- English Grammar
- Reported Speech

Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Class 5 English Grammar Chapter 7 Reported Speech
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 English Grammar Chapter 7 Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect Speech) updated for session 2024-25. State boards and CBSE students can take the benefits of these contents clearing their doubts. Lots of illustrations are given for practice the concepts.
Class 5 English Grammar Chapter 7 Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect)
- Class 5 English Grammar Chapter 7 Direct and Indirect Speech
- Class 5 English Grammar Chapter 7 Revision Book
- Class 5 English Grammar Main Page
- Class 5 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
| Class: 5 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 7 | Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect) |
The following paragraphs illustrate the two ways in which we can report the words of a speaker.
- 1. Teacher said, “Have you done your homework?” Student said, “Sorry, teacher, I could not complete it.” Teacher said, “Why couldn’t you complete your homework? Now get out of my class!”
- 2. The teacher asked the student if he had done his homework. The student apologised that he could not do his homework. On knowing this, the teacher angrily asked him the reason for not doing the homework and asked him to get out of the class.
In 1, we give the exact words used by the speaker. This is called the Direct Speech. In 2, we do not give the exact words of the speaker but give only the substance of what he said. This is called the Indirect Speech or Narration.
The following rules will help you in changing Direct Speech into Indirect: Rule 1: If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the Verb in the Reported Speech is not changed at all. Direct: Meena says, “There is no water in the jug.” Indirect: Meena says that there is no water in the jug.
Rule 2: If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the Verb in the Reported Speech is also in the Past Tense. The matter inside the inverted comma will change as under. 1. The Simple Present becomes the Simple Past; as: Direct: Teacher said, “Kitty works very hard.” Indirect: Teacher said that Kitty worked very hard.
Rule 3: (Exception to Rule 2.) If the reported speech contains some universal or habitual fact, then the Simple Present in the Reported Speech is not changed into the corresponding Simple Past, but remains unchanged. Direct: The Mother Teresa said, “Charity begins at home.” Indirect: The Mother Teresa said that Charity begins at home.
Rule 4: Students may carefully note the following in order to understand the change of persons. First Person is changed into the person of the subject. Second Person is changed into the person of the object. For the Third Person, there is no change.
Rule 5: In the Reported Speech ‘said to’ changes to “told”, thus: Direct: He said to me, “I will go there tomorrow.” Indirect: He told me that he would go there the next day.
Rule 6: In the Reported Speech the words expressing nearness are changed into words expressing distance or remoteness, thus: ex.: This- changes into- that
| words expressing nearness | words expressing distance or remoteness |
|---|---|
| This | that |
| These | those |
| Here | there |
| Now | then |
| Today | that day |
| Tomorrow | the next day |
| words expressing nearness | words expressing distance or remoteness |
|---|---|
| Yesterday | the previous day or the day before |
| Last night | the previous night or the night before |
| Ago | before |
| Just | then |
| Come | go |
| Next month | the following month. |
What is reported speech and its type in Chapter 7 Class 5 English Grammar?
Reported speech is the way we can express our thoughts. There are two type of reported speeches: (i). Direct Speech (ii). Indirect speech
What is the main difference between direct and indirect speeches in Class 5 Grammar Chapter 7?
Direct speech: in the direct speech sentences we give the exact words used by the speaker. This is called the Direct Speech. Ex.: Meena says, “There is no water in the jug.” Indirect speech: in the indirect speech sentences we do not give the exact words of the speaker but give only the substance of what he said. This is called the Indirect Speech or Narration. Ex.: Meena says that there is no water in the jug.
What is the indirect form of Present Perfect in 5th Grammar Chapter 7?
The Present Perfect becomes the Past Perfect; when sentence changes from direct speech to indirect speech. Ex.: Direct: Srikant said. “Mini has done his work.” Indirect: Srikant said that Mini had done his work.
In what condition Simple Present in the Reported Speech is not changed into the corresponding Simple Past in Class 5 Grammar?
If the reported speech contains some universal or habitual fact, then the Simple Present in the Reported Speech is not changed into the corresponding Simple Past, but remains unchanged. Ex.: Direct: The Mother Teresa said, “Charity begins at home.” Indirect: The Mother Teresa said that Charity begins at home.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education


Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common thing in the English language. We do it almost every day, in conversation and in writing. The problem is, sometimes there can be some confusion around the topic. So today we’ll take a look at reported speech: what it is, how to use it, and we’ll give some interactive exercises of reported speech too, so you can see how it looks in everyday conversations or writing.
Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we are referring to something that was said either by ourselves or by someone else in the past. An example of this might be ‘he said that he was going shopping. This type of speech is used very frequently during both spoken and written examples of English and it is an important part of the language which any English student will find useful to learn. In this section, we are going to look at types of reported speech as well as how we can use it.
What is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when we tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, we use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used, and we’ll try to use different ones throughout this article to show you some examples, but you can always do some research too if you want to learn more examples for yourself.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that we use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. So, we’ll look at some grammar change examples below and highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When we use reported speech, we are usually talking about the past (because obviously, the person who spoke originally spoke in the past). The verbs therefore usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Reported Speech Rules
When changing from direct to indirect speech, you need to change the grammar in certain ways. In this section, we are going to be looking a little more closely at direct and indirect speech and how they are used.
Verb Tense Changes in Reported Speech

If the reporting verb is in the present tense, then very little needs to be done to the direct speech sentence to change it. Here’s an example.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
Here nothing really needed to be changed except the pronoun, because you are now talking about somebody else, so ‘I’ becomes ‘She’ or ‘He’. The tense is still the same because ‘says’ is the present tense version of the reporting verb. But what happens if the sentence needs to be changed to past tense?
