

How to Tackle an Essay (an ADHD-friendly Guide)
6 steps and tips.
Most of the college students I work with have one major assignment type that gets them stuck like no other: the dreaded essay. It has become associated with late nights, requesting extensions (and extensions on extensions), feelings of failure, and lots of time lost staring at a screen. This becomes immensely more stressful when there is a thesis or capstone project that stands between you and graduation.
The good news?
An essay doesn’t have to be the brick wall of doom that it once was. Here are some strategies to break down that wall and construct an essay you feel good about submitting.
Step 1: Remember you’re beginning an essay, not finishing one.
Without realizing it, you might be putting pressure on yourself to have polished ideas flow from your brain onto the paper. There’s a reason schools typically bring up having an outline and a rough draft! Thoughts are rarely organized immediately (even with your neurotypical peers, despite what they may say). Expecting yourself to deliver a publishing-worthy award winner on your first go isn’t realistic. It’s allowed to look messy and unorganized in the beginning! There can be unfinished thoughts, and maybe even arguments you aren’t sure if you want to include. When in doubt, write it down.
Step 2: Review the rubric
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the assignment is asking you to include and to focus on. If you don’t have an understanding of it, it’s better to find out in advance rather than the night before the assignment is due. The rubric is your anchor and serves as a good guide to know “when you can be done.” If you hit all the marks on the rubric, you’re looking at a good grade.
I highly recommend coming back to the rubric multiple times during the creative process, as it can help you get back on track if you’ve veered off in your writing to something unrelated to the prompt. It can serve as a reminder that it’s time to move onto a different topic - if you’ve hit the full marks for one area, it’s better to go work on another section and return to polish the first section up later. Challenge the perfectionism!
Step 3: Divide and conquer
Writing an essay is not just writing an essay. It typically involves reading through materials, finding sources, creating an argument, editing your work, creating citations, etc. These are all separate tasks that ask our brain to do different things. Instead of switching back and forth (which can be exhausting) try clumping similar tasks together.
For example:
Prepping: Picking a topic, finding resources related to topic, creating an outline
Gathering: reading through materials, placing information into the outline
Assembling: expanding on ideas in the outline, creating an introduction and conclusion
Finishing: Make final edits, review for spelling errors and grammar, create a title page and reference page, if needed.
Step 4: Chunk it up
Now we’re going to divide the work EVEN MORE because it’s also not realistic to expect yourself to assemble the paper all in one sitting. (Well, maybe it is realistic if you’re approaching the deadline, but we want to avoid the feelings of panic if we can.) If you haven’t heard of chunking before, it’s breaking down projects into smaller, more approachable tasks.
This serves multiple functions, but the main two we are focusing on here is:
- it can make it easier to start the task;
- it helps you create a timeline for how long it will take you to finish.
If you chunk it into groups and realize you don’t have enough time if you go at that pace, you’ll know how quickly you’ll need to work to accomplish it in time.
Here are some examples of how the above categories could be chunked up for a standard essay. Make sure you customize chunking to your own preferences and assignment criteria!
Days 1 - 3 : Prep work
- Day 1: Pick a topic & find two resources related to it
- Day 2: Find three more resources related to the topic
- Day 3: Create an outline
Days 4 & 5 : Gather
- Day 4: Read through Resource 1 & 2 and put information into the outline
- Day 5: Read through Resource 3 & 4 and put information into the outline
Days 6 - 8 : Assemble
- Day 6: Create full sentences and expand on Idea 1 and 2
- Day 7: Create full sentences and expand on Idea 3 and write an introduction
- Day 8: Read through all ideas and expand further or make sentence transitions smoother if need be. Write the conclusion
Day 9: Finish
- Day 9: Review work for errors and create a citation page
Hey, we just created an outline about how to make an outline - how meta!
Feel like even that is too overwhelming? Break it down until it feels like you can get started. Of course, you might not have that many days to complete an assignment, but you can do steps or chunks of the day instead (this morning I’ll do x, this afternoon I’ll do y) to accommodate the tighter timeline. For example:
Day 1: Pick a topic
Day 2: Find one resource related to it
Day 3: Find a second resource related to it
Step 5: Efficiently use your resources
There’s nothing worse than stockpiling 30 resources and having 100 pages of notes that can go into an essay. How can you possibly synthesize all of that information with the time given for this class essay? (You can’t.)
Rather than reading “Article A” and pulling all the information you want to use into an “Article A Information Page,” try to be intentional with the information as you go. If you find information that’s relevant to Topic 1 in your paper, put the information there on your outline with (article a) next to it. It doesn’t have to be a full citation, you can do that later, but we don’t want to forget where this information came from; otherwise, that becomes a whole mess.
By putting the information into the outline as you go, you save yourself the step of re-reading all the information you collected and trying to organize it later on.
*Note: If you don’t have topics or arguments created yet, group together similar ideas and you can later sort out which groups you want to move forward with.
Step 6: Do Some Self-Checks
It can be useful to use the Pomodoro method when writing to make sure you’re taking an adequate number of breaks. If you feel like the 25 min work / 5 min break routine breaks you out of your flow, try switching it up to 45 min work / 15 min break. During the breaks, it can be useful to go through some questions to make sure you stay productive:
- How long have I been writing/reading this paragraph?
- Does what I just wrote stay on topic?
- Have I continued the "write now, edit later" mentality to avoid getting stuck while writing the first draft?
- Am I starting to get frustrated or stuck somewhere? Would it benefit me to step away from the paper and give myself time to think rather than forcing it?
- Do I need to pick my energy back up? Should I use this time to get a snack, get some water, stretch it out, or listen to music?
General Tips:
- If you are having a difficult time trying to narrow down a topic, utilize office hours or reach out to your TA/professor to get clarification. Rather than pulling your hair out over what to write about, they might be able to give you some guidance that speeds up the process.
- You can also use (and SHOULD use) office hours for check-ins related to the paper, tell your teacher in advance you’re bringing your rough draft to office hours on Thursday to encourage accountability to get each step done. Not only can you give yourself extra pressure - your teacher can make sure you’re on the right track for the assignment itself.
- For help with citations, there are websites like Easybib.com that can help! Always double check the citation before including it in your paper to make sure the formatting and information is correct.
- If you’re getting stuck at the “actually writing it” phase, using speech-to-text tools can help you start by transcribing your spoken words to paper.
- Many universities have tutoring centers and/or writing centers. If you’re struggling, schedule a time to meet with a tutor. Even if writing itself isn’t tough, having a few tutoring sessions scheduled can help with accountability - knowing you need to have worked on it before the tutoring session is like having mini deadlines. Yay, accountability!
Of course, if writing just isn’t your jam, you may also struggle with motivation . Whatever the challenge is, this semester can be different. Reach out early if you need help - to your professor, a tutor, an ADHD coach , or even a friend or study group. You have a whole team in your corner. You’ve got this, champ!

Explore more

The Science of Slumber: Delving into Why We Sleep

How Do Gaming Mechanics Impact Mental Health?

Helping ADHD teens sleep better

Best Mindfulness Resources: ADHD Coach Favorites
Need help? Call us at (833) 966-4233
- Anxiety therapy
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Depression counseling
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
- Grief & loss counseling
- Relational therapy
- View all specialties & approaches
Thriveworks has earned 65+ awards (and counting) for our leading therapy and psychiatry services.
We’re in network with most major insurances – accepting 585+ insurance plans, covering 190 million people nationwide.
Thriveworks offers flexible and convenient therapy services, available both online and in-person nationwide, with psychiatry services accessible in select states.
Find the right provider for you, based on your specific needs and preferences, all online.
If you need assistance booking, we’ll be happy to help — our support team is available 7 days a week.
Discover more
ADHD is my superpower: A personal essay
Our clinical and medical experts , ranging from licensed therapists and counselors to psychiatric nurse practitioners, author our content, in partnership with our editorial team. In addition, we only use authoritative, trusted, and current sources. This ensures we provide valuable resources to our readers. Read our editorial policy for more information.
Thriveworks was established in 2008, with the ultimate goal of helping people live happy and successful lives. We are clinician-founded and clinician-led. In addition to providing exceptional clinical care and customer service, we accomplish our mission by offering important information about mental health and self-improvement.
We are dedicated to providing you with valuable resources that educate and empower you to live better. First, our content is authored by the experts — our editorial team co-writes our content with mental health professionals at Thriveworks, including therapists, psychiatric nurse practitioners, and more.
We also enforce a tiered review process in which at least three individuals — two or more being licensed clinical experts — review, edit, and approve each piece of content before it is published. Finally, we frequently update old content to reflect the most up-to-date information.

A Story About a Kid
In 1989, I was 7 years old and just starting first grade. Early in the school year, my teacher arranged a meeting with my parents and stated that she thought that I might be “slow” because I wasn’t performing in class to the same level as the other kids. She even volunteered to my parents that perhaps a “special” class would be better for me at a different school.
Thankfully, my parents rejected the idea that I was “slow” out of hand, as they knew me at home as a bright, talkative, friendly, and curious kid — taking apart our VHS machines and putting them back together, filming and writing short films that I’d shoot with neighborhood kids, messing around with our new Apple IIgs computer!
The school, however, wanted me to see a psychiatrist and have IQ tests done to figure out what was going on. To this day, I remember going to the office and meeting with the team — and I even remember having a blast doing the IQ tests. I remember I solved the block test so fast that the clinician was caught off guard and I had to tell them that I was done — but I also remember them trying to have me repeat numbers back backwards and I could barely do it!
Being Labeled
The prognosis was that I was high intelligence and had attention-deficit disorder (ADD). They removed the hyperactive part because I wasn’t having the type of behavioral problems like running around the classroom (I’ll cover later why I now proudly identify as hyperactive). A week later, my pediatrician started me on Ritalin and I was told several things that really honestly messed me up.
I was told that I had a “learning disability” — which, to 7-year-old me, didn’t make any sense since I LOVED learning! I was told that I would take my tests in a special room so that I’d have fewer distractions. So, the other kids would watch me walk out of the classroom and ask why I left the room when tests were happening — and they, too, were informed that I had a learning disability.
As you can imagine, kids aren’t really lining up to be friends with the “disabled” kid, nor did they hold back on playground taunts around the issue.
These were very early days, long before attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) was well known, and long before people had really figured out how to talk to kids with neurodiversities . And as a society, we didn’t really have a concept that someone who has a non-typical brain can be highly functional — it was a time when we didn’t know that the world’s richest man was on the autism spectrum !
Growing Past a Label
I chugged my way through elementary school, then high school, then college — getting consistent B’s and C’s. What strikes me, looking back nearly 30 years later, is just how markedly inconsistent my performance was! In highly interactive environments, or, ironically, the classes that were the most demanding, I did very well! In the classes that moved the slowest or required the most amount of repetition, I floundered.
Like, I got a good grade in the AP Biology course with a TON of memorization, but it was so demanding and the topics were so varied and fast-paced that it kept me engaged! On the opposite spectrum, being in basic algebra the teacher would explain the same simple concept over and over, with rote problem practice was torturously hard to stay focused because the work was so simple.
And that’s where we get to the part explaining why I think of my ADHD as a superpower, and why if you have it, or your kids have it, or your spouse has it… the key to dealing with it is understanding how to harness the way our brains work.
Learning to Thrive with ADHD
Disclaimer : What follows is NOT medical advice, nor is it necessarily 100% accurate. This is my personal experience and how I’ve come to understand my brain via working with my therapist and talking with other people with ADHD.
A Warp Speed Brain
To have ADHD means that your brain is an engine that’s constantly running at high speed. It basically never stops wanting to process information at a high rate. The “attention” part is just an observable set of behaviors when an ADHD person is understimulated. This is also part of why I now openly associate as hyperactive — my brain is hyperactive! It’s constantly on warp speed and won’t go any other speed.
For instance, one of the hardest things for me to do is fill out a paper check. It’s simple, it’s obvious, there is nothing to solve, it just needs to be filled out. By the time I have started writing the first stroke of the first character, my mind is thinking about things that I need to think about. I’m considering what to have for dinner, then I’m thinking about a movie I want to see, then I come up with an email to send — all in a second.
I have to haullll myself out of my alternate universe and back to the task at hand and, like a person hanging on the leash of a horse that’s bolting, I’m struggling to just write out the name of the person who I’m writing the check to! This is why ADHD people tend to have terrible handwriting, we’re not able to just only think about moving the pen, we’re in 1,000 different universes.
On the other hand, this entire blog post was written in less than an hour and all in one sitting. I’m having to think through a thousand aspects all at once. My dialog: “Is this too personal? Maybe you should put a warning about this being a personal discussion? Maybe I shouldn’t share this? Oh, the next section should be about working. Should I keep writing more of these?”
And because there is so much to think through and consider for a public leader like myself to write such a personal post, it’s highly engaging! My engine can run at full speed. I haven’t stood up for the entire hour, and I haven’t engaged in other nervous habits I have like picking things up — I haven’t done any of it!
This is what’s called hyperfocus, and it’s the part of ADHD that can make us potentially far more productive than our peers. I’ve almost arranged my whole life around making sure that I can get myself into hyperfocus as reliably as possible.
Harnessing What My Brain Is Built For
Slow-moving meetings are very difficult for me, but chatting in 20 different chat rooms at the same time on 20 different subjects is very easy for me — so you’ll much more likely see me in chat rooms than scheduling additional meetings. Knowing what my brain is built for helps me organize my schedule, work, and commitments that I sign up for to make sure that I can be as productive as possible.
If you haven’t seen the movie “Everything Everywhere All At Once,” and you are ADHD or love someone who is, you should immediately go watch it! The first time I saw it, I loved it, but I had no idea that one of its writers was diagnosed with ADHD as an adult , and decided to write a sci-fi movie about an ADHD person! The moment I read that it was about having ADHD my heart exploded. It resonated so much with me and it all made sense.
Practically, the only real action in the movie is a woman who needs to file her taxes. Now, don’t get me wrong — it’s a universe-tripping adventure that is incredibly exciting, but if you even take a step back and look at it, really, she was just trying to do her taxes.
But, she has a superpower of being able to travel into universes and be… everywhere all at once. Which is exactly how it feels to be in my mind — my brain is zooming around the universe and it’s visiting different thoughts and ideas and emotions. And if you can learn how to wield that as a power, albeit one that requires careful handling, you can do things that most people would never be able to do!
Co-workers have often positively noted that I see solutions that others miss and I’m able to find a course of action that takes account of multiple possibilities when the future is uncertain (I call it being quantum brained). Those two attributes have led me to create groundbreaking new technologies and build large teams with great open cultures and help solve problems and think strategically.
It took me until I was 39 to realize that ADHD isn’t something that I had to overcome to have the career I’ve had — it’s been my superpower .
Keep up-to-date on the latest in mental health
Tap into the wisdom of our experts — subscribe for exclusive wellness tips and insights.
Blog signup for Active Campaign (blog page)
- Email Address
Published Jul 15, 2022

