
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction

Early waste disposal
Developments in waste management, composition and properties, generation and storage.
- Collecting and transporting
- Transfer stations
- Furnace operation
- Energy recovery
- Sorting and shredding
- Digesting and processing
- Constructing the landfill
- Controlling by-products
- Importance in waste management

- What role can living organisms play in environmental engineering?

solid-waste management
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Engineering LibreTexts - Solid Waste Management
- Frontiers - Solid Waste Management in Indian Himalayan Region: Current Scenario, Resource Recovery, and Way Forward for Sustainable Development
- DigitalCommons at UMaine - Solid Waste Management (SWM) Options: The Economics of Variable Cost and Conventional Pricing Systems in Maine
- European Commission - Solid waste management
- The World Bank - Solid Waste Management
- Table Of Contents

solid-waste management , the collecting, treating, and disposing of solid material that is discarded because it has served its purpose or is no longer useful. Improper disposal of municipal solid waste can create unsanitary conditions, and these conditions in turn can lead to pollution of the environment and to outbreaks of vector-borne disease—that is, diseases spread by rodents and insects . The tasks of solid-waste management present complex technical challenges. They also pose a wide variety of administrative, economic, and social problems that must be managed and solved.
Historical background
In ancient cities, wastes were thrown onto unpaved streets and roadways, where they were left to accumulate. It was not until 320 bce in Athens that the first known law forbidding this practice was established. At that time a system for waste removal began to evolve in Greece and in the Greek-dominated cities of the eastern Mediterranean. In ancient Rome , property owners were responsible for cleaning the streets fronting their property. But organized waste collection was associated only with state-sponsored events such as parades. Disposal methods were very crude, involving open pits located just outside the city walls. As populations increased, efforts were made to transport waste farther out from the cities.
After the fall of Rome, waste collection and municipal sanitation began a decline that lasted throughout the Middle Ages . Near the end of the 14th century, scavengers were given the task of carting waste to dumps outside city walls. But this was not the case in smaller towns, where most people still threw waste into the streets. It was not until 1714 that every city in England was required to have an official scavenger. Toward the end of the 18th century in America, municipal collection of garbage was begun in Boston , New York City , and Philadelphia . Waste disposal methods were still very crude, however. Garbage collected in Philadelphia, for example, was simply dumped into the Delaware River downstream from the city.
A technological approach to solid-waste management began to develop in the latter part of the 19th century. Watertight garbage cans were first introduced in the United States, and sturdier vehicles were used to collect and transport wastes. A significant development in solid-waste treatment and disposal practices was marked by the construction of the first refuse incinerator in England in 1874. By the beginning of the 20th century, 15 percent of major American cities were incinerating solid waste. Even then, however, most of the largest cities were still using primitive disposal methods such as open dumping on land or in water.
Technological advances continued during the first half of the 20th century, including the development of garbage grinders, compaction trucks, and pneumatic collection systems. By mid-century, however, it had become evident that open dumping and improper incineration of solid waste were causing problems of pollution and jeopardizing public health . As a result, sanitary landfills were developed to replace the practice of open dumping and to reduce the reliance on waste incineration. In many countries waste was divided into two categories, hazardous and nonhazardous, and separate regulations were developed for their disposal. Landfills were designed and operated in a manner that minimized risks to public health and the environment. New refuse incinerators were designed to recover heat energy from the waste and were provided with extensive air pollution control devices to satisfy stringent standards of air quality. Modern solid-waste management plants in most developed countries now emphasize the practice of recycling and waste reduction at the source rather than incineration and land disposal.
Solid-waste characteristics
The sources of solid waste include residential, commercial, institutional, and industrial activities. Certain types of wastes that cause immediate danger to exposed individuals or environments are classified as hazardous; these are discussed in the article hazardous-waste management . All nonhazardous solid waste from a community that requires collection and transport to a processing or disposal site is called refuse or municipal solid waste (MSW). Refuse includes garbage and rubbish. Garbage is mostly decomposable food waste; rubbish is mostly dry material such as glass, paper, cloth, or wood. Garbage is highly putrescible or decomposable, whereas rubbish is not. Trash is rubbish that includes bulky items such as old refrigerators, couches, or large tree stumps. Trash requires special collection and handling.
Construction and demolition (C&D) waste (or debris) is a significant component of total solid waste quantities (about 20 percent in the United States), although it is not considered to be part of the MSW stream. However, because C&D waste is inert and nonhazardous, it is usually disposed of in municipal sanitary landfills.

Another type of solid waste, perhaps the fastest-growing component in many developed countries, is electronic waste , or e-waste, which includes discarded computer equipment, televisions , telephones , and a variety of other electronic devices. Concern over this type of waste is escalating. Lead , mercury , and cadmium are among the materials of concern in electronic devices, and governmental policies may be required to regulate their recycling and disposal.
Solid-waste characteristics vary considerably among communities and nations. American refuse is usually lighter, for example, than European or Japanese refuse. In the United States paper and paperboard products make up close to 40 percent of the total weight of MSW; food waste accounts for less than 10 percent. The rest is a mixture of yard trimmings, wood, glass, metal, plastic, leather, cloth, and other miscellaneous materials. In a loose or uncompacted state, MSW of this type weighs approximately 120 kg per cubic metre (200 pounds per cubic yard). These figures vary with geographic location, economic conditions, season of the year, and many other factors. Waste characteristics from each community must be studied carefully before any treatment or disposal facility is designed and built.
Rates of solid-waste generation vary widely. In the United States , for example, municipal refuse is generated at an average rate of approximately 2 kg (4.5 pounds) per person per day. Japan generates roughly half this amount, yet in Canada the rate is 2.7 kg (almost 6 pounds) per person per day. In some developing countries the average rate can be lower than 0.5 kg (1 pound) per person per day. These data include refuse from commercial, institutional, and industrial as well as residential sources. The actual rates of refuse generation must be carefully determined when a community plans a solid-waste management project.
Most communities require household refuse to be stored in durable, easily cleaned containers with tight-fitting covers in order to minimize rodent or insect infestation and offensive odours. Galvanized metal or plastic containers of about 115-litre (30-gallon) capacity are commonly used, although some communities employ larger containers that can be mechanically lifted and emptied into collection trucks. Plastic bags are frequently used as liners or as disposable containers for curbside collection. Where large quantities of refuse are generated—such as at shopping centres, hotels, or apartment buildings—dumpsters may be used for temporary storage until the waste is collected. Some office and commercial buildings use on-site compactors to reduce the waste volume.
- Environmental Engineering
- Engineering
- Waste Management
Introduction to Waste Management
- Publisher: international Youth Ambassadors Foundation
- ISBN: 978-9957-67-886-9

- Jordan University of Science and Technology
Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Int J Sustain Dev Plann

- Paolo Canfora
- Pierre Gaudillat

- John Pichtel

- N.P. Cheremisinoff
- Forbes R. McDougall
- Peter R. White
- Dr. M. Franke
- K Vizayakumar
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

Waste Management, Types, Process, Objective, Different Methods
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. Check details on waste management here in this article.

Table of Contents
Waste Management
Waste management encompasses a multidisciplinary approach that integrates engineering principles, economics, urban and regional planning, management techniques, and social sciences. Its objective is to minimize the overall wastage within the system under consideration. A systematic waste management approach should address all types of resources at every stage. Notably, material constitutes a significant portion of the total production cost, making the management of wasted materials critically important (Arora, 2004).
According to the Environmental Protection Act of 1990, waste is defined as any undesirable material. This includes scrap material, effluents, or any surplus substance or item requiring disposal due to being damaged, worn out, contaminated, or otherwise polluted. Wastes are essentially those substances or objects that no longer serve a purpose within the business cycle or chain of utility. For instance, glass bottles that are returned or reused in their original form are not considered waste, whereas glass bottles collected by the public and sent for remoulding are classified as waste until they have been recovered. The Department of the Environment identifies four broad categories of potential waste:
- Items that are worn but still functional and can be used for their intended purpose (potentially after repair).
- Substances or items that can be immediately utilized for purposes other than by specialized waste recovery entities. For example, ash from a power station used in building materials.
- Degraded substances or items that can only be utilized by specialized waste recovery establishments. These remain classified as waste, even if sent for recovery for value, such as contaminated solvents or scrap. They are only considered recovered when the process is complete.
- Substances that the possessor no longer wants and for which they must pay for proper disposal.
Types of Waste
The rapid pace of economic development has led to an improved standard of living worldwide. This, in turn, has resulted in increased material consumption and subsequently, higher waste generation. Solid waste materials generated, particularly in urban areas, include:
- Organic waste
- Plastic waste
- Metal waste materials
- Glass waste materials
- Paper waste materials
- Electronic waste
- Other materials like ash, sand, grit, etc.
Waste Management Process
Ensuring Environmental Health and Resource Recovery. Waste management encompasses the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, or disposal of materials generated through human activity. This process is primarily aimed at mitigating their impact on both human health and the environment. Additionally, waste management strives to extract valuable resources from these materials. It covers a wide range of substances, including solid, liquid, gaseous, and radioactive, each requiring specialized methods and expertise for proper handling.
Studies have shown that waste management practices vary depending on factors like a nation’s level of development, urban or rural settings, and whether the waste is generated by residential or industrial sources. Typically, local government authorities oversee the management of non-hazardous waste from homes and institutions in metropolitan areas, while generators of non-hazardous commercial and industrial waste usually handle its management.
An efficient waste management system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of various interconnected systems. These systems are vital for tasks such as waste containment and leachate management. Without regular examination, maintenance, improvement, and assessment of the components of a waste management system, even the most well-designed unit may not function optimally.
Effective implementation of a waste management system can lead to reduced costs in both the short and long term, provide protection for workers and local communities, and foster positive community relations. Furthermore, a successful waste management system necessitates the establishment of procedures for monitoring performance and tracking progress towards clearly defined environmental objectives.
Objective of Waste Management
The primary aim of waste management is to reduce waste generation, ultimately striving for an ideal system. Conversely, resource management seeks to maximize the efficient use of available resources. Both waste and resource management share a common objective: the optimal utilization of resources to enhance system efficiency and growth. However, their approaches differ (Arora, 2004).
To accomplish this objective, it is crucial to:
- Prevent the generation of waste.
- Encourage the reuse of waste.
- Support the biological recovery and material recycling of waste.
- Promote the energy utilization of waste that isn’t suitable for recycling.
- Ensure that the treatment and disposal of waste do not result in any harmful impacts.
Management literature has established that resource and waste management are interdependent and complement each other in achieving these goals.
Different Methods of waste disposal
The different methods of waste disposal have been mentioned below:
- In the age-old ritual of waste management, the Landfill emerges as a solemn guardian. It cradles our refuse in vacant urban spaces, a sacred resting place for our discarded tales. Covered in a quilt of soil, it guards against the specter of contamination. And trees, nature’s sentinels, are called upon, their roots tenderly embracing the soil, fortifying this sanctuary.
- The Landfill, if choreographed with care, waltzes as an economical and hygienic custodian of our waste. Yet, in the chaos of urban life, unplanned landfills sprout like wildflowers in forgotten corners, birthing environmental and health specters. Poisonous gases escape, toxic secrets seep, and the once vibrant vegetation bows in sorrow. The Landfill, a testament to our stewardship, a tale of caution, a dance of contradictions.
Incineration
- It is a carefully controlled process of burning or thermally treating mostly organic substances at high temperatures to release water, CO2, and thermal energy.
- Advantages: Produces power and is useful for handling big amounts of dangerous organic waste.
- Disadvantages: The installation is expensive (high equipment and labor costs) and produces harmful gases (HCL, CO, and SO2).
This process changes the condition of the solid into a liquid, and the liquid into a gas. The creation of energy can then be done using these treatment byproducts.
Gasification
The substance to be treated is immediately transformed into SynGas (synthetic gas), which is made up of carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Bioremediation
Utilizing living creatures, primarily microbes, to transform environmental pollutants into less hazardous forms is known as bioremediation. For instance, a pseudonymous microbe may break down artificial pesticide.
The use of bioremediation techniques reduces exposure hazards for workers because they are more affordable than conventional approaches and allow for the on-site treatment of contaminants.
Waste Management UPSC
Waste management can be accomplished in one of two ways: trash reduction or recycling. Less waste will need to be transferred to landfills and incinerators if waste reduction and recycling efforts are consistent. As a result, there will be a significant decrease in the emission of greenhouse gases and other types of pollution. There will be less new product manufacturing as a result of reuse and recycling of existing items.
Sharing is caring!
Waste Management FAQs
What are the 4 types of waste management.
The 4 types of waste management are - Landfills, Recycling, Incineration and Composting
What is meant by waste management?
Waste management refers to the various schemes to manage and dispose of wastes. It can be by discarding, destroying, processing, recycling, reusing, or controlling wastes.
What are the 5 waste management techniques?
They include refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose, and recycle.
Why is waste management important?
Reducing waste will not only protect the environment but will also save on costs or reduce expenses for disposal.
What is modern waste management?
Modern waste management strategies are geared towards sustainability.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Trending Event
- UPSC EPFO PA Result 2024
- UPSC CMS Result 2024
- SSC Stenographer Apply Online 2024
- SSC Stenographer Notifcation 2024
- IB SA MTS Final Result 2024
- UPSC CAPF AC Admit 2024
- UKPSC Answer Key 2024

Recent Posts

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
SSC CGL 2024
- SSC CGL Exam 2024
- SSC CGL Syllabus 2024
- SSC CGL Cut off
- SSC CGL Apply Online
- SSC CGL Salary
- SSC CGL Previous Year Question Paper
- SSC MTS 2024
- SSC MTS Apply Online 2024
- SSC MTS Syllabus 2024
- SSC MTS Salary 2024
- SSC MTS Eligibility Criteria 2024
- SSC MTS Previous Year Paper
SSC Stenographer 2024
- SSC Stenographer Notfication 2024
- SSC Stenographer Syllabus 2024
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle Resources for Students and Educators
The following are resources for students and educators on reducing, reusing, and recycling.
On this page:
Recycle City
Planet protectors club, teach english, teach about the environment, science fair fun, learning by doing: students take greening to the community, the quest for less: activities and resources for teaching k-8, tools to reduce waste in schools, pack a waste free lunch.
- Life of a Soccer Ball
Additional Resources for Students and Educators
This large document includes factsheets, activities, and teaching notes for 6-8 th grade teachers. (Educators, K-8)

The Life of a Soccer Ball

Learn about the life cycle of a soccer ball - from obtaining raw materials through manufacture, packaging, distribution, useful life, and disposal. Also available in Spanish.
- EPA's Environmental Education website.
- Environmental Resources for Students.
- Food Matters Action Kit developed by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation.
Educating Youth About Wasted Food
- Recycle Home
- Reduce and Reuse Basics
- Recycling Basics and Benefits
- Frequent Questions on Recycling
- How Do I Recycle...
- What You Can Do
- Used Electronics
- Used Batteries
- Food Waste Prevention
- Composting at Home
- Students and Educators

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
115 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Waste management is a crucial issue in today's world, as the amount of waste produced continues to grow at an alarming rate. From household trash to industrial waste, finding sustainable solutions for managing and reducing waste is essential for protecting the environment and public health.
If you're tasked with writing an essay on waste management, you may be struggling to come up with a topic that is both interesting and relevant. To help you get started, here are 115 waste management essay topic ideas and examples that you can use as inspiration for your own writing:
- The importance of proper waste management in protecting the environment
- The impact of waste management on public health
- Strategies for reducing household waste
- The role of recycling in waste management
- The benefits of composting for waste reduction
- The challenges of managing electronic waste
- The environmental impact of plastic waste
- The economic benefits of sustainable waste management practices
- The ethical implications of waste disposal methods
- The role of government in regulating waste management
- The impact of waste management on climate change
- The potential for waste-to-energy technologies to reduce landfill waste
- The importance of educating the public about waste management
- The role of businesses in implementing sustainable waste management practices
- The social justice implications of waste management
- The impact of waste management on wildlife and ecosystems
- The benefits of using biodegradable materials to reduce waste
- The challenges of managing construction and demolition waste
- The potential for using waste as a resource in circular economy models
- The role of technology in improving waste management processes
- The impact of food waste on global hunger and food security
- The benefits of implementing zero-waste initiatives in communities
- The role of NGOs in promoting sustainable waste management practices
- The potential for using drones to monitor and manage waste
- The impact of waste management on water quality
- The benefits of community-based waste management programs
- The challenges of managing hazardous waste
- The potential for using blockchain technology to track waste disposal
- The role of education in promoting sustainable waste management practices
- The impact of waste management on air quality
- The benefits of waste segregation and sorting programs
- The challenges of managing medical waste
- The potential for using robots to automate waste sorting processes
- The role of public-private partnerships in improving waste management
- The impact of waste management on urban planning and development
- The benefits of using anaerobic digestion to process organic waste
- The challenges of managing electronic waste in developing countries
- The potential for using machine learning algorithms to optimize waste collection routes
- The role of social media in raising awareness about waste management issues
- The impact of waste management on biodiversity conservation
- The benefits of implementing extended producer responsibility programs
- The challenges of managing marine litter
- The potential for using satellite imagery to monitor illegal waste dumping
- The role of indigenous communities in sustainable waste management practices
- The impact of waste management on land degradation
- The benefits of using biochar to improve soil quality
- The challenges of managing radioactive waste
- The potential for using 3D printing to create products from recycled materials
- The role of artists in raising awareness about waste management issues
- The impact of waste management on social inequality
- The benefits of implementing pay-as-you-throw waste pricing schemes
- The challenges of managing agricultural waste
- The potential for using blockchain technology to create a transparent waste management system
- The role of citizen science in monitoring waste pollution
- The impact of waste management on tourism
- The benefits of using drones to collect and transport waste
- The challenges of managing industrial waste
- The potential for using gene editing technologies to break down plastic waste
- The role of policymakers in promoting sustainable waste management practices
- The impact of waste management on public perception of cities
- The benefits of using algae to clean up wastewater
- The challenges of managing construction and demolition waste in urban areas
- The potential for using artificial intelligence to optimize waste management processes
- The role of community gardens in reducing food waste
- The impact of waste management on mental health
- The benefits of using green roofs to reduce stormwater runoff
- The challenges of managing asbestos waste
- The potential for using drones to monitor landfill sites
- The role of youth groups in promoting waste management education
- The impact of waste management on renewable energy production
- The benefits of implementing waste audits in businesses
- The challenges of managing wastewater treatment sludge
- The potential for using geospatial technologies to map waste hotspots
- The role of religious organizations in promoting waste reduction
- The impact of waste management on indigenous rights
- The benefits of using blockchain technology to create a circular economy
- The challenges of managing pharmaceutical waste
- The potential for using robots to clean up ocean plastic pollution
- The role of community activists in advocating for waste management reform
- The impact of waste management on green jobs creation
- The benefits of using drones to monitor illegal waste dumping
- The challenges of managing construction and demolition waste in rural areas
- The potential for using satellite imagery to track waste flows
- The role of citizen science in monitoring air quality near waste facilities
- The impact of waste management on water scarcity
- The benefits of using biopesticides to control pests in waste management facilities
- The challenges of managing medical waste in conflict zones
- The potential for using machine learning algorithms to predict waste generation patterns
- The role of grassroots organizations in promoting waste reduction
- The impact of waste management on mental well-being
- The benefits of using drones to monitor illegal waste dumping in remote areas
- The challenges of managing electronic waste in rural communities
- The potential for using blockchain technology to create a decentralized waste management system
- The role of community gardens in promoting sustainable waste management practices
- The impact of waste management on social cohesion
- The benefits of using drones to monitor waste collection routes
- The challenges of managing hazardous waste in developing countries
- The potential for using machine learning algorithms to optimize waste sorting processes
- The role of social entrepreneurs in developing innovative waste management solutions
- The benefits of using blockchain technology to create a transparent waste management system
These waste management essay topic ideas and examples cover a wide range of issues and perspectives, giving you plenty of options to explore in your writing. Whether you're interested in the environmental, social, economic, or technological aspects of waste management, there's sure to be a topic that piques your interest. Good luck with your essay, and happy writing!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade
Chapter 13: Solid and Hazardous Waste
13.2 waste management strategies.
The long-recognized hierarchy of management of wastes, in order of preference consists of prevention, minimization, recycling and reuse, biological treatment, incineration, and landfill disposal (see Figure below ).

[Figure 1] Hierarchy of Waste Management Figure shows the hierarchy of management of wastes in order or preference, starting with prevention as the most favorable to disposal as the least favorable option. Source: Drstuey via Wikimedia Commons
Waste Prevention
The ideal waste management alternative is to prevent waste generation in the first place. Hence, waste prevention is a basic goal of all the waste management strategies. Numerous technologies can be employed throughout the manufacturing, use, or post-use portions of product life cycles to eliminate waste and, in turn, reduce or prevent pollution. Some representative strategies include environmentally conscious manufacturing methods that incorporate less hazardous or harmful materials, the use of modern leakage detection systems for material storage, innovative chemical neutralization techniques to reduce reactivity, or water saving technologies that reduce the need for fresh water inputs.
Waste Minimization
In many cases, wastes cannot be outright eliminated from a variety of processes. However, numerous strategies can be implemented to reduce or minimize waste generation. Waste minimization, or source reduction, refers to the collective strategies of design and fabrication of products or services that minimize the amount of generated waste and/or reduce the toxicity of the resultant waste. Often these efforts come about from identified trends or specific products that may be causing problems in the waste stream and the subsequent steps taken to halt these problems. In industry, waste can be reduced by reusing materials, using less hazardous substitute materials, or by modifying components of design and processing. Many benefits can be realized by waste minimization or source reduction, including reduced use of natural resources and the reduction of toxicity of wastes.
Waste minimization strategies are extremely common in manufacturing applications; the savings of material use preserves resources but also saves significant manufacturing related costs. Advancements in streamlined packaging reduces material use, increased distribution efficiency reduces fuel consumption and resulting air emissions. Further, engineered building materials can often be designed with specific favorable properties that, when accounted for in overall structural design, can greatly reduce the overall mass and weight of material needed for a given structure. This reduces the need for excess material and reduces the waste associated with component fabrication.
The dry cleaning industry provides an excellent example of product substitution to reduce toxic waste generation. For decades, dry cleaners used tetrachloroethylene, or “perc” as a dry cleaning solvent. Although effective, tetrachloroethylene is a relatively toxic compound. Additionally, it is easily introduced into the environment, where it is highly recalcitrant due to its physical properties. Further, when its degradation occurs, the intermediate daughter products generated are more toxic to human health and the environment.
Because of its toxicity and impact on the environment, the dry cleaning industry has adopted new practices and increasingly utilizes less toxic replacement products, including petroleum-based compounds. Further, new emerging technologies are incorporating carbon dioxide and other relatively harmless compounds. While these substitute products have in many cases been mandated by government regulation, they have also been adopted in response to consumer demands and other market-based forces.
Recycling and Reuse
Recycling refers to recovery of useful materials such as glass, paper, plastics, wood, and metals from the waste stream so they may be incorporated into the fabrication of new products. With greater incorporation of recycled materials, the required use of raw materials for identical applications is reduced. Recycling reduces the need of natural resource exploitation for raw materials, but it also allows waste materials to be recovered and utilized as valuable resource materials. Recycling of wastes directly conserves natural resources, reduces energy consumption and emissions generated by extraction of virgin materials and their subsequent manufacture into finished products, reduces overall energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to the global climate change, and reduces the incineration or landfilling of the materials that have been recycled. Moreover, recycling creates several economic benefits, including the potential to create job markets and drive growth.
Common recycled materials include paper, plastics, glass, aluminum, steel, and wood. Additionally, many construction materials can be reused, including concrete, asphalt materials, masonry, and reinforcing steel. “Green” plant-based wastes are often recovered and immediately reused for mulch or fertilizer applications. Many industries also recover various by-products and/or refine and “re-generate” solvents for reuse. Examples include copper and nickel recovery from metal finishing processes; the recovery of oils, fats, and plasticizers by solvent extraction from filter media such as activated carbon and clays; and acid recovery by spray roasting, ion exchange, or crystallization. Further, a range of used food-based oils are being recovered and utilized in “biodiesel” applications.
Numerous examples of successful recycling and reuse efforts are encountered every day. In some cases, the recycled materials are used as input materials and are heavily processed into end products. Common examples include the use of scrap paper for new paper manufacturing, or the processing of old aluminum cans into new aluminum products. In other cases, reclaimed materials undergo little or no processing prior to their re-use.
Some common examples include the use of tree waste as wood chips, or the use of brick and other fixtures into new structural construction. In any case, the success of recycling depends on effective collection and processing of recyclables, markets for reuse (e.g. manufacturing and/or applications that utilize recycled materials), and public acceptance and promotion of recycled products and applications utilizing recycled materials.
Biological Treatment
Landfill disposal of wastes containing significant organic fractions is increasingly discouraged in many countries, including the United States. Such disposal practices are even prohibited in several European countries. Since landfilling does not provide an attractive management option, other techniques have been identified. One option is to treat waste so that biodegradable materials are degraded and the remaining inorganic waste fraction (known as residuals) can be subsequently disposed or used for a beneficial purpose.
Biodegradation of wastes can be accomplished by using aerobic composting, anaerobic digestion, or mechanical biological treatment (MBT) methods. If the organic fraction can be separated from inorganic material, aerobic composting or anaerobic digestion can be used to degrade the waste and convert it into usable compost. For example, organic wastes such as food waste, yard waste, and animal manure that consist of naturally degrading bacteria can be converted under controlled conditions into compost, which can then be utilized as natural fertilizer. Aerobic composting is accomplished by placing selected proportions of organic waste into piles, rows or vessels, either in open conditions or within closed buildings fitted with gas collection and treatment systems. During the process, bulking agents such as wood chips are added to the waste material to enhance the aerobic degradation of organic materials. Finally, the material is allowed to stabilize and mature during a curing process where pathogens are concurrently destroyed. The end-products of the composting process include carbon dioxide, water, and the usable compost material.
Compost material may be used in a variety of applications. In addition to its use as a soil amendment for plant cultivation, compost can be used remediate soils, groundwater, and stormwater. Composting can be labor-intensive, and the quality of the compost is heavily dependent on proper control of the composting process. Inadequate control of the operating conditions can result in compost that is unsuitable for beneficial applications. Nevertheless, composting is becoming increasingly popular; composting diverted 82 million tons of waste material away the landfill waste stream in 2009, increased from 15 million tons in 1980. This diversion also prevented the release of approximately 178 million metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2009 – an amount equivalent to the yearly carbon dioxide emissions of 33 million automobiles.
In some cases, aerobic processes are not feasible. As an alternative, anaerobic processes may be utilized. Anaerobic digestion consists of degrading mixed or sorted organic wastes in vessels under anaerobic conditions. The anaerobic degradation process produces a combination of methane and carbon dioxide (biogas) and residuals (biosolids). Biogas can be used for heating and electricity production, while residuals can be used as fertilizers and soil amendments. Anaerobic digestion is a preferred degradation for wet wastes as compared to the preference of composting for dry wastes. The advantage of anaerobic digestion is biogas collection; this collection and subsequent beneficial utilization makes it a preferred alternative to landfill disposal of wastes. Also, waste is degraded faster through anaerobic digestion as compared to landfill disposal.
Another waste treatment alternative, mechanical biological treatment (MBT), is not common in the United States. However, this alternative is widely used in Europe. During implementation of this method, waste material is subjected to a combination of mechanical and biological operations that reduce volume through the degradation of organic fractions in the waste. Mechanical operations such as sorting, shredding, and crushing prepare the waste for subsequent biological treatment, consisting of either aerobic composting or anaerobic digestion. Following the biological processes, the reduced waste mass may be subjected to incineration.
Incineration
Waste degradation not only produces useful solid end-products (such as compost), degradation by-products can also be used as a beneficial energy source. As discussed above, anaerobic digestion of waste can generate biogas, which can be captured and incorporated into electricity generation. Alternatively, waste can be directly incinerated to produce energy. Incineration consists of waste combustion at very high temperatures to produce electrical energy. The byproduct of incineration is ash, which requires proper characterization prior to disposal, or in some cases, beneficial re-use. It is widely used in developed countries due to landfill space limitations. It is estimated that about 130 million tons of waste are annually combusted in more than 600 plants in 35 countries. Further, incineration is often used to effectively mitigate hazardous wastes such as chlorinated hydrocarbons, oils, solvents, medical wastes, and pesticides.
|
|
|
| The incinerated waste is turned into energy. | The fly ash (airborne particles) has high levels of toxic chemicals, including dioxin, cadmium and lead. |
| The volume of waste is reduced. | The initial construction costs are high. |
Despite the advantages, incineration is often viewed negatively because of high initial construction costs, and emissions of ash, which is toxic (see Table above ). Currently, many ‘next generation” systems are being researched and developed, and the USEPA is developing new regulations to carefully monitor incinerator air emissions under the Clean Air Act.
Landfill Disposal
Despite advances in reuse and recycling, landfill disposal remains the primary waste disposal method in the United States. As previously mentioned, the rate of MSW generation continues to increase, but overall landfill capacity is decreasing. New regulations concerning proper waste disposal and the use of innovative liner systems to minimize the potential of groundwater contamination from leachate infiltration and migration have resulted in a substantial increase in the costs of landfill disposal. Also, public opposition to landfills continues to grow, partially inspired by memories of historic uncontrolled dumping practices the resulting undesirable side effects of uncontrolled vectors, contaminated groundwater, unmitigated odors, and subsequent diminished property values.
Figure 1: Modern Landfill
Landfills can be designed and permitted to accept hazardous wastes in accordance with RCRA Subtitle C regulations, or they may be designed and permitted to accept municipal solid waste in accordance with RCRA Subtitle D regulations. Regardless of their waste designation, landfills are engineered structures consisting of bottom and side liner systems, leachate collection and removal systems, final cover systems, gas collection and removal systems, and groundwater monitoring systems. An extensive permitting process is required for siting, designing and operating landfills. Post-closure monitoring of landfills is also typically required for at least 30 years. Because of their design, wastes within landfills are degraded anaerobically. During degradation, biogas is produced and collected. The collection systems prevent uncontrolled subsurface gas migration and reduce the potential for an explosive condition. The captured gas is often used in cogeneration facilities for heating or electricity generation. Further, upon closure, many landfills undergo “land recycling” and redeveloped as golf courses, recreational parks, and other beneficial uses.
Wastes commonly exist in a dry condition within landfills, and as a result, the rate of waste degradation is commonly very slow. These slow degradation rates are coupled with slow rates of degradation-induced settlement, which can in turn complicate or reduce the potential for beneficial land re-use at the surface. Recently, the concept of bioreactor landfills has emerged, which involves recirculation of leachate and/or injection of selected liquids to increase the moisture in the waste, which in turn induces rapid degradation. The increased rates of degradation increase the rate of biogas production, which increases the potential of beneficial energy production from biogas capture and utilization.
- 15.2 Waste Management Strategies. Authored by : Kamala Doru0161ner. Provided by : ck-12. Located at : https://www.ck12.org/user:zg9yc25lckbnbwfpbc5jb20./book/Essentials-of-Environmental-Science/section/15.2/ . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Waste hierarchy. Authored by : Drstuey. Provided by : ck-12. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Waste_hierarchy.svg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
Essay on Waste Management for Students and Teacher
500+ essay on waste management.
Essay on Waste Management -Waste management is essential in today’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is getting doubled day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people.
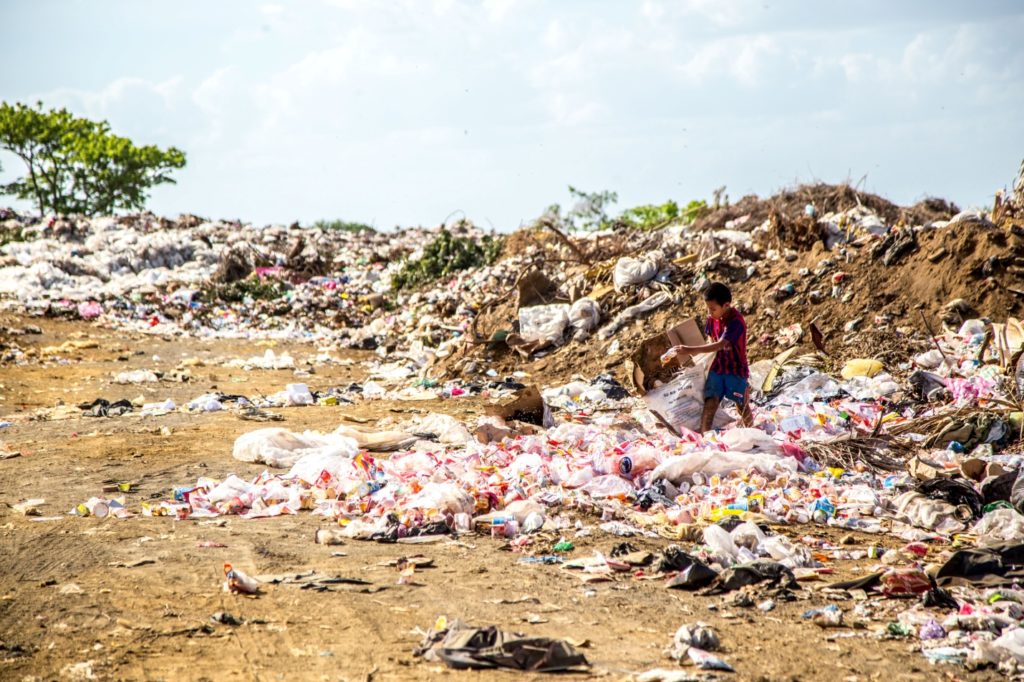

For instance, people living in slums are very close to the waste disposal area. Therefore there are prone to various diseases. Hence, putting their lives in danger. In order to maintain a healthy life, proper hygiene and sanitation are necessary. Consequently, it is only possible with proper waste management .
The Meaning of Waste Management
Waste management is the managing of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. Some of them are Landfills, Recycling , Composting, etc. Furthermore, these methods are much useful in disposing of the waste without causing any harm to the environment.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Methods for Waste Management
Recycling – Above all the most important method is the recycling of waste. This method does not need any resources. Therefore this is much useful in the management of waste . Recycling is the reusing of things that are scrapped of. Moreover, recycling is further converting waste into useful resources.

Landfills – Landfills is the most common method for waste management. The garbage gets buried in large pits in the ground and then covered by the layer of mud. As a result, the garbage gets decomposed inside the pits over the years. In conclusion, in this method elimination of the odor and area taken by the waste takes place.
Composting – Composting is the converting of organic waste into fertilizers. This method increases the fertility of the soil. As a result, it is helpful in more growth in plants. Furthermore it the useful conversion of waste management that is benefiting the environment.
Advantages of Waste Management
There are various advantages of waste management. Some of them are below:
Decrease bad odor – Waste produces a lot of bad odor which is harmful to the environment. Moreover, Bad odor is responsible for various diseases in children. As a result, it hampers their growth. So waste management eliminates all these problems in an efficient way.
Reduces pollution – Waste is the major cause of environmental degradation. For instance, the waste from industries and households pollute our rivers. Therefore waste management is essential. So that the environment may not get polluted. Furthermore, it increases the hygiene of the city so that people may get a better environment to live in.
Reduces the production of waste -Recycling of the products helps in reducing waste. Furthermore, it generates new products which are again useful. Moreover, recycling reduces the use of new products. So the companies will decrease their production rate.
It generates employment – The waste management system needs workers. These workers can do various jobs from collecting to the disposing of waste. Therefore it creates opportunities for the people that do not have any job. Furthermore, this will help them in contributing to society.
Produces Energy – Many waste products can be further used to produce energy. For instance, some products can generate heat by burning. Furthermore, some organic products are useful in fertilizers. Therefore it can increase the fertility of the soil.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Waste Management

- Updated on
- May 11, 2023

Every year, the amount of waste is doubling because of the increasing population around the world. The 3Rs, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle should be followed to help in waste management. Waste management is the need of the hour and should be followed by individuals globally. This is also a common essay topic in the school curriculum and various academic and competitive exams like IELTS , TOEFL , SAT , UPSC , etc. In this blog, let us explore how to write an essay on Waste Management.
This Blog Includes:
Tips for writing an essay on waste management , what is the meaning of waste management, essay on waste management in 200 words, essay on waste management in 300 words .
To write an impactful and scoring essay, here are some tips on how to manage waste and write a good essay:
- The initial step is to write an introduction or background information about the topic
- You must use a formal style of writing and avoid using slang language.
- To make an essay more impactful, write dates, quotations, and names to provide a better understanding
- You can use jargon wherever it is necessary, as it sometimes makes an essay complicated
- To make an essay more creative, you can also add information in bulleted points wherever possible
- Always remember to add a conclusion where you need to summarise crucial points
- Once you are done, read through the lines and check spelling and grammar mistakes before submission
Waste management is the management of waste by disposal and recycling of it. It requires proper techniques while keeping in mind the environmental situations. For example, there are various methods and techniques through which the waste is disposed of. Some of these are Landfills, Recycling, Composting, etc. These methods are useful in disposing of waste without causing any harm to the environment.
Sample Essays on Waste Management
To help you write a perfect essay that would help you score well, here are some sample essays to give you an idea about the same.
One of the crucial aspects of today’s society is waste management. Due to a surge in population, the waste is generated in millions of tons day by day and affects the lives of a plethora of people across the globe. Mostly the affected people live in slums that are extremely close to the waste disposal areas; thus, they are highly prone to communicable and non-communicable diseases. These people are deprived of necessities to maintain a healthy life, including sanitation and proper hygiene.
There are various methods and techniques for disposing of waste including Composting, Landfills, Recycling, and much more. These methods are helpful in disposing of waste without being harmful to the environment. Waste management is helpful in protecting the environment and creating safety of the surrounding environment for humans and animals. The major health issue faced by people across the world is environmental pollution and this issue can only be solved or prevented by proper waste management so that a small amount of waste is there in the environment. One of the prominent and successful waste management processes, recycling enables us not only in saving resources but also in preventing the accumulation of waste. Therefore it is very important to teach and execute waste management.
The basic mantra of waste management is” Refuse, Reuse, Reduce, Repurpose, and Recycle”. Waste management is basically the collection or accumulation of waste and its disposal. This process involves the proper management of waste including recycling waste generated and even generating useful renewable energy from it. One of the most recent initiatives taken by various countries at the local, national and international levels, waste management is a way of taking care of planet earth. This responsible act helps in providing a good and stable environment for the present and future generations. In India, most animals get choked and struggle till death because they consume waste on the streets.
So far many lives are lost, not only animals but also humans due to a lack of proper waste management. There are various methods and techniques for disposing of waste including Composting, Landfills, Recycling, and much more. These methods are helpful in disposing of waste without being harmful to the environment. Waste management is helpful in protecting the environment and creating safety of the surrounding environment for humans and animals. This process of waste management evolved due to industrialization as prior to these inventions simple burying was sufficient for disposing of waste.
One of the crucial things to control waste is creating awareness among people and this can only be achieved only when the governments and stakeholders in various countries take this health issue seriously. To communicate with various communities and reach each end of the country, the message can be communicated through media and related platforms. People also need to participate in waste management procedures by getting self-motivated and taking care of activities of daily living. These steps to create consciousness about waste management are crucial to guarantee the success and welfare of the people and most importantly our planet earth.
Check Out Popular Essay Topics
- Essay on Population Explosion
- Essay on My Hobby
- Essay on Human Rights
- Essay On Sikkim
- Essay on Disaster Management
- Essay on Democracy
- Essay on Child Labour
- Essay on Global Warming
- Essay on Women’s Empowerment
- Essay on My Aim in Life
- Essay on India
- Essay on Education System
We hope this blog has helped you structure a terrific essay on waste management. Planning to ace your IELTS, get expert tips from coaches at Leverage Live by Leverage Edu .
Sonal is a creative, enthusiastic writer and editor who has worked extensively for the Study Abroad domain. She splits her time between shooting fun insta reels and learning new tools for content marketing. If she is missing from her desk, you can find her with a group of people cracking silly jokes or petting neighbourhood dogs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet

When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best waste management topic ideas & essay examples, 💡 interesting topics to write about waste management, 👍 good essay topics on waste management.
- E-Waste Management for the Local Environment The negative consequence of poor e-waste management, such as poor e-waste disposal, might cue the thoughts of the locals on the need to improve on their environmental awareness, thus joining the local environmental organization proposed.
- E-Waste Management in the School Environment Recycling Recycling is one of the best ways of managing e-waste in the school. Specifically, the school should roll out a comprehensive campaign on the need to dump the e-wastes in these bins.
- Disposal of Electronic Waste There has been a growing call for industry players to effect proper disposal of e-wastes, or to find alternative uses of the wastes, such as recycling and separating the components of the electronic devices for […]
- Solid Waste Management in the Dubai Municipality The aim of this paper is to examine the extent of managing the effects of solid waste within the Dubai Municipality.
- The Importance of Zero Waste Management The introduction gets the audience acquainted with the general idea of the paper and the key concept investigated. The major purpose of the zero-waste approach is the arrangement of a circular flow of materials, thereby […]
- Environmental Protection and Waste Management The analysis also focuses on the intellectual behaviour of people regarding the environmental effects of waste. There is lack of strong basis for scientific findings and current guidance is causing the environmental challenges to become […]
- Sustainability and Waste Management Secondly, this approach can decrease the cost of energy, and this opportunity is important for the economic sustainability of the country.
- Effective Waste Management Steps Step 6: To guarantee the effective reuse of the waste, it is necessary to pay attention to the containers for storing the waste and to the method used for reusing the substances.
- Waste Management in Australia Numerous materials that end up in landfills determine the types of waste-to-energy management practices that should be executed to save the environment from pollution and devastation.
- Management of E-Waste The school can contact the vendors and suppliers of such equipment for disposal. The school can identify the surplus equipment and organize a local auction to dispose them off.
- Possible Solutions to the Problem of Solid Waste Management Basing on the Comparison of the Situation in the USA and the European Countries To overcome the issue of solid waste management, the USA and the European countries practice the collection, transportation, recycling of the waste at the local and regional levels, with focusing on the competitiveness of the […]
- Campus Waste Management The current agreement with the surrounding community on the problem of waste management is based on such principles as the reduction of the waste and its division according the recycling standards.
- Electronic Waste Management and Recycling In this modern era, going green is the main concern of companies and thus a stance for competition for the majority.
- E-Waste Disposal in US E-waste disposal is destroying the environment in various ways depending on the type of the electronic disposed and the method of disposal.
- African Towns’ Waste Management: Port Said, Egypt The report addresses problems in developing African countries in general and the city of Port Said in particular. In Port Said, waste collection is done by local authority employees and is largely dependent on two […]
- Healthcare Waste Management and International Pacts Where a private contractor is involved in the collection, transportation, and disposal of the waste, the duty of care principle requires the health care facility to conduct supervision to ensure that the processes are carried […]
- Nepal’s Waste Management Alternatives For this reason, the group embarked on a research and a number of discussions with EWB to come up with the best design to address the problem of waste management in the area.
- Illegal Hazardous Waste Management Cases It may include the illegal storage of waste under the guise of valuable materials or the illegal dumping of refuse into surroundings.
- Horizon Company’s Energy and Waste Management The same analogy is true for its high-energy demand because Horizon’s use of fossil fuel and electricity to power its organisational processes contribute to the depletion of the earth’s resources.
- Electronic Waste Management in China According to Liu et al, one of the major areas of concern in environmental conservation is the massive generation of electronic wastes.
- Solid Waste Management: Hazardous Waste Management It is the purpose of this paper to discuss the issue of improper trash disposal practices and the human health problems that such practices may cause in the community.
- Poor Waste Disposal and Pollution in California For instance, the rapid increase in the number of factories and industries in California has led to more waste products in the state.
- Medical Waste Disposal: Steps and Regulations Medical waste is “waste sufficiently capable of causing infection during handling and disposal”. Genotoxic Highly dangerous waste that can be teratogenic, carcinogenic, or mutagenic.
- The Nuclear Waste Management Policy The increase in the nations’ potential will aid in their industrialization and enable them to contribute more significantly to the settlement of the nuclear waste problem.
- Dental Offices’ Waste Management Practices A dental office also has to train its employees to ensure that they are aware of the importance of effective waste management to minimize the likelihood of pollution.
- Food Waste Management: Impact on Sustainability and Climate Change How effective is composting food waste in enhancing sustainability and reducing the effects of climate change? The following key terms are used to identify and scrutinize references and study materials.”Food waste” and sustain* “Food waste” […]
- Efficient Strategies to Improve Waste Management in Qatar Restaurants The primary aim of the study is to determine the effective strategies that can be used to improve waste management in restaurants operating in Qatar.
- Sustainable Waste Management Benefits In this study, the scholar’s aims include: to know the impacts of workable management of leftover in project-based corporations, including how it profits organisations and the various methods firms use to sustain the environment.
- Household Hazardous Waste Disposal Strategies People are informed about the area of the collection facilities and the types of materials that are permissible and inadmissible at the collection site.
- Waste Management and Policy Improvement Suggestions However, the existing framework does not allow for rigid and sufficient control of the waste management strategies, particularly in regard to organizational e-waste management and e-waste disposal in families.
- The Issue of Waste Management at Events This paper considers the importance of gradually reducing the volume of waste generated at events and the possibility of attracting investors to the field of waste recycling at events.
- Waste Management Sustainability in the UK Fashion Industry In spite of the presence of the overarching goal, the exact nature and direction of sustainable policies may vary across different contexts and regions of the globe.
- Reign of Recycling and Waste Management Problem Despite the established opinion about the benefits of recycling, John Tierney, the author of the article, debates the advantages of this process.
- Solid Waste Disposal: Alternative Methods From this perspective, the necessity to recycle specific types of waste is easier to explain to the citizens than the benefits of incineration, as the former approach is more explicit.
- Environmental Effect & Waste Management Survey The result shows that most respondents are aware of some of the issues caused by environmental waste and lack of recycling.
- On Waste Management: “The Big Necessity” by Rose George To accomplish this three major issues are addressed; the author’s points as well as my intention, things I have learned from the book as well as my thoughts, and lastly the benefits of the book.
- Waste Disposal: Deductions, Legal Fees S 8-1 Positive and Negative limbs: First positive limb: The extent to which outgoing expenses are incurred in gaining or producing assessable income.
- Waste Management and Hazardous Releases The study assesses the credibility of the area to sustain the facility and the effect on the public health and environment.
- Radioactive Medical Waste Management The discovery of the potential of radionuclides in the management of medical conditions has seen an increase in the use of radionuclides in medical facilities.
- Transpacific Waste Management Facility The company has a wide range of waste removal, management, and disposal arrangements that have been fully certified to manage liquid and hazardous waste materials.
- Waste Management Practices: The Shire of Collie Most of the regions within the proximity of the Shire of Collie undertake drastic measures to control the growth of the waste management problem.
- Waste Management in Developing Nations: A Need Assessment Plan Information gathering is very important as it will tell the current methods of waste management present in the community and the existing resources.
- E-Waste Management in the US: In Search of a Financial Model This paper defines and considers the peculiar characteristics of electronic waste or E-Waste, and invites particular reference to the system of E-Waste management followed by the US federal government and the member States.
- Mapping Environmental Justice: Water and Waste Management Environmental justice describes a set of values, rules and actions which place the responsibility for the dangers to the environmental health on citizens from all ethnicities and socioeconomic classes of the society and guarantee them […]
- Analysis of the Hazardous Waste Management in American States The report particularly mirrors the relationship of the number of waste generators and total hazardous waste generated by the state, generators versus waste generated, and waste shipped versus a number of regions within the States.
- Liquid Waste Disposal and Ground Water Contamination The following picture illustrates the contamination of water by the liquid waste disposed by The Davis Liquid Waste Analysis of the two case studies reveals that there was ground water in glacial deposits contamination by […]
- Evaluation and Enhancement of E-Waste Management in Dubai The following are some of the possible research methods that can be used to evaluate how to enhance e-waste management in the United Arab Emirates, specifically in the city of Dubai.
- Waste Management: Building Information Modeling The amount of waste generated in construction and demolition processes is enormous and is considered the largest portion of global waste.
- Waste Management in Food Processing: Different Types of Wastes and Recycling Ways Even though countries use a variety of ways to manage waste, the research suggests that they are not sufficiently effective and the accumulating waste poses a danger to the well-being of the population.
- Metalico Inc.’s Sustainability and Waste Management The other types of scrap metal are distributed to the other facilities in various states. Since this company is a scrap metal recycling facility, it protects the environment against pollution.
- Etihad Airways Company’s Waste Management Approach Moreover, one of the core values of the company is its determination to create a sustainable system that will minimize the impact of the company’s operations on the environment.
- Waste Management in Australia: International Lessons This report is based on the extensive literature survey of the waste management sector in Australia and helps to develop an understanding of the achievements made by the country in the chosen sector. Many developed […]
- Ford’s Waste Disposal in Ringwood Mines Landfill Site In 1984, the area was placed on the Superfund priority list by the Environmental Protection Agency in order to clean up the contamination; however, several attempts of land recovery made by Ford failed as pockets […]
- Deep Borehole Disposal for Nuclear Waste 22It is noteworthy that the issue of the feasibility of these projects is still questionable, and the US is unique in actually preparing to test it.
- Hazardous Waste Disposal in the United States The purpose of this report is to present the results of the investigation of the Hanford vitrification plant, a construction projct of Bechtel Corporation.
- Food and Water Waste Disposal in NYC As Grogan observes, many of the problems that are associated with the process of waste disposal are due to the corruption in the state government.
- Waste Management and Action Plan: SP AusNet’s Offices Besides, the report outlines the protocols and procedures for conducting waste management audits such as visual inspection of the current waste boxes and disposal bins.
- Geelong Resource Recovery Centre: Waste Management The Organogram of the facility supports the waste disposal system. Consequently, some waste materials are not transported to the landfill facility.
- Transpacific, Australian Waste Disposal Agency The services department is classified into the general waste disposal, hazardous waste disposal unit, industrial waste disposal and other waste disposal unit. In accordance with the Waste Management Act, the company has the certification and […]
- Nuclear Waste Management Ethical Dilemmas However, the creation of energy through nuclear reactions leads to the production of radioactive by-products that are dangerous to the environment.
- Hazardous Material Waste Management Issues For example, nuclear wastes that are generated during the production of nuclear energy are highly hazardous to people and the environment.
- Benefit Corporation’s Waste Management Owing to the new changes in the operational nature of this company, there is an urgent need to oversee the wellbeing of the immediate environment.
- Hazardous Waste Management Policy at ASU Understanding the seriousness of the issue and the importance of the correct policy applied towards such aspect of work as hazardous waste management, I have read the policy Arizona State University presents.
- Nuclear Waste Disposal Methods The main challenge associated with the nuclear energy is the disposal of the resultant waste. The question of nuclear waste management remains a challenging one given that projections indicate a possible rise in the use […]
- Solid Waste Management in Canada The paper researches and examines the issue of privatization in solid waste management in Canada. The article reveals crucial debates on the issue of privatization of solid waste management.
- “Management Models of Municipal Solid Waste: A Review Focusing on Socio Economic Factors” by Cherian and Jacob Numerous factors impact the quality and results of solid waste management, and the goal of Cherian and Jacob is to review them.
- Introducing E-Waste Management Course in the College The objective of the course would be to ensure that the youths are responsible for the management of wastes, especially the electronic wastes.
- Waste Management Plan – Archivision Garbage collection is inappropriate while the firm produces a great amount of paper and ink wastes, not to mention the food waste and from other activities in the kitchen and in the suites.
- Global Solid Waste Problem and Management Effectiveness in the collection of solid wastes depends on the rate of production of the wastes and availability of resources and equipment to facilitate this collection.
- Waste Disposal of Victoria City Since the quality of wastes is above the amount which is allowed for disposal through the council, the company should begin by getting waste disposal certificate and observe the rules of disposing the hazardous wastes.
- E-Waste Management Plan for Melbourne School For instance, the e-waste sensitization unit may be encouraged to advice the stakeholders of the school to observe the basic rules of e-waste disposal such as collection of these wastes in designated containers or collection […]
- Sustainability and Waste Management: University of Queensland At the time of the collection of the waste from the bins, the bins are over 50% full, with the general waste bins being 95% full.
- Refinery Wastewater Management Water processing plants that use chemical processes to manage the waste water have now turned to the use of zero-effluent techniques of waste management that ensure that the waste water can be re-used and the […]
- Waste Management in Rye Facility The main aim of Rye facility is to foster waste recovery together with the provision of tipping services to people within the municipality.
- Waste Management in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi The government in the emirate should formulate regulations governing waste management and restricting any form of disposal that could be harmful to the environment.
- A Comparative Analysis of American and Chinese Waste Management Methods In addition, the use of recycling reduces the chances of a country to make use of land fill and incineration and promotes the usability of waste materials again and again.
- The Intel Corporation Waste Management Plan in the Workplaces This paper presents a discussion of the intensity of the seriousness of these problems with reference to a case study of waste management in Jones Cafe 5 and the Ronler Acres Cafe 3 workplaces. The […]
- Technologies in Improving Air Quality Management Due to Waste Water In this regard, the Eastern Research Group says the temperature of the environment and the physical design of the wastewater treatment facilities have a role to play in the intensity of the pollution In Canada, […]
- Project Management: A Platform Project for Waste Recycling in SMEs and Public Companies Seeing how the manufacturing process includes the location of the resources and the transportation of the given resources to the end customer and, in fact, cannot be viewed outside the manufacturing process, it will be […]
- Sustainability and Waste Management in the Australian Construction Industry In Australia, there is the National Waste Policy that the Waste Management Association of Australia together with the government has put forth to responsibly manage wastes in the country.
- Waste Management Strategies in Australia This is because the population of the country is increasing leading to the creation of more waste. The increase in the quantity of waste generated in the country has a direct link to the increase […]
- The Bamako Convention: Management of Hazardous Waste Materials Movement In the recent past, many countries have been accused of damping hazardous waste in the form of nuclear waste in various parts of the world especially oceans and in third world countries this trend is […]
- Waste Management, Inc. Analysis and Recommendations The company had expressed interest in acquiring its competitor Republic Services, Inc in July 2008 placing a bid of $34 per share, however, this offer was rejected and the company made another attempt in August […]
- Management Recycling of the Waste The requirement of this assignment was to collect and recycle different kinds of household items from the trash. In the first week five plastic cups were collected, which were kept in the storage area.
- Comparison of Secondary and Tertiary Waste Water Management Both the secondary and tertiary treatment methods utilize a number of processes to make each step a success but tertiary treatment is never usually a necessity because it depends on the toxicity of the source […]
- Landfill Essay Titles
- Deforestation Research Ideas
- Atmosphere Questions
- Endangered Species Questions
- Osmosis Research Topics
- Water Pollution Research Topics
- Ecosystem Essay Topics
- Poisoning Essay Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/waste-management-essay-topics/
"97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/waste-management-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/waste-management-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/waste-management-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "97 Waste Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/waste-management-essay-topics/.
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Pedro Reynolds-Cuellar
Departments
- Edgerton Center
As Taught In
- Sustainability
- Environmental Policy
- Urban Planning
- The Developing World
Learning Resource Types
D-lab: waste, first reflection paper: waste technology, first reflection.
Subject: Waste Management Technology
Use this reflection to explore a waste management technology with one of three lenses:
- Technologies for a specific material stream - Choose one material and examine the technologies used to process / treat that material
- Technology Case Study - Choose three areas (cities, communities, government jurisdiction) and compare the technologies used in the three areas
- Specific Technology - Explore a technology in depth, its application, scale of use and considerations for purchase and implementation (like cost, size, etc.)
- 4–5 pages; 4 pages in writing, more with charts / graphs
- Helvetica size 12, 1.5 spacing or less
Evaluated on
- Scope of paper
- Synthesis of material presented
- Integration of class content
- Background of technology and its application
- Detailed analysis and synthesis of researched materials that showcases the secondary sources you used to research a technology
- What gaps need to be filled in the existing research in regards to the technology featured in your research?
- What are the limitations of the technology?
- What other innovations (system, technology, policy) could help the technology, material processing or waste management need that you researched?

