Essay Papers Writing Online
A comprehensive guide to writing a response essay that will help you ace your academic assignments.

Writing a response essay can be a challenging task, as it requires you to analyze a piece of literature, a movie, an article, or any other work and provide your personal reaction to it. This type of essay allows you to express your thoughts and feelings about the content you’re responding to, and it can help you develop critical thinking and analytical skills.
In order to craft a compelling response essay, you need to carefully read and understand the work you’re responding to, identify key themes and arguments, and formulate a clear and coherent response. This guide will provide you with tips and strategies to help you write an effective response essay that engages your readers and communicates your ideas effectively.

Key Elements of a Response Essay
A response essay typically includes the following key elements:
- Introduction: Begin with a brief summary of the text you are responding to and your main thesis statement.
- Summary: Provide a concise summary of the text, focusing on the key points and arguments.
- Analysis: Analyze and evaluate the text, discussing its strengths, weaknesses, and the effectiveness of its arguments.
- Evidence: Support your analysis with evidence from the text, including quotes and examples.
- Personal Reaction: Share your personal reaction to the text, including your thoughts, feelings, and opinions.
- Conclusion: Sum up your response and reiterate your thesis statement, emphasizing the significance of your analysis.
By incorporating these key elements into your response essay, you can effectively engage with the text and provide a thoughtful and well-supported response.
Understanding the Assignment
Before you start writing your response essay, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the assignment requirements. Read the prompt carefully and identify the main objectives of the assignment. Make sure you understand what the instructor expects from your response, whether it is a critical analysis of a text, a personal reflection, or a synthesis of different sources.
Pay attention to key elements such as:
- The topic or subject matter
- The purpose of the response
- The audience you are addressing
- The specific guidelines or formatting requirements
Clarifying any doubts about the assignment will help you focus your response and ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria for a successful essay.
Analyzing the Prompt
Before you start writing your response essay, it is crucial to thoroughly analyze the prompt provided. Understanding the prompt is essential for crafting a coherent and well-structured response that addresses the key points effectively. Here are some key steps to consider when analyzing the prompt:
- Carefully read the prompt multiple times to fully grasp the main question or topic that needs to be addressed.
- Identify the key words and phrases in the prompt that will guide your response and help you stay focused on the main theme.
- Consider any specific instructions or requirements outlined in the prompt, such as the length of the essay, the format to be used, or the sources to be referenced.
- Break down the prompt into smaller parts or components to ensure that you cover all aspects of the question in your response.
- Clarify any terms or concepts in the prompt that are unclear to you, and make sure you have a solid understanding of what is being asked of you.
By analyzing the prompt carefully and methodically, you can ensure that your response essay is well-structured, focused, and directly addresses the main question or topic at hand.
Developing a Thesis Statement

One of the most critical aspects of writing a response essay is developing a clear and strong thesis statement. A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of your essay. It sets the tone for your entire response and helps guide your reader through your arguments.
When developing your thesis statement, consider the following tips:
| 1. | Identify the main topic or issue you will be responding to. |
| 2. | State your position or stance on the topic clearly and concisely. |
| 3. | Provide a brief preview of the key points or arguments you will present in your essay to support your thesis. |
Remember, your thesis statement should be specific, focused, and debatable. It should also be located at the end of your introduction paragraph to ensure it captures the reader’s attention and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
Structuring Your Response
When structuring your response essay, it’s essential to follow a clear and logical format. Start with an introduction that provides background information on the topic and presents your thesis statement. Then, organize your body paragraphs around key points or arguments that support your thesis. Make sure each paragraph focuses on a single idea and provides evidence to back it up.
After presenting your arguments, include a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your thesis. Remember to use transitions between paragraphs to ensure a smooth flow of ideas. Additionally, consider the overall coherence and cohesion of your response to make it engaging and easy to follow for the reader.
Main Body Paragraphs

When writing the main body paragraphs of your response essay, it’s essential to present your arguments clearly and logically. Each paragraph should focus on a separate point or idea related to the topic. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, and then provide supporting evidence or examples to reinforce your argument.
- Make sure to organize your paragraphs in a coherent and sequential manner, so that your essay flows smoothly and is easy for the reader to follow.
- Use transition words and phrases, such as “furthermore,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand,” to connect your ideas and create a cohesive structure.
- Cite sources and provide proper references to strengthen your arguments and demonstrate the credibility of your analysis.
Remember to analyze and evaluate the information you present in each paragraph, rather than simply summarizing it. Engage critically with the texts, articles, or sources you are referencing, and develop your own perspective or interpretation based on the evidence provided.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
How to Write a Critical Response Essay With Examples and Tips
- Icon Calendar 20 July 2024
- Icon Page 5910 words
- Icon Clock 27 min read
A critical response essay is an important type of academic essay, which instructors employ to gauge the students’ ability to read, react, and respond critically and express their opinions. Firstly, this guide begins with a detailed definition of a critical response paper and an extensive walkthrough of source analysis and its format. Next, the manual breaks down the writing process into the pre-writing, writing, and post-writing stages and discusses each stage in extensive detail. Finally, the article provides practical examples of an outline and a paper itself, which implement the writing strategies and guidelines of critical response writing. After the examples provided, there is a brief overview of documentation styles for people to use in their papers. Hence, students need to learn how to write a perfect critical response essay to follow its criteria.
What Is a Critical Response Essay and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a critical response essay presents a writer’s reaction to the content of an article, text, book, story, film, artwork, play, performance, or any other piece of writing and the author’s strategy for achieving his or her intended purpose. Basically, this type of paper goes beyond mere summary and response, requiring the writer to engage deeply with the material to assess its merits and shortcomings (Wallace & Wray, 2021). The main purpose of writing a critical response essay is to develop a reasoned argument that expresses the writer’s analysis and critique. Moreover, a critical response to a piece of any text under review demands an analysis, interpretation, and synthesis of a reading (Ogbonnaya & Brown, 2023). These parts allow readers to develop their personal positions and reactions concerning the extent to which an author of a specific work creates a desired effect on the audience, establishing it implicitly or explicitly at the beginning. Mostly, students assume that a critical reaction revolves around the identification of flaws, but this aspect only represents one dimension of writing (Davies, 2022). In turn, a critical response in an essay should identify both the strengths and weaknesses of the work under analysis and present them without exaggerating their significance.
Source Analysis

