmacher.org/infographic/2017/abortion-rates-income .
More accurately, because almost 60% of those having an abortion already have at least one child, they cannot afford the costs of another child. Jerman J, Jones RK & Onda T, Characteristics of U.S. Abortion Patients in 2014 and Changes Since 2008 , Guttmacher Inst. (2016), https://www.guttmacher.org/report/characteristics-us-abortion-patients-2014 .
Bearak J et al., Unintended pregnancy and abortion by income, region, and the legal status of abortion: estimates from a comprehensive model for 1990–2019 , 8 lancet global health 9 (2020).
An unintended pregnancy is one that occurred when a woman wanted to become pregnant in the future but not at the time she became pregnant (‘wanted later’) or one that occurred when she did not want to become pregnant then or at any time in the future (‘unwanted’). See Unintended Pregnancy in the United States , Guttmacher Inst. (Jan. 2017), https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/unintended-pregnancy-united-states . In recent years, this frame has been problematized by calling into view the reality that, for many people, pregnancies are not so much planned as they are responded to. That is to say, the relevant question is not whether it was intended, but whether it is wanted or unwanted. See Abigail R.A. Aiken, et al., Rethinking the Pregnancy Planning Paradigm: Unintended Conceptions or Unrepresentative Concepts? , 48 Perspect Sex Reprod Health 147–151 (2016).
See generally Unintended Pregnancy Rates Declined Globally from 1990 to 2014 , Guttmacher Inst. (Mar. 5, 2018), https://www.guttmacher.org/news-release/2018/unintended-pregnancy-rates-declined-globally-1990-2014 .
Between the 1990s and 2020, abortion rates declined by almost 40%. See Sabrina Tavernise, Why Women Getting Abortions Now Are More Likely to Be Poor , N.Y Times (July 9, 2019), https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/09/us/abortion-access-inequality.html . In the years since 2010 alone, rates have declined by almost 20%. Elizabeth Nash & Joerg Dreweke, The U.S. Abortion Rate Continues to Drop: Once Again, State Abortion Restrictions Are Not the Main Driver , Guttmacher Inst. (Sept. 18, 2019), https://www.guttmacher.org/gpr/2019/09/us-abortion-rate-continues-drop-once-again-state-abortion-restrictions-are-not-main . Scholars are divided in their explanations for the decline, which vary from increasingly effective contraceptive practices to declines in rates of sexual activity. See Pam Belluck, America’s Abortion Rate Has Dropped to its Lowest Ever , N.Y. Times (Sept. 20, 2019), https://www.nytimes.com/2019/09/18/health/abortion-rate-dropped.html ; see also Diana Greene Foster, Dramatic Decreases in US Abortion Rates: Public Health Achievement or Failure? , 107 Am J. Public Health 1860 (2017); Alia E. Dastagir, Fewer Women are having abortions. Why? , USA Today (June 13, 2019), https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2019/06/13/abortion-law-fewer-women-having-abortions-why/1424236001/ ; Doug Stanglin, US Abortion Rate is at its Lowest, but Restrictive Laws aren’t the Likely Cause, Study Says , USA Today (Sept. 18, 2019), https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2019/09/18/number-of-abortions-us-drops-guttmacher-institute-study/2362316001/ .
See U.S. Abortion Rate Continues to Decline, Hits Historic Low, Guttmacher Inst. (Jan. 17, 2017), https://www.guttmacher.org/news-release/2017/us-abortion-rate-continues-decline-hits-historic-low .
See Guttmacher Inst., supra note 15. Although poor Americans have higher rates of unintended pregnancy for a range of reasons, central among them is that they struggle to access contraception. See Michele Troutman, Saima Rafique & Torie Comeaux Plowden, Are Higher Unintended Pregnancy Rates Among Minorities a Result of Disparate Access to Contraception? , Contracept Reprod Med 5, no. 16 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1186/s40834-020-00118-5 (describing the factors underlying the disparate rates of unintended pregnancy by race and class). One finds evidence of this struggle in the data on contraceptive use among sexually active women not seeking pregnancy. While 90% of those covered by private health insurance and 87% of those covered by Medicaid use contraception, that figure drops to 81% for those who have no insurance coverage. Megan L. Kavanaugh & Emma Pliskin, Use of Contraception Among Reproductive-aged Women in the United States , 2014 and 2016 , Guttmacher Inst. (July, 2020). On the cost of contraception, see Eliana Kosova, How Much Do Different Kinds of Birth Control Cost Without Insurance? , Nat’l Women’s Health Network (Nov. 17, 2017), https://nwhn.org/much-different-kinds-birth-control-cost-without-insurance/ (noting that the most effective methods, long-acting implants and devices, cost upwards of $800, and that oral contraceptives can cost up to $600 per year).
Cost is not the only barrier to contraception, ranging from cost to personal preferences. For example, Black women tend to report higher rates of dissatisfaction with existing contraceptive options, putting them at further disadvantage in terms of risk of unwanted pregnancy. Andrea V. Jackson, Deborah Karasek, Christine Dehlendorf, and Diana Greene Foster, Racial and Ethnic Differences in Women’s Preferences for Features of Contraceptive Methods , 93 Contraception 406–411 (2016).
See Colleen L. MacCallum-Bridges & Claire Margerison, The Affordable Care Act Contraception Mandate & Unintended Pregnancy in Women of Reproductive Age: An Analysis of the National Survey of Family Growth, 2008–2010 v. 2013–2015 , 101 Contraception 34–39 (2020) (Overall, the odds of experiencing unintended pregnancy decreased 15% from the pre-mandate to post-mandate period); See also Susan Christiansen, The Impact of the Affordable Care Act Contraceptive Mandate on Fertility and Abortion Rates (Dec. 2020) (Ph.D. dissertation, Johns Hopkins University), https://jscholarship.library.jhu.edu/handle/1774.2/63939 (last visited Jan. 28, 2022).
See Molly Jong-Fast, The Anti-Birth Control Movement Is the New Anti-Abortion Movement , Vogue (July 1, 2021), https://www.vogue.com/article/anti-birth-control-movement .
Burwell v. Hobby Lobby Stores, Inc., 573 U.S. 682 (2014) (striking down the ACA’s contraception mandate because it ‘created a substantial burden’ on Hobby Lobby’s religious freedom and it was not the ‘least restrictive means of satisfying the government’s interests.’) . See eg Tom Cohen, Hobby Lobby Ruling Much More Than Abortion , Cnn Politics (July 2, 2014), https://www.cnn.com/2014/07/02/politics/scotus-hobby-lobby-impacts/index.html (describing anti-abortion advocates opposition to contraception mandates).
See Carole Joffe, Failing to Embed Abortion Care in Mainstream Medicine Made it Politically Vulnerable , Wash. Post (Jan. 11, 2022), https://www.washingtonpost.com/outlook/2022/01/11/failing-embed-abortion-care-mainstream-medicine-made-it-politically-vulnerable/ (describing the range in quality of abortion providers when abortion was illegal).
See Elizabeth G. Raymond et al., Efficacy of Misoprostol Alone for First-Trimester Medical Abortion: A Systematic Review , 133 Obstet Gynecol 133–147 (2019).
Id. (This consolidated report of existing research finds that misoprostol alone successfully terminates a pregnancy in 93% of cases).
See How to Buy Abortion Pills That Are Safe and Effective , https://www.ipas.org/our-work/abortion-self-care/abortion-with-pills/how-to-buy-abortion-pills-that-are-safe-and-effective/ (Noting that manufacturers sell the pills to pharmacies for very little cost—less than $0.05 per pill—and that the highest sales price found in a recent study was $2 per pill).
See eg Celina Schocken, Business Case: Investing in Production of High Quality Misoprostol for Low-Resource Settings , Concept. Found. (Dec. 2014), https://www.conceptfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/BusinessCase_Misoprostol_web.pdf (describing misoprostol’s vital role in treating postpartum hemorrhage); see also Essential Medicines List includes Misoprostol tablets for use during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum care , World Health Organization, https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/essential-medicines-list-includes-misoprostol-tablets-for-use-during-pregnancy-childbirth-and-postpartum-care .
Beverly Winikoff & Wendy Sheldon, Use of Medicines Changing the Face of Abortion , Guttmacher Inst. (Sept. 2012), https://www.guttmacher.org/journals/ipsrh/2012/09/use-medicines-changing-face-abortion . For a description of the misoprostol market in countries where abortion is illegal, see Michelle Oberman, What Happens When Abortion is Banned? , N.Y. Times (May 31, 2018), https://www.nytimes.com/2018/05/31/opinion/sunday/abortion-banned-latin-america.html .
See Gilda Sedgh et al., Induced Abortion: Incidence and Trends Worldwide from 1995 to 2008 , 379 The Lancet 625, 625 (2012) (comparing the one out of three pregnancies in Central America end in abortion with one out of five in the United States); see also Susheela Singh et al., Abortion Worldwide: A Decade of Uneven Progress , Guttmacher Inst. (Oct. 2009), http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/Abortion-Worldwide.pdf .
There is evidence of an expanding market in misoprostol in the U.S. See Caroline Kitchener, Self-Managed Abortion Could be the Future—But it’s Very Hard to Talk About , The Lily (Dec. 20, 2021), https://www.thelily.com/self-managed-abortion-could-be-the-future-but-its-very-hard-to-talk-about/ . See also, Erica Hellerstein, The Rise of the DIY Abortion in Texas , The Atlantic (June 27, 2014), https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2014/06/the-rise-of-the-diy-abortion-in-texas/373240/ .
Kari White et al., Initial Impacts of Texas’ Senate Bill 8 on Abortions in Texas and at Out-of State Facilities , Texas Policy Evaluation Project (Oct. 2021), http://sites.utexas.edu/txpep/files/2021/11/TxPEP-brief-SB8-inital-impact.pdf .
In the immediate aftermath of Prohibition–evidenced by mortality rates, mental health, and crime statistics–alcohol consumption fell to approximately 30% of its pre-Prohibition level. But this drop in alcohol consumption was short-lived. Within a few years after Prohibition, alcohol consumption had increased to 60–70% of its pre-Prohibition level. See Annika Nekalson, Prohibition was a Failed Experiment in Moral Governance, The Atlantic (Jan. 16, 2020), https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2020/01/prohibition-was-failed-experiment-moral-governance/604972/ .
See Nash & Dreweke, supra note 19, regarding the various reasons behind declining abortion rates.
See Greene Foster, Stop Saying , supra note 6; see also Greene Foster, The Turnaway Study, supra note 2.
Hence the insistence of the reproductive justice movement that advocates center the goals of racial justice. RJ Squared. For a detailed description of the ways in which structural inequities circumscribe the reproductive choices of poor women and women of color, see Jamila K. Taylor, Structural Racism and Maternal Health Among Black Women , 48 Journal Of Law, Medicine & Ethics 506–517 (2020).
See generally, Katrina Kimport, No Real Choice: How Culture And Politics Matter For Reproductive Autonomy (2021) (positing that for the most marginalized Americans faced with an unwanted pregnancy, the question is not whether to have an abortion or have a baby, but rather, whether they can actually get an abortion or not).
At oral argument, Justice Barrett said, “Both Roe and Casey emphasized the burdens of parenting, and insofar as you and many of your amici focus on the ways in which the forced parenting, forced motherhood would hinder women’s access to the workplace and to equal opportunities, it’s also focused on the consequences of parenting and the obligations of motherhood that flow from pregnancy. Why don’t the safe haven laws take care of that problem?” Transcript of Oral Argument at 56, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health, No. 19–1392. For a compelling analysis and indictment of safe haven laws, see Laury Oaks, Giving Up Baby: Safe Haven Laws, Motherhood, And Reproductive Justice (2015); see also Lizzie Widdicombe, The Baby-Box Lady of America , The New Yorker (Dec. 18, 2021) https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/the-baby-box-lady-of-america .
See Mardie Caldwell, Open Adoption is a Win-Win Situation (Apr. 7, 2018), https://mardiecaldwell.com/open-adoption-is-a-win-win-situation/ ; see also Julia D. Hejduk, Gift Motherhood, the Prius, and the Peace Corps: Reducing Abortion by Incentivizing Adoption , The Public Discourse (Sept. 27, 2017), https://www.thepublicdiscourse.com/2017/09/20054/ .
Id . On the merits, what limited scholarly evidence there is on adoption runs counter to this rosy characterization of adoption’s outcomes, at least for birth mothers. See eg Are Birth Mothers Satisfied with Decisions to Place Children for Adoption? , Science Daily (June 8, 2018), https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/06/180608131605.htm (a longitudinal study of birth mothers that found women reported a mean satisfaction of 3.11 on a scale of 1–5). See also Gretchen Sisson, ‘Choosing Life’: Birth Mothers on Abortion and Reproductive Choice , 25 Women’s Health Issues 349–54 (2015) (a study involving in-depth interviews with 40 women who had placed infants for adoption from 1962 to 2009. The majority of the participants–many of whom placed their babies in closed adoptions, which are less typical today–described their adoption experiences as ‘predominantly negative,’ a response that Sisson attributes in part to the reality that adoption is not a preferred course of action, but rather, something chosen by those who feel they have no other options).
Olga Khazan, Why So Many Women Choose Abortion Over Adoption , The Atlantic (May 20, 2019). ( https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2019/05/why-more-women-dont-choose-adoption/589759 ; S ee also Olga Khazan, The New Question Haunting Adoption , The Atlantic (Oct. 22, 2020), https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2021/10/adopt-baby-cost-process-hard/620258/ (‘Since the mid-1970s—the end of the so-called baby-scoop era, when large numbers of unmarried women placed their children for adoption—the percentage of never-married women who relinquish their infants has declined from nearly 9% to less than 1%.’).
See Elizabeth Wildsmith, Jennifer Manlove et al., Dramatic Increase in the Proportion of Births Outside of Marriage in the United States from 1990 to 2016 , Child Trends (Aug. 8, 2018), https://www.childtrends.org/publications/dramatic-increase-in-percentage-of-births-outside-marriage-among-whites-hispanics-and-women-with-higher-education-levels#:∼:text=Recent%20estimates%20show%20that%20about , worldwide%20(Chamie%2C%202017). The most rapid growth is among white women: as of 2016, 28% of all births to white women were non-marital. See also Khazan , supra note 43 (Starting in the 1970s, single white women became much less likely to relinquish their babies at birth: nearly a fifth of them did so before 1973; by 1988, just 3% did).
Khazan, Id .
The Turnaway Study is a longitudinal study examining the effects of unintended pregnancy on women’s lives. For the study and its findings, see Greene Foster, The Turnaway Study, supra note 2.
See id . See also Diana Greene Foster, What Happens When It’s Too Late to Get an Abortion , N.Y. Times (Nov. 22, 2021), https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/22/opinion/abortion-supreme-court-women-law.html .
See Gretchen Sisson, Lauren Ralph, Heather Gould & Diana Greene Foster, Adoption Decision Making among Women Seeking Abortion, 27 Women’s Health Issues 136 (2017).
See Women’s Access to Abortion Improves Children’s Lives , Ansirh (Jan. 2019), https://www.ansirh.org/sites/default/files/publications/files/womens_access_to_abortion_improves_childrens_lives.pdf .
See generally Kayla Patrick, National Snapshot: Poverty Among Women & Families , National Women’s Law Center, https://nwlc.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Poverty-Snapshot-Factsheet-2017.pdf . (The poverty rate for female-headed families with children was 36.5%, compared to 22.1% for male-headed families with children and 7.5% of families headed by married couples with children).
Robin Bleiweis, Diana Boesch & Alexandra C. Gaines, The Basic Facts About Women in Poverty , American Progress (Aug. 3, 2020), https://www.americanprogress.org/article/basic-facts-women-poverty/ .
See American Academy of Pediatrics, Council on Community Pediatrics, Poverty and Child Health in the United States , Pediatrics 137 no. 4 (2016): e20160339.
See kimport, supra note 39, at 37, and generally.
See Leah Outten, Birth Mothers and the Adoption Option , Focus On The Family (Nov. 9, 2021), https://www.focusonthefamily.com/pro-life/the-adoption-option-birth-mothers-need-your-support/ ; Stephanie McCrummen, A Maternity Ranch is Born: How Evangelical Women in Texas are Mobilizing for a Future Without Abortion , Wash. Post (Nov. 16, 2021), https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2021/11/16/evangelical-women-texas-abortion/?utm_campaign=wp_post_most&utm_medium=email&utm_source=newsletter&wpisrc=nl_most&carta-url=https%3A%2F%2Fs2.washingtonpost.com%2Fcar-ln-tr%2F354c967%2F6193e9909d2fdab56b8e7f16%2F5a1f90909bbc0f4d5203bb72%2F8%2F73%2F6193e9909d2fdab56b8e7f16 . see also Michelle Oberman, The Women the Abortion War Leaves Out , N.Y. Times (Jan. 11, 2018), https://www.nytimes.com/2018/01/11/opinion/sunday/abortion-crisis-pregnancy-centers.html (describing Oklahoma City’s Rose Home, a pro-life organization that houses up to five pregnant women and their children at any given time).
See Outten, supra note 54. See also Eleanor Bartow, 12 Pro-Life Truths to Counter Every Abortion Myth , The Federalist (Oct. 11, 2021) https://thefederalist.com/2021/10/11/12-pro-life-truths-to-counter-every-abortion-myth/ (where Bartow asserts adoption is ‘a better option than killing an unborn child’ because there are many ‘loving, screened, financially stable parents [who] are waiting to adopt babies.’).
See Sue Halpern, How Republicans Became Anti-Choice , The N.Y. Rev. (Nov. 8, 2018), https://www.nybooks.com/articles/2018/11/08/how-republicans-became-anti-choice/ (reviewing Reversing Roe , a documentary film directed and produced by Ricki Stern and Annie Sundberg).
See Robert Reich, Republicans, So Called party of Family Values, Do Not Support Needy Families , The Guardian (Jul. 18, 2021), https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/jul/18/child-allowance-payments-american-rescue-plan-republicans
See eg Richard Garnett, supra note 4. See also Hadley Arkes, in One Untrue Thing , Nat’l Rev. (Aug. 1, 2007), https://www.nationalreview.com/2007/08/one-untrue-thing-nro-symposium/ , (‘[T]he law does not need to invoke the harshest penalties for the sake of teaching moral lessons.’).
§315, Penal Law, 5737–1977, LSI Special Volume (1977), as amended (Isr.),
https://knesset.gov.il/review/data/eng/law/kns8_penallaw_eng.pdf [ https://perma.cc/N9QZ-8JEV ].
Or at least it would do so if the law were interpreted in a way that strictly limited abortion access. Instead, as I explain elsewhere, the committees close to 100% of the requests they receive, making legal abortion readily available in the country. See Oberman, supra note 2, at 172.
And they do. Recall that Israel has the highest fertility rates of any country in the OECD. Families have an average of 3.1 children. See Family Database: Fertility Rates , Org. Econ. Coop. Dev., https://www.oecd.org/els/family/SF_2_1_Fertility_rates.pdf [ https://perma.cc/5J2Y-YGWG ] (last updated June 2021).
See Maternity Leave , Kol Zchut, https://www.kolzchut.org.il/en/Maternity_Leave [ https://perma.cc/Q29Q-T6Q6 ] (last visited June 19, 2021).
See Childcare in Israel , Expat.Com (Sept. 18, 2017) https://www.expat.com/en/guide/middle-east/israel/15420-childcare-in-israel.html [ https://perma.cc/2Z7S-SJCK ] (describing the relative level of state support that young Israeli families receive, compared to the U.S.). See also, Register to State Recognized Daycare and Afternoon Care, and Request State Participation in Tuition Fees , Gov. IL, https://www.gov.il/en/service/registration_for_day_care_centers_and_nurseries1 (last updated Feb. 7, 2020) (Israeli government website describing eligibility for state supported day care). Rates of enrollment in both day care and preschool are among the highest in the developed world. Indeed, preschool enrollment rates are double that of the OECD average. https://issuu.com/bernardvanleerfoundation/docs/publication_taub_center_early_childhood_education_ (at 27).
See, eg Children , Nat’l Ins. Inst. Of Isr., https://www.btl.gov.il/English%20Homepage/Benefits/Children/Pages/default.aspx [ https://perma.cc/8KE2-3K8L ] (last visited on Dec. 19, 2021). Although these policies may not significantly offset the costs of having a child, surely, they are a benefit to Israel’s poorest families.
The only government support for those who have babies lies in family medical leave, which promises twelve weeks of unpaid leave time after the birth of a child. See Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), 29 U.S.C. § 2612.
