SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
A critical review of research on student self-assessment.

- Educational Psychology and Methodology, University at Albany, Albany, NY, United States
This article is a review of research on student self-assessment conducted largely between 2013 and 2018. The purpose of the review is to provide an updated overview of theory and research. The treatment of theory involves articulating a refined definition and operationalization of self-assessment. The review of 76 empirical studies offers a critical perspective on what has been investigated, including the relationship between self-assessment and achievement, consistency of self-assessment and others' assessments, student perceptions of self-assessment, and the association between self-assessment and self-regulated learning. An argument is made for less research on consistency and summative self-assessment, and more on the cognitive and affective mechanisms of formative self-assessment.
This review of research on student self-assessment expands on a review published as a chapter in the Cambridge Handbook of Instructional Feedback ( Andrade, 2018 , reprinted with permission). The timespan for the original review was January 2013 to October 2016. A lot of research has been done on the subject since then, including at least two meta-analyses; hence this expanded review, in which I provide an updated overview of theory and research. The treatment of theory presented here involves articulating a refined definition and operationalization of self-assessment through a lens of feedback. My review of the growing body of empirical research offers a critical perspective, in the interest of provoking new investigations into neglected areas.

Defining and Operationalizing Student Self-Assessment
Without exception, reviews of self-assessment ( Sargeant, 2008 ; Brown and Harris, 2013 ; Panadero et al., 2016a ) call for clearer definitions: What is self-assessment, and what is not? This question is surprisingly difficult to answer, as the term self-assessment has been used to describe a diverse range of activities, such as assigning a happy or sad face to a story just told, estimating the number of correct answers on a math test, graphing scores for dart throwing, indicating understanding (or the lack thereof) of a science concept, using a rubric to identify strengths and weaknesses in one's persuasive essay, writing reflective journal entries, and so on. Each of those activities involves some kind of assessment of one's own functioning, but they are so different that distinctions among types of self-assessment are needed. I will draw those distinctions in terms of the purposes of self-assessment which, in turn, determine its features: a classic form-fits-function analysis.
What is Self-Assessment?
Brown and Harris (2013) defined self-assessment in the K-16 context as a “descriptive and evaluative act carried out by the student concerning his or her own work and academic abilities” (p. 368). Panadero et al. (2016a) defined it as a “wide variety of mechanisms and techniques through which students describe (i.e., assess) and possibly assign merit or worth to (i.e., evaluate) the qualities of their own learning processes and products” (p. 804). Referring to physicians, Epstein et al. (2008) defined “concurrent self-assessment” as “ongoing moment-to-moment self-monitoring” (p. 5). Self-monitoring “refers to the ability to notice our own actions, curiosity to examine the effects of those actions, and willingness to use those observations to improve behavior and thinking in the future” (p. 5). Taken together, these definitions include self-assessment of one's abilities, processes , and products —everything but the kitchen sink. This very broad conception might seem unwieldy, but it works because each object of assessment—competence, process, and product—is subject to the influence of feedback from oneself.
What is missing from each of these definitions, however, is the purpose of the act of self-assessment. Their authors might rightly point out that the purpose is implied, but a formal definition requires us to make it plain: Why do we ask students to self-assess? I have long held that self-assessment is feedback ( Andrade, 2010 ), and that the purpose of feedback is to inform adjustments to processes and products that deepen learning and enhance performance; hence the purpose of self-assessment is to generate feedback that promotes learning and improvements in performance. This learning-oriented purpose of self-assessment implies that it should be formative: if there is no opportunity for adjustment and correction, self-assessment is almost pointless.
Why Self-Assess?
Clarity about the purpose of self-assessment allows us to interpret what otherwise appear to be discordant findings from research, which has produced mixed results in terms of both the accuracy of students' self-assessments and their influence on learning and/or performance. I believe the source of the discord can be traced to the different ways in which self-assessment is carried out, such as whether it is summative and formative. This issue will be taken up again in the review of current research that follows this overview. For now, consider a study of the accuracy and validity of summative self-assessment in teacher education conducted by Tejeiro et al. (2012) , which showed that students' self-assigned marks tended to be higher than marks given by professors. All 122 students in the study assigned themselves a grade at the end of their course, but half of the students were told that their self-assigned grade would count toward 5% of their final grade. In both groups, students' self-assessments were higher than grades given by professors, especially for students with “poorer results” (p. 791) and those for whom self-assessment counted toward the final grade. In the group that was told their self-assessments would count toward their final grade, no relationship was found between the professor's and the students' assessments. Tejeiro et al. concluded that, although students' and professor's assessments tend to be highly similar when self-assessment did not count toward final grades, overestimations increased dramatically when students' self-assessments did count. Interviews of students who self-assigned highly discrepant grades revealed (as you might guess) that they were motivated by the desire to obtain the highest possible grades.
Studies like Tejeiro et al's. (2012) are interesting in terms of the information they provide about the relationship between consistency and honesty, but the purpose of the self-assessment, beyond addressing interesting research questions, is unclear. There is no feedback purpose. This is also true for another example of a study of summative self-assessment of competence, during which elementary-school children took the Test of Narrative Language and then were asked to self-evaluate “how you did in making up stories today” by pointing to one of five pictures, from a “very happy face” (rating of five) to a “very sad face” (rating of one) ( Kaderavek et al., 2004 . p. 37). The usual results were reported: Older children and good narrators were more accurate than younger children and poor narrators, and males tended to more frequently overestimate their ability.
Typical of clinical studies of accuracy in self-evaluation, this study rests on a definition and operationalization of self-assessment with no value in terms of instructional feedback. If those children were asked to rate their stories and then revise or, better yet, if they assessed their stories according to clear, developmentally appropriate criteria before revising, the valence of their self-assessments in terms of instructional feedback would skyrocket. I speculate that their accuracy would too. In contrast, studies of formative self-assessment suggest that when the act of self-assessing is given a learning-oriented purpose, students' self-assessments are relatively consistent with those of external evaluators, including professors ( Lopez and Kossack, 2007 ; Barney et al., 2012 ; Leach, 2012 ), teachers ( Bol et al., 2012 ; Chang et al., 2012 , 2013 ), researchers ( Panadero and Romero, 2014 ; Fitzpatrick and Schulz, 2016 ), and expert medical assessors ( Hawkins et al., 2012 ).
My commitment to keeping self-assessment formative is firm. However, Gavin Brown (personal communication, April 2011) reminded me that summative self-assessment exists and we cannot ignore it; any definition of self-assessment must acknowledge and distinguish between formative and summative forms of it. Thus, the taxonomy in Table 1 , which depicts self-assessment as serving formative and/or summative purposes, and focuses on competence, processes, and/or products.
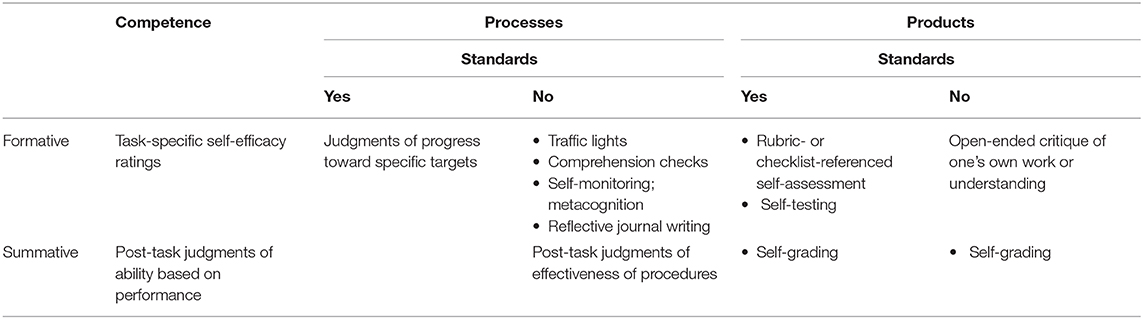
Table 1 . A taxonomy of self-assessment.
Fortunately, a formative view of self-assessment seems to be taking hold in various educational contexts. For instance, Sargeant (2008) noted that all seven authors in a special issue of the Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions “conceptualize self-assessment within a formative, educational perspective, and see it as an activity that draws upon both external and internal data, standards, and resources to inform and make decisions about one's performance” (p. 1). Sargeant also stresses the point that self-assessment should be guided by evaluative criteria: “Multiple external sources can and should inform self-assessment, perhaps most important among them performance standards” (p. 1). Now we are talking about the how of self-assessment, which demands an operationalization of self-assessment practice. Let us examine each object of self-assessment (competence, processes, and/or products) with an eye for what is assessed and why.
What is Self-Assessed?
Monitoring and self-assessing processes are practically synonymous with self-regulated learning (SRL), or at least central components of it such as goal-setting and monitoring, or metacognition. Research on SRL has clearly shown that self-generated feedback on one's approach to learning is associated with academic gains ( Zimmerman and Schunk, 2011 ). Self-assessment of the products , such as papers and presentations, are the easiest to defend as feedback, especially when those self-assessments are grounded in explicit, relevant, evaluative criteria and followed by opportunities to relearn and/or revise ( Andrade, 2010 ).
Including the self-assessment of competence in this definition is a little trickier. I hesitated to include it because of the risk of sneaking in global assessments of one's overall ability, self-esteem, and self-concept (“I'm good enough, I'm smart enough, and doggone it, people like me,” Franken, 1992 ), which do not seem relevant to a discussion of feedback in the context of learning. Research on global self-assessment, or self-perception, is popular in the medical education literature, but even there, scholars have begun to question its usefulness in terms of influencing learning and professional growth (e.g., see Sargeant et al., 2008 ). Eva and Regehr (2008) seem to agree in the following passage, which states the case in a way that makes it worthy of a long quotation:
Self-assessment is often (implicitly or otherwise) conceptualized as a personal, unguided reflection on performance for the purposes of generating an individually derived summary of one's own level of knowledge, skill, and understanding in a particular area. For example, this conceptualization would appear to be the only reasonable basis for studies that fit into what Colliver et al. (2005) has described as the “guess your grade” model of self-assessment research, the results of which form the core foundation for the recurring conclusion that self-assessment is generally poor. This unguided, internally generated construction of self-assessment stands in stark contrast to the model put forward by Boud (1999) , who argued that the phrase self-assessment should not imply an isolated or individualistic activity; it should commonly involve peers, teachers, and other sources of information. The conceptualization of self-assessment as enunciated in Boud's description would appear to involve a process by which one takes personal responsibility for looking outward, explicitly seeking feedback, and information from external sources, then using these externally generated sources of assessment data to direct performance improvements. In this construction, self-assessment is more of a pedagogical strategy than an ability to judge for oneself; it is a habit that one needs to acquire and enact rather than an ability that one needs to master (p. 15).
As in the K-16 context, self-assessment is coming to be seen as having value as much or more so in terms of pedagogy as in assessment ( Silver et al., 2008 ; Brown and Harris, 2014 ). In the end, however, I decided that self-assessing one's competence to successfully learn a particular concept or complete a particular task (which sounds a lot like self-efficacy—more on that later) might be useful feedback because it can inform decisions about how to proceed, such as the amount of time to invest in learning how to play the flute, or whether or not to seek help learning the steps of the jitterbug. An important caveat, however, is that self-assessments of competence are only useful if students have opportunities to do something about their perceived low competence—that is, it serves the purpose of formative feedback for the learner.
How to Self-Assess?
Panadero et al. (2016a) summarized five very different taxonomies of self-assessment and called for the development of a comprehensive typology that considers, among other things, its purpose, the presence or absence of criteria, and the method. In response, I propose the taxonomy depicted in Table 1 , which focuses on the what (competence, process, or product), the why (formative or summative), and the how (methods, including whether or not they include standards, e.g., criteria) of self-assessment. The collections of examples of methods in the table is inexhaustive.
I put the methods in Table 1 where I think they belong, but many of them could be placed in more than one cell. Take self-efficacy , for instance, which is essentially a self-assessment of one's competence to successfully undertake a particular task ( Bandura, 1997 ). Summative judgments of self-efficacy are certainly possible but they seem like a silly thing to do—what is the point, from a learning perspective? Formative self-efficacy judgments, on the other hand, can inform next steps in learning and skill building. There is reason to believe that monitoring and making adjustments to one's self-efficacy (e.g., by setting goals or attributing success to effort) can be productive ( Zimmerman, 2000 ), so I placed self-efficacy in the formative row.
It is important to emphasize that self-efficacy is task-specific, more or less ( Bandura, 1997 ). This taxonomy does not include general, holistic evaluations of one's abilities, for example, “I am good at math.” Global assessment of competence does not provide the leverage, in terms of feedback, that is provided by task-specific assessments of competence, that is, self-efficacy. Eva and Regehr (2008) provided an illustrative example: “We suspect most people are prompted to open a dictionary as a result of encountering a word for which they are uncertain of the meaning rather than out of a broader assessment that their vocabulary could be improved” (p. 16). The exclusion of global evaluations of oneself resonates with research that clearly shows that feedback that focuses on aspects of a task (e.g., “I did not solve most of the algebra problems”) is more effective than feedback that focuses on the self (e.g., “I am bad at math”) ( Kluger and DeNisi, 1996 ; Dweck, 2006 ; Hattie and Timperley, 2007 ). Hence, global self-evaluations of ability or competence do not appear in Table 1 .
Another approach to student self-assessment that could be placed in more than one cell is traffic lights . The term traffic lights refers to asking students to use green, yellow, or red objects (or thumbs up, sideways, or down—anything will do) to indicate whether they think they have good, partial, or little understanding ( Black et al., 2003 ). It would be appropriate for traffic lights to appear in multiple places in Table 1 , depending on how they are used. Traffic lights seem to be most effective at supporting students' reflections on how well they understand a concept or have mastered a skill, which is line with their creators' original intent, so they are categorized as formative self-assessments of one's learning—which sounds like metacognition.
In fact, several of the methods included in Table 1 come from research on metacognition, including self-monitoring , such as checking one's reading comprehension, and self-testing , e.g., checking one's performance on test items. These last two methods have been excluded from some taxonomies of self-assessment (e.g., Boud and Brew, 1995 ) because they do not engage students in explicitly considering relevant standards or criteria. However, new conceptions of self-assessment are grounded in theories of the self- and co-regulation of learning ( Andrade and Brookhart, 2016 ), which includes self-monitoring of learning processes with and without explicit standards.
However, my research favors self-assessment with regard to standards ( Andrade and Boulay, 2003 ; Andrade and Du, 2007 ; Andrade et al., 2008 , 2009 , 2010 ), as does related research by Panadero and his colleagues (see below). I have involved students in self-assessment of stories, essays, or mathematical word problems according to rubrics or checklists with criteria. For example, two studies investigated the relationship between elementary or middle school students' scores on a written assignment and a process that involved them in reading a model paper, co-creating criteria, self-assessing first drafts with a rubric, and revising ( Andrade et al., 2008 , 2010 ). The self-assessment was highly scaffolded: students were asked to underline key phrases in the rubric with colored pencils (e.g., underline “clearly states an opinion” in blue), then underline or circle in their drafts the evidence of having met the standard articulated by the phrase (e.g., his or her opinion) with the same blue pencil. If students found they had not met the standard, they were asked to write themselves a reminder to make improvements when they wrote their final drafts. This process was followed for each criterion on the rubric. There were main effects on scores for every self-assessed criterion on the rubric, suggesting that guided self-assessment according to the co-created criteria helped students produce more effective writing.
Panadero and his colleagues have also done quasi-experimental and experimental research on standards-referenced self-assessment, using rubrics or lists of assessment criteria that are presented in the form of questions ( Panadero et al., 2012 , 2013 , 2014 ; Panadero and Romero, 2014 ). Panadero calls the list of assessment criteria a script because his work is grounded in research on scaffolding (e.g., Kollar et al., 2006 ): I call it a checklist because that is the term used in classroom assessment contexts. Either way, the list provides standards for the task. Here is a script for a written summary that Panadero et al. (2014) used with college students in a psychology class:
• Does my summary transmit the main idea from the text? Is it at the beginning of my summary?
• Are the important ideas also in my summary?
• Have I selected the main ideas from the text to make them explicit in my summary?
• Have I thought about my purpose for the summary? What is my goal?
Taken together, the results of the studies cited above suggest that students who engaged in self-assessment using scripts or rubrics were more self-regulated, as measured by self-report questionnaires and/or think aloud protocols, than were students in the comparison or control groups. Effect sizes were very small to moderate (η 2 = 0.06–0.42), and statistically significant. Most interesting, perhaps, is one study ( Panadero and Romero, 2014 ) that demonstrated an association between rubric-referenced self-assessment activities and all three phases of SRL; forethought, performance, and reflection.
There are surely many other methods of self-assessment to include in Table 1 , as well as interesting conversations to be had about which method goes where and why. In the meantime, I offer the taxonomy in Table 1 as a way to define and operationalize self-assessment in instructional contexts and as a framework for the following overview of current research on the subject.
An Overview of Current Research on Self-Assessment
Several recent reviews of self-assessment are available ( Brown and Harris, 2013 ; Brown et al., 2015 ; Panadero et al., 2017 ), so I will not summarize the entire body of research here. Instead, I chose to take a birds-eye view of the field, with goal of reporting on what has been sufficiently researched and what remains to be done. I used the references lists from reviews, as well as other relevant sources, as a starting point. In order to update the list of sources, I directed two new searches 1 , the first of the ERIC database, and the second of both ERIC and PsychINFO. Both searches included two search terms, “self-assessment” OR “self-evaluation.” Advanced search options had four delimiters: (1) peer-reviewed, (2) January, 2013–October, 2016 and then October 2016–March 2019, (3) English, and (4) full-text. Because the focus was on K-20 educational contexts, sources were excluded if they were about early childhood education or professional development.
The first search yielded 347 hits; the second 1,163. Research that was unrelated to instructional feedback was excluded, such as studies limited to self-estimates of performance before or after taking a test, guesses about whether a test item was answered correctly, and estimates of how many tasks could be completed in a certain amount of time. Although some of the excluded studies might be thought of as useful investigations of self-monitoring, as a group they seemed too unrelated to theories of self-generated feedback to be appropriate for this review. Seventy-six studies were selected for inclusion in Table S1 (Supplementary Material), which also contains a few studies published before 2013 that were not included in key reviews, as well as studies solicited directly from authors.
The Table S1 in the Supplementary Material contains a complete list of studies included in this review, organized by the focus or topic of the study, as well as brief descriptions of each. The “type” column Table S1 (Supplementary Material) indicates whether the study focused on formative or summative self-assessment. This distinction was often difficult to make due to a lack of information. For example, Memis and Seven (2015) frame their study in terms of formative assessment, and note that the purpose of the self-evaluation done by the sixth grade students is to “help students improve their [science] reports” (p. 39), but they do not indicate how the self-assessments were done, nor whether students were given time to revise their reports based on their judgments or supported in making revisions. A sentence or two of explanation about the process of self-assessment in the procedures sections of published studies would be most useful.
Figure 1 graphically represents the number of studies in the four most common topic categories found in the table—achievement, consistency, student perceptions, and SRL. The figure reveals that research on self-assessment is on the rise, with consistency the most popular topic. Of the 76 studies in the table in the appendix, 44 were inquiries into the consistency of students' self-assessments with other judgments (e.g., a test score or teacher's grade). Twenty-five studies investigated the relationship between self-assessment and achievement. Fifteen explored students' perceptions of self-assessment. Twelve studies focused on the association between self-assessment and self-regulated learning. One examined self-efficacy, and two qualitative studies documented the mental processes involved in self-assessment. The sum ( n = 99) of the list of research topics is more than 76 because several studies had multiple foci. In the remainder of this review I examine each topic in turn.
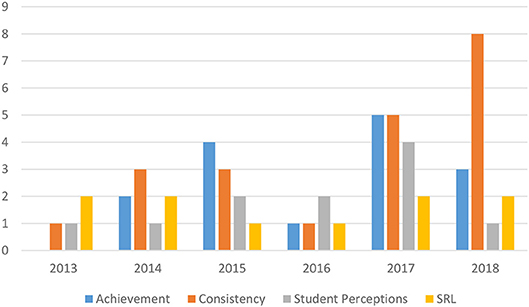
Figure 1 . Topics of self-assessment studies, 2013–2018.
Consistency
Table S1 (Supplementary Material) reveals that much of the recent research on self-assessment has investigated the accuracy or, more accurately, consistency, of students' self-assessments. The term consistency is more appropriate in the classroom context because the quality of students' self-assessments is often determined by comparing them with their teachers' assessments and then generating correlations. Given the evidence of the unreliability of teachers' grades ( Falchikov, 2005 ), the assumption that teachers' assessments are accurate might not be well-founded ( Leach, 2012 ; Brown et al., 2015 ). Ratings of student work done by researchers are also suspect, unless evidence of the validity and reliability of the inferences made about student work by researchers is available. Consequently, much of the research on classroom-based self-assessment should use the term consistency , which refers to the degree of alignment between students' and expert raters' evaluations, avoiding the purer, more rigorous term accuracy unless it is fitting.
In their review, Brown and Harris (2013) reported that correlations between student self-ratings and other measures tended to be weakly to strongly positive, ranging from r ≈ 0.20 to 0.80, with few studies reporting correlations >0.60. But their review included results from studies of any self-appraisal of school work, including summative self-rating/grading, predictions about the correctness of answers on test items, and formative, criteria-based self-assessments, a combination of methods that makes the correlations they reported difficult to interpret. Qualitatively different forms of self-assessment, especially summative and formative types, cannot be lumped together without obfuscating important aspects of self-assessment as feedback.
Given my concern about combining studies of summative and formative assessment, you might anticipate a call for research on consistency that distinguishes between the two. I will make no such call for three reasons. One is that we have enough research on the subject, including the 22 studies in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) that were published after Brown and Harris's review (2013 ). Drawing only on studies included in Table S1 (Supplementary Material), we can say with confidence that summative self-assessment tends to be inconsistent with external judgements ( Baxter and Norman, 2011 ; De Grez et al., 2012 ; Admiraal et al., 2015 ), with males tending to overrate and females to underrate ( Nowell and Alston, 2007 ; Marks et al., 2018 ). There are exceptions ( Alaoutinen, 2012 ; Lopez-Pastor et al., 2012 ) as well as mixed results, with students being consistent regarding some aspects of their learning but not others ( Blanch-Hartigan, 2011 ; Harding and Hbaci, 2015 ; Nguyen and Foster, 2018 ). We can also say that older, more academically competent learners tend to be more consistent ( Hacker et al., 2000 ; Lew et al., 2010 ; Alaoutinen, 2012 ; Guillory and Blankson, 2017 ; Butler, 2018 ; Nagel and Lindsey, 2018 ). There is evidence that consistency can be improved through experience ( Lopez and Kossack, 2007 ; Yilmaz, 2017 ; Nagel and Lindsey, 2018 ), the use of guidelines ( Bol et al., 2012 ), feedback ( Thawabieh, 2017 ), and standards ( Baars et al., 2014 ), perhaps in the form of rubrics ( Panadero and Romero, 2014 ). Modeling and feedback also help ( Labuhn et al., 2010 ; Miller and Geraci, 2011 ; Hawkins et al., 2012 ; Kostons et al., 2012 ).
An outcome typical of research on the consistency of summative self-assessment can be found in row 59, which summarizes the study by Tejeiro et al. (2012) discussed earlier: Students' self-assessments were higher than marks given by professors, especially for students with poorer results, and no relationship was found between the professors' and the students' assessments in the group in which self-assessment counted toward the final mark. Students are not stupid: if they know that they can influence their final grade, and that their judgment is summative rather than intended to inform revision and improvement, they will be motivated to inflate their self-evaluation. I do not believe we need more research to demonstrate that phenomenon.
The second reason I am not calling for additional research on consistency is a lot of it seems somewhat irrelevant. This might be because the interest in accuracy is rooted in clinical research on calibration, which has very different aims. Calibration accuracy is the “magnitude of consent between learners' true and self-evaluated task performance. Accurately calibrated learners' task performance equals their self-evaluated task performance” ( Wollenschläger et al., 2016 ). Calibration research often asks study participants to predict or postdict the correctness of their responses to test items. I caution about generalizing from clinical experiments to authentic classroom contexts because the dismal picture of our human potential to self-judge was painted by calibration researchers before study participants were effectively taught how to predict with accuracy, or provided with the tools they needed to be accurate, or motivated to do so. Calibration researchers know that, of course, and have conducted intervention studies that attempt to improve accuracy, with some success (e.g., Bol et al., 2012 ). Studies of formative self-assessment also suggest that consistency increases when it is taught and supported in many of the ways any other skill must be taught and supported ( Lopez and Kossack, 2007 ; Labuhn et al., 2010 ; Chang et al., 2012 , 2013 ; Hawkins et al., 2012 ; Panadero and Romero, 2014 ; Lin-Siegler et al., 2015 ; Fitzpatrick and Schulz, 2016 ).
Even clinical psychological studies that go beyond calibration to examine the associations between monitoring accuracy and subsequent study behaviors do not transfer well to classroom assessment research. After repeatedly encountering claims that, for example, low self-assessment accuracy leads to poor task-selection accuracy and “suboptimal learning outcomes” ( Raaijmakers et al., 2019 , p. 1), I dug into the cited studies and discovered two limitations. The first is that the tasks in which study participants engage are quite inauthentic. A typical task involves studying “word pairs (e.g., railroad—mother), followed by a delayed judgment of learning (JOL) in which the students predicted the chances of remembering the pair… After making a JOL, the entire pair was presented for restudy for 4 s [ sic ], and after all pairs had been restudied, a criterion test of paired-associate recall occurred” ( Dunlosky and Rawson, 2012 , p. 272). Although memory for word pairs might be important in some classroom contexts, it is not safe to assume that results from studies like that one can predict students' behaviors after criterion-referenced self-assessment of their comprehension of complex texts, lengthy compositions, or solutions to multi-step mathematical problems.
The second limitation of studies like the typical one described above is more serious: Participants in research like that are not permitted to regulate their own studying, which is experimentally manipulated by a computer program. This came as a surprise, since many of the claims were about students' poor study choices but they were rarely allowed to make actual choices. For example, Dunlosky and Rawson (2012) permitted participants to “use monitoring to effectively control learning” by programming the computer so that “a participant would need to have judged his or her recall of a definition entirely correct on three different trials, and once they judged it entirely correct on the third trial, that particular key term definition was dropped [by the computer program] from further practice” (p. 272). The authors note that this study design is an improvement on designs that did not require all participants to use the same regulation algorithm, but it does not reflect the kinds of decisions that learners make in class or while doing homework. In fact, a large body of research shows that students can make wise choices when they self-pace the study of to-be-learned materials and then allocate study time to each item ( Bjork et al., 2013 , p. 425):
In a typical experiment, the students first study all the items at an experimenter-paced rate (e.g., study 60 paired associates for 3 s each), which familiarizes the students with the items; after this familiarity phase, the students then either choose which items they want to restudy (e.g., all items are presented in an array, and the students select which ones to restudy) and/or pace their restudy of each item. Several dependent measures have been widely used, such as how long each item is studied, whether an item is selected for restudy, and in what order items are selected for restudy. The literature on these aspects of self-regulated study is massive (for a comprehensive overview, see both Dunlosky and Ariel, 2011 and Son and Metcalfe, 2000 ), but the evidence is largely consistent with a few basic conclusions. First, if students have a chance to practice retrieval prior to restudying items, they almost exclusively choose to restudy unrecalled items and drop the previously recalled items from restudy ( Metcalfe and Kornell, 2005 ). Second, when pacing their study of individual items that have been selected for restudy, students typically spend more time studying items that are more, rather than less, difficult to learn. Such a strategy is consistent with a discrepancy-reduction model of self-paced study (which states that people continue to study an item until they reach mastery), although some key revisions to this model are needed to account for all the data. For instance, students may not continue to study until they reach some static criterion of mastery, but instead, they may continue to study until they perceive that they are no longer making progress.
I propose that this research, which suggests that students' unscaffolded, unmeasured, informal self-assessments tend to lead to appropriate task selection, is better aligned with research on classroom-based self-assessment. Nonetheless, even this comparison is inadequate because the study participants were not taught to compare their performance to the criteria for mastery, as is often done in classroom-based self-assessment.
The third and final reason I do not believe we need additional research on consistency is that I think it is a distraction from the true purposes of self-assessment. Many if not most of the articles about the accuracy of self-assessment are grounded in the assumption that accuracy is necessary for self-assessment to be useful, particularly in terms of subsequent studying and revision behaviors. Although it seems obvious that accurate evaluations of their performance positively influence students' study strategy selection, which should produce improvements in achievement, I have not seen relevant research that tests those conjectures. Some claim that inaccurate estimates of learning lead to the selection of inappropriate learning tasks ( Kostons et al., 2012 ) but they cite research that does not support their claim. For example, Kostons et al. cite studies that focus on the effectiveness of SRL interventions but do not address the accuracy of participants' estimates of learning, nor the relationship of those estimates to the selection of next steps. Other studies produce findings that support my skepticism. Take, for instance, two relevant studies of calibration. One suggested that performance and judgments of performance had little influence on subsequent test preparation behavior ( Hacker et al., 2000 ), and the other showed that study participants followed their predictions of performance to the same degree, regardless of monitoring accuracy ( van Loon et al., 2014 ).
Eva and Regehr (2008) believe that:
Research questions that take the form of “How well do various practitioners self-assess?” “How can we improve self-assessment?” or “How can we measure self-assessment skill?” should be considered defunct and removed from the research agenda [because] there have been hundreds of studies into these questions and the answers are “Poorly,” “You can't,” and “Don't bother” (p. 18).
I almost agree. A study that could change my mind about the importance of accuracy of self-assessment would be an investigation that goes beyond attempting to improve accuracy just for the sake of accuracy by instead examining the relearning/revision behaviors of accurate and inaccurate self-assessors: Do students whose self-assessments match the valid and reliable judgments of expert raters (hence my use of the term accuracy ) make better decisions about what they need to do to deepen their learning and improve their work? Here, I admit, is a call for research related to consistency: I would love to see a high-quality investigation of the relationship between accuracy in formative self-assessment, and students' subsequent study and revision behaviors, and their learning. For example, a study that closely examines the revisions to writing made by accurate and inaccurate self-assessors, and the resulting outcomes in terms of the quality of their writing, would be most welcome.
Table S1 (Supplementary Material) indicates that by 2018 researchers began publishing studies that more directly address the hypothesized link between self-assessment and subsequent learning behaviors, as well as important questions about the processes learners engage in while self-assessing ( Yan and Brown, 2017 ). One, a study by Nugteren et al. (2018 row 19 in Table S1 (Supplementary Material)), asked “How do inaccurate [summative] self-assessments influence task selections?” (p. 368) and employed a clever exploratory research design. The results suggested that most of the 15 students in their sample over-estimated their performance and made inaccurate learning-task selections. Nugteren et al. recommended helping students make more accurate self-assessments, but I think the more interesting finding is related to why students made task selections that were too difficult or too easy, given their prior performance: They based most task selections on interest in the content of particular items (not the overarching content to be learned), and infrequently considered task difficulty and support level. For instance, while working on the genetics tasks, students reported selecting tasks because they were fun or interesting, not because they addressed self-identified weaknesses in their understanding of genetics. Nugteren et al. proposed that students would benefit from instruction on task selection. I second that proposal: Rather than directing our efforts on accuracy in the service of improving subsequent task selection, let us simply teach students to use the information at hand to select next best steps, among other things.
Butler (2018 , row 76 in Table S1 (Supplementary Material)) has conducted at least two studies of learners' processes of responding to self-assessment items and how they arrived at their judgments. Comparing generic, decontextualized items to task-specific, contextualized items (which she calls after-task items ), she drew two unsurprising conclusions: the task-specific items “generally showed higher correlations with task performance,” and older students “appeared to be more conservative in their judgment compared with their younger counterparts” (p. 249). The contribution of the study is the detailed information it provides about how students generated their judgments. For example, Butler's qualitative data analyses revealed that when asked to self-assess in terms of vague or non-specific items, the children often “contextualized the descriptions based on their own experiences, goals, and expectations,” (p. 257) focused on the task at hand, and situated items in the specific task context. Perhaps as a result, the correlation between after-task self-assessment and task performance was generally higher than for generic self-assessment.
Butler (2018) notes that her study enriches our empirical understanding of the processes by which children respond to self-assessment. This is a very promising direction for the field. Similar studies of processing during formative self-assessment of a variety of task types in a classroom context would likely produce significant advances in our understanding of how and why self-assessment influences learning and performance.
Student Perceptions
Fifteen of the studies listed in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) focused on students' perceptions of self-assessment. The studies of children suggest that they tend to have unsophisticated understandings of its purposes ( Harris and Brown, 2013 ; Bourke, 2016 ) that might lead to shallow implementation of related processes. In contrast, results from the studies conducted in higher education settings suggested that college and university students understood the function of self-assessment ( Ratminingsih et al., 2018 ) and generally found it to be useful for guiding evaluation and revision ( Micán and Medina, 2017 ), understanding how to take responsibility for learning ( Lopez and Kossack, 2007 ; Bourke, 2014 ; Ndoye, 2017 ), prompting them to think more critically and deeply ( van Helvoort, 2012 ; Siow, 2015 ), applying newfound skills ( Murakami et al., 2012 ), and fostering self-regulated learning by guiding them to set goals, plan, self-monitor and reflect ( Wang, 2017 ).
Not surprisingly, positive perceptions of self-assessment were typically developed by students who actively engaged the formative type by, for example, developing their own criteria for an effective self-assessment response ( Bourke, 2014 ), or using a rubric or checklist to guide their assessments and then revising their work ( Huang and Gui, 2015 ; Wang, 2017 ). Earlier research suggested that children's attitudes toward self-assessment can become negative if it is summative ( Ross et al., 1998 ). However, even summative self-assessment was reported by adult learners to be useful in helping them become more critical of their own and others' writing throughout the course and in subsequent courses ( van Helvoort, 2012 ).
Achievement
Twenty-five of the studies in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) investigated the relation between self-assessment and achievement, including two meta-analyses. Twenty of the 25 clearly employed the formative type. Without exception, those 20 studies, plus the two meta-analyses ( Graham et al., 2015 ; Sanchez et al., 2017 ) demonstrated a positive association between self-assessment and learning. The meta-analysis conducted by Graham and his colleagues, which included 10 studies, yielded an average weighted effect size of 0.62 on writing quality. The Sanchez et al. meta-analysis revealed that, although 12 of the 44 effect sizes were negative, on average, “students who engaged in self-grading performed better ( g = 0.34) on subsequent tests than did students who did not” (p. 1,049).
All but two of the non-meta-analytic studies of achievement in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) were quasi-experimental or experimental, providing relatively rigorous evidence that their treatment groups outperformed their comparison or control groups in terms of everything from writing to dart-throwing, map-making, speaking English, and exams in a wide variety of disciplines. One experiment on summative self-assessment ( Miller and Geraci, 2011 ), in contrast, resulted in no improvements in exam scores, while the other one did ( Raaijmakers et al., 2017 ).