1. Questions That Guide Source Analysis
Writers engage in textual analysis through critical reading. Hence, students undertake this reading to answer three primary questions:
- What does the author say or show unequivocally?
- What does the author not say or show outright but implies intentionally or unintentionally in the text?
- What do I think about responses to the previous two questions?
Readers should strive to comprehensively answer these questions with the context and scope of a critical response essay. Basically, the need for objectivity is necessary to ensure the student’s analysis does not contain any biases through unwarranted or incorrect comparisons (Ogbonnaya & Brown, 2023). Nonetheless, the author’s pre-existing knowledge concerning the topic is crucial in facilitating the process of critical reading. In turn, the generation of answers to three guiding questions occurs concurrently throughout the close reading of an assigned text or other topics.
2. Techniques of Critical Reading
Previewing, reading, and summarizing are the main methods of critical reading. Basically, previewing a text allows readers to develop some familiarity with the content of any paper, which they gain through exposure to content cues, publication facts, important statements, and authors’ backgrounds (Fort, 1971). In this case, readers may take notes of questions that emerge in their minds and possible biases related to prior knowledge. Then, reading has two distinct stages: first reading, rereading, and annotating. In this case, students read an assigned text at an appropriate speed for the first time with minimal notetaking. After that, learners reread a text to identify core and supporting ideas, key terms, and connections or implied links between ideas while making detailed notes (Lauritzen, 2021). Lastly, writers summarize their readings into the main points by using their own words to extract the meaning and deconstruct reaction papers into meaningful parts. As such, writers should avoid bias in a critical response essay because it undermines the objectivity and credibility of the entire analysis, and, before writing a paper, they should ask themselves the next minor guiding questions:
- What is the author’s background?
- What is the purpose of the source?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What is the main argument or thesis?
- What evidence does the author use to support their argument?
- How does the source fit into the broader context?
- What assumptions does the author make?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
- How does the author address counterarguments or alternative perspectives?
- What is the overall impact or significance of the source?
3. Creating a Critical Response
Up to this point, source analysis is a blanket term that represents the entire process of developing a critical response. Mainly, the creation of a reaction paper involves analysis, interpretation, and synthesis, which occur as distinct activities (Lauritzen, 2021). In this case, students analyze their readings by breaking down texts into elements with distilled meanings and obvious links to a thesis statement. During analysis, writers may develop minor guiding questions under first and second guiding questions, which are discipline-specific. Then, learners focus on interpretations of elements to determine their significance to an assigned text as a whole, possible meanings, and assumptions under which they may exist (Lauritzen, 2021). Finally, they create connections through the lens of relevant pre-existing knowledge, which represents a version of the element’s interconnection that they perceive to be an accurate depiction of a text. In turn, the length of a critical response essay varies by academic level and the specific requirements of the course or instructor. Here are general guidelines for the length of critical response essays at different academic levels:
High School
- Pages: 2-4 pages
- Words: 500-1,000 words
College (Undergraduate)
- Pages: 3-5 pages
- Words: 750-1,500 words
University (Upper Undergraduate)
- Pages: 5-8 pages
- Words: 1,500-2,500 words
Master’s
- Pages: 8-12 pages
- Words: 2,500-4,000 words
- Pages: 12-20 pages
- Words: 4,000-8,000 words
Critical Response Essay Format
| Introduction | Introduce the work under analysis with its title and author, including a brief summary in 1-2 sentences, to provide further context. | In a well-known novel “To Kill a Mockingbird,” Harper Lee explores sensitive themes of racial injustice among people and their moral growth. |
| Thesis Statement | Present your main argument or perspective on the work. | Lee uses Atticus Finch as one of the central characters to highlight the pervasive racial injustices of the American South. |
| Summary of the Work | Provide a concise summary of the work, focusing on key points relevant to your analysis. | The novel presents the main character of Scout Finch, a young girl, as she grows up in a racially divided town and witnesses that her father defends a Black man accused of rape. |
| Analysis: Theme | Discuss the main themes of the work and how they are developed. | The theme of racial injustice is central to the novel, and it is illustrated through the trial of Tom Robinson. |
| Analysis: Characters | Examine the main characters and their development. | Atticus Finch embodies moral integrity, serving as a role model for his children and the community. |
| Analysis: Techniques | Analyze some literary techniques used by the author (e.g., symbolism, imagery, narrative style). | Lee uses symbolism, such as the ‘mockingbird,’ to represent innocence and the destruction caused by evil. |
| Personal Reflection | Reflect on your personal response to the work and explain how it resonated with you and why. | The novel’s portrayal of justice and morality deeply impacted me, prompting me to reflect on my own beliefs. |
| Supporting Evidence | Provide specific examples and quotes from the work or other credible sources to support your analysis and reflections. | Finch says, “You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view… .” |
| Conclusion | Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and provide final thoughts on the work’s significance. | Through its strong themes and compelling characters, Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird” remains an outstanding example of literature concerning justice and human dignity. |
Note: Analysis sections can be added, deleted, or combined with each other in 1 paragraph depending on the type of the source under review and assignment requirements. Other sections must be provided to ensure writers follow the key rules of critical reading criteria.
Critical Response Essay Outline Template
I. Introduction
A. Summary of an article. B. Thesis statement.
A. First body paragraph
- The idea for the first paragraph.
- Evidence for the first point from an article.
- Interpretation of the evidence.
B. Second body paragraph
- The idea for the second paragraph.
- Evidence for the second point from an article.
C. Third body paragraph
- The idea for the third paragraph.
- Evidence for the third point from an article.
III. Conclusion
A. Summary of three points that form a body section. B. Closing remarks.
The presence of a summary in the introduction and an interpretation for each piece of evidence are defining features of a critical response essay. Typically, the introduction, being one of 5 parts of an essay, does not contain a succinct summary of a source that an author uses in body paragraphs (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). In this case, the incorporation of a summary and response in the introduction paragraph provides the audience with specific information concerning the target article. Specifically, such a work differs from other response papers because it emphasizes the provision of reasonable judgments of a text rather than the testing and defense of one’s evaluations or arguments (Wallace & Wray, 2021). In turn, writers do not provide evaluation for their judgments, which implies critical responses may be different but correct if a specific interpretation is reasonable to the audience.
Expanding an Outline Format Into a Critical Response Essay
1. introduction.
The introductory paragraph in a critical response essay consists of two primary sections: a summary of an article and a thesis statement. Firstly, a summary of an article consists of the text’s central argument and the purpose of the presentation of the argument (Davies, 2022). Basically, students should strive to distill the main idea and purpose of the text into a few sentences because the length of the introduction is approximately 10% of the essay’s word count. Then, a summary provides the audience with adequate background information concerning an article, which forms a foundation for announcing the student’s primary idea. In this case, writers may include an additional sentence between a summary and a thesis statement to establish a smooth flow in the opening paragraph (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). However, learners should not quote thesis and purpose statements because it results in a fragmented introduction, which is unappealing to readers and ineffective.
- All body paragraphs have in a critical response essay four main elements: the writer’s idea, meaningful evidence from a reading text, interpretation of the evidence, and a concluding statement.
A. Writer’s Idea
The writer’s idea for a paragraph appears in the first sentence of a paragraph, which is a topic sentence. For example, if students know how to write a topic sentence, they present readers with a complete and distinct idea that proves or supports a thesis statement (Davies, 2022). In this case, authors should carefully word their topic sentences to ensure there is no unnecessary generalization or spillovers of ideas from other paragraphs. Notably, all the topic sentences in the body of a critical response essay share a logical relationship that allows the audience to easily follow the development of the central idea of a paper.
B. Evidence
Students should provide evidence that supports the idea they propose in the topic sentence. Basically, the evidence for all body paragraphs is the product of critical reading of an article, which allows writers to identify meaningful portions of a text (Wallace & Wray, 2021). During the presentation of evidence, learners should ascertain that the contextual meaning of paraphrases or quotations is not lost because such a strategy will harm interpretations that follow after it. In turn, critical response essays must not contain lengthy or numerous quotations unless the meaning or intended effect of a quotation is not replicable upon paraphrasing.
C. Interpretation
Interpretation segments of paragraphs allow writers to explain the significance of the evidence to the topic sentence. In a critical response essay, the interpretation is the equivalent of an author revealing the possible assumptions behind a text paraphrase and commenting on whether or not he or she finds them reasonable (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Moreover, students make inferences concerning their meaning in the context of the entire narrative and its relation to the paragraph’s idea. In turn, learners should refrain from reading too much into a piece of evidence because it may result in false or unreasonable inferences.
D. Concluding Sentence
The concluding statement is the final sentence of any paragraph. In this case, the primary role of the concluding sentence is to emphasize the link between the topic sentence, evidence, interpretation, and the paper’s central idea (Davies, 2022). Besides, the concluding statement should not contain an in-text citation because it does not introduce new evidence to support the topic sentence. Therefore, authors use concluding sentences to maintain the unity between body paragraphs and a critical response essay in its entirety.
3. Conclusion
The conclusion comprises three core elements: a restatement of a thesis statement, a summary of the main points that writers present in body paragraphs, and closing remarks. In particular, the first sentence of the conclusion draws the attention of the audience to the central idea, which an author proposes in a thesis statement (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). Then, students review the main points of their papers to demonstrate that written arguments in body paragraphs adequately support a thesis statement. Moreover, writers should summarize the main points of a paper in the same order they appear in the main part and guarantee logical patterns in the body are readily discernible in summary. Finally, learners make their closing remarks, which creates a sense of wholesomeness in a critical response essay or ties a paper to a larger relevant discourse.
Writing Steps of a Critical Response Essay
Step 1: pre-writing, a. analysis of writing situation.
Objective. Before a student begins writing a critical response essay, he or she must identify the main reason for communication to the audience by using a formal essay format. Basically, the primary purposes of writing reaction papers are explanation and persuasion, and it is not uncommon for two objectives to overlap (Davies, 2022). However, one of the purposes is usually dominant, which implies it plays a crucial role in the wording, evidence selection, and perspective on a topic. In turn, students should establish their purposes in the early stages of the writing process because the purpose has a significant effect on the essay writing approach. Beginning a critical response essay correctly also effectively sets an appropriate tone and provides a clear direction for the whole analysis (Fort, 1971). All opening sentences must introduce the subject, set the context, and hint at the writer’s perspective or main argument. Here are ten examples of starting sentences:
- The famous narrative of [Title] by [Author] shows [main theme], revealing [author’s message or argument].
- In [Title], [Author] masterfully employs [literary device] to explore [theme or issue], prompting readers to consider [related question or implication].
- The powerful depiction of [subject] in [Title] by [Author] challenges conventional views on [topic], offering a new perspective on [specific aspect].
- Through [Title], [Author] presents a compelling argument about [issue], using [specific elements] to underscore [main point or message].
- The thought-provoking themes of [Title] by [Author] allow readers to critically assess [related topic or issue], shedding light on [specific aspect].
- In [Title], [Author] explores the complexities of [subject], using [specific technique] to highlight [main idea or argument].
- The evocative imagery in [Title] by [Author] serves to illustrate [theme], encouraging readers to reflect on [related issue or question].
- By examining [specific aspect] in [Title], [Author] effectively critiques [related issue], providing valuable insights into [main point].
- The dynamic characters and intricate plot of [Title] by [Author] offer a rich exploration of [theme], challenging readers to think critically about [related topic].
- In [Title], [Author] uses [specific technique] to convey [main idea], ultimately arguing that [related point or implication].
Audience. Students should establish a good understanding of the audience’s expectations, characteristics, attitudes, and knowledge in anticipation of the writing process. Basically, learning the audience’s expectations enables authors to meet the organizational demands, ‘burden of proof,’ and styling requirements (Lauritzen, 2021). In college writing, it is the norm for all essays to attain academic writing standards. Then, the interaction between characteristics and attitudes forces students to identify a suitable voice, which is appreciative of the beliefs and values of the audience (Davies, 2022). Lastly, writers must consider the level of knowledge of the audience while starting a critical response essay because it has a direct impact on the context, clarity, and readability of a paper. Consequently, writing a critical response essay for classmates is quite different from a paper that an author presents to a multi-disciplinary audience.
Define a topic. Topic selection is a critical aspect of the prewriting stage to respond. Ideally, assignment instructions play a crucial role in topic selection, especially in higher education institutions. For example, when writing a critical response essay, instructors may choose to provide students with a specific article or general instructions to guide learners in the selection of relevant reading sources (Wallace & Wray, 2021). In this case, students may not have opportunities for independent topic selection in former circumstances. However, by considering the latter assignment conditions, learners may need to identify a narrow topic to use in article selection. Moreover, students should take adequate time to do preliminary research, which gives them a ‘feel’ of the topic, for example, 19th-century literature. Next, writers narrow down the scope of the topic based on their knowledge and interests, for example, short stories by black female writers from the 19 th century.
B. Research and Documentation
Find sources. Once a student has a topic, he or she can start the process of identifying an appropriate article. Basically, choosing a good source for writing a critical response essay is much easier when aided with search tools on the web or university repository (Davies, 2022). In this case, learners select keywords or other unique qualities of an article and develop a search filter. Moreover, authors review abstracts or forewords of credible sources to determine their suitability based on their content (Ogbonnaya & Brown, 2023). Besides content, other factors constrain the article selection process: the word count for a critical response essay and a turnaround time. In turn, if an assignment has a fixed length of 500 words and a turnaround time of one week, it is not practical to select a 200-page source despite content suitability.
Content selection. The process of selecting appropriate content from academic sources relies heavily on the purpose of a critical response essay. Basically, students must select evidence that they will include in a paper to support their claims in each paragraph (Wallace & Wray, 2021). However, writers tend to let a source speak through the use of extensive quotations or summaries, which dilutes a synthesis aspect of a critical reaction essay. Instead, learners should take a significant portion of time to identify evidence from reliable sources, which are relevant to the purpose of an essay (Davies, 2022). In turn, a student who is writing a critical response essay to disagree with one or more arguments will select different pieces of evidence as compared to a person who is writing to analyze the overall effectiveness of the work.
Annotated bibliography. An annotated bibliography is vital to the development of a critical response essay because it enables students to document useful information that they encounter during research. During research and documentation stages for a critical response essay, annotated bibliographies contain the main sources for a paper and other sources that contribute to the knowledge base of an author, even though these sources will not appear in reference lists (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Mostly, a critical response paper has only one source. However, an annotated bibliography contains summaries of other sources, which may inform the author’s response through the development of a deep understanding of a topic. In turn, an annotated bibliography is quite useful when an individual is writing a critical response to an article on an unfamiliar topic.
Step 2: Writing a Critical Response Essay
A. organization.
Thesis . A thesis statement sentence is a crucial component of a critical response essay because it presents the student’s purpose, argument, and the conclusion that he or she draws from the textual evidence. In this case, the thesis statement is the response to the thesis question, which an author creates from assignment instructions (Davies, 2022). After completing the research stage, students can develop a tentative thesis statement to act as a starting point for the writing stage. Usually, tentative thesis statements undergo numerous revisions during the writing stage, which is a consequence of the refinement of the main idea during the drafting. In turn, these examples of sentence starters can help writers to craft a strong thesis statement that clearly defines a critical response lens and the main argument or insight:
- In [Title], [Author] effectively/ineffectively uses [element] to convey [theme or message], prompting readers to … .
- Through [specific technique or element], [Title] by [Author] offers a compelling critique/endorsement of [issue or theme], illustrating that … .
- The portrayal of [character/element] in [Title] by [Author] serves as a powerful commentary on [issue or theme] because of … .
- In [Title], [Author] explores [theme or issue] through [specific technique or narrative], demonstrating … .
- The [specific element] in [Title] by [Author] highlights the complexities of [theme or issue], suggesting that … .
- By examining [element or aspect] in [Title], [Author] provides a better insight into [theme or issue], challenging readers to consider…
- In [Title], [Author] uses [literary device or technique] to address [theme or issue], ultimately arguing … .
- The narrative structure of [Title] by [Author] effectively/ineffectively conveys [theme or message], encouraging readers to … .
- Through the lens of [specific perspective], [Title] by [Author] reveals the intricacies of [theme or issue] and suggests that … .
- In [Title], [Author] employs [specific technique] to critique/celebrate [issue or theme], making a particular situation when … .
Weigh the evidence. Based on the tentative thesis, an author evaluates the relative importance of collected pieces of textual evidence to the central idea. Basically, students should distinguish between general and specific ideas to ascertain that there exists a logical sequence of presentation, which the audience can readily grasp (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Firstly, for writing a critical response essay, learners should identify general ideas and establish specific connections that exist between each general idea and specific details, which support a central claim. Secondly, writers should consider some implications of ideas as they conduct a sorting process and remove evidence that does not fit. Moreover, students fill ‘holes’ that are present due to the lack of adequate supporting evidence to conclude this stage.
Create an outline. An essay outline is a final product of weighing the significance of the evidence in the context of the working thesis statement. In particular, a formal outline is a preferred form of essay structure for a critical response paper because it allows for detailed documentation of ideas while maintaining a clear map of connections (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). During the formation of an outline, students use a systematic scheme of indentation and labeling all the parts of an outline structure. In turn, this arrangement ensures elements that play the same role are readily discernible at a glance, for example, primary essay divisions, secondary divisions, principle supporting points, and specific details.
Drafting. The drafting step involves the conversion of the one-sentence ideas in an outline format into complete paragraphs and, eventually, a critical reaction essay. In this case, there is no fixed approach to writing the first draft. Moreover, students should follow a technique they find effective in overcoming the challenge of starting to write a critical response essay (Davies, 2022). Nonetheless, it is good practice to start writing paragraphs that authors believe are more straightforward to include regardless of specific positions they hold on an outline. In turn, learners should strive to write freely and be open to new ideas despite the use of an outline. During drafting, the conveyance of meaning is much more important than the correctness of the draft.
Step 3: Post-Writing
Individual revision. An individual revision process focuses on the rethinking and rewriting of a critical response essay to improve the meaning and structure of a paper. Essentially, students try to review their papers from a perspective of readers to ensure the level of detail, relationship and arrangement of paragraphs, and the contribution of the minor ideas to the thesis statement attain the desired effect (Campbell & Latimer, 2023). In this case, the use of a checklist improves the effectiveness of individual revision. Moreover, a checklist contains 12 main evaluation categories: assignment, purpose, audience and voice, genre, thesis, organization, development, unity, coherence, title, introduction, and conclusion.
Collaborative revision. Collaborative revision is a revision strategy that covers subconscious oversight that occurs during individual revision. During an individual revision of a critical response essay, writers rely on self-criticism, which is rarely 100% effective because writers hold a bias that their works are of high quality (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Therefore, subjecting an individual’s work to peer review allows students to collect critique from an actual reader who may notice problems that an author may easily overlook. In turn, learners may provide peer reviewers with a checklist to simplify the revision process.
Editing . The editing step requires authors to examine the style, clarity, and correctness of a critical response essay. In particular, students review their papers to ascertain their conformance with the guidelines of formal essay writing and the English language (Davies, 2022). Moreover, sentence fragments, subject-verb agreement, dangling modifiers, incorrect use of punctuation, vague pronoun references, and parallelism are common grammar issues that learners eliminate during editing. Then, writers confirm that their critical reaction essays adhere to referencing style guidelines for citation and formatting, such as the inclusion of a title page, appropriate in-text citation, and proper styling of bibliographic information in the reference list (Wallace & Wray, 2021). In turn, students must proofread a critical response paper repeatedly until they find all errors because such mistakes may divert the audience’s attention from the content of a paper and consider the following criteria to ensure a comprehensive and reflective piece:
- Clear Thesis Statement: Present a clear and concise thesis statement that reflects your overall response to an assigned text or experience, outlining your main argument or perspective.
- Personal Connection: Describe your personal connection to the subject matter and explain how the text or experience resonates with your own experiences, feelings, or beliefs.
- Summary of the Source: Provide a brief summary of the source under analysis you are responding to, highlighting key points relevant to your response.
- Detailed Analysis: Analyze specific elements of the source that are important to you, including characters, themes, settings, or any other aspects that lead to a strong reaction.
- Supporting Evidence: Use quotes, examples, or references from the work under review or other credible sources to support your response and personal reflections on the actual content.
- Emotional and Intellectual Reflection: Balance your emotional reactions with intellectual analysis and reflect on why certain aspects make you feel a particular way and explore any deeper meanings or implications.
- Organization: Ensure your essay is well-organized, with a clear and strong introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion that ties everything together.
- Clarity and Coherence: Write clearly and coherently, making sure your ideas flow logically from one point to the next, avoiding ambiguity, and ensure each paragraph transitions smoothly.
- Personal Voice: Maintain a personal and engaging tone throughout the entire composition, making your writing genuine and authentic.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your writing and reflect on the overall impact of the source on your thoughts and feelings or discuss any changes in perspective or insights gained.
Example of Writing a Critical Response Essay
Topic: American Capitalism: The New Face of Slavery
I. Sample Introduction
Capitalism is a dominant characteristic of the American economy. In this case, Matthew Desmond’s article “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation” discusses the role of slavery in shaping contemporary business practices. Specifically, the author attempts to convince the audience that the brutality of American capitalism originates from slavery. In turn, Desmond lays a strong but simple foundation for his argument, which ensures that the audience can conceptualize the link between plantation slavery and contemporary American capitalistic practices.
II. Example of Body Paragraphs
A. American Capitalism
Early in the article, Desmond informs readers of the high variability in the manifestation of capitalism in societies, which creates the impression that American capitalism is a choice. For example, Desmond (2019) argues that the brutality of American capitalism is simply one of the possible outcomes of a society built on capitalistic principles because other societies implement the same principles in a manner that is liberating, protective, and democratic. Moreover, Desmond begins his argument by eliminating a popular presumption that exploitation and oppression are unavoidable outcomes of capitalism. In turn, this strategic move to establish this fact is in the introductory section of the article because it invites the audience to rethink the meaning of capitalism. Furthermore, its plants doubt regarding the ‘true’ meaning of capitalism outside the context of American society.
B. Slavery and American’s Economic Growth
After establishing that the perception of capitalism through the lens of American society has some bias, Desmond proceeds to provide detailed evidence to explain the attempt to camouflage the obvious link between slavery and America’s economic growth. For instance, Desmond (2019) notes the role of Alfred Chandler’s book, The Visible Hand, and Caitlin Rosenthal’s book, Accounting for Slavery, in breaking the link between management practices in plantations and modern corporations by suggesting that the current business practices are a consequence of the 19th-century railroad industry. In this case, Desmond uses this evidence to make a logical appeal to the audience, which makes his argument more convincing because he explains the reason behind the exclusion of slavery in the discourse on modern industry. As a result, Desmond dismisses one of the main counterarguments against his central argument, which increases his persuasive power.
C. Input vs. Output Dynamic
Desmond emphasizes the link between slavery and American capitalism to readers by using the simple input vs. output dynamic throughout the article. For example, Desmond (2019) compares the Plantation Record and Account Book to the heavy digital surveillance techniques in modern workplaces because they collect data, which the employers use to maximize productivity while minimizing inputs. In particular, the comparison reveals that employers did not stop the practice of reducing laborers into units of production with fixed productivity thresholds. Moreover, the constant repetition of the theme of low input and high output dominates the body paragraphs, which makes it nearly impossible for readers to lose sight of the link between slavery and business practices under American capitalism. In turn, the simplification of the underlying logic in Desmond’s argument ensures its clarity to the audience.
III. Sample Conclusion
Desmond carefully plans the presentation of his argument to the audience, which allows readers to follow the ideas easily. In particular, the author starts with a call for readers to set aside any presumptions concerning capitalism and its origin. Then, Desmond provides the audience with an alternative narrative with support from seminal texts in slavery and economics. On the whole, Desmond manages to convince the audience that the American capitalistic society is merely a replica rather than an aberration of slavery.
Citing Sources in a Critical Response Essay
A critical response essay contains specific thoughts of the article’s author and direct words of the text’s author. In this case, students must conduct proper documentation to ensure readers can distinguish between these two types of ‘voices’ (Wallace & Wray, 2021). Moreover, documentation prevents incidents of plagiarism. Usually, instructors mention a referencing technique that students should use while writing a critical response paper. However, if assignment instructions do not identify a specific documentation style, writers should use a referencing technique that is acceptable for scholarly writing in their disciplines.
In-text citation:
- Parenthetical: (Desmond, 2019).
- Narrative: Desmond (2019).
- Desmond, M. (2019, August 12). In order to understand the brutality of American capitalism, you have to start on the plantation. New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html
- Parenthetical: (Desmond par. 1).
- Narrative: Desmond argues . . . (par. 1).
Works Cited:
- Desmond, Matthew. “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation.” New York Times , 14 Aug. 2019, www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html.
Harvard Referencing
- Parenthetical: (Desmond 2019).
Reference List:
- Desmond, M 2019, ‘In order to understand the brutality of American capitalism, you have to start on the plantation,’ New York Times . Available from: <https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html>. [06 June 2024].
Chicago/Turabian
In-text citation (footnote):
- 1. Matthew Desmond, “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation,” New York Times , August 14, 2019, https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html.
Bibliography:
- Desmond, Matthew. “In Order to Understand the Brutality of American Capitalism, You Have to Start on the Plantation.” New York Times . August 14, 2019. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/08/14/magazine/slavery-capitalism.html.
Final Provisions on a Critical Response Essay
- Adequate reading is a precursor for writing an effective critical response essay.
- Students must conduct adequate research on a topic to develop a proper understanding of a theme, even if only one article appears on the reference list.
- Notetaking or annotation is a good practice that aids students in extracting meaning from an article.
- Writers should plan for all activities in the writing process to ascertain they have adequate time to move through all the stages.
- An outline is an organizational tool, which learners must use to establish the sequence of ideas in such a paper.
- The purpose of a critical response essay has a significant impact on the selection of evidence and the arrangement of body paragraphs.
- Students should prioritize revision and editing, which represent opportunities to refine the content of composition and remove mechanical issues.
- Collaborative and individual revision are equally important because they play different roles in the writing of a good paper.
- Evidence selection is dependent on the purpose and thesis statement of a critical response essay.
Campbell, K. H., & Latimer, K. (2023). Beyond the five-paragraph essay . Routledge.
Davies, M. (2022). Writing critical reviews: A step-by-step guide. In S tudy skills for international postgraduates (pp. 194–207). Bloomsbury. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312965969
Fort, K. (1971). Form, authority, and the critical essay. College English , 32 (6), 629–639. https://www.jstor.org/stable/374316
Lauritzen, J. (2021). Read, write, and cite . Kendall Hunt Publishing Company.
Ogbonnaya, C., & Brown, A. D. (2023). Editorial: Crafting review and essay articles for Human Relations . Human Relations , 76 (3), 365–394. https://doi.org/10.1177/00187267221148440
Wallace, M., & Wray, A. (2021). Critical reading and writing for postgraduates . Sage.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

723 Informative Essay Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 8 September 2020
- Icon Page 6759 words

Character Analysis Essay: Student Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 6 September 2020
- Icon Page 6256 words
📕 Studying HQ
How to write a Response Essay.
Carla johnson.
- June 13, 2023
- How to Guides
A response essay is an important part of academic writing because they give students a chance to think about the ideas and arguments in a text and give their own thoughts and opinions on the subject. Response essays are different from other types of essays because students not only have to summarize the text, but also analyze and evaluate it in a critical way.
These essays are important because they help students learn how to think critically, improve their writing skills, and deal with complicated ideas and arguments. In this article, we’ll talk about how to write response essays and give students tips, examples, and ideas for topics to help them learn this important skill.
In this article, readers will learn what response essays are, how to write a good response essay, and what kinds of topics are good for this type of assignment. By the end of this article, readers will know exactly what it takes to write a good response essay and have the tools and knowledge they need to confidently take on this type of assignment.
What You'll Learn
What is a Response Essay?
In a response essay, the writer talks about how they feel about a certain text, article, or book. The goal of a response essay is to analyze the text critically and share the writer’s thoughts and opinions about the topic.
Response essays are different from argumentative and expository essays in that the writer must give their own opinion on the topic. Even though a summary of the text is often part of a response essay, it is not the main point.
An introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion are the most important parts of a response essay. The introduction should give background information about the text and include a thesis statement that shows the writer’s opinion about the text. The writer’s argument should be backed up by evidence and examples from the text in the body paragraphs. The conclusion should restate the essay’s main points and give a final opinion on the text.
Elements of a Response Essay
To write an effective response essay, it is important to include several key elements in the essay . These include:
Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on the text, including the author, title, and publication date. It should also include a thesis statement that expresses the writer’s opinion about the text.
Body Paragraphs: The writer’s argument should be backed up by evidence and examples from the text in the body paragraphs. It’s important to think critically about the text and give specific examples to back up the writer’s ideas and opinions. Each paragraph in the body should be about a different part of the text, and the writer should use transitions to link the paragraphs and keep the flow of ideas smooth.
Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points of the essay and provide a final opinion on the text. It should not introduce any new ideas or information, but rather provide closure for the reader and reinforce the writer’s thesis statement .
Thesis Statement: The thesis statement is a critical component of a response essay, as it expresses the writer’s opinion on the text. The thesis statement should be clear, concise, and focused on the main argument of the essay. It should provide a roadmap for the reader and guide the writer’s analysis and evaluation of the text.
Evidence and Examples: In a response essay, the writer’s argument needs to be backed up by evidence and examples from the text. The writer should back up their ideas and thoughts with specific examples and quotes from the text. It is important to think carefully about the evidence and explain how it backs up the writer’s argument .
Writing a response essay means carefully analyzing and judging a piece of writing, as well as being able to say what you think and feel about it. By including the key points talked about in this article, writers can effectively communicate their ideas and make sense of complicated texts.
Don’t forget to use clear, concise language, give specific examples and proof, and stick to the main point of your essay . With these tips, writers can learn how to write response essays and effectively respond to academic texts in their writing.
How to Write a Response Essay
Writing a response essay can be a challenging task, but it can also be a rewarding one. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a response essay:
Before you start writing your response essay, it is important to read the text carefully and take notes on important ideas and concepts . Consider the main argument of the text and evaluate the evidence and examples used to support it. Think about your own experiences and opinions on the subject matter and how they relate to the text.
Once you’re done with your planning, you can start writing your response essay. Start with an introduction that tells what the text is about and includes a clear thesis statement that shows what you think about it. Use body paragraphs to analyze and evaluate the text critically , using evidence and examples from the text to support your arguments. Use transitions between paragraphs to make sure the ideas flow smoothly. Finish with a summary of your main points and your final thoughts on the text.
After you finish the first draft of your essay, you should go back and fix any mistakes. Read your essay carefully , making sure there are no spelling or grammar mistakes and that it makes sense. Think about how your essay is put together and make any changes you need to make sure your argument is clear and well-supported. It’s important to follow a clear and logical format when setting up and organizing your response essay. Start with an introduction that gives background information about the text and a thesis statement that is clear and focused. Use the body paragraphs to back up your thesis statement with evidence and examples from the text, and make sure to use clear, concise language. Use transitions to link your paragraphs and keep your ideas moving smoothly. Finish with a summary of your main points and your final thoughts on the text. When writing a response essay, common mistakes to avoid include summarizing the text instead of analyzing and evaluating it, not giving specific examples and evidence to back up your arguments, and not revising and editing your essay carefully .
Response Essay Examples
Here are 10 fascinating response essay examples from different academic fields:
1. The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers” by Jane Smith
2. “The Role of Art in Society” by John Doe
3. “The Ethics of Genetic Engineering” by Sarah Johnson
4. The Importance of Education in Developing Countries” by Michael Brown
5. The Significance of the Civil Rights Movement” by Angela Davis
6. “The Future of Renewable Energy” by David Lee
7. The Effects of Climate Change on Marine Life” by Rachel Wilson
8. The Impact of Technology on Human Relationships” by Emily Jones
9. “The Role of Women in Politics” by Susan Lee
10. The Importance of Cultural Diversity in the Workplace” by Maria Hernandez
Each of these response essay examples provides a clear and focused thesis statement that expresses the writer’s opinion on the subject matter. The body paragraphs use specific examples and evidence from the text to support the arguments, and the conclusion summarizes the main points of the essay and provides a final opinion on the subject.
For example, in “The Ethics of Genetic Engineering” by Sarah Johnson, the thesis statement is clear and focused: “Genetic engineering poses ethical dilemmas that must be carefully considered before any scientific advances are made.” The body paragraphs provide specific examples and evidence to support this argument, such as the potential for genetic discrimination and the unknown long-term effects of genetic engineering. The conclusion summarizes the main points of the essay and provides a final opinion on the subject, emphasizing the need for caution and ethical considerations in genetic engineering.
Readers can use these examples to learn how to write effective response essays in their own academic fields. They can also analyze the key features of each example, such as the use of specific examples and evidence to support the argument, and use these techniques in their own writing. By learning from these examples, readers can become skilled response essay writers and effectively engage with complex texts in their academic writing.
Response Essay Topics
Here are 50 response essay topics that are sure to impress your professors:
1. The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
2. The Ethics of Animal Testing
3. The Role of Government in Healthcare
4. The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture
5. The Importance of Diversity in the Workplace
6. The Role of Art in Society
7. The Impact of Technology on Education
8. The Ethics of Cloning
9. The Significance of the Civil Rights Movement
10. The Future of Renewable Energy
11. The Effects of Immigration on the Economy
12. The Role of Women in Politics
13. The Impact of Video Games on Youth
14. The Ethics of Capital Punishment
15. The Importance of Voting Rights
16. The Effects of Globalization on Culture
17. The Role of Religion in Society
18. The Impact of Technology on Human Relationships
19. The Ethics of Stem Cell Research
20. The Significance of the Women’s Suffrage Movement
21. The Future of Space Exploration
22. The Effects of Social Media on Politics
23. The Role of Education in Reducing Poverty
24. The Importance of Mental Health Awareness
25. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Job Market
26. The Ethics of Euthanasia
27. The Significance of the American Revolution
28. The Future of Self-Driving Cars
29. The Effects of Income Inequality on Society
30. The Role of Media in Shaping Public Opinion
31. The Impact of COVID-19 on Education
32. The Ethics of Gene Editing
33. The Importance of Free Speech in Democracy
34. The Effects of Technology on Privacy
35. The Role of Sports in Society
36. The Impact of Climate Change on Public Health
37. The Ethics of Cybersecurity
38. The Significance of the Industrial Revolution
39. The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
40. The Effects of Social Media on Body Image
41. The Role of Animal Rights in Society
42. The Importance of Cultural Diversity in the Workplace
43. The Impact of Technology on Mental Health
44. The Ethics of Abortion
45. The Significance of the Women’s Rights Movement
46. The Future of Green Energy
47. The Effects of Immigration on Cultural Identity
48. The Role of Music in Society
49. The Impact of Technology on Privacy
50. The Ethics of Human Cloning
Each of these topics is interesting and important, providing ample opportunity for critical analysis and evaluation. They cover a broad range of subjects, including social issues, technology, ethics, history, and the environment . By choosing one of these topics for your response essay, you can demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in the subject matter and engage with complex ideas and arguments.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is the difference between a response essay and a summary.
A response essay requires critical analysis and evaluation of a text, while a summary simply provides a brief overview of the text. In a response essay, the writer provides their own opinions and thoughts on the text, while in a summary, the writer remains objective and simply summarizes the main points of the text.
2. What is the appropriate tone for a response essay?
The tone for a response essay should be professional and objective, while also expressing the writer’s personal opinions and thoughts. It is important to remain respectful and avoid using emotional language, while also conveying a sense of passion and engagement in the subject matter.
3. What are some tips for writing a strong conclusion for a response essay?
A strong conclusion for a response essay should summarize the main points of the essay and provide a final opinion on the text. It should also provide closure for the reader and reinforce the writer’s thesis statement. To write a strong conclusion, it is important to avoid introducing any new ideas or information and to end on a strong and memorable note.
Response Essay Outline and Structure
A clear and logical structure is essential for writing an effective response essay. Here is a sample response essay outline:
I. Introduction
A. Background information on the text
B. Thesis statement
II. Body Paragraph 1
A. Topic sentence
B. Evidence and examples from the text
C. Analysis and evaluation of evidence
III. Body Paragraph 2
IV. Body Paragraph 3
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of main points
B. Final opinion on the text
This outline can be customized for different topics and purposes by adjusting the number of body paragraphs and the amount of evidence and analysis required for each paragraph. For example, a more complex topic may require additional body paragraphs with more evidence and analysis, while a simpler topic may only require two or three body paragraphs.
Transitions are also important for maintaining a clear and logical structure in a response essay. Transitions help to connect the paragraphs and ensure a smooth flow of ideas. Some effective transition words and phrases to use in a response essay include “furthermore,” “in addition,” “however,” “on the other hand,” and “finally.”
In conclusion, response essays are an important part of academic writing that require critical analysis and evaluation of a particular text. To write an effective response essay, it is important to include key components such as an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. It is also important to use a clear and logical structure, including transitions between paragraphs, to ensure that the essay is easy to read and understand.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter.
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us
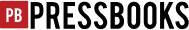
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
24 How do I Write a Response Essay?
Pre-writing steps:
- Read the essay prompt carefully.
- Activate schema
Actively read the assigned article.
Analyze the article to determine the rhetorical situation.
- Consider your own thoughts about the article.
- Decide how you want to respond.
Conference #1
Structure your essay.
- Outline the essay you want to write.
Draft a working thesis.
Drafting the essay:
Write a summary of the article as your introduction.
Write 3 or more body paragraphs in response to the article.
Review your draft so far.
Write the conclusion to summarize your thoughts.
Revising steps:
Peer review
Conference #2
- Revise your essay.
- Proofread your essay.
—————————————–
Read the essay prompt carefully
- Highlight or note the important points
- Ask questions for any part that isn’t clear to you.
- Retrieve your assigned article.
Activate schema.
- Skim and scan the article to identify the topic and the author(s). Look for subtitles and boldly printed words. Read the author’s bio which is often located at the beginning or at the end of the article. Identify the publication. Read the first sentence of each paragraph. Ask yourself, “Am I familiar with this topic?” This will help you to activate your schema.
- identify the key points and ideas
- make note of where you agree or disagree
- highlight impactful sentences to quote the author later
- paraphrase the author’s words
- summarize the article
- What is the message?
- What is the context?
- Who is the author?
- What is the author’s purpose?
- What is the structure of the text?
- Who is the audience?
Consider your own thoughts about the author and their message.
- What do I think about this topic?
- Is this author trustworthy?
- Is the article written to inform or persuade me?
- If it is written to persuade, on which points do I agree or disagree?
- Is the author biased?
- Does the article have an objective or subjective tone?
- What did I like or dislike about what the author has written in this article?
- What made the most sense to me? What was confusing about this article?
Decide how to respond.
There are several ways in which to respond to an article. You may choose a type of response from the following list:
- Before/After- Discuss your thoughts about this topic before you read the article, then explain what you learned from the article using evidence from the text.
- Persuasion- Discuss which parts of the articles you found convincing and/or which parts of the article you did not find convincing.
- Agreement or Disagreement- Discuss an idea that the author presented to which you agree or disagree. If there were two points of view that were presented, explain which one you agree with and explain why.
- Affect- Explain the emotional effect that the article had on you. Explain why you responded that way including your own background and your own thoughts/ experiences.
- Association- Share something from the article that is similar to your own experience. Or relate the information to a different article that you have read before this article.
- Most students wait until they have a draft, but seriously, this is the best time to talk to a writing tutor about your project.
- HCC has several options for free tutoring. Best choice: after class, drop in at the Composition and Learning Center (CLC) in Duncan Hall 210. This is staffed by current HCC English professors, and you can talk to one for 10-20 minutes about your assignment and your ideas for your topic, and what to include in your essay.
- There are also drop-in tutors at the Learning Assistance Center (LAC) in RCF 340.
- an introduction- a summary paragraph of the article
- a response- 3 or more body paragraphs responding to the author
- a conclusion- a concluding paragraph summing up your thoughts.
Outline the essay your want to write.
- Use the structure of the response essay to determine the order of each paragraph. Gather your notes. Review the way you chose to respond. Write a main idea statement for each paragraph of your essay. Then, list (using bullet points) the details that you want to include under each main idea statement. You can also list relevant quotes from the article that support your ideas.
- A thesis includes your topic and what you are going to say about this topic.
- A thesis always has two parts: a topic AND something important about this topic that your essay is going to discuss.
- A thesis is NEVER a question.
- Use your notes and the rhetorical situation of the article to write a summary. Begin with an introductory sentence that introduces the publisher, author, topic, purpose, and the main idea of the article.
- Next, write a few sentences to describe the key points the author made to support the main idea.
- End your summary with your thesis.
- During your pre-writing, you decided how you might want to respond to the article. Use your outline to draft your body paragraphs. Use your synthesis skills to corporate relevant quotes from the article into paragraphs to support your ideas.
- Is your summary of the article concise, objective, and accurate?
- Do your body paragraphs respond to the article?
- Do you have a main idea for each of the body paragraphs?
- Do the sentences in each paragraph support each main idea?
- This question is extremely important. If you find that you did not respond to the article in the way you had originally planned, revise your thesis.
- End your essay by summarizing the main points you shared in your body paragraphs.
- A classmate; a friend; a relative: ask someone to read over your work. Note their questions as they read.
- At the very least, read your essay aloud to yourself, stopping when you get tripped up in words or sentences. Consider how to make these rough spots easier to read.
- Schedule a conference with your instructor, or drop in on their student/office hours, or send them a Zoom request to talk about any questions you have about your draft.
- You can also drop in at the CLC in DH210 or LAC in RCF 340 to have a conference with a tutor.
Revise your essay
- Look at your outline: have you forgotten anything?
- Do a paragraph outline of just main idea sentences for each paragraph: you’ll have a 5-7 sentence summary of your whole essay.
Proofread your essay
- take on an objective tone?
- introduce the article properly?
- capture the main point of the article?
- respond to the article?
- capture your thoughts and opinions?
- begin with a main idea statement followed by detail?
- include quotes from the article?
- concisely review your thoughts about the article?
- Major grammar errors include run-on sentences, comma splices, and sentence fragments.
- You are responsible for running Grammarly or another grammar/spellcheck before your essay is submitted.
- Your instructors want to focus on improving your WRITING—not technical errors that machines can catch easily.
- Use Modern Language Association (MLA) guidelines for formatting your academic essay and for any in-text citations or a Works Cited page.
College Reading & Writing: A Handbook for ENGL- 090/095 Students Copyright © by Yvonne Kane; Krista O'Brien; and Angela Wood. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Home ➔ How to Write an Essay ➔ Response (Reaction) Paper
Response Paper Guide
A response paper, also called a reaction paper, is a unique form of written assignment often encountered in academic settings. Its primary aim is to prompt the writer to articulate their perspective, analysis, and personal reflection on a given text, which could be an article, book, film, or another form of media.

- A response paper is a critical reflection on a specific piece of work. It goes beyond mere summary, urging the writer to engage with the text deeper, analyzing its content, and expressing a personalized viewpoint.
- The purpose of a response paper is multifaceted. It demonstrates the writer’s understanding of the text, allowing for the expression of personal thoughts and opinions. It also encourages the development of critical reading skills, fostering the ability to evaluate arguments, identify strengths and weaknesses in a text, and articulate a reasoned response to its ideas.
- In academic contexts, response papers are valuable tools for assessing a student’s comprehension, analytical abilities, and engagement with course material. They allow students to synthesize and interpret information, enhancing their ability to argue effectively and thoughtfully.
- Beyond academia, response essays hold relevance in various professional fields, particularly those that require critical analysis and thoughtful reflection on texts and concepts. For example, in journalism, research, and policy-making, crafting coherent and insightful responses to texts is crucial for informing decisions, presenting arguments, and contributing to scholarly and public discourse.
Response papers are a vital component of both academic and professional landscapes, offering a platform for critical engagement, thoughtful analysis, and the expression of personalized viewpoints on diverse topics and texts.
Types of Response Papers
Response papers come in various formats, each designed to cater to different analytical needs and perspectives. This section provides an overview of the various types of response essays, highlighting their unique features and objectives. These types include:
- Focuses on breaking down the text into its core components to examine and interpret its structure, themes, and techniques. This type of response requires a deep analysis of elements like symbolism, language use, and narrative structure.
- Involves analyzing two or more texts to identify similarities and differences. This type of response paper emphasizes understanding each text in the context of the others, comparing themes, styles, or arguments.
- Centers on the writer’s feelings, experiences, and opinions related to the text. It is subjective, allowing the writer to connect personal life experiences or beliefs with the content of the text.
- Seeks to offer a more profound meaning or a new perspective on the text. This type often involves exploring underlying themes, hidden messages, or the broader implications of the text’s message.
- Focuses on evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of a text. It involves a balanced analysis, offering both praise and constructive criticism based on evidence from the text and other scholarly sources.
- Encourages the writer to reflect on the text and its impact on their thinking or perspective. This type often includes personal reflections, connecting the text to broader life experiences or societal issues.
- Involves constructing an argument either in support of or against the main claims of the text. This type requires the writer to present clear arguments backed by evidence to persuade the reader of their viewpoint.
- Extends beyond the primary text by incorporating external sources such as scholarly articles, books, or interviews. This type of response paper enriches the analysis with additional perspectives and evidence, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Each type of response paper serves a specific purpose and requires a different approach. Understanding these variations allows writers to choose the most suitable type for their objectives and the text they are responding to, enhancing the depth and quality of their analysis and reflection.
Pre-Writing Steps
The pre-writing process phase is a critical step in crafting a response paper. It sets the foundation for a well-structured and insightful paper. This section outlines the key pre-writing steps: thorough reading and analysis of the text, effective note-taking and highlighting, developing a clear thesis statement, and creating a structured outline.
- The first and foremost step is to read and analyze the text thoroughly. This involves more than a cursory glance; it requires deep engagement with the text’s content, structure, and style. Pay close attention to the author’s main arguments, themes, and the use of language. Consider the context in which the text was written and its relevance to contemporary issues.
- While reading, taking detailed notes and highlighting key points is crucial. This practice helps in organizing thoughts and forming a basis for the response. Jot down initial reactions, questions, and observations. Highlight significant quotes, evidence, and arguments that stand out. This step is instrumental in identifying patterns and crucial insights within the text.
- A thesis statement forms the backbone of your response paper. It should clearly articulate your main argument or perspective regarding the text. This statement should be based on your analysis and personal viewpoint. Ensure that it is specific, focused, and reflective of your engagement with the text. A well-crafted thesis statement guides the direction of your argument and provides coherence to your paper.
- An outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and structuring your paper. It helps map out the paper’s flow, ensuring that each point and argument is logically placed. The outline should include an introduction that presents the thesis, body paragraphs that expand on your arguments with evidence from the text, and a conclusion that ties together your main points and reiterates the thesis.
These pre-writing steps are integral to writing a response paper that is coherent, well-argued, and reflective of a deep engagement with the text. They provide a structured approach to dissecting and understanding the text, enabling a more nuanced and informed response.

Write the Introduction
The introduction of a response paper sets the tone for the entire essay and is crucial for capturing the reader’s interest. It should be engaging, informative, and clearly state the purpose of your paper.
- Begin the introductory paragraph with a compelling hook : a thought-provoking question, a striking fact, or a brief anecdote related to the text. This captures the reader’s attention and piques their curiosity.
- Provide a brief overview or preview of the main points you will discuss, creating intrigue and setting expectations for the reader.
- Introduce the text by mentioning the author, title, and publication details. This provides the reader with necessary background information.
- Offer a brief summary of the text’s main argument or theme, setting the stage for your response. This helps readers who may not be familiar with the text understand your perspective.
- Conclude the introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement . This statement should briefly present your main argument or reaction to the text.
- Ensure that your thesis reflects your analysis and viewpoint, providing a roadmap for the rest of your response essay.
Craft the Body of the Paper
The body of a response paper is where you delve into your analysis and argument, supported by evidence from the text.
- Support your arguments with relevant quotes, examples, and details from the text. This demonstrates a thorough understanding and provides a solid foundation for your analysis.
- Explain how each piece of evidence is relevant to your argument, making connections explicit.
- Critically engage with the text, analyzing key themes, arguments, and stylistic elements. Discuss how these aspects support or contradict your thesis statement.
- Interpret the text in the context of your argument, offering a unique perspective or insight.
- Consider potential counterarguments or differing interpretations of the text. Acknowledge these perspectives and provide reasoned responses to them.
- This approach demonstrates critical thinking and adds depth to your analysis.
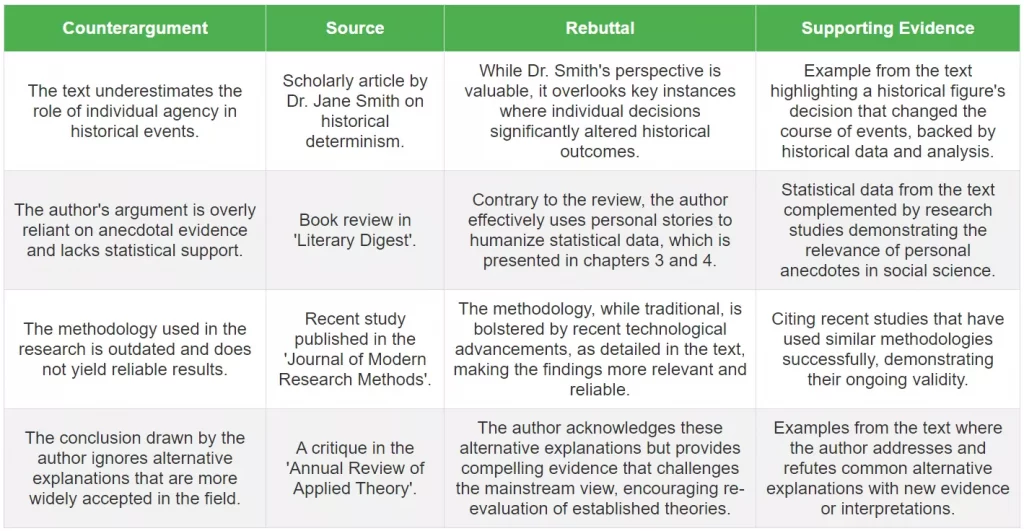
The Summary and Response Format
A response paper’s summary and response format involves two distinct sections: a summary of the text and a personal reaction or critique.
- Start with a concise summary that covers the main ideas of the text. This should be neutral and factual, providing a foundation for your response.
- Avoid including your opinions in the summary; focus on the author’s arguments and key points.
- The response section is where you present your analysis and viewpoints. Here, engage critically with the text, offering your interpretations and evaluations.
- Back up your opinions with evidence, and relate them to the main themes or arguments of the text.
- One common format is to present the summary and response in separate blocks: first summarizing the text, followed by your response.
- Alternatively, you can integrate the summary and response, addressing each main point of the text and immediately following with your reaction.
Conclude the Paper
The conclusion of a response paper is where you wrap up your analysis and restate your main points.
- Briefly summarize the main arguments of your paper, reinforcing how they support your thesis.
- Avoid introducing new ideas; focus on bringing closure to the points you’ve already made.
- Restate your thesis to reflect the insights and arguments you have presented in the body of the paper.
- This reaffirms your stance and provides a coherent end to your response essay.
- Conclude with a final thought or question that leaves the reader pondering your perspective or the text itself.
- This creates a lasting impression, encouraging further reflection on the topic.

Read for more insights:
- Graff, G., & Birkenstein, C. (2014). They Say / I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing. W. W. Norton & Company. This book provides a comprehensive guide to academic writing, focusing on argumentation and the integration of one’s own voice with others’ ideas, which is crucial for response papers.
- Rosenwasser, D., & Stephen, J. (2011). Writing Analytically . Cengage Learning. This text offers strategies for developing analytical skills in writing, which are essential for crafting effective response papers.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., & Williams, J. M. (2016). The Craft of Research, Fourth Edition . University of Chicago Press. This book is valuable for response paper writing as it guides developing a research question, gathering evidence, and constructing an argument.
- Lunsford, A. A. (2020). The Everyday Writer . Bedford/St. Martin’s. This guide provides practical advice on the nuts and bolts of writing, including structure and style, which are key components of a well-written response paper.
- Harris, M. (2017). Rewriting: How To Do Things With Texts, Second Edition . Utah State University Press. This book delves into revising and rewriting texts, a crucial skill for refining response papers and strengthening arguments.
Was this article helpful?
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Summary/Response Essays: Overview
A summary/response essay may, at first, seem like a simplistic exercise for a college course. But the truth is that most academic writing requires us to successfully accomplish at least two tasks: summarizing what others have said and presenting what you have to say. Because of this, summarizing and responding are core skills that every writer should possess.
Being able to write an effective summary helps us make sense of what others have to say about a topic and how they choose to say it. As writers, we all need to make an effort to recognize, understand, and consider various perspectives about different issues. One way to do this is to accurately summarize what someone else has written, but accomplishing this requires us to first be active and engaged readers.
Along with the other methods covered in the Reading Critically chapter , writing a good summary requires taking good notes about the text. Your notes should include factual information from the text, but your notes might also capture your reactions to the text—these reactions can help you build a thoughtful and in-depth response.
Responding to a text is a crucial part of entering into an academic conversation. An effective summary proves you understand the text; your response allows you to draw on your own experiences and prior knowledge so that you can talk back to the text.
As you read, make notes, and summarize a text, you’ll undoubtedly have immediate reactions. Perhaps you agree with almost everything or find yourself frustrated by what the author writes. Taking those reactions and putting them into a piece of academic writing can be challenging because our personal reactions are based on our history, culture, opinions, and prior knowledge of the topic. However, an academic audience will expect you to have good reasons for the ways you have responded to a text, so it’s your responsibility to critically reflect on how you have reacted and why.
The ability to recognize and distinguish between types of ideas is key to successful critical reading.
Types of Ideas You Will Encounter When Reading a Text
- Fact: an observable, verifiable idea or phenomenon
- Opinion: a judgment based on fact
- Belief: a conviction or judgment based on culture or values
- Prejudice: an opinion (judgment) based on logical fallacies or on incorrect, insufficient information
After you have encountered these types of ideas when reading a text, your next job will be to consider how to respond to what you’ve read.
Four Ways to Respond to a Text
- Reflection. Did the author teach you something new? Perhaps they made you look at something familiar in a different way.
- Agreement. Did the author write a convincing argument? Were their claims solid, and supported by credible evidence?
- Disagreement. Do you have personal experiences, opinions, or knowledge that lead you to different conclusions than the author? Do your opinions about the same facts differ?
- Note Omissions. If you have experience with or prior knowledge on the topic, you may be able to identify important points that the author failed to include or fully address.
You might also analyze how the author has organized the text and what the author’s purposes might be, topics covered in the Reading Critically chapter .
Key Features
A brief summary of the text.
Include Publication Information. An effective summary includes the author’s name, the text’s title, the place of publication, and the date of publication—usually in the opening lines.
Identify Main Idea and Supporting Ideas. The main idea includes both the topic of the text and the author’s argument, claim, or perspective. Supporting ideas help the author demonstrate why their argument or claim is true. Supporting ideas may also help the audience understand the topic better, or they may be used to persuade the audience to agree with the author’s viewpoints.
Make Connections Between Ideas. Remember that a summary is not a bullet-point list of the ideas in a text. In order to give your audience a complete idea of what the author intended to say, you need to explain how ideas in the text are related to one another. Consider using transition phrases.
Be Objective and Accurate. Along with being concise, a summary should be a description of a text, not an evaluation. While you may have strong feelings about what the author wrote, your goal in a summary is to objectively capture what was written. Additionally, a summary needs to accurately represent the ideas, opinions, facts, and judgments presented in a text. Don’t misrepresent or manipulate the author’s words.
Do Not Include Quotes. Summaries are short. The purpose of a summary is for you to describe a text in your own words . For this reason, you should focus on paraphrasing rather than including direct quotes from the text in your summary.
Thoughtful and Respectful Response to the Text
Consider Your Reactions. Your response will be built on your reactions to the text, so you need to carefully consider what reactions you had and how you can capture those reactions in writing.
Organize Your Reactions. Dumping all of your reactions onto the page might be useful to just get your ideas out, but it won’t be useful for a reader. You need to organize your reactions. For example, you might develop sections that focus on where you agree with the author, where you disagree, how the author uses rhetoric, and so on.
Create a Conversation. Avoid the trap of writing a response that is too much about your ideas and not enough about the author’s ideas. Your response should remain engaged with the author’s ideas. Keep the conversation alive by making sure you regularly reference the author’s key points as you talk back to the text.
Be Respectful. We live in an age when it’s very easy to anonymously air our grievances online, and we’ve seen how Reddit boards, YouTube comments, and Twitter threads can quickly devolve into disrespectful, toxic spaces. In a summary/response essay, as in other academic writing, you are not required to agree with everything an author writes—but you should state your objections and reactions respectfully. Imagine the author is standing in front of you, and write your response as if you value and respect their ideas as much as you would like them to value and respect yours.
Distinguish Between an Author’s Ideas and Your Own
Signal Phrases. A summary/response essay, especially your response, will include a mix of an author’s ideas and your ideas. It’s important that you clearly distinguish which ideas in your essay are yours, which are the author’s, and even others’ ideas that the author might be citing. Signal phrases are how you accomplish this. Remember to use the author’s last name and an accurate verb.
Examples of Signal Phrases
Poor Signal Phrases: “They say…” “The article states…” “The author says…”
Effective Signal Phrases: “Smith argues…” “Baez believes…” “Henning references Chan Wong’s research about…”
Drafting Checklists
These questions should help guide you through the stages of drafting your summary/response essay.
- Have you identified all the necessary publication information for the text that you will need for your summary?
- Have you identified the text’s main ideas and supporting ideas?
- What were your initial reactions to the text?
- What new perspectives do you have on the topic covered in the text?
- Do you ultimately agree or disagree with the author’s points? A little of both?
- Has the author omitted any points or ideas they should have covered?
- Has the author organized their text effectively for their purpose?
- Have they used rhetoric effectively for their audience?
- Have your reactions to the text changed since you first read it? Why or why not?
Writing and Revising
- Does your summary clearly tell your reader the author’s name, the text’s title, the place of publication, and the publication data?
- Has your summary effectively informed your reader about the text’s main ideas and supporting ideas? Have you made the connections between those ideas clear for your reader by using effective transition phrases?
- Would your reader think your summary is objective and accurate?
- You haven’t included any quotes in your summary, right?
- Does your response present your reactions to the text in an organized way that will make sense to your reader?
- Does your response create a conversation between you and the author by regularly referencing ideas from the text?
- Would your reader think that your response is respectful of the author’s ideas, opinions, and beliefs?
- Have you used signal phrases to help your reader recognize which ideas are the author’s and which ideas are yours?
- Have you carefully proofread your essay to correct any grammar, mechanics, punctuation, and spelling errors?
- Have you formatted your document appropriately and used citations when necessary?
Sources Used to Create this Chapter
Parts of this chapter were remixed from:
- First-Year Composition by Leslie Davis and Kiley Miller, which was published under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
Starting the Journey: An Intro to College Writing Copyright © by Leonard Owens III; Tim Bishop; and Scott Ortolano is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write a Response Paper
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Most of the time when you are tasked with an essay about a book or article you've read for a class, you will be expected to write in a professional and impersonal voice. But the regular rules change a bit when you write a response paper.
A response (or reaction) paper differs from the formal review primarily in that it is written in the first person . Unlike in more formal writing, the use of phrases like "I thought" and "I believe" is encouraged in a response paper.
You'll still have a thesis and will need to back up your opinion with evidence from the work, but this type of paper spotlights your individual reaction as a reader or viewer.
Read and Respond
Grace Fleming
For a response paper, you still need to write a formal assessment of the work you're observing (this could be anything created, such as a film, a work of art, a piece of music, a speech, a marketing campaign, or a written work), but you will also add your own personal reaction and impressions to the report.
The steps for completing a reaction or response paper are:
- Observe or read the piece for an initial understanding.
- Mark interesting pages with a sticky flag or take notes on the piece to capture your first impressions.
- Reread the marked pieces and your notes and stop to reflect often.
- Record your thoughts.
- Develop a thesis.
- Write an outline.
- Construct your essay.
It may be helpful to imagine yourself watching a movie review as you're preparing your outline. You will use the same framework for your response paper: a summary of the work with several of your own thoughts and assessments mixed in.
The First Paragraph
After you have established an outline for your paper, you need to craft the first draft of the essay using all the basic elements found in any strong paper, including a strong introductory sentence .
In the case of a reaction essay, the first sentence should contain both the title of the work to which you are responding and the name of the author.
The last sentence of your introductory paragraph should contain a thesis statement . That statement will make your overall opinion very clear.
Stating Your Opinion
There's no need to feel shy about expressing your own opinion in a position paper, even though it may seem strange to write "I feel" or "I believe" in an essay.
In the sample here, the writer analyzes and compares the plays but also manages to express personal reactions. There's a balance struck between discussing and critiquing the work (and its successful or unsuccessful execution) and expressing a reaction to it.
Sample Statements
When writing a response essay, you can include statements like the following:
- I felt that
- In my opinion
- The reader can conclude that
- The author seems to
- I did not like
- This aspect didn't work for me because
- The images seemed to
- The author was [was not] successful in making me feel
- I was especially moved by
- I didn't understand the connection between
- It was clear that the artist was trying to
- The soundtrack seemed too
- My favorite part was...because
Tip : A common mistake in personal essays it to resort to insulting comments with no clear explanation or analysis. It's OK to critique the work you are responding to, but you still need to back up your feelings, thoughts, opinions, and reactions with concrete evidence and examples from the work. What prompted the reaction in you, how, and why? What didn't reach you and why?
- What Is Expository Writing?
- 10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- How to Write a Great Process Essay
- List of Topics for How-to Essays
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Personal Narrative
- How to Outline and Organize an Essay
- Overused and Tired Words
- Writing a History Book Review
- Structure of a Descriptive Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay Topics
- Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech (With Topic Ideas)
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- Venn Diagrams to Plan Essays and More
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
English Works
Writing a text response essay: notes, tips and sample paras
In a text response essay, you will be assessed on your ability to develop an argument/discussion relating to a prompt, your ability to analyse themes, issues and characters in an insightful way, your ability to identity an author’s intentions and unpack their narrative devices.

Remember, the reason you are studying your particular text is because it contains complex and thoughtful themes. You must discuss the text’s complexity, but in a systematic way. Start with the simple and obvious points and then show a progression of thoughts.
If you are getting around a mid-range C-B, you may need to work on:
Topic sentences
- Sharper and more analytical topic sentences. Make sure they directly answer the question and set up a paragraph that will develop the main theme in a thoughtful and profound way.
- Make sure that each topic sentence has a different focus so as to avoid repetition. In a B-range essay there is often considerable repetition of ideas.
- Evidence: you must be as analytical as possible and avoid general statements. Show an insightful knowledge of the text by choosing key evidence/insightful/ ambivalent examples in the text to support the topic sentence.
- Build your discussion around the author’s intentions, purpose, narrative devices. These will keep the focus on analysis rather than summary.
- Be sure to show readers/assessors that you are capable of precise and accurate analysis of characters, themes and significant moments/turning points in a text’s narrative.
The flow of ideas throughout the paragraph
- Take each topic sentence and brainstorm the points/quotes/insights that you must include in the paragraph. Group together similar ideas and then delve deeper.
- Make sure that your paragraph flows. Do not just cobble together a list of statements or quotes. Make sure that each point follows and adds to the previous point.
- Make sure you give priority to the narrative devices.
- Do not just add irrelevant details in order to pad the paragraph; or if there are two perspectives/views on the statement, include them separately.
- Please see sample paras on Romeo and Juliet.
- Awkward phrases: work on sophistication of expression. Avoid clumsy verb phrases. Use nominals. Work at incorporating quotes into the grammatical construction of your sentence. Use a combination of short, snappy sentences and longer sentences. Do not lose control of the subject. See Notes on Improving Expression.
Write a 1-2 page summary of the “most important” or key points/issues in the text. Ask yourself, if you had to write a response on this text, what could you absolutely not leave out, or omit to mention (taking into account that given the prompt, you may make a short or longer reference to this key piece of evidence/quote/views/values.)
- See Writing a Comparative Essay
- See Romeo and Juliet : Study Page
- See Macbeth: Study Page
Return to the Homework Tasks Page
For Sponsorship and Other Enquiries
Keep in touch.
Response Essay Examples
A response essay is a sub-genre of critical writing. It describes your impressions from a book, movie, art, music, research paper, or any other creation. Its distinctive feature is the unlimited subjectivity allowing you to express whatever emotions the analyzed object has evoked. It is the main difference from a standard critical essay which is more objective and requires argumentation.
The structure of a response essay is not too strict. Still, it usually consists of two parts: source overview and personal response to the reading.
Below you can find an extensive list of response essay examples. Please be sure to reference the source whenever you decide to quote any part of them.
75 Best Response Essay Examples
“supersize your child” by richard hayes.
- Subjects: Evolution of Humans Sciences
- Words: 1189
Richard Hayes: Supersize Your Child
- Words: 1210
Applying Learning Models in a Particular Setting
- Subjects: Education Learning Challenges
- Words: 1167
Indecent Behavior in Moral Standards
- Subjects: Ethics Sociology
Lady Anne Clifford’s Life and Family
- Subjects: British Literature Literature
- Words: 1414
Students’ Creativity: Imagination
- Subjects: Education Study Courses and Education Programs
Propaganda in the Democratic Society
- Subjects: Entertainment & Media Journalism
The Negative Consequences of Employing High School Students in Fast Food Restaurants
- Subjects: Business Management
Monstrous and Human Relationship in “The Odyssey”
- Subjects: Literature Plays
“The Odyssey”: The Relationship Between the Monstrous and the Human
Culture and business practices in asia.
- Subjects: Business Employees Management
Kant’s Prolegomena Concerning Any Future Metaphysics
- Subjects: Philosophical Theories Philosophy
- Words: 2271
Relationship Between Body and Consciousness by Jean-Paul Sartre
- Subjects: Philosophical Concept Philosophy
- Words: 1407
Lanling Xiaoxiao Sheng: The Plum in the Golden Vase
- Subjects: Literature World Literature
- Words: 1678
The Church as a Forgiving Community
- Subjects: Religion Religion, Culture & Society
“Integrative Approaches to Psychology and Christianity” by David N. Entwistle
Family and marriage therapy.
- Subjects: Family Psychology Psychology
- Words: 1898
Jackson and His Environment
- Subjects: Behavior Psychology
- Words: 2212
Death Penalty Role in the Criminal Justice System
- Subjects: Politics & Government Social & Political Theory
Job Analysis and Selection
Leading with soul response.
- Words: 1147

Explanation of Cancer Disease
- Subjects: Health & Medicine Oncology
“The Thatcher Revolution” by Earl A. Reitan
- Subjects: History Western Europe
- Words: 1900
Leadership and Communication
Animals with rich histories.
- Subjects: Environment Environmental Studies
Psychology, Theology, and Spirituality in Christian Counseling
- Subjects: Literature on Religion Religion
- Words: 1152
Satellite Dishes Company Marketing Process
- Subjects: Business Marketing
Empowerment of Students for Their Motivation
- Subjects: Academic Performance Education
A Global Health Discussion: Ebola
- Subjects: Epidemiology Health & Medicine
Americans With Disabilities Act
- Subjects: Interpersonal Communication Episodes Psychology
“What is Academic Language?” by James Paul Gee
- Subjects: American Literature Literature
“Revisiting the Commons: Local Lessons, Global Challenges”
- Subjects: Ecology Environment
Climate Change and Corporate World
- Subjects: Climate Change Environment
- Words: 1139
Vision for Your Teaching and Learning & Role as a Teacher-Leader or Teacher-Researcher
- Subjects: Education Teacher Career
- Words: 1129
Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) in Reducing the Effects of Climate Change
- Subjects: Disasters Environment
Slaughterhouse-Five Movie Analysis
- Subjects: Art Film Studies
Overcoming the Tyranny of Segregated Minds in Desegregated Schools
- Subjects: Education Education Issues
Living Buddha, Living Christ
Experience of reggio emilia critique.
- Subjects: Education Education System
The Art of Pastoring
- Subjects: Religion Religious Education
- Words: 3679
History From the Inside Out: Prison Life in Nineteenth-Century by L. Goldsmith
- Subjects: History United States
Gender Violence in the News
- Subjects: Sociology Violence
- Words: 1195
The End of History: Views of the Philosophers
- Words: 1963
Antecedents and Outcomes of Entrepreneurial and Market Orientations in a Non-Profit Context
Children in at-risk families.
- Subjects: Family, Life & Experiences Parenting
Families With Members Who Experience Disabilities
- Subjects: Family Members Family, Life & Experiences
“The Experience of Space and Time”
Positivism and interpretivism.
- Subjects: Sciences Scientific Method
Team Learning as a Way of Education
- Subjects: Challenges of Psychology Psychology
Japanese Soldiers in the World War II
- Subjects: Asia History
Origins of Religion
- Words: 1384
Napoleon Bonaparte in his study
- Subjects: Art Paintings
- Words: 1105
System Thinking: Contributing to the Learning Organization
- Subjects: Business Management Priorities
Using Leadership to Improve Ethical Performance
- Subjects: Business Business Ethics
- Words: 1234
Hispanic Americans: Racial Status
- Subjects: Immigration Sociology
Race and Ethnic Relations: American and Global Perspective
- Subjects: Culture Ethnicity Studies
“With Training and Development for All” by Goodman and Preston
- Subjects: Business Global Scale Management
Why No Apple in Europe?
- Subjects: Social Movements Sociology
Last Night I dreamt of Peace
- Subjects: Historical Figures History
Narrative of the Captivity and Restoration of Mrs Mary Rowlandson
Three cups of tea, insights on green automotive development.
- Subjects: Engineering Tech & Engineering
Capitalism: A Love Story: A Reflective Paper
- Subjects: Economic Systems & Principles Economics
Ethnography Reflection
- Subjects: Anthropology Sciences
- Words: 1710
Misery – Anton Chekhov. Analysis of Summary and Themes
- Subjects: Dramatic Literature Literature
Infantile Sexuality: Thumb Sucking
- Subjects: Development Psychology
Pride and Arrogance in the “Oedipus the King” by Sophocles
The corporation & our media, not theirs.
- Subjects: Documentaries Entertainment & Media
- Words: 1109
Maldoror and the Completed Works of the Comte de Lautréamont
- Words: 1390
Folklore: Contemporary Legends
- Subjects: Literature Modernist Literature
- Words: 1641
Gods and Humans: Myths of Ancient Rome and Greece
- Subjects: Comparative Literature Literature
Summary: James Wertsch’s “The Multivoicedness of Meaning”.
Social networks benefits and disadvantages.
- Subjects: Sociological Issues Sociology
- Words: 1122
The Problem of Global Overpopulation
Molto agitato: the mayhem behind the music at the metropolitan opera.
- Subjects: Art Music Industry
- Words: 1112
- How It Works
- Essay Examples
What Response Essays Are and How to Tackle Them
Writing a response essay might seem like a challenging task at first. Firstly, you need to understand to a great extent what the study that you are responding to is talking about and then make sure that you write an insightful, true to the source essay about it. Even if you need to write a response essay as part of your homework for faculty studies or high school assignments or you want to exercise your argumentative skills, it might seem like a lot of work at first. However, having in mind a clear structure of your future response essay is essential.
Before beginning to go through the main structure points that you need to check when writing a response essay, there are some tips that you need to know and that will help you lay your thoughts on paper in a more efficient way. First of all, after reading the essay or the article that you are responding to, you need to settle on whether you want to attack the ideas presented in that article or to agree with them. Based on that, you will structure the components of your response essay. For example, if your response essay is talking about protecting the environment and you want to show your agreement with the ideas presented in the original essay, then you should build your response essay around the idea of consolidating the thoughts in the main source.
Secondly, it is important that your readers clearly understand your position after reading your response essay. This means that you need to expose all possible arguments which might strengthen or attack the ideas presented in the main article. In order for you to achieve a strong position, it might be helpful to also expose a personal experience that can be related to the topic you are writing an essay about. This will not only make your argument points stronger but will also help your readers empathize with your writing. Also, it is important that you keep in mind that your response essay should be a response to something you have read, something that is a hot topic at the moment in various social contexts or something that has been debated for a long time and you want to present a new approach to things.
You also have to keep in mind that the more knowledge you show to your audience in your response essay about the author and the topic that is being debated, the more credibility you will gain. Read some cause or effect essay topics to get inspired. This is why it is important to also present a context in your response essay, such as details about the author and the paper you are choosing to respond to. Finally, after debating the ideas of the original text, you can also choose to talk about the effectiveness of the source text. It can be about how the main paper managed to reach the audience, if the writing style was effective, and how the author you are responding to had chosen to expose their ideas.
If we were to summarize the main points you should keep in mind before starting to tackle the components of a response essay, these would be:
- Make sure to clearly expose your position regarding the article or paper you are responding to
- Don’t forget to expose the personal experiences or thoughts that might help you relate to the matter in question and your reader to empathize with your way of writing
- Prove that you have knowledge about the author of the main text and can put your response essay in a context
- Evaluate the main text’s effectiveness and how it managed to reach the audience
Get Started: Write an Introduction
One important thing when writing a response essay is the way you structure the introduction. This is one of the key parts of your essay, as it embodies the topic you are about to debate and the premises you are basing your essay on. The introduction will make your audience decide if they want to keep reading your response essay or not. This is why it is important that you keep in mind the following tips:
- Introduction is all about catching your audience’s attention
- It should provide a brief description of the topic
- You should be able to briefly summarize your thesis
- Don’t forget to give a short description of the author and the article you are responding to
It might be the case that the source article that you are about to discuss contains several parts or has different ideas which can be debated and your response article refers only to a part of them. In this case, don’t forget to also mention this. Do not forget that you need to keep it short and catchy.
How to Make Your Introduction Catchy – Introduction Ideas
Writing a catchy introduction that will make your reader read the whole response article is challenging. This is why you will find here some ideas to start with, such as:
- Making use of a statistic: some puzzling conclusion that researchers might have reached at some point and which is relevant to the topic you are about to respond to.
- Citing someone who is related to the area of expertise of your topic or is known for having deep knowledge about the topic. The more popular the person you are citing is, the more efficient your introduction will be.
- Story-telling or reproducing a dialogue might also help, provided they are relevant and short.
- Starting with a question or with a situation regarding the topic you are about to talk about might also be a good introduction idea.
You might even want to combine some of these ideas and write your introduction based on an example and a statistic or any other possible combination. Whatever you choose, make sure it stays to the point and is catchy to the eye of the reader.
How You Can Connect Introduction to Conclusion
Another important aspect that you need to consider when writing your introduction to the response essay is that you need to somehow connect it to the conclusion. In order for you to achieve a perfectly cyclic response essay, you need to find a way to make the two feel correspondent. This will help your response essay have a “frame” and will help your writing style be more efficient.
It might be a bit difficult at first to start with an introduction and end with a conclusion that are connected, mostly if you want to write very long and thorough response essays. However, one important suggestion that might help is to always make sure that before starting off your response essay, you are clear about the ideas and position you want to present. This will help you avoid changing your position as you advance in writing your essay and make your introduction and conclusion connected, giving a sense of symmetry to your text.
Below you can find some examples of how you can connect your introduction with the conclusion:
- If you are writing about the usage of mobile devices in our everyday life, you could start your introduction by exposing a real-life experience, maybe someone who is driving to work on a normal day and is stuck in traffic. You could start by asking your readers what they would do on their phones as they wait in traffic and end with several possible outcomes of this scenario.
- If you are choosing to present an essay about a personal experience and you start with an introduction about how a certain day started in your life, you could end your essay with how that day ended. This way, you will make sure you keep your readers connected to the story and have their attention all throughout the essay.
- If you decide to write about any other topic, such as a topic of national importance or even an environmental topic, you could start by stating the facts to which you want to draw the attention and end with the facts about the current situation or how it can be improved.
How to Write a Strong Thesis
After making sure that you have caught your readers’ attention, it is all about making it clear to them what your position regarding the source article is. However, you should also provide a context to your response article by mentioning details about the author and the main ideas in the article that you have chosen to respond to. It can be that you are choosing to respond only partially, to a few of the ideas presented there, so this is the reason why it is important to clearly state the ideas of the article you want to respond to. Make sure to give an account of whatever it is debated in the article, by presenting the information in an objective way. At this point, it is more important for your readers to understand what you are trying to agree or disagree with than hear your personal opinion. Also, exposing the ideas of the source text in an objective, impersonal way will help your readers decide for themselves if the position you are taking is one that they would take or not.
Afterwards, it is vital that you expose what is known as “thesis statement” by allocating one paragraph in which you clearly state if you agree or disagree with the main topic presented in the source text. This should start with “I agree/I don’t agree with” and should be followed by a short and powerful message about the main reason why you are taking this position regarding that text.
The next step is to talk more about the reasons you are considering attacking or agreeing with the ideas presented in the original text. This can be done by either reviewing what the author is saying or just expanding on the main ideas. You can, for example, try to understand why the author has reached a certain conclusion that you are debating by trying to relate it to the author’s background or career. It can be that the author has chosen to promote oil drilling because they work in a factory that wants to make this process a sustainable one. It is important that you stay true to your debate and present the situation from both points of view: yours and the author’s.
How to Respond to Articles – Ideas
After tackling the introduction and the conclusion, the main body of your response essay is left to deal with. This is mainly the way in which you choose to present the source text and where you are standing regarding it. It is up to you if you choose to agree or disagree, however, what you have to keep in mind is that you need to be consistent and stay true to the topic you have chosen to debate.
One way to do that is to map the main three components of the response essay, namely, the introduction, body, and conclusion. Here are some helpful suggestions on how to structure your responding ideas:
- Whether you agree or disagree, you can state 3 or more reasons for which you are doing so. Make sure to start each new paragraph and allocate enough space for your ideas to be clearly distinguished and stated.
- If you are partially agreeing or disagreeing, make sure to always mention that so that your readers will clearly understand your position.
- It is always important to see how the author’s ideas managed to reach the audience and in which ways the ideas were brought forward.
How to Better Structure the Body of the Response Essay
Make sure to utilize evidence to back-up your thesis. In order to do this, you can use quotes, author tags or simply rely on other readings and give references.
Make sure that you achieve a personal voice throughout the text. This can be done by differentiating yourself from the author and using author tags.
By using author tags, you communicate to your readers the fact that it is the author you are responding to who has a certain idea or it is their article that makes this reference. You can use any of these suggestions when talking about someone’s article:
- The author mentions
- The author refers to
- The author is suggesting
- The author writes
- The author asks
- The author recommends
- The author is presenting
- The author points out
- The author relates
- The author pleads
- The author denies
- The author’s remarks point to
- The author explains
Write a Conclusion Your Readers Won’t Forget
One important thing to keep in mind when writing a conclusion to your response essay is that you shouldn’t repeat the arguments in the same form in which you have presented them in the body. Offering a conclusion to your response article is still needed, as this will help your readers make a clear decision whether they agree or disagree with the ideas presented in your response essay.
Besides making sure that your essay is built around a very powerful introduction and a conclusion that sums up the main ideas of your position regarding this essay, you can also:
- Present the topic that you have been debating throughout the essay in a broader perspective; for example, if the topic you are tackling is national, you can connect this topic to the situation in other countries worldwide
- Promote an organization or an event that has some influence on the topic you have been responding to
- Present the current situation of the topic you are talking about and ring the alarm if anything needs to be done about it
- Summarize how your arguments shed a new light on the topic
A Brief Summary of How a Response Essay Should Look Like
Keeping everything in mind, the essential parts of a response essay and the main suggestions that you have to keep in mind when starting to write are:
- Paragraph 1: The first part of the introduction which needs to be vivid, catchy and reflect the point you are about to make.
- Paragraph 2: Provide a context to your response essay: details about the source-text and the author and what the main points in the article are.
- State your position regarding the ideas presented in the introduction and if you agree with the author’s take on the matter or not.
- Clearly mention if you are going to question the author’s position or expand on the author’s account of the facts.
- Give clear arguments pro or against the matter and allocate one paragraph to each of these arguments.
- Use statistics, story-telling, research findings, scientific discoveries, and any other tools suggested in this article.
- Provide an insightful and catchy conclusion that correlates with the introduction you have chosen for your response essay.

