ESL Speaking
Games + Activities to Try Out Today!
in Activities for Adults · Activities for Kids

Tell your Story | ESL Speaking Activity to Practice Reported Speech
If you’re looking for a reported speech speaking activity, look no further than tell your story . It’s a fun reported speech activity to try out with your higher-level ESL or EFL students. Keep on reading for all the details you need to know about teaching indirect speech!
Speaking Activity to Practice Reported Speech
You can often find a unit on reported speech in most intermediate-level English textbooks. But, it’s not that easy to design some ESL activities to practice this. Not to worry. Keep on reading for one of the best reported speech activities to try out with your students.
Check out one of my favourites: “Tell a Story.” It’s fun, and engaging, and creates some great opportunities for students to practice this important skill. Reported speech activities don’t have to be terrible any longer! Have some fun with reported speech ESL.
Reported Speech ESL Speaking Activity
Skills: Writing/reading/speaking/listening Time: 15-30 minutes Level: Intermediate to Advanced Materials Required: Nothing
Have students write something interesting. Some examples are the most embarrassing moment, the scariest thing you’ve ever done, your dream for the future, future predictions , etc. Base it on whatever topic you are studying in class that day. Make it clear to the students that it should be something they’re willing to share with the entire class so as not to write something very private.
Then, distribute the stories to other people in the class. Then the students have to go around the class, finding the person whose story they have by asking questions. Once they find that person, they have to ask them three interesting questions about the story. And the person who originally wrote the story has to answer them of course.
I like this part of it because it gets students up and out of their seats, moving around and talking to different people. It gets boring sitting down all the time and talking to only 1 person! It’s ideal for those sleepy classes that you might have on Friday afternoon or those ones who are just waking up on Monday morning.
Reported speech ESL activities
Teaching Tips for Tell Your Story:
Emphasize to students that they are to practice asking good questions. For example, “USA?” is not a good question, while, “Did you study abroad in the USA?” is much better. Full sentences are the key here.
Also, emphasize that students should think of interesting follow-up questions that expand upon their knowledge about that situation. This involves reading carefully so they can avoid asking about things that are already mentioned.
You can give your students a couple of minutes before the activity starts to write down a few questions based on the paper they received to help facilitate this. Based on the topic you’ve assigned for the story, there should be some obvious ones that they’d want to ask.
This activity provides an excellent opportunity for your students to work on reported speech. This is something that high-level students are often surprisingly weak at. If you have a small class (less than 10), students can report what they learned about their partner to everyone.
If larger, students can tell their seating partner what they learned. For example, students might say something like, “I talked to Min-Ji. She told me that she got in a car accident last year. She said that it was really scary, but thankfully nobody got injured seriously.”
Please enable JavaScript
Procedure for this Reported Speech Activity:
- Have students write an interesting story based on a certain topic. Adjust for length and difficulty depending on your students.
- Collect stories and redistribute them–one per student, making sure a student does not get their own story.
- Students go around the class asking people if that is their story. For example, “Did you get in a car accident when you were little?”
- When they find the person, they must ask them three interesting follow-up questions about it.
- Do the optional variation of having students tell other people what they learned about their classmate in order to practice using reported speech.
- Follow-up with a worksheet, other activity or homework assignment.
Do You Like this Reported Speech ESL Speaking Activity?
- Amazon Kindle Edition
- Bolen, Jackie (Author)
- English (Publication Language)
- 148 Pages - 03/09/2016 (Publication Date)
If you like this ESL speaking activity to help your students practice reported speech, then you’re going to love this book: 101 ESL Activities: For Teenagers and Adults . It’s lesson planning made easy, guaranteed. The key to better English classes is a wide variety of engaging and interactive games and activities and this book will help you get there in style.
There are dozens of top-quality ESL games and activities for teenagers and adults that are organized into various categories: reading, writing, speaking, writing, warm-ups, and 4-skills. You’re sure to find something that will work for any level of students or topic.
You can get the book on Amazon in both print and digital formats. The (cheaper!) digital copy can be read on any device by downloading the free Kindle reading app. It’s super easy to have fun, engaging ESL activities with you anywhere you go.
Or, buy the book and keep it as a handy reference on your bookshelf, or teacher supply room. You can check out 101 ESL Activities for yourself over on Amazon:
Teaching Reported Speech FAQs
There are a number of common questions that people have about reported speech games and activities for English learners. Here are the answers to some of the most popular ones.
What is reported speech in English?
Reported speech is when we talk about or repeat what someone else has said using our own words.
Why do we use reported speech?
We use reported speech to share information, statements, or questions that someone else has said.
What changes occur when turning direct speech into indirect speech?
Pronouns, tense, and time expressions often change for indirect speech.
Can you give an example of direct speech changing to reported speech?
Direct: She said, “I am going to the store.” Reported: She said that she was going to the store.
What happens to the pronouns in reported speech?
Pronouns usually change to match the perspective of the speaker in reported speech.
How do you shift tenses in reported speech?
Generally, you shift the tense back one step. For example, present simple becomes past simple.
Do all time expressions remain the same in indirect speech?
No, time expressions usually change, e.g., “now” becomes “then,” “today” becomes “that day.”
What’s the reporting verb?
The verb that introduces indirect speech can be things like, “said,” “told,” “asked.”
Can questions be reported too?
Yes, questions can be reported using reporting verbs like “asked” or “wondered.”
How do you report imperative sentences?
Imperative sentences are reported using the verb “to” + infinitive, or with phrases like “ordered” or “told.”
What’s the key to successfully teaching indirect speech to ESL students?
Practice and exposure through various exercises and real-life examples are crucial for understanding indirect speech.
Reported speech games and activities for ESL
Tell your Story English Speaking Activity: Have your Say!
What do you think of this activity to practice ESL reported speech? Is it a good one or do you have another reported speech lesson plan activity that you’d like to recommend? Leave a comment below and let us know your thoughts. We’d love to hear from you.
Also be sure to give this article a share on Facebook, Pinterest, or Twitter. It’ll help other busy teachers, like yourself find this useful resource.
Last update on 2024-08-04 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
About Jackie
Jackie Bolen has been teaching English for more than 20 years to students in South Korea and Canada. She's taught all ages, levels and kinds of TEFL classes. She holds an MA degree, along with the Celta and Delta English teaching certifications.
Jackie is the author of more than 100 books for English teachers and English learners, including 101 ESL Activities for Teenagers and Adults , Great Debates for ESL/EFL , and 1001 English Expressions and Phrases . She loves to share her ESL games, activities, teaching tips, and more with other teachers throughout the world.
You can find her on social media at: YouTube Facebook Pinterest Instagram
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Our Top-Seller
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
More ESL Activities
Feeling under the weather: english dialogue & practice questions, meeting someone new dialogue (for english learners), english dialogue: talking about vacation plans, esl classroom management tips and tricks, about, contact, privacy policy.
Jackie Bolen has been talking ESL speaking since 2014 and the goal is to bring you the best recommendations for English conversation games, activities, lesson plans and more. It’s your go-to source for everything TEFL!
About and Contact for ESL Speaking .
Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
Email: [email protected]
Address: 2436 Kelly Ave, Port Coquitlam, Canada

- Become an Affiliate
- Join our Team
- Online Platform Tutorial
- TEFL Courses
- Contact Us / FAQ
Forgot Username or Password
- Active vs. Passive Voice
- Adverbial Clauses
- Adverbial Phrases
- Be Going To Statements
- Be Going To Wh Questions
- Be Going To Yes/No Questions
- Be Going To & Present Continuous
- Comparatives
- Superlatives
- Comparatives & Superlatives
- Zero Conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third Conditional
- Mixed Conditionals
- Future Continuous
- Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Simple
- Future Tenses
- Future Time Clauses
- Gerunds & Infinitives
- Have Got & Has Got
- I wish & If only
- Imperatives
- Irregular Verbs
- Narrative Tenses
- Noun Clauses
- Noun Phrases
- Passive Voice
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple & Continuous
- Past Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Past Simple Passive
- Past Simple Regular Verbs
- Past Simple Was and Were
- Past Simple Wh Questions
- Past Simple Yes/No Questions
- Past Simple vs. Past Continuous
- Past Simple vs. Present Perfect
- Past Tense Review
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Present Perfect - Ever and Never
- Present Perfect - For and Since
- Present Perfect - Just, Yet & Already
- Present Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Present Simple Passive
- Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
- Present Simple vs. Present Perfect
- Present Simple Wh Questions
- Present Simple Yes/No Questions
- Present Tense Review
- Question Words
- Relative Clauses
- Reported Speech
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Tag Questions
- There is & There are
- Wh Questions
- Abstract Nouns
- Adjective-Noun Collocations
- Adjectives of Feeling & Emotion
- Adjectives of Opinion
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Adjective Opposites
- Adjective Order
- Adjective-Preposition Collocations
- -ed and -ing Adjectives
- Adverb-Adjective Collocations
- Adverb Order
- Adverbs of Affirmation & Negation
- Adverbs of Degree
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Time
- Articles - a, an, the
- Causative Verbs
- Collective Nouns
- Common & Proper Nouns
- Compound Adjectives
- Compound Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Countable & Uncountable Nouns
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Dependent Prepositions
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Intensifiers & Mitigators
- Interjections
- Modal Verbs of Ability
- Modals of Deduction & Speculation
- Modals of Necessity
- Modals of Obligation & Prohibition
- Modals of Possibility & Certainty
- Onomatopoeia
- Parts of Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
- Possessives
- Prepositions of Movement
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Proper Adjectives
- Quantifiers
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Sense Verbs and Adjectives
- Singular & Plural Nouns
- So and Such
- Subject & Object Pronouns
- Too and Enough
- Transition Words
- Verb-Noun Collocations
- Agreeing & Disagreeing
- Asking Permission
- At the Dentist's
- At the Doctor's
- Being Polite
- Classroom Language
- Complaining & Apologizing
- Complimenting
- Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
- Describing Character & Personality
- Describing People's Appearance
- Describing Places
- Describing Things
- Etiquette and Manners
- Getting Around
- Getting to Know You
- Giving Advice
- Giving Directions
- Giving Opinions
- Giving Personal Information
- Greetings & Introductions
- Indirect Questions
- Likes and Dislikes
- Making Arrangements
- Making Decisions
- Making Excuses
- Making Invitations
- Making Offers & Promises
- Making Requests
- Making Suggestions
- Online Communication
- Ordering Food & Drink
- Social Media
- Telephoning
- Times and Dates
- British English vs. American English
- Cities, Towns & Places
- Clothes & Fashion
- Computers & Smartphones
- Countries & Nationalities
- Crime, Law & Punishment
- Cultural Celebrations
- Daily Routines
- Everyday Objects
- Family & Relationships
- Food & Drink
- Going Out & Entertainment
- Health & Fitness
- Hobbies & Free Time
- Houses, Rooms & Furniture
- Jobs & the Workplace
- Love, Romance & Dating
- Modes of Transport
- Parts of the Body
- Reading Comprehension
- Shapes & Measurements
- The Natural World
- Time Expressions
- TV & Film
- Valentine's Day
- Academic Collocations
- Academic Phrasal Verbs
- Academic Reading Comprehension
- AWL Sublist 1 & 2
- Cause and Effect Essays
- Compare and Contrast Essays
- Discussion Essays
- Discussion Skills
- Discussions Practice
- Essay Writing
- Paragraph Writing
- Persuasive Essays
- Presentation Skills
- Problem Solution Essays
- Punctuation
- Reading Skills
- Referenced Essays
- Study Skills
- The Writing Process
- Business Collocations
- Business Emails
- Business Idioms
- Business Meetings
- Business Negotiations
- Business Phrasal Verbs
- Closing a Presentation
- Describing Graphs & Charts
- Presentation Language & Structure
- Resumes, CVs & Email Cover Letters
- Starting a Presentation
- Talking about Companies
- Talking About Jobs
- Answer Games
- Brainstorming Games
- Category Games
- Classic Childhood Games
- Counting Games
- Describing Games
- Drawing Games
- Drilling Activity Games
- First Day of Class Games
- Flashcard Games
- Grammar Games
- Hangman Games
- Listening Games
- Miming Games
- Music Games
- Question & Answer Games
- Sentence Race Games
- Spelling Games
- TV Game Shows
- Vocabulary Games
- Word Association Games
- Yes/No Question Games
- Classroom Interaction Patterns
- Classroom Management
- Concept Checking
- Cultural Awareness
- Developing Students' Listening Skills
- Developing Students' Reading Skills
- Developing Students' Speaking Skills
- Eliciting Techniques
- ESL Dictations
- How to Introduce a Lesson
- How to Use Music in ESL Class
- Lesson Planning
- Making Teaching Materials Relevant
- Problems Learning English
- Teaching English Idioms
- Teaching English Vocabulary
- Teaching Large Classes
- Teaching Mixed-Ability Classes
- Teaching Small Classes
- The First Day of Class
- Using Correction in Class
- Using Song Gap Fills
- Online Membership
- ESL Essentials eBook Series
Reported Speech ESL Games, Activities and Worksheets
- Pre-intermediate ( A2 )
- Intermediate ( B1 )
- Upper-intermediate ( B2 )

But he told me...
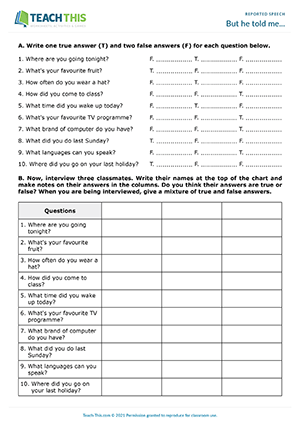
Esl reported speech activity - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions, forming sentences, true or false, guessing - group work - pre-intermediate (a2) - 40 minutes.
Double Trouble
Esl direct and indirect speech game - grammar and speaking: pelmanism, reforming sentences, controlled practice - group work - pre-intermediate (a2) - 20 minutes.

ESL Reported Speech Game - Grammar and Speaking: Reading and Responding to Statements, Forming Sentences, Controlled Practice - Pre-intermediate (A2) - 35 minutes

You said...
Esl reported speech game - grammar and speaking: miming, guessing, forming sentences - group and pair work - pre-intermediate (a2) - 25 minutes.

Report This
Esl reported speech activity - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions, forming sentences - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 25 minutes.

Reporting Modal Verbs
Esl reporting modal verbs worksheet - grammar exercises: identifying, matching, gap-fill, rewriting sentences, writing a paragraph - intermediate (b1) - 30 minutes.

Run and Report
Esl reported speech activity - reading, speaking and grammar: running dictation, rewriting sentences - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 25 minutes.

Somebody told me that...
Esl reported speech activities - speaking activity: asking and answering questions - grammar game: forming sentences, guessing - group work - intermediate (b1) - 40 minutes.
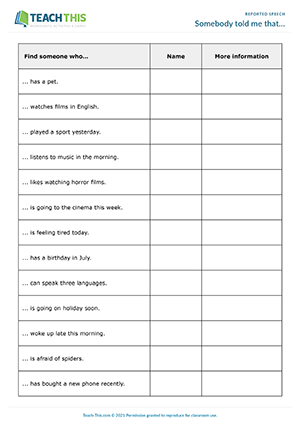
Telephone Messages
Esl reported speech game - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions from prompts, freer practice - group work - intermediate (b1) - 25 minutes.
Trip Around the World
Esl reported speech activity - grammar, speaking and writing: writing questions and answers, role-play, interview, writing a short article - group and pair work - intermediate (b1) - 45 minutes.

What did they say?
Esl reported speech game - grammar and speaking: asking and answering questions from prompts, writing sentences, controlled and freer practice - group work - intermediate (b1) - 45 minutes.

What did you ask me?
Esl reported speech activity - grammar, speaking and writing: asking and answering questions, writing sentences - pair work - intermediate (b1) - 40 minutes.

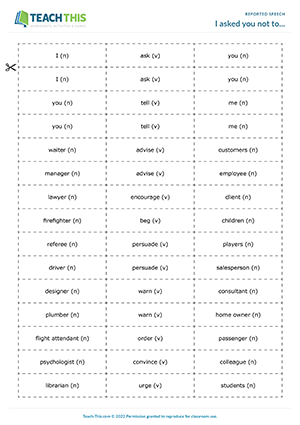
I asked you not to...
Esl reported speech game - grammar: forming sentences from prompts - group work - upper-intermediate (b2) - 45 minutes.
Infinitive Clauses Practice
Esl infinitive clauses worksheet - grammar exercises: binary choice, gap-fill, matching, unscrambling, rewriting sentences - upper-intermediate (b2) - 25 minutes.

Listening In
Esl reported speech game - grammar: sentence completion, guessing - group and pair work - upper-intermediate (b2) - 25 minutes.

Sign up for our monthly newsletter and keep up-to-date with our latest resources, news and website features.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Latest Free Resources
Upper-intermediate (B2)
Elementary (A1-A2)
Latest Member Resources
Talking about companies, here's what our members are saying....
There are a lot of resources that are useful for teaching English. I downloaded the games which are handy and use them in my classes. With the games, my students never skip class or feel tired to learn English. The resources for teaching English helped my students progress in grammar, vocabulary, writing and comprehension. They also helped me a lot to guide my students to learn in a practical way.
I am an ESOL teacher, and the resources have helped my classes enormously. In particular, the speaking activities were a great help for my intermediate students before their exam. The website is user-friendly, and I will continue to utilise the resources - next term is reading and comprehension, so I will be looking for more resources from you. Thank you for such helpful activities and worksheets. They save me a lot of time in class preparation.
Teach This is an absolutely brilliant website, offering a vast amount of high-quality content, much of it free. Everyone involved in its creation deserves commendation. The leadership's vision has my deepest respect and gratitude. It's undoubtedly the best resource for English teachers, with its clear layout, easy navigation, concise messaging, and lack of invasive advertising - rare qualities that Teach This has perfected.
When I need to add or change an activity from my school’s curriculum, I always turn to TeachThis. While our curriculum is usually very good, it sometimes doesn’t fit well with my students. With TeachThis, I can easily find activities that match my topic and level, and the resources make my classes more interesting and varied. I look forward to the monthly newsletter and exploring new materials for inspiration. Please keep it up!
I like the efficiency and organization of the website. The resources cater to various levels with topic-based options for higher levels. The worksheets are very engaging and the answer keys are particularly helpful for teacher. The resources are also highly specific to levels and outcomes, making planning much easier. Finding what I need is simple and time-saving with the keyword search feature. Everything is clear and straightforward.
The easy and ready-to-go materials have helped me a lot during the last few years. Most of all I like the grammar games that activate my pupils and keep them engaged. My lessons have become way more playful and varied. Additionally, I like the grammar worksheets which I use to consolidate what I have worked on during class. The website is very user-friendly, and I have never had any difficulties finding what I was looking for.
A friend told me about the site, and it's awesome. I have found the Business English resources especially engaging and relevant for my students as the materials help them understand business writing and terms. My teaching experience has also improved from using the games on the site as they allow me to teach in a fun way. The user experience is outstanding. Great job!
I found Teach-This a long time ago when I started teaching. It's always had great resources. I really appreciate the grammar materials, board games, and group activities. They've saved me lots of time on lesson planning. The materials are easy to use and understand, making my job much simpler. The best thing is that many resources can be downloaded for free. I've used it for around 8 years, and it consistently offers great content.
I use the resources from the Games Section as part of my daily 30-minute morning warm-up activities, and I've received rave reviews for using them. The games help me maintain student interest and participation and leave the students feeling happy and awake. I like everything about the site, and customer support is very effective as they respond in time.
Teach-This is one of the best EFL websites I've found. It's extremely user-friendly, and I always find what I need quickly. I like the design, and the content is fun, engaging and original. I am very thankful for all your work and generosity by making some resources free. I always recommend this website to my fellow teachers. Your work is really helpful, and I value it enormously.
I like the grammar-focused resources the most as they save me time. The resources also inspire me. If I see an interesting grammar activity, I often rework it for other grammar rules. I like the fact that I simply pay a flat fee, and I can download whatever I want. Teach-This really is a great timesaver. I know that if I am in need of resources for my students, I can go to Teach-This and find something interesting.
Getting familiar with the site and how to use the resources is not difficult. I found the writing skills resources to be the most valuable as they have enhanced my teaching of this skill. The website is elaborate and full of all types of resources to help me teach English. When I contacted customer support, they were super-fast to deal with my enquiry. So overall, I recommend it.
I have found the grammar and vocabulary resources the most valuable. They have improved my teaching experience because they are easy to use and well-organized. The materials are very engaging for my students. The website is also very user-friendly. The best thing about Teach-This is that it offers ready-made worksheets for busy teachers, and the content is well-organized and full of information.
I'm really glad I found the Teach-This website. The materials in the General English section have proven to be really helpful and made my classes more engaging. The materials are well-structured and cover a wide range of topics, making it easy to keep my students interested and motivated. Overall, my experience using your resources has been great.
My first impression of the website was that it was amazing. The games and activities have really improved my teaching. The resources are engaging and relevant to my students’ needs, and I find the website easy to use and navigate. Thanks.
I discovered the site on Google when I was searching for question games and reading activities. It has been very helpful. The activities are awesome and have benefited me and my students by making my classes more fun. I am now less stressed about preparing for classes as the ready-made resources offer me everything I need. I give the site five out of five for user-friendliness. It is very easy to navigate and find what I need.
I would like to thank you for making a fantastic website. I particularly enjoy teaching the functional language materials, which have been very helpful in my classes. The resources have significantly improved my students' communication skills in daily life, so it was rewarding to see them benefit in this way. It feels great to be able to make a difference in my students' lives. Please keep up the good work.
- Have got & Has got
- Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation
- Concrete nouns
- Sense Verbs & Adjectives
- AWL Sublist 1 and 2
- Talking about Jobs
- TEFL Certification & Courses
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common aspect of the English language. You use it nearly every day, both in conversations and in writing. This reference covers key sections about reported speech, including what it is, examples, rules, and verb tense changes. You’ll also learn about modal verbs, changes in time and place, and different reporting verbs.
Reported Speech

What Is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when you tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, you use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that you use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When using reported speech, you are usually talking about the past. The verbs, therefore, usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Another example :
- Direct speech: She is doing her homework .
- Reported speech: He said (that) she was doing her homework.
Table of Changes :
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| I am | He said he was |
| I have | She said she had |
| I will | They said they would |
Reported Speech Rules
Verb tense changes in reported speech.
When the reporting verb is in the present tense, only small changes are needed.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, you need to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the main verb.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
The tenses generally move backward as follows:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Past Simple | |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Past Perfect | |
| Past Simple | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past Perfect | Past Perfect (remains unchanged) |
For sentences about the future, you also need to change the future verbs.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Here are the changes for future tenses:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Will | Would |
| Will be | Would be |
| Will have | Would have |
| Will have been | Would have been |
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Modal verbs also change when used in reported speech.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Can | Could |
| Could | Could (unchanged) |
| Have to | Had to |
| Must | Must/Had to |
| May | Might |
| Might | Might (unchanged) |
| Should | Should (unchanged) |
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
Some modal verbs do not need to change tense because they fit naturally.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Here are both correct and incorrect examples of reported speech for clarity:
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
To correct these:
- Add ‘me’: He told me he should go to the park.
- Remove ‘me’ or add ‘to’: He said he should go to the park or He said to me he should go to the park.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
References to time and place often need to change when you use indirect speech. Here is a useful guide to these changes:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Here | There |
| This | That |
| Tomorrow | The following day/ The next day |
| Next week | The following week/ The week after |
| Yesterday | The previous day/ The day before |
| Last week | The previous week/ The week before |
| Ago | Previously/ Before |
| Tonight | That night |
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
In some cases, verb tenses do not change when you report speech indirectly. Here are the key instances:
- When the introductory verb is in the present , present perfect , or future .
- When the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- When the reported sentence contains a time clause .
- If the verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to , and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
Reporting verbs are crucial in indirect speech. Here is a list categorized by their usage:
- Basic Verbs : Tell, say, ask
- Verb + that + clause : Complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest
- Verb + to + infinitive : Agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : Advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn
- Verb + “ing” form : Admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest
- Verb + how : Explain to somebody
Reported Questions
When converting questions from direct to indirect speech, you follow rules similar to those for statements. Verbs used include inquire, wonder, want to know, ask.
Reported Commands and Requests
Commands and requests in Indirect Speech are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive . Common reporting verbs include order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid.
Pronoun and tense changes are needed when shifting from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
| past simple | I bought a car | She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. |
| past continuous | I was walking along the street | She said (that) she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | I haven't seen Julie | She said (that) she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | I had taken English lessons before | She said (that) she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | I'll see you later | She said (that) she would see me later. |
| would* | I would help, but... | She said (that) she would help but... |
| can | I can speak perfect English | She said (that) she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | I could swim when I was four | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
| should* | I should call my mother | She said (that) she should call her mother |
| might* | I might be late | She said (that) she might be late |
| must | I must study at the weekend | She said (that) she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
| Where is the Post Office, please? | She asked me where the Post Office was. |
| What are you doing? | She asked me what I was doing. |
| Who was that fantastic man? | She asked me who that fantastic man had been. |
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
| Do you love me? | He asked me if I loved him. |
| Have you ever been to Mexico? | She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico. |
| Are you living here? | She asked me if I was living here. |
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
| Please don't smoke. | She asked me not to smoke. |
| Could you bring my book tonight? | She asked me to bring her book that night. |
| Could you pass the milk, please? | She asked me to pass the milk. |
| Would you mind coming early tomorrow? | She asked me to come early the next day. |
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don't worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don't smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method

Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
| Simple present “I to go home.” | Simple past She said she to go home. |
| Present continuous “I a good book.” | Past continuous She said she a good book. |
| Simple past “I pasta for dinner last night.” | Past perfect She said she pasta for dinner the night before. |
| Present perfect “I just cleaning my room.” “My mother never to Japan.” | Past perfect She said she just cleaning her room. She said her mother never to Japan. |
| Can/can’t “I meet with you next Monday.” “Sorry, I talk now; I’m at work.” | Could/couldn’t She said she meet with me next Monday. She said she talk at the moment because she was at work. |
| Will/won’t “I pick him up from the airport.” “I tell anyone your secret.” | Would/wouldn’t She said she pick him up from the airport. She said she tell anyone my secret. |
| Should “You apologize.” | Should She said I apologize. |
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to Backshift in Reported Speech
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

British vs. American English Spelling

100 Superlatives: List & Examples

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.

Reported speech activities
ESL Reported Speech Games
Let’s get into the best activities and games for English learners.

#1: Reported Speech Board Game
I love to play board games in real life which is why I also like to play them with my students! It’s super easy to make your own to use for just about any grammatical point, including this concept.
In this case, fill the board with a bunch of statements like the following:
- Sister-has boyfriend
- Friend-fired from job
- Dad-playing golf tomorrow
Then, students have to make a reported speech statement using the information. It’s fun, engaging and a nice way to give students some practice with this important concept.
Check out this simple ESL board game so you can see how easy it is to make your own:
ESL Board Game .
#2: Ball Toss
This is a simple but versatile activity that’s perfect for reported speech. I write down a number of questions on the beach ball. Then, students take turns tossing the ball to each other and the person that catches it has to answer the question under their right thumb.
To add a reported speech element, have another student (the one who threw the ball?) report on that student’s answer. It’s simple but effective! Check it out:
Ball Toss Activity .
#3: Is that Sentence Correct
If you want to focus on forms, then consider using this simple error correction activity. Write some sentences that use the target grammar. Some have errors while others do not. Students have to find the incorrect ones and make the required changes.
It’s possible to do this in class, or for a homework activity. Have a look here:
Is that Sentence Correct?
#4: Running Dictation
Please enable JavaScript
#5: Mixed Up Sentences
Making good sentences using reported speech can be a little bit tricky. If you want to focus on forms, consider using this simple activity.
Write some sentences on the board of PowerPoint, but mix them up in terms of the order. Students have to work quickly to put them in the correct order and the first time to finish is the winner. It also makes a nice homework assignment. Try it out for yourself:
Mixed Up Sentences .
- Amazon Kindle Edition
- Bolen, Jackie (Author)
- English (Publication Language)
- 92 Pages - 09/27/2020 (Publication Date)
#6: Man/Woman on the Street Interview Activity
If you want to level up the typical ESL interview activity, consider using Man or Woman on the Street. Then, to make it into a reported speech activity, have students tell someone else about what they heard. It’s fun, engaging, and lends itself well to this grammar point. Find out more:
Man/Woman on the Street Activity .
#7: Concentration
This is a fun memory game that’s ideal for a whole bunch of different grammar or vocabulary points. On one card, write down a statement, and then on the other, write down the correct form.
- I have a boyfriend (She told me that she has a boyfriend).
Make a number of these sets. I usually do 8 of them per group of 4. Then, students play a matching memory game. Learn more here:
Concentration Game .
#8: Vocabulary Auction
#9: find someone who bingo game.
This is a nice icebreaker activity that can also be used for some practice with this grammar point. Students have to circulate around the class, asking their classmates questions to find people to fill their Bingo grid.
To make this into a reported speech activity, have students report some of the things they learned about their classmates to a partner (bigger classes) or to the entire class (smaller classes). Find out more about it:
Find Someone Who Bingo Game .
#10: More Ideas for Teaching English
#11: dictogloss and reported speech.
This is a challenging ESL activity that’s perfect for developing listening skills. It also lends itself to almost any vocabulary set or grammatical point, including this one.
Find (or write) a passage of people talking about something that they heard.. Then, put students into pairs and read it out at a faster than normal pace. Students take notes and then attempt to recreate what they heard. Repeat the process again. Finally, they can compare what they have with the original. Check it out:
Dictogloss Activity .
#12: Surveys and Reported Speech
I love to use surveys and questionnaires in my classes. They’re engaging, student-centred and cover a range of skills in a single activity. They’re also great for working on this concept if you get each student to tell their partner some of the things they learned about their classmates.
This is a simple way to cover a new concept but have a quick review of this grammar point as well. Take a look at this activity:
ESL Surveys .
ESL games and activities
#13: Brochure Scanning Activity
This is a nice activity if you have a bunch of different travel brochures. Have students quickly scan them to find important information. For example:
- number of days
Then, have students use reported speech to tell their partner about the trip. Find out more:
Brochure Scanning Activity .
#14: ESL Review Games and Activities
#15: daily routine activities and reported speech.
In terms of topics to combine with this concept, daily routine is one of the best. It’s very simple to set up activities that lead to sentences like the following:
- Tim told me that he gets up at 7 am.
- Jenny said that she usually sleeps in on the weekends.
For some more ideas, have a look here:
Daily Routine ESL Activities .
#16: Error Correction Relay Race
This is a simple activity that takes something old (error correction) and makes it new again. Students have to work in teams to fix errors in a number of reported speech sentences. The first team to make all the corrections is the winner!
Want to give it a try? Learn more:
Error Correction Relay Race .
#17: Dialogue Substitution
#18: news reporting.
Provide students with news headlines or short news articles. Ask them to transform from direct speech (quoted speech) to reported speech (indirect speech) when retelling the news. This activity helps students practice the appropriate changes in verb tenses, pronouns, and time and place references.
#19: Interview and Report
Pair students up and ask them to conduct mock interviews. Afterward, have them report the interview to a different partner using reported speech. This activity allows students to practice converting direct speech into reported while maintaining the meaning and context of the conversation.
#20: Picture Stories
Provide students with a series of pictures that depict a sequence of events. Ask them to create a story using reported speech to describe what is happening in each picture. This activity encourages students to use this language in a narrative context and practice converting direct speech into reported speech.
#21: Role Plays
Create role play scenarios where students take on different roles and engage in conversations. Afterward, ask them to report the conversations to another person using reported speech. This activity allows students to practice converting direct speech into reported speech in a context that mimics real-life situations.
#22: Song Lyrics Transformation
Choose a song that contains direct speech and ask students to rewrite the lyrics using reported speech. This activity helps students practice converting direct speech in songs into reported speech while exploring the meaning and context of the lyrics.
Online Practice for Reported Speech
There are a number of sites for online practice and quizzes that cover this. They are excellent resources to recommend to students who want a little bit of extra practice. Check it out here:
Perfect English Grammar
Exam English
My English Pages
Reported Speech ESL Lesson Plans
There are lots of nice lesson plans. Here are some of the best ones to consider using:
Lingua House
Reported Speech Worksheets
If you’re a busy teacher then you’re going to know what a huge time saver it can be to use worksheets that other teachers have made. Here are some of the top picks:
ISL Collective
English Grammar
There are a number of common questions that people have about using this method of speech. Here are the answers to some of the most popular ones.
What is reported speech ESL?
Reported speech ESL is when we tell someone what another person said. You often have to use a tense that is further back in time (backshift) and may also need to change the pronouns.
What are some examples of reported speech?
Some examples of reported speech are the following:
- They said you didn’t want to come.
- My mom told me that she was angry at my dad.
- I asked her what her plans were.

How do you teach reported speech?
To teach reported speech, first set the context with a short video clip, discussion question, etc. Then, explain the grammar rules for it and do some controlled practice. Finally, use an ESL game or activity that allows students to practice further.
What are the types of reported speech?
The types of reported speech are direct speech and indirect speech.
Tips for Teaching Reported Speech To English Learners
Teaching reported speech to ESL learners can be challenging, as it involves a shift in verb tense and pronoun usage. Here are some tips to make the teaching process more effective and engaging.
Start with Direct Speech
Begin by introducing and reviewing direct speech, which is the original statement or question spoken by someone. Ensure students are familiar with the use of quotation marks and the appropriate verb tenses in direct speech.
Introduce Reporting Verbs
Teach students a variety of reporting verbs such as say, tell, ask, explain, suggest, etc. Explain the different patterns that follow these reporting verbs, including the use of direct objects, indirect objects, and prepositions.
Present Tense Changes
Demonstrate how to change verb tenses when reporting speech. Provide clear examples of how present simple changes to past simple, present continuous changes to past continuous, and so on. Reinforce the importance of maintaining accuracy in verb tense changes.
Practice Conversion of Pronouns
Show students how pronouns change when reporting speech. Explain the transformation from the speaker’s pronouns (I, you, we) to the appropriate pronouns in reported speech (he, she, they). Emphasize the use of possessive pronouns when necessary.
Provide Contextualized Examples
Use authentic materials, such as dialogues, interviews, or news articles, to provide meaningful examples of reported speech. This helps students understand the purpose and practical application in real-life situations.
Use Reporting Structures
Teach students reporting structures, such as reporting statements, reporting questions, and reporting commands. Practice transforming direct speech into reported speech using these structures and provide opportunities for students to generate their own examples.
Focus on Reporting Verbs of Perception
Highlight reporting verbs of perception like see, hear, feel, notice, etc., which require a change in verb tense but do not require reporting the exact words. Provide examples to help students understand the difference between reporting statements and reporting verbs of perception.
Incorporate Speaking and Writing Activities
Encourage students to practice reported speech through role-plays, interviews, or storytelling activities. Assign writing tasks where students report a conversation or summarize an article using reported speech.
Address Common Errors
Be aware of common errors students make when learning reported speech, such as incorrect verb tense changes or pronoun usage. Provide corrective feedback and offer opportunities for targeted practice to overcome these challenges.
Review and Reinforce
Regularly review with students and provide opportunities for reinforcement through quizzes, games, or interactive exercises. Repetition and reinforcement are key to solidifying understanding and application of this language.
Did you like these Reported Speech Activities?
- 87 Pages - 10/24/2019 (Publication Date)
Yes? Thought so. Then you’re going to love this book on Amazon: 39 No-Prep/Low-Prep ESL Grammar Activities for Teenagers and Adults . It’s the book you need if you want to have more engaging and interactive grammar lessons.
You can find the book in both digital and print formats. Keep a copy on the bookshelf in your office to use as a handy reference guide. Or, take the e-version with you to your favourite coffee shop for some lesson planning on the go.
Whatever the case, get ready for some ESL grammar teaching awesome in your life. Head over to Amazon to find out more about it:
Have your Say about Reported Speech Games and Activities
What do you think about these activities? Are they a winner, or do you have another one that you’d like to recommend? Leave a comment below and let us know what you think. We’d love to hear from you.
Also, be sure to give this article a share on Facebook, Pinterest, or Twitter. It’ll help other busy English teachers, like yourself find this useful resource.
Last update on 2022-07-17 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
About Jackie
Jackie Bolen has been teaching English for more than 20 years to students in South Korea and Canada. She's taught all ages, levels and kinds of TEFL classes. She holds an MA degree, along with the Celta and Delta English teaching certifications.
Jackie is the author of more than 100 books for English teachers and English learners, including Business English Vocabulary Builder , 67 ESL Conversation Topics ,and 39 No-Prep/Low-Prep ESL Speaking Activities for Teenagers and Adults . She loves to share her ESL games, activities, teaching tips, and more with other teachers throughout the world.
You can find her on social media at: YouTube Facebook Instagram
Top Selling ESL Activity Book
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
More ESL Activities and Games
Past continuous activities, games, worksheets & lesson plans esl, thanksgiving esl activities, games, worksheets, lesson plans, esl number games and activities | teaching english numbers & maths, second conditional activities, games, worksheets & questions, about, contact, privacy policy.
Best-selling author and English teacher Jackie Bolen has been talking ESL activities and games since 2015. The goal is to bring you the best ideas, lesson plans, and activity recommendations for your TEFL classes.
Get in touch: About + Contact
Privacy Policy and Terms of Use
Email: [email protected]
Address: 2436 Kelly Ave, Port Coquitlam, Canada
100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
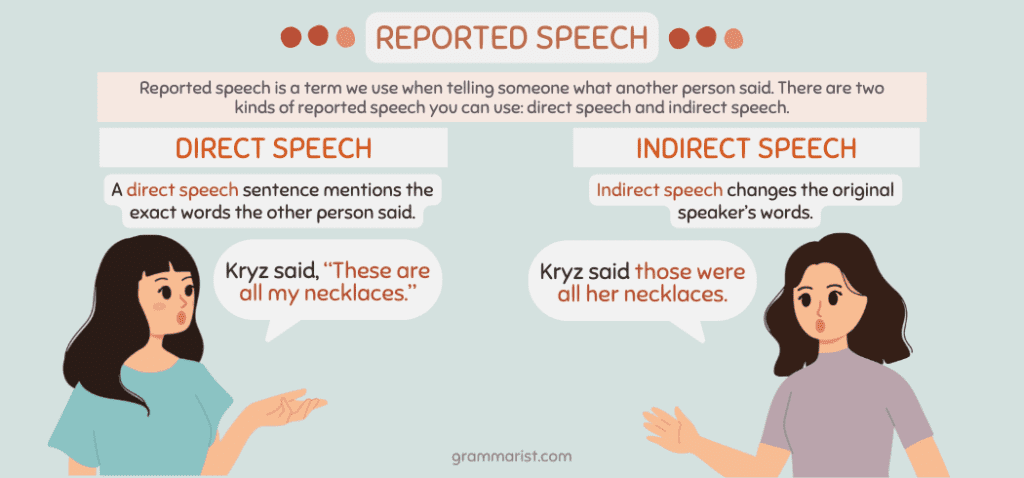
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
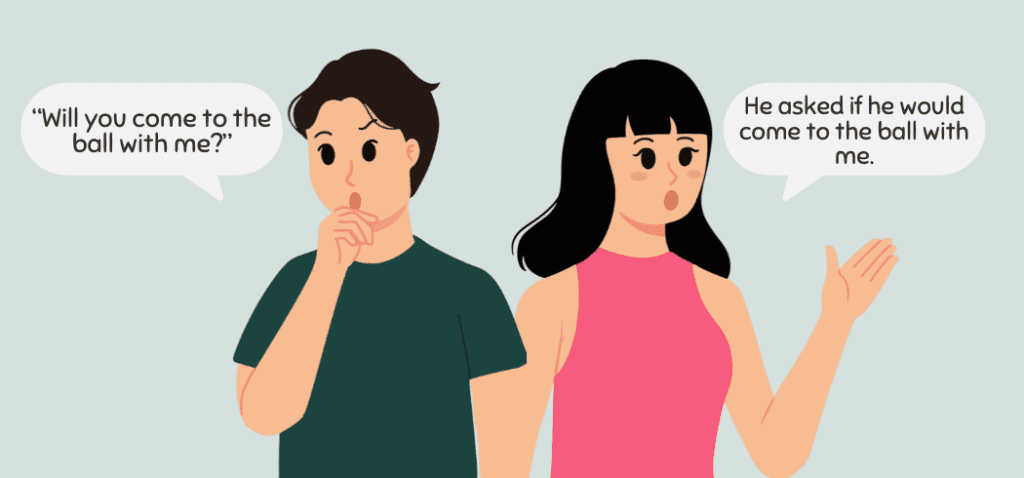
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- English ESL Worksheets
- Speaking Practice
- Discussion starters, speaking cards
- Reported Speech (Indirect speech)
4 Reported Speech (Indirect speech), Discussion starters, speaking cards, Speaking Practice English ESL worksheets pdf & doc
Fun Ways of Practising Reported Speech
1. Reported speech reversi Prepare cards with reported speech on one side and direct speech of the same sentence on the other. Students have to correctly say what is on the other side to turn it over and score one point. There are many games you can play with these cards, including the TEFL version of Reversi/ Othello that was first described by Mario Rinvolucri in Grammar Games and that is the subject of an upcoming article of mine.
2. Go betweens This is also a game from a classic TEFL supplementary book that can easily be done without access to the book (in this case Intermediate Communication Games). Two students have such a problem with each other that they are refusing to speak, and another student shuttles between them trying to find a compromise. The two students need to be sitting so far apart that they can’t hear the other people speak and so really need to listen to the peacemaker, e.g. by sitting in different rooms or one half of the students sitting in the corridor. Making both sides have complaints about the other and giving out roleplay cards can also help set up this activity well, as can having different groups of students working on different situations so that they can’t listen into the neighbouring teams. Possible situations to roleplay include students who have problems with the other students’ behaviour in class (speaking too much, not speaking enough, holding up the lesson because they haven’t done their homework, distracting the teacher from the lesson plan by asking questions, etc- maybe leading onto discussion of good classroom behaviour), neighbours, neighbouring countries, married couples, or suppliers and customers who are near breaking point in their relationship. This can also be used for non-conflict negotiations such as premarital contracts or price negotiations. Note that students usually get into this activity so much that they completely forget about Reported Speech, so you might want to do this as a controlled activity where they must make an effort to use the structures you have presented.
3. What they told you Give the students a list of people they have probably been spoken to by in their lives (e.g. teachers, policemen, future employers, immigration officers and market researchers) or brainstorm such a list onto the board. Students choose one of the people on the list and say things that this person really said to them, e.g. “He asked me whether I wanted a single or return”, and the other students guess which person from the list was speaking. As a more challenging extension, they can continue the game with people not on the list. This can also be done as Twenty Questions, e.g. “Has this person ever asked you whether you were carrying any drugs?” This game links well with the vocabulary of jobs or practising situational language such as “At the airport”. The same game can also be done with the vocabulary of relationships like “colleague”, “acquaintance” and “classmate”.
4. Reported speech pairwork dictation This idea lacks the fun element of the other games here (unless you choose or write an amusing dialogue or one with a surprising twist), but is easy to do and check and can lead to examination of things we usually leave out of reported speech such as “well” and “yes”. It can also be a lead in to the similar but more fun activities below. Student A has one person’s part of a dialogue and Student B has the other person’s part, and they convert their part into reported speech and tell their partner what the person on their worksheet said so that their partner can convert it back into direct speech (in their heads) and write it down in the gaps on their sheet. At the end when they check their worksheets with each other they should have identical dialogues written down. This activity can be made more challenging by one of the students having their half of the dialogue in mixed up order.
5. Reported speech pairwork dictation same or different A more intellectually challenging version of pairwork dictation is giving students similar but not identical direct speech sentences on Student A and Student B sheets. They dictate them to each other in reported speech and work together to decide if the original two sentences were the same or not, e.g. Student A reports “Do you feel happy?” as “He asked me whether I felt happy” and Student B reports “Are you feeling happy?” as “He asked me if I was feeling happy”, and they decide together that the original sentences were different (without ever telling their partner exactly what is on their sheet). You can add some trick questions where the direct speech sentences are different but the reported speech versions are the same, e.g. “I have been there” and “I was there” or “I was there that day” and “I have been there today”. They might feel robbed if you include sentences like this as it will stop them finishing the game successfully, but they will really pay attention when you bring that grammar point up later!
6. Pairwork dictation match the sentences Another good way of using sentences that sound similar when converted into reported speech (either correctly or wrongly) is to put the same direct speech sentences on Student A’s and Student B’s worksheets but mixed up and labelled 1 to 10 (for example) on one student’s and a to j on the other. They then dictate them to each other in reported speech and decide which ones are the same.
7. Pairwork dictation match the dialogue pairs Rather than matching identical sentences as above, you can add extra language and challenge by the students trying to match up typical functional language sentence pairs such as “Would you like anything else?” on Student A’s sheet and “No, that’s all thanks” on Student B’s. The sentences on their worksheets can be given in reported speech for them just to read out and convert back to direct speech in their heads while trying to work out which typical sentences or (more challenging) be given as direct speech for them to convert to reported speech when they tell them to their partner as in the games above.
8. Reported Speech sentence completion guessing game Give the students a list of sentence stems that should be completed with reported speech such as “I forgot to tell someone…”, “ or “Someone told me that I…”. They complete as many sentences as they can and then read out only the part they have written for the other students to guess which sentence that comes from.
9. Guess the backshift Students tell their partner(s) something that was said to them in direct speech (maybe using the air speech marks gesture), and their partner(s) convert it into reported speech, using the right kind of backshift or not by guessing whether it is something that is generally true about them, whether it is something their brother always says to them or whether it was a one off thing that is no longer true, e.g. choosing to convert “My brother said ‘You look sad’” to “Your brother said that you looked sad” or “Your brother (often) says that you look sad/ your brother once said that you always look sad” depending on whether they think that is generally true or not.
10. The … thing he ever said Give prompts containing superlatives for real things people said to them, e.g. “The worst thing your siblings have said to you” or “The best advice you have ever had”. Students tell their partner(s) one of these things, and their partners guess which prompt it refers to.
11. Referring to who guessing game Students report something they said or heard about someone else, e.g. gossip about someone famous, news about a politician, a reviewer’s opinion on someone’s acting or a colleague slagging off their boss, and the other students guess who was being spoken about.
12. Which occasion Students tell their partners something that was said to them at an important time, e.g. when they graduated from university or the first time their parents talked to them about sex, and their partners guess which occasion that thing was said at. The list of occasions can be given as a worksheet or brainstormed onto the board. This topic can easily be extended into an interesting cross cultural discussion on the traditional lack of school graduation ceremonies in the UK etc.
13. And this is how I felt sentence completion Students report something that was said to them or they heard that they had a strong emotional reaction to and the other students guess what their reaction was. This ties in well with a lesson on adjectives, and you can maybe give them a worksheet with some suggested adjectives on or brainstorm them before the activity, such as “… and I felt sad/ hungry/ romantic/ nostalgic/ old/ young/ flattered”
14. Reported mingling Almost any mingling activity (e.g. Find Someone Who) can be extended to include reported speech by people reporting back to their partners or the class what they learnt. Before doing this you will need to decide whether you want to encourage them to use Reported Speech or whether it is something you hope will come up naturally and that you might bring up later in an error correction stage.
15. Real or imagined reported speech This one works well with students whose memories freeze under the stress of speaking English or who don’t want to give away too much personal information. Students report something from prompts such as those described above, and then the other students guess whether that was really said to them or whether it was just made up.
You may also like:
- Yet Another 15 Games for Reported Speech
- More Reported Speech Games
- 15 Fun Ways of Practising the Past Perfect

11 Comments
thank for the material. it can add my knowledge. it used for may activity
The worksheets link I gave is still working, but the other parts of the article are now here: https://www.tefl.net/elt/ideas/games/games-reported-speech/ https://www.tefl.net/elt/ideas/games/reported-speech-games/
Great ideas shared, Alex!
I’ll try “And this is how I felt” with a twist to be carried out with my online students. I’ll include as a prompt: watching a short video like the ones that appear on Instagram (emotionally charged), for them to react to and report what was said and how it made them feel.
Let’s see how it works! Many thanks for the inspiration :)
Thanks, great ideas to use in my classroom.
Great ideas!! I will definetely try some in my classrrom. Thanks!!
Great ideas, thanks! I incorporated a few themes into a find someone who to start the topic of reported speech:
Find someone who:
1. Can remember some good advice they received
2. Has overheard an interesting conversation recently
3. Has had an interesting discussion recently
4. Knows some celebrity gossip
5. Has heard a joke in English
Parts Two and Three of this article are here:
http://www.tefl.net/elt/ideas/games/reported-speech-games/
http://www.tefl.net/elt/ideas/games/games-reported-speech/
And there are some worksheets here:
https://tefltastic.wordpress.com/worksheets/grammar/reported-speech/
excellent ideas, i will try some of them in my class today. thank you
Great activities. I tried “This is How I felt” as a follow-up and it really worked. Thanks
Hey there, speaking of Reversi games, I just posted a variation for teachers to use in one-to-one classes.
http://strictly4myteacherz.wordpress.com/2009/01/10/phrasal-verb-reversi-for-one-to-one/
Leave a comment
Email * (not published)
Reported Speech and Indirect Requests Listening and Speaking Exercises
Indirect questions and reported speech are two aspects of English grammar that can be a little tricky. Practice with pictures and listening using multiple intelligences can help make lessons more entertaining and engaging.
1 Reported speech listening/speaking (with audio and answers)
Subscribe to eslflow.
Subscribe to get full access to the latest and best resources from eslflow.com . There are no ads in the newsletter and you will receive entertaining, high quality, and up-to-date teaching resources regularly. And, if you subscribe, you will be supporting the eslflow website.
Reported Speech Guide
| Variations | Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | “I live in Paris.” | He said that he lived in Paris. |
| Present Continuous | “I am reading a book,” she said. | She said that she was reading a book. |
| Past Simple | “I went to the park,” John said. | John said that he had gone to the park. |
| Past Continuous | “I was playing soccer,” he said. | He said that he had been playing soccer. |
| Present Perfect | “I have seen that movie,” she said. | She said that she had seen that movie. |
| Past Perfect | “I had finished my homework,” he said. | He said that he had finished his homework. |
| Will | “I will call you later,” she said. | She said that she would call me later. |
| Can | “I can swim,” he said. | He said that he could swim. |
| Must | “You must leave now,” she said. | She said that I had to leave then. |
| Yes/No Questions | “Did you finish your homework?” he asked. | He asked if I had finished my homework. |
| Imperatives | “Close the door,” he said. | He told me to close the door. |
Introduction to reported speech practice worksheet (PDF)
2 Reported speech brainstorm (with audio and possible answers)
Indirect questions.
| Variations | Direct Question | Indirect Question |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple (to do) | What do you do for a living? | I’d like to know what you do for a living. |
| Present Simple (to be) | Who is your best friend? | Can you tell me who your best friend is? |
| Present Continuous | What are you doing right now? | I was wondering what you are doing right now. |
| Past Simple (to do) | What did you do last weekend? | Could you let me know what you did last weekend? |
| Past Simple (to be) | Who was your teacher last year? | I’d be interested to know who your teacher was last year. |
| Present Perfect | What have you done today? | I’m curious to know what you have done today. |
| Yes/No Questions (to do) | Do you like reading? | Can you tell me if you like reading? |
| Yes/No Questions (to be) | Are you okay? | Could you tell me if you are okay? |
| Will | Will it rain tomorrow? | Do you know if it will rain tomorrow? |
Introduction indirect questions practice (PDF)
3 Indirect questions (with answers and audio)
Indirect questions listening/speaking (PDF)
4 Indirect questions challenge(with audio and answers)
Indirect questions challenge (PDF)
5 Celebrity interview: advanced reported speech with academic reporting verbs (with audio and answers)
This is a more advanced reported speech exercise for listening/speaking or writing students. I’ve noticed that even quite good students often have trouble using a variety of reporting verbs. In this exercise, students listen to a interview with a celebrity and write sentences using the specified reporting verbs.
Related Resources:
6 reporting verbs (sorting), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
RECENT ESL EXERCISES
Reported speech
Mar Blancafort Engelfried
Grammar guide and exercises to practice. I hope you find it useful!
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF
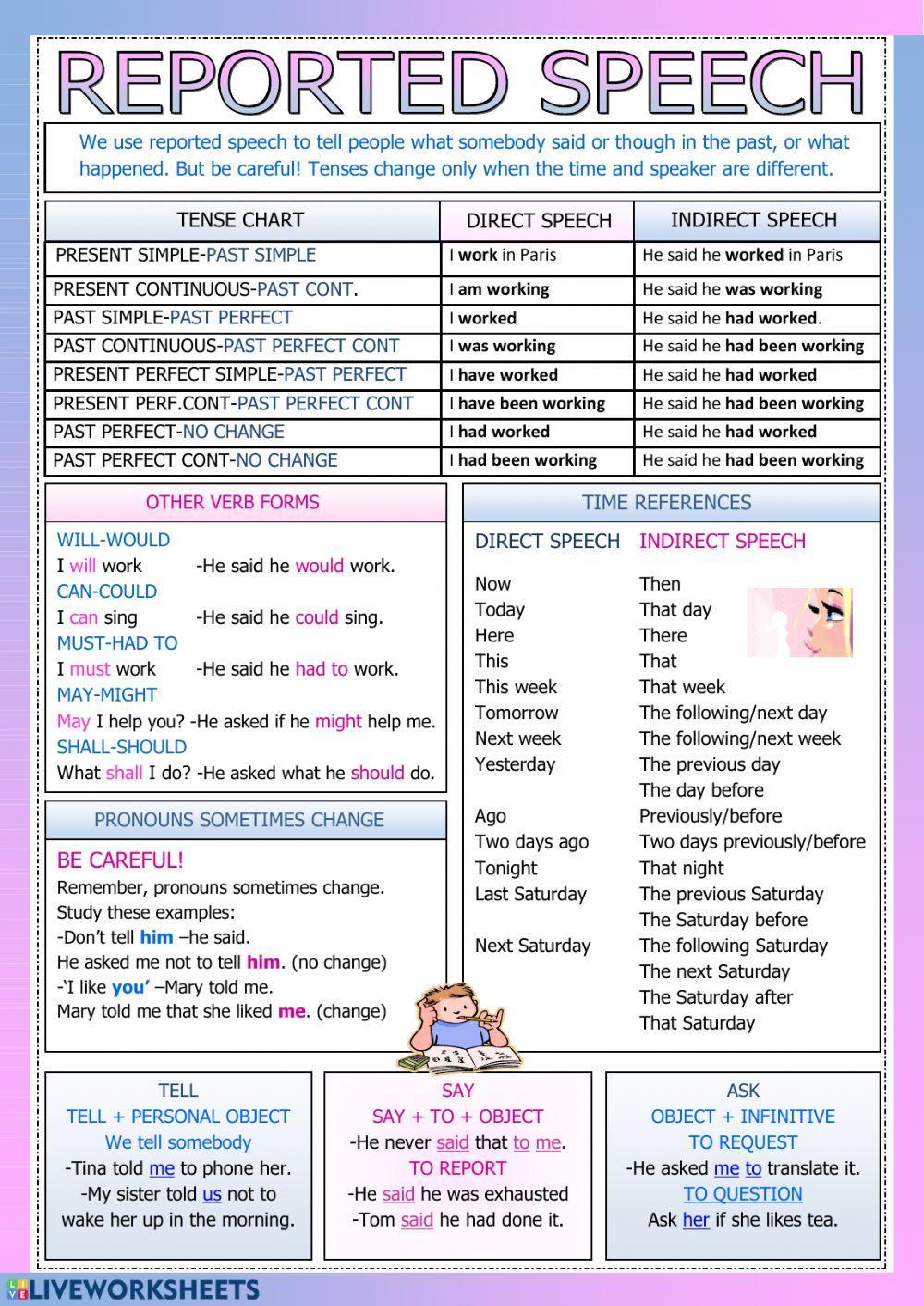
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
direct | indirect | reported clause | |
statement | ) I was tired. | -clause | |
question | . . | clause clause clause | |
command | . | -infinitive clause |
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| not very happy at work.’ | not very happy at work. |
| going home.’ | going home. |
| be late.’ | be late. |
| been working,’ she said. | . |
| to make her so angry?’ he asked. | to make her so angry. |
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
direct | indirect | |
present simple | → | past simple |
present continuous | → | past continuous |
present perfect simple | → | past perfect simple |
present perfect continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
past simple | → | past perfect simple |
past continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
future (will) | → | future-in-the-past (would) |
past perfect | ↔ | past perfect (no change) |
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Direct speech | Indirect speech |
| already left. |
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
direct speech | indirect speech | change | |
| be there,’ he promised. | be there. | becomes |
| need more money.’ I open it?’ she asked. | need more money. open it. | usually becomes in reported questions, becomes |
| see you at 2.30,’ he added. | see me at 2.30. | becomes |
| be back later,’ she said. wait in the hallway,’ he said. | be back later. wait in the hallway. | (possibility) becomes (permission) becomes |
| pay by 30th April.’ be awful to live in such a noisy place,’ she said. | pay by 30th April. be awful to live in such a noisy place. | (obligation) usually becomes (speculation) does not change |
| sell it for about 2,000 euros,’ he said. | sell it for about 2,000 euros. | no change |
| go there immediately,’ she said. | go there immediately. | no change |
| buy it if I had the money,’ he said. | buy it if he had the money. | no change |
| snow tonight,’ he warned. | snow that night. | no change |
| come till six o’clock,’ he said. | come till six o’clock. | no change |
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
direct | indirect | |
| don’t want to shock people,’ Tom said. | said he didn’t want to shock people. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| ’ll look after Toby,’ I said. | said I would look after Toby. | same speaker (no change) |
| need to be here at nine o’clock,’ George told Beatrice. | told Beatrice she needed to be there at nine o’clock. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| hope you will join us tonight,’ I said to James. | told James I hoped he would join us that night. | same speaker (no change to ; changes to ) |
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| .’ | the next/following day. |
| this moment in time.’ | . |
| .” | . |
| ,’ the boy protested. | . |
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
direct | indirect | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect speech: typical errors
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
a day that you spend somewhere that is not your home or usual place of work

It’s not really my thing (How to say you don’t like something)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Reported speech exercises
Examples from our community, 3,566 results for 'reported speech exercises'.
Harris speech fails to win over critics in Democrats' biggest rift, Gaza
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Andrea Shalal; Additional reporting by Kanishka Singh in Washington; Editing by Kat Stafford, Heather Timmons, Daniel Wallis and Raju Gopalakrishnan
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Kanishka Singh is a breaking news reporter for Reuters in Washington DC, who primarily covers US politics and national affairs in his current role. His past breaking news coverage has spanned across a range of topics like the Black Lives Matter movement; the US elections; the 2021 Capitol riots and their follow up probes; the Brexit deal; US-China trade tensions; the NATO withdrawal from Afghanistan; the COVID-19 pandemic; and a 2019 Supreme Court verdict on a religious dispute site in his native India.

Unidentified drone shot down over Iraq's Kirkuk, police say
Iraq's air defences shot down an unmanned drone on Thursday in the northern city of Kirkuk, two police sources told Reuters, triggering an investigation into the identity of the drone.

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- U.S. Open Tennis
- College football
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Highlights from Election 2024: RFK Jr. says he is suspending, not ending his campaign. His campaign says he ‘has not endorsed Trump’
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. says he’s suspending his independent presidential bid and is backing Donald Trump. Kennedy said Friday in Arizona that his internal polls show his presence in the race would hurt Trump and help Democratic nominee Kamala Harris.
- Copy Link copied
Today’s live coverage has ended. See what you missed below and find the latest on the 2024 presidential election at apnews.com.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has announced he is suspending, not ending, his campaign for president and will seek to remove his name from the ballot in battleground states because he believes his presence in the race would help Democratic nominee Vice President Kamala Harris.
Kennedy and Donald Trump will appear miles apart in Arizona on Friday amid speculation that Kennedy will endorse him.
Meanwhile, Harris accepted her party’s nomination and offered her policy agenda on the fourth and final night of the Democratic National Convention on Thursday.
What to know today:
- Takeaways from the DNC: Harris told voters they have a chance to chart a “new way forward” as Americans this November, as she looked to introduce herself to voters and prosecute her case against Republican Donald Trump . Supporters turned out in white to mark the moment.
- By the numbers: In a close election campaign with both sides looking for an edge, the party with more viewers watching their convention would seem to have an important sign of success. But historically speaking, that measurement means next to nothing.
- Trump and RFK Jr. in Arizona: Donald Trump will hold a rally in Glendale, AZ, hours after Robert F. Kennedy Jr. spoke in the same state . Trump’s campaign has teased that he will be joined by “a special guest,” though neither campaign responded to whether Kennedy would be that guest.
At the Phoenix event after Kennedy suspended his presidential bid, longtime RFK Jr. supporter Bruce Brimacombe said he is now an undecided voter.
The 64-year-old said what he heard was not Kennedy throwing his support behind Trump but rather an idea.
“It’s not going to Trump,” Brimacombe said. “It’s going to a unity idea of bringing things together. That’s a big difference.”
At his campaign stop Friday in Las Vegas, Trump sought to reclaim his vow to eliminate taxes on tips for service industry workers.
It’s a promise that Trump shared in June at a Las Vegas rally that Harris later echoed when speaking to her own supporters at a rally earlier this month on the campus of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas.
“In our case, we mean it,” Trump said. “Somebody I know just copied it. You know that’s not going to happen.”
The Culinary Workers Union, a political powerhouse in Nevada representing 60,000 service-industry employees at hotels and casinos, has endorsed Harris. But on Friday, Trump said, “Can we get the Culinary Union to maybe vote for Trump?”
The union did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Trump’s campaign has released a new memo from pollster Tony Fabrizio that argues Kennedy’s decision to suspend his campaign and endorse Trump will benefit the former president across battleground states.
“This is good news for President Trump and his campaign – plain and simple,” he writes.
Trump, who is campaigning in Las Vegas, said he’d just got a “very nice” endorsement from RFK Jr. that he’ll be talking about in Arizona.
“That was very nice,” he said. “That’s big.”
Dozens of his supporters packed inside a Mexican and Italian fusion restaurant cheered.
As Kennedy shared what he called an “agonizing” and “heart-wrenching decision to suspend my campaign and to support President Trump,” it evoked another decision he had described as difficult for himself and his family — when he left the Democratic Party to run as an independent.
When he announced that move last fall, he said it was “very painful to let go of the party of my uncles, my father, my grandfather and both of my great-grandfathers.”
During Friday’s announcement, he noted that joining the Trump campaign would be a “difficult sacrifice for my wife and children.”
Democratic presidential nominee Kamala Harris and her husband, Doug Emhoff, are greeting supporters at Chicago’s Soldier Field before the vice president returns to Washington.
Harris accepted her party’s presidential nomination in a speech Thursday night to close out the Democratic National Convention.
Several dozen supporters and community leaders awaited Harris’ arrival in the parking lot of Soldier Field.Some are wearing “Harris for President” T-shirts as the vice president goes down the line shaking hands, greeting people and posing for photos.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. said Friday he’s suspending his independent presidential bid and will seek to remove his name from the ballot in battleground states because he believes his presence in the race would help Democratic nominee Kamala Harris.
He said his supporters can continue to back him in the majority of states where they are unlikely to sway the outcome. Kennedy took steps to withdraw his candidacy in at least two states late this week, Arizona and Pennsylvania.
Kennedy said the move followed conversations with Donald Trump over the past few weeks.
Before the speech, his campaign had said in a Pennsylvania court filing Friday that he would be endorsing Trump for president. However, a spokesperson for Kennedy said the court filing had been made in error.
“Mr. Kennedy has not endorsed President Trump,” said spokesperson Stefanie Spear. “The filing was made by an attorney and not reviewed by the campaign.” She said the filing would be updated.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s campaign said in a Pennsylvania court filing Friday that he’s endorsing Donald Trump for president.
The campaign also requested that he be removed from the Pennsylvania ballot, though it wasn’t immediately clear that he was officially dropping out of the race. It came a day after he sought to be removed from Arizona’s ballot. He is running as an independent.
Kennedy is set to speak in Arizona shortly “about the present historical moment and his path forward,” according to his campaign. Hours later, Trump will hold a rally in neighboring Glendale. Trump’s campaign has teased that he’ll be joined by “a special guest,” though neither campaign responded to messages about whether Kennedy would be that guest.
Victor Marani, a 64-year-old retiree from Rio Del Mar, California, said he flew to Phoenix for Kennedy’s news conference after receiving an invitation from the independent candidate’s campaign.
“I learned a long time ago, don’t speculate until you hear what he has to say,” Marani said.
Marani, who identified himself as state chairman of the American Independent Party, said he would continue to support Kennedy.
“He’s not dropping out of California,” Marani said. “He’s on the ballot.”
In a close election campaign with both sides looking for an edge, the party with more people watching their midsummer convention would seem to have an important sign of success.
Yet historically speaking, that measurement means next to nothing.
Eight times over the past 16 presidential election cycles dating back to 1960, the party with the most popular convention among television viewers won in November. Eight times they lost.
Through the first three nights of each convention this summer, the Democrats averaged 20.6 million viewers, the Nielsen company said. Republicans averaged 17 million in July. The estimate for Thursday night, highlighted by Vice President Kamala Harris’ acceptance speech , is due later Friday.
“It’s one of those interesting things about covering politics is that you see these indicators about what really matters, and a lot of times it doesn’t,” said veteran journalist Jeff Greenfield, who covered the Democrats this week for Politico.
▶ Read more about convention viewership
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. and Donald Trump are set to appear miles apart in Arizona on Friday as speculation grows that Kennedy could drop his independent presidential bid and endorse the Republican nominee.
Kennedy is scheduled to speak at 2 p.m. Eastern time in Phoenix “about the present historical moment and his path forward,” according to his campaign. Hours later, Trump will hold a rally in neighboring Glendale. Trump’s campaign has teased that he’ll be joined by “a special guest,” though neither campaign responded to messages about whether Kennedy would be that guest.
Kennedy withdrew from the ballot in Arizona late Thursday, less than a week after he submitted well more than the required number of signatures to appear on the ballot. But his critics raised questions about the validity of some of the signatures, and the involvement of a pro-Kennedy super PAC to collect them risked potentially running afoul of rules against coordination between candidates and independent political groups.
▶ Read more about Robert F. Kennedy Jr.
This comes as the vulnerable three-term lawmaker seeks to distance himself from his party’s leaders ahead of the November election.
Tester said he was focused on his own race and it shouldn’t be about national politics. He faces a stiff challenge in November from Republican Tim Sheehy in a contest that could help decide control of the closely-divided Senate.
Tester made the remarks Thursday just hours before Harris accepted the Democratic nomination in Chicago, following President Joe Biden’s withdrawal from the race last month. The moderate lawmaker didn’t attend the convention and was the sole Democratic delegate from Montana to withhold a vote backing Harris for president.
“It’s about making sure we have a Montanan back in Washington, D.C., representing Montana values,” Tester told reporters during a news conference in Hamilton, Montana, about prescription drug costs, the Missoulian reported .
Tester supported Biden in 2020 but called for him to drop out of this year’s election following the president’s stumbling performance in a June debate against Trump.
Trump visited Montana two weeks ago seeking to boost Sheehy, a former U.S. Navy SEAL who moved to Montana a decade ago and founded an aerial firefighting company.
With anger over the war in Gaza simmering, Vice President Kamala Harris tried to defuse one of the most divisive issues within the Democratic Party on the biggest political stage of her life.
Her remarks Thursday night in her speech accepting the party’s presidential nomination hewed closely to previous statements on the conflict, which began when Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7.
Harris said she “will always stand up for Israel’s right to defend itself and I will always ensure Israel has the ability to defend itself.” She’s opposed restrictions on arms sales to Israel.
Then Harris pivoted to the destruction Israel has caused in Gaza, where 40,000 Palestinians have been killed.
“So many innocent lives lost,” she said. “Desperate, hungry people fleeing for safety, over and over again. The scale of suffering is heartbreaking.”
Harris said she was working with President Joe Biden on a cease-fire deal that would also release hostages held by Hamas, a step toward helping Palestinians “realize their right to dignity, security, freedom, and self-determination.”
▶ Read more about Harris and war in Gaza
Comey writes in a social media post that the Democratic nominee has “made me feel like it’s finally morning in America.”
Comey was fired by Trump in 2017 as the FBI was investigating potential ties between Russia and the Republican president’s 2016 campaign. He’s since become a public critic of Trump, writing frequently about what he says is Trump’s disdain for the rule of law and democratic norms.
Comey was a senior Justice Department official during the administration of Republican President George W. Bush. But in the last several years, he’s encouraged others to vote for Democrats.
In a post Friday on X, Comey wrote: “Everyone who cares about the rule of law and America’s indispensable role in the world should vote for Harris and Walz. I will.”
Donald Trump is changing his tune on Georgia’s Republican governor after delivering a series of blistering attacks at a rally just weeks ago.
In a social media post, Trump thanked Gov. Brian Kemp “for all of your help and support in Georgia, where a win is so important to the success of our Party and, most importantly, our Country.”
“I look forward to working with you, your team, and all of my friends in Georgia to help MAKE AMERICA GREAT AGAIN!” he wrote.
Trump’s words marked a major departure from his comments at a rally earlier this month , where Trump tore into the governor in an Atlanta arena that is only blocks from the Georgia Capitol, blaming him for his narrow 2020 loss in the state.
▶ Read more about Trump and Gov. Kemp
Pro-Palestinian protests during the final hours of the Democratic National Convention began Thursday night much like they had earlier this week — largely peaceful with a family-friendly atmosphere.
The crowd of thousands slowly snaked through residential areas surrounding the United Center. Some wore red T-shirts that said “Not In Our Name” while others held signs that said “End U.S. Aid to Israel.” Pausing at the edge of a park to turn toward the convention center, they chanted: “DNC, you will see. Palestine will be free.”
There was heavy police presence as protesters walked the blocks by the United Center, including at a park where a small group of activists breached an outer perimeter fence earlier in the week. In addition to police on bikes along the route, about 100 officers in riot gear and more than 20 law enforcement vehicles followed the marchers.
At Union Park ahead of the march, the grassy field teemed with Palestinian flags, and a speaker system played Palestinian dance songs. The gathering was organized by the Coalition to March on the DNC, a group of more than 200 organizations that also ran a similar event on Monday night.
Read more about Thursday night’s demonstrations outside of the DNC
Vice President Kamala Harris , on the night she became the first woman of Black and South Asian heritage to be a major party’s presidential nominee, didn’t explicitly mention the racial and gender firsts she would set if elected to the White House.
Instead, she opted for direct mentions of her multiracial background and upbringing. She paid tribute to her roots as the daughter of a brown woman and Caribbean man. She honored the multicultural village of “aunties” and “uncles” in California’s Bay Area. And following her speech, the relatives who joined her onstage for the traditional balloon drop included people of different and often multiple, overlapping races, like Harris herself. Western attire and saris were worn side by side.
It was a way for Harris and others at the convention to display her personal story while offering a visual political message that could appeal to a broad swath of people who see themselves in families like hers. Around 12.5% of U.S. residents identified as two or more races in 2022, up from 3% a decade earlier, according to the U.S. Census Bureau’s most comprehensive survey of American life.
▶ Read more about Harris’ racial and cultural identity
If you think you’re seeing a lot of women wearing white during the final night of the Democratic National Convention in Chicago, you don’t need to adjust your television set. There was a coordinated effort among female delegates and Democratic supporters as they arrived at the United Center on Thursday afternoon.
Harris’ nominating convention has been a four-day romp imbued with a party-like atmosphere and a sense of optimism. It’s safe to say that it would have been a much different gathering were Biden the party’s nominee.
Democrats have been through emotional whiplash since Biden bowed out of the race last month, clearing the path for Harris.
For months Democrats had been despondent about Biden’s polling and his underwhelming speaking appearances. And many Democrats were convinced that Trump could run away with the election.
Contrast that with the convention being held to nominate Harris in Chicago: Laughter filled the air, the mood was electric and searing jokes at Trump’s expense flowed freely. The event has also drawn an A-list slate of talent, from John Legend to Pink.
Not to be forgotten: There also have been words of caution about the hard work ahead.
Pro-Palestinian delegates never got the chance to take the stage and address the convention. It was a reflection of how the party has tried to avoid one of the more divisive issues of this election season as the U.S. alliance with Israel has become a political flashpoint.
Israel’s response to the Oct. 7, 2023, attack by Hamas has spurred outrage over mass casualties and human rights violations in Gaza , and pro-Palestinian demonstrators have marched outside the arena each day.
“Uncommitted” delegate Abbas Alawieh had been in talks with DNC officials about speaking to the hall. After being rejected, he and other delegates chose to spend Wednesday night on the sidewalk outside the convention hall in protest.
Harris and Biden have both called for a cease-fire and the release of hostages taken in the October raid. On Wednesday, the parents of one of the young men being held hostage in Gaza addressed the convention.
The convention didn’t just formally mark the exit of 81-year-old Biden from the campaign. It served as a showcase for the younger Democrats in the political talent pool.
Speakers included swing state up-and-comers like Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer, who was scheduled for prime-time slot Thursday. Others featured during the week: Pennsylvania Gov. Josh Shapiro and Arizona Sen. Mark Kelly, both of whom made the short list when Harris was searching for a running mate.
Michigan Attorney General Dana Nessel brought down the house with her address earlier in the week when she warned Republicans and the U.S. Supreme Court, “You can pry this wedding band from my cold, dead, gay hand!”
There were also rising blue-state celebrities like California Gov. Gavin Newsom, Maryland Gov. Wes Moore, Angela Alsobrooks, Maryland’s Democratic nominee for an open Senate seat, and 34-year-old New York Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, seen as representing a new generation of Democrats.
It was only a few years ago that Democrats worried they had too little talent in the pipeline, after scores of officeholders were wiped out in the off-year elections under President Barack Obama. But they’ve seen a resurgence in the Trump era.
Polling shows voters have consistently felt Republicans are better on the economy — a perception that Democrats are trying to fix.
High inflation hounded Biden’s popularity. Now Trump is trying to assign the blame to Harris as well, going so far as to call her a communist by nicknaming her “Comrade Kamala” and misleadingly claiming a relatively healthy economy is actually in tatters.
It’s not clear how well Trump’s criticism will stick to Harris, but Democrats tried to show her economic credentials on Thursday.
The Democrats’ argument is that Harris can do more for the middle class and entrepreneurs as the party tries to reframe social issues as economic ones.
Harris wants to provide $25,000 in down payment assistance for first-time homebuyers. “She knows housing is a human right and a pathway to the middle class,” Marcia Fudge, the former secretary of Housing and Urban Development, told the convention.
Inflation has been a persistent challenge for Democrats and the message Thursday was that greedy companies are to blame.
DNC delegates of color in Chicago are welcoming the ‘historic’ nature of Kamala Harris’ rise to the top of the Democratic presidential ticket. Political barriers will be broken if Harris becomes the first female president who is also multiracial.
The Democratic National Convention wraps up Thursday with Vice President Kamala Harris accepting her party’s presidential nomination. She is the first Black woman and first person of South Asian descent to be nominated, and supporters turned out in white to mark the moment.
Ahead of Harris’ appearance in the convention hall, rising Democratic stars were to address the crowd, along with survivors of mass shootings and others who were showcasing different issues. Republican Rep. Adam Kinzinger, who voted to impeach Donald Trump and sat on the House committee investigating the Jan. 6 attacks , also was scheduled to speak.
The crowded lineup reflects the immense work Democrats have before them as they’ve stood up a fresh presidential campaign in just under a month since President Joe Biden bowed out of the race.
▶ Read more about some of the takeaways from the Democrats’ final night
Some protestors jeered at a crowd of convention attendees as they left the arena.
One woman folded her Harris-Walz sign over her head as the group chanted “cease-fire now” and “shame on you.”
After her speech, Harris went to another part of the United Center and briefly addressed a group of staffers and supporters at a postconvention speech party.
“We just decided that we would celebrate our anniversary with all of you,” said Harris who accepted the Democratic presidential nomination on her and her husband Doug Emhoff’s 10th wedding anniversary.
The party included former Hillary Clinton aide Huma Abedin and a former co-host of The View, Desirée Rogers.
“Our fight is deeply and truly borne out of love of country,” Harris said, adding, “celebrate tonight” and “it’s been a wonderful convention.”
As much as her campaign is about joy, Harris devoted a considerable chunk of her speech to what she said were the risks of another Trump term, calling the election “one of the most important in the life of our nation.”
Her focus on Trump showed that fear remains a powerful motivator for many voters and she wants to tap into that.
Harris described how Trump inspired the Jan. 6, 2021, assault on the U.S. Capitol and his fraud conviction. She talked about his willingness to deploy the military against U.S. citizens — and the ability to do so with immunity from criminal consequences due to a recent Supreme Court ruling.
“Just imagine: Donald Trump with no guardrails,” she warned.
A few dozen protesters fought briefly with Chicago police on the edge of Union Park.
The small group, leftover from the earlier demonstration, planned to march toward the convention center, but they were blocked by rows of police in riot gear who pushed into the group, shouting, “Move back.”
Several of the protesters surged forward, with some swinging wooden signs down on the officers. The group has since retreated to the park, where an organizer said they plan to regroup. Police have ordered all media to leave the area, warning over a loudspeaker, “If you fail to comply, you will be in violation of the law and we will place you into custody.”
Within moments of Harris finishing her speech, the Trump campaign sent out a fundraising email titled “Worst speech ever!”
“Farewell to America if we have President Kamala!” it proclaimed.
In a letter to anti-abortion leaders during his 2016 campaign, Trump expressed his commitment to this view by vowing to sign the Pain-Capable Unborn Child Protection Act . The then-Republican president advocated for the bill again in 2018 , at that year’s annual March for Life festival in Washington, saying he “strongly supported the House of Representatives Pain-Capable bill, which would end painful, late-term abortions nationwide.”
Trump said that he would “call upon the Senate to pass this important law and send it to my desk for signing.” The bill, which included exceptions for saving the life of a pregnant woman, as well as rape or incest, was passed by the House in 2017 but failed to move forward in the Senate.
During her DNC acceptance speech, Harris said of Trump that the former president would “ban medication abortion and enact a nationwide abortion ban with or without Congress.”
While Trump has said in the past that he would support a national ban on abortion, he made clear his changed position on Thursday’s Fox & Friends: “I would never. There will not be a federal ban. This is now back in the states where it belongs.”
In April, he said that he would leave the issue up to the states in a video on his Truth Social platform.
Days later, asked by a reporter upon arriving in Atlanta whether he would sign a national abortion ban , Trump shook his head and said, “No.”
But just a month earlier Trump suggested that he’d support a national ban on abortion around 15 weeks of pregnancy . He also often brags about appointing the Supreme Court justices who overturned Roe v. Wade.
Trump has previously supported a federal ban on abortion at 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Trump told CBS News on Monday that he would not enforce the Comstock Act to restrict the sale of abortion medication by mail. The act, originally passed in 1873, was revived in an effort to block the mailing of mifepristone, the pill used in more than half of U.S. abortions.
The image of a mixed-race family joining the candidate on stage as she accepts the nomination to potentially be the first Black and Asian American female president is a political first in many ways.
“I do not limit access to birth control or I.V.F. - THAT IS A LIE, these are all false stories that she’s making up, that I’ve never even heard of,” wrote Trump, who appointed the judges who overturned Roe V. Wade. “I TRUST WOMEN, ALSO, AND I WILL KEEP WOMEN SAFE!” he wrote.
Trump has been offering commentary on the speech on his social media network.
He has repeatedly questioned why she didn’t implement the policies she’s proposing while serving as vice president.
“Why didn’t she do something about the things of which she complains?” he asked.
After speaking for about 37 minutes, Harris wrapped up her speech and was joined on stage by her husband, Doug Emhoff, along with running mate Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz and his wife, Gwen.
Family members began to play with some of the 100,000 red, white and blue balloons that began to cascade from netting where they’d been held in the ceiling all week.
Harris made a forceful defense of Ukraine and NATO in her speech as she lambasted Trump’s past comments on the war in Ukraine.
“As President, I will stand strong with Ukraine and our NATO allies,” Harris said.
Harris touted that five days before Russia invaded Ukraine, “I warned President Zelenskyy” and helped lead the U.S. diplomatic response in rallying “more than 50 countries.”
The DNC has restricted access to the United Center, which is at capacity, in the final hours of the convention, according to the Chicago Fire Department.
A fire department spokesperson said on X that the decision was made by the DNC in consultation with Chicago fire officials. He said both city fire and DNC officials would continue to monitor the situation.
Crowds of credentialed journalists were photographed outside the United Center, where they were not allowed entry into the stadium. The United Center can hold about 23,500 people.
In a stunning departure from the Biden campaign, Harris made the U.S.'s most forceful message yet on the ongoing war between Israel and Hamas.
Kamala Harris addressed the Israel-Hamas war during her DNC speech, calling for the release of Israeli hostages as well as a cease-fire in Gaza.
The vice president said that she would “always stand up for Israel’s right to defend itself,” while pushing for the release of the hostages and the implementation of a cease-fire deal.
“At the same time, what has happened in Gaza in the last 10 months is devastating, so many innocent lives lost,” Harris said. “Desperate, hungry people fleeing to safety over and over again. The scale of suffering is heartbreaking.”
Border security has been a major point of GOP criticism for Harris and her campaign, but the Democrat is drawing big cheers from her arena of delegates for her border plans.
Harris said, “I know we can live up to our proud heritage as a nation of immigrants and reform our broken immigration system.”
She also criticized Trump for his own actions, saying he “ordered his allies in Congress to kill” a border bill.
“Well, I refuse to play politics with our security,” she said, pledging to “bring back the bipartisan border security bill” and saying she’d sign it into law.
Guests sitting in the vice president’s box for her acceptance speech at the Democratic National Convention include her vice-presidential running mate, Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz and his wife, Gwen; her in-laws, Barb and Mike Emhoff; Arizona Sen. Mark Kelly and his wife, Gabby Giffords; and childhood friends Wanda Kagan and Stacey Johnson-Batiste; the mayors of Philadelphia and Madison, Wisconsin; and several members of the House of Representatives, according to Harris’ campaign.
While Harris is in the middle of her nomination acceptance speech inside the Democratic National Convention, protestors outside have staged an impromptu sit-in on Chicago’s Ashland Avenue.
The man leading it, who declined to be identified, said he initially sat because he was exhausted from hours of marching. Before long, about 100 others had joined him, singing “Which Side Are You On?” over bongo players and an electric guitar. While police initially called on the group to disburse, they retreated after the request was ignored.
The loudest reaction came when Harris pledged to help shepherd voting-rights legislation through Congress despite several failed attempts in the last few years.

