

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.
It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'

Is homework a necessary evil?
After decades of debate, researchers are still sorting out the truth about homework’s pros and cons. One point they can agree on: Quality assignments matter.
By Kirsten Weir
March 2016, Vol 47, No. 3
Print version: page 36

- Schools and Classrooms
Homework battles have raged for decades. For as long as kids have been whining about doing their homework, parents and education reformers have complained that homework's benefits are dubious. Meanwhile many teachers argue that take-home lessons are key to helping students learn. Now, as schools are shifting to the new (and hotly debated) Common Core curriculum standards, educators, administrators and researchers are turning a fresh eye toward the question of homework's value.
But when it comes to deciphering the research literature on the subject, homework is anything but an open book.
The 10-minute rule
In many ways, homework seems like common sense. Spend more time practicing multiplication or studying Spanish vocabulary and you should get better at math or Spanish. But it may not be that simple.
Homework can indeed produce academic benefits, such as increased understanding and retention of the material, says Duke University social psychologist Harris Cooper, PhD, one of the nation's leading homework researchers. But not all students benefit. In a review of studies published from 1987 to 2003, Cooper and his colleagues found that homework was linked to better test scores in high school and, to a lesser degree, in middle school. Yet they found only faint evidence that homework provided academic benefit in elementary school ( Review of Educational Research , 2006).
Then again, test scores aren't everything. Homework proponents also cite the nonacademic advantages it might confer, such as the development of personal responsibility, good study habits and time-management skills. But as to hard evidence of those benefits, "the jury is still out," says Mollie Galloway, PhD, associate professor of educational leadership at Lewis & Clark College in Portland, Oregon. "I think there's a focus on assigning homework because [teachers] think it has these positive outcomes for study skills and habits. But we don't know for sure that's the case."
Even when homework is helpful, there can be too much of a good thing. "There is a limit to how much kids can benefit from home study," Cooper says. He agrees with an oft-cited rule of thumb that students should do no more than 10 minutes a night per grade level — from about 10 minutes in first grade up to a maximum of about two hours in high school. Both the National Education Association and National Parent Teacher Association support that limit.
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
In a recent study of Spanish students, Rubén Fernández-Alonso, PhD, and colleagues found that students who were regularly assigned math and science homework scored higher on standardized tests. But when kids reported having more than 90 to 100 minutes of homework per day, scores declined ( Journal of Educational Psychology , 2015).
"At all grade levels, doing other things after school can have positive effects," Cooper says. "To the extent that homework denies access to other leisure and community activities, it's not serving the child's best interest."
Children of all ages need down time in order to thrive, says Denise Pope, PhD, a professor of education at Stanford University and a co-founder of Challenge Success, a program that partners with secondary schools to implement policies that improve students' academic engagement and well-being.
"Little kids and big kids need unstructured time for play each day," she says. Certainly, time for physical activity is important for kids' health and well-being. But even time spent on social media can help give busy kids' brains a break, she says.
All over the map
But are teachers sticking to the 10-minute rule? Studies attempting to quantify time spent on homework are all over the map, in part because of wide variations in methodology, Pope says.
A 2014 report by the Brookings Institution examined the question of homework, comparing data from a variety of sources. That report cited findings from a 2012 survey of first-year college students in which 38.4 percent reported spending six hours or more per week on homework during their last year of high school. That was down from 49.5 percent in 1986 ( The Brown Center Report on American Education , 2014).
The Brookings report also explored survey data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress, which asked 9-, 13- and 17-year-old students how much homework they'd done the previous night. They found that between 1984 and 2012, there was a slight increase in homework for 9-year-olds, but homework amounts for 13- and 17-year-olds stayed roughly the same, or even decreased slightly.
Yet other evidence suggests that some kids might be taking home much more work than they can handle. Robert Pressman, PhD, and colleagues recently investigated the 10-minute rule among more than 1,100 students, and found that elementary-school kids were receiving up to three times as much homework as recommended. As homework load increased, so did family stress, the researchers found ( American Journal of Family Therapy , 2015).
Many high school students also seem to be exceeding the recommended amounts of homework. Pope and Galloway recently surveyed more than 4,300 students from 10 high-achieving high schools. Students reported bringing home an average of just over three hours of homework nightly ( Journal of Experiential Education , 2013).
On the positive side, students who spent more time on homework in that study did report being more behaviorally engaged in school — for instance, giving more effort and paying more attention in class, Galloway says. But they were not more invested in the homework itself. They also reported greater academic stress and less time to balance family, friends and extracurricular activities. They experienced more physical health problems as well, such as headaches, stomach troubles and sleep deprivation. "Three hours per night is too much," Galloway says.
In the high-achieving schools Pope and Galloway studied, more than 90 percent of the students go on to college. There's often intense pressure to succeed academically, from both parents and peers. On top of that, kids in these communities are often overloaded with extracurricular activities, including sports and clubs. "They're very busy," Pope says. "Some kids have up to 40 hours a week — a full-time job's worth — of extracurricular activities." And homework is yet one more commitment on top of all the others.
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up."
Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well. Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, Internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs, says Lea Theodore, PhD, a professor of school psychology at the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia. They are less likely to have computers or a quiet place to do homework in peace.
"Homework can highlight those inequities," she says.
Quantity vs. quality
One point researchers agree on is that for all students, homework quality matters. But too many kids are feeling a lack of engagement with their take-home assignments, many experts say. In Pope and Galloway's research, only 20 percent to 30 percent of students said they felt their homework was useful or meaningful.
"Students are assigned a lot of busywork. They're naming it as a primary stressor, but they don't feel it's supporting their learning," Galloway says.
"Homework that's busywork is not good for anyone," Cooper agrees. Still, he says, different subjects call for different kinds of assignments. "Things like vocabulary and spelling are learned through practice. Other kinds of courses require more integration of material and drawing on different skills."
But critics say those skills can be developed with many fewer hours of homework each week. Why assign 50 math problems, Pope asks, when 10 would be just as constructive? One Advanced Placement biology teacher she worked with through Challenge Success experimented with cutting his homework assignments by a third, and then by half. "Test scores didn't go down," she says. "You can have a rigorous course and not have a crazy homework load."
Still, changing the culture of homework won't be easy. Teachers-to-be get little instruction in homework during their training, Pope says. And despite some vocal parents arguing that kids bring home too much homework, many others get nervous if they think their child doesn't have enough. "Teachers feel pressured to give homework because parents expect it to come home," says Galloway. "When it doesn't, there's this idea that the school might not be doing its job."
Galloway argues teachers and school administrators need to set clear goals when it comes to homework — and parents and students should be in on the discussion, too. "It should be a broader conversation within the community, asking what's the purpose of homework? Why are we giving it? Who is it serving? Who is it not serving?"
Until schools and communities agree to take a hard look at those questions, those backpacks full of take-home assignments will probably keep stirring up more feelings than facts.
Further reading
- Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987-2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62. doi: 10.3102/00346543076001001
- Galloway, M., Connor, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81 (4), 490–510. doi: 10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
- Pope, D., Brown, M., & Miles, S. (2015). Overloaded and underprepared: Strategies for stronger schools and healthy, successful kids . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Letters to the Editor
- Send us a letter
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School’s In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Bu alum chompon boonnak runs mahaniyom, one of greater boston’s hottest thai restaurants, champion of indie films, china scholar merle goldman dies, cfa alum jonathan knight is head of games for the new york times, is our democracy at risk americans think so. bu experts talk about why—and the way forward, a commitment to early childhood education, reading list: alum bonnie hammer publishes 15 lies women are told at work —plus fiction, poetry, and short stories, one good deed: jason hurdich (cas’97) is uniting the deaf community, one cup at a time, space force general b. chance saltzman is a bu alum, using glamour for good: alum’s nonprofit organization brings clothes and beauty products to those in need, gallery: shea justice (cfa’93), oscar-nominated actor hong chau (com’01) stars in new action-comedy the instigators, alum’s new book recounts the battle for inclusion in boy scouts, feedback: readers weigh in on a bu superager, the passing of otto lerbinger, and alum’s book fat church, law alum steven m. wise, who fought for animal rights, dies, pups wearing custom-designed veterinary collars get star treatment in alum’s new coffee-table book, opening doors: ellice patterson (questrom’17), an alum’s new memoir recounts six decades of beatlemania, bu alum in paris keeping olympians’ minds sharp and healthy, erika jordan departs bu alumni engagement office to return to california.
- Second Opinion
- Research & Innovation
- Patients & Families
- Health Professionals
- Recently Visited
- Segunda opinión
- Refer a patient
- MyChart Login
Healthier, Happy Lives Blog
Sort articles by..., sort by category.
- Celebrating Volunteers
- Community Outreach
- Construction Updates
- Family-Centered Care
- Healthy Eating
- Heart Center
- Interesting Things
- Mental Health
- Patient Stories
- Research and Innovation
- Safety Tips
- Sustainability
- World-Class Care
About Our Blog
- Back-to-School
- Pediatric Technology
Latest Posts
- Pediatrician Insights on Childhood Sleep Problems
- Stanford Children’s Eases Needle Jabs With the Buddy Guard Device
- Young Adult Turns Short Bowel Into Motivator for Full Life
- Menstruation, Birth Control, Mental Health Top Team USA Female Athletes’ Research Agenda
- Two Sisters Return to the Bay Area to Work Together in the Johnson Center for Pregnancy and Newborn Services

Health Hazards of Homework
March 18, 2014 | Julie Greicius Pediatrics .

A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework “experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.”
Those health problems ranged from stress, headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems, to psycho-social effects like dropping activities, not seeing friends or family, and not pursuing hobbies they enjoy.
In the Stanford Report story about the research, Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Experimental Education , says, “Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good.”
The study was based on survey data from a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in California communities in which median household income exceeded $90,000. Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night.
“It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today’s workplace,” says Neville Golden, MD , chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. “This landmark study shows that excessive homework is counterproductive, leading to sleep deprivation, school stress and other health problems. Parents can best support their children in these demanding academic environments by advocating for them through direct communication with teachers and school administrators about homework load.”
Related Posts

Top-ranked group group in Los Gatos, Calif., is now a part of one of the…

The Stanford Medicine Children’s Health network continues to grow with our newest addition, Town and…
- Julie Greicius
- more by this author...
Connect with us:
Download our App:
ABOUT STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Leadership Team
- Vision, Mission & Values
- The Stanford Advantage
- Government and Community Relations
LUCILE PACKARD FOUNDATION FOR CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Get Involved
- Volunteering Services
- Auxiliaries & Affiliates
- Our Hospital
- Send a Greeting Card
- New Hospital
- Refer a Patient
- Pay Your Bill

Also Find Us on:
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Code of Conduct
- Price Transparency
- Stanford School of Medicine
- Stanford Health Care
- Stanford University
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is Therapy Homework?
Astrakan Images / Getty Images
Types of Therapy That Involve Homework
If you’ve recently started going to therapy , you may find yourself being assigned therapy homework. You may wonder what exactly it entails and what purpose it serves. Therapy homework comprises tasks or assignments that your therapist asks you to complete between sessions, says Nicole Erkfitz , DSW, LCSW, a licensed clinical social worker and executive director at AMFM Healthcare, Virginia.
Homework can be given in any form of therapy, and it may come as a worksheet, a task to complete, or a thought/piece of knowledge you are requested to keep with you throughout the week, Dr. Erkfitz explains.
This article explores the role of homework in certain forms of therapy, the benefits therapy homework can offer, and some tips to help you comply with your homework assignments.
Therapy homework can be assigned as part of any type of therapy. However, some therapists and forms of therapy may utilize it more than others.
For instance, a 2019-study notes that therapy homework is an integral part of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) . According to Dr. Erkfitz, therapy homework is built into the protocol and framework of CBT, as well as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) , which is a sub-type of CBT.
Therefore, if you’re seeing a therapist who practices CBT or DBT, chances are you’ll regularly have homework to do.
On the other hand, an example of a type of therapy that doesn’t generally involve homework is eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy. EMDR is a type of therapy that generally relies on the relationship between the therapist and client during sessions and is a modality that specifically doesn’t rely on homework, says Dr. Erkfitz.
However, she explains that if the client is feeling rejuvenated and well after their processing session, for instance, their therapist may ask them to write down a list of times that their positive cognition came up for them over the next week.
"Regardless of the type of therapy, the best kind of homework is when you don’t even realize you were assigned homework," says Erkfitz.
Benefits of Therapy Homework
Below, Dr. Erkfitz explains the benefits of therapy homework.
It Helps Your Therapist Review Your Progress
The most important part of therapy homework is the follow-up discussion at the next session. The time you spend reviewing with your therapist how the past week went, if you completed your homework, or if you didn’t and why, gives your therapist valuable feedback on your progress and insight on how they can better support you.
It Gives Your Therapist More Insight
Therapy can be tricky because by the time you are committed to showing up and putting in the work, you are already bringing a better and stronger version of yourself than what you have been experiencing in your day-to-day life that led you to seek therapy.
Homework gives your therapist an inside look into your day-to-day life, which can sometimes be hard to recap in a session. Certain homework assignments keep you thinking throughout the week about what you want to share during your sessions, giving your therapist historical data to review and address.
It Helps Empower You
The sense of empowerment you can gain from utilizing your new skills, setting new boundaries , and redirecting your own cognitive distortions is something a therapist can’t give you in the therapy session. This is something you give yourself. Therapy homework is how you come to the realization that you got this and that you can do it.
"The main benefit of therapy homework is that it builds your skills as well as the understanding that you can do this on your own," says Erkfitz.
Tips for Your Therapy Homework
Below, Dr. Erkfitz shares some tips that can help with therapy homework:
- Set aside time for your homework: Create a designated time to complete your therapy homework. The aim of therapy homework is to keep you thinking and working on your goals between sessions. Use your designated time as a sacred space to invest in yourself and pour your thoughts and emotions into your homework, just as you would in a therapy session .
- Be honest: As therapists, we are not looking for you to write down what you think we want to read or what you think you should write down. It’s important to be honest with us, and yourself, about what you are truly feeling and thinking.
- Practice your skills: Completing the worksheet or log are important, but you also have to be willing to put your skills and learnings into practice. Allow yourself to be vulnerable and open to trying new things so that you can report back to your therapist about whether what you’re trying is working for you or not.
- Remember that it’s intended to help you: Therapy homework helps you maximize the benefits of therapy and get the most value out of the process. A 2013-study notes that better homework compliance is linked to better treatment outcomes.
- Talk to your therapist if you’re struggling: Therapy homework shouldn’t feel like work. If you find that you’re doing homework as a monotonous task, talk to your therapist and let them know that your heart isn’t in it and that you’re not finding it beneficial. They can explain the importance of the tasks to you, tailor your assignments to your preferences, or change their course of treatment if need be.
"When the therapy homework starts 'hitting home' for you, that’s when you know you’re on the right track and doing the work you need to be doing," says Erkfitz.
A Word From Verywell
Similar to how school involves classwork and homework, therapy can also involve in-person sessions and homework assignments.
If your therapist has assigned you homework, try to make time to do it. Completing it honestly can help you and your therapist gain insights into your emotional processes and overall progress. Most importantly, it can help you develop coping skills and practice them, which can boost your confidence, empower you, and make your therapeutic process more effective.
Get Help Now
We've tried, tested, and written unbiased reviews of the best online therapy programs including Talkspace, BetterHelp, and ReGain. Find out which option is the best for you.
Conklin LR, Strunk DR, Cooper AA. Therapist behaviors as predictors of immediate homework engagement in cognitive therapy for depression . Cognit Ther Res . 2018;42(1):16-23. doi:10.1007/s10608-017-9873-6
Lebeau RT, Davies CD, Culver NC, Craske MG. Homework compliance counts in cognitive-behavioral therapy . Cogn Behav Ther . 2013;42(3):171-179. doi:10.1080/16506073.2013.763286
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.

How to Use Homework to Support Student Success
Covid has brought many changes in education. what does it mean for homework.
Posted January 12, 2022 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
- Why Education Is Important
- Take our ADHD Test
- Find a Child Therapist
- Generally, homework should include about 10 minutes per night per grade level.
- The value of homework is debated, with questions about the right amount and potential for inequity.
- Families should view homework as a communication tool, strive to be good helpers, and monitor balance.
School assignments that a student is expected to do outside of the regular school day—that’s homework. The general guideline is 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level beginning after kindergarten. This amounts to just a few minutes for younger elementary students to up to 2 hours for high school students.
The guidance seems straightforward enough, so why is homework such a controversial topic? School disruptions, including extended periods of remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, have magnified the controversies yet also have provided an opportunity to rethink the purpose and value of homework.
Debates about the value of homework center around two primary issues: amount and inequity.
First, the amount of assigned homework may be much more than the recommended guidelines. Families report their children are stressed out over the time spent doing homework. Too much homework can challenge well-being given the restricted time available for sleep, exercise, and social connection. In a 2015 study , for example, parents reported their early elementary children received almost three times the recommended guidelines. In high school, researchers found an average of three hours of homework per night for students living in economically privileged communities.
Second, homework can perpetuate inequities. Students attending school in less economically privileged communities may receive little to no homework, or have difficulty completing it due to limited access to needed technology. This can translate into fewer opportunities to learn and may contribute to gaps in achievement.
There isn’t a ton of research on the effects of homework, and available studies certainly do not provide a simple answer. For example, a 2006 synthesis of studies suggested a positive influence between homework completion and academic achievement for middle and high school students. Supporters also point out that homework offers additional opportunities to engage in learning and that it can foster independent learning habits such as planning and a sense of responsibility. A more recent study involving 13-year-old students in Spain found higher test scores for those who were regularly assigned homework in math and science, with an optimal time around one hour—which is roughly aligned with recommendations. However, the researchers noted that ability to independently do the work, student effort, and prior achievement were more important contributors than time spent.
Opponents of homework maintain that the academic benefit does not outweigh the toll on well-being. Researchers have observed student stress, physical health problems, and lack of life balance, especially when the time spent goes over the recommended guidelines. In a survey of adolescents , over half reported the amount and type of homework they received to be a primary source of stress in their lives. In addition, vast differences exist in access and availability of supports, such as internet connection, adult assistance, or even a place to call home, as 1.5 million children experience homelessness in the United States.
The COVID-19 pandemic has re-energized discussion about homework practices, with the goal to advance recommendations about how, when, and with whom it can be best used. Here’s a summary of key strategies:
Strategies for Educators
Make sure the tasks are meaningful and matched. First, the motto “ quality over quantity ” can guide decisions about homework. Homework is not busy-work, and instead should get students excited about learning. Emphasize activities that facilitate choice and interest to extend learning, like choose your own reading adventure or math games. Second, each student should be able to complete homework independently with success. Think about Goldilocks: To be effective, assignments should be just right for each learner. One example of how do this efficiently is through online learning platforms that can efficiently adjust to skill level and can be completed in a reasonable amount of time.
Ensure access to resources for task completion. One step toward equity is to ensure access to necessary resources such as time, space, and materials. Teach students about preparing for homework success, allocating classroom time to model and practice good study habits such as setting up their physical environment, time management , and chunking tasks. Engage in conversations with students and families to problem-solve challenges When needed, connect students with homework supports available through after-school clubs, other community supports, or even within a dedicated block during the school day.
Be open to revisiting homework policies and practices. The days of penalizing students for not completing homework should be long gone. Homework is a tool for practicing content and learning self- management . With that in mind, provide opportunities for students to communicate needs, and respond by revising assignments or allowing them to turn in on alternative dates. Engage in adult professional learning about high-quality homework , from value (Should I assign this task?) to evaluation (How should this be graded? Did that homework assignment result in expected outcomes?). Monitor how things are going by looking at completion rates and by asking students for their feedback. Be willing to adapt the homework schedule or expectations based on what is learned.

Strategies for Families
Understand how to be a good helper. When designed appropriately, students should be able to complete homework with independence. Limit homework wars by working to be a good helper. Hovering, micromanaging, or doing homework for them may be easiest in the moment but does not help build their independence. Be a good helper by asking guiding questions, providing hints, or checking for understanding. Focus your assistance on setting up structures for homework success, like space and time.
Use homework as a tool for communication. Use homework as a vehicle to foster family-school communication. Families can use homework as an opportunity to open conversations about specific assignments or classes, peer relationships, or even sleep quality that may be impacting student success. For younger students, using a daily or weekly home-school notebook or planner can be one way to share information. For older students, help them practice communicating their needs and provide support as needed.
Make sure to balance wellness. Like adults, children need a healthy work-life balance. Positive social connection and engagement in pleasurable activities are important core principles to foster well-being . Monitor the load of homework and other structured activities to make sure there is time in the daily routine for play. Play can mean different things to different children: getting outside, reading for pleasure, and yes, even gaming. Just try to ensure that activities include a mix of health-focused activities such as physical movement or mindfulness downtime.

Sandra M. Chafouleas, Ph.D., is a Distinguished Professor in the Neag School of Education at the University of Connecticut.
- Find Counselling
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- Richmond - Tweed
- Newcastle - Maitland
- Canberra - ACT
- Sunshine Coast
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Homework – Top 3 Pros and Cons
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
Homework as a Mental Health Concern It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health practitioners, especially those who work in schools. Over the years, we have tried to emphasize the idea that schools need to ensure that homework is designed as "motivated practice," and parents need to avoid turning homework into a battleground. These views are embedded in many of the Center documents. At this time, we hope you will join in a discussion of what problems you see arising related to homework and what you recommend as ways to deal with such problems, what positive homework practices you know about, and so forth. Read the material that follows, and then, let us hear from you on this topic. Contact: [email protected] ######################### As one stimulus, here's a piece by Sharon Cromwell from Education World prepared for teachers " The Homework Dilemma: How Much Should Parents Get Involved? " http://www.education-world.com/a_curr/curr053.shtml . What can teachers do to help parents help their children with homework? Just what kind of parental involvement -- and how much involvement -- truly helps children with their homework? The most useful stance parents can take, many experts agree, is to be somewhat but not overly involved in homework. The emphasis needs to be on parents' helping children do their homework themselves -- not on doing it for them. In an Instructor magazine article, How to Make Parents Your Homework Partner s, study-skills consultant Judy Dodge maintains that involving students in homework is largely the teacher's job, yet parents can help by "creating a home environment that's conducive to kids getting their homework done." Children who spend more time on homework, on average, do better academically than children who don't, and the academic benefits of homework increase in the upper grades, according to Helping Your Child With Homework , a handbook by the Office of Education Research and Improvement in the U.S. Department of Education. The handbook offers ideas for helping children finish homework assignments successfully and answers questions that parents and people who care for elementary and junior high school students often ask about homework. One of the Goals 2000 goals involves the parent/school relationship. The goal reads, "Every school will promote partnerships that will increase parental involvement and participation in promoting the social, emotional, and academic growth of children." Teachers can pursue the goal, in part, by communicating to parents their reasons for assigning homework. For example, the handbook states, homework can help children to review and practice what they have learned; prepare for the next day's class; use resources, such as libraries and reference materials; investigate topics more fully than time allows in the classroom. Parents can help children excel at homework by setting a regular time; choosing a place; removing distractions; having supplies and resources on hand; monitoring assignments; and providing guidance. The handbook cautions against actually doing the homework for a child, but talking about the assignment so the child can figure out what needs to be done is OK. And reviewing a completed assignment with a child can also be helpful. The kind of help that works best depends, of course, partly on the child's age. Elementary school students who are doing homework for the first time may need more direct involvement than older students. HOMEWORK "TIPS" Specific methods have been developed for encouraging the optimal parental involvement in homework. TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) Interactive Homework process was designed by researchers at Johns Hopkins University and teachers in Maryland, Virginia, and the District of Columbia to meet parents' and teachers' needs, says the Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin . The September 1997 bulletin reported the effects of TIPS-Language Arts on middle-grade students' writing skills, language arts report card grades, and attitudes toward TIPS as well as parents' reactions to interactive homework. TIPS interactive homework assignments involve students in demonstrating or discussing homework with a family member. Parents are asked to monitor, interact, and support their children. They are not required to read or direct the students' assignments because that is the students' responsibility. All TIPS homework has a section for home-to-school communication where parents indicate their interaction with the student about the homework. The goals of the TIPS process are for parents to gain knowledge about their children's school work, students to gain mastery in academic subjects by enhancing school lessons at home, and teachers to have an understanding of the parental contribution to student learning. "TIPS" RESULTS Nearly all parents involved in the TIPS program said TIPS provided them with information about what their children were studying in school. About 90 percent of the parents wanted the school to continue TIPS the following year. More than 80 percent of the families liked the TIPS process (44 percent a lot; 36% a little). TIPS activities were better than regular homework, according to 60 percent of the students who participated. About 70 percent wanted the school to use TIPS the next year. According to Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin , more family involvement helped students' writing skills increase, even when prior writing skills were taken into account. And completing more TIPS assignments improved students' language arts grades on report cards, even after prior report card grades and attendance were taken into account. Of the eight teachers involved, six liked the TIPS process and intended to go on using it without help or supplies from the researchers. Furthermore, seven of the eight teachers said TIPS "helps families see what their children are learning in class." OTHER TIPS In "How to Make Parents Your Homework Partners," Judy Dodge suggests that teachers begin giving parent workshops to provide practical tips for "winning the homework battle." At the workshop, teachers should focus on three key study skills: Organizational skills -- Help put students in control of work and to feel sure that they can master what they need to learn and do. Parents can, for example, help students find a "steady study spot" with the materials they need at hand. Time-management skills -- Enable students to complete work without feeling too much pressure and to have free time. By working with students to set a definite study time, for example, parents can help with time management. Active study strategies -- Help students to achieve better outcomes from studying. Parents suggest, for instance, that students write questions they think will be on a test and then recite their answers out loud. Related Resources Homework Without Tears by Lee Canter and Lee Hauser (Perennial Library, 1987). A down-to-earth book by well-known experts suggests how to deal with specific homework problems. Megaskills: How Families Can Help Children Succeed in School and Beyond by Dorothy Rich (Houghton Mifflin Company, 1992). Families can help children develop skills that nurture success in and out of school. "Helping Your Student Get the Most Out of Homework" by the National PTA and the National Education Association (1995). This booklet for teachers to use with students is sold in packages of 25 through the National PTA. The Catalog item is #B307. Call 312-549-3253 or write National PTA Orders, 135 South LaSalle Street, Dept. 1860, Chicago, IL 60674-1860. Related Sites A cornucopia of homework help is available for children who use a computer or whose parents are willing to help them get started online. The following LINKS include Internet sites that can be used for reference, research, and overall resources for both homework and schoolwork. Dr. Internet. The Dr. Internet Web site, part of the Internet Public Library, helps students with science and math homework or projects. It includes a science project resource guide Help With Homework. His extensive listing of Internet links is divided into Language Art Links, Science Links, Social Studies Links, Homework Help, Kids Education, and Universities. If students know what they are looking for, the site could be invaluable. Kidz-Net... Links to places where you can get help with homework. An array of homework help links is offered here, from Ask Dr. Math (which provides answers to math questions) to Roget's Thesaurus and the White House. Surfing the Net With Kids: Got Questions? Links to people -- such as teachers, librarians, experts, authors, and other students -- who will help students with questions about homework. Barbara J. Feldman put together the links. Kidsurfer: For Kids and Teens The site, from the National Children's Coalition, includes a Homework/Reference section for many subjects, including science, geography, music, history, and language arts. Homework: Parents' Work, Kid's Work, or School Work? A quick search of this title in the Education Week Archives and you'll find an article presenting a parent's viewpoint on helping children with homework. @#@#@#@@# As another stimulus for the discussion, here is an excerpt from our online continuing education module Enhancing Classroom Approaches for Addressing Barriers to Learning ( https://smhp.psych.ucla.edu ) Turning Homework into Motivated Practice Most of us have had the experience of wanting to be good at something such as playing a musical instrument or participating in a sport. What we found out was that becoming good at it meant a great deal of practice, and the practicing often was not very much fun. In the face of this fact, many of us turned to other pursuits. In some cases, individuals were compelled by their parents to labor on, and many of these sufferers grew to dislike the activity. (A few, of course, commend their parents for pushing them, but be assured these are a small minority. Ask your friends who were compelled to practice the piano.) Becoming good at reading, mathematics, writing, and other academic pursuits requires practice outside the classroom. This, of course, is called homework. Properly designed, homework can benefit students. Inappropriately designed homework, however, can lead to avoidance, parent-child conflicts, teacher reproval, and student dislike of various arenas of learning. Well-designed homework involves assignments that emphasize motivated practice. As with all learning processes that engage students, motivated practice requires designing activities that the student perceives as worthwhile and doable with an appropriate amount of effort. In effect, the intent is to personalize in-class practice and homework. This does not mean every student has a different practice activity. Teachers quickly learn what their students find engaging and can provide three or four practice options that will be effective for most students in a class. The idea of motivated practice is not without its critics. I don't doubt that students would prefer an approach to homework that emphasized motivated practice. But �� that's not preparing them properly for the real world. People need to work even when it isn't fun, and most of the time work isn't fun. Also, if a person wants to be good at something, they need to practice it day in and day out, and that's not fun! In the end, won't all this emphasis on motivation spoil people so that they won't want to work unless it's personally relevant and interesting? We believe that a great deal of learning and practice activities can be enjoyable. But even if they are not, they can be motivating if they are viewed as worthwhile and experienced as satisfying. At the same time, we do recognize that there are many things people have to do in their lives that will not be viewed and experienced in a positive way. How we all learn to put up with such circumstances is an interesting question, but one for which psychologists have yet to find a satisfactory answer. It is doubtful, however, that people have to experience the learning and practice of basic knowledge and skills as drudgery in order to learn to tolerate boring situations. Also in response to critics of motivated practice, there is the reality that many students do not master what they have been learning because they do not pursue the necessary practice activities. Thus, at least for such individuals, it seems essential to facilitate motivated practice. Minimally, facilitating motivated practice requires establishing a variety of task options that are potentially challenging -- neither too easy nor too hard. However, as we have stressed, the processes by which tasks are chosen must lead to perceptions on the part of the learner that practice activities, task outcomes, or both are worthwhile -- especially as potential sources of personal satisfaction. The examples in the following exhibit illustrate ways in which activities can be varied to provide for motivated learning and practice. Because most people have experienced a variety of reading and writing activities, the focus here is on other types of activity. Students can be encouraged to pursue such activity with classsmates and/or family members. Friends with common interests can provide positive models and support that can enhance productivity and even creativity. Research on motivation indicates that one of the most powerful factors keeping a person on a task is the expectation of feeling some sense of satisfaction when the task is completed. For example, task persistence results from the expectation that one will feel smart or competent while performing the task or at least will feel that way after the skill is mastered. Within some limits, the stronger the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more likely practice will be pursued even when the practice activities are rather dull. The weaker the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more the practice activities themselves need to be positively motivating. Exhibit � Homework and Motivated Practice Learning and practicing by (1) doing using movement and manipulation of objects to explore a topic (e.g., using coins to learn to add and subtract) dramatization of events (e.g., historical, current) role playing and simulations (e.g., learning about democratic vs. autocratic government by trying different models in class; learning about contemporary life and finances by living on a budget) actual interactions (e.g., learning about human psychology through analysis of daily behavior) applied activities (e.g., school newspapers, film and video productions, band, sports) actual work experience (e.g., on-the-job learning) (2) listening reading to students (e.g., to enhance their valuing of literature) audio media (e.g., tapes, records, and radio presentations of music, stories, events) listening games and activities (e.g., Simon Says; imitating rhymes, rhythms, and animal sounds) analyzing actual oral material (e.g., learning to detect details and ideas in advertisements or propaganda presented on radio or television, learning to identify feelings and motives underlying statements of others) (3) looking directly observing experts, role models, and demonstrations visual media visual games and activities (e.g., puzzles, reproducing designs, map activities) analyzing actual visual material (e.g., learning to find and identify ideas observed in daily events) (4) asking information gathering (e.g., investigative reporting, interviewing, and opinion sampling at school and in the community) brainstorming answers to current problems and puzzling questions inquiry learning (e.g., learning social studies and science by identifying puzzling questions, formulating hypotheses, gathering and interpreting information, generalizing answers, and raising new questions) question-and-answer games and activities (e.g., twenty questions, provocative and confrontational questions) questioning everyday events (e.g., learning about a topic by asking people about how it effects their lives) O.K. That's should be enough to get you going. What's your take on all this? What do you think we all should be telling teachers and parents about homework? Let us hear from you ( [email protected] ). Back to Hot Topic Home Page Hot Topic Home Page --> Table of Contents Home Page Search Send Us Email School Mental Health Project-UCLA Center for Mental Health in Schools WebMaster: Perry Nelson ([email protected])

Homework can be bad for your mental health. Should we get rid of it?
- Teachers are taking to social media apps like TikTok to take a stand against the idea
- Heavy workloads can be extra stressful for students, especially during the Covid-19 pandemic
Latest Articles
Face off: should universities get rid of applications fees, gay penguin sphen, 11, dies in australia, leaving behind his partner, 150,400 hongkongers use bn(o) option to emigrate to britain, your voice: olympics aftermath, seine pollution, starbucks’ new ceo, hong kong set for hotter autumn thanks to the effects of climate change, international baccalaureate body undertakes steps to resolve time zone cheating.

It’s no secret that homework can be a pain. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about their workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn’t assign it because the “whole premise of homework is flawed.”
Do students need homework to learn?
For starters, he says he can’t grade work on “even playing fields” when students’ home environments can be vastly different.
“Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that’s what a lot of homework is, it’s busy work,” he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. “You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18.”
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Chinese schoolgirl uses robot to do her homework
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be “detrimental” for students and cause a “big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health.”
“More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies,” she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it’s not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
“The research shows that there’s really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom,” he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
Should Hong Kong introduce a zero-homework policy?
“Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they’re doing a minimum of three hours, and it’s taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person’s mental and emotional health.”
Catchings, who taught Primary Three to Secondary 6 for 12 years, says she’s seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
“Not having homework was something that I always admired from French students (and) French schools, because that helped students really have time off and disconnect from school,” she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a secondary school teacher for 10 years.
“I don’t think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless, busy work-type homework. That’s something that needs to be scrapped entirely,” she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
- entertainment
- journalism resources
- latest reports
- learning resources
- college & uni life
- career advice
trending topics
Thanks for visiting! GoodRx is not available outside of the United States. If you are trying to access this site from the United States and believe you have received this message in error, please reach out to [email protected] and let us know.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Dear Life Kit
- Life Skills

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
What to do if you're struggling with your mental health at work

Jordan-Marie Smith

Andee Tagle

When you're not in the right headspace, being at work can be difficult.
Whether it's depression, burnout, anxiety or something else, struggling with your mental health while you're waiting tables or sitting behind a desk can disrupt your life and your job.
But there's a stigma to taking time off to care for your mental health that's not present with physical health. The mindset is, "Just work, work, work, push through it and get to the other end and deal with it," says Jody Adewale, a Los Angeles-based psychologist and medical advisor for the mental health advocacy foundation, Made of Millions .
Addressing your mental health needs is important — and human. "It's not a character flaw or a character defect or a sign of weakness," says Adewale. "It's something that everyone I think on this planet will experience at one point or another in their life."
Life Kit asked mental health professionals how to spot an issue and what the options are when you do.
While we know there's no such thing as the perfect job, there are tools for both employees and managers to make work a better place to be.
1. Look for signs of declining mental health
First, check-in with your body. Are you more tense than usual? Do you lose sleep or not eat as much?
Even if you aren't the person experiencing poor mental health, you can be a good coworker by taking note of the five signs of emotional suffering.
- Personality change in a way that seems drastic
- Agitation or uncharacteristically angry demeanor
- Withdrawn from social interaction
- Poor hygiene (substance abuse or physical hygiene)
- Feelings of hopelessness
These five signs from the national mental health non-profit Give an Hour are clear ways to determine if it's time to check in with your colleague or tend to your own mental health issues, says Hassel Aviles, the co-founder of Not 9 to 5 , a global non-profit focusing on mental health advocacy for the foodservice and hospitality sector.

Burnout Isn't Just Exhaustion. Here's How To Deal With It
And you don't need to mark every item on this list – spotting even one could be a reason to check in with yourself or someone you care about. From there, do some triage and be honest with yourself.
Could it help to switch up some habits? Do you need to vent to a friend, get some more movement or minimize social media time ? Or, is it time to raise a concern at the office?
2. Have a conversation with a trusted person who can introduce you to resources
After realizing that you need help, reach out to a colleague that you trust.
A loyal and reliable coworker can help you vent or think things through. If you need more help, a supervisor might be the best person to talk to, given they may be informed about resources that could help with mental health. Human resources can be a good option as well, but be mindful that HR typically has the company's best interest in mind, Adewale says.
If your employer is retaliating against you because of your mental health condition, you can contact the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission to file a claim.
One way to address your needs is to use the DEAR method in a meeting with HR, management or your trusted coworker.
- D - Describe the situation using facts.
- E - Express how the situation made you feel or how it affected you.
- A - Assert your needs.
- R - Reinforce the outcome and how it will be a win-win.
Part two of this method follows the acronym MAN, and will help remind you of mindset in these conversations:
- M - Be mindful of your words, and stay in the present moment.
- A - Be assertive. If you're raising a mental health issue at work, it's important for everyone involved, so stand your ground!
- N - Negotiate. Your office might not be able to shift to your ideal hours, but perhaps you could work together to set firmer boundaries for emails or start actually honoring lunch breaks. Work with your manager to find solutions.

How To Start Therapy
And remember, your boss or your coworker is not your therapist in this situation. If you get a burn or a cut at the office, you wouldn't expect your supervisor to know how to treat you, says Aviles. They are there to direct you to help.
One resource your trusted person may point you to is an employee assistance program or EAP. This is a service that many companies have. It provides employees with a handful of therapy sessions at no charge.
3. Sometimes you need to take a break
If therapy isn't enough, it might help to take time off from work. It could be anywhere from one day to several months, but taking time to process, rest, heal and seek proper treatment can make all the difference.
A good start to pursuing this option is to ask your human resources department about short-term disability leave. Short-term disability leave allows you to take time off for a sickness or injury, including your mental health

You aren't lazy. You just need to slow down
Vermont journalist Siobhan Neela-Stock took over two months off work to heal from a less-than-ideal work environment. When she tweeted about it, she was flooded with positive responses. Some were from people who want to take time off from work and other notes were from people who had.
Neela-Stock says more and more people are discussing mental health leave as a viable option.
"I guess the good thing about this silver lining is that we're, again, talking about it more and we're realizing that a lot of us are going through this. And, that there is a way out," Neela-Stock said.
4. Create a psychologically safe workplace
The quickest path to mentally healthy workers is mentally healthy workspaces.
"Psychological safety" is a term coined by researcher Amy Edmondson . It focuses on the need to create safe environments at work, where people can share how they are actually doing without the threat of losing out on a promotion or big project.
Aviles says employers and employees can create psychological safety anywhere–from an office to a kitchen. It all depends on if you're able to be vulnerable with each other.

Leadership At Work Is An Art Form. Here's How To Practice It.
Remember that It's also important to engage with your team by centering voices that are most affected by something. Employers don't need to have all of the answers, but they should be transparent and open to feedback.
One last tip: It's okay to make mistakes. In a psychologically safe environment, an employee learns from their mistakes and uses the opportunity to grow. This is the opposite of the top-down approach where the boss chastises an employee for making mistakes.
"And that is what creates innovation. That is what fosters creativity that is with us to really grow, that psychological safety in the workplace," says Aviles.
Here's a non-exhaustive list of resources for workplace mental health:
- The CDC offers a wealth of resources , including a glossary of terms and suggestions for managers.
- Did you know you can train in mental health first aid? Here's where to find training and mental health aid resources.
- Made of Millions is a global mental health advocacy group that offers lots of training and resources. Here's their letter to your manager , and here's their global directory of resources .
- Not 9 to 5 is a global non-profit focusing on mental health advocacy in the foodservice and hospitality sectors. Their website offers a lot of great workplace mental health resources .
- Here's a breakdown of how to implement psychological safety in the workplace , from ShiftCollab , a therapy collective
- For an explanation of your rights in regards to mental health protection in the workplace, check out the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission .
The podcast portion of this story was produced by Andee Tagle.
We'd love to hear from you. If you have a good life hack, leave us a voicemail at 202-216-9823 or email us at [email protected] . Your tip could appear in an upcoming episode.
If you love Life Kit and want more, subscribe to our newsletter .
- Life Kit: Health
- Life Kit: Life Skills
5 Benefits of Journaling for Mental Health

In fact, studies show that time spent journaling about our deepest thoughts and feelings can even reduce the number of sick days we take off work (Sohal, Singh, Dhillon & Gill, 2022).
Research suggests that journaling can help us accept rather than judge our mental experiences, resulting in fewer negative emotions in response to stressors (Ford, Lam, John, & Mauss, 2018; Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005).
This article explores the numerous benefits of journaling and introduces guidance and techniques to support clients as they attempt to express how they feel and think.
Before you start reading, we thought you might like to download our three Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF) for free . These science-based exercises will equip you and those you work with, with tools to manage stress better and find a healthier balance in your life.
This Article Contains:
Why is journaling good for you, 5 surprising benefits of journaling, how to journal for optimal mental health, getting started – journaling prompts, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Journaling is a widely used non-pharmacological tool for coaching and counseling and the treatment of mental illness. Two forms of journaling are particularly commonplace in psychotherapy (Sohal et al., 2022):
- Expressive writing Typically performed over three or four sessions to access the client’s innermost feelings and thoughts; focusing on the emotional experience than events, people, or objects.
- Gratitude journaling Involving a focus on the positive aspects of life through capturing situations, events, and interactions for which we are grateful.
Keeping a record of personal thoughts and feelings is particularly helpful in supporting mental health by (WebMD.com, 2021):
- Reducing anxiety
- Breaking away from a nonstop cycle of obsessive thinking and brooding
- Improving the awareness and perception of events
- Regulating emotions
- Encouraging awareness
- Boosting physical health
The positive effects of journaling can even be felt when not performed daily – helping the individual better understand their needs and boosting their wellbeing (Tartakovsky, 2022).
Research on Journaling
Studies show that by capturing our thoughts and feelings on paper, “participants often reveal a considerable range and depth of emotional trauma” (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005, p. 339).
Indeed, while the experience of writing can be upsetting, clients report they find it valuable and meaningful and, ultimately, a valuable part of the acceptance process.
In fact, based on client self-reports, research suggests a wide range of physical, cognitive, and emotional benefits from expressive writing (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005):
- Lowered blood pressure
- Improved lung and liver function
- Less time spent in hospital
- Better moods
- Improved psychological wellbeing
- Fewer depressive and avoidance symptoms
- Reduced stress-related visits to the doctor
- Less work absenteeism
- Less time out of work following job loss
- Higher student grade averages
Not only that, but research into gratitude journaling suggests that “study participants who regularly drew their attention to aspects of their lives that made them feel blessed increased their positivity” (Fredrickson, 2010, p. 187). However, a caveat exists. Recording what makes us feel grateful every day can become monotonous, even zapping positivity. A few days a week may be sufficient.
The Psychology Behind Journaling
“Research has consistently linked the habitual tendency to accept one’s mental experiences with greater psychological health” (Ford et al., 2018, p. 2). Study findings suggest that accepting our feelings is linked to better psychological health and positive therapeutic outcomes, including improved moods and reduced anxiety.
And this is where journaling can help. It can promote acceptance–and mindful acceptance in particular–which is a valuable and effective way of getting unstuck, freeing ourselves to move forward (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
While the exact mechanisms involved in journaling that confer physical and mental health benefits are not clear, the following psychological processes may be involved, to a greater or lesser degree (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005):
- Emotional catharsis An emotional release of unconscious conflicts through venting negative feelings.
- Increased cognitive processing Time spent creating coherent narratives of what has happened.
- Repeated exposure Increased and prolonged exposure to stressful events may lead to a reduction in harmful thoughts and feelings.
- Emotional inhibition Actively inhibiting negative emotions takes a considerable effort, further stressing the body and mind. Confronting them may support cognitive integration and further understanding.
For each suggestion, there is supporting and contradictory evidence. The benefits of journaling seem apparent, yet the mechanisms beneath are yet to be fully understood (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005; Tartakovsky, 2022).

Easy to implement and get started, it can benefit clients experiencing different mental health issues (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005; Ford et al., 2018):
Journaling for Anxiety
Journaling has proven popular and effective for treating clients experiencing anxiety, possibly because of an improved acceptance of negative emotions and a more helpful emotional response to stress (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005; Ford et al., 2018).
One meta-review of research studies suggests that journaling may be a more effective treatment for anxiety in women than men (yet both groups have a positive effect) and that doing so for longer than 30 days may maximize mental wellbeing benefits (Sohal et al., 2022).
Journaling for Depression
Research suggests that expressive writing and gratitude journaling can reduce symptoms of depression, providing an effective intervention for clients receiving treatment in therapy.
As with anxiety, such interventions also appeared more effective when lasting longer than 30 days. While benefits may not be as great as for anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), journaling still appears to be a valuable intervention (Sohal et al., 2022).
Journaling for Stress Management
Journaling can support coping and reduce the impact of stressful events – potentially avoiding burnout and chronic anxiety. Studies link writing privately about stressful events and capturing thoughts and emotions on paper with decreased mental distress.
When journaling for stress management , processing our emotions in written form may even increase the likelihood that we reach out for social support. This, in turn, leads to emotional healing and improved resilience to stress (WebMD.com, 2021).
Journaling for Reflection
When stressed or consumed by negative thoughts, it’s difficult to view our situation objectively. Writing in a journal can help us create the space and distance needed to reflect on what has happened, where we are, and what is ahead.
Journaling may create sufficient cognitive defusion –looking at thoughts rather than being in them–to create the separation needed to accept our feelings and commit to the changes we need to make (Tartakovsky, 2022).
Journaling for Recovery
Research suggests that journaling, particularly expressive writing, can help those experiencing or recovering from the emotional trauma associated with PTSD (Sohal et al., 2022).
Another innovative approach combined journaling with visualization and appeared to offer lasting support to war veterans (Mims, 2015).
Other findings confirm journaling as a valuable and effective intervention for recovery from addiction.
A 2022 paper highlighted the ability of journaling to support the recovery of women in residential treatment for substance use disorders. Results showed that the intervention “helped participants to recognize what was positive about recovery, to achieve meaningful short-term goals, and to experience a sense of optimism and pride in their accomplishments” (Krentzman, Hoeppner, Hoeppner, & Barnett, 2022, p. 1).
6 Ways to process your feelings in writing – Therapy in a Nutshell
Despite the clear benefits of journaling for easing distress, we are often less willing to capture how we feel on paper when we are struggling the most.
After all, it’s not always pleasant. We are revisiting thoughts and emotions that we may have been avoiding. In fact, we may feel sad, upset, guilty, or anxious immediately after time spent writing. And yet, in the long term, journaling offers us better psychological and physical health (Newman, 2020).
The following guidelines should ease the first-timer into the process and make it less daunting (Newman, 2020; WebMD.com, 2021; Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005):

Guidance for mental health practitioners working with clients:
- Expressive writing can be set as homework, between, or immediately before or after sessions.
- Encourage the client to find somewhere quiet and peaceful, away from distractions.
- Set a goal of writing three or four times a week – potentially on consecutive days.
- Carve out 30 minutes–even during a busy day–with 20 for writing and 10 for reflection and composing.
- Let the client choose what they want to write about, for example, a stressful or traumatic event.
- Do not impose a structure on their writing – encourage them to choose their own format.
- Clarify that what the client writes is private; it will only be read if they choose to share.
- Do not judge what they capture and choose to offer up for discussion – and keep feedback to a minimum.

Download 3 Free Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to manage stress better and find a healthier balance in their life.
Download 3 Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Guidance for the client:
- Pick the time of day that suits you best to write in the journal; setting a regular time is helpful but accept that it may be necessary to be flexible.
- Start by expressing your feelings, allowing yourself time to name each one. Then move on to observing your thoughts and any patterns of thinking that might characterize you.
- Start small. Begin by writing for only a few minutes on a subject of your choice – perhaps the day’s events or something that has been troubling you.
- Create and express what you want from life and how you feel. There are no rules, and there is no wrong way of doing this.
- Do not worry about spelling and punctuation – no one is here to judge you.
- Choose a medium that suits you. Use a journal app , write on paper, use a computer, or record your spoken thoughts.
- Accept that, at times, you may feel upset as you write. And that’s ok. Take a break if you need to. While this process will not fix all your problems, it will help you learn more about yourself.
We should explain to the client that expressive writing can sometimes lead to short-term distress despite the long-term benefits. Clients should be encouraged to stop writing if they find no benefits or the practice is too distressing (Baikie & Wilhelm, 2005).

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO

“For the next four days, I would like you to write down how you feel and think about your most traumatic experience or a significant emotional issue that has profoundly impacted you.
If you can, try to let go, capturing your deepest emotions and thoughts, including how you relate to those closest to you, your past, present, and future, and how you have been and would like to be. Feel free to carry one topic across multiple days or, if you prefer, choose a new one for each.
Your writing will remain confidential, so please do not worry about spelling, grammar, or style. You are not being judged so try to write honestly and openly.”
Specific and individual prompts can be helpful for clients if they are new to journaling or are struggling to get started. Begin by answering one or more of the following questions (Tartakovsky, 2022; Newman, 2020):
- How do the changes in your life make you feel? And how are you handling changes at work, at home, and in relationships?
- What are you most anxious or uncertain about? Where is that coming from, and how are you coping?
- What three things are you most grateful for today, or what three good things have happened to you today?
- What are your favorite memories from your own or your children’s lives?
- Name something you fear and why?
- What do you enjoy doing and why?
- How would you describe yourself from the perspective of someone close to you?
- What would your very best day look like and why?
- How would a difficult situation be handled if you were being your very best self?
- If you woke up tomorrow having everything you truly wanted, what would it look like?

17 Exercises To Reduce Stress & Burnout
Help your clients prevent burnout, handle stressors, and achieve a healthy, sustainable work-life balance with these 17 Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises [PDF].
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
We have many journaling resources available for therapists providing support to clients wanting to address mental health issues.
Gratitude often plays a large part in journaling. Why not download our free gratitude pack and try out the powerful tools contained within, including:
- Experiencing Awe Feelings of awe can arise in response to experiences that appear vast (including landscapes, such as the sea, mountains, and night sky) and can profoundly impact our gratitude. Ask the client to recall a time when they experienced awe and to write about their experience in detail.
- Fostering admiration in couples Maintaining fondness and respect in a relationship can help support the love within a couple. This exercise encourages positivity within the relationship and helps form a strong emotional bond.
Other free resources include:
- Gratitude Journal Use this worksheet Gratitude Journal as a prompt to help clients capture those aspects of their lives for which they are most grateful.
- Self Esteem Journal for Adults Use this sheet to note down meaningful daily activities and reflect on them to enhance client self-knowledge.
- Self-Love Journal These ten self-love prompts encourage emotional expression, mood boosting, and de-stressing within the client.
More extensive versions of the following tools are available with a subscription to the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , but they are described briefly below:
- Journaling Through Grief in 40 Days Losing someone special from our lives is one of the most distressing human experiences. Journaling through grief allows the individual to step back and reflect on what they have been going through from multiple perspectives.
The 40 days of journaling also provide a lasting record of their journey for later reflection.
- Strength journaling Personal strengths can be reinforced and developed through attending to them and exploring the ways in which one has used them in real, everyday life.
Use the seven days of prompts to write about what has gone well and the strengths that may have played a role in the successful outcome.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others manage stress without spending hours on research and session prep, this collection contains 17 validated stress management tools for practitioners . Use them to help others identify signs of burnout and create more balance in their lives.
Journaling as an intervention has many benefits, supporting physical and mental wellbeing, resilience, and greater emotional awareness and understanding.
To begin with, clients may be uncertain regarding revisiting difficult emotions or situations. And yet, with support and confirmation that their innermost thoughts and feelings remain private, they will grow more confident in capturing their deepest thoughts and better able to manage their anxiety and stressful situations.
Journaling encourages space from negative or self-critical thinking, allowing the client to see that what they think and feel is not who they are but something they are experiencing.
Journaling allows the client to see that what they think and feel is not who they are but something they are experiencing. It provides a space where a client can view their negative or self-critical thinking as just that – thoughts.
With practice, journaling can help process emotions–even ones that have been avoided or held back–and lead to a better understanding of how to proceed.
If your clients are not already doing so, task them with capturing how they think and feel in written form through either expressive writing or gratitude journaling. The client does not need to spend a great deal of time on it every day; even twenty minutes, three to four times a week, will have a positive and lasting effect.
Encourage them to reflect on what they have written later on, becoming better at understanding that difficult feelings will pass, and it is not the situation or specific stressors that cause us difficulty but our perception of them.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF) for free .
- Baikie, K., & Wilhelm, K. (2005). Emotional and physical health benefits of expressive writing. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment , 11(5), 338-346.
- Ford, B. Q., Lam, P., John, O. P., & Mauss, I. B. (2018). The psychological health benefits of accepting negative emotions and thoughts: Laboratory, diary, and longitudinal evidence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 115(6), 1075-1092.
- Forsyth, J. P., & Eifert, G. H. (2016). The Mindfulness & Acceptance Workbook for Anxiety: A Guide to Breaking Free from Anxiety, Phobias & Worry Using Acceptance & Commitment Therapy . Oakland, CA: New Harbinger Publications.
- Fredrickson, B. (2010). Positivity: Groundbreaking research reveals how to release your inner optimist and thrive . Richmond: Oneworld.
- Krentzman, A. R., Hoeppner, B. B., Hoeppner, S. S., & Barnett, N. P. (2022). Development, feasibility, acceptability, and impact of a positive psychology journaling intervention to support addiction recovery. The Journal of Positive Psychology , 1-19.
- Mims, R. (2015). Military veteran use of visual journaling during recovery. Journal of Poetry Therapy , 28(2), 99-111.
- Newman, K. (2020). How journaling can help you in hard times . Retrieved September 2, 2022, from https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/article/item/how_journaling_can_help_you_in_hard_times
- Sohal, M., Singh, P., Dhillon, B. S., & Gill, H. S. (2022). Efficacy of journaling in the management of mental illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Family Medicine and Community Health , 10(1).
- Tartakovsky, M. (2022, February 22). 15 benefits of journaling and tips for getting started . Retrieved September 2, 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/benefits-of-journaling
- WebMD.com. (2021). How journaling can help ease anxiety and encourage healing . Retrieved September 2, 2022, from https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/mental-health-benefits-of-journaling
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
What to put in a journal entry. I just stare at the blank page..nothing comes to mind. Not sure how this helps anything.
Hi Kimberly,
You don’t have to start journaling all by yourself! This is why there are many prompts and examples out there that can help you get started. To get inspired, feel free to check out the following blog articles that we wrote to give you a head start: – “ Writing Therapy: How to Write and Journal Therapeutically ” – “ Journaling for Mindfulness: 44 Prompts, Examples & Exercises ” – “ Self-Esteem Journals, Prompts, PDFs, and Ideas ”
I hope this helps!
Kind regards, Julia | Community Manager
It’s great that you elaborate on how journaling could benefit our mental health since it reduces anxiety. Recently, I’ve been busy with my job, and I barely go out with my friends, so I think I’m trapped in a bubble I’ve built, and I want to break it free. I think that keeping a journal could help me become more aware of what’s going on in my life, as you mentioned, so I’ll buy one later today.
I am glad that this article could inspire you to try journaling! I’m sorry to hear that you feel trapped, but we really stand by the mental benefits and feel it can be such a great de-stressor when we feel overwhelmed.
I wish you luck on your journaling journey!
Kind regards, -Caroline | Community Manager
These are some of the benefits that I have experienced myself. I started journaling with no expectations, but it turned out to be really great step toward my self-care journey. That day I decided to share the knowledge with other people as well. I created a blog named Your Mental Health Pal where I share mental health-related topics.
Thanks for a great well put together article. I’ve been journaling for 34 years which began while I was depressed on bed rest due to a high risk pregnancy. The act of journaling has been quite therapeutic for me to the degree that I now teach others how to do it. I’ve also created a collection of journals to share with others.
Your hard work in putting together this informative piece is very much appreciated. THANK YOU!
This is great. Thank you so much.
My life is too big for me and shrinking at the same time! Its the rollercoaster ride that I waited in line for so long to ride that when I realized that I couldn’t see when or how it would end I had no choice but to get on it anyway! I am 64, and my father died 6 years ago and told me I could see him one time for 5 minutes and that was it! He never spoke and I just left and said I hope you feel better. Since then my wife had an affair and divorced me, and now I take care of my 88 year old mom who is dying of c.o.p.d. and has not left the house in a year! My brother lives 4 blocks away and hasn’t come over in the 2 1/2 years he has lived here. I live in a small town that has no interests in things that make life a place of wonder and passion! Its like a graveyard where the dead still walk around but never speak but they are comfortable not thinking, just walking. Besides that, my relatives don’t like me for whatever reasons and every day brings a sunrise and sunset, alone. Thanks for letting me throw up into the starless void. Did I tell you that my friends all wanted me to do standup comedy! True story! Mel Blanc’ who did the voices for bugs bunny and most of those character’s has written on his grave stone” thats all folks!”
Ted from what you have written I hear loneliness despite there being people around. I wonder if there may be a community you may connect with locally? Or start one? Best wishes as you continue to explore
Thank you for sharing Ted. I love your witty humor as a way to cope but life does sound stressful and a tad lonely. Are there fun activities or meet-up groups you can go to? Like a hiking group, a fitbit/walking challenge group? writing seminar? or better yet standup comedy (they do have amateur night). I think connecting outside your immediate circle would be good to being in some light and laughter….. just a thought….
Can I get some help with my feelings I need a journal online that guesses my feelings.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Recognizing High-Functioning Anxiety & 6 Tools to Manage It
As our lives get busier and busier and more and more crises develop on the world stage, we are seeing reports of increasing incidences of [...]

Moving From Chronic Stress to Wellbeing & Resilience
Stress. It can be as minute as daily hassles, car trouble, an angry boss, to financial strain, a death or terminal illness. The ongoing stressors [...]

3 Burnout Prevention Strategies for Type A Personality
Highly driven, goal-oriented, and somewhat impatient? You may be dealing with a Type A personality. Having a Type A personality comes with a mixed bag [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (52)
- Coaching & Application (39)
- Compassion (23)
- Counseling (40)
- Emotional Intelligence (21)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (18)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (16)
- Mindfulness (40)
- Motivation & Goals (41)
- Optimism & Mindset (29)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (23)
- Positive Education (36)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Parenting (14)
- Positive Psychology (21)
- Positive Workplace (35)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (29)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (33)
- Theory & Books (42)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (54)

- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Stress Exercises Pack
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
More From Forbes
Better mental health for kids starts with good school-life balance.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
All work and no play? Turns out it’s just as bad for students as it is for employees.
Many teens need better school-life balance
We hear about employees’ need for healthy work/life balance all the time. If we as adults don’t have adequate time to unplug and relax, we run the risk of burnout.
But what many parents don’t realize is that their kids have the exact same need to strike a happy medium between what they have to do (school) and what they want to do (life). Kids can and do get burned out, too.
According to new research by Pearson , many students and parents aren’t on the same page when it comes to the boundaries between school and life. While 80% of parents believe their teens have good school-life balance, only 45% of teens agree.
“The disconnect can come from parents perceiving the time students spend on school work vs. other activities (leisure or otherwise) as relatively balanced compared to what they see in their own lives,” says Dr. Lorna Bryant, Head of Career Solutions, Pearson’s Virtual Learning division, “where work far exceeds the time they have for other responsibilities they need and want to prioritize.”
Dr. Bryant and I connected for a conversation about why kids are hungry for better school-life boundaries—and how parents can better support that need. Here’s what we covered.
Balance Supports Direction
Russian troops captured one of ukraine’s dutch armored vehicles, rode it back into battle—and promptly got killed, apple iphone 16 pro: new design echoed in latest leak, the sound of failure at sonos.
Many parents are pushing their kids to work harder at school because they want their kids to have enjoyable, financially stable careers—a laudable goal. But the foundation of a rewarding career is actually a healthy school-life balance.
The research found that students with a strong school/life balance often have a clearer understanding of their future aspirations, with 76% knowing what career they want to pursue. Conversely, more than a fourth (29%) report fair to very poor school/life balance and say it’s having a negative impact on their ability to start career planning.
In pushing their kids to do more, some parents may be trying to help their kids avoid their own mistakes. Of those surveyed, 72% wished they had explored different careers before they graduated, 67% regret that they didn’t learn better time management skills, and 64% would have balanced their time better between academics and extracurriculars.
Dr. Bryant believes that, unlike their parents, today’s young people see ‘balance’ as being able to connect what they’re learning academically with what they’re passionate about.
“Without being able to identify how schoolwork aligns with a passion that can turn into a career, they will continue to feel an imbalance and heightened anxiety about their future, which is so pronounced in this generation,” she says. “This conundrum is something their parents might not quite understand based on their view that ‘work’ and ‘life’ are wholly distinct from one another.”
Students Can’t Fix Their Own Imbalance
It's one thing for adults to work on improving their work/life balance, but this is more challenging for students who 1.) don’t have as much control over their day-to-day activities, and 2.) may lack the knowledge and resources to organize their time effectively. That’s why it’s so critical for parents to actively participate in helping their children develop this lifelong skill.
“Fifty-one percent of students reported that anxiety/stress is the most significant barrier to their school-life balance, which 52% also report is best supported by engaging with peers, friends, and fellow students in both online and offline settings,” says Dr. Bryant. “In a world so digitally focused, these learners see the value in connecting with others but likely need guidance to understand how to continue to manage these relationships during busy times.”
They also need tools to learn discipline, says Dr. Bryant. “Implementing strategies to organize schoolwork and using a planner or technology to help them segment their time were the next most common tactics that 43% of students mentioned would be useful.”
Of course, students don’t know what they don’t know about the resources out there that can help them make the most of their time. “This is where parents, counselors and teachers can step in and provide guidance,” says Dr. Bryant.
Action Steps For Parents
While it’s clear that parents play a significant role in helping teens gain the healthy school-life balance they need, the steps to make it happen may not be so evident. Here are some practical actions parents can take to better support their children’s social and emotional needs alongside their academic achievement:
- Reconsider the definition of ‘wasted time.’ “Extracurriculars or even in-school activities and experiences that allow their students to make real-world connections and hone and demonstrate durable skills are almost as important as strictly academic endeavors,” says Dr. Bryant. To take that point even further—even your child’s epic videogaming skills might contribute to their future career aspirations.
- Do career exploration together. “The research shows that teens want their parents to be involved in their career exploration by helping them find jobs (48%) and sharing resources (43%),” says Dr. Bryant. “This type of parent involvement can also increase communication with students and close the wide gap between how students and parents view the student’s school-life balance.”
- Make everything count. “Show them how to be intentional about their choices and tie experiences that might seem unrelated (part-time jobs, job shadowing, mentorships) to what they are currently learning and preparing for beyond school,” Dr. Bryant urges. In other words, the world is a classroom, too.
Above all, parents should recognize that all work and no play is just as rough on kids as it is on adults. By supporting their healthy school/life balance now, we can equip the next generation to set strong boundaries in their future professional lives.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Close Menu Search
- Recommend a Story

The Lion's Roar
May 24 Party Like It’s 1989: Lions Capture the 2024 Diamond Classic
May 24 Why Does the Early 20th Century Tend to Spark Nostalgia?
May 24 O.J Simpson Dead at 76: Football Star Turned Murderer
May 24 NAIA Bans Transgender Women From Women’s Sports
May 24 From Papyrus to Ashes: The Story of the Great Library of Alexandria
How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health
Jessica Amabile '24 , Staff Writer March 25, 2022
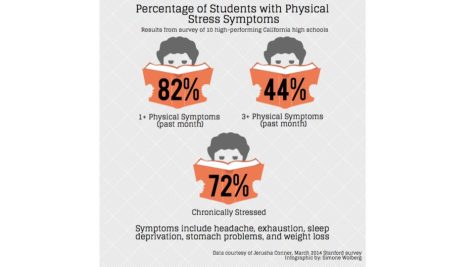
“[Students] average about 3.1 hours of homework each night,” according to an article published by Stanford . Teens across the country come home from school, exhausted from a long day, only to do more schoolwork. They sit at their computers, working on homework assignments for hours on end. To say the relentless amount of work they have to do is overwhelming would be an understatement. The sheer amount of homework given has many negative impacts on teenagers.
Students have had homework for decades, but in more recent years it has become increasingly more demanding. Multiple studies have shown that students average about three hours of homework per night. The Atlantic mentioned that students now have twice as much homework as students did in the 1990s. This is extremely detrimental to teens’ mental health and levels of stress. Students have a lot to do after school, such as spending time with family, extracurricular activities, taking care of siblings or other family members, hanging out with friends, or all of the above. Having to juggle all of this as well as hours on end of homework is unreasonable because teenagers already have enough to think or worry about.
According to a student- run survey conducted in Cherry Hill West, students reported that they received the most homework in math, history, and language arts classes. They receive anywhere from 1 to 4 or more hours of homework every day, but only about 22.7% somewhat or strongly agree that it helps them learn. Of the students who participated, 63.6% think schools should continue to give out homework sometimes, while 27.3% said they should not give out homework at all. In an open-ended response section, students had a lot to say. One student wrote, “I think we should get homework to practice work if we are seen struggling, or didn’t finish work in class. But if we get homework, I think it just shows that the teacher needs more time to teach and instead of speeding up, gives us more work.” Another added, “Homework is important to learn the material. However, too much may lead to the student not learning that much, or it may become stressful to do homework everyday.” Others wrote, “The work I get in chemistry doesn’t help me learn at all if anything it confuses me more,” and “I think math is the only class I could use homework as that helps me learn while world language is supposed to help me learn but feels more like a time waste.” A student admitted, “I think homework is beneficial for students but the amount of homework teachers give us each day is very overwhelming and puts a lot of stress on kids. I always have my work done but all of the homework I have really changes my emotions and it effects me.” Another pointed out, “you are at school for most of your day waking up before the sun and still after all of that they send you home each day with work you need to do before the next day. Does that really make sense[?]”
As an article from Healthline mentioned, “Researchers asked students whether they experienced physical symptoms of stress… More than 80 percent of students reported having at least one stress-related symptom in the past month, and 44 percent said they had experienced three or more symptoms.” If school is causing students physical symptoms of stress, it needs to re-evaluate whether or not homework is beneficial to students, especially teenagers. Students aren’t learning anything if they have hours of “busy work” every night, so much so that it gives them symptoms of stress, such as headaches, weight loss, sleep deprivation, and so on. The continuous hours of work are doing nothing but harming students mentally and physically.

The mental effects of homework can be harmful as well. Mental health issues are often ignored, even when schools can be the root of the problem. An article from USA Today contained a quote from a licensed therapist and social worker named Cynthia Catchings, which reads, “ heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.” Mental health problems are not beneficial in any way to education. In fact, it makes it more difficult for students to focus and learn.
Some studies have suggested that students should receive less homework. To an extent, homework can help students in certain areas, such as math. However, too much has detrimental impacts on their mental and physical health. Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, has a suggestion. She mentioned, “I don’t think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That’s something that needs to be scrapped entirely,” she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments,” according to USA Today . Students don’t have much control over the homework they receive, but if enough people could explain to teachers the negative impacts it has on them, they might be convinced. Teachers need to realize that their students have other classes and other assignments to do. While this may not work for everything, it would at least be a start, which would be beneficial to students.
The sole purpose of schools is to educate children and young adults to help them later on in life. However, school curriculums have gone too far if hours of homework for each class are seen as necessary and beneficial to learning. Many studies have shown that homework has harmful effects on students, so how does it make sense to keep assigning it? At this rate, the amount of time spent on homework will increase in years to come, along with the effects of poor mental and physical health. Currently, students do an average of 3 hours of homework, according to the Washington Post, and the estimated amount of teenagers suffering from at least one mental illness is 1 in 5, as Polaris Teen Center stated. This is already bad enough–it’s worrisome to think it could get much worse. Homework is not more important than physical or mental health, by any standards.
What time should high school should start?
- 7:00 AM or earlier
- 7:30 AM (Current Start Time)
- After 9:00 AM
View Results
- Polls Archive
Comments (0)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Eight Ways You Can Feel More Hopeful—Even in Dark Times
Should we maintain hope in uncertain times?
These days, this question is at the forefront of my mind—and probably many other people’s. Especially when we face political polarization, humanitarian crises at our borders, and the prospect of a warming planet, it’s easy to despair rather than hope.
But, according to William Miller, professor emeritus at the University of New Mexico, this is the wrong approach to what ails us. In his new book, 8 Ways to Hope , he explains why we should hope and how to cultivate a hopeful outlook.

“The essence of hope is envisioned betterment, and it serves us well,” writes Miller. “It comes hardwired in human nature to dream a better future, helping us to carry on and survive.”
Why we need hope
As Miller defines it, hope is not a naive approach to seeing the world, where we ignore problems and engage in “wishful thinking.” Instead, hope is a complex response, involving “feeling, thought, action, vision, a life force, and a way of seeing or being.”
Having hope, as opposed to living in fear or being cynical, he argues, helps us to see possibility in present-day circumstances and not become overwhelmed. People who feel hopeful are good problem-solvers , more resilient and persistent , more engaged and productive at work, more creative and adaptable , and better at recovering from adversity . For these reasons and others, inculcating more hope in ourselves means we’re better equipped to handle problems and enjoy life more.
“Given the plethora of positive characteristics with which it is associated, hope might be considered a master virtue,” writes Miller. “It is a positive orientation of mind and heart toward your own future or that of the world at large.”
Being hopeful can be contagious, too, affecting how others look at what’s possible. For example, Miller recounts a study where staff at an in-patient alcohol treatment center were given the hopeful message that certain patients in their care were more likely to improve. After treatment was over, those patients did, indeed, have fewer drinking episodes, longer periods of abstinence, and higher rates of employment than other patients. But it turns out the staff had been duped—those patients actually had no better chance of improvement than any others. Just infusing hope changed the course of treatment.
While some may doubt the benefits of hope, Miller suggests that a dour view of the future often becomes a kind of self-fulfilling prophecy . For example, he says, believing that people are against you may cause you to act subtly (or not-so-subtly) more hostile toward them, and your behavior can actually cause them to react negatively toward you. Unfortunately, writes Miller, “[These negative] expectations, like a virus, can replicate themselves in an individual or group, often without awareness, and mightily resist effort to remove them.”
How to hope
Since there are good reasons to hope, it’s helpful to understand the many facets of hope, writes Miller. Each of these can play a role in creating or maintaining hope in ourselves and others.
Desire. Hope involves wanting a future outcome that could potentially manifest (even if it seems unlikely). Miller, who spent much of his career helping people overcome alcoholism, found hope for success to be an important element of recovery—and desire to be an important precursor for hope. If his patients didn’t think it was that important to quit drinking—if they really didn’t desire sobriety—it was harder to get them to take the necessary steps to change.
“Desire can create hope, and hope encourages us to take action,” he writes.
In that sense, getting clear about what you desire may be an important starting point. One way to do that is to try the Magic Wand or Best Possible Self exercises.

To find your purpose, imagine a better world
Probability. Since we can’t know what the future holds, there is always uncertainty. But, to some extent, believing that a positive outcome has a good probability of coming to pass can make us more hopeful about it.
However, probability can also be deceiving. We’re all different in our need for certainty, which affects when we will allow ourselves to be hopeful—and it may vary depending on the situation, too. For example, if we’re entering a risky surgery, we may research every corner of the internet seeking reassurance before being hopeful or just trust our surgeon’s expertise.
When it comes to assessing the probability of a hoped-for outcome, we should keep in mind our biases, such as the tendency to only seek information that confirms our views (like ignoring the science around vaccine safety) and our prejudices (like assuming our surgeon’s race or gender is a sign of their competence).
We also shouldn’t assume what’s probable based only on past experiences. For example, women gained the right to vote in the U.S., and Northern Ireland brokered a peace agreement, despite past failures. Having hope can change our odds, he says, so we needn’t let probability determine it.
“Hope not only anticipates but also shapes the future,” he writes.
Possibility. Hope is not just about what’s probable, but also what’s possible. Being willing to keep hope alive can affect everything from your health to a peace treaty, says Miller.
For example, myriad research finds that keeping hope alive in medical situations can affect how much pain a patient feels and whether or not they’ll be “cured.” In fact, Miller cites an interesting review of many placebo studies that found people can experience significant pain relief on placebos if they’re hopeful about them, even though the placebo isn’t active.
“In perceiving and pursuing possibilities, the seemingly improbable can happen because, at least in part, what you see is what you get,” writes Miller. “Seeing a possible pathway forward is both a source and a product of hope .”
Optimism. While hope can be situational, optimism is a facet of being hopeful that is more like a personality trait, writes Miller. Optimistic people seem to experience a lot of benefits, including greater well-being and resilience, and better health and work performance .
When optimists face negative news, they still look for hopeful information surrounding it, and that can inspire them not to lose hope. Pessimists, in contrast, can get lost in negative news and feel hopeless or helpless. But all of us might do well to not overly focus on negative news, as it can affect our mental health and discourage optimism in others, too.
“Collective optimism can rise or fall within a group or population, affecting people’s willingness to invest in the future,” writes Miller.
To practice more optimism, you can try the Finding Silver Linings exercise.

Finding Silver Linings
Change your outlook on a negative event—and enjoy less stress
Trust. Trust might look like seeing people around you as generally trustworthy or believing that things will generally work out, even if sometimes they don’t. In that way, it requires something different from other facets of hope.
“Probability is a calculation, possibility a vision, desire a wish, and optimism a predisposition,” writes Miller. “Trust is more like a decision, a risky choice to entrust your well-being to the safekeeping of another.”
Trust can build relationships and encourage cooperation, which is good for collective action. While not everyone or everything is necessarily trustworthy, we often get better results if we allow ourselves to be vulnerable and accept the uncertainty that comes with trust, writes Miller. Giving into fear, in contrast, may keep us stuck and unhappy.
“Mutual trust is closely related to happiness in personal relationships, organizations, and nations,” he writes. “You [can] choose to trust despite doubts and fear. If the risk is rewarded, trusting can open the door to further trust just as fear begets more fear.”
Meaning and purpose. Having a sense of meaning or purpose in life can also foster hope, writes Miller. While different in tenor, they both help affect how we see ourselves in relationship to the world around us.
“Perceiving meaning in life can provide a sense of coherence, recognition, and comprehension in whatever is happening,” writes Miller, while “purpose in life includes a personal role in the present and future.”
When people have a strong sense of meaning or purpose, it helps them see a bigger picture and avoid giving up after facing obstacles or setbacks. For example, if you are a woman who’s faced discrimination, you may find meaning and purpose in the fight for equality and be less inclined to step away from that fight—even if you become discouraged.
As with optimism, purposeful people seem to experience many benefits, including less chance of developing dementia and better mental and physical health. Purpose can give us the fuel to hope (and work toward) something better, as can meaning.
“Meaning draws on your deeply held beliefs and values, painting a larger picture than the particulars of the present,” says Miller. “It provides a larger context within which to understand current adversity, a bit like zooming up to a certain altitude that affords a broader view.”
For cultivating a sense of purpose, you can try the Affirming Important Values or Life Crafting practices.

Life Crafting
Sharpen your sense of purpose by defining and committing to your goals
Perseverance. While other facets of hope are more about how we think and feel, perseverance is more about action, writes Miller. “To persevere is to continue trying despite obstacles or opposition, to pursue what is difficult even after many optimists and realists have long since lost hope,” he writes.
While hope can spark action, action can also spark hope. For example, when people are depressed (and feeling hopeless), one of the treatment approaches is simply to activate them—to get them to move or engage in pleasant activities, whether or not they feel like it. Doing those activities can provide hope, as people see that their mood is not permanent but can fluctuate.
When we persevere, we are more likely to succeed, because we are willing to consider alternate paths if the path we’d hoped to take was blocked, writes Miller.
Hope beyond hope. While all entryways into hopefulness can be good, there is something to be gained from having hope even when the cause seems lost, writes Miller.
“The core characteristic of hope beyond hope is a refusal, regardless of current reality, to give up and succumb to hopelessness, cynicism, or despair,” he writes.
While it may be hard sometimes to imagine hoping when things are so rough, one can look to exemplars from history who overcame the odds by keeping hope alive, writes Miller—for example, Martin Luther King Jr., Mahatma Gandhi, or Mother Teresa. Not only did these people keep hope alive, they worked in community to help bring about the changes they wanted to see.
Practicing hope is particularly important when we face difficulties that seem insurmountable, writes Miller. Visioning what we want, collaborating with others, practicing patience, and being dogged in our actions can make all the difference in what happens in our future.
“Ultimately hope seeks to keep faith with deeply held values and without regard to attachment to immediate outcomes,” he writes. “It is a conviction that something better is ultimately possible for us collectively.”
About the Author

Jill Suttie
Jill Suttie, Psy.D. , is Greater Good ’s former book review editor and now serves as a staff writer and contributing editor for the magazine. She received her doctorate of psychology from the University of San Francisco in 1998 and was a psychologist in private practice before coming to Greater Good .
You May Also Enjoy

Three Ways to Feel More Hopeful as an Educator

How Hope Can Keep You Happier and Healthier

Are Your Hopes Too High for the New Year?

Can We Be Hopeful and Courageous in the Face of Climate Change?

Seven Ways to Feel Hopeful About Climate Change

Americans Still Have Hope for Democracy, Despite Everything
Fostering and supporting mental health, focusing on empowerment, well-being and suicide prevention
Is it time to get rid of homework mental health experts weigh in, august 17 , 2021.
It’s no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
- Student Success
- Health & Wellness
Survey: Getting a Grip on the Student Mental Health Crisis
Recent Student Voice survey data from Inside Higher Ed finds large numbers of students are experiencing poor mental health, but is this a generational shift or a larger systemic problem in higher education?
By Ashley Mowreader
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

Student mental health concerns and demand for mental health services have both grown—is this a crisis, and what does that mean for colleges and universities?
FotoDuets/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Over the past decade, student mental health has grown as a retention concern for higher education leaders as young people nationally report higher rates of anxiety, depression , loneliness and suicidal ideation .
Recent data from Inside Higher Ed ’s 2024 Student Voice survey of 5,025 undergraduates, conducted by Generation Lab in May, found two in five students say their mental health is impacting their ability to focus, learn and perform academically “a great deal,” and one in 10 students rate their mental health as “poor.”
While states and institutions have invested unprecedented dollars and resources into improving student wellness, identifying the source of college students’ declining mental wellness rates is a challenge for administrators and learners alike.
Inside Higher Ed asked students and college presidents what factors are driving an increased demand for mental health services on college campuses, and the results from the two surveys highlight generational differences in language around mental health, the power of online spaces and the need for a communitywide focus on wellness.
Methodology
Inside Higher Ed ’s annual Student Voice survey was fielded in May in partnership with Generation Lab and had 5,025 total student respondents.
The sample includes over 3,500 four-year students and 1,400 two-year students. Over one-third of respondents are post-traditional (attending a two-year institution or 25 or older in age), 16 percent are exclusively online learners, and 40 percent are first-generation students. Over half (52 percent) of respondents are white, 15 percent are Hispanic, 14 percent are Asian American or Pacific Islanders, 11 percent are Black, and 8 percent are another race (international student or two or more races).
The complete data set, with interactive visualizations, is available here . In addition to questions about health and wellness , the survey asked students about their academics , college experience and preparation for life after college.
Survey says: When asked what factors are the biggest drivers of the “college mental health crisis” or high demand for student mental health services in recent years, 42 percent of Student Voice respondents said the need to balance personal, economic and family duties with schoolwork. ( This was also the No. 1 stressor students reported in the survey ).
Other top drivers, as reported by students, include increased academic stress (37 percent), prevalence of social media (33 percent) and an increase in loneliness (29 percent). Around one-quarter of respondents believe current economic events and generational differences in how students cope with stress are significant factors in the student mental health crisis.
College presidents, on the other hand, pointed to generational changes in the student experience. Inside Higher Ed ’s 2024 Presidents Survey found 86 percent of college leaders (n=362) believe social media is very or extremely influential in the demand for mental health services, followed by decreased socialization skills caused by COVID-19 (74 percent), loneliness (68 percent), pre-existing mental health conditions (62 percent), declining student resilience (62 percent) and the need to balance personal, economic and family duties with schoolwork (59 percent). Only 42 percent of presidents thought academic stress was highly influential.
Mental health experts say these results aren’t entirely off base, with changing demographics of learners in higher education and a growing consciousness of larger societal issues.
“If you ask administrators like me, we’re used to the traditional, normal college student development issues, which is what the college students are saying is what’s hard,” explains James Raper, vice president for health, well-being, access and prevention at Emory University. “‘How do I learn to be a more full human and take all those responsibilities on and be at a university and figure out how to hold that down?’”
At the same time, college leaders should understand that the nature of being a young adult has changed, which impacts students’ mental health.
“Young people are dealing with a completely different world than we were when we were younger,” says Laura Erickson-Schroth, chief medical officer at the Jed Foundation. “Some of the same stressors exist, of course—there are always going to be things going on in your family or with relationships. But young people are thinking about a lot of things that didn’t exist.”
Some of those worries are external, such as climate change, racial justice, reproductive rights, campus protests and anti-LGBTQ+ legislation. Others are more personal, such as a global rise in loneliness among young people and teens spending less time in person with their friends outside of school.
What’s in a crisis? A 2022 survey by TimelyCare (formerly TimelyMD) found 88 percent of college students believe there is a mental health crisis on college campuses.
Doug Everhart, director of student wellness and health promotion at the University of California, Irvine, pushes back against the idea of a crisis, because “language is what helps perpetuate this whole issue,” he says. “We keep saying ‘mental health crisis,’ and we perpetuate that thought by continuing to label it that way.”
For better or for worse, language around mental health has changed as health care professionals and other advocates have worked to address the stigma of mental illness.
Editors’ Picks
- MIT’s Incoming Freshman Class Is Less Diverse, Data Shows
Borrowers Reeling After Appeals Court Declines to Clarify Order
- Library Faculty Eliminated Amid ‘Fiscal Insanity’ at Western Illinois
“Part of this mental health crisis that we’re all talking about on campus is a definitional one,” says Melissa Saunders, assistant director for clinical services at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “Because the term ‘mental health,’ which used to refer to traditional mental illness, like a mood disorder or something significant, has now been used much more broadly, to refer to mental and emotional discomfort that comes from the ordinary stressors of life.”
As language around mental health evolves to be more inclusive and widespread, young people are more comfortable talking about mental health. Active Minds is one example of this work, bringing together student advocates on campuses across the country to discuss mental health and provide peer support.
“We are an organization that is led by young people, so if young people are telling us that they’re in a mental health crisis, we believe them first and foremost,” says Trace Terrell, higher education and policy intern for Active Minds. “If that’s their experience, then we’re going to address their experience directly.”
May data from JED found, among 13- to 17-year-olds, stigma is not a top concern in seeking mental health care. Among Student Voice respondents, 16 percent say the destigmatization of seeking mental health services is one of the drivers of increased demand for support.
Data on students with disabilities finds there is a greater number of students receiving accommodations for mental and emotional disabilities. A May report from the U.S. Government Accountability Office found the number of postsecondary students with depression increased 226 percent from 2004 to 2020. A 2022 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services study found the number of children (ages 3 to 17) diagnosed with anxiety and depression grew by around 29 percent and 27 percent, respectively.
Only 12 percent of Student Voice participants say “more pre-existing health conditions” is one of the biggest drivers of the college mental health crisis. Fifteen percent point to a rise in self-diagnoses.
The role of social media: One in three Student Voice respondents believe social media has played a role in the rise of the college student mental health crisis, compared to 86 percent of presidents.
On the plus side, social media can be a space for students to connect with one another, find support and learn more about their interests or world events. It’s also an accepted norm in today’s culture.
“We all use social media all the time,” Erickson-Schroth says. “It’s the water we swim in at this point. We live our lives online in so many ways.”
Raper believes the challenges with students and social media go deeper than scrolling Instagram or Facebook.
“Forget the function of social media itself on a phone, but the presence of constant information in our brains, on developing brains, makes it harder,” Raper says. “Whether you’re exposed to that first when you’re 8 [years old] or 30, it makes it harder to do the normal life things.”
Electronic stimuli can make it challenging to engage in healthy mental practices, such as mindfulness and contemplative practices. Teaching those skills is a priority for Raper and his team, he says. “They need to catch up—that’s been harder for them, that ability to be bored.”
In normalizing mental health concerns, social media has been both a tool and a detriment, with more learners aware of what mental illness could look like but also more likely to self-determine they have a disorder based on what they see online.
“We have seen a tendency in the last five years or so for students to self-diagnose based on what they’re seeing on TikTok, particularly , but other social medias,” Saunders says. “There’s almost a disorder of the year on TikTok. A couple of years ago, it was autism , and then it was OCD. [Students are] getting a lot of information online, and then matching what they’re feeling at the moment with what they think is a major mental illness, when in fact it’s not.”
Terrell, an undergraduate student at Johns Hopkins, has experienced this firsthand, supporting friends as they struggle with symptoms of poor mental health.
“People can experience anxiety, but having an anxiety disorder is completely different. People can feel sad for long periods of time, but that doesn’t necessarily qualify as depression,” he explains. “It’s really important for us to teach young people how to get it right when they’re talking about it and how to accurately express their emotions.”
A culture of care: Experts agree getting ahead of the mental health crisis takes a community effort, catered to the institution and its students.
“We don’t want to engage just the individual well-being issue,” Raper from Emory says. “It’s not just ‘Go to counseling.’ We have to create a community that supports this.”
JED is seeing “unprecedented numbers” of college campuses reaching out to the organization, looking to make mental health and suicide prevention a priority. “They’re excited to think about this on a large scale in ways that they weren’t before,” Erickson-Schroth says.
The presidents’ survey found 57 percent of leaders agree somewhat or strongly that their institution has enough clinical capacity to meet the mental health needs of their undergraduate population. Seven in 10 respondents also indicate they have invested in wellness facilities or services to promote overall well-being on campus since 2020.
Emory will roll out a new well-being framework in the fall, helping students practice and reflect on eight dimensions of wellness while involving the entire campus community.
UC Irvine is piloting an initiative this fall, as well. It encourages social development of students by creating informal conversation spaces for students, faculty and staff members to engage and bond over shared interests and hobbies.
“Our hypothesis is that it’s going to improve communication, improve relationships and take down these barriers for connection and engagement that currently prevent them from doing [wellness and self-care],” Everhart says.
Active Minds is also working to start conversations with students in middle school, getting ahead of student crises by empowering them with education and programming.
Read more about institutional interventions to support student mental health here.

The order blocked the Biden administration’s SAVE plan and raised questions about the Education Department’s authorit
Share This Article
More from health & wellness.

Student Wellness Tip: Investing in Graduate Student Mental Health
Campus leaders at Ohio State University are using state funding to bolster resources and services for graduate

Listen: Campus Facilities Promote Inclusion, Mental Health of Students
In the latest Voices of Student Success episode, learn about how colleges are working to better student well-being th

Funding Student Success: Scholarships for Former Foster Youth
California created a scholarship for students with foster care history attending public, four-year institutions in th
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
- Imposter Syndrome: Causes, Types, and Coping Tips
- Autism at Work: Overcoming Challenges
Ageism and Age Discrimination
Bullying at work, interviewing techniques and tips, job networking tips, finding the right career.
- Disability at Work: Cope with Challenges and Thrive
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
The link between work and mental health
Signs and symptoms of a mental health issue at work, coping with work-related mental health problems, how to care for your mental health at work, mental health and working at home, how to talk to your employer about mental health, mental health in the workplace.
Are you struggling with anxiety, depression, burnout, or bullying at work? There are ways to cope with a toxic workplace, ease the stress of remote working, and improve your work-life balance.

Work can play a huge role in your overall health and welfare. In addition to the financial benefits, your job can add meaning, structure, and purpose to your life. It can also provide you with a sense of identity, bolster your self-esteem, and offer an important social outlet.
However, working in a negative environment can have the opposite effect and take a heavy toll on your emotional health. Long hours, understaffing, a lack of support, and harassment in the workplace can ramp up your stress levels and contribute to mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse. These problems have only been exacerbated by the pandemic and the major shifts in our working habits over the last couple of years. Many of us have spent months adapting to the new stressors of working remotely, for example, only to now have to re-adjust to commuting and working onsite again. It’s left us feeling tense, unhappy, and worried about the future and how we spend our days.
Just as work can impact your mental health, so too, your mental health can affect your work, impacting your job performance and productivity. In fact, recent estimates suggest mental health issues cost the global economy $1 trillion annually in lost productivity, absenteeism, and staff turnover.
For most of us, a lot about our workplace environment remains outside our control. The culture at work is established by those in senior positions above us and we often feel unable to speak out without fear of judgment or risking our jobs. But whether your mental health issues are caused by your workplace or stem from elsewhere and are affecting your performance at work, there are steps you can take to care for yourself and protect your well-being. With these tips you can learn to talk to your employer about mental health, cope with common challenges at work, increase your resilience, and better strive to fulfill your potential—in the workplace and beyond.
Workplace risk factors for mental health
Common work-related challenges that can negatively impact your mental health include:
- Long, inflexible hours, short-staffing due to cutbacks or unfilled vacancies, or an ever-increasing workload.
- Working remotely with no clear separation between work and personal time.
- A toxic workplace that fosters bullying, harassment, or abuse.
- Lack of training or guidance for the role you’re expected to fulfill.
- Limited or unclear communication from management about tasks, goals, or decision-making.
- Lack of support, shortage of equipment or other job resources, or unsafe working practices.
We all have bad days at work from time to time, days when nothing seems to go right. You may have difficulty focusing, feel overly stressed, irritable, or unappreciated, or lack the energy and motivation to complete even the most basic task. But if this is how you feel day after day, it can be a red flag that something is wrong.
Many mental health problems can creep up on you slowly. You can get so used to feeling frazzled, anxious, and downbeat at work that it starts to feel “normal”. But ignoring the early signs of a problem won’t make it go away; it will just become worse over time, leaving you vulnerable to illnesses and other health problems, causing burnout , and damaging your job performance, relationships, and home life.
While the symptoms of mental health problems can vary wildly according to the condition and the person experiencing them, it’s important to be aware of any changes to how you’re thinking, feeling, and behaving. If you identify with several of the following symptoms in yourself (or in a work colleague or employee), it could indicate that it’s time to reach out for help.
- Decline in your performance at work. You struggle to function in your daily duties at work (as well as at home or social life).
- Trouble concentrating and thinking. You have problems focusing on tasks or experience difficulties with your memory, thinking, or even changes to your speech patterns.
- Changes in your appetite or sleeping patterns. Struggling with insomnia, sleeping too much, sudden changes in how much you eat, or relying more and more on drugs and alcohol to cope.
- Changes in your mood. You feel hopeless, helpless, on-edge, or experience uncharacteristic mood swings or even suicidal thoughts.
- Loss of interest in activities. You lose interest in aspects of your work that you previously enjoyed, quit hobbies you used to love, or withdraw from friendships and social activities. This could be accompanied by pronounced apathy.
- Fear or nervousness. You feel overly suspicious of others at work or socially, or feel suddenly nervous and fearful in certain situations.
- Increased sensitivity. You’re more sensitive to sights and sounds and try to avoid any situations that are over-stimulating.
- Unusual behavior. You feel disconnected to your surroundings, exhibit uncharacteristic, unusual, or out of control behavior, see or hear things that aren’t real.
- Unexplained aches and pains, such as headaches, upset stomach, or muscle pain.
When stress, harassment, or mental health problems negatively affect your performance, relationships, and physical functioning at work, you may feel isolated, overwhelmed, and struggle to know where to turn. But you’re far from being alone.
Recent surveys suggest that about one in five US adults report having a mental health issue each year while 70% experience symptoms of stress. While most people never seek help, there are steps you can take today to start improving how you feel.
While some stress can provide you with the focus and energy to meet deadlines and challenges at work, too much can take a toll on your health and productivity. When you’re constantly worried about being laid off, having to work longer and longer hours, or feeling under pressure at work all the time, your mood, personal life, and job performance will suffer.
No matter how stressful your job is right now, there are ways you can relieve the pressure, lower your stress levels, and regain a sense of control. Read Stress at Work .
It’s normal to feel down or unhappy every now and then, but feeling like you’re in a black hole, hopeless and helpless, could be a sign of depression. When you’re depressed, you feel so listless and despairing that it impacts your ability to work, eat, sleep, and find enjoyment in life. Just getting out of bed in the morning can seem overwhelming.
But as bleak as things may seem at the moment, there are steps you can take to boost your mood, overcome feelings of sadness and despair, and regain a sense of hope. Read Coping with Depression .
Like stress, not all anxiety is bad. In manageable doses, it can help you face a challenging situation, such as a job interview or important presentation. But when you’re plagued by constant worrying, negative thoughts, or an overwhelming sense of tension or panic, it can interfere with your daily life and ability to perform in the workplace. Anxiety can drain you emotionally, leave you feeling nervous and restless, and trigger insomnia, headaches, stomachaches, and muscle tension.
Whatever type of anxiety disorder you’re facing, there are ways to turn off anxious thoughts and find calm again. Read: Anxiety Disorders and Anxiety Attacks .
Bullying or harassment
When bullying, abuse, or harassment occur in the workplace, it can create a hostile environment and have a damaging impact on your mood, outlook, and overall health and well-being. Whether you’re being targeted because of your gender, race, sexual orientation, or religion, you may work in constant fear, feel compelled to take time off sick whenever possible, or even want to quit, regardless of the financial consequences.
While you may feel powerless to put a stop to bullying and harassment, especially when the perpetrator is a boss or high-performing colleague, there are steps you can take to regain control. Document the negative behavior, seek support from any coworkers who’ve witnessed it, and then approach someone higher-ranking than the bully or abuser—whether that’s a manager, director, or sympathetic HR person. Read: Bullying at Work .
Are you self-medicating your problems?
When feelings of tension, fear, hopelessness, or grief start to impact your work life, it can often be tempting to try to find the easiest way to cope on your own. For many of us, that means taking a pill or pouring a drink. While self-medicating your problems can sometimes offer some short-term relief, over time it only creates more difficulties.
Whether you turn to alcohol, illegal drugs, prescription medications, or even food to change the way that you feel, there are healthier and more effective ways of improving your mood and coping with your problems. Read: Self-Medicating Depression, Anxiety, and Stress .
When you’re feeling stressed and overwhelmed by the demands of work, taking time away—using personal or sick days or taking some vacation time—can help you to recharge and avoid burnout . However, if you have a persistent mental health issue, such as depression or anxiety, you’re going to need more than just a few days off.
Caring for your mental health in the workplace isn’t just about dealing with immediate mental health problems, either. It’s also about promoting well-being. Even if you’re not facing a mental health challenge right now, taking steps to care for your emotional health can help you build resilience, improve your work performance, and provide you the tools to better cope with uncertainty and challenges in the future. The following tips can help:
Switch off. Whether you’re working onsite or remotely, it’s important to strike a healthy work-life balance. That means taking regular breaks throughout the day and switching off your screens when the work day is over. Instead of making yourself available 24/7 to respond to work calls, emails, or other messages, it’s important to focus on friends and family and take the time to relax, recharge, and enjoy yourself.
Practice relaxation techniques. Relaxing and recharging requires more than just zoning out on the couch in front of the TV. To reduce the damaging effects of stress and protect your mental health, you need to activate your body’s relaxation response. This can be done by practicing a relaxation technique such as meditation, deep breathing, rhythmic exercise, or yoga.
Take care of yourself. Getting enough quality sleep at night , eating a healthy, nutritious diet , and regularly exercising can make a huge difference to your mental health—at work and beyond. These are also aspects of your life that you have more control over than many things in your workplace. The more effort you put into self-care, the better you’ll feel. If necessary, talk to a therapist about building self-care strategies.
Find meaning and purpose in your work. Even if you don’t love your job, you can still find ways to derive meaning and purpose from the work that you do. Try to focus on how your work helps others, for example, provides an important product or service, or the relationships you enjoy with your coworkers. Looking for opportunities to get more training or take job-related classes can also help you to find more meaning in your work.
[Read: Finding the Right Career]
Try to connect and collaborate. As human beings, we crave connection. Developing mutually supportive relationships with your coworkers, collaborating as a team, and having fun together can help ease stress and bolster your mood at work. If you’re not close to your colleagues, make the effort to pool resources on projects, work closer together, and be more social during breaks and outside the workplace.
Build resiliency. The more resilient you are, the better you’re able to tolerate the feelings of stress, anxiety, and hopelessness that can be generated by problems at work. Building resilience can also help you from setbacks in your career or personal life and help you maintain a positive outlook. Rather than being a macho quality, resilience is something that requires effort to build and maintain over time.
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, more and more of us have found ourselves working from home. While it can be gratifying to be free of the daily commute and its related expenses, there are still plenty of drawbacks to working remotely that can take a toll on your mental health.
Many people feel isolated away from the workplace, disconnected from the support and social aspects of being among colleagues. It can be extremely stressful living and working in the same place every day, especially if it’s a small space, you’re looking after young children, or you have other family members also working from home. Endless back-to-back virtual meetings, longer work hours, and feeling the need to always be “on” can also be a drain on your time, mood, and outlook.
Whether you’re working from home full-time or just intermittently, there are steps you can take to ensure you protect your mental health and make it a more productive and enjoyable experience.
Maintain a regular work routine. When you’re working from home, it can be very difficult to establish a boundary between work and home time, so many people find themselves worker much longer hours. To maintain a sense of normalcy, try to keep regular office hours, starting and finishing at the same time every day. Some people find it useful to go for a walk before starting work in the morning and then again after finishing work in the evening. It can help you mentally switch from work to home mode and vice versa.
Schedule breaks and set boundaries. Just because your desk is at home, it doesn’t mean you always have to be available. Set aside time to take a break from your screens and have lunch, for example, and then turn off your phone and computer when you’re done for the day. Try to leave time between virtual meetings so they don’t feel so overwhelming.
Establish a dedicated work space. Even if you don’t have a separate room that you can use for a home office, try to reserve a space that you can use just for work, rather than working at the kitchen table, for example. You’ll find it easier to keep to your routine and separate your work and home life.
Look for opportunities to work outside the home. If you’re missing being around other people, try working at a coffee shop or library, or renting a co-working space.
Schedule face-to-face time with your co-workers. To counter the sense of isolation, arrange regular meetings or social events where you can see your colleagues in-person and catch-up. If you freelance, reach out to other freelancers on social media and arrange face-to-face get-togethers.
If your emotional state is impacting your ability to perform at work, you may decide that it’s time to talk to your boss, especially if it’s your work environment that’s causing the problem. However, many of us are understandably reticent about talking to others about our mental health, especially our supervisors or employers. You may fear that you’ll be negatively judged, your reputation will suffer, or your career damaged.
There also remains a stigma attached to mental health that can make it difficult to open up in the same way you would about a physical health issue. Some people view feeling stressed, depressed, anxious, or traumatized as some kind of character flaw, something to be ashamed of. But the truth is that 80% of us will experience a diagnosable mental health condition at some point in our lives. So, whether you’re aware of it or not, the chances are that your boss has or will experience a mental health issue, either directly themselves or in someone very close to them.
This has never been truer than it is now. The stress and upheaval of the COVID-19 pandemic has seen mental health problems skyrocket. Very few of us have remained untouched. Yet, thankfully, more and more people are feeling able to share what they’re going through, helping to reduce the stigma of what are normal human conditions.
Talking to your boss
Mental health and substance abuse cost companies billions of dollars each year, so it’s in your employer’s interest to listen and take steps to improve the workplace whenever they can.
How much you choose to disclose will largely depend on your employer’s personality, the level of trust in your relationship with them, and your own comfort levels. If it’s your boss who’s causing the problem—bullying, harassing, or creating a dysfunctional environment—you’ll want to approach his superior or someone in your company’s HR department.
It can also help to:
Choose the right time to talk. Find a quiet time at work to approach your employer, when they’re more likely to be calm and not stressed. That may be at the end of the week, for example, when things are winding down, rather than during peak hours or ahead of a pressing deadline. Try to schedule a time when you’re both free of distractions and unlikely to be interrupted.
[Read: Effective Communication]
Focus on your work performance. Instead of simply listing all your complaints, explain to your boss how specific conditions are impacting your ability to perform in your job. For example, you could explain how sudden changes in your duties and responsibilities have created high levels of stress or exacerbated your panic attacks.
Offer concrete solutions whenever possible. Suggest changes your boss can make to help you improve your work performance. For example, if you need to see your therapist without arriving late for work, asking for flexible hours or to work at home on certain days of the week could be a practical solution. Or, if you’re overworked due to understaffing, suggest which low-priority tasks you could skip or delegate to ensure you don’t fall behind.
Remember there’s strength in numbers. If any co-workers are also being bullied, harassed, or suffering in a negative environment, approaching your employer as a group can add weight to your voice.
Be understanding of your employer. These are stressful, demanding times for all of us. The pandemic has changed much about how we work and the “new normal” seems to be changing all the time. So, don’t expect your boss to immediately have all the answers. Allow them the chance to think about what you’ve told them, but make sure you set a time for a follow-up session.
Speak to a Licensed Therapist
BetterHelp is an online therapy service that matches you to licensed, accredited therapists who can help with depression, anxiety, relationships, and more. Take the assessment and get matched with a therapist in as little as 48 hours.
Know your legal rights
Depending on your country or state of residence, you may have a legal right to receive reasonable accommodations to help you fulfill your duties at work. While it’s always better to adopt a conciliatory rather than confrontational tone with your employer, researching your legal position can add authority to any reasonable requests you make. See the “Get more help” section below for resources.
Call the NAMI HelpLine at 1-800-950-6264.
Call the Mind Infoline at 0300 123 3393 or SANEline at 07984 967 708.
Call the Sane Helpline at 1800 187 263.
Call Healthline at 0800 611 116.
Call Wellness Together Canada at 1-866-585-0445.
Call the Mental Health helpline at 1800-599-0019 or the Vandrevala Foundation Helpline at 1860 2662 345.
More Information
- Stress in America - 2021 survey by the American Psychological Association. (APA)
- Mental Health in the Workplace - The work-related effects of mental health disorders and stress—and what you can do about them. (CDC)
- Employer resources - Tools, resources, and information for employers to promote and support the mental health of their employees. (Center for Workplace Mental Health)
- Depression, PTSD, & Other Mental Health Conditions in the Workplace: Your Legal Rights - Legal tips in the U.S. from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. (USEEOC)
- Supporting mental health at work - Legal advice in the UK on dealing with workplace mental health. (Acas)
- Anxiety Disorders. (2013). In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . American Psychiatric Association. Link
- Depressive Disorders. (2013). In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . American Psychiatric Association. Link
- Greenberg, Paul E., Andree-Anne Fournier, Tammy Sisitsky, Crystal T. Pike, and Ronald C. Kessler. “The Economic Burden of Adults with Major Depressive Disorder in the United States (2005 and 2010).” The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 76, no. 2 (February 2015): 155–62. Link
- Kessler, Ronald C. “The Costs of Depression.” The Psychiatric Clinics of North America 35, no. 1 (March 2012): 1–14. Link
- Lipari, Rachel N. “Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health,” 2019, 114. Link
- “2015 Stress in America Snapshot.” Accessed September 29, 2021 Link
- Schaefer, Jonathan D., Avshalom Caspi, Daniel W. Belsky, Honalee Harrington, Renate Houts, L. John Horwood, Andrea Hussong, Sandhya Ramrakha, Richie Poulton, and Terrie E. Moffitt. “Enduring Mental Health: Prevalence and Prediction.” Journal of Abnormal Psychology 126, no. 2 (February 2017): 212–24. Link
More in Work & Career
Imposter syndrome.
What to do when you feel like a fraud at work, school, or in relationships

Autism at Work
Overcoming challenges and finding success in the workplace

How to challenge ageism in the workplace and in daily life

How to deal with a workplace bully

Prepare for and feel more confident during the interview

How to find a rewarding job by building powerful relationships

How to choose or change career paths and find job satisfaction

Disability at Work
How to cope with challenges and thrive

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.

COMMENTS
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer ...
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for ...
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The ...
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Health Hazards of Homework. Pediatrics. A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework "experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.".
Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. The researchers asked students whether they experienced physical symptoms of stress, such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep ...
Mental health experts weigh in. August 16 2021, by Sara M Moniuszko. It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental ...
Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework. Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation ...
Below, Dr. Erkfitz shares some tips that can help with therapy homework: Set aside time for your homework: Create a designated time to complete your therapy homework. The aim of therapy homework is to keep you thinking and working on your goals between sessions. Use your designated time as a sacred space to invest in yourself and pour your ...
Key points. Generally, homework should include about 10 minutes per night per grade level. The value of homework is debated, with questions about the right amount and potential for inequity ...
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies' Home Journal, decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but ...
Homework as a Mental Health Concern. It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health ...
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer ...
The relationship between homework compliance and therapy outcomes: An updated meta-analysis. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 34(5), 429-438. Ribbers, A., & Waringa, A. (2015). E-coaching: Theory and practice for a new online approach to coaching. Routledge. Shapiro, S. L. (2020). Rewire your mind: Discover the science and practice of mindfulness.
Yes. Generally, the link between homework and achievement scores is stronger for math compared to subjects like English and history. For middle school students especially, math homework can strengthen school performance. There is not a lot of research into the quality of homework. Most experts agree that homework should be reinforcing what kids ...
3. Sometimes you need to take a break. If therapy isn't enough, it might help to take time off from work. It could be anywhere from one day to several months, but taking time to process, rest ...
There is a non-linear relationship between homework time and adolescent mental health. • Homework negatively impacts adolescent mental health, but only when exceeding about 1 h and 15 min. ... 3=Yes, and the equipment is in good condition. 2.182: 0.636: 5.2.5. Descriptive statistics. Table 2 presents the definitions of the variables and ...
Improving the awareness and perception of events. Regulating emotions. Encouraging awareness. Boosting physical health. The positive effects of journaling can even be felt when not performed daily - helping the individual better understand their needs and boosting their wellbeing (Tartakovsky, 2022).
Housework is linked to sharper memory, attention span, and better leg strength, and by extension, greater protection against falls, in older adults, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Open. The findings were independent of other regular recreational and workplace physical activities, and active commuting.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they ...
Discover how a balanced school-life approach can improve kids' mental health. Learn strategies for fostering well-being and success both in and out of the classroom. Subscribe To Newsletters
Understanding good mental health. Your mental health influences how you think, feel, and behave in daily life. It also affects your ability to cope with stress, overcome challenges, build relationships, and recover from life's setbacks and hardships. Strong mental health isn't just the absence of mental health problems.
The mental effects of homework can be harmful as well. Mental health issues are often ignored, even when schools can be the root of the problem. An article from USA Today contained a quote from a licensed therapist and social worker named Cynthia Catchings, which reads, " heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the ...
Based on your brain activity, scientists can now predict your emotions and how strong they are in response to a stimulus. Five Ways Parents Can Help Kids Navigate Social Media August 20, 2024. Parents can help mitigate some of the harm that social media may be doing to young people's mental health.
Good vs. Bad emotions. ... Consult your physician or a mental health expert for advice and treatments. Certain kinds of therapy that could be beneficial include cognitive behavior therapy (CBT ...
August 17, 2021. Anxiety Children Covid-19 Mental Health Depression Mental Health. It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Explore our unique guides to identify symptoms, causes, and treatment for your condition, and discover how to take charge of your mental health.
Survey says: When asked what factors are the biggest drivers of the "college mental health crisis" or high demand for student mental health services in recent years, 42 percent of Student Voice respondents said the need to balance personal, economic and family duties with schoolwork. (This was also the No. 1 stressor students reported in the survey).
With these tips you can learn to talk to your employer about mental health, cope with common challenges at work, increase your resilience, and better strive to fulfill your potential—in the workplace and beyond. Workplace risk factors for mental health. Common work-related challenges that can negatively impact your mental health include: