The State of the Barangay Health Centers of Tanauan City, Batangas: An In-Depth Study
- DSpace Home
- Department of Social Sciences
- BA Development Studies
Show simple item record
| dc.contributor.author | Barrera, Maita Florence A. | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2022-11-17T01:17:23Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2022-11-17T01:17:23Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2008-03 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://dspace.cas.upm.edu.ph:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/1783 | |
| dc.description.abstract | Health is a basic human right. It determines the productivity of the work force; hence, it is one of the major factors of economic development. In this case, quality health care should be accessible to all. Efforts to increase the accessibility of the health care system from the side of the government have been made, like the devolution of the health care system through the introduction of rural health units and the Barangay Health Centers in virtue of the Primary Health Care system which was introduced in the 1970s. The Barangay Health Center is the lowest branch of the organizational setup of the Primary Health Care system; hence it is where the first contact of the health care system with patient occurs. It administers free basic health services like maternal health care, immunization programs and free medicines, and is concerned with the improvement and maintenance of the basic health indicators of the people. The Barangay Health Centers then are of utmost importance when it comes to the health care of the people from distant or rural areas who cannot afford to go to hospitals which are usually located in cities. The accessibility of the Barangay Health Centers of Tanauan city is greatly affected by their geographic distance from the people. Hence, the Barangay Health Centers and the organization attempts of the City Health Office and Local Government Unit are only accessible to those who live near the Barangay Health Centers. This proves to be problematic to those who live far from the Barangay Health Centers since they only comprise the minority of those who avail of the free health services. The accessibility of the Barangay Health Centers of Tanauan city, then, is the major concern of this research. Twenty out of the forty three Barangay Health Centers of Tanauan city are used as representatives of the Barangay Health Centers ofTanauan city as a whole. | en_US |
| dc.title | The State of the Barangay Health Centers of Tanauan City, Batangas: An In-Depth Study | en_US |
| dc.type | Thesis | en_US |

Files in this item
This item appears in the following collection(s).
- BA Development Studies Bachelor thesis of BA Development Studies
Search DSpace
All of dspace.
- Communities & Collections
- By Issue Date
This Collection

Health Center Management System Capstone Project Document
Introduction.
In the current time people can’t imagine their life without technology. The technology sector has changed and developed many products. A computer is an example of technology that helps people in many ways. People use computers to finish office works, for business and also for entertainment. Computers helps us makes manual process easier and efficient.
Most of us already engage ourselves in the developing state of our environment. As we go on to our study, we ask several people on how modern technology affects their daily activities, one of those are the health centers which is having a lot of daily activities. Our system focuses on how the health center personnel can convey an effective service to its people in a manageable span of time. It also emphasizes with the registration of ongoing patients, together with their SMS notification wherein they will be easily notified about their appointments, changes of schedule and follow- up reminders. In addition to that are the health center personnel can easily manage their time and can give effective and efficient satisfaction to their patients with the help of our system.
Background of the Study
Barangay health center is a community based and patient directed organization. It is usually the first point of contact between residents of the community and other health care facility levels. Barangay Estefania health center provides consultation, immunization and prenatal. They are using manual procedure to get information from their patients. Barangay health center service is regulated by the DOH. Every health center is equipped to provide primary level of health care.
We developed this system in order to make the health center acquire modern technology, to consume the time works and easily deliver monthly reports and records. The provision of high-quality health care services is an increasingly difficult challenge and outcomes of health care services. It is a key to inform government officials by having a modern technology and other decision making more accurate about health-related issues. Health services researchers examine the access to care, and easily to processes the outcomes of health services for individuals and populations.
Statement of the Objective
The Automated process of Health Center will be a big help to them, that was the main objectives of our system to get out from manual process, and to implement a new way of method to the center.
The study aims to develop a system that allows to:
- Organize the record list and easily to find the previous Records.
- Lessen the time to find their Records in log book and their paper works.
- Easy to get information by using SMS notification.
Conceptual Framework
The goal of this study is to make the Health Center automated from manual process. This system can record and send SMS notification.
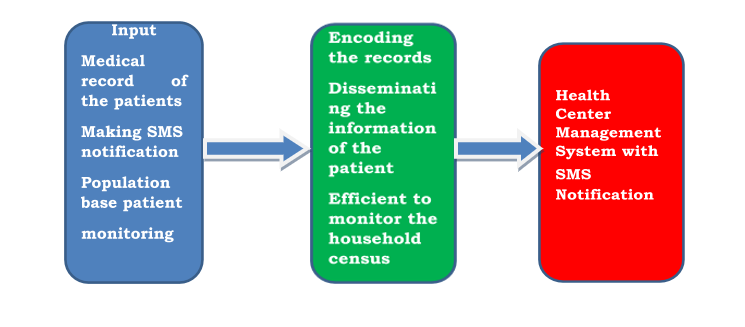
Scope and Delimitation
This system has the following scope and limitations:
Scope
This study consists of SMS notification, records and similar nature of transaction and processes of barangay health center. For the patient information database, the report generates a purpose and also SMS Notification. This system can be use by the personnel of the Barangay Estefania Health Center. Through SMS Notification they will know the information and schedule activities for the patient and with upcoming events. The SMS notification will transmit the message through the patient about the program from the health center.
Delimitation
This study does not cover the previous years patients records. Only the volunteer can access the system. Volunteers are the ones to make or set appointment of the patient. Once the SMS notification is sent to the patient, the patient can’t reply to the sent message. There is also possibility of SMS failure due to coverage of signals. It also covered maintenance good for 6 months.
Significance of the study
The study will be significant to the following identified beneficiaries:
Patient . They will never forget their schedule for their next visit at the center, it’s because the center have already the system that can sent a notification for all their patients. They have a timely record for just a one click ahead where records can be easily and ready to print out.
BHW . Makes their paper works secure, time consumption manageable, and most of all avoiding human errors and misinformation of the patients records. The main purpose of this is making the reports for the supplies in the center, like the medicines. Is considered as the most informative system in all barangays. By the SMS, it also ease the barangay personnel to send the information to the people. It is needed for health assistance and guidelines for the national investment of technology for the system to be fully functional. Improve client services satisfaction.
Future Researcher . This may acquired the same study, useful research in the future and recommendation of study.
Definition of Terms
To provide understanding of the following terms used below conceptually and operationally.
Data- Conceptually, as a general concept refers to the fact that some existing information or knowledge is represented or coded in some form, suitable for better usage or processing.
Operationally, is a collection of information that organized so that it can easily be accessed, manage and update.
Record- Conceptually, a thing constituting a piece of evidence about the past, especially an account of an act or occurrence kept in writing or some other permanent form.
Operationally, files where you will find information regarding patients.
SMS Notification- Conceptually, is also commonly referred to as a text message. With a SMS you can send a message of up to 160 characters to another device.
Operationally, contains information date, time and change of schedule.
System- Conceptually A set of principle or procedure according to which something is done an organized scheme or method.
Operationally, automated filling of records for easy access.
Review Of Related Literature
This chapter includes concepts of related study in the system that show or present the information about the Barangay Health Center with SMS Notification.
LOCAL RELATED STUDIES
- Patient Record Management System
TAB FUSION RMS modules handle everything from entry level tracking to advanced imaging all with enhanced security and optimized workflow. Easy to access patients records management software solution. It can use unity of the entire spectrum of medical records that your institution needs. Make retrieval and viewing of patient (or staff) information easy and secure. Ensures the right information is in the right hands at the right time. Deliver easy to use transparent reporting in a variety of formats. Tab Corporate Headquarters- 2002
http://www.ameshealthcarerecords.com/record-management-system/
- SMS Delivers Patient Support in Many Form
The SMS advantages in Health Care institutions want to connect with their patients via SMS should pay attention to these figures. SMS can help with many aspect of the healthcare process, such as sending patient’s appointment and follow-up reminders, information about schedule changes, timely medical advice and more. SMS also has the advantage of making communication feel more personal, since messages are sent to individual phones.
Sharon Hurley Hall- February 17, 2016
https://www.mobilecommon.com/blog/2016 /02/sms-delivers-patient-support-many-forms/
FOREIGN RELATED STUDIES
- Clinic Management System outpatient Management System
It is design to be tool for doctors and also registrar to manage their out patient. Design to provide better service to patient, patient details and other vital information for group clinic such as registration process. Lessen the workload of registrar, where all data are easier to receive without time wasting compare to the manual process where data about patient need to be search in the archive, where required extra effort and time.
Nurzety Aqtar Ahmad Azuan- March 2005
https://sourcetorge.net/project/clinicmanagement
- The Helpful Patients Record System: Problem Oriented and Knowledge Based
A helpful Patients Record System is a problem oriented and knowledge based system which provides the clinician with situation- specific information from the patient record, relevant to the activity within the patient care process. They suggest extending the data model of current patient record system. Knowledge for recognizing and interpreting care situation. Knowledge for how clinician work and what information they need means to rank information according to its relevance in a system situation. Elizabeth Bayelgan-2002
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nin.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2244287
Related System Summary Table
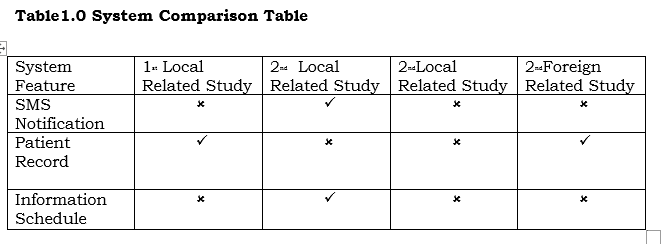
Related System
This table shows the features of our system based on the researcher analysis in the comparison of related system according to Barangay Health Center with SMS Notification Management System.
The system that in the related studies, both local and foreign in the system feature they present of each local and foreign that connected to the systems. The 2 nd local related study the patient can access SMS Notification. The 1 st local and 2 nd foreign related study has patient record. Only the second local related study has information schedule. Base on the research both related study doesn’t have similarities in our system.
Methodology
This chapter is to show the flow of system and techniques applied in this study. The purpose explains the use and the process of developing of the system.
System Development Life cycle (SDLC) was designed to build on one another, it is a framework defining tasks performed at each step in the software development process. SDLC is a structure followed by a development team within the software organization. It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain and replace specific software by incremental waterfall model.
Development process is structures that impose the development of software. Describing approaches to a variety of tasks or activities that take place during the process. The basic activities or task of development software process are as follow Planning, Analysis, Design, Development, Testing, Implementation and Maintenance phases.
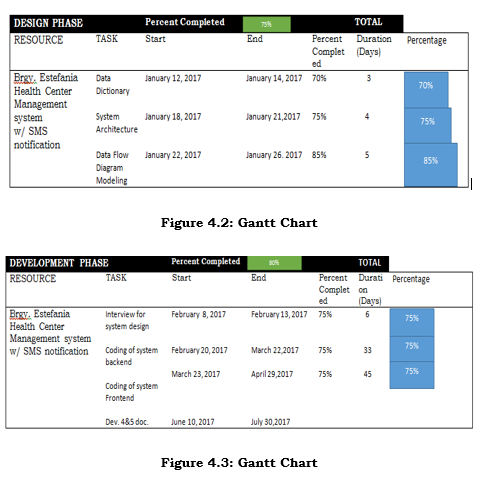
Planning Phase
The project will start upon discussion of the group about the kind of system we will be developing. The group already come up with a list of company we will be visiting for an interview. After that we will come up with the title for our defense.
Analysis phase
This phase, the researcher will start collecting data and information needed for the system. Involved the flow of the system, as well as their role and responsibility and current process that is being adopted by the health center in daily operation.
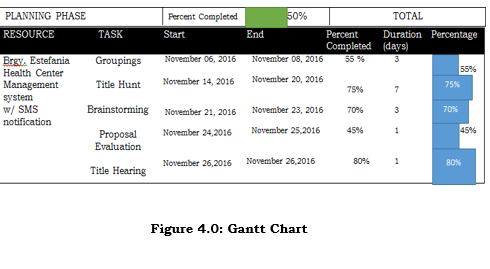
Design Phase

Waterfall Model
Figure 2.0: Incremental Waterfall Model
This phase, we design for the system. We will make a Dataflow that will modify how the system flow. And the Software requirement specification this is the reference of the system architect to come up with the design for the system.
