- Digital Marketing
- Facebook Marketing
- Instagram Marketing
- Ecommerce Marketing
- Content Marketing
- Data Science Certification
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data Analytics
- Graphic Design
- Adobe Illustrator
- Web Designing
- UX UI Design
- Interior Design
- Front End Development
- Back End Development Courses
- Business Analytics
- Entrepreneurship
- Supply Chain
- Financial Modeling
- Corporate Finance
- Project Finance
- Harvard University
- Stanford University
- Yale University
- Princeton University
- Duke University
- UC Berkeley
- Harvard University Executive Programs
- MIT Executive Programs
- Stanford University Executive Programs
- Oxford University Executive Programs
- Cambridge University Executive Programs
- Yale University Executive Programs
- Kellog Executive Programs
- CMU Executive Programs
- 45000+ Free Courses
- Free Certification Courses
- Free DigitalDefynd Certificate
- Free Harvard University Courses
- Free MIT Courses
- Free Excel Courses
- Free Google Courses
- Free Finance Courses
- Free Coding Courses
- Free Digital Marketing Courses

25 Digital Transformation Case Studies [2024]
In a world where technology relentlessly reshapes our world, businesses that fail to adapt are destined for obsolescence. These 15 digital transformation case studies present a thrilling narrative of change, charting the journeys of companies that dared to embrace the digital frontier. Each story unfolds as a high-stakes gamble where traditional practices are disrupted, often under the threat of imminent collapse. These businesses, spanning diverse industries from retail to agriculture, engaged in transformative practices not just to survive but to radically reinvent themselves. As we explore these narratives, consider them as a playbook for disruption, illustrating the necessity of digital evolution and its perils and promises.
25 Digital Transformation Case Studies
1. nordstrom: reinventing retail through digital customer experiences.
Nordstrom, an upscale American chain of department stores, has long been known for its commitment to customer service. As digital technologies evolved, Nordstrom embraced a digital transformation strategy to enhance its customer experience and seamlessly integrate online and in-store shopping.
Transformation
a. Omni-channel Integration: Nordstrom invested heavily in creating a seamless omni-channel experience. They enhanced their capabilities to monitor inventory in real-time both in stores and online, enabling customers to verify product availability and reserve items for in-store pickup.
b. Mobile App Enhancements: The Nordstrom mobile app was enhanced with features like “Style Boards,” a digital tool allowing salespeople to create and share personalized fashion recommendations virtually.
c. Data Analytics: Using advanced data analytics, Nordstrom acquired deep insights into customer preferences and shopping behaviors. This enabled them to tailor their marketing efforts and enhance customer engagement effectively.
The digital initiatives paid off by enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction. The ability to shop seamlessly between online and physical stores improved the overall shopping experience, increasing sales and customer loyalty.
Related: Evolution of Digital Transformation
2. Mayo Clinic: Digital Innovation in Healthcare
The Mayo Clinic is recognized worldwide for its specialized medical care. Faced with the growing need for healthcare modernization and improved patient outcomes, Mayo Clinic initiated a comprehensive digital transformation.
a. Telemedicine: Adopting telemedicine technologies was accelerated, allowing patients to consult with Mayo Clinic specialists remotely. This was specifically crucial during pandemic scenarios
b. Electronic Health Records (EHR): Mayo Clinic implemented a state-of-the-art EHR system to streamline patient information management across all points of care, improving coordination and treatment outcomes.
c. AI and Machine Learning: They embraced AI technologies for diagnostic imaging, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine, aiming to enhance diagnosis accuracy and patient care planning.
The digital transformation at Mayo Clinic has significantly enhanced patient accessibility, care coordination, and efficiency. Telemedicine has expanded its reach, particularly to those unable to travel for medical care, and AI integration has improved diagnostic and treatment precision.
3. Ford Motor Company: Embracing Digital Manufacturing and Connected Cars
Ford, a century-old automotive manufacturer, faced increasing competition from traditional car manufacturers and new tech-driven entrants like Tesla. In response, Ford launched an aggressive digital transformation strategy to revamp its manufacturing processes and product offerings.
a. Smart Factories: Ford introduced advanced manufacturing techniques in its factories, employing robotics, AI, and IoT to enhance production efficiency and flexibility. Using connected sensors and predictive analytics helped minimize downtime and optimize maintenance.
b. Connected Cars: Ford increased its investment in developing connected car technologies, which enable vehicles to communicate with one another and with infrastructure, enhancing safety and driving experiences. Features include remote services, real-time traffic updates, and emergency response systems.
c. Electric Vehicles (EV) Innovation: To align with global sustainability trends, Ford accelerated its development of electric vehicles, supported by a digital ecosystem that offers an integrated network of charging stations and a smart, user-friendly interface for managing vehicle charging.
Ford’s digital transformation has improved its manufacturing efficiency and positioned it as a leader in the future mobility space, with advancements in connected cars and a strong focus on electric vehicles. These efforts have helped Ford stay competitive in a rapidly evolving automotive landscape.
4. Singapore’s Public Utilities Board (PUB): Digital Water Management
Singapore’s Public Utilities Board (PUB) is responsible for the collection, development, distribution, and reclamation of water in Singapore, a nation with limited natural resources. The Public Utilities Board (PUB) initiated a digital transformation project aimed at boosting sustainability and efficiency in water management.
a. Smart Water Metering: Implementing smart meters across the city-state enabled real-time water usage monitoring, helping to detect leaks early and educate consumers about their water consumption patterns.
b. Automated Water Quality Monitoring: PUB deployed sensors throughout the water supply network to continuously monitor water quality and operational parameters, utilizing AI to predict and address potential issues before they impact consumers.
c. Virtual Singapore: PUB participated in the ‘Virtual Singapore’ project, which features a dynamic three-dimensional city model and a collaborative data platform incorporating hydrological models to simulate water movements and accumulation. This contribution enhances flood management and urban planning.
These technological advancements have made Singapore’s water management system one of the most efficient and sustainable in the world. The integration of digital tools has enabled PUB to ensure a continuous, safe water supply and effective management of the nation’s water resources, even as demand grows and climate challenges intensify.
Related: Impact of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Sector
5. Netflix: Pioneering the Streaming Revolution
Netflix started as a DVD rental service by mail but transformed into a global streaming giant. As consumer preferences shifted from physical rentals to digital streaming, Netflix pivoted its business model to focus on online content delivery and original programming.
a. Streaming Technology: Netflix invested heavily in developing robust streaming technology, capable of delivering high-quality video content over the internet. This technology adjusts to the user’s bandwidth, ensuring an uninterrupted viewing experience.
b. Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Utilizing big data analytics and machine learning, Netflix analyzes vast amounts of data on viewer preferences to recommend personalized content and to decide which new series and films to produce.
c. Original Content: Transitioning from licensing to producing original content, Netflix created a wide array of popular shows and movies, becoming a major player in the entertainment industry, with its productions receiving critical acclaim and awards.
Netflix’s focus on technology and data-driven content creation has changed how people consume entertainment and how it’s produced. It has grown into one of the most significant entertainment platforms globally, with a vast subscriber base that enjoys content across many genres and languages.
6. DBS Bank: Leading Digital Banking in Asia
DBS Bank, the biggest bank in Southeast Asia, faced intense competition from traditional banks and new fintech startups. In response, DBS embarked on a comprehensive digital transformation journey to redefine banking in a digital world.
a. Digital-Only Banking: DBS launched Digibank, a mobile-only bank in India and Indonesia, which offers a paperless, signatureless, and branchless banking experience. This initiative aimed to tap into the mobile-savvy population in these countries.
b. API Platform: DBS was one of the first banks in Asia to create a comprehensive banking API platform, allowing businesses to integrate banking services into their applications seamlessly, enhancing customer experiences, and creating new revenue streams.
c. Data-Driven Insights: Leveraging big data, DBS provides personalized financial advice to customers. They use AI to offer tailored investment and savings solutions based on individual spending habits and financial goals.
DBS’s digital initiatives have set a new standard in the banking industry, significantly improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiencies. Their digital-first approach has attracted millions of new customers, particularly among the tech-savvy younger demographic, and has solidified their position as a leader in the digital banking space.
7. Domino’s Pizza: From Pizza Company to Tech Company
Domino’s Pizza recognized the importance of technology in the fast-food industry early and embarked on an ambitious digital transformation to become more than just a pizza company. They aimed to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and increase sales through digital channels.
a. Online Ordering System: Domino’s developed an innovative digital ordering system with a website, mobile app, and voice-recognition system. This system made ordering pizzas quick and easy for customers.
b. Pizza Tracker: Domino’s introduced the “Pizza Tracker,” a feature that enables customers to follow their orders in real-time from preparation through delivery, thereby increasing transparency and boosting customer engagement.
c. AI and Automation: To reduce delivery times and costs, Domino’s has experimented with artificial intelligence and automation technologies, including chatbots for ordering and robotic units for pizza delivery.
These digital initiatives have transformed Domino’s into a tech-forward company, significantly boosting online sales. They have also improved operational efficiencies and customer satisfaction, keeping Domino’s competitive in a fiercely contested market.
Related: Pros and Cons of Digital Transformation
8. Delta Airlines: Enhancing Travel Experience with Digital Solutions
Delta Airlines, one of the largest airlines worldwide, has consistently sought to leverage technology to better its operational efficacy and customer service. Recognizing the evolving needs of modern travelers, Delta has invested in digital technologies to enhance the passenger experience.
a. Mobile App Innovations: Delta’s mobile app includes features like check-in, boarding pass access, flight tracking, and notifications about gate changes or delays, making travel more manageable and less stressful for passengers.
b. RFID Baggage Tracking: Delta implemented Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for baggage handling. This tech upgrade provides customers with real-time updates on their checked luggage and significantly reduces the rate of lost or misdirected bags.
c. Biometrics for Seamless Travel: Delta has introduced biometric boarding at several airports, using facial recognition technology to speed up the boarding process while enhancing security.
Delta’s digital transformation efforts have improved customer satisfaction by making flying more pleasant less stressful and enhancing operational efficiencies. The use of advanced technology has solidified Delta’s reputation as an innovator in the airline industry.
9. Nike: Revolutionizing Retail with Digital Engagement
Nike, a leading sports apparel and equipment manufacturer, faced the challenge of staying relevant in a rapidly changing retail landscape dominated by digital engagement and e-commerce. Nike embarked on an aggressive digital transformation strategy to maintain its market leadership and connect with a global audience.
a. Nike+ Ecosystem: Nike developed the Nike+ ecosystem, which includes apps for fitness tracking, coaching, and community engagement. These apps collect data that Nike uses to improve customer engagement, tailor marketing efforts, and enhance product development.
b. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Sales: Nike boosted its direct-to-consumer channel through its website and mobile app, enhancing the customer shopping experience with personalized recommendations based on user activity and preferences.
c. Augmented Reality: Nike introduced augmented reality features in its app, allowing customers to try on shoes virtually, ensuring a better fit and reducing return rates.
Nike’s focus on digital has dramatically shifted its sales strategy, significantly increasing its direct-to-consumer revenue. The personalized and connected experiences have fostered brand loyalty and enabled Nike to gather valuable customer data to drive future product and marketing strategies.
10. Southern California Edison: Powering Up Grid Modernization
Southern California Edison (SCE), one of the biggest electric utilities in the U.S., needed to address aging infrastructure, regulatory pressures, and increasing demand for renewable energy sources. SCE launched a digital transformation initiative to modernize its electrical grid to improve reliability, efficiency, and sustainability.
a. Smart Grid Technology: SCE implemented a smart grid with advanced metering infrastructure, digital sensors, and automated controls throughout the network. This technology provides SCE with real-time data to manage energy flow and respond to issues efficiently.
b. Renewable Integration: The utility company enhanced its grid to handle more renewable energy sources. Digital tools help manage the variability and intermittency of renewables like solar and wind.
c. Customer Engagement Platforms: SCE developed online tools and mobile applications that give customers detailed insights into their energy usage, helping them manage consumption and reduce costs.
SCE’s digital initiatives have enhanced grid reliability and efficiency, which is crucial for incorporating renewable energy. These initiatives have enabled consumers to take a more active role in managing their energy consumption, supporting broader sustainability objectives and compliance with regulatory standards.
Related: Use of Digital Transformation in Real Estate
11. L’Oréal: Digital Beauty Transformation
L’Oréal, the world’s largest cosmetics company, recognized the need to digitally transform to maintain its leadership and respond to changing consumer behaviors, particularly the rise of e-commerce and digital-first beauty brands.
a. Virtual Try-On Technology: L’Oréal acquired the augmented reality and artificial intelligence company ModiFace, which offered customers virtual try-on features for makeup and hair color, enhancing the online shopping experience.
b. Personalized Marketing: Using AI-driven analytics, L’Oréal was able to offer personalized product recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns, improving customer engagement and satisfaction.
c. E-commerce and Social Selling: L’Oréal expanded its e-commerce presence and integrated social media selling platforms, enabling customers to purchase products directly through social media ads and influencers, tapping into the social commerce trend.
These digital initiatives have improved L’Oréal’s engagement with tech-savvy consumers and boosted online sales significantly. The company has stayed competitive in a rapidly evolving beauty market, ensuring that digital and physical retail strategies complement each other.
12. The New York Times: Navigating the Shift to Digital Journalism
As the media landscape shifted from print to digital, The New York Times faced the challenge of adapting to changing reader habits and the decline of traditional newspaper revenue from ads and subscriptions.
a. Digital Subscription Model: The NYT introduced a digital subscription model, which has become a significant revenue stream. It allows them to cater to global readers online, surpassing the limitations of print distribution.
b. Enhanced Digital Content: The publication expanded its digital offerings, including podcasts, video content, and interactive journalism, providing a more comprehensive media experience that appeals to a broader audience.
c. Data Analytics: Using data analytics, The NYT can understand reader preferences and engagement, tailoring content and marketing strategies to increase subscriber retention and attract new readers.
The shift to a digital-first approach has rejuvenated The New York Times, turning it into a model for successful and effective digital transformation in the media industry. It has stabilized its revenue and expanded its audience globally, showcasing its adaptability and innovation in journalism.
13. DHL: Logistics and Supply Chain Innovation
DHL, a global leader in logistics, faced the challenge of adapting to the rapidly evolving demands of e-commerce and global trade. DHL embarked on a digital transformation journey to streamline operations and improve customer service to maintain its competitive edge.
a. Internet of Things (IoT) and Robotics: DHL invested in IoT technologies to enhance tracking and monitoring of shipments. Robotics solutions were integrated into warehouses to automate sorting and packaging processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
b. Predictive Analytics: By implementing predictive analytics, DHL improved its logistics planning capabilities. This technology helps anticipate delays and optimize routes in real-time, significantly reducing delivery times.
c. Customer Interaction Platforms: DHL upgraded its customer service platforms, introducing chatbots and AI-driven support systems to provide quick and reliable customer service around the clock.
These innovations have improved operational efficiencies and enhanced client satisfaction by providing more accurate and timely delivery services. DHL’s adoption of advanced technologies has solidified its position as a leader in the logistics sector, capable of handling the complexities of modern supply chains.
Related: Predictions About the Future of Digital Transformation
14. U.S. Social Security Administration (SSA): Enhancing Public Services Through Digital Outreach
The U.S. Social Security Administration, which provides financial support to millions of Americans, faced challenges in service accessibility and administrative efficiency. The SSA initiated a digital transformation strategy to address these issues and better serve the public.
a. Online Services Expansion: The SSA expanded its online platform to allow users to apply for benefits, manage their accounts, and access services without visiting a physical office. This was particularly vital during the COVID-19 pandemic.
b. Digital Documentation: The transition to digital documentation systems helped reduce paperwork, streamline processes, and increase the speed and accuracy of processing claims and applications.
c. Data Security Enhancements: With increased digital interactions, the SSA invested heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive personal information and prevent fraud.
The SSA’s digital transformation has significantly improved accessibility to services, allowing beneficiaries to manage their benefits easily and securely from home. These changes have also improved the agency’s efficiency and reduced operational costs, ensuring sustainability and responsiveness to public needs.
15. John Deere: Digital Agriculture and Smart Farming Solutions
John Deere, a leading agricultural machinery manufacturer, identified the potential of digital technologies to revolutionize farming. John Deere embarked on a digital transformation journey to maintain its leadership in the industry and help farmers increase productivity and sustainability.
a. Precision Agriculture: John Deere developed advanced precision agriculture technologies, integrating GPS and IoT sensors into their equipment. These technologies empower farmers to continuously monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns in real-time, enhancing the efficiency of planting, watering, and harvesting activities.
b. Data Analytics Platforms: The company introduced platforms that analyze data collected from farm equipment to provide actionable insights, aiding farmers make informed decisions about crop management and resource allocation.
c. Autonomous Machines: John Deere invested in developing autonomous tractors and combined harvesters. These machines can operate with minimal human oversight, increasing efficiency and reducing the labor needed for various farming operations.
John Deere’s digital innovations have profoundly impacted the agricultural sector. Farmers using these advanced tools can achieve higher crop yields, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact. The company’s commitment to integrating digital technologies into its products has solidified its position as a leader in the agricultural machinery industry, ensuring that it continues to match the evolving requirements of modern agriculture.
16. IKEA: Enhancing the Furniture Shopping Experience with Digital Tools
IKEA, known for its flat-pack furniture and home accessories, aimed to bridge the gap between online and in-store shopping to enhance customer experience and streamline operations.
a. Virtual Reality Showrooms: IKEA implemented virtual reality tools that allow customers to see how furniture would appear in their homes before buying, which has improved customer satisfaction and reduced return rates.
b. Online Planning Tools: They developed online tools for room planning and furniture customization, helping customers design their living spaces and make informed decisions remotely.
c. Supply Chain Optimization: Utilizing AI and machine learning, IKEA optimized its supply chain processes, reducing costs and improving delivery times with better inventory management and distribution strategies.
These digital strategies have markedly boosted IKEA’s online sales and enhanced customer engagement. By providing immersive and interactive digital tools, IKEA has improved the shopping experience, leading to greater customer loyalty and market competitiveness.
Related: Digital Transformation Statistics
17. HSBC: Digital Transformation in Global Banking
HSBC, one of the world’s largest banking and financial services organizations, faced the challenge of modernizing its services to meet the expectations of a digitally savvy customer base and to compete with emerging fintech companies.
a. Global Banking App: HSBC launched a new mobile banking app providing a comprehensive range of services, including foreign currency exchange, global transfers, and real-time account management.
b. Blockchain for Trade Finance: They adopted blockchain technology to streamline and secure international trade finance processes, significantly reducing the time and cost of transactions.
c. AI-Driven Fraud Detection: Implementing cutting-edge AI algorithms, HSBC enhanced its security measures by predicting and preventing fraudulent transactions in real-time.
HSBC’s digital transformation has led to a more agile and secure banking experience, attracting a younger demographic and enhancing global customer satisfaction. Integrating advanced technologies has also positioned HSBC as a leader in digital innovation within the banking sector.
18. Adobe: Transforming Creative Industries with Cloud-Based Solutions
Adobe, a leader in creative software, recognized the need to transition from traditional desktop applications to a more flexible, cloud-based model to cater to the evolving demands of creative professionals globally.
a. Adobe Creative Cloud: Adobe shifted its suite of creative tools, such as Photoshop and Illustrator, to a subscription-based service, Adobe Creative Cloud. This shift allowed users to access their tools and files from any device and facilitated real-time collaboration.
b. AI and Machine Learning Enhancements: Incorporating AI technologies like Adobe Sensei, Adobe enhanced features across its products to improve user experience, offering capabilities such as automated image editing and smart design suggestions.
c. Education and Community Building: Adobe expanded its training resources and community features, providing extensive tutorials, live sessions, and a platform for creatives to share work and insights, fostering a collaborative environment.
Adobe’s shift to the cloud has revolutionized how creative content is produced, shared, and monetized, significantly enhancing productivity and creativity among professionals. This transformation has solidified Adobe’s leadership in the digital creative market, broadening its user base and increasing customer engagement.
19. Walmart: Revolutionizing Retail with Omnichannel Strategies
Walmart, the world’s largest retailer, aimed to integrate its vast network of physical stores with digital technologies to provide a seamless shopping experience and compete with e-commerce giants like Amazon.
a. Enhanced E-commerce Platform: Walmart upgraded its online platform to facilitate an efficient, user-friendly shopping experience, featuring a robust mobile app that integrates with in-store services.
b. Advanced Inventory Management: Utilizing IoT and AI, Walmart implemented advanced inventory systems to optimize stock levels and logistics, ensuring product availability and rapid fulfillment.
c. Pickup and Delivery Services: They expanded their pickup and delivery options, allowing customers to order online and choose convenient, flexible methods for receiving their purchases, including curbside pickup and same-day delivery.
Walmart’s digital transformation has significantly enhanced customer convenience, driving increased online and in-store sales. By leveraging technology to bridge the gap amidst physical and digital retail, Walmart has strengthened its market position and customer loyalty, setting a new standard in the retail sector.
Related: Digital Transformation in Telecom Case Studies
20. Siemens: Advancing Industrial Automation with Digital Twin Technology
Siemens, a global powerhouse in electrical engineering and electronics, recognized the need to innovate in industrial automation to maintain its leadership in the market. They aimed to leverage digital technologies to enhance manufacturing processes and product development.
a. Digital Twin Implementation: Siemens implemented digital twin technology, which generates virtual models of physical systems to simulate, forecast, and enhance the performance of machines and processes before their actual deployment.
b. IoT and Edge Computing: They integrated IoT with edge computing in their manufacturing operations to gather and analyze data at the source, improving real-time decision-making and operational efficiency.
c. Customizable Automation Solutions: Siemens developed a range of customizable automation solutions tailored to the particular needs of industries, facilitating greater flexibility and efficiency in production processes.
Siemens’ adoption of digital twin technology and IoT has revolutionized its approach to industrial automation, significantly decreasing time to market and operational costs while improving product quality and innovation. This strategic digital transformation has solidified Siemens’ position as a leader in smart industrial solutions, driving growth and sustainability in the sector.
21. Toyota: Pioneering Mobility Solutions with Connected Vehicle Technology
Toyota, a leading global automaker, sought to enhance vehicle safety, efficiency, and user experience by integrating advanced digital technologies into their vehicles, aiming to transition from a car manufacturer to a mobility solutions provider.
a. Connected Car Platform: Toyota developed a connected car platform that integrates telemetry, real-time data monitoring, and vehicle management systems to enhance the driving experience and improve vehicle maintenance.
b. Autonomous Driving Development: They significantly increased their investment in research and development for autonomous driving technologies to develop safer and more efficient transportation solutions.
c. Sustainable Mobility Solutions: Emphasizing sustainability, Toyota expanded its hybrid and electric vehicle offerings, supported by digital tools that help manage energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
Toyota’s digital transformation has significantly improved vehicle functionality and safety, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Their focus on connected and autonomous technologies has positioned Toyota at the forefront of the next generation of mobility solutions, driving innovation in the automotive industry.
22. Unilever: Digital Sustainability and Supply Chain Innovation
Background .
Unilever, a global leader in consumer goods, aimed to enhance its sustainability practices and supply chain efficiency by embedding digital technologies. This initiative supports their commitment to environmental sustainability and efficient resource management.
a. Sustainable Sourcing Platform: Unilever developed a digital platform to trace the sourcing of raw materials, ensuring they meet sustainability standards. This system helps manage supplier relationships and certifications, promoting ethical sourcing practices.
b. AI-Driven Demand Forecasting: Leveraging AI to improve demand forecasting accuracy, Unilever optimized production and inventory management, reducing waste and improving delivery timelines.
c. Eco-Efficient Operations: By implementing IoT devices in manufacturing facilities, Unilever monitors and reduces energy usage, water consumption, and carbon emissions, enhancing the environmental impact of its production processes.
Unilever’s digital sustainability and supply chain management initiatives have improved operational efficiencies and significantly advanced its corporate responsibility goals. These efforts have helped Unilever reduce its environmental footprint, increase transparency in its supply chain, and strengthen its brand reputation among eco-conscious consumers.
Related: Digital Transformation in Finance Case Studies
23. Philips: Transforming Healthcare with Connected Care Solutions
Philips, a global leader in health technology, focused on transforming the healthcare industry by integrating digital solutions into its products and services. This strategic change was designed to improve patient care and boost operational efficiency in healthcare facilities around the globe.
Transformation
a. Connected Health Devices: Philips expanded its line of connected health devices, including wearable technology for remote patient monitoring, that allows healthcare providers to track patient vitals and conditions in real time.
b. Cloud-Based Platforms: They developed cloud-based platforms that facilitate the sharing and analyzing of health data across systems, improving collaboration between healthcare professionals and enabling more informed decision-making.
c. AI-Enhanced Diagnostics: Implementing artificial intelligence in diagnostic equipment, Philips has improved the accuracy and speed of patient diagnostics, aiding in early detection and personalized treatment plans.
Philips’ digital transformation has significantly improved patient care and healthcare efficiency. Their connected care solutions have made health services more accessible, particularly in remote areas, and enhanced the ability of medical professionals to provide timely and effective treatment. This strategic digital integration supports Philips’ mission to improve billions of lives through meaningful innovation.
24. BASF: Driving Chemical Innovation with Digital Lab and Process Optimization
BASF, one of the largest chemical producers in the world, aimed to enhance innovation and efficiency in its chemical processes and product development by leveraging digital technologies. This initiative was a key component of their wider strategy to maintain a competitive advantage and promote sustainable operations.
a. Digital Labs: BASF implemented digital labs that use virtual simulations and modeling to accelerate chemical research and development, reducing the time and resources required for experimental trials.
b. Process Automation and IoT: They enhanced their manufacturing processes through advanced process automation integrated with IoT sensors, enabling for real-time monitoring and control of chemical processes, which improves safety and efficiency.
c. Predictive Maintenance: BASF implemented predictive maintenance capabilities in their facilities using machine learning algorithms. This technology anticipates equipment failures before they happen, reducing downtime and extending the life of their machinery.
BASF’s adoption of digital technologies in its laboratories and production facilities has significantly boosted innovation and operational efficiency. These advancements have enabled BASF to produce higher-quality chemical products faster and more sustainably, reinforcing its position as a leader in the global chemical industry.
25. Coca-Cola: Refreshing Consumer Engagement with Digital Marketing and Analytics
Coca-Cola, one of the world’s most iconic beverage brands, recognized the need to adapt to changing consumer behaviors and expectations, particularly in the digital age. They aimed to engage consumers more effectively and personalize their marketing efforts.
a. Digital Engagement Platforms: Coca-Cola developed digital platforms and mobile applications to engage directly with consumers, offering personalized promotions, loyalty rewards, and interactive brand experiences.
b. Data-Driven Marketing: Leveraging big data analytics, Coca-Cola refined its marketing strategies to target consumers more precisely based on their preferences and behaviors. This approach allowed for more effective ad placements and campaign optimizations.
c. Social Media Integration: Coca-Cola enhanced its presence by creating dynamic and interactive content tailored to global markets, increasing engagement and loyalty.
Coca-Cola’s digital transformation in marketing has significantly increased consumer engagement and brand visibility. Their use of advanced analytics and digital platforms has enabled more personalized and effective marketing campaigns, reinforcing Coca-Cola’s position as a leading global brand in the beverage industry.
Related: Digital Transformation in Aviation Case Studies
The stories of these 15 companies culminate in a powerful testament to the transformative impact of digital technology. Each case study highlights the pivotal role of innovation in securing market leadership and underscores the broader implications for industries at large. Through their transformative journeys, these firms reveal that achieving digital excellence is a challenging endeavor, yet it is abundant with opportunities for growth and reinvention. This collection serves as both a beacon and a warning: embracing change isn’t optional to thrive in the digital era; it’s imperative.
- Top 12 Free Marine Biology Courses [2024]
- Tim Walz Education [Deep Analysis][2024]
Team DigitalDefynd
We help you find the best courses, certifications, and tutorials online. Hundreds of experts come together to handpick these recommendations based on decades of collective experience. So far we have served 4 Million+ satisfied learners and counting.
Pros and Cons of being a Chief Digital Officer [2024]