Ben Casselman, Child Tax Credit’s Extra Help Ends, Just as Covid Surges Anew , N.Y. Times (last updated Jan. 3, 2022), https://www.nytimes.com/2022/01/02/business/economy/child-tax-credit.html .
Ali Safawi & Cindy Reyes, States Must Continue Recent Momentum to Further Improve TANF Benefit Levels , Cntr on Budget & Pol’y Priorities (updated Dec. 2, 2021), https://www.cbpp.org/research/family-income-support/states-must-continue-recent-momentum-to-further-improve-tanf-benefit .
For signs that anti-abortion advocates are beginning to grapple with the need to take systemic realities into account, see Tish Harrison Warren, The Systemic Realities Created by Legal Abortion , N.Y. Times (Jan. 22, 2022), https://www.nytimes.com/2022/01/22/opinion/roe-legal-abortion.html .
See Richard H. McAdams , A Focal Point Theory of Expressive Law, 86 V.A. L. Rev.1649, 1713–28 (2000) (applying expressive law theory to smoking bans and landlord liability law). See generally Richard H. McAdams, The Expressive Powers Of Law: Theories And Limits (2015).
He offers little evidence, by way of proof. However, numerous studies both domestically and worldwide document an association between smoking bans and an overall decline in smoking rates, including a reduction in smoking by smokers. See eg Thomas W. Carton, Michael Dardon, et al., Comprehensive Indoor Smoking Bans and Smoking Prevalence: Evidence from the BRFSS , 2 J Health Econ. 535–56 (2016); see also Silke Anger, Michael Kvasnicka, Thomas Seidler, One Last Puff? Public Smoking Bans and Smoking Behavior , 30 J Health Econ. 591–601 (2011).
See McAdams, supra note 70, at 197.
These lawmakers also must contend with considerable public opposition to their position. As of 2020, 79% of Americans say that the decision to have an abortion is best left to women, not lawmakers, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation study from 2020. See Ariana Eunjung Cha & Emily Guskin, Most Americans Want Abortion to Remain Legal, but Back S ome State Restrictions , Wash. Post (Jan. 22, 2020), https://www.washingtonpost.com/health/2020/01/22/most-americans-want-abortion-remain-legal-back-some-state-restrictions/ .
See McAdams, supra note 70, at 180.
Recreational cannabis is legal in 18 states, while 11 states criminalize it. (See https://disa.com/map-of-marijuana-legality-by-state for a breakdown of the various jurisdictions’ laws). Experts estimate that at least 15 states will keep abortion legal, and perhaps even expand abortion rights, regardless of the absence of a Constitutional right. https://www.guttmacher.org/state-policy/explore/abortion-policy-absence-roe .
Kimport, supra note 37, at 28 and 62–69.
See eg Anna North, All the Near-Total Abortion Bans Passed This Year Have Now Been Blocked in Court, Vox (updated Oct. 29, 2019), https://www.vox.com/2019/10/2/20895034/alabama-abortion-ban-blocked-georgia-law ; see also Sean Murphy, Oklahoma Supreme Court Blocks 3 New Anti-Abortion Laws, ABC News (Oct. 25, 2021), https://abcnews.go.com/Health/wireStory/oklahoma-supreme-court-blocks-anti-abortion-laws-80779946 .
See Chotiner, supra note 5. See also O. Carter Snead, in One Untrue Thing , Nat’l Rev. (Aug. 1, 2007), https://www.nationalreview.com/2007/08/one-untrue-thing-nro-symposium/ (Offering a pragmatic justification for not punishing self-abortion: ‘[T]he public is more willing to accept a law that punishes doctors rather than mothers. Pro-lifers can thus achieve their goal of ending abortion without provoking a political backlash.’).
Although there are legal strategies a government might employ in response to overseas entities that sell abortion medicines to U.S. consumers (eg border patrol agents or diplomatic pressure), we learn from both the heroin and the fentanyl epidemics that the government’s options in the face of high demand are limited. See Claire Felter, Backgrounder: The U.S. Opioid Epidemic , The Council on Foreign Relations, (Sept. 8, 2021), https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/us-opioid-epidemic .
Stephanos Bibas, Prosecutorial Regulation Versus Prosecutorial Accountability , 157 U. Pa. L. Rev. 959 (2009).
Stephanos Bibas, The Need for Prosecutorial Discretion , 19 Temp. Pol. & Civ. Rts. Rev. 369, 371 (2010).
See Leslie Reagan, When Abortion Was A Crime: Women, Medicine, And Law In The United States, 1867–1973 (1997), at 114, 164.
See From Hospital to Jail: The Impact on Women of El Salvador’s Total Criminalization of Abortion , 22 Repr. Health Matters 52–60 (2014); see also Oberman, supra note 2 , at 8–10 and 49–55 (describing similar patterns in Chile and El Salvador).
See Oberman , supra note 2, at 44.
See Repr. Health Matters, supra note 83.
See eg Chelsea Becker’s prosecution for murder, following stillbirth allegedly caused by methamphetamine use. Judge Dismisses Murder Charge Against Califronia Mother After Stillbirth , N.Y. Times (May 21, 2021), https://www.nytimes.com/2021/05/20/us/chelsea-becker-stillbirth-murder-charges-california.html .
They may also conscript doctors into law enforcement. See Michelle Oberman, Abortion Bans, Doctors, and the Criminalization of Patients ,48 Hastings Ctr. Rep.5 (2018); see also Oberman, Her Body Our Laws, supra note 2, at 43–67 for a discussion of how reports from doctors to police in El Salvador overwhelmingly involve poor, marginalized women.
Priscilla Thompson & Alexandra Turcios Cruz, How an Oklahoma Women’s Miscarriage Put a Spotlight on Racial Disparities in Prosecutions , Nbc News (Nov. 5, 2021), https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/woman-prosecuted-miscarriage-highlights-racial-disparity-similar-cases-rcna4583 . For a detailed discussion of these cases, see Lynn M. Paltrow & Jeanne Flavin, Arrests of and Forced Interventions on Pregnant Women in the United States, 1973–2005: Implications for Women’s Legal Status and Public Health , 38 J. Health Pol., Pol’y And L. 299, 304–05 (2013) (discussing these findings and the limitations of the research which led the authors to conclude that their findings represent a substantial undercount of cases). See also Michele Goodwin, Policing The Womb: Invisible Women And The Criminalization Of Motherhood (2020).
See Arrests and Prosecutions of Pregnant Women, 1973–2020 , Napw (Sept.18, 2021), https://www.nationaladvocatesforpregnantwomen.org/arrests-and-prosecutions-of-pregnant-women-1973-2020/ (summarizing the range of cases). See also Lynn M. Paltrow, Constitutional Rights for the ‘Unborn’ Would Force Women to Forfeit Theirs , Ms. Magazine (Apr. 15, 2021), https://msmagazine.com/2021/04/15/abortion-constitutional-rights-unborn-fetus-14th-amendment-womens-rights-pregnant/ (The rate of arrests and prosecutions is increasing. ‘From 2006–2020, we have documented over 1000 such arrests—more than double in half as many years. Black, Brown and low-income, rural white women are the typical targets of these arrests.’).
Thompson & Turcios Cruz, supra note 85 (noting that the Black defendants were also significantly more likely to be charged with felonies than white women, with 85% of Black women receiving felony charges compared to 71% of white women); see also Lynn M. Paltrow, Roe v. Wade and the New Jane Crow: Reproductive Rights in the Age of Mass Incarceration , 103 Am. J. Pub. Health 17, 19 (2013). Note that healthcare experts object strenuously to these prosecutions on the grounds that they deter people from seeking treatment essential both to their own welfare and to that of the fetus. See eg Katherine C. Arnold, Viewpoint: Criminalizing Young Women is not the Way to Improve Birth Outcomes , The Oklahoman (Dec. 26, 2021, 5:00 AM), https://www.oklahoman.com/story/opinion/2021/12/26/viewpoint-prosecuting-oklahoma-women-who-miscarry-wrong/8930865002/ .
While beyond the scope of this Article, it bears noting the range of options that state lawmakers have given prosecutors, when it comes to abortion crimes, outlawing things like purchasing abortion medicine, or aiding and assisting an abortion. See eg Emily Bazelon, A Mother in Jail for Helping her Daughter Have an Abortion , N.Y. Times (Sept. 22, 2014), https://www.nytimes.com/2014/09/22/magazine/a-mother-in-jail-for-helping-her-daughter-have-an-abortion.html . See also Sabrina Tavernese, Citizens, not the State, Will Enforce New Abortion Law in Texas , N.Y. Times (Nov. 1, 2021), https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/09/us/abortion-law-regulations-texas.html (Describing the ways that Texas S.B. Eight criminalizes all those who aid and assist abortion, and quoting Prof. Melissa Murray, ‘If the barista at Starbucks overhears you talking about your abortion, and it was performed after six weeks, that barista is authorized to sue the clinic where you obtained the abortion and to sue any other person who helped you, like the Uber driver who took you there.’).
See Paltrow , supra note 91. See generally Michele Bratcher Goodwin, Invisible Women: Mass Incarceration’s Forgotten Casualties , 94 Tex. L. Rev. (2015).
See Race & Justice News: Eliminating Crack/Cocaine Sentencing Disparity The Sentencing Project (July 27, 2021), https://www.sentencingproject.org/news/race-justice-news-senate-hearing-crack-cocaine-sentencing-disparity/ (summarizing the ongoing work toward sentencing equality in drug crimes, starting with the 2010 Fair Sentencing Act). On the negative downstream consequences of race bias in drug law enforcement, Republican Governor Asa Hutchinson noted that racial disparities, “undermined community confidence in the fairness of the criminal justice system. I talked with drug task force officers and front-line agents at the DEA who said this sense of injustice had a real impact in the fight against illegal drugs; it made it more difficult for agents to build trust and work with informants in the areas most impacted by the crack epidemic. The disparity in sentencing led to more harm than help in our federal anti-crime efforts.” ( Gov. Asa Hutchinson: It’s Time to Fix an Old Wrong and End the Disparity Between Crack and Cocaine Offenses , Fox News (June 8, 2021)), https://www.foxnews.com/opinion/end-crack-cocaine-offenses-gov-asa-hutchinson .
See Caroline Kitchener, The Texas Abortion ban has a Medical Exception. But some Doctors Worry it’s too Narrow to use, The Lily, Oct. 22, 2021 (describing existing legal protections and the limitations of Texas S.B. 8’s ‘medical emergency’ exception to its abortion ban), https://www.thelily.com/the-texas-abortion-ban-has-a-medical-exception-but-some-doctors-worry-its-too-narrow-to-use/ .
See Michael Asimow, Federal, Administrative Adjudication Outside The Administrative Procedure Act 3–4 (2019) (classifying these hearings into three categories, according to level of formal process).
See Kari White, Subasri Narasimhan, Sophie A. Hartwig, Erin Carroll, Alexandra McBrayer, Samantha Hubbard, Rachel Rebouché, Melissa Kottke & Kelli Stidham Hall, Parental Involvement Policies for Minors Seeking Abortion in the Southeast and Quality of Care , Sexuality Rsch. & Soc. Pol’y (Jan. 18, 2021), https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s13178-021-00539-0.pdf .
See David S. Cohen & Carole Joffe, Obstacle Course: The Everyday Struggle To Get An Abortion In America 209 (2020) (quoting Ohio doctor Chrisse France, decrying this standard in U.S. practice today; ‘She cannot be seen at our public hospital unless pretty much she’s going to die today or maybe tomorrow’).
See Kari White, Subasri Narasimhan, Sophie A. Hartwig, Erin Carroll, Alexandra McBrayer, Samantha Hubbard, Rachel Rebouché, Melissa Kottke & Kelli Stidham Hall, Parental Involvement Policies for Minors Seeking Abortion in the Southeast and Quality of Care , Sexuality Rsch. & Soc. Pol’y (Feb., 2021) (noting the impact of these policies in delaying access to early abortion among those ultimately deemed eligible to end their pregnancies).
See Herbert L. Packer & Ralph J. Gampell, Therapeutic Abortion: A Problem in Law and Medicine , 11 Stan. L. Rev. 417, 418, 421 (1959). (Explaining that hospitals developed protocols at least in part as a defensive measure: to protect themselves from potential downstream criminal or civil liability). See also, Carole Joffe, Doctors Of Conscience 31 (1995) (describing how doctors who performed abortions illegally would do so outside of the hospital setting, but legal abortions that met the test of necessary to save life would necessarily have been performed in a hospital, thereby implicating both medical and hospital oversight).
See generally Packer & Gampell, id . at 418 . (Noting these questions, among others: Is the procedure limited to cases where its purpose is to avoid shortening the pregnant woman’s life? If so, how do we determine whether carrying the child to term will shorten life? If not, what other considerations are relevant? Is a threat to health necessarily a threat to life? Must the threat to life (or health) be on account of a somatic illness? Or is the woman’s mental condition also to be considered? If so, is a probability that suicide will ensue a justification for therapeutic abortion?). For a searing indictment of U.S. therapeutic abortion committee practices in the mid-twentieth century, see Rickie Solinger, ‘A Complete Disaster:’ Abortion and the Politics of Hospital Abortion Committees, 1950–1970 , 19 Feminist Stud. 241 (1993).
See Packer & Gampell, supra note 100, at 449. (‘[R]eputable members of the medical profession may well find it galling that their freedom from criminal and civil liability turns merely on the nonenforcement of provisions of the law which, on their face, appear to embrace the conduct in question.’). Texas’s S.B. 8 law employs such a threat by way of subjecting doctors who provide abortions after six weeks to civil suit. See Sabrina Tavernese, supra note 75.
Id. at 421 (citing Alan F. Guttmacher, The Shrinking Non-Psychiatric Indications for Therapeutic Abortion , in Therapeutic Abortion 12 (Rosen, ed. 1954)).
Id . at 430. Their study concluded with a call for law reform—a call that was echoed by their Canadian counterparts in the 1977 Badgley report, which found “gross inequities existed in the availability of therapeutic abortion to the women of Canada.” W.D.S. Thomas, The Badgley Report on the Abortion Law, 116 Can. Med. Ass’n. J. 966, 966 (1977).
See Carole Joffe and Jody Steinauer, Evan Texas Allows Abortions to Protect a Woman’s Life. Or Does It? , N.Y. Times (Sept. 12, 2021), https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/12/opinion/abortion-texas-roe.html (describing how contemporary abortion bans will likewise challenge medical integrity).
See Oberman, supra note 2, at 13–42 (describing the highly public Salvadoran case of Beatriz, a woman forced to continue a life-threatening pregnancy until her doctors agreed that death was imminent, which then triggered her right to self-defense, permitting doctors to end her pregnancy).
For a thoughtful consideration of the constitutional protections owed to one who is pregnant, when abortion is illegal, see Meghan Boone, Reproductive Due Process , 88 Geo. Wash. L. Rev. 511, 526 (2020) (‘Beyond its flexibility and ability to evolve, a third feature of due process is simply its function as a catchall constitutional backstop for determining the fairness of government action’).
See Matthews v. Eldridge, 424 U.S. 319, 335 (1976) (“Identification of the specific dictates of due process generally requires consideration of three distinct factors: first, the private interest that will be affected by the official action; second, the risk of erroneous deprivation of such interest through the procedures used, and probable value, if any, of additional or substitute procedural safeguards; and, finally, the Government’s interest, including the function involved and the fiscal and administrative burdens that the additional or substitute procedural requirements would entail.”). See also Simona Grossi, Procedural Due Process , 13 Seton Hall Cir. Rev. 155, 158 (2017) (‘[A]…procedural law that is not supported by logic, fairness, and efficiency considerations,…violates due process.’).
See Chotiner, supra note 5, (citing Marjorie Dannenfelser).
See eg Box v. Planned Parenthood, 139 S. Ct. 1780 at 1783 (Thomas, J., concurring) (supporting an Indiana law banning abortion on grounds of fetal anomaly by invoking the state’s ‘compelling interest in preventing abortion from becoming a tool of modern-day eugenics.’).
See eg Eli Rosenberg, Clarence Thomas Tried to Link Abortion to Eugenics. Seven Historians Told the Post He’s Wrong , Wash. Post (May 30, 2019, 9:50 PM), https://www.washingtonpost.com/history/2019/05/31/clarence-thomas-tried-link-abortion-eugenics-sevenhistorians-told-post-hes-wrong [ https://perma.cc/5DNR-PJT5 ]; Imani Gandy, When It Comes to Birth Control and Eugenics, Clarence Thomas Gets It All Wrong , Rewire (May 29, 2019, 5:11 PM), https://rewire.news/ablc/2019/05/29/when-it-comes-to-birth-control-and-eugenics-clarencethomas-gets-it-all-wrong [ https://perma.cc/3HZ3-689B ]; Lydia O’Connor, What Justice Clarence Thomas Gets Wrong About Eugenics and Abortion , Huff. Post (May 29, 2019, 5:50 PM), https://www.huffpost.com/entry/clarence-thomas-eugenics-abortion_n_5ced6c87e4b0356205a07182 [ https://perma.cc/6AHJ-MS5U ].
See Melissa Murray, Race-ing Roe: Reproductive Justice, Racial Justice, and the Battle for Roe v. Wade , 134 Harv. L. Rev. 2025 (2021) (providing a compelling response to the eugenics charge); see also Jennifer L. Holland, Tiny You: A Western History Of The Anti-Abortion Movement (2020) (arguing that the goals of the anti-abortion movement are deeply entwined with those of the white supremacy movement). Indeed, one might find evidence of racism in the suggestion that adoption is the best solution for poor Black and brown babies, which echoes the U.S. Indian Adoption Project of 1958–1967, under which as many as one-third of indigenous children were separated from their families. 85% of those children were placed in non-native homes or institutions. See Stephanie Woodward, Native Americans Expose The Adoption Era and Repair Its Devastation , Indian Country Today (updated Sept. 13, 2018), https://indiancountrytoday.com/archive/native-americans-expose-the-adoption-era-and-repair-its-devastation .
Reproductive Justice–Sister Song https://www.sistersong.net/reproductive-justice . See also, Mission and Vision , If, When, How, https://www.ifwhenhow.org/about/mission-vision/ [ https://perma.cc/3RRJ-LKT5 ] (last visited Dec. 21, 2021) (A leading reproductive justice organization, their vision statement reads: ‘We envision a transformation of the legal systems and institutions that perpetuate oppression into structures that realize justice, and a future when all people can self-determine their reproductive lives free from discrimination, coercion, or violence.’).
They might begin by looking to Germany. Not, as Chief Justice Roberts suggested in the Dobbs oral argument, because its law restricting abortion to 12 weeks’ gestation is a good compromise. (Transcript of Oral Argument at 53–55, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health, No. 19-1392). Rather, because of the story of how anti-abortion German lawmakers concluded that the best way to deter abortion was to enact, along with a partial ban, “a suite of services that had to be made available to women and families as part of any law regulating abortion: financial assistance for stay-at-home parents; a guaranteed return to a parent’s prior job if he or she took off up to three years to care for a child; extended day care and extensive tax credits for day care costs; increases for child support payments; extended paid leave to care for sick children; reemployment guarantees for empty nesters; sex education services; and a host of other measures relating to adoption, housing and taxation.” Jamal Greene, How Rights Went Wrong: Why Our Obsession With Rights Is Tearing America Apart 130 (2021).
See Chotiner interview, supra note 5. (“We make sure there’s child care in the first few years of that child’s life that’s cheap or free. That’s going to look very different in Minnesota than it does in Georgia. In Minnesota, there very well may be a political appetite for passing more state-supported aid…. There is not a one-size-fits-all when it comes to…how the needs of women will be met. That is vital work for the pro-life movement, and the Republican Party.”).
See Isaac Chotiner, How Pandemics Change History , The New Yorker (Mar. 3, 2020), https://www.newyorker.com/news/q-and-a/how-pandemics-change-history (quoting Frank M. Snowden).
Author notes
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| April 2022 | 49 |
| May 2022 | 2,191 |
| June 2022 | 3,863 |
| July 2022 | 2,219 |
| August 2022 | 959 |
| September 2022 | 1,528 |
| October 2022 | 1,936 |
| November 2022 | 2,280 |
| December 2022 | 1,666 |
| January 2023 | 801 |
| February 2023 | 994 |
| March 2023 | 1,161 |
| April 2023 | 1,163 |
| May 2023 | 848 |
| June 2023 | 572 |
| July 2023 | 578 |
| August 2023 | 492 |
| September 2023 | 714 |
| October 2023 | 1,391 |
| November 2023 | 1,501 |
| December 2023 | 958 |
| January 2024 | 997 |
| February 2024 | 1,282 |
| March 2024 | 1,374 |
| April 2024 | 1,576 |
| May 2024 | 917 |
| June 2024 | 481 |
| July 2024 | 547 |
| August 2024 | 920 |
| September 2024 | 237 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations

- Online ISSN 2053-9711
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press and Harvard, Duke and Stanford Law Schools
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

THE PRINCETON LEGAL JOURNAL
Princeton Legal Journal > The Forum
4 Prin.L.J.F. 12
The First Amendment and the Abortion Rights Debate
Sofia Cipriano
Spring 2024
Following Dobbs v. Jackson ’s (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are protected by various state constitutions’ free exercise clauses — and, by extension, the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. While reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is undoubtedly strategic, the Free Exercise Clause is not the only place to locate abortion rights: the Establishment Clause also warrants further investigation.
Roe anchored abortion rights in the right to privacy — an unenumerated right with a long history of legal recognition. In various cases spanning the past two centuries, t he Supreme Court located the right to privacy in the First, Fourth, Fifth, Ninth, and Fourteenth Amendments . Roe classified abortion as a fundamental right protected by strict scrutiny, meaning that states could only regulate abortion in the face of a “compelling government interest” and must narrowly tailor legislation to that end. As such, Roe ’s trimester framework prevented states from placing burdens on abortion access in the first few months of pregnancy. After the fetus crosses the viability line — the point at which the fetus can survive outside the womb — states could pass laws regulating abortion, as the Court found that “the potentiality of human life” constitutes a “compelling” interest. Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992) later replaced strict scrutiny with the weaker “undue burden” standard, giving states greater leeway to restrict abortion access. Dobbs v. Jackson overturned both Roe and Casey , leaving abortion regulations up to individual states.
While Roe constituted an essential step forward in terms of abortion rights, weaknesses in its argumentation made it more susceptible to attacks by skeptics of substantive due process. Roe argues that the unenumerated right to abortion is implied by the unenumerated right to privacy — a chain of logic which twice removes abortion rights from the Constitution’s language. Moreover, Roe’s trimester framework was unclear and flawed from the beginning, lacking substantial scientific rationale. As medicine becomes more and more advanced, the arbitrariness of the viability line has grown increasingly apparent.
As abortion rights supporters have looked for alternative constitutional justifications for abortion rights, the First Amendment has become increasingly more visible. Certain religious groups — particularly Jewish groups — have argued that they have a right to abortion care. In Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida , a religious rights group argued that Florida’s abortion ban (HB 5) constituted a violation of the Florida State Constitution: “In Jewish law, abortion is required if necessary to protect the health, mental or physical well-being of the woman, or for many other reasons not permitted under the Act. As such, the Act prohibits Jewish women from practicing their faith free of government intrusion and thus violates their privacy rights and religious freedom.” Similar cases have arisen in Indiana and Texas. Absent constitutional protection of abortion rights, the Christian religious majorities in many states may unjustly impose their moral and ethical code on other groups, implying an unconstitutional religious hierarchy.
Cases like Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida may also trigger heightened scrutiny status in higher courts; The Religious Freedom Restoration Act (1993) places strict scrutiny on cases which “burden any aspect of religious observance or practice.”
But framing the issue as one of Free Exercise does not interact with major objections to abortion rights. Anti-abortion advocates contend that abortion is tantamount to murder. An anti-abortion advocate may argue that just as religious rituals involving human sacrifice are illegal, so abortion ought to be illegal. Anti-abortion advocates may be able to argue that abortion bans hold up against strict scrutiny since “preserving potential life” constitutes a “compelling interest.”
The question of when life begins—which is fundamentally a moral and religious question—is both essential to the abortion debate and often ignored by left-leaning activists. For select Christian advocacy groups (as well as other anti-abortion groups) who believe that life begins at conception, abortion bans are a deeply moral issue. Abortion bans which operate under the logic that abortion is murder essentially legislate a definition of when life begins, which is problematic from a First Amendment perspective; the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment prevents the government from intervening in religious debates. While numerous legal thinkers have associated the abortion debate with the First Amendment, this argument has not been fully litigated. As an amicus brief filed in Dobbs by the Freedom From Religion Foundation, Center for Inquiry, and American Atheists points out, anti-abortion rhetoric is explicitly religious: “There is hardly a secular veil to the religious intent and positions of individuals, churches, and state actors in their attempts to limit access to abortion.” Justice Stevens located a similar issue with anti-abortion rhetoric in his concurring opinion in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services (1989) , stating: “I am persuaded that the absence of any secular purpose for the legislative declarations that life begins at conception and that conception occurs at fertilization makes the relevant portion of the preamble invalid under the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the Federal Constitution.” Judges who justify their judicial decisions on abortion using similar rhetoric blur the line between church and state.
Framing the abortion debate around religious freedom would thus address the two main categories of arguments made by anti-abortion activists: arguments centered around issues with substantive due process and moral objections to abortion.
Conservatives may maintain, however, that legalizing abortion on the federal level is an Establishment Clause violation to begin with, since the government would essentially be imposing a federal position on abortion. Many anti-abortion advocates favor leaving abortion rights up to individual states. However, in the absence of recognized federal, constitutional protection of abortion rights, states will ban abortion. Protecting religious freedom of the individual is of the utmost importance — the United States government must actively intervene in order to uphold the line between church and state. Protecting abortion rights would allow everyone in the United States to act in accordance with their own moral and religious perspectives on abortion.
Reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is the most viable path forward. Anchoring abortion rights in the Establishment Clause would ensure Americans have the right to maintain their own personal and religious beliefs regarding the question of when life begins. In the short term, however, litigants could take advantage of Establishment Clauses in state constitutions. Yet, given the swing of the Court towards expanding religious freedom protections at the time of writing, Free Exercise arguments may prove better at securing citizens a right to an abortion.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Cell Rep Med
- v.4(1); 2023 Jan 17