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare





























IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
solid waste. solid-waste management, the collecting, treating, and disposing of solid material that is discarded because it has served its purpose or is no longer useful. Improper disposal of municipal solid waste can create unsanitary conditions, and these conditions in turn can lead to pollution of the environment and to outbreaks of vector ...
Introduction to Waste Management. Waste disposal leads to direct an d in direct environmental impacts, such as land. occupation, resource depletion, a mplification of global warming due to methane ...
Waste management encompasses the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, or disposal of materials generated through human activity. This process is primarily aimed at mitigating their impact on both human health and the environment. Additionally, waste management strives to extract valuable resources from these materials.
This booklet is a step-by-step guide to help you design an exciting science fair project that focuses on the 3Rs of waste management—reduce, reuse, and recycle. Use your science fair project to show how the 3Rs lead to resource conservation. ... journal writing assignments, and other educational tools related to preventing and reusing waste ...
1. Recognize the elements of solid waste management systems, including waste generation, storage, collection, and landfilling 2. Describe the purpose of landfill components and design protective elements of a landfill 3. Analyze solid waste management systems to determine appropriate use of incineration, composting and recycling. 4.
To help you get started, here are 115 waste management essay topic ideas and examples that you can use as inspiration for your own writing: The importance of proper waste management in protecting the environment. The impact of waste management on public health. Strategies for reducing household waste.
The ideal waste management alternative is to prevent waste generation in the first place. Hence, waste prevention is a basic goal of all the waste management strategies. Numerous technologies can be employed throughout the manufacturing, use, or post-use portions of product life cycles to eliminate waste and, in turn, reduce or prevent pollution.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Methods for Waste Management. Recycling - Above all the most important method is the recycling of waste. This method does not need any resources. Therefore this is much useful in the management of waste. Recycling is the reusing of things that are scrapped of.
process that involves collecting, reprocessing, and/or recovering certain waste materials (e.g., glass, metal, plastics, paper) to make new materials or products. Some recycled organic materials are rich in nutrients and can be used to improve soils. The conversion of waste materials into soil additives is called composting.
Essay on Waste Management in 300 Words. The basic mantra of waste management is" Refuse, Reuse, Reduce, Repurpose, and Recycle". Waste management is basically the collection or accumulation of waste and its disposal. This process involves the proper management of waste including recycling waste generated and even generating useful renewable ...
The negative consequence of poor e-waste management, such as poor e-waste disposal, might cue the thoughts of the locals on the need to improve on their environmental awareness, thus joining the local environmental organization proposed. Zero Waste Management. The objective of a zero waste lifestyle is to reduce waste on the environment.
f waste management.Bring some waste. aterials from home. This can be kitchen waste (for example, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, some food leftovers) and discarded articles of use, such as empty jars of plastic or/and glass, used pa. er, torn cloth etc.• Bury those items in the school garden, or in a bucket or flower pot, and cover them w.
Principles of Waste Management. Waste management principles include following: Waste Hierarchy. The first and vital principle of waste management refers to the 3 R's, Reuse, Recycle, Reduce.The waste hierarchy is represented in the form of a pyramid because the basic premise is the promotion of integrated methods to prevent waste generation.
First Reflection. Subject: Waste Management Technology. Use this reflection to explore a waste management technology with one of three lenses: Technologies for a specific material stream - Choose one material and examine the technologies used to process / treat that material; Technology Case Study - Choose three areas (cities, communities, government jurisdiction) and compare the technologies ...
Solid waste management is an essential part of every society, but it is also one of the most neglected one. An in-depth understanding of the subject is required to tackle the current solid waste management crisis effectively. ... Average assignment score = 25% of average of best 8 assignments out of the total 12 assignments given in the course.
Waste management is that the generation, prevention, characterization, monitoring, treatment, handling, use and residual disposition of solid wastes. There are varied sorts of solid waste as well restaurant, residential, institutional, commercial, agricultural, and special health care, home risky wastes, waste product sludge. The term typically ...
Municipal solid waste (MSW) generation in the city is 4634.52 tons/day. This study aims to explore current MSW management scenario which is found one of the most underestimated sectors of Dhaka City Corporation (DCC) - the responsible authority for MSW management. Overall operational and collection efficiency of DCC MSW management is 45% and ...
Waste Management employees evacuated the facility. Officials haven't shared any information about the fire. A Spokane Fire Department spokesperson didn't immediately respond to a request for more ...
Waste Management Home. Residential. Commercial. Sustainability & Recycling. About Us. Support. Search. WM Support Center Find quick solutions to our top support requests: Find a Solution. Choose a topic and we'll guide you toward the right solution. Request Service. Check Service Status. Bulk Pickup. Missed Pickup.
This assessment indicates that the solid waste management system in Gaza has collapsed. There is no access to the major landfills, and waste accumulates at more than 140 temporary dumping sites which causes serious health and environmental risks, including a spike in diarrheal illness and in acute respiratory infections.
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Waste Management (WM-1.48%) reported second-quarter results that fell short of Wall Street expectations. Investors are moving on, sending shares of WM down 6% as of 10:45 a.m. ET.
Eco-Vista Landfill was purchased by WM in 2000. The property was first permitted for landfill activities in 1979. The 609-acre property includes a 147-acre Class I Municipal Solid Waste Landfill and a 60-acre Class 4 Construction and Demolition Debris (C&D) Landfill, Composting Area, Recycling Drop-off Station, Landfill Gas-to-Energy Facility and a Certified Wildlife Habitat area.
Top Elektrostal Art Museums: See reviews and photos of Art Museums in Elektrostal, Russia on Tripadvisor.
On July 24, Waste Management will be releasing earnings for the most recent quarter. In terms of EPS, 18 analysts are predicting earnings of $1.83 per share compared to earnings of $1.52 per share ...
In the formative period of the KSSO (2009-2013), the General Staff leadership extensively studied the development, training and methods used by the special forces of the world's leading military powers. Finally, in March 2013, the KSSO was formally created and subordinated directly to the CGS (Novosti Rossiya, February 28, 2019).
OAK RIDGE, Tenn. - Joshua Vajda, an employee of Oak Ridge Office of Environmental Management (OREM) contractor UCOR, recently earned a top honor from the American Nuclear Society for contributions that benefit U.S. Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management (EM) sites nationwide. The American Nuclear Society Special Award recognizes an individual for contributions in research or ...
The European Commission announced on Tuesday it intends to begin infringement proceedings against member states failing to meet current waste management targets by sending them letters of formal notice letters.. The targets, detailed in the Waste Framework Directive, the Directive on Waste and Electronic Equipment, and the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive, impose legally binding ...
Toronto-based waste management company GFL Environmental Inc. GFL-T is ruling out a sale of the entire company to private buyers, but is considering running an auction for its environmental ...
Waste Management has generated $6.11 earnings per share over the last year ($6.11 diluted earnings per share) and currently has a price-to-earnings ratio of 34.0. Earnings for Waste Management are expected to grow by 9.93% in the coming year, from $7.25 to $7.97 per share. Waste Management has not formally confirmed its next earnings ...