- History Essay Topics
- Types of Sentences and Punctuation
- Sociology Essay Topics
- How to Write a Dissertation
- How to Write the Stanford University Application Essays in 2018


Introduction
Goals and Goal Setting
Goals Common to All RST Writers
Other Goals to Consider
Defining My Own Goals
Advice about Assignments
Getting Started: Listing Topics to Write about in the Tutorial
Narrative One: Personal Piece on a Significant Experience
Narrative Two: Academic Piece on a Significant Experience
Summary/Response One
Summary/Response Two
Tutorial Evaluation Postscript
On Using the Resources for Writers
Generating and Developing Ideas
Finding/Expressing Main Ideas
Showing v. Telling Sentences
Focusing Topic Sentences
Thesis Statements
Reading Strategies
Assessing Your Reading Strategies
Summarizing
Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays
Discourse Analysis Worksheet
Trade Magazines
Selecting Readings
A summary is a concise paraphrase of all the main ideas in an essay. It cites the author and the title (usually in the first sentence); it contains the essay's thesis and supporting ideas; it may use direct quotation of forceful or concise statements of the author's ideas; it will NOT usually cite the author's examples or supporting details unless they are central to the main idea. Most summaries present the major points in the order that the author made them and continually refer back to the article being summarized (i.e. "Damon argues that ..." or "Goodman also points out that ... "). The summary should take up no more than one-third the length of the work being summarized.
The Response:
A response is a critique or evaluation of the author's essay. Unlike the summary, it is composed of YOUR opinions in relation to the article being summarized. It examines ideas that you agree or disagree with and identifies the essay's strengths and weaknesses in reasoning and logic, in quality of supporting examples, and in organization and style. A good response is persuasive; therefore, it should cite facts, examples, and personal experience that either refutes or supports the article you're responding to, depending on your stance.
Two Typical Organizational Formats for Summary/Response Essays:
1. Present the summary in a block of paragraphs, followed by the response in a block:
Intro/thesis Summary (two to three paragraphs) Agreement (or disagreement) Disagreement (or agreement) Conclusion
Note: Some essays will incorporate both agreement and disagreement in a response, but this is not mandatory.
2. Introduce the essay with a short paragraph that includes your thesis. Then, each body paragraph summarizes one point and responds to it, and a conclusion wraps the essay up.
Intro/thesis Summary point one; agree/disagree Summary point two; agree/disagree Summary point three; agree/disagree Conclusion
How to Write a Response Paper: Understanding the Basics

Writing a response paper is an important task for students. It allows them to critically analyze a text, express their thoughts and opinions, and improve their writing skills. In this comprehensive guide, our ‘ write my essay ’ experts will explore the basics of how to write a response paper, pre-writing steps, and crafting a winning introduction, body, and conclusion. So, let's dive in and discover a flawless response paper at the end!
Defining What is a Response Paper
A response paper is a written assignment that requires the student to read a text and respond to it by expressing their views on the topic. It can be a stand-alone assignment or part of a larger project. When writing a response paper, it is important to remember the audience you are writing for. Are you writing for your professor, classmates, or a broader audience? This will help you tailor your writing style and tone accordingly.
Moreover, this kind of academic assignment should not only summarize the text but also provide a critical analysis of its main arguments and ideas. It should demonstrate your understanding of the text and your ability to engage with it in a thoughtful and meaningful way.
Purpose of Crafting a Response Paper
Writing response papers aims to demonstrate your understanding of the text, give your opinions and thoughts, and provide evidence to support your claims. In addition, this type of paper can help you develop critical reading skills and formulate coherent arguments. By engaging with the text, you can identify its strengths and weaknesses, evaluate its claims, and form your own opinions about the topic.
Furthermore, crafting response paper examples can be a valuable exercise in self-reflection. It allows you to articulate your thoughts and feelings about a particular topic and can help you better understand your values and beliefs.
Types of Response Papers
There are various types of response papers, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements. These include:

- Personal response : Here, you express your personal opinions, thoughts, and emotions about the text. This type of paper allows you to engage with the text more personally and explore your reactions to it.
- Critical response : Involves analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting the text to provide a critique. This type of paper requires you to engage with the text more objectively and analytically, focusing on its strengths and weaknesses and providing evidence to support your claims.
- Research-based response : Research-based response paper examples involve using external sources to support your claims. This type of paper requires you to engage with the text and supplement your analysis with evidence from other sources, such as scholarly articles, books, or interviews.
Too Overwhelmed with Academic Assignments?
Let our professional writers take the burden off your shoulders, order an essay and rest easy knowing that your assignment is in capable hands!
How to Write a Response Paper: Pre-Writing Steps
Before diving into the writing process, laying a strong foundation through effective pre-writing steps is crucial. These initial stages not only provide clarity and structure but also enhance the overall quality of your response. And if you aren’t sure how to write a reaction paper , these steps can also be employed for your assignment.

Carefully Read and Analyze the Text
The first step in response paper creation is to carefully read and analyze the text. This involves more than just reading the words on the page; it requires critical thinking and analysis. As you read, pay attention to the author's tone, style, and use of language. Highlight important points, take notes, and identify the author's main argument and themes. Consider the context in which the text was written and how it relates to contemporary issues.
For example, if you are reading a historical document, think about how it reflects the social and political climate of the time. If you are reading a work of fiction, consider how the characters and plot relate to larger themes and ideas. By carefully analyzing the text, you will be better equipped to write a thoughtful and insightful response.
Take Notes and Highlight Key Points
Another important step is to take notes while reading, as it helps you organize your thoughts and ideas. As you read through the text, jot down your reactions, questions, and observations. Highlight key points, evidence, and quotes that support the author's argument. This will make it easier to refer back to specific parts of the text when you are writing your response.
Additionally, taking notes can help you identify patterns and connections between different parts of the text. This can be especially helpful when you are trying to develop your thesis statement and outline.
Develop a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a central argument that you will be making in your paper. It should be clear and concise and provide direction for your essay. Your thesis statement should be based on your analysis of the text and should reflect your own perspective.
When developing your thesis statement, consider the main argument of the text and how you agree or disagree with it. Think about the evidence and examples that the author uses to support their argument and how you might use those same examples to support your own argument. Your thesis statement should be specific and focused and should guide the rest of your essay.
Create an Outline
If you want to unlock the most important tip on how to ace a response paper perfection, it lies in creating