Sometimes it is necessary to change the reporting verb into the past tense if what was said is no longer relevant, or was said sometime in the past. Here are the changes that would need to be made.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
As well as changing the pronouns here, we’ve had to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the verb. So, ‘says’ becomes ‘said’ and ‘like’ becomes ‘liked’.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, verb tense forms usually need to change. The tenses generally move backward in this way:
- Present Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense
- Present Continuous Tense into Past Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Continuous Tense into Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense (the tense remains unchanged)
If somebody is talking about what will happen in the future then, again, you will need to change the tense of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Notice how ‘shall’ and “will” become ‘would’ here in order for it to make sense.
- Will into Would
- Will be into Would be
- Will have into Would have
- Will have been into Would have been
Modal verbs actually have a very interesting relationship with reported speech, so we’ll look at that below too.
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
We’ve already covered modal verbs in another article, but it’s interesting to see how they are changed in reported speech.
- Can into Could
- Could (The verb remains unchanged)
- Have to into Had to
- Must into Must/Had to
- May into Might
- Might (The verb remains unchanged)
- Should (The verb remains unchanged)
Let’s take a look at some examples.
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb ‘will’ being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb ‘will’ and the reporting verb ‘ask’ are both written in the past tense. So, ‘will’ becomes ‘would’ and ‘ask’ becomes ‘asked’. It’s important in reported speech to make sure that each part of the sentence is in the same tense.
Sometimes though, modal verbs do not need to change tense because they already read correctly. Here’s an example.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Notice that nothing needed to be changed here to fit the past tense reporting verb ‘told’. ‘Should’ does not need to be changed grammatically for either sentence to make sense. But you will notice that because we decided to use the reporting verb ‘told’ instead of ‘said’, we had to include the pronoun ‘me’ for it to make sense.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
Both of these sentences make grammatical sense, because we added the pronoun ‘me’ after ‘told’ in the first sentence, but we didn’t after ‘said’ in the second one. Here is the incorrect versions so you can see why it doesn’t work grammatically:
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
In order to make the top one make sense, we need to add ‘me’ like we did in the correct examples above. In order to make the second one make sense, we would either have to remove ‘me’ like we did in the correct one above, or we would have to add another word. So that it looked like this.
- Reported speech: He said to me he should go to the park.
The above sentence makes sense, but sometimes you have to watch your wording of certain things to make sure that you aren’t over-speaking/writing. This can be a problem if you are trying to get your point across quickly. You should always choose the option that is quickest to say/write because it sounds/looks better and you run less risk of making a grammatical mistake.
This guide could not possibly be extensive, because there are many grammar rules that need to be followed when reporting speech, but they vary wildly. The take-home message should really be that when reporting speech, it is important to think carefully about what you are going to say or write, so you know it makes sense. Hopefully, this guide served as a good starting point though, so you can identify reported speech now, and start to think about which grammar rules are applied.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
Time and place references often have to change in Indirect Speech
- Now –> Then
- Today –> That day
- Here –> There
- This –> That
- Tomorrow –> The following day/ The next day/ The day after
- Next week –> The following week/ The next week/ The week after
- Yesterday –> The previous day/ The day before
- Last week –> The previous week/ The week before
- Ago –> Previously/ Before
- Tonight –> That night
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
There is no change in verb tenses in Indirect Speech when:
- The introductory verb is in the Present, Present Perfect or Future .
- If the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- The reported sentence contains a time clause .
- The verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
List of reporting verbs in reported speech.
- Tell, say, ask.
- Verb + that + clause : complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest.
- Verb + to + infinitive : agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim.
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn.
- Verb + “ing” form : admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/ of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest.
- Verb + how : explain to somebody.
Reported Questions in English
When you are changing a question from direct speech into indirect speech, you follow the same kinds of rules as for statements.
To report a question , we use verbs such as inquire, wonder, want to know, ask…
Reported Commands and Requests in English
Reported Orders, Commands, and Requests are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive.
The reporting verbs for the orders/ commands/ requests are order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid…
When we change from direct to indirect speech, the pronoun and tense changes are also needed.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
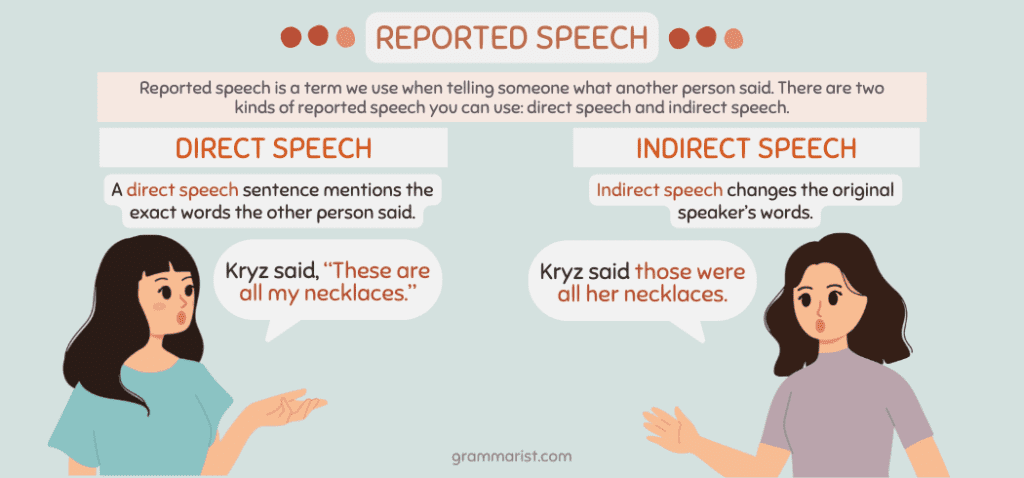
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.