Delegates cheer as Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris speaks during the Democratic National Convention Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024, in Chicago. (AP Photo/Brynn Anderson)
For Harris’ key moment, there are many color-coordinated options around the United Center.
Delegates have vertical blue signs with “Kamala” written out. Many people have added American flags handed out earlier in the night atop the post holding those blue signs, hoisting the flags further aloft.
Delegates in the seats directly in front of Harris — between the stage and the platform that holds a number of cameras broadcasting the convention — have smaller rectangular signs reading “Harris-Walz.”
In her speech, Harris touched on what has become the central policy issue of her vice presidency and now her campaign: the risk to reproductive rights.
“Tonight in America, too many women are not able to make those decisions,” she said.
“And let’s be clear about how we got here: Donald Trump handpicked members of the United States Supreme Court to take away reproductive rights.” She added, “One must ask why exactly is it that they don’t trust women? Well, we trust women.”
“The middle class is where I come from,” Harris said, describing for delegates how her late mother kept a “strict budget” and “we lived within our means.”
She said her mother taught her and her sister, Maya, that opportunity is not available to everyone.
But now Harris promises to create an “opportunity economy,” where she said, “everyone has the chance to compete and a chance to succeed.”
She also promised a “middle-class tax cut.”

Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris speaks during the Democratic National Convention Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024, in Chicago. (AP Photo/Brynn Anderson)
“We are not going back” chants broke out in the venue as Harris criticized Trump’s record and began outlining her vision for the nation.
“We are charting a new way forward, forward to a future with a strong middle class,” Harris said. “And building that middle class will be a defining goal of my presidency.”
Harris is issuing warnings about how Trump’s prior willingness to violate the law indicates a willingness for a reckless second term if he’s elected to the White House again.
The former prosecutor listed off Trump’s conviction in the New York fraud case, as well as the judgment against him in the E. Jean Carroll case.
“Just imagine Donald Trump with no guardrails and how he would use the immense powers of the presidency of the United States, not to improve your life, not to strengthen our national security but to serve the only client that he has ever had: himself,” Harris warned.
The prosecutor in Harris surfaced during the speech when, in referring to Trump, she referred several times to “his explicit intent.”

Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris speaks during the Democratic National Convention Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024, in Chicago. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Advertisement
Oprah Winfrey, in a Convention Debut, Calls Harris ‘the Best of America’
The surprise appearance by the television legend was closely held by Democratic organizers. Ms. Winfrey even rehearsed her speech wearing sunglasses and a face mask.
- Share full article
Oprah Celebrates Kamala as a Child of Immigrants
Oprah winfrey spoke on the third night of the democratic convention. she gave kamala harris a full-throated endorsement, saying that voting for her is “common sense.”.
I’ve lived in Mississippi, in Tennessee, in Wisconsin, Maryland, Indiana, Florida, Hawaii, Colorado, California and sweet home, Chicago, Ill. I’ve seen racism and sexism and income inequality and division. I’ve not only seen it at times, I’ve been on the receiving end of it. We are not so different from our neighbors. When a house is on fire, we don’t ask about the homeowner’s race or religion. We don’t wonder who their partner is or how they voted — no. We just try to do the best we can to save them. We’re going to be teaching our daughters and sons about how this child of an Indian mother and a Jamaican father, two idealistic, energetic immigrants. Immigrants — how this child grew up to become the 47th president of the United States. That is the best of America.

By Michael M. Grynbaum
Reporting from Chicago
- Aug. 21, 2024
The television legend Oprah Winfrey returned to prime time on Wednesday in a surprise appearance at the Democratic National Convention, calling on Americans to choose “optimism over cynicism” and “inclusion over retribution” as she endorsed the candidacy of Vice President Kamala Harris, whose life story Ms. Winfrey deemed “the best of America.”
Ms. Winfrey, a billionaire media mogul who built her career in Chicago, had never before spoken at a national convention. Her speech was carefully kept under wraps by Democratic organizers, including a cloak-and-dagger act during rehearsals in which one of the most famous women in America crept into the United Center wearing a hat, sunglasses and a face mask.
When Ms. Winfrey said hello to Representative Nancy Pelosi of California, Ms. Pelosi had no idea who she was at first, according to Ms. Winfrey’s friend Gayle King, the CBS anchor.
The obvious excitement in the crowd when Ms. Winfrey emerged on Wednesday evening was a reminder of her power as a public speaker and a widely recognized icon of optimism, particularly among the female and Black voters that Ms. Harris is hoping to turn out in big numbers on Election Day.
Ms. Winfrey’s speech touched on school integration, the preservation of democracy, and civil rights icons like John Lewis. Dressed in a purple outfit, she appeared to direct her remarks toward the country’s political independents, a cohort to which she said she belonged.
“Decency and respect are on the ballot in 2024, and just plain common sense,” Ms. Winfrey said, before building to a climactic passage that evoked the energy of her daytime talk show, which ended in 2011.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
BusyTeacher.org

“He Said What?” Top 10 ESL Activities for Reported Speech

He said…She said…He asked her if, when, where or what… Reported Speech, also known as Indirect Speech, is not one the most fun to teach.
What ESL teachers usually do is simply have one student supply a statement or ask a question and then have another student report what was said/asked. However, there are others ways to practice Reported Speech , more creative and engaging ways, which should prevent students tuning out and help them tune in to the lesson.
Try These Top 10 ESL Activities for Reported Speech
Reported speech card games.
For some students, the best way to learn Reported Speech is by reading the statements they have to report. This is why we often write them on the board. Try these card games instead! For the first game, prepare a set of index card each with a direct speech statement on one side and the indirect statement on the other. Divide students into pairs. Student A picks up a card and reads the direct statement. Student B must change what they heard into an indirect statement. Student A checks B’s reply on the back of the card. The team with the most correct points wins.
You may also try this easier version. Write the direct statements on index cards and their indirect versions on another set of cards. Divide the class into two teams. Each student must pick up a card and find the matching statement. You can make this more challenging by using statements that are similar but in different tenses.
What Did They Ask You?
Ask students to brainstorm a list of people who might ask them questions and what those questions might be: a police officer, their mother/father, a teacher, a taxi driver, etc., Then a student reports something that someone asked, without revealing who it was: This person asked me if I had my driver’s license . Students must guess it was the police officer: The police officer asked you if you had your driver’s license .

Words to Live by
Give students snippets of things that famous people have said about their lives and experiences. Students read them out loud and then take turns reporting what someone said: Einstein said peace could not be kept by force. He said it could only be achieved by understanding. “The future rewards those who press on. I don't have time to feel sorry for myself. I don't have time to complain. I'm going to press on,” said former President Obama. President Obama said that the future rewards those who press on, that he does not have time to complain and is going to press on.
Celebrity Buzz
Hand out several copies of entertainment magazines or the showbiz section of the newspaper. Students must read through them and find at least one juicy bit of celebrity gossip to report to the rest of the class: Miley Cyrus said she was officially engaged to her boyfriend . To make this into a game, ask students to withhold the celebrity’s name and have the other students guess: Which famous celebrity said she was engaged to boyfriend Liam Hemsworth?
Take advantage of story time by asking students to report on what some of the main characters said/asked in the stories or works they are reading : What did the Evil Queen ask the magic mirror? She asked it who the fairest of them all was .
Student Reporter
Any budding reporters can have the chance to show off their reporting skills with this fun activity. Divide students into pairs. One student will be the reporter and the other will be someone worthy of an exclusive interview:
- A famous actress
- A rich entrepreneur
- An Olympic athlete and so on.

Ask each student to write Dear Abby letter asking for advice on a problem ; ask them to use Reported Speech in their letter: My parents said we were moving to another country but I don’t want to move . Students then exchange letters and reply to a classmate’s problem: Don’t be afraid to tell your parents how you feel . Students get their original problem letters back and report to the class on what Dear Abby said: Dear Abby told me not to be afraid to tell my parents how I feel . With this activity you are giving your students two opportunities to use Reported Speech.
I Heard it Through the Grapevine
One student whispers something to a classmate: I love chocolate more than anything else . This student whispers it to another: Juan said he loved chocolate more than anything else . The whispering continues through the grapevine, until it reaches the last student who must then say the original statement in direct speech. If there are differences, they must find out who made the mistake: Karen said Juan loved chocolate more than life itself. - I said he loved it more than anything else .
Comic Strip Gaps
To prepare for this activity cut out comic strips from a newspaper or print some you find online. Then use some liquid paper to white out what some of the characters say in their speech bubbles. Write these lines down on separate cards. Students pick up a card and try to match it to a character: Garfield said he wanted to eat lasagna .
First you need some flashcards with sentences in direct or indirect speech, a basic timer and a bean bag or ball. Have the students stand in a circle. Give the first one a bean bag or the ball and set the timer for a random interval, even a short one — one minute or even six seconds, or you can even vary the intervals to make it more interesting — depending on the size of your class. When the timer stops, the student holding the bean bag must read one of the flashcards and convert it into the opposite e.g., direct speech to indirect speech, or the other way round. If they are wrong, they must leave the circle. You can vary the game by changing the flashcards to contain other words where students would need to come with sentences containing, say for example, superlative adjectives , add suffixes , countable and uncountable nouns .
Try not to give your students random direct statements to report.
Each of the activities suggested above should establish a situation, a context that should help your students see just how useful Reported Speech really is.
If you have any activities that have worked for you, please share them below!
Like it? Tell your friends:
How to teach reported speech - statements.

