
Technology and the self
Tomorrow people
For the entire 20th century, it had felt like telepathy was just around the corner. Why is that especially true now?
Roger Luckhurst

Space exploration
Mind-bending speed is the only way to reach the stars – here are three ways to do it

Film and visual culture
An augmented-reality filter reveals the hidden movements all around us

The skyhook solution
Space junk surrounds Earth, posing a dangerous threat. But there is a way to turn the debris into opportunity
Angelos Alfatzis

Computing and artificial intelligence
A scientist’s poor eyesight helped fuel a revolution in computer ‘vision’

Future of technology
Is this the future of space travel? Take a luxury ‘cruise’ across the solar system

The final ethical frontier
Earthbound exploration was plagued with colonialism, exploitation and extraction. Can we hope to make space any different?
Philip Ball

Artificial ‘creativity’ is unstoppable. Grappling with its ethics is up to us
Give the drummer some
As AI drum machines embrace humanising imperfections, what does this mean for ‘real’ drummers and the soul of music?
Jack Stilgoe

With human help, AIs are generating a new aesthetics. The results are trippy

What does an AI make of what it sees in a contemporary art museum?

Ecology and environmental sciences
Producing food while restoring the planet – a glimpse of farming in the future

The environment
The power of shit
Our excrement is a natural, renewable and sustainable resource – if only we can overcome our visceral disgust of it
Lina Zeldovich
When an AI rejects him for life insurance, Mitch wonders if he can escape his fate

Learn from machine learning
The world is a black box full of extreme specificity: it might be predictable but that doesn’t mean it is understandable
David Weinberger

Stories and literature
The cliché writes back
Machine-written literature might offend your tastes but until the dawn of Romanticism most writers were just as formulaic
Yohei Igarashi

Algorithms are sensitive. People are specific. We should exploit their respective strengths

Tech companies shroud their algorithms in secrecy. It’s time to pry open the black box

How vulnerable is the world?
Sooner or later a technology capable of wiping out human civilisation might be invented. How far would we go to stop it?
Nick Bostrom & Matthew van der Merwe
Zoom and gloom
Sitting in a videoconference is a uniformly crap experience. Instead of corroding our humanity, let’s design tools to enhance it
Robert O’Toole
A handful of executives control the ‘attention economy’. Time for attentive resistance

Where did the grandeur go?
Superlative things were done in the past century by marshalling thousands of people in the service of a vision of the future
Martin Parker

Ceramic coral reefs and sawdust houses – the architects 3D-printing the future from scratch
Algorithms associating appearance and criminality have a dark past
Catherine Stinson
Feb 13, 2023

200-500 Word Example Essays about Technology
Got an essay assignment about technology check out these examples to inspire you.
Technology is a rapidly evolving field that has completely changed the way we live, work, and interact with one another. Technology has profoundly impacted our daily lives, from how we communicate with friends and family to how we access information and complete tasks. As a result, it's no surprise that technology is a popular topic for students writing essays.
But writing a technology essay can be challenging, especially for those needing more time or help with writer's block. This is where Jenni.ai comes in. Jenni.ai is an innovative AI tool explicitly designed for students who need help writing essays. With Jenni.ai, students can quickly and easily generate essays on various topics, including technology.
This blog post aims to provide readers with various example essays on technology, all generated by Jenni.ai. These essays will be a valuable resource for students looking for inspiration or guidance as they work on their essays. By reading through these example essays, students can better understand how technology can be approached and discussed in an essay.
Moreover, by signing up for a free trial with Jenni.ai, students can take advantage of this innovative tool and receive even more support as they work on their essays. Jenni.ai is designed to help students write essays faster and more efficiently, so they can focus on what truly matters – learning and growing as a student. Whether you're a student who is struggling with writer's block or simply looking for a convenient way to generate essays on a wide range of topics, Jenni.ai is the perfect solution.
The Impact of Technology on Society and Culture
Introduction:.
Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives and has dramatically impacted how we interact, communicate, and carry out various activities. Technological advancements have brought positive and negative changes to society and culture. In this article, we will explore the impact of technology on society and culture and how it has influenced different aspects of our lives.
Positive impact on communication:
Technology has dramatically improved communication and made it easier for people to connect from anywhere in the world. Social media platforms, instant messaging, and video conferencing have brought people closer, bridging geographical distances and cultural differences. This has made it easier for people to share information, exchange ideas, and collaborate on projects.
Positive impact on education:
Students and instructors now have access to a multitude of knowledge and resources because of the effect of technology on education . Students may now study at their speed and from any location thanks to online learning platforms, educational applications, and digital textbooks.
Negative impact on critical thinking and creativity:
Technological advancements have resulted in a reduction in critical thinking and creativity. With so much information at our fingertips, individuals have become more passive in their learning, relying on the internet for solutions rather than logic and inventiveness. As a result, independent thinking and problem-solving abilities have declined.
Positive impact on entertainment:
Technology has transformed how we access and consume entertainment. People may now access a wide range of entertainment alternatives from the comfort of their own homes thanks to streaming services, gaming platforms, and online content makers. The entertainment business has entered a new age of creativity and invention as a result of this.
Negative impact on attention span:
However, the continual bombardment of information and technological stimulation has also reduced attention span and the capacity to focus. People are easily distracted and need help focusing on a single activity for a long time. This has hampered productivity and the ability to accomplish duties.
The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies has been one of the most significant technological developments of the past several decades. These cutting-edge technologies have the potential to alter several sectors of society, including commerce, industry, healthcare, and entertainment.
As with any new and quickly advancing technology, AI and ML ethics must be carefully studied. The usage of these technologies presents significant concerns around privacy, accountability, and command. As the use of AI and ML grows more ubiquitous, we must assess their possible influence on society and investigate the ethical issues that must be taken into account as these technologies continue to develop.
What are Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning?
Artificial Intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence in machines designed to think and act like humans. Machine learning is a subfield of AI that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
The impact of AI and ML on Society
The use of AI and ML in various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and retail, has brought many benefits. For example, AI-powered medical diagnosis systems can identify diseases faster and more accurately than human doctors. However, there are also concerns about job displacement and the potential for AI to perpetuate societal biases.
The Ethical Considerations of AI and ML
A. Bias in AI algorithms
One of the critical ethical concerns about AI and ML is the potential for algorithms to perpetuate existing biases. This can occur if the data used to train these algorithms reflects the preferences of the people who created it. As a result, AI systems can perpetuate these biases and discriminate against certain groups of people.
B. Responsibility for AI-generated decisions
Another ethical concern is the responsibility for decisions made by AI systems. For example, who is responsible for the damage if a self-driving car causes an accident? The manufacturer of the vehicle, the software developer, or the AI algorithm itself?
C. The potential for misuse of AI and ML
AI and ML can also be used for malicious purposes, such as cyberattacks and misinformation. The need for more regulation and oversight in developing and using these technologies makes it difficult to prevent misuse.
The developments in AI and ML have given numerous benefits to humanity, but they also present significant ethical concerns that must be addressed. We must assess the repercussions of new technologies on society, implement methods to limit the associated dangers, and guarantee that they are utilized for the greater good. As AI and ML continue to play an ever-increasing role in our daily lives, we must engage in an open and frank discussion regarding their ethics.
The Future of Work And Automation
Rapid technological breakthroughs in recent years have brought about considerable changes in our way of life and work. Concerns regarding the influence of artificial intelligence and machine learning on the future of work and employment have increased alongside the development of these technologies. This article will examine the possible advantages and disadvantages of automation and its influence on the labor market, employees, and the economy.
The Advantages of Automation
Automation in the workplace offers various benefits, including higher efficiency and production, fewer mistakes, and enhanced precision. Automated processes may accomplish repetitive jobs quickly and precisely, allowing employees to concentrate on more complex and creative activities. Additionally, automation may save organizations money since it removes the need to pay for labor and minimizes the danger of workplace accidents.
The Potential Disadvantages of Automation
However, automation has significant disadvantages, including job loss and income stagnation. As robots and computers replace human labor in particular industries, there is a danger that many workers may lose their jobs, resulting in higher unemployment and more significant economic disparity. Moreover, if automation is not adequately regulated and managed, it might lead to stagnant wages and a deterioration in employees' standard of life.
The Future of Work and Automation
Despite these difficulties, automation will likely influence how labor is done. As a result, firms, employees, and governments must take early measures to solve possible issues and reap the rewards of automation. This might entail funding worker retraining programs, enhancing education and skill development, and implementing regulations that support equality and justice at work.
IV. The Need for Ethical Considerations
We must consider the ethical ramifications of automation and its effects on society as technology develops. The impact on employees and their rights, possible hazards to privacy and security, and the duty of corporations and governments to ensure that automation is utilized responsibly and ethically are all factors to be taken into account.
Conclusion:
To summarise, the future of employment and automation will most certainly be defined by a complex interaction of technological advances, economic trends, and cultural ideals. All stakeholders must work together to handle the problems and possibilities presented by automation and ensure that technology is employed to benefit society as a whole.
The Role of Technology in Education
Introduction.
Nearly every part of our lives has been transformed by technology, and education is no different. Today's students have greater access to knowledge, opportunities, and resources than ever before, and technology is becoming a more significant part of their educational experience. Technology is transforming how we think about education and creating new opportunities for learners of all ages, from online courses and virtual classrooms to instructional applications and augmented reality.
Technology's Benefits for Education
The capacity to tailor learning is one of technology's most significant benefits in education. Students may customize their education to meet their unique needs and interests since they can access online information and tools.
For instance, people can enroll in online classes on topics they are interested in, get tailored feedback on their work, and engage in virtual discussions with peers and subject matter experts worldwide. As a result, pupils are better able to acquire and develop the abilities and information necessary for success.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the numerous advantages of technology in education, there are also obstacles and considerations to consider. One issue is the growing reliance on technology and the possibility that pupils would become overly dependent on it. This might result in a lack of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, as students may become passive learners who only follow instructions and rely on technology to complete their assignments.
Another obstacle is the digital divide between those who have access to technology and those who do not. This division can exacerbate the achievement gap between pupils and produce uneven educational and professional growth chances. To reduce these consequences, all students must have access to the technology and resources necessary for success.
In conclusion, technology is rapidly becoming an integral part of the classroom experience and has the potential to alter the way we learn radically.
Technology can help students flourish and realize their full potential by giving them access to individualized instruction, tools, and opportunities. While the benefits of technology in the classroom are undeniable, it's crucial to be mindful of the risks and take precautions to guarantee that all kids have access to the tools they need to thrive.
The Influence of Technology On Personal Relationships And Communication
Technological advancements have profoundly altered how individuals connect and exchange information. It has changed the world in many ways in only a few decades. Because of the rise of the internet and various social media sites, maintaining relationships with people from all walks of life is now simpler than ever.
However, concerns about how these developments may affect interpersonal connections and dialogue are inevitable in an era of rapid technological growth. In this piece, we'll discuss how the prevalence of digital media has altered our interpersonal connections and the language we use to express ourselves.
Direct Effect on Direct Interaction:
The disruption of face-to-face communication is a particularly stark example of how technology has impacted human connections. The quality of interpersonal connections has suffered due to people's growing preference for digital over human communication. Technology has been demonstrated to reduce the usage of nonverbal signs such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and other indicators of emotional investment in the connection.
Positive Impact on Long-Distance Relationships:
Yet there are positives to be found as well. Long-distance relationships have also benefited from technological advancements. The development of technologies such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and social media has made it possible for individuals to keep in touch with distant loved ones. It has become simpler for individuals to stay in touch and feel connected despite geographical distance.
The Effects of Social Media on Personal Connections:
The widespread use of social media has had far-reaching consequences, especially on the quality of interpersonal interactions. Social media has positive and harmful effects on relationships since it allows people to keep in touch and share life's milestones.
Unfortunately, social media has made it all too easy to compare oneself to others, which may lead to emotions of jealousy and a general decline in confidence. Furthermore, social media might cause people to have inflated expectations of themselves and their relationships.
A Personal Perspective on the Intersection of Technology and Romance
Technological advancements have also altered physical touch and closeness. Virtual reality and other technologies have allowed people to feel physical contact and familiarity in a digital setting. This might be a promising breakthrough, but it has some potential downsides.
Experts are concerned that people's growing dependence on technology for intimacy may lead to less time spent communicating face-to-face and less emphasis on physical contact, both of which are important for maintaining good relationships.
In conclusion, technological advancements have significantly affected the quality of interpersonal connections and the exchange of information. Even though technology has made it simpler to maintain personal relationships, it has chilled interpersonal interactions between people.
Keeping tabs on how technology is changing our lives and making adjustments as necessary is essential as we move forward. Boundaries and prioritizing in-person conversation and physical touch in close relationships may help reduce the harm it causes.
The Security and Privacy Implications of Increased Technology Use and Data Collection
The fast development of technology over the past few decades has made its way into every aspect of our life. Technology has improved many facets of our life, from communication to commerce. However, significant privacy and security problems have emerged due to the broad adoption of technology. In this essay, we'll look at how the widespread use of technological solutions and the subsequent explosion in collected data affects our right to privacy and security.
Data Mining and Privacy Concerns
Risk of Cyber Attacks and Data Loss
The Widespread Use of Encryption and Other Safety Mechanisms
The Privacy and Security of the Future in a Globalized Information Age
Obtaining and Using Individual Information
The acquisition and use of private information is a significant cause for privacy alarm in the digital age. Data about their customers' online habits, interests, and personal information is a valuable commodity for many internet firms. Besides tailored advertising, this information may be used for other, less desirable things like identity theft or cyber assaults.
Moreover, many individuals need to be made aware of what data is being gathered from them or how it is being utilized because of the lack of transparency around gathering personal information. Privacy and data security have become increasingly contentious as a result.
Data breaches and other forms of cyber-attack pose a severe risk.
The risk of cyber assaults and data breaches is another big issue of worry. More people are using more devices, which means more opportunities for cybercriminals to steal private information like credit card numbers and other identifying data. This may cause monetary damages and harm one's reputation or identity.
Many high-profile data breaches have occurred in recent years, exposing the personal information of millions of individuals and raising serious concerns about the safety of this information. Companies and governments have responded to this problem by adopting new security methods like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Many businesses now use encryption and other security measures to protect themselves from cybercriminals and data thieves. Encryption keeps sensitive information hidden by encoding it so that only those possessing the corresponding key can decipher it. This prevents private information like bank account numbers or social security numbers from falling into the wrong hands.
Firewalls, virus scanners, and two-factor authentication are all additional security precautions that may be used with encryption. While these safeguards do much to stave against cyber assaults, they are not entirely impregnable, and data breaches are still possible.
The Future of Privacy and Security in a Technologically Advanced World
There's little doubt that concerns about privacy and security will persist even as technology improves. There must be strict safeguards to secure people's private information as more and more of it is transferred and kept digitally. To achieve this goal, it may be necessary to implement novel technologies and heightened levels of protection and to revise the rules and regulations regulating the collection and storage of private information.
Individuals and businesses are understandably concerned about the security and privacy consequences of widespread technological use and data collecting. There are numerous obstacles to overcome in a society where technology plays an increasingly important role, from acquiring and using personal data to the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. Companies and governments must keep spending money on security measures and working to educate people about the significance of privacy and security if personal data is to remain safe.
In conclusion, technology has profoundly impacted virtually every aspect of our lives, including society and culture, ethics, work, education, personal relationships, and security and privacy. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning has presented new ethical considerations, while automation is transforming the future of work.
In education, technology has revolutionized the way we learn and access information. At the same time, our dependence on technology has brought new challenges in terms of personal relationships, communication, security, and privacy.
Jenni.ai is an AI tool that can help students write essays easily and quickly. Whether you're looking, for example, for essays on any of these topics or are seeking assistance in writing your essay, Jenni.ai offers a convenient solution. Sign up for a free trial today and experience the benefits of AI-powered writing assistance for yourself.
Start Writing With Jenni Today
Sign up for a free Jenni AI account today. Unlock your research potential and experience the difference for yourself. Your journey to academic excellence starts here.
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
©Getty Images
Future technology: 22 ideas about to change our world
The future is coming, and sooner than you think. These emerging technologies will change the way we live, how we look after our bodies and help us avert a climate disaster.
Technology moves at a relentlessly fast pace in the modern world. It can sometimes feel like every single day there are new technologies and innovations that will change our futures forever. But in a steady stream of announcements about new massive futuristic technological upgrades and cool gadgets , it is easy to lose track of the amazing ways the world is progressing.
For instance, there are artificial intelligence programs writing poems from scratch and making images from nothing more than a worded prompt. There are 3D-printed eyes, new holograms, lab-grown food and brain-reading robots.
All of this just scratches the surface of what is out there, so we've curated a guide to the most exciting future technologies, listing them all below.
Necrobotics
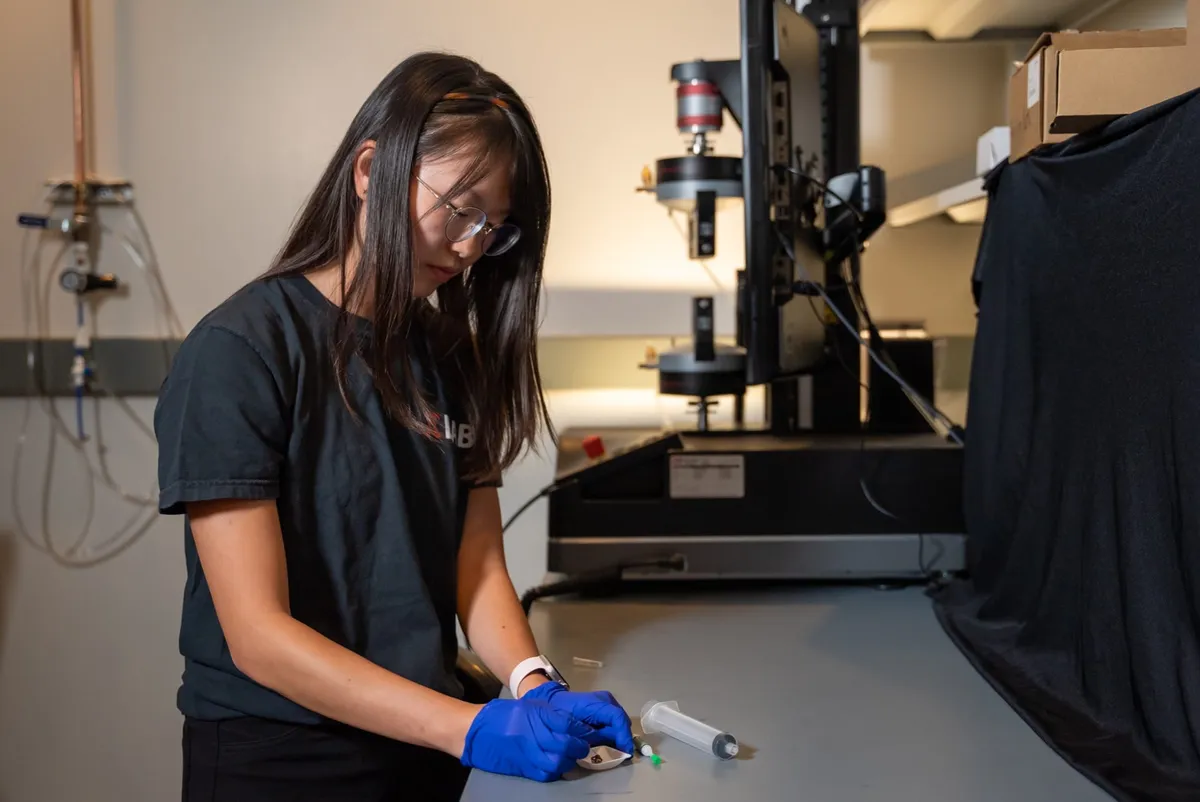

Sometimes new future technologies can offer amazing development, with the possibility of changing the future... while also being incredibly creepy.
This is one way to describe the idea of necrobotics which, as the name suggests, involves turning dead things into robots . While this sounds like a plot to a creepy horror film, this is a technology being explored at Rice University.
A team of researchers turned a dead spider into a robot-like gripper, given the ability to pick up other objects. To achieve this, they take a spider and inject it with air. This works because spiders use hydraulics to force their version of blood (haemolymph) into their limbs, making them extend.
Right now this concept is in its infant stages, but it could mean a future where dead animals are used to further science... it all feels very Frankeinstein-like!
Sand batteries

Not every technology bettering our future has to be complicated, some are simple, yet extremely effective.
One of these kind of technologies has come from some Finnish engineers who have found a way to turn sand into a giant battery.
These engineers piled 100 tons of sand into a 4 x 7 metre steel container. All of this sand was then heated up using wind and solar energy.
This heat can then be distributed by a local energy company to provide warmth to buildings in nearby areas. Energy can be stored this way for long periods of time.
All of this occurs through a concept known as resistive heating. This is where a material is heated by the friction of electrical currents.
Sand and any other non-super conductor are warmed by the electricity passing through them generated heat than can be used for energy.
E-skin could help us hug long-distance friends
While modern technology allows us to communicate verbally and visually almost anywhere in the world, there is currently no reliable method of sharing the sense of touch across long distances. Now, a wireless soft e-skin developed by engineers at the City University of Hong Kong could one day make giving and receiving hugs over the internet a reality.
The e-skin is studded with flexible actuators that sense the wearer’s movements and convert them into electrical signals. These signals can then be sent to another e-skin system via Bluetooth, where the actuators convert them into mechanical vibrations that mimic the initial movements. The system could be used to allow friends and family to ‘feel’ each other over long distances, the researchers say.
Researchers at the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented what they're calling a 'novel, wireless, skin-interfaced olfactory feedback system '. In other words, VR attachments that let you smell stuff.
The smells are generated by the devices heating and melting odorous wax that releases adjustable concentrations of stink. There are two versions of this tech. One is 'mounted' on your upper lip for easy access to your nostrils, and the other is a facemask-like design with hundreds of different odour combinations.
The university said their new tech has a broad range of applications that includes online teaching and 4D movie watching. That's right, in the future, you'll not only be able to watch your favourite movies in VR, you'll also be able to smell them. Now that's immersion!
Catapulting satellites into space
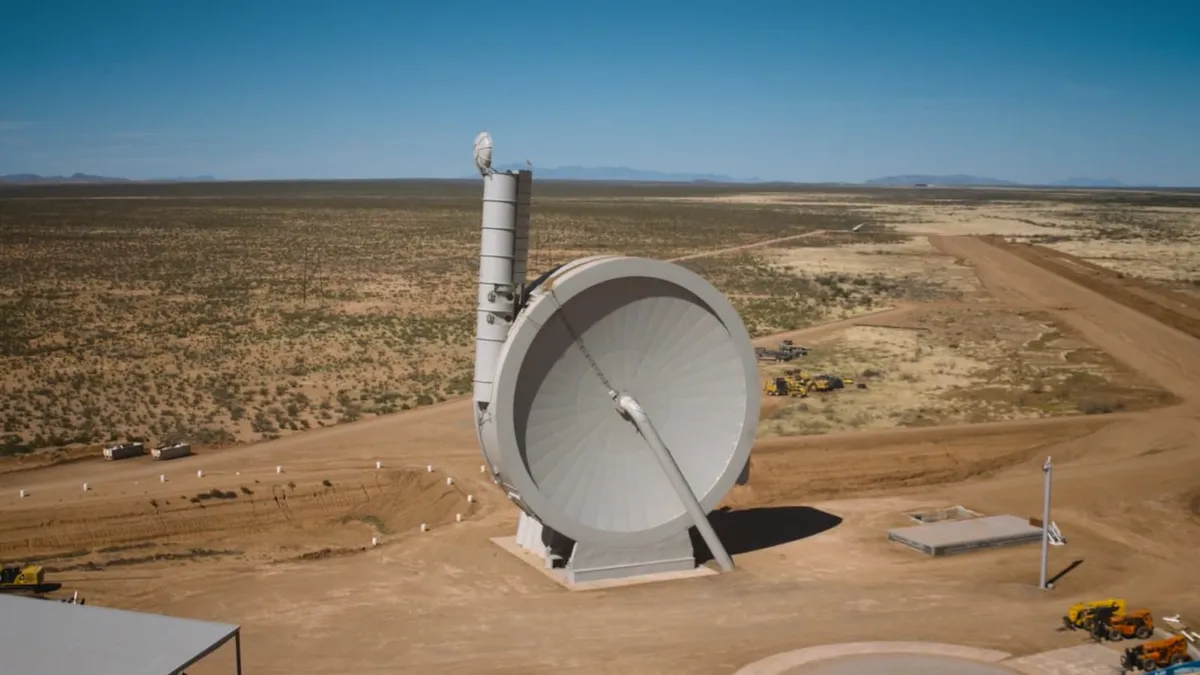

Who would have thought the best way to get satellites into space was with a makeshift catapult! Okay, it is a lot smarter than a catapult but the technology exists in a similar way.
SpinLaunch is a prototype system for getting satellites or other payloads up into space. It does this by using kinetic energy instead of the usual technique of using chemical fuel found in traditional rockets. This technology could be capable of spinning payloads at 8,000km/h and 10,000G, then launching them skyward through a large launch tube.
Of course, small rocket engines will still be required for payloads to reach orbit, but SpinLaunch has claimed this system cuts down on the fuel and infrastructure by an impressive 70 per cent.
The company has signed an agreement with NASA and is now testing the system.
Xenotransplantation
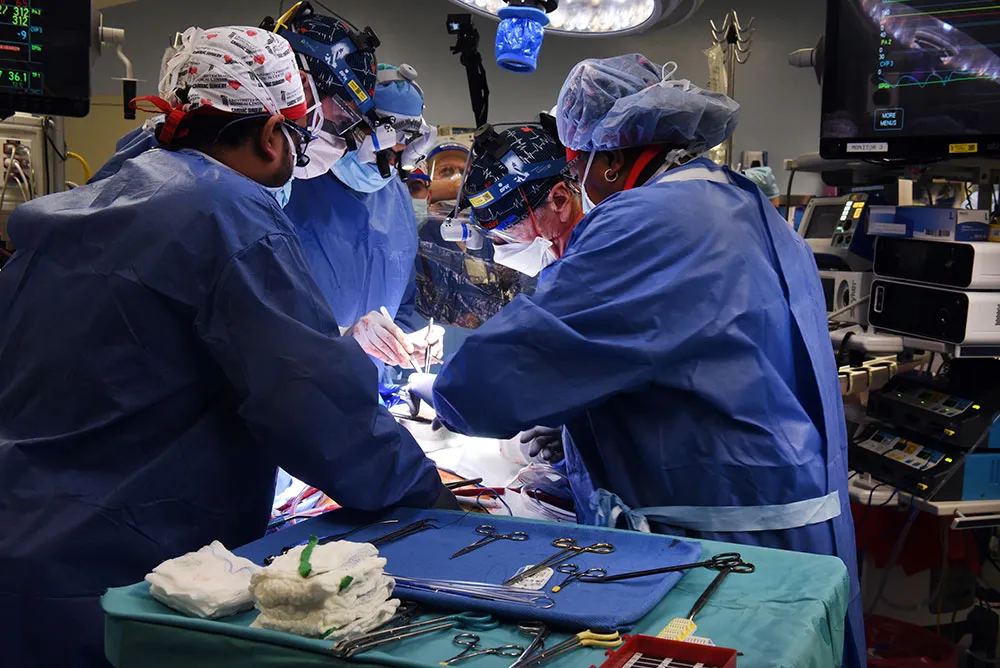
Inserting the heart of a pig into a human feels like a bad idea, and yet, this is one of the latest medical procedures that is seeing rapid progress.
Xenotransplantation - the procedure of transplanting, implementing or infusing a human with cells, tissues or organs from an animal source - has the potential to revolutionise surgery.
One of the most common procedures performed so far is the insertion of a pig's heart into a human. This has now successfully happened twice. However, one of the patients was only alive for a few months, and the second is still being observed.
In these surgeries, the heart cannot be instantly put into a human, gene-editing needs to take place first. Certain genes need to be knocked out of the heart and human genes need to be added, mainly around immune acceptance and genes to prevent excessive growth of heart tissue.
Right now, these surgeries are risky and there is no certainty around success. However, in the near future, we could see xenotransplants happening on a regular basis, providing hearts or tissues from animals to humans in need of it.
AI image-generation

As artificial intelligence continues to perform jobs just as well as humans, there is a new industry to add to the list – the world of art. Researchers at the company OpenAI have created a software that is able to create images from just worded prompts.
Type in ‘a dog wearing a cowboy hat singing in the rain’ and you’ll get a host of completely original images that fit that description. You can even choose what style of art your request will come back in. However, the technology isn't perfected and still has issues, like when we gave it poor prompts on designing cartoon characters .
This technology known as Dall-E is now its second iteration and the team behind it plans to continue developing it further. In the future, we could see this technology used to create art exhibitions, for companies to get quick, original illustrations or of course, to revolutionise the way we create memes on the internet.
There is also technology known as Midjourney , a AI image generator that creates gothic masterpieces with a simple text prompt. We are truly living in the future.
Brain reading robots
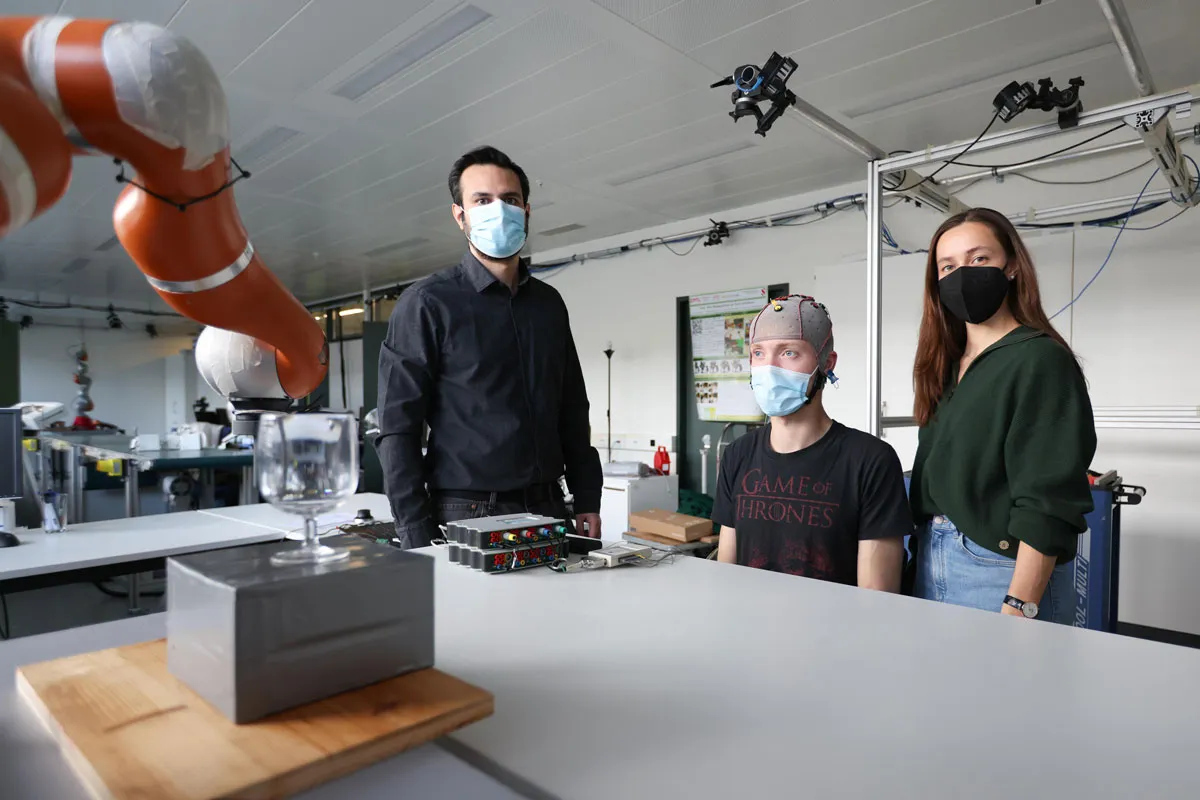

No longer a science fiction trope, the use of brain reading technology has improved hugely in recent years. One of the most interesting and practical uses we’ve seen tested so far comes from researchers at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL).
Thanks to a machine-learning algorithm, a robot arm and a brain-computer interface, these researchers have managed to create a means for tetraplegic patients (those who can’t move their upper or lower body) to interact with the world .
In tests, the robot arm would perform simple tasks like moving around an obstacle. The algorithm would then interprets signals from the brain using an EEG cap and automatically determine when the arm had made a move that the brain considered incorrect, for example moving too close to the obstacle or going too fast.
Over time the algorithm can then adjust to the individuals preferences and brain signals. In the future this could lead to wheelchairs controlled by the brain or assistance machines for tetraplegic patients.
3D printed bones
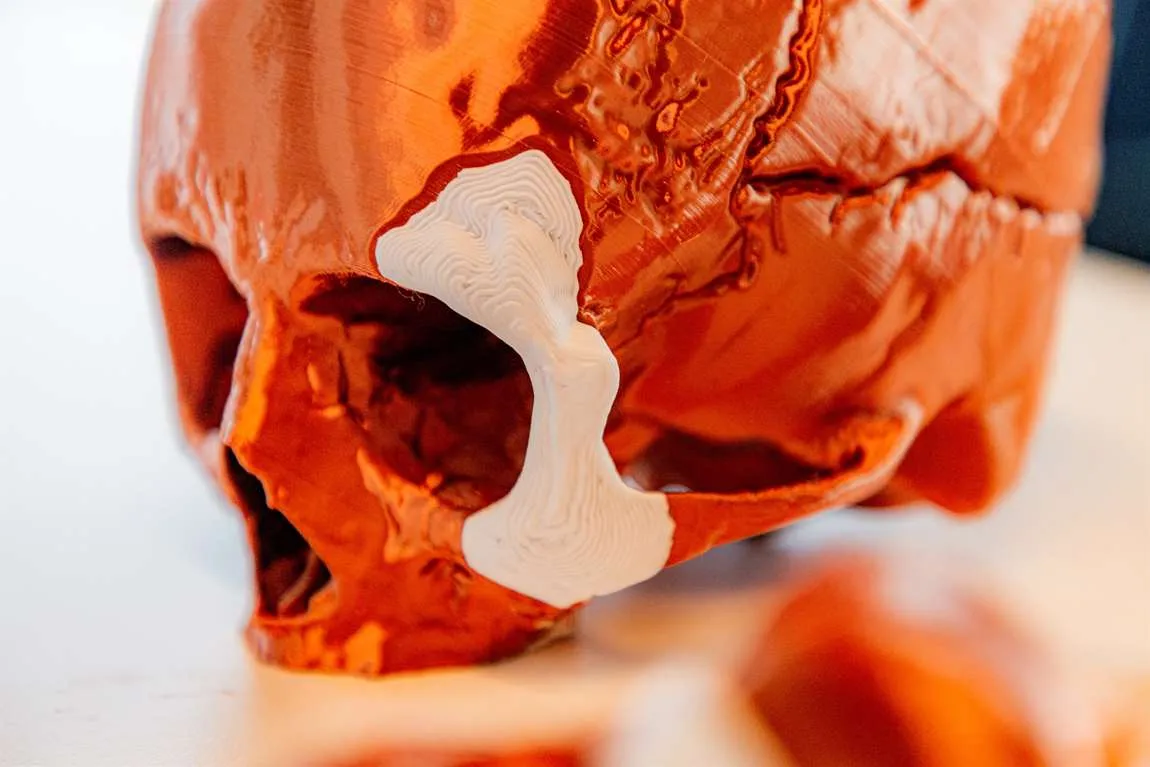
3D printing is an industry promising everything from cheap house building through to affordable rugged armour, but one of the most interesting uses of the technology is the building of 3D printed bones.
The company Ossiform specialises in medical 3D printing, creating patient-specific replacements of different bones from tricalcium phosphate – a material with similar properties to human bones.
Using these 3D printed bones is surprisingly easy. A hospital can perform an MRI which is then sent to Ossiform who create a 3D model of the patient-specific implant that is needed. The surgeon accepts the design and then once it is printed, it can be used in surgery.
What is special about these 3D printed bones is that because of the use of tricalcium phosphate, the body will remodel the implants into vascularised bone. That means they will enable the full restoration of function that the bone it is replacing had. To achieve the best integration possible, the implants are of a porous structure and feature large pores and canals for cells to attach to and reform bone.
3D-printed food that takes the cake
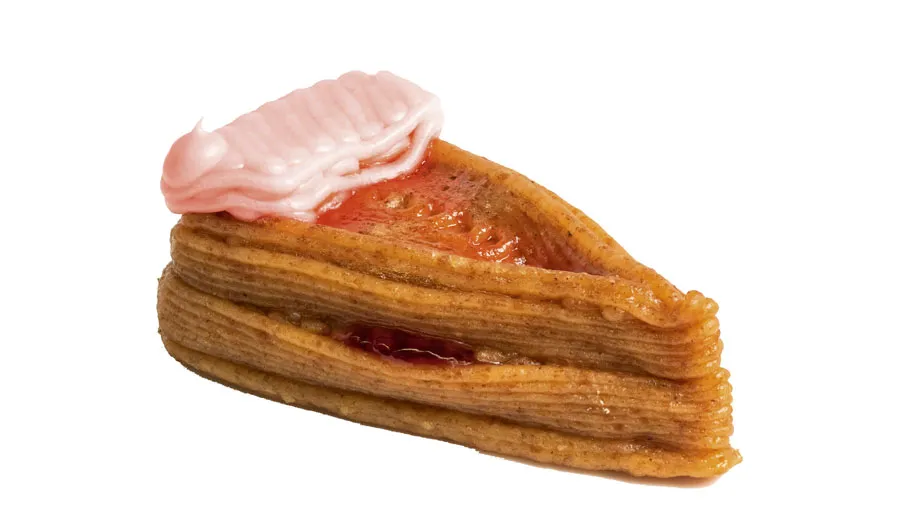

What’s for dinner tonight? Soon it could be a piece of 3D-printed, laser-cooked cake. Researchers at Columbia University School of Engineering have created a device that can construct a seven-ingredient cheesecake using food inks and then cook it to perfection using a laser.
Their creation contained banana, jam, peanut butter and Nutella. Tasty. The technology could one day be used to create personalised meals for everyone from professional athletes to patients with dietary conditions, or could be useful for those who are simply short on time.
Natural language Processing
Natural language processing is the big new trend taking over the internet. While you've most likely seen it in use in Google's autocomplete software, or when your smartphone offers a prediction of what you are trying to type, it is capable of much smarter things.
OpenAI is a company that is at the forefront of artificial intelligence, originally taking the internet by storm with its image generator Dall-E 2 . Now it is back, making a chatbot known as ChatGPT , creating poems from scratch, explaining complex theories with ease and having full-length conversations like it is a human.
ChatGPT is powered by a software known as GPT-3, trained on billions of examples of texts, then taught how to form coherent and logical sentences.
ChatGPT is an example of AI and its future. It has proven its ability to make completely new websites from scratch, write entire length books and even make jokes... although, it clearly still hasn't mastered humour yet.
Boom-free supersonic flight
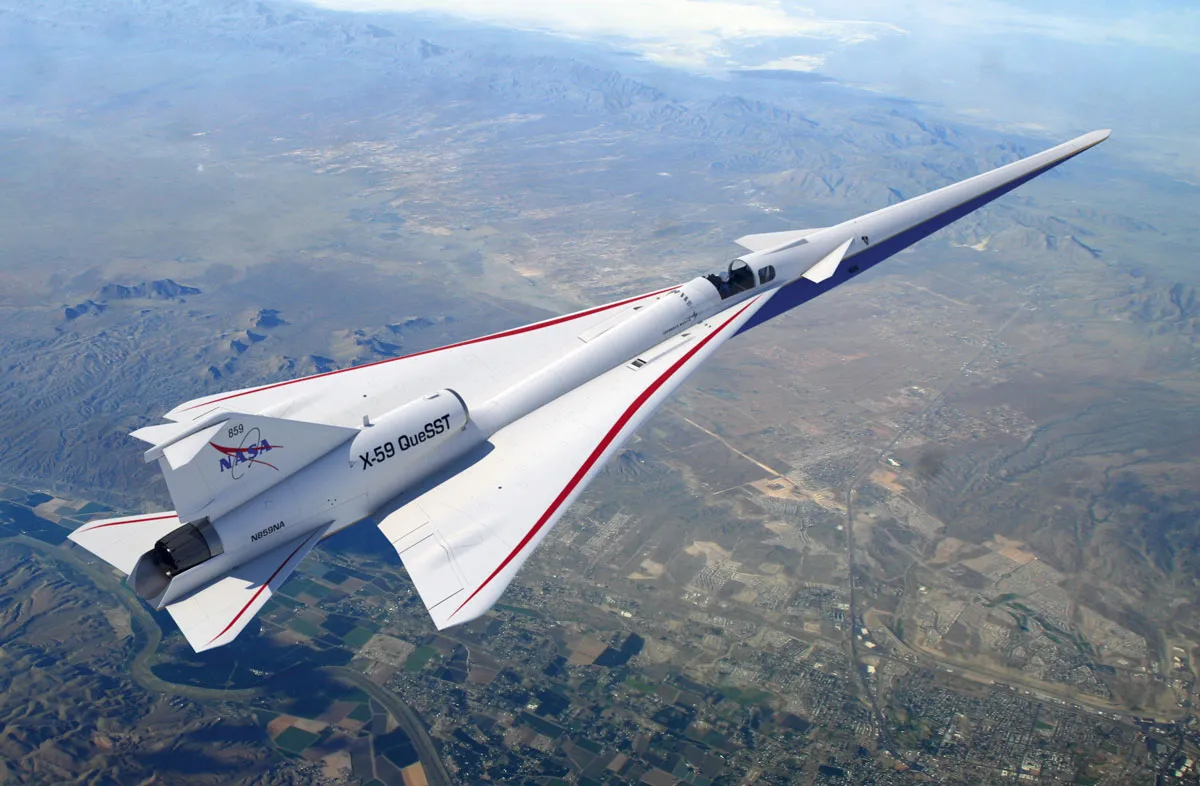

NASA’s X-59 ‘quiet’ supersonic aircraft is set to take to the skies for its first test flight at the Armstrong Flight Research Center later this year. The plane is currently being assembled in a hangar at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California.
Its fuselage, wings and tail have been specially designed to control the airflow around the plane as it flies, with the ultimate aim of preventing a loud sonic boom from disturbing people on the ground below when it breaks the sound barrier. If the initial test goes to plan, the space agency aims to carry out further test flights over inhabited areas to gauge the public’s response to aircraft in 2024.
Digital "twins" that track your health
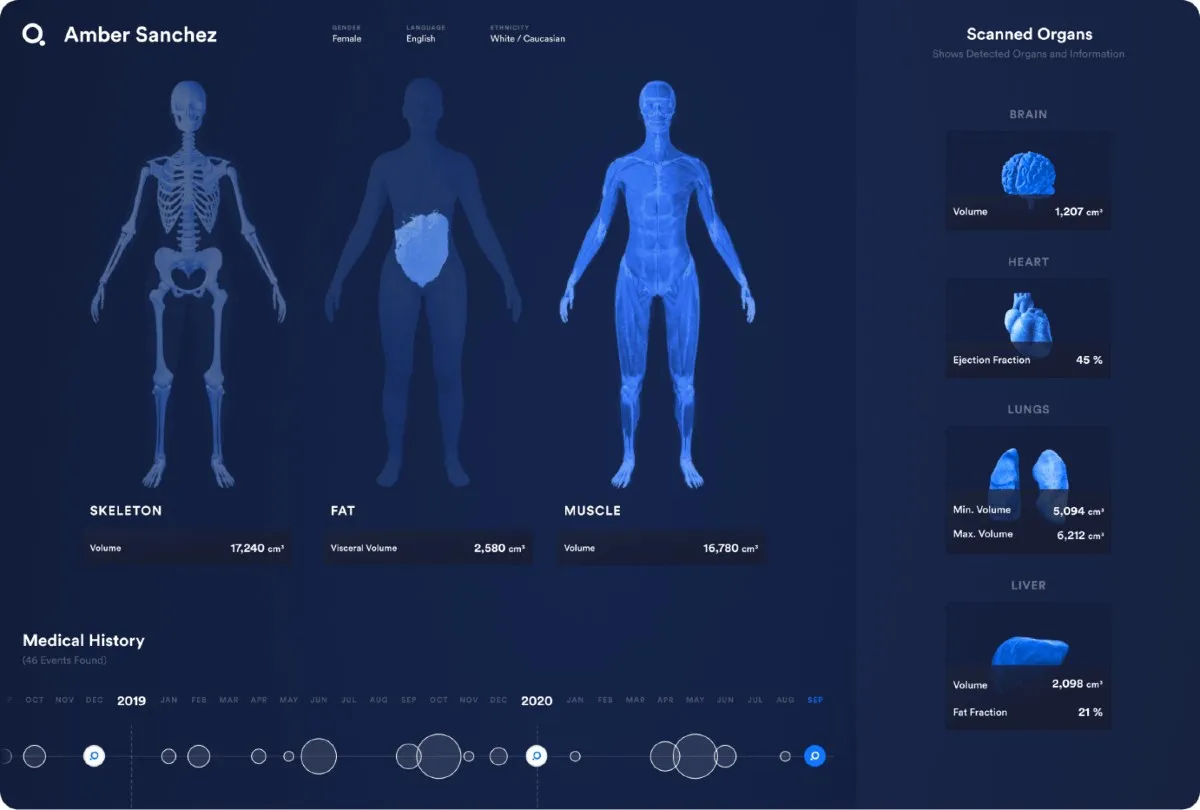
In Star Trek , where many of our ideas of future technology germinated, human beings can walk into the medbay and have their entire body digitally scanned for signs of illness and injury. Doing that in real life would, say the makers of Q Bio, improve health outcomes and alleviate the load on doctors at the same time.
The US company has built a scanner that will measure hundreds of biomarkers in around an hour, from hormone levels to the fat building up in your liver to the markers of inflammation or any number of cancers. It intends to use this data to produce a 3D digital avatar of a patient's body – known as a digital twin – that can be tracked over time and updated with each new scan.
Q Bio CEO Jeff Kaditz hopes it will lead to a new era of preventative, personalised medicine in which the vast amounts of data collected not only help doctors prioritise which patients need to be seen most urgently, but also to develop more sophisticated ways of diagnosing illness. Read an interview with him here.
Direct air capture
Through the process of photosynthesis, trees have remained one of the best ways to reduce the levels of CO2 in the atmosphere. However, new technology could perform the same role as trees, absorbing carbon dioxide at greater levels while also taking up less land.
This technology is known as Direct Air Capture (DAC). It involves taking carbon dioxide from the air and either storing the CO 2 in deep geological caves under ground, or using it in combination with hydrogen to produce synthetic fuels.
While this technology has great potential, it has a lot of complications right now. There are now direct air capture facilities up and running, but the current models require a huge amount of energy to run. If the energy levels can be reduced in the future, DAC could prove to be one of the best technological advances for the future of the environment.
Green funerals
Sustainable living is becoming a priority for individuals squaring up to the realities of the climate crisis, but what about eco-friendly dying? Death tends to be a carbon-heavy process, one last stamp of our ecological footprint. The average cremation reportedly releases 400kg of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, for example. So what's a greener way to go?
In Washington State in the US, you could be composted instead. Bodies are laid in chambers with bark, soil, straw and other compounds that promote natural decomposition. Within 30 days, your body is reduced to soil that can be returned to a garden or woodland. Recompose, the company behind the process, claims it uses an eighth of the carbon dioxide of a cremation.
An alternative technology uses fungi. In 2019, the late actor Luke Perry was buried in a bespoke "mushroom suit" designed by a start-up called Coeio. The company claims its suit, made with mushrooms and other microorganisms that aid decomposition and neutralise toxins that are realised when a body usually decays.
Most alternative ways of disposing of our bodies after death are not based on new technology; they're just waiting for societal acceptance to catch up. Another example is alkaline hydrolysis, which involves breaking the body down into its chemical components over a six-hour process in a pressurised chamber. It's legal in a number of US states and uses fewer emissions compared with more traditional methods.
Energy storing bricks
Scientists have found a way to store energy in the red bricks that are used to build houses.
Researchers led by Washington University in St Louis, in Missouri, US, have developed a method that can turn the cheap and widely available building material into “smart bricks” that can store energy like a battery.
Although the research is still in the proof-of-concept stage, the scientists claim that walls made of these bricks “could store a substantial amount of energy” and can “be recharged hundreds of thousands of times within an hour”.
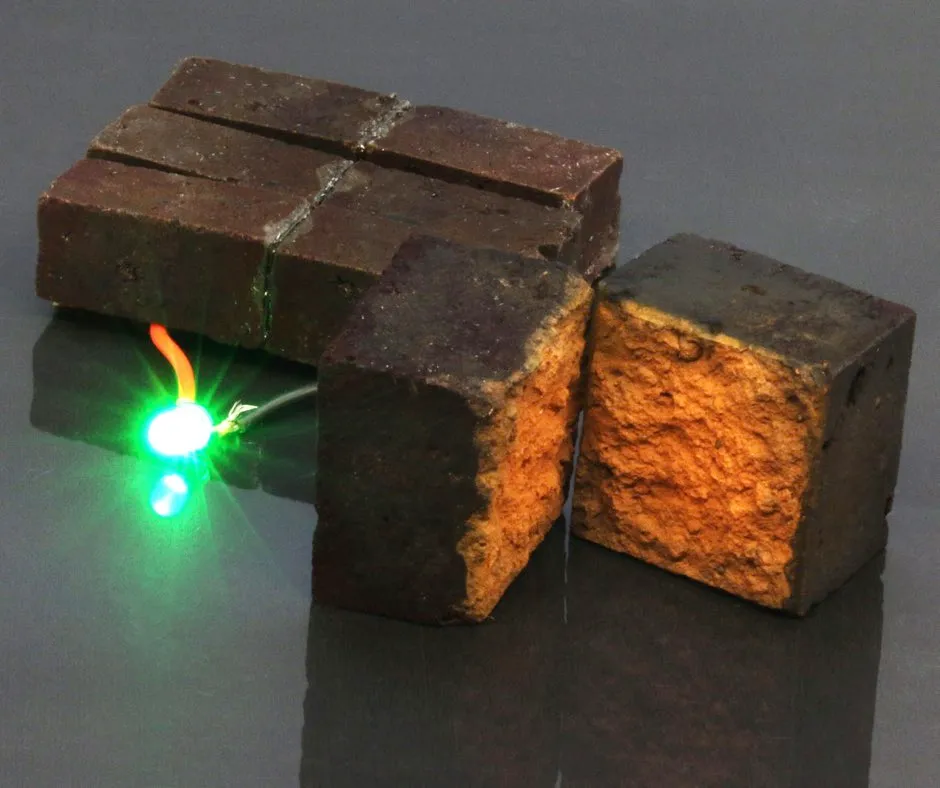
The researchers developed a method to convert red bricks into a type of energy storage device called a supercapacitor.
This involved putting a conducting coating, known as Pedot, onto brick samples, which then seeped through the fired bricks’ porous structure, converting them into “energy storing electrodes”.
Iron oxide, which is the red pigment in the bricks, helped with the process, the researchers said.
Self-healing 'living concrete'

Scientists have developed what they call living concrete by using sand, gel and bacteria.
Researchers said this building material has structural load-bearing function, is capable of self-healing and is more environmentally friendly than concrete – which is the second most-consumed material on Earth after water.
The team from the University of Colorado Boulder believe their work paves the way for future building structures that could “heal their own cracks, suck up dangerous toxins from the air or even glow on command”.
Fuel from thin air
Chemical engineers from Switzerland’s École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne have created a prototype device that can produce hydrogen fuel from the water found in air.
Inspired by leaves, the device is made from semiconducting materials that harvest energy from sunlight and use it to produce hydrogen gas from water molecules found in the atmosphere. The gas could then, potentially, be converted for use as liquid fuels.
Internet for everyone
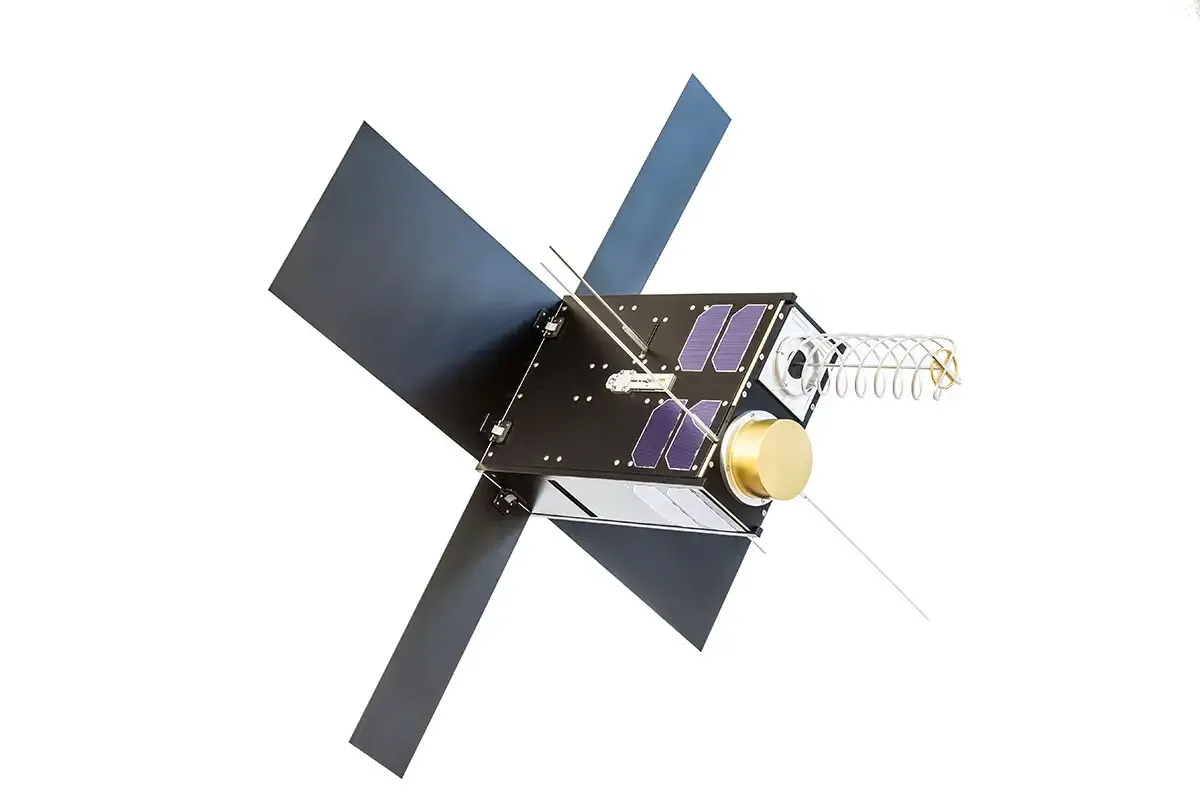

We can’t seem to live without the internet (how else would you read sciencefocus.com?), but still only around half the world’s population is connected. There are many reasons for this, including economic and social reasons, but for some the internet just isn’t accessible because they have no connection.
Google is slowly trying to solve the problem using helium balloons to beam the internet to inaccessible areas, while Facebook has abandoned plans to do the same using drones, which means companies like Hiber are stealing a march. They have taken a different approach by launching their own network of shoebox-sized microsatellites into low Earth orbit, which wake up a modem plugged into your computer or device when it flies over and delivers your data.
Their satellites orbit the Earth 16 times a day and are already being used by organisations like The British Antarctic Survey to provide internet access to very extreme of our planet.
Read more about future technology:
- Dude, where’s my flying car? 11 future technologies we’re still waiting for
- Exciting new green technology of the future
- Future tech: The most exciting innovations from CES 2022
3D-printed eye tissue
Researchers at the National Eye Institute in the US have produced retinal tissue using stem cells and 3D bioprinting. The new technique may help scientists model the human eye to better understand – and develop treatments for – diseases and conditions that affect people’s vision, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
The researchers created tissue found in the outer blood-retina barrier, which is the area AMD is known to start in, by printing stem cells taken from patients into a gel and allowing them to grow over several weeks. They are currently using the tissue to study the progression of AMD and are experimenting with adding additional cell types to model more of the human eye.
Car batteries that charge in 10 minutes
Fast-charging of electric vehicles is seen as key to their take-up, so motorists can stop at a service station and fully charge their car in the time it takes to get a coffee and use the toilet – taking no longer than a conventional break.
But rapid charging of lithium-ion batteries can degrade the batteries, researchers at Penn State University in the US say.This is because the flow of lithium particles known as ions from oneelectrode to another to charge the unit and hold the energy ready for use does not happen smoothly with rapid charging at lower temperatures.
However, they have now found that if the batteries could heat to 60°C for just 10 minutes and then rapidly cool again to ambient temperatures, lithium spikes would not form and heat damage would be avoided.
The battery design they have come up with is self-heating, using a thin nickel foil which creates an electrical circuit that heats in less than 30 seconds to warm the inside of the battery.The rapid cooling that would be needed after the battery is charged would be done using the cooling system designed into the car.
Their study, published in the journal Joule , showed they could fully charge an electrical vehicle in 10 minutes.
Artificial neurons on silicon chips
Scientists have found a way to attach artificial neurons onto silicon chips, mimicking the neurons in our nervous system and copying their electrical properties.
“Until now neurons have been like black boxes, but we have managed to open the black box and peer inside,” said Professor Alain Nogaret , from the University of Bath, who led the project.
“Our work is paradigm-changing because it provides a robust method to reproduce the electrical properties of real neurons in minute detail.
“But it’s wider than that, because our neurons only need 140 nanowatts of power. That’s a billionth the power requirement of a microprocessor, which other attempts to make synthetic neurons have used.
Researchers hope their work could be used in medical implants to treat conditions such as heart failure and Alzheimer’s as it requires so little power.
- 11 future technologies we’re still waiting for
- CES 2023: The 10 gadgets that will change the future
- Disco fridges and tech that wants you to pee on it: The 7 weirdest gadgets announced at CES 2023
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
Technology and Its Impact in the World Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Technology impacts, works cited.
Technology is defined as the use of tools, techniques and methods of organization in solving real world problems, which aims at performing specific tasks.
Technology has a profound root in the society; this is because today’s world relies on the advances in technology. These advances in technology in today’s world has sped people’s lives and made the world a smaller place to live in as it makes different locations closer to one another.
In addition, the fact that technology has become omnipresent in the world today due to its widespread use, is vital because it helps people in carrying out their chores in their daily livelihood. It is therefore important that the technology that exists be easily adaptable and able to solve the current world issues as human progress rate is increasing at an alarming rate (Oak 1).
The advances in technology have brought huge changes in the world today. Some of the areas where technology has brought important changes are as follows. First, technology has enabled the world in automating its critical processes in industries and households. The automobile industry has evolved from mechanical to automated automobiles simply because of the driving force that is technology.
Technology is applicable in performing tasks that are not accessible to man and are vital in automating crucial industrial processes. The technologies that are applicable when performing these crucial tasks include the use of robotics and artificial intelligence in carrying out challenging tasks such as space exploration and mining (Oak 1).
Another positive effect of technology is that it has changed the manner of communication. This has been made possible through the use computer technology; computers have the ability to process huge chunks of data at one go. Information digitization has proved to be a vital technology platform since it has made it possible in storing information and helps in enriching the information quality.
The advances in technology enable harnessing of water from natural sources to homes through robust transmission systems. Technology has brought the discovery of electricity that is important in lighting up the world. Electricity is easily generated by using renewable energy resources.
On the other hand, with all the advances in technology, it is unimaginable that technology has its side effects in the society even when the world is at the epitome of technology. In the medical technology world, technology can affect and also harm patients in cases where it involves a machine that has radiation rays.
On environmental technology, there is a lot of waste in terms of chemicals, which directly go back to the environment. Lastly, technology has a negative impact on people since they tend to be lazy and rely mostly on technology (Oak 1).
In conclusion, the advances brought about by technologies, which are the Internet, cell phones, and notebook computers are vital necessity for daily living. Due to these advances, it is easy for us to forget about those who suffer while attempting to provide for their basic needs, such as clean water, food and health care.
It is a good gesture by the developed world to make use of their technologies to help the underprivileged groups of people in the society. Through the continuous use of these technologies, there are advances that targets medical services, improved economy based on the Internet, emerging technologies in information systems sector, advanced farming methods and industrial sectors.
More importantly, educational needs for the people are taken into consideration by these technologies, since they help them become prosperous nations who do not require help from others but are able to get their own resources. Moreover, transferring technology from the developed world to the developing world has various benefits. There will be improvement in living standards, production efficiency and become a base for economic growth (Oak 1).
Oak, Manali. “ Positive Effects of Technology on Society .” Buzzle. 2011. Web.
- The Evolution of the Automobile & Its Effects on Society
- Inventions That the World Would Do Without
- Telecommunications: The Case of SewWorld
- The Evolution of Electricity
- Electricity Is the Most Important Invention
- How Computers Affect Our Lives
- Nanotechnology and its Perspectives in Connecticut
- Purchasing or Leasing Computer Equipment: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Ethical and Illegal Computer Hacking
- Autonomous Controller Robotics: The Future of Robots
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, June 11). Technology and Its Impact in the World. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-in-the-world/
"Technology and Its Impact in the World." IvyPanda , 11 June 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-in-the-world/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Technology and Its Impact in the World'. 11 June.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Technology and Its Impact in the World." June 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-in-the-world/.
1. IvyPanda . "Technology and Its Impact in the World." June 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-in-the-world/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Technology and Its Impact in the World." June 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-technology-in-the-world/.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Technology is such a ubiquitous part of modern life that it can often feel like a force of nature, a powerful tidal wave that users and consumers can ride but have little power to guide its direction. It doesn’t have to be that way.
Go to the web site to view the video.
Stanford scholars say that technological innovation is not an inevitable force that exercises power over us. Instead, in a new book, they seek to empower all of us to create a technological future that supports human flourishing and democratic values.
Rather than just accept the idea that the effects of technology are beyond our control, we must recognize the powerful role it plays in our everyday lives and decide what we want to do about it, said Rob Reich , Mehran Sahami and Jeremy Weinstein in their new book System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can Reboot (Harper Collins, 2021). The book integrates each of the scholars’ unique perspectives – Reich as a philosopher, Sahami as a technologist and Weinstein as a policy expert and social scientist – to show how we can collectively shape a technological future that supports human flourishing and democratic values.
Reich, Sahami and Weinstein first came together in 2018 to teach the popular computer science class, CS 181: Computers, Ethics and Public Policy . Their class morphed into the course CS182: Ethics, Public Policy and Technological Change , which puts students into the role of the engineer, policymaker and philosopher to better understand the inescapable ethical dimensions of new technologies and their impact on society.
Now, building on the class materials and their experiences teaching the content both to Stanford students and professional engineers, the authors show readers how we can work together to address the negative impacts and unintended consequences of technology on our lives and in society.
“We need to change the very operating system of how technology products get developed, distributed and used by millions and even billions of people,” said Reich, a professor of political science in the School of Humanities and Sciences and faculty director of the McCoy Family Center for Ethics in Society . “The way we do that is to activate the agency not merely of builders of technology but of users and citizens as well.”
How technology amplifies values
Without a doubt, there are many advantages of having technology in our lives. But instead of blindly celebrating or critiquing it, the scholars urge a debate about the unintended consequences and harmful impacts that can unfold from these powerful new tools and platforms.
One way to examine technology’s effects is to explore how values become embedded in our devices. Every day, engineers and the tech companies they work for make decisions, often motivated by a desire for optimization and efficiency, about the products they develop. Their decisions often come with trade-offs – prioritizing one objective at the cost of another – that might not reflect other worthy objectives.
For instance, users are often drawn to sensational headlines, even if that content, known as “ clickbait ,” is not useful information or even truthful. Some platforms have used click-through rates as a metric to prioritize what content their users see. But in doing so, they are making a trade-off that values the click rather than the content of that click. As a result, this may lead to a less-informed society, the scholars warn.
“In recognizing that those are choices, it then opens up for us a sense that those are choices that could be made differently,” said Weinstein, a professor of political science in the School of Humanities & Sciences, who previously served as deputy to the U.S. ambassador to the United Nations and on the National Security Council Staff at the White House during the Obama administration.
Another example of embedded values in technology highlighted in the book is user privacy.
Legislation adopted in the 1990s, as the U.S. government sought to speed progress toward the information superhighway, enabled what the scholars call “a Wild West in Silicon Valley” that opened the door for companies to monetize the personal data they collect from users. With little regulation, digital platforms have been able to gather information about their users in a variety of ways, from what people read to whom they interact with to where they go. These are all details about people’s lives that they may consider incredibly personal, even confidential.
When data is gathered at scale, the potential loss of privacy gets dramatically amplified; it is no longer just an individual issue, but becomes a larger, social one as well, said Sahami, the James and Ellenor Chesebrough Professor in the School of Engineering and a former research scientist at Google.
“I might want to share some personal information with my friends, but if that information now becomes accessible by a large fraction of the planet who likewise have their information shared, it means that a large fraction of the planet doesn’t have privacy anymore,” said Sahami. “Thinking through these impacts early on, not when we get to a billion people, is one of the things that engineers need to understand when they build these technologies.”
Even though people can change some of their privacy settings to be more restrictive, these features can sometimes be difficult to find on the platforms. In other instances, users may not even be aware of the privacy they are giving away when they agree to a company’s terms of service or privacy policy, which often take the form of lengthy agreements filled with legalese.
“When you are going to have privacy settings in an application, it shouldn’t be buried five screens down where they are hard to find and hard to understand,” Sahami said. “It should be as a high-level, readily available process that says, ‘What is the privacy you care about? Let me explain it to you in a way that makes sense.’ ”
Others may decide to use more private and secure methods for communication, like encrypted messaging platforms such as WhatsApp or Signal. On these channels, only the sender and receiver can see what they share with one another – but issues can surface here as well.
By guaranteeing absolute privacy, the possibility for people working in intelligence to scan those messages for planned terrorist attacks, child sex trafficking or other incitements of violence is foreclosed. In this case, Reich said, engineers are prioritizing individual privacy over personal safety and national security, since the use of encryption can not only ensure private communication but can also allow for the undetected organization of criminal or terrorist activity.
“The balance that is struck in the technology company between trying to guarantee privacy while also trying to guarantee personal safety or national security is something that technologists are making on their own but the rest of us also have a stake in,” Reich said.
Others may decide to take further control over their privacy and refuse to use some digital platforms altogether. For example, there are increasing calls from tech critics that users should “delete Facebook.” But in today’s world where technology is so much a part of daily life, avoiding social apps and other digital platforms is not a realistic solution. It would be like addressing the hazards of automotive safety by asking people to just stop driving, the scholars said.
“As the pandemic most powerfully reminded us, you can’t go off the grid,” Weinstein said. “Our society is now hardwired to rely on new technologies, whether it’s the phone that you carry around, the computer that you use to produce your work, or the Zoom chats that are your way of interacting with your colleagues. Withdrawal from technology really isn’t an option for most people in the 21st century.”
Moreover, stepping back is not enough to remove oneself from Big Tech. For example, while a person may not have a presence on social media, they can still be affected by it, Sahami pointed out. “Just because you don’t use social media doesn’t mean that you are not still getting the downstream impacts of the misinformation that everyone else is getting,” he said.
Rebooting through regulatory changes
The scholars also urge a new approach to regulation. Just as there are rules of the road to make driving safer, new policies are needed to mitigate the harmful effects of technology.
While the European Union has passed the comprehensive General Data Protection Regulation (known as the GDPR) that requires organizations to safeguard their users’ data, there is no U.S. equivalent. States are trying to cobble their own legislation – like California’s recent Consumer Privacy Act – but it is not enough, the authors contend.
It’s up to all of us to make these changes, said Weinstein. Just as companies are complicit in some of the negative outcomes that have arisen, so is our government for permitting companies to behave as they do without a regulatory response.
“In saying that our democracy is complicit, it’s not only a critique of the politicians. It’s also a critique of all of us as citizens in not recognizing the power that we have as individuals, as voters, as active participants in society,” Weinstein said. “All of us have a stake in those outcomes and we have to harness democracy to make those decisions together.”
System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can Reboot is available Sept. 7, 2021.
Media Contacts
Melissa De Witte, Stanford News Service: [email protected]
Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Impact of Technology — How Technology Has Changed Our Lives
How Technology Has Changed Our Lives
- Categories: Impact of Technology
About this sample

Words: 1130 |
Updated: 9 November, 2023
Words: 1130 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read
Table of contents
Hook examples for technology essay, technology essay example.
- A Digital Revolution: Enter the era of smartphones, AI, and the Internet of Things, where technology is the driving force. Join me as we explore how technology has transformed our lives and the profound impact it has on society.
- An Intriguing Quote: Arthur C. Clarke once said, "Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic." Let's delve into the magical world of modern technology and how it shapes our daily existence.
- The Paradox of Connectivity: Technology promises to connect us, yet it can also lead to isolation. Explore with me the paradox of our hyperconnected world and how it affects our relationships, both online and offline.
- The Impact on Work and Leisure: Discover how technology has revolutionized our work environments, blurring the lines between office and home. Together, we'll examine the changing landscape of leisure and entertainment in the digital age.
- Looking Ahead: As technology continues to advance, what lies on the horizon? Join me in discussing the future implications of emerging technologies and how they will further reshape our world in the years to come.
The Dark Side of Technological Advancement
- Increased Bullying
- Lack of Privacy
- Constant Distraction
Balancing Technology in Our Lives
Works cited.
- Anderson, M. (2018). The Effects of Technology on Teenagers. Verywell Family.
- Brown, B. W., & Bobkowski, P. S. (2011). Older and newer media: Patterns of use and effects on adolescents’ health and well-being. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(1), 95-113.
- Calvillo, D. P., & Downey, R. G. (2010). Mobile phones and interruption in college classrooms: Instructors’ attitudes, beliefs, and practices. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(2), 223-231.
- Clarke-Pearson, K., & O'Keeffe, G. (2011). The impact of social media on children, adolescents, and families. Pediatrics, 127(4), 800-804.
- Livingstone, S., & Smith, P. K. (2014). Annual research review: Harms experienced by child users of online and mobile technologies: The nature, prevalence and management of sexual and aggressive risks in the digital age. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 55(6), 635-654.
- Oulasvirta, A., Rattenbury, T., Ma, L., & Raita, E. (2012). Habits make smartphone use more pervasive. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 16(1), 105-114.
- Przybylski, A. K., & Weinstein, N. (2017). A large-scale test of the goldilocks hypothesis: Quantifying the relations between digital-screen use and the mental well-being of adolescents. Psychological Science, 28(2), 204-215.
- Rosen, L. D., Lim, A. F., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2011). An empirical examination of the educational impact of text message-induced task switching in the classroom: Educational implications and strategies to enhance learning. Psicologia Educativa, 17(2), 163-177.
- Schulte, B. (2018). The human costs of bringing smartphones to every student. The Atlantic.
- Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among US adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(1), 3-17.
Video Version

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1757 words
3 pages / 1252 words
3 pages / 1670 words
3 pages / 1487 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Impact of Technology
In recent decades, technological advancements have transformed the daily lives of Americans, exerting profound influence on political, economic, and social aspects of modern society. These changes have been primarily driven by [...]
Technology is a blend of two Greek words, techne and logos. In Greek, the word techne alludes to the utilization of an instrument, or the usage of an art or logic, and logos alludes to a word or discussion about a specific [...]
Computers can be amongst best creation man has ever made. With different features and abilities that makes life easier for us as human beings; like performing tasks ranging from searching up questions on the internet to [...]
Over the past three decades, video games have become a massive pop culture sensation among younger individuals. As David Deutsch, author of “Playing Video Games Benefits Children,” explains, “They provide something for which [...]
In recent years, the use of Nano-technology (Nano-particles, Nano-material and Nano-additives) has attracted attention of scholars, engineers, and scientists in all scientific fields such as chemistry, medicine, material, [...]
Scholars still question the positive and negative effects of the Internet to the society until today. The Internet had always been a great help to the present generation. The population assumes it is the most notable invention [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Dean’s Office
- External Advisory Council
- Computing Council
- Extended Computing Council
- Undergraduate Advisory Group
- Break Through Tech AI
- Building 45 Event Space
- Infinite Mile Awards: Past Winners
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Educating Computing Bilinguals
- Online Learning
- Industry Programs
- AI Policy Briefs
- Envisioning the Future of Computing Prize 2024
- SERC Symposium 2023
- SERC Case Studies
- SERC Scholars Program
- SERC Group Leaders
- Common Ground Subjects
- For First-Year Students and Advisors
- For Instructors: About Common Ground Subjects
- Common Ground Award for Excellence in Teaching
- New & Incoming Faculty
- Faculty Resources
- Faculty Openings
- Search for: Search
- MIT Homepage
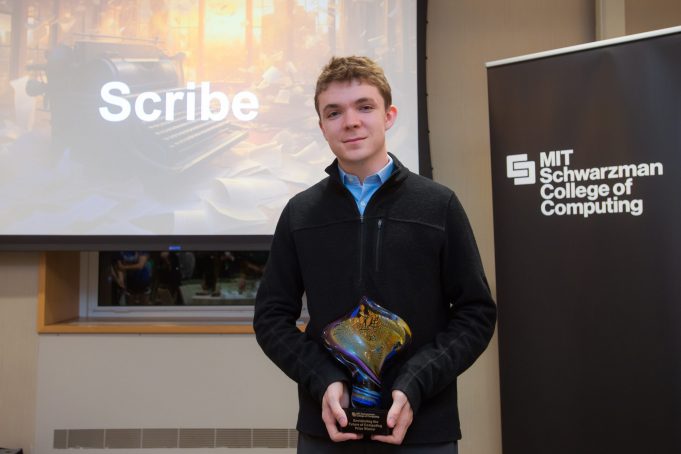
Envisioning the future of computing

MIT students share ideas, aspirations, and vision for how advances in computing stand to transform society in a competition hosted by the Social and Ethical Responsibilities of Computing.
How will advances in computing transform human society?
MIT students contemplated this impending question as part of the Envisioning the Future of Computing Prize — an essay contest in which they were challenged to imagine ways that computing technologies could improve our lives, as well as the pitfalls and dangers associated with them.
Offered for the first time this year, the Institute-wide competition invited MIT undergraduate and graduate students to share their ideas, aspirations, and vision for what they think a future propelled by advancements in computing holds. Nearly 60 students put pen to paper, including those majoring in mathematics, philosophy, electrical engineering and computer science, brain and cognitive sciences, chemical engineering, urban studies and planning, and management, and entered their submissions.
Students dreamed up highly inventive scenarios for how the technologies of today and tomorrow could impact society, for better or worse. Some recurring themes emerged, such as tackling issues in climate change and health care. Others proposed ideas for particular technologies that ranged from digital twins as a tool for navigating the deluge of information online to a cutting-edge platform powered by artificial intelligence, machine learning, and biosensors to create personalized storytelling films that help individuals understand themselves and others.
Conceived of by the Social and Ethical Responsibilities of Computing (SERC), a cross-cutting initiative of the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing in collaboration with the School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences (SHASS), the intent of the competition was “to create a space for students to think in a creative, informed, and rigorous way about the societal benefits and costs of the technologies they are or will be developing,” says Caspar Hare, professor of philosophy, co-associate dean of SERC, and the lead organizer of the Envisioning the Future of Computing Prize. “We also wanted to convey that MIT values such thinking.”
Prize winners
The contest implemented a two-stage evaluation process wherein all essays were reviewed anonymously by a panel of MIT faculty members from the college and SHASS for the initial round. Three qualifiers were then invited to present their entries at an awards ceremony on May 8, followed by a Q&A with a judging panel and live in-person audience for the final round.
The winning entry was awarded to Robert Cunningham ’23, a recent graduate in math and physics, for his paper on the implications of a personalized language model that is fine-tuned to predict an individual’s writing based on their past texts and emails. Told from the perspective of three fictional characters: Laura, founder of the tech startup ScribeAI, and Margaret and Vincent, a couple in college who are frequent users of the platform, readers gained insights into the societal shifts that take place and the unforeseen repercussions of the technology.
Cunningham, who took home the grand prize of $10,000, says he came up with the concept for his essay in late January while thinking about the upcoming release of GPT-4 and how it might be applied. Created by the developers of ChatGPT — an AI chatbot that has managed to capture popular imagination for its capacity to imitate human-like text, images, audio, and code — GPT-4, which was unveiled in March, is the newest version of OpenAI’s language model systems.
“GPT-4 is wild in reality, but some rumors before it launched were even wilder, and I had a few long plane rides to think about them! I enjoyed this opportunity to solidify a vague notion into a piece of writing, and since some of my favorite works of science fiction are short stories, I figured I’d take the chance to write one,” Cunningham says.
The other two finalists , awarded $5,000 each, included Gabrielle Kaili-May Liu ’23, a recent graduate in mathematics with computer science, and brain and cognitive sciences, for her entry on using the reinforcement learning with human feedback technique as a tool for transforming human interactions with AI; and Abigail Thwaites and Eliot Matthew Watkins, graduate students in the Department of Philosophy and Linguistics, for their joint submission on automatic fact checkers, an AI-driven software that they argue could potentially help mitigate the spread of misinformation and be a profound social good.
“We were so excited to see the amazing response to this contest. It made clear how much students at MIT, contrary to stereotype, really care about the wider implications of technology, says Daniel Jackson, professor of computer science and one of the final-round judges. “So many of the essays were incredibly thoughtful and creative. Robert’s story was a chilling, but entirely plausible take on our AI future; Abigail and Eliot’s analysis brought new clarity to what harms misinformation actually causes; and Gabrielle’s piece gave a lucid overview of a prominent new technology. I hope we’ll be able to run this contest every year, and that it will encourage all our students to broaden their perspectives even further.”
Fellow judge Graham Jones, professor of anthropology, adds: “The winning entries reflected the incredible breadth of our students’ engagement with socially responsible computing. They challenge us to think differently about how to design computational technologies, conceptualize social impacts, and imagine future scenarios. Working with a cross-disciplinary panel of judges catalyzed lots of new conversations. As a sci-fi fan, I was thrilled that the top prize went to a such a stunning piece of speculative fiction!”
Other judges on the panel for the final round included:
- Dan Huttenlocher, dean of the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing;
- Aleksander Madry, Cadence Design Systems Professor of Computer Science;
- Asu Ozdaglar, deputy dean of academics for the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing and head of the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science;
- Georgia Perakis, co-associate dean of SERC and the William F. Pounds Professor of Management; and
- Agustin Rayo, dean of the MIT School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences.
Honorable mentions
In addition to the grand prize winner and runners up, 12 students were recognized with honorable mentions for their entries, with each receiving $500.
The honorees and the title of their essays include:
- Alexa Reese Canaan, Technology and Policy Program, “A New Way Forward: The Internet & Data Economy”;
- Fernanda De La Torre Romo, Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, “The Empathic Revolution Using AI to Foster Greater Understanding and Connection”;
- Samuel Florin, Mathematics, “Modeling International Solutions for the Climate Crisis;”
- Claire Gorman, Department of Urban Studies and Planning (DUSP), “Grounding AI- Envisioning Inclusive Computing for Soil Carbon Applications”;
- Kevin Hansom, MIT Sloan School of Management, “Quantum Powered Personalized Pharmacogenetic Development and Distribution Model”;
- Sharon Jiang, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), “Machine Learning Driven Transformation of Electronic Health Records”;
- Cassandra Lee, Media Lab, “Considering an Anti-convenience Funding Body”;
- Martin Nisser, EECS, “Towards Personalized On-Demand Manufacturing;
- Andi Qu, EECS, “Revolutionizing Online Learning with Digital Twins”;
- David Bradford Ramsay, Media Lab, “The Perils and Promises of Closed Loop Engagement”;
- Shuvom Sadhuka, EECS, “Overcoming the False Trade-off in Genomics: Privacy and Collaboration”; and
- Leonard Schrage, DUSP, “Embodied-Carbon-Computing.”
The Envisioning the Future of Computing Prize was supported by MAC3 Impact Philanthropies.
Related Stories

Tech at the edge: Trends reshaping the future of IT and business
It is easy to become numb to the onslaught of new technologies hitting the market, each with its own promise of changing (more often “revolutionizing”) the business world. But our analysis of some of the more meaningful tech trends lays out a convincing case that something significant is happening. 1 Michael Chui, Roger Roberts, and Lareina Yee, “ McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022 ,” McKinsey, August 24, 2022.
These tech trends are generally accelerating the primary characteristics that have defined the digital era: granularity, speed, and scale. But it’s the magnitude of these changes—in computing power, bandwidth, and analytical sophistication—that is opening the door to new innovations, businesses, and business models.
The emergence of cloud and 5G , for example, exponentially increases compute power and network speeds that can enable greater innovation. Developments in the metaverse of augmented and virtual reality open the doors to virtual R&D via digital twins , for example, and immersive learning. Advances in AI, machine learning, and software 2.0 (machine-written code) bring a range of new services and products, from autonomous vehicles to connected homes, well within reach.
Much ink has been spilled on identifying tech trends, but less attention has been paid to the implications of those changes. To help understand how management will need to adapt in the face of these technology trends in the next three to five years, we spoke to business leaders and leading thinkers on the topic. We weren’t looking for prognostications; we wanted to explore realistic scenarios, their implications, and what senior executives might do to get ready.
The discussions pinpointed some broad, interrelated shifts, such as how technology’s radically increasing power is exerting a centrifugal force on the organization, pushing innovation to expert networks at the edges of the company; how the pace and proliferation of these innovations calls for radical new approaches to continuous learning built around skills deployed at points of need; how these democratizing forces mean that IT can no longer act as a centralized controller of technology deployment and operations but instead needs to become a master enabler and influencer; and how these new technologies are creating more data about, and touchpoints with, customers, which is reshaping the boundaries of trust and requiring a much broader understanding of a company’s security responsibilities.
1. Innovation at the edge
Key tech trends.
We estimate that 70 percent of companies will employ hybrid or multicloud management technologies, tools, and processes . 2 “ The top trends in tech ,” McKinsey, June 15, 2021. At the same time, 5G will deliver network speeds that are about ten times faster than current speeds on 4G LTE networks, 3 Irina Ivanova, “What consumers need to know about this week’s AT&T–Verizon 5G rollout,” CBS News, January 20, 2022. with expectations of speeds that are up to 100 times faster with 40 times faster latency. 4 “5G speed: 5G vs. 4G performance compared,” Tom’s Guide, June 1, 2021. By 2024, more than 50 percent of user touches will be augmented by AI-driven speech, written word, or computer-vision algorithms , 5 “ The top trends in tech ,” June 15, 2021. while global data creation is projected to grow to more than 180 zettabytes by 2025, up from 64.2 zettabytes in 2020. 6 “Amount of data created, consumed, and stored 2010–2025,” Statista Research Department, May 23, 2022. The low-code development platform market‘s compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is projected at about 30 percent through 2030. 7 “Global $187 billion low-code development platform market to 2030,” GlobeNewswire, November 10, 2020.
Shift: Innovation develops around personal networks of experts at the porous edge of the organization and is supported by capabilities that scale the benefits across the business.
These technologies promise access to virtually unlimited compute power and massive data sets, as well as a huge leap in bandwidth at low cost, making it cheaper and easier to test, launch, and scale innovations quickly. The resulting acceleration in innovation will mean that companies can expect more disruptions from more sources. Centralized strategic and innovation functions cannot hope to keep pace on their own. Companies will need to be much more involved in networks outside their organizations to spot, invest in, and even acquire promising opportunities.
Corporate venture-capital (VC) funds with centralized teams have looked to find and fund innovation, but their track record has been spotty, often because the teams lack the requisite skills and are simply too far removed from the constantly evolving needs of individual business units. Instead, companies will need to figure out how to tap their front lines, particularly business domain experts and technologists, to enable them to act, in effect, as the business’s VC arm. That’s because the people who are writing code and building solutions are often well plugged into strong external networks in their fields and have the expertise to evaluate new developments. One pharma company, for example, taps its own expert researchers in various fields, such as gene expression, who know well the people outside the company who are leaders in the field.
While companies will need to create incentives and opportunities for engineers to build up and engage with their networks, the key focus must be on empowering teams so they can spend their allocated budget as they see fit—for example, experimenting and failing without penalty (within boundaries) and deciding on technologies to meet their goals (within prescribed guidelines).
The IT organization of the future can play an important role in building up a scaling capability to make that innovation work for the business, something that has traditionally been a challenge. Individual developers or small teams working fast don’t tend to naturally think about how to scale an application. That issue is likely to be exacerbated as nontechnical users working in pockets across organizations use low-code/no-code (LC/NC) applications to design and build programs with point-and-click or pull-down-menu interfaces.
One pharma company has taken this idea to heart by giving local business units the flexibility to run with a nonstandard idea when it has proven to be better than what the company is already doing. In return for that flexibility, the business unit must commit to helping the rest of the organization use the new idea, and IT builds it into the company’s standards.
In considering how this scaling capability might work, companies could, for example, assign advanced developers to “productize” applications by refactoring code so they can scale. IT leadership can provide tools and platforms, reusable-code libraries that are easily accessible, and flexible, standards-based architecture so that innovations can be scaled across the business more easily.
Questions for leadership
- What incentives will best encourage engineers and domain experts to develop, maintain, and tap into their networks?
- What processes are in place for tracking and managing VC activity at the edge?
- What capabilities do you need to identify innovation opportunities and “industrialize” the best ones so they can be shared across the organization?
For more on how to empower workers at the edge, see “ Tech companies innovate at the edge. Legacy companies can too ,” in Harvard Business Review.
Would you like to learn more about McKinsey Digital ?
2. a perpetual-learning culture.
Advances in AI, machine learning, robotics, and other technologies have increased the pace of change tenfold . By 2025, we estimate that 50 billion devices will be connected to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), while 70 percent of manufacturers are expected to be using digital twins regularly (by 2022). 8 “ The top trends in tech ,” June 15, 2021. Some 70 percent of new applications will use LC/NC technologies by 2025, up from less than 25 percent in 2020. 9 “Gartner says cloud will be the centerpiece of new digital experiences,” Gartner, November 10, 2021. The global metaverse revenue opportunity could approach $800 billion in 2024, up from about $500 billion in 2020. 10 Bloomberg Intelligence, “Metaverse may be $800 billion market, next tech platform,” Bloomberg, December 1, 2021. This proliferation of technological innovations means we can expect to experience more progress in the next decade than in the past 100 years combined, according to entrepreneur and futurist Peter Diamandis. 11 Peter Diamandis and Steven Kotler, The Future Is Faster than You Think: How Converging Technologies Are Transforming Business, Industries, and Our Lives , New York: Simon & Schuster, 2020.
Shift: Tech literacy becomes core to every role, requiring learning to be continuous and built at the level of individual skills that are deployed at the point of need.
With the pace and proliferation of technologies pushing innovation to the edge of the organization, businesses need to be ready to incorporate the most promising options from across the front lines. This will create huge opportunities, but only for those companies that develop true tech intelligence through a perpetual-learning culture. The cornerstone of this effort includes training all levels of personnel, from “citizen developers” working with easy-to-use LC/NC tools or in entirely new environments such as the metaverse, to full-stack developers and engineers, who will need to continually evolve their skills to keep up with changing technologies. We’re already seeing situations where poorly trained employees use LC/NC to churn out suboptimal products.
While there will always be a need for more formalized paths for foundational learning, we anticipate an acceleration in the shift from teaching curricula periodically to continuous learning that can deliver varying technical skills across the entire organization. In practice, that will mean orienting employee development around delivering skills. This requires breaking down a capability into its smallest sets of composite skills. One large tech company, for example, created 146,000 skills data points for the 1,200 technical skills it was assessing.
The key point is that these skills “snippets”—such as a block of code or a video of a specific negotiating tactic—need to be integrated into the workflow so that they’re delivered when needed. This might be called a “LearnOps” approach, where learning is built into the operations. This integration mentality is established at Netflix, where data scientists partner directly with product managers, engineering teams, and other business units to design, execute, and learn from experiments. 12 Netflix Technology Blog , “Experimentation is a major focus of data science across Netflix,” blog entry by Martin Tingley et al., January 11, 2022.
As important as being able to deploy learning is building a learning culture by making continuous learning expected and easy to do. The way top engineers learn can be instructive. This is a community that is highly aware of the need to keep their skills up to date. They have ingrained habits of sharing code, and they gravitate to projects where they can learn. One advantage of using open source, for example, is the built-in community that constantly updates and reviews code. In the same spirit, we’re seeing companies budget extra time to allow people to try new tools or technologies when they’re building a product. Other companies are budgeting for “learning buffers” to allow for setbacks in product development that teams can learn from. 13 “ The big boost: How incumbents successfully scale their new businesses ,” McKinsey, August 27, 2020.
Netflix, which makes broad, open, and deliberate information sharing a core value, built the Netflix experimentation platform as an internal product that acts as a repository of solutions for future teams to reuse. It has a product manager and innovation road map, with the goal of making experimentation a simple and integrated part of the product life cycle. 14 Netflix Technology Blog , “Netflix: A culture of learning,” blog entry by Martin Tingley et al., January 25, 2022.
To support this kind of continuous learning and experimentation, companies will need to accept mistakes. The art will be in limiting the impact of potentially costly mistakes, such as the loss or misuse of customer data. IT will need to architect protocols, incentives, and systems to encourage good behaviors and reduce bad ones. Many companies are beginning to adopt practices such as automated testing to keep mistakes from happening in the first place ; creating spaces where mistakes won’t affect other applications or systems, such as isolation zones in cloud environments ; and building in resiliency protocols.
- Do you have a list of the most important skills your business needs?
- What is the minimum level of learning needed for advanced users of analytics and manipulators of data?
- How do you track what people are learning and whether that learning is effective and translating into better performance?
3. IT as a service
It is estimated that the global cloud microservices platform market will generate $4.2 billion in revenue by 2028, up from $952 million in 2020. 15 Cloud microservice platform market report , Research Dive, November 2021. GitHub has more than 200 million code repositories and expects 100 million software developers by 2025. 16 Paul Krill, “GitHub expects more than 100 million software developers by 2025,” InfoWorld, December 3, 2020. Nearly 90 percent of developers already use APIs. 17 Christina Voskoglou, “APIs have taken over software development,” Nordic APIs, October 27, 2020. Software 2.0 creates new ways of writing software and reduces complexity. Software sourced by companies from cloud-service platforms, open repositories, and software as a service (SaaS) is growing at a CAGR of 27.5 percent from 2021 to 2028. 18 Software as a service (SaaS) market, 2021–2028 , Fortune Business Insights, January 2022.
Shift: IT becomes the enabler of product innovation by serving small, interoperable blocks of code.
When innovation is pushed to the edge and a perpetual-learning culture permeates an organization, the role of IT shifts dramatically. IT can’t support this dynamic environment by sticking to its traditional role as a controlling entity managing technology at the center. The premium will now be on IT’s ability to enable innovation, requiring a shift in its traditional role as protector of big tech assets to a purveyor of small blocks of code. The gold standard of IT effectiveness will be its ability to help people stitch together snippets of code into a useful product.
We are already seeing what that might look like. Employees at G&J Pepsi-Cola Bottlers with little to no experience at software development created an app that examines images of a store shelf to identify the number and type of bottles on it, then automatically restocks it based on historic trends. 19 Adam Burden, “Low code/no code could reshape business innovation,” VentureBeat, February 5, 2022. One pharmaceutical company grew its low-code platform base from eight users to 1,400 in just one year . Business users outside of IT are now building applications with thousands of monthly sessions. 20 Shivam Srivastava, Kartik Trehan, Dilip Wagle, and Jane Wang, “ Developer Velocity: How software excellence fuels business performance ,” McKinsey, April 20, 2020. Companies that empower “citizen developers” score 33 percent higher on innovation compared with bottom-quartile companies that don’t provide that level of support, according to a McKinsey survey. 21 Shivam Srivastava, Kartik Trehan, Dilip Wagle, and Jane Wang, “ Developer Velocity: How software excellence fuels business performance ,” McKinsey, April 20, 2020.
These developments point toward much more of a “buffet” approach to technology, where IT builds useful blocks of reusable code, sometimes assembles them into specific products, and makes them available through a user-friendly cataloging system for the business to use to create the products it needs. IT provides guiderails, such as API standards and directives on the environments in which the code might be most useful; protects the most sensitive information, such as customer data and financial records; and tracks their adoption. This tracking capability will become particularly crucial as bots, AI, algorithms, and APIs proliferate. Transparency isn’t sufficient. IT will need to make sense of all the activity through advanced tech performance and management capabilities and the development of new roles, such as data diagnosticians and bot managers.
This IT-as-a-service approach puts the product at the center of the operating model, requiring a commitment to organizing IT around product management . Some companies have been moving in this direction. But reaching the scale needed to support fast-paced and more diffuse innovation will require a deeper commitment to product owners, working with leaders in the business side of the house, to run teams with real P&L responsibility. Many organizations, from traditional enterprises to digital natives, have found that putting in place product leaders who set overall product and portfolio strategy, drive execution, and empower product owners to drive innovation aligned with business outcomes and P&L metrics can increase the return on the funding that flows to technology delivery and quicken the pace of innovation.
- Do you have a vision for how the role of the IT organization will change to enable democratization of technology?
- How will you elevate the role of the technology product manager, and do you have a road map for developing that role?
- What systems will you need to put in place to manage and track the use, reuse, and performance of code?

McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022
4. expanded trust boundaries.
It was estimated that almost 100 percent of biometrics-capable devices (such as smartphones) will be using biometrics for transactions by 2022. 22 “Usage of biometric technology in transactions with mobile devices worldwide 2016–2022”, Statista Research Department, June 13, 2022. The effectiveness of these technologies has advanced dramatically, with the best facial-identification algorithms having improved 50 times since 2014. 23 William Crumpler, “How accurate are facial recognition systems—and why does it matter?” Center for Strategies and International Studies (CSIS), April 14, 2020. These developments are contributing to profound unease in the relationship between technology and consumers of technology. The Pearson Institute and the Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research shows that “about two-thirds of Americans are very or extremely concerned about hacking that involves their personal information, financial institutions, government agencies, or certain utilities.” 24 Chuck Brooks, “More alarming cybersecurity stats for 2021!” Forbes , October 24, 2021.
Shift: Trust expands to cover a broader array of stakeholder concerns and become an enterprise-wide responsibility.
These enormous shifts in technology power and capacity will create many more touchpoints with customers and an exponential wave of new data about customers. Even as IT’s role within the organization becomes more that of an enabler, the expanding digital landscape means that IT must broaden its trust capabilities around security, privacy, and cyber . To date, consumers have largely embraced the convenience that technology provides, from ordering a product online to adjusting the temperature in their homes remotely to monitoring their health through personal devices. In exchange for these conveniences, consumers have traditionally been willing to provide some personal information. But a steady undercurrent of privacy and trust concerns around these ever-more-sophisticated conveniences is raising the stakes on the broad topic of trust. Consumers are becoming more aware of their identity rights, making decisions based on values, and demanding the ethical use of data and responsible AI .
The most obvious concern is around cybersecurity , an ongoing issue that is already on the board-level agenda. But tech-driven trust issues are much broader and are driven by three characteristics. One is the sheer quantity of personal data, such as biometrics, that companies and governments collect, creating concerns about privacy and data misuse. The second is that personal security issues are becoming more pervasive in the physical world. Wired homes, connected cars, and the Internet of Medical Things, for example, are all vectors for attack that can affect people’s well-being. Third is the issue that advanced analytics seem too complex to be understood and controlled, leading to deep unease about people’s relationship with technology. This issue is driving the development of “ explainable AI ” and the movement to debias AI.
Adding to the complexity is the frequent need to manage and secure trust across an entire ecosystem of technologies. Take the wired home, for example. The proliferation of devices—think virtual assistants, security, communications, power management, and entertainment systems—means that a large group of providers will need to agree on standards for managing, in effect, an interconnected security net in the home.
These developments require a complex extension of the boundaries of trust. The significant advantages that many incumbents enjoy—existing relationships with customers and proprietary data—are at risk unless businesses rethink how they manage and nurture that trust. Companies need to consider putting identity and trust management at the core of their customer experience and business processes. That can happen effectively only when companies assign a dedicated leader with real power and board-level prioritization with enterprise-wide responsibility across the entire trust and security landscape. Given the tech underpinnings of this trust environment, IT will need to play a key role in monitoring and remediating, such as assessing the impact of new legislation on AI algorithms, tracking incidents, identifying the number and nature of high-risk data-processing activities and automated decisions, and—perhaps most important—monitoring consumer trust levels and the issues that affect them.
- Who is responsible for the enterprise-wide trust and risk landscape?
- How have you integrated your efforts around customer trust with overall cybersecurity processes?
- What privacy, trust, and security processes are in place to manage the entire life cycle of your data?
It is inevitable that the pace of technological change will continue to accelerate. The successful technology leader of the future will not simply need to adopt new technologies but to build capabilities to absorb continuous change and make it a source of competitive advantage.
Steve Van Kuiken is a senior partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Digital twins: From one twin to the enterprise metaverse

Why digital trust truly matters

IoT value set to accelerate through 2030: Where and how to capture it
- Essay On Technology
Essay on Technology
500+ words essay on technology.
The word technology comes from the two Greek words, ‘techne’ and ‘logos’. Techne means art, skills, or craft, and Logos means a word, saying, or expression that expresses inward thought. Thus, technology means the skill to convey an idea to reach a goal. But nowadays, the term technology mainly signifies the knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems, and organisation methods to solve a problem. Today, technological advancement has provided the human race with the ability to control and adapt to their natural environment. In this Essay on Technology, students will know the importance of technology, its advantages and disadvantages and the future of technology.
How Has Technology Changed Our Lives?
Various innovations and development took place in the field of technology which has made a significant impact on our lives in different ways. With the invention of technology, we become more powerful. We have the ability to transform the environment, extend our lifetime, create big and interconnected societies and even explore various new things about the universe. Today, we use technology from morning to evening, from the simplest nail cutter to television and personal laptop. Technology has touched all aspects of our lives, whether it is mobile phones, kettles, kitchen microwaves, electric cookers, television, water heaters, remote control, fridge, and other larger communication systems such as internet facilities, railways, air routes, and so on. Thus, technology plays an extremely crucial role in the lives of human beings.
Advantages of Technology
The advancement in technology has made our lives easier, more comfortable and enjoyable. It has reduced the effort and time required to complete a task, thus enhancing the quality and efficiency of work. Technology has become a part of our life and benefited us in many ways. Today, we can communicate with people living in any city or country. Communication has become much faster and easier as we are just a click away from people. In education, technology has played a vital role, especially during the COVID-19 breakdown period. It has brought virtual and online classes for students and teachers across the globe to share knowledge, ideas and resources online. Moreover, technology has made it easier for students to understand complex concepts with the help of virtualisation, graphics, 3D animation and diagrams.
Technology is considered to be the driving force behind improvements in the medical and healthcare field. Modern machines have helped doctors to perform operations successfully. Due to technology, the lifespan of the common person has increased. There are many more sectors, such as banking, automation, automobile, and various industries, where technology is making significant changes and helping us.
Disadvantages of Technology
Although we have so many advantages of technology, there are also disadvantages. Robots and machines have taken over the job of many people. Instead of bringing people together, technology has made them socially isolated. People now spend most of their time on smartphones or computers rather than interacting with other people. Technology in education has reduced the intellectual and analytical ability of students. It is like spoon-feeding to students as they don’t have the reasoning and aptitude skills to think differently. Technology has raised the issue of internet privacy. So, one has to be very careful while using banking passwords to make online transactions.
Future of Technology
The future of technology seems to be exciting but also scary. Futuristic predictions in technology can dish out some exciting or scary visions for the future of machines and science. Technology will either enhance or replace the products and activities that are near and dear to us. The answer to our technological dilemma about what will be the upcoming technological innovation in the future is not surprising. In the past, technology was mainly focused on retaining more information and efficient processing, but in the future, it will be based on industrial robots, artificial intelligence, machine learning, etc.
Technology alone cannot help in building a better world. The collateral collaboration of machines and human effort is required for the progress and prosperity of the nation. We need to develop a more robust management system for the efficient functioning of technology.
Practise CBSE Essays on more topics to improve the writing section. Students can get the latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S website. They can also download the BYJU’S App for interactive study videos.
Frequently Asked Questions on Technology Essay
What is the simple definition of technology.
The real-time application of science and knowledge is how technology can be defined in simple terms.
Which country is ranked first in technological advancement?
Finland ranks top in technological advancement ahead of the USA according to the UNDP.
Why is the development of technology important?
Technology has now become an important part of our lives and thus technical and technological advancements are essential to take us forward in all aspects.
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Technology Essay

Essay on Technology
The word "technology" and its uses have immensely changed since the 20th century, and with time, it has continued to evolve ever since. We are living in a world driven by technology. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization, along with cultural changes. Technology provides innovative ways of doing work through various smart and innovative means.
Electronic appliances, gadgets, faster modes of communication, and transport have added to the comfort factor in our lives. It has helped in improving the productivity of individuals and different business enterprises. Technology has brought a revolution in many operational fields. It has undoubtedly made a very important contribution to the progress that mankind has made over the years.
The Advancement of Technology:
Technology has reduced the effort and time and increased the efficiency of the production requirements in every field. It has made our lives easy, comfortable, healthy, and enjoyable. It has brought a revolution in transport and communication. The advancement of technology, along with science, has helped us to become self-reliant in all spheres of life. With the innovation of a particular technology, it becomes part of society and integral to human lives after a point in time.
Technology is Our Part of Life:
Technology has changed our day-to-day lives. Technology has brought the world closer and better connected. Those days have passed when only the rich could afford such luxuries. Because of the rise of globalisation and liberalisation, all luxuries are now within the reach of the average person. Today, an average middle-class family can afford a mobile phone, a television, a washing machine, a refrigerator, a computer, the Internet, etc. At the touch of a switch, a man can witness any event that is happening in far-off places.
Benefits of Technology in All Fields:
We cannot escape technology; it has improved the quality of life and brought about revolutions in various fields of modern-day society, be it communication, transportation, education, healthcare, and many more. Let us learn about it.
Technology in Communication:
With the advent of technology in communication, which includes telephones, fax machines, cellular phones, the Internet, multimedia, and email, communication has become much faster and easier. It has transformed and influenced relationships in many ways. We no longer need to rely on sending physical letters and waiting for several days for a response. Technology has made communication so simple that you can connect with anyone from anywhere by calling them via mobile phone or messaging them using different messaging apps that are easy to download.
Innovation in communication technology has had an immense influence on social life. Human socialising has become easier by using social networking sites, dating, and even matrimonial services available on mobile applications and websites.
Today, the Internet is used for shopping, paying utility bills, credit card bills, admission fees, e-commerce, and online banking. In the world of marketing, many companies are marketing and selling their products and creating brands over the internet.
In the field of travel, cities, towns, states, and countries are using the web to post detailed tourist and event information. Travellers across the globe can easily find information on tourism, sightseeing, places to stay, weather, maps, timings for events, transportation schedules, and buy tickets to various tourist spots and destinations.
Technology in the Office or Workplace:
Technology has increased efficiency and flexibility in the workspace. Technology has made it easy to work remotely, which has increased the productivity of the employees. External and internal communication has become faster through emails and apps. Automation has saved time, and there is also a reduction in redundancy in tasks. Robots are now being used to manufacture products that consistently deliver the same product without defect until the robot itself fails. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technology are innovations that are being deployed across industries to reap benefits.
Technology has wiped out the manual way of storing files. Now files are stored in the cloud, which can be accessed at any time and from anywhere. With technology, companies can make quick decisions, act faster towards solutions, and remain adaptable. Technology has optimised the usage of resources and connected businesses worldwide. For example, if the customer is based in America, he can have the services delivered from India. They can communicate with each other in an instant. Every company uses business technology like virtual meeting tools, corporate social networks, tablets, and smart customer relationship management applications that accelerate the fast movement of data and information.
Technology in Education:
Technology is making the education industry improve over time. With technology, students and parents have a variety of learning tools at their fingertips. Teachers can coordinate with classrooms across the world and share their ideas and resources online. Students can get immediate access to an abundance of good information on the Internet. Teachers and students can access plenty of resources available on the web and utilise them for their project work, research, etc. Online learning has changed our perception of education.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a paradigm shift using technology where school-going kids continued their studies from home and schools facilitated imparting education by their teachers online from home. Students have learned and used 21st-century skills and tools, like virtual classrooms, AR (Augmented Reality), robots, etc. All these have increased communication and collaboration significantly.
Technology in Banking:
Technology and banking are now inseparable. Technology has boosted digital transformation in how the banking industry works and has vastly improved banking services for their customers across the globe.
Technology has made banking operations very sophisticated and has reduced errors to almost nil, which were somewhat prevalent with manual human activities. Banks are adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) to increase their efficiency and profits. With the emergence of Internet banking, self-service tools have replaced the traditional methods of banking.
You can now access your money, handle transactions like paying bills, money transfers, and online purchases from merchants, and monitor your bank statements anytime and from anywhere in the world. Technology has made banking more secure and safe. You do not need to carry cash in your pocket or wallet; the payments can be made digitally using e-wallets. Mobile banking, banking apps, and cybersecurity are changing the face of the banking industry.

Manufacturing and Production Industry Automation:
At present, manufacturing industries are using all the latest technologies, ranging from big data analytics to artificial intelligence. Big data, ARVR (Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality), and IoT (Internet of Things) are the biggest manufacturing industry players. Automation has increased the level of productivity in various fields. It has reduced labour costs, increased efficiency, and reduced the cost of production.
For example, 3D printing is used to design and develop prototypes in the automobile industry. Repetitive work is being done easily with the help of robots without any waste of time. This has also reduced the cost of the products.
Technology in the Healthcare Industry:
Technological advancements in the healthcare industry have not only improved our personal quality of life and longevity; they have also improved the lives of many medical professionals and students who are training to become medical experts. It has allowed much faster access to the medical records of each patient.
The Internet has drastically transformed patients' and doctors’ relationships. Everyone can stay up to date on the latest medical discoveries, share treatment information, and offer one another support when dealing with medical issues. Modern technology has allowed us to contact doctors from the comfort of our homes. There are many sites and apps through which we can contact doctors and get medical help.
Breakthrough innovations in surgery, artificial organs, brain implants, and networked sensors are examples of transformative developments in the healthcare industry. Hospitals use different tools and applications to perform their administrative tasks, using digital marketing to promote their services.
Technology in Agriculture:
Today, farmers work very differently than they would have decades ago. Data analytics and robotics have built a productive food system. Digital innovations are being used for plant breeding and harvesting equipment. Software and mobile devices are helping farmers harvest better. With various data and information available to farmers, they can make better-informed decisions, for example, tracking the amount of carbon stored in soil and helping with climate change.
Disadvantages of Technology:
People have become dependent on various gadgets and machines, resulting in a lack of physical activity and tempting people to lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle. Even though technology has increased the productivity of individuals, organisations, and the nation, it has not increased the efficiency of machines. Machines cannot plan and think beyond the instructions that are fed into their system. Technology alone is not enough for progress and prosperity. Management is required, and management is a human act. Technology is largely dependent on human intervention.
Computers and smartphones have led to an increase in social isolation. Young children are spending more time surfing the internet, playing games, and ignoring their real lives. Usage of technology is also resulting in job losses and distracting students from learning. Technology has been a reason for the production of weapons of destruction.
Dependency on technology is also increasing privacy concerns and cyber crimes, giving way to hackers.

FAQs on Technology Essay
1. What is technology?
Technology refers to innovative ways of doing work through various smart means. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization. It has helped in improving the productivity of individuals and businesses.
2. How has technology changed the face of banking?
Technology has made banking operations very sophisticated. With the emergence of Internet banking, self-service tools have replaced the traditional methods of banking. You can now access your money, handle transactions, and monitor your bank statements anytime and from anywhere in the world. Technology has made banking more secure and safe.
3. How has technology brought a revolution in the medical field?
Patients and doctors keep each other up to date on the most recent medical discoveries, share treatment information, and offer each other support when dealing with medical issues. It has allowed much faster access to the medical records of each patient. Modern technology has allowed us to contact doctors from the comfort of our homes. There are many websites and mobile apps through which we can contact doctors and get medical help.
4. Are we dependent on technology?
Yes, today, we are becoming increasingly dependent on technology. Computers, smartphones, and modern technology have helped humanity achieve success and progress. However, in hindsight, people need to continuously build a healthy lifestyle, sorting out personal problems that arise due to technological advancements in different aspects of human life.

Essay on Future of Artificial Intelligence
Students are often asked to write an essay on Future of Artificial Intelligence in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
100 Words Essay on Future of Artificial Intelligence
Introduction.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the science of making machines think and learn like humans. It’s an exciting field that’s rapidly changing our world.
Future Possibilities
In the future, AI could take over many jobs, making our lives easier. Robots could clean our houses, and AI could help doctors diagnose diseases.
Challenges Ahead
The future of AI is promising, but we need to navigate it carefully to ensure it benefits everyone.
250 Words Essay on Future of Artificial Intelligence
Ai in everyday life.
The future of AI holds promising advancements in everyday life. We can expect more sophisticated personal assistants, smarter home automation, and advanced healthcare systems. AI will continue to streamline our lives, making mundane tasks more efficient.
AI in Business
In business, AI will revolutionize industries by automating processes and creating new business models. Predictive analytics, customer service, and supply chain management will become more efficient and accurate. AI will also enable personalized marketing, enhancing customer experience and retention.
AI in Ethics and Society
In conclusion, the future of AI is a blend of immense potential and challenges. It will transform our lives and businesses, but also necessitates careful consideration of ethical and societal implications. As we move forward, it is essential to foster a global dialogue about the responsible use and governance of AI.
500 Words Essay on Future of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed from a fringe scientific concept into a commonplace technology, permeating every aspect of our lives. As we stand on the precipice of the future, it becomes crucial to understand AI’s potential trajectory and the profound implications it might have on society.
The Evolution of AI
The current focus is on developing General AI, machines that can perform any intellectual task that a human being can. While we are yet to achieve this, advancements in Deep Learning and Neural Networks are bringing us closer to this reality.
AI in the Future
In the future, AI is expected to become more autonomous and integrated into our daily lives. We will see AI systems that can not only understand and learn from their environment but also make complex decisions, solve problems, and even exhibit creativity.
Implications and Challenges
However, the future of AI is not without its challenges. As AI systems become more autonomous, we must grapple with ethical issues. For instance, who is accountable if an AI system makes a mistake? How do we ensure that AI systems are fair and unbiased?
Moreover, as AI continues to automate tasks, there are concerns about job displacement. While AI will undoubtedly create new jobs, it will also render many existing jobs obsolete. Therefore, societies must prepare for this transition by investing in education and training.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
All About Technology Essay
Personal Technology Essay Blog
Home » Education » Writing an Essay About Future Technology
Writing an Essay About Future Technology
A Technology Past Present and Future Essay is a type of essay that is written to answer questions such as: What is the importance of technology in the future? How can technology affect people’s lives today? Who will benefit from the future of technology?
There are many different types of technology that exist today. Some of these include computers, radio, television, cellular phones, and satellite television. Each of these has their own unique characteristics, and each is very useful in society.
These different things have been developed over time, and the information about all of these things is constantly changing. Some things are important, while others are not. Technology is always changing. As a writer, you must keep up with the changing times so that your essays will be timeless and still relevant.
One of the best ways to write a technology essay is to discuss all of the different topics that are relevant to the topic. This way, you will have information about what was around when the technology was developed, and you can explain the various characteristics that were discovered. This will also allow for an argument as to why certain things are important today, while others were not known about at the time.
In your essay, you must describe the development of the technologies that you are discussing, including how the development progressed over time. You must also explain the different reasons that people used the technology. It is important to show a progression of technology from past to present, and then to the future.
Past technology that is being discussed is always going to be considered. Because technology has changed so much, there is always a different way to think about technology than there was in the past. For example, you might have a technology essay about how the computer changed the world, or you might have an essay about how the cell phone changed the world. There are several different types of technology that are used in society, and everyone should have an opportunity to use them.
Because of the technological advancements that are happening each day, people in society have more opportunity to use these things that have changed. People who are not familiar with a new invention can become knowledgeable about the invention through the use of an internet. The Internet is one of the most widely used inventions in society, and is used for both research and learning.
The future of technology is in everyone’s hands. If you write an essay about the future of technology, it is very important that you understand the future of technology, and how it will affect the world. The people that will read this essay will be able to predict the future of the technologies that will be available to them and what they will do.
When you talk about the future of technology, you must give yourself some time to write your essay. You need to consider how the future will change the present and what changes it will bring about. It is important to write your essay in such a way that it is interesting to read. A good way to learn about the future is to read the past in order to see what the past has taught us.
Some people think that writing about the future is a bit difficult. While some people think that it is, other people think that it is not. There are some people who believe that there are many different opinions on the future of technology, and how it affects the present. It is true that there are many different people that believe that there are two different visions of the future of technology, and they have a good reason for this.
Some people may think that current technology has gotten better because they have been able to develop the latest gadgets and tools. They are right in some cases, but there are also many people that believe that these gadgets are not as useful as they used to be. This is because the technology has changed, and the tools that were once helpful are now obsolete.
When you write your essay , it is very important to consider the future. Whether you write it for school or for a school assignment, you want to give your readers some hope. You want to give your readers a clear picture of what their lives will be like in the future, so that they can know if the future is something that is exciting.
Technology Advantages and Disadvantages Essay
Essay on Effects of Technology on Human Beings
- Essay Editor
Exploring the Impact of Technology on Finding New Ways to Connect People
1. introduction.
Consumer engagement in science can be hard to come by. Most people's minds are taken up with their day-to-day lives, not with the policy implications of the most recent energy deal or the rather complicated functioning of a carbon market. There is a reported public appetite for energy research, but to engage people's minds, we need to offer them congruence with busy lives. Modern technology can make that link, through SMS, through voice telephony, and on the web, literally bringing engagement into the home, working environment, and itinerant lifestyles of our modern world. We live in a world defined by technology. We communicate, research, learn, teach, and deliver ourselves through it. Our relationship with technology also competes for our time. It can take us out of our local environment, can link us to people and knowledge across continents. However, for energy in developing countries, our development paradigm is very local. Energy comes in large, spatially defined infrastructure. Our consumption of energy happens at a local scale. We use our own small networks to organize the consumption of what is brought to us by larger systems. Until recent years, we have used simpler and quite rigid technology to regulate our consumption. Web services and other interactive technology can help us simplify customer relationships but cannot easily act as a replacement for the physical interaction between system operators and customers during power failures.
2. Historical Perspectives on Communication Technologies
The earliest form of communication technology—writing on the clay tablet—left messages across time, greatly expanding the range of our interpersonal connections. As writing on clay tablets evolved into writing on paper, reading and writing transformed our capacity to connect with people who were absent from us either in terms of time or space. Our ancestors began to depend on a type of relationship in which they communicated with people that they did not know. Consequently, they developed new kinds of questions in addition to creating new ways to answer them. From our contemporary retrospective, we can appreciate that their historical turn to questions about how we know and connect with others left an important sociocultural and ecological legacy. One way that we can begin to understand historical contexts is to look at old technologies with new questions. Such historical approaches can be usefully analogous to the advice that the noted anthropologist Clifford Geertz gave to his students when they wanted to explore a strange culture—look at new things with old questions. Since few of us share historical contexts with clay tablets, Phoenician script, or papyrus, we have quickly encountered some challenges in trying to use this historical approach to study the impacts of new communication technologies on the nature of interpersonal connections in the present. These challenges have stimulated us to identify other questions that complicate anything the historical record might usefully illuminate. The ancient Greeks, who lived closely in small city-states and kept written archives that provide much of what we know about surrounding cultures at that time, can help us think through some of the questions we have begun to address through our exploratory historical inquiries.
3. Current Technological Innovations in Connecting People
In most cases, utilizing technology to connect geographically distant individuals involves leveraging our natural media. Voice communication has been part of the telecommunications network since Alexander Graham Bell's historic invention. Voice communication, both in wired and wireless form, is available to everyone. Other media, such as letter writing and face-to-face communication enabled by travel, have been augmented by additional transportation and transmission capabilities. Wireline and wireless methods now supplement traditional face-to-face contacts through the Internet or similar services such as intranets. By incorporating internet browsing capability into cellphones and personal digital assistants, two-way communication media are intermingled with the presentation of information. Integrated systems also incorporate data presentation with either event-derived or scheduled voice and data transmission capabilities. Technological innovations include wireless wearable biophysical environmental sensing and communication systems aimed at providing a proactive and integrated approach to wellness management to achieve a shift from treatment to wellness-centered health care. By continuously and unobtrusively monitoring an extensive set of biophysical and environmental parameters at any location, these systems allow healthcare professionals and coaches to identify health risks early, taking corrective actions before health problems have advanced. Each biophysical parameter can be monitored using one or more reliable sensor technologies, such as radio-frequency-based comma (electrical conductivity of body), temperature, heart rate, motion, SpOss (oxygen saturation), and blood pressure sensors. A dedicated body area network (BAN), which seamlessly interfaces with the resident cellular and ad-hoc networks, collects data from wearable and environmentally placed sensors, transmitting local alarm notifications and data to remote healthcare and wellness professionals or coaches. The BAN organizes the collected data streams and provides inter BAN and intercellular communication synchronized with operators' availability for the notification-specific and data-mediated local actions. Caregiver notifications and voice and video communications may occur via ad-hoc, cellular calls, or using Voice over IP (VoIP) technology, with data, voice, and video communications dynamically adjusting the data bandwidth based on a live assessment of the transmitted sensor data and video link quality. Suns (stimulants, drugs, and other essential) reminders can also be issued, serving as medication adherence support. Notification alerts can be sent out remotely based on analysis of the biophysical parameter data, health profiles, and other users' data. Data can be stored in local terminals and/or centrally managed databases for further analysis, to assess health issues, and to tailor information and interventions toward health promotion. Technology has reduced or addressed issues of privacy and security related to any personal healthcare information that is not contained in the transmitted and locally stored data or processes.
4. Social Implications of Technology-Mediated Communication
When assessing the impact of TMC on people's social lives, there is a wealth of both positive and negative ways in which such technologies can factor. TMC can be used to maintain existing relationships with family and friends, and can be especially important for geographically separated, socially isolated, or peripatetic people, and (together with associated systems such as distance learning tools and Web 2.0 based applications) it can be used to maintain and develop new relationships that have been recently formed face to face or to support active participation within current interest groups, communities, and settings. However, TMC can also be associated with tensions and harmful effects such as a perceived erosion of social skills, lack of perception of privacy, social surveillance, and risks of cyberstalking. When looking at the social uses of new technologies, it is not only the technology itself that can lead to such claims, especially when it is accessed, used, and implemented. Sometimes social benefits and negative effects arise from a combination of situational and technology-oriented user perspectives together with the choices of settings where the technologies are utilized. Users carry with them the constraints and opportunities of both personal and environmental circumstances, and grapple with normative and aesthetic standards about how technologies can and should be used. Given all the evidence indicating that all the potential ways in which people can be in touch with each other more often, meet more often, and better understand each other despite the inherent restrictions of the technological medium at our disposal, the search for effective and ethical solutions for interconnectivity using technology should remain a primary focus of analysis and discussion of these networks.
5. Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Age
With the rise of social media, there are numerous new opportunities but also a range of challenges that we need to address. Research on Facebook, leading the world's most extensive social network, can illustrate the issues. The average Facebook user has 130 friends and is connected to many general interest and niche groups. The possibilities for meaningful relationships and for participation in groups or causes that would have been less likely had it not been for social connections are vast. We can also access high-quality commercial information in an efficient manner. Facebook enables a more profound understanding of other cultures, ethnicities, and sexual orientations. At the same time, it is well documented that many social media users feel uncomfortable with the fact different providers can unevenly treat us if we have divergent political views, are of different ages or sexual orientations or have distinct tastes in movies, sports teams, or vivid histories. Fake accounts and 'deep fakes' undermine our confidence in what we read and see. Social media can also enhance social comparison, increase negative perceptions of our bodies, and enable our natural impulse to favor what is known and similarity over the never-before experienced. Rising levels of addiction may lead to excessive screen time and problems with memory, eyesight, difficulty in sleeping and a loss of real-life social connections. Finally, the non-profit or niche content we value may disappear or be less high quality should the economics of Internet advertising change.
6. Future Trends in Technology for Connecting People
As with all technology trends - if we take AI as an example - interest has been shown both by commercially-driven companies as well as the research community. Yet another approach for connecting individuals is being researched by neuroscientists. In their lab in London, the researchers are investigating the use of audio and olfactory information to create interactions and sharing among individuals. Compelling sound and smell experiences often feed our fascination for travel, and this provides a strong lean-in for search terms for conversations and digital sharing among users. These approaches could serve in collaboration, entertainment, and also in the fields of health and well-being, and may bring interactive experiences to places where privacy and trust may already exist to help guide the need for creating social links.
Related articles
The impact of electronic communication on social interactions.
1. Introduction The internet is the decisive technology of the Information Age, and with the explosion of wireless communication in the early twenty-first century, we can say that humankind is now almost entirely connected, albeit with great levels of inequality in terms of access, use, and effectiveness. On the one hand, the internet is an open network with complex global governance and distributive mechanisms. Additionally, the development of the internet has enabled social networks within cy ...
The Role of Achievement in Mathematics Education: Exploring Strategies for Success
1. Introduction Mathematics achievement has long been an issue of national concern in the United States. As early as 1983, A Nation at Risk indicated that nearly 20% of all 17-year-olds in the United States lacked the competency in mathematics expected of a 13-year-old. Other nations had also expressed concern about their students' mathematical competence and had embarked on national reforms of their mathematics education. Particularly in the United States, the federal government, with Robert T ...
The Impact of Patent Law on Innovation and Economic Growth in the Technology Industry
1. Introduction Both the patent system and the contribution of patents to innovation and economic growth in the technology industry are subjects of wide-ranging debate. The requirement for every inventor to conduct a patent search prior to commencing an invention suggests the importance of patented technology in future innovation. Furthermore, costs associated with the development and marketing of technology are generally high, but benefits of technology can be put to use by other parties for l ...
The Impact of Technology on Modern Society
1. Introduction The role of technology in our society is important. In the past few decades, advancements in technology have pushed the boundaries of what is possible. It has altered the way humans interact and makes significant changes in the ways we communicate, work, and play, so as to change the way we live. The changes brought about to our society have been both positive and negative. Without doubt, the conversation must begin with the history of technology. From the dark ages to the age o ...
The Impact of Technological Change on Cultural Values
1. Introduction As with markets, governments, and other workaday institutions, culture is changing. It is changing rapidly and in some unexpected ways. The changes come from many sources, including a growing world population; increased production and consumption of information and culture across the globe; the emergence of a global youth culture, which is pioneered by Western and Japanese producers of cultural products; the spread of new communication technologies; the rise of a global popular ...
La importancia de preservar la naturaleza en el siglo XXI
1. Introducción El mundo y sus constantes cambios han evolucionado desde la aparición del hombre. Este hecho ha figurado una alteración en los mecanismos de autorregulación del planeta que ha modificado sus formas ecológicas de vida. La naturaleza ha experimentado y experimenta a día de hoy diferentes avatares. Estos no sólo son explicados por su propia biología evolutiva sino que al igualar el planeta hay que añadir cambios y alteraciones por parte de la comunidad de sistemas vivos entre los q ...
The Importance of Mathematics in Secondary Education
1. Introduction There was a time when mathematics enjoyed a much improved reputation. It was highly respected, and the word mathematician was reserved for highly educated thinkers capable of solving the most difficult problems. It was the mathematical activity of laying the foundation of philosophical, theoretical, and practical issues. With the advent of the sciences and the continued development of the activities associated with them, mathematics took on the role of underlying the complete st ...
1. Introduction Impact of technology on modern society Like any society, modern society is a product of history. And this self-identity is not determined by its material culture or indeed by the artifacts it has produced, but by the attitude of its members to these artifacts. And the impact of these novel technological artifacts, it is contended, is sufficient to effect a modest social revolution. The thesis of this paper is that any concept of technology is loaded to some extent with at least ...
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
Job title of the future: Weather maker
One scientist leads a project to increase winter snowfall so that desert towns in the US West will have water in summer.
- Mara Johnson-Groh archive page

Much of the western United States relies on winter snowpack to supply its rivers and reservoirs through the summer months. But with warming temperatures, less and less snow is falling—a recent study showed a 23% decline in annual snowpack since 1955. By some estimates, runoff from snowmelt in the western US could decrease by a third between now and the end of the century, meaning less water will be available for agriculture, hydroelectric projects, and urban use in a region already dealing with water scarcity.
That’s where Frank McDonough comes in. An atmospheric research scientist, McDonough leads a cloud-seeding program at the Desert Research Institute (DRI) that aims to increase snowfall in Nevada and the Eastern Sierras. Snow makers like McDonough and others who generate rain represent a growing sector in a parched world.
Instant snow: Cloud seeding for snow works by injecting a tiny amount of silver iodide dust into a cloud to help its water vapor condense into ice crystals that grow into snowflakes. In other conditions, water molecules drawn to such particles coalesce into raindrops. McDonough uses custom-made, remotely operated machines on the ground to heat up a powdered form of the silver iodide that’s released into the air. Dust—or sometimes table salt—can also be released from planes.
Old tech, new urgency: The precipitation-catalyzing properties of silver iodide were first explored in the 1940s by American chemists and engineers, but the field remained a small niche. Now, with 40% of people worldwide affected by water scarcity and a growing number of reservoirs facing climate stress, cloud seeding is receiving global interest. “It’s becoming almost like, hey, we have to do this, because there’s just too many people and too many demands on these water resources,” says McDonough. A growing number of government-run cloud-seeding programs around the world are now working to increase rainfall and snowpack, and even manipulating the timing of precipitation to prevent large hailstorms, reduce air pollution, and minimize flood risk. The private sector is also taking note: One cloud-seeding startup, Rainmaker, recently raised millions.
Keep Reading
Most popular.