After the analyzing the data and information its already read for database program, the proponent were able to plan the interface and start on its design.
Development Phase
This phase is to analyzed the information and the initial design of the system, creating database and using coding in order for the system to work
Testing Phase
This phase is the testing of the system to the administrator or BHW of health center where defects are identified and retested of the system. Until it achieve the standard quality of the system.
Implementation Phase
This phase is presented to the user by the features and system details of documentation. After the documentations, the developers conduct the seminar or survey to the user of the system to test and to check the error in the software. This error will be fix to formal software and to give it to the BHW/ administrator when the system is correctly implemented.
Maintenance Phase
In this phase, the system require maintenance, edit and delete made by administration or BHW of the system are considered for its enhancement. For the purpose, maintenance of the system is updated only for 6 months.
User’s Acceptance Survey
The system were improved the record of patient and the services in BHW. The Health Center should be enhanced with the activities, the operations of the application of patient with the SMS notification
Requirements Specification
Operational feasibility.
The goals of this system study are to develop the following functionalities:
- Provides an information schedule for the patient which may help for the patient to know their schedule.
- Provide the medicine and services for the patients.
- An SMS notification and mobile application that can be accessed in anywhere through the individual mobile phone.
- Generates a monthly and weekly patient record.
- The health center that provides a free consultation, immunization, pre-natal check up and other services that help for the patient.
Program Environment
HTML is the standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications . With Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and JavaScript , it forms a triad of cornerstone technologies for the Worldwide Web. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render them into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document.
CSS the Cascading Style Sheets Specification (CSS) is a computer language that is used to write formatting instructions. It is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors, layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices, such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML and can be used with any XML-based markup language.
PHP is a widely-used open source general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and can be embedded HTML. PHP is a general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited to server-side web development, in which case PHP generally runs on a web server. Any PHP code in a requested file is executed by the PHP runtime, usually to create dynamic web page content or dynamic images used on websites or elsewhere.
MySQL is an open source relational database management system that uses structure query language, the most popular language for adding, accessing, and processing data in a database. MySQL is noted mainly for its speed, reliability, and flexibility. It is fast, robust and scalable relational database management system.
Technical Feasibility
Hardware specification (maximum requirement)
- Quad Core Processor
- Android 5.0 version up to latest version
- Dual Core Processor
- 4GB Ram (internal Memory)
- 320GB Hard drive
Software specification (maximum requirement)
- Google chrome version 6.3.2
- Mozilla firefox 17.6
- Windows 8.0 Pro
System Architecture
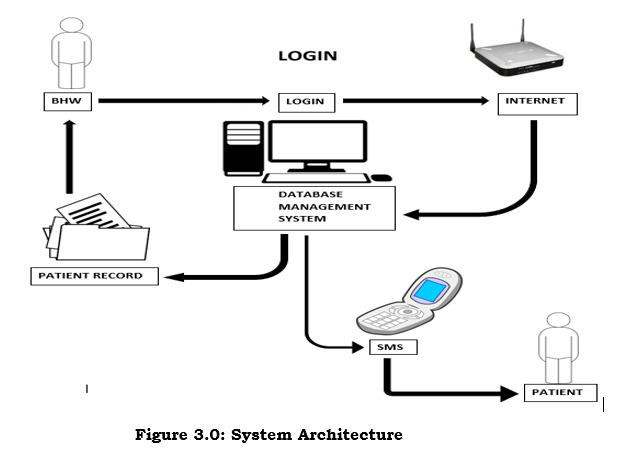
The health center management system will display the network design for the user and end up for the patient. It shows that the system needs the patient to access through internet connection and mobile phone to be able to get information for the efficiency to deliver the information schedule and services.
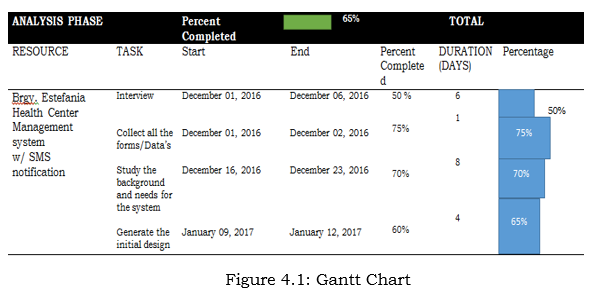
Analysis Phase
Design and Developmental Phase
Gantt Chart
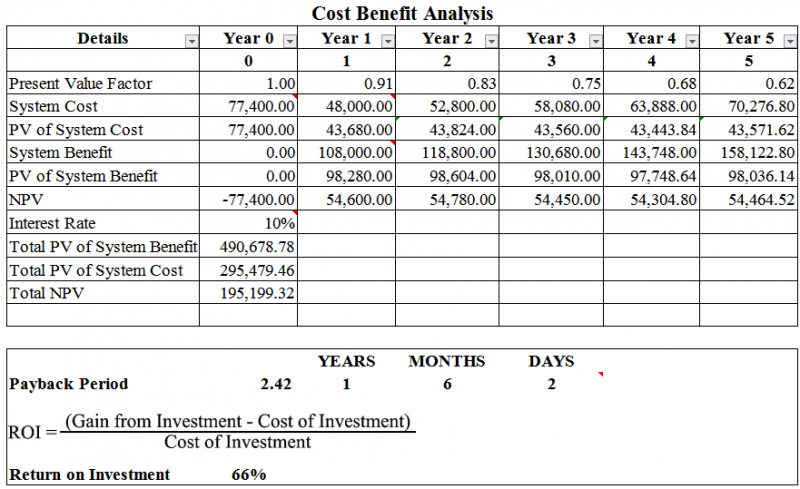
Cost Benefit Analysis
Cost Benefits Analysis or CBA is the estimation and total equivalent money value of the benefits and costs of the system in order to determine its worth.
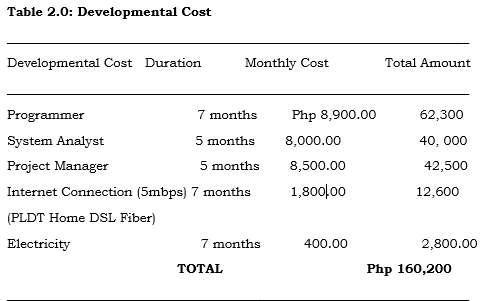
Table 2.4: Cost Benefit Analysis
Database Model

Entity Relationship Diagram
Figure 5.0: Entity Relationship Diagram
This figure shows the relationship of each entity. The data gathered into individual entities become basis record and entities. Necessary attributes that simplify the data in the system.
Data Flow Diagram
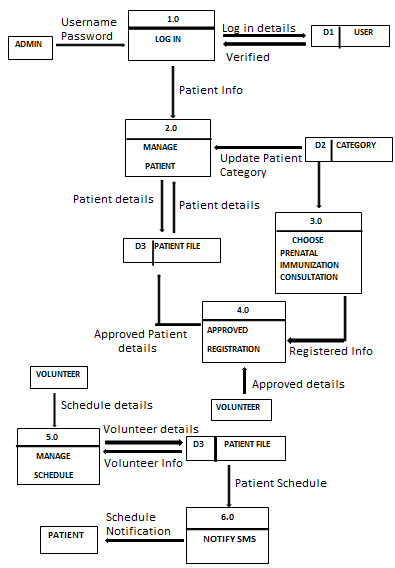
Figure 6.0: Data Flow Diagram
This Data flow diagram shows the process between the admin and the volunteer.
Data Dictionary
Table 3.0: Data Dictionary of the System
______________________________________________________________________________
Data field Type Description
Administrator
Id int(11) Id number of Student
Username varchar(50) Unique name to access administrator
Password varchar(50) Unique key to access administrator
| Id Username Password | int(11) varchar(50) varchar(50) | Id number of student Unique name to access Unique key to access administrator |
| Prenatal Id First Name Last Name Husband Name Age Address MenstrualHx Menarche Cycle Flow Duration Dysmenorrhea ObgyneHx Past MedicalHx | int(11) text(25) text(25) varchar(50) int(2) varchar(100) varchar(50) varchar(50) varchar(50) varchar(50) datetime(6) varchar(50) text(100) varchar(100) | Refers to the number ID patient to register Refers to the first name of the patient Refers to the last name of the patient Refers to the name of husband of the patient Refers to the age of the patient Private address for the Patient Refers to the menstrualhx Refers to the first occurrence of the patients first menstruation Refers to the cycle Refers to the flow of blood Refers to the duration Refers to the dsymenorrhe Refers to the obgynehx Refers to the past medication of the patient |
| Id Prenatal Id Fundamental heartbeat Fatal Height Weight BP Temperature Presentation Complaint Date Appointment | int(11) int(11) varchar(11) varchar(25) varchar(25) varchar(25) text(100) text(100) datetime(6) | Refers to the number ID patient to register Patient prenatal ID Refers to the fundamental heartbeat Refers to the fatal height Refers to the weight Refers to the blood pressure Refers to the presentation Refers to the complaint Refers to the appointment date |
| Id First Name Last Name Gender Mother’s Name Father’s Name Date first Seen Birth date Birth Weight Place of delivery Address Type of delivery | int(11) text(25) text(25) text(25) text(25) text(25) datetime(6) date(6) varchar(25) varchar(50) varchar(50) text(50) | Refers to the number ID patient to register Refers to the first name of the child Refers to the last name of the child Refers to the gender Refers to the mother’s name Refers to the father’s name Refers to the date first seen Refers to the birthday Refers to the birth weight Refers to the place of delivery Private address for the patient Refers to type of delivery |
| Id Immunization ID Service ID Number of Visit Visit Date | int(11) int(11) int(11) varchar(25) datetime(6) | Refers to the number ID of patient to register Patients immunization id Patients service id Refers to number of visit Refers to the date visited |
| Id Service Name | int(11) text(25) | Refers to the number ID of patient to register Refers to the name of service |
| Id First Name Last Name Address Head of the family Occupation Age Date of Birth Number of living child Date Weight BP Temperature | int(11) text(25) text(25) varchar(50) text(25) text(25) int(2) date(6) int(11) date(6) varchar(11) varchar(25) varchar(50 | Refers to the number ID of patient to register Refers to patients first name Refers to patients last name Private address for the patient Refers to the name of the head of the family Refers to the occupation Refers to the age of patient Refers to the date of birth of the patient Refers to the number of living child Refers to the date of consultation Refers to the weight of the patient Refers to the blood pressure Refers to the patients temperature |
Presentation, Analysis, and Presentation of Data
This chapter will exhibit the result of the User’s Survey conducted for the system to the Barangay Health Worker and Nurses.
Presentation
The researcher demonstrates the system’s functionality to the randomly selected respondents. The researcher observed how the respondents respond to the system and perform about technology to the system. In the User’s Acceptance Survey provided by capstone adviser researcher evaluate those respondents, gathered some data and to distinguish the level of acceptance of the proposed system.
Data Analysis
This section presents the analysis of data gathered from the respondents of Barangay Health Worker and Nurses.
Characteristics of the Respondents
The population composed of the Barangay Health Worker and Nurses. The researcher got twenty respondents from the Barangay Health Worker and Nurses.
Table 4.0 Frequency of Respondents
| Respondents | Frequency |
| Nurses/ BNS BHW Total | 3 17 20 |
This table shows the frequency who has answered the User Acceptance Survey. The researcher got total 20 of respondents.
Interpretation of Data
The instrument to access the perception of the users in terms (5) categories namely: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Quality, Timeless and Productivity.
The first category composed of four(4) items, second category composed of three(3) items, third category composed of four(4) items, and then the fourth and fifth category composed of four(4) items with the rating scale was 1 to 5 which are 5 as very satisfied, 4 as satisfies, 3 as neutral, 2 as dissatisfies and 1 as very dissatisfied.
Table 6.0 Rating Scale
Range of Mean Verbal Interpretation
4.21-5.00 Very Satisfied
3.41-4.20 Satisfied
2.61-3.40 Neutral
1.81-2.60 Dissatisfied
1.00-1.80 Very Dissatisfied
This table shows the range of mean and its verbal interpretation.
Table 7.0 Survey Result of Effectiveness
Effectiveness
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 TOTAL
Mean 4.0 3.55 4.0 4.0 4.0125
Table 7.0 shows that effectiveness as a whole has an average mean of 4.0125 as very satisfied that the users were highly satisfied after the testing.
Table 7.1 Survey Result for Efficiency
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 TOTAL
Mean 3.7 4.0 4.0 3.90
The table above shows that efficiency as a whole average mean of 3.90 as a satisfied with the efficiency of the system after the testing.
Table 8.0 Survey Result Quality
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 TOTAL
Mean 4.0 4.0 4.0 3.75 3.9375
This table shows the survey result for the systems quality recorded a total mean of 3.9375 which is interpreted that the users were satisfied with the systems quality after using it.
Table 9.0 Survey Result Timeliness
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 TOTAL
Mean 3.85 4.0 4.0 3.85 3.925
This table shows the survey result for the systems timeliness accounted a total mean of 3.925 which is interpreted that the user were satisfied with the efficiency of the system aster testing it.
Table 10.0 Survey Result Productivity
Productivity
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 TOTAL
Mean 3.85 3.9 4.2 4.1 4.0125
This table shows the survey result for the systems productivity as a whole has an average of 4.0125 which is interpreted that the user were satisfied with the systems productivity after testing it.
Summary of Findings, Conclusion and Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary or the research work undertaken the recommendation and conclusion of an outgrowth of study.
Summary of Findings
This study was conducted purposes of making reliable for Brgy.Estefania Center w/ SMS Notification System. It will be beneficial for Barangay Estefania Health Center workers can work efficiently and access patient records. The system generates the records and can secure the records of the patients. The researcher utilize the interview technique was used for gathering data and also the Users Acceptance Survey serves as elements for collecting data.
The findings of users experience with the system of effectiveness got a total of 4.0125 which is interpreted as a very satisfied for the level of users experience towards the system efficiency got total rating of 3.90 as satisfied. In the term of system quality got total rating of 3.9375 being satisfied for the timeless the users rate of 3.925 as a satisfied and also the productivity got rating of 4.0125 as a very satisfied. The total of whole system proposed was a big help for generating time records and managing the record of patient and also obtaining the security of the records through having restriction between the BNS/ Nurse and BHW.
They prepare as much and gathered all the files of patients that recommended the Health Center. The Brgy. Health Center typically shows the information that given into the patients. They notice the system was been essential in managing the records of every patient in Barangay Health Center.
Share This Post!
- Capstone Project
Recent Posts
Boarding house management system: simplify your life as a landlord, revolutionizing the hospitality industry: top 50 it projects for hotel and tourism, inn management and reservation system capstone project document.
- Student Academic Discipline System Capstone Project Document
- Events Tabulation System Capstone Project Document
- November 2022
- February 2022
- September 2020
- August 2020
Share This Event!
About the author: capstoneguide.
Related Posts

Leave A Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

THE LEVEL OF SATISFACTION IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF BARANGAY HEALTH CENTER SERVICES AND PROGRAMS

Related Papers
Abigail Gandol
Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal
Allain D Fonte , Donna Mae E. Tulaytay
This research study aims to investigate the level of satisfaction among residents of isolated mountain barangays in Cebu City regarding healthcare services. The identified barangays for this study are Bonbon, Sudlon 1, Sudlon 2, and Sinsin. By distributing survey questionnaires to randomly selected participants from each barangay, the study sought to assess residents' satisfaction levels with respect to healthcare services provided within their respective communities. The study employed a mixed-methods approach, incorporating both quantitative and qualitative data collection techniques. The questionnaires were designed to measure various aspects of healthcare services, including accessibility, quality of care, healthcare personnel, facilities, and overall satisfaction. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics to examine the quantitative data. Qualitative data were analyzed using thematic analysis to identify recurring themes and patterns in participants' responses. The preliminary findings of the study indicated that residents' satisfaction levels with healthcare services in these isolated mountain barangays varied across different aspects. While some residents expressed overall satisfaction, others identified specific areas that required improvement. Accessibility, availability of healthcare personnel, quality of care, and the adequacy of healthcare facilities emerged as critical factors influencing residents' satisfaction. The research findings have important implications for policymakers, healthcare providers, and local government units in improving healthcare services in isolated mountain barangays. The study provides valuable insights into residents' perceptions, allowing for targeted interventions and the development of strategies to address the identified areas of concern.
Marecon Viray
Governance has been defined as “the manner in which power is exercised in the management of the country’s economic and social resources for development”. However, governance is not simply about how government conducts business in its own sphere. It is also about how government interacts with civil society. It tells how well government has encouraged and facilitated people’s participation not only in the delivery of services but also in evaluation and monitoring of government performance itself. In spite of technological advancement in information systems, people remain the most important factor in private and public organization. None of these techniques or management methods is effective unless they are administered and carried out by competent Barangay officials. Considering the importance of human power development, The City Government of Bayugan, Agusan del Sur conducted training programs, leadership seminars, and other Seminar-Workshop to fully reach the competence of leadershi...
Cognizance Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies
Gener Udanga
Barangay Pili, Mogpog, Marinduque, a former mining area, continues to seek mediation measures from the government for improved service delivery and community life. The Citizen Satisfaction Index System (CSIS) assesses community needs and service requirements based on Section 17 of the Local Government Code. However, its limited use restricts data availability for barangay-level decision-making. This paper examines the satisfaction level of Barangay Pili residents with local government programs and services, providing a basis for policy formulation and priority setting. A CSIS-inspired questionnaire was used to gather data through survey research. Results revealed that VAWC Desk services received the lowest mean of 2.22, indicating a low level of satisfaction. Barangay leaders are encouraged to prioritize this service in program and policy formulation.
Journal of Academic Research
Jyanee Loi Yecla
A study was conducted to evaluate the performance in the delivery of health services of the LGU of Banga, Aklan. The samples were determined by adopting the Multi-Stage Random Probability Sampling technique. The targeted 150 respondents were proportionately allocated in each barangay. The qualified sample respondents were selected using the Kish Grid. Female respondents were targeted for even-numbered questionnaires, while male respondents were targeted for odd-numbers. The four major core concepts namely, awareness, availment, satisfaction, and need for action were used in measuring the rating of the respondents and presented in frequency and percentage distributions. The study concluded that the citizens are highly aware of the health services and programs in Banga, Aklan. There is high awareness of free basic medicine or low-cost medicine program, but low on prevention and management of communicable and noncommunicable diseases, basic dental/oral hygiene, and family planning. The LGU should continuously take action to improve citizens’ awareness of the program. The availment of health services and programs, on the other hand, was low. This infers that there should be additional effort to notify and persuade the citizens to avail of the health services. Overall satisfaction with health programs and services is high. Despite of this, the local government should continuously take action to sustain and even better the programs and services, most especially on the prevention of diseases, basic dental/oral hygiene, and family planning.
Liceo journal of higher education research
Joussie Bermio
The study was conducted to determine the implementation of Barangay Health Workers’ Benefits and Incentives Act of 1995 (Republic Act 7883) in Santa, Ilocos Sur for the Calendar Year 2014. The respondents were the 44 BHWs of Santa, Ilocos Sur. Results shows tha there is the high extent of implementation of RA 7883. The local and provincial governments are supportive of the BHWs. The BHWs are not aware of their privileges as provided by RA 7883. No significant relationship exists between the level of awareness and the personal profile and benefits and incentives, as well as the awareness of benefits and incentives and extent of implementation of RA 7883. The extent of administrative support is related to the implementation of RA 7883. It is recommended therefore that RA 7883 be fully discussed during meetings with the BHWs by the Municipal Health Office staff. The Department of Health (DOH) should coordinate with the LGU of Santa for the allocation of allowances of BHWs. There sh...
Technium Social Sciences Journal
MNur Alamsyah
This study aims to determine how the implementation of Village Fund policies in addressing the problems of community health development in Donggala Regency, Central Sulawesi Province. The technique for determining informants in this area was carried out after determining the sample area by referring to the Village Minister Regulation (Permendesa) Number 2 of 2016 concerning the Developing Village Index (IDM), which maps Villages into the Village category. Donggala Regency has three categories of villages, namely: very disadvantaged villages, underdeveloped villages, and developing villages. And for each Village Category, informants were determined purposively, as was the technique of determining informants at the Health Office and the Community Development and Village Government (DPMD) Office, informants were determined purposively. The results of the study concluded that the implementation of public health development policies in Donggala Regency was not well realized, however, in ...
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives
Kyu Jae Lee
Annalyn Almirol Lachica
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.

RELATED PAPERS
dedi syafikri
Italian Journal of Public Health
Enrico Reginato
Philippine Journal of Development
Allan Layug
Harry Santos
Suripto suripto
PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences
Gina Maria Carmona Salazar
International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science (IJRISS)
Ronel G Dagohoy
Bernard Pagsuguiron
Olive Chester Cuya-Antonio
Kasmad Kamal
Ijetrm Journal
Mae Eleonor
IMRaD Journal
DR. DAVID C . BUENO
International Conference on Public Organization V (Asia Pacific Society for Public Affairs)
Daisy Besing
Hikmawan Suryanto
Journal of Resources Development and Management
Ahmad Siboy, SH., MH
Jurnal Sistem Teknik Industri
willy tambunan
Gayle Apolinar
IJESRT Journal
University of Cagayan Valley
John Carl Manding
The Journal of Development Communication
Ivan N . Gallegos , Merle Dawn Comidoy
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Visual Basic .NET
Barangay Health Center Information System
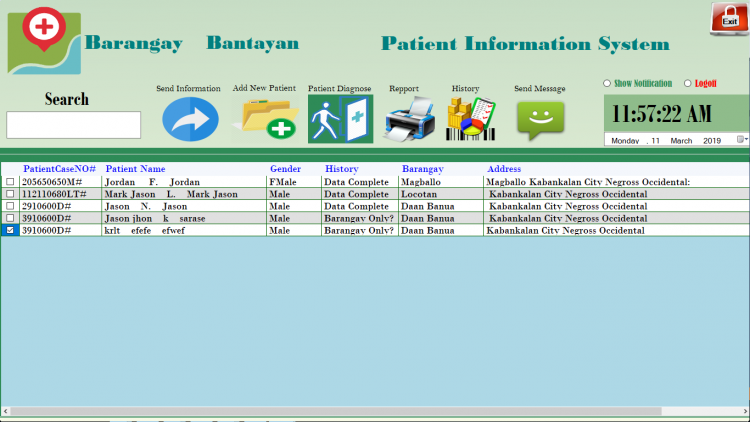
These are the following features of the system
- Manage Patients
- Manage Users
- Patient Diagnosis
- Patient Medical History
- Print List of Patient Diagnosis
- Print Sum of Patient has Diagnosis Based on Graph
Note: Due to the size or complexity of this submission, the author has submitted it as a .zip file to shorten your download time. After downloading it, you will need a program like Winzip to decompress it.
Virus note: All files are scanned once-a-day by SourceCodester.com for viruses, but new viruses come out every day, so no prevention program can catch 100% of them.
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY, PLEASE:
1. Re-scan downloaded files using your personal virus checker before using it. 2. NEVER, EVER run compiled files (.exe's, .ocx's, .dll's etc.)--only run source code.