Why Move from Digital Marketing to Digital Transformation? [2024]

Role of Business Analytics in Digital Transformation [2024]

Is Digital Transformation a Good Career Option for Women? [2024]

20 Reasons Why You Must Study Digital Transformation [2024]

Driving Digital Transformation with AR & VR [2024]
The Whatfix Blog | Drive Digital Adoption
- CIO CIO CIO Blog Explore all new CIO, change, and ITSM content on our enterprise digitalization blog hub. Explore by Category Business Processes Change Management Digital Adoption Digital Transformation ERP Healthcare Transformation ITSM Insurance Transformation Procurement
- Employee Experience Employee Experience EX Blog Explore all new employee experience related content on our EX blog hub. Explore by category Employee Onboarding Employee Training HCM HR & People Ops Instructional Design Learning Technology Performance Support Skill Development CRM Sales Ops
- CX & Product Product CX & Product Ops Blog Explore all new CX and product-related content on our CX and product manager hub. Explore by category Product Ops Support Technical Documentation User Feedback User Onboarding
- Resources Customer Experience What Is a Digital Adoption Platform? Learn how DAPs enable technology users in our ultimate guide. Resources Case Studies eBooks Podcasts White Papers
- Explore Whatfix What Is Whatfix? Whatfix DAP Create contextual in-app guidance in the flow of work with Whatfix DAP. Mirror Easily create simulated application experiences for hands-on IT training with Whatfix Mirror. Product Analytics Analyze how users engage with desktop and web apps with no-code event tracking. Resources About Us Pricing Userization Whatfix AI
- Digital Transformation
8 Examples of Innovative Digital Transformation Case Studies (2024)
- Published: January 19, 2022
- Updated: August 21, 2024