Happy birthday, baby! What the future holds for those born today
An intelligent digital agent could be a companion for life—and other predictions for the next 125 years.
- Kara Platoni archive page

This researcher wants to replace your brain, little by little
The US government just hired a researcher who thinks we can beat aging with fresh cloned bodies and brain updates.
- Antonio Regalado archive page

Here’s how people are actually using AI
Something peculiar and slightly unexpected has happened: people have started forming relationships with AI systems.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page

Google DeepMind trained a robot to beat humans at table tennis
It was able to draw on vast amounts of data to refine its playing style and adjust its tactics as matches progressed.
- Rhiannon Williams archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
- Trends Summit
White Papers
- Continuing Education
- Sustainability
The Future of Data Center Cooling: Embracing Emerging Technologies while Maintaining Air Cooling

As the data center industry evolves and artificial intelligence (AI) workloads become increasingly common, the topic of cooling technologies has gained significant attention. While liquid cooling is often seen as the future, it is essential to recognize that air cooling, which has served the industry for decades, still has its place. In this article, we will explore the benefits of hybrid designs and the importance of embracing emerging technologies while planning for the future.
The Five to Ten-Year Plan
Looking at future goals, data center planning requires a long-term vision and consideration of future needs. This applies not only to hyperscale, edge, and enterprise facility operators, but also to colocation facilities engaging with their customers. Conversations surrounding future goals, needs, and requirements are vital to make informed choices about cooling technologies.
Air Cooling Innovation: Going Beyond Perimeter Cooling
Air cooling technology has not stagnated; it has evolved over the years to meet increasingly demanding requirements. The advent of row cooling has allowed for higher-density racks, with successful implementations of 40-50 kW racks. Critical factors such as containment or perimeter units can help optimize air cooling performance.
Embracing Hybrid Cooling Solutions for Modern Data Centers
Contrary to popular belief, air cooling is not going away anytime soon. Enterprise data centers, which don't require extensive cooling, form a significant portion of the industry. It is unrealistic to assume that all data centers will switch entirely to liquid cooling. Instead, air and liquid cooling tailored to specific application requirements will likely be the norm.
Hybrid designs offer a practical approach when the specific cooling requirements are uncertain. By combining air and liquid cooling systems, organizations can maintain flexibility. This approach provides the opportunity to adapt to changing needs, whether it be incorporating liquid cooling in the future or optimizing existing air-cooled systems. While hybrid designs may involve additional upfront costs, the long-term benefits and flexibility outweigh the initial investment.
Retrofitting data centers to add liquid cooling capabilities can be expensive. It is better to plan ahead and design your data centers in a way that can accommodate both liquid and air-cooling technologies. In this hybrid design, you can cool racks of 50 kW and below efficiently with air cooling technologies. Anything above 80 kW will have to be cooled with liquid cooling technologies.
Evaluating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Assessing the total cost of ownership is crucial when choosing between air and liquid cooling. While liquid cooling may provide more efficient cooling, evaluating overall costs, including construction expenses involved in changing the data center layout is essential. Each organization must consider factors like load availability, space constraints, predicted future demand, and energy efficiency to decide the most cost-effective cooling solution.
Day-to-day operations and downtime maintenance are key aspects of data center operation, and their impact on downtime cannot be ignored. Liquid cooling systems often require specific procedures, such as working with oil-based single-phase immersion systems, which can pose challenges for routine maintenance. While two-phase systems offer hermetically sealed solutions, they may still incur additional costs. It is essential to compare the maintenance requirements of different cooling technologies when making decisions.
The Importance of Planning for the Future
In an ever-changing landscape, planning plays a crucial role. With different regulations and sustainability standards in each country, a one-size-fits-all approach is not feasible. Lack of standardization and the evolving nature of cooling technologies require organizations to plan ahead. Organizations can bridge the current gap in the industry by focusing on future needs, making specific requirements, and ensuring the right specifications.
While emerging technologies like single-phase and direct-to-chip cooling gain attention in the data center industry, air cooled cooling technologies retain their significance. The future of cooling lies in embracing hybrid designs that combine air and liquid cooling, offering flexibility and adaptability. Organizations can make informed decisions and optimize their data centers by engaging in conversations about future goals and needs. It is crucial to remember that planning for the future and embracing new technologies while still utilizing the proven benefits of air cooling will shape the success of data centers in the years to come.

Danielle Rossi
Danielle Rossi is Global Director – Mission Critical Cooling for Trane . Danielle has 17+ years in data center solution design and engineering for hyperscale, colocation, enterprise, edge, and government environments. In her current role, Danielle manages global mission-critical cooling products and processes to provide a standardized deliverable for customers executing projects worldwide.
Trane® – by Trane Technologies – continues to innovate its HVAC systems & controls and energy services for mission critical customers. With over 37,000 employees in 58 countries and serving approximately 100 countries in 2023, Trane is well-positioned to support hyperscale and co-location data centers with their cooling needs across the globe.
Continue Reading
The Eight Trends That Will Shape the Data Center Industry in 2021
Google Building More Data Centers for Massive Future Clouds
Sponsored recommendations.
NECA Manual of Labor Rates Chart
Electrical Conduit Cost Savings: A Must-Have Guide for Engineers & Contractors
Conduit Sweeps and Elbows for Data Centers and Utilities
Prefabricated Conduit Duct Banks Enable Smooth and Safe Electrical Installation for a Data Center
Voices of the industry.

Bridging the Gap: With Local Grids Stretched to the Limit, Data Centers Need a Plan for Reliable Supplemental Power
Latest in sponsored.

Liquid Cooling: A Sustainable Revolution in Data Center Efficiency

New Strategies in Design to Meet the Demands of AI Data Centers

Podcast: The Dynamics of Exascale Data Centers

Enhancing Resiliency For the Energy Transition
Investing in Edge Computing: It’s Still Early, Investors Say
Vapor IO’s Edge Data Centers Power a Network of Drones
Roundtable: Will 5G Accelerate the Data Center Sector?
More From Forbes
Is the future of the american city in making shoes portland’s answer is ‘yes’.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
In a time when global supply chains are under unprecedented strain, the " Made in Old Town " project in Portland, Oregon, represents a bold new vision for American manufacturing—one that combines cutting-edge digital production technologies, like 3D printing, with the growing trend of reshoring. The result may redefine U.S. cities altogether.
A New Urban Model
Old Town in Portland, once the city's manufacturing hub, has faced economic decline and underutilization of its historic buildings, becoming a " net drain on civic resources ." Despite these challenges, its rich industrial heritage and strategic location near Portland's thriving footwear and apparel industry make it the ideal site for the Made in Old Town project.
An illustration of the Made in Old Town location.
At the heart of this initiative is the idea of transforming urban centers into vibrant ecosystems where production, retail, and living spaces coexist in harmony. Matthew Claudel, founder of civic design firm Field States and a key architect of the Made in Old Town project, highlights how this approach not only addresses the post-COVID urban economy but also reimagines how cities function.
“Cities were initially a place where you have manufacturing, retail, and housing all in one unit,” Claudel explains. “We’re exploring what the next generation of cities will look like, creating something that is truly an integrated ecosystem.”
This vision draws from historical urban models but is powered by the latest in digital manufacturing technology. The integration of 3D printing, for instance, allows for manufacturing to occur in a way that is “lightweight, environmentally clean, and has a very small footprint,” enabling production facilities to be embedded directly within city neighborhoods. The result is a dense, vibrant downtown where products are conceived, designed, and manufactured in close proximity to local consumers.
Ransomware Gang Targets Google Chrome Users In Surprise New Threat Twist
Today’s nyt mini crossword clues and answers for tuesday, august 27th, new details emerge about why ‘the acolyte’ was cancelled, reshoring through innovation.
Elias Stahl, CEO and Co-Founder of HILOS , sees this project as a blueprint for reshoring manufacturing in the U.S., particularly in industries that have become highly globalized, such as footwear and apparel.
“We’re living at a real inflection point for supply chains,” Stahl notes. “There’s a massive opportunity for the industry to work closely again with brands and their suppliers to build the next supply chain for the 21st century—one that is sustainable, on-demand, and close to the market.”
An illustration of HILOS's future location at Made in Old Town.
HILOS, a company that started as a 3D-printed footwear brand, now sits at the center of this transformation. The company uses HP's Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) printers to create soles from thermoplastic polyurethane derived from 80% recycled material and which can be fully recycled after use. This technology allows HILOS to produce shoes on-demand, eliminating overproduction and reducing waste by streamlining the manufacturing process from 65 parts across 360 steps to just five parts in 12 steps. By fulfilling orders within 72 hours, HILOS not only meets consumer demand quickly but also sets a new standard for sustainable and agile manufacturing in the footwear industry.
In turn, HILOS is helping to develop what Stahl describes as “the lowest cost and most scaled form of not just 3D footwear, but even U.S.-based footwear production.” This capability is critical for reshoring efforts, as it addresses two major barriers: cost and capacity.
The XII Modular Sandal by HILOS and Unknown Union, featuring three 3D printed parts and 80 percent ... [+] reclaimed material.
Sustainability at Scale
Sustainability is a cornerstone of the Made in Old Town project, with 3D printing playing a key role in reducing waste and making production more responsive to market demands. Noel Kinder, former Chief Sustainability Officer for Nike and a member of the Made in Old Town stewardship committee, emphasizes the importance of this technology in achieving environmental goals.
“I’ve always been fascinated by 3D printing and where that would fit in the footwear supply chain,” Kinder says. “HILOS has done a really nice job of proving that it can fit at scale and finally reach the promise that has been out there for so long.”
This promise includes the potential to drastically reduce the environmental footprint of manufacturing by enabling localized production, reducing the need for transportation, and minimizing excess inventory through on-demand production. The project has already garnered substantial support, receiving $2 million in state funding, with plans to scale significantly in the coming years.
A Model for the Future
The Made in Old Town project is a clear vision for the future of Portland’s Old Town neighborhood. The development is designed to spark the future of clean, environmentally sustainable footwear and apparel manufacturing while transforming the neighborhood for the better. Grounded in high-quality urban design and inclusive wealth-building for Portland’s community, the project will strategically invest in vacant and under-utilized properties, transforming four Portland city blocks into a world-class sustainable industry campus.
In total, this mixed-use development will encompass 323,000 square feet across nine buildings, including 80,000 square feet of advanced manufacturing space and 110,000 square feet of workforce housing. Alongside anchor manufacturing companies, the Made in Old Town district will be home to dozens of small businesses—from creative brands to tier-two suppliers. The project’s integration of various functions—manufacturing, retail, logistics, and housing—creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that supports both the local economy and the broader goals of reshoring.
The implications of the Made in Old Town project extend far beyond Portland. As Claudel points out, this model could be replicated in other American cities, each with its unique industrial heritage.
“Regions across the country have their own unique heritage of manufacturing,” he explains. “This is a roadmap that every American city can use to embrace the future with technological possibility, job creation, and tapping into craft and that heritage culture of making.”
The timing for such initiatives is particularly opportune, given the significant federal support for infrastructure revitalization and reshoring efforts. The Biden Administration’s Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, now two years into implementation, has allocated over $306 billion into state and local projects, with much of this funding aimed at rebuilding and modernizing critical infrastructure.
With 80% of competitive grant funding still available, cities across the U.S. have an unprecedented opportunity to secure resources that can support projects like Made in Old Town. This influx of federal investment aligns with the goals of reshoring and sustainable urban redevelopment, providing the financial backbone needed to turn such ambitious visions into reality.
Indeed, the success of this project could signal a broader shift in how manufacturing is approached in the U.S., blending the benefits of advanced technologies with a resurgence of local production. It’s a vision that, if realized, could redefine urban economies and make reshoring not just a possibility, but a reality.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
National Security
Why the us isn't ready for the wars of the future, according to experts.