Add new comment
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 22 March 2024
Drug-resistant tuberculosis: a persistent global health concern
- Maha Farhat ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3871-5760 1 , 2 ,
- Helen Cox 3 na1 ,
- Marwan Ghanem 1 na1 ,
- Claudia M. Denkinger 4 , 5 ,
- Camilla Rodrigues 6 ,
- Mirna S. Abd El Aziz 4 ,
- Handaa Enkh-Amgalan 7 ,
- Debrah Vambe 8 ,
- Cesar Ugarte-Gil 9 ,
- Jennifer Furin 10 &
- Madhukar Pai ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3667-4536 11
Nature Reviews Microbiology ( 2024 ) Cite this article
6265 Accesses
3 Citations
165 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Bacterial evolution
- Clinical microbiology
- Infectious-disease epidemiology
Drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) is estimated to cause 13% of all antimicrobial resistance-attributable deaths worldwide and is driven by both ongoing resistance acquisition and person-to-person transmission. Poor outcomes are exacerbated by late diagnosis and inadequate access to effective treatment. Advances in rapid molecular testing have recently improved the diagnosis of TB and drug resistance. Next-generation sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis has increased our understanding of genetic resistance mechanisms and can now detect mutations associated with resistance phenotypes. All-oral, shorter drug regimens that can achieve high cure rates of drug-resistant TB within 6–9 months are now available and recommended but have yet to be scaled to global clinical use. Promising regimens for the prevention of drug-resistant TB among high-risk contacts are supported by early clinical trial data but final results are pending. A person-centred approach is crucial in managing drug-resistant TB to reduce the risk of poor treatment outcomes, side effects, stigma and mental health burden associated with the diagnosis. In this Review, we describe current surveillance of drug-resistant TB and the causes, risk factors and determinants of drug resistance as well as the stigma and mental health considerations associated with it. We discuss recent advances in diagnostics and drug-susceptibility testing and outline the progress in developing better treatment and preventive therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
195,33 € per year
only 16,28 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
Rifampicin Resistant Tuberculosis in Lesotho: Diagnosis, Treatment Initiation and Outcomes
Global burden of disease due to rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a mathematical modeling analysis
Peto, H. M., Pratt, R. H., Harrington, T. A., LoBue, P. A. & Armstrong, L. R. Epidemiology of extrapulmonary tuberculosis in the United States, 1993–2006. Clin. Infect. Dis. 49 , 1350–1357 (2009).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment — Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Treatment, 2022 Update. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240063129 (2022).
WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment — Drug-susceptible Tuberculosis Treatment. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240048126 (2022).
WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 3: Diagnosis — Rapid Diagnostics For Tuberculosis Detection, 2021 Update. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240029415 (2021).
Cohen, K. A., Manson, A. L., Desjardins, C. A., Abeel, T. & Earl, A. M. Deciphering drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using whole-genome sequencing: progress, promise, and challenges. Genome Med. 11 , 45 (2019).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cohen, K. A. et al. Extensive global movement of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains revealed by whole-genome analysis. Thorax 74 , 882–889 (2019).
Short-course chemotherapy in pulmonary tuberculosis: a controlled trial by the British Thoracic and Tuberculosis Association. Lancet 305 , 119–124 (1975).
Zhang, Y. The magic bullets and tuberculosis drug targets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 45 , 529–564 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729 (2022).
Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021 (2021).
Boehme, C. C. et al. Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 363 , 1005–1015 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
The Use of Molecular Line Probe Assay for the Detection of Resistance to Isoniazid and Rifampicin: Policy Update. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241511261 (2016).
Dixit, A. et al. Estimation of country-specific tuberculosis antibiograms using genomic data. Preprint at medRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.23.21263991 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
O’Connor, C. & Brady, M. F. Isoniazid. StatPearls [Internet] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32491549/ (updated 8 April 2022).
Yee, D. et al. Incidence of serious side effects from first-line antituberculosis drugs among patients treated for active tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 167 , 1472–1477 (2003).
Murray, J. F., Schraufnagel, D. E. & Hopewell, P. C. Treatment of tuberculosis: a historical perspective. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 12 , 1749–1759 (2015).
Jacobson, K. R. et al. Treatment outcomes of isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis patients, Western Cape Province, South Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 53 , 369–372 (2011).
Ahmad, N., Ahuja, S. & Akkerman, O. Treatment correlates of successful outcomes in pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet 392 , 821–834 (2018).
Stagg, H. R. et al. Fluoroquinolones and isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis: implications for the 2018 WHO guidance. Eur. Respir. J. 54 , 1900982 (2019).
WHO Treatment Guidelines for Isoniazid-resistant Tuberculosis: Supplement to the WHO Treatment Guidelines for Drug-resistant Tuberculosis. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550079 (2018).
Meeting Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on the Definition of extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis, 27-29 October 2020. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240018662 (2021).
Global Tuberculosis Report 2023. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240083851 (2023).
Murray, C. J. et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399 , 629–655 (2022).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Knight, G. M., McQuaid, C. F., Dodd, P. J. & Houben, R. Global burden of latent multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: trends and estimates based on mathematical modelling. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19 , 903–912 (2019).
WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement: Report of a Subgroup Meeting on Methods Used by WHO to Estimate TB Disease Burden, 11-12 May 2022, Geneva, Switzerland. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240057647 (2022).
Global Tuberculosis Report 2015. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565059 (2015).
Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131 (2020).
Villegas, L. et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment outcomes of isoniazid- and rifampicin-mono-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in Lima, Peru. PLoS ONE 11 , e0152933 (2016).
Sharling, L., Marks, S. M., Goodman, M., Chorba, T. & Mase, S. Rifampin-resistant tuberculosis in the United States, 1998-2014. Clin. Infect. Dis. 70 , 1596–1605 (2019).
Ismail, N. A. et al. Prevalence of drug-resistant tuberculosis and imputed burden in South Africa: a national and sub-national cross-sectional survey. Lancet Infect. Dis. 18 , 779–787 (2018).
Dean, A. S. Prevalence and genetic profiles of isoniazid resistance in tuberculosis patients: a multicountry analysis of cross-sectional data. PLoS Med. 17 , e1003008 (2020).
Subbaraman, R., Jhaveri, T. & Nathavitharana, R. R. Closing gaps in the tuberculosis care cascade: an action-oriented research agenda. J. Clin. Tuberc. Mycobact. Dis. 19 , 100144 (2020).
Google Scholar
Subbaraman, R. et al. Constructing care cascades for active tuberculosis: a strategy for program monitoring and identifying gaps in quality of care. PLoS Med. 16 , e1002754 (2019).
Naidoo, P. et al. The South African tuberculosis care cascade: estimated losses and methodological challenges. J. Infect. Dis. 216 , S702–S713 (2017).
Subbaraman, R. et al. The tuberculosis cascade of care in India’s public sector: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 13 , e1002149 (2016).
Migliori, G. B. et al. Gauging the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tuberculosis services: a global study. Eur. Respir. J. 58 , 2101786 (2021).
Daniels, B. et al. Use of standardised patients to assess quality of healthcare in Nairobi, Kenya: a pilot, cross-sectional study with international comparisons. BMJ Glob. Health 2 , e000333 (2017).
Daniels, B., Kwan, A. & Pai, M. Lessons on the quality of tuberculosis diagnosis from standardized patients in China, India, Kenya, and South. Afr. J. Clin. Tuberc. Mycobact. Dis. 16 , 100109 (2019).
Boffa, J. et al. Quality of care for tuberculosis and HIV in the private health sector: a cross-sectional, standardised patient study in South Africa. BMJ Glob. Health 6 , e005250 (2021).
Kwan, A. et al. Variations in the quality of tuberculosis care in urban India: a cross-sectional, standardized patient study in two cities. PLoS Med. 15 , e1002653 (2018).
Daniels, B. et al. Tuberculosis diagnosis and management in the public versus private sector: a standardised patients study in Mumbai, India. BMJ Glob. Health 7 , 009657 (2022).
Demers, A. M. et al. Drug susceptibility patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from adults with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and implications for a household contact preventive therapy trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 21 , 205 (2021).
Step up for TB 2020 report: Tuberculosis Policies in 37 Countries. Médecins Sans Frontières & Stop TB Partnership https://msfaccess.org/step-tb-tb-policies-37-countries-4th-ed (2020).
Omar, S. V., Ismail, F., Ndjeka, N., Kaniga, K. & Ismail, N. A. Bedaquiline-resistant tuberculosis associated with Rv0678 mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 386 , 93–94 (2022).
Ismail, N. A. et al. Assessment of epidemiological and genetic characteristics and clinical outcomes of resistance to bedaquiline in patients treated for rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22 , 496–506 (2022).
Azimi, T. et al. Linezolid resistance in multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis : a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13 , 955050 (2022).
Chesov, E. et al. Emergence of bedaquiline resistance in a high tuberculosis burden country. Eur. Respir. J. 59 , 2100621 (2022).
Mallick, J. S., Nair, P., Abbew, E. T., Van Deun, A. & Decroo, T. Acquired bedaquiline resistance during the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 4 , dlac029 (2022).
Jenkins, H. E. & Yuen, C. M. The burden of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 22 , 3–6 (2018).
WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis, Module 5: Management of Tuberculosis in children and Adolescents. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240046764 (2022).
Dodd, P. J., Mafirakureva, N., Seddon, J. A. & McQuaid, C. F. The global impact of household contact management for children on multidrug-resistant and rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis cases, deaths, and health-system costs in 2019: a modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 10 , 1034–1044 (2022).
Dookie, N., Rambaran, S., Padayatchi, N., Mahomed, S. & Naidoo, K. Evolution of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis : a review on the molecular determinants of resistance and implications for personalized care. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73 , 1138–1151 (2018).
Casali, N. et al. Evolution and transmission of drug-resistant tuberculosis in a Russian population. Nat. Genet. 46 , 279–286 (2014).
Cohen, K. A. et al. Evolution of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis over four decades: whole genome sequencing and dating analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from KwaZulu-Natal. PLoS Med. 12 , e1001880 (2015).
Jiang, Q. et al. The evolution and transmission dynamics of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in an isolated high-plateau population of Tibet, China. Microbiol. Spectr. 11 , e03991-22 (2023).
Ektefaie, Y., Dixit, A., Freschi, L. & Farhat, M. R. Globally diverse Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance acquisition: a retrospective geographical and temporal analysis of whole genome sequences. Lancet Microbe 2 , e96–e104 (2021).
Auld, S. C. et al. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa: genomic evidence supporting transmission in communities. Eur. Respir. J. 52 , 1800246 (2018).
Kendall, E. A., Fofana, M. O. & Dowdy, D. W. Burden of transmitted multidrug resistance in epidemics of tuberculosis: a transmission modelling analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 3 , 963–972 (2015).
Yang, C. et al. Transmission of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Shanghai, China: a retrospective observational study using whole-genome sequencing and epidemiological investigation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 17 , 275–284 (2017).
Becerra, M. C. et al. Transmissibility and potential for disease progression of drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis : prospective cohort study. BMJ 367 , l5894 (2019).
Atre, S. R. et al. Tuberculosis pathways to care and transmission of multidrug resistance in India. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 205 , 233–241 (2022).
El Halabi, J. et al. Measuring health-care delays among privately insured patients with tuberculosis in the USA: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 21 , 1175–1183 (2021).
Odone, A. et al. Acquired and transmitted multidrug resistant tuberculosis: the role of social determinants. PLoS ONE 11 , e0146642 (2016).
Bayer, R. & Wilkinson, D. Directly observed therapy for tuberculosis: history of an idea. Lancet 345 , 1545–1548 (1995).
Pasipanodya, J. G., Srivastava, S. & Gumbo, T. Meta-analysis of clinical studies supports the pharmacokinetic variability hypothesis for acquired drug resistance and failure of antituberculosis therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 55 , 169–177 (2012).
Srivastava, S., Pasipanodya, J. G., Meek, C., Leff, R. & Gumbo, T. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis not due to noncompliance but to between-patient pharmacokinetic variability. J. Infect. Dis. 204 , 1951–1959 (2011).
McKay, B., Castellanos, M., Ebell, M., Whalen, C. C. & Handel, A. An attempt to reproduce a previous meta-analysis and a new analysis regarding the impact of directly observed therapy on tuberculosis treatment outcomes. PLoS ONE 14 , e0217219 (2019).
Manson, A. L. et al. Genomic analysis of globally diverse Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains provides insights into the emergence and spread of multidrug resistance. Nat. Genet. 49 , 395–402 (2017).
Dreyer, V. et al. High fluoroquinolone resistance proportions among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis driven by dominant L2 Mycobacterium tuberculosis clones in the Mumbai Metropolitan Region. Genome Med. 14 , 95 (2022).
Cox, H. et al. Potential contribution of HIV during first-line tuberculosis treatment to subsequent rifampicin-monoresistant tuberculosis and acquired tuberculosis drug resistance in South Africa: a retrospective molecular epidemiology study. Lancet Microbe 2 , e584–e593 (2021).
Wang, Z. et al. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Luoyang, China. Front. Public Health 11 , 1117101 (2023).
Hang, N. T. L. et al. Primary drug-resistant tuberculosis in Hanoi, Viet Nam: present status and risk factors. PLoS ONE 8 , e71867 (2013).
Vashakidze, L. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for drug resistance among hospitalized tuberculosis patients in Georgia. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 13 , 1148–1153 (2009).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Andrews, J. R. et al. Predictors of multidrug-and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in a high HIV prevalence community. PLoS ONE 5 , e15735 (2010).
Mesfin, E. A. et al. Drug-resistance patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and associated risk factors among multi drug-resistant tuberculosis suspected patients from Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 13 , e0197737 (2018).
Mbuh, T. P. et al. Predictors of drug-resistant tuberculosis among high-risk population diagnosed under national program conditions in the Littoral region, Cameroon. BioMed. Res. Int. 2021 , 8817442 (2021).
Skrahina, A. et al. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Belarus: the size of the problem and associated risk factors. Bull. World Health Organ. 91 , 36–45 (2013).
Urrego, J. et al. The impact of ventilation and early diagnosis on tuberculosis transmission in Brazilian prisons. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 93 , 739–746 (2015).
Kerubo, G., Amukoye, E., Niemann, S. & Kariuki, S. Drug susceptibility profiles of pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from patients in informal urban settlements in Nairobi, Kenya. BMC Infect. Dis. 16 , 583 (2016).
Oliveira, O. et al. Using Bayesian spatial models to map and to identify geographical hotspots of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Portugal between 2000 and 2016. Sci. Rep. 10 , 16646 (2020).
Jenkins, H. E. et al. Assessing spatial heterogeneity of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in a high-burden country. Eur. Respir. J. 42 , 1291–1301 (2013).
Alene, K. A., Viney, K., McBryde, E. S. & Clements, A. C. A. Spatial patterns of multidrug resistant tuberculosis and relationships to socio-economic, demographic and household factors in northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 12 , e0171800 (2017).
Paleckyte, A., Dissanayake, O., Mpagama, S., Lipman, M. C. & McHugh, T. D. Reducing the risk of tuberculosis transmission for HCWs in high incidence settings. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 10 , 106 (2021).
Escombe, A. R. et al. Tuberculosis transmission risk and infection control in a hospital emergency department in Lima, Peru. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 14 , 1120–1126 (2010).
Telisinghe, L. et al. High tuberculosis prevalence in a South African prison: the need for routine tuberculosis screening. PLoS ONE 9 , e87262 (2014).
Dheda, K. et al. The epidemiology, pathogenesis, transmission, diagnosis, and management of multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and incurable tuberculosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 5 , 291–360 (2017).
Houben, R. M. G. J. & Glynn, J. R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of molecular epidemiological studies of tuberculosis: development of a new tool to aid interpretation. Trop. Med. Int. Health 14 , 892–909 (2009).
Chen, S. et al. Risk factors for multidrug resistance among previously treated patients with tuberculosis in eastern China: a case-control study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 17 , e1116-20 (2013).
Pradipta, I. S., Forsman, L. D., Bruchfeld, J., Hak, E. & Alffenaar, J. W. Risk factors of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 77 , 469–478 (2018).
Lomtadze, N. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the Republic of Georgia: a population-based study. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 13 , 68–73 (2009).
Lee, E. G. et al. Age-stratified anti-tuberculosis drug resistance profiles in South Korea: a multicenter retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 20 , 446 (2020).
Behr, M. A., Edelstein, P. H. & Ramakrishnan, L. Revisiting the timetable of tuberculosis. BMJ 362 , k2738 (2018).
Oladimeji, O. et al. Gender and drug-resistant tuberculosis in Nigeria. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 8 , 104 (2023).
McQuaid, C. F., Horton, K. C., Dean, A. S., Knight, G. M. & White, R. G. The risk of multidrug-or rifampicin-resistance in males versus females with tuberculosis. Eur. Respir. J. 56 , 2000626 (2020).
O’Donnell, M. R. et al. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in women, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17 , 1942–1945 (2011).
Gandhi, N. R. et al. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis as a cause of death in patients co-infected with tuberculosis and HIV in a rural area of South Africa. Lancet 368 , 1575–1580 (2006).
Kolla, B. P., Oesterle, T., Gold, M., Southwick, F. & Rummans, T. Infectious diseases occurring in the context of substance use disorders: a concise review. J. Neurol. Sci. 411 , 116719 (2020).
Soboka, M. et al. Substance use disorders and adherence to antituberculosis medications in Southwest Ethiopia: a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 11 , e043050 (2021).
Mekonnen, H. S. & Azagew, A. W. Non-adherence to anti-tuberculosis treatment, reasons and associated factors among TB patients attending at Gondar town health centers, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 11 , 691 (2018).
Chaves Torres, N. M., Quijano Rodríguez, J. J., Porras Andrade, P. S., Arriaga, M. B. & Netto, E. M. Factors predictive of the success of tuberculosis treatment: a systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 14 , e0226507 (2019).
Dixit, A. et al. Modern lineages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis were recently introduced in Western India and demonstrate increased transmissibility. Preprint at medRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.04.22268645 (2022).
Casali, N. et al. Microevolution of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in Russia. Genome Res. 22 , 735–745 (2012).
Gygli, S. M. et al. Publisher Correction: prisons as ecological drivers of fitness-compensated multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Nat. Med. 27 , 1308–1308 (2021).
Loiseau, C. et al. The relative transmission fitness of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a drug resistance hotspot. Nat. Commun. 14 , 1988 (2023).
Gygli, S. M., Borrell, S., Trauner, A. & Gagneux, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis : mechanistic and evolutionary perspectives. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 , 354–373 (2017).
Li, S. et al. CRISPRi chemical genetics and comparative genomics identify genes mediating drug potency in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Nat. Microbiol. 7 , 766–779 (2022).
Nguyen, L. & Pieters, J. Mycobacterial subversion of chemotherapeutic reagents and host defense tactics: challenges in tuberculosis drug development. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 49 , 427–453 (2009).
Morris, R. P. et al. Ancestral antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102 , 12200–12205 (2005).
Mailaender, C. et al. The MspA porin promotes growth and increases antibiotic susceptibility of both Mycobacterium bovis BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Microbiology 150 , 853–864 (2004).
Rodriguez-Rivera, F. P., Zhou, X., Theriot, J. A. & Bertozzi, C. R. Visualization of mycobacterial membrane dynamics in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 , 3488–3495 (2017).
Madsen, C. T. et al. Methyltransferase Erm(37) slips on rRNA to confer atypical resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . J. Biol. Chem. 280 , 38942–38947 (2005).
Wang, F., Cassidy, C. & Sacchettini, J. C. Crystal structure and activity studies of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis beta-lactamase reveal its critical role in resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50 , 2762–2771 (2006).
Chambers, H. F., Kocagoz, T., Sipit, T., Turner, J. & Hopewell, P. C. Activity of amoxicillin/clavulanate in patients with tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26 , 874–877 (1998).
Donald, P. R. & Sirge, F. A. Early bactericidal activity of amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid in patients with sputum smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 33 , 466–469 (2001).
Hugonnet, J.-E., Tremblay, L. W., Boshoff, H. I., Barry, C. E. & Blanchard, J. S. Meropenem-clavulanate is effective against extensively drug-desistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Science 323 , 1215–1218 (2009).
Vargas, R. Jr et al. Phase variation as a major mechanism of adaptation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120 , e2301394120 (2023).
Vargas, R. Jr Role of epistasis in amikacin, kanamycin, bedaquiline, and clofazimine resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65 , e0116421 (2021).
Farhat, M. R. et al. Genetic determinants of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their diagnostic value. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 194 , 621–630 (2016).
Nebenzahl-Guimaraes, H., Jacobson, K. R., Farhat, M. R. & Murray, M. B. Systematic review of allelic exchange experiments aimed at identifying mutations that confer drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69 , 331–342 (2013).
Kadura, S. et al. Systematic review of mutations associated with resistance to the new and repurposed Mycobacterium tuberculosis drugs bedaquiline, clofazimine, linezolid, delamanid and pretomanid. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75 , 2031–2043 (2020).
Zhang, Y. & Yew, W. W. Mechanisms of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 13 , 1320–1330 (2009).
Green, A. G. et al. Analysis of genome-wide mutational dependence in naturally evolving Mycobacterium tuberculosis populations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 40 , msad131 (2023).
Barilar, I. et al. Quantitative measurement of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals genetic determinants of resistance and susceptibility in a target gene approach. Nat. Commun. 15 , 488 (2024).
Farhat, M. R. et al. GWAS for quantitative resistance phenotypes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals resistance genes and regulatory regions. Nat. Commun. 10 , 2128 (2019).
Walker, T. M. et al. The 2021 WHO catalogue of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex mutations associated with drug resistance: a genotypic analysis. Lancet Microbe 3 , e265–e273 (2022).
Ghodousi, A. et al. Isoniazid resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a heterogeneous phenotype composed of overlapping MIC distributions with different underlying resistance mechanisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63 , e00092-19 (2019).
Spitaleri, A., Ghodousi, A., Miotto, P. & Cirillo, D. M. Whole genome sequencing in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Ann. Transl. Med. 7 , S197 (2019).
Farhat, M. R. et al. Gyrase mutations are associated with variable levels of fluoroquinolone resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . J. Clin. Microbiol. 54 , 727–733 (2016).
Chen, M. L. et al. Beyond multidrug resistance: leveraging rare variants with machine and statistical learning models in Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance prediction. EBioMedicine 43 , 356–369 (2019).
Green, A. G. et al. A convolutional neural network highlights mutations relevant to antimicrobial resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Nat. Commun. 13 , 3817 (2022).
Yang, Y. et al. Machine learning for classifying tuberculosis drug-resistance from DNA sequencing data. Bioinformatics 34 , 1666–1671 (2018).
Gröeschel, M. I. et al. GenTB: a user-friendly genome-based predictor for tuberculosis resistance powered by machine learning. Genome Med. 13 , 138 (2021).
Safi, H. et al. Phase variation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis glpK produces transiently heritable drug tolerance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116 , 19665–19674 (2019).
Hicks, N. D. et al. Clinically prevalent mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis alter propionate metabolism and mediate multidrug tolerance. Nat. Microbiol. 3 , 1032–1042 (2018).
Liu, Q. et al. Tuberculosis treatment failure associated with evolution of antibiotic resilience. Science 378 , 1111–1118 (2022).
Kreutzfeldt, K. M. et al. CinA mediates multidrug tolerance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Nat. Commun. 13 , 2203 (2022).
Martini, M. C. et al. Loss of RNase J leads to multi-drug tolerance and accumulation of highly structured mRNA fragments in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . PLoS Pathog. 18 , e1010705 (2022).
Andersson, D. I., Nicoloff, H. & Hjort, K. Mechanisms and clinical relevance of bacterial heteroresistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 17 , 479–496 (2019).
Vargas, R. et al. In-host population dynamics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex during active disease. eLife 10 , e61805 (2021).
Nimmo, C. et al. Dynamics of within-host Mycobacterium tuberculosis diversity and heteroresistance during treatment. EBioMedicine 55 , 102747 (2020).
Engelthaler, D. M. et al. Minority Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotypic populations as an indicator of subsequent phenotypic resistance. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 61 , 789–791 (2019).
WHO Standard: Universal Access to Rapid Tuberculosis Diagnostics. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240071315 (2023).
Report of the 16th Meeting of the Strategic and Technical Advisory Group for Tuberculosis 2016. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/report-of-the-16th-meeting-of-the-strategic-and-technical-advisory-group-for-tb (2016).
Jacobson, K. R. et al. Implications of failure to routinely diagnose resistance to second-line drugs in patients with rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis on Xpert MTB/RIF: a multisite observational study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 64 , 1502–1508 (2017).
Oga-Omenka, C. et al. Factors influencing diagnosis and treatment initiation for multidrug-resistant/rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis in six sub-Saharan African countries: a mixed-methods systematic review. BMJ Glob. Health 5 , e002280 (2020).
Svadzian, A., Sulis, G., Gore, G., Pai, M. & Denkinger, C. M. Differential yield of universal versus selective drug susceptibility testing of patients with tuberculosis in high-burden countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 5 , e003438 (2020).
Kim, S. J. Drug-susceptibility testing in tuberculosis: methods and reliability of results. Eur. Respir. J. 25 , 564–569 (2005).