It would be easy to overgeneralize and claim that the question about the effect of self-assessment on learning has been answered, but there are unanswered questions about the key components of effective self-assessment, especially social-emotional components related to power and trust ( Andrade and Brown, 2016 ). The trends are pretty clear, however: it appears that formative forms of self-assessment can promote knowledge and skill development. This is not surprising, given that it involves many of the processes known to support learning, including practice, feedback, revision, and especially the intellectually demanding work of making complex, criteria-referenced judgments ( Panadero et al., 2014 ). Boud (1995a , b) predicted this trend when he noted that many self-assessment processes undermine learning by rushing to judgment, thereby failing to engage students with the standards or criteria for their work.
Self-Regulated Learning
The association between self-assessment and learning has also been explained in terms of self-regulation ( Andrade, 2010 ; Panadero and Alonso-Tapia, 2013 ; Andrade and Brookhart, 2016 , 2019 ; Panadero et al., 2016b ). Self-regulated learning (SRL) occurs when learners set goals and then monitor and manage their thoughts, feelings, and actions to reach those goals. SRL is moderately to highly correlated with achievement ( Zimmerman and Schunk, 2011 ). Research suggests that formative assessment is a potential influence on SRL ( Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick, 2006 ). The 12 studies in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) that focus on SRL demonstrate the recent increase in interest in the relationship between self-assessment and SRL.
Conceptual and practical overlaps between the two fields are abundant. In fact, Brown and Harris (2014) recommend that student self-assessment no longer be treated as an assessment, but as an essential competence for self-regulation. Butler and Winne (1995) introduced the role of self-generated feedback in self-regulation years ago:
[For] all self-regulated activities, feedback is an inherent catalyst. As learners monitor their engagement with tasks, internal feedback is generated by the monitoring process. That feedback describes the nature of outcomes and the qualities of the cognitive processes that led to those states (p. 245).
The outcomes and processes referred to by Butler and Winne are many of the same products and processes I referred to earlier in the definition of self-assessment and in Table 1 .
In general, research and practice related to self-assessment has tended to focus on judging the products of student learning, while scholarship on self-regulated learning encompasses both processes and products. The very practical focus of much of the research on self-assessment means it might be playing catch-up, in terms of theory development, with the SRL literature, which is grounded in experimental paradigms from cognitive psychology ( de Bruin and van Gog, 2012 ), while self-assessment research is ahead in terms of implementation (E. Panadero, personal communication, October 21, 2016). One major exception is the work done on Self-regulated Strategy Development ( Glaser and Brunstein, 2007 ; Harris et al., 2008 ), which has successfully integrated SRL research with classroom practices, including self-assessment, to teach writing to students with special needs.
Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick (2006) have been explicit about the potential for self-assessment practices to support self-regulated learning:
To develop systematically the learner's capacity for self-regulation, teachers need to create more structured opportunities for self-monitoring and the judging of progression to goals. Self-assessment tasks are an effective way of achieving this, as are activities that encourage reflection on learning progress (p. 207).
The studies of SRL in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) provide encouraging findings regarding the potential role of self-assessment in promoting achievement, self-regulated learning in general, and metacognition and study strategies related to task selection in particular. The studies also represent a solution to the “methodological and theoretical challenges involved in bringing metacognitive research to the real world, using meaningful learning materials” ( Koriat, 2012 , p. 296).
Future Directions for Research
I agree with ( Yan and Brown, 2017 ) statement that “from a pedagogical perspective, the benefits of self-assessment may come from active engagement in the learning process, rather than by being “veridical” or coinciding with reality, because students' reflection and metacognitive monitoring lead to improved learning” (p. 1,248). Future research should focus less on accuracy/consistency/veridicality, and more on the precise mechanisms of self-assessment ( Butler, 2018 ).
An important aspect of research on self-assessment that is not explicitly represented in Table S1 (Supplementary Material) is practice, or pedagogy: Under what conditions does self-assessment work best, and how are those conditions influenced by context? Fortunately, the studies listed in the table, as well as others (see especially Andrade and Valtcheva, 2009 ; Nielsen, 2014 ; Panadero et al., 2016a ), point toward an answer. But we still have questions about how best to scaffold effective formative self-assessment. One area of inquiry is about the characteristics of the task being assessed, and the standards or criteria used by learners during self-assessment.
Influence of Types of Tasks and Standards or Criteria
Type of task or competency assessed seems to matter (e.g., Dolosic, 2018 , Nguyen and Foster, 2018 ), as do the criteria ( Yilmaz, 2017 ), but we do not yet have a comprehensive understanding of how or why. There is some evidence that it is important that the criteria used to self-assess are concrete, task-specific ( Butler, 2018 ), and graduated. For example, Fastre et al. (2010) revealed an association between self-assessment according to task-specific criteria and task performance: In a quasi-experimental study of 39 novice vocational education students studying stoma care, they compared concrete, task-specific criteria (“performance-based criteria”) such as “Introduces herself to the patient” and “Consults the care file for details concerning the stoma” to vaguer, “competence-based criteria” such as “Shows interest, listens actively, shows empathy to the patient” and “Is discrete with sensitive topics.” The performance-based criteria group outperformed the competence-based group on tests of task performance, presumably because “performance-based criteria make it easier to distinguish levels of performance, enabling a step-by-step process of performance improvement” (p. 530).
This finding echoes the results of a study of self-regulated learning by Kitsantas and Zimmerman (2006) , who argued that “fine-grained standards can have two key benefits: They can enable learners to be more sensitive to small changes in skill and make more appropriate adaptations in learning strategies” (p. 203). In their study, 70 college students were taught how to throw darts at a target. The purpose of the study was to examine the role of graphing of self-recorded outcomes and self-evaluative standards in learning a motor skill. Students who were provided with graduated self-evaluative standards surpassed “those who were provided with absolute standards or no standards (control) in both motor skill and in motivational beliefs (i.e., self-efficacy, attributions, and self-satisfaction)” (p. 201). Kitsantas and Zimmerman hypothesized that setting high absolute standards would limit a learner's sensitivity to small improvements in functioning. This hypothesis was supported by the finding that students who set absolute standards reported significantly less awareness of learning progress (and hit the bull's-eye less often) than students who set graduated standards. “The correlation between the self-evaluation and dart-throwing outcomes measures was extraordinarily high ( r = 0.94)” (p. 210). Classroom-based research on specific, graduated self-assessment criteria would be informative.
Cognitive and Affective Mechanisms of Self-Assessment
There are many additional questions about pedagogy, such as the hoped-for investigation mentioned above of the relationship between accuracy in formative self-assessment, students' subsequent study behaviors, and their learning. There is also a need for research on how to help teachers give students a central role in their learning by creating space for self-assessment (e.g., see Hawe and Parr, 2014 ), and the complex power dynamics involved in doing so ( Tan, 2004 , 2009 ; Taras, 2008 ; Leach, 2012 ). However, there is an even more pressing need for investigations into the internal mechanisms experienced by students engaged in assessing their own learning. Angela Lui and I call this the next black box ( Lui, 2017 ).
Black and Wiliam (1998) used the term black box to emphasize the fact that what happened in most classrooms was largely unknown: all we knew was that some inputs (e.g., teachers, resources, standards, and requirements) were fed into the box, and that certain outputs (e.g., more knowledgeable and competent students, acceptable levels of achievement) would follow. But what, they asked, is happening inside, and what new inputs will produce better outputs? Black and Wiliam's review spawned a great deal of research on formative assessment, some but not all of which suggests a positive relationship with academic achievement ( Bennett, 2011 ; Kingston and Nash, 2011 ). To better understand why and how the use of formative assessment in general and self-assessment in particular is associated with improvements in academic achievement in some instances but not others, we need research that looks into the next black box: the cognitive and affective mechanisms of students who are engaged in assessment processes ( Lui, 2017 ).
The role of internal mechanisms has been discussed in theory but not yet fully tested. Crooks (1988) argued that the impact of assessment is influenced by students' interpretation of the tasks and results, and Butler and Winne (1995) theorized that both cognitive and affective processes play a role in determining how feedback is internalized and used to self-regulate learning. Other theoretical frameworks about the internal processes of receiving and responding to feedback have been developed (e.g., Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick, 2006 ; Draper, 2009 ; Andrade, 2013 ; Lipnevich et al., 2016 ). Yet, Shute (2008) noted in her review of the literature on formative feedback that “despite the plethora of research on the topic, the specific mechanisms relating feedback to learning are still mostly murky, with very few (if any) general conclusions” (p. 156). This area is ripe for research.
Self-assessment is the act of monitoring one's processes and products in order to make adjustments that deepen learning and enhance performance. Although it can be summative, the evidence presented in this review strongly suggests that self-assessment is most beneficial, in terms of both achievement and self-regulated learning, when it is used formatively and supported by training.
What is not yet clear is why and how self-assessment works. Those of you who like to investigate phenomena that are maddeningly difficult to measure will rejoice to hear that the cognitive and affective mechanisms of self-assessment are the next black box. Studies of the ways in which learners think and feel, the interactions between their thoughts and feelings and their context, and the implications for pedagogy will make major contributions to our field.
Author Contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and has approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2019.00087/full#supplementary-material
1. ^ I am grateful to my graduate assistants, Joanna Weaver and Taja Young, for conducting the searches.
Admiraal, W., Huisman, B., and Pilli, O. (2015). Assessment in massive open online courses. Electron. J. e-Learning , 13, 207–216.
Google Scholar
Alaoutinen, S. (2012). Evaluating the effect of learning style and student background on self-assessment accuracy. Comput. Sci. Educ. 22, 175–198. doi: 10.1080/08993408.2012.692924
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Al-Rawahi, N. M., and Al-Balushi, S. M. (2015). The effect of reflective science journal writing on students' self-regulated learning strategies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 10, 367–379. doi: 10.12973/ijese.2015.250a
Andrade, H. (2010). “Students as the definitive source of formative assessment: academic self-assessment and the self-regulation of learning,” in Handbook of Formative Assessment , eds H. Andrade and G. Cizek (New York, NY: Routledge, 90–105.
Andrade, H. (2013). “Classroom assessment in the context of learning theory and research,” in Sage Handbook of Research on Classroom Assessment , ed J. H. McMillan (New York, NY: Sage), 17–34. doi: 10.4135/9781452218649.n2
Andrade, H. (2018). “Feedback in the context of self-assessment,” in Cambridge Handbook of Instructional Feedback , eds A. Lipnevich and J. Smith (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 376–408.
PubMed Abstract
Andrade, H., and Boulay, B. (2003). The role of rubric-referenced self-assessment in learning to write. J. Educ. Res. 97, 21–34. doi: 10.1080/00220670309596625
Andrade, H., and Brookhart, S. (2019). Classroom assessment as the co-regulation of learning. Assessm. Educ. Principles Policy Pract. doi: 10.1080/0969594X.2019.1571992
Andrade, H., and Brookhart, S. M. (2016). “The role of classroom assessment in supporting self-regulated learning,” in Assessment for Learning: Meeting the Challenge of Implementation , eds D. Laveault and L. Allal (Heidelberg: Springer), 293–309. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-39211-0_17
Andrade, H., and Du, Y. (2007). Student responses to criteria-referenced self-assessment. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 32, 159–181. doi: 10.1080/02602930600801928
Andrade, H., Du, Y., and Mycek, K. (2010). Rubric-referenced self-assessment and middle school students' writing. Assess. Educ. 17, 199–214. doi: 10.1080/09695941003696172
Andrade, H., Du, Y., and Wang, X. (2008). Putting rubrics to the test: The effect of a model, criteria generation, and rubric-referenced self-assessment on elementary school students' writing. Educ. Meas. 27, 3–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-3992.2008.00118.x
Andrade, H., and Valtcheva, A. (2009). Promoting learning and achievement through self- assessment. Theory Pract. 48, 12–19. doi: 10.1080/00405840802577544
Andrade, H., Wang, X., Du, Y., and Akawi, R. (2009). Rubric-referenced self-assessment and self-efficacy for writing. J. Educ. Res. 102, 287–302. doi: 10.3200/JOER.102.4.287-302
Andrade, H. L., and Brown, G. T. L. (2016). “Student self-assessment in the classroom,” in Handbook of Human and Social Conditions in Assessment , eds G. T. L. Brown and L. R. Harris (New York, NY: Routledge), 319–334.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Baars, M., Vink, S., van Gog, T., de Bruin, A., and Paas, F. (2014). Effects of training self-assessment and using assessment standards on retrospective and prospective monitoring of problem solving. Learn. Instruc. 33, 92–107. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2014.04.004
Balderas, I., and Cuamatzi, P. M. (2018). Self and peer correction to improve college students' writing skills. Profile. 20, 179–194. doi: 10.15446/profile.v20n2.67095
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The Exercise of Control . New York, NY: Freeman.
Barney, S., Khurum, M., Petersen, K., Unterkalmsteiner, M., and Jabangwe, R. (2012). Improving students with rubric-based self-assessment and oral feedback. IEEE Transac. Educ. 55, 319–325. doi: 10.1109/TE.2011.2172981
Baxter, P., and Norman, G. (2011). Self-assessment or self deception? A lack of association between nursing students' self-assessment and performance. J. Adv. Nurs. 67, 2406–2413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2011.05658.x
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bennett, R. E. (2011). Formative assessment: a critical review. Assess. Educ. 18, 5–25. doi: 10.1080/0969594X.2010.513678
Birjandi, P., and Hadidi Tamjid, N. (2012). The role of self-, peer and teacher assessment in promoting Iranian EFL learners' writing performance. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 37, 513–533. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2010.549204
Bjork, R. A., Dunlosky, J., and Kornell, N. (2013). Self-regulated learning: beliefs, techniques, and illusions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 64, 417–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143823
Black, P., Harrison, C., Lee, C., Marshall, B., and Wiliam, D. (2003). Assessment for Learning: Putting it into Practice . Berkshire: Open University Press.
Black, P., and Wiliam, D. (1998). Inside the black box: raising standards through classroom assessment. Phi Delta Kappan 80, 139–144; 146–148.
Blanch-Hartigan, D. (2011). Medical students' self-assessment of performance: results from three meta-analyses. Patient Educ. Counsel. 84, 3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2010.06.037
Bol, L., Hacker, D. J., Walck, C. C., and Nunnery, J. A. (2012). The effects of individual or group guidelines on the calibration accuracy and achievement of high school biology students. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 37, 280–287. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2012.02.004
Boud, D. (1995a). Implementing Student Self-Assessment, 2nd Edn. Australian Capital Territory: Higher Education Research and Development Society of Australasia.
Boud, D. (1995b). Enhancing Learning Through Self-Assessment. London: Kogan Page.
Boud, D. (1999). Avoiding the traps: Seeking good practice in the use of self-assessment and reflection in professional courses. Soc. Work Educ. 18, 121–132. doi: 10.1080/02615479911220131
Boud, D., and Brew, A. (1995). Developing a typology for learner self-assessment practices. Res. Dev. High. Educ. 18, 130–135.
Bourke, R. (2014). Self-assessment in professional programmes within tertiary institutions. Teach. High. Educ. 19, 908–918. doi: 10.1080/13562517.2014.934353
Bourke, R. (2016). Liberating the learner through self-assessment. Cambridge J. Educ. 46, 97–111. doi: 10.1080/0305764X.2015.1015963
Brown, G., Andrade, H., and Chen, F. (2015). Accuracy in student self-assessment: directions and cautions for research. Assess. Educ. 22, 444–457. doi: 10.1080/0969594X.2014.996523
Brown, G. T., and Harris, L. R. (2013). “Student self-assessment,” in Sage Handbook of Research on Classroom Assessment , ed J. H. McMillan (Los Angeles, CA: Sage), 367–393. doi: 10.4135/9781452218649.n21
Brown, G. T. L., and Harris, L. R. (2014). The future of self-assessment in classroom practice: reframing self-assessment as a core competency. Frontline Learn. Res. 3, 22–30. doi: 10.14786/flr.v2i1.24
Butler, D. L., and Winne, P. H. (1995). Feedback and self-regulated learning: a theoretical synthesis. Rev. Educ. Res. 65, 245–281. doi: 10.3102/00346543065003245
Butler, Y. G. (2018). “Young learners' processes and rationales for responding to self-assessment items: cases for generic can-do and five-point Likert-type formats,” in Useful Assessment and Evaluation in Language Education , eds J. Davis et al. (Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press), 21–39. doi: 10.2307/j.ctvvngrq.5
CrossRef Full Text
Chang, C.-C., Liang, C., and Chen, Y.-H. (2013). Is learner self-assessment reliable and valid in a Web-based portfolio environment for high school students? Comput. Educ. 60, 325–334. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.012
Chang, C.-C., Tseng, K.-H., and Lou, S.-J. (2012). A comparative analysis of the consistency and difference among teacher-assessment, student self-assessment and peer-assessment in a Web-based portfolio assessment environment for high school students. Comput. Educ. 58, 303–320. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2011.08.005
Colliver, J., Verhulst, S, and Barrows, H. (2005). Self-assessment in medical practice: a further concern about the conventional research paradigm. Teach. Learn. Med. 17, 200–201. doi: 10.1207/s15328015tlm1703_1
Crooks, T. J. (1988). The impact of classroom evaluation practices on students. Rev. Educ. Res. 58, 438–481. doi: 10.3102/00346543058004438
de Bruin, A. B. H., and van Gog, T. (2012). Improving self-monitoring and self-regulation: From cognitive psychology to the classroom , Learn. Instruct. 22, 245–252. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2012.01.003
De Grez, L., Valcke, M., and Roozen, I. (2012). How effective are self- and peer assessment of oral presentation skills compared with teachers' assessments? Active Learn. High. Educ. 13, 129–142. doi: 10.1177/1469787412441284
Dolosic, H. (2018). An examination of self-assessment and interconnected facets of second language reading. Read. Foreign Langu. 30, 189–208.
Draper, S. W. (2009). What are learners actually regulating when given feedback? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 40, 306–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8535.2008.00930.x
Dunlosky, J., and Ariel, R. (2011). “Self-regulated learning and the allocation of study time,” in Psychology of Learning and Motivation , Vol. 54 ed B. Ross (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press), 103–140. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385527-5.00004-8
Dunlosky, J., and Rawson, K. A. (2012). Overconfidence produces underachievement: inaccurate self evaluations undermine students' learning and retention. Learn. Instr. 22, 271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2011.08.003
Dweck, C. (2006). Mindset: The New Psychology of Success. New York, NY: Random House.
Epstein, R. M., Siegel, D. J., and Silberman, J. (2008). Self-monitoring in clinical practice: a challenge for medical educators. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 28, 5–13. doi: 10.1002/chp.149
Eva, K. W., and Regehr, G. (2008). “I'll never play professional football” and other fallacies of self-assessment. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 28, 14–19. doi: 10.1002/chp.150
Falchikov, N. (2005). Improving Assessment Through Student Involvement: Practical Solutions for Aiding Learning in Higher and Further Education . London: Routledge Falmer.
Fastre, G. M. J., van der Klink, M. R., Sluijsmans, D., and van Merrienboer, J. J. G. (2012). Drawing students' attention to relevant assessment criteria: effects on self-assessment skills and performance. J. Voc. Educ. Train. 64, 185–198. doi: 10.1080/13636820.2011.630537
Fastre, G. M. J., van der Klink, M. R., and van Merrienboer, J. J. G. (2010). The effects of performance-based assessment criteria on student performance and self-assessment skills. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 15, 517–532. doi: 10.1007/s10459-009-9215-x
Fitzpatrick, B., and Schulz, H. (2016). “Teaching young students to self-assess critically,” Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association (Washington, DC).
Franken, A. S. (1992). I'm Good Enough, I'm Smart Enough, and Doggone it, People Like Me! Daily affirmations by Stuart Smalley. New York, NY: Dell.
Glaser, C., and Brunstein, J. C. (2007). Improving fourth-grade students' composition skills: effects of strategy instruction and self-regulation procedures. J. Educ. Psychol. 99, 297–310. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.99.2.297
Gonida, E. N., and Leondari, A. (2011). Patterns of motivation among adolescents with biased and accurate self-efficacy beliefs. Int. J. Educ. Res. 50, 209–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ijer.2011.08.002
Graham, S., Hebert, M., and Harris, K. R. (2015). Formative assessment and writing. Elem. Sch. J. 115, 523–547. doi: 10.1086/681947
Guillory, J. J., and Blankson, A. N. (2017). Using recently acquired knowledge to self-assess understanding in the classroom. Sch. Teach. Learn. Psychol. 3, 77–89. doi: 10.1037/stl0000079
Hacker, D. J., Bol, L., Horgan, D. D., and Rakow, E. A. (2000). Test prediction and performance in a classroom context. J. Educ. Psychol. 92, 160–170. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.92.1.160
Harding, J. L., and Hbaci, I. (2015). Evaluating pre-service teachers math teaching experience from different perspectives. Univ. J. Educ. Res. 3, 382–389. doi: 10.13189/ujer.2015.030605
Harris, K. R., Graham, S., Mason, L. H., and Friedlander, B. (2008). Powerful Writing Strategies for All Students . Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Harris, L. R., and Brown, G. T. L. (2013). Opportunities and obstacles to consider when using peer- and self-assessment to improve student learning: case studies into teachers' implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 36, 101–111. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2013.07.008
Hattie, J., and Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Rev. Educ. Res. 77, 81–112. doi: 10.3102/003465430298487
Hawe, E., and Parr, J. (2014). Assessment for learning in the writing classroom: an incomplete realization. Curr. J. 25, 210–237. doi: 10.1080/09585176.2013.862172
Hawkins, S. C., Osborne, A., Schofield, S. J., Pournaras, D. J., and Chester, J. F. (2012). Improving the accuracy of self-assessment of practical clinical skills using video feedback: the importance of including benchmarks. Med. Teach. 34, 279–284. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.658897
Huang, Y., and Gui, M. (2015). Articulating teachers' expectations afore: Impact of rubrics on Chinese EFL learners' self-assessment and speaking ability. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 3, 126–132. doi: 10.11114/jets.v3i3.753
Kaderavek, J. N., Gillam, R. B., Ukrainetz, T. A., Justice, L. M., and Eisenberg, S. N. (2004). School-age children's self-assessment of oral narrative production. Commun. Disord. Q. 26, 37–48. doi: 10.1177/15257401040260010401
Karnilowicz, W. (2012). A comparison of self-assessment and tutor assessment of undergraduate psychology students. Soc. Behav. Person. 40, 591–604. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2012.40.4.591
Kevereski, L. (2017). (Self) evaluation of knowledge in students' population in higher education in Macedonia. Res. Pedag. 7, 69–75. doi: 10.17810/2015.49
Kingston, N. M., and Nash, B. (2011). Formative assessment: a meta-analysis and a call for research. Educ. Meas. 30, 28–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-3992.2011.00220.x
Kitsantas, A., and Zimmerman, B. J. (2006). Enhancing self-regulation of practice: the influence of graphing and self-evaluative standards. Metacogn. Learn. 1, 201–212. doi: 10.1007/s11409-006-9000-7
Kluger, A. N., and DeNisi, A. (1996). The effects of feedback interventions on performance: a historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psychol. Bull. 119, 254–284. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.119.2.254
Kollar, I., Fischer, F., and Hesse, F. (2006). Collaboration scripts: a conceptual analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 18, 159–185. doi: 10.1007/s10648-006-9007-2
Kolovelonis, A., Goudas, M., and Dermitzaki, I. (2012). Students' performance calibration in a basketball dribbling task in elementary physical education. Int. Electron. J. Elem. Educ. 4, 507–517.
Koriat, A. (2012). The relationships between monitoring, regulation and performance. Learn. Instru. 22, 296–298. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2012.01.002
Kostons, D., van Gog, T., and Paas, F. (2012). Training self-assessment and task-selection skills: a cognitive approach to improving self-regulated learning. Learn. Instruc. 22, 121–132. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2011.08.004
Labuhn, A. S., Zimmerman, B. J., and Hasselhorn, M. (2010). Enhancing students' self-regulation and mathematics performance: the influence of feedback and self-evaluative standards Metacogn. Learn. 5, 173–194. doi: 10.1007/s11409-010-9056-2
Leach, L. (2012). Optional self-assessment: some tensions and dilemmas. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 37, 137–147. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2010.515013
Lew, M. D. N., Alwis, W. A. M., and Schmidt, H. G. (2010). Accuracy of students' self-assessment and their beliefs about its utility. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 35, 135–156. doi: 10.1080/02602930802687737
Lin-Siegler, X., Shaenfield, D., and Elder, A. D. (2015). Contrasting case instruction can improve self-assessment of writing. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 63, 517–537. doi: 10.1007/s11423-015-9390-9
Lipnevich, A. A., Berg, D. A. G., and Smith, J. K. (2016). “Toward a model of student response to feedback,” in The Handbook of Human and Social Conditions in Assessment , eds G. T. L. Brown and L. R. Harris (New York, NY: Routledge), 169–185.
Lopez, R., and Kossack, S. (2007). Effects of recurring use of self-assessment in university courses. Int. J. Learn. 14, 203–216. doi: 10.18848/1447-9494/CGP/v14i04/45277
Lopez-Pastor, V. M., Fernandez-Balboa, J.-M., Santos Pastor, M. L., and Aranda, A. F. (2012). Students' self-grading, professor's grading and negotiated final grading at three university programmes: analysis of reliability and grade difference ranges and tendencies. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 37, 453–464. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2010.545868
Lui, A. (2017). Validity of the responses to feedback survey: operationalizing and measuring students' cognitive and affective responses to teachers' feedback (Doctoral dissertation). University at Albany—SUNY: Albany NY.
Marks, M. B., Haug, J. C., and Hu, H. (2018). Investigating undergraduate business internships: do supervisor and self-evaluations differ? J. Educ. Bus. 93, 33–45. doi: 10.1080/08832323.2017.1414025
Memis, E. K., and Seven, S. (2015). Effects of an SWH approach and self-evaluation on sixth grade students' learning and retention of an electricity unit. Int. J. Prog. Educ. 11, 32–49.
Metcalfe, J., and Kornell, N. (2005). A region of proximal learning model of study time allocation. J. Mem. Langu. 52, 463–477. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2004.12.001
Meusen-Beekman, K. D., Joosten-ten Brinke, D., and Boshuizen, H. P. A. (2016). Effects of formative assessments to develop self-regulation among sixth grade students: results from a randomized controlled intervention. Stud. Educ. Evalu. 51, 126–136. doi: 10.1016/j.stueduc.2016.10.008
Micán, D. A., and Medina, C. L. (2017). Boosting vocabulary learning through self-assessment in an English language teaching context. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 42, 398–414. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2015.1118433
Miller, T. M., and Geraci, L. (2011). Training metacognition in the classroom: the influence of incentives and feedback on exam predictions. Metacogn. Learn. 6, 303–314. doi: 10.1007/s11409-011-9083-7
Murakami, C., Valvona, C., and Broudy, D. (2012). Turning apathy into activeness in oral communication classes: regular self- and peer-assessment in a TBLT programme. System 40, 407–420. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2012.07.003
Nagel, M., and Lindsey, B. (2018). The use of classroom clickers to support improved self-assessment in introductory chemistry. J. College Sci. Teach. 47, 72–79.
Ndoye, A. (2017). Peer/self-assessment and student learning. Int. J. Teach. Learn. High. Educ. 29, 255–269.
Nguyen, T., and Foster, K. A. (2018). Research note—multiple time point course evaluation and student learning outcomes in an MSW course. J. Soc. Work Educ. 54, 715–723. doi: 10.1080/10437797.2018.1474151
Nicol, D., and Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: a model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Stud. High. Educ. 31, 199–218. doi: 10.1080/03075070600572090
Nielsen, K. (2014), Self-assessment methods in writing instruction: a conceptual framework, successful practices and essential strategies. J. Res. Read. 37, 1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9817.2012.01533.x.
Nowell, C., and Alston, R. M. (2007). I thought I got an A! Overconfidence across the economics curriculum. J. Econ. Educ. 38, 131–142. doi: 10.3200/JECE.38.2.131-142
Nugteren, M. L., Jarodzka, H., Kester, L., and Van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2018). Self-regulation of secondary school students: self-assessments are inaccurate and insufficiently used for learning-task selection. Instruc. Sci. 46, 357–381. doi: 10.1007/s11251-018-9448-2
Panadero, E., and Alonso-Tapia, J. (2013). Self-assessment: theoretical and practical connotations. When it happens, how is it acquired and what to do to develop it in our students. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 11, 551–576. doi: 10.14204/ejrep.30.12200
Panadero, E., Alonso-Tapia, J., and Huertas, J. A. (2012). Rubrics and self-assessment scripts effects on self-regulation, learning and self-efficacy in secondary education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 22, 806–813. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.04.007
Panadero, E., Alonso-Tapia, J., and Huertas, J. A. (2014). Rubrics vs. self-assessment scripts: effects on first year university students' self-regulation and performance. J. Study Educ. Dev. 3, 149–183. doi: 10.1080/02103702.2014.881655
Panadero, E., Alonso-Tapia, J., and Reche, E. (2013). Rubrics vs. self-assessment scripts effect on self-regulation, performance and self-efficacy in pre-service teachers. Stud. Educ. Evalu. 39, 125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.stueduc.2013.04.001
Panadero, E., Brown, G. L., and Strijbos, J.-W. (2016a). The future of student self-assessment: a review of known unknowns and potential directions. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 28, 803–830. doi: 10.1007/s10648-015-9350-2
Panadero, E., Jonsson, A., and Botella, J. (2017). Effects of self-assessment on self-regulated learning and self-efficacy: four meta-analyses. Educ. Res. Rev. 22, 74–98. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2017.08.004
Panadero, E., Jonsson, A., and Strijbos, J. W. (2016b). “Scaffolding self-regulated learning through self-assessment and peer assessment: guidelines for classroom implementation,” in Assessment for Learning: Meeting the Challenge of Implementation , eds D. Laveault and L. Allal (New York, NY: Springer), 311–326. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-39211-0_18
Panadero, E., and Romero, M. (2014). To rubric or not to rubric? The effects of self-assessment on self-regulation, performance and self-efficacy. Assess. Educ. 21, 133–148. doi: 10.1080/0969594X.2013.877872
Papanthymou, A., and Darra, M. (2018). Student self-assessment in higher education: The international experience and the Greek example. World J. Educ. 8, 130–146. doi: 10.5430/wje.v8n6p130
Punhagui, G. C., and de Souza, N. A. (2013). Self-regulation in the learning process: actions through self-assessment activities with Brazilian students. Int. Educ. Stud. 6, 47–62. doi: 10.5539/ies.v6n10p47
Raaijmakers, S. F., Baars, M., Paas, F., van Merriënboer, J. J. G., and van Gog, T. (2019). Metacognition and Learning , 1–22. doi: 10.1007/s11409-019-09189-5
Raaijmakers, S. F., Baars, M., Schapp, L., Paas, F., van Merrienboer, J., and van Gog, T. (2017). Training self-regulated learning with video modeling examples: do task-selection skills transfer? Instr. Sci. 46, 273–290. doi: 10.1007/s11251-017-9434-0
Ratminingsih, N. M., Marhaeni, A. A. I. N., and Vigayanti, L. P. D. (2018). Self-assessment: the effect on students' independence and writing competence. Int. J. Instruc. 11, 277–290. doi: 10.12973/iji.2018.11320a
Ross, J. A., Rolheiser, C., and Hogaboam-Gray, A. (1998). “Impact of self-evaluation training on mathematics achievement in a cooperative learning environment,” Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association (San Diego, CA).
Ross, J. A., and Starling, M. (2008). Self-assessment in a technology-supported environment: the case of grade 9 geography. Assess. Educ. 15, 183–199. doi: 10.1080/09695940802164218
Samaie, M., Nejad, A. M., and Qaracholloo, M. (2018). An inquiry into the efficiency of whatsapp for self- and peer-assessments of oral language proficiency. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 49, 111–126. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12519
Sanchez, C. E., Atkinson, K. M., Koenka, A. C., Moshontz, H., and Cooper, H. (2017). Self-grading and peer-grading for formative and summative assessments in 3rd through 12th grade classrooms: a meta-analysis. J. Educ. Psychol. 109, 1049–1066. doi: 10.1037/edu0000190
Sargeant, J. (2008). Toward a common understanding of self-assessment. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 28, 1–4. doi: 10.1002/chp.148
Sargeant, J., Mann, K., van der Vleuten, C., and Metsemakers, J. (2008). “Directed” self-assessment: practice and feedback within a social context. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 28, 47–54. doi: 10.1002/chp.155
Shute, V. (2008). Focus on formative feedback. Rev. Educ. Res. 78, 153–189. doi: 10.3102/0034654307313795
Silver, I., Campbell, C., Marlow, B., and Sargeant, J. (2008). Self-assessment and continuing professional development: the Canadian perspective. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 28, 25–31. doi: 10.1002/chp.152
Siow, L.-F. (2015). Students' perceptions on self- and peer-assessment in enhancing learning experience. Malaysian Online J. Educ. Sci. 3, 21–35.
Son, L. K., and Metcalfe, J. (2000). Metacognitive and control strategies in study-time allocation. J. Exp. Psychol. 26, 204–221. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.26.1.204
Tan, K. (2004). Does student self-assessment empower or discipline students? Assess. Evalu. Higher Educ. 29, 651–662. doi: 10.1080/0260293042000227209
Tan, K. (2009). Meanings and practices of power in academics' conceptions of student self-assessment. Teach. High. Educ. 14, 361–373. doi: 10.1080/13562510903050111
Taras, M. (2008). Issues of power and equity in two models of self-assessment. Teach. High. Educ. 13, 81–92. doi: 10.1080/13562510701794076
Tejeiro, R. A., Gomez-Vallecillo, J. L., Romero, A. F., Pelegrina, M., Wallace, A., and Emberley, E. (2012). Summative self-assessment in higher education: implications of its counting towards the final mark. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 10, 789–812.
Thawabieh, A. M. (2017). A comparison between students' self-assessment and teachers' assessment. J. Curri. Teach. 6, 14–20. doi: 10.5430/jct.v6n1p14
Tulgar, A. T. (2017). Selfie@ssessment as an alternative form of self-assessment at undergraduate level in higher education. J. Langu. Linguis. Stud. 13, 321–335.
van Helvoort, A. A. J. (2012). How adult students in information studies use a scoring rubric for the development of their information literacy skills. J. Acad. Librarian. 38, 165–171. doi: 10.1016/j.acalib.2012.03.016
van Loon, M. H., de Bruin, A. B. H., van Gog, T., van Merriënboer, J. J. G., and Dunlosky, J. (2014). Can students evaluate their understanding of cause-and-effect relations? The effects of diagram completion on monitoring accuracy. Acta Psychol. 151, 143–154. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2014.06.007
van Reybroeck, M., Penneman, J., Vidick, C., and Galand, B. (2017). Progressive treatment and self-assessment: Effects on students' automatisation of grammatical spelling and self-efficacy beliefs. Read. Writing 30, 1965–1985. doi: 10.1007/s11145-017-9761-1
Wang, W. (2017). Using rubrics in student self-assessment: student perceptions in the English as a foreign language writing context. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 42, 1280–1292. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2016.1261993
Wollenschläger, M., Hattie, J., Machts, N., Möller, J., and Harms, U. (2016). What makes rubrics effective in teacher-feedback? Transparency of learning goals is not enough. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 44–45, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.11.003
Yan, Z., and Brown, G. T. L. (2017). A cyclical self-assessment process: towards a model of how students engage in self-assessment. Assess. Evalu. High. Educ. 42, 1247–1262. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2016.1260091
Yilmaz, F. N. (2017). Reliability of scores obtained from self-, peer-, and teacher-assessments on teaching materials prepared by teacher candidates. Educ. Sci. 17, 395–409. doi: 10.12738/estp.2017.2.0098
Zimmerman, B. J. (2000). Self-efficacy: an essential motive to learn. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 25, 82–91. doi: 10.1006/ceps.1999.1016
Zimmerman, B. J., and Schunk, D. H. (2011). “Self-regulated learning and performance: an introduction and overview,” in Handbook of Self-Regulation of Learning and Performance , eds B. J. Zimmerman and D. H. Schunk (New York, NY: Routledge), 1–14.
Keywords: self-assessment, self-evaluation, self-grading, formative assessment, classroom assessment, self-regulated learning (SRL)
Citation: Andrade HL (2019) A Critical Review of Research on Student Self-Assessment. Front. Educ. 4:87. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2019.00087
Received: 27 April 2019; Accepted: 02 August 2019; Published: 27 August 2019.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2019 Andrade. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Heidi L. Andrade, handrade@albany.edu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Advertisement
The power of assessment feedback in teaching and learning: a narrative review and synthesis of the literature
- Original Paper
- Published: 09 March 2021
- Volume 1 , article number 75 , ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Michael Agyemang Adarkwah ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8201-8965 1
4490 Accesses
14 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Assessment feedback is heralded as an integral facilitator of teaching and learning. Despite the acknowledgement of its crucial role in education, there are inconsistencies in its powerful impact in teaching and learning: the role of the categories of feedback, the role of providers of feedback, constituents of effective feedback, and barriers to effective feedback. The focus of the narrative synthesis is to examine these different dimensions of assessment feedback and its powerful role in teaching and learning. A narrative evidence involving 82 studies was presented in thematic themes identified in literature. From the comprehensive review of the literature, the concept of assessment feedback and how it contributes to school effectiveness is thoroughly discussed. The article presents assessment feedback as a valuable factor for educators and students seeking to ensure continuous school improvement. It was found that a blended form of formative and summative feedback can improve teaching and learning. Feedback in any form should be specific, timely, frequent, supportive, and constructive. Negative feedback can distort learning, affective states of the recipient of feedback, and the job performance of employees. Findings from the review can assist researchers, authors, and readers of feedback reviews in the conceptualization of the role of assessment feedback in education. The study concludes with pedagogical implications for teaching and learning practice.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Formative Assessment and Feedback Strategies