Abortion bans and their impacts: A view from the United States
Laura j. frye.
1 Gynuity Health Projects, New York, NY, USA
Beverly Winikoff
A retrospective study of abortion facilities in and around Texas by White et al. 1 and a spatial analysis by Rader et al. 2 are combined to illustrate the detrimental effects of abortion bans enacted in the United States.
Abortion restrictions have been introduced in various forms across many states for years, but since June 2022, when the right to abortion was no longer federally protected, we have seen a rapid increase in these restrictions. We are just starting to quantify and qualify their effects. Two recent studies published in JAMA offer early indications of the effects of draconian bans.
In “Association of Texas’ 2021 Ban on Abortion in Early Pregnancy with the Number of Facility-Based Abortion in Texas and Surrounding States,” White et al. used a large dataset containing information before and after the passage of SB8 in September 2021. 1 This bill banned most abortions after 6 weeks in the state of Texas. The data presented in this article allow for a careful examination of the law’s effects, and the authors paint a picture of how rapidly destabilizing such bans can be. The study clearly shows that, in the immediate aftermath of SB8’s implementation, there was both an absolute drop in documented abortions and a shift in the location of abortions as Texans went to neighboring states for medical care.
The paper explicitly examines abortions after 12 weeks as an important indicator of change, not because of the small decrease in safety and efficacy with increasing gestational durations, but rather because of the major increase in burdens to affected individuals (cost, time, travel) and to clinics (resources, scheduling) with gestations beyond this point.
A clearer and more detailed sense of how these patient travel dynamics play out can be found in the “Estimated Travel Time and Spatial Access to Abortion Facilities in the US Before and After the Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Decision” by Rader et al., which uses simulation and spatial analysis to measure changes in surface travel time to the closest abortion facility before and after the June 2022 Dobbs decision. 2
The average travel time to reach the nearest abortion facility significantly increased in the simulated post-Dobbs world, and, while the median change from 11 to 17 min is not jaw dropping, the spread of the data and the extremes of the curve are where the biggest problems lie. The authors show a doubling of the number of individuals who must travel more than 60 min to access abortion care. Then, through sensitivity analyses on geographic heterogeneity, they illustrate some of the extreme increases in travel time for people in the South, as in Texas, with a mean increase of over 7 h.
While the White paper notes that their data did not include individual-level demographic information (and thus was not able to explore the disparate effects of the ban on various subpopulations), the Raden paper is able to shed some light on the disproportionate impacts of abortion restrictions by use of census data. The latter paper shows that longer travel times occur more frequently in populations without insurance, with lower incomes, and who are racial and ethnic minorities. Documentation of these effects is important for advocacy, policy change, and resource allocation.
The White et al. paper wisely uses care in describing the data they have as “documented facility-based abortions,” acknowledging the now-frequent practice of non-facility-based self-managed abortion with pills. Similarly, Rader et al. note that their data are predicated on the idea of traveling to a physical facility and do not account for the mailing of pills to a person’s home. The TelAbortion study from 2016 to 2021 provided evidence on the safety and efficacy of direct-to-patient telemedicine abortion with mailing of pills, 3 , 4 and the FDA now allows for this method of abortion pill provision. We also know that self-managed abortion can be a safe and effective option 5 and is currently common in the United States. 6 , 7 There is increasing interest in determining its role in the care landscape. 8 , 9 , 10 Moving forward, it would be beneficial to see more information on how remote provision of care and self-management play into the dynamics illustrated in these articles.
These two papers, used together, can help prepare clinics in protective states for the influx of affected individuals as additional oppressive laws are passed in other states. The lessons documented only grow in relevance as the map of the United States darkens with more and more states passing restrictive abortion laws. We can use these data both to decry the negative and disproportionate effect of these bans and to call for action to prepare receiving clinics in protective states as they take on the care of more people who are denied medical services in their home states.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
- How to Order
Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Abortion
How To Write A Persuasive Essay On Abortion
10 min read
-9248.jpg&w=640&q=75)
People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
A Catalogue of 300 Best Persuasive Essay Topics for Students
Persuasive Essay Outline - A Complete Guide
30+ Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
Learn to Write a Persuasive Essay About Business With 5 Best Examples
Check Out 14 Persuasive Essays About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you about to write a persuasive essay on abortion but wondering how to begin?
Writing an effective persuasive essay on the topic of abortion can be a difficult task for many students.
It is important to understand both sides of the issue and form an argument based on facts and logical reasoning. This requires research and understanding, which takes time and effort.
In this blog, we will provide you with some easy steps to craft a persuasive essay about abortion that is compelling and convincing. Moreover, we have included some example essays and interesting facts to read and get inspired by.
So let's start!
- 1. How To Write a Persuasive Essay About Abortion?
- 2. Persuasive Essay About Abortion Examples
- 3. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Abortion
- 4. Persuasive Topics about Abortion
- 5. Facts About Abortion You Need to Know
How To Write a Persuasive Essay About Abortion?
Abortion is a controversial topic, with people having differing points of view and opinions on the matter. There are those who oppose abortion, while some people endorse pro-choice arguments.
It is also an emotionally charged subject, so you need to be extra careful when crafting your persuasive essay.
Before you start writing your persuasive essay, you need to understand the following steps.
Step 1: Choose Your Position
The first step to writing a persuasive essay on abortion is to decide your position. Do you support the practice or are you against it? You need to make sure that you have a clear opinion before you begin writing.
Once you have decided, research and find evidence that supports your position. This will help strengthen your argument.
Check out the video below to get more insights into this topic:
Step 2: Choose Your Audience
The next step is to decide who your audience will be. Will you write for pro-life or pro-choice individuals? Or both?
Knowing who you are writing for will guide your writing and help you include the most relevant facts and information. Additionally, understanding your audience will help you craft a focused thesis statement that clearly addresses their concerns and perspectives.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Step 3: Make an Outline & Define Argument
Now that you have chosen your position and identified your audience, it’s time to craft your argument. Start by clearly defining your stance on the issue and outlining the reasons behind your belief. Use evidence to support each of your claims, such as facts, statistics, or expert opinions.
To organize your thoughts, create a persuasive essay outline that maps out the structure of your essay.
For instance, your persuasive essay on abortion outline might include:
- Introduction: Present the topic and state your thesis.
- Body Paragraph 1: Explain your first supporting argument and provide evidence.
- Body Paragraph 2: Discuss your second supporting argument with additional evidence.
- Body Paragraph 3: Address opposing arguments and provide counterarguments to refute them.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate why your position is valid.
By outlining your essay, you ensure that your argument is logical and well-structured, making your essay more balanced and convincing.
Step 4: Format Your Essay
Once you have the argument ready, it is time to craft your persuasive essay. Follow a standard format for the essay , with an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Make sure that each paragraph is organized and flows smoothly. Use clear and concise language, getting straight to the point.
Step 5: Proofread and Edit
The last step in writing your persuasive essay is to make sure that you proofread and edit it carefully. Look for spelling, grammar, punctuation, or factual errors and correct them. This will help make your essay more professional and convincing.
These are the steps you need to follow when writing a persuasive essay on abortion. It is a good idea to read some examples before you start so you can know how they should be written.
Continue reading to find helpful examples.
Persuasive Essay About Abortion Examples
To help you get started, here are some example persuasive essays on abortion that may be useful for your own paper.
Abortion laws are a contentious issue, and persuasive arguments often revolve around the balance between individual rights and moral considerations. Advocates for more permissive abortion laws argue that these laws are essential for safeguarding women’s health and personal autonomy. Access to safe and legal abortion services allows individuals to make critical decisions about their own bodies and futures. Restrictive laws can lead to unsafe, unregulated procedures, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities and exacerbating health disparities. Moreover, persuasive arguments against overly restrictive abortion laws emphasize that personal circumstances vary widely. Women facing unplanned pregnancies may encounter complex situations, including health risks or severe financial hardship. In such cases, the ability to choose abortion can be crucial for their well-being and that of their families. Opponents of restrictive laws often argue that decisions about abortion should be made by individuals in consultation with their healthcare providers, rather than by lawmakers who may not fully understand the personal or medical intricacies involved. In conclusion, persuasive arguments for more flexible abortion laws highlight the importance of personal choice and access to safe medical procedures, advocating for a legal framework that respects individual rights and promotes public health. |
Here is another short persuasive essay about abortion:
Abortion remains one of the most polarizing issues in contemporary discourse, and a persuasive argument against it often centers on the moral and ethical considerations surrounding the sanctity of life. Opponents of abortion argue that life begins at conception and that every embryo or fetus has an inherent right to life. This perspective asserts that terminating a pregnancy is a profound moral wrong, akin to ending a human life. From a moral standpoint, many believe that the potential for human life deserves protection regardless of the circumstances surrounding conception. They argue that adoption presents a viable alternative for those who cannot or choose not to raise a child, ensuring that the unborn have the opportunity to live and contribute to society. Additionally, some argue that the availability of abortion can lead to a devaluation of human life in general. They contend that societies should focus on strengthening support systems for pregnant individuals, such as improved access to prenatal care and financial assistance, rather than offering abortion as an option. In conclusion, the argument against abortion emphasizes the ethical obligation to protect potential life and advocate for alternatives that respect both the unborn and the needs of individuals facing unplanned pregnancies. |
Persuasive Essay About No To Abortion
Persuasive Speech on Abortion
Legal Abortion Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay About Abortion in the Philippines
Persuasive Essay about legalizing abortion
You can also read m ore persuasive essay examples to imp rove your persuasive skills.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Abortion
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that presents both sides of an argument. These essays rely heavily on logic and evidence.
Here are some examples of short argumentative essays with an introduction, body, and conclusion that you can use as a reference in writing your own argumentative essay.
The debate over whether abortion should be made illegal is a deeply divisive issue, marked by moral, ethical, and legal considerations. On one hand, proponents of making abortion illegal argue that it is a moral and ethical wrong, asserting that the fetus has a right to life from conception. They contend that every potential life should be protected, and that alternatives such as adoption provide viable options for those facing unwanted pregnancies. Conversely, those opposed to making abortion illegal argue that such a move would infringe on personal autonomy and reproductive rights. They believe that individuals should have the freedom to make decisions about their own bodies, including whether to continue or terminate a pregnancy. Making abortion illegal could lead to unsafe, unregulated procedures, disproportionately affecting low-income women and those without access to safe medical care. Historical evidence suggests that criminalizing abortion does not eliminate it but drives it underground, where it becomes much riskier. Ultimately, the debate centers on balancing ethical considerations with personal rights. While the protection of potential life is important, ensuring safe, legal access to abortion respects individual autonomy and public health. |
Let’s take a look at another short example:
Legalizing abortion remains one of the most contentious issues in modern society, with passionate arguments on both sides. Advocates for legalizing abortion assert that it is a fundamental right for individuals to have control over their own bodies. They argue that access to safe and legal abortion services is essential for protecting women’s health and autonomy. By legalizing abortion, individuals can make informed decisions based on their personal circumstances, including financial stability, health risks, and life goals. Additionally, legalizing abortion helps prevent unsafe, illegal procedures that can lead to severe health complications or even death. Historical data indicates that restrictive abortion laws do not eliminate abortions but drive them underground, where they become significantly more dangerous. On the other hand, opponents of legalization often argue that abortion ends a potential life and is therefore morally wrong. They advocate for alternatives such as adoption and assert that society has a responsibility to protect the unborn. However, the ethical and moral arguments must be balanced with practical considerations. Legalizing abortion ensures that individuals can access safe, regulated medical care and make personal decisions without facing undue risks. It respects the autonomy of individuals while also considering their health and well-being, making it a crucial component of a just and equitable society. |
Here are some PDF examples that you can download and read for free!
Abortion Persuasive Essay Introduction
Argumentative Essay About Abortion Conclusion
Argumentative Essay About Abortion Pdf
Argumentative Essay About Abortion in the Philippines
Argumentative Essay About Abortion - Introduction
Persuasive Topics about Abortion
If you are looking for some topics to write your persuasive essay on abortion, here are some examples:
- Should abortion be legal in the United States?
- Is it ethical to perform abortions, considering its pros and cons?
- What should be done to reduce the number of unwanted pregnancies that lead to abortions?
- Is there a connection between abortion and psychological trauma?
- What are the ethical implications of abortion on demand?
- How has the debate over abortion changed over time?
- Should there be legal restrictions on late-term abortions?
- Does gender play a role in how people view abortion rights?
- Is it possible to reduce poverty and unwanted pregnancies through better sex education?
- How is the anti-abortion point of view affected by religious beliefs and values?
These are just some of the potential topics that you can use for your persuasive essay on abortion. Think carefully about the topic you want to write about and make sure it is something that interests you.
Check out m ore persuasive essay topics that will help you explore other things that you can write about!
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Facts About Abortion You Need to Know
Here are some facts about abortion that will help you formulate better arguments.
- According to the Guttmacher Institute , 1 in 4 pregnancies end in abortion.
- The majority of abortions are performed in the first trimester.
- Abortion is one of the safest medical procedures, with less than a 0.5% risk of major complications.
- In the United States, 14 states have laws that restrict or ban abortion of most forms after 20 weeks gestation.
- Seven out of 198 nations allow elective abortions after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- In places where abortion is highly illegal, more women die during childbirth and due to complications resulting from pregnancy.
- A majority of pregnant women who opt for abortions do so for financial and social reasons.
- According to estimates, 56 million abortions occur annually.
In conclusion, these are some of the examples, steps, and topics that you can use to write a persuasive essay. Make sure to do your research thoroughly and back up your arguments with evidence. This will make your essay more professional and convincing.
Need the services of a persuasive essay writing service ? We've got your back!
MyPerfectWords.com provides help to students in the form of professionally written essays. Our persuasive essay writer can craft quality persuasive essays on any topic, including abortion.
So, just ask our experts ' do my essay ' and get professional help.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to start a persuasive essay about abortion.
To start a persuasive essay about abortion, begin with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader's attention and clearly presents the topic. Provide some background information on the issue and state your thesis statement, which should outline your position on the matter. Ensure your introduction sets up the argument you will be making throughout the essay.
What is a good argument for abortion?
A good argument for abortion could be that it is a woman’s choice to choose whether or not to have an abortion. It is also important to consider the potential risks of carrying a pregnancy to term.
What is a good hook for an essay about abortion?
A good hook for an essay might involve a thought-provoking question, a startling statistic, or a powerful quote. For example:
- "Did you know that nearly one in four women will have an abortion by age 45? This staggering statistic highlights the urgency of the abortion debate."
- "‘The right to choose is fundamental,’ argues many pro-choice advocates. But how does this stand against the moral objections of pro-life supporters?"
What is a persuasive speech about legalizing abortion?
A persuasive speech about legalizing abortion argues for the importance of granting individuals the right to make autonomous decisions regarding their reproductive health. It emphasizes that legalizing abortion ensures safe, regulated medical procedures, protects women's health, and supports personal autonomy. The speech often highlights the risks associated with illegal abortions, the need for access to healthcare, and the ethical consideration of allowing individuals to choose based on their unique circumstances.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