Mary Louise Kelly
Katia Riddle

NPR's Mary Louise Kelly speaks to General Mark Milley, the former Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and Eric Schmidt, the former CEO of Google, about how technology is transforming warfare.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
Securing data and preserving privacy in cloud IoT-based technologies an analysis of assessing threats and developing effective safeguard
- Open access
- Published: 27 August 2024
- Volume 57 , article number 269 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Mayank Pathak 1 ,
- Kamta Nath Mishra 1 &
- Satya Prakash Singh 1
1 Altmetric
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a powerful technology adopted in various industries. Applications of the IoT aim to enhance automation, productivity, and user comfort in a cloud and distributive computing environment. Cloud computing automatically stores and analyzes the large amounts of data generated by IoT-based applications. Cloud computing has become a crucial component of the information age through easier data administration and storage. Currently, government agencies, commercial enterprises, and end users are rapidly migrating their data to cloud environments. This may require end-user authentication, greater safety, and data recovery in the event of an attack. A few issues were discovered by authors after analysis and assessments of various aspects of the published research papers. The research analysis reveals that the existing methods need to be further improved to address the contemporary dangers related to data security and privacy. Based on the research reports, it can be stated that safe end-to-end data transmission in a cloud-IoT environment requires modifications and advancements in the design of reliable protocols. Upcoming technologies like blockchain, machine learning, fog, and edge computing mitigate data over the cloud to some level. The study provides a thorough analysis of security threats including their categorization, and potential countermeasures to safeguard our cloud-IoT data. Additionally, the authors have summarized cutting-edge approaches like machine learning and blockchain technologies being used in the data security privacy areas. Further, this paper discusses the existing problems related to data privacy and security in the cloud-IoT environment in today’s world and their possible future directions.
Explore related subjects
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The speedy development of technology and Internet of Things (IoT)-based devices in organizations and enterprises give rise to progressive increases in various types of data. IoT has become a vital part of human life and it can be sensed in our day-to-day activities. It was said by Kumar et al. ( 2019 ) that IoT is a revolutionary approach that has changed numerous aspects of human life. It makes our lives easy and secure by handling various applications of smart city societies including pollution control , smart transportation , smart industries , smart home security systems , smart water supply , and many more systems. The small amount of data accumulates and gives rise to Big Data which is stored, processed, and analyzed by a set of technologies. Big Data is a large volume of data generated by IoT sensors , servers , social media , and medical equipment, etc . Cloud computing is internet-based computing that enables inexpensive, reliable, easy, simple, and convenient accessibility to the resource (Albugmi et al. 2016 ). Cloud computing provides service, and reduces infrastructure maintenance overheads. Apart from this it also provides better performance to the end users and flexibility for storing data over the cloud. However, storing highly confidential Big Data obtained from IoT devices , medical data , and server data over the cloud may pose threats to attackers. Therefore, data security is a most important concern when a large or bulk of confidential data is to be stored in the cloud (Sumithra and Parameswari 2022 ).
Cyber attacks target IoT devices that impact stakeholders, and they may damage physical systems, m-health, and economic systems severely. Earlier events show that IoT devices hold numerous vulnerabilities. Many manufacturers struggle to protect IoT devices from vulnerabilities (Schiller et al. 2022a ). Cloud computing integrates distributed computing, grid computing, and utility computing to establish a shared virtual resource pool (Sun 2019 ). There are privacy and security issues in these cases because the owners have no control over the information and tasks carried out on the platform. Various privacy protection methods have been introduced such as encryption , access control , cryptography , and digital signature but they are not strong enough, as a result, attackers easily break through the security wall and harm the data over the cloud.
The authors of the research papers reviewed various methods and suggested some measures and directions to protect the data in cloud computing and edge computing environments (Ravi Kumar et al. 2018 ; Zhang et al. 2018 ). Through this study, the author found that data privacy , data remoteness , data leakage , and data segregation are crucial problems that may exist. The survey paper (Hong-Yen and Jiankun 2019 ) addressed modern privacy and preserving models to focus on numerous privacy-interrelated frameworks to be implemented in practice.
As a contribution, the current paper aims to accomplish the following objectives:
To examine existing security frameworks , standards , and techniques that incorporate different standards across multiple areas of cloud-IoT technologies.
To explore and discuss open-ended challenges in a Cloud-IoT-based environment concerning securities and privacy.
To present and discuss the classification of challenges in Cloud-IoT environments after evaluating the performance of existing literature. It also provides solutions for the identified open-ended challenges and addresses future security concerns related to Cloud-IoT technologies.
The following are the Research Questions ( RQs ) that the researchers tried to investigate through the current research paper:
RQ 1 : To Investigate how IoT , Big Data , and Cloud computing technologies are interconnected, and how security can be a major concern when data is stored in a cloud environment.
RQ 2 : What are the security objectives for the data security and privacy domain?
RQ 3 : What are the privacy concerns for end-users in cloud-IoT-based environments?
RQ 4 : What is the role of edge computing in enhancing privacy in a cloud-IoT environment?
RQ 5 : What are vulnerabilities that exist in the cloud-IoT infrastructure?
RQ 6 : What are the current research trends and areas of focus?
RQ 7 : What are Advancements in security threat detection and avoidance ?
RQ 8 : How machine learning can be a useful tool in detecting vulnerabilities within a cloud-IoT environment?
RQ 9 : How can blockchain technology be an effective measure of data security and privacies?
RQ 10 : What are Current Issues in Data Security and Privacy?
Regarding the remaining portion of the document, Sect. 2 describes the methodology of this research work. Section 3 discusses the characteristics of a research paper and explains how the current paper differs from others. Section 4 talks about security goals in the Cloud-IoT environment. Section 5 discusses the taxonomy related to Cloud-IoT environment which includes Big Data and IoT along with its applications in various domains. Section 6 is a comprehensive study of various attacks in the Cloud-IoT environment. Section 7 (A) explores the study of various research trends through Table 1 . Section 7 (B) describes attack vectors and mitigation strategies through Table 2 . Section 8 presents an in-depth analysis of digital forensics. Section 9 talks about the machine learning and Blockchain technologies-based approaches used for threat detection and recovery. Section 10 covers the current challenges in data security and privacy, and it provides a brief description of possible solutions listed in Table 3 . Further, this section highlights the research gaps identified by the author in Table 4 . Conclusions and future research work are discussed in Sect. 11 .
2 Methodology: a systematic approach
The methodology is the systematic approach that is used by the author to conduct research, analyze the data, and frame conclusions. The methodology section covers the boundary area of methods and approaches that are followed by the author to write the current research paper. The methodology of this research paper is as follows: To examine IoT security challenges and threats author searched numerous kinds of literature on IoT security. For this keyword IoT, Cloud-IoT security was used for standard survey papers that were published in reputed journals like IEEE, Elsevier, Springer, and many more. After completing this task, the author examined numerous techniques and methodologies presented in those survey papers critically analyzed the facts, and algorithms, and selected a set of relevant topics that is important from a security perspective, provided with the help of the author’s individual experience in the sphere of security. In addition to this, the author introduced various standard approaches that are recognized in the sphere of security for protection against threats. At last, the author utilized Internet-based search techniques to find the most appropriate security products. The Methodology of the current paper is divided into three standard stages as follows.
Phase 1 Identification of the study area, formulation of the research questions, sampling, and establishing the primary search approach or standards.
Phase 2 Using the search strategy or criterion about existing literature, carrying out keyword searches, Boolean searches involving the combination of keywords and phrases with the operators “AND”, and “OR”, and database searches, assessing the results, and formulating selection criteria.
Phase 3 Finding and evaluating approved literature, articles, papers, websites, and web documents by the chosen primary research topic.
Figure 1 shows the distribution of references over the year. The figure portrays which year the researcher’s paper was selected to prepare the current paper. The author selected the previous research paper from year 2016 to 2024, a recently published paper. The author reviewed the paper which includes published journal and conference papers. The author searched, examined, and analyzed the paper was included in the references section of the manuscript.
Reference timeline
2.1 Inclusion/exclusion criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria aim to identify the research studies that correspond with the questions under investigation. The primary studies were identified using the inclusion criteria that we are presenting. The exclusion criteria were left out since they represent the negative version of the inclusion criteria that were specified.
Inclusion Criteria
IC 1 : Publications released on and after the year 2016.
IC 2 : Publications that have been published in peer-reviewed journals, conferences, workshops, etc.
IC 3 : English-language articles published.
IC 4 : Articles that are required to contain an abstract and title.
IC 5 : Publication that specifically addresses the subject topic such as data security, privacies encryption decryption, machine learning, blockchain, or research problems.
IC 6 : Research with subject-specific keywords included.
IC 7 : Systematic reviews, theoretical analysis, and empirical study.
Exclusion Criteria
EX 1 : Articles that are loosely connected to the research question or do not answer it.
EX 2 : Articles whose complete text cannot be accessed.
EX 3 : Articles not available in English.
EX 4 : Articles that were released almost ten years ago.
EX 5 : Studies with poor ratings or serious methodological errors.
EX 6 : Articles that don’t explicitly address privacy and data security concerns is excluded.
EX 7 : To prevent prejudice from incorporating the same study more than once, remove duplicate publications.
2.2 Algorithms, tools, and techniques Implemented
Alogrithm 1 : RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are a few examples of the particular encryption techniques used in the studies.
Alogrithm 2 : Determine which machine learning techniques—such as anomaly detection methods (e.g., k-means clustering, isolation forests)—are utilized to detect data breaches or to ensure data security.
Tool 1 : To manage and organize references, use programs like Scispace, Citation Gecko, and Open Knowledge Map.
Tool 2 : To create visual representations of the data in MS Excel (graph).
Tool 3 : To check Grammar and Spelling Grammarly software tools are used.
Tool 4 : To draw the picture tools such as Paint, Smart Draw, and Origin-Lab are used.
Tool 5 : iThenticate is used for Plagiarism detection.
Techniques for Search
Technique 1 : Use Boolean operators and specified keywords to search IEEE Xplore, Scopus, and Google Scholar. The following query is an example: “data security” AND “privacies” AND (encryption OR data protection) AND “2016–2024”.
3 Advancing IoT, Big Data, and cloud integration: novelty in current research
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, the convergence of the IoT, Big Data, and Cloud computing stands at the forefront of innovation. Each domain, when studied individually, offers significant advancements and benefits. However, the integration of these technologies opens up unprecedented possibilities, presenting both opportunities and challenges. This research work provides the novel aspects of combining IoT , Big Data , and Cloud computing . Further, the paper highlights the transformative impact on various industries and emerging security concerns. This study aims to uncover new insights and propose solutions to ensure the safe and efficient deployment of integrated systems by exploring how these technologies interact. The major contributions of the current research paper are as follows:
Integration of IoT, Big Data, and Cloud Computing : The paper examines the combined effects and security threats of integrating IoT, Big Data, and Cloud computing.
Role Analysis : It offers an in-depth analysis of how IoT, Big Data, and Cloud storage work together.
Data Flow : The paper explores the process where data generated from IoT devices becomes Big Data and is subsequently stored in the Cloud.
Security Threats : It highlights the potential security threats during the transmission and storage of data.
Proposed Protections : The authors propose standard approaches to protect against potential attacks that could compromise the data.
Digital Forensics : The paper discusses digital forensics as a method to preserve and analyze digital data post-attack, aiding in tracing the attacker’s footprint and identifying patterns and trends.
Recent Data Security Technologies : In this research work, the authors addressed new technologies that have the potential to significantly reduce threats in cloud-IoT environments.
Research Focus : Authors determine the researcher’s field of expertise methodically.
4 Security goals in Cloud-IoT environments: a comprehensive overview
Security in Cloud-IoT environments is paramount due to the interconnected nature of devices and the vast amount of sensitive data they generate and process. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services has become a major challenge as cloud computing and IoT devices become more integrated into everyday life and vital infrastructure. In an ever-changing digital ecosystem, this comprehensive overview seeks to explore the major security objectives, difficulties, and tactics that are crucial for protecting Cloud-IoT environments.
Figure 2 shows security objectives in a cloud environment. To guarantee the confidentiality, integrity, availability, and general security of data, applications, and resources hosted in the cloud, security objectives for a cloud environment are essential. These goals assist businesses in defining their security objectives and directing the application of suitable security solutions. For the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services hosted in the cloud, security objectives for the environment are crucial. These goals aid organizations in developing a framework for putting security measures in place and in defining their security objectives. To respond to changing threats and keep a solid security posture in the cloud, it is essential to regularly assess and update security goals and procedures.
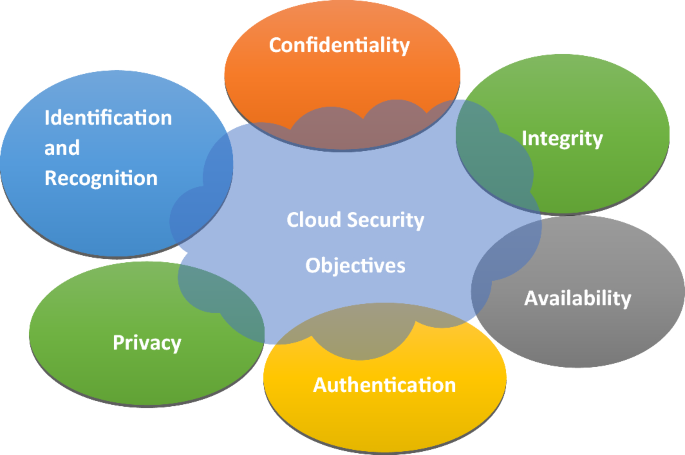
Security objective in cloud environment
Confidentiality Confidentiality refers to safeguarding or protecting critical data from unauthorized access. The information will only be revealed or accessible to those persons who are authorized (Schiller et al. 2022a ).
Identification and Recognition Identification is a unique way to provide attributes to users or devices to differentiate from other users. Recognition is related to the validation of the claimed identity. When a user gives a password, it matches with the saved password and identifies an individual (Schiller et al. 2022a ).
Privac: To safeguard the privacy of individual data, security measures are implemented. It also ensures that data must be responsibly handled. It involves protecting personnel information (Schiller et al. 2022a ).
Authentication: The authentication measures procedure involves confirming the identities of individuals and protecting against unauthorized access. It involves the user providing a username and password (Schiller et al. 2022a ).
Availability Availability refers to the accessibility and usage of data when required by an authenticated person. It involves maintaining availability includes protecting against denial of service, downtime, and disruptions that can hamper the availability of data (Schiller et al. 2022a ).
Integrity Integrity ensures that data should be consistent, accurate, and unchangeable throughout its lifecycle. It also ensures the trustworthiness of the data (Schiller et al. 2022a ).
Case studies that demonstrate how these security goals are implemented in practice are described below:
Estonia’s e-Residency Program: e-Residents receive a government-issued digital ID that is stored on a blockchain. This ID allows them to securely sign documents, access Estonian e-services, and run a business remotely.
MediLedger in Pharmaceutical Supply Chain: MediLedger uses blockchain, a decentralized ledger, to ensure data integrity and transparency.
Civic’s blockchain-based identity verification: It allows users to create and verify digital identities. Further, Enigma uses secure multi-party computation ( sMPC ) on the blockchain to ensure that data can be shared and analyzed without being exposed.
5 Taxonomy of Cloud-IoT environment
In the rapidly growing landscape of the Cloud-IoT environment, understanding the taxonomy is significant for navigating the complexities of connected devices and realizing their full potential in the swift diversification of the Cloud-IoT ecosystem.
5.1 The relationship between IoT, Big Data, and cloud computing
There is a strong synergistic relationship between Cloud Computing, Big Data, and the IoT, with each technology augmenting the other’s capabilities. IoT enables data collection which is uploaded to the cloud for storage and processing. These bulk data are accumulated in the cloud and form a large volume of data known as Big Data. Big Data tools and techniques are applied to these bulk data for processing and scrutiny of data on the cloud. Real-time monitoring and analysis are made possible by the convergence of cloud computing, Big Data, and IoT. This makes it possible to respond and act quickly, which optimizes processes, boosts productivity, and enhances user experiences.
Figure 3 illustrates the relationship between the IoT devices that are placed at remote locations. Data is generated from IoT devices which are stored and analysed on the cloud using Big Data tools. Finally, after processing data on the cloud decision is made. IoT, Big Data, and cloud computing work together to create a potent trio that propels efficiency and innovation in a wide range of sectors, including manufacturing, agriculture, smart cities, and healthcare.
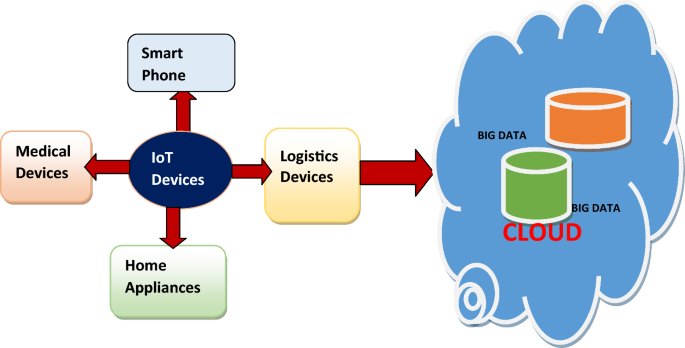
Relationship between IoT, Big Data, and cloud computing
5.1.1 Understanding the dynamics of Big Data
Big Data in a few years come out as an ideal that has provided an enormous amount of data and provided a chance to enhance and refine decision-making applications. Big Data offers great value and has been considered as being a driving force behind economic growth and technological innovation (Dutkiewicz et al. 2022 ). Machines and humans both contribute to data through online records, closed-circuit television streaming, and other means. Social media and smartphones create enormous amounts of data every minute (Ram Mohan et al. 2018 ). Big Data is a large amount of data that is fast and complex. These data are not easy to process using conventional methods. Today Giant Companies substantial portion of the value advanced from data generated by the company which is continually examined to produce better and advanced products. A prime example of Big Data is the New York Stock Exchange, which creates one terabyte of fresh trade data daily. Big Data characteristics are defined by the 4 V’s i.e. Volume, Variety, Velocity, and Veracity which is shown in the figure below. Big Data involves three main actions integration, managing, and analysis.
Figure 4 A and B illustrate the essential 4 V’s i.e. Variety, Volume Velocity, and Veracity of Big Data through 4 blocks. Volume block represents the size of data that grows exponentially such as Peta byte, Exa byte, etc. It represents how much information is present. The volume of data is increasing exponentially. Velocity block shows that data is streaming into the server for analysis and the outcome is only useful if the delay is short. It is used to portray how fast information can be available. Data must be generated quickly and should also be processed rapidly. For example, a healthcare monitoring system in which sensors record the activities that occur in our body and if an abnormal situation occurs needs a quick reaction. Variety blocks represent, a variety of data and various formats, types, and structures of data that exist such as sensor data, PDF, photo, video, social media data, time series, etc. The veracity block ensures that data should be consistent, relevant, and complete in itself. Hence, the error can be minimized accurate results can be produced and decisions can be taken through analysis of the result.
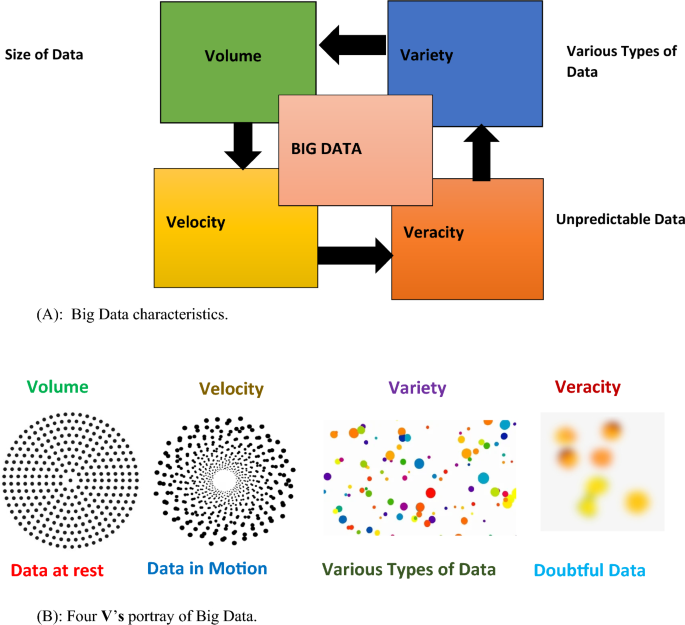
A Big Data characteristics. B Four V’s portray of Big Data
Apart from its several advantages Big Data faces security challenges as well such as attackers can damage or steal information where a large volume of data is stored such as cloud and fog. An attacker can steal data and he/she can attempt to study and analyze data and thereafter can change the outcome of the result accordingly. Therefore special protection and privacy of data such as cryptographic defense mechanisms should be provided so that data can be kept safe and secure (Kaaniche and Laurent 2017 ). The healthcare industry is one of the most promising areas where Big Data may be used to effect change. Large-scale medical data holds great promise for bettering patient outcomes, anticipating epidemics, gaining insightful knowledge, preventing avoidable diseases, lowering healthcare costs, and enhancing overall quality of life. To address security and privacy threats in healthcare, the author has provided some suggested strategies and approaches that have been documented in the literature, while also outlining their drawbacks (Abouelmehdi et al. 2018 ).
5.1.2 Connecting the world: the evolution and impact of the Internet of Things
The development of the Internet of Things has revolutionized the Internet market around the world. The Internet of Things is a device that when connected to the Internet transmits, receives, and stores data over the cloud. The Internet of Things is embedded with several devices such as sensors, physical devices, and software to control the devices. IoT can be device can include anything that contains a UID (Unique Identification Number) that can be used to in identify uniquely over the internet. IoT devices have several benefits such as high efficiency, providing more business opportunities, high productivity, increased mobility, and many more. Apart from the above-mentioned benefits, IoT devices can also be deployed to monitor tool execution and find and diagnose the issues before any major break happens in the functioning of the device, also in addition it reduces maintenance costs and thereby increases the throughput. IoT devices can able to gather large volumes of data beyond any human can think of it. As the world is developing data is considered to be an oil for the development of any country, so to cope with new challenges IoT devices should also be made smarter than traditional devices which can able to guide and make decisions. To achieve such objectives IoT devices should be accompanied by machine learning and artificial intelligence technology to enhance the performance of the device and to make sense of collected data.
Figure 5 illustrates the key components of IoT devices. The components are the building blocks of IoT which is shown in the diagram. These “DGCAU” components collectively facilitate the working of the IoT devices. Each component is significant in terms of productivity, data collection, monitoring, and connectivity. In Fig. 5 ‘D’ stands for IoT Device. IoT devices are those which are such as medical equipment, smart meters, home security systems, smart lights, etc. which are used to collect data. The second ‘G’ stands for Gateway which is similar to a centralized hub that is used to interconnect IoT devices and sensors to the cloud. Advanced gateway facilitates data flow in both directions between IoT devices and the cloud. ‘C’ indicates the cloud aids in the storage of data and simultaneously analyzing data. Rapid processing and strong control mechanisms enable cloud-enabled IoT devices to minimize the risk of attack. User identities and data are protected by strict authentication methods, encryption tools, and biometric authentication in Internet of Things devices. ‘A’ signifies the Analysis of data that was stored in the cloud to determine the outcome. Analysis tool studies large amounts of data and produces useful information, which is helpful in decision-making. The last component ‘U’ represents the user interface or UI module that facilitates the user to administer the IoT device with which they are interacting. it is generally a graphical user interface that includes a display screen, mouse, keyboard, etc.
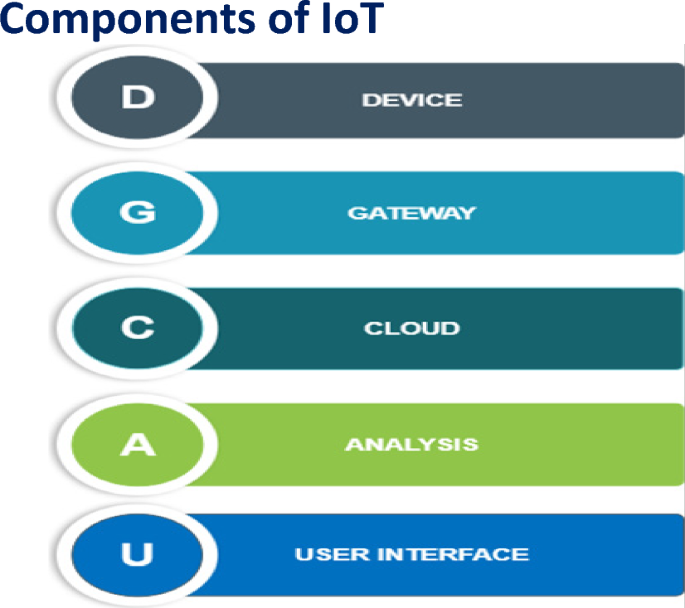
Key components of the Internet of Things
Figure 6 shows the various applications of the IoT which are technology paradigms used to interconnect the devices with the Internet, collect data, share data, transmit data, and act upon data. IoT has enormous application in day-to-day life therefore enabling us to perform our work widely and conveniently . Smart Lighting IoT can be used to operate the light remotely through a smartphone. Transportation IoT is used to track vehicles and goods in real-time. IoT finds application in health which enables doctors to monitor the patients remotely. In Logistics IoT helps to keep track of goods and vehicle devices. IoT is useful for smart framing because IoT sensors can monitor, measure, and track soil moisture, nutrients needed for crop fertilization, and irrigation needs. IoT devices used in retail monitor the department’s real-time inventory level and stock and forward orders when a product is discovered to be out of stock. With features like motion sensors, doorbell cameras, and video surveillance , smart home security systems employ the Internet of Things to monitor and secure houses. IoT is used by smart grids to increase the effectiveness and dependability of electricity delivery. Water quality indicators like pH, turbidity, chlorine levels, and pollutants are continuously monitored by IoT sensors. Smart meters with IoT capabilities allow for real-time monitoring of utility consumption. IoT equipment on autonomous vehicles processes sensor data in real time. This entails reading and assessing the environment to make deft choices regarding safety, navigation, and vehicle control. Wearable gadgets gather information on activities, health, and other topics before sending it for analysis to smartphones or the cloud for processing.
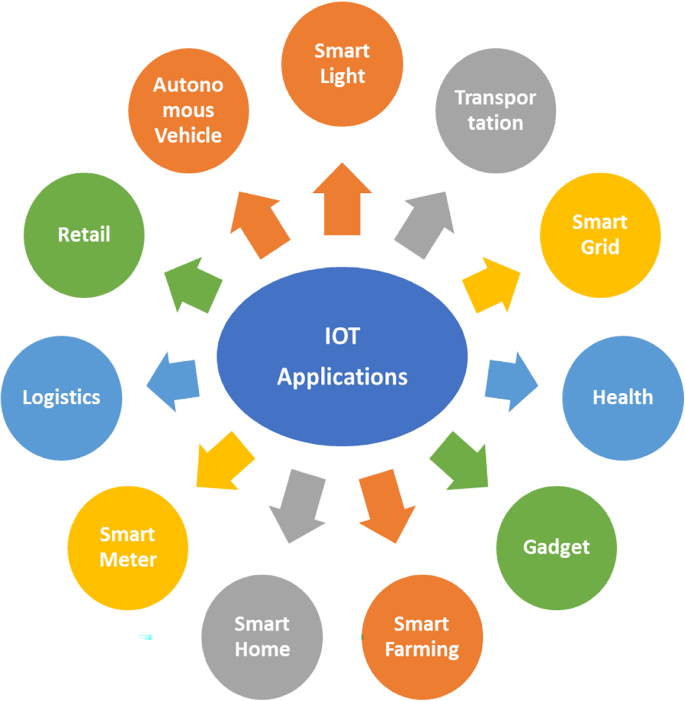
Internet of Things applications
Apart from the benefits of IoT devices in day-to-day life, IoT devices suffer security threats as well. The rapid growth of IoT devices has revolutionized how we interact with technology. As the number of IoT devices increases the security concern also increases simultaneously. The author addresses the issue of sharing sensitive data securely for designated recipients in the context of the Blockchain Internet of Things (B-IoT) (Yin et al. 2022 ). The author has scrutinized the security flaws in computer systems based on cloud, blockchain, IoT, and fog computing (Mishra et al. 2022 ; Yao 2022 ; Abdulkader 2022 ). Security challenges and threats in IoT and cloud environments addressed by various authors are presented in the papers (Pandey et al. 2023 ; Ray and Dutta 2020 ; Bedi et al. 2021 ). Cloud Computing and IoT Using Attribute-Based Encryption approaches are developed by authors found to be very effective in the security domain (Mihailescu et al. 2022 ; Henze et al. 2017 ). The author presents D-CAM, a solution for achieving distributed configuration, authorization, and management across borders between IoT networks (Simsek 2023 ). The study presented by the author is a novel handshake protocol for the broker-based publish/subscribe paradigm in the Internet of Things that offers key exchange-based authentication, authorization, and access control (Shin and Kwon 2020 ; Stergiou et al. 2018 ).The goal of a systematic literature review (SLR) paper is to examine the body of research on cloud computing security, risks, and difficulties that are presented by authors (Wang 2021 ). The primary issue in the cloud environment has been confirmed to be data access, despite the security measures being deemed dependable (Javid et al. 2020 ; Gai et al. 2021 ; Shukla 2022 ). We suggested an effective data access control method that uses optimal homomorphic encryption (HE) to get around this issue (Gnana Sophia et al. 2023 ). The paper highlights the edge computing security and privacy requirements (Yahuza et al. 2020 ). Multiple encryption techniques are presented by the authors which are significant in protecting privacy and data security (Sharma et al. 2019 ; Silva et al. 2018 ; Bertino 2016 ). The author proposes a distributed machine learning-oriented data integrity verification scheme (DML-DIV) to ensure the integrity of training data (Zhao and Jiang 2020 ). The researcher introduced an identity-based (ID-based) RDIC protocol including security against a malicious cloud server which is presented in the paper (Yu et al. 2017 ; Sookhak et al. 2018 ). The authors studied various security challenges concerning IoT devices, Big Data generated by IoT devices, and cloud and presented them in the paper (Akmal et al. 2021 ; Awaysheh et al. 2022 ; Tang 2020 ; Shi 2018 ).
5.2 Navigating the cloud: exploring the world of cloud computing
Cloud Computing refers to Internet-based computing, where shared resources data, software, and information are to the customer and devices on demand. The term “cloud” used to appear on the Internet. Huge memory space and inexpensive, high-performance computing are made possible by the cloud computing paradigm. Users can get cost savings and productivity benefits to manage projects and develop collaborations by moving their local data management system to cloud storage and utilizing cloud-based services. Information and knowledge extraction is greatly aided by computing infrastructure, particularly cloud computing. The services for cloud computing are provided using the network, generally the Internet. The characteristics of cloud computing include broad network access, on-demand service, rapid elasticity, and many more. With the help of the cloud, numerous services are accessible to clients. Broadly there are three types of services offered that enable the client to use software, platform, and infrastructure. Several types of cloud can be subscribed to by anyone as per the requirement of an individual or any organization. These include private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid cloud. Private cloud solely owned by any business houses. In this type of cloud infrastructure software is preserved on a private network and hardware and software entirely belong to the organization. Public clouds are commonly cloud services that are allotted to various subscribers. Third-party owned and operated the cloud resource.
The public cloud is mostly used for online office applications, testing, development, etc. A hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private clouds, which is implemented by a couple of interrelated organizations. Common types of cloud services are presented through the 3-layer architecture of Cloud Services in Fig. 7 and each one is discussed.
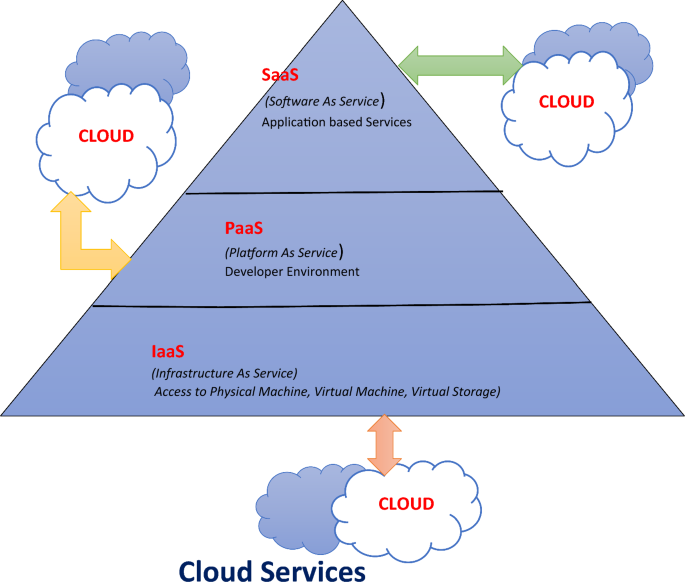
3-Layer architecture of cloud services
Figure 7 exhibits the different types of cloud and services provided by the cloud. The figure conveys the three-layer architecture of the cloud. IaaS makes virtualized computing resources available via the internet, enabling customers to pay-as-you-go access and manage the essential parts of the infrastructure. These resources often include storage, networking, virtual machines, and other things. Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing architecture that offers developers a platform and environment to create, deploy, and manage applications. PaaS provides a variety of tools and services that speed up and improve the efficiency of the application development process. A cloud computing approach called Software as a Service (SaaS) allows users to access software programs online. SaaS has many benefits, including affordability, scalability, and accessibility.
Because crucial data is processed and stored on the cloud, for instance in Internet of Things applications, it also poses security and privacy issues (Alouffi et al. 2021 ; Hamzah Amlak and Kraidi Al-Saedi 2023 ; Yu et al. 2022 ). Cloud security is an important area where authors have tried to find the best possible solution through their research they have highlighted the challenges of possible solutions to the problem through finding and investigation in the paper (Gupta et al. 2022 ; Chaowei et al. 2017 ; Wang et al. 2021 ).
To ensure the integrity of data kept in the cloud, the author’s study proposes an effective public auditing technique that makes use of Third third-party auditor (TPA) (Reddy 2018 ; Hiremath and Kunte 2017 ; Yan and Gui 2021 ). The author proposes an efficient certificate-based data integrity auditing protocol for cloud-assisted WBANs (wireless body area networks (Li and Zhang 2022 ). The author proposed a secure architecture by associating DNA cryptography, HMAC, and a third-party auditor to provide security and privacy (Kumar 2021 ; Duan et al. 2019 ). Adversaries are always coming up with new ways to get access to users’ devices and data through developing technologies like the cloud, edge, and IoT. The author discussed various attacks along with security solutions (Pawlicki et al. 2023 ). The paper highlights the research challenges and directions concerning cyber security to build a comprehensive security model for Electronic health records (Chenthara et al. 2019 ; Hou et al. 2020 ; Ishaq et al. 2021 ; Jusak et al. 2022 ). The author mentioned the research and analysis of privacy-preserving data mining (PPDM) and classified using various approaches for data modification in the research paper (Binjubeir et al. 2020 ).
Even with all the benefits mentioned, there are security and privacy issues while using cloud computing (Nanda et al. 2020 ; Himeur et al. 2022 ). The issue of data security and privacy for Big Data is complicated by the use of cloud computing for Big Data management, storage, and applications. Since cloud services are typically offered on a common infrastructure, there is always potential for new attacks, both internal and external, such as password theft or application programming interface (API) flaws. The author has proposed a software architecture model by using approaches like hardware security extensions (Intel SGX) and homomorphic encryption. To improve data security in large data cloud environments and defend against threats, a virtualization design and related tactics are suggested by the author. The TID (Token Identification) model developed by the author provides security to the data. The user has various access rights as a client. The authentication access token establishes a connection with the user account after the user logs into the cloud network. The researchers have developed the Remote Data Checking (RDC) technique, which uses the sampling technique to evaluate the integrity of data that is outsourced across remote servers. Authors developed the techniques for remote data auditing that are very beneficial in ensuring the integrity and dependability of the data that is outsourced. Data, auditing, monitoring, and output these elements are all included in the DAMO taxonomy. The author in his paper offers a unique security-by-design framework for the implementation of BD (Big Data) frameworks via cloud computing (Big Cloud) (Ye et al. 2021 ). Various data security issues in the Big Data cloud computing environment are addressed by the authors in his paper. Various methods for safeguarding privacy and data security in public clouds are covered in the article (Jain et al. 2016 ). A multi-cloud architecture with privacy and data security enabled is suggested by the author. To increase user security on SNg (Social Networking) by utilizing techniques that can give data about BD technology (Big Data) greater privacy. This approach is described by the author in the paper along with various metrics and usage-related outcomes. The author examines financial risk analysis and related regulatory studies using blockchain and Big Data technologies. A secure cloud environment can be achieved by using a hybrid cryptographic system (HCS), which combines the advantages of symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