Let’s Be Indirect: Teachers’ Top 9 Fun and Creative Activities for Practicing Reported Speech

Don’t Get to the Point: Teaching Indirect Questions

Watch CBS News
Hillary Clinton says "the future is here, it's in our grasp," in energetic DNC speech
By Kaia Hubbard
August 19, 2024 / 10:40 PM EDT / CBS News
Washington — Former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton , who herself came close to becoming the first woman president eight years ago, said Monday that the future is "in our grasp," delivering an energetic speech at the first night of the Democratic National Convention .
"This is our time, America," Clinton said. "This is when we stand up. This is when we break through. The future is here, it's in our grasp, let's go win it."
Clinton's speech came as Democrats showed a united front behind Vice President Kamala Harris after she replaced President Biden at the top of the ticket.
Clinton, who took the stage to a lengthy and warm reception of cheers from the crowd, said, "Something is happening in America — you can feel it," calling it "something we've worked for and dreamed of for a long time."
Eight years after she accepted the party's nomination for president at the Democratic convention in Philadelphia, Clinton said "we are writing a new chapter in America's story" with the nomination of Harris — who is the first woman of color to be nominated as a major party's presidential candidate.

In her remarks, Clinton took the audience through a short history of women shattering glass ceilings in politics — from gaining the ability to vote to her nomination in 2016, which she said called the "honor of my life."
"Nearly 66 million Americans voted for a future where there are no ceilings on our dreams," Clinton said. "And afterwards, we refused to give up on America … we kept our eyes on the future."
"Well, my friends, the future is here," she added, urging Americans to send Harris to the White House.
Like many other Democrats before her on Monday, Clinton painted a stark picture of the future of the nation under Harris versus a second Trump administration. She told voters they face a choice between uniting as "we the people" or fracturing into "us versus them." And she said, "Kamala has the character, experience, and vision to lead us forward."
Clinton, who lost her presidential bid to former President Donald Trump in 2016 and has been the target of Trump's ire for years, said it "is no surprise" that the former president "is lying about Kamala's record, he is mocking her name and her laugh."
"Sounds familiar," she quipped with a shrug. "But, we have him on the run now. So, no matter what the polls say, we can't let up."
The former secretary of state said Harris' victory would have meaning far beyond just one individual, saying it would uplift the nation by "opening the promise of America wide enough for everyone."
"Together we put a lot of cracks in the highest, hardest glass ceiling," Clinton said. "And tonight, tonight so close to breaking through once and for all, I want to tell you what I see through all those cracks, and why it matters for each and every one of us."
"I see freedom," she said. "On the other side of that glass ceiling is Kamala Harris raising her hand and taking the oath of office as the 47th president of the United States."
The convention comes less than a month after Mr. Biden dropped out of the race and promptly endorsed Harris as his replacement at the top of the ticket. Clinton and her husband, former President Bill Clinton, quickly endorsed Harris' bid for the presidency.
Clinton celebrated Mr. Biden as well on Monday, saying he "brought dignity, decency and confidence back to the White House."
"He showed what it means to be a true patriot," Clinton said. "Thank you. Joe Biden, for your lifetime of service and leadership."
- Hillary Clinton
- Democratic Party
- Democratic National Convention
Kaia Hubbard is a politics reporter for CBS News Digital, based in Washington, D.C.
More from CBS News

JD Vance says Kamala Harris "can go to hell" over Afghanistan withdrawal

Harris girds for battle with Trump over union workers and their Big Labor bosses

RFK Jr. wants off the ballot in 10 states. Some battlegrounds are saying no

More than 200 former Bush, McCain and Romney staffers endorse Harris
RFK Jr. is planning to drop out of the 2024 presidential race and endorse Trump
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. intends to end his independent presidential campaign and endorse former President Donald Trump, according to two sources familiar with the plans.
The sources cautioned that talks are ongoing but said there will be clarity by the end of the week. One of the sources said the campaigns are working toward a joint appearance.
The decision to drop out will end the most prominent third-party candidacy in the race. Kennedy announced Wednesday that he will give a campaign speech addressing “his path forward,” days after his running mate said the campaign faced a choice about staying in the election or dropping out to back Trump .
Kennedy’s campaign announced he will hold the event in Phoenix on Friday. Trump, meanwhile, is also set to host an event on Friday night, in Glendale, a Phoenix suburb.
Nicole Shanahan, Kennedy's running mate, said Tuesday that the ticket is weighing two options. One is to stay in the race and "risk" a Harris-Walz presidency, as she put it in a podcast interview, while the other is to drop out of the race and "join forces" with Trump.
Persuading Kennedy to back Trump has been an ongoing project of Trump's eldest son, Donald Jr., former Fox News host Tucker Carlson and wealthy donor Omeed Malik, according to a source familiar with the efforts who requested anonymity to divulge internal campaign deliberations. The three men have worked behind the scenes in meetings and calls with both principals to negotiate Kennedy’s exit and endorsement, the source said.
Trump's running mate, Sen. JD Vance of Ohio, said in an interview Wednesday that "there's been a lot of communication back and forth" between Kennedy and his campaign.
"I haven’t spoken to RFK personally, but I know there’s been a lot of communication back and forth between RFK, between the campaign, between this campaign," Vance said. "Look, our argument to RFK, and I’ll make it right now, because, of course, he hasn’t dropped out yet, is, look: If you want a Democratic Party that protected American workers and stood for strong borders, maybe disagreed with Republicans on things like tax policy, that party doesn’t exist anymore."
Vance also said Trump wouldn't promise a Cabinet position for Kennedy's endorsement.
And Tuesday, Trump told CNN that he would be open to Kennedy's joining his administration if he is elected. Asked whether he'd consider putting Kennedy in the administration if he backed him and he won, Trump said, “I probably would." He added, "I like him a lot. I respect him a lot."
Mary Beth Cahill, a senior adviser to the Democratic National Committee, slammed Kennedy in a statement: “Desperate men do desperate things. RFK Jr. was recruited by MAGA, funded by MAGA, and parroted MAGA talking points. No one should be shocked if he formalizes his relationship in an attempt to maintain relevance.”
Trump and Kennedy met in Milwaukee last month during the Republican convention, which came days after the assassination attempt against Trump.
"I know the president's been working hard for that, but it's completely separate from whether RFK gets a Cabinet position," Vance said. "It's about welcoming a lot of those Democrats who feel abandoned by the party of Kamala Harris."
Kennedy's presence on the campaign trail has been minimal in recent weeks. He hasn't hosted a public, campaign-sponsored event since early July, and Shanahan hasn't been seen on the trail in months. Kennedy's standing in public polling has slipped, too.
The campaign has faced a string of damaging stories, from groping allegations against Kennedy from a former family babysitter to the bizarre story that Kennedy picked up a bear carcass on the side of the road years ago and used it to stage a bicycle accident in New York's Central Park.
In a podcast interview , Kennedy didn't specifically deny the groping allegation, which surfaced in a Vanity Fair article in July, saying: "I am not a church boy. I am not running like that. I have said I had a very, very rambunctious youth. I said in my announcement speech that I have so many skeletons in my closet that if they could all vote, I could run for king of the world."
"I'm not going to comment on it," he added when asked again about the specific allegation.
And he also faces financial troubles. The campaign closed July with almost $3.5 million in debt, according to the most recent campaign finance report. Those documents also show that Shanahan, who has been pouring her own millions into the campaign, received a refund of almost $1 million in July.
Kennedy's endeavor for ballot access in all 50 states has also hit a roadblock. He was recently disqualified from the ballot in New York state when a judge ruled that his home address used on signature petitions wasn't his place of residency.
Vaughn Hillyard is a correspondent for NBC News.
Dasha Burns is a correspondent for NBC News.
Katherine Koretski is a 2024 NBC News campaign embed.
Alec Hernández is a 2024 NBC News campaign embed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Procedure for this Reported Speech Activity: Have students write an interesting story based on a certain topic. Adjust for length and difficulty depending on your students. Collect stories and redistribute them-one per student, making sure a student does not get their own story.
ESL Reported Speech Activity - Grammar and Speaking: Asking and Answering Questions, Forming Sentences, True or False, Guessing - Group Work - Pre-intermediate (A2) - 40 minutes. In this entertaining reported speech speaking activity, students interview each other giving true or false answers and then use reported speech to compare what the ...
Reported Speech Card Games. For some students, the best way to learn Reported Speech is by reading the statements they have to report. This is why we often write them on the board. Try these card games instead! For the first game, prepare a set of index card each with a direct speech statement on one side and the indirect statement on the other.
Reported speech is a very common aspect of the English language. You use it nearly every day, both in conversations and in writing. This reference covers key sections about reported speech, including what it is, examples, rules, and verb tense changes.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
The types of reported speech are direct speech and indirect speech. Tips for Teaching Reported Speech To English Learners. Teaching reported speech to ESL learners can be challenging, as it involves a shift in verb tense and pronoun usage. Here are some tips to make the teaching process more effective and engaging. Start with Direct Speech
Yes, and you report it with a reporting verb. He said he wanted to know about reported speech. I said, I want and you changed it to he wanted. Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present continuous changes to the past continuous; the present perfect changes to the past perfect; can changes to could; will changes ...
Reported speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
For example: Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken. Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting.
Shaken not stirred.". "The power of Christ compels you!". "Remember: What happens in Vegas stays in Vegas.". 3. Reported Speech Cards. This is another fun speaking activity that will help students learn reported speech. Hand out slips of paper to students. One side of the paper is a direct speech sentence. One student reads out the ...
409 Reported Speech (Indirect speech) English ESL worksheets pdf & doc. SORT BY. Most popular. TIME PERIOD. All-time. Zmarques. Reported Speech. It consists of seven. 103443 uses. estrelapolar. REPORTED SPEECH - CH. An easy way to teach. 49910 uses. dobrawaa. Reported Speech - a . This is a boardgame . 47261 uses. Zmarques. Reported Speech.
reported speech. turn dialogue into request reported speech. 312 uses. A selection of English ESL reported speech (indirect speech) printables with discussion starters, speaking cards, speaking practice.
Fun Ways of Practising Reported Speech. By Alex Case. Alex Case offers 15 ideas for getting learners to use indirect speech. 1. Reported speech reversi. Prepare cards with reported speech on one side and direct speech of the same sentence on the other. Students have to correctly say what is on the other side to turn it over and score one point.
Level: Intermediate (B1-B2) Type of English: General English. Tags: reported speech Grammar practice. Publication date: 08/17/2021. This worksheet teaches reported speech. The rules for changing the tense of the verb from direct speech are presented and practised. The worksheet is suitable for both classroom practice and self-study.
1 Reported speech listening/speaking (with audio and answers) Reported speech is an essential but sometimes overlooked aspect of English grammar. This is a fairly elementary exercise. Students can try to complete the speech bubbles. Then they can listen to the audio to compare answers. Reported speech (PDF)
Country code: ES. Country: Spain. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Reported speech (2013113) From worksheet author: Grammar guide and exercises to practice. I hope you find it useful! Other contents: Indirect speech.
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
10,000+ results for 'speaking reported speech'. Reported Speech Speaking cards. by Ednauvapds. Reported speech Quiz. by Mariela98. Reported Speech Spin the wheel. by Wordwallgrupo3. Higher Education ELA. Reported Speech Quiz.
articulation Speech Speech therapy. /k/ All Positions Spin the wheel. by Powellselah. Speech Production Speech therapy. High Frequency SH Words Spin the wheel. by Holly17. articulation Speech Speech therapy. Function of Object (field of 3/4) Quiz. by Wileyspeech.
The trio of Tennessee lawmakers known as the "Tennessee Three" were expected to get a primetime speaking slot at Thursday's Democratic National Convention, but the group is expected to be bumped ...
Uncommitted delegates and their allies had pushed unsuccessfully for a prime-time speaking slot at the Democratic National Convention (DNC) to address the latest bloodshed in the decades old ...
The speech on Friday will be the Kennedy campaign's first public event since early July. It comes as Kennedy has struggled to gain traction since Harris took over the top of the Democratic ticket.
Afghanistan's Taliban has banned women from looking at men and speaking loudly in public and inside their homes.. In a 114-page document of new orders seen by The Telegraph, the regime announced ...
Harris accepted her party's presidential nomination in a speech Thursday night to close out the Democratic National Convention. ... the Missoulian reported. ... After speaking for about 37 minutes, Harris wrapped up her speech and was joined on stage by her husband, Doug Emhoff, along with running mate Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz and his wife ...
Ms. Winfrey's speech touched on school integration, the preservation of democracy, and civil rights icons like John Lewis. Dressed in a purple outfit, she appeared to direct her remarks toward ...
For some students, the best way to learn Reported Speech is by reading the statements they have to report. This is why we often write them on the board. Try these card games instead! For the first game, prepare a set of index card each with a direct speech statement on one side and the indirect statement on the other. Divide students into pairs.
Clinton's speech came as Democrats showed a united front behind Vice President Kamala Harris after she replaced President Biden at the top of the ticket. Clinton, who took the stage to a lengthy ...
Independent presidential candidate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. is set to make a campaign speech addressing "his path forward" on Friday, after his running mate mentioned the possibility of dropping out ...