With the rapid pace of technological advancement, every organization needs to undergo digital transformation and, most likely, transform multiple times to stay relevant and competitive.
However, before you can reap the benefits of new technology, you must first get your customers and employees to adapt to this change successfully—and here lies a significant digital transformation challenge.
Organizations thriving in this digital-first era have developed digital innovation strategies prioritizing the change management mindset. This paradigm shift implies that organizations should continuously explore improving business processes .
8 Best Examples of Digital Transformation Case Studies in 2024
- Amazon Business
- Under Armour
- Internet Brands®
- Michelin Solutions
8 Examples of Inspiring Digital Transformation Case Studies
While digital transformation presents unique opportunities for organizations to innovate and grow, it also presents significant digital transformation challenges . Also, digital maturity and levels of digital transformation by sector vary widely.
If you have the budget, you can consider hiring a digital transformation consulting company to help you plan your digitization. However, the best way to develop an effective digital transformation strategy is to learn by example.
Here are the 8 inspiring digital transformation case studies to consider when undertaking transformation projects in 2024:
1. Amazon extended the B2C model to embrace B2B transactions with a vision to improve the customer experience.
Overview of the digital transformation initiative
Amazon Business is an example of how a consumer giant transitions to the B2B space to keep up with the digital customer expectations. It provides a marketplace for businesses to purchase from Amazon and third parties. Individuals can also make purchases on behalf of their organizations and integrate order approval workflows and reporting.
The approach
- Amazon created a holistic marketplace for B2B vendors by offering over 250 million products ranging from cleaning supplies to industrial equipment.
- It introduced free two-day shipping on orders worth $49 or more and exclusive price discounts. It further offered purchase system integration, tax-exemption on purchases from select qualified customers, shared payment methods, order approval workflows, and enhanced order reporting.
- Amazon allowed manufacturers to connect with buyers & answer questions about products in a live expert program.
- Amazon could tap the B2B wholesale market valued between $7.2 and $8.2 trillion in the U.S. alone.
- It began earning revenue by charging sales commissions ranging from 6-15% from third-party sellers, depending on the product category and the order size.
- It could offer more personalized products for an improved customer experience.
2. Netflix transformed the entertainment industry by offering on-demand subscription-based video services to its customers.
Like the video rental company Blockbuster, Netflix also had a pay-per-rental model, which included DVD sales and rent-by-mail services. However, Netflix anticipated a change in customer demand with rising digitalization and provided online entertainment, thereby wiping out Blockbuster – and the movie rental industry – entirely.
- In 2007, Netflix launched a video-on-demand streaming service to supplement their DVD rental service without any additional cost to their subscriber base.
- It implemented a simple and scalable business model and infused 10% of its budget in R&D consistently.
- The company has an unparalleled recommendation engine to provide a personalized and relevant customer experience.
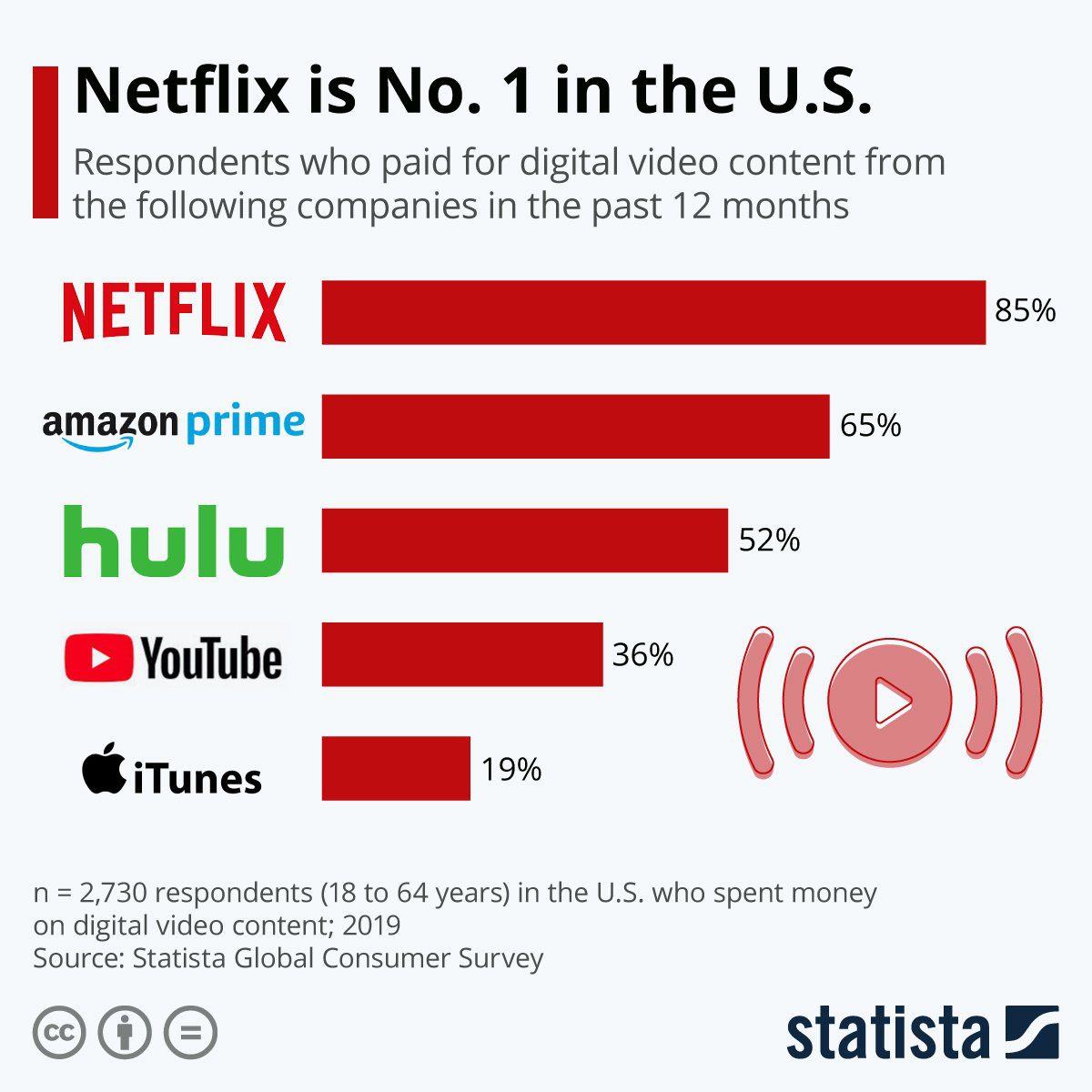
- Netflix is the most popular digital video content provider, leading other streaming giants such as Amazon, Hulu, and Youtube with over 85% market share.
- Netflix added a record 36 million subscribers directly after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
3. Tesla uses connected car technology and over-the-air software updates to enhance customer experience, enable cost savings, and reduce carbon emissions.
No digital transformation discussion is complete without acknowledging the unconventional ideas implemented by Elon Musk. Tesla was a huge manifestation of digital transformation as the core motive was to prove that electric cars are better than their gasoline counterparts both in looks and performance.
Over the years, Tesla has innovated continuously to improve its product, make itself more economical, and reduce its carbon footprint.
- Tesla is the only auto manufacturer globally, providing automatic over-the-air firmware updates that allow its cars to remotely improve their safety, performance, and infotainment capabilities. For example, the OTA update could fix Tesla’soverheating issues due to power fluctuation.
- Tesla launched an autopilot feature to control the speed and position of the car when on highways to avoid potential accidents. However, the user still has to hold the wheel; the vehicle controls everything else. This connected car technology has created an intelligent data platform and smart autonomous driving experience.
- Tesla further ventured into a data-driven future, and it uses analytics to obtain actionable insights from demand trends and common complaints. A noteworthy fact is that the company has been collecting driving data from all of its first and second-generation vehicles. So far, Tesla has collected driving data on 8 billion miles while Google’s autonomous car project, Waymo , has accumulated data on 10 million miles.
- Tesla’s over-the-air updates reduce carbon emissions by saving users’ dealer visits. Additionally, these updates save consumers time and money.
- Tesla delivered a record 936,172 vehicles in 2021, an 87 % increase over the 499,550 vehicle deliveries made in 2020.
4. Glassdoor revolutionized the recruitment industry by allowing employees to make informed decisions.
Glassdoor is responsible for increasing transparency in the workplace and helping people find the right job by allowing them to see millions of peer-to-peer reviews on employers, including overall company culture, their CEOs, benefits, salaries, and more.
- Glassdoor gathers and analyzes employee reviews on employers to provide accurate job recommendations to candidates and vice-versa. It also allows recruitment agencies and organizations to download valuable data points for in-depth analysis & reporting.
- It further introduced enhanced profiles as a paid program, allowing companies to customize their content on the Glassdoor profiles, including job listings, “Why is it the Best Place to Work” tabs, social media properties, and more. This gives companies a new, innovative way to attract and recruit top talent.
- Glassdoor created the largest pool of interview questions, salary insights, CEO ratings, and organizational culture via a peer-to-peer network, making it one of the most trustworthy, extensive jobs search and recruiting platforms – and one of the most well-recognized review sites
- Glassdoor leverages its collected data for labor market research in the US. Its portfolio of Fortune’s “Best Companies to Work For” companies outperformed the S&P 500 by 84.2%, while the “Best Places to Work” portfolio outperformed the overall market by 115.6%.
5. Under Armour diversified from an athletic apparel company to a new data-driven digital business stream to transform the fitness industry.
Under Armour introduced the concept of “Connected Fitness” by providing a platform to track, analyze and share personal health data directly to its customers’ phones.
- Under Armour acquired several technology-based fitness organizations such as MapMyFitness, MyFitnessPal, and European fitness app Endomondo for a combined $715 million to obtain the required technology and an extensive customer database to get its fitness app up and running. The application provides a stream of information to Under Armour, identifying fitness and health trends. For example, Under Armour (Baltimore) immediately recognized a walking trend that started in Australia, allowing them to deploy localized marketing and distribution efforts way before their competitors knew about it.
- Under Armour merged its physical and digital offerings to provide an immersive customer experience via products such as Armourbox. The company urged its customers to go online and share their training schedule, favorite shoe style, and fitness goals. It used advanced analytics to send customers new shoes or apparel on a subscription basis, offering customers a more significant value over their lifetime.
- It additionally moved to an agile development model and data center footprint with the ERP SAP HANA .
- Under Armour additionally leveraged Dell EMC’s Data Protection and Dell Technologies to help fuel digital innovation and find peak value from its data.
- Under Armour created a digital brand with a strong consumer focus, agility, and change culture.
- With the Connected Fitness app, it provided a customer experience tailored to each consumer.
6. Internet Brands® subsidiary Baystone Media leverages Whatfix DAP to drive product adoption of its healthcare businesses.
Baystone Media provides end-to-end marketing solutions for healthcare companies by providing a low-cost, high-value subscription offering of Internet Brands® to promote their practices digitally. Baystone Media empowers its customers by offering a codeless creation of personalized websites. However, as its userbase is less tech-savvy, customers were unable to make the most of their solution.
The idea was to implement a solution for Baystone Media & its sister companies to enable its clients to navigate its platforms easily. In addition to PDFs and specific training videos, the search was on for a real-time interactive walkthrough solution, culminating with Whatfix .
Baystone media saw a 10% decrease in inbound calls and a 4.17% decrease in support tickets, giving them the runway to spend more time enhancing its service for the clients.
7. Sophos implemented Salesforce to streamline its business and manage customer relations more effectively.
Sophos went live with Salesforce to accelerate its sales process , enhance sales productivity , and increase the number of accounts won. However, the complex interface and regular updates of Salesforce resulted in a decreased ROI.
- Sophos implemented Whatfix to provide interactive, on-demand training that helped users learn in the flow of work. The 24*7 availability of on-demand self-support, contextual guidance, and smart tips allowed Sophos to manage its new CRM implementation effectively.
- It unified internal communications using Whatfix content. First, they created walkthroughs for the basic functionality of Salesforce such as lead management, opportunities, etc. Next, they moved to slightly more complex features that their users were uncomfortable with and created guided walkthroughs and smart pop-ups. Sophos also used Whatfix to align the sales and product management teams by embedding videos and other media to unify product communication instead of relying on various communication tools.
- Sophos experienced a reduction in sales operations support tickets globally by 15% (~12,000 tickets). It saved 1070 man-hours and achieved an ROI of 342%.
8. Michelin Solutions uses IoT & AI to provide customers with a more holistic mobility experience.
The digital strategy of Michelin Solutions has essentially centered around three priorities:
- Creating a personalized relationship with customers and end-users
- Developing new business models
- Improving their existing business processes
- AI is extensively used in R&D, enabling the digital supply chain driven through digital manufacturing and predictive maintenance. For example, connected bracelets assist machine operators with the manufacturing process.
- It deployed sophisticated robots to take over the clerical tasks and leveraged advanced analytics to become a data-driven organization.
- Offerings such as Effifuel & Effitires resulted in significant cost savings and improved overall vehicle efficiency.
- Michelin Solutions carefully enforced cultural change and launched small pilots before the change implementation .
- Effifuel led to extra savings for organizations and doubled per-vehicle profits.
- A reduction in fuel consumption by 2.5 L per 100km was observed which translates into annual savings of €3,200 for long-haul transport (at least 2.1% reduction in the total cost of ownership & 8 tonnes in CO2 emissions).
- Michelin Solutions shifted its business model from selling tires to a service guaranteeing performance, helping it achieve higher customer satisfaction, increased loyalty, and raised EBITDA margins.
Each industry & organization faces unique challenges while driving digital transformation initiatives. Each organization must find a personalized solution and the right digital transformation model when implementing new technology. Their challenges can prepare you better for the potential roadblocks, but the specific solutions will need to be personalized according to your business requirements.
Open communication with your customers and employees will help you spot potential issues early on, and you can use case studies like these as a starting point.
If you would like to learn how you can achieve these results by using a digital adoption platform , then schedule a conversation with our experts today.
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user adoption and provide on-demand customer support


Home / Resources / ISACA Journal / Issues / 2021 / Volume 5 / Technology Modernization Digital Transformation Readiness and IT Cost Savings
Case study: technology modernization, digital transformation readiness and it cost savings.

“Digital Distinction” is a major trend for growing, medium-sized organizations, with growth requiring a well-executed digital platform enabled by foresight, leadership and accountability that helps ensure that societal needs are addressed with limited input resources. 1
This digital distinction story was performed with limited resources in a multiservice urban Aboriginal agency (the Agency) providing holistic, culture-based programs and services for Aboriginal children and families. The Agency strives to provide a life of quality, well-being, healing, and self-determination for children and families in the Toronto, Ontario, Canada, urban Aboriginal community by implementing a service model that is culture based and respects the values of Aboriginal people, the extended family and the right to self-determination.
The Agency faced considerable technology challenges at the start of the pandemic-induced lockdowns. The mandatory move to a remote service model stressed the existing IT infrastructure to such an extent that it exposed issues such as network bottlenecks, Wi-Fi interruptions and landline unreliability, all of which compromised the ability of social workers to perform their duties. It had become evident to management that the Agency needed significant digital transformation as part of the journey toward the increasing virtualization of social services and a much-needed modernization of its base IT infrastructure.
To be effective, however, digital transformation must build on an IT foundation that ensures reliable and sustainable outcomes. While IT modernization is a necessary condition for digital transformation readiness, 2 it is not a sufficient condition. Readiness must identify and address all IT operating model gaps 3 before innovation; unfortunately, many organizations undertaking transformation are not ready for innovation. 4
An unprepared organization is likely to see its digital transformations flounder;
…barely one in eight are successful. Even worse, only 3 percent of … 1,733 business executives … report any success at sustaining the change required for successful digital transformation…. 5
Thus, the Agency needed improved digital capabilities to support its growth and to increase its agility in response to the pandemic, so it engaged an experienced digital transformation consultancy with one executive from the group serving in the role of interim chief information officer (CIO).
The CIO title of the 1980s 6 has evolved to become one of vision as part of enterprise strategy, of managing risk as part of enterprise risk and of managing a governed high-performance team to sustain today’s ever more complex IT ecosystems. The modern CIO creates new operating models and helps the organization become data-driven. 7 The CIO takes the organization forward “… in ways that extract the maximum value from the information on hand…to make better decisions, faster” 8 as articulated in the new data strategy.
This case study articulates all the listed requirements of the modern CIO from vision to risk management to creating high performance teams as part of IT operating model modernization. Furthermore, down the road, there will be sufficient material for a future case study to document the path of the organization to achieving fit-for-purpose data for data-driven decision-making and improved reporting efficiency.
THE AGENCY’S INTERIM CIO’S FIRST STEP WAS…TO ESTABLISH THE ORGANIZATION’S CURRENT STATE TO DETERMINE ITS STATE OF READINESS FOR THE REQUIRED DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION.
The challenge: assessing the current state.
One cannot create a strategy without knowing the current state. The Agency’s interim CIO’s first step was, therefore, to establish the organization’s current state to determine its state of readiness for the required digital transformation. While tools facilitating readiness include staff surveys, 9 benchmarking and determining the business case for IT change, a survey was selected as the right tool to learn about the organization’s IT challenges (what the users experience), its IT priorities (what the users want fixed first) and its IT value chain performance (how IT creates value for the organization) through the lens of four different levels of stakeholders. The survey was distributed to staff at all levels; the output presented an end-user view of the organization’s current state.
The four key findings from the survey across these categories were:
- The organization’s executives had different perceptions of the frequency of the top IT challenges compared to the rest of the staff complement ( figure 1 ). This could be given that they were more aware of the negative impact of various IT failures on their mandate.
- The frontline staff were the most supportive of prioritizing all of the top items compared to management, who saw the priorities differently ( figure 2 ). This highlights the importance of engaging with people most actively using technology and not to depend only on management feedback for insights in this respect.
- The supervisor level experienced the severity of most of the shortcomings along the IT value chain ( figure 3 ).
- One of the major challenges experienced by end users was that it took too long for IT to fix IT issues, with users perceiving that it was getting worse. The same held for the network; network reliability was decreasing ( figure 4 ).

The fact that the survey highlighted IT challenges such as poor service request and incident management (the service desk item in figure 1 ) is more important than it may seem at first glance. As part of the journey to making IT more approachable and customer-centric, it is important that the service desk works flawlessly, as it is a major driver of staff (customer) satisfaction, which, incidentally, should be a key IT metric for any CIO.