How To Win Any Argument About Abortion

So you're talking to someone who says something ignorant . And while you know that they're in the wrong, your words escape you. To make sure that doesn't happen, we've compiled a series of reference guides with the most common arguments — and your counter-arguments — for the most hot-button issues. Ahead, how to argue the pro-choice position .
Common Argument #1: A fetus is a human being, and human beings have the right to life, so abortion is murder.
The Pro-Choice Argument: I'm probably not going to convince you that a fetus isn't a life, as that's basically the most intractable part of this whole debate, so I'll be brief:
- A fetus can't survive on its own. It is fully dependent on its mother's body, unlike born human beings.
- Even if a fetus was alive, the "right to life" doesn't imply a right to use somebody else's body. People have the right to refuse to donate their organs , for example, even if doing so would save somebody else's life.
- The "right to life" also doesn't imply a right to live by threatening somebody else's life. Bearing children is always a threat the life of the mother (see below).
- A "right to life" is, at the end of the day, a right to not have somebody else's will imposed upon your body. Do women not have this right as well?
Common Argument #2: If a woman is willing to have sex, she's knowingly taking the risk of getting pregnant, and should be responsible for her actions.
The Pro-Choice Argument: You're asserting that giving birth is the "responsible" choice in the event of a pregnancy, but that's just your opinion. I'd argue that if a mother knows she won't be able to provide for her child, it's actually more responsible to have an abortion, and in doing so prevent a whole lot of undue suffering and misery.
But let's look at this argument a bit further. If you think getting an abortion is "avoiding responsibility," that implies that it's a woman's responsibility to bear a child if she chooses to have sex. That sounds suspiciously like you're dictating what a woman's role and purpose is, and a lot less like you're making an argument about the life of a child.
Common Reply : No, because women can practice safe sex and avoid getting pregnant. If she refuses to use contraception and gets pregnant as a result, that's her fault, and her responsibility.
Your Rebuttal: Not everyone has easy access to contraception , nor does everyone have a good enough sex education class to know how to use it or where to obtain it. But let's just suppose, for the sake of argument, that everyone had access to free contraception and knew how to use it correctly.
Even then, no contraception is 100% effective. Presumably, you oppose abortions even in cases where contraception fails (and it does sometimes fail, even when used perfectly). If that's true, you're saying that, by merely choosing to have sex — with or without a condom — a woman becomes responsible for having a child. And that's a belief that has everything to do with judging a woman's behavior, and nothing to do with the value of life.
Common Argument #3: But I'm OK with abortions in cases of rape .
The Pro-Choice Argument: Why only in those cases? Are the lives of children who were conceived by rape worth less than the lives of children who were willfully conceived? If preserving the life of the child takes primacy over the desires of the mother — which is what you're saying if you if you oppose any legal abortions — then it shouldn't matter how that life was conceived.
Common Argument #4: "If it's a legitimate rape, the female body has ways to try to shut that whole thing down."
Your Response: Go home, Todd Akin , you're drunk.
Common Argument #5: Adoption is a viable alternative to abortion.
The Pro-Choice Argument: This implies that the only reason a woman would want to get an abortion is to avoid raising a child, and that isn't the case. Depending on the circumstances, the mere act of having a child in a hospital can cost between $3,000 and $37,000 in the United States. Giving birth is dangerous, too: In the United States, pregnancy complications are the sixth most common cause of death for women between the ages of 20 and 34.
Even before birth, there are costs to pregnancy. In addition to the whole "carrying another human being around in your stomach for nine months" thing, many women, particularly teens, are shunned and shamed for their pregnancies — not only by friends, families, employers, and classmates, but also by advertisements in the subway . There's also the risk of violent retribution from abusive partners and parents.
In short, there are a lot of reasons a woman might seek an abortion. Adoption doesn't address all of them.
Common Argument #6: When abortion is legal, women just use it as a form of birth control.
The Pro-Choice Argument: Do you have evidence of this? Considering that contraceptives are cheaper, easier, less painful, less time-consuming, less emotionally taxing, and more readily available than abortions, it seems odd to suggest that women who've already decided to use birth control would select abortion as their preferred method. It's more likely the opposite: Historical and contemporary data suggests that women will seek abortions regardless of whether or not they're legal, but that when birth control and contraceptives are more widely accessible, abortion rates go down.
Common Argument #7: Abortions are dangerous.
The Pro-Choice Argument: When performed by trained professionals, abortions are one of the safest procedures in medicine, with a death rate of less than 0.01%. The risk of dying while giving birth is roughly 13 times higher. Abortions performed by people without the requisite skills and training, however, are extremely unsafe. An estimated 68,000 women die every year from back alley abortions, which are generally most common when abortion is illegal and/or inaccessible.
If you'd like to examine the health impact of banning abortion, consider Romania, which banned abortions in 1966. That policy remained in place for about 23 years, during which time over 9,000 women died from unsafe abortions , and countless others were permanently injured. That's around two women dying every day. When the policy was reversed, maternal mortality rate plummeted to one-eighth of what it was at its peak under the no-abortion policy.
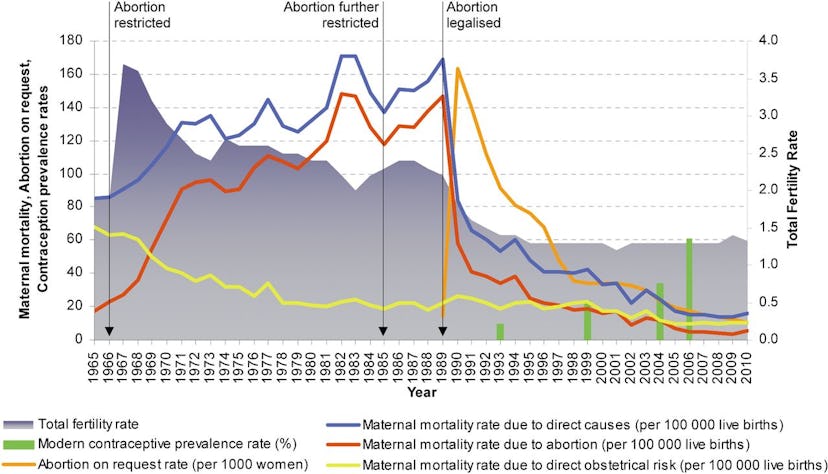
Abortions and maternal death rates in Romania, 1965-2010. Image credit: BMJ Group
The negative health effects of prohibiting abortion don't end with the mothers. Romania's abortion ban sparked a nationwide orphan crisis, as roughly 150,000 unwanted newborns were placed in nightmarish state-run orphanages . Many of those orphans now suffer from severe mental and physical health problems, including reduced brain size, schizoaffective disorder, and sociopathy.
When abortion is illegal, it becomes exponentially more unsafe for both women and their children. You may not like the fact that women will seek abortions even when they're illegal, but it is undeniably a fact nonetheless.
Common Argument #8: What if Winston Churchill or Martin Luther King had been aborted?
Your Response: Are you saying abortion policy should be influenced by how good of a person a fetus ends up becoming? If that's the case, what if Joseph Stalin or Pol Pot had been aborted?
Common Argument #9: Many women who get abortions regret their decision later on.
The Pro-Choice Argument: This is a pretty common argument. As with shaming of teen moms, it pops up in subway ads.
This is a bad argument. Should the government ban people from doing things they sometimes regret? Think of everything you've ever regretted — not moving after college, dating the wrong person — and ask yourself if you wish there had been a law to prevent you from doing that thing. You probably don't, because you probably believe people should be able to choose their own paths in life regardless of whether they regret those choices later on. I agree, which is part of why I'm pro-choice .
Common Argument #10: Taxpayers shouldn't be forced to pay for things they find morally disagreeable.
The Pro-Choice Argument: By that rationale, America also shouldn't have a military, since that's funded by taxes, and many taxpayers find American foreign policy morally disagreeable. Also, the Hyde Amendment prevents most public funds from going toward abortions. But that's a moot point, because these are two separate arguments. Believing that abortion should be legal doesn't require you to also believe that taxpayer dollars should fund abortions.
Common Argument #11: What if your mother had aborted you?
The Pro-Choice Argument: Well, if I'd never come into existence in the first place, I probably wouldn't have any strong feelings on the matter. Anyway, I love my mother very much and respect her right to make whatever decisions are right for her body and life.
The best pro-choice arguments , in summary:
- A "right to life" doesn't imply a right to use someone else's body to sustain a life.
- Women do not have a "responsibility" to have children, and certainly don't assume such a responsibility by virtue of deciding to have sex.
- Outlawing abortion is very dangerous, both for women and their children.
- Adoption still requires women to carry a baby to term and then give birth, both of which are also inherently dangerous.
- Abortions, on the other hand, are quite safe.
- Banning abortion violates a woman's right to control her own body.
This article was originally published on March 5, 2014
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
As the Supreme Court considers Roe v. Wade, a look at how abortion became legal

Nina Totenberg

The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey , the court's major decisions over the last half-century that guarantee a woman's right to an abortion nationwide. J. Scott Applewhite/AP hide caption
The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey , the court's major decisions over the last half-century that guarantee a woman's right to an abortion nationwide.
For nearly a half-century, abortion has been a constitutional right in the United States. But this week, the U.S. Supreme Court hears arguments in a Mississippi case that directly challenges Roe v. Wade and subsequent decisions.
Those rulings consistently declared that a woman has a constitutional right to terminate a pregnancy in the first two trimesters of pregnancy when a fetus is unable to survive outside the womb. But with that abortion right now in doubt, it's worth looking back at its history.
Abortion did not become illegal in most states until the mid to late 1800s. But by the 1960s, abortion, like childbirth, had become a safe procedure when performed by a doctor, and women were entering the workforce in ever larger numbers.
Still, being pregnant out of wedlock was seen as scandalous, and women increasingly sought out abortions, even though they were illegal. What's more, to be pregnant often meant that women's educations were stunted, as were their chances for getting a good job. Because of these phenomena, illegal abortion began to skyrocket and became a public health problem. Estimates of numbers each year ranged from 200,000 to over a million, a range that was so wide precisely because illegal procedures often went undocumented.
At the time, young women could see the perils for themselves. Anyone who lived in a college dormitory back then might well have seen one or more women carried out of the dorm hemorrhaging from a botched illegal abortion.
George Frampton clerked for Justice Harry Blackmun the year that his boss authored Roe v. Wade , and he remembers that until Roe , "those abortions had to be obtained undercover if you had a sympathetic doctor" and you were "wealthy enough." But most abortions were illegal and mainly took place "in backrooms by abortion quacks" using "crude tools" and "no hygiene."
By the early to mid-1960s, Frampton notes, thousands of women in large cities were arriving at hospitals, bleeding and often maimed.
One woman, in an interview with NPR, recalled "the excruciatingly painful [illegal] procedure," describing it as "the equivalent of having a hot poker stuck up your uterus and scraping the walls." She remembered that the attendant had to "hold her down on the table."
The result, says Frampton, was that by the mid-1960s, a reform movement had begun, aimed at decriminalizing abortion and treating it more like other medical procedures. Driving the reform movement were doctors, who were concerned about the effect that illegal abortions were having on women's health. Soon, the American Law Institute — a highly respected group of lawyers, judges and scholars — published a model abortion reform law supported by major medical groups, including the American Medical Association.
Many states then began to loosen their abortion restrictions. Four states legalized abortion, and a dozen or so adopted some form of the model law, which permitted abortion in cases of rape, incest and fetal abnormality, as well as to save the life or health of the mother.
By the early 1970s, when nearly half the states had adopted reform laws, there was a small backlash. Still, as Frampton observes, "it wasn't a big political or ideological issue at all."
In fact, the justices in 1973 were mainly establishment conservatives. Six were Republican appointees, including the court's only Catholic. And five were generally conservative, as defined at the time, including four appointed by President Richard Nixon. Ultimately, the court voted 7-to-2 that abortion is a private matter to be decided by a woman during the first two trimesters of her pregnancy.
That framework has remained in place ever since, with the court repeatedly upholding that standard. In 1992, it reiterated the framework yet again, though it said that states could enact some limited restrictions — for example, a 24-hour waiting period — as long as the restrictions didn't impose an "undue burden" on a woman's right to abortion.
Frampton says that the court established the viability framework because of the medical consensus that a fetus could not survive outside the womb until the last trimester. He explains that "the justices thought that this was going to dispose of the constitutional issues about abortion forever."
Although many had thought that fetal viability might change substantially, that has not happened. But in the years that followed, the backlash to the court's abortion decisions grew louder and louder, until the Republican Party, which had earlier supported Roe , officially abandoned it in 1984.
Looking at the politicization of the Supreme Court nomination and confirmation process in recent years, one can't help but wonder whether Roe played a part in that polarization. What does Frampton think?
"I'm afraid," he concedes, "that analysis is absolutely spot on. I think they [the justices] saw it as a very important landmark constitutional decision but had no idea that it would become so politicized and so much a subject of turmoil."
Just why is abortion such a controversial issue in the United States but not in so many other countries where abortion is now legal? Florida State University law professor Mary Ziegler, author of Abortion and the Law in America , points out that in many countries, the abortion question has been resolved through democratic means — in some countries by national referendum, in others by parliamentary votes and, in some, by the courts. In most of those countries, however, abortions, with some exceptions, must be performed earlier, by week 12, 15 or 18.
But — and it is a big but — in most of those countries, unlike in the U.S., national health insurance guarantees easy access to abortions.
Lastly, Ziegler observes, "there are a lot of people in the United States who have a stake in our polarized politics. ... It's a way to raise money. It's a way to get people out to the polls."
And it's striking, she adds, how little our politics resemble what most people say they want. Public opinion polls consistently show that large majorities of Americans support the right to abortion in all or most cases. A poll conducted last May by the Pew Research Center found 6 in 10 Americans say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. And a Washington Post -ABC poll conducted last month found that Americans by a roughly 2-to-1 margin say the Supreme Court should uphold its landmark Roe v. Wade decision.
But an NPR poll conducted in 2019 shows just how complex — and even contradictory — opinions are about abortion. The poll found that 77% of Americans support Roe . But that figure dropped to 34% in the second trimester. Other polls had significantly higher support for second trimester abortions. A Reuters poll pegged the figure at 47% in 2021. And an Associated Press poll found that 49% of poll respondents supported legal abortion for anyone who wants one "for any reason," while 50% believed that this should not be the case. And 86% said they would support abortion at any time during a pregnancy to protect the life or health of the woman.
All this would seem to suggest that there is overwhelming support for abortion rights earlier in pregnancy, but less support later in pregnancy, and overwhelming support for abortions at any time to protect the life or, importantly, the health of the mother. That, however, is not where the abortion debate is in the 25 or so states that have enacted very strict anti-abortion laws, including outright bans, in hopes that the Supreme Court will overturn Roe .
Opinion: When I talked about my pre-Roe abortion, other women’s stories poured out: ‘You are the only person I’ve ever told’

- Copy Link URL Copied!
The summer of 1965, the first gynecologist I went to for a diaphragm turned me down. He was within his rights — birth control had only just become legal for married people, and contraception for unmarried people like me would remain against the law until 1972. With the support of a growing feminist movement, single women with financial resources and medical access managed to get the pill anyway and rode the wave of the summer of love, exulting in the sexual revolution. “Make Love Not War” demanded not only peace in Vietnam but liberation from restraints on sex and dread of unwanted pregnancy.
But a diaphragm could slip or have a hole in it. Condoms were considered ineffective and impaired our pleasure and freedom. Intrauterine devices were not in general use. You might skip a birth control pill one day or two days and find yourself pregnant, which is what happened to me. Or sleep with one’s boyfriend and be edged into unwanted sex with someone else and not know who impregnated you. That also happened to me.


Column: Warren Hern is one of the country’s few late-term abortion doctors. This is what drives him
Through half a century of death threats and derision, Warren Hern has never stopped providing women with critically needed healthcare.
Aug. 21, 2024
White and privileged enough to pay what I remember as $2,000, I maneuvered a “therapeutic abortion,” a loophole in the law that allowed abortion for the health of the woman. Typically, the strategy was mental health. I’m sure I told the psychiatrist I didn’t want to marry the father and that I could not care for a child. The obstetrician agreed to perform the procedure, asked me on the operating table if I wanted to go through with it, and told me not to tell anyone. I told only the friends who drove me to the hospital.
The story still amazes me. Who was that 23-year-old woman who managed to get a safe abortion all on her own? What was the impact of that decision on the rest of my life? I thought little about it until recently, when I realized my students and other younger women had no idea what it had been like back in the day. What to tell them? I remember being alone. I remember feeling scared. I had paid for the abortions of a couple of women I knew and driven a friend to an illegal one in New Jersey. She ended up in the hospital, bleeding badly. “I damn near died,” she told me, 55 years later.

Calmes: Why Trump’s ‘leave it to the states’ abortion stance ties him in knots
Trump’s hapless and contradictory flailing on abortion is a prime signal: This man shouldn’t get another term.
Sept. 5, 2024
I did not know, when I sought to terminate my pregnancy in New Haven, Conn., that a month before in New York City 12 women had gone public about their abortions at a “speak-out,” or that in Chicago an underground collective called the Janes was arranging safe abortions, free to those who could not afford them. Fear of pregnancy haunted everything beyond a kiss, as did stories of women sent away to have children they gave up for adoption, women who died from botched procedures, boyfriends who wouldn’t help pay, boyfriends who would.
The most radical position on abortion before Roe vs. Wade was repeal not reform — the argument being that any abortion law, no matter how liberal, denied women control of our own bodies. After Roe, abortion opponents took control of the discourse, muddling the clarity of the simple fact that one’s body is one’s own. In 1977, the Hyde Amendment, which denied federal funds for abortion, further reinforced the disparity between women who could afford the procedure and those who could not. Demands for parental consent denied young women autonomy. Amid clinic bombings, the pro-choice movement seemed unable to effectively call out the cruelty of antiabortion rhetoric that privileged the life of an unborn child over that of an unrealized woman or overburdened mother.

Column: Two years after the Supreme Court’s abortion decision, meet the expert on post-Roe America
UC Davis law professor and historian Mary Ziegler has become one of the country’s leading authorities on the abortion issue. She sees a push-pull between judges, anti-abortion lawmakers and Americans who by and large favor abortion rights.
June 23, 2024
Those of us who’d had abortions were made somehow inaudible. “Write a poem,” a friend said to me on our way to Washington for the 1992 March for Women’s Lives, an event prompted by a challenge to a Pennsylvania abortion rights law brought to the Supreme Court . Half a million rallied and Roe was preserved. I’d hardly talked about my abortion, let alone written about it, but I remembered my long-ago loneliness. The poem recounted the sex that led to my 1969 abortion and a visit to a post-Roe women-run clinic. I remember the power of the audience response when I read it aloud and my surprise when a young editor wrote me, saying that her magazine’s decision to publish it had been controversial.
With the Dobbs decision, public speech about abortion is no longer rare. What was silence has become an uproar. The new back alley is a flight you can’t afford to a state where abortion is legal, or a hospital room where you’re left to bleed out because your miscarriage is too late to be legally assisted by professionals.
On a recent women’s mobilization call for Kamala Harris supporters, two women told their stories — both were hospitalized for late-term miscarriages, both abandoned by doctors who feared criminal charges. “I nearly died,” one of the women said. “I was lucky,” said the other.
During the last two years, when I’ve told women I was writing about my pre-Roe abortion, stories poured out: Mine was in a dentist’s office; I had to go to Puerto Rico; mine was botched and I was so alone. That I’d prompted these revelations was surprise enough. More unnerving was that in almost every instance, the woman would lean forward: “You are the only person I’ve ever told,” she’d confide. “Only you will know,” a woman in her 50s whispered to me at a book signing last week.
Though friends who knew me in my 20s tell me I always seemed confident, it’s amazing to me that I was able to make such a decision on my own behalf before I even had a self. Now in my 70s, I realize that moment helped to form me, a woman who has made many decisions against the grain. I still seem confident to friends, but every time an important choice presents itself, I churn back to that long-ago lonely girl. How stunning now to join that mobilizing call where the importance of decisions like mine were acknowledged, where my life as a single working woman was not odd or unusual, where I was invited to shout as one of many.
Honor Moore is on the graduate writing faculty at the New School. Her newest book is “ A Termination .”
More to Read

Column: The abortion pill is safe. Is your uterus?
June 13, 2024
How treatment of miscarriages is upending the abortion debate
April 25, 2024

Inside an Arizona abortion clinic: Uncertainty looms and optimism reigns
April 22, 2024
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Calmes: Listen up, Kamala — let Trump beat Trump
Sept. 8, 2024

Abcarian: From ‘fridgescaping’ to egg parties, we’ve become social-media-driven parodies of ourselves

World & Nation
The controversial Catholic ‘postliberal’ thinkers who helped shape JD Vance’s views
Sept. 7, 2024

Judge’s ruling imperils Missouri abortion rights ballot initiative
Sept. 6, 2024
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- America’s Abortion Quandary
2. Social and moral considerations on abortion
Table of contents.
- 1. Americans’ views on whether, and in what circumstances, abortion should be legal
- Public views of what would change the number of abortions in the U.S.
- A majority of Americans say women should have more say in setting abortion policy in the U.S.
- How do certain arguments about abortion resonate with Americans?
- In their own words: How Americans feel about abortion
- 3. How the issue of abortion touches Americans personally
- Acknowledgments
- Methodology
Relatively few Americans view the morality of abortion in stark terms: Overall, just 7% of all U.S. adults say abortion is morally acceptable in all cases, and 13% say it is morally wrong in all cases. A third say that abortion is morally wrong in most cases, while about a quarter (24%) say it is morally acceptable most of the time. About an additional one-in-five do not consider abortion a moral issue.
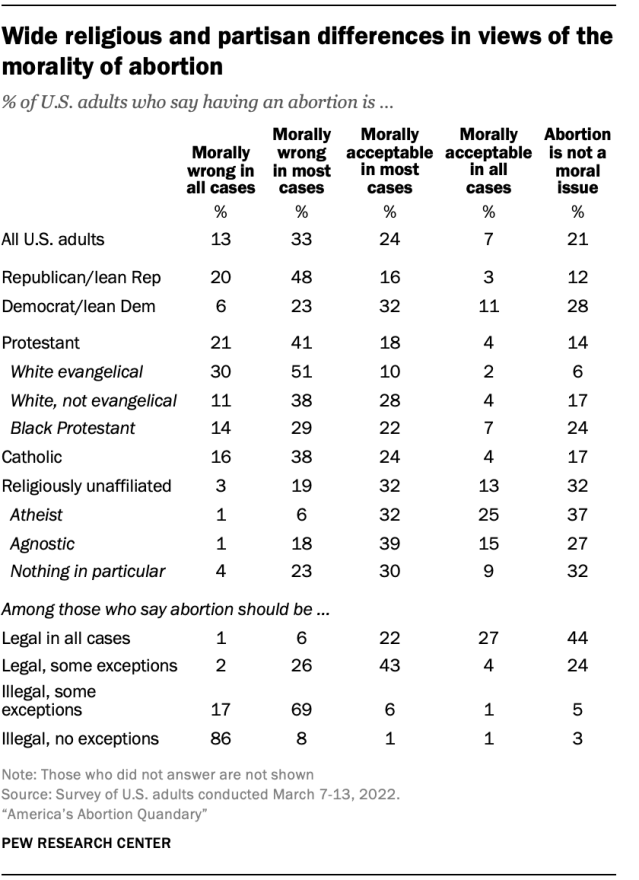
There are wide differences on this question by political party and religious affiliation. Among Republicans and independents who lean toward the Republican Party, most say that abortion is morally wrong either in most (48%) or all cases (20%). Among Democrats and Democratic leaners, meanwhile, only about three-in-ten (29%) hold a similar view. About four-in-ten Democrats say abortion is morally acceptable in most (32%) or all (11%) cases, while an additional 28% say abortion is not a moral issue.
White evangelical Protestants overwhelmingly say abortion is morally wrong in most (51%) or all cases (30%). A slim majority of Catholics (53%) also view abortion as morally wrong, but many also say it is morally acceptable in most (24%) or all cases (4%), or that it is not a moral issue (17%). And among religiously unaffiliated Americans, about three-quarters see abortion as morally acceptable (45%) or not a moral issue (32%).
There is strong alignment between people’s views of whether abortion is morally wrong and whether it should be illegal. For example, among U.S. adults who take the view that abortion should be illegal in all cases without exception, fully 86% also say abortion is always morally wrong. The prevailing view among adults who say abortion should be legal in all circumstances is that abortion is not a moral issue (44%), though notable shares of this group also say it is morally acceptable in all (27%) or most (22%) cases.
Most Americans who say abortion should be illegal with some exceptions take the view that abortion is morally wrong in most cases (69%). Those who say abortion should be legal with some exceptions are somewhat more conflicted, with 43% deeming abortion morally acceptable in most cases and 26% saying it is morally wrong in most cases; an additional 24% say it is not a moral issue.
The survey also asked respondents who said abortion is morally wrong in at least some cases whether there are situations where abortion should still be legal despite being morally wrong. Roughly half of U.S. adults (48%) say that there are, in fact, situations where abortion is morally wrong but should still be legal, while just 22% say that whenever abortion is morally wrong, it should also be illegal. An additional 28% either said abortion is morally acceptable in all cases or not a moral issue, and thus did not receive the follow-up question.
Across both political parties and all major Christian subgroups – including Republicans and White evangelicals – there are substantially more people who say that there are situations where abortion should still be legal despite being morally wrong than there are who say that abortion should always be illegal when it is morally wrong.