The information on this page is not intended to replace assistance, diagnosis, or treatment from a clinical or medical professional. Readers are urged to seek professional help if they are struggling with a mental health condition or another health concern.
If you’re in a crisis, do not use this site. Please call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or use these resources to get immediate help.
162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples
Looking for ADHD topics to write about? ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) is a very common condition nowadays. It is definitely worth analyzing.
🔝 Top 10 ADHD Research Topics
🏆 best adhd essay examples, 💡 most interesting adhd topics to write about, 🎓 exciting adhd essay topics, 🔥 hot adhd topics to write about, 👍 adhd research paper topics, ❓ research questions about adhd.
In your ADHD essay, you might want to focus on the causes or symptoms of this condition. Another idea is to concentrate on the treatments for ADHD in children and adults. Whether you are looking for an ADHD topic for an argumentative essay, a research paper, or a dissertation, our article will be helpful. We’ve collected top ADHD essay examples, research paper titles, and essay topics on ADHD.
- ADHD and its subtypes
- The most common symptoms of ADHD
- The causes of ADHD: genetics, environment, or both?
- ADHD and the changes in brain structures
- ADHD and motivation
- Treating ADHD: the new trends
- Behavioral therapy as ADHD treatment
- Natural remedies for ADHD
- ADD vs. ADHD: is there a difference?
- Living with ADHD: the main challenges
- Learning Disabilities: Differentiating ADHD and EBD As for the most appropriate setting, it is possible to seat the child near the teacher. It is possible to provide instructions with the help of visual aids.
- Bright Not Broken: Gifted Kids, ADHD, and Autism It is possible to state that the book provides rather a high-quality review of the issues about the identification, education, and upbringing of the 2e children.
- Everything You Need to Know About ADHD The frontal hemisphere of the brain is concerned with coordination and a delay in development in this part of the brain can lead to such kind of disorder.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD / ADHD) Some critics maintain that the condition is a work of fiction by the psychiatric and pharmacists who have taken advantage of distraught families’ attempts to comprehend the behaviour of their children to dramatise the condition.
- Psychology: Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder It is important to pay attention to the development of proper self-esteem in children as it can negatively affect their development and performance in the future.
- ADHD and Its Effects on the Development of a Child In particular, this research study’s focus is the investigation of the impact of household chaos on the development and behavior of children with ADHD.
- The History of ADHD Treatment: Drug Addiction Disorders Therefore, the gathered data would be classified by year, treatment type, and gender to better comprehend the statistical distribution of the prevalence of drug addiction.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Recommended Therapy The condition affects the motivational functioning and abnormal cognitive and behavioural components of the brain. Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex contributed to a lack of alertness and shortened attention in the brain’s short-term memory.
- Rhetorical Modes Anthology on Attention Deficit Disorder It clearly outlines the origin and early symptoms of the disorder and the scientist who discovered attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Summary & Validity: This article describes the causes of hyperactivity disorder and the potential factors […]
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a Young Girl The particular objective was to assist Katie in becoming more focused and capable of finishing her chores. The patient received the same amount of IR Ritalin and was required to continue taking it for an […]
- Similarities and Differences: SPD, ADHD, and ASD The three disorders, Sensory Processing Disorder, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, and Autism Spectrum Disorder, are often confused with each other due to the connections and similarities that exist.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Awareness According to Sayal et al, ADHD is common in young boys as it is easier to identify the problem. The disorder is well-known, and there is no struggle to identify the problem.
- Assessing the Personality Profile With ADHD Characteristics On the contrary, the study was able to understand significant changes in the emotional states and mood of the children when the observations and the tests ended.
- Aspects of ADHD Patients Well-Being This goal can be achieved through the help of mental health and behavioral counselors to enhance behavioral modification and the ability to cope with challenges calmly and healthily.
- ADHD and Problems With Sleep This is because of the activity of a person in the middle of the day and the condition around them. The downside of the study is that the study group included 52 adults with ADHD […]
- The Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Treatment It has been estimated that when medicine and therapy are applied as treatment together, the outcomes for children with ADHD are excellent.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Organization’s Mission Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder is an organization that is determined to handle individuals affected by ADHD. The organization was founded in 1987 following the rampant frustration and isolation that parents experienced due to […]
- Case Conceptualization: Abuse-Mediated ADHD Patient The case provides insight into the underlying causes of James’s educational problems and the drug abuse of his parents. The case makes it evident that the assumption from the first case conceptualization about James’s ADHD […]
- Change: Dealing With Patients With ADHD In the current workplace, the most appropriate change would be the increase in the awareness of nurses regarding the methods of dealing with patients with ADHD.
- Dealing With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Although my experience is not dramatic, it clearly shows how untreated ADHD leads to isolation and almost depression. However, the question arises of what is the norm, how to define and measure it.
- Parents’ Perception of Attending an ADHD Clinic The main principles of the clinic’s specialists should be an objective diagnosis of the neurological status of the child and the characteristics of his/her behavior, the selection of drug treatment only on the basis of […]
- ADHD: Mental Disorder Based on Symptoms The DSM-5 raised the age limit from 6 to 12 for qualifying the disorder in children and now requires five instead of six inattentive or hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
- Understanding Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Thus, the smaller sizes of the reviewed brain structures associated with ADHD result in problems with attention, memory, and controlling movement and emotional responses.
- Effective Therapies for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder The problem at hand is that there is a need to determine which of the therapies administered is effective in the management of ADHD.
- Participants of “ADHD Outside the Laboratory” Study The participants in the testing group and those in the control group were matched for age within 6 months, for IQ within 15 points and finally for performance on the tasks of the study.
- Variables in “ADHD Outside the Laboratory” Study The other variables are the videogames, matching exercise and the zoo navigation exercise used to test the performance of the boys.
- Different Types of Diets and Children’s ADHD Treatment The last factor is a trigger that can lead to the development of a child’s genes’ reaction. Thus, diet is one of the factors that can help prevent the development of ADHD.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children The consistent utilization of effective praises and social rewards indeed results in the behavioral orientation of the child following the treatment goals.
- Vyvanse – ADD and ADHD Medicine Company Analysis It is produced by Shire and New River Pharmaceuticals in its inactive form which has to undergo digestion in the stomach and through the first-pass metabolic effect in the liver into L-lysine, an amino acid […]
- Dealing With the Disruptive Behaviors of ADHD and Asperger Syndrome Students While teaching in a class that has students with ADHD and Asperger syndrome, the teacher should ensure that they give instructions that are simple and easy to follow.
- Current Issues in Psychopharmacology: Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder This is the area that is charged with the responsibility for vision control as well as a regulation of one’s brain’s ability to go to aresynchronize’ and go to rest.
- Cognitive Psychology and Attention Deficit Disorder On top of the difficulties in regulating alertness and attention, many individuals with ADD complain of inabilities to sustain effort for duties.
- Adult and Paediatric Psychology: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder To allow children to exercise their full life potential, and not have any depression-caused impairment in the social, academic, behavioral, and emotional field, it is vital to reveal this disorder as early in life, as […]
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Biological Testing The research, leading to the discovery of the Biological testing for ADHD was conducted in Thessaloniki, Greece with 65 children volunteering for the research. There is a large difference in the eye movement of a […]
- Issues in the Diagnosis of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children Concept theories concerning the nature of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder influence treatment, the approach to the education of children with ADHD, and the social perception of this disease.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Care Controversy The objective of this study was to assess the efficacy, in terms of symptoms and function, and safety of “once-daily dose-optimized GXR compared with placebo in the treatment of children and adolescents aged 6 17 […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Interventions The authors examine a wide range of past studies that reported on the effects of peer inclusion interventions and present the overall results, showing why further research on peer inclusion interventions for children with ADHD […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in a Child A child counselor works with children to help them become mentally and emotionally stable. The case that is examined in this essay is a child with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Drug-Free Therapy The proposed study aims to create awareness of the importance of interventions with ADHD among parents refusing to use medication. The misperceptions about ADHD diagnosis and limited use of behavioral modification strategies may be due […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Psychosocial Interventions The mentioned components and specifically the effects of the condition on a child and his family would be the biggest challenge in the case of Derrick.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Comorbidities Due to the effects that ADHD has on patients’ relationships with their family members and friends, the development of comorbid health problems becomes highly possible.
- Medicating Kids to Treat ADHD The traditional view is that the drugs for the disorder are some of the safest in the psychiatric practice, while the dangers posed by untreated ADHD include failure in studies, inability to construct social connections, […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Signs and Strategies Determining the presence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a child and addressing the disorder is often a rather intricate process because of the vagueness that surrounds the issue.
- Cognitive Therapy for Attention Deficit Disorder The counselor is thus expected to assist the self-reflection and guide it in the direction that promises the most favorable outcome as well as raise the client’s awareness of the effect and, by extension, enhance […]
- “Stress” Video and “A Natural Fix for ADHD” Article There certainly are some deeper reasons for people to get stressed, and the video documentary “Stress: Portrait of a Killer” and the article “A Natural Fix for A.D.H.D”.by Dr.
- Attention Deficit Disorder: Diagnosis and Treatment The patient lives with her parents and 12-year-old brother in a middle-class neighborhood. Her father has a small business, and her mother works part-time in a daycare center.
- Treatment of Children With ADHD Because of the lack of sufficient evidence concerning the effects of various treatment methods for ADHD, as well as the recent Ritalin scandal, the idea of treating children with ADHD with the help of stimulant […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Medicalization This paper discusses the phenomenon of medicalization of ADHD, along with the medicalization of other aspects perceived as deviant or atypical, it will also review the clash of scientific ideas and cultural assumptions where medicalization […]
- Medication and Its Role in the ADHD Treatment Similar inferences can be inferred from the findings of the research conducted by Reid, Trout and Schartz that revealed that medication is the most appropriate treatment of the symptoms associated with ADHD.
- Children With Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder The purpose of the present research is to understand the correlation between the self-esteem of children with ADHD and the use of medication and the disorder’s characteristics.
- Natural Remedies for ADHD The key peculiarity of ADHD is that a patient displays several of these symptoms, and they are observed quite regularly. Thus, one can say that proper diet can be effective for the treatment of attention […]
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy in Children With ADHD The study revealed that the skills acquired by the children in the sessions were relevant in the long term since the children’s behaviors were modeled entirely.
- Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Real? In fact, the existence of the condition, its treatment and diagnosis, have been considered controversial topics since the condition was first suggested in the medical, psychology and education.
- Is Attention Deficit Disorder a Real Disorder? When Medicine Faces Controversial Issues In addition, it is necessary to mention that some of the symptoms which the children in the case study displayed could to be considered as the ones of ADHD.
- Foods That Effect Children With ADHD/ ADD Therefore, it is the duty of parents to identify specific foods and food additives that lead to hyperactivity in their children.
- Toby Diagnosed: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder The symptoms of the disorder are usually similar to those of other disorder and this increases the risks of misdiagnosing it or missing it all together.
- Identifying, Assessing and Treating Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder For these criteria to be effective in diagnosing a child with ADHD, the following symptoms have to be present so that the child can be labelled as having ADHD; the child has to have had […]
- ADHD Should Be Viewed as a Cognitive Disorder The manifestation of the disorder and the difficulties that they cause, as posited by the American Psychiatric Association, are typically more pronounced when a person is involved in some piece of work such as studying […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Influence on the Adolescents’ Behavior That is why the investigation was developed to prove or disprove such hypotheses as the dependence of higher rates of anxiety of adolescents with ADHD on their diagnosis, the dependence of ODD and CD in […]
- Stroop Reaction Time on Adults With ADHD The model was used to investigate the effectiveness of processes used in testing interference control and task-set management in adults with ADHD disorder.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Causes Family studies, relationship studies of adopted children, twin studies and molecular research have all confirmed that, ADHD is a genetic disorder.
- Diagnosis and Treatment of ADHD The diagnosis of ADHD has drawn a lot of attention from scientific and academic circles as some scholars argue that there are high levels of over diagnosis of the disorder.
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder As it would be observed, some of the symptoms associated with the disorder for children would differ from those of adults suffering from the same condition in a number of ways.
- Working Memory in Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Whereas many studies have indicated the possibility of the beneficial effects of WM training on people with ADHD, critics have dismissed them on the basis of flawed research design and interpretation.
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: The Basic Information in a Nutshell In the case with adults, however, the definition of the disorder will be quite different from the one which is provided for a child ADHD.
- How ADHD Develops Into Adult ADD The development of dominance is vital in processing sensations and information, storage and the subsequent use of the information. As they become teenagers, there is a change in the symptoms of ADHD.
- Medical Condition of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder A combination of impulsive and inattentive types is referred to as a full blown ADHD condition. To manage this condition, an array of medical, behavioral, counseling, and lifestyle modification is the best combination.
- Effects of Medication on Education as Related to ADHD In addition, as Rabiner argues, because of the hyperactivity and impulsivity reducing effect of ADHD drugs, most ADHD suffers are nowadays able to learn in an indistinguishable class setting, because of the reduced instances of […]
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Treatment Generally the results indicate that children with ADHD had a difficult time in evaluating time concepts and they seemed to be impaired in orientation of time.
- The Ritalin Fact Book: Stimulants Use in the ADHD Treatment Facts presented by each side of the critical issue The yes side of the critical issue makes it clear that the drugs being used to control ADHD are harmful as they affect the normal growth […]
- Behavior Modification in Children With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Introduction The objective of the article is to offer a description of the process of behavior modification for a child diagnosed with ADHD.
- What Is ADHD and How Does It Affect Kids
- The Benefits of Physical Activities in Combating the Symptoms of ADHD in Students
- The Effects of Exercise and Physical Activity as Intervention for Children with ADHD
- What Are the Effects of ADHD in the Classroom
- Are Children Being Diagnosed with ADHD too Hastily
- The Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on ADHD
- Understanding ADHD, Its Effects, Symptoms, and Approach to Children with ADHD
- ADHD Stimulant Medication Abuse and Misuse Among U.S. Teens
- Severity of ADHD and Anxiety Rise if Both Develop
- The Best Approach to Dealing with Attention Deficit/Herpactivity Disorder or ADHD in Children
- An Analysis of the Potential Causes and Treatment Methods for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Young Children
- The Best Way to Deal with Your Child Who Struggles with ADHD
- Response Inhibition in Children with ADHD
- Behavioral and Pharmacological Treatment of Children with ADHD
- Symptoms And Symptoms Of ADHD, Depression, And Anxiety
- Bioethics in Intervention in the Deficit Attention Hyperkinetic Disorder (ADHD)
- The Effects of Children’s ADHD on Parents’ Relationship Dissolution and Labor Supply
- The Effects of Pharmacological Treatment of ADHD on Children’s Health
- The Educational Implications Of ADHD On School Aged Children
- Differences in Perception in Children with ADHD
- The Effects Of ADHD On Children And Education System Child
- Students With ADD/ADHD and Class Placement
- The Advantage and Disadvantage of Using Psychostimulants in the Treatment of ADHD
- How to Increase Medication Compliance in Children with ADHD
- Effective Teaching Strategies for Students with ADHD
- Scientists Probe ADHD Treatment for Long Term Management of the Disease
- Should Stimulants Be Prescribed for ADHD Children
- The Rise of ADHD and the an Analysis of the Drugs Prescribed for Treatment
- The Correlation Between Smoking During Pregnancy And ADHD
- Exploring Interventions Improving Workplace Behavior In Adults With ADHD
- The Promise of Music and Art in Treating ADHD
- The Struggle Of ADHD Medication And Over Diagnosis
- The Problems of Detecting ADHD in Children
- The Harmful Effects of ADHD Medication in Children
- The Symptoms and Treatment of ADHD in Children and Teenagers
- The Impact of Adult ADD/ADHD on Education
- The Experience of Having the ADHD Disorder
- The Young Children And Children With ADHD, And Thinking Skills
- The Use of Ritalin in Treating ADD and ADHD
- The Ethics Of Giving Children ADHD Medication
- The Importance of Correctly Diagnosing ADHD in Children
- The Rise in ADHD Diagnosis and Treatment within the United States of America
- The World of ADHD Children
- The Use of Drug Therapies for Children with ADHD
- What Are the Effects of ADHD in the Classroom?
- Does ADHD Affect Essay Writing?
- What Are the Three Main Symptoms of ADHD?
- How Does ADHD Medication Affect the Brain?
- What Can ADHD Lead To?
- Is ADHD Legitimate Medical Diagnosis or Socially Constructed Disorder?
- How Does Art Help Children With ADHD?
- What Are the Four Types of ADHD?
- Can Sports Affect Impulse Control in Children With ADHD?
- What Age Does ADHD Peak?
- How Can You Tell if an Adult Has ADHD?
- Should Antihypertensive Drugs Be Used for Curing ADHD?
- How Does ADHD Affect Cognitive Development?
- Is Adult ADHD a Risk Factor for Dementia or Phenotypic Mimic?
- How Are People With ADHD Seen in Society?
- Can Additional Training Help Close the ADHD Gender Gap?
- How Does School Systems Deal With ADHD?
- Are Children With Low Working Memory and Children With ADHD Same or Different?
- How Does ADHD Affect School Performance?
- Should Children With ADHD Be Medicated?
- How Does Society View Children With ADHD?
- What Do Researches Tell Us About Students With ADHD in the Chilean Context?
- Why Should Teachers Understand ADHD?
- Does DD/ADHD Exist?
- What Are Some Challenges of ADHD?
- Why Is ADHD an Important Topic to Discuss?
- Is ADHD Born or Developed?
- Can ADHD Cause Lack of Emotion?
- Does ADHD Affect Females?
- Is ADHD on the Autism Spectrum?
- Neuropsychology Topics
- Bipolar Disorder Research Ideas
- Pathogenesis Research Ideas
- Abnormal Psychology Paper Topics
- Schizophrenia Essay Topics
- Dissociative Identity Disorder Essay Topics
- Cognitive Therapy Essay Topics
- Emotional Intelligence Paper Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 20). 162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adhd-essay-topics/
"162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 20 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adhd-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples'. 20 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples." February 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adhd-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples." February 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adhd-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "162 ADHD Essay Topics & Examples." February 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/adhd-essay-topics/.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Psychiatry & Mental Health — Adhd
ADHD ( Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) Essay Examples
Adhd essay topics and outline examples, essay title 1: understanding adhd: causes, symptoms, and treatment.
Thesis Statement: This research essay aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), including its possible causes, common symptoms, and various treatment approaches.
- Introduction
- Defining ADHD: An Overview
- Possible Causes of ADHD: Genetic, Environmental, and Neurological Factors
- Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing ADHD in Children and Adults
- Treatment Options: Medication, Behavioral Therapy, and Lifestyle Interventions
- The Impact of ADHD on Daily Life: School, Work, and Relationships
- Current Research and Future Directions in ADHD Studies
- Conclusion: Enhancing Understanding and Support for Individuals with ADHD
Essay Title 2: ADHD in Children: Educational Challenges and Supportive Strategies
Thesis Statement: This research essay focuses on the educational challenges faced by children with ADHD, explores effective strategies for supporting their learning, and highlights the importance of early intervention.
- Educational Implications of ADHD: Academic, Social, and Emotional Impact
- Supportive Classroom Strategies: Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) and 504 Plans
- Teacher and Parent Collaboration: Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
- Alternative Learning Approaches: Montessori, Waldorf, and Inclusive Education
- ADHD Medication in the Educational Context: Benefits and Considerations
- Early Intervention and the Role of Pediatricians and School Counselors
- Conclusion: Nurturing Academic Success and Well-Being in Children with ADHD
Essay Title 3: ADHD in Adulthood: Challenges, Coping Strategies, and Stigma
Thesis Statement: This research essay examines the often overlooked topic of ADHD in adults, discussing the challenges faced, coping mechanisms employed, and the impact of societal stigma on individuals with adult ADHD.
- ADHD Persisting into Adulthood: Recognizing the Symptoms
- Challenges Faced by Adults with ADHD: Work, Relationships, and Self-Esteem
- Coping Strategies and Treatment Options for Adult ADHD
- The Role of Mental Health Support: Therapy, Coaching, and Self-Help
- ADHD Stigma and Misconceptions: Impact on Diagnosis and Treatment
- Personal Stories of Triumph: Overcoming ADHD-Related Obstacles
- Conclusion: Raising Awareness and Providing Support for Adults with ADHD
A Negative Critique on ADHD Diagnosis and Treatment
Rethinking adhd: balancing medication with holistic interventions, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Understanding ADHD: an Informative Overview
The effect of adhd on the life of an individual, analysis of treatment decisions for a child with adhd, the effects of methylphenidate on adults with adhd, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Personal Experience of The Struggles Associated with Asperger's Syndrome and ADHD
Adhd: the child/teacher struggle, the importance of online schooling for add/adhd students, reduction of inhibitory control in people with adhd, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Negative Effects Associated with Prescription Drugs on Children with ADHD
How fidgeting actually contributes to a lack of focus in students, diagnosing dyscalculia and adhd diagnosis in schools, the issue of social injustice of misdiagnosed children with adhd, understanding adhd: a comprehensive analysis, behavioral disorders: causes, symptoms, and support.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by excessive amounts of inattention, carelessness, hyperactivity (which evolves into inner restlessness in adulthood), and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing, and otherwise age-inappropriate.
The major symptoms are inattention, carelessness, hyperactivity (evolves into restlessness in adults), executive dysfunction, and impulsivity.
The management of ADHD typically involves counseling or medications, either alone or in combination. While treatment may improve long-term outcomes, it does not get rid of negative outcomes entirely. Medications used include stimulants, atomoxetine, alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists, and sometimes antidepressants. In those who have trouble focusing on long-term rewards, a large amount of positive reinforcement improves task performance.ADHD stimulants also improve persistence and task performance in children with ADHD.
Relevant topics
- Mental Health
- Schizophrenia
- Stress Management
- Drug Addiction
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Our Mission
Writing Strategies for Students With ADHD
Here are six challenges and solutions, based on task simplicity and clear instruction, for helping students with ADHD develop their essay-writing skills.

Too often, students with ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) get labeled as "problem students." They often get shuffled into special education programs even if they show no signs of developmental disability. Though these students' brains do work differently, studies prove that it doesn't preclude them from being highly intelligent. That means teachers should pay special attention to help students with ADHD discover their potential and deal with the challenges they face in their learning process.
As essay writing is both the most common and the most complicated assignment for students, writing instruction for students with ADHD requires special efforts. Each step of writing process may present certain difficulties for these young people. Here are some practical solutions for teachers to encourage, motivate, and focus their students on writing process.
1. Difficulty Concentrating on Assignment
Research proves that ADHD doesn’t result in less intelligence, but rather in difficulties controlling emotions, staying motivated, and organizing the thoughts. So a teacher's first task is teaching students focus enough on a writing assignment.
Solution: Give clear, concise instructions.
When assigning an essay or other writing project, be specific and clear about what you expect. Don't leave a lot of room for interpretation. Instead of the assignment "Write about a joyous moment," include instructions in your writing prompt, such as:
- Think about the last time you felt happy and joyful.
- Describe the reasons for your happiness.
- What exactly made you feel joy?
- What can that feeling be compared to?
Make sure every student knows that he or she should come to you directly with any questions. Plan to take extra time reviewing the instructions with students one to one, writing down short instructions along the way.
2. Difficulty Organizing Thoughts on Paper
Several studies have found that students with ADHD struggle with organizing their thoughts and mental recall. These students can often speak well and explain their thoughts orally, but not in writing.
Solution: Get them organized from the start.
Start each project with a simple note system. Give students the freedom to take their own notes and review them together if possible. Have students pay special attention to filing these notes in a large binder, folder, or other method for making storage and retrieval simple.
To help students understand how to organize their written thoughts, teach them mind mapping . A semantic mind map for an essay may include major nouns, verbs, and adjectives, as well as phrases to use in writing each paragraph. Some introductory and transition sentences will also come in handy. Another step after mind mapping is advanced outlining . Begin and end the initial outline with the words "Intro" and "Conclusion" as placeholders. Then have students expand that outline on their own.
3. Difficulty With Sustained Work on a Single Task
ADHD can make it difficult for students to focus on long-term goals, leading to poor attention and concentration when the task requires work for an extended period of time.
Solution: Create small, manageable milestones.
Since accomplishing a five-page essay takes a lot of time, you can chop it into smaller, easier-to-manage pieces that can be worked on in rotation. Each piece may be checked separately if time allows. Treating every issue and section as an independent task will prevent students from feeling overwhelmed as they work toward a larger goal.
4. Difficulty in Meeting Deadlines
Deadlines are the things that discourage students with ADHD, as they work on assignments more slowly than their classmates, are often distracted, and tend to procrastinate.
Solution: Allow for procrastination.
It may sound ridiculous, but build procrastination into the writing process by breaking up the work and allowing for extra research, brainstorming, and other activities which diversify students' work while still focusing on the end result.
5. Spelling Issues
Students with ADHD often have difficulties with writing, especially in terms of spelling. The most common issues are reversing or omitting letters, words, or phrases. Students may spell the same word differently within the same essay. That's why lots of attention should be paid to spelling.
Solution: Encourage spell checkers, dictionaries, and thesaurus.
There are plenty of writing apps and tools available to check spelling and grammar. As a teacher, you can introduce several apps and let students choose which ones work better for writing essays. When checking the submitted papers and grading the work, highlight the spelling mistakes so that students can pay special attention to the misspelled words and remember the correct variant.
6. Final Editing Issues
Students with ADHD may experience problems during the final editing of their work since, by this time, they will have read and reviewed it several times and may not be paying attention to mistakes.
Solution: Teach them to review their writing step by step.
Take an essay template as an example and show students how to revise it. Go through the editing process slowly, explaining the "why" behind certain changes, especially when it comes to grammatical issues. Assign students the task of revising each other's essays so that when they revise their own final draft, they'll know what to pay attention to and what common mistakes to look for.
Addressing the challenges unique to students with ADHD will help these students find ways to handle their condition effectively and even use it to their advantage. Their unique perspective can be channeled into creative writing, finding new solutions to problems, and most of all, finding, reaching, and even exceeding their goals and fulfilling their full potential.

The Impact of ADHD on Academic Performance
The importance of advocating for your child with their educators..
Posted February 17, 2023 | Reviewed by Tyler Woods
- What Is ADHD?
- Take our ADHD Test
- Find a therapist to help with ADHD
- ADHD symptoms contribute to poor academic performance.
- The symptoms of inattentive-type ADHD make it difficult diagnose in school-age children.
- Advocating for your child with educators can improve their academic performance.
- Working with your child’s ADHD is key to their academic success.
A major concern for parents of ADHD children is their performance in school, and parents often worry over criticizing their children for behaviors like difficulty finishing homework . Poor academic performance can result in failing grades, skipping school, dropping out of high school, or not attending college.
Inattentive-type ADHD is difficult to identify
Children with the inattentive subtype of ADHD can fly under the radar at school and at home with symptoms of inattention, forgetfulness, and disorganization. Michael Jellineck, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, has estimated children with ADHD could receive as many as 20,000 corrections for their behavior in school by the time they are 10 years old. The symptom of inattentive-type ADHD, including behaviors like disappearing to the bathroom or nurse’s office during class to avoid a disliked task, are difficult to identify correctly as the inattentive subtype and can often be confused with other behavioral problems.
According to the Centers for Disease Control 2017 report, nine out of ten children with ADHD received classroom accommodations in school. However, most children with ADHD are not in special education programs and their teachers may know little about ADHD behaviors. Knowledge of ADHD, including symptoms, behaviors, prognosis, and treatment, varies among teachers (Mohr-Jennsen et al., 2019), and educators are most knowledgeable about the “hallmark” symptoms of ADHD, like students fidgeting or squirming in their seat and being easily distracted by extraneous stimuli (Scuitto et al., 2016).
Advocating for your child
Since my son’s inattentive ADHD is not outwardly apparent (i.e., he isn’t hyperactive or disruptive in the classroom), advocating for him, and teaching him to advocate for himself, is one of my most important jobs as a parent. I was inspired by the story of a father who would send letters to his son’s teachers explaining the boy’s learning disability. Knowing my son’s performance did not always reflect his capabilities, I emailed my son’s middle and high school teachers at the beginning of each semester detailing his ADHD, his weaknesses, and, most importantly, his strengths. I was pleasantly surprised that the reaction from many of my son’s teachers over the years was positive; they were grateful for parental communication and support. Teachers with a greater understanding of ADHD recognize the benefit of behavioral and educational treatments and are more likely to help their students (Ohan et al., 2008). In my son’s case, educators who either had ADHD themselves, or sought to learn about it, had the biggest impact in terms of my son’s academic success.
Practical strategies for common academic struggles
Due to the executive function deficits that accompany ADHD, our kids cannot just “try harder” to get good grades. They are already working harder than their peers to stay afloat in school. According to Mayes and Calhoun (2000) more than half of ADHD children struggle with written expression, my son included. Executive function deficits in ADHD make organizing ideas, planning, and editing difficult. I helped my son by having him talk it out when he had to write an essay for school (this was also an accommodation in his 504 plan to help him answer essay questions on tests and other assignments). I would start by asking him to tell me one fact about his essay’s topic. I found that he knew what he wanted to say, but organizing his thoughts on the page was an overwhelming and difficult task for him. I would furiously type while he talked, then gave him the notes, making it much easier for him to compose his essay. Another strategy was to have him incorporate something about a topic he was interested in, if possible. Anytime my son could write something about outer space or rockets he struggled less, even being selected as a national finalist in a NASA-sponsored essay contest about traveling to Mars.
Approximately 25-40% of patients with ADHD have major reading and writing difficulties, and ADHD frequently co-occurs with other learning disabilities like dyslexia, which makes reading difficult. In addition, the inattention symptoms of ADHD likely interfere with reading ability, resulting in reading the same paragraph over and over without retaining the information. As parents, we have to accept that our ADHD kids learn differently and not be concerned with the traditional, or 'right' way of doing something. My son retained information from required reading in school much better when he listened to an audiobook, rather than trying to painstakingly read the book. What did it matter if my son read the book or listened to it being read? Let’s take a cue from our ADHD kids and think outside the box.
Learning to work with my son’s ADHD gave me a better understanding of his strengths and weaknesses when it came to his academic performance. As a result, I was a better advocate for him and was able to work with his teachers to ensure his academic success.
Albert, M., Rui, P., & Ashman, J.J. (2017). Physician office visits for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents Aged 4–17 Years: United States, 2012–2013 . National Center for Health Statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/ databriefs/db269.htm.
Mayes, S.D. & Calhoun, S. (2000, April). Prevalence and degree of attention and learning problems in ADHD and LD. ADHD Reports , 8 (2).
Mohr-Jensen, C., Steen-Jensen, T., Bang Schnack, M., &Thingvad, H. (2019). What do primary and secondary school teachers kno about ADHD in children? Findings from a systematic review and a representative, nationwide sample of Danish teachers. Journal of Attention Disorders 23(3): 206-219.
Ohan, J. L., Cormier, N., Hepp, S. L., Visser, T. A. W., & Strain, M. C. (2008). Does knowledge about attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder impact teachers' reported behaviors and perceptions? School Psychology Quarterly, 23 (3), 436–449.
Sciutto, M.J., Terjesen, M.D., Kučerová, A., Michalová, Z., Schmiedeler, S., Antonopoulou, K., Shaker, N.Z., Lee, J., Lee, K., Drake, B., & Rossouw, J. (2016). Cross-national comparisons of teachers’ knowledge and misconceptions of ADHD. International Perspectives in Psychology 5(1): 34-50.

Kristin Wilcox, Ph.D. , is the author of Andrew's Awesome Adventures with His ADHD Brain . She has studied ADHD medications and drug abuse behavior at Emory University and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- What is ADHD?
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common mental disorders affecting children. Symptoms of ADHD include inattention (not being able to keep focus), hyperactivity (excess movement that is not fitting to the setting) and impulsivity (hasty acts that occur in the moment without thought). ADHD is considered a chronic and debilitating disorder and is known to impact the individual in many aspects of their life including academic and professional achievements, interpersonal relationships, and daily functioning (Harpin, 2005). ADHD can lead to poor self-esteem and social function in children when not appropriately treated (Harpin et al., 2016). Adults with ADHD may experience poor self-worth, sensitivity towards criticism, and increased self-criticism possibly stemming from higher levels of criticism throughout life (Beaton, et al., 2022). Of note, ADHD presentation and assessment in adults differs; this page focuses on children.
An estimated 8.4% of children and 2.5% of adults have ADHD (Danielson, 2018; Simon, et al., 2009). ADHD is often first identified in school-aged children when it leads to disruption in the classroom or problems with schoolwork. It is more commonly diagnosed among boys than girls given differences in how the symptoms present. However, this does not mean that boys are more likely to have ADHD. Boys tend to present with hyperactivity and other externalizing symptoms whereas girls tend to have inactivity.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Many children may have difficulties sitting still, waiting their turn, paying attention, being fidgety, and acting impulsively. However, children who meet diagnostic criteria for ADHD, differ in that their symptoms of hyperactivity, impulsivity, organization, and/or inattention are noticeably greater than expected for their age or developmental level. These symptoms lead to significant suffering and cause problems at home, at school or work, and in relationships. The observed symptoms are not the result of an individual being defiant or not being able to understand tasks or instructions.
There are three main types of ADHD:
- Predominantly inattentive presentation.
- Predominantly hyperactive/impulsive presentation.
- Combined presentation.
A diagnosis is based on the presence of persistent symptoms that have occurred over a period of time and are noticeable over the past six months. While ADHD can be diagnosed at any age, this disorder begins in childhood. When considering the diagnosis, the symptoms must be present before the individual is 12 years old and must have caused difficulties in more than one setting. For instance, the symptoms can not only occur at home.
Inattentive type
Inattentive refers to challenges with staying on task, focusing, and organization. For a diagnosis of this type of ADHD, six (or five for individuals who are 17 years old or older) of the following symptoms occur frequently:
- Doesn’t pay close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in school or job tasks.
- Has problems staying focused on tasks or activities, such as during lectures, conversations or long reading.
- Does not seem to listen when spoken to (i.e., seems to be elsewhere).
- Does not follow through on instructions and doesn’t complete schoolwork, chores or job duties (may start tasks but quickly loses focus).
- Has problems organizing tasks and work (for instance, does not manage time well; has messy, disorganized work; misses deadlines).
- Avoids or dislikes tasks that require sustained mental effort, such as preparing reports and completing forms.
- Often loses things needed for tasks or daily life, such as school papers, books, keys, wallet, cell phone and eyeglasses.
- Is easily distracted.
- Forgets daily tasks, such as doing chores and running errands. Older teens and adults may forget to return phone calls, pay bills and keep appointments.
Hyperactive/impulsive type
Hyperactivity refers to excessive movement such as fidgeting, excessive energy, not sitting still, and being talkative. Impulsivity refers to decisions or actions taken without thinking through the consequences. For a diagnosis of this type of ADHD, six (or five for individuals who are 17 years old or older) of the following symptoms occur frequently:
- Fidgets with or taps hands or feet, or squirms in seat.
- Not able to stay seated (in classroom, workplace).
- Runs about or climbs where it is inappropriate.
- Unable to play or do leisure activities quietly.
- Always “on the go,” as if driven by a motor.
- Talks too much.
- Blurts out an answer before a question has been finished (for instance may finish people’s sentences, can’t wait to speak in conversations).
- Has difficulty waiting for his or her turn, such as while waiting in line.
- Interrupts or intrudes on others (for instance, cuts into conversations, games or activities, or starts using other people’s things without permission). Older teens and adults may take over what others are doing.
Combined type
This type of ADHD is diagnosed when both criteria for both inattentive and hyperactive/impulse types are met.
ADHD is typically diagnosed by mental health providers or primary care providers. A psychiatric evaluation will include a description of symptoms from the patient and caregivers, completion of scales and questionnaires by patient, caregivers and teachers, complete psychiatric and medical history, family history, and information regarding education, environment, and upbringing. It may also include a referral for medical evaluation to rule out other medical conditions.
It is important to note that several conditions can mimic ADHD such as learning disorders, mood disorders, anxiety, substance use, head injuries, thyroid conditions, and use of some medications such as steroids (Austerman, 2015). ADHD may also co-exist with other mental health conditions, such as oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder, anxiety disorders, and learning disorders (Austerman, 2015). Thus, a full psychiatric evaluation is very important. There are no specific blood tests or routine imaging for ADHD diagnosis. Sometimes, patients may be referred for additional psychological testing (such as neuropsychological or psychoeducational testing) or may undergo computer-based tests to assess the severity of symptoms.
The Causes of ADHD
Scientists have not yet identified the specific causes of ADHD. While there is growing evidence that genetics contribute to ADHD and several genes have been linked to the disorder, no specific gene or gene combination has been identified as the cause of the disorder. However, it is important to note that relatives of individuals with ADHD are often also affected. There is evidence of anatomical differences in the brains of children with ADHD in comparison to other children without the condition. For instance, children with ADHD have reduced grey and white brain matter volume and demonstrate different brain region activation during certain tasks (Pliszka, 2007). Further studies have indicated that the frontal lobes, caudate nucleus, and cerebellar vermis of the brain are affected in ADHD (Tripp & Wickens, 2009). Several non-genetic factors have also been linked to the disorder such as low birth weight, premature birth, exposure to toxins (alcohol, smoking, lead, etc.) during pregnancy, and extreme stress during pregnancy.
ADHD treatment usually encompasses a combination of therapy and medication intervention. In preschool-age and younger children, the recommended first-line approach includes behavioral strategies in the form of parent management training and school intervention. Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT) is an evidence-based therapy modality to help young children with ADHD and oppositional defiant disorder.
According to current guidelines, psychostimulants (amphetamines and methylphenidate) are first-line pharmacological treatments for the management of ADHD (Pliszka, 2007). In preschool-aged patients with ADHD, amphetamines are the only FDA-approved medication, although guidelines suggest that methylphenidate rather than amphetamines may be helpful if behavioral interventions prove insufficient. Alpha agonists (clonidine and guanfacine) and the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, atomoxetine, are the other FDA-approved options for treating ADHD. There are newer FDA-approved medications for ADHD treatment, including Jornay (methylphenidate extended-release) which is taken at night and starts the medication effect the next morning, Xelstrym (dextroamphetamine) which is an amphetamine patch, Qelbree (viloxazine) which is a non-stimulant, Adhansia (methylphenidate hydrochloride), Dyanavel (amphetamine extended-release oral suspension), Mydayis (mixed salts amphetamine product), and Cotempla (methylphenidate extended-release orally disintegrating tablets).
Many children and families can alternate between various medication options depending on the efficacy of treatment and tolerability of the medication. The goal of treatment is to improve symptoms to restore functioning at home and at school.
ADHD and School-Aged Children
Teachers and school staff can provide parents and doctors with information to help evaluate behavior and learning problems and can assist with behavioral training. However, school staff cannot diagnose ADHD, make decisions about treatment or require that a student take medication to attend school. Only parents and guardians can make those decisions with the child’s health care clinician.
Students whose ADHD impairs their learning may qualify for special education under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act or for a Section 504 plan (for children who do not require special education) under the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Children with ADHD can benefit from study skills instruction, changes to the classroom setup, alternative teaching techniques and a modified curriculum.
ADHD and Adults
Many children diagnosed with ADHD will continue to meet criteria for the disorder later in life and may show impairments requiring ongoing treatment (Pliszka, 2007). However, sometimes a diagnosis of ADHD is missed during childhood. Many adults with ADHD do not realize they have the disorder. A comprehensive evaluation typically includes a review of past and current symptoms, a medical exam and history, and use of adult rating scales or checklists. Adults with ADHD are treated with medication, psychotherapy or a combination. Behavior management strategies, such as ways to minimize distractions and increase structure and organization, and support from immediate family members can also be helpful.
ADHD is a protected disability under the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This means that institutions receiving federal funding cannot discriminate against those with disabilities. Individuals whose symptoms of ADHD cause impairment in the work setting may qualify for reasonable work accommodations under ADA.
Related Conditions
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Disruptive, impulse control and conduct disorders
- Social communication disorder
- Specific learning disorder
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) . 2013.
- Austerman J. ADHD and behavioral disorders: Assessment, management, a nd an update from DSM-5 . Cleve Clin J Med. 2015 Nov;82(11 Suppl 1):S2-7.
- Beaton, D. M., Sirois, F., & Milne, E. (2022). Experiences of criticism in adults with ADHD: A qualitative study . PloS one, e0263366.
- Danielson, M.L., et al. Prevalence of Parent-Reported ADHD Diagnosis and Associated Treatment Among U.S. Children and Adolescents, 2016. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, Volume 47, 2018 - Issue 2.
- Harpin VA. (2005). The effect of ADHD on the life of an individual, their family, and community from preschool to adult life. Arch Dis Child. 90 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i2-7.
- Harpin V, Mazzone L, Raynaud JP, Kahle J, Hodgkins P. (2013). Long-Term Outcomes of ADHD: A Systematic Review of Self-Esteem and Social Function . J Atten Disord. 20(4):295-305.
- Pliszka S; AACAP Work Group on Quality Issues. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder . J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007 Jul;46(7):894-921.
- Simon, V. , Czobor, P. , Bálint, S. , et al: : Prevalence and correlates of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry194(3):204–211, 2009
- Tripp, G., Wickens, J.R. Neurobiology of ADHD . Neuropharmacology. 2009 Dec;57(7-8):579-89.
- Wolraich, M.L., Hagan, J.F.J., Allan, C., et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics. 2019;144(4).
Physician Review
Rana Elmaghraby, M.D.
Stephanie Garayalde, M.D.
More on ADHD
- Children and Adults with ADHD (CHADD): Online ADHD Training for Parents
- Parent's Medication Guide: ADHD – from APA and AACAP (.pdf)
- National Institutes on Mental Health (NIMH) - ADHD
- Attention Deficit Disorder Association (ADDA)
- ADDitude Magazine - Directory of parent support
- American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP)
Medical leadership for mind, brain and body.
Mobile menu.
- Psychiatrists
- Residents & Medical Students
- Patients and Families
- Advocacy & APAPAC
- Diversity & Health Equity
- Research & Registry
- Meetings & Events
- Search Directories & Databases
- International
- Medical Students
- What is Psychiatry?
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Addiction and Substance Use Disorders
- Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
- Alcohol Use Disorder
- Anxiety Disorders
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Bipolar Disorders
- Climate Change and Mental Health Connections
- Coping After Disaster
- Disruptive, Impulse-Control and Conduct Disorders
- Dissociative Disorders
- Domestic Violence
- Eating Disorders
- E-Cigarettes and Vaping
- Gambling Disorder
- Gender Dysphoria
- Helping a Loved One Cope with Mental Illness
- Hoarding Disorder
- Integrated Behavioral Healthcare
- Intellectual Disability
- Internet Gaming
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Opioid Use Disorder
- Perinatal Depression (formerly Postpartum)
- Personality Disorders
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prolonged Grief Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
- Sleep Disorders
- Somatic Symptom Disorder
- Specific Learning Disorders
- Stigma, Prejudice and Discrimination Against People with Mental Illness
- Suicide Prevention
- Technology Addictions: Social Media, Online Gaming, and More
- Warning Signs of Mental Illness
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- What is Mental Illness?
- What is Psychotherapy?
- What is Telepsychiatry?
- La Salud Mental
- Childhood Disorders: Medication Guides for Parents
- Lifestyle to Support Mental Health
- Member Benefits
- Honorary Fellowship (FAPA & DFAPA)
- Awards & Leadership Opportunities
- Get Involved
- Directories, Contact Info & FAQs
- District Branches
- APA's Vision, Mission, Values, and Goals
- Meet Our Organization
- Read APA Organization Documents and Policies
- Work At APA
- About APA's Headquarters
- Policy Finder
- News Releases
- Messages from the APA President
- Reporting on Mental Health Conditions
- Goldwater Rule
- Annual Meeting Press Registration + Guidelines
- APA Public Opinion Polls
- Reporter Toolkit: Recommendations on Covering the AAPI Community
- Comunicados de prensa en español
- APA Annual Meeting
- APA Communities
- APA Foundation
- APA JobCentral
- APA Learning Center
- APA Publishing
- Center for Workplace Mental Health
- Melvin Sabshin, M.D. Library & Archives
- Psychiatric News
- Psychiatry Online
- Annual Meeting
- APA On Demand
- At the APA Educational Series
- Books and Journals
- Certification and Licensure
- Diversity and Health Equity Education Resources
- Meeting Submission and Guidelines
- Mental Health Innovation Zone
- The Mental Health Services Conference
- The Virtual Immersive
- Virtual Paid Courses
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Covid-19 / Coronavirus
- Digital Mental Health
- Helping Patients Access Care
- Media and Communications
- Mental Health Apps
- Mental Health Parity
- Practice Management
- Professional Interests
- Quality Improvement
- Risk Management
- Social Media
- Sunshine Act
- Telepsychiatry
- The Clozapine Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program
- Transition to Practice and Early Career Resources
- Well-being and Burnout
- Mental Health and Faith Community Partnership
- Mental Health Equity Looking Beyond Series
- Minority and Underrepresented (M/UR) Caucuses
- Moore Equity in Mental Health Initiative
- News and Updates
- Striving for Excellence Series
- AMNet: Addiction Medicine Practice Based Research Network
- PsychPRO: APA's Mental Health Registry
- Research Colloquium for Junior Psychiatrist Investigators
- Perinatal Mental Health Toolkit
- Psychiatric Bed Crisis Report
- Advocacy Action Center
- Congressional Advocacy Network
- Election Resource Center
- Federal Affairs
- State Affairs
- Implementing 9-8-8
- Advocacy Update Webinars
- 2025 Annual Meeting
- The 2024 Mental Health Services Conference
- Addressing Structural Racism Town Hall Series
- APA Meetings App
- Governance Meetings
- Mental Health Equity Fireside Chat Series
- Moore Equity in Mental Health 5K
- Policy & Practice Insights Series
- September Component Meetings
- Social Determinants of Mental Health Town Hall Series
- Amicus Briefs
- Assembly Directory
- Component Directory
- Conference Publications
- Library and Archive
- Member Directory
- Member Obituaries
- Practice Guidelines
- Resource Documents
- International Trainees
- International Humanitarian Opportunities
- Global Mental Health
- International Medical Graduates Resources
- Residents' Journal
- Featured Publications
- APAF Fellowships
- External Fellowships and Awards
- Helping Residents Cope with a Patient Suicide
- Vacant Resident Positions
- Leadership Positions
- SET for Success
- Apply for Psychiatric Residency
- Choosing a Career in Psychiatry
- Building a Career in Psychiatry
- Medical Student Programs
- Resident-Fellow Census
- Transitioning to Residency During COVID-19
- What Is a Substance Use Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Addiction and Substance Use Disorders
- What Are Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease?
- Expert Q&A: Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
- What are Anxiety Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Anxiety Disorders
- Expert Q&A: ADHD
- What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Autism Spectrum Disorder
- What Are Bipolar Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Bipolar Disorder
- How Extreme Weather Events Affect Mental Health
- Who Is Affected by Climate Change?
- What Is Depression?
- Expert Q&A: Depression
- What are Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders
- What Are Dissociative Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Dissociative Disorders
- What are Eating Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Eating Disorders
- What is Gambling Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Gambling Disorder
- What is Gender Dysphoria?
- Expert Q&A: Gender Dysphoria
- What is Hoarding Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Hoarding Disorder
- What is Intellectual Disability?
- Expert Q&A: Intellectual Disability
- What Is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- What is Perinatal Depression (formerly Postpartum)?
- Expert Q&A: Perinatal Depression
- What are Personality Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Personality Disorders
- What is Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
- Expert Q&A: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- What is Schizophrenia?
- Expert Q&A: Schizophrenia
- What are Sleep Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Sleep Disorders
- What is Somatic Symptom Disorder?
- Expert Q&A: Somatic Symptom Disorder
- What Are Specific Learning Disorders?
- Expert Q&A: Specific Learning Disorders
- What is Technology Addiction?
- Expert Q&A: Technology Addiction
- Cigarrillos electrónicos y vapeo
- Trastorno del espectro autista
- Trastorno por consumo de alcohol
- Trastorno por consumo de opioides
- Trastorno de estrés postraumático (TEPT)
- Adicción a la tecnología: redes sociales, juegos en línea, y más
- ¿Qué es la psiquiatría?
- Conexiones entre el cambio climático y la salud mental
- Más temas de salud mental
- General Members
- Early Career Psychiatrists
- Residents and Fellows
- International Resident-Fellows
- Semi-Retired and Retired
- View Your Profile
- Resident-Fellow Members
- Fellow of the APA
- Distinguished Fellow of the APA
- International Fellow of the APA
- International Distinguished Fellow of the APA
- 2024 Class of Honorary Fellows
- 2025 APA National Elections
- Councils, Committees and Components
- Resident-Fellow Leadership Opportunities
- Advocacy and APAPAC
- APA/APAF Fellowships
- APA Insider Sessions
- APA Specialty Interest Caucuses, Listservs & Communities
- Leadership, Equity and Diversity Institute
- Mentorship Program for APA/APAF Fellows
- Research Colloquium
- Contact Your Membership Specialist
- Contact Your District Branch
- Membership FAQs
- Semi-Retired and Retired FAQs
- Lump Sum Dues
- 2025 APA Dues Rate Changes FAQs
- District Branch Resources
- District Branch Dues for General Members
- District Branch Dues for Residents and Fellows
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

Writing Problems Common for Students With ADHD
damircudic / E+ / Getty Images
- ADHD and Writing Skills
- Common Challenges
- Helpful Writing Strategies
Children with ADHD are more likely to develop writing problems than children without ADHD, regardless of gender. Among both boys and girls with ADHD who also have a reading disability, however, girls have an even higher chance of developing a written language disorder, creating even more challenges for girls in the classroom.
At a Glance
ADHD is a form of neurodivergence that can make writing more challenging for some students. ADHD traits can affect a student's ability to concentrate, meet deadlines, stay on task, and stay organized, impacting their writing skills. Keep reading to learn more about how ADHD can affect children's writing skills—and how appropriate accommodations and support can help these students succeed.
ADHD Can Impact Skills Important for Writing
The technique of expressing oneself through writing is quite a complex, multi-step process. It requires integrating several skills, including:
- Planning, analyzing, and organizing thoughts
- Prioritizing and sequencing information
- Remembering and implementing correct spelling, punctuation, and grammar rules
- Fine motor coordination
As students age and move into high school and college , the expectations around writing become even more demanding. Essays and reports that require students to communicate what they know on paper factor more prominently into the curriculum.
It is no wonder that writing can create such anxiety in students with ADHD. Simply starting the process and getting ideas and thoughts out of their head in an organized manner and down on paper can feel like an uphill battle.
This can create problems for students with ADHD since research has found that writing abilities longitudinally predict the academic outcomes of kids with this form of neurodivergence .
Signs of Writing Problems in Kids With ADHD
Some of the signs that a student might be struggling with their writing due to ADHD characteristics include:
- Taking longer than their classmates to complete their work
- Producing less written work—shorter reports, less "discussion" on discussion questions, and fewer sentences on each test question—as compared to their peers without ADHD
- Struggling to turn in written assignments by the required deadline
- Making spelling errors due to rushing through the writing process or not being able to stay on task
- Failing to proofread and edit assignments before turning them in
ADHD Challenges That May Lead to Writing Difficulties
Why is it so tough for students with ADHD to produce well-crafted, thoughtful, carefully edited writing? Here are nine of the top reasons:
- Keeping ideas in mind long enough to remember what one wants to say
- Maintaining focus on the "train of thought" so the flow of the writing does not veer off course
- Keeping in mind the big picture of what you want to communicate while manipulating the ideas, details, and wording
- With the time and frustration it can take to complete work, there is often no time (or energy) remaining to check over the details, edit assignments, and make corrections.
- Students with ADHD generally have problems with focus and attention to detail, making it likely that they will make errors in spelling, grammar, or punctuation.
- If a child is impulsive, they may also rush through schoolwork. As a result, papers are often filled with "careless" mistakes.
- The whole proofreading and editing process can be quite tedious, so if students attempt to review work, they may easily lose interest and focus.
- Challenges with fine motor coordination can complicate writing ability further. Many students with ADHD struggle with fine motor coordination, resulting in slower, messier penmanship that can be very difficult to read.
- Simply sustaining the attention and mental energy required for writing can be a struggle for someone with ADHD.
Research indicates that it is less the overt behavioral traits (like restlessness and impulsivity) that influence writing problems in kids with ADHD. Instead, it is typically struggles with executive functions (such as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and attentional control) that play the most significant role in causing writing problems for kids with ADHD.
Writing Strategies for Kids With ADHD
Students with ADHD can work on strategies to improve writing skills that address common learning problems that can interfere with written language expression. Appropriate accommodations and support can help students with ADHD manage the challenges that might affect their writing abilities. Some strategies that can help include:
Giving Clear Instructions
Students with ADHD benefit from having concise instructions that clearly outline the steps to follow in an assignment. Breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable chunks can also help.
Help With Organization
Organizational strategies like outlining can help. Some people may find index cards breaking down writing tasks into small steps helpful, but students with ADHD often get bogged down if they have to deal with many smaller tasks. In such instances, setting a timer and devoting a specific block of time to writing can be a great way to make progress on writing tasks without getting overwhelmed.
Provide Extra Time
Because students with ADHD may take longer with writing assignments, providing extra time to complete these tasks can be a helpful accommodation that helps ensure academic sucess. This can give kids the time they need to produce quality work and finish their assignments.
Extra time, clear instructions, and help with organization can help kids with ADHD managing writing assignments more easily. However, it is important to remember that each kid is different. Experimenting with different methods and supports can help each child figure out what works best for them.
Keep in Mind
It is important to remember that while students with ADHD might struggle with writing skills, having the right accommodations and support can help them succeed in academic settings. Finding ways to support kids in overcoming their writing challenges can help them manage their ADHD effectively, foster more positive academic self-esteem, and strengthen their writing skills.
Molitor SJ, Langberg JM, Evans SW. The written expression abilities of adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder . Res Dev Disabil . 2016;51-52:49-59. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2016.01.005
Molitor SJ, Langberg JM, Bourchtein E, Eddy LD, Dvorsky MR, Evans SW. Writing abilities longitudinally predict academic outcomes of adolescents with ADHD . Sch Psychol Q . 2016;31(3):393-404. doi:10.1037/spq0000143
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ADHD in the classroom: Helping children succeed in school .
Mokobane M, Pillay BJ, Meyer A. Fine motor deficits and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in primary school children . S Afr J Psychiatr . 2019;25:1232. doi:10.4102/sajpsychiatry.v25i0.1232
Soto EF, Irwin LN, Chan ESM, Spiegel JA, Kofler MJ. Executive functions and writing skills in children with and without ADHD . Neuropsychology . 2021;35(8):792-808. doi:10.1037/neu0000769
By Keath Low Keath Low, MA, is a therapist and clinical scientist with the Carolina Institute for Developmental Disabilities at the University of North Carolina. She specializes in treatment of ADD/ADHD.
Celebrating 25 Years
- Join ADDitude
- |

- What Is ADHD?
- The ADHD Brain
- ADHD Symptoms
- ADHD in Children
- ADHD in Adults
- ADHD in Women
- Find ADHD Specialists
- Symptom Checker Tool
- Symptom Tests
- More in Mental Health
- ADHD Medications
- Medication Reviews
- Natural Remedies
- ADHD Therapies
- Managing Treatment
- Treating Your Child
- Success @ School 2024
- Behavior & Discipline
- Positive Parenting
- Schedules & Routines
- School & Learning
- Health & Nutrition
- Teens with ADHD
- More on ADHD Parenting
- Do I Have ADD?
- Getting Things Done
- Time & Productivity
- Relationships
- Organization
- Health & Nutrition
- More for ADHD Adults
- Free Webinars
- Free Downloads
- Newsletters
- Guest Blogs
- eBooks + More
- Search Listings
- Add a Listing
- News & Research
- For Clinicians
- For Educators
- ADHD Directory
- Manage My Subscription
- Get Back Issues
- Digital Magazine
- Gift Subscription
- Renew My Subscription
- ADHD Parenting
How to Apply to College When You Have ADHD
Applying to college is stressful for everyone — if your child has adhd, you’re probably concerned about finding a school that’s a great fit for his personality and academic performance. here, tips for putting his best foot forward during the application process..
As a teen with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), you were able to take the SATs untimed and you earned a good score.
But academic challenges in high school have left you with a so-so grade point average. Now, wary of the college admissions process in general, you’re wondering whether or not to disclose the fact that you have ADHD.
Or perhaps you’re the parent of this teen. How do you begin this process? How can you help your child find the best school to fit his ADHD needs and personality?
Two words always apply to college planning: Start early. According to the HEATH Resource Center , the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) requires that the Individualized Education Program (IEP) team begin to consider post-secondary school goals when the student is entering high school! Even if your teen is further along in his high-school career, here are a number of cool-headed strategies you can employ when facing application time.
Create a Top List of Colleges
Talk with your teen and members of her IEP team to decide what level of services she’d feel comfortable with in college. If your teen was recently diagnosed, it will be helpful to compare semesters before and after interventions were in place — what made the biggest difference? Many colleges provide as-needed services for students with ADHD and/or learning disabilities while others offer structured programs.
Keep in mind that colleges are not obliged to alter their program requirements for students with learning disabilities once they have been admitted. Therefore, you’re advised to take a realistic view of your teen’s unique interests and abilities during the early stages of the decision process. The fact that your child may be admitted to a specific school doesn’t mean he will thrive there. Pursue colleges that will meet your child’s needs.
Develop a “hot list” of six to 12 colleges or universities that offer such programs and/or student supports. Find out the ranges of standardized test scores and GPAs for those admitted, keeping in mind that there’s probably a margin of flexibility.
After you’ve determined what your child needs in a school, refine your list by figuring out what she wants . Your teen should have a clear idea of her academic strengths and weaknesses. Students with ADHD tend to do better in subjects they enjoy, so this can be a clue as to a possible major in college. Highlight the schools on your list that offer a course of study in this field. Then consider extracurricular opportunities. Does your child play a sport or participate in drama club? Would he prefer to stay close to home or venture out to another state (or coast!)? Does in-state tuition make the most sense for your family? Contact the student activities offices to see what’s available outside the classroom, and talk to the offices of financial aid to see what type of package each school can offer.
Visit as many of the schools on your list as you can. In Learning How to Learn: Getting Into and Surviving College When You Have a Learning Disorder , Joyanne Cobb advises prospective freshmen that “College is not just a place to get an education, but a home and lifestyle for four years or more.” An afternoon or an overnight stay on a campus will give you a much better feel for the school than the colorful brochure you received in the mail.
After the data collection part of the application process, sit down with your teen and go over the “hot list,” which by now should include a range of significant factors (entrance difficulty, available majors, financial considerations, location, athletics, activities, and community resources). Evaluate the list and begin ranking the schools by desirability.
Should You Reveal Your ADHD Diagnosis on College Applications?
Before your teen begins to fill out applications, he needs to determine whether or not to disclose the fact that he has ADHD. If he’s applying to specialized schools for students with learning disabilities, or if a school requires documentation of ADHD or a learning disability before it will provide on-campus services, the answer is obvious. But if he requires only minor accommodations, he’ll want to give some thought to this decision.
By law, colleges and universities cannot deny entrance solely based on disabilities — but they are also, by law, under no obligation to alter their admissions standards. Translated, this means that students with disabilities must meet the same criteria established by admissions committees for all prospective students.
However, most colleges do take note of extenuating personal circumstances, such as ADHD. Colleges and universities often maintain some leeway with regard to the qualifications for prospective students. The staff at the HEATH Resource Center suggests that high school students with learning disabilities consider disclosure, in order to show how their academic strengths and personalities mesh with their chosen curricula. A savvy student is in a position to enhance his applications by making a statement of purpose. By putting the proper spin on his learning difficulties, a student can show how, through proper diagnosis and tenacity, he has turned setbacks into triumphs.
Keep in mind that your child’s personal statement, test scores, transcript, and recommendations are each just a part of the larger picture. A student with ADHD may have a high GPA, but low SAT scores, or vice versa, but neither situation need define him. By disclosing his disabilities and putting forth a detailed plan for managing his ADHD and/or learning disabilities at the college level, a student may tacitly amend discrepancies within his admissions packet. Unless admissions committees are aware that such schisms exist, the candidate may be summarily rejected.
Ready…Set…Apply!
A candidate must complete an application form for each school he wishes to apply to. Many institutions still use their own form, which you can request by mail, by telephone, or via the Web, but many schools now accept the Common Application . Submitted electronically or in hard copy, this is now the accepted application form for nearly 700 selective colleges and universities.
Most colleges expect their applicants to supplement their application with an official transcript of classes and grades, a personal essay, and two letters of recommendation from teachers, counselors, or other adults who can comment on the student’s scholastic ability. Additionally, colleges and universities may be especially interested in evidence of a candidate’s community service, extracurricular activities, sports participation, or other talents.
Successful Marketing
A vital part of the application process is distinguishing the applicant. Accommodative services granted by a testing agency to students with ADHD or learning disabilities are solely meant to give students equal footing in that section of the application process. From there, it’s up to the student to set himself apart, to highlight his assets and bring his top-notch qualities to the attention of the admissions team. If your teen’s SATs aren’t stellar, do all you can to help him play up his other strengths.
- The importance of the on-campus interview cannot be overstressed. Role-play questions to get your teen’s confidence up before the appointment.
- If your student has a mentor or a special relationship with a particular teacher, have him request a letter of recommendation from that adult. A heartfelt recommendation that comments on a student’s personality as well as his in-class performance can catch the eye of the admissions office.
- Your child’s extracurricular participation can set him apart from the rest of the applicant pool. Remember to mention his activities that take place outside of school — Eagle-Scout status or a steady after-school job says a lot about commitment and responsibility.
Also, remember that a high level of interest in a particular institution is an attractive quality in an applicant. If possible, participate in formal activities for prospective students, such as overnight stays or campus tours. Applying for early decision or early action at her first-choice college also implies serious interest, and might give her a winning edge.
Final Thoughts
Parents, remember that your own network of contacts can be beneficial. The recommendations of relatives, friends, and alumni of your selected institutions won’t guarantee admission, but they may improve a student’s chances of acceptance. Students, remember that actions affect outcomes. Continue to play a proactive role in the high school-to-college transition — seeking out appropriate supports, assessing your growth — even after the application process is over and you’re finishing up senior year.
Most students with ADHD and/or learning disabilities have realistic concepts of their strengths and weaknesses and will be able to identify the school that seems “right.” In the end, trust your instincts about a school and about the focus of your application. Help your teen coordinate an application that zeroes in on who he is and what he has to offer, and prepare to find sweet surprises in your mailbox come spring of senior year.
Survival Guide for College Students with ADHD & LD (Magination Press), by Kathleen Nadeau, Ph.D.
ADD and the College Student (Magination Press), by Patricia Quinn, M.D.
Learning How to Learn: Getting into and Surviving College When You Have a Learning Disability (Child & Family Press), by Joyanne Cobb
Testing Tips
Contact the PSAT, SAT, or ACT boards to secure a testing environment to meet your child’s needs for standardized testing. Accommodations may include:
- Individual administration of the test
- Computerized, audio, or large-print test editions
- Extended testing time
ADHD in College: Read These Next

Read These ADHD Articles! The 25 Most Influential Reads from ADDitude’s First 25 Years

[ADHD Ages & Stages] How to Avoid Symptom Collisions at College & Work

ADDitude's Top 10 Webinars of 2022

Top Webinars in ADDitude's History
Adhd newsletter, success @ school, strategies for homework, accommodations, ieps, working with school & more..
It appears JavaScript is disabled in your browser. Please enable JavaScript and refresh the page in order to complete this form.

ADHD and Graduate Writing
What this handout is about.
This handout outlines how ADHD can contribute to hitting the wall in graduate school. It describes common executive function challenges that grad students with ADHD might experience, along with tips, strategies, and resources for navigating the writing demands of grad school with ADHD.
Challenges for graduate students with ADHD
Many graduate students hit the wall (lose focus, productivity, and direction) when they reach the proposal, thesis, or dissertation phase—when they have a lot of unstructured time and when their external accountability system is gone. Previously successful strategies aren’t working for them anymore, and they aren’t making satisfactory progress on their research.
In many ways, hitting the wall is a normal part of the grad school experience, but ADHD, whether diagnosed or undiagnosed, can amplify the challenges of graduate school because success depends heavily on executive functioning. ADHD expert Russell Barkley explains that people with ADHD have difficulty with some dimensions of executive function, including working memory, motivation, planning, and problem solving. For grad students, those difficulties may emerge as these kinds of challenges:
- Being forgetful and having difficulty keeping things organized.
- Not remembering anything they’ve read in the last few hours or the last few minutes.
- Not remembering anything they’ve written or the argument they’ve been developing.
- Finding it hard to determine a research topic because all topics are appealing.
- Easily generating lots of new ideas but having difficulty organizing them.
- Being praised for creativity but struggling with coherence in writing, often not noticing logical leaps in their own writing.
- Having difficulty breaking larger projects into smaller chunks and/or accurately estimating the time required for each task.
- Difficulty imposing structure on large blocks of time and finishing anything without externally set deadlines.
- Spending an inordinate amount of time (like 5 hours) developing the perfect plan for accomplishing tasks (like 3 hours of reading).
- Having trouble switching tasks—working for hours on one thing (like refining one sentence), often with no awareness of time passing.
- Conversely, having trouble focusing on a single task–being easily distracted by external or internal competitors for their attention.
- Being extremely sensitive to or upset by criticism, even when it’s meant to be constructive.
- Struggling with advisor communications, especially when the advisors don’t have a strict structure, e.g., establishing priorities, setting clear timelines, enforcing deadlines, providing timely feedback, etc.
If you experience these challenges in a way that is persistent and problematic, check out our ADHD resources page and consider talking to our ADHD specialists at the Learning Center to talk through how you can regain or maintain focus and productivity.
Strategies for graduate students with ADHD
Writing a thesis or dissertation is a long, complex process. The list below contains a variety of strategies that have been helpful to grad students with ADHD. Experiment with the suggestions below to find what works best for you.
Reading and researching
Screen reading software allows you to see and hear the words simultaneously. You can control the pace of reading to match your focus. If it’s easier to focus while you’re physically active, try using a screen reader so you can listen to journal articles while you take a walk or a run or while you knit or doodle–or whatever movement helps you focus. Find more information about screen readers and everything they can do on the ARS Technology page .
Citation management systems can help you keep your sources organized. Most systems enable you to enter notes, add tags, save pdfs, and search. Some allow you to annotate pdfs, export to other platforms, or collaborate on projects. See the UNC Health Sciences Library comparison of citation managers to learn more about options and support.
Synthesis matrix is a fancy way of saying “spreadsheet,” but it’s a spreadsheet that helps you keep your notes organized. Set the spreadsheet up with a column for the full citations and additional columns for themes, like “research question,” “subjects,” “theoretical perspective,” or anything that you could productively document. The synthesis matrix allows you to look at all of the notes on a single theme across multiple publications, making it easier for you to analyze and synthesize. It saves you the trouble of shuffling through lots of highlighted articles or random pieces of paper with scribbled notes. See these example matrices on Autism , Culturally Responsive Pedagogy , and Translingualism .
Topic selection
Concept maps (also called mind maps) represent information visually through diagrams, flowcharts, timelines, etc. They can help you document ideas and see relationships you might be interested in pursuing. See examples on the Learning Center’s Concept Map handout . Search the internet for “concept-mapping software” or “mind-mapping software” to see your many choices.
Advisor meetings can help you reign in all of the interesting possibilities and focus on a viable, manageable project. Try to narrow the topics down to 3-5 and discuss them with your advisor. Be ready to explain why each interests you and how you would see the project developing. Work with your advisor to set goals and a check-in schedule to help you stay on track. They can also help you sort what needs to be considered now and what’s beyond the scope of the dissertation—tempting though it may be to include everything possible.
Eat the elephant one bite at a time. Break the dissertation project down into bite-sized pieces so you don’t get overwhelmed by the enormity of the whole project. The pieces can be parts of the text (e.g., the introduction) or the process (e.g., brainstorming or formatting tables). Enlist your advisor, other grad students, or anyone you think might help you figure out manageable chunks to work on, discuss reasonable times for completion, and help you set up accountability systems.
Tame perfectionism and separate the processes . Writers with ADHD will often try to perfect a single sentence before moving on to the next one, to the point that it’s debilitating. Start with drafting for ideas, knowing that you’re going to write a lot of sentences that will change later. Allow the ideas to flow, then set aside times to revise for ideas and to polish the prose.
List questions you could answer as a way of brainstorming and organizing information.
Make a slideshow of your key points for each section, chapter, or the entire dissertation. Hit the highlights without getting mired in the details as you draft the big picture.
Give a presentation to an imaginary (or real) audience to help you flesh out your ideas and try to articulate them coherently. The presentation can be planned or spontaneous as a brainstorming strategy. Give your presentation out loud and use dictation software to capture your thoughts.
Use dictation software to transcribe your speech into words on a screen. If your brain moves faster than your fingers can type, or if you constantly backspace over imperfectly written sentences, dictation software can capture the thoughts as they come to you and preserve all of your phrasings. You can review, organize, and revise later. Any device with a microphone (like your phone) will do the trick. See various speech to text tools on the ARS Technology page .
Turn off the monitor and force yourself to write for five, ten, twenty minutes, or however long it takes to dump your brain onto the screen. If you can’t see the words, you can’t scrutinize and delete them prematurely.
Use the Pomodoro technique . Set a timer for 25 minutes, write as much as you can during that time, take a five-minute break, and then do it again. After four 25-minute segments, take a longer break. The timer puts a helpful limit on the writing session that can motivate you to produce. It also keeps you aware of the passage of time, helping you stay focused and keeping your time more structured.
Sprints or marathons? Some people find it helpful to break down the writing process into smaller tasks and work on a number of tasks in smaller sprints. However, some people with ADHD find managing a number of tasks overwhelming, so for them, a “marathon write” may be a good idea. A marathon write doesn’t have to mean last-minute writing. Try to plan ahead, stock up on food for as many days as you plan to write, and think about how you’ll care for yourself during the long stretch of writing.
Minimize distractions . Turn off the internet, find a suitable place (quiet, ambient noise, etc.), minimize disruptions from other people (family, office mates, etc.), and use noise-canceling headphones or earplugs if they help. If you catch your thoughts wandering, write down whatever is distracting and you can attend to it later when you finish.
Seek feedback for clarity . Mind-wandering is a big asset for people with ADHD as it boosts creativity. Expansive, big-picture thinking is also an asset because it allows you to imagine complex systems. However, these things can also make graduate students with ADHD struggle with maintaining logical coherence. When you ask for feedback, specify logical coherence as a concern so your reader has a focus. If you’d like to look at your logic before you seek feedback, see our 2-minute video on reverse outlining .
Seek feedback for community . Talking to people about your ideas for writing will help you stay connected at a time when it’s easy to fade into a dark hole. Check out this handout on getting feedback .
Time management and accountability
Enlist your advisor . Graduate students with ADHD might worry about the perception that they’re “gaming the system” if they disclose their ADHD. Or they might struggle with an advisor with a more hands-off mentoring style. It will be helpful to be explicit about your neurodiversity and your potential need for a structure. Ask your advisor to clarify the expectations specifically (even quantify them), and work with them to come up with a clear timeline and a regular check-in schedule.
Enlist other mentors . Your advisor may be less understanding and/or may not be able to provide enough structure, or you may think it’s a good idea to have more than one person on your structure team. Look for other mentors on your faculty (inside or outside of your committee), and talk to senior grad students about their strategies.
Pay attention to your body rhythms . When do you feel most creative? Most focused? Most energetic? Or the least creative, focused, energetic? What activities could you engage in during those times? How can you do them consistently?
Think about task vs. time . It can be difficult to estimate how long a task is going to take, so think about setting a time limit for working on something. Set a timer, work for that amount of time, and change tasks when the time is over.
Tame hyperfocus . If you have trouble switching tasks, ask a friend or colleague to “interrupt” you, or figure out a system you can use to interrupt yourself. For example, when you find yourself trying to fix a sentence for 30 minutes, you can call a friend for a brief conversation about another topic. People with ADHD often find this helps them to look at the work from a more objective perspective when they return to it.
Set SMART goals . Check out the handout on setting SMART goals to help you set up a regular research and writing routine.
Set up a reward system . Tie your research or writing goal to an enjoyable reward. Note that it can also be pre-ward – something you do beforehand that will help you feel refreshed and motivated to work.
Find accountability buddies . These can be people you update on your progress or people you meet with to get work done together. Oftentimes, the simple presence of other people is able to motivate and keep us focused. This “body-doubling” strategy is particularly helpful for people with ADHD. Look for events like the Dissertation Boot Camp or IME Writing Wednesdays .
Find virtual accountability partners . There are a number of online platforms to connect you with virtual work partners. See this article on strategies and things to consider.
Use productivity and focus apps . Check out some recommendations among the Learning Center’s ADHD/LD Resources . To find the best options for you, try Googling “Apps for focus and productivity” to find reviews of timers and other focus apps.
Learn more about accountability . See the Learning Center’s Accountability Strategies page for great information and resources.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Barkley, R. (2022, July 11). What is executive function? 7 deficits tied to ADHD . ADDitude: Inside the ADHD Mind. https://www.additudemag.com/7-executive-function-deficits-linked-to-adhd/
Hallowell, E. and Ratey, J. (2021). ADHD 2.0: New science and essential strategies for thriving with distraction—from childhood through adulthood . Random House Books.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
P: 323-325-1525 | E: [email protected]