Technical Manual for Drug Susceptibility Testing of Medicines Used in the Treatment of Tuberculosis. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241514842 (2018).
Yu, H.-J. et al. Performance evaluation of the BACTEC MGIT 960 system for rifampin drug-susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using the current WHO critical concentration. J. Clin. Microbiol. 61 , e01086-22 (2023).
Shea, J. et al. Low-level rifampin resistance and rpoB mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis : an analysis of whole-genome sequencing and drug susceptibility test data in New York. J. Clin. Microbiol. 59 , e01885-20 (2021).
Torrea, G. et al. Variable ability of rapid tests to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis rpoB mutations conferring phenotypically occult rifampicin resistance. Sci. Rep. 9 , 11826 (2019).
Automated Real-time Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology for Rapid and Simultaneous Detection of Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF System: Policy Statement. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241501545 (2011).
Rapid Implementation of the Xpert MTB/RIF Diagnostic Test: Technical and Operational “How-to”; Practical Considerations. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241501569 (2011).
Dorman, S. E. et al. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: a prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 18 , 76–84 (2018).
Albert, H. et al. Development, roll-out and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF for tuberculosis: what lessons have we learnt and how can we do better? Eur. Respir. J. 48 , 516–525 (2016).
Zifodya, J. S. et al. Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021 , CD009593 (2021).
Penn-Nicholson, A. et al. A prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study for the Truenat tuberculosis assays. Eur. Respir. J. 58 , 2100526 (2021).
Gomathi, N. S. et al. Validation of an indigenous assay for rapid molecular detection of rifampicin resistance in presumptive multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Indian J. Med. Res. 152 , 482–489 (2020).
Molbio Diagnostics: Molbio launches Truenat MTB-INH test for drug resistance in TB patients. Health News, ET HealthWorld https://health.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/diagnostics/molbio-launches-truenat-mtb-inh-test-for-drug-resistance-in-tb-patients/96963161 (2023).
Theron, G. et al. Feasibility, accuracy, and clinical effect of point-of-care Xpert MTB/RIF testing for tuberculosis in primary-care settings in Africa: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 383 , 424–435 (2014).
Yoon, C. et al. Impact of Xpert MTB/RIF testing on tuberculosis management and outcomes in hospitalized patients in Uganda. PLoS ONE 7 , e48599 (2012).
Di Tanna, G. L. et al. Effect of Xpert MTB/RIF on clinical outcomes in routine care settings: individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 7 , e191–e199 (2019).
Churchyard, G. J. et al. Xpert MTB/RIF versus sputum microscopy as the initial diagnostic test for tuberculosis: a cluster-randomised trial embedded in South African roll-out of Xpert MTB/RIF. Lancet Glob. Health 3 , 450–457 (2015).
Cattamanchi, A. et al. Multicomponent strategy with decentralized molecular testing for tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 385 , 2441–2450 (2021).
Penn-Nicholson, A. et al. Detection of isoniazid, fluoroquinolone, ethionamide, amikacin, kanamycin, and capreomycin resistance by the Xpert MTB/XDR assay: a cross-sectional multicentre diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22 , 242–249 (2022).
Cao, Y. et al. Xpert MTB/XDR: a 10-color reflex assay suitable for point-of-care settings to detect isoniazid, fluoroquinolone, and second-line-injectable-drug resistance directly from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-positive sputum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 59 , e02314-20 (2021).
De Vos, M. et al. Comparative analytical evaluation of four centralized platforms for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 59 , e02168-20 (2021).
Meaza, A. et al. Evaluation of genotype MTBDRplus VER 2.0 line probe assay for the detection of MDR-TB in smear positive and negative sputum samples. BMC Infect. Dis. 17 , 280 (2017).
Nathavitharana, R. R. et al. Accuracy of line probe assays for the diagnosis of pulmonary and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 49 , 1601075 (2017).
Driesen, M. et al. Evaluation of a novel line probe assay to detect resistance to pyrazinamide, a key drug used for tuberculosis treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 24 , 60–64 (2018).
Willby, M. J. et al. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pncA mutations by the Nipro Genoscholar PZA-TB II assay compared to conventional sequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62 , e01871-17 (2018).
Catalogue of Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex and their Association with Drug Resistance, 2nd edn. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240082410 (2023).
Ismail, N. et al. Genetic variants and their association with phenotypic resistance to bedaquiline in Mycobacterium tuberculosis : a systematic review and individual isolate data analysis. Lancet Microbe 2 , e604–e616 (2021).
An, Q., Lin, R., Yang, Q., Wang, C. & Wang, D. Evaluation of genetic mutations associated with phenotypic resistance to fluoroquinolones, bedaquiline, and linezolid in clinical Mycobacterium tuberculosis : a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 34 , 214–226 (2023).
Gan, W. C., Ng, H. F. & Ngeow, Y. F. Mechanisms of linezolid resistance in mycobacteria. Pharmaceuticals 16 , 784 (2023).
CRyPTIC Consortium & The 100,000 Genomes Project. Prediction of susceptibility to first-line tuberculosis drugs by DNA sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 379 , 1403–1415 (2018).
Pankhurst, L. J. Rapid, comprehensive, and affordable mycobacterial diagnosis with whole-genome sequencing: a prospective study. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 , 49–58 (2016).
Use of Targeted Next-generation Sequencing to Detect Drug-resistant Tuberculosis: Rapid Communication. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240076372 (2023).
The Use of Next-Generation Sequencing for the Surveillance of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: An Implementation Manual. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240078079 (2023).
Dippenaar, A. et al. Nanopore sequencing for Mycobacterium tuberculosis : a critical review of the literature, new developments, and future opportunities. J. Clin. Microbiol. 60 , e00646-21 (2022).
Sanchez-Padilla, E. et al. Detection of drug-resistant tuberculosis by Xpert MTB/RIF in Swaziland. N. Engl. J. Med. 372 , 1181–1182 (2015).
Ng, K. C. et al. Xpert Ultra can unambiguously identify specific rifampin resistance-conferring mutations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56 , 10–1128 (2018).
Daum, L. T. et al. Next-generation sequencing for characterizing drug resistance-conferring Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes from clinical isolates in the Ukraine. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56 , e00009-18 (2018).
Tagliani, E. et al. Culture and next-generation sequencing-based drug susceptibility testing unveil high levels of drug-resistant-TB in Djibouti: results from the first national survey. Sci. Rep. 7 , 17672 (2017).
Walker, T. M. et al. Whole-genome sequencing to delineate Mycobacterium tuberculosis outbreaks: a retrospective observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 13 , 137–146 (2013).
Mahomed, S., Mlisana, K., Cele, L. & Naidoo, K. Discordant line probe genotypic testing vs culture-based drug susceptibility phenotypic testing in TB endemic KwaZulu-Natal: impact on bedside clinical decision making. J. Clin. Tuberc. Mycobact. Dis. 20 , 100176 (2020).
Milimo, D. et al. Diagnosis of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: discordant results by diagnostic methods. Afr. J. Lab. Med. 7 , 1–4 (2018).
Votintseva, A. A. et al. Same-day diagnostic and surveillance data for ttuberculosis via whole-genome sequencing of direct respiratory samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 55 , 1285–1298 (2017).
Brown, A. C. et al. Rapid whole-genome sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates directly from clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 53 , 2230–2237 (2015).
Doyle, R. M. et al. Direct whole-genome sequencing of sputum accurately identifies drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis faster than MGIT culture sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56 , e00666–18 (2018).
Goig, G. A. et al. Whole-genome sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis directly from clinical samples for high-resolution genomic epidemiology and drug resistance surveillance: an observational study. Lancet Microbe 1 , e175–e183 (2020).
Van Rie, A. et al. Sequencing mycobacteria and algorithm-determined resistant tuberculosis treatment (SMARTT): a study protocol for a phase-IV pragmatic randomized controlled patient management strategy trial. Trials 23 , 864 (2022).
Sibandze, D. B. et al. Rapid molecular diagnostics of tuberculosis resistance by targeted stool sequencing. Genome Med. 14 , 52 (2022).
Iyer, A. et al. Operationalising targeted next-generation sequencing for routine diagnosis of drug-resistant TB. Public Health Action. 13 , 43–49 (2023).
Cox, H. et al. Whole-genome sequencing has the potential to improve treatment for rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis in high-burden settings: a retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 60 , e02362–21 (2022).
Kwong, J. C., McCallum, N., Sintchenko, V. & Howden, B. P. Whole genome sequencing in clinical and public health microbiology. Pathology 47 , 199–210 (2015).
Conradie, F. et al. Treatment of highly drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 382 , 893–902 (2020).
Nyang’wa, B.-T. et al. A 24-week, all-oral regimen for rifampin-resistant tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 387 , 2331–2343 (2022).
Padmapriyadarsini, C. et al. Bedaquiline, delamanid, linezolid and clofazimine for treatment of pre-extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 76 , e938–e946 (2022).
Pym, A. S. et al. Bedaquiline in the treatment of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur. Respir. J. 47 , 564–574 (2016).
Schnippel, K. et al. Effect of bedaquiline on mortality in South African patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 6 , 699–706 (2018).
Ndjeka, N. et al. High treatment success rate for multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis using a bedaquiline-containing treatment regimen. Eur. Respir. J. 52 , 1801528 (2018).
Ndjeka, N. et al. Treatment outcomes 24 months after initiating short bedaquiline-containing or injectable-containing rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis treatment regimens: a retrospective cohort study in South Africa. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22 , 1042–1051 (2022).
Zhao, Y. et al. Improved treatment outcomes with bedaquiline when substituted for second-line injectable agents in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a retrospective cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 68 , 1522–1529 (2019).
Conradie, F. et al. Bedaquiline–pretomanid–linezolid regimens for drug-resistant tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 387 , 810–823 (2022).
Esmail, A. et al. An all-oral 6-month regimen for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a multicenter, randomized controlled clinical trial (the NExT study). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 205 , 1214–1227 (2022).
Goodall, R. L. et al. Evaluation of two short standardised regimens for the treatment of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis (STREAM stage 2): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 400 , 1858–1868 (2022).
WHO Operational Handbook on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment of Drug-resistant Tuberculosis. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240006997 (2020).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02589782 (2021).
Clinical Trial Results Offer Hope to DR-TB patients with short, effective treatment. Médecins Sans Frontières https://www.msf.org/clinical-trial-finds-short-effective-safe-DR-TB-treatment (2022).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02333799 (2020).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03086486 (2023).
Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Clinical Trials Progress Report. RESIST-TB https://www.resisttb.org/clinical-trials-progress-report (2023).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02619994 (2019).
Mok, J. et al. 9 months of delamanid, linezolid, levofloxacin, and pyrazinamide versus conventional therapy for treatment of fluoroquinolone-sensitive multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-END): a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 2/3 non-inferiority trial in South Korea. Lancet 400 , 1522–1530 (2022).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04062201 (2022).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02754765 (2023).
Guglielmetti, L. et al. Evaluating newly approved drugs for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (endTB): study protocol for an adaptive, multi-country randomized controlled trial. Trials 22 , 651 (2021).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03896685 (2022).
ShORRT Initiative. Tropical Disease Research https://tdr.who.int/activities/shorrt-research-package (2022).
Tuberculosis Treatment: 2023 Pipeline Report. Treatment Action Group https://www.treatmentactiongroup.org/resources/pipeline-report/2023-pipeline-report/ (2023).
WHO Operational Handbook on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment — Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Treatment, 2022 Update. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240065116 (2022).
Maugans, C. et al. Best practices for the care of pregnant people living with TB. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 27 , 357–366 (2023).
Patankar, S. et al. Making the case for all-oral, shorter regimens for children with drug-resistant tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 208 , 130–131 (2023).
Turkova, A. et al. Shorter treatment for nonsevere tuberculosis in African and Indian children. N. Engl. J. Med. 386 , 911–922 (2022).
Management of Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis in Children: A Field Guide. Sentinel Project on Pediatric Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis https://sentinel-project.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/DRTB-Field-Guide-2021_v5.pdf (2022).
Furin, J., Tommasi, M. & Garcia-Prats, A. J. Drug-resistant tuberculosis: will grand promises fail children and adolescents? Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2 , 237–238 (2018).
Karo, B. et al. Isoniazid (INH) mono-resistance and tuberculosis (TB) treatment success: analysis of European surveillance data, 2002 to 2014. Eur. Surveill. 24 , 1800392 (2019).
Gegia, M., Winters, N., Benedetti, A., Soolingen, D. & Menzies, D. Treatment of isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis with first-line drugs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 17 , 223–234 (2017).
Furin, J., Cox, H. & Pai, M. Tuberculosis. Lancet 393 , 1642–1656 (2019).
WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis: Module 1: Prevention: Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240001503 (2020).
Guidelines for Programmatic Management of Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment in India. National TB Elimination Programme https://tbcindia.gov.in/WriteReadData/l892s/Guidelines%20for%20Programmatic%20Management%20of%20Tuberculosis%20Preventive%20Treatment%20in%20India.pdf (2021).
Latent Tuberculosis Infection: Updated and Consolidated Guidelines for Programmatic Management. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550239 (2018).
Kherabi, Y., Tunesi, S., Kay, A. & Guglielmetti, L. Preventive therapy for contacts of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Pathogens 11 , 1189 (2022).
Huang, C. C. et al. Isoniazid preventive therapy in contacts of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 202 , 1159–1168 (2020).
Seddon, J. A. et al. Levofloxacin versus placebo for the prevention of tuberculosis disease in child contacts of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: study protocol for a phase-III cluster randomised controlled trial (TB-CHAMP). Trials 19 , 693 (2018).
Fox, G. J. et al. Levofloxacin versus placebo for the treatment of latent tuberculosis among contacts of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (the VQUIN MDR trial): a protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 10 , e033945 (2020).
First Effective Treatment to Prevent Multidrug-Resistant TB. UCL News https://www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2023/nov/first-effective-treatment-prevent-multidrug-resistant-tb (2023).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03568383 (2023).
WHO announces forthcoming updates on tuberculosis preventive treatment. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/news/item/13-02-2024-who-announces-forthcoming-updates-on-tuberculosis-preventive-treatment (2024).
Zimmerman, E., Smith, J., Banay, R., Kau, M. & Garfin, A. M. C. G. Behavioural barriers and perceived trade-offs to care-seeking for tuberculosis in the Philippines. Glob. Public Health 17 , 210–222 (2022).
Daftary, A., Frick, M., Venkatesan, N., & Pai, M. Fighting TB stigma: we need to apply lessons learnt from HIV activism. BMJ Glob. Health 2 , e000515 (2017).
Pradhan, A. et al. Internalized and perceived stigma and depression in pulmonary tuberculosis: do they explain the relationship between drug sensitivity status and adherence? Front. Psychiatry 13 , 869647 (2022).
Redwood, L. et al. Depression, stigma and quality of life in people with drug-susceptible TB and drug-resistant TB in Vietnam. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 25 , 461–467 (2021).
Daftary, A., Padayatchi, N. & O’Donnell, M. Preferential adherence to antiretroviral therapy over tuberculosis treatment: a qualitative study of drug-resistant TB/HIV co-infected patients in South Africa. Glob. Public Health 9 , 1107–1116 (2014).
Susanto, T. D. et al. Anxiety and depression level of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) in two hospitals in Banten province, Indonesia. Dialogues Health 2 , 100115 (2023).
Walker, I. et al. Depression and anxiety in patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Nepal: an observational study. Public Health Action 9 , 42–48 (2019).
Sommerland, N. et al. Evidence-based interventions to reduce tuberculosis stigma: a systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 21 , S81–S86 (2017).
As’hab, P. P., Keliat, B. A. & Wardani, I. Y. The effects of acceptance and commitment therapy on psychosocial impact and adherence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients. J. Public Health Res. 11 , 2737 (2022).
Thomas, B. E. et al. Psycho-socio-economic issues challenging multidrug resistant tuberculosis patients: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 11 , e0147397 (2016).
Udwadia, Z. & Furin, J. Quality of drug-resistant tuberculosis care: gaps and solutions. J. Clin. Tuberc. Mycobact. Dis. 16 , 100101 (2019).
Pai, M., Dewan, P. K. & Swaminathan, S. Transforming tuberculosis diagnosis. Nat. Microbiol. 8 , 756–759 (2023).
McKenna, L. et al. The 1/4/6x24 campaign to cure tuberculosis quickly. Nat. Med. 11 , 2337 (2023).
Zaunbrecher, M. A., Sikes, R. D. Jr, Metchock, B., Shinnick, T. M. & Posey, J. E. Overexpression of the chromosomally encoded aminoglycoside acetyltransferase eis confers kanamycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106 , 20004–20009 (2009).
Miotto, P. et al. A standardised method for interpreting the association between mutations and phenotypic drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Eur. Respir. J. 50 , 1701354 (2017).
Rifat, D. et al. Mutations in fbiD (Rv2983) as a novel determinant of resistance to pretomanid and delamanid in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65 , e01948–20 (2020).
Plinke, C. et al. embCAB sequence variation among ethambutol-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates without embB306 mutation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65 , 1359–1367 (2010).
Safi, H. et al. Evolution of high-level ethambutol-resistant tuberculosis through interacting mutations in decaprenylphosphoryl-β-D-arabinose biosynthetic and utilization pathway genes. Nat. Genet. 45 , 1190–1197 (2013).
Srivastava, S., Ayyagari, A., Dhole, T. N., Nyati, K. K. & Dwivedi, S. K. emb nucleotide polymorphisms and the role of embB306 mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to ethambutol. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 299 , 269–280 (2009).
Grant, S. S. et al. Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenases EthA and MymA are required for activation of replicating and non-replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibitors. Cell Chem. Biol. 23 , 666–677 (2016).
Dover, L. G. et al. EthA, a common activator of thiocarbamide-containing drugs acting on different mycobacterial targets. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 1055–1063 (2007).
Vilchèze, C. et al. Mycothiol biosynthesis is essential for ethionamide susceptibility in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Mol. Microbiol. 69 , 1316–1329 (2008).
Zhang, Y., Dhandayuthapani, S. & Deretic, V. Molecular basis for the exquisite sensitivity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to isoniazid. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93 , 13212–13216 (1996).
Ando, H., Miyoshi-Akiyama, T., Watanabe, S. & Kirikae, T. A silent mutation in mabA confers isoniazid resistance on Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Mol. Microbiol. 91 , 538–547 (2014).
Vilchèze, C. et al. Altered NADH/NAD + ratio mediates coresistance to isoniazid and ethionamide in mycobacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49 , 708–720 (2005).
Reeves, A. Z. et al. Aminoglycoside cross-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis due to mutations in the 5′ untranslated region of whiB7 . Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57 , 1857–1865 (2013).
Liu, J. et al. Mutations in efflux pump Rv1258c (tap) cause resistance to pyrazinamide, isoniazid, and streptomycin in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Front. Microbiol. 10 , 216 (2019).
Gopal, P. et al. Pyrazinamide triggers degradation of its target aspartate decarboxylase. Nat. Commun. 11 , 1661 (2020).
Scorpio, A. & Zhang, Y. Mutations in pncA , a gene encoding pyrazinamidase/nicotinamidase, cause resistance to the antituberculous drug pyrazinamide in tubercle bacillus. Nat. Med. 2 , 662–667 (1996).
Wong, S. Y. et al. Functional role of methylation of G518 of the 16S rRNA 530 loop by GidB in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57 , 6311–6318 (2013).
Catalogue of Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex and their Association with Drug Resistance. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240028173 (2021).
Farhat, M. R. et al. Rifampicin and rifabutin resistance in 1003 Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 74 , 1477–1483 (2019).
Nahid, P. et al. Treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis. An Official ATS/CDC/ERS/IDSA clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 200 , e93–e142 (2019).
Download references
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Helen Cox, Marwan Ghanem.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Maha Farhat & Marwan Ghanem
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
Maha Farhat
Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine, Wellcome Centre for Infectious Disease Research and Division of Medical Microbiology, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
Division of Infectious Disease and Tropical Medicine, Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany
Claudia M. Denkinger & Mirna S. Abd El Aziz
German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), partner site Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany
Claudia M. Denkinger
P.D. Hinduja Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Mumbai, India
Camilla Rodrigues
Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
Handaa Enkh-Amgalan
National TB Control Programme, Manzini, Eswatini
Debrah Vambe
School of Public and Population Health, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX, USA
Cesar Ugarte-Gil
Department of Global Health and Social Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Jennifer Furin
McGill International TB Centre, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Madhukar Pai
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.P., M.F., H.C., C.M.D., J.F. and M.G. wrote the article and, together with C.R. and M.S.A.E.A. researched data for the article. All authors contributed substantially to the discussion of the content and reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Madhukar Pai .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Microbiology thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
Clinicaltrials.gov: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Refers to the delivery of anti-tuberculosis drug treatment under direct observation of health workers, community workers or family members with the goal of improving adherence.
(XDR-TB). Defined as multidrug-resistant or rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis with further resistance to fluoroquinolones and to either bedaquiline or linezolid or both (key second-line drugs).
(Hr-TB). Defined as resistance to isoniazid and susceptibility to rifampicin.
(MDR-TB). Defined as resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid, the two most important first-line drugs used to treat tuberculosis (TB), regardless of resistance to other TB drugs.
Defined as multidrug-resistant or rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis with resistance to fluoroquinolones.
(RMR-TB). Defined as resistance to rifampicin (Rif), with susceptibility to isoniazid.
(RR-TB). Defined as resistance to rifampicin (Rif), regardless of resistance to other tuberculosis (TB) drugs. Individuals with RR-TB are treated with regimens similar to those for multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) and are therefore grouped with MDR-TB as MDR/RR-TB.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Farhat, M., Cox, H., Ghanem, M. et al. Drug-resistant tuberculosis: a persistent global health concern. Nat Rev Microbiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-024-01025-1
Download citation
Accepted : 12 February 2024
Published : 22 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-024-01025-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Microbiology newsletter — what matters in microbiology research, free to your inbox weekly.
- Word of the day
- Random word
Definitions
From the american heritage® dictionary of the english language, 5th edition..
- A city of south-central Russia on the Irtysh River. On the Trans-Siberian Railroad, it is a major river port and transportation hub. The city was founded in 1716.
from Wiktionary , Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
- proper noun Seventh largest city in Russia , centre of Omsk oblast .
from WordNet 3.0 Copyright 2006 by Princeton University. All rights reserved.
- noun a city in the Asian part of Russia
Etymologies
Sorry, no etymologies found.

Help support Wordnik (and make this page ad-free) by adopting the word Omsk .
The Czech-born Jagr, 36, a right wing who has topped rosters for the Pittsburgh Penguins, the Washington Capitals, and the New York Rangers since 1990, is now playing for Avangard Omsk , of the new Continental Hockey League, in Omsk, Siberia.
Jagr, wearing number 68 to commemorate the Prague Spring, waits to play in Omsk . Image credit: Utkin Igor/Itar-Tass Photo/Corbis
Watch them smile to themselves as they refute objections and expound implications of Stalin's monetary policy on rural electrification in Omsk . If there are two of them in the car, you just might do a Gemini and climb out the window to pull off a carjacking.
Archive 2007-11-01 2007
Astrology and Traffic Tie-ups 2007
Ultimately, he said it was a matter of stability, that he wanted a three-year contract and a place to call home, even if that means going to an outpost like Omsk , which is far more a part of Siberia than continental Europe.
Archive 2008-07-01 James Mirtle 2008
Nine-time NHL All-Star Jaromir Jagr shocked the hockey world in 2008 when he joined Avangard Omsk at age 36, before rejoining the NHL this summer.
Hockey Stars Killed in Russian Crash Gregory L. White 2011
The firebrand championing the indigenous Komi people was none other than Yury Spiridonov, an ethnically Russian oil miner and party worker, born in Omsk and educated in Sverdlovsk, who had once gotten into trouble for snapping at someone who tried to address him in Komi: “Speak in a way that can be understood.”
The Return Daniel Treisman 2011
Before returning to the NHL this season with the Philadelphia Flyers, Jagr had played three years for Avangard Omsk , a franchise in Russia's Kontinental Hockey League.