A comparison of the actual ratio with the benchmark ratios above confirmed a historical underinvestment in IT. Reducing underinvestment in IT and addressing the associated risk areas while building future IT capabilities should be high, not only on the CIO’s agenda via IT governance, but on the board’s agenda, given the implications for enterprise governance.
The Solution: Addressing the Priority Current State Shortcomings
As a result of the current state findings, the CIO reconsidered improvements and developments that may impact the entire IT operating model. A restitution strategy was developed to address as many of the identified priority shortcomings as possible in the shortest possible time.
ADDRESSING THE NETWORK SHORTCOMINGS REQUIRED SIGNIFICANT PLANNING AND ACTIVITY, GIVEN THAT THE NETWORK WOULD NEED TO BE MODERNIZED WHILE THE AGENCY WAS STILL PERFORMING ITS MANDATE.
Restitution is about partnerships, though, another modern CIO imperative. Non-IT senior leaders are just as accountable for decisions and the delivery of ongoing IT services. 12 In other words, restitution is an organizational challenge rather than only an IT challenge, a fact that impacted the nature of the stakeholders identified to oversee the initiative. The more a CIO engages in stakeholder relationships with the goal of forging partnerships, the more effective the broad diversity of IT initiatives within the CIO’s portfolio must almost automatically become.
In this case, restitution was performed in 1) a technology stream and 2) an IT governance stream. (A data governance stream was also recently introduced but will not be explored further here.) The relationship between the CIO and IT governance took a major leap forward a decade ago when it was explicitly considered in South Africa’s King III code for corporate governance. 13 However, more than five years later, the focus still tended to be on the use of IT in regulation and compliance, 14 rather than being about the organizational performance and value creation mechanism it is meant to be.
Aligned with digital transformation principles, specifically around the operating model readiness, 15 restitution was not only about technology, but also about other important components of the organization’s operating model, such as people, process and governance.
Technology Stream
From the current state analysis, the Agency’s legacy technology landscape suffered extended maintenance, support, integration, security, and agility risk and constraints. Technology modernization projects ( figure 5 ) were identified for the Agency to address these issues while also addressing most of the user-defined IT priorities identified in the survey.

One of the CIO’s primary objectives was to measure the benefits of each IT intervention, whether they be through enhanced activity, cost savings, risk mitigation or potentially even revenue generation. Cost and activity benefits, where the interventions are complete, are highlighted for the various interventions the Agency undertook.
Network Remediation The annual operating cost of the Agency’s new network is 48 percent of the cost of the old network—savings driven largely by deploying a modern network technology with standardizing network devices using a modern network protocol.
The old network had nonstandard devices that were unmaintained, outdated with no active support, not configured according to industry best practices and had no redundancy. Furthermore, it suffered bottlenecks, single points of failure and cybersecurity vulnerabilities, with costly management implications.
Addressing the network shortcomings required significant planning and activity, given that the network would need to be modernized while the Agency was still performing its mandate. It involved an initial network discovery process that, for example, identified Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, the devices linked to the IP addresses, the functions and roles of various servers, the portfolio of critical applications, and network-based processes that needed to be mapped out and well understood. Backout plans and vendor escalation processes were created. Replacing more than 50 switches and several firewalls within a 36-hour window was challenging, especially for a new network topology in an overall process that took up to a year when including the planning and vendor identification/selection processes.
Network remediation addressed technical cybersecurity vulnerabilities, fault tolerance and failover readiness with redundancy. It also provided greater bandwidth, scalability and manageability, with Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) technology proving to be more secure and providing higher performance compared to the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) technology it replaced. While bandwidth demand tripled during the pandemic, it was all reliably and seamlessly accommodated within the new network architecture.
Strategically, the organization seeks to share its IT environment with smaller social services agencies that might be insufficiently funded to develop appropriately functional IT platforms. The Platform as a Service (PaaS) aspiration required a network architecture designed to handle traffic at scale and the recognition that an additional network engineer would be needed to bring this aspiration to life.
Human Productivity Tools The annual operating cost of the Agency’s new human productivity tools (HPTs) is 39 percent of the cost of the old HPTs.
The old portfolio of HPTs was a disparate set of vendor solutions that were difficult to support, offered relatively little functionality, challenged the implementation of integrated security, and were costly to manage.
A key consideration was to ensure that all data stayed within Canada. A hybrid approach was followed leveraging Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) with Azure that allowed for failover from on-premises to the cloud, while moving all users’ mailboxes and enabling the additional functionality into production. This parallel process took six months from planning and vendor identification to deployment.
The Agency’s new Software as a Service (SaaS) HPT offered vast improvements in functionality across multiple end-user devices, such as facilitating engagement and teamwork; application interoperability; and facilitating a single approach to cybersecurity by means of integrated identity and access management. This deployment is a critical lever for successful digital transformation given benefits such as performance, scalability, security, and reliable and integrated support from the vendor. 16
Case Management A single case management system to integrate the agency’s two case management systems was identified ( figure 5 ). Two systems were deployed as a means to address the data collection shortcomings in each. To address this, a thorough business requirements document (BRD) will be created to facilitate a request for proposal (RFP) process to identify whether an integrated case management tool is available. (This will not be discussed further as it is a separate, significantly larger project that has only recently been instantiated.)
Document Management A document and content management system— coupled with appropriate workflows and governance—was needed to manage the intranet; perform as a repository for digitized, historical paper-based case files; perform document management; and provide a basis for operational metadata management and the organization’s data dictionary. A feasible tool and functionality was included in the software package provided for the HPT stream, coming in as a cost saving relative to the next best alternative. A decision was taken to use this tool given this cost benefit. A configuration and deployment plan was not yet in place at the time of writing.
Incident Management An incident management tool had been deployed at the Agency but without supporting processes or governance. There was no ticket escalation process, no ticket auto-allocation process and no feedback loop to the requester that a ticket had been received. The following were established as part of the Agency’s IT department’s emerging ITIL- alignment aspirations to improve incident management performance:
- Defined incident management processes
- Defined incident management responsibilities
- Feedback loops with workflows
- Service-level agreement (SLA)-driven ticket auto-escalation
The operational impact of these changes is evident in figure 6 . Within seven months after implementation and as the subject of continuous improvement during that time and beyond, the average ticket closing time had decreased from 34 days to three days according to the system logs, and the average ticket assignment time had decreased from 140 minutes to nine minutes according to the same logs. There are further initiatives to use more of the functionality of the selected tool in the future.

Additional service desk functionality deployed at the Agency includes IT asset management and a configuration management database.
THE ANNUAL OPERATING COST OF THE AGENCY’S NEW MONITORING AND PATCHING SYSTEM IS 30 PERCENT OF THE COST OF THE OLD VENDOR SOLUTION.
Monitoring and Patching System The annual operating cost of the Agency’s new monitoring and patching system is 30 percent of the cost of the old vendor solution.
Driven by continuity risk factors such as poor outage monitoring and alerting, poor device monitoring, and poor vendor responsiveness, as well as cybersecurity risk factors such as poor patching, the Agency sought and deployed a tool to fulfill these requirements with remote management capability.
The technology was selected based on a review of this specific technology landscape according to various IT research organizations. Then, deploying the monitoring tool required making changes to the firewall to allow agents to communicate. Furthermore, a cache server was set up to reduce the bandwidth implications of all the computers in the Agency requiring similar updates, thereby reducing the possibility of network congestion. Planning, vendor identification and deployment took less than three months.
Cloud The annual operating cost of the Agency’s new cloud data center is 45 percent of the cost of the on-premises data center, driven by the higher support and equipment costs of maintaining an on-premises environment.
THE ANNUAL OPERATING COST OF THE AGENCY’S NEW CLOUD DATA CENTER IS 45 PERCENT OF THE COST OF THE ON-PREMISES DATA CENTER.
The Agency had historically entered into a five-year contract for its data center, with further expenditure required for power to eight servers, hosting facilities and equipment, an uninterruptible power supply, and management time for maintenance and management. The risk of the data center being an operational bottleneck was considerable. The real push for a work-in-progress cloud migration was driven by the pandemic.
The selection of the cloud vendor was based on a review of the findings by various IT research organizations and the need to ensure interoperability between the various tools that were about to be deployed in the cloud. For the software tools, a primary driver was the effectiveness of the solution to serve well in a Software as a Service (SaaS) paradigm, which will be the foundation for the type of incremental transformational functionality envisaged as a strategic driver of future IT at the Agency.
Configuring a cloud infrastructure requires configuration activities such as subscribing to the services, creating virtual machine(s), the virtual private network (VPN) and the VPN gateway. Additional services that were migrated to the cloud or deployed to the cloud include the HPTs, the monitoring and patching services, and the mail system. The planning, vendor identification and deployment was performed within four months.
The operational, scale and cost advantages of the cloud at a stated availability of 99.999 percent were implemented as a desirable alternative to on-premises services, given that the modern CIO’s role is to create an environment that facilitates on-demand technology and related services. 17 The potential of this migration for future Platform as a Service (PaaS) services, virtual computing, storage and on-demand functionality positions the organization well for an enhanced digital future.
Telephony Telephony depends on a stable network, and the organization is now ready to address its telephony shortcomings. An architecture and plan to migrate between the current state and the proposed state for telephony is being developed, with the major goals being scalability as part of the PaaS vision for the organization and redundancy, given, the always- on requirement of child welfare services.
Financial Summary IT underinvestment introduces significant risk and inefficiencies into an organization. The technology modernization stream not only addressed technology risk at the Agency, it also eliminated architectural inefficiencies and high-cost structures, as demonstrated by the annual cost savings achieved ( figure 7 ).

While cost savings of up to 13 percent are expected in technology modernization, 18 savings of 18 percent were realized.
IT Governance Stream
IT governance ensures that IT produces the value expected of it. While IT governance was introduced as a mechanism for CIO oversight of the technology deployments, less tangible activities were also established by means of the IT governance stream to help establish a vision for IT, to reduce IT risk and to extend the people capabilities of the IT department.
The following sections detail the measures taken to help ensure reduced-risk value delivery from IT.
Policies and Processes Procedural and cybersecurity-related updates were made to the Agency’s IT policy. Processes were also co-created with human resources (HR) (e.g., onboarding, offboarding) and with operations (e.g., IT-facilitated process design for the handling of all possibilities of incoming telephone calls) to ensure that handovers to IT and back to HR and operations were clear, and that people had been identified in the process to accept handovers.
If an operational process needs engagement with IT, operations must co-design the process with IT to manage expectations and to reduce operational risk. Failing to do this will result in failed processes, given no awareness or clarity of IT’s role in the process.
AS A RISK CONTROL, A PASSWORD VAULT WAS CREATED FOR ALL APPLICATION AND SYSTEM PASSWORDS, SUPPORTED BY A PROCESS THAT COULD BE ACCESSED BY THE EXECUTIVE TEAM IN AN EMERGENCY.
Risk Management Risk management is a key pillar of effective IT governance. Together with policies and procedures as a critical part of effective risk management, 19 IT implemented a risk management process—Identify, Assess, Respond, Control, Monitor—with a living risk register as a monitoring and communication tool as a means to help minimize potentially negative differences between expected IT outcomes and the actual IT outcomes. The process emphasized assigning responsibility for a risk control at the point where risk is realized. Periodic IT governance meetings were established as a means to monitor changes in IT environment risk and to monitor the effectiveness of the risk controls.
Key administrator passwords held in people’s heads was a major operational and sustainability risk. As a risk control, a password vault was created for all application and system passwords, supported by a process that could be accessed by the executive team in an emergency.
Structure and People People are the most critical part of IT because they determine whether something is done well. To effect and to sustain digital transformation, IT staff must have digital mindsets; 20 be inclined to testing and learning, innovation, and agility; 21 have diverse technology knowledge, deep data skills, rich process skills, and end-to-end mindsets that includes teamwork, courage, and change management. 22
Sustainable digital transformation, thus, requires “t- shaped” people—staff with deep knowledge of their areas of expertise and broad knowledge that they can apply to solve the types of new problems that emerge under transformation. 23 T-shaped people are especially important in small IT teams, where broad knowledge overlap mitigates the continuity risk of a small staff complement.
Digital transformation demands agility—people fluidly structuring around problems or challenges in cross-functional teams 24, 25 rather than constrained within traditional organizational structures. Compromising on IT competence has been described as a subtle and even a dangerous issue in digital transformation. 26
“Build the organization,” “run the organization” and “transform the organization” 27 was adopted as the IT structure paradigm. Bespoke definitions for “run the organization” and “build the organization” were developed to define their purpose and scope for the organization ( figure 8 ).

While the Agency’s IT organization managed day-to-day operations (run) and performed technology modernization projects (build) like those in figure 8 , it had unsustainable transformation. Given the organization’s growth and expansion aspirations, “transform the organization” was established as a full-time role, and an experienced leader was recruited to focus on strategy and architecture to help define the organization’s broader digital capabilities.
Strategy and Architecture The current state of the Agency was such that it had no clear IT strategy and no clear IT architecture. Many different applications had been acquired from a wide variety of vendors over time to serve specific point purposes but with no consideration for aspects such as architectural fit, integrated cybersecurity management and interoperability. The historical approach to IT tended to be tactical, with no consideration of how the tactical deployments would impact the Agency’s overall IT risk profile.
While this worked reasonably well in a low-stress IT environment, the diverse flaws in the approach quickly became apparent at the start of the pandemic—especially to end users who suffered service interruptions—when network volumes escalated significantly under work-from-home orders.
All interventions documented in the Technology Stream section were part of a significantly more architected approach—specifically around cybersecurity and interoperability—that included business cases as part of the supporting documentation and a comparison with next-best technology alternatives.
THE HISTORICAL APPROACH TO IT TENDED TO BE TACTICAL, WITH NO CONSIDERATION OF HOW THE TACTICAL DEPLOYMENTS WOULD IMPACT THE AGENCY’S OVERALL IT RISK PROFILE.
It is useful to note that unarchitected IT is a primary driver of technology debt; 28 an unwelcome gift to current IT management from former IT management as experienced in the Agency’s current IT state. While appropriate IT vendor diversity should be supported in the interest of good IT risk management, this should occur within a strategically architected framework. IT strategy and IT architecture can sustainably reduce IT risk and improve business continuity.
Data Governance Stream Digital transformation consumes data and produces more data that not only serves general reporting and decision-making, but also potentially serves government policy direction. While data were not initially identified as a problem at the Agency, a data strategy has been developed in response to some data issues identified ( figure 9 ), and in line with a vision for data for the organization. (The data strategy will not be covered further in this case study beyond the limited discussion that follows.)

CIOs strive for data consistency, data availability, information resource control and information flow visibility. 29 Not addressing data challenges results in delayed and/or incorrect data-driven decision- making and productivity compromises, and incurs unnecessary IT effort to resolve issues arising from bad data.
As a first step toward addressing data challenges, the Agency articulated its unique perspective of the drivers of a data culture as an output of a facilitated workshop series. Some of the behavioral considerations include:
- Mistrust about what data could communicate; could they show performance levels that are lower than perceived?
- That data have not been seen as something that can add value
- That data are removed from the people whose lives they represent
- That data capture is only seen as a necessary part of getting the job done, rather than as a vital part of the data value chain
- That data are not seen as distinct from IT, with operational and strategic best practices distinct from those applicable to data
It is important that ways to address these behavioral considerations are included in the organization’s data strategy. The implementation of the cultural aspect is an overarching workstream for the data work that needs to be performed over the upcoming years to create an environment rich in fit- for-purpose data. Overall, IT culture is the single greatest risk—and, therefore, critical success factor (CSF)—not only for IT governance, 30 but possibly for data governance, too.
Key Results and Benefits
As outlined, successful digital transformation requires the barriers to an effective digital strategy—processes, technology, people and governance, in that order 31 —to be addressed. Without a sound IT operating model foundation, digital transformation will exacerbate IT operating model shortcomings with predictable consequences. Figure 10 summarizes the major IT outcomes achieved. Note that the column “Technology and/or Governance Intervention” in the figure refers to the relevant item in the Technology Stream section or the Governance Stream section.

Figure 10 item 10 refers to technical cybersecurity vulnerabilities. However, the Desjardins breach in Canada 32, 33 is a shocking reminder of the scale of breach possible in the presence of even the best technological responses. People vulnerabilities are, thus, addressed through the newly established SOC at the Agency, mandated to address people matters such as cybersecurity training and to perform vendor due diligence. This closes the loop on the cybersecurity vulnerabilities identified as part of the network remediation workstream.
Other noteworthy outcomes include digital forms with workflows for efficient forms processing compared to paper forms, and improved secure video conferencing.
What Is Next?
With many of the primary activities in figure 10 having been achieved in six months across nearly 20 regional sites, there is still more work to do, with some of the major considerations being:
- Telephony, as discussed
- Case management, as discussed
- Laptop standardization, all staff
- Addressing stable and reliable power
- Modernizing the data infrastructure as the foundation required for the implementation of an organizationwide data strategy
DIGITAL DISTINCTION’ AND COST SAVINGS WERE ACHIEVED WITH LIMITED RESOURCES IN A LIMITED TIMEFRAME, AN UNUSUAL ACHIEVEMENT IRRESPECTIVE OF ORGANIZATION SIZE OR RESOURCES.
Of these, the data infrastructure will likely be the highest cost future intervention. This will require not only technology, but a full data operating model to support the growing day-to-day requirements for data and reporting in the organization. From a CIO perspective, formally aligned organizational strategy and IT strategy interventions ultimately help minimize digital strategy execution gaps, 34 the difference between what an organization aspires to achieve strategically, and what it actually achieves.
Organizations trust the CIO to ensure that the technology ecosystem is a functional and reliable enabler of the organization’s operations. 35 This means that the role has significant fiduciary responsibilities requiring high performing, t-shaped people. Digital transformation needs executive support and visibility, and credit is due to the head of the organization, the head of finance and administration, and the head of human resources (HR) for their encouragement during some of the darkest hours of this process. Thanks are due also to the extraordinary performance of a small, but mighty and highly motivated IT team willing to go so significantly beyond the extra mile for months on end.
This case study details the types of CIO leadership needed for digital transformation readiness and technology modernization, aligned with an approach published in ISACA ® Journal . 36 “Digital distinction” and cost savings were achieved with limited resources in a limited timeframe, an unusual achievement irrespective of organization size or resources. The organization is now positioned to increasingly redirect IT spend from operations to digital innovation 37 as reward for its courageous efforts.
1 El Tarabishy, A.; “The Top 10 Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Trends for 2021,” International Council for Small Business, 6 July 2020, https://icsb.org/toptrends2021 2 Avanade, “IT Modernization: Critical to Digital Transformation,” March 2017, https://www.avanade.com/-/media/asset/white-paper/avanade-it-modernization-whitepaper.pdf 3 Pearce, G.; “Digital Transformation Governance: What Boards Must Know,” Governance Institute of Australia, vol. 72, no. 5, 2020, https://www.governanceinstitute.com.au/resources/governance-directions/volume-72-number-5/digital-transformation-governance-what-boards-must-know/ 4 Bendor-Samuel, P.; “Four Guidelines for Success in Innovation in Digital Transformation,” Forbes , 23 July 2019, https://www.forbes.com/sites/peterbendorsamuel/2019/07/23/four-guidelines-for-success-in-innovation-in-digital-transformation/#61401a511aa9 5 Pearce, G.; “Attaining Digital Transformation Readiness,” ISACA ® Journal , vol. 1, 2020, https://www.isaca.org/archives 6 Rivier University Nashua, New Hampshire, USA, “The Growing Importance of a CIO in Today’s Evolving Business World,” Boston Business Journal , 16 March 2020, https://www.bizjournals.com/boston/news/2020/03/16/the-growing-importance-of-a-cio-in-today-s.html 7 Op cit McLaughlin 8 Op cit Rivier University 9 Ibid. 10 Morley, L.; “How Much Should a Company Spend on IT?,” Techvera, https://blog.techvera.com/company-it-spend 11 Avasant Research; “IT Spending as a Percentage of Revenue by Industry, Company Size, and Region,” Computer Economics , https://www.computereconomics.com/article.cfm?id=2626 12 CIO Journal , “The Role of Senior Leaders in IT Governance,” The Wall Street Journal , 22 June 2015, https://deloitte.wsj.com/articles/the-role-of-senior-leaders-in-it-governance-1434945783?tesla=y 13 IT Governance Network; “The CIO and IT Governance,” https://www.itgovernance.co.za/3/index.php/general-articles/176-the-cio-and-it-governance 14 De Haes, S.; A. Joshi; T. Huygh; S. Jansen; Board Level IT Governance Research Project , Antwerp Management School, Belgium, September 2016, https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/be/pdf/2018/05/Corporate_Governance_Codes_and_Digital_leadership.pdf 15 Op cit Pearce, “Attaining Digital Transformation Readiness” 16 Sharma, A.; “Application Modernization: One of the Critical Levers of Digital Transformation,” CIO , 30 July 2020, https://cio.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/strategy-and-management/application-modernization-one-of-the-critical-levers-of-digital-transformation/77253867 17 Dogan, C.; From the Basement to the Cloud: The Role of the CIO Over Four Decades , Deloitte Consulting, USA, 2018, https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/ar/Documents/technology/THE-ROLE-OF-THE-CIO-OVERF-OUR-DECADES.pdf 18 Op cit Avanade 19 Amadei, L.; “Why Policies and Procedures Matter,” Risk Management , 1 November 2016, http://www.rmmagazine.com/2016/11/01/why-policies-and-procedures-matter/ 20 Op cit Dogan 21 Annacone, A.; “The Four Types of Digital Transformation,” TechNexus on Linkedin, 19 June 2019, https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/4-types-digital-transformation-andrew-annacone/ 22 Davenport, T. H.; T. C. Redman; “Digital Transformation Comes Down to Talent in Four Key Areas,” Harvard Business Review , 21 May 2020, https://hbr.org/2020/05/digital-transformation-comes-down-to-talent-in-4-key-areas 23 Rowles, D.; T. Brown; Building Digital Culture , Kogan Page, United Kingdom, 2017 24 Ghosh, A.; “Digital Transformation of the Workplace,” India Inc., 19 November 2020, https://indiaincgroup.com/digital-transformation-of-the-workplace/ 25 Penfold, P.; “HR Strategies That Help Digital Transformation Succeed,” People Matters, 22 November 2019, https://www.peoplemattersglobal.com/article/hr-technology/hr-strategies-that-help-digital-transformation-succeed-23829 26 Op cit Rowles and Brown 27 Apptio, IT Financial Metrics Primer , USA, https://dsimg.ubm-us.net/envelope/151893/296392/1390318118_WP_-_Apptio_IT_Financial_Metrics_Primer.pdf 28 Dalal, V.; R. Patenge; K. Krishnakanthan; “Tech Debt: Reclaiming Tech Equity,” McKinsey Digital, 6 October 2020, https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/tech-debt-reclaiming-tech-equity# 29 Op cit Dogan 30 Pearce, G.; “The Sheer Gravity of Underestimating Culture as an IT Governance Risk,” ISACA Journal , vol. 3, 2019, https://www.isaca.org/archives 31 Op cit Pearce, “Attaining Digital Transformation Readiness” 32 The Canadian Press, “Desjardins Says Employee Who Stole Personal Data Also Accessed Credit Card Info,” BNN Bloomberg, 10 December 2019, https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/desjardins-says-employee-who-stole-personal-data-also-accessed-credit-card-info-1.1360652 33 The Canadian Press, “Series of Gaps Allowed Massive Desjardins Data Breach, Privacy Watchdog Says,” CTV News, 14 December 2020, https://www.ctvnews.ca/business/series-of-gaps-allowed-massive-desjardins-data-breach-privacy-watchdog-says-1.5230179 34 Pearce, G.; “Digital Governance: Closing the Digital Strategy Execution Gap,” ISACA Journal , vol. 2, 2020, https://www.isaca.org/archives 35 Edelman, D. J.; “CIO in Focus: A Global Study,” USA, 2020, https://www.edelman.com/expertise/technology/cio-in-focus 36 Op cit Pearce, “Attaining Digital Transformation Readiness” 37 Halfteck, D.; “Six Steps to Ensure IT Readiness to Drive Digital Transformation,” Access IT Automation, 16 May 2019
Guy Pearce, CGEIT, CDPSE
Has served on governance boards in banking, financial services and a not-for-profit, and as chief executive officer (CEO) of a financial services organization. He has taken an active role in digital transformation since 1999, experiences that led him to create a digital transformation course for the University of Toronto School of Continuing Studies (Ontario, Canada) in 2019. Consulting in digital transformation and governance, Pearce shares more than a decade of experience in data governance and IT governance as an author and as a speaker. He was awarded the ISACA® 2019 Michael Cangemi Best Author award for contributions to IT governance, and he is chief digital officer and chief data officer at Convergence.Tech.
Richard Fullerton, AWS CSA, ITIL, MCAAA, VCP-DCV
Is the IT manager at Native Child and Family Services of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. He is a solutions-oriented IT professional with more than 20 years of experience in the organization and delivery of end-to-end IT projects involving data migrations, server upgrades and configurations, and enterprise-scale software and hardware installations. His areas of expertise include cloud (AWS, Azure, Office 365), virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V, Citrix), and identity and access management. Fullerton is an experienced technical team leader in matrix organizations. He is the recipient of multiple Distinguished Service and Project Leadership awards, and the recipient of a Service Excellence award.

- Get IGI Global News

- All Products
- Book Chapters
- Journal Articles
- Video Lessons
- Teaching Cases

Journal of Cases on Information Technology (JCIT)
Export reference.

- Data Management
- Distance Learning
- E-commerce technologies
- E-Government
- E-Learning Technologies
- End User Computing
- Human Side of IT
- Information security and ethics
- Internet Technologies
- Issues of emerging technology
- IT in business
- IT in developing countries
- IT in government
- IT in libraries
- IT in organizations
- IT in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
- IT in the classroom
- IT in the healthcare industry
- Legal issues of IT
- Multimedia in Education
- Social Networks
- Web-Enabled Technologies

- Timely Publication: Quick Turnarounds & Prompt Peer Review (No Embargoes)
- Continuous Support: In-House, Personalized Service Throughout the Entire Process
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Proprietary Technologies & Integrations With Major Open Access Platforms
- Diverse Options: Individual APCs, Platinum Funding, Institutional Open Access Agreements, & More
- Research Advancement First: IGI Global Prioritizes Research Over Profit by Forfeiting Subscription Revenue
- Unmatched Transparency: Comprehensive Visibility in Processes, Licensing, & More
- Rapid Transformation: IGI Global is One of Few Publishers That Have Completed the Open Access Transition
- Independence and Integrity: IGI Global is Committed to Maintaining its Autonomy as an Independent Publisher
- Medium-Sized, Yet Powerful: IGI Global Offers Advantages of a Medium-Sized Publisher With the Reach of a Larger Publisher
Payment of the APC fee (directly to the publisher) by the author or a funding body is not required until AFTER the manuscript has gone through the full double-anonymized peer review process and the Editor(s)-in-Chief at his/her/their full discretion has/have decided to accept the manuscript based on the results of the double-anonymized peer review process.
In the traditional subscription-based model, the cost to the publisher to produce each article is covered by the revenue generated by journal subscriptions. Under OA, all the articles are published under a Creative Commons (CC BY) license; therefore, the authors or funding body will pay a one-time article processing charge (APC) to offset the costs of all of the activities associated with the publication of the article manuscript, including:
- Digital tools used to support the manuscript management and review process
- Typesetting, formatting and layout
- Online hosting
- Submission of the journal's content to numerous abstracts, directories, and indexes
- Third-party software (e.g. plagiarism checks)
- Editorial support which includes manuscript tracking, communications, submission guideline checks, and communications with authors and reviewers
- All promotional support and activities which include metadata distribution, press releases, promotional communications, web content, ads, fliers, brochures, postcards, etc. for the journal and its published contents
- The fact that all published articles will be freely accessible and able to be posted and disseminated widely by the authors
- Professional line-by-line English language copy editing and proofreading*
*This service is only performed on article manuscripts with fully paid (not discounted or waived) APC fees.
To assist researchers in covering the costs of the APC in OA publishing, there are various sources of OA funding. Additionally, unlike many other publishers, IGI Global offers flexible subsidies, 100% Open Access APC funding, discounts, and more. Learn More
I have been associated with JCIT (and its predecessor ACIT) for the past five years as an author, reviewer and, now, associate editor. JCIT provides a rich collection of IT cases on a wide range of IT topics. Over this time I've seen the rigor of the review process, and I'm confident in the quality of the end product. Faculty in the IT discipline can count on JCIT to provide valuable teaching tools for their undergraduate and graduate classes.
Real-life examples of information technology are the life blood of rich postgraduate work that is challenging, relevant, and interesting for students. The Journal of Cases in Information Technology provides such real life examples and it is being continually updated and added to. The Journal of Cases in Information Technology is an important academic resource which I turn to when setting postgraduate course work.
The Journal of Cases on Information Technology (JCIT) is owned and published by IGI Global.
Journal of Cases on Information Technology (JCIT) is editorially independent, with full authority of the journal's content falling to the Editor-in-Chief and the journal's Editorial Board .
The In-House Editorial Office manages the publishing operations of the journal.
IGI Global 701 East Chocolate Avenue Hershey, PA 17033 USA
Principal Contact Grace Long Managing Editor of Journal Development IGI Global Phone: (717) 533-8845 ext. 147 E-mail: [email protected]
Support Contact Tessa Eberlein Development Editor - Journal of Cases on Information Technology (JCIT) IGI Global Phone: 717-533-8845 E-mail: [email protected]
This site uses cookies to improve your experience. By viewing our content, you are accepting the use of cookies. To help us insure we adhere to various privacy regulations, please select your country/region of residence. If you do not select a country we will assume you are from the United States. View our privacy policy and terms of use.

Digital Transformation in Healthcare
N2Growth Blog
MAY 12, 2023
As the healthcare industry continues to undergo rapid changes, driven by advancements in technology and evolving patient needs, it is crucial for healthcare organizations to stay ahead of the curve. However, implementing telemedicine requires the proper infrastructure, technology , and traditional healthcare delivery model changes.
Executive Evolution: How Performance Coaching Transforms Leadership
OCTOBER 26, 2023
Rapid technological advancements, globalization, and changing consumer demands are just a few factors contributing to the constant flux in the corporate landscape. One of the key obstacles lies in the ever-changing business environment.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Trending Sources
- Leading Blog
- Let's Grow Leaders
- Leadership Freak
Rich Gee Group
- Leading in Context
- Great Results Team Building
Tanveer Naseer
- Sales Wolf Blog
- Women on Business

Unlocking Digital Leadership: CIO Executive Search
As organizations increasingly rely on technology to drive growth and innovation, the role of digital leaders has become paramount. Digital leadership is not limited to technology -driven companies; businesses across industries recognize the need for influential digital leaders to stay competitive in the market.

Developing a Leadership Training Program for High Potentials: A Case Study
Great Leadership By Dan
SEPTEMBER 15, 2011
Developing a Leadership Training Program for High Potentials: A Case Study . Let’s look at a case study of a manufacturing company that saw the need for a leadership development program for their high potential employees. Case Study : XYZ Widget Manufacturing Corporation. Background Information .

AI for Execs: Navigating the Future of Business.
OCTOBER 8, 2023
For executives, AI isn't just about technology ; it's about transformation. AI specialists can provide insights into what technologies to adopt, how to integrate them, and how to avoid potential pitfalls. The book also includes case studies from companies that have successfully implemented AI.

Executive Search in the Legal Sector: Uncovering Excellence
DECEMBER 8, 2023
The Role of Technology in Enhancing the Executive Search Process for Legal Professionals Technology has become an invaluable tool in the executive search process for legal professionals. One of the key ways technology enhances the executive search process is through data analysis.

Drowning in Information While Thirsting for Communication
The Practical Leader
AUGUST 25, 2021
Are you over- informing and under communicating? Many managers confuse information and communication: Information Technology /. Information Technology is critical today. Find ways to condense information dumps/updates so you can truly communicate — talk to, not at, each other. Communication.