How to Improve the Efficacy of Student Feedback
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Adalberon E (2020) Providing assessment feedback to pre-service teachers: a study of examiners’ comments. Assess Eval Higher Educ. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2020.1795081
Article Google Scholar
Al-Hattami AA (2019) The perception of students and faculty staff on the role of constructive feedback. Int J Instr 12(1):885–894. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2019.12157a
Alt D, Raichel N (2020) Higher education students’ perceptions of and attitudes towards peer assessment in multicultural classrooms. Asia-Pacific Educ Res 29(6):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-020-00507-z
Aoun C, Vatanasakdakul S, Ang K (2016) Feedback for thought: examining the influence of feedback constituents on learning experience. Stud High Educ 43(1):72–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2016.1156665
Atwater LE, Brett JF (2006) 360-Degree feedback to leaders: does it relate to changes in employee attitudes? Group Organ Manag 31(5):578–600. https://doi.org/10.1177/1059601106286887
Bader M, Burner T, Iversen SH (2019) Student perspectives on formative feedback as part of writing portfolios. Assess Eval 44(7):1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2018.1564811
Banister C (2020) Exploring peer feedback processes and peer feedback meta-dialogues with learners of academic and business English. Lang Teach Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362168820952222
Beran TN, Rokosh JL (2009) Instructors’ perspectives on the utility of student ratings of instruction. Instr Sci 37(2):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-007-9045-2
Bergil AS, Atlib I (2012) Different perspectives about feedback on teaching. Procedia 46:5833–5839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.524
Black P, Wiliam D (1998) Assessment and classroom learning. Assess Educ 5(1):7–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969595980050102
Bohndick C, Menne CM, Kohlmeyer S, Buhl HM (2019) Feedback in internet-based self-assessments and its effects on acceptance and motivation. J Further Higher Educ 44(6):717–728. https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2019.1596233
Boud D, Falchikov N (1989) Quantitative studies of student self-assessment in higher education: a critical analysis of findings. High Educ 18:529–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00138746
Brown G, Harris LR, Harnett JA (2012) Teacher beliefs about feedback within an Assessment for Learning environment: endorsement of improved learning over student well-being. Teach Teach Educ 28(7):968–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2012.05.003
Carless D, Boud D (2018) The development of student feedback literacy: enabling uptake of feedback. Assess Eval Higher Educ 43(8):1315–1325. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2018.1463354
Chan JC, Lam S-F (2010) Effects of different evaluative feedback on students’ self-efficacy in learning. Instr Sci 38:37–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-008-9077-2
Cohen VB (1985) A reexamination of feedback in computer-based instruction: implications for instructional design. Educ Technol 25(1):33–37
Google Scholar
Colbran S, Gilding A, Colbran S (2016) Animation and multiple-choice questions as a formative feedback tool for legal education. Law Teach 51(3):249–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/03069400.2016.1162077
Cooper NJ (2000) Facilitating learning from formative feedback in level 3 assessment. Assess Eval Higher Educ 25(3):279–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/713611435
Crisp BR (2007) Is it worth the effort? How feedback influences students’ subsequent submission of assessable work. Assess Eval Higher Educ 32(5):571–581. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930601116912
Deeley SJ (2013) Summative co-assessment: a deep learning approach to enhancing employability skills and attributes. Act Learn High Educ 15(1):39–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787413514649
Donaldson ML, Papay JP (2015) An idea whose time had come: negotiating teacher evaluation reform in New Haven, Connecticut. Am J Educ 122(1):39–70. https://doi.org/10.1086/683291
Ellegaard M, Damsgaard L, Bruun J, Johannsen BF (2017) Patterns in the form of formative feedback and student response. Assess Eval Higher Educ 43(5):727–744. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2017.1403564
Evans C (2013) Making sense of assessment feedback in higher education. Rev Educ Res 83(1):70–120. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654312474350
Fedor DB, Davis WD, Maslyn JM, Mathieson K (2001) Performance improvement efforts in response to negative feedback: the roles of source power and recipient self-esteem. J Manage 27(1):79–97. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920630102700105
Flodén J (2016) The impact of student feedback on teaching in higher education. Assess Eval Higher Educ 42(7):1054–1068. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2016.1224997
Fluckiger J, Vigil YT, Pasco R, Danielson K (2010) Formative feedback: involving students as partners in assessment to enhance learning. Coll Teach 58(4):136–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/87567555.2010.484031
Frank B, Simper N, Kaupp J (2017) Formative feedback and scaffolding for developing complex problem solving and modelling outcomes. Eur J Eng Educ 43(4):552–568. https://doi.org/10.1080/03043797.2017.1299692
Gaertner H (2014) Effects of student feedback as a method of self-evaluating the quality of teaching. Stud Educ Eval 42:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2014.04.003
Gibbs G, Simpson C (2005) Conditions under which assessment supports students’ learning. Learn Teach Higher Educ 1:3–31
Gibbs JC, Taylor JD (2016) Comparing student self-assessment to individualized instructor feedback. Act Learn High Educ 17(2):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787416637466
Goh K, Walker R (2018) Written teacher feedback: reflections of year seven music students. Austral J Teach Educ 43(12):30–41
Halverson R (2010) School formative feedback systems. Peabody J Educ 85(2):130–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/01619561003685270
Hamilton IR (2009) Automating formative and summative feedback for individualised assignments. Campus-Wide Inf Syst 26(5):355–364. https://doi.org/10.1108/10650740911004787
Harlen W, James M (1997) Assessment and Learning: differences and relationships between formative and summative assessment. Assess Educ 4(3):365–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594970040304
Harris LR, Brown GT, Harnett JA (2015) Analysis of New Zealand primary and secondary student peer- and self-assessment comments: applying Hattie and Timperley’s feedback model. Assess Educ 22(2):265–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594X.2014.976541
Harrison CJ, Könings KD, Schuwirth L, Wass V, Vleuten C (2015) Barriers to the uptake and use of feedback in the context of summative assessment. Adv Health Sci Educ 20:229–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-014-9524-6
Hattie J (2008) Visible learning: a synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge, Oxford
Book Google Scholar
Hattie J, Timperley H (2007) The power of feedback. Rev Educ Res 77(1):81–112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487
Hellrung K, Hartig J (2013) Understanding and using feedback – a review of empirical studies concerning feedback from external evaluations to teachers. Educ Res Rev 9:174–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2012.09.001
Hoban G, Hastings G (2006) Developing different forms of student feedback to promote teacher reflection: a 10-year collaboration. Teach Teach Educ 22(8):1006–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2006.04.006
Hoo H-T, Tan K, Deneen C (2020) Negotiating self- and peer-feedback with the use of reflective journals: an analysis of undergraduates’ engagement with feedback. Assess Eval Higher Educ 45(3):431–446. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2019.1665166
Huang S-C (2015) Understanding learners’ self-assessment and self-feedback on their foreign language speaking performance. Assess Eval Higher Educ 41(6):803–820. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2015.1042426
Karlsen KH (2017) The value of oral feedback in the context of capstone projects in design education. Des Technol Educ 22(3):1–23
Kluger AN, DeNisi A (1996) The effects of feedback interventions on performance: a historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psycholog Bull 119(2):254–284. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.119.2.254
Kmet LM, Cook IS, Lee RC (2004) Standard quality assessment criteria for evaluating primary research papers from a variety of fields. Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research, Alberta
Koka A, Hein V (2006) Perceptions of teachers’ positive feedback and perceived threat to sense of self in physical education: a longitudinal study. Eur Phys Educ Rev 12(2):333–346. https://doi.org/10.1177/1356336X06065180
Kyaruzi F, Strijbos J-W, Ufer S, Brown GT (2019) Students’ formative assessment perceptions, feedback use and mathematics performance in secondary schools in Tanzania. Assess Educ 26(3):278–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594X.2019.1593103
Lepper MR, Chabay RW (1985) Intrinsic motivation and instruction: Conflicting views on the role of motivational processes in computer-based education. Educ Psychol 20(4):217–230. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep2004_6
Lipnevich AA, Smith JK (2009) Effects of differential feedback on students’ examination performance. J Exp Psychol 15(4):319–333. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017841
Liu Y, Visone J, Mongillo MB, Lisi P (2019) What matters to teachers if evaluation is meant to help them improve? Stud Educ Eval 61:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2019.01.006
Lutovac S, Kaasila R, Komulainen J, Maikkola M (2017) University lecturers’ emotional responses to and coping with student feedback: a Finnish case study. Eur J Psychol Educ 32:235–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-016-0301-1
Mahfoodh OH (2017) “I feel disappointed”: EFL university students’ emotional responses towards teacher written feedback. Assess Writ 31:53–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2016.07.001
May T (2013) Identifying the characteristics of written formative feedback used by assessors in work-based qualifications. J Vocat Educ Train 65(1):18–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/13636820.2012.727855
McCarthy J (2017) Enhancing feedback in higher education: students’ attitudes towards online and in-class formative assessment feedback models. Act Learn High Educ 18(2):127–141. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787417707615
McKevitt CT (2013) Engaging students with self-assessment and tutor feedback to improve performance and support assessment capacity. J Univ Teach Learn Pract 13(1):1–20
Merry S, Orsmond P (2008) Students’ attitudes to and usage of academic feedback provided via audio files. Biosci Educ 1:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3108/beej.11.3
Mireles-Rios R, Becchio JA (2018) The evaluation process, administrator feedback, and teacher self-efficacy. J School Leadership 28(4):462–487. https://doi.org/10.1177/105268461802800402
Mireles-Rios R, Becchio JA, Roshandel S (2019) Teacher evaluations and contextualized self-efficacy: classroom management, instructional strategies and student engagement. J School Adm Res Dev 4(1):6–17
Montgomery JL, Baker W (2007) Teacher-written feedback: student perceptions, teacher self-assessment, and actual teacher performance. J Second Lang Writing 16(2):82–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2007.04.002
Moreno R (2004) Decreasing cognitive load for novice students: effects of explanatory versus corrective feedback in discovery-based multimedia. Instr Sci 32(1):99–113. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRUC.0000021811.66966.1d
Mubayrik HF (2020) New trends in formative-summative evaluations for adult education. SAGE Open. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020941006
Narciss S, Huth K (2004) How to design informative tutoring feedback for multi-media learning. In: Niegemann HM, Leutner D, Brunken R (eds) Instructional design for multimedia learning. Waxmann, Munster, NY, pp 181–195
Nicol D, Thomson A, Breslin C (2014) Rethinking feedback practices in higher education: a peer review perspective. Assess Eval Higher Educ 39(1):102–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.795518
O’Donovan BM, Outer BD, Price M, Lloyd A (2020) What makes good feedback good? Stud High Educ. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2019.1630812
O’Neill G, McEvoy E, Maguire T (2020) Developing a national understanding of assessment and feedback in Irish higher education. Irish Educ Stud. https://doi.org/10.1080/03323315.2020.1730220
Pagano R, Paucar-Caceres A (2013) Using systems thinking to evaluate formative feedback in UK higher education: the case of classroom response technology. Innov Educ Teach Int 50(1):94–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2012.748332
Panhoon S, Wongwanich S (2014) An analysis of teacher feedback for improving teaching quality in primary schools. Procedia 116:4124–4130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.902
Percell JC (2017) Lessons from alternative grading: essential qualities of teacher feedback. Clearing House 90(4):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.2017.1304067
Perera J, Lee N, Win K, Wijesuriya L (2008) Formative feedback to students: the mismatch between faculty perceptions and student expectations. Med Teach 30:395–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590801949966
Perera L, Nguyen H, Watty K (2014) Formative feedback through summative tutorial-based assessments: the relationship to student performance. Account Educ 23(5):424–442. https://doi.org/10.1080/09639284.2014.947093
Peters M, Godfrey C, Khalil H, McInerney P, Parker D, Baldini Soares C (2015) Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Based Healthc 13:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050
Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A, Petticrew M, Arai L, Rodgers M, Duffy S (2006) Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. A Product from the ESRC Methods Programme Version 1: b92
Popham J (2008) Transformative assessment. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Instruction, Alexandria, VA
Qunayeer HS (2019) Supporting postgraduates in research proposals through peer feedback in a Malaysian university. J Further Higher Educ 44(7):956–970. https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2019.1627299
Rand J (2017) Misunderstandings and mismatches: the collective disillusionment of written summative assessment feedback. Res Educ 97(1):33–48. https://doi.org/10.1177/0034523717697519
Robins L, Smith S, Kost A, Combs H, Kritek PA, Klein EJ (2019) Faculty perceptions of formative feedback from medical students. Teach Learn Med 32(2):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10401334.2019.1657869
Ryan JJ, Anderson JA, Birchler AB (1980) Student evaluation: the faculty responds. Res High Educ 12(4):317–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00976185
Sadler RD (1989) Formative assessment and the design of instructional systems. Instr Sci 18:119–144
Schweinberger K, Quesel C, Mahler S, Höchli A (2017) Effects of feedback on process features of school quality: a longitudinal study on teachers’ reception of school inspection of Swiss compulsory schools. Stud Educ Eval 55:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2017.07.004
Shute VJ (2007) Focus on formative feedback. Research Report. Educational Testing Service, Princeton, NJ
Shute VJ (2008) Focus on formative feedback. Rev Educ Res 78(1):153–189. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654307313795
Skovholt K (2018) Anatomy of a teacher–student feedback encounter. Teach Teach Educ 69:142–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2017.09.012
Tan FD, Whipp PR, Gagné M, Van Quaquebeke N (2020) Expert teacher perceptions of two-way feedback interaction. Teach Teach Educ 87:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2019.102930
Taras M (2008) Summative and formative assessment: perceptions and realities. Act Learn High Educ 9(2):172–192. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787408091655
Tasker TQ, Herrenkohl LR (2016) Using peer feedback to improve students’ scientific inquiry. J Sci Teacher Educ 27:35–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10972-016-9454-7
Van den Hurk HT, Houtveen AA, Van de Grift WJ (2016) Fostering effective teaching behavior through the use of data-feedback. Teach Teach Educ 60:444–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2016.07.003
Van der Kleij FM, Adie LE, Cumming JJ (2019) A meta-review of the student role in feedback. Int J Educ Res 98:303–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.09.005
Watling C, Driessen E, Vleuten CP, Vanstone M, Lingard L (2013) Beyond individualism: professional culture and its influence on feedback. Med Educ 47(6):585–594. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.12150
Weaver MR (2006) Do students value feedback? Student perceptions of tutors’ written responses. Assess Eval Higher Educ 31(3):379–394. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930500353061
White HD (1994) Scientific communication and literature retrieval. In: Cooper H, Hedges LV (eds) The handbook of research synthesis. Russell Sage Foundation, New York NY, pp 41–55
Wiggins G (2011) Giving students a voice: The power of feedback to improve teaching. Educ Horiz 89(3):23–26
Winstone NE, Boud D (2020) The need to disentangle assessment and feedback in higher education. Stud High Educ. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2020.1779687
Yorke M (2003) Formative assessment in higher education: Moves towards theory and the enhancement of pedagogic practice. High Educ 45(4):477–501. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023967026413
Zhong Q, Yan M, Zou F (2019) The effect of teacher feedback on the simple past tense acquisition in senior high school students’ english writing. World J Educ 9(3):30–37. https://doi.org/10.5430/wje.v9n3p30
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Southwest University, No. 2 Tianzhu Street, Beibei District, Chongqing, China
Michael Agyemang Adarkwah
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Michael Agyemang Adarkwah .
Ethics declarations
Data availability.
All data analysed or generated are included in the paper.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.

Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Adarkwah, M.A. The power of assessment feedback in teaching and learning: a narrative review and synthesis of the literature. SN Soc Sci 1 , 75 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-021-00086-w
Download citation
Received : 09 September 2020
Accepted : 12 February 2021
Published : 09 March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-021-00086-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Formative assessment
- Summative assessment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 09 September 2024
The human costs of the research-assessment culture
- Rachel Brazil 0
Rachel Brazil is a freelance journalist in London, UK.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Illustration: Stephan Schmitz
You have full access to this article via your institution.
The term ‘REF-able’ is now in common usage in UK universities. “Everyone’s constantly thinking of research in terms of ‘REF-able’ outputs, in terms of ‘REF-able’ impact,” says Richard Watermeyer, a sociologist at the University of Bristol, UK. He is referring to the UK Research Excellence Framework (REF), which is meant to happen every seven years and is one of the most intensive systems of academic evaluation in any country. “Its influence is ubiquitous — you can’t escape it,” says Watermeyer. But he and other scholars around the world are concerned about the effects of an extreme audit culture in higher education, one in which researchers’ productivity is continually measured and, in the case of the REF, directly tied to research funding for institutions. Critics say that such systems are having a detrimental effect on staff and, in some cases, are damaging researchers’ mental health and departmental collegiality.
Unlike other research benchmarking systems, the REF results directly affect the distribution of around £2 billion (US$2.6 billion) annually, creating high stakes for institutions. UK universities receive a significant proportion of their government funding in this way (in addition to the research grants awarded to individual academics).

Research assessment toolkit
Since its inception, the REF methodology has been through several iterations. The rules about which individuals’ work must be highlighted have changed, but there has always been a focus on peer-review panels to assess outputs. Since 2014, a team in each university department has been tasked with selecting a dossier of research outputs and case studies that must demonstrate societal impact. These submissions can receive anything from a four-star rating (for the most important, world-leading research) to just one star (the least significant work, of only national interest). Most departments aim to include three- or four-star submissions, often described as ‘REF-able’.
But the process is time-consuming and does not come cheap. The most recent REF, in 2021, was estimated to have cost £471 million. Tanita Casci, director of the Research Strategy & Policy Unit at the University of Oxford, UK, acknowledges that it’s resource-intensive, but says that it’s still a very efficient way of distributing funds, compared with the cost of allocating money through individual grant proposals. “I don’t think the alternative is better,” she concludes. The next exercise has been pushed back a year, until 2029, with planned changes to include a larger emphasis on assessment of institutional research culture.

Tanita Casci says the UK REF assessment is an efficient way to distribute funding. Credit: University of Oxford
Many UK academics see the REF as adding to an already highly competitive and stressful environment. A 2021 survey of more than 3,000 researchers (see go.nature.com/47umnjd ) found that they generally felt that the burdens of the REF outweighed the benefits. They also thought that it had decreased academics’ ability to follow their own intellectual interests and disincentivized the pursuit of riskier, more-speculative work with unpredictable outcomes.
Some other countries have joined the assessment train — with the notable exception of the United States, where the federal government does not typically award universities general-purpose research funding. But no nation has chosen to copy the REF exactly. Some, such as the Netherlands, have instead developed a model that challenges departments to set their own strategic goals and provide evidence that they have achieved them.
Whatever the system, few assessments loom as large in the academic consciousness as the REF. “You will encounter some institutions where, if you mention the REF, there’s a sort of groan and people talk about how stressed it’s making them,” says Petra Boynton, a research consultant and former health-care researcher at University College London.
Strain on team spirit
Staff collating a department’s REF submission, selecting the research outputs and case studies to illustrate impact, can find themselves in an uncomfortable position, says Watermeyer. He was involved in his own department’s 2014 submission and has published a study of the REF’s emotional toll 1 . It’s a job that most academics take on “with trepidation”, he says. It can change how they interact with colleagues and how colleagues view and interact with them.
“You’re trying to make robust, dispassionate, critical determinations of the quality of research. Yet at the back of your mind, you are inescapably aware of the implications of the judgements that you’re making in terms of people’s research identities, their careers,” says Watermeyer. In his experience, people can get quite defensive. That scrutiny of close colleagues’ work “can be really disruptive and damaging to relationships”.

UK research assessment is being reformed — but the changes miss the mark
Watermeyer often found himself not only adjudicating on work but also acting as a counsellor. “You have to attend to the emotional labour that’s involved; you’re responsible for people’s welfare and well-being,” and no training is provided, he says. A colleague might think that their work has met expectations, only to find that assessors disagree. “I’ve been in situations where there are tears,” Watermeyer recalls. “People break down.”
For university support staff, the REF also looms large. Sometimes, more staff must be hired near the submission deadline to cope with the workload. “It is an unbelievable pressure cooker,” particularly at small institutions, says Julie Bayley, former director of research-impact development at the University of Lincoln, UK. Bayley was responsible for overseeing 50 case studies to demonstrate the impact of Lincoln’s research, and describes this as akin to preparing evidence for a legal case. “You are having to prove, to a good level of scrutiny, that this claim is true,” Bayley says. This usually involves collecting testimonial letters from organizations or individuals who can vouch for the research impact, something she sometimes did on behalf of researchers who feared straining the external relationships they had developed.
Boynton says there can be an upside. “There’s something really exciting about putting together [a case study] that shows you did something amazing,” she says. But she also acknowledges that those whose research is not put forward can feel as if their work doesn’t matter or is not respected, and that can be demoralizing.
The clamour about achieving four stars can skew attitudes about research achievements. Bayley recounts a senior academic tearfully showing her an e-mail from his supervisor that read, “It’s all well and good that you’ve changed national UK policy, but unless you change European policy, it doesn’t count.” She says her own previous research on teenage pregnancy met with similar responses because it involved meeting real needs at the grass-roots level, rather than focusing on national policy. “That’s the bit I find most heartbreaking. Four-star is glory for the university, but four-star is not impact for society,” says Bayley.
The picking and choosing between individual researchers has implications for departments. “That places some people on the ‘star player competition winner’ side and, particularly where resources are limited, that means those people get more support” from their departments, explains Bayley. She has witnessed others being asked to pick up the teaching workload of researchers who are selected to produce impact case studies for a REF submission. Boynton agrees: “It’s not a collegiate, collective thing — it’s divisive.”
Hidden contributions
Research assessment can also affect work that universities often consider ‘non-REF-able’. Simon Hettrick, a research software engineer at the University of Southampton, UK, was in this position in 2021. He collaborates with researchers to produce crucial software for their work. But, he says, universities find it hard to look beyond academic papers as the metric for success even though there are 21 categories of research output that can be considered, including software, patents, conference proceedings and digital and visual media.
In the 2021 REF, publications made up about 98.5% of submissions. Hettrick says that although other submissions are encouraged, universities tend not to select the alternatives, presumably out of habit or for fear they might not be judged as favourably.