- ADHD Coworking Sessions
- ADHD Coaching
- ADHD Coaching For College Students
- Strengths-Based Approach
- How To Get Started

ADHD College Students: Use This Strategy To Write Papers
ADHD College Students : Here at ADHD Collective, we love highlighting the experiences and perspectives of like-minded people with ADHD. Izzy Walker started attending the weekly coworking sessions we launched in March 2020 when the COVID-19 pandemic began. She showed up week after week and put in the hard work as she neared the semester’s end at University. When she accepted my invitation to share what she learned with our readers, I was thrilled, and I know you will be too. Please share Izzy’s helpful tips in your social circles, if you know a college student with ADHD who could benefit.
ADHD and College
Making it to university was a milestone I often thought I would never make. However, my experience was gloomy. Everything was disproportionately difficult, lectures were a confusing din, and every assignment was a mammoth struggle.
I changed university naively thinking it would be different somewhere else. It wasn’t. But it was there at my new university that my story of hope began, as one friend saw the immense struggle I was having and suggested that it could be ADHD.
This conversation was a catalyst for change, and set the ball rolling for me in my journey. It led to a heck of a lot of personal research, but also a meeting with an Educational Psychologist who after a series of testing gave me the diagnosis of ADHD and Dyspraxia .
When I read these words I felt an odd, overwhelming sense of relief. I wasn’t dumb, lazy, incapable, or ‘just not cut out to study’.
School reports year after year would echo the words, ‘distracted and distracting’, ‘capable but often off-task’, and ‘constantly questioning’. On paper I was doing well, the product of my work was good, so no flags had been raised, but deep down behind closed doors I was not doing well, the process was far from good. This has been the case throughout the whole of my education, and I just put it down to my capability.
Since diagnosis I have finished my 1 st assignment, and then my 2 nd , and then my 3 rd , and I am now looking onwards to my final year before being a qualified teacher. This time with hope and acceptance of who I am and who I can be with the right strategies and support in place.
Here are some that I have found the most game-changing when working on projects/assignments:
Give Yourself a New Deadline
I set myself a deadline a few days (at least) before the actual one. I have a real tendency to be scrambling right to the last minute and this helps avoid a lot of stress.
The whole point of this was to prevent a lot of unnecessary scrambling and stress. This also gave me time to edit (more on that later).
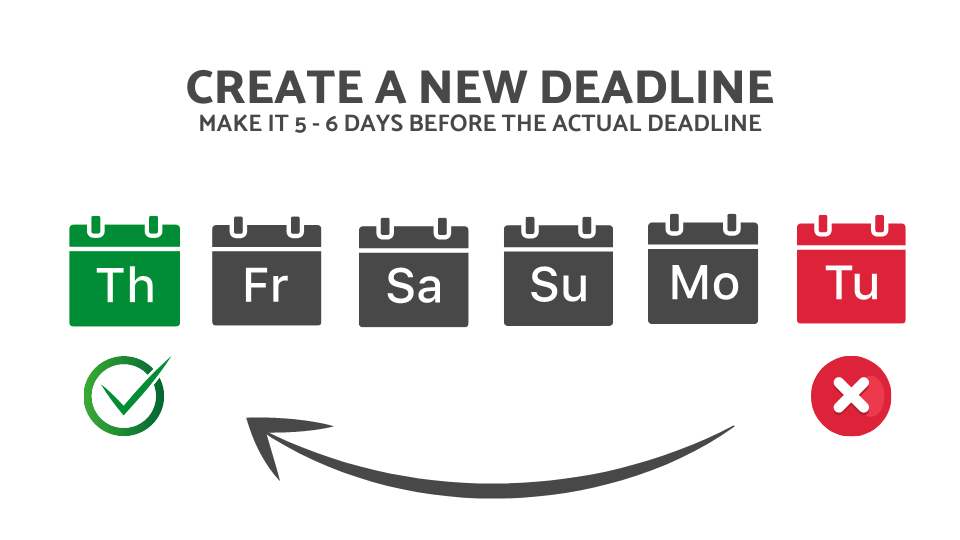
As much as you can, it’s helpful to treat this earlier date as your actual deadline. One way I did this was only scheduling this earlier date on the calendar so it felt more real.
By finishing 5-6 days early, it offered me a window of time for editing and getting it ready to turn in. It also gave time to improve the paper should I have any middle of the night revelations…which I so often do!
Break Your Paper Down into Smaller Pieces
When I was presented with a 5,000 word assignment I felt immediately overwhelmed. I broke the assignment down into sections and assigned a word count to each one.
when I considered what my paper actually entailed, it didn’t seem so bad. Here's what the requirements consisted of:
- Introduction - 1 section
- Argument FOR - 3 sections
- Argument AGAINST - 3 sections
- Conclusion - 1 Section
- Total length of the paper had to be 5,000 words.
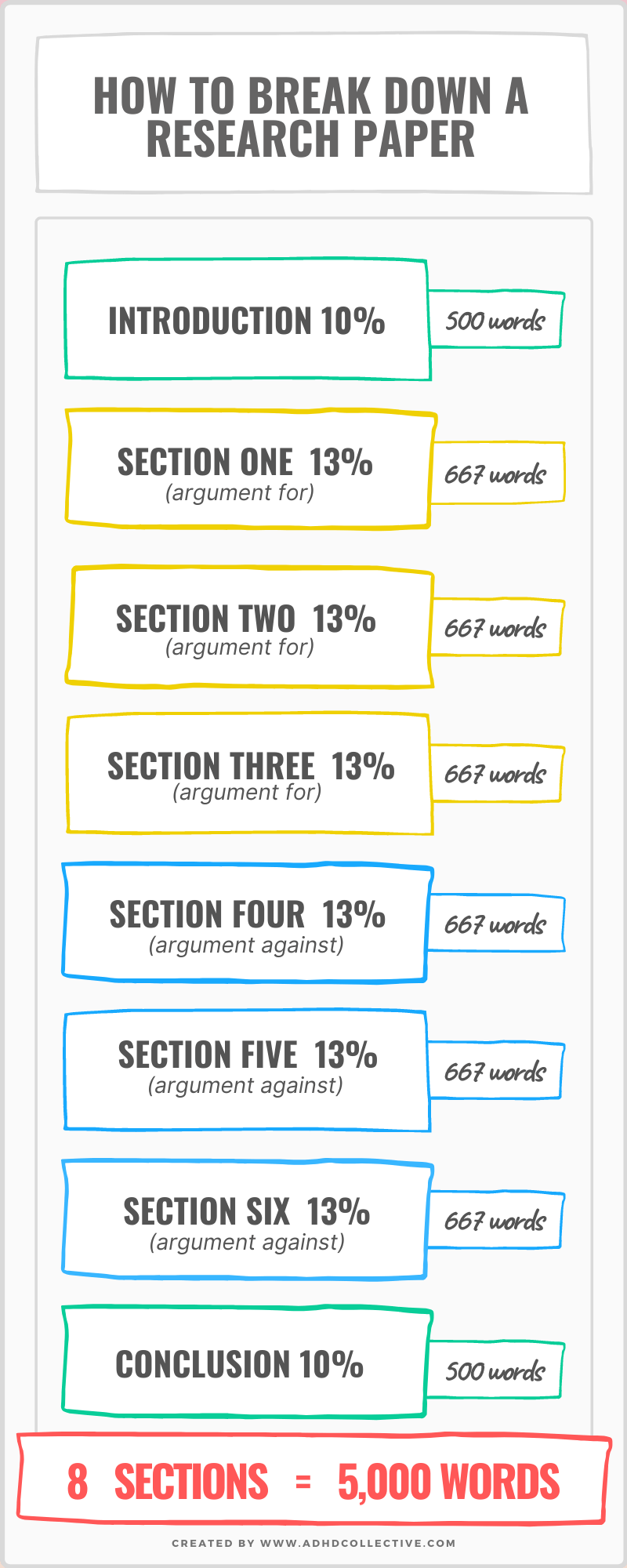
It may seem very overly meticulous, but by spending 30 minutes doing this prevented what could have been HOURS of cutting back word count in the editing stages, and could also run the risk of having no clear structure.
I am a waffler, so without this structure, I would probably have gone WAY over the word limit anyway.
I also went one step further by writing a title for each of the points (on my plan only) and any key things I wanted/needed to mention.
For example, in an assignment on why outdoor learning should be a part of the primary curriculum, my points would be titled ‘educational benefits’, ‘health benefits’ and ‘social benefits’.
The contrary points could be titled ‘behavioural issues’, ‘lack of funding’, and ‘lack of training’. By breaking it down into bite size chunks I felt it was much more manageable.
Focus on One Section a Day
After breaking it down, I dedicated a day to each of the sections. For example, intro – Monday, section 1 – Tuesday, etc.
From my experience, I have found that having a specific measurable target makes it almost like a game. I found it very motivating watching the word count for that section going down as I typed.
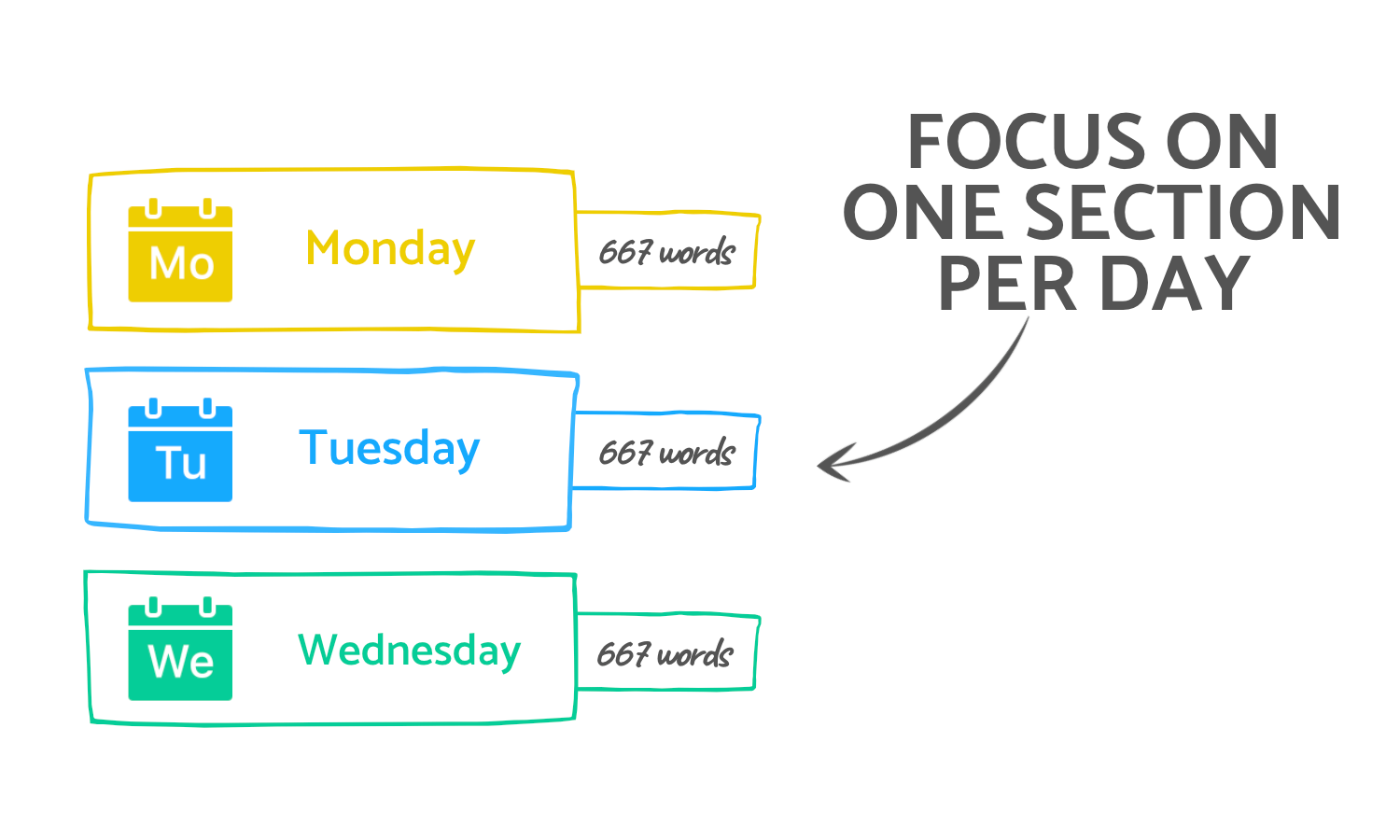
By scheduling the sections out and putting them in my calendar, it allowed me to know when this assignment could realistically be finished by, rather than taking a guess and hoping for the best.
When I woke up, I was thinking, 'I have to write 650 words today!’ rather than ‘oh my goodness 5,000 words!?
I would recommend doing this step as soon as you get the assignment and the deadline date…even if you do nothing else towards it, so that you know when you must start.
Set a Mid-Way Checkpoint
it will save you a LOT of time in the editing stages if you do a little editing as you go along.
With the word count on this particular assignment being so big, I thought it would be wise to set a mid-way checkpoint to read through everything so far and make changes as necessary.
Normally, this would be done at the end but I knew I would have lost all interest and motivation by this point…so it would be better to save myself such a huge job. This also filled me with confidence because when I was writing the second half of the assignment and needed the extra boost, I knew that the first half was to a good standard.
Do Something Every Day (No Matter How Small)
I’m not going to lie, not everyday was as straightforward as ‘write one section a day’.
Some days I was crippled by demotivation, lethargy and not wanting to do ANYTHING.
The key times I noticed this was if I had worked too hard the previous day or if I had hit a difficult part. Believe me, working TOO hard is a THING.
My biggest piece of advice is…know your limits!
I’m no ADHD scientist, but I find my brain must be working harder because of the increased effort I am investing to even stand a chance of being able to concentrate.
Whilst I may feel just about fine at the time, the next day it takes its toll…big time…and maybe the work I did in my ‘overtime’ wasn’t even of the best quality anyway.
"If you just aren’t feeling it, do just one sentence, or find just one piece of theory. Just do one something ..."
This is another reason why my structured plan was really useful because it prevented me from unnecessarily going overboard…and meant that there was no real reason to anyway as I was already on track to finish on time.
If it’s the latter reason, that I’ve hit a difficult part, then there is nothing worse than putting it off another day because this ‘mental wall’ will just get HIGHER.
What did I find useful? If you just aren’t feeling it…do just ONE sentence, or find just ONE piece of theory you just use. Just do ONE something…so then you can feel at least partially accomplished and it’s not a blank section for when you do get back to it.
Best case scenario…that ONE something, could roll into TWO or THREE or FOUR somethings…and before you know it that section is done. Often it is just starting that is the difficult bit.
But worse case scenario…you tried and you can give it another shot tomorrow when your brain is a bit fresher. Productive days happen, utilise these and ride the waves…as do unproductive days…don’t allow the guilt to creep in.
Declutter Your Workspace
I even went to the extreme of removing the pen pot off the desk…in front of me all I had was paper, 1 pen, my lamp, and my laptop.
Minimalism has been a saviour for me during this time of discovering what works for me and what doesn’t. I’ve come to the conclusion that reducing physical clutter consequently reduces mental clutter. I also found the inverse to be true too, clearing my physical space gave me mental clarity.

Whilst this is a visible practice in much of my life, it is especially apparent with my workspace . You’d be amazed what I can get distracted by when writing an assignment…even something as small and monotonous as a pen pot!
Firstly…I would recommend to ALWAYS have a work station with a proper chair when you are writing an assignment and never work from your bed. You must set yourself up for success.
Secondly, I have only the bare essentials in front of me…a pen, a lamp, paper, and my laptop. By keeping it minimal it also means it is easily portable if you want to ‘hot seat’ in your own house if you get bored of that scenery!
Use ADHD Coworking Sessions (and the Pomodoro Technique)
At the start of lockdown I stumbled upon a weekly coworking group ran by Adam from ADHD Collective. I can honestly put down a lot of my success to this…it was amazing!
Firstly, I felt so understood because the group was aimed at people with ADHD. This meant that everyone could share their experiences and not feel judged, but instead find themselves in a supportive community where they could also ask advice.
Each session was 2 hours long and attracted between 4 and 12 people, depending on the week.
It would start with each person sharing (with specifics) what task they wanted to achieve within the next 25 minute block.
By being specific it allowed for a strong element of accountability because at the end of the block, Adam, the ADHD coach and group host would check your progress and whether you had achieved what you wanted to achieve.
Working in 25 minute blocks is often referred to as the Pomodoro Technique . Whilst everyone else in the group is sharing their progress, it gives your brain the opportunity for a short break before starting the next block.
By having short bursts of activity I was able to concentrate and thus achieve more than I would have done if I tried to work for hours without breaks.
Additionally, having the accountability was an incentive for me because it was motivation and almost turned it into a game to try and get the activity finished in time.
I hope these college writing tips give you several options that might help you with your ADHD experience.
Now over to you!
Share the tools, strategies, and tips in the comments below that have helped you in your own journey with ADHD and college writing!