Asked about the impact a number of policy changes would have on the number of abortions in the U.S., nearly two-thirds of Americans (65%) say “more support for women during pregnancy, such as financial assistance or employment protections” would reduce the number of abortions in the U.S. Six-in-ten say the same about expanding sex education and similar shares say more support for parents (58%), making it easier to place children for adoption in good homes (57%) and passing stricter abortion laws (57%) would have this effect.
While about three-quarters of White evangelical Protestants (74%) say passing stricter abortion laws would reduce the number of abortions in the U.S., about half of religiously unaffiliated Americans (48%) hold this view. Similarly, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say this (67% vs. 49%, respectively). By contrast, while about seven-in-ten unaffiliated adults (69%) say expanding sex education would reduce the number of abortions in the U.S., only about half of White evangelicals (48%) say this. Democrats also are substantially more likely than Republicans to hold this view (70% vs. 50%).
Democrats are somewhat more likely than Republicans to say support for parents – such as paid family leave or more child care options – would reduce the number of abortions in the country (64% vs. 53%, respectively), while Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say making adoption into good homes easier would reduce abortions (64% vs. 52%).
Majorities across both parties and other subgroups analyzed in this report say that more support for women during pregnancy would reduce the number of abortions in America.
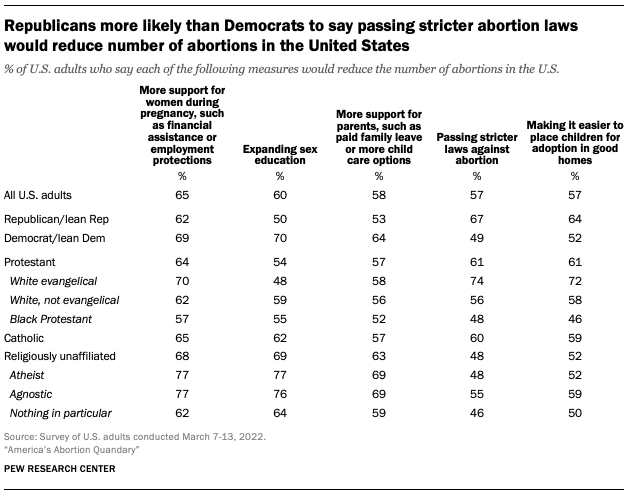
More than half of U.S. adults (56%) say women should have more say than men when it comes to setting policies around abortion in this country – including 42% who say women should have “a lot” more say. About four-in-ten (39%) say men and women should have equal say in abortion policies, and 3% say men should have more say than women.
Six-in-ten women and about half of men (51%) say that women should have more say on this policy issue.
Democrats are much more likely than Republicans to say women should have more say than men in setting abortion policy (70% vs. 41%). Similar shares of Protestants (48%) and Catholics (51%) say women should have more say than men on this issue, while the share of religiously unaffiliated Americans who say this is much higher (70%).
Seeking to gauge Americans’ reactions to several common arguments related to abortion, the survey presented respondents with six statements and asked them to rate how well each statement reflects their views on a five-point scale ranging from “extremely well” to “not at all well.”
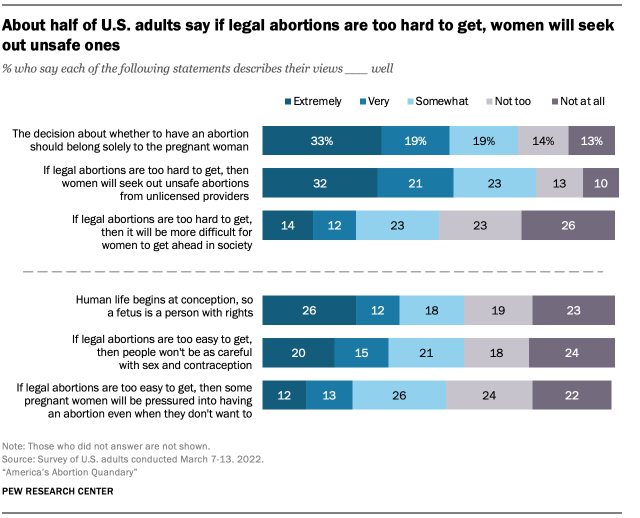
The list included three statements sometimes cited by individuals wishing to protect a right to abortion: “The decision about whether to have an abortion should belong solely to the pregnant woman,” “If legal abortions are too hard to get, then women will seek out unsafe abortions from unlicensed providers,” and “If legal abortions are too hard to get, then it will be more difficult for women to get ahead in society.” The first two of these resonate with the greatest number of Americans, with about half (53%) saying each describes their views “extremely” or “very” well. In other words, among the statements presented in the survey, U.S. adults are most likely to say that women alone should decide whether to have an abortion, and that making abortion illegal will lead women into unsafe situations.
The three other statements are similar to arguments sometimes made by those who wish to restrict access to abortions: “Human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights,” “If legal abortions are too easy to get, then people won’t be as careful with sex and contraception,” and “If legal abortions are too easy to get, then some pregnant women will be pressured into having an abortion even when they don’t want to.”
Fewer than half of Americans say each of these statements describes their views extremely or very well. Nearly four-in-ten endorse the notion that “human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights” (26% say this describes their views extremely well, 12% very well), while about a third say that “if legal abortions are too easy to get, then people won’t be as careful with sex and contraception” (20% extremely well, 15% very well).
When it comes to statements cited by proponents of abortion rights, Democrats are much more likely than Republicans to identify with all three of these statements, as are religiously unaffiliated Americans compared with Catholics and Protestants. Women also are more likely than men to express these views – and especially more likely to say that decisions about abortion should fall solely to pregnant women and that restrictions on abortion will put women in unsafe situations. Younger adults under 30 are particularly likely to express the view that if legal abortions are too hard to get, then it will be difficult for women to get ahead in society.
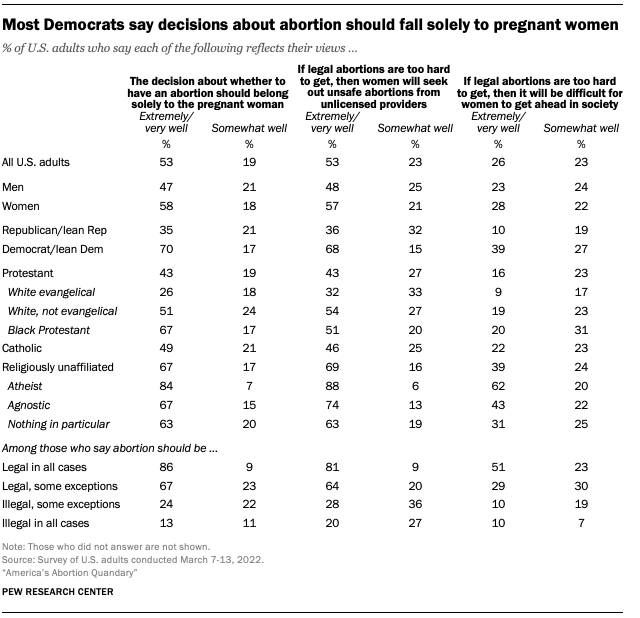
In the case of the three statements sometimes cited by opponents of abortion, the patterns generally go in the opposite direction. Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say each statement reflects their views “extremely” or “very” well, as are Protestants (especially White evangelical Protestants) and Catholics compared with the religiously unaffiliated. In addition, older Americans are more likely than young adults to say that human life begins at conception and that easy access to abortion encourages unsafe sex.
Gender differences on these questions, however, are muted. In fact, women are just as likely as men to say that human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights (39% and 38%, respectively).
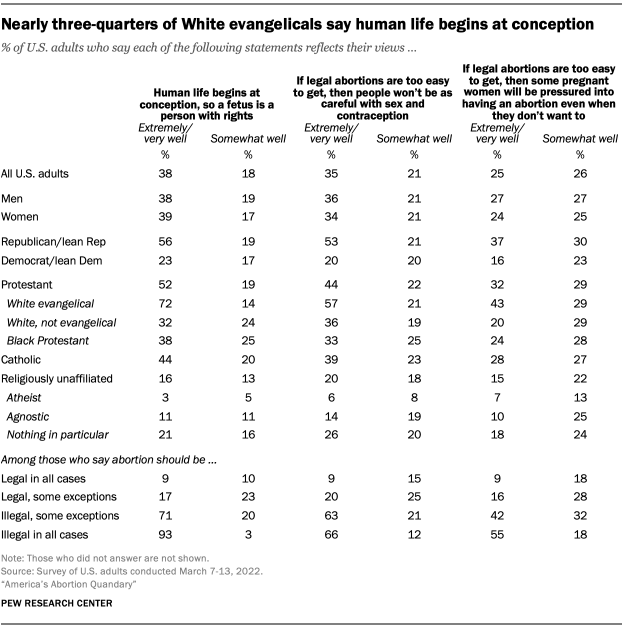
Analyzing certain statements together allows for an examination of the extent to which individuals can simultaneously hold two views that may seem to some as in conflict. For instance, overall, one-in-three U.S. adults say that both the statement “the decision about whether to have an abortion should belong solely to the pregnant woman” and the statement “human life begins at conception, so the fetus is a person with rights” reflect their own views at least somewhat well. This includes 12% of adults who say both statements reflect their views “extremely” or “very” well.
Republicans are slightly more likely than Democrats to say both statements reflect their own views at least somewhat well (36% vs. 30%), although Republicans are much more likely to say only the statement about the fetus being a person with rights reflects their views at least somewhat well (39% vs. 9%) and Democrats are much more likely to say only the statement about the decision to have an abortion belonging solely to the pregnant woman reflects their views at least somewhat well (55% vs. 19%).
Additionally, those who take the stance that abortion should be legal in all cases with no exceptions are overwhelmingly likely (76%) to say only the statement about the decision belonging solely to the pregnant woman reflects their views extremely, very or somewhat well, while a nearly identical share (73%) of those who say abortion should be illegal in all cases with no exceptions say only the statement about human life beginning at conception reflects their views at least somewhat well.
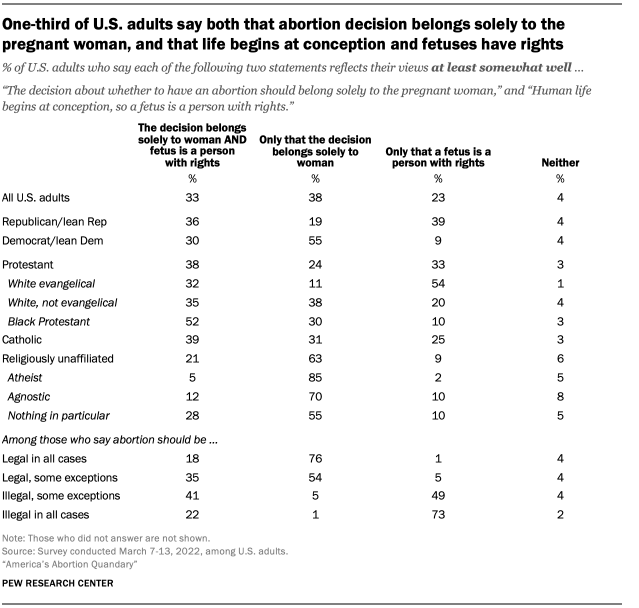
When asked to describe whether they had any other additional views or feelings about abortion, adults shared a range of strong or complex views about the topic. In many cases, Americans reiterated their strong support – or opposition to – abortion in the U.S. Others reflected on how difficult or nuanced the issue was, offering emotional responses or personal experiences to one of two open-ended questions asked on the survey.
One open-ended question asked respondents if they wanted to share any other views or feelings about abortion overall. The other open-ended question asked respondents about their feelings or views regarding abortion restrictions. The responses to both questions were similar.
Overall, about three-in-ten adults offered a response to either of the open-ended questions. There was little difference in the likelihood to respond by party, religion or gender, though people who say they have given a “lot” of thought to the issue were more likely to respond than people who have not.
Of those who did offer additional comments, about a third of respondents said something in support of legal abortion. By far the most common sentiment expressed was that the decision to have an abortion should be solely a personal decision, or a decision made jointly with a woman and her health care provider, with some saying simply that it “should be between a woman and her doctor.” Others made a more general point, such as one woman who said, “A woman’s body and health should not be subject to legislation.”
About one-in-five of the people who responded to the question expressed disapproval of abortion – the most common reason being a belief that a fetus is a person or that abortion is murder. As one woman said, “It is my belief that life begins at conception and as much as is humanly possible, we as a society need to support, protect and defend each one of those little lives.” Others in this group pointed to the fact that they felt abortion was too often used as a form of birth control. For example, one man said, “Abortions are too easy to obtain these days. It seems more women are using it as a way of birth control.”
About a quarter of respondents who opted to answer one of the open-ended questions said that their views about abortion were complex; many described having mixed feelings about the issue or otherwise expressed sympathy for both sides of the issue. One woman said, “I am personally opposed to abortion in most cases, but I think it would be detrimental to society to make it illegal. I was alive before the pill and before legal abortions. Many women died.” And one man said, “While I might feel abortion may be wrong in some cases, it is never my place as a man to tell a woman what to do with her body.”
The remaining responses were either not related to the topic or were difficult to interpret.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Christianity
- Evangelicalism
- Political Issues
- Politics & Policy
- Protestantism
- Religion & Abortion
- Religion & Politics
- Religion & Social Values
Americans see many federal agencies favorably, but Republicans grow more critical of Justice Department
9 facts about americans and marijuana, nearly three-quarters of americans say it would be ‘too risky’ to give presidents more power, biden nears 100-day mark with strong approval, positive rating for vaccine rollout, biden begins presidency with positive ratings; trump departs with lowest-ever job mark, most popular, report materials.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Newsletters
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
- Labor Day sales
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Crossing state lines to get an abortion is a new legal minefield, with courts to decide if there’s a right to travel
Almost half of the states in the country have made it harder to get an abortion since the Supreme Court in 2022 overturned the federal right to get an abortion. Fourteen states ban abortions in almost all circumstances, and another eight in almost all cases after 6 to 18 weeks of pregnancy .
Nonetheless, the number of abortions provided in the U.S. has actually grown since the court’s Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision, rising 11% since 2020, to over 1 million abortions a year .
This increase can partially be explained by the fact that the number of people who crossed state lines to get abortions more than doubled from 81,000 in 2020 to 171,000 in 2023 .
Justice Brett Kavanaugh wrote in the 2022 Dobbs decision that states cannot legally prevent their residents from going to another state to get an abortion, because he believes there is a “constitutional right to interstate travel.”
The U.S. Constitution does not, however, explicitly recognize a “right to interstate travel.” But the Supreme Court has issued decisions as far back as 1867 that can be interpreted to protect this right – and some scholars are confident that such a right exists.
But that hasn’t stopped states such as Idaho and Tennessee from enacting laws that make it harder to travel for an abortion – and some people have even attempted to legally punish their own partners for traveling to end a pregnancy .
As law professors who teach about reproductive justice , we view attempts to restrict abortion travel as one of the frontiers in the anti-abortion rights movement, raising new legal questions for courts to unravel.
States push to stop abortion travel
Idaho bans abortion at all stages of pregnancy . In April 2023, it also became the first state to impose travel restrictions with what it called an “abortion trafficking” law.
This law prevents people from helping minors who are not their children get abortions – without parental consent – including in another state.
Idaho’s attorney general has interpreted the law to mean that health care providers cannot refer patients to abortion clinics in other states. And based on this interpretation, the new law also means that a grandparent or teacher, for example, could not provide advice to a pregnant teenager.
An abortion access fund and a few others have challenged this law, saying that it violates the First Amendment and infringes on pregnant patients’ constitutional right to travel.
A federal district court temporarily blocked the law from going into effect in November 2023, but the case is currently being appealed at the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals .
More recently, in July 2024, Tennessee enacted copycat legislation , which is also being challenged .
Other states – Alabama, Mississippi and Oklahoma – have considered similar abortion trafficking laws but so far have not enacted any.
A spiraling effect
Idaho’s and Tennessee’s laws don’t directly prevent interstate travel, because they focus on people helping minors get an abortion. But some abortion rights activists still say these laws could lead to more explicit bans on interstate travel for abortion.
In the meantime, four Texas counties and a handful of Texas cities are imposing what they call “ abortion trafficking laws .”
Under these laws, people can sue anyone who travels through their cities or counties to get an abortion in another state. Supporters of these laws describe “abortion trafficking” in broad terms, because as one anti-abortion activist has said, “ the unborn child is always taken against their will ” by a pregnant person.
This understanding of “abortion trafficking” effectively treats the fetus as a person, in line with other fetal personhood efforts by anti-abortion rights groups. They are also carefully crafted to avoid constitutional challenges.
In some cases, it is individual people, not states, who are trying to block people from traveling to get an abortion.
In February 2024 , for example, a man named Collin Davis tried to prevent his ex-partner from traveling from Texas to Colorado to get an abortion .
While Davis failed to prevent the abortion, he later filed a lawsuit to investigate his ex-partner and people who assisted her in having the procedure . His goal is to “ pursue wrongful-death claims against anyone involved in the killing of his unborn child .”
An uncertain future
As the courts consider whether it is legal to ban interstate travel for abortion, it is useful to consider the 1975 Supreme Court case, Bigelow v. Virginia .
This case materialized after a Virginia newspaper published an advertisement for an abortion clinic in New York. The state of Virginia convicted the managing editor for violating a Virginia law that made it a misdemeanor for any person “by publication, lecture, advertisement, or by the sale or circulation of any publication” to encourage getting an abortion.
The Supreme Court struck down the Virginia law as violating the First Amendment, and it also noted that Virginia could not “ prevent its residents from traveling to New York to obtain” an abortion or “prosecute them for going there .” This language about the right to travel was not, however, essential to the court’s final decision, so it can’t necessarily be relied upon.
The Bigelow case was also decided just a few years after Roe v. Wade established a constitutional right to abortion. Such a right no longer exists after Dobbs.
This legal situation raises uncertainty about whether and how the Supreme Court would protect the right to travel for abortion.
States trying to protect abortion rights
There are approximately 22 states that have responded to other states’ abortion bans and other restrictive measures on interstate travel by adopting statutes called “shield” laws. These laws seek to prevent states with abortion bans from investigating their residents’ efforts to get an abortion in the shield state.
Along these same lines, the Biden administration issued a rule in 2024 that protects the privacy of people’s personal health information with respect to abortion when such care is legal.
The Dobbs decision returned the question of abortion to the states. But it has not settled many other legal issues related to abortion, such as whether there is a right to travel to get an abortion.
This article is republished from The Conversation , a nonprofit, independent news organization bringing you facts and trustworthy analysis to help you make sense of our complex world. It was written by: Naomi Cahn , University of Virginia and Sonia Suter , George Washington University
Anti-abortion rights activists navigate a new, post-Roe landscape, as state bans mean they can ‘save babies’
One year after the fall of Roe v. Wade, abortion care has become a patchwork of confusing state laws that deepen existing inequalities
As president, Harris could not easily make Roe v. Wade federal law − but she could still make it easier to get an abortion
The authors do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Argumentative Essay
Jazatte Dalisay is a ninth-grade student at the Manhattan Center for Science and Mathematics. This essay was composed in a class tutored by James Traub, a long-time PEN Member and coordinator of PEN’s Writers in the Schools program.
Women’s rights have greatly evolved throughout the centuries. As of 2014, women in the U.S. are entitled to their right to decide when to have a child. But there is a constant debate on whether or not abortion should remain legal in the United States. The legalization of abortion has not only kept women from danger, but has provided women with a concrete solution to unplanned pregnancies and protects their civil rights. Taking abortion off the shelf of opportunity for women will only make them seek illicit and dangerous methods to abort an unwanted child and takes away the ability of women to decide what to do with their own bodies.
It is understandable why some might think abortion is an inhumane act that is unnecessary and unlawful, especially since there are alternatives. Adoption has been seen as the perfect solution to unplanned pregnancies; women can simply give their unwanted child away to someone who wants it. With adoption, infertile couples get another chance at making a family, and the child still has a chance at life. This would seem to be the most logical, and humane thing to do. So why does abortion exist?
What people who are pro-life fail to see is the psychological and emotional damage that is inflicted on the woman during the pregnancy. If abortion were to be banned, women who have gotten pregnant through rape and/or incest would have to withstand the shame and pain of knowing that an unwanted child is growing inside them. Victims would be forced to have a constant reminder of their rape. A recent study shows that rape victims are 13 times more likely to attempt suicide, and 26 times more likely to abuse substances such as alcohol and drugs (mscu.edu). Banning abortion would mean destroying the chances of women who are victims of rape to get closure. The psychological and emotional stress can fuel their desperation to rid themselves of the fetus and make them go to great lengths to do that. According to Daniel R. Mishell, Jr., MD, Chair of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, “before abortion was legalized women would frequently try to induce abortions by using coat hangers, knitting needles, or radiator flush, or by going to unsafe “back-alley” abortionists.” In the end, banning abortion will not stop women from trying to rid themselves of the fetus, but just put their own well-being in jeopardy.
Abortion is also a concrete solution to unplanned pregnancies. Though the use of contraceptions, such as the morning-after pill, have been proven to work, it is not always as effective. “Fifty-one percent of women who have abortions had used a contraceptive method in the month they got pregnant, most commonly condoms (27 percent) or a hormonal method (17 percent)” (guttmacher.org). Often, women and teenage girls are too afraid to speak up or don’t even know that they are pregnant, and once they realize they are, it’s already too late—contraceptions are not effective after a certain amount of time. Abortion is their last chance of terminating the pregnancy in a safe and legal way.
Lastly, keeping abortion legal protects women’s rights. Women have full control over their bodies, meaning what they do with them is their decision. If abortion were illegal, women would be stripped of this right. According to Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O’Conner, “The ability of women to participate equally in the economic and social life of the Nation has been facilitated by their ability to control their reproductive lives” (procon.org). Abortion is also viewed as a fundamental right under law. The Constitution gives “a guarantee of certain areas or zones of privacy,” and that “This right of privacy…is broad enough to encompass a woman’s decision whether or not to terminate her pregnancy” (procon.org). Making abortion illegal means robbing women of their rights.
Keeping abortion legal ensures a woman’s safety when faced with unplanned pregnancies, provides hope for rape victims and helps them in moving on with their lives, and protects women’s rights. Making abortion illegal does not stop women from trying to terminate a pregnancy, nor does it save lives. Rather, it does the opposite — illegalizing abortion puts women in danger and prevents them from having control over their own bodies.
Join PEN America Today
Defend free expression, support persecuted writers, and promote literary culture.