Figure 8 shows a hierarchical structure created to handle and process data and applications efficiently depending on how close they are to the user or the source of the data. “Hierarchical edge computing” refers to the interplay between these three layers, cloud, fog, and edge. The Cloud Layer is a centralized data processing center that provides abundant computing and storage capacity for handling and storing enormous volumes of data as well as running sophisticated applications. The growths of the Internet and its associated ideas, such as edge computing, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things, have had a permanent impact. The cloud layer is a highly scalable data center that is perfect for managing large-scale applications and services because they can extend horizontally to manage increased workloads.
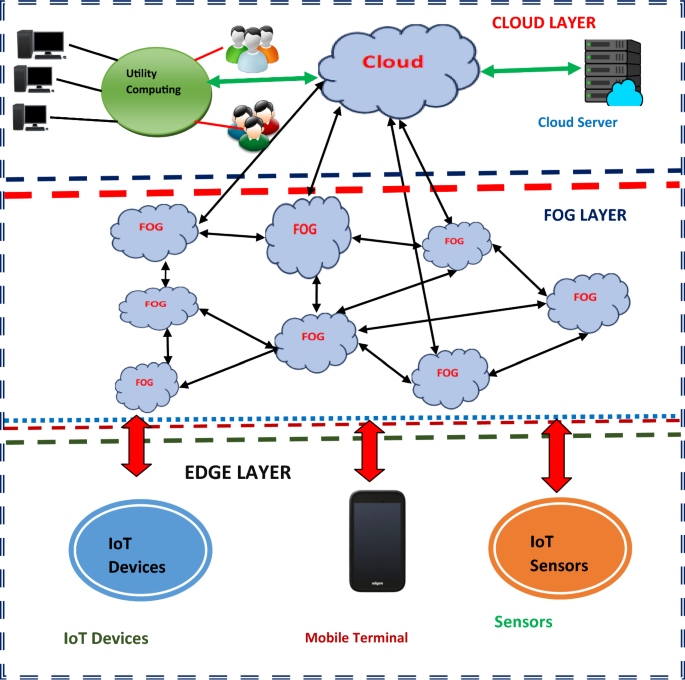
Hierarchical edge computing
The fog Layer is an intermediate layer after the cloud layer which spreads and distributes processing responsibilities among several local servers or devices, which can be very useful for IoT applications with many data sources. Fog computing is ideal for latency-sensitive applications that demand quick responses. Virtual components called cloudlets are employed in fog computing. Fog computing has emerged as a promising paradigm in overcoming the growing challenges (e.g., low latency, location awareness, and geographic distribution) arising from many real-world IoT applications, by extending the cloud to the network edge. To facilitate data offloading and computation, these virtual computers offer a micro data centre close to mobile devices (Lu et al. 2020 ). Fog computing offers new insights into the extension of cloud computing systems by procuring services to the edges of the network. It shortens the time it takes for data to go to the cloud and back by processing it closer to the source. The edge layer, which is frequently located adjacent to IoT medical devices themselves (Muzammal et al. 2018 ), is the one that is nearest to the data source or end users. A promising paradigm that expands on cloud computing capabilities is edge computing. It processes data instantly, allowing for extremely quick replies devices, sensor devices, and industrial machinery, mobile terminals are examples of edge devices that can function autonomously and make decisions in the present without relying on a central cloud infrastructure (Ghaffar et al. 2020 ; Jiang et al. 2016 ). Big Data applications are a risk for cyber security assaults, as these attacks directly affect applications utilized across several sectors, such as Big Data analytics. The authors presented a novel data encryption approach, which is known as Dynamic Data Encryption Strategy (D2ES) to protect and safeguard the data which proves promising in cloud computing. Encrypted data can be obtained by cryptography methods, enabling secure communication links within the networking system. Researchers suggested the blockchain-based Shamir threshold cryptography solution for IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) data protection. An improved data security in mobile edge computing, the Fine-Grained Access Control mechanism (FGAC) is suggested to guarantee data security during data access (Ahmed et al. 2021 ).To analyze and investigate the data reduction at the fog level, researchers attempted to create a model. This researcher has successfully applied methods including artificial intelligence, principal component analysis (PCA), and the Naïve Bayesian classifier for data reduction.
6 Exploring the complex landscape of Cloud-IoT threats: an in-depth analysis
Security concerns are growing along with the integration of Cloud Computing and the IoT. Numerous dangers and vulnerabilities that might compromise the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of data and services are brought about by the junction of these two technologies. We examine the subtleties, possible effects, and vital necessity of strong security measures to protect against changing hazards in interconnected environments as we delve into the complex nature of Cloud-IoT security concerns in this analysis.
Figure 9 illustrates the numerous types of attacks that can take place in the cloud. These Attacks can harm the cloud service provider as well as cloud customers. The attacker is an individual who attempts to use a cloud infrastructure, platform, or service’s vulnerabilities or flaws for nefarious reasons in the world of cloud computing. Because they frequently house significant data and offer computational resources that may be used for a variety of purposes, such as launching cyber-attacks, stealing confidential information, or causing disruption, cloud systems are very alluring targets for attackers. For different purposes, including data theft, service interruption, or resource exploitation, attackers target cloud environments. To breach cloud systems, attackers use a range of methods and tactics. These attack methods can include insider threats, sniffer attacks password change SQL-Ingestion, Eavesdropping, malware, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, phishing, and more (Basit et al. 2021 ; Ullah et al. 2019 ; Jahromi et al. 2021 ).
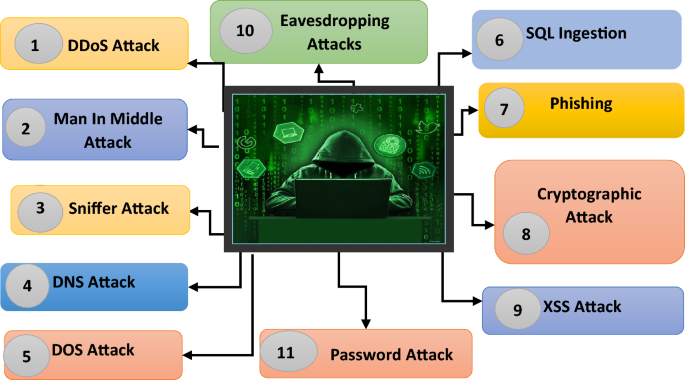
Threats in cloud computing environment
DDOS Attack A distributed denial-of-service attack aims to disrupt regular network operations by flooding the network with traffic. Denial-of-service attacks aim to prevent end users from accessing the network.
Man-in-Middle Attack In a man-in-middle attack, the attacker generally modifies the conversation between the two parties. In a man-in-the-middle attack, attackers generally eavesdrop on sensitive information and alter the conversation. The integrity and security of sensitive data are seriously threatened by MitM attacks.
Sniffer Attack It is an attack in which an unauthorized person intercepts and gains control over network traffic. The goal is to capture and examine the data when it passes over the network.
DNS Attack The domain name system attacks the domain name system, which is responsible for converting human name readable to IP address. DNS attacks have the potential to affect the DNS infrastructure’s availability, integrity, and confidentiality, which could cause interruptions to internet services.
DOS Attack A Denial of Service (DoS) assault involves the exploitation of a single source, typically a compromised device or computer, to overwhelm a target’s resources and cause a loss of service.
SQL Ingestion In SQL (Structure Query Language Ingestion), attackers ingest harmful code inside the parameters of a web application. The main goal of attackers is to manipulate SQL databases. In this type of attack, the attacker gains the advantage of bad input, which enables the attacker to execute the SQL command.
Phishing Attack In Phishing attackers use some trick to expose delicate information, for example, username, personal information, password, and credit card details. Phishing attacks sometimes use the personas of reliable companies, banks, or websites to trick people into doing things that could jeopardize their security.
Cryptographic Attacks Cryptography is important to ensure confidentiality and integrity and authenticate the user. The attacker exploits vulnerability or weakness in the existing system. Attackers compromise the security of cryptographic systems.
XSS Attacks Cross-site scripting (XSS) is one of the serious attacks that occur when vulnerable code which is in the form of a script is injected into the web page of the user. The objective of the attacker is to steal sensitive information about the user by running the scripting code in the user’s browse.
Eavesdropping Attacks Eavesdropping is a kind of attack in which attacker unauthorized person tries to listen to or sniff the conversation between two people and steal information. In this type of attack, the attacker even manipulates the information.
Password Change Request Interception Attack The assailant attempts to intercept legitimate users’ password changes. Interception of this kind could happen during a browser-server conversation.
7 Exploring research trends and areas of focus
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, researchers and academics are continually exploring new trends and areas of focus within their respective fields. To keep ahead of new difficulties, seize opportunities, and encourage innovation, this investigation is essential. We explore the current research trends and areas of attention in a variety of disciplines in this overview, offering insight into the cutting-edge subjects that are influencing the direction of technological and scientific advancement. After scrutinizing the number of published research papers we came across various domains in which researchers have worked and proposed various security frameworks.
Table 1 represents the research work and focus of various researchers in field security. From the table above it can be concluded that researcher have focused on Cloud Computing and their finding are more concentrated on Cloud security and the Internet of Things. The researcher primarily focused on the development of security algorithms to protect the data from being damaged or corrupted by cyber attackers. Through study, it was found that researchers have developed innovative techniques by making use of machine learning techniques, and blockchain technology to safeguard data developed for the Internet of Things.
Cryptography is another eminent way to protect our data. Researchers have created algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data prominently so that data can be safely transmitted over the network. A method like PSEBVC: Provably Secure ECC and Biometric Based Authentication Framework is developed by the author as a countermeasure for attacks.
In the digital landscape, the risks of cyber-attacks are growing enormously which is becoming a challenge for both organizations and individuals. A comprehensive examination of attack vectors and mitigation strategies is essential for understanding and effectively countering these attacks (Wylde et al. 2022a , b ). Through an analysis of numerous attack pathways and related mitigation techniques including artificial intelligence-based solutions discussed in paper (Al Hamid et al. 2017 ; Abed and Anupam 2022 ). This research paper aims to offer important insights on how to enhance security and defend against cyber threats in a constantly changing security environment. The objective of this analysis is to provide individuals and organizations with the necessary knowledge and tools to improve their digital security and minimize risks in the constantly changing threat landscape. To do this, each attack mechanism is thoroughly examined, and appropriate remedies are explored through Table 2 .
Table 2 is a complete description of the investigation of the several research papers related to security threats that exist, various categories of attackers that occur on the cloud, and countermeasures that can be taken to prevent attacks summarized in the Table by the author. The table shows how attacks affect the data and what standard approaches were developed by researchers to protect data.
8 Unveiling the intricacies of digital forensics in Cloud-IoT environments
Digital Forensics is a branch of forensic science that concentrates on recovery of data, analysis of data and exhibit the digital evidence that is found on electronic devices. The IoT Forensics can be identified as part of Digital Forensics. The objective of IoT Forensics is to explore digital information in an authorized manner. IoT forensics data can be accumulated through IoT devices, sensors, networks, and cloud. There are some differences between security, IoT, and forensics. The protection against physical and logical security threats is provided by IoT security adopts multiple methods to protect from threats and minimize attacks (Unal et al. 2018 ). Forensics examines the data present in the devices and recreates the happenings by utilizing investigative methods to preserve and analyze digital data. Post-mortem examinations are the main focus of forensics i.e. discovering shortcomings that emerged from the event. Forensic experts obtain digital proof throughout the actual event with the help of standard approaches used in forensic analyses of physical proofs of electronic data to determine and reframe the events by storing and analysis of digital information using different methods of investigation. Some authors have presented detailed studies to investigate the forensic issues in cloud computing and provide possible solutions, and guidelines, including existing case studies (Morioka and Sharbaf 2016 ; Al-Dhaqm et al. 2021 ). The paper offers an enhanced blockchain-based IoT digital forensics architecture that builds the Blockchain’s Merkle tree using the fuzzy hash in addition to the traditional hash for authentication (Mahrous et al. 2021 ). Authors Almutairi and Moulahi ( 2023 ) trained models locally using federated learning on data stored on the IoT devices using a dataset created to simulate attacks in the IoT environment. In order to make the blockchain lightweight, the authors next carried out aggregation via blockchain by gathering the parameters from the IoT gateway (Almutairi and Moulahi 2023 ).
The IoT has revolutionized various sectors through seamless device interactions, yet it has introduced significant security and privacy challenges. Traditional security measures often fall short due to IoT’s distinct characteristics like heterogeneity and resource limitations. Danish Javed et al. ( 2024a ) explored the synergy of quantum computing, federated learning, and 6G networks to bolster IoT security. Quantum computing enhanced encryption, while federated learning preserved data privacy by keeping training data on local devices. Leveraging 6G’s high-speed, low-latency capabilities allows for secure, real-time data processing among IoT devices. The study also reviewed recent advancements, proposed a framework for integrating these technologies, and discussed future directions for IoT security. Recent innovations in network communication have revolutionized the industrial sector with automatic communication through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) . Despite its benefits, the increased connectivity and use of low-power devices in IIoT heighten vulnerability to attacks, and its diverse nature complicates centralized threat detection. To tackle this, authors Javed et al. ( 2023 ) proposed a fog-based Augmented Intelligence (IA) defense mechanism that uses GRU and BiLSTM deep learning classifiers for anomaly detection and secure communication. This framework (Cu-GRU-BiLSTM), which achieved up to 99.91% accuracy, surpassed existing threat detection methods, proving its effectiveness for securing IIoT environments (Javeed et al. 2023 ).
Further, the hybrid approach proposed by Danish Javed et al. ( 2024b ) enhances intrusion detection in federated learning (FL) for IoT by addressing existing limitations. Here, CNNs identify local intrusion patterns by extracting spatial features, while BiLSTM captures sequential patterns and temporal dependencies. Using a zero-trust model, data stays on local devices, and only the learned weights are shared with the centralized FL server. The server then combines updates to improve the global model’s accuracy. Tests on CICIDS2017 and Edge-IIoTset datasets show this method outperforms centralized and federated deep learning-based IDS.
9 Advancements in security threat detection and avoidance
With the constant advancement in sophistication of cyber attacks, enterprises, and individuals alike are obliged to use innovative methods and technologies to detect, prevent, and mitigate potential security breaches. Threat detection is seeing tremendous breakthroughs, enabling defenders to keep one step ahead of malicious actors. These advancements include machine learning algorithms and behavior analysis methodologies. This ongoing change emphasizes how crucial it is to take preventative action to protect sensitive data and maintain digital trust in an environment where dangers are becoming more complicated.
9.1 Harnessing the power of machine learning
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing models and algorithms that enable computers to learn from data and make decisions or predictions without having to be explicitly programmed to do so. As a result, machine learning algorithms are beneficial when dealing with vast amounts of data since, after being trained on the data (Ali et al. 2020 ), the trained model uses its learning experience to present precise outcomes on new data. Data generated by IoT devices may suffer from threats (Safaei Yaraziz et al. 2023 ). Today Machine Learning proves to be one of the strongest tools to identify threats and maintain the integrity of data in transmission. The foundation of machine learning is the algorithms that are used to train the models. The first step in using machine learning to address a problem is gathering data. Next come tasks like data preparation, data analysis, training, testing, and eventually deploying the model for real-world application. Two types of ML problems can be solved by supervised machine learning algorithms: regression and classification. Classification is used to solve problems with binary target variables ( yes / no ), while Regression ML algorithms are used to address problems of similar nature when the target variable is continuous. A phishing attack has become one of the most prominent attacks faced by internet users, and governments. The attacker(s) transmits URL(s) to the intended victims via text messaging, social networking, or spam messages. They do this by mimicking the behavior of authentic websites when creating website pages. Malware attack during data in transit is a common type of attacks that can manipulate the data and damage the data. To prevent such attacks ML model can be one of the tools to identify such attacks and prevent them to such extents. Machine Learning algorithms have been used to build several intrusion detection systems, improving the systems’ ability to identify threats and enabling uninterrupted business operations (Pathak et al. 2023 ). Despite many benefits that SDN(Software-Defined Networking) offers such as offer nimble and adaptable network growth, malicious attacks that can eventually prevent network services are unavoidable (Unal et al. 2018 ). Machine learning has been used in several studies to detect distributed denial of service (DDoS) threats in SDN (Software-Defined Networking) environments (Morioka and Sharbaf 2016 ). ML models are being trained on numerous datasets to build models that can detect cloud attacks with elevated accuracy. Various classifier is implemented in the ML model to identify attacks such as SVM, Decision tree, K-NN (K-Nearest Neighbour), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), random forests, and many more. The use of random forest and K-NN classification approaches enables malware detection method proofs to be 99.7% accuracy and 99.9% in several cases (Abed and Anupam 2022 ; Morioka and Sharbaf 2016 ). These classifiers can be used with different feature engineering and feature selection strategies to create machine learning models that effectively handle certain security issues and enhance overall cyber security posture.
Figure 10 represents security threat detection using machine learning algorithms and models. The automatic detection of potential security threats and abnormalities within a file system using machine learning techniques uses a predictive model to identify the threat and classifies it as a malware file or harmless file over the system. Data breaches and other security problems can be prevented because of their ability to assist enterprises in detecting and responding to threats more quickly and effectively. In this process, it involves two important stages. The first stage is the Training stage where the model is being trained using different files. Files are sent as input to train the model. Numerous machine learning algorithms, such as decision trees, random forests, support vector machines (SVM), neural networks, and others, can be used for training the model. After the model is trained, then comes to the security stage where an unknown file is given to the model for analysis the file. For the detection of security threats, supervised learning techniques like classification and regression are frequently used. The machine learning model generates notifications for security professionals to investigate when it spots a potential security danger or abnormality. Automated responses to lessen or control the crisis may also be triggered based on how serious the threat is. Deep learning approach is used to detect pirated software and malware-infected files across the IoT network. Using color picture visualization, the deep CNN is utilized to identify harmful infections in Internet of Things networks. Secure video transmission over the cloud is discussed in the paper (Hossain et al. 2018 ). Researchers have developed Holistic Big Data Integrated Artificial Intelligent Modelling (HBDIAIM) to provide and improve privacy and security in data management (Chen et al. 2021 ). The previously developed model falls short in providing adequate data privacy and security, keeping this shortcoming in mind author (Yazdinejad et al. 2024a ) developed an Auditable Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning (AP2FL) model tailored for electronics in healthcare. AP2FL model provides secure training and aggregation processes on the server side as well as the client side. Thereby protecting and minimizing the risk of data leakage. Researchers primarily focus on Machine learning-based threat detection models to address the challenges within Consumer IoT. Using Federation Learning (FL) techniques data privacy in Consumer IoT is maintained (Namakshenas et al. 2024 ). The author suggests an approach to attack detection that makes use of deep learning (DL) algorithms to identify false data injection (FDI) assaults (Sakhnini et al. 2023 ). In the research paper, the author utilizes federated learning to automatically search for threats in blockchain-based IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) networks using a threat-hunting framework we call block hunter (Yazdinejad et al. 2022 ).
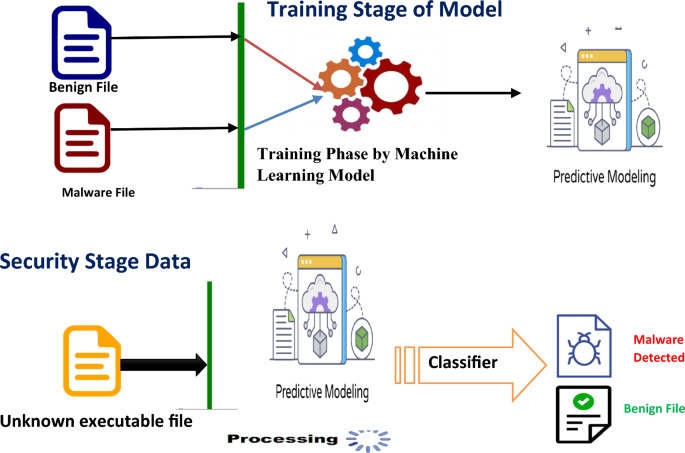
Security threat detection using machine learning technique
Real-life applications of machine learning in malware detection
AT&T Uses machine learning to protect networks and find malware that targets telecom infrastructure.
Mayo Clinic A healthcare organization that implements machine learning techniques to safeguard patient data from malware attacks and unauthorized access.
Bank of America Employs AI and machine learning to improve cyber security safeguards, identifying malware and averting breaches in data.
Cylance A cyber security firm that heavily relies on machine learning to identify and eradicate malware. To identify threats instantly, its algorithm is trained on an extensive dataset of both malicious and benign files.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) AWS uses machine learning techniques to identify threats, examining the logs and network traffic.
Symantec An American consumer-based software company that employs machine learning techniques to identify and categorize malware.
National Security Agency (NSA) To improve national cyber security, the National Security Agency (NSA) uses cutting-edge machine learning algorithms to identify and analyze malware.
9.2 Unlocking the power of blockchain: a cutting-edge safeguard technique for enhanced security in the digital landscape
Blockchain is an emerging decentralized technology that securely stores and authenticates transactions across a network of computers. Its decentralized and open structure makes it a viable option for many companies looking to improve digital security, efficiency, and trust. Although cloud computing is becoming more and more popular for processing and storing data, security, and privacy are still big issues because of the possibility of hostile assaults on wireless and mobile communication networks. Data transfer privacy and system security are improved by using blockchain technology. To put it briefly, a blockchain is auditable, can function as a distributed ledger with digitally signed data, and allows changes to be tracked back to the original data to ensure security. This demonstrates that the security of data may be guaranteed by blockchain technology (Safaei Yaraziz et al. 2023 ). The suggested IAS protocol is developed on top of blockchain technology to guarantee the security and authenticity of data transmission in cloud computing. A potential solution to the security and privacy problems in the Internet of Things is blockchain technology (Williams et al. 2022 ; Waheed et al. 2020 ). For every transaction including proper authentication, data can pass through the blockchain distributed ledger thanks to blockchain technology, which does away with the idea of an IoT central server. Blockchain technology could provide a more effective answer to the issues that IoT systems confront. Transactional privacy, decentralization, the immutability of data, non-repudiation, transparency, pseudonymity, and traceability, as well as integrity, authorization, system transparency, and fault tolerance, are the primary security features of blockchain technology. The Smart contact is verified, put into use, and then shared as a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) over a Pier-to-Pier (P2P) network as a function of blockchain (Wylde et al. 2022b ). The authors created and put into use smart, secure fuzzy blockchain architecture. This framework makes use of a unique fuzzy DL model, improved adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS)-based attack detection, fuzzy matching (FM), and fuzzy control system (FCS) for network attack detection (Yazdinejad et al. 2023 ).
Figure 11 illustrates the specification of blockchain technology concerning cloud environment. Blockchain is a distributed ledger across a peer-to-peer network. Blockchain features can help cloud services reach their full potential and address the many problems that arise. A collection of connected building blocks that are coupled and arranged in an appropriate linear sequence is used to keep a detailed record of all transactions. Decentralization, Security, transparency, availability, traceability, and many more are the essential features of blockchain technology which is highlighted by the figure presented by the author.
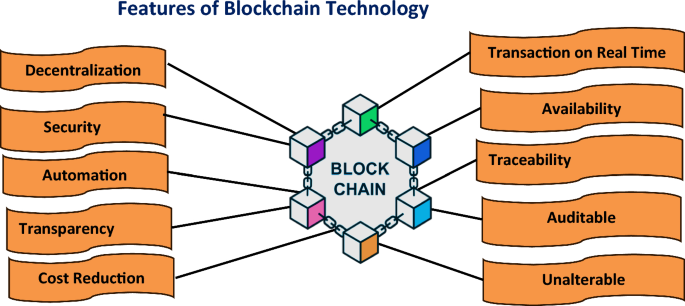
Specifications of blockchain technology
Decentralization Decentralization in blockchain technologies refers to the dividing of control and decision-making across the network users instead of concentrating on the centralized entity. It addresses the limitations of a centralized system in which security is compromised.
Security The network architecture of blockchain technology provides security by minimizing the risk of failure. The allocated characteristics of blockchain strengthen the security. Attacks on any nodes are less likely to put the entire network at risk.
Automation An intelligent system automates the carrying out of the consensus, and removes the requirement of human intervention. Smart contact enhances transaction efficiency. It automatically implements the terms and conditions of the agreement whenever conditions or terms are fulfilled.
Transparency The transactions made on blockchain appeared to every participant over the network. The method not only provides trust and security to the data but also promotes accountability which helps to gain the faith of the user.
Cost Reduction In conventional systems, the settlement of financial transactions might take several days, causing delays and capital lockups. Blockchain eliminates the need for drawn-out clearing and settlement procedures by enabling very immediate transaction settlement.
Transaction in Real Time Transactions in real time can be made over the network. Real-time transaction implements techniques like Proof-of-stake to attain quick acknowledgment of transactions. This technique permits fast agreement among nodes on the validity of transactions.
Availability Transaction availability guarantees a user’s ability to communicate with the network and complete transactions dependably. Availability may still be impacted by network maintenance, upgrades, and sporadic problems.
Traceability Traceability features of blockchain enable to provide of transparent transactions. The transaction can be can be traced by the user. Blockchain is helpful in industries where the origin, transportation, and ownership of assets need to be accurately recorded and validated because of its traceability capabilities.
Auditable Real-time transaction auditing is made possible by the blockchain ledger’s transparency and immutability. At any time, participants can check the transaction history.
Unalterable The ability of blockchain to keep a safe and impenetrable record of transactions is one of its unchangeable features. Once information is posted to the blockchain, it is impossible to change, guaranteeing the information’s integrity and immutability.
Figure 12 portrays the basic components of blockchain. These components work in agreement to form a secure ledger system. Blockchain technology comprises those elements that work in agreement to formulate a secure and decentralized ledger. Supply chain management, decentralized applications, voting systems, healthcare, and property registration are the major applications of technology. Each component plays an important role in blockchain functioning.
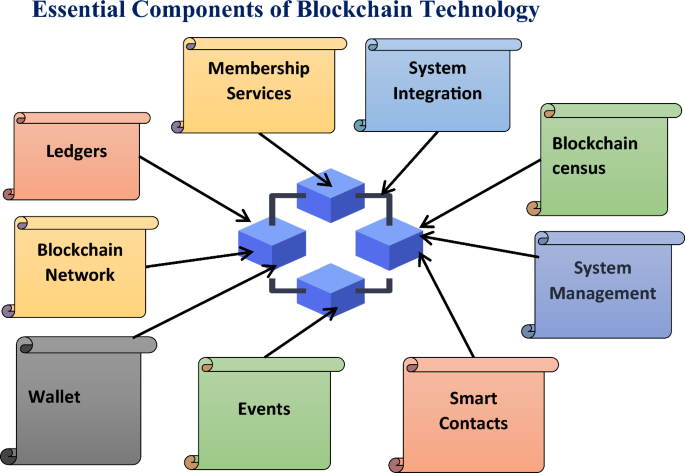
Basic building blocks for blockchain
Ledgers Ledgers in blockchain technology are used to maintain transparency of the record in transactions. Every node contains a replica of the complete ledger, protecting it from being altered or any kind of fraud. The ledger with the help of a chain of blocks carries out transactions; blocks represent every transaction in ledgers.
Blockchain Network In a Blockchain network, the user is referred to as nodes. All the users collectively validate the transaction and record the transaction in a synchronized manner. Blocks are depositors for a cluster of transactions. Blocks contain a timestamp, which is of location of preciously occurred transactions and a cryptographic has for the current blocks.
Wallet Blockchain technology wallets are tools that let users manage and store funds safely. It enables users to access the public and private keys, facilitating the blockchain’s ability to transfer and receive crypto-currency. There are two types of wallets Hot Wallets: Easy for frequent transactions and internet-connected. Cold wallets are offline and thought to be safer for storing money over time.
Events Events are essential for improving the automation, transparency, and usability of blockchain systems. They give decentralized networks a way to communicate and update in real time. The execution of smart contracts or modifications to the ledger’s current state is frequently linked to blockchain events.
Smart Contacts The blockchain records the complete history of smart contract execution, making it transparent and auditable. It has numerous applications such as in supply chain, finance, etc. Based on predetermined criteria, smart contracts carry out actions.
System Management Blockchain technology’s system management characteristics include a variety of operations and procedures meant to guarantee the safety, effectiveness, and appropriate operation of the blockchain network. These characteristics are essential to preserving the dependability and integrity of decentralized systems.
Blockchain Census The blockchain’s consensus techniques, like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), help make the system resistant to censorship. By requiring a distributed agreement from all network users, these mechanisms make it more difficult for one party to control or restrict transactions.
System Integration Establishing seamless connectivity between different blockchain networks and between blockchain technology and traditional systems is the aim of blockchain system integration. The successful communication and information sharing between diverse systems is greatly dependent upon standards, protocols, and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
Membership Services Membership services features of blockchain technology a functions and features for a member or participant management in a blockchain network. It is used to manage access control, rights, and user identity on the network. The elements of the blockchain ecosystem enhance its overall security, governance, and usefulness.
Figure 13 shows the internal workings of the blockchain technology which is used to perform any kind of transaction over the cloud securely. The figure above is a step-by-step explanation of how the transaction takes place over the cloud. In step 1 , first of all, the transaction is generated by any one of the users and request is the directed to the server for processing further. In step 2 , the server after receiving the transaction request creates a block that can appear for the transaction. Next step i.e. step 3 a chain or interconnect block is created using algorithms to authenticate the user and ensure that the request is being made by the authenticated user. Further, in step 4 , this block is distributed to other users or groups of users to grant permission for the transaction to happen. Once the group of users grants permission the transaction or block will be successfully added to the existing blocks that are shown in step 5 in the above figure. If any user disapproves or denies it, then the block will not be added to the existing chain. The modification that has taken place is permanent and cannot be modified further. Therefore, it ensures data security in the cloud environment.
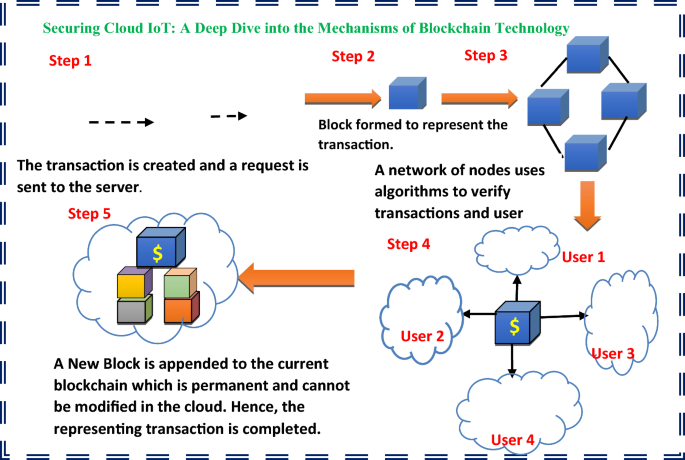
Functioning of blockchain technology in Cloud IoT systems
Real-World Applications of Blockchain Technology in Enhancing Security and Data Protection is as follows:
Walmart Walmart one of the retail companies collaborated with IBM to implement blockchain technology to track the movement of products, maintain food safety, and minimizes the possibility of contamination.
MedRec MedRec is an MIT-developed blockchain-based electronic medical record system that gives individuals more control over their health information while maintaining confidentiality and privacy.Allows for real-time transactions and decentralized energy management by utilizing blockchain to increase the security and efficiency of energy distribution.
Ripple Ripples operates in the financial sector. It uses blockchain techniques to protect the data and enables real-time secure payment.
Follow My Vote Follow My Vote creates a safe, open, and verifiable online voting system using blockchain technology.
uPort uPort is a blockchain-based self-governing identity platform that empowers people to take control of their online personas while improving security and privacy.
10 Unveiling the challenges: addressing current issues in data security and privacy within the Cloud IoT environment
10.1 open ended problems.
The open-ended problems and primary issues about data security and privacy in cloud IoT systems are summarized in Table 3 . Table 3 also provides targeted solutions to address each challenge, thereby ensuring a robust and secure cloud-IoT ecosystem.
10.2 Research gaps
The research gaps of data security and privacy preservation in cloud-IoT technologies are described in Table 4 .
11 Conclusions
The IoT is on the verge of substantial expansion, necessitating secure data transfer and robust cloud storage solutions. As IoT devices become more widespread, the need for enhanced cloud security is critical. Current methods, while helpful, do not fully address modern threats, thus requiring the development of more advanced protective systems. Manufacturers can improve security by creating products grounded in a detailed assessment of IoT security risks and objectives. Effective measures include the implementation of strong authentication methods like One Time Password (OTP) features and robust cryptographic systems. While Machine Learning (ML) is widely used for data protection in various sectors, it faces challenges such as scalability issues with small data sets. Integrating ML with homomorphic encryption shows promise but needs further development. The evolving sophistication of hackers compels reliance on ML and AI for defense strategies. Additionally, blockchain technology, supported by platforms like Ethereum and Hyper-ledger Fabric, offers considerable potential for enhancing security, though more research is necessary to standardize these techniques.
The authors recommend three key solutions:
Develop new security standards and frameworks for cloud-based and IoT devices to tackle modern security challenges.
Create more efficient ML models for real-time attack prediction.
Design robust privacy protection protocols for blockchain technology to safeguard sensitive data.
The authors encountered several limitations during their research, including restricted access to relevant literature, challenges in avoiding plagiarism, difficulties in summarizing a large body of research, integrating information logically, and keeping up with the latest studies.
Data availability
The data and material used in this paper are appropriately referred to and described in this paper.
Code availability
The source code/custom code/software application will be provided when required.
Abdulkader ZA (2022) Cloud data security mechanism using the lightweight cryptography. Optik 271:170084
Article Google Scholar
Abdulsalam YS, Hedabou M (2021) Decentralized data integrity scheme for preserving privacy in cloud computing. In 2021 International conference on security, pattern analysis, and cybernetics (SPAC), Chengdu, China, pp 607–612
Abed AK, Anupam A (2022) Review of security issues in the Internet of Things and artificial intelligence-driven solutions. Internet Technol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/spy2.285
Abouelmehdi K, Beni-Hessane A, Khaloufi H (2018) Big healthcare data: preserving security and privacy. J Big Data 5:1
Ahmed W et al (2021) Security in next generation mobile payment systems: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 9:115932–115950
Ahmad W, Rasool A, Javed AR, Baker T, Jalil Z (2022) Cyber security in IoT-based cloud computing: a comprehensive survey. Electronics 11:16
Akmal M, Syangtan B, Alchouemi A (2021) Enhancing the security of data in cloud computing environments using Remote Data Auditing. In: 2021 IEEE 6th International conference on innovative technology in intelligent system and industrial applications (CITISIA), Sydney, Australia, pp 1–10
Alabdulatif A, Thilakarathne NN, Kalinaki K (2023) A novel cloud enabled access control model for preserving the security and privacy of medical Big Data. Electronics 12:2646
Albugmi A, Alassafi MO, Walters R, Wills G (2016) Data security in cloud computing. 2016 Fifth International conference on future generation communication technologies (FGCT), London, UK, pp. 55–59
Al-Dhaqm A et al (2021) Digital forensics subdomains: the state of the art and future directions. IEEE Access 9:152476–152502