Izzy Walker
Izzy Walker is a trainee teacher in her final year at University in Newcastle, UK. When not studying, she can be found on spontaneous adventures, and meeting new people! To follow her as she navigates through the adventures of ADHD, student life, and teacher...find her on Instagram at @if.walker
Thank you so much.
I am an over 50 returning student trying to finish my undergraduate degree. I never knew I had ADHD until I started taking classes that required retention, organizing, and WRITING. At times, I even wondered if I lacked the skills to even finish. I, at times, self sabotage myself of success because of my struggles. I truly appreciate you sharing your experience. I’ve become desperate and will try anything at this point. I’m just glad to know that others understand my journey. Thank you for sharing.
Thanks for this! In addition to these, I also find it really helpful to keep a “Random thoughts” notepad near me to jot down unrelated urges as I have them. Things like “refill water bottle” or “text Casey back” will still be there in 25 minutes, and knowing in advance that thoughts like ‘this will only take a second’ are lies makes them easier to put on the back burner.
Wow. Thank you, so much, Izzy. I developed ADHD only 3 years ago from a medication. I also decided to go back to college as a mom of 3 boys and the mental exhaustion and burnout is no joke. Papers have been the most challenging and this is the single most helpful tool I’ve found yet. I could feel the relief wash over me as I read through your guide. I feel inspired to tackle my papers in a new way now.
Hi, I am a mid-career student here going back for an MA part-time, while also working. I’ve never been formally diagnosed, but I tick all the boxes and I know now it is why I struggled with papers in college the first time around and why I developed so many systems to be organized in my work life. Was feeling a little burned out today while writing an academic paper and was looking for advice. I was amazed to see that your system is very similar to what I’ve been doing for myself to get through paper-writing! It’s reinforcing in a very good way. Thank you for sharing this. Best of luck to everyone with finding the solutions and tricks that work for them.
Hi Espy, appreciate the comment. Very cool to hear your intuitive system is similar (nice intuition!). If an additional accountability/community component would ever be useful, you’re always invited to our Wednesday ADHD Coworking Sessions. They’re free and we do them every Wednesday (you can sign up for upcoming sessions here: https://adhdcollective.com/adhd-coworking-session-online/ ). Would love to have you, Espy!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Health Topics
- Brochures and Fact Sheets
- Help for Mental Illnesses
- Clinical Trials
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
What is adhd.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is marked by an ongoing pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development. People with ADHD experience an ongoing pattern of the following types of symptoms:
- Inattention means a person may have difficulty staying on task, sustaining focus, and staying organized, and these problems are not due to defiance or lack of comprehension.
- Hyperactivity means a person may seem to move about constantly, including in situations when it is not appropriate, or excessively fidgets, taps, or talks. In adults, hyperactivity may mean extreme restlessness or talking too much.
- Impulsivity means a person may act without thinking or have difficulty with self-control. Impulsivity could also include a desire for immediate rewards or the inability to delay gratification. An impulsive person may interrupt others or make important decisions without considering long-term consequences.
What are the signs and symptoms of ADHD?
Some people with ADHD mainly have symptoms of inattention. Others mostly have symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity. Some people have both types of symptoms.
Many people experience some inattention, unfocused motor activity, and impulsivity, but for people with ADHD, these behaviors:
- Are more severe
- Occur more often
- Interfere with or reduce the quality of how they function socially, at school, or in a job
Inattention
People with symptoms of inattention may often:
- Overlook or miss details and make seemingly careless mistakes in schoolwork, at work, or during other activities
- Have difficulty sustaining attention during play or tasks, such as conversations, lectures, or lengthy reading
- Not seem to listen when spoken to directly
- Find it hard to follow through on instructions or finish schoolwork, chores, or duties in the workplace, or may start tasks but lose focus and get easily sidetracked
- Have difficulty organizing tasks and activities, doing tasks in sequence, keeping materials and belongings in order, managing time, and meeting deadlines
- Avoid tasks that require sustained mental effort, such as homework, or for teens and older adults, preparing reports, completing forms, or reviewing lengthy papers
- Lose things necessary for tasks or activities, such as school supplies, pencils, books, tools, wallets, keys, paperwork, eyeglasses, and cell phones
- Be easily distracted by unrelated thoughts or stimuli
- Be forgetful in daily activities, such as chores, errands, returning calls, and keeping appointments
Hyperactivity-impulsivity
People with symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity may often:
- Fidget and squirm while seated
- Leave their seats in situations when staying seated is expected, such as in the classroom or the office
- Run, dash around, or climb at inappropriate times or, in teens and adults, often feel restless
- Be unable to play or engage in hobbies quietly
- Be constantly in motion or on the go, or act as if driven by a motor
- Talk excessively
- Answer questions before they are fully asked, finish other people’s sentences, or speak without waiting for a turn in a conversation
- Have difficulty waiting one’s turn
- Interrupt or intrude on others, for example in conversations, games, or activities
Primary care providers sometimes diagnose and treat ADHD. They may also refer individuals to a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or clinical psychologist, who can do a thorough evaluation and make an ADHD diagnosis.
For a person to receive a diagnosis of ADHD, the symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity must be chronic or long-lasting, impair the person’s functioning, and cause the person to fall behind typical development for their age. Stress, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression, and other physical conditions or illnesses can cause similar symptoms to those of ADHD. Therefore, a thorough evaluation is necessary to determine the cause of the symptoms.
Most children with ADHD receive a diagnosis during the elementary school years. For an adolescent or adult to receive a diagnosis of ADHD, the symptoms need to have been present before age 12.
ADHD symptoms can appear as early as between the ages of 3 and 6 and can continue through adolescence and adulthood. Symptoms of ADHD can be mistaken for emotional or disciplinary problems or missed entirely in children who primarily have symptoms of inattention, leading to a delay in diagnosis. Adults with undiagnosed ADHD may have a history of poor academic performance, problems at work, or difficult or failed relationships.
ADHD symptoms can change over time as a person ages. In young children with ADHD, hyperactivity-impulsivity is the most predominant symptom. As a child reaches elementary school, the symptom of inattention may become more prominent and cause the child to struggle academically. In adolescence, hyperactivity seems to lessen and symptoms may more likely include feelings of restlessness or fidgeting, but inattention and impulsivity may remain. Many adolescents with ADHD also struggle with relationships and antisocial behaviors. Inattention, restlessness, and impulsivity tend to persist into adulthood.
What are the risk factors of ADHD?
Researchers are not sure what causes ADHD, although many studies suggest that genes play a large role. Like many other disorders, ADHD probably results from a combination of factors. In addition to genetics, researchers are looking at possible environmental factors that might raise the risk of developing ADHD and are studying how brain injuries, nutrition, and social environments might play a role in ADHD.
ADHD is more common in males than females, and females with ADHD are more likely to primarily have inattention symptoms. People with ADHD often have other conditions, such as learning disabilities, anxiety disorder, conduct disorder, depression, and substance use disorder.
How is ADHD treated?
While there is no cure for ADHD, currently available treatments may reduce symptoms and improve functioning. Treatments include medication, psychotherapy, education or training, or a combination of treatments.
For many people, ADHD medications reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity and improve their ability to focus, work, and learn. Sometimes several different medications or dosages must be tried before finding the right one that works for a particular person. Anyone taking medications must be monitored closely by their prescribing doctor.
Stimulants. The most common type of medication used for treating ADHD is called a “stimulant.” Although it may seem unusual to treat ADHD with a medication that is considered a stimulant, it works by increasing the brain chemicals dopamine and norepinephrine, which play essential roles in thinking and attention.
Under medical supervision, stimulant medications are considered safe. However, like all medications, they can have side effects, especially when misused or taken in excess of the prescribed dose, and require an individual’s health care provider to monitor how they may be reacting to the medication.
Non-stimulants. A few other ADHD medications are non-stimulants. These medications take longer to start working than stimulants, but can also improve focus, attention, and impulsivity in a person with ADHD. Doctors may prescribe a non-stimulant: when a person has bothersome side effects from stimulants, when a stimulant was not effective, or in combination with a stimulant to increase effectiveness.
Although not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically for the treatment of ADHD, some antidepressants are used alone or in combination with a stimulant to treat ADHD. Antidepressants may help all of the symptoms of ADHD and can be prescribed if a patient has bothersome side effects from stimulants. Antidepressants can be helpful in combination with stimulants if a patient also has another condition, such as an anxiety disorder, depression, or another mood disorder. Non-stimulant ADHD medications and antidepressants may also have side effects.
Doctors and patients can work together to find the best medication, dose, or medication combination. To find the latest information about medications, talk to a health care provider and visit the FDA website .
Psychotherapy and psychosocial interventions
Several specific psychosocial interventions have been shown to help individuals with ADHD and their families manage symptoms and improve everyday functioning.
For school-age children, frustration, blame, and anger may have built up within a family before a child is diagnosed. Parents and children may need specialized help to overcome negative feelings. Mental health professionals can educate parents about ADHD and how it affects a family. They also will help the child and his or her parents develop new skills, attitudes, and ways of relating to each other.
All types of therapy for children and teens with ADHD require parents to play an active role. Psychotherapy that includes only individual treatment sessions with the child (without parent involvement) is not effective for managing ADHD symptoms and behavior. This type of treatment is more likely to be effective for treating symptoms of anxiety or depression that may occur along with ADHD.
Behavioral therapy is a type of psychotherapy that aims to help a person change their behavior. It might involve practical assistance, such as help organizing tasks or completing schoolwork, or working through emotionally difficult events. Behavioral therapy also teaches a person how to:
- Monitor their own behavior
- Give oneself praise or rewards for acting in a desired way, such as controlling anger or thinking before acting
Parents, teachers, and family members also can give feedback on certain behaviors and help establish clear rules, chore lists, and structured routines to help a person control their behavior. Therapists may also teach children social skills, such as how to wait their turn, share toys, ask for help, or respond to teasing. Learning to read facial expressions and the tone of voice in others, and how to respond appropriately can also be part of social skills training.
Cognitive behavioral therapy helps a person learn how to be aware and accepting of one’s own thoughts and feelings to improve focus and concentration. The therapist also encourages the person with ADHD to adjust to the life changes that come with treatment, such as thinking before acting, or resisting the urge to take unnecessary risks.
Family and marital therapy can help family members and spouses find productive ways to handle disruptive behaviors, encourage behavior changes, and improve interactions with the person with ADHD.
Parenting skills training (behavioral parent management training) teaches parents skills for encouraging and rewarding positive behaviors in their children. Parents are taught to use a system of rewards and consequences to change a child’s behavior, to give immediate and positive feedback for behaviors they want to encourage, and to ignore or redirect behaviors they want to discourage.
Specific behavioral classroom management interventions and/or academic accommodations for children and teens have been shown to be effective for managing symptoms and improving functioning at school and with peers. Interventions may include behavior management plans or teaching organizational or study skills. Accommodations may include preferential seating in the classroom, reduced classwork load, or extended time on tests and exams. The school may provide accommodations through what is called a 504 Plan or, for children who qualify for special education services, an Individualized Education Plan (IEP).
To learn more about the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), visit the U.S. Department of Education’s IDEA website .
Stress management techniques can benefit parents of children with ADHD by increasing their ability to deal with frustration so that they can respond calmly to their child’s behavior.
Support groups can help parents and families connect with others who have similar problems and concerns. Groups often meet regularly to share frustrations and successes, to exchange information about recommended specialists and strategies, and to talk with experts.
The National Resource Center on ADHD, a program of Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (CHADD®) supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), has information and many resources. You can reach this center online or by phone at 1-866-200-8098.
Learn more about psychotherapy .
Tips to help kids and adults with ADHD stay organized
Parents and teachers can help kids with ADHD stay organized and follow directions with tools such as:
- Keeping a routine and a schedule. Keep the same routine every day, from wake-up time to bedtime. Include times for homework, outdoor play, and indoor activities. Keep the schedule on the refrigerator or a bulletin board. Write changes on the schedule as far in advance as possible.
- Organizing everyday items. Have a place for everything, (such as clothing, backpacks, and toys), and keep everything in its place.
- Using homework and notebook organizers. Use organizers for school material and supplies. Stress to your child the importance of writing down assignments and bringing home necessary books.
- Being clear and consistent. Children with ADHD need consistent rules they can understand and follow.
- Giving praise or rewards when rules are followed. Children with ADHD often receive and expect criticism. Look for good behavior and praise it.
For adults:
A professional counselor or therapist can help an adult with ADHD learn how to organize their life with tools such as:
- Keeping routines.
- Making lists for different tasks and activities.
- Using a calendar for scheduling events.
- Using reminder notes.
- Assigning a special place for keys, bills, and paperwork.
- Breaking down large tasks into more manageable, smaller steps so that completing each part of the task provides a sense of accomplishment.
How can I find a clinical trial for ADHD?
Clinical trials are research studies that look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat diseases and conditions. The goal of clinical trials is to determine if a new test or treatment works and is safe. Although individuals may benefit from being part of a clinical trial, participants should be aware that the primary purpose of a clinical trial is to gain new scientific knowledge so that others may be better helped in the future.
Researchers at NIMH and around the country conduct many studies with patients and healthy volunteers. We have new and better treatment options today because of what clinical trials uncovered years ago. Be part of tomorrow’s medical breakthroughs. Talk to your health care provider about clinical trials, their benefits and risks, and whether one is right for you.
To learn more or find a study, visit:
- NIMH’s Clinical Trials webpage : Information about participating in clinical trials
- Clinicaltrials.gov: Current Studies on ADHD : List of clinical trials funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) being conducted across the country
- Join a Study: Children - ADHD : List of studies being conducted on the NIH Campus in Bethesda, MD
Where can I learn more about ADHD?
Free brochures and shareable resources.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: What You Need to Know: This brochure provides information about attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, teens, and adults including symptoms, how it is diagnosed, causes, treatment options, and resources to find help for yourself or your child.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults: What You Need to Know : This brochure provides information about attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults including symptoms, how ADHD is diagnosed, causes, treatment options, and resources to find help for yourself or someone else. Also available en español .
- Shareable Resources on ADHD : These digital resources, including graphics and messages, can be used to spread the word about ADHD and help promote awareness and education in your community.
- Mental Health Minute: ADHD : Take a mental health minute to learn about ADHD.
- NIMH Expert Discusses Managing ADHD : Learn the signs, symptoms, and treatments of ADHD as well as tips for helping children and adolescents manage ADHD during the pandemic.
Federal resources
- ADHD : CDC offers fact sheets, infographics, and other resources about the signs, symptoms, and treatment of children with ADHD.
- ADHD : (MedlinePlus – also available en español .)
Research and statistics
- Journal Articles : This webpage provides information on references and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine).
- ADHD Statistics : This web page provides statistics about the prevalence and treatment of ADHD among children, adolescents, and adults.
Last Reviewed: September 2023
Unless otherwise specified, the information on our website and in our publications is in the public domain and may be reused or copied without permission. However, you may not reuse or copy images. Please cite the National Institute of Mental Health as the source. Read our copyright policy to learn more about our guidelines for reusing NIMH content.
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Warren Magnus ; Saad Nazir ; Arayamparambil C. Anilkumar ; Kamleh Shaban .
Affiliations
Last Update: August 8, 2023 .
- Continuing Education Activity
The diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been surrounded by controversy over the last century. Over the past 30 years, however, a consensus has been developed regarding both the existence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and the symptoms and signs that define it. Additionally, research has increased knowledge of the neurochemical and physiologic causes of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. This has led to the development of techniques for effective management of the condition. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in collaborating to provide well-coordinated care and enhance outcomes for affected patients.
- Outline the pathophysiology of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Explain how to evaluate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Review treatment considerations for patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Summarize the importance of enhancing coordination amongst the interprofessional team, caregiver, and patient to provide optimal care to patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Introduction
Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a psychiatric condition that has long been recognized as affecting children's ability to function. Individuals suffering from this disorder show patterns of developmentally inappropriate levels of inattentiveness, hyperactivity, or impulsivity. Although there used to be two different diagnoses of Attention Deficit Disorder vs. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, the DSM IV combined this into one disorder with three subtypes: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive, or combined type.
The symptoms begin at a young age and usually include lack of attention, lack of concentration, disorganization, difficulty completing tasks, being forgetful, and losing things. These symptoms should be present before the age of 12, have lasted six months, and interfere with daily life activities in order to be labeled as 'ADHD.' This must be present in more than one setting (i.e., at home and school, or school and after-school activities). It can have large consequences, including social interactions, increased risky behaviors, loss of jobs, and difficulty achieving in school.
ADHD must be considered within the context of what is developmentally and culturally appropriate for a person. It is considered a dysfunction of executive functioning, predominantly a frontal lobe activity. Therefore, patients with ADHD show disability not only in attention and focus but also in decision making and emotional regulation. Children with ADHD can have difficulty with social interactions, can be easily frustrated, and can be impulsive. They are often labeled as "trouble makers."
ADHD is not a new condition and has been called different names throughout history. It was labeled as 'minimal brain dysfunction' in the 1930s and has ever since changed names to ADD and ADHD, respectively. [1] Its prevalence has increased over time, with a seeming spike in the 1950s as school became more standardized for children.
It is important to diagnose and treat the disorder at a young age so that the symptoms do not persist into adulthood and cause other comorbid conditions. The treatment for the disorder is mostly related to stimulants and psychotherapy. [2] This review would further shed light upon the causal factors, pathophysiology, and management of ADHD.