Why Didn't New York Keep Jagr? Mike Sielski 2011
Related Words
Log in or sign up to add your own related words.
hypernyms (3)
Words that are more generic or abstract.
- urban center
Word visualization
Log in or sign up to get involved in the conversation. It's quick and easy.
- About Wordnik
- @[email protected]
- github.com/wordnik
- Send Us Feedback!
- Need Support?
- Advanced Search
Wordnik is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization, EIN #47-2198092.
The New Order: Last Days of Europe Wiki
Attention everyone, The New Order: Last Days of Europe Wiki on Fandom will no longer be used, except for TNO Styled GFX Icons . The new wiki is located at https://tno.wiki.gg/ and please claim your old username (with contributions) at https://tno.wiki.gg/wiki/Special:ClaimExternalAccount/ .

Omsk , officially the Siberian Black League , is a warlord state in Western Siberia. Occupying the territory of the former Omsk Oblast, it borders Tomsk to the north, the Kazakh SSR to the south, Tyumen to the east, and Novosibirsk to the west.
- 2.1 National spirits
- 2.2 Cabinet
- 3.1 Generals
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union , the city of Omsk, initially held by the West Siberian People's Republic , was seized by a league of ultranationalists sharing views of anti-German sentiment and revanchism. Led by Dmitry Karbyshev 's All-Russian Black League, upon the seizing of Omsk, the ultranationalist regime had to industrialize and fortify it. In a way, some could say it's nothing but a fortified city in which the Black League militarizes and prepares for its future conflicts.
The political system of Omsk is governed as a militarist one-party state since its founding, ruled by Karbyshev and his like-minded comrades of the All-Russian Black League, an organization fanatically devoted to revanchism against the Greater Germanic Reich . However, at heart, Karbyshev is a Russian and while he sought to create an ultranationalist military state to take revenge against Germany, he did not account for the despots that wished to claim as much power as possible from him. Karbyshev is represented in-game as a dying man soon to fall, due to him leading a brutal military dictatorship, while being opposed to the radical rhetoric of his officer clique. The Black League has since become an ultranationalist state, even more radical in their hatred of Germany. Due to Karbyshev's declining health, many of the other officers have gained massive influence in the leadership of Omsk. The reality is that Karbyshev started a movement that assumed it was able to change the hearts of the despots with nationalism rather than terror; but it has since been corrupted beyond his visions, and there is little he can do to stop the train of degeneracy. Indeed, once Karbyshev dies and Omsk is still around, actual ultranationalist and General Dmitry Yazov will assume leadership of the Black League and prevent the despotic cliques from growing.
Under the sheer doctrine of anti-German sentiment, the theory of the “Great Trial” in Omsk comes in. This is where the warlord state will prepare for its final assault on the Reich, as revenge for the “First Trial” which brought the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the “Second Trial” being the West Russian War . Their hatred doesn't stop with just Germany, but it includes many who collaborated with them. Some officers of the Black League even go as far as to want to destroy the United States for not helping enough during the Great Patriotic War. In preparation for their war with Germany, they are expectant of nuclear strikes and so have started to construct massive metro tunnels to double as shelter from the warheads and radioactive fallout. The resolve of the Black League cannot be stopped, even with the threat of nuclear war.
Omsk is one of the hardest paths in TNO, due to it being weaker than a lot of the surrounding warlords and being unable to conduct diplomacy at all. To reunite Russia, Omsk will have to fight every single state in its way. Their end goal is the complete extermination of the Reich and the German people, and they will stop at nothing to reach this. They are hard-coded for hostility and are always at war with someone, but an AI Omsk will almost always never be successful. Despite being founded on nothing but hatred, when they unify Western Siberia and start to emerge on the international stage, they actually try to conceal their ideology and ambitions from foreign influences. They stick with a nondescript name of the “West Siberian Provisional Authority” under the guise of a protective military authority and switch their ideology to “Despotism”.
National spirits
| During the Last Trial, each of us saw and faced Hell on Earth. The Nazis razed our cities, slaughtered our families, and shattered the Union we worked so hard to build. And as the world unraveled around us, we resolved to never again allow the Teuton to despoil our homes. Never again would we tremble in fear as the jackboot trampled on our soil. Whatever the cost, whatever the sacrifice, the day of the will come. On that day, they will feel our terrible vengeance. | |
| Our backs are pressed against the wall, our supplies run low, and yet morale is as high as ever. Each and every son and daughter of the Black League know their mission and know they have nothing to lose, for the Last Trial already robbed them of everything. This simple truth has transformed the League from a band of disgruntled veterans to an army with discipline unparalleled in the Russian wastes. We will survive our current, dire circumstances, we will rebuild what was lost, and when the comes, we will repay our enemies for every life lost. | |
| It is a sad fact that the founder of the Black League, General Karbyshev, is not as young as he once was. As he has aged, though his mind is as sharp as ever, his body has become frail and weak. The people weep to know that he is not long for this world; and yet not all is lost. The loyal sons and daughters of the Black League's officer corps are glad to receive and deliver General Karbyshev's orders, and even to reinterpret them when the General's mind has slipped. |
| Cabinet member | Role | Ideology | Trait(s) and effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head of government | Political Protege Political Power Gain: | ||
| Viktor Abakumov | Foreign minister | Iron-Fisted Brute | |
| Alexander Kharkhardin | Economy minister | Corrupt Kleptocrat | |
| Konstantin Valukhin | Security minister | Prince of Terror Political Power Gain: |
After Dmitry Yazov comes to power and purges the Black League's old guard, the cabinet changes to:
| Cabinet member | Role | Ideology | Trait(s) and effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head of government | Devoted Follower Political Power Gain: Stability: | ||
| Foreign minister | The Cloak-n-Dagger Schemer: | ||
| Evgeny Pitovranov | Economy minister | Military Entrepreneur: Infrastructure Construction Speed: | |
| Security minister | Template:Spymaster |
Omsk has at least eleven generals.
- Ironically, according to a former developer of West Siberia, Omsk at one point had a National Socialist path as a "sane" option, due to now-former head developer Pink Panzer wanting every region in Western Siberia to have multiple paths. This was changed after the other developers convinced him to have Omsk only have one path.
- Omsk was partially inspired by the Armenian Secret Army for the Liberation of Armenia , a militant group that aspired to carve out an ethnic Armenian homeland in eastern Turkey.
| • Nations as of January 1st, 1962 | |
| Americas | • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • |
|---|---|
| Europe | • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • |
| Africa | • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • |
| Middle East | • • • • • • • • |
| Central Asia | • • • • • • • |
| Siberia | • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • |
| East Asia | • • • • • • • |
| South Asia | • • • • |
| Southeast Asia & Oceania | • • • • • • • • • |
| Antarctica | • • • • • |
- 1 SS State of Burgundy
- 2 Sergey Taboritsky
- 3 TNO Styled GFX Icons

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Barangay Basak Health Center Management System provides first aid, maternal and child health care, diagnosis of social diseases, and other basic health services to all the members of its community. Barangay Basak Health Center is using a manual system in terms of implementing medical services, health programs, health monitoring and profiling ...
This study intends to improve the existing manual way of Barangay Villamonte Health Center. The Barangay Health Management System is an automated information system that is designed for keeping, and evaluating the residents' heath records. Conceptual Framework. Figure 1 : Conceptual Framework of BHMS.
The document proposes a Barangay Health Center Management System (BHCMS) to help manage patient records at the Barangay Basak Health Center. Currently, the health center uses a manual system for medical services, health programs, monitoring, and patient profiling. This causes issues with accuracy, efficiency, bulk filing, and queueing. The proposed system would provide a user-friendly ...
BARANGAY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 15 Definition of Terms BARANGAY. It is the smallest administrative division of the Philippines; a native Filipino term for a village or district. The barangay is subdivided to purok's or zone, it manages by the barangay chairman and his fellow officials and secretary and treasurer. BMS.
A Guide for the Establishment of a Barangay Health Management Council: An Initiative to Strengthen the Health System and Improve Services at the Barangay Level through Better Health Leadership, Management, and Governance. Submitted to the US Agency for International Development by the Systems for Improved Access to
3 PROJECT STRUCTURE 3.1 Components The proposed system is divided into multiple functionalities that is intended majority of the transactions performed in a barangay health services center to further help the barangay health workers. As such were also referred from the forms, documents and roles of responsibilities made known to the proponent.
BARANGAY HEALTH CENTER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (BHCMS) A System Design Project Presented to the Faculty of College of Computer Engineering University of Cebu - Lapulapu and Mandaue A.C., Cortes, Looc, Mandaue City, Cebu In Partial Fulfilment Of the Requirements for System Analysis and Design By ANTASUDA, VAN BARRIENTOS, MICHAEL JOHN CABALHUG, VERLIN GRACE DOROY, FLORIE MAE MARCH 2020 INTRODUCTION
Based on the thorough evaluation of the experts and respondents, the Barangay Integrated Management System with Mobile Support is highly usable, secured, efficient, and provides a fast and easy way to manage residents' profile, manage public information, manage supplies, manage complaints, set appointments, manage medical transactions, and ...
The Barangay Health Center is the lowest branch of the organizational setup of the Primary Health Care system; hence it is where the first contact of the health care system with patient occurs. It administers free basic health services like maternal health care, immunization programs and free medicines, and is concerned with the improvement and ...
Barangay health center is a community based and patient directed organization. It is usually the first point of contact between residents of the community and other health care facility levels. Barangay Estefania health center provides consultation, immunization and prenatal. They are using manual procedure to get information from their patients.
Current System Use. Barangay Basak Health Center is using a manual system in terms of implementing medical services, health programs, health monitoring and profiling. These transactions as implemented by nurse in-charge. and barangay health workers in their station are done manually. Also the archiving of the Patient's records
It encompassed the residents of Barangay Five, Zone 6-A who visits the Health Center for maternal check-up, immunization services, family planning, environmental sanitation, National Tuberculosis Program, Rabies Prevention and Control Program, Dengue Prevention and Control Program and Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control Program.
Thesis barangay management system for barangay 905 sta. ana, manila software proposal presented to the faculty of the college of computer studies and systems ... generate statistical reports such as (to- tal population of the Barangay, reported cases (offenses against the law), health re- ports, the total number of voters registered on the ...
884 Words4 Pages. PERCEPTION ON THE SERVICES OF. BARANGAY MAKILING HEALTH CENTER. A Thesis presented to the College of Business and Accountancy. In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree. Bachelor of Science in Business Administration. Major in Marketing Management.
This Barangay Health Center Information System is an automated system that aims to help health workers and midwife in-charge in organizing and monitoring the medical records of patients in every barangays and reduce the hours during the consultation process. This system ensures that records are well secured in a centralized database wherein an authorized health worker can easily check the ...
Research on Barangay Hall and Health Center Design - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the requirements and design considerations for barangay halls and health centers in the Philippines. It provides examples of floor plans for spaces commonly found in barangay halls like daycare centers, offices, and ...
The document discusses the challenges of writing a thesis on a Barangay Management Information System, including the extensive research, analysis, and attention to detail required. It notes how developing such a thesis takes time and expertise to properly identify the research problem, conduct literature reviews, gather and analyze data, and present findings. Additionally, drafting and ...
The global impact of household contact management for children on multidrug-resistant and rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis cases, deaths, and health-system costs in 2019: a modelling study ...
Download Citation | On Apr 1, 2019, Victor S. Kuzevanov published Management of the Architectural Branch of the Administrative Center of Omsk Oblast in the 1930s-1940s | Find, read and cite all ...
The Czech-born Jagr, 36, a right wing who has topped rosters for the Pittsburgh Penguins, the Washington Capitals, and the New York Rangers since 1990, is now playing for Avangard Omsk, of the new Continental Hockey League, in Omsk, Siberia.. Exile 2008. The Czech-born Jagr, 36, a right wing who has topped rosters for the Pittsburgh Penguins, the Washington Capitals, and the New York Rangers ...
Omsk, officially the Siberian Black League, is a warlord state in Western Siberia. Occupying the territory of the former Omsk Oblast, it borders Tomsk to the north, the Kazakh SSR to the south, Tyumen to the east, and Novosibirsk to the west. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the city of Omsk, initially held by the West Siberian People's Republic, was seized by a league of ...