Using Modals
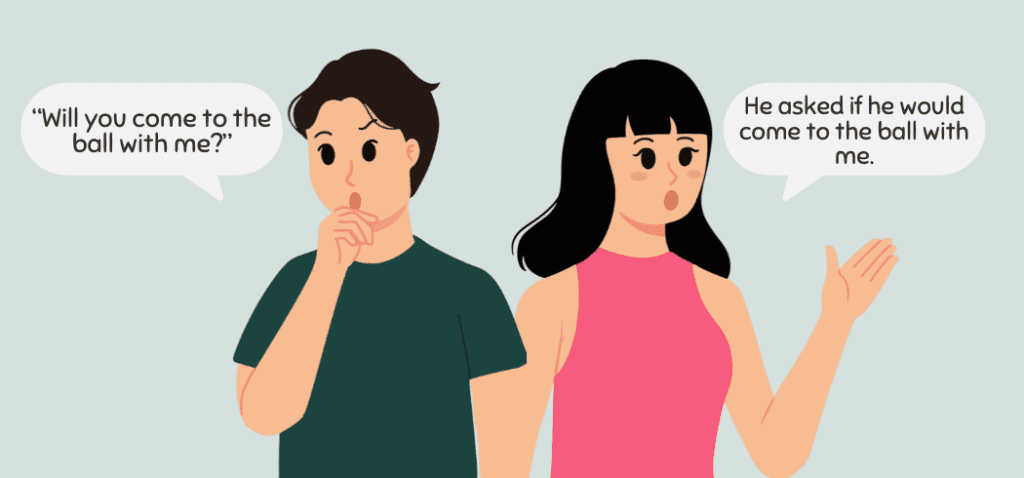

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
| past simple | I bought a car | She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. |
| past continuous | I was walking along the street | She said (that) she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | I haven't seen Julie | She said (that) she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | I had taken English lessons before | She said (that) she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | I'll see you later | She said (that) she would see me later. |
| would* | I would help, but... | She said (that) she would help but... |
| can | I can speak perfect English | She said (that) she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | I could swim when I was four | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
| should* | I should call my mother | She said (that) she should call her mother |
| might* | I might be late | She said (that) she might be late |
| must | I must study at the weekend | She said (that) she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
| Where is the Post Office, please? | She asked me where the Post Office was. |
| What are you doing? | She asked me what I was doing. |
| Who was that fantastic man? | She asked me who that fantastic man had been. |
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
| Do you love me? | He asked me if I loved him. |
| Have you ever been to Mexico? | She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico. |
| Are you living here? | She asked me if I was living here. |
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
| Please don't smoke. | She asked me not to smoke. |
| Could you bring my book tonight? | She asked me to bring her book that night. |
| Could you pass the milk, please? | She asked me to pass the milk. |
| Would you mind coming early tomorrow? | She asked me to come early the next day. |
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don't worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don't smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheet for Class 5 with Answers
We’re talking about Direct and Indirect Worksheet for Class 5. These worksheets help us learn how to talk to others in different ways. They’re super useful for improving grammar skills. Whether you’re a student or a teacher, these worksheets can make learning easier. Thank you!
Answers are given below with each exercise; refer to them to see if your answers are right.
Exercise 1 – Simple Present Tense
Jump ahead to:
Change the following sentences from direct to indirect speech
- Mother said, ”The dinner is ready.”
- Tom said to me, ”I want to become an engineer.”
- She said, ”I love this song.”
- She said, “I enjoy reading books.”
- He said, “I always eat breakfast at 8 AM.”
- They said, “We visit our grandparents every weekend.”
- Mary said, “I like to watch movies on Fridays.”
- Alex said, “I play the guitar in a band.”
- He said to me, ”I live in the city center.”
- She said, ”I don’t want to go.”
- Mother said that the dinner was ready.
- Tom told me that he wanted to become an engineer.
- She said that she loved that song.
- She said that she enjoyed reading books.
- He said that he always ate breakfast at 8 AM.
- They said that they visited their grandparents every weekend.
- Mary said that she liked to watch movies on Fridays.
- Alex said that he played the guitar in a band.
- He told me that he lived in the city center.
- She said that she didn’t want to go.
Exercise 2 – Present Continuous Tense
- Deepa said, ”Aakash is playing with his cousin.”
- Jayesh said to his mother, ”I am feeling an engineer.”
- My mother said, “I am going to take a short nap.”
- She said, ”I am going home.”
- Michael said to Tom, ”My father is helping me in study.”
- Teacher said, ”I am speaking to the Principal.”
- They said, ”We are shopping in Khan Market.”
- He said, ”I am making the map of Pakistan.”
- Ahmed said, ”I am winding the watch.”
- The fishermen said, ”We are catching fish.”
- Deepa said that Aakash was playing with his cousin.
- Jayesh told his mother that he was feeling like an engineer.
- My mother said that she was going to take a short nap.
- She said that she was going home.
- Michael told Tom that my father was helping him in study.
- Teacher said that she was speaking to the principal.
- They said that they were shopping in Khan Market.
- He said that he was making the map of Pakistan.
- Ahmed said that he was winding the watch.
- The fisherman said that they were catching fish.
Exercise 3 – Present Perfect Tense
- He told me, “I have been to London.”
- They said, ”We have planned to visit the museum.”
- Nikita said to me, ”I have finished my school project.”
- She said, ”I have lived in Delhi.”
- She said, ”You have a great sense of humour.”
- The poor man said, ”I have no money.”
- Boss said, ”I have some work.”
- She said, ”I have seen the Taj Mahal.”
- He said, ”I have watched the Avengers movie.”
- Grandma said, ”Dad has made breakfast.”
- He told me that I had been to London.
- They said that they had planned to visit the museum.
- Nikita told me that she had finished her school project.
- She said that she had lived in Delhi.
- She said that You had a great sense of humour.
- The poor man said that he had no money.
- Boss said that he had some work.
- She said that she had seen the Taj Mahal.
- He said that he had watched the Avengers movie.
- Grandma said that Dad had made breakfast.
Exercise 4 – Simple Past Tense
- My father said, ”I arrived in the morning.”
- Azhar said, ”I went to the cinema yesterday.”
- Robin said to me, ”They went to watch the circus last week.”
- They said to him, ”We won the game.”
- The man said, ”I dropped my wallet in the bus.”
- He said, ”I lost my keys yesterday.”
- Jill said to Ted , ” I did not sing well yesterday.”
- He said, ”The bell rang an hour ago.”
- The teacher said to his students, ”Did you finish your exercise?”
- She said, ”I did not say that.”
- My father said that I had arrived in the morning.
- Azhar said that he had gone to the cinema that day.
- Robin told me that they had gone to watch the circus the week before.
- They told him that they had won the game.
- The man said that he had dropped my wallet in the bus.
- He said that he had lost his keys that day.
- Jill told Ted that he had not sung well that day.
- He said that the bell had rung an hour before.
- The teacher asked his students if they had finished their exercise.
- She said that she had not said that.
Exercise 5 – Past Continuous Tense
- They said, ”I was living in Delhi.”
- They said, ”We were enjoying the weather.”
- She said, “I was studying for my exams all night.”
- John said, “They were cooking dinner when the power went out.”
- Sarah said, “I was watching a movie when you called.”
- They shouted, “We were waiting for the bus for over an hour!”
- The children exclaimed, “We were playing in the park when it started raining.”
- He mentioned, “I was working on my project until late last night.”
- She asked, “What were you doing at the time of the accident?”
- Tom said to Mary, “We were traveling around Europe during the summer.”
- She said that she had been living in Delhi.
- They said that they had been enjoying the weather.
- She said that she had been studying for her exams all night.
- John said that they had been cooking dinner when the power went out.
- Sarah said that she had been watching a movie when I called.
- They complained that they had been waiting for the bus for over an hour.
- The children said that they had been playing in the park when it started raining.
- He mentioned that he had been working on his project until late last night.
- She asked what I had been doing at the time of the accident.
- Tom told Mary that they had been traveling around Europe during the summer.
Exercise 6 – Simple Future Tense
- He said, “ I will study the book.”
- She said, ”I will buy a computer.”
- He promised, ”I will always love you.”
- They exclaimed, “We will celebrate the success with a party!”
- Jane said, “I will call you as soon as I reach home.”
- He said, ”I will see you later.”
- He said, ” I shall be in Paris on Monday.”
- She said, “I will visit my grandparents next weekend.”
- The teacher announced, “We will have a quiz on Friday.”
- He promised, “I will finish the project by tomorrow.”
- He said that he would study the book.
- She said that she would buy a computer.
- He promised that he would always love her.
- They exclaimed that they would celebrate the success with a party.
- Jane said that he would call you as soon as she reached home.
- He said that he would see me later.
- He said that he should be in Paris on Monday.
- She said that she would visit her grandparents the following weekend.
- The teacher announced that they would have a quiz on Friday.
- He promised that he would finish the project by the next day.
Exercise 7 – Rewrite the Sentences from Direct to Indirect Speech
Read the sentences given below and rewrite them from direct to indirect speech
- Father said, “I am going to the park for a walk.”
- Praveen says, “I play football every evening.”
- Rohan said, ”There is a dog inside the house.”
- She said, ”I don’t know.”
- They said , ”They have taken exercise.”
- She said, ”I am waiting for Michael.”
- He said, ”I was walking along the street.”
- He said, “I bought a car.”
- Mary said, ”I will study.”
- She said, “My mother is not very well.”
- Father said that he was going to the park for a walk.
- Praveen said that he played football every evening.
- Rohan said that there was a dog inside the house.
- She said that she didn’t know.
- They said that they had taken exercise .
- She said that she was waiting for Michael.
- He said that he had been walking along the street.
- He said that he had bought a car.
- Mary said that he would study.
- She said that my mother was not very well.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Simple English Grammar

- Direct Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech Online Exercise for Grade 5
Change the following direct speech sentences into indirect speech sentences. This work out will make you understand the concept of the language more efficiently:
- Usha Madam said to us, “We will go to picnic tomorrow”.
- Pappu said, “I am watching the cricket match”.
- Billu said, “I am munching a softy”.
- Tannu said to me, “I am very busy now”.
- The guests said, “Our room is large and airy”.
- Aditi said, “I can solve this sum”.
- Piyush said to his teacher, “May I go outside the classroom to meet my father?”
- Kamal said, “I am writing my notes’’.
- Sanju Said, “I shall sit by the river bank”.
- The children came home and said, “We are very hungry”.
- Chitra said to her son, “I am preparing dosas for you”.
- The cop uncle said, “The thief has been arrested yesterday”.
- Mr. Gupta said to the banker, “I will repay the loan within one year”.
- Martha said to me, “I shall meet you tomorrow for dinner”.
- Weeping Charu said, “I have lost the precious ring in the hall”.
- Usha Madam said to us that we would go to picnic the next day.
- Pappu said that he was watching the cricket match.
- Billu said that he was munching a softy.
- Tannu said to me that he was very busy then. [Note: ‘Now’ changes to ‘Then’ in the indirect speech.]
- The guests said that their room was large and airy.
- Aditi said that she could solve that sum.
- Piyush asked to his teacher if he might go outside the classroom to meet his father.
- Kamal said that he was writing his notes.
- Sanju Said that he should sit by the river bank.
- The children came home and said that they were very hungry.
- Chitra said to her son that she was preparing dosas for him.
- The cop uncle informed that the thief had been arrested the previous day.
- Mr. Gupta said to the banker that he would repay the loan within one year.
- Martha said to me that she should meet me the next day for dinner.
- Weeping Charu said that she had lost the precious ring in the hall
Direct and Indirect Speech Online Exercise for Class 4
Nouns: instruction.
Related posts
Direct and indirect speech online exercise for class 6, direct and indirect speech, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Reported Questions
Reported speech, 10.2k plays, quotation marks in dialogue, 3rd - 5th , quotation marks, offering help, indirect questions, professional development .

DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH
10 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Direct Speech is..
the reporting of speech by using similar words to the speaker.
the reporting of speech by rephrasing what the speaker said.
the reporting of speech by repeating the exact words of the speaker.
the reporting of speech at the exact time it was said.
Indirect speech is also known as what?
Repeated speech
Repeated statements
Reported speech
Reported statements
Speech marks are needed for what?
Direct Speech
Indirect Speech
My mom told me, "Clean your room now."
My mom told me that clean my room now.
My mom told me to clean my room then.
My mom told me if clean my room then.
The man asked the clerk, "Do you sell teapot in this store?"
The man asked the clerk if he sold teapot in that store.
The man asked the clerk that he sold teapot in that store.
No correct answer
Which indirect speech statement reports this: Lana said, "I am leaving New York City."
Lana said that she is leaving New York City.
Lana will be leaving New York City.
Lana said that she was leaving New York City.
X : "What does she say to you?"
Y : She told me ......
She needed help
She needs help
She had needed help
She has needed help
I asked, "Mom, can I have some ice-cream?"
I asked mom to have some ice-cream.
I asks whether mom can have some ice-cream.
I asked mom whether I could have some ice-cream.
I asks mom whether I can have some ice-cream.
Prince Harry said, "I bought a beautiful ring for Meghan yesterday."
Prince Harry said that he had bought a beautiful ring for Meghan yesterday.
Prince Harry said that he had bought a beautiful ring for Meghan the previous day.
Prince Harry said that he bought a beautiful ring for Meghan the previous day.
Prince Harry said he had bought a beautiful ring for Meghan yesterday.
Change to indirect speech. Eric said, "I eat a bowl of salad."
Eric said that he eats a bowl of salad.
Eric said that he ate a bowl of salad.
Eric said he ate a bowl of salad.
Eric said that he eat a bowl of salad.
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
- Kindergarten
- Greater Than Less Than
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Place Value
- Subtraction
- Punctuation
- 1st Grade Reading
- 2nd Grade Reading
- 3rd Grade Reading
- Cursive Writing
- Alphabet Coloring
- Animals Coloring
- Birthday Coloring
- Boys Coloring
- Buildings Coloring
- Cartoons Coloring
- Christmas Coloring
- Country Flag Coloring
- Country Map Coloring
- Disney Coloring
- Fantasy Coloring
- Food Coloring
- Girls Coloring
- Holidays Coloring
- Music Coloring
- Nature Coloring
- New Year Coloring
- People Coloring
- Religious Coloring
- Sports Coloring
- Toys Coloring
- Transportation Coloring
- US Sports Team Coloring
- Valentine Day Coloring
Reported Speech For Grade 5 With Answer
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Reported Speech For Grade 5 With Answer .
Some of the worksheets for this concept are Reported statements mixed exercise, Direct indirect speech, Direct and indirect speech, Reported speech work, Reported speech rs 1, Reported speech ejercicios, Grammar challenge, Reported speech.
Found worksheet you are looking for? To download/print, click on pop-out icon or print icon to worksheet to print or download. Worksheet will open in a new window. You can & download or print using the browser document reader options.
1. Reported Statements Mixed Exercise
2. direct . indirect speech, 3. direct and indirect speech, 4. reported speech worksheet, 5. reported speech rs 1 -, 6. reported speech ejercicios -, 7. grammar challenge, 8. reported speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Yakub Susanto
Change the sentences.
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF

The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
5th Class English Direct and Indirect Speech Question Bank
Done direct and indirect speech total questions - 30.

| Select the correct options that show the change from the direct to the indirect speech. |
A) Minu said, "Her house was nearby." done clear
B) Minu said that my house is nearby. done clear
C) Minu said that her house was nearby. done clear
D) Minu said, "that her house was nearby." done clear
A) Raju said that "he has many toys." done clear
B) Raju said that he had many toys. done clear
C) Raju said that I have many toys. done clear
D) Raju said that he has many toys. done clear
A) Vinni said that she will go to see my grandma tomorrow. done clear
B) Vinni said, "that she will go to see my grandma tomorrow." done clear
C) Vinni said that I will go to see my grandma the next day. done clear
D) Vinni said that she would go to see her grandma the next day. done clear
A) Ali said that our English teacher was new. done clear
B) Ali said that their English teacher was new. done clear
C) Ali said, "that our English teacher is new." done clear
D) Ali said that our English teacher is new. done clear
A) Hari said that we have a class today. done clear
B) Hari said, "that they have a class today." done clear
C) Hari said that they had a class that day. done clear
D) Hari said that they have a class this day. done clear
A) Madhu said that they were learning these grammar rules. done clear
B) Madhu said that they were learning those grammar rules. done clear
C) Madhu said that they are learning those grammar rules. done clear
D) Madhu said, "that they are learning those grammar rules." done clear
A) Vani said that she was painting now. done clear
B) Vani said, "that I am painting the picture now." done clear
C) Vani said that, "I am painting the picture now." done clear
D) Vani said that she was painting the picture then. done clear
A) Mother said that, "he buys books." done clear
B) Mother said that he buys books. done clear
C) Mother said that I bought books. done clear
D) Mother said that he bought books. done clear
A) The boy said that we'll take your book tomorrow. done clear
B) The boy said that, "they will take their book the next day." done clear
C) The boy said that they would take her book tomorrow. done clear
D) The boy said that they would take her book the next day. done clear
A) Anu says, "that we lived in the heart of the city. done clear
B) Anu says that they had lived in the heart of the city. done clear
C) Anu says that they live in the heart of the city. done clear
D) Anu said that they lived in the heart of the city. done clear
| Select the correct options that show the change from the Indirect to the Direct speech. |
A) He said, "Your house is nearby." done clear
B) He said to the teacher that "Your house is nearby." done clear
C) He said, "My house was nearby." done clear
D) He said, "My house is nearby." done clear
A) Raj Kaur said, "We had a singing clock at home." done clear
B) Raj Kaur said, "They had a singing clock at home." done clear
C) Raj Kaur said, "We have a singing clock at home." done clear
D) Raj Kaur said, "That we have a singing clock at home." done clear
A) "I am as wise as his brother," said Ravi. done clear
B) "I am as wise as my brother," said Ravi. done clear
C) "He is as wise as his brother," said Ravi. done clear
D) "He was as wise as your brother," said Ravi. done clear
A) Ashok said, "They'll go to the film tomorrow." done clear
B) Ashok said, "We would go to the film tomorrow." done clear
C) Ashok said, "We will go to the film the next day." done clear
D) Ashok said, "We will go to the film tomorrow." done clear
A) Vinay said, "Our library had many books." done clear
B) Vinay said, "Our library has many books." done clear
C) Vinay said, "My library had many books." done clear
D) Vinay said, "Their library has many books." done clear
A) The newsreader said, "The President was visiting my native place today." done clear
B) The newsreader said, "The President was visiting his native place today." done clear
C) The newsreader said, "The President is visiting his native place today." done clear
D) The newsreader said, "The President is visiting his native place that day." done clear
A) Ram's mother said, "She'll take him to the zoo the next day." done clear
B) Ram's mother said, "that she'll take you to the zoo tomorrow." done clear
C) Ram's mother said, "I would take you to the zoo tomorrow." done clear
D) Ram's mother told Ram, "I'll take you to the zoo tomorrow." done clear
A) Mohit said, "They are going to Mumbai by air." done clear
B) Mohit said, "We are going to Mumbai by air." done clear
C) Mohit said, "We were going to Mumbai by air." done clear
D) Mohit said, "We went to Mumbai by air." done clear
A) Payal said, "I live in a village." done clear
B) Payal said me, "I lived in a village." done clear
C) Payal said to me, "She lived in a village." done clear
D) Payal told to me, "I live in a village." done clear
A) Ram said, "I'll present a gift to her." done clear
B) Ram said, "He'll present a gift to her." done clear
C) Ram said, "I will present a gift to you." done clear
D) Ram said, "I would present a gift to her." done clear
| Select the correct options that show the change from the Direct speech to the reported speech. |
A) Vinay said he and Ramu gone to the beach yesterday. done clear
B) Vinay said that he and Ramu had gone to the beach the day before. done clear
C) Ramu and he went to the beach the day before he said. done clear
D) Vinay said that he and Ramu goes to the beach the day before. done clear
A) Akhil said that they would go swimming the next day. done clear
B) Akhil said that they would go swimming the day before. done clear
C) they had gone for swimming said Akhil. done clear
D) Akhil said that they went swimming the day before. done clear
A) Divya says her mother worked as a pharmacist. done clear
B) Divya said that her mother is working as a pharmacist. done clear
C) Divya said that her mother worked as a pharmacist. done clear
D) Divya said that her mother works as a pharmacist. done clear
A) Amith told that he was having dinner when his father came home. done clear
B) Amith said that he has been having dinner when his father came home. done clear
C) Amith said that he had dinner when his father came home. done clear
D) Amith said that he had been having dinner when his father came home. done clear
A) Jim said a snake has almost bitten him in the forest the day before. done clear
B) Jim said that a snake had almost bitten him in the forest the day before. done clear
C) A snake almost bit me in the forest the next day said Jim. done clear
D) Jim says a snake almost bit him in the forest the day before. done clear
A) Maryam said that their class would start the following week. done clear
B) Maryam said that her class would start the following week. done clear
C) Maryam said that their class will have started the following week. done clear
D) Maryam said that their class would start the week before. done clear
A) Rajesh said that they cannot enter the museum without a pass. done clear
B) Rajesh said that he could not enter the museum without a pass. done clear
C) Rajesh said that they could not enter the museum without a pass. done clear
D) Rajesh said that they will not enter the museum without a pass. done clear
A) John asked what Kiran was doing. done clear
B) John said what Kiran was doing. done clear
C) John asked what Kiran had been doing. done clear
D) John asked what Kiran has been doing. done clear
A) The teacher said to the boy where he was that afternoon. done clear
B) The teacher asked the boy as to where he had been that afternoon. done clear
C) The teacher asked the boy where he has been that afternoon. done clear
D) Where have you been asked the teacher to the boy. done clear
A) Kavya told her son to close the windows as it was raining. done clear
B) Kavya said to her son to close the windows as it had been raining. done clear
C) Kavya told her son to close the windows as it had rained. done clear
D) Kavya told her son to close the windows as it is raining. done clear
Download Complete Course
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Who is Yusuf Dikec, the Turkish shooter who went viral at the 2024 Olympics?
Turkey’s Savval Ilayda Tarhan, left, and Yususf Dikec compete in the 10m air pistol mixed team gold medal event at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Tuesday, July 30, 2024, in Chateauroux, France. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Turkey’s Savval Ilayda Tarhan, left, and Yususf Dikec pose for a photograph after winning the silver medal in the 10m air pistol mixed team event at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Tuesday, July 30, 2024, in Chateauroux, France. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Turkey’s Sevval Ilayda Tarhan, left, and teammate Yusuf Dikec prepare to compete in the 10m air pistol mixed team qualification round at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Monday, July 29, 2024, in Chateauroux, France. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
L to R on the podium, Turkey’s Savval Ilayda Tarhan and Yususf Dikec, Serbia’s Zorana Arunovic and Damir Mikec, and India’s Manu Bhaker and Sarabjot Singh pose for a photograph after the medal ceremony of the 10m air pistol mixed team event at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Tuesday, July 30, 2024, in Chateauroux, France. Serbia won the gold medal, while Turkey and India won the silver and the bronze respectively. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
R to L, India’s Sarabjot Singh uses his phone to take a selfie with teammate Manu Bhaker, Serbia’s Damir Mikec and Zorana Arunovic, and Turkey’s Yususf Dikec and Savval Ilayda Tarhan after the medal ceremony of the 10m air pistol mixed team event at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Tuesday, July 30, 2024, in Chateauroux, France. Serbia won the gold medal, while Turkey and India won the silver and the bronze respectively. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
- Copy Link copied
Want more Olympics? Sign up for our daily Postcards from Paris newsletter.
CHATEAUROUX, France (AP) — Turkish pistol shooter Yusuf Dikec has gone viral on social media for his seemingly casual attitude while shooting his way to a silver medal at the 2024 Olympics.
The most-shared images show Dikec shooting in a T-shirt with one hand in his pocket, a seemingly standard pair of glasses and an impassive look on his face. He’s been likened to a regular guy competing at the Olympics, or even a hitman.
The 51-year-old is no newcomer, though. He’s competed at every Summer Olympics since 2008.
Some memes contrast Dikec with his Serbian opponent Damir Mikec, who was wearing a blinder over one eye, a lens over the other and a large pair of ear defenders.
Did Dikec win a medal?
He did, and it made history.
Dikec and Sevval Ilayda Tarhan won the silver medal in mixed team 10-meter air pistol shooting Tuesday. It was Turkey’s first-ever medal in Olympic shooting.
Mikec and Zorana Arunovic won gold for Serbia. The bronze went to India’s Manu Bhaker and Sarabjot Singh.
Unlike Dikec, his teammate Tarhan was competing with large ear defenders and a visor, as well as braids in the red and white colors of the Turkish flag. She was shooting with one hand in her pocket, too.
Dikec was 13th in his individual event and is now done at the Paris Olympics. He’s looking ahead to the next Games in 2028, though. “I hope next in Los Angeles (for) a gold medal,” he said Tuesday.
What does he think about going viral?
Dikec seems to be embracing the trend, reposting a video compilation of Turkish-language memes about him to his Instagram page.
The shooting events were held around three hours’ drive south of Paris. Dikec and Tarhan made the journey to the French capital Wednesday, where they were greeted with cheers at the Champions Park , an open-air venue where medalists celebrate with fans.
Why didn’t Dikec wear more gear?
Shooters have some freedom about how they dress for competition.
Catch up on the latest from Day 11 of the 2024 Paris Olympics:
- Boxing: Imane Khelif, the Algerian boxer who has faced misconceptions about her gender, returns to the ring.
- Basketball: Lebron James, seeking his fourth Olympic medal, will lead the U.S. men’s basketball team in a quarterfinal game against Brazil.
- Keep up : Follow along with our Olympics medal tracker and list of winners. Check out the Olympic schedule of events.
Many shooters at the Olympic range in Chateauroux, central France, choose to wear visors to reduce the glare of the lights or so-called blinders over one eye to get a better focus for the eye which is looking down the sights.
It’s not quite true that Dikec wasn’t wearing any shooting gear. He had yellow earplugs to block out distractions while he shot in the final. They just weren’t visible from the angle of the image which went viral.
Just like Dikec, Chinese rifle shooter Liu Yukun won a gold medal Thursday wearing earplugs but no blinder or visor.
Have other shooters gone viral at the 2024 Olympics?
Yes, South Korean pistol shooter Kim Yeji’s confident demeanor and dramatic stance have brought praise on social media for her “main character energy”.
“The Olympic #shootingsport stars we didn’t know we needed,” the official Olympics account on X posted Thursday with pictures of Kim and Dikec.
Kim won silver in the women’s 10-meter air pistol event Sunday behind her South Korean teammate Oh Ye Jin. Kim and Oh are roommates and Kim said she was pleased Oh got the gold because she sees her like a “youngest sibling”.
Kim is set to compete again Friday in qualification for the women’s 25-meter pistol event.
AP Summer Olympics: https://apnews.com/hub/2024-paris-olympic-games

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
1. The Simple Present becomes the Simple Past; as: Direct: Teacher said, "Kitty works very hard.". Indirect: Teacher said that Kitty worked very hard. Rule 3: (Exception to Rule 2.) If the reported speech contains some universal or habitual fact, then the Simple Present in the Reported Speech is not changed into the corresponding Simple ...