Here’s Why Corporate Video Production Is Essential for Your Business
Strategy Driven
AUGUST 15, 2024
Videos have become a vital tool for businesses, offering a dynamic way to engage, inform , and connect with both current and potential customers. Studies show that people are more likely to watch and retain information from video content than from other formats. That’s where corporate video production comes into play.

Why Boutique Executive Search Firms Outperform Global Behemoth’s
APRIL 19, 2024
This deep understanding informs every aspect of our search, from the criteria we use to evaluate candidates to the way we position the opportunity to attract top talent. Unlike global firms, where clients may be passed off to junior associates, at N2Growth, clients work directly with our top leadership throughout the entire search process.

Changing The Talent Equation: From Expense to Asset
JUNE 10, 2024
Employees who receive ongoing training are better equipped to handle new challenges, adapt to technological advancements, and drive innovation within the organization. 2: IBM's Reskilling Programs IBM recognized the need to adapt to rapid technological changes and invested heavily in reskilling its workforce.

Maximizing ROI with Advanced Data Techniques in Family Offices
JULY 5, 2024
By analyzing this data, family offices can identify emerging trends, predict market movements, and make informed investment decisions. These technologies can process large datasets at incredible speeds, uncover patterns, and generate predictive models. GDPR, CCPA) is paramount.

A Technology Case Study: Implementing What the Customer Wants
JULY 27, 2011
In order for any change to occur – whether it’s a decision to purchase a product, or an implementation to add new technology – whatever touches the ultimate solution must buy-in to the change. In 1983, in London, I started up a body shop/recruitment company to support the ‘new’ language and ’4GL’ support technology called Focus.

The Beauty of Efficiency: Transforming Cosmetic Fulfillment Processes
AUGUST 7, 2024
Track and Trace : Provide customers with tracking information for their orders. This keeps them informed about the status of their shipment and reduces the number of customer inquiries. Leveraging Technology for Fulfillment Efficiency Technology plays a crucial role in transforming cosmetic fulfillment processes.

Key Strategies for Aspiring Entrepreneurs Considering Franchise Ownership
APRIL 27, 2024
Additionally, perusing information from established platforms specializing in the franchise sector can offer rich insights into a franchise opportunity and what it takes to succeed. Technology Integration in Franchises The infusion of technology into franchise operations is an accelerating trend redefining industry standards.

Collaboration for Change: Multi-Sector Partnerships in Sustainable Medical and Sharps Waste Management
OCTOBER 13, 2023
Case Study : Houston’s Multi-Sector Approach In Houston, this collaborative spirit is palpable. The Global Perspective: Lessons from Abroad While Houston offers a compelling case study , it’s essential to recognize global efforts.

Things to Consider When Relocating a Business
FEBRUARY 6, 2024
Look for a company with a strong track record in commercial moves, evidenced by customer reviews and case studies . Keep your team informed about the moving schedule and what is expected from them. For customers, keep them informed about how the move might affect them, if at all. Communication is key here.

How to Minimize Business Disruption When Upgrading Tech
SEPTEMBER 18, 2020
With technology moving at such a rapid rate these days, you can’t afford to allow your hardware and software to become old and stale. However, when you do get round to upgrading your technology , it is all too easy for it to cause business disruptions. Hire the Right Tech Team. Plan and Test. Prepare for Future Upgrades.

How To Get Started With Digital Transformation
The Horizons Tracker
JULY 29, 2021
Given this mixed record of success and the inherent complexity of adopting technologies that can often be a world away from what you are used to, it’s perhaps understandable that many managers are reluctant to venture down such an uncertain path. Using digital technology to better engage with customers and sell more effectively.

Outsourcing Manual Link Building Service for Your Business
DECEMBER 26, 2023
Lastly, ask for case studies or client testimonials. They will also inform you of the impact they’re having on your site’s SEO. You can make informed decisions that best suit your business. Suppose they’re writing a blog post about the latest developments in cloud technology .


Coaching Executives: The Essence of Nurturing Leadership
DECEMBER 22, 2023
Case Study : The Transformational Impact of Empathy A compelling example can be found in a tech startup CEO who underwent executive coaching. A comprehensive study involving 242 technology -intensive knowledge-based firms (t-KIBS) has shed light on this transformative strategy.

Inviting New Voices to the Table: HR as a Strategic Partner
NOVEMBER 26, 2023
With the way trends and technology keep adapting, having strong control over the human resources invested in a company and planning for the long term can be just as crucial a decision as planning a new product launch or seeking a profitable business deal. Investment in HR Technology Another investment avenue is in HR technology .

The Art of Conducting a Comprehensive Training Needs Analysis
MAY 15, 2024
By regularly conducting training needs analyses, organizations can cultivate a culture of continuous learning and development, empowering employees to stay up-to-date with industry trends, technological advancements, and evolving business requirements. The Three Levels of Training Needs Analysis What is traning needs anaylsis?

Why Doctors Today Need Managerial Skills
JUNE 23, 2022
There’s a thirst for this type of information among clinicians,” they explain. For instance, the early months of the pandemic saw rapid digital transformation in medicine, with technologies such as telehealth introduced in double quick time. These technologies were hugely valuable, but did require a change in mindset from physicians.

2020 Top CHRO List – The People Leaders To Watch
SEPTEMBER 28, 2020
While Chief Digital/ Technology Officers or Chief Marketing Officers are often tagged with the innovator label, it is the CHRO who is the real innovator in 2020. Remember, it’s the people and culture who enable technology and marketing success – not the other way around. ?. Selection Methodology.

Boosting Productivity: Generative AI’s Impact On The Workplace
MAY 26, 2023
Generative AI , also known as artificial intelligence encompasses technology that possesses the ability to be ‘trained’ to tackle inquiries through text or other outputs. Instead of financial analysts spending 80 percent of their time running reports, they can be freed up to help businesses make better- informed decisions.”
The Center for Leadership Studies Announces New Program for Empowering Accountability Through Situational Leadership® Practices
The Center For Leadership Studies
APRIL 25, 2023
Situational Performance Ownership is available in four critical modalities—in-person instructor-led training (ILT), virtual instructor-led training (vILT), digital blended and self-paced—and the program’s modern design features accessibility compliance, reinforcement and practice, facilitator feedback as well as engaging case study videos.

The Key Software Tools Modern Business Owners Should Embrace In 2021
MARCH 4, 2021
The modern business world relies on technology and with the rise in remote work , caused in part by the Coronavirus, more companies across the corporate landscape have needed to embrace innovative software solutions to stay productive and cost-efficient. As such, all businesses should consider cloud cost management software.

12 HR Podcasts You Should Listen to Right Away
APRIL 13, 2020
They help to develop HR skills and teach interesting information about recruitment and talent management. The Jim Stroud Podcast is hosted by Jim Stroud himself and shares essential thoughts and insights about the cultural trends and emerging technology that influence the world of professionalism. The Jim Stroud Podcast.

Key Elements for a Successful Employee Training Program
AUGUST 14, 2023
Effective training materials are not just informative ; they are engaging, interactive, and tailored to the needs of your learners. Use real-life examples, case studies , and anecdotes to illustrate key concepts and make the content relatable. Monitoring Progress: Are We There Yet? Congratulations!

Vanity Phone Numbers’ Effect on Customer Recall and Business Branding
FEBRUARY 29, 2024
They transform ordinary contact information into memorable catchphrases that stick with consumers long after the advertisement has ended. Studies have revealed that ease of communication is critical to customer satisfaction, and vanity numbers address this need effectively.

What is the effectiveness of Every Door direct mail?
DECEMBER 1, 2022
Try doing research or surveys to learn more about their needs and interests, and use that information when creating content for your EDDM marketing materials. Case studies of successful EDDM campaigns. With these tips, you can immediately start seeing better results from your EDDM campaigns.

Eforms 101: Everything You Need To Know About eForms
JANUARY 21, 2020
The age of 3D printing has been around for a while, yet the vast majority of businesses are still stuck on technology invented millennia ago. One of the primary uses of paper in businesses is for creating forms that help collect information . They Enable Quick Release Of Essential Business Information . But what is an eForm?

Learning Methods | Vital Learning
Chart Your Course
SEPTEMBER 7, 2013
Technology continues to evolve, creating many new options for delivering training. Our facilitator guides provide all the information trainers need to deliver effective courses, including: Complete instructions about how to conduct the course. Today, people consume content in a variety of formats.

10 Learning and Development Books for 21st Century Leaders & Organizations
Experience to Lead
MAY 19, 2022
Packed with plentiful case studies and dynamic games, this guide is the perfect resource for anyone wishing to train others and to improve their own cultural competency. This resource is perfect for world leaders who wish to understand technological trends- all through a powerfully humanitarian lens. Robert Kohls.

5 Ways to Better Manage Your Field Workforce in the Cloud
JULY 31, 2017
However, determining which technology tools to use — and how to make it all work for your team — is another animal altogether. But the process also provides a means to update your inventory, so your field reps have the latest information on the road. A service like Import.io Manage Expense Reporting On-the-Go.

Three Key Criteria for Choosing the Right Custom Learning Partner
DECEMBER 4, 2020
In this category, the information you are looking for should answer the question, “What can they do?” By applying this transferable knowledge and expertise, design teams can work with you to create immersive role- and industry-specific case studies , simulations and application activities that are relevant and relatable to your learners.

Dave Ulrich on The Four Waves of HR
OCTOBER 26, 2012
Technology Proponent – All organizations seem to have difficulty in handling and transferring the massive amounts of information they accumulate. This is especially true in HR, and HR Professionals must find ways to effectively use technology to understand and strengthen the talent within the organization.

How Impactful Is Machine Learning In Today’s Business World?
NOVEMBER 14, 2018
Since 2012, with the proliferation of Python in general software development, Machine Learning has become the biggest trend in the technology world. An interesting case study would be related to bridging loans , given the fact that fast-paced finance is heavily looked after by many clients. Service Providers. About the Author.

Case Study: Follow Dubious Orders or Speak Up?
Harvard Business Review
APRIL 20, 2017
Mr. Moon (as Susan had been told to call him by her half-Korean father, Don) was the Seoul office manager of Zantech, a technology security firm with headquarters in Amsterdam. Editor's Note This fictionalized case study will appear in a forthcoming issue of Harvard Business Review, along with commentary from experts and readers.

CMI Singapore: Updates from the Board
Chartered Management Institute
NOVEMBER 14, 2023
The discussions explored various issues, challenges and opportunities facing managers and leaders across a diverse set of areas – technology and digital, travel, business and the regional economy. Where should I start? We know that helping the community around you bolsters your business success.

Dave Ulrich on The Five Waves of HR

Steve Jobs, the Immediate Case Study
OCTOBER 14, 2011
In all kinds of places this past week — from Twitter feeds to boardrooms — people discussed Steve Jobs's career at Apple as a kind of informal but very important case study . This is not surprising, given his contributions to technology and the lasting impact he'll have on the way we communicate.

Engaging Culture One Conversation At A Time
JANUARY 15, 2013
They fully describe each element, and provide case studies and actionable takeaways. Intimacy means that talk takes place face-to-face: informally , between two people or in small groups. Profoundly social by nature, interactive talk both elicits responses and provides a means for participants to pass on information .

Stop Decorating the Fish
Skip Prichard
MAY 10, 2021
They start by sharing the “Seductive Seven” which is a list of common tactics organizations may use to respond to problems: More technology . For example, we can see data dashboards, organization charts, spreadsheets, new strategic plans, or the latest new technology trend bouncing around social media. The Seductive Seven. More money.
Stay Connected
Join 5,000+ Insiders by signing up for our newsletter
- Participate in Leadership Digital
- Add a Source
- Add a Resource
- Fri. Aug 30
- Thu. Aug 29
- Wed. Aug 28
- Tue. Aug 27
- Aug 17 - Aug 23
- Productivity
- Development
- More Topics
Input your email to sign up, or if you already have an account, log in here!
Enter your email address to reset your password. a temporary password will be e‑mailed to you., be in the know on.
Leadership Digital
Expert insights. Personalized for you.
We organize all of the trending information in your field so you don't have to. Join 5,000+ users and stay up to date on the latest articles your peers are reading.

Get the good stuff
Subscribe to the following Leadership Digital newsletters:
You must accept the Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions to proceed.

You know about us, now we want to get to know you!
Check your mail, we've sent an email to . please verify that you have received the email..
We have resent the email to
Let's personalize your content
Use social media to find articles.
We can use your profile and the content you share to understand your interests and provide content that is just for you.
Turn this off at any time. Your social media activity always remains private.
Let's get even more personalized
Choose topics that interest you., so, what do you do.
Are you sure you want to cancel your subscriptions?
Cancel my subscriptions
Don't cancel my subscriptions
Changing Country?
Accept terms & conditions.
It looks like you are changing your country/region of residence. In order to receive our emails, you must expressly agree. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the unsubscribe link at the bottom of our emails.
You appear to have previously removed your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions.
We noticed that you changed your country/region of residence; congratulations! In order to make this change, you must accept the Aggregage Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. Once you've accepted, then you will be able to choose which emails to receive from each site .
You must choose one option
Please choose which emails to receive from each site .
- Update All Sites
- Update Each Site
Please verify your previous choices for all sites
Sites have been updated - click Submit All Changes below to save your changes.
We recognize your account from another site in our network , please click 'Send Email' below to continue with verifying your account and setting a password.
You must accept the Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions to proceed.
This is not me
Ethics, Society, & Technology Case Studies
At the McCoy Family Center for Ethics in Society, we believe that researchers, founders, and technologists—present and future—should be expected to confront and gain a deeper understanding of the ethical, social, and political dimensions of technologies. We aim to prepare the next generation of leaders to take on these challenges by integrating ethical and societal implications into the development, deployment, and governance of technology.
To support this mission, the Ethics, Society, and Technology Initiatives are creating a high-quality production of open-source ethics, policy, and technology case studies for use in university and industry settings. Through the Ethics, Society, and Technology (EST) Case Study Program a talented team of case writers develop and prototype case studies that address pressing ethical and sociotechnical issues in the technology field by drawing on secondary and primary sources of research materials.
EST case studies explore written stories that wrestle with business decisions, design and technical implementation, regulatory compliance and limitations, and individual participation in the technology industry and workforce. These stories can range from real-life scenarios to fictionalized ones based on composite experiences and stories.
Previous and current projects include:
- Algorithmic Decision-Making and Accountability
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Facial Recognition
- Fizz: Social Media Growth
- Generative AI: Navigating the Technology Industry
- Juul Labs: A Design & Marketing Case Study
- Private Platforms
- Ethics and Profits: The Case of Meta and Teens
- Vaccine Distribution: A Case Study in Algorithmic Priorities
- Voting Registration: A Case Study in Data Representation
If you use any of these case studies and have feedback on them, please feel free to send the case writing team an email at estinitiatives [at] stanford.edu (estinitiatives[at]stanford[dot]edu) .
These case studies are made possible in part by Frank McCourt in association with Stanford’s partnership with the Project Liberty Institute .