Al Hamid HA, Rahman SMM, Hossain MS, Almogren A, Alamri A (2017) A security model for preserving the privacy of medical Big Data in a healthcare cloud using a fog computing facility with pairing-based cryptography. IEEE Access 5:22313–22328
Ali J, Roh BH, Lee B, Oh J, Adil M (2020) A machine learning framework for prevention of software-defined networking controller from DDoS attacks and dimensionality reduction of Big Data. In: 2020 International conference on information and communication technology convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea (South), pp 515–519
Almutairi W, Moulahi T (2023) Joining federated learning to blockchain for digital forensics in IoT. Computers 12:157
Alnaim AK, Alwakeel AM (2023) Machine-learning-based IoT–edge computing healthcare solutions. Electron MDPI 12:1027
Google Scholar
Alouffi B, Hasnain M, Alharbi A, Alosaimi W, Alyami H, Ayaz M (2021) A systematic literature review on cloud computing security: threats and mitigation strategies. IEEE Access 9:57792–57807
Alrasheed SH, Aiedalhariri M, Adubaykhi SA, El Khediri S (2022) Cloud computing security and challenges: issues, threats, and solutions. In: 2022 5th Conference on cloud and Internet of Things (CIoT), Marrakech, Morocco, pp 166–172
Alzoubi YI, Ahmad AAA, Jaradat A (2021) Fog computing security and privacy issues, open challenges, and blockchain solution: an overview. Int J Electr Comput Eng (IJECE) 11(6):5081–5088
Andrew J, Karthikeyan J (2019) Privacy-preserving Internet of Things: techniques and applications. Int J Eng Adv Technol (IJEAT) 8(6):3229
Arora A, Khanna A, Rastogi A, Agarwal A (2017) Cloud security ecosystem for data security and privacy. In: 2017 7th International conference on cloud computing, data science & engineering - confluence, Noida, India, IEEE, pp 288–292
Atiewi S, Al-Rahayfeh AA, Almiani M, Yussof S, Alfandi O, Abugabah A, Jararweh Y (2020) Scalable and secure Big Data IoT system based on multifactor authentication and lightweight cryptography. IEEE Access 8:113498–113511
Awaysheh FM, Aladwan MN, Alazab M, Alawadi S, Cabaleiro JC, Pena TF (2022) Security by design for Big Data frameworks over cloud computing. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 69(6):3676–3693
Ayofe Azeez NA, Vyver CVD (2019) Security and privacy issues in e-health cloud-based system: a comprehensive content analysis. Egyptian Inform J 20(2):97–108
Basit A, Zafar M, Liu X et al (2021) A comprehensive survey of AI-enabled phishing attacks detection techniques. Telecommun Syst 76:139–154
Bedi RK, Singh J, Gupta SK (2021) An efficient and secure privacy-preserving multi-cloud storage framework for mobile devices. Int J Comput Appl 43:1–11
Bertino E (2016) Big Data security and privacy. In: 2016 IEEE International conference on Big Data (Big Data), Washington, DC, USA, pp 3–3
Binjubeir M, Ahmed AA, Ismail MAB, Sadiq AS, Khurram Khan M (2020) Comprehensive survey on Big Data privacy protection. IEEE Access 8:20067–20079
Butpheng C, Yeh K-H, Xiong H (2020) Security and privacy in IoT-cloud-based e-health systems—a comprehensive review. Symmetry MDPI 12:1191
Campos EM, Saura PF, González-Vidal A, Hernández-Ramos JL, Bernabé JB, Baldini G, Skarmeta A (2022) Evaluating federated learning for intrusion detection in Internet of Things: review and challenges. Comput Netw 203:108661
Cha SC, Hsu TY, Xiang Y, Yeh K-H (2019) Privacy enhancing technologies in the Internet of Things: perspectives and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J 6(2):2159–2187
Chaowei Y, Qunying H, Zhenlong L, Kai L, Fei H (2017) Big Data and cloud computing: innovation opportunities and challenges. Int J Digit Earth. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2016.1239771
Chen J, Ramanathan L, Alazab M (2021) Holistic Big Data integrated artificial intelligent modelling to improve privacy and security in data management of smart cities. Microprocess Microsyst 81:103722
Chen Q, Wu L, Jiang C (2022) ES-PPDA: an efficient and secure privacy-protected data aggregation scheme in the IoT with an edge-based XaaS architecture. J Cloud Comp 11:20
Chenthara S, Ahmed K, Wang H, Whittaker F (2019) Security and privacy-preserving challenges of e-health solutions in cloud computing. IEEE Access 7:74361–74382
Choudhury T, Gupta A, Pradhan S, Kumar P, Rathore YS (2017) Privacy and security of Cloud-Based Internet of Things (IoT). In: 2017 3rd International conference on computational intelligence and networks (CINE), Odisha, India, pp 40–45
Duan H, Zheng Y, Wang C, Yuan X (2019) Treasure collection on foggy islands: building secure network archives for Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J 6(2):2637–2650
Dutkiewicz L et al (2022) Privacy-preserving techniques for trustworthy data sharing: opportunities and challenges for future research. In: Curry E, Scerri S, Tuikka T (eds) Data spaces. Springer, Cham
Gai K, Qiu M, Zhao H (2021) Privacy-preserving data encryption strategy for Big Data in mobile cloud computing. IEEE Transact Big Data 7(4):678–688
Ghaffar Z, Ahmed S, Mahmood K, Islam SH, Hassan MM, Fortino G (2020) An improved authentication scheme for remote data access and sharing over cloud storage in cyber-physical-social-systems. IEEE Access 8:47144–47160
Gnana Sophia S, Thanammal KK, Sujatha SS (2023) Secure storage and accessing the data in the cloud using optimized homomorphic encryption. J Control Decision. https://doi.org/10.1080/23307706.2022.2078436
Gupta I, Singh AK, Lee C-N, Buyya R (2022) Cloud computing research center, secure data storage and sharing techniques for data protection in cloud environments: a systematic review, analysis, and future directions. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3188110
Hamzah Amlak GM, Kraidi Al-Saedi KH (2023) Data mining techniques for cloud privacy preservation. Int J Intell Syst Appl Eng 11(6s):246–256
Hassija V, Chamola V, Saxena V, Jain D, Goyal P, Sikdar B (2019) A survey on IoT security: application areas, security threats, and solution architectures. IEEE Access 7:82721–82743
Henze M, Wolters B, Matzutt R, Zimmermann T, Wehrle K (2017) Distributed configuration, authorization and management in the cloud-based Internet of Things. 2017 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ICESS, Sydney, NSW, Australia, pp 185–192
Himeur Y, Sohail SS, Bensaali F, Amira A, Alazab M (2022) Latest trends of security and privacy in recommender systems: a comprehensive review and future perspectives. Comput Secur 118:102746
Hiremath S, Kunte S (2017) A novel data auditing approach to achieve data privacy and data integrity in cloud computing. In: 2017 International conference on electrical, electronics, communication, computer, and optimization techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, pp 306–310
Hong-Yen T, Jiankun H (2019) Privacy-preserving Big Data analytics a comprehensive survey. J Parallel Distribut Comput 134:207–218
Hossain MS, Muhammad G, Abdul W, Song B, Gupta BB (2018) Cloud-assisted secure video transmission and sharing framework for smart cities. Futur Gener Comput Syst 83:596–606
Hou Y, Garg S, Hui L, Jayakody DNK, Jin R, Hossain MS (2020) A data security enhanced access control mechanism in mobile edge computing. IEEE Access 8:136119–136130
Hurrah NN, Parah SA, Sheikh JA, Al-Turjman F, Muhammad K (2019) Secure data transmission framework for confidentiality in IoTs. Ad Hoc Netw 95:101989
Ishaq A, Qadeer B, Shah MA, Bari N (2021) A comparative study on securing electronic health records (EHR) in cloud computing. In: 2021 26th International conference on automation and computing (ICAC), Portsmouth, United Kingdom, pp 1–7
Jahromi AN, Karimipour H, Dehghantanha A, Choo K-KR (2021) Toward detection and attribution of cyber-attacks in iot-enabled cyber-physical systems. IEEE Internet Things J 8(17):13712–13722
Jain SK, Kesswani N (2023) A noise-based privacy-preserving model for the Internet of Things. Complex Intell Syst 9:3655–3679
Jain P, Gyanchandani M, Khare N (2016) Big Data privacy: a technological perspective and review. J Big Data 3:25
Jain P, Gyanchandani M, Khare N (2019) Enhanced secured map reduce layer for Big Data privacy and security. J Big Data 6:30
Javeed D, Gao T, Saeed MS, Khan MT (2023) FOG-Empowered augmented-intelligence-based proactive defensive mechanism for IoT-enabled smart industries. IEEE Internet Things J 10(21):18599–18608. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3288563
Javeed D, Saeed MS, Ahmad I, Adil M, Kumar P, Najmul Islam AKM (2024a) Quantum-empowered federated learning and 6G wireless networks for IoT security: Concept, challenges and future directions. Futur Gener Comput Syst 160:577–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2024.06.023
Javeed D, Saeed MS, Adil M, Kumar P, Jolfaei A (2024b) A federated learning-based zero trust intrusion detection system for Internet of Things. Ad Hoc Netw 162:103540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2024.103540
Javid T, Faris M, Beenish H, Fahad M (2020) Cybersecurity and data privacy in the cloudlet for preliminary healthcare Big Data analytics. In: 2020 International Conference on Computing and Information Technology (ICCIT-1441), Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, pp 1–4
Jeong J, Joo JWJ, Lee Y, Son Y (2019) Secure cloud storage service using bloom filters for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 7:60897–60907
Jiang Q, Kumar N, Ma J, Shen J, He D, Chilamkurti N (2016) A privacy-aware two-factor authentication protocol based on elliptic curve cryptography for wireless sensor networks. Int J Network Mgmt. https://doi.org/10.1002/nem.1937
Jusak J, Mahmoud SS, Laurens R, Alsulami M, Fang Q (2022) A new approach for secure cloud-based electronic health record and its experimental testbed. IEEE Access 10:1082–1095
Kaaniche N, Laurent M (2017) Data security and privacy preservation in cloud storage environments based on cryptographic mechanisms. Comput Commun 111:120–141
Kabir AA, Elmedany M, Sharif W, Saeed M (2023) Securing IoT devices against emerging security threats: challenges and mitigation techniques. J Cyber Secur Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/23742917.2023.2228053
Karie NM, Sahri NM, Yang W, Valli C, Kebande VR (2021) A review of security standards and frameworks for IoT-based smart environments. IEEE Access 9:121975–121995
Kaur K, Syed A, Mohammad A, Halgamuge MN (2017) Review: an evaluation of major threats in cloud computing associated with Big Data. In: 2017 IEEE 2nd International conference on Big Data analysis (ICBDA), Beijing, China, pp 368–372
Khan S, Parkinson S, Qin Y (2017) Fog computing security: a review of current applications and security solutions. J Cloud Comp 6:19
Khan HK, Pradhan R, Chandavarkar BR (2021) Hybrid cryptography for cloud computing. In: 2021 2nd International conference for emerging technology (INCET), Belagavi, India, pp 1–5
Krishnaraj N, Sangeetha S (2022) A study of data privacy in Internet of Things using privacy preserving techniques with its management. Int J Eng Trends Technol 70(3):54–65
Kumar S, Tiwari P, Zymbler M (2019) Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology enhancement: a review. J Big Data 6:111
Kumar A (2021) Framework for data security using DNA cryptography and HMAC technique in cloud computing. In: 2021 Second International conference on electronics and sustainable communication systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, pp 898-903
Kumar V, Alameemi AMA, Kumari A, Ahmad M, Falah MW, Abd El-Latif AA (2022) PSEBVC: provably secure ECC and biometric based authentication framework using smartphone for vehicular cloud environment. IEEE Access 10:84776–84789
Kumar A, Khan SB, Pandey SK et al (2023) Development of a cloud-assisted classification technique for the preservation of secure data storage in smart cities. J Cloud Comp 12:92
Li Y, Zhang F (2022) An efficient certificate-based data integrity auditing protocol for cloud-assisted WBANs. IEEE Internet Things J 9(13):11513–11523
Lin J, Yu W, Zhang N, Yang X, Zhang H, Zhao W (2017) A survey on Internet of Things: architecture, enabling technologies, security and privacy, and applications. IEEE Internet Things J 4(5):1125–1142
Loai AT, Gokay S (2021) Reconsidering Big Data security and privacy in cloud and mobile cloud systems. J King Saud Univ Comput Inform Sci 33(7):810–819
Lone AN, Mustajab S, Alam M (2023) A comprehensive study on cybersecurity challenges and opportunities in the IoT world. Secur Privacy 6:e318
Lu X, Pan Z, Xian H (2020) An efficient and secure data sharing scheme for mobile devices in cloud computing. J Cloud Comp 9:60
Mahfoudhi S, Frehat M, Moulahi T (2019) Enhancing cloud of things performance by avoiding unnecessary data through artificial intelligence tools. In: 2019 15th International wireless communications & mobile computing conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, pp 1463–1467
Mahrous WA, Farouk M, Darwish SM (2021) An enhanced blockchain-based IoT digital forensics architecture using fuzzy hash. IEEE Access 9:151327–151336
Majeed A, Khan S, Hwang SO (2022) Toward privacy preservation using clustering based anonymization: recent advances and future research outlook. IEEE Access 10:53066–53097
Mei R, Yan HB, He Y, Wang Q, Zhu S, Wen W (2022). Considerations on evaluation of practical cloud data protection. CONCERT 2022. In: Communications in computer and information science, vol 1699. Springer, Singapore
Mihailescu MI, Nita SL, Asalomia BL, Rogobete MG, Racuciu C (2022) Customized authorization process for cloud computing and IoT using attribute-based encryption. In: 2022 14th International conference on electronics, computers and artificial intelligence (ECAI), IEEE Ploiesti, Romania, pp 1–4
Mishra JK, Janarthanan MC (2023) Cloud computing security: machine and deep learning models analysis. Macromol Symp 407:2100521
Mishra K, Bhattacharjee V, Saket S et al (2022) Cloud and Big Data security system’s review principles: a decisive investigation. Wireless Pers Commun 126:1013–1050
Mishra A, Jabar TS, Alzoubi YI, Mishra KN (2023) Enhancing privacy-preserving mechanisms in cloud storage: a novel conceptual framework. Concurr Computat Pract Exper. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.7831
Moqurrab SA, Tariq N, Anjum A et al (2022) A Deep learning-based privacy-preserving model for smart healthcare in Internet of medical things using fog computing. Wireless Pers Commun 126:2379–2401
Morioka E, Sharbaf MS (2016) Digital forensics research on cloud computing: An investigation of cloud forensics solutions. In: 2016 IEEE symposium on technologies for homeland security (HST), Waltham, MA, USA, pp 1–6
Moulahi T, El Khediri S, Ullah Khan R, Zidi S (2021) A fog computing data reduction level to enhance the cloud of things performance. Int J Commun Syst 34(9):e4812
Muzammal SM et al (2018) Counter measuring conceivable security threats on smart healthcare devices. IEEE Access 6:20722–20733
Nadian-Ghomsheh A, Farahani B, Kavian M (2021) A hierarchical privacy-preserving IoT architecture for vision-based hand rehabilitation assessment. Multimed Tools Appl 80:31357–31380
Namakshenas D, Yazdinejad A, Dehghantanha A, Srivastava G (2024) Federated quantum-based privacy-preserving threat detection model for consumer Internet of Things. IEEE Trans Consum Electron. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2024.3377550
Nanda P, He X, Yang LT (2020) Security, trust and privacy in cyber (STPCyber): future trends and challenges. Futur Gener Comput Syst 109:446–449
Nasiraee H, Ashouri-Talouki M (2022) Privacy-preserving distributed data access control for CloudIoT. IEEE Trans Dependable Secure Comput 19(4):2476–2487
Navin Prasad S, Rekha C (2023) Blockchain-based IAS protocol to enhance security and privacy in cloud computing. Measur Sens 28:100813
Niu L, Wang F, Li J, Han T, Liu D (2019) Development of agricultural Internet of Things monitoring system combining cloud computing and WeChat technology. In: 2019 IEEE 8th Joint international information technology and artificial intelligence conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, pp 1457–1460
Ogunniye G, Kokciyan N (2023) A survey on understanding and representing privacy requirements in the Internet-of-Things. J Art Intell Res 76:163–192
Pandey NK, Kumar K, Saini G et al (2023) Security issues and challenges in a cloud of things-based applications for industrial automation. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-023-05285-7
Pathak M, Mishra KN, Singh SP, Mishra A (2023) An automated smart centralised vehicle security system for controlling the vehicle thefts/hacking using IOT and facial recognition. In: 2023 International conference on computational intelligence and knowledge economy (ICCIKE), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, pp 516–521
Pawlicki M, Pawlicka A, Kozik R, Choraś M (2023) The survey and meta-analysis of the attacks, transgressions, countermeasures, and security aspects common to the Cloud Edge and IoT. Neurocomputing 551:126533
Pioli L, Dorneles CF, de Macedo DDJ et al (2022) An overview of data reduction solutions at the edge of IoT systems: a systematic mapping of the literature. Computing 104:1867–1889
Quach S, Thaichon P, Martin KD et al (2022) Digital technologies: tensions in privacy and data. J of the Acad Mark Sci 50:1299–1323
Rachit BS, Ragiri PR (2021) Security trends in Internet of Things: a survey. SN Appl Sci 3:121
Radoglou Grammatikis PI, Sarigiannidis PG, Moscholios ID (2019) Securing the Internet of Things: challenges, threats and solutions. Internet of Things 5:41–70
Rahman SMM, Hossain MA, Hassan MM, Alamri A, Alghamdi A, Pathan M (2016) Secure privacy vault design for distributed multimedia surveillance system. Futur Gener Comput Syst 55:344–352
Ram Mohan P, Murali Krishna S, Siva Kumar AP (2018) Privacy preservation techniques in Big Data analytics: a survey. J Big Data 5:33
Ravi Kumar P, Herbert Raj P, Jelciana P (2018) Exploring data security issues and solutions in cloud computing. Procedia Comput Sci 125:691–697
Ray SM, Dutta S (2020) Big Data security issues from the perspective of IoT and cloud computing: a review. Recent Adv Comput Sci Commun. https://doi.org/10.2174/2666255813666200224092717
Reddy Y (2018) Big Data security in cloud environment. In: 2018 IEEE 4th International Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud (BigDataSecurity), IEEE International conference on high performance and smart computing, (HPSC) and IEEE international conference on intelligent data and security (IDS), Omaha, NE, USA, pp 100–106
Rejin PR, Paul RD, Alavi AH (2019) Verification of data integrity and co-operative loss recovery for secure data storage in cloud computing. Cogent Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2019.1654694
Rodríguez E, Otero B, Canal R (2023) A survey of machine and deep learning methods for privacy protection in the Internet of Things. Sensors 23:1252
Roslin Dayana K, Shobha Rani P (2023) Secure cloud data storage solution with better data accessibility and time efficiency. Automatika J Control Measur Electron Comput Commun 64(4):751–758
Sadhu PK, Yanambaka VP, Abdelgawad A (2022) Internet of Things: security and solutions survey. MDPI Sens 22:7433
Safaei Yaraziz M et al (2023) Recent trends towards privacy-preservation in the Internet of Things, its challenges and future directions. IET Circuits Devices Syst 17(2):53–61
Sakhnini J et al (2023) A generalizable deep neural network method for detecting attacks in industrial cyber-physical systems. IEEE Syst J 17(4):5152–5160
Sarwar K, Yongchareon S, Jian Yu, Rehman SU (2021) A survey on privacy preservation in fog-enabled Internet of Things. ACM Comput Surv 55(1):2
Schiller E, Andy A, Jara F, Jonathan S, Michael Z, Burkhard S (2022a) Landscape of IoT security. Comput Sci Rev 44:100467
Schiller E, Aidoo A, Fuhrer J, Stahl J, Ziörjen M, Stiller B (2022b) Landscape of IoT security. Comput Sci Rev Internet Things 44:100467
Selvarajan S, Srivastava G, Khadidos AO et al (2023) An artificial intelligence lightweight blockchain security model for security and privacy in IIoT systems. J Cloud Comp 12:38
Sharma Y, Gupta H and Khatri S. K. (2019) A Security Model for the Enhancement of Data Privacy in Cloud Computing. 2019 Amity international conference on artificial intelligence (AICAI), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, IEEE, pp 898–902
Shi Y (2018) Data security and privacy protection in public cloud. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, pp 4812–4819
Shin S, Kwon T (2020) A privacy-preserving authentication, authorization, and key agreement scheme for wireless sensor networks in 5G-integrated Internet of Things. IEEE Access 8:67555–67571
Shukla RS (2022) IoT based designing of secure data storage system in distributed cloud system with Big Data using cryptography algorithm. In: 2022 11th International conference on system modeling & advancement in research trends (SMART), Moradabad, India, pp 264-270
Sicari S, Rizzardi A, Coen-Porisini A (2022) Insights into security and privacy towards fog computing evolution. Comput Secur 120:102822
Silva LV, Barbosa P, Marinho R (2018) Security and privacy aware data aggregation on cloud computing. J Internet Serv Appl 9:6
Simsek I (2023) Zero-knowledge and identity-based authentication, authorization, access control, and key exchange for publish/subscribe in Internet of Things. In: 2023 6th conference on cloud and Internet of Things (CIoT), Lisbon, Portugal, pp 47–54
Singh N, Singh AK (2018) Data privacy protection mechanisms in cloud. Data Sci Eng 3:24–39
Sookhak M, Yu FR, Zomaya AY (2018) Auditing Big Data storage in cloud computing using divide and conquer tables. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 29(5):999–1012
Stergiou C, Psannis KE, Xifilidis T, Plageras AP, Gupta BB (2018) Security and privacy of Big Data for social networking services in the cloud. IEEE INFOCOM 2018—IEEE conference on computer communications workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Honolulu, HI, USA, pp 438–443
Sumithra R, Parameswari R (2022) Data privacy and data protection security algorithms for Big Data in the cloud. Int J Health Sci 6(S2):7613–7621
Sun PJ (2019) Privacy protection and data security in cloud computing: a survey, challenges, and solutions. IEEE Access 7:147420–147452
Tahirkheli AI, Shiraz M, Hayat B, Idrees M, Sajid A, Ullah R, Ayub N, Kim K-I (2021) A survey on modern cloud computing security over smart city networks: threats, vulnerabilities, consequences, countermeasures, and challenges. Electronics 10:1811
Tang Z (2020) A preliminary study on data security technology in Big Data cloud computing environment. In: 2020 International conference on Big Data & artificial intelligence & software engineering (ICBASE) IEEE, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 27–30
Thabit F, Alhomdy S, Jagtap S (2021) A new data security algorithm for cloud computing based on genetics techniques and logical-mathematical functions. Int J Intell Netw Sci Direct 2:18–33
Tian Y, Kaleemullah MM, Rodhaan MA, Song B, Al-Dhelaan A, Ma T (2019) A privacy-preserving location service for cloud-of-things system. J Parallel Distrib Comput 123:215–222
Ullah F et al (2019) Cyber security threats detection in Internet of Things using deep learning approach. IEEE Access 7:124379–124389
Unal E, Sen-Baidya S, Hewett R (2018) Towards prediction of security attacks on software defined networks: a Big Data analytic approach. In: 2018 IEEE International conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, pp 4582–4588
Waheed N, He X, Ikram M, Usman M, Hashmi SS, Usman M (2020) Security and privacy in IoT using machine learning and blockchain: threats and countermeasures. ACM Comput Surv 53(6):122
Wang H (2021) Research on risk and supervision of financial Big Data application based on cloud computing. In: 2021 IEEE International conference on advances in electrical engineering and computer applications (AEECA), Dalian, China, pp 507–510
Wang F, Wang H, Xue L (2021) Research on data security in Big Data cloud computing environment. In: 2021 IEEE 5th advanced information technology, electronic and automation control conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, pp 1446–1450
Wang Y, Ni K, Wang X, Zhu J (2022) Design of automatic weather monitoring and forecasting system based on Internet of Things and Big Data. In: 2022 International conference on sustainable computing and data communication systems (ICSCDS), Erode, India, pp 979–982
Wazid M, Das AK, Hussain R, Succi G, Rodrigues JJPC (2019) Authentication in cloud-driven IoT-based Big Data environment: survey and outlook. J Syst Architect 97:185–196
Williams P, Dutta IK, Daoud H, Bayoumi M (2022) A survey on security in the Internet of Things with a focus on the impact of emerging technologies. Internet Things 19:100564
Wylde V, Rawindaran N, Lawrence J et al (2022a) Cybersecurity, data privacy, and blockchain: a review. SN Comput Sci 3:127
Wylde V, Rawindaran N, Lawrence J, Balasubramanian R, Prakash E, Jayal A, Khan I, Hewage C, Platts J (2022b) Cybersecurity, data privacy, and blockchain: a review. SN Comput Sci 3:127
Xiao Y, Jia Y, Liu C, Cheng X, Yu J, Lv W (2019) Edge computing security: state of the art and challenges. Proc IEEE 107(8):1608–1631
Xie Q, Zhang C, Jia X (2023) Security-aware and efficient data deduplication for edge-assisted cloud storage systems. IEEE Trans Serv Comput 16(03):2191–2202
Yahuza M et al (2020) Systematic review on security and privacy requirements in edge computing: state of the art and future research opportunities. IEEE Access 8:76541–76567
Yan H, Gui W (2021) Efficient identity-based public integrity auditing of shared data in cloud storage with user privacy preserving. IEEE Access 9:45822–45831
Yao H (2022) Data storage security system based on cloud computing. In: 2022 IEEE 2nd International conference on electronic technology, communication and information (ICETCI), Changchun, China, pp 1220–1223
Yazdinejad A, Dehghantanha A, Parizi RM, Hammoudeh M, Karimipour H, Srivastava G (2022) Block hunter: federated learning for cyber threat hunting in blockchain-based IIoT networks. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 18(11):8356–8366
Yazdinejad A, Dehghantanha A, Parizi RM, Srivastava G, Karimipour H (2023) Secure intelligent fuzzy blockchain framework: effective threat detection in IoT networks. Comput Ind 144:2023
Yazdinejad A, Dehghantanha A, Srivastava G (2024a) AP2FL: auditable privacy-preserving federated learning framework for electronics in healthcare. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 70(1):2527–2535
Yazdinejad A, Dehghantanha A, Srivastava G, Karimipour H, Parizi RM (2024b) Hybrid privacy-preserving federated learning against irregular users in next-generation Internet of Things. J Syst Architect 148:103088
Ye C, Cao W, Chen S (2021) Security challenges of blockchain in Internet of Things: systematic literature review. Trans Emerging Tel Tech 32:e4177
Yin H, Chen E, Zhu Y, Zhao C, Feng R, Yau SS (2022) Attribute-based private data sharing with script-driven programmable ciphertext and decentralized key management in blockchain Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J 9(13):10625–10639
Yu Y et al (2017) Identity-based remote data integrity checking with perfect data privacy preserving for cloud storage. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 12(4):767–778
Yu K et al (2022) A blockchain-based shamir’s threshold cryptography scheme for data protection in industrial Internet of Things settings. IEEE Internet Things J 9(11):8154–8167
Zaman S et al (2021) Security threats and artificial intelligence based countermeasures for Internet of Things networks: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 9:94668–94690
Zarandi MA, Dara Rozita A, Evan F (2020) A survey of machine learning-based solutions to protect privacy in the Internet of Things. Comput Secur 96:101921
Zhang J, Chen B, Zhao Y, Cheng X, Hu F (2018) Data security and privacy-preserving in edge computing paradigm: survey and open issues. IEEE Access 6:18209–18237
Zhang W, Jin S (2020) Research and application of data privacy protection technology in cloud computing environment based on attribute encryption. In: 2020 IEEE International conference on power, intelligent computing and systems (ICPICS), Shenyang, China, pp 994–996
Zhao X-P, Jiang R (2020) Distributed machine learning oriented data integrity verification scheme in cloud computing environment. IEEE Access 8:26372–26384
Zhou J, Cao Z, Dong X, Vasilakos AV (2017) Security and privacy for cloud-based IoT: challenges. IEEE Commun Mag 55(1):26–33
Zhu H et al (2019) A secure and efficient data integrity verification scheme for Cloud-IoT based on short signature. IEEE Access 7:90036–90044
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Jharkhand, India
Mayank Pathak, Kamta Nath Mishra & Satya Prakash Singh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Mayank Pathak, Kamta Nath Mishra and Satya Prakash Singh have equally contributed in writing this paper after having various discussions.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kamta Nath Mishra .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest.
Being the corresponding author I declare that there is no conflict of interest with any person or organization for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Pathak, M., Mishra, K.N. & Singh, S.P. Securing data and preserving privacy in cloud IoT-based technologies an analysis of assessing threats and developing effective safeguard. Artif Intell Rev 57 , 269 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10908-x
Download citation
Accepted : 06 August 2024
Published : 27 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10908-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Blockchain technologies
- Cloud computing
- Data breach
- Data securities
- Digital forensic
- Fog computing
- Internet of Things
- Machine learning
- Privacy protection
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
COMMENTS
100 Words Essay on Future Technology What is Future Technology? Future technology means the new inventions and ideas that will change how we live. Think of robots, smart cars, and computers that can learn. These things are not common now, but in the future, they might be everywhere, helping us in ways we can't imagine yet. ...
5. ChatGPT-like tech will become the norm. Large language models will become a given because they lower the cost of artificial intelligence (AI) by allowing you to have multiple models over one base, giving you a speed advantage, says Krishna. "Beyond language is going to be a given, language because code can be a form of language and then ...
essay. Future of technology. Learn from machine learning. The world is a black box full of extreme specificity: it might be predictable but that doesn't mean it is understandable. ... essay. Technology and the self. Zoom and gloom. Sitting in a videoconference is a uniformly crap experience. Instead of corroding our humanity, let's design ...
Science has profoundly modified education. For one, technology has notably multiplied get right of entry to education. In medieval times, books had been uncommon and only an elite few had to get admission to academic opportunities. Individuals had to tour to centers of learning to get an education.
But writing a technology essay can be challenging, especially for those needing more time or help with writer's block. ... while automation is transforming the future of work. In education, technology has revolutionized the way we learn and access information. At the same time, our dependence on technology has brought new challenges in terms of ...
Changes in travel. Innovation in Science and Technology will also change travel. People will be traveling on sky car that will be cruising comfortably at a speed of 300Miles per hour using regular fuel. The sky car will be equipped with onboard computers and will be fully automated. This means that one will not need a license to fly the sky car.
The world is still figuring out the right technology base for long-duration ESSs, but there are multiple options: flow batteries, non-lithium-ion non-flow batteries, gravity-based ESSs, heat-based ESSs and hydrogen-and a winner, or winners are sure to emerge. In short, the future for how we build cities is charged with potential.
In conclusion, technology has brought many benefits to different aspects of our lives, from communication and education to work and health. However, the increasing reliance on technology has also raised concerns over privacy, security, and addiction. It is essential to strike a balance between the benefits and drawbacks that come with technology.
How do I start an essay about technology It is a good idea to start your technology advancement with a hook. One option is to use a quote, like the following one by Albert Einstein: "It has become appallingly obvious that our technology has exceeded our humanity." One more option is to use an exciting fact like the following one: Over 6,000 ...
Future technology: 22 ideas about to change our world - BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Get a custom essay on Technology and Its Impact in the World. Technology has a profound root in the society; this is because today's world relies on the advances in technology. These advances in technology in today's world has sped people's lives and made the world a smaller place to live in as it makes different locations closer to one ...
The future of technology looks promising, with advancements like quantum computing and nanotechnology on the horizon. These developments will further revolutionize our lives, paving the way for a future that is as exciting as it is unpredictable. In conclusion, the rise of technology is a testament to human ingenuity and the quest for progress.
We all have the power to shape the future of technology, say Stanford scholars. Three Stanford professors want people to press control-alt-delete on how we think about our relationship to Big Tech ...
500 Words Essay on Modern Technology ... Conclusion: The Future of Modern Technology. In conclusion, modern technology, despite its potential drawbacks, is an integral part of our lives. It has the power to drive societal change, foster economic growth, and enhance the quality of life. As we navigate the digital age, it is crucial to strike a ...
Hook Examples for Technology Essay. A Digital Revolution: Enter the era of smartphones, AI, and the Internet of Things, where technology is the driving force. Join me as we explore how technology has transformed our lives and the profound impact it has on society. An Intriguing Quote: Arthur C. Clarke once said, "Any sufficiently advanced ...
Robert Cunningham '23, a recent graduate in math and physics, is the winner of the Envisioning the Future of Computing Prize. Cunningham's essay was among nearly 60 entries submitted for the first-ever essay competition that challenged MIT students to imagine ways that computing technologies could improve our lives, as well as the pitfalls and dangers associated with them.
Technologies are becoming increasingly complicated and increasingly interconnected. Cars, airplanes, medical devices, financial transactions, and electricity systems all rely on more computer software than they ever have before, making them seem both harder to understand and, in some cases, harder to control. Government and corporate surveillance of individuals and information processing ...
Key tech trends. We estimate that 70 percent of companies will employ hybrid or multicloud management technologies, tools, and processes. 2 At the same time, 5G will deliver network speeds that are about ten times faster than current speeds on 4G LTE networks, 3 with expectations of speeds that are up to 100 times faster with 40 times faster ...
Essay on Technology: 500+ Words Essay on Technology is provided here to help students get familiar with the advantages and disadvantages of technology and use it in the right direction. Go through it and write more essays on similar topics. ... The future of technology seems to be exciting but also scary. Futuristic predictions in technology ...
Essay on Technology. The word "technology" and its uses have immensely changed since the 20th century, and with time, it has continued to evolve ever since. We are living in a world driven by technology. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization, along with cultural changes.
Abstract. Emerging technologies are not the danger. Failure of human imagination, optimism, energy, and creativity is the danger. Why the future doesn't need us: Our most powerful 21st-century technologies—robotics, genetic engineering, and nanotech—are threatening to make humans an endangered species.
500 Words Essay on Future of Artificial Intelligence Introduction. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed from a fringe scientific concept into a commonplace technology, permeating every aspect of our lives. As we stand on the precipice of the future, it becomes crucial to understand AI's potential trajectory and the profound ...
If you write an essay about the future of technology, it is very important that you understand the future of technology, and how it will affect the world. The people that will read this essay will be able to predict the future of the technologies that will be available to them and what they will do. When you talk about the future of technology ...
1. Introduction Both the patent system and the contribution of patents to innovation and economic growth in the technology industry are subjects of wide-ranging debate. The requirement for every inventor to conduct a patent search prior to commencing an invention suggests the importance of patented technology in future innovation.
Founded at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1899, MIT Technology Review is a world-renowned, independent media company whose insight, analysis, reviews, interviews and live events ...
Organizations can make informed decisions and optimize their data centers by engaging in conversations about future goals and needs. It is crucial to remember that planning for the future and embracing new technologies while still utilizing the proven benefits of air cooling will shape the success of data centers in the years to come.
An illustration of HILOS's future location at Made in Old Town. Image courtesy of Travis Dang, Sera Architects. HILOS, a company that started as a 3D-printed footwear brand, now sits at the center ...
NPR's Mary Louise Kelly speaks to General Mark Milley, the former Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and Eric Schmidt, the former CEO of Google, about how technology is transforming warfare.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a powerful technology adopted in various industries. Applications of the IoT aim to enhance automation, productivity, and user comfort in a cloud and distributive computing environment. Cloud computing automatically stores and analyzes the large amounts of data generated by IoT-based applications. Cloud computing has become a crucial component of the information ...