Simon Hettrick says evaluations should include more contributions such as software. Credit: Simon Hettrick
The result is that those in roles similar to Hettrick’s feel demotivated. “You’re working really hard, without the recognition for that input you’re making,” he says. To counter this, Hettrick and others launched an initiative called The hidden REF that ran a 2021 competition to spotlight important work unrecognized by the REF, garnering 120 submissions from more than 60 universities. The competition is being run again this year .
In April, Hettrick and his colleagues wrote a manifesto asking universities to ensure that at least 5% of their submissions for the 2029 REF are ‘non-traditional outputs’. “That has been met with some consternation,” he says.
Regarding career advancement, REF submissions should not feed into someone’s prospects, according to Casci, who says that universities make strong efforts to separate REF assessments from decisions about individuals’ career progression. But “it’s a grey area” in Watermeyer’s experience; “it might not be reflected within formal promotional criteria, but I think it’s the accepted unspoken reality”. He thinks that academic researchers lacking ‘REF-able’ three- or four-star outputs are unlikely to be hired by any “serious research institution” — severely limiting their career prospects and mobility.
Watermeyer says the consequences for these individuals will vary. Some institutions try to boost the ratings of early-career academics by putting them on capacity-building programmes, including buddying schemes to foster collaborations with more ‘REF-able’ colleagues. But, for more senior staff, the downside could be a performance review. “People might be ‘encouraged’ to reconsider their research role, if they find themselves unable to satisfy the three-star criteria,” he says.
There’s a similar imperative for a researcher’s work to be used as an impact case study. “If your work is not selected for that competition, you lose the currency for your own progression,” says Bayley.
The REF also exacerbates inequalities that already exist in research, says Emily Yarrow, an organizational-behaviour researcher at Newcastle University Business School, UK. “There are still gendered impacts and gendered effects of the REF, and still a disproportionate negative impact on those who take time out of their careers, for example, for caring responsibilities, maternity leave.” A 2014 analysis she co-authored of REF impact case studies in the fields of business and management showed that women were under-represented: just 25% of studies with an identifiable lead author were led by women 2 . Boynton also points out that there are clear inequalities in the resources available to institutions to prepare for the REF, causing many researchers to feel that the system is unfair.

Emily Yarrow found that women were under-represented in research-evaluation case studies. Credit: Toby Long
Although not all the problems researchers face can be attributed to the REF, it certainly contributes to what some have called an epidemic of poor mental health among UK higher-education staff. A 2019 report (see go.nature.com/3xsb78x ) highlighted the REF as causing administrative overload for some and evoking a heightened, ever-present fear of ‘failure’ for others.
UK research councils have acknowledged the criticisms and have promised changes to the 2029 REF. Steven Hill, chair of the 2021 REF Steering Group at Research England in Bristol, UK, which manages the REF exercise, says these changes will “rebalance the exercise’s definition of research excellence, to focus more on the environment needed for all talented people to thrive”. Hill also says they will implement changes to break “the link between individuals and submissions” because there will no longer be a minimum or maximum number of submissions for each researcher. The steering group aims to provide more support in terms of how REF guidance is applied by institutions, to dispel misconceptions about requirements. “Some institutions frame their performance criteria in REF terms and place greater requirements on staff than are actually required by REF,” Hill says.
Other ways forward
Similar to the REF, the China Discipline Evaluation (CDE) occurs every four to five years. Yiran Zhou, a higher-education researcher at the University of Cambridge, UK, has studied attitudes to the CDE 3 and says there are pressures in China to produce the equivalent of ‘REF-able’ research and similar concerns about the impact on academics. China relies much more on conventional quantitative publication metrics, but researchers Zhou interviewed criticized the time wasted in producing CDE impact case studies. Those tasked with organizing this often had to bargain with colleagues to collect the evidence they needed. “Then, they owe personal favours to them, like teaching for one or two hours,” says Zhou.
Increased competition has become a concern among Chinese universities, and Zhou says the government has decided not to publicize the results of the most recent CDE, only informing the individual universities. And, Zhou says, some of those she spoke to favoured dropping the assessment altogether.

Mammoth UK research assessment concludes as leaders eye radical shake up
In 2022, Australia did just that. Ahead of the country’s 2023 Excellence in Research for Australia (ERA) assessment, the government announced that it would stop the time-consuming process and start a transition to examine other “modern data-driven approaches, informed by expert review”. In October 2023, the Australian Research Council revealed a blueprint for a new assessment system and was investigating methods for smarter harvesting of evaluation data. It also noted that any data used would be “curated”, possibly with the help of artificial intelligence.
Some European countries are moving away from the type of competitive process exemplified by the REF. “For the Netherlands, we hope to move from evaluation to development” of careers and departmental strategies, says Kim Huijpen, programme manager for Recognition and Reward for the Universities of the Netherlands, based in The Hague, and a former chair of the working group of the Strategy Evaluation Protocol (SEP), the research evaluation process for Dutch universities. In the SEP, institutions organize subject-based research-unit evaluations every six years, but the outcome is not linked to government funding.
The SEP is a benchmarking process. Each research group selects indicators and other types of evidence related to its strategy and these, along with a site visit, provide the basis for review by a committee of peers and stakeholders. The protocol for 2021–27 has removed the previous system of grading. “We wanted to get away from this kind of ranking exercise,” explains Huijpen. “There’s a lot of freedom to deepen the conversation on quality, the societal relevance and the impact of the work — and it’s not very strict in how you should do this.”
The Research Council of Norway also runs subject-based assessments every decade, including institutional-level metrics and case studies, to broadly survey a field. “From what I hear from colleagues, the Norwegian assessment is much milder than the REF. Although it’s similar in what is looked at, it doesn’t feel the same,” says Alexander Refsum Jensenius, a music researcher at the University of Oslo. That’s probably because there is no direct link between the assessment and funding.
Refsum Jensenius has been involved in the Norwegian Career Assessment Matrix , a toolbox developed in 2021 by Universities Norway, the cooperative body of 32 accredited universities. It isn’t used to assess departments, but it demonstrates a fresh, broader approach.
What differentiates it from many other assessments is that in addition to providing evidence, there is scope for a researcher to outline the motivations for their research directions and make their own value judgements on achievements. “You cannot only have endless lists of whatever you have been doing, but you also need to reflect on it and perhaps suggest that some of these things have more value to you,” says Refsum Jensenius. For example, researchers might add context to their publication list by highlighting that opportunities to publish their work are limited by its interdisciplinary nature. There is also an element of continuing professional development to identify a researcher’s skills that need strengthening. Refsum Jensenius says this approach has been welcomed in the Norwegian system. “The toolbox is starting to be adopted by many institutions, including the University of Oslo, for hiring and promoting people.”
For many UK researchers, this more nurturing, reflective method of assessment might feel a million miles away from the REF, but that’s not to say that the REF process does not address ways to improve an institution’s research environment. Currently, one of the three pillars of assessment involves ‘people, culture and environment’, which includes open science, research integrity, career development and equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) concerns. Since 2022, there have been discussions on how to better measure and incentivize good practice in these areas for the next REF.
Bayley thinks the REF can already take some credit for an increased emphasis on EDI issues at UK universities. “I will not pretend for a second it’s sorted, but EDI is now so commonly a standing item on agendas that it’s far more present than it ever was.”
But she is less sure that the REF has improved research culture overall. For example, she says after the 2014 REF, when the rules changed to require that contributions from all permanent research staff be submitted, she saw indications that some universities were gaming the system in a way that disadvantaged early-career researchers. Junior staff members were left on precarious temporary contracts, and she has seen examples of institutions freezing staff numbers to avoid the need to submit more impact case studies. “I’ve seen that many times across many universities, which means the early-career entry points for research roles are reduced.”
“The REF is a double-edged sword,” concludes Bayley. The administrative burden and pressures it brings are much too high, but it does provide a way to allocate money that gives smaller institutions more of a chance, she says. After the 2021 REF, even though top universities still dominated, many received less of the pot than previously, whereas some newer, less prestigious universities performed strongly. The biggest increase was at Northumbria University in Newcastle, where ‘quality-related’ funding rose from £7 million to £18 million.
For Watermeyer, the whole process is counterproductive, wasting precious resources and creating a competitive, rather than a collaborative, culture that might not tolerate the most creative thinkers. He would like to see it abolished. Hettrick is in two minds, because “the realist in me says it is necessary to explain to the taxpayer what we’re doing with their money”. He says the task now is to do the assessment more cheaply and more effectively.
Other research communities might not agree. As Huijpen points out, “there’s quite a lot of assessments in academic life, there are a lot of moments within a career where you are assessed, when you apply for funding, when you apply for a job”. From her perspective, it’s time to opt for less ranking and more reflection.
Nature 633 , 481-484 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-02922-4
Watermeyer, R., Derrick, G. E. & Batalla, M. B. Res. Eval. 31 , 498–506 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Davies, J., Yarrow, E. & Syed, J. Gend. Work Organ. 27 , 129–148 (2020).
Zhou, Y. High. Educ. 88 , 1019–1035 (2024).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management
- Institutions
- Peer review

The grassroots organizations continuing the fight for Ukrainian science
Career Feature 11 SEP 24

How a struggling biotech company became a university ‘spin-in’
Career Q&A 10 SEP 24

Massive Attack’s science-led drive to lower music’s carbon footprint
Career Feature 04 SEP 24

Why I’m committed to breaking the bias in large language models
Career Guide 04 SEP 24
Binning out-of-date chemicals? Somebody think about the carbon!
Correspondence 27 AUG 24

No more hunting for replication studies: crowdsourced database makes them easy to find
Nature Index 27 AUG 24

Can South Korea regain its edge in innovation?
Nature Index 21 AUG 24

What will it take to open South Korean research to the world?

How South Korea can support female research leaders
Gathering Outstanding Overseas Talents, Innovating to Lead the Future
The 16th Peiyang Young Scientist Forum and the 2024 Tianjin University High-Level Forum for University Faculty, Postdoctoral Fellows...
Tianjin, China
Tianjin University (TJU)
High-level Talent Recruitment dedicated to teaching & research
College of Water Sciences, Beijing Normal University
Beijing, China
OSU Neurology Clayton C. Wagner Parkinson’s Disease Research Professorship
Columbus, Ohio
The Ohio State University (OSU)
Professor/Associate Professor/Assistant Professor/Senior Lecturer/Lecturer
The School of Science and Engineering (SSE) at The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-Shenzhen) sincerely invites applications for mul...
Shenzhen, China
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK Shenzhen)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Publish?
- About Research Evaluation
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
1. introduction, what is meant by impact, 2. why evaluate research impact, 3. evaluating research impact, 4. impact and the ref, 5. the challenges of impact evaluation, 6. developing systems and taxonomies for capturing impact, 7. indicators, evidence, and impact within systems, 8. conclusions and recommendations.
- < Previous
Assessment, evaluations, and definitions of research impact: A review
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Teresa Penfield, Matthew J. Baker, Rosa Scoble, Michael C. Wykes, Assessment, evaluations, and definitions of research impact: A review, Research Evaluation , Volume 23, Issue 1, January 2014, Pages 21–32, https://doi.org/10.1093/reseval/rvt021
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This article aims to explore what is understood by the term ‘research impact’ and to provide a comprehensive assimilation of available literature and information, drawing on global experiences to understand the potential for methods and frameworks of impact assessment being implemented for UK impact assessment. We take a more focused look at the impact component of the UK Research Excellence Framework taking place in 2014 and some of the challenges to evaluating impact and the role that systems might play in the future for capturing the links between research and impact and the requirements we have for these systems.
When considering the impact that is generated as a result of research, a number of authors and government recommendations have advised that a clear definition of impact is required ( Duryea, Hochman, and Parfitt 2007 ; Grant et al. 2009 ; Russell Group 2009 ). From the outset, we note that the understanding of the term impact differs between users and audiences. There is a distinction between ‘academic impact’ understood as the intellectual contribution to one’s field of study within academia and ‘external socio-economic impact’ beyond academia. In the UK, evaluation of academic and broader socio-economic impact takes place separately. ‘Impact’ has become the term of choice in the UK for research influence beyond academia. This distinction is not so clear in impact assessments outside of the UK, where academic outputs and socio-economic impacts are often viewed as one, to give an overall assessment of value and change created through research.
an effect on, change or benefit to the economy, society, culture, public policy or services, health, the environment or quality of life, beyond academia
Impact is assessed alongside research outputs and environment to provide an evaluation of research taking place within an institution. As such research outputs, for example, knowledge generated and publications, can be translated into outcomes, for example, new products and services, and impacts or added value ( Duryea et al. 2007 ). Although some might find the distinction somewhat marginal or even confusing, this differentiation between outputs, outcomes, and impacts is important, and has been highlighted, not only for the impacts derived from university research ( Kelly and McNicol 2011 ) but also for work done in the charitable sector ( Ebrahim and Rangan, 2010 ; Berg and Månsson 2011 ; Kelly and McNicoll 2011 ). The Social Return on Investment (SROI) guide ( The SROI Network 2012 ) suggests that ‘The language varies “impact”, “returns”, “benefits”, “value” but the questions around what sort of difference and how much of a difference we are making are the same’. It is perhaps assumed here that a positive or beneficial effect will be considered as an impact but what about changes that are perceived to be negative? Wooding et al. (2007) adapted the terminology of the Payback Framework, developed for the health and biomedical sciences from ‘benefit’ to ‘impact’ when modifying the framework for the social sciences, arguing that the positive or negative nature of a change was subjective and can also change with time, as has commonly been highlighted with the drug thalidomide, which was introduced in the 1950s to help with, among other things, morning sickness but due to teratogenic effects, which resulted in birth defects, was withdrawn in the early 1960s. Thalidomide has since been found to have beneficial effects in the treatment of certain types of cancer. Clearly the impact of thalidomide would have been viewed very differently in the 1950s compared with the 1960s or today.
In viewing impact evaluations it is important to consider not only who has evaluated the work but the purpose of the evaluation to determine the limits and relevance of an assessment exercise. In this article, we draw on a broad range of examples with a focus on methods of evaluation for research impact within Higher Education Institutions (HEIs). As part of this review, we aim to explore the following questions:
What are the reasons behind trying to understand and evaluate research impact?
What are the methodologies and frameworks that have been employed globally to assess research impact and how do these compare?
What are the challenges associated with understanding and evaluating research impact?
What indicators, evidence, and impacts need to be captured within developing systems
What are the reasons behind trying to understand and evaluate research impact? Throughout history, the activities of a university have been to provide both education and research, but the fundamental purpose of a university was perhaps described in the writings of mathematician and philosopher Alfred North Whitehead (1929) .
‘The justification for a university is that it preserves the connection between knowledge and the zest of life, by uniting the young and the old in the imaginative consideration of learning. The university imparts information, but it imparts it imaginatively. At least, this is the function which it should perform for society. A university which fails in this respect has no reason for existence. This atmosphere of excitement, arising from imaginative consideration transforms knowledge.’
In undertaking excellent research, we anticipate that great things will come and as such one of the fundamental reasons for undertaking research is that we will generate and transform knowledge that will benefit society as a whole.
One might consider that by funding excellent research, impacts (including those that are unforeseen) will follow, and traditionally, assessment of university research focused on academic quality and productivity. Aspects of impact, such as value of Intellectual Property, are currently recorded by universities in the UK through their Higher Education Business and Community Interaction Survey return to Higher Education Statistics Agency; however, as with other public and charitable sector organizations, showcasing impact is an important part of attracting and retaining donors and support ( Kelly and McNicoll 2011 ).
The reasoning behind the move towards assessing research impact is undoubtedly complex, involving both political and socio-economic factors, but, nevertheless, we can differentiate between four primary purposes.
HEIs overview. To enable research organizations including HEIs to monitor and manage their performance and understand and disseminate the contribution that they are making to local, national, and international communities.
Accountability. To demonstrate to government, stakeholders, and the wider public the value of research. There has been a drive from the UK government through Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE) and the Research Councils ( HM Treasury 2004 ) to account for the spending of public money by demonstrating the value of research to tax payers, voters, and the public in terms of socio-economic benefits ( European Science Foundation 2009 ), in effect, justifying this expenditure ( Davies Nutley, and Walter 2005 ; Hanney and González-Block 2011 ).
Inform funding. To understand the socio-economic value of research and subsequently inform funding decisions. By evaluating the contribution that research makes to society and the economy, future funding can be allocated where it is perceived to bring about the desired impact. As Donovan (2011) comments, ‘Impact is a strong weapon for making an evidence based case to governments for enhanced research support’.
Understand. To understand the method and routes by which research leads to impacts to maximize on the findings that come out of research and develop better ways of delivering impact.
The growing trend for accountability within the university system is not limited to research and is mirrored in assessments of teaching quality, which now feed into evaluation of universities to ensure fee-paying students’ satisfaction. In demonstrating research impact, we can provide accountability upwards to funders and downwards to users on a project and strategic basis ( Kelly and McNicoll 2011 ). Organizations may be interested in reviewing and assessing research impact for one or more of the aforementioned purposes and this will influence the way in which evaluation is approached.
It is important to emphasize that ‘Not everyone within the higher education sector itself is convinced that evaluation of higher education activity is a worthwhile task’ ( Kelly and McNicoll 2011 ). The University and College Union ( University and College Union 2011 ) organized a petition calling on the UK funding councils to withdraw the inclusion of impact assessment from the REF proposals once plans for the new assessment of university research were released. This petition was signed by 17,570 academics (52,409 academics were returned to the 2008 Research Assessment Exercise), including Nobel laureates and Fellows of the Royal Society ( University and College Union 2011 ). Impact assessments raise concerns over the steer of research towards disciplines and topics in which impact is more easily evidenced and that provide economic impacts that could subsequently lead to a devaluation of ‘blue skies’ research. Johnston ( Johnston 1995 ) notes that by developing relationships between researchers and industry, new research strategies can be developed. This raises the questions of whether UK business and industry should not invest in the research that will deliver them impacts and who will fund basic research if not the government? Donovan (2011) asserts that there should be no disincentive for conducting basic research. By asking academics to consider the impact of the research they undertake and by reviewing and funding them accordingly, the result may be to compromise research by steering it away from the imaginative and creative quest for knowledge. Professor James Ladyman, at the University of Bristol, a vocal adversary of awarding funding based on the assessment of research impact, has been quoted as saying that ‘…inclusion of impact in the REF will create “selection pressure,” promoting academic research that has “more direct economic impact” or which is easier to explain to the public’ ( Corbyn 2009 ).
Despite the concerns raised, the broader socio-economic impacts of research will be included and count for 20% of the overall research assessment, as part of the REF in 2014. From an international perspective, this represents a step change in the comprehensive nature to which impact will be assessed within universities and research institutes, incorporating impact from across all research disciplines. Understanding what impact looks like across the various strands of research and the variety of indicators and proxies used to evidence impact will be important to developing a meaningful assessment.
What are the methodologies and frameworks that have been employed globally to evaluate research impact and how do these compare? The traditional form of evaluation of university research in the UK was based on measuring academic impact and quality through a process of peer review ( Grant 2006 ). Evidence of academic impact may be derived through various bibliometric methods, one example of which is the H index, which has incorporated factors such as the number of publications and citations. These metrics may be used in the UK to understand the benefits of research within academia and are often incorporated into the broader perspective of impact seen internationally, for example, within the Excellence in Research for Australia and using Star Metrics in the USA, in which quantitative measures are used to assess impact, for example, publications, citation, and research income. These ‘traditional’ bibliometric techniques can be regarded as giving only a partial picture of full impact ( Bornmann and Marx 2013 ) with no link to causality. Standard approaches actively used in programme evaluation such as surveys, case studies, bibliometrics, econometrics and statistical analyses, content analysis, and expert judgment are each considered by some (Vonortas and Link, 2012) to have shortcomings when used to measure impacts.
Incorporating assessment of the wider socio-economic impact began using metrics-based indicators such as Intellectual Property registered and commercial income generated ( Australian Research Council 2008 ). In the UK, more sophisticated assessments of impact incorporating wider socio-economic benefits were first investigated within the fields of Biomedical and Health Sciences ( Grant 2006 ), an area of research that wanted to be able to justify the significant investment it received. Frameworks for assessing impact have been designed and are employed at an organizational level addressing the specific requirements of the organization and stakeholders. As a result, numerous and widely varying models and frameworks for assessing impact exist. Here we outline a few of the most notable models that demonstrate the contrast in approaches available.
The Payback Framework is possibly the most widely used and adapted model for impact assessment ( Wooding et al. 2007 ; Nason et al. 2008 ), developed during the mid-1990s by Buxton and Hanney, working at Brunel University. It incorporates both academic outputs and wider societal benefits ( Donovan and Hanney 2011 ) to assess outcomes of health sciences research. The Payback Framework systematically links research with the associated benefits ( Scoble et al. 2010 ; Hanney and González-Block 2011 ) and can be thought of in two parts: a model that allows the research and subsequent dissemination process to be broken into specific components within which the benefits of research can be studied, and second, a multi-dimensional classification scheme into which the various outputs, outcomes, and impacts can be placed ( Hanney and Gonzalez Block 2011 ). The Payback Framework has been adopted internationally, largely within the health sector, by organizations such as the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the Dutch Public Health Authority, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and the Welfare Bureau in Hong Kong ( Bernstein et al. 2006 ; Nason et al. 2008 ; CAHS 2009; Spaapen et al. n.d. ). The Payback Framework enables health and medical research and impact to be linked and the process by which impact occurs to be traced. For more extensive reviews of the Payback Framework, see Davies et al. (2005) , Wooding et al. (2007) , Nason et al. (2008) , and Hanney and González-Block (2011) .
A very different approach known as Social Impact Assessment Methods for research and funding instruments through the study of Productive Interactions (SIAMPI) was developed from the Dutch project Evaluating Research in Context and has a central theme of capturing ‘productive interactions’ between researchers and stakeholders by analysing the networks that evolve during research programmes ( Spaapen and Drooge, 2011 ; Spaapen et al. n.d. ). SIAMPI is based on the widely held assumption that interactions between researchers and stakeholder are an important pre-requisite to achieving impact ( Donovan 2011 ; Hughes and Martin 2012 ; Spaapen et al. n.d. ). This framework is intended to be used as a learning tool to develop a better understanding of how research interactions lead to social impact rather than as an assessment tool for judging, showcasing, or even linking impact to a specific piece of research. SIAMPI has been used within the Netherlands Institute for health Services Research ( SIAMPI n.d. ). ‘Productive interactions’, which can perhaps be viewed as instances of knowledge exchange, are widely valued and supported internationally as mechanisms for enabling impact and are often supported financially for example by Canada’s Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, which aims to support knowledge exchange (financially) with a view to enabling long-term impact. In the UK, UK Department for Business, Innovation, and Skills provided funding of £150 million for knowledge exchange in 2011–12 to ‘help universities and colleges support the economic recovery and growth, and contribute to wider society’ ( Department for Business, Innovation and Skills 2012 ). While valuing and supporting knowledge exchange is important, SIAMPI perhaps takes this a step further in enabling these exchange events to be captured and analysed. One of the advantages of this method is that less input is required compared with capturing the full route from research to impact. A comprehensive assessment of impact itself is not undertaken with SIAMPI, which make it a less-suitable method where showcasing the benefits of research is desirable or where this justification of funding based on impact is required.
The first attempt globally to comprehensively capture the socio-economic impact of research across all disciplines was undertaken for the Australian Research Quality Framework (RQF), using a case study approach. The RQF was developed to demonstrate and justify public expenditure on research, and as part of this framework, a pilot assessment was undertaken by the Australian Technology Network. Researchers were asked to evidence the economic, societal, environmental, and cultural impact of their research within broad categories, which were then verified by an expert panel ( Duryea et al. 2007 ) who concluded that the researchers and case studies could provide enough qualitative and quantitative evidence for reviewers to assess the impact arising from their research ( Duryea et al. 2007 ). To evaluate impact, case studies were interrogated and verifiable indicators assessed to determine whether research had led to reciprocal engagement, adoption of research findings, or public value. The RQF pioneered the case study approach to assessing research impact; however, with a change in government in 2007, this framework was never implemented in Australia, although it has since been taken up and adapted for the UK REF.
In developing the UK REF, HEFCE commissioned a report, in 2009, from RAND to review international practice for assessing research impact and provide recommendations to inform the development of the REF. RAND selected four frameworks to represent the international arena ( Grant et al. 2009 ). One of these, the RQF, they identified as providing a ‘promising basis for developing an impact approach for the REF’ using the case study approach. HEFCE developed an initial methodology that was then tested through a pilot exercise. The case study approach, recommended by the RQF, was combined with ‘significance’ and ‘reach’ as criteria for assessment. The criteria for assessment were also supported by a model developed by Brunel for ‘measurement’ of impact that used similar measures defined as depth and spread. In the Brunel model, depth refers to the degree to which the research has influenced or caused change, whereas spread refers to the extent to which the change has occurred and influenced end users. Evaluation of impact in terms of reach and significance allows all disciplines of research and types of impact to be assessed side-by-side ( Scoble et al. 2010 ).
The range and diversity of frameworks developed reflect the variation in purpose of evaluation including the stakeholders for whom the assessment takes place, along with the type of impact and evidence anticipated. The most appropriate type of evaluation will vary according to the stakeholder whom we are wishing to inform. Studies ( Buxton, Hanney and Jones 2004 ) into the economic gains from biomedical and health sciences determined that different methodologies provide different ways of considering economic benefits. A discussion on the benefits and drawbacks of a range of evaluation tools (bibliometrics, economic rate of return, peer review, case study, logic modelling, and benchmarking) can be found in the article by Grant (2006) .
Evaluation of impact is becoming increasingly important, both within the UK and internationally, and research and development into impact evaluation continues, for example, researchers at Brunel have developed the concept of depth and spread further into the Brunel Impact Device for Evaluation, which also assesses the degree of separation between research and impact ( Scoble et al. working paper ).
Although based on the RQF, the REF did not adopt all of the suggestions held within, for example, the option of allowing research groups to opt out of impact assessment should the nature or stage of research deem it unsuitable ( Donovan 2008 ). In 2009–10, the REF team conducted a pilot study for the REF involving 29 institutions, submitting case studies to one of five units of assessment (in clinical medicine, physics, earth systems and environmental sciences, social work and social policy, and English language and literature) ( REF2014 2010 ). These case studies were reviewed by expert panels and, as with the RQF, they found that it was possible to assess impact and develop ‘impact profiles’ using the case study approach ( REF2014 2010 ).
From 2014, research within UK universities and institutions will be assessed through the REF; this will replace the Research Assessment Exercise, which has been used to assess UK research since the 1980s. Differences between these two assessments include the removal of indicators of esteem and the addition of assessment of socio-economic research impact. The REF will therefore assess three aspects of research:
Environment
Research impact is assessed in two formats, first, through an impact template that describes the approach to enabling impact within a unit of assessment, and second, using impact case studies that describe the impact taking place following excellent research within a unit of assessment ( REF2014 2011a ). HEFCE indicated that impact should merit a 25% weighting within the REF ( REF2014 2011b ); however, this has been reduced for the 2014 REF to 20%, perhaps as a result of feedback and lobbying, for example, from the Russell Group and Million + group of Universities who called for impact to count for 15% ( Russell Group 2009 ; Jump 2011 ) and following guidance from the expert panels undertaking the pilot exercise who suggested that during the 2014 REF, impact assessment would be in a developmental phase and that a lower weighting for impact would be appropriate with the expectation that this would be increased in subsequent assessments ( REF2014 2010 ).
The quality and reliability of impact indicators will vary according to the impact we are trying to describe and link to research. In the UK, evidence and research impacts will be assessed for the REF within research disciplines. Although it can be envisaged that the range of impacts derived from research of different disciplines are likely to vary, one might question whether it makes sense to compare impacts within disciplines when the range of impact can vary enormously, for example, from business development to cultural changes or saving lives? An alternative approach was suggested for the RQF in Australia, where it was proposed that types of impact be compared rather than impact from specific disciplines.
Providing advice and guidance within specific disciplines is undoubtedly helpful. It can be seen from the panel guidance produced by HEFCE to illustrate impacts and evidence that it is expected that impact and evidence will vary according to discipline ( REF2014 2012 ). Why should this be the case? Two areas of research impact health and biomedical sciences and the social sciences have received particular attention in the literature by comparison with, for example, the arts. Reviews and guidance on developing and evidencing impact in particular disciplines include the London School of Economics (LSE) Public Policy Group’s impact handbook (LSE n.d.), a review of the social and economic impacts arising from the arts produced by Reeve ( Reeves 2002 ), and a review by Kuruvilla et al. (2006) on the impact arising from health research. Perhaps it is time for a generic guide based on types of impact rather than research discipline?
What are the challenges associated with understanding and evaluating research impact? In endeavouring to assess or evaluate impact, a number of difficulties emerge and these may be specific to certain types of impact. Given that the type of impact we might expect varies according to research discipline, impact-specific challenges present us with the problem that an evaluation mechanism may not fairly compare impact between research disciplines.
5.1 Time lag
The time lag between research and impact varies enormously. For example, the development of a spin out can take place in a very short period, whereas it took around 30 years from the discovery of DNA before technology was developed to enable DNA fingerprinting. In development of the RQF, The Allen Consulting Group (2005) highlighted that defining a time lag between research and impact was difficult. In the UK, the Russell Group Universities responded to the REF consultation by recommending that no time lag be put on the delivery of impact from a piece of research citing examples such as the development of cardiovascular disease treatments, which take between 10 and 25 years from research to impact ( Russell Group 2009 ). To be considered for inclusion within the REF, impact must be underpinned by research that took place between 1 January 1993 and 31 December 2013, with impact occurring during an assessment window from 1 January 2008 to 31 July 2013. However, there has been recognition that this time window may be insufficient in some instances, with architecture being granted an additional 5-year period ( REF2014 2012 ); why only architecture has been granted this dispensation is not clear, when similar cases could be made for medicine, physics, or even English literature. Recommendations from the REF pilot were that the panel should be able to extend the time frame where appropriate; this, however, poses difficult decisions when submitting a case study to the REF as to what the view of the panel will be and whether if deemed inappropriate this will render the case study ‘unclassified’.
5.2 The developmental nature of impact
Impact is not static, it will develop and change over time, and this development may be an increase or decrease in the current degree of impact. Impact can be temporary or long-lasting. The point at which assessment takes place will therefore influence the degree and significance of that impact. For example, following the discovery of a new potential drug, preclinical work is required, followed by Phase 1, 2, and 3 trials, and then regulatory approval is granted before the drug is used to deliver potential health benefits. Clearly there is the possibility that the potential new drug will fail at any one of these phases but each phase can be classed as an interim impact of the original discovery work on route to the delivery of health benefits, but the time at which an impact assessment takes place will influence the degree of impact that has taken place. If impact is short-lived and has come and gone within an assessment period, how will it be viewed and considered? Again the objective and perspective of the individuals and organizations assessing impact will be key to understanding how temporal and dissipated impact will be valued in comparison with longer-term impact.
5.3 Attribution
Impact is derived not only from targeted research but from serendipitous findings, good fortune, and complex networks interacting and translating knowledge and research. The exploitation of research to provide impact occurs through a complex variety of processes, individuals, and organizations, and therefore, attributing the contribution made by a specific individual, piece of research, funding, strategy, or organization to an impact is not straight forward. Husbands-Fealing suggests that to assist identification of causality for impact assessment, it is useful to develop a theoretical framework to map the actors, activities, linkages, outputs, and impacts within the system under evaluation, which shows how later phases result from earlier ones. Such a framework should be not linear but recursive, including elements from contextual environments that influence and/or interact with various aspects of the system. Impact is often the culmination of work within spanning research communities ( Duryea et al. 2007 ). Concerns over how to attribute impacts have been raised many times ( The Allen Consulting Group 2005 ; Duryea et al. 2007 ; Grant et al. 2009 ), and differentiating between the various major and minor contributions that lead to impact is a significant challenge.
Figure 1 , replicated from Hughes and Martin (2012) , illustrates how the ease with which impact can be attributed decreases with time, whereas the impact, or effect of complementary assets, increases, highlighting the problem that it may take a considerable amount of time for the full impact of a piece of research to develop but because of this time and the increase in complexity of the networks involved in translating the research and interim impacts, it is more difficult to attribute and link back to a contributing piece of research.

Time, attribution, impact. Replicated from ( Hughes and Martin 2012 ).
This presents particular difficulties in research disciplines conducting basic research, such as pure mathematics, where the impact of research is unlikely to be foreseen. Research findings will be taken up in other branches of research and developed further before socio-economic impact occurs, by which point, attribution becomes a huge challenge. If this research is to be assessed alongside more applied research, it is important that we are able to at least determine the contribution of basic research. It has been acknowledged that outstanding leaps forward in knowledge and understanding come from immersing in a background of intellectual thinking that ‘one is able to see further by standing on the shoulders of giants’.
5.4 Knowledge creep
It is acknowledged that one of the outcomes of developing new knowledge through research can be ‘knowledge creep’ where new data or information becomes accepted and gets absorbed over time. This is particularly recognized in the development of new government policy where findings can influence policy debate and policy change, without recognition of the contributing research ( Davies et al. 2005 ; Wooding et al. 2007 ). This is recognized as being particularly problematic within the social sciences where informing policy is a likely impact of research. In putting together evidence for the REF, impact can be attributed to a specific piece of research if it made a ‘distinctive contribution’ ( REF2014 2011a ). The difficulty then is how to determine what the contribution has been in the absence of adequate evidence and how we ensure that research that results in impacts that cannot be evidenced is valued and supported.
5.5 Gathering evidence
Gathering evidence of the links between research and impact is not only a challenge where that evidence is lacking. The introduction of impact assessments with the requirement to collate evidence retrospectively poses difficulties because evidence, measurements, and baselines have, in many cases, not been collected and may no longer be available. While looking forward, we will be able to reduce this problem in the future, identifying, capturing, and storing the evidence in such a way that it can be used in the decades to come is a difficulty that we will need to tackle.
Collating the evidence and indicators of impact is a significant task that is being undertaken within universities and institutions globally. Decker et al. (2007) surveyed researchers in the US top research institutions during 2005; the survey of more than 6000 researchers found that, on average, more than 40% of their time was spent doing administrative tasks. It is desirable that the assignation of administrative tasks to researchers is limited, and therefore, to assist the tracking and collating of impact data, systems are being developed involving numerous projects and developments internationally, including Star Metrics in the USA, the ERC (European Research Council) Research Information System, and Lattes in Brazil ( Lane 2010 ; Mugabushaka and Papazoglou 2012 ).
Ideally, systems within universities internationally would be able to share data allowing direct comparisons, accurate storage of information developed in collaborations, and transfer of comparable data as researchers move between institutions. To achieve compatible systems, a shared language is required. CERIF (Common European Research Information Format) was developed for this purpose, first released in 1991; a number of projects and systems across Europe such as the ERC Research Information System ( Mugabushaka and Papazoglou 2012 ) are being developed as CERIF-compatible.
In the UK, there have been several Jisc-funded projects in recent years to develop systems capable of storing research information, for example, MICE (Measuring Impacts Under CERIF), UK Research Information Shared Service, and Integrated Research Input and Output System, all based on the CERIF standard. To allow comparisons between institutions, identifying a comprehensive taxonomy of impact, and the evidence for it, that can be used universally is seen to be very valuable. However, the Achilles heel of any such attempt, as critics suggest, is the creation of a system that rewards what it can measure and codify, with the knock-on effect of directing research projects to deliver within the measures and categories that reward.
Attempts have been made to categorize impact evidence and data, for example, the aim of the MICE Project was to develop a set of impact indicators to enable impact to be fed into a based system. Indicators were identified from documents produced for the REF, by Research Councils UK, in unpublished draft case studies undertaken at King’s College London or outlined in relevant publications (MICE Project n.d.). A taxonomy of impact categories was then produced onto which impact could be mapped. What emerged on testing the MICE taxonomy ( Cooke and Nadim 2011 ), by mapping impacts from case studies, was that detailed categorization of impact was found to be too prescriptive. Every piece of research results in a unique tapestry of impact and despite the MICE taxonomy having more than 100 indicators, it was found that these did not suffice. It is perhaps worth noting that the expert panels, who assessed the pilot exercise for the REF, commented that the evidence provided by research institutes to demonstrate impact were ‘a unique collection’. Where quantitative data were available, for example, audience numbers or book sales, these numbers rarely reflected the degree of impact, as no context or baseline was available. Cooke and Nadim (2011) also noted that using a linear-style taxonomy did not reflect the complex networks of impacts that are generally found. The Goldsmith report ( Cooke and Nadim 2011 ) recommended making indicators ‘value free’, enabling the value or quality to be established in an impact descriptor that could be assessed by expert panels. The Goldsmith report concluded that general categories of evidence would be more useful such that indicators could encompass dissemination and circulation, re-use and influence, collaboration and boundary work, and innovation and invention.
While defining the terminology used to understand impact and indicators will enable comparable data to be stored and shared between organizations, we would recommend that any categorization of impacts be flexible such that impacts arising from non-standard routes can be placed. It is worth considering the degree to which indicators are defined and provide broader definitions with greater flexibility.
It is possible to incorporate both metrics and narratives within systems, for example, within the Research Outcomes System and Researchfish, currently used by several of the UK research councils to allow impacts to be recorded; although recording narratives has the advantage of allowing some context to be documented, it may make the evidence less flexible for use by different stakeholder groups (which include government, funding bodies, research assessment agencies, research providers, and user communities) for whom the purpose of analysis may vary ( Davies et al. 2005 ). Any tool for impact evaluation needs to be flexible, such that it enables access to impact data for a variety of purposes (Scoble et al. n.d.). Systems need to be able to capture links between and evidence of the full pathway from research to impact, including knowledge exchange, outputs, outcomes, and interim impacts, to allow the route to impact to be traced. This database of evidence needs to establish both where impact can be directly attributed to a piece of research as well as various contributions to impact made during the pathway.
Baselines and controls need to be captured alongside change to demonstrate the degree of impact. In many instances, controls are not feasible as we cannot look at what impact would have occurred if a piece of research had not taken place; however, indications of the picture before and after impact are valuable and worth collecting for impact that can be predicted.
It is now possible to use data-mining tools to extract specific data from narratives or unstructured data ( Mugabushaka and Papazoglou 2012 ). This is being done for collation of academic impact and outputs, for example, Research Portfolio Online Reporting Tools, which uses PubMed and text mining to cluster research projects, and STAR Metrics in the US, which uses administrative records and research outputs and is also being implemented by the ERC using data in the public domain ( Mugabushaka and Papazoglou 2012 ). These techniques have the potential to provide a transformation in data capture and impact assessment ( Jones and Grant 2013 ). It is acknowledged in the article by Mugabushaka and Papazoglou (2012) that it will take years to fully incorporate the impacts of ERC funding. For systems to be able to capture a full range of systems, definitions and categories of impact need to be determined that can be incorporated into system development. To adequately capture interactions taking place between researchers, institutions, and stakeholders, the introduction of tools to enable this would be very valuable. If knowledge exchange events could be captured, for example, electronically as they occur or automatically if flagged from an electronic calendar or a diary, then far more of these events could be recorded with relative ease. Capturing knowledge exchange events would greatly assist the linking of research with impact.
The transition to routine capture of impact data not only requires the development of tools and systems to help with implementation but also a cultural change to develop practices, currently undertaken by a few to be incorporated as standard behaviour among researchers and universities.
What indicators, evidence, and impacts need to be captured within developing systems? There is a great deal of interest in collating terms for impact and indicators of impact. Consortia for Advancing Standards in Research Administration Information, for example, has put together a data dictionary with the aim of setting the standards for terminology used to describe impact and indicators that can be incorporated into systems internationally and seems to be building a certain momentum in this area. A variety of types of indicators can be captured within systems; however, it is important that these are universally understood. Here we address types of evidence that need to be captured to enable an overview of impact to be developed. In the majority of cases, a number of types of evidence will be required to provide an overview of impact.
7.1 Metrics
Metrics have commonly been used as a measure of impact, for example, in terms of profit made, number of jobs provided, number of trained personnel recruited, number of visitors to an exhibition, number of items purchased, and so on. Metrics in themselves cannot convey the full impact; however, they are often viewed as powerful and unequivocal forms of evidence. If metrics are available as impact evidence, they should, where possible, also capture any baseline or control data. Any information on the context of the data will be valuable to understanding the degree to which impact has taken place.
Perhaps, SROI indicates the desire to be able to demonstrate the monetary value of investment and impact by some organizations. SROI aims to provide a valuation of the broader social, environmental, and economic impacts, providing a metric that can be used for demonstration of worth. This is a metric that has been used within the charitable sector ( Berg and Månsson 2011 ) and also features as evidence in the REF guidance for panel D ( REF2014 2012 ). More details on SROI can be found in ‘A guide to Social Return on Investment’ produced by The SROI Network (2012) .
Although metrics can provide evidence of quantitative changes or impacts from our research, they are unable to adequately provide evidence of the qualitative impacts that take place and hence are not suitable for all of the impact we will encounter. The main risks associated with the use of standardized metrics are that
The full impact will not be realized, as we focus on easily quantifiable indicators
We will focus attention towards generating results that enable boxes to be ticked rather than delivering real value for money and innovative research.
They risk being monetized or converted into a lowest common denominator in an attempt to compare the cost of a new theatre against that of a hospital.
7.2 Narratives
Narratives can be used to describe impact; the use of narratives enables a story to be told and the impact to be placed in context and can make good use of qualitative information. They are often written with a reader from a particular stakeholder group in mind and will present a view of impact from a particular perspective. The risk of relying on narratives to assess impact is that they often lack the evidence required to judge whether the research and impact are linked appropriately. Where narratives are used in conjunction with metrics, a complete picture of impact can be developed, again from a particular perspective but with the evidence available to corroborate the claims made. Table 1 summarizes some of the advantages and disadvantages of the case study approach.
The advantages and disadvantages of the case study approach
| Benefits . | Considerations . |
|---|---|
| Uses quantitative and qualitative data | Automated collation of evidence is difficult |
| Allows evidence to be contextualized and a story told | Incorporating perspective can make it difficult to assess critically |
| Enables assessment in the absence of quantitative data | Time-consuming to prepare and assess |
| Allows collation of unique datasets | Difficult to compare like with like |
| Preserves distinctive account or disciplinary perspective | Rewards those who can write well, and/or afford to pay for external input |
| Benefits . | Considerations . |
|---|---|
| Uses quantitative and qualitative data | Automated collation of evidence is difficult |
| Allows evidence to be contextualized and a story told | Incorporating perspective can make it difficult to assess critically |
| Enables assessment in the absence of quantitative data | Time-consuming to prepare and assess |
| Allows collation of unique datasets | Difficult to compare like with like |
| Preserves distinctive account or disciplinary perspective | Rewards those who can write well, and/or afford to pay for external input |
By allowing impact to be placed in context, we answer the ‘so what?’ question that can result from quantitative data analyses, but is there a risk that the full picture may not be presented to demonstrate impact in a positive light? Case studies are ideal for showcasing impact, but should they be used to critically evaluate impact?
7.3 Surveys and testimonies
One way in which change of opinion and user perceptions can be evidenced is by gathering of stakeholder and user testimonies or undertaking surveys. This might describe support for and development of research with end users, public engagement and evidence of knowledge exchange, or a demonstration of change in public opinion as a result of research. Collecting this type of evidence is time-consuming, and again, it can be difficult to gather the required evidence retrospectively when, for example, the appropriate user group might have dispersed.
The ability to record and log these type of data is important for enabling the path from research to impact to be established and the development of systems that can capture this would be very valuable.
7.4 Citations (outside of academia) and documentation
Citations (outside of academia) and documentation can be used as evidence to demonstrate the use research findings in developing new ideas and products for example. This might include the citation of a piece of research in policy documents or reference to a piece of research being cited within the media. A collation of several indicators of impact may be enough to convince that an impact has taken place. Even where we can evidence changes and benefits linked to our research, understanding the causal relationship may be difficult. Media coverage is a useful means of disseminating our research and ideas and may be considered alongside other evidence as contributing to or an indicator of impact.
The fast-moving developments in the field of altmetrics (or alternative metrics) are providing a richer understanding of how research is being used, viewed, and moved. The transfer of information electronically can be traced and reviewed to provide data on where and to whom research findings are going.
The understanding of the term impact varies considerably and as such the objectives of an impact assessment need to be thoroughly understood before evidence is collated.
While aspects of impact can be adequately interpreted using metrics, narratives, and other evidence, the mixed-method case study approach is an excellent means of pulling all available information, data, and evidence together, allowing a comprehensive summary of the impact within context. While the case study is a useful way of showcasing impact, its limitations must be understood if we are to use this for evaluation purposes. The case study does present evidence from a particular perspective and may need to be adapted for use with different stakeholders. It is time-intensive to both assimilate and review case studies and we therefore need to ensure that the resources required for this type of evaluation are justified by the knowledge gained. The ability to write a persuasive well-evidenced case study may influence the assessment of impact. Over the past year, there have been a number of new posts created within universities, such as writing impact case studies, and a number of companies are now offering this as a contract service. A key concern here is that we could find that universities which can afford to employ either consultants or impact ‘administrators’ will generate the best case studies.
The development of tools and systems for assisting with impact evaluation would be very valuable. We suggest that developing systems that focus on recording impact information alone will not provide all that is required to link research to ensuing events and impacts, systems require the capacity to capture any interactions between researchers, the institution, and external stakeholders and link these with research findings and outputs or interim impacts to provide a network of data. In designing systems and tools for collating data related to impact, it is important to consider who will populate the database and ensure that the time and capability required for capture of information is considered. Capturing data, interactions, and indicators as they emerge increases the chance of capturing all relevant information and tools to enable researchers to capture much of this would be valuable. However, it must be remembered that in the case of the UK REF, impact is only considered that is based on research that has taken place within the institution submitting the case study. It is therefore in an institution’s interest to have a process by which all the necessary information is captured to enable a story to be developed in the absence of a researcher who may have left the employment of the institution. Figure 2 demonstrates the information that systems will need to capture and link.
Research findings including outputs (e.g., presentations and publications)
Communications and interactions with stakeholders and the wider public (emails, visits, workshops, media publicity, etc)
Feedback from stakeholders and communication summaries (e.g., testimonials and altmetrics)
Research developments (based on stakeholder input and discussions)
Outcomes (e.g., commercial and cultural, citations)
Impacts (changes, e.g., behavioural and economic)

Overview of the types of information that systems need to capture and link.
Attempting to evaluate impact to justify expenditure, showcase our work, and inform future funding decisions will only prove to be a valuable use of time and resources if we can take measures to ensure that assessment attempts will not ultimately have a negative influence on the impact of our research. There are areas of basic research where the impacts are so far removed from the research or are impractical to demonstrate; in these cases, it might be prudent to accept the limitations of impact assessment, and provide the potential for exclusion in appropriate circumstances.
This work was supported by Jisc [DIINN10].
Google Scholar
Google Preview
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| January 2017 | 90 |
| February 2017 | 153 |
| March 2017 | 323 |
| April 2017 | 108 |
| May 2017 | 153 |
| June 2017 | 226 |
| July 2017 | 163 |
| August 2017 | 282 |
| September 2017 | 381 |
| October 2017 | 441 |
| November 2017 | 553 |
| December 2017 | 1,824 |
| January 2018 | 1,960 |
| February 2018 | 2,322 |
| March 2018 | 3,092 |
| April 2018 | 3,790 |
| May 2018 | 3,419 |
| June 2018 | 2,710 |
| July 2018 | 2,952 |
| August 2018 | 3,328 |
| September 2018 | 2,402 |
| October 2018 | 2,169 |
| November 2018 | 2,618 |
| December 2018 | 1,910 |
| January 2019 | 1,778 |
| February 2019 | 1,858 |
| March 2019 | 2,443 |
| April 2019 | 3,265 |
| May 2019 | 3,305 |
| June 2019 | 2,399 |
| July 2019 | 2,311 |
| August 2019 | 2,464 |
| September 2019 | 1,854 |
| October 2019 | 1,387 |
| November 2019 | 1,222 |
| December 2019 | 825 |
| January 2020 | 1,245 |
| February 2020 | 1,125 |
| March 2020 | 971 |
| April 2020 | 626 |
| May 2020 | 805 |
| June 2020 | 1,025 |
| July 2020 | 1,085 |
| August 2020 | 1,324 |
| September 2020 | 1,737 |
| October 2020 | 3,544 |
| November 2020 | 1,885 |
| December 2020 | 1,353 |
| January 2021 | 1,198 |
| February 2021 | 1,216 |
| March 2021 | 1,300 |
| April 2021 | 1,060 |
| May 2021 | 1,192 |
| June 2021 | 809 |
| July 2021 | 827 |
| August 2021 | 855 |
| September 2021 | 1,128 |
| October 2021 | 1,353 |
| November 2021 | 962 |
| December 2021 | 733 |
| January 2022 | 840 |
| February 2022 | 974 |
| March 2022 | 1,220 |
| April 2022 | 1,084 |
| May 2022 | 986 |
| June 2022 | 845 |
| July 2022 | 642 |
| August 2022 | 725 |
| September 2022 | 761 |
| October 2022 | 854 |
| November 2022 | 702 |
| December 2022 | 554 |
| January 2023 | 720 |
| February 2023 | 637 |
| March 2023 | 644 |
| April 2023 | 628 |
| May 2023 | 616 |
| June 2023 | 550 |
| July 2023 | 481 |
| August 2023 | 497 |
| September 2023 | 439 |
| October 2023 | 728 |
| November 2023 | 499 |
| December 2023 | 502 |
| January 2024 | 554 |
| February 2024 | 724 |
| March 2024 | 609 |
| April 2024 | 691 |
| May 2024 | 607 |
| June 2024 | 467 |
| July 2024 | 548 |
| August 2024 | 659 |
| September 2024 | 199 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1471-5449
- Print ISSN 0958-2029
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The purpose of. an evaluation is to judge the quality of a pe rformance or work product against a. standard. The fundamental nature of assessment is that a mentor values helping a. mentee and is ...
Research design specifics, such as research questions, instruments, and analysis methods; • Research sample, such as number of schools, teachers, and students; • Type(s) of formative assessment approach: DBDM and/or AfL; • Results, such as the evidence with regard to the role of the teacher in formative assessment (i.e., the prerequisites
Classroom assessment research often presents assessment literacy as a task for initial or in-service teacher education: to improve assessment, we must strengthen teachers' knowledge and skills as assessors (DeLuca & Volante, 2016; Xu & Brown, 2016). While this is a laudable goal, participating teachers emphasised that assessment literacy is ...
This article is a review of research on student self-assessment conducted largely between 2013 and 2018. The purpose of the review is to provide an updated overview of theory and research. The treatment of theory involves articulating a refined definition and operationalization of self-assessment. The review of 76 empirical studies offers a ...
Introduction. Assessment for learning (AfL) and differentiated instruction (DI) both imply a focus on learning processes and learning needs and affect student learning positively (Corno, Citation 2008; Ruiz-Primo & Furtak, Citation 2006; Tomlinson et al., Citation 2003; Black & Wiliam, Citation 1998; Yin et al., Citation 2014).Not surprisingly, both practices have been highlighted ...
Research on authentic assessment has explored various aspects including design, scoring, effects on teaching and learning, professional development, validity, reliability, and costs. Those are relative to authentic assessment (used interchangeably with performance assessment) in the classroom and will be reviewed.
Smith's (2013) formula determined that the number of respondents needed for a reliable representation of the population. The formula for an unknown population was 'Necessary sample size = (Z-score)2 x StdDev x (1-StdDev) / (margin of error)2'. The Z-score was 1.96, which corresponds to a confidence level of 95%.
Abstract. Assessment in its various forms has always been a central part of educational practice. Evidence gleaned from the empirical literature suggests that assessment, especially high stakes external assessment has effect on how teachers teach and consequently, how students learn. Through focus group discussions, this paper draws upon the ...
The paper contributes to the extant literature on assessment feedback by highlighting the integral role it plays in improving teaching and learning in the education field. The article is intended for educators (school administrators/leaders and teachers) and students whose goal is to facilitate teaching and learning for school effectiveness.
Villarroel and colleagues (Citation 2018) systematically reviewed core concepts across 112 papers to propose that authentic assessments are ... and Brown Citation 2014; Villarroel et al. Citation 2018), though some research on specific assessment strategies such as blogs emphasises the value of creativity in content and format in engaging ...
The purpose of this conceptual article is twofold. First, we articulate the interplay between feedback literacy and self-assessment based on a reframing and integration of the two concepts. Secondly, we unfold the self-assessment process into three steps: (1) determining and applying assessment criteria, (2) self-reflection, and (3) self ...
In this paper, a methodology for characterizing assessment environments at an engineering program level that is able to distinguish between weak, average, and talented students has been presented. Also an Assessment Experience Questionnaire (AEQ) that is competent of measuring students' learning response has been presented.
This paper explored how machine learning methods facilitate PE, intelligent assessment and data-intensive research in education. By using machine learning, especially DL models, in adaptive ITS, the learning paths can be changed dynamically and personalized based on the learner's progress and pace.
Research assessment can also affect work that universities often consider 'non-REF-able'. ... universities find it hard to look beyond academic papers as the metric for success even though ...
This paper examines six interrelated topics, denoted as follows: the definitional. issue, the effectiveness issue, the domain dependency issue, the measurement issue, the professional development ...
the proposed outcomes and reward mechanisms associated with assessment tasks and feedback. This paper proposes that teachers should strive to incorporate four different types of assessment tasks throughout a programme of study, namely diagnostic, formative, integrative and summative tasks, and that the outcomes and ... (Center for Research on
This research sought to examine classroom assessment designs that might make assessment inclusive. A critical literature review was conducted identifying 13 research papers where outcomes of inclusive assessment were reported. Included studies focussed on students with disabilities, international and linguistically diverse students.
In this paper, a methodology for characterizing assessment environments at an engineering program level that is able to distinguish between weak, average, and talented students has been presented.
(Research Centre, In Education, University of Calicut), Kerala, India [email protected] Mob: 9447847053 Abstract Assessment is an integral part of any teaching learning process. Assessment has large number of functions to perform, whether it is formative or summative assessment. This paper analyse the
A very different approach known as Social Impact Assessment Methods for research and funding instruments through the study of Productive Interactions (SIAMPI) was developed from the Dutch project Evaluating Research in Context and has a central theme of capturing 'productive interactions' between researchers and stakeholders by analysing ...
Evaluation. Teachers need assessment and evaluation results to assist them to plan, implement, and revise their classroom instruction. They also use these results to better meet the needs, often diverse, of their students, identify scholarship recipients, and advise students on what courses to take for. 9.
ation and Research Relationships and Definitions in the Field of Student AfairsAnn. E. LundquistThe terms assessment, evaluation, and research can mean many things to many people. There is not one agreed-upon definition in higher education for each of these terms, but, as the field of student afairs has evolved, and, as the emphasis on using ...
This study investigates teachers' assessment methods and the challenges they encounter in assessing learning in an Ethiopian university. A convergent parallel mixed-method research design was used ...
Classroom assessment is a continual activity for teachers to improve the quality of instruction and motivate students to learn (Gronlund, 2006). Although there is a great deal of research on teachers' assessment practices, few empirical research attempts have been made to link assessment practices to achievement goals.
* This paper was derived from the doctoral dissertation by Ceyhun Ozan conducted under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Remzi ... According to the research results, formative assessment was the third most influential factor among 138 factors for students' achievement. In the same order, feedback, which
This paper considers assessment of research quality by focusing on definition and. solution of research problems. W e develop and discuss, across different classes of. problems, a set of general ...