Indirect Speech - Ravi said that all had been looking at the magician. Direct Speech - Jimmy said, "All the boys were shouting.". Indirect Speech - Jimmy said that all the boys had been shouting. 7. Shall is changed into should; will is changed into would. Direct Speech - Radha said, "I will open the door."
Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later. In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb 'will' being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb 'will' and the reporting verb 'ask' are both written in the past tense. So, 'will' becomes 'would' and 'ask' becomes 'asked'.
Speech: Direct And Indirect | English Grammar & Composition Grade 5 | PeriwinkleWatch our other videos:English Stories for Kids: https://www.youtube.com/play...
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I'll break each down for you. A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example: Kryz said, "These are all my necklaces.". Indirect speech changes the original speaker's words. For example: Kryz said those were all ...
Grade 5 Language Study, Semester 2 1 | P a g e Direct and Indirect (Reported) Speech Revision Activity 1: The following sentences are written in Direct Speech. Change them to Indirect Speech. 1. The boy said, "I have to learn to sail." 2. The teacher said, "You still have to do your work." 3.
English Grammar Reported Speech For Class 5- Download Free PDF With Solutions. To speak and communicate in English, it is highly important to learn the language. Speaking can be done in many ways, like direct speech, indirect speech, active voice, or passive voice. Class 5 English Chapter 7 is about reported speech, which is a part of direct ...
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Learn about reported speech, how it can be used, and how it differs from direct speech. Reported speech relays the words of others without direct quotation. Recently Viewed and Downloaded › Recently Viewed › Recently Downloaded . ... Grade 5 . 11 - 14 years old . Grade 6 - Grade 7 . 14+ years old . High School
English Grammar Class 5Reported SpeechToday we will study. n exciting topic "Reported speech". Reported speech refers to how we ha. e interpreted the words of the speaker. In simple terms, Reported speech refers to reporting the speech of the speaker i.e. whether conveying directly the words of the speaker or indirectly conveying.
Reported speech Reported speech. chkotro Member for 3 years 8 months Age: 14+ Level: GRADE 5. Language: English (en) ID: 595977. 16/12/2020. Country code: GR. Country: Greece. School subject: English language (1061957) Main content: Grammar (2013237) From worksheet author: LANGUAGE PRACTICE. Other contents: DIRECT SPEECH ...
In this video, you will learn about what reported speech means, about the types pf specch [ direct and indirect speech], and about the changes made when cha...
1 'I work in a bank.' ⇒ He said that he in a bank. 2 'I am working today.' ⇒ She told us she that day. 3 'I've been ill for a couple of weeks.' ⇒ He told me he for a couple of weeks. 4 'I was at the doctor all morning.' ⇒ She told me that she at the doctor all morning. 5 'I'll lend you the money.' ⇒ He told me he me the money.
Shaken not stirred.". "The power of Christ compels you!". "Remember: What happens in Vegas stays in Vegas.". 3. Reported Speech Cards. This is another fun speaking activity that will help students learn reported speech. Hand out slips of paper to students. One side of the paper is a direct speech sentence. One student reads out the ...
Exercise 4 - Simple Past Tense. Exercise 5 - Past Continuous Tense. Exercise 6 - Simple Future Tense. Exercise 7 - Rewrite the Sentences from Direct to Indirect Speech. Change the following sentences from direct to indirect speech. Mother said, "The dinner is ready.". Tom said to me, "I want to become an engineer.". She said ...
Reported Speech Reported Speech. anikajaiswal06 Member for 2 years 7 months ... Age: 10-12. Level: Grade 5-6. Language: English (en) ID: 1711132. 06/12/2021. Country code: IN. Country: India. School subject: English language (1061957) Main content: Reported speech (2012149) From worksheet author: It's very easy. Loading ad... Share / Print ...
Reported speech. SARAEM Member for 4 years 6 months Age: 10-12. Level: Grade 5. Language: English (en) ID: 454227. 28/10/2020. Country code: PE. Country: Peru. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Reported speech (2013113) From worksheet author: Choose the best answer. ...
Direct and Indirect Speech Online Exercise for Grade 5. by Admin July 17, 2022 0 3056. Share 4. Change the following direct speech sentences into indirect speech sentences. This work out will make you understand the concept of the language more efficiently: Usha Madam said to us, "We will go to picnic tomorrow".
30 seconds. 1 pt. Direct Speech is.. the reporting of speech by using similar words to the speaker. the reporting of speech by rephrasing what the speaker said. the reporting of speech by repeating the exact words of the speaker. the reporting of speech at the exact time it was said. 2. Multiple Choice.
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Reported Speech For Grade 5 With Answer. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Reported statements mixed exercise, Direct indirect speech, Direct and indirect speech, Reported speech work, Reported speech rs 1, Reported speech ejercicios, Grammar challenge, Reported speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech. Yakub Susanto. Member for 2 years 11 months Age: 9-15. Level: Grade 5. Language: English (en) ID: 2169802. 08/10/2022. Country code: ID. Country: Indonesia. School subject: English language (1061957) Main content: Reported speech (2012149) From worksheet author: Change the sentences. ...
Select the correct options that show the change from the Direct speech to the reported speech. "Close the windows as it is raining," Kavya told her son. A) Kavya told her son to close the windows as it was raining. done clear. B) Kavya said to her son to close the windows as it had been raining. ...
5 of 5 | . R to L, India's Sarabjot Singh uses his phone to take a selfie with teammate Manu Bhaker, Serbia's Damir Mikec and Zorana Arunovic, and Turkey's Yususf Dikec and Savval Ilayda Tarhan after the medal ceremony of the 10m air pistol mixed team event at the 2024 Summer Olympics, Tuesday, July 30, 2024, in Chateauroux, France.