The etiology of ADHD is related to a variety of factors that include both a genetic and an environmental component. It is one of the most heritable conditions in terms of psychiatric disorders. There is a much greater concordance in monozygotic twins than dizygotic. Siblings have twice the risk of having ADHD than the general population. Similarly, viral infections, smoking during pregnancy, nutritional deficiency, and alcohol exposure in the fetus have also been explored as possible causes of the disorder. There are no consistent findings on brain imaging of patients with ADHD. The number of dopaminergic receptors has also been implicated in the development of the disorder whereby research has shown that the receptors are decreased in the frontal lobes in individuals with ADHD. [3] [1] There is also evidence for the role of noradrenergic receptor involvement in ADHD.
- Epidemiology
The subtypes of attention deficit disorders are found to have a different rate of prevalence in a group of individuals suffering from the disorders. It is found that the inattentive subtype is prevalent in about 18.3% of the total patients while hyperactive/impulsive and combined represent 8.3% and 70%, respectively. It is also found that the inattentive subtype is more common amongst the female population. The disorders (collectively) are found in a 2:1 male to female ratio as per different researches. [4] It is prevalent in around 3%-6% of the adult population. [5] It is one of the most prevalent disorders found in childhood. There is some evidence that ADHD is more prevalent in the United States than in other developed countries.
- Pathophysiology
ADHD is associated with cognitive and functional deficits that relate to diffuse abnormalities in the brain. The anterior cingulate gyrus and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLFPC) are found to be small in individuals who are suffering from ADHD. It is thought that these changes account for the deficits in goal-directed behavior. Moreover, activity in the frontostriatal region is also reduced in these individuals as measured by fMRI. It is important to understand these pathophysiological mechanisms so that the pharmacotherapy is directed onto them. [6] It is important to remember that ADHD is a clinical diagnosis. There are no standard laboratory or imaging results among patients with ADHD.
- History and Physical
In order to diagnose ADHD, it is very important to take a relevant history of the concerned individual. ADHD is diagnosed in children based upon their history, where the children face difficulty in at least 6 of the 9 symptoms as mentioned in DSM 5. Inattentive symptoms include: not paying close attention to tasks, missing small details, rushing through tasks, not seeming to listen when spoken to, difficulty organizing things, not finishing work, dislikes or avoids tasks that take sustained mental effort, losing thins, or being forgetful. Hyperactive symptoms include: fidgeting, feeling like an "internal motor" is always going, leaving their seat, climbing on things, being loud, blurting out answers, talking excessively or out of turn, having trouble waiting their turn, interrupts, or intrudes on others. These symptoms must be present in multiple settings.
In adults, however, these core symptoms may be missing, and they may manifest as other problems such as procrastination, mood instability, and low self-esteem. They will likely be more impulsive in nature or inattentive, as the hyperactivity symptoms can be better controlled. The symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity will likely be elicited when doing a proper history of childhood but may have been missed.
ADHD interferes with functioning and development. This can be included in adults who do not work and is often dismissed in this population. For example, a stay-at-home mom may have difficulty getting her children to school on time, organizing her home, paying attention while driving, etc., which affects her functioning and daily life even though she is not at work or school. It is important to take this into consideration when making a diagnosis.
Different scales are used to measure the problems that patients with ADHD are suffering from. One such example is the Brown Attention Deficit Disorder Scale which includes common areas that these individuals face difficulty in and can be used in adults to identify the disorder. For children, the Vanderbilt ADHD scale is often used as it has both a teacher and parent component. A physical examination, on the other hand, is not as useful in the diagnosis of ADHD, but it can still be used to exclude medical causes such as thyroid problems. It could also help to identify any medical issue that could thereby direct the treatment options. For example, individuals with hypertension may not opt for stimulants as a treatment option. [7] [8] [9]
ADHD is a disorder that is diagnosed clinically and does not have any specific laboratory or radiologic tests. The neuropsychological tests are not as sensitive for diagnosing the disorder, and hence the disorder should be diagnosed based upon the history of the patient. [7] The evaluation of the patient with ADHD is usually done with different rating scales and multiple informants who may include the teachers and parents. It is necessary for a clinician to look for other disorders as they may be a cause for the symptoms that a child is exhibiting. It should not be diagnosed in the context of symptoms from another disorder, for example, a psychotic episode or manic episode.
DSM 5: Types of ADHD
- Predominantly inattentive
- Predominantly impulsive or hyperactive
- Combination of the above
- The onset is usually before age 12
- Symptoms present at school, work, or home
- The disturbance causes significant impairment in social, occupational, and academic functioning.
- The disorder is not accounted for by any other behavior disorder.
- Treatment / Management
Pharmacological therapy remains the mainstay of treatment for patients who have ADHD. It is divided into two major categories, which fall into stimulants or non-stimulants. Stimulants are further broken into amphetamines and methylphenidates. Both types of stimulants block the reuptake of dopamine at the presynaptic membranes and postsynaptic membranes. Amphetamines also directly release dopamine. Stimulants are the mainstay of treatment for ADHD. They are effective in about 70% of patients. There is a number needed to treat of 2. There are multiple formulations of each subtype of stimulants, including immediate-release and extended-release, long-acting, or sustained release. Side effects of stimulants include changes in blood pressure, decreasing appetite and sleep, and risk of dependency. However, there is an increased risk of substance use in patients with ADHD and studies show treating with a stimulant decreases their overall lifetime risk of substance abuse. Because stimulants are controlled substances, providers often are hesitant to use them. However, repeated evidence has shown how imperative it is to try stimulants in ADHD.
There have been concerns regarding stimulant use in patients with seizures. However, recent studies showed that stimulant use for ADHD is safe in epilepsy. [10] [11]
There can be an increase in the frequency of tics in patients with ADHD and Tic disorders. Adding alpha agonists may help to reduce tics. [12]
Of the non-stimulant option, there are also two types: antidepressants and alpha agonists. Within the antidepressant category, atomoxetine is is the best known and works as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It is known to be effective in many trials as a treatment option for ADHD, though not nearly as effective as stimulants. It also has minimal antidepressant effects. It is often used in children who don't tolerate stimulants or have anxiety. Other antidepressants include bupropion, which targets dopamine and serotonin, and TCAs, which are the last choice options. These work by targeting norepinephrine.
Lastly, alpha agonists such as clonidine and guanfacine can be used as an effective treatment for ADHD. However, these are associated with multiple cardiovascular effects like lowering blood pressure, sedation (clonidine more than guanfacine), weight gain, dizziness, etc. They are found to be more effective in younger children than adults. [6]
Psychosocial treatment is the other form of treatment that is used for individuals suffering from the disorder. This form of treatment includes psycho-education for the family and patient and cognitive-behavioral training programs designed specifically for the patient to achieve short and long-term goals. Research has found that these training programs prove to be very effective when used along with pharmacotherapy. However, unlike other psychiatric disorders, there is strong evidence for medication management without therapy as being the most efficacious. [13] [14] [15]
The FDA has just approved the trigeminal nerve stimulation system for children not on medications. The device generates a low-level electrical pulse which suppresses hyperactivity.
There is no diet that has been found to improve ADHD
- Differential Diagnosis
It is important to differentiate ADHD from other clinical disorders as it can have symptoms that may overlap with them. Mood disorders such as depression and anxiety can be misdiagnosed in a patient with ADHD as these symptoms (inattention and poor focus, memory loss, distractibility, etc.) generally persist in individuals with the disorder. Substance abuse disorders should also be carefully examined as children with ADHD are prone to substance abuse. It is important to rule out hearing disorders, learning disorders, and developmental disorders from ADHD. [6]
The prognosis of ADHD is variable depending upon the age of the individual who is experiencing the symptoms. It is seen that the symptoms of ADHD persist into the teenage years and may involve the social and academic domains of life. Two-fifths of the patients continue experiencing the symptoms in the teenage years, whereas a quarter of them are also diagnosed with a concurrent antisocial disorder. However, an important trend in the long term was also noted whereby the symptoms of the patients with ADD decreased in adulthood by about 50%. The general rule of thumb is that 50% of patients "grow out of" ADHD, especially with treatment, and another 25% do not need treatment into adulthood. This is theorized twofold; first, that stimulants help improve the development of the frontal lobe over time, and second that adults often choose careers that don't require sustained attention. In adulthood, these patients are able to achieve their educational and vocational goals. [16]
Treatment of ADHD has also been shown to improve symptoms of oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. It has shown a decreased risk of substance use.
However, untreated ADHD can cause persisting dysfunction and devastating consequences included but are not limited to long-term inability to work, increased car accidents, and increased substance use. [17] [18]
- Deterrence and Patient Education
Patients with ADHD must be followed up regularly to check upon their symptoms and comorbidities. In order to achieve treatment goals, the role of patient education cannot be emphasized enough. For children who have ADHD, the parents should be formally educated about the disorder so that they understand the concept behind the diagnosis. Medication treatment can only be optimized if there is an ongoing interaction between the primary caregiver and the family. [19]
- Pearls and Other Issues
ADHD is often a very easily treated disorder that is highly stigmatized in society. Proper diagnosis and treatment can change the lives of patients who suffer from these.
Providers should not be hesitant to try stimulant medications. They are highly effective and can be very safe when properly prescribed.
ADHD has multiple comorbidities, including anxiety, depression, and conduct disorder. Treatment of ADHD can improve the symptoms of these other disorders.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
ADHD is a condition that can be managed, but the protocols for managing it must be followed effectively in order to achieve a fruitful result. The management involves an interprofessional team that includes the specialist psychiatrist, pediatrician, pharmacist, and other health care professionals, including nurse practitioners who help in diagnosing the disorder. The collaboration on the part of the family and the health care team becomes important so as to know the exact history of the events that the patient has gone through.
The team should then make up a management plan that may include a pharmacologic treatment, a psychosocial intervention, or both. The comorbid disorders of ADHD would have to be analyzed by the team as depression, and anxiety disorders are much more common in this set of population. In order to make a diagnosis of ADHD, regular follow-ups with the primary caregiver of the child should be scheduled along with the child. The clinician can then ascertain and evaluate the child himself and clinically co-relate it to the findings as provided by the caregiver. This can further be taken to a specialist psychiatrist, whereby a confirmatory diagnosis can be made. This would then involve a set of other healthcare professionals such as a psychologist or a trained psychotherapist along with the psychiatrist. The treatment plan is then formulated by the team, and the caregiver himself is given an important role along with the healthcare team. The caregiver has to observe the patient and help in noticing the changes that the child may exhibit. Hence, it can be concluded that an integrated healthcare plan should be followed for the diagnosis and treatment of ADHD so that the long-term goals of the treatment can be achieved. [20]
Open communication between the interprofessional team is the key to improve outcomes. The team should have a conference as that everyone knows what message is to be sent to the caregiver, who often gets upset with mixed messages.
Despite decades of research, the outcomes for patients with ADHD are guarded. Noncompliance with medications is common, and follow-up is difficult as many patients seek alternative treatments. Many parents do not trust the drugs and often seek alternative care. There is no question that currently available treatments do help some patients improve functionally. Still, without treatment, the individuals continue to deteriorate and eventually end up in financial, legal, and social difficulties. [4] [21] [22]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Warren Magnus declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Saad Nazir declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Arayamparambil Anilkumar declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Kamleh Shaban declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Magnus W, Nazir S, Anilkumar AC, et al. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Validity of DSM-IV attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom dimensions and subtypes. [J Abnorm Psychol. 2012] Validity of DSM-IV attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom dimensions and subtypes. Willcutt EG, Nigg JT, Pennington BF, Solanto MV, Rohde LA, Tannock R, Loo SK, Carlson CL, McBurnett K, Lahey BB. J Abnorm Psychol. 2012 Nov; 121(4):991-1010. Epub 2012 May 21.
- A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Assessing the Efficacy and Safety of Viloxazine Extended-Release Capsules in Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. [CNS Drugs. 2022] A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Assessing the Efficacy and Safety of Viloxazine Extended-Release Capsules in Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Nasser A, Hull JT, Chaturvedi SA, Liranso T, Odebo O, Kosheleff AR, Fry N, Cutler AJ, Rubin J, Schwabe S, et al. CNS Drugs. 2022 Aug; 36(8):897-915. Epub 2022 Jul 27.
- Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, including an assessment of evening and morning behavior: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. [Pediatrics. 2004] Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, including an assessment of evening and morning behavior: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Kelsey DK, Sumner CR, Casat CD, Coury DL, Quintana H, Saylor KE, Sutton VK, Gonzales J, Malcolm SK, Schuh KJ, et al. Pediatrics. 2004 Jul; 114(1):e1-8.
- Review Practical considerations for the evaluation and management of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults. [Encephale. 2020] Review Practical considerations for the evaluation and management of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults. Weibel S, Menard O, Ionita A, Boumendjel M, Cabelguen C, Kraemer C, Micoulaud-Franchi JA, Bioulac S, Perroud N, Sauvaget A, et al. Encephale. 2020 Feb; 46(1):30-40. Epub 2019 Oct 11.
- Review [Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)]. [Encephale. 2009] Review [Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)]. Emond V, Joyal C, Poissant H. Encephale. 2009 Apr; 35(2):107-14. Epub 2008 Jul 7.
Recent Activity
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - StatPearls Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Breaking Barriers: My Battle with ADHD. In a prize-winning essay about overcoming obstacles, a child with attention deficit disorder explains the effects of ADHD on his life. From enlisting the help of family members to keeping a journal, this is how Jack Prey manages his diagnosis. By Jack Prey Verified Updated on May 15, 2020.
Step 2: Review the rubric. Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the assignment is asking you to include and to focus on. If you don't have an understanding of it, it's better to find out in advance rather than the night before the assignment is due. The rubric is your anchor and serves as a good guide to know "when you can be ...
A Warp Speed Brain. To have ADHD means that your brain is an engine that's constantly running at high speed. It basically never stops wanting to process information at a high rate. The "attention" part is just an observable set of behaviors when an ADHD person is understimulated. This is also part of why I now openly associate as ...
ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) is a very common condition nowadays. It is definitely worth analyzing. In your ADHD essay, you might want to focus on the causes or symptoms of this condition. Another idea is to concentrate on the treatments for ADHD in children and adults.
ADHD continues to be diagnosed by careful history with an understanding of the developmental presentation of normal behavior and symptoms of the disorder. ADHD has been reconceptualized as a more chronic condition with approximately one-half of children continuing to exhibit symptoms and impairment of the disorder into adulthood 39, 40..
ADHD increases the risk of substance misuse disorders 1.5-fold (2.4-fold for smoking) and problematic media use 9.3-fold in adolescence 55 56 and increases the risk of becoming obese 1.23-fold for adolescent girls. 57 58 59 It is also associated with different forms of dysregulated eating in children and adolescents.
Essay Title 2: ADHD in Children: Educational Challenges and Supportive Strategies Thesis Statement: This research essay focuses on the educational challenges faced by children with ADHD, explores effective strategies for supporting their learning, and highlights the importance of early intervention.
1. Introduction. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) presenting with inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. It can be classified in three subtypes, depending on the intensity of the symptoms: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, and combined [ 1, 2 ].
Studies suggest that more than half of children with attention deficit disorder (ADHD or ADD) struggle with writing.These students may have an overflow of creative ideas, but often struggle when it comes to getting these ideas onto paper.. Children with ADHD have a hard time getting started — and following through — on writing assignments because they have difficulty picking essay topics ...
Here are some practical solutions for teachers to encourage, motivate, and focus their students on writing process. 1. Difficulty Concentrating on Assignment. Research proves that ADHD doesn't result in less intelligence, but rather in difficulties controlling emotions, staying motivated, and organizing the thoughts.
Knowledge of ADHD, including symptoms, behaviors, prognosis, and treatment, ... I helped my son by having him talk it out when he had to write an essay for school (this was also an accommodation ...
A robust body of evidence suggests that children with ADHD are at increased risk for other co-occurring conditions, including depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders (Asherson et al., 2016; Costa Dias et al., 2013).Additionally, ADHD is associated with lower educational or occupational achievement, reduced social functioning (Costa Dias et al., 2013; Franke et al., 2018), and ...
Of note, ADHD presentation and assessment in adults differs; this page focuses on children. An estimated 8.4% of children and 2.5% of adults have ADHD (Danielson, 2018; Simon, et al., 2009). ADHD is often first identified in school-aged children when it leads to disruption in the classroom or problems with schoolwork.
Adhd Essay. Sort By: Page 1 of 50 - About 500 essays. Better Essays. Adhd And Comprehension Strategies For Students With Adhd. 5462 Words; 22 Pages; Adhd And Comprehension Strategies For Students With Adhd. ADHD and Comprehension JVT2 Task 2 Jennifer Blake July 19, 2015 A Written Project Presented to the Faculty of the Teachers College of ...
ADHD is a form of neurodivergence that can make writing more challenging for some students. ADHD traits can affect a student's ability to concentrate, meet deadlines, stay on task, and stay organized, impacting their writing skills. Keep reading to learn more about how ADHD can affect children's writing skills—and how appropriate ...
Writing challenges with ADHD. The signs and symptoms of ADHD center around inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. So, when presented with a writing task, the following symptoms may hinder ...
Most students with ADHD and/or learning disabilities have realistic concepts of their strengths and weaknesses and will be able to identify the school that seems "right.". In the end, trust your instincts about a school and about the focus of your application. Help your teen coordinate an application that zeroes in on who he is and what he ...
You learn to live in kind cohabitation so you can do what you need to do, whether it's crafting a personal essay on ADHD or putting away a load of laundry. Sometimes, the former is easier than ...
Abstract. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a complex disorder, which can be seen as a disorder of life time, developing in preschool years and manifesting symptoms (full and/or partial) throughout the adulthood; therefore, it is not surprising that there are no simple solutions. The aim of this paper is to provide a short and ...
In many ways, hitting the wall is a normal part of the grad school experience, but ADHD, whether diagnosed or undiagnosed, can amplify the challenges of graduate school because success depends heavily on executive functioning. ADHD expert Russell Barkley explains that people with ADHD have difficulty with some dimensions of executive function ...
ADHD College Students: Here at ADHD Collective, we love highlighting the experiences and perspectives of like-minded people with ADHD. Izzy Walker started attending the weekly coworking sessions we launched in March 2020 when the COVID-19 pandemic began. She showed up week after week and put in the hard work as she neared the semester's end at University.
Adults with undiagnosed ADHD may have a history of poor academic performance, problems at work, or difficult or failed relationships. ADHD symptoms can change over time as a person ages. In young children with ADHD, hyperactivity-impulsivity is the most predominant symptom.
Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a psychiatric condition that has long been recognized as affecting children's ability to function. Individuals suffering from this disorder show patterns of developmentally inappropriate levels of inattentiveness, hyperactivity, or impulsivity. Although there used to be two different diagnoses of Attention Deficit Disorder vs. Attention ...