Support for the freedom to read with exclusive designs by Todd Parr, Mike Curato, Art Spiegelman, and more!
Are you an artist at risk or know someone who is?
CONTACT ARC

The ‘Truth Sandwich’ and 11 Other Ways to Combat Election Misinformation with your Reporting

Russia Escalates Crackdown on Free Expression with Publisher Shutdowns

PEN America Speaks: How We Defended And Celebrated Free Expression the Week Of Aug. 26

PEN America’s Russian Independent Media Archive: Preserving Words of Those Who Can’t Speak
7 big issues at stake in the 2024 election

WASHINGTON — The policy contrasts between President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump are sharpening as the general election campaign gets fully underway.
But what does the choice represent for ordinary voters and the economic and cultural issues they care about? A rematch between the Democratic incumbent and his Republican predecessor may feel uninspiring to many voters, but the policy stakes are enormous for tens of millions of Americans — and the world.
Here are seven big issues at stake in the 2024 election.
The contrast: Biden favors federal abortion protections; Trump opposes them. Trump supported nationwide restrictions on abortion as president but now downplays the need for a federal ban, as Republicans are divided over the issue. Biden does not support federal limits.
Biden has championed the Women’s Health Protection Act, a bill to protect abortion rights in all 50 states under federal law and prohibit medically unnecessary hurdles to accessing the procedure. He has asked voters to send him a Democratic Congress that supports legal abortion to achieve that.
Trump has boasted that he "broke Roe v. Wade" by picking three of the five Supreme Court justices who overturned it, delivering on a four-decade goal of the GOP. More recently, Trump has openly fretted that the backlash may cost him and his party the election. Last week, Trump said the issue should be left to states, a shift from his support for nationwide restrictions when he was president. His new stance has drawn pushback from GOP allies, like Sen. Lindsey Graham, of South Carolina , and anti-abortion-rights advocates, who say that he is wrong and that Republicans should not be deterred from their long-standing goal of enacting some nationwide abortion limits.
Some Republicans downplay the prospects of federal abortion restrictions’ passing Congress, even if they win full control. Biden and his allies are telling voters to look at the GOP’s long history of championing federal restrictions and not their recent rhetoric.
Immigration
The contrast: Trump has promised a sweeping crackdown on illegal immigration and tougher executive actions; Biden is asking Congress to give him more tools to manage an overwhelmed border and create new legal pathways to immigrate to the U.S.
Trump has called existing border laws an existential threat to the U.S., saying migrants are “ poisoning the blood of our country” and bringing new “ languages .” His campaign website says: “President Trump will shut down Biden’s border disaster. He will again end catch-and-release, restore Remain in Mexico , and eliminate asylum fraud. In cooperative states, President Trump will deputize the National Guard and local law enforcement to assist with rapidly removing illegal alien gang members and criminals.”
After having rescinded some of Trump's policies, Biden has recently shifted to support stricter immigration laws as the system remains overwhelmed. He championed a bipartisan bill to raise the bar for gaining asylum, grant more U.S. resources to process asylum claims and turn away migrants who do not qualify, and empower the president to temporarily shut down the border if migration levels hit certain triggers. (Republicans blocked the bill in the Senate amid lobbying by Trump , who wants to use the border as an election issue.) Biden has also endorsed the U.S. Citizenship Act , which would grant a pathway to citizenship for people in the U.S. illegally if they pass background checks and pay their taxes.
Fundamentally, Trump has aligned with forces who want less immigration into the country, while Biden has embraced the belief that immigrants make the U.S. better.
Health care and prescription drugs
The contrast: Biden wants to extend Affordable Care Act provisions and empower Medicare to negotiate more prescription drugs; Trump has aggressively criticized the ACA but not offered a health care plan.
Biden, who was vice president when the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, sees it as a cherished achievement to protect and strengthen. The law, also known as "Obamacare," which has extended coverage to 45 million people through subsidies, insurance mandates and a Medicaid expansion, continues to face conservative opposition.
Separately, Biden has touted a provision in his party-line Inflation Reduction Act that empowers Medicare to negotiate lower prices for 10 prescription drugs. He said he wants to boost that to 50 if he is re-elected, with the goal of $200 billion in savings.
Trump spent his four years as president fighting unsuccessfully to repeal and unravel the law — through legislation and executive action and endorsing lawsuits to wipe it out. In November, Trump called for revisiting plans to "terminate" the ACA . He has recently sought to downplay that and insists he only wants to improve the law. But he has not offered a health care plan. Many of his GOP allies in Congress still favor repealing or undoing the ACA, including a budget by the Republican Study Committee, which boasts about 80% of the House GOP conference as members, including Speaker Mike Johnson, of Louisiana.
The contrast: Trump's 2017 tax cuts expire at the end of next year, and he has called for extending them; Biden has called for raising taxes on families earning over $400,000 to fund various priorities.
A series of Trump tax cuts, which Republicans passed on a party-line basis in 2017, expire at the end of 2025. Congress and the winner of the election will decide what happens to them.
In a recent private speech to wealthy donors, Trump s aid his policies include "extending the Trump tax cuts" if he is elected, according to a Trump campaign official. That would preserve lower rates across the income spectrum, with the biggest benefits for top earners.
Biden has attacked that law as a giveaway to the wealthiest Americans, vowing to make "big corporations and the very wealthy finally pay their fair share." He has backed a corporate tax rate hike from 21% to 28% and said that "nobody earning less than $400,000 will pay an additional penny in federal taxes." Biden is also calling for a $3,600-per-child tax cut for families, an $800 average tax break for "front-line workers" and a 25% minimum tax on billionaires, according to a newly released campaign plank.
The expiration of the Trump tax cuts will restore the unlimited federal deduction for state and local taxes, which Republicans had capped at $10,000 in the 2017 law. Republicans broadly support preserving the cap, with some exceptions, while most Democrats want to lift it.
Judges and the Supreme Court
The contrast: Their track records tell a clear story. Trump has picked young conservative judges to serve on the federal bench, while Biden has picked liberals with a focus on professional and personal diversity.
One of the clearest contrasts is what kinds of judges Trump and Biden would pick for lifetime appointments on the federal courts. A simple way for voters to think about it is whether they prefer new judges with the conservative views of Justice Neil Gorsuch, Trump's first Supreme Court pick, or with the liberal views of Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson, Biden's (so far only) high court pick.
As president, Trump nominated young conservative judges who will serve for generations. Biden has focused on finding judges with diverse backgrounds and résumés, including more civil rights lawyers and public defenders.
Perhaps the biggest question is whether a Supreme Court vacancy will open up in the next four years. The presidential election winner and the party that controls the Senate would fill it.
The contrast: Trump is pushing a 10% across-the-board tariff on imports; Biden's White House opposes that, saying it would raise inflation.
Trump, long a skeptic of U.S. trade deals, has proposed to impose a 10% tariff on all imported goods if he returns to the White House. He recently told Fox News that it could be 60% — or potentially “more than that” — on imports of Chinese goods.
Biden opposes that idea. In a memo over the weekend, the White House slammed the idea of "across-the-board tariffs that would raise taxes and prices by $1,500 per American family," without naming Trump; it referred to an estimate by the Center for American Progress, a liberal think tank, that Trump's 10% tax on imports could cost an average American household $1,500 per year.
Biden, instead, has sought to boost domestic manufacturing with major federal investments in semiconductors and electric vehicles.
Foreign policy and NATO
The contrast: Biden favors Ukraine aid, while Trump is skeptical of it; Biden supports NATO and a traditional view of American power, while Trump has criticized NATO and voiced some isolationist views.
The clearest example of the foreign policy differences between the two concerns the fate of Ukraine, which is running low on ammunition and says it needs U.S. assistance to continue holding off Russia’s aggression. Biden is an ardent proponent of helping Ukraine, while Trump has poured cold water on U.S. aid to Ukraine and successfully pressured House Republicans to block it since they took the majority in January 2023.
And that points to a deeper divide: Biden is an outspoken supporter of the NATO alliance as a bulwark against adversaries like Russia and China and of preserving the post-World War II order. Trump has dialed up his criticisms of NATO and aligned with a growing isolationist wing in the U.S. that wants to be less involved in global affairs. Trump recently said that as president, he “would encourage” Russia “to do whatever the hell they want” to member countries who are “delinquent” in their dues.
Sahil Kapur is a senior national political reporter for NBC News.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Views on whether abortion should be legal, and in what ...
Opinion | The Case Against Abortion
Key facts about the abortion debate in America
So, should abortion be legal or illegal? As a college student, I recognize the importance of discussing the contentious issue of abortion and its legality.The complexity of this topic calls for a thoughtful examination of various perspectives, as well as a thorough understanding of the historical, legal, ethical, socio-economic, and personal aspects that are intricately intertwined with the ...
The battle to make abortion illegal has been waged over a surprisingly nebulous assumption that banning abortion would, in itself, lead to meaningful changes in the practice of abortion in America. ... And if we stay true to the patterns laid out in this essay, those faces will be disproportionately poor, Black and brown women and children.
Persuasion and the law. A majority of Americans favor some restrictions on abortion but support Roe v. Wade, according to national polls. But activists dedicated to the goal of ending abortion in ...
By Sofia Cipriano — Following Dobbs v. Jackson's (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are ...
Pro-Choice Does Not Mean Pro-Abortion: An Argument for ...
Legal and social barriers that impede access to safe abortions are detrimental to the health and survival of women and girls; thus, constructing policies ensuring access to safe abortion services should be an urgent priority. Placing undue hurdles between women and access to abortion care is associated with undesirable health outcomes.
Human Rights Watch released a new question-and-answer document that articulates the human rights imperative, guided by international law, to ensure access to abortion, which is critical to ...
In "Association of Texas' 2021 Ban on Abortion in Early Pregnancy with the Number of Facility-Based Abortion in Texas and Surrounding States," White et al. used a large dataset containing information before and after the passage of SB8 in September 2021. 1 This bill banned most abortions after 6 weeks in the state of Texas.
Do You Think That Abortion Should Be Made Illegal? An Argumentative Essay. The debate over whether abortion should be made illegal is a deeply divisive issue, marked by moral, ethical, and legal considerations. On one hand, proponents of making abortion illegal argue that it is a moral and ethical wrong, asserting that the fetus has a right to ...
How Abortion Views Are Different
The best pro-choice arguments, in summary: A "right to life" doesn't imply a right to use someone else's body to sustain a life. Women do not have a "responsibility" to have children, and ...
Abortion Rights - Amnesty International ... Abortion Rights
Published June 8, 2022 Updated July 1, 2022. The United States Supreme Court overruled the landmark Roe v. Wade case on June 24, eliminating the constitutional right to abortion in a monumental ...
The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey, the court's major decisions ...
Why Lawmakers Should Legalize Abortion
Abortion is a common medical or surgical intervention used to terminate pregnancy. Although a controversial and widely debated topic, approximately 73 million induced abortions occur worldwide each year, with 29% of all pregnancies and over 60% of unintended pregnancies ending in abortion. Abortions are considered safe if they are carried out using a method recommended by WHO, appropriate to ...
See where abortions are legal or banned
The most radical position on abortion before Roe vs. Wade was repeal not reform — the argument being that any abortion law, no matter how liberal, denied women control of our own bodies.
2. Social and moral considerations on abortion
Access to legal abortion in the US now depends on where you are. As of August 2024, 17 states have outlawed nearly all abortions, banning the procedure at six weeks of pregnancy or earlier.
Yes. Legal restrictions on abortion often result in more illegal abortions, which may also be unsafe and may drive higher maternal mortality and morbidity. As a result, lack of access to safe and ...
Iowa and Idaho have passed abortion trafficking laws that stop people from helping minors get abortions. These laws open the door for questions about the right to travel to get an abortion.
This essay was composed in a class tutored by James Traub, a long-time PEN Member and coordinator of PEN's Writers in the Schools program. ... If abortion were illegal, women would be stripped of this right. According to Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O'Conner, "The ability of women to participate equally in the economic and social life ...
7 big issues at stake in the 2024 election
(THE CONVERSATION) Almost half of the states in the country have made it harder to get an abortion since the Supreme Court in 2022 overturned the federal right to get an abortion. Fourteen states ...
Ms. Cheney, a daughter of former Vice President Dick Cheney, is a member of a private and deeply conservative political family. She is pro-gun and anti-abortion and favors a stronger national defense.