- Technology Ethics Cases
- Markkula Center for Applied Ethics
- Focus Areas
- Technology Ethics
- Technology Ethics Resources
Find case studies illustrating dilemmas in technology and ethics.
Case studies are also available on Internet Ethics .
For permission to reprint cases, submit requests to [email protected] .
Looking to draft your own case studies? This template provides the basics for writing ethics case studies in technology (though with some modification it could be used in other fields as well).
A fitness tracker aimed at children raises issues of design ethics, incentives, and more.
AI-generated text, voices, and images used for entertainment productions and impersonation raise ethical questions.
Ethical questions arise in interactions among students, instructors, administrators, and providers of AI tools.
Which stakeholders might benefit from a new age of VR “travel”? Which stakeholders might be harmed?
Case study on the history making GameStop short and stock price surge that occurred during January 2021.
As PunkSpider is pending re-release, ethical issues are considered about a tool that is able to spot and share vulnerabilities on the web, opening those results to the public.
With URVR recipients can capture and share 360 3D moments and live them out together.
VR rage rooms may provide therapeutic and inexpensive benefits while also raising ethical questions.
A VR dating app intended to help ease the stress and awkwardness of early dating in a safe and comfortable way.
Ethical questions pertaining to the use of proctoring software in online teaching.
- More pages:
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. You must have JavaScript enabled in your browser to utilize the functionality of this website.
- My Wishlist
- Customer Login / Registration
FB Twitter linked in Youtube G+

- ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
- MARKETING MANAGEMENT
- STATISTICS FOR MANAGEMENT
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
- OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- BRAND MANAGEMENT
- MARKETING RESEARCH
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP & STARTUPS
- CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
- BANKING & FINANCIAL SERVICES
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
- ADVERTISING
- BUSINESS ANALYTICS
- BUSINESS ETHICS
- DIGITAL MARKETING
- HEALTHCARE MANAGEMENT
- SALES AND DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT
- FAMILY BUSINESS
- MEDIA AND ENTERTAINMENT
- CORPORATE CASES
- Case Debate
- Course Case Maps
- Sample Case Studies
- IIM KOZHIKODE
- VINOD GUPTA SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT, IIT KHARAGPUR
- GSMC - IIM RAIPUR
- IMT GHAZIABAD
- INSTITUTE OF PUBLIC ENTERPRISE
- IBM Corp. & SAP SE
- Classroom Classics
- Free Products
- Case Workshops
- Home
- Case Categories

Leveraging IT for Corporate Banking Business Benchmarking
Making it happen @ bpcl kochi refinery: defining new paradigms of operational excellence through it transformation.
- last 6 months (0)
- last 12 months (0)
- last 24 months (0)
- older than 24 months (2)
- INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (2)
- CASE STUDY (2)
Information
- Collaborations
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Case Format
- Pricing and Discount
- Subscription Model
- Case Writing Workshop
- Case Submission
- Reprint Permissions
CUSTOMER SERVICE
| Monday - Friday | : | 09:00 AM - 05:30 PM (IST) |
Phone: +91 9626264881
Email: [email protected]
ET CASES develops customized case studies for corporate organizations / government and non-government institutions. Once the query is generated, one of ET CASES’ Case Research Managers will undertake primary/secondary research and develop the case study. Please send an e-mail to [email protected] to place a query or get in touch with us.
Don’t miss out!
Be the first to hear about new cases, special promotions and more – just pop your email in the box below.

Case Studies of Information Technology Application in Education
Utilising the Internet, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, and Cloud in Challenging Times
- © 2023
- Yang Shen 0 ,
- Xin Yin 1 ,
- Yu Jiang 2 ,
- Lingkai Kong 3 ,
- Sheng Li 4 ,
- Haijun Zeng 5
Collaborative Innovation Center of Assessment for Basic Education Quality, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Capital Normal University, Beijing, China
Center for educational technology and resource development, ministry of education, beijing, china, the joint laboratory for mobile learning, china mobile communications corporation, ministry of education, beijing, china, national engineering center of cyberlearning and intelligent technology, beijing normal university, beijing, china.
- Illustrates the development of basic education informatization in China
- Examines the construction and application of educational informatization in various regions in China
- Demonstrates the potential of applying information technology to transform education processes
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Educational Technology (LNET)
8430 Accesses
5 Citations
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
About this book
Similar content being viewed by others.

The Innovative Influence of Technologies on Education in China: Ongoing and Outlook

Section Introduction: Paradigms for Researching Information Technology in Education

- Application of Internet in education
- Application of big data in education
- Application of cloud in education
- Application of AI in education
- Project-based learning
- Integration of Urban and Rural Education
- "Internet +" Teaching
- Smart Classroom
- Cloud Platform for Rural Education
- Independent learning
Table of contents (43 chapters)
Front matter, case study for the application of internet in education, based on information technology, “learning–speaking” action plan: from “micro-class community” began.
- Yang Shen, Xin Yin, Yu Jiang, Lingkai Kong, Sheng Li, Haijun Zeng
Adaptive Evaluation System APP Development: Achieve Project-Based Learning
“micro-course of teaching group”: promote balanced development of education in different regions, “1 + n” compulsory courses special delivery class: exploring the integration of urban and rural education, the four rules of normalization of “internet +” teaching, disciplines are fully covered by mobile terminals, a new way of informatization for poor schools of ethnic minorities, digital-based “garden of the grass” school-based curriculum development, urban and rural assistance, across the straits, the practice of digital campus under the background of the new policy of college entrance examination, a new educational model of “classified classes online”, walk into the “internet + subjects” classroom, diverse star-rating online review, “qr code” application in education and teaching, case study for the application of big data in education, “data” runs: in smart classrooms, teachers and teaching, smart classroom: find the teaching methodology for teaching students according to their aptitude, information technology: let students discover their beauty, authors and affiliations.
Lingkai Kong, Sheng Li
Haijun Zeng
About the authors
YIN Xin is the technical director of the Technology Transfer Center of Capital Normal University, China, and a part-time researcher of the National Engineering Research Center of Cyberlearning and Intelligent Technology. His research interests are intelligent education, transformation of scientific and technological achievements, and intellectual property management.
JIANG Yu is an associate researcher of the Center for Educational Technology and Resource Development, Ministry of Education, P.R. China(National Center for Educational Technology) , and the deputy secretary-general of the Online Education Committee of the China Federation of Internet Societies. His main research interests are online education and learning science.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Case Studies of Information Technology Application in Education
Book Subtitle : Utilising the Internet, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, and Cloud in Challenging Times
Authors : Yang Shen, Xin Yin, Yu Jiang, Lingkai Kong, Sheng Li, Haijun Zeng
Series Title : Lecture Notes in Educational Technology
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9650-4
Publisher : Springer Singapore
eBook Packages : Education , Education (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2023
Hardcover ISBN : 978-981-19-9649-8 Published: 16 March 2023
Softcover ISBN : 978-981-19-9652-8 Published: 17 March 2024
eBook ISBN : 978-981-19-9650-4 Published: 15 March 2023
Series ISSN : 2196-4963
Series E-ISSN : 2196-4971
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XVI, 271
Number of Illustrations : 7 b/w illustrations, 94 illustrations in colour
Topics : Education, general , Computers and Education , Sociology of Education
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Search bar.
- Legal Queries
- Files
- Online Law Courses
- Lawyers Search
- Legal Dictionary
- The Indian Penal Code
- Juvenile Justice
- Negotiable Instruments
- The 3 New Criminal Laws
- Matrimonial Laws
- Data Privacy
- Court Fees Act
- Commercial Law
- Criminal Law
- Procedural Law
- The Constitutional Expert
- Matrimonial
- Writs and PILs
- CrPC Certification Course
- Criminal Manual
- Execution U/O 21
- Transfer of Property
- Domestic Violence
- Muslim Laws
- Indian Constitution
- Arbitration
- Matrimonial-Criminal Law
- Indian Evidence Act
- Live Classes
- Writs and PIL

Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn
Share on Email
Supinder Singh
Important Cases On Information Technology Act, 2000

Key Takeaways
- Primarily, Information Technology Act, 2000 provides the basic legal framework for electronic transactions in India. Along with this Act, various rules notified under this Act play a significant role in regulating the digital space.
- The rights of copyright owners cannot be restricted by Section 79 of the IT Act, 2000. So, intermediaries who infringe copyrights of anyone cannot seek protection under this section.
- Banyan Tree case Judgment is a Landmark for determining the jurisdiction of the court,where neither party to a suit, claiming online copyright infringement, resides within the territorial jurisdiction of such court.
- Union Government notified Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021. But these Rules have been challenged by various organizations as being violative of Fundamental Rights.
Introduction
Information Technology Act, 2000 (hereinafter referred to as “IT Act) was enacted in India to provide legal recognition to transactions carried out through electronic mediums, and to facilitate the electronic filing of documents with the Government Agencies. It was enacted after the General Assembly of the United Nations adopted the ‘Model Law on Electronic Commerce’ through a resolution. This Act was largely based on the Model Law that was adopted by the UN.In this article, I will discuss some Important Case Laws inIT Act, of 2000.
Important Case Laws on Information Technology Act, 2000
1. state of tamil nadu v. dr. l prakash (w.p.m.p.no. 10120 of 2002).
In this case, an FIR was registered against Dr. L Prakash under Section 67 of the IT Act, 2000 read with Section 4 & 6 of the Indecent Representation of Women Act, Section 27 of the Arms Act, and Sections 120B & 506 (2) of the IPC. The said case was registered as Dr. L Prakash was accused of making pornographic videos and then sending those to the US & France for publication on pornographic websites.
The Fast Track Court convicted the accused under the aforesaid provisions and sentenced him to undergo imprisonment for life. A fine of Rs. 1.27 lakh was also imposed on him.
This case is a landmark in the Cyber Crime Law as it was the first time that pornographic websites and their brokers were targeted in India.
2. Amar Singh v. Union of India [(2011) 4 AWC 3726 SC]
In this case, the petitioner had alleged that his calls were being tapped unauthorizedly by his telecom service provider. He had claimed that the alleged tapping was violating his fundamental right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution of India. The service provider had argued that it was complying with the government orders. This case is important in the context of Sections 69, 69A, and 69B of the IT Act, 2000.
The court observed that a telecom service provider performs a function of public nature. It is his inherent duty to act carefully and in a responsible manner. Furthermore, it was observed that when the orders of the government ‘to tap calls’ have gross mistakes, then the service provider must verify the authenticity of such orders. The court also directed the Central Government to frame certain directions/guidelines to prevent unauthorized interception of calls.
3. Nirmaljit Singh Narula v. Indijobs at Hubpages.Com [CS (OS) 871 / 2012]
This case relates to an alleged defamatory article published by Defendant against the Petitioner (popularly known as ‘Nirmal Baba’). It is an important case in the context of Section 79 of the IT Act, 2000 since the petitioner had sent a legal notice to the intermediary, on whose website the ‘defamatory’ article was published. The intermediary refused to remove the ‘defamatory’ article, so the instant case was filed.
The court held that an intermediary is obliged to remove unlawful content from its website if it receives a notice from the affected party, claiming that any illegal content is being circulated through the intermediary’s service. An intermediary is not liable for 3rd party content if it removes such content upon receiving notice.
In this case, an injunction was issued against Defendant barring it from publishing any further defamatory content against the Petitioner, and the intermediary was ordered to produce the IP log of the 3rd party user who had published the ‘defamatory’ article.
4. Vyakti Vikas Kendra, India Public v. Jitender Bagga [CS (OS) No. 1340 / 2012]
It was also a case of online defamation . In this case, it was alleged that the defendants had published online some defamatory material against ‘Shri Ravi Shanker, owner of Art of Living Foundation’. The Petitioners had prayed for damages along with a mandatory & permanent injunction against the Defendants.
The Court observed that an intermediary is bound to comply with Information Technology (Intermediaries Guidelines) Rules, 2011. These rules require that an intermediary must not allowthe publication of any defamatory or libelous information on its platform. So, in this case, the court passed an interim order in the favor of the petitioner.
5. Super Cassettes Industries Ltd. v. Myspace Inc. [CS (OS) No. 2682/2008]
The plaintiff approached the court as Defendant was allegedly infringing the copyright of the plaintiff. The plaintiff alleged that the defendant’s website generates revenue by making available infringing copies of copyrighted media to the public. It was also contended that the defendant encourages the users to share such type of content with the public.
One of the primary issues between the parties was – Whether the acts of the defendant as an intermediatory are protected under the provisions of Section 79 of the IT Act, 2000.
The court observed that the rights of copyright owners cannot be restricted by Section 79 of the IT Act, 2000. The aforesaid Section does not save the defendants from liability in case of infringing acts due to the proviso of Section 81 of the IT Act.
6. Banyan Tree v. A. Murali Krishna Reddy & Anr, [2010 (42) PTC 361 (Del)]
In this case, the plaintiff had filed a suit claiming that the defendant was passing off its word mark ‘Banyan Tree’ through its online website. In this case, neither the plaintiff nor the Defendant was located within the local limits of Territorial Jurisdiction of the court (before which the suit was brought).
So, the court had to decide on the question that in what circumstances does the hosting of a universally accessible website by the Defendants gives jurisdiction to the forum court, if the Plaintiff is not carrying on business within the territorial jurisdiction of the forum court.
The court answered that for the purposes of a passing-off action, the plaintiff will have to show that the defendant has “purposefully availed” itself of the jurisdiction of the forum court.Further, it will have to be proved by the plaintiff that Defendant operated the website to conclude a commercial transaction with the website users. The plaintiff will also have to show that the operation of such a website resulted in injury to the Plaintiff in the forum state.
7. Writs challenging the validity of Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021
In 2021, the Union Government notified these rules by using its power under Section 87 of the IT Act, 2000. These rules supersede the Information Technology (Intermediaries Guidelines) Rules, 2011. With these rules, the Government seeks to regulate the Social Media intermediaries, the Digital news media, and the online streaming platforms.
These rules provide that the social media intermediaries need to follow an internal grievance redressal mechanism. These intermediaries are also required to share the information of the person, who originated an objectionable message in cases of serious offences, with the Government.
The rules provide that the Intermediaries who do not comply with the rules will lose the immunity available to them under Section 79 of the IT Act. Furthermore, the rules require the Digital News Media to follow a code of ethics and also set up an Internal grievance redressal system.
These rules have been challenged by various organizations including WhatsApp, The Quint, LiveLaw, and Foundation for Independent Journalists. The decisions in these cases will determine the further course of the jurisprudence in the field of Information Technology in India.
8. Shreya Singhal v. Union of India [AIR 2015 SC 1523]
In this case, the constitutionality of Section 66A of the IT Act, 2000 was challenged. The petitioner contended that this section infringes their fundamental right to freedom of speech and expression. It was submitted that the restrictions imposed by the said section are not even saved or allowed by Article 19 (2) of the Constitution. Another primary contention put forward by the petitioner was that the said section suffers from the vice of vagueness because the terms used in the Section cannot be defined. So, that creates a wide scope for arbitrary and whimsical action by the State against a large number of innocent persons.It was also argued that the said Section violates the Right to Equality provided by Article 14 since the Section unreasonably differentiates between the people who use the internet and the people who use other mediums of communication.
Respondent, on the other hand, argued that the legislature is in the best position to understand the needs of the people. So, the court must not interfere in the legislative process until there is a clear violation of rights provided under Part III of the Constitution of India. It was submitted that the presumption is also in the favor of the constitutionality of a statute and that the mere possibility of abuse of a particular provision of a statute cannot be a valid ground to declare it invalid.
After hearing detailed arguments from both sides, the Hon’ble Supreme Court struck down Section 66A of the IT Act, 2000 in its entirety as being violative of Article 19 (1) (A). It is observed that the said Section is not saved under Article 19 (2).However, the court upheld the constitutional validity of Sections 69A and 79 of the IT Act, 2000 along with the IT (Procedure & Safeguards for Blocking for Access of Information by Public) Rules, 2009.
9. M/s Gujarat Petrosynthese Ltd &Anr.v. Union of India [2014 (1) Kar L J 121]
This case relates to a writ petition filed by the petitioner praying the court to issue a writ of mandamus directing the appointment of Chairperson to the Cyber Appellate Tribunal (CAT) by the Central Government. The petitioners submitted that due to the absence of the CAT Chairperson, their appeal was not being heard.They, further, submitted that the Government of India hadfailed to take necessary action to make the Cyber Appellate Tribunal operational.By relying on Section 49 of the IT Act, 2000, it was argued that the process of appointment of CAT chairperson must be initiated by the Central Government.
The counsel appearing for the Respondent submitted that the Government would take all the necessary actions for filling up the post of the Chairperson of the Cyber Appellate Tribunal within 6 months from the day of the submission. After hearing the parties, the Karnataka High Court observed that no direction needed to be issued, but it remarked that considering the delay of more than 2 years, the respondent must appoint the CAT Chairperson with a “sense of urgency”.
10. CBI v. Arif Azim (Sony Sambandh case) [(2008) 150 DLT 769]
In this case, the accused had stolen the credit card details of Barbara Campa. He then used that stolen card to purchase products from a website (sony-sambandh.com) owned by Sony India Private Limited. When the transaction was disputed by Barbara, the credit card company informed Sony about the same. So, Sony reportedthe case of Internet Fraud and Cheating to the CBI. CBI, on its part, initiated an investigation u/s 418, 419, and 420 of the IPC. The Court convicted the accused under the said Sections for the offence of cyber fraud. This case particularly relates to Section 66C of the IT Act, 2000, which covers the dishonest & fraudulent usage of electronic passwords, signatures,and other unique identification features of any person (Identity Theft).
11. State of Tamil Nadu v. Suhas Katti [CC No. 4680 of 2004]
In this case, a complaint was filed by the victim u/s 67 of the IT Act and Section 469 & 509 of the IPC, 1860. It was alleged that the accused posted obscene messages related to the victim in various groups with the intention to harass the woman. He also shared her phone number and created a fake account in her name to cause disrepute to her. The court convicted the accused under the aforementioned Sections. This case is a landmark since it inspired people around the country to come forward and file cases related to harassment on the Internet.
12. SMC Pneumatics (India) Pvt Ltd v.Jogesh Kwatra [CM APPL No. 33474 of 2016]
In this case, the defendant was an ex-employee of the plaintiff company. It was alleged that the defendant was sending defamatory, obscene, derogatory, and abusive emails to Plaintiff. The plaintiff submitted that the emails were intended to cause disrepute to its Managing Director. The accused was identified to be the sender of the emails after an investigation by a private computer expert. So, a suit seeking a perpetual injunction against the defendant was filed in the court.However, the said suit was dismissed by the court citing the lack of electronic evidence, linking the derogatory emails with the defendants.
13. Avnish Bajaj v. State (NCT) of Delhi [(2008) 150 DLT 769]
This petition was filed under Section 482, CrPC for getting annulled the criminal prosecution initiated against the Managing Director of a Company/Website (baazee.com) under Section 292 of the IPC and Section 67 of the IT Act, 2000. The Website provided an online marketplace for buyers and sellers to interact.The Petitioner argued that since the Website Company was not made an accused in the case, the petitioner could not be made liable with the aid of Section 85, IT Act. The respondent-State, on the other hand, argued that since the petitioner failed to ensure an adequate filter on its website for filtering obscene content, so, he cannot escape legal consequences. It was also submitted that the crime is grievous and must not go unpunished based on some technicalities.
The court observed that the IPC does not recognize the concept of an automatic criminal liability attaching to the director where the company is an accused. So, the petitioner was discharged from offences under the IPC. However, regarding the liability of the petitioner under Section 67 of the IT Act, the court observed that the law recognizes the deemed criminal liability of the directors even if the company is not arraigned as an accused in a case. So, it was held that the prosecution of the petitioner under Section 67 read with Section 85, IT Act will continue.
14. Christian Louboutin SAS v. Nakul Bajaj &Ors [(2018) 253 DLT 728]
One of the primary issues before the court, in this case, was whether Defendant was protected u/s 79 of the IT Actto use thePlaintiff’s trademark, images, and logos. The court observed that Defendant’s website (Darveys.com) exercised complete control over the products it sold and its role is much more than that of just an intermediary. To enjoy immunity u/s 79 of the IT Act, e-commerce websites must operate with care & caution. The basic thumb rule to claim exemption u/s 79 of the IT Act, is to ensure that the entity does not actively participate in the selling process.
15. Nasscom v. Ajay Sood & Ors. [119 (2005) DLT 596]
This is a case of Cheating by personation by using a computer resource under Section 66D, IT Act, 2000. In this case, the petitioner had prayed for a permanent injunction against the defendant, restraining him from sending “fraudulent Emails” under the trademark ‘NASSCOM” belonging to the petitioner. It was alleged that the defendants were posing as NASSCOM to obtain personal data from various addresses for head-hunting. The parties, later, on compromised and a consent decree was passed. This is a landmark judgment because the court declared ‘phishing’ on the internet to be an illegal act, against which an ‘injunction’ could be granted and damages could also be awarded. The court described ‘Phishing’ as a form of internet fraud where a person misrepresents the identity of a legitimate party (like a bank or an insurance company) to extract personal data from a user. It also deliberated upon the fact that there is no legislation in India dealing particularly with ‘phishing’.
16. Department of Electronics and Information Technology v. Star India Pvt. Ltd. [R.P. 131/2016 in FAO(OS) 57/2015]
This case dealt with the live telecast of cricket matches. The primary issue between the parties was regarding the extent of the ban that could be imposed on the website of a person infringing the trademark of another.The respondent pushed for a ‘domain’ ban, citing that it is relatively easy for ‘internet pirates’ to change the URLs of the infringing content as compared to the domain names. The court observed that the websites which are known to be rogue i.e., the ones that host “predominantly infringing content”, could be blocked completely, rather than resorting to URL blocking.The court described such websites to be ‘rogue’ that is hardly carrying on any lawful business and in their entirety/to a large extent are resorting to piracy.
17. Kent Systems Ltd. and Ors. v. Amit Kotak and Ors. 2017 (69) PTC 551 (Del)
In this case, the court observed that the IT Rules, do not oblige an intermediary to screen/remove all content/information hosted on its portal for infringement of rights of all persons who have complained to the intermediary at any point in time. The only obligation is to remove the infringing information/content upon receipt of a complaint from the Rights Holder. The court ultimately concluded that to require an intermediary to do compulsory screening of infringing content would amount to unreasonable interference with the right of the said intermediary to carry on its business.
18. Google India Pvt. Ltd. v. M/S Vishaka Industries Limited [Second Appeal No. 505 of 2016]
The basic facts of the case were that a person had published certain defamatory articles aimed at the Respondent and some politicians of the country, in a group hosted by Google (Appellant). The respondent had issued a notice to the Appellant to block the aforementioned defamatory content, but the appellant did not make any effort in that regard.Keeping that in regard, the High Court passed an order in the favor of the Respondent while observing that the Petitioner could not claim any exemption under Section 79 of the IT Act.
19. State v. Mohd. Afzal & Ors. [2003 (71) DRJ 178]
This is an important case concerning Section 2 (ha) of the IT Act, 2000 that defines ‘Communication Device’. It relates to the trial of the persons accused in the 2001 Parliament House Attack. It was argued by the accused that computers &digital evidence could not be regarded as reliable, as they could be easily tampered with. So, they claimed it to be unreliable for a criminal trial. The Court dismissed the contentions of the accused by observing that the misuse or tampering of the evidence has to be established by the challenger.Further, it was held that the theoretical and generic doubts could not be cast on the evidence of the prosecution.
20. Syed Asifuddin& Ors. v. State of Andhra Pradesh & Anr. [2005 Cr LJ 4314]
This case relates to the tampering of low-cost hand sets that were being handed out by the Reliance Infocomm, with a lock-in period of 3 years. The petitioners, in this case, were accused of an offence under section 65 of the IT Act, for allegedly tampering with the source code of the aforesaid Reliance Infocomm handsets to wean away customers from Reliance Infocommto TATA Indicom. The petitioners, in the instant petition, prayed for the quashing of the criminal investigation. However, the court observed that unless the investigation is shown to be illegal, it cannot ordinarily be quashed. So, the court refused to quash the investigation under section 65 of the IT Act, 2000 and directed the police to complete the investigation within a period of 3 months.
21. Dharamvir v. Central Bureau of Investigation [148 (2008) DLT 289]
This case primarily relates to ‘Electronic Record’ defined under section2 (t) of the IT Act, 2000. In this case, the main question before the court was that of the admissibility & reliability of the digital evidence in a legal proceeding. A CD was presented before the court that contained telephonic conversations copied from a hard disk.The court observed that the recording of the telephone call and the hard disks constitute electronic records that can be used as evidence.
22. P.R Transport Agency v. Union of India & Ors. [AIR 2006 All 23]
This case relates to Section 13 (5) of the IT Act, 2000. In this case, Bharat Coking Coal Ltd. held an e-auction for coal. The petitioner’s bid was accepted for a particular lot of coal and the letter of acceptance was issued by email to the petitioner. Later on, some conflict arose andthe allocation was canceled. So, petitioners approached the High Court of Allahabad. The Bharat Coking Ltd. put up an objection regarding the jurisdiction of the Court, contending that no part of the cause of action arose within Uttar Pradesh. The Court observed that since the acceptance was received at Varanasi (UP), it had the jurisdiction to entertain the case. Further, it was observed that for the purpose of Section 13 (5) of the IT Act, the place of business is relevant and not the location of the information system.
23. Umashankar Sivasubramanian v. ICICI Bank (Petition No. 2462 of 2008)
In this case, the petitioner received an email from ICICI Bank asking for his Internet Banking username and password. The petitioner replied to the email with the aforementioned details and later on found that he was defrauded of Rs. 6.46 Lakhs. So, he filed a complaint against ICICI Bank with the adjudicating authority for getting compensation. The Adjudicating Authority found ICICI Bank to be guilty of offences under section 85 read with Section 43 of the IT Act, 2000 and directed it to pay Rs. 12.85 lakh to the petitioner.
In this way, various courts around the country have interpreted the provisions of the IT Act, 2000 according to the facts and circumstances of the particular cases. Along with the provisions of the IT Act, the rules notified by the Government also play a significant role in regulating the digital space.With the rapid advent of technology, Cyber Laws are becoming more and more relevant. There is a need for these laws to keep evolving with the latest developments in Information Technology.

Click here to Get More Content on LCI Android App

41623 Views
Category Others , Other Articles by - Supinder Singh
Recent Articles
- How to Protect Yourself Legally from Unfair Termination
- Understanding Labor Rights: A Guide to Ensuring Fair Pay for Workers
- Get Quick Cash Fast! Apply For Small Instant Personal Loans Online And Get Your Funds Today
- Cryptocurrency And Blockchain Technology: Legal Challenges And Opportunities In The Digital Asset Era
- The Union Public Service Commission: Constitutional Framework, Functions, And Evolving Role In India's Civil Service Recruitment
- The Legal And Ethical Implications Of Deepfake Technology: A Comprehensive Overview
- If An Accused Given Bail In Multiple Cases Is Unable To Find Multiple Sureties, Condition Of Multiple Sureties Be Balanced With Article 21: SC
- SC Directs Police Chiefs To Take Action Against Erring Officials For Arrests In Violation Of S.41/41A CrPC & SC Guidelines
- Lawyers Abstaining From Work To Condole Death Will Be Contempt Of Court: Allahabad HC
- The Doctrine Of Judicial Precedent And It's Declining Credibility
More »

Popular Articles
- SC Most Strongly Castigates And Reprimands West Bengal State Government For Mishandling Horrific Case
- Mere Denial In Affidavit Doesn't Attract Offence Under Section 193 IPC
- Protecting Those Who Protect Us: Advocating For Healthcare Worker Safety
- The Legal And Ethical Implications Of Artificial Intelligence In The Justice System
- Mumbai Tragedy Spotlights Healthcare Crisis. A Mother And Child Lost To Negligence. High Court Seeks Answers
LCI Articles
You can also submit your article by sending to email
Browse by Category
- Business Law
- Constitutional Law
- Labour & Service Law
- Legal Documents
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Property Law
- Top Members
- Share Files
- LCI Online Learning
Member Strength 969953 and growing..
- We are Hiring
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 LAWyersclubindia.com. Let us grow stronger by mutual exchange of knowledge.
Lawyersclubindia Search
Whatsapp groups, login at lawyersclubindia.

Alternatively, you can log in using:


COMMENTS
Information Technology New research on information technology from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including the HealthCare.gov fiasco, online privacy concerns, and the civic benefits of technologies that utilize citizen-created data.
Technology. Today, business and technology are inextricably linked. And keeping pace with the emerging technology landscape can be difficult for even the most tech-savvy leaders. Deloitte can help. Our technology professionals have deep experience applying technologies to help you achieve your business goals. Email a customized link that shows ...
Related: Conclusion The stories of these 15 companies culminate in a powerful testament to the transformative impact of digital technology. Each case study highlights the pivotal role of innovation in securing market leadership and underscores the broader implications for industries at large.
Here are the 8 best digital transformation examples & case studies to help you strategize for your transformation initiatives.
Case Study: Technology Modernization, Digital Transformation Readiness and IT Cost Savings. Author: Guy Pearce, CGEIT, CDPSE, and Richard Fullerton, AWS CSA, ITIL, MCAAA, VCP-DCV. Date Published: 27 August 2021. Related: COBIT. "Digital Distinction" is a major trend for growing, medium-sized organizations, with growth requiring a well ...
Technological Innovation New research on technological innovation from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including using data mining to improve productivity, why business IT innovation is so difficult, and the business implications of the technology revolution.
Technology is such an integral part of so many industries now that business executives can't afford to leave all the digital know-how to their tech teams. Andy Wu explains the five essential principles of computer science that all leaders need to grasp to gain an edge.
4 Technology Consulting Case Studies The best way to learn about technology consulting is to read case studies. Examples demonstrate how partnership with a technology consulting company positively impacts efficiency, customer satisfaction, and the bottom line.
Real-world case studies are important to complement the academic skills and knowledge acquired by computer science students. In this paper we relate our experiences with a course specifically ...
The Journal of Cases on Information Technology (JCIT) publishes comprehensive, real-life teaching cases, empirical and applied research-based case studies, and case studies based on individual, organizational, and societal experiences related to the utilization and management of information technolo...
Case studies. Monash IT has worked with a range of industry partners and demonstrated that our IT research and expertise can profoundly impact any type of organisation. Commercial. We have made technical processes more efficient and improved how businesses interpret big data.
Top content on Case Study, Information and Technology as selected by the Leadership Digital community.
EST case studies explore written stories that wrestle with business decisions, design and technical implementation, regulatory compliance and limitations, and individual participation in the technology industry and workforce. These stories can range from real-life scenarios to fictionalized ones based on composite experiences and stories.
This study replicates and extends that study and thereby adds to the body of knowledge on the nature of information technology acquisition at universities. Levy (1988) used a single-case design for the study at the University of Arizona.
Information Technology Case Studies, Information Technology Case Study, ICMR develops Case Studies, Micro Case Studies, Latest Case Studies, Best Selling Case Studies, Short Case Studies, business research reports, courseware - in subjects like Information Technology Cases, Marketing, Finance, Human Resource Management, Operations, Project Management, Business Ethics, Business strategy ...
For permission to reprint cases, submit requests to [email protected]. Looking to draft your own case studies? This template provides the basics for writing ethics case studies in technology (though with some modification it could be used in other fields as well).
Information technology case studies (IT case studies) demonstrate the examples of effective use of information technology resources, successful deployment of IT, in addition to failures as a result of inefficient use and management of IT resources in companies.
AA comparative ticular geographic case study information was designed system (GIS) to assess in two the neighboring consequences county of government implementing or a par ganizations. Respondents reported radically different experiences with, and consequences of, the GIS technology. In North County, participants considered GIS to be responsible for trans forming the way that work was ...
However the strongest evidence and opinion across the entire research study, including the case studies, related to staff time, staff development and understanding the management of learning where IT resources are a key feature of learning and teaching.
This study explores the complex dualities in digital education, focusing on the case study of Singapore. It highlights the ethical issues surrounding the integration of information and communication technology (ICT), especially artificial intelligence, in the education sector. The paper presents a theoretical framework to explore these dualities, examining how they have been navigated in ...
Abstract —The present study is conducted among 283 students. from University of Zabol to identify the harm and ethical and. social issues i n the field of information tec hnology and to classify ...
This collection of case studies not only reflects the current trend of informatization application moving from 'universal application' to 'integrated innovation' but also uncovers the potential of applying information technology to transform education processes, innovate education environment, and optimize education governance.
Abstract Qualitative case study methodology enables researchers to conduct an in-depth exploration of intricate phenomena within some specific context. By keeping in mind research students, this article presents a systematic step-by-step guide to conduct a case study in the business discipline. Research students belonging to said discipline face issues in terms of clarity, selection, and ...
Important Case Laws on Information Technology Act, 2000. 1. State of Tamil Nadu v. Dr. L Prakash (W.P.M.P.No. 10120 of 2002) In this case, an FIR was registered against Dr. L Prakash under Section 67 of the IT Act, 2000 read with Section 4 & 6 of the Indecent Representation of Women Act, Section 27 of the Arms Act, and Sections 120B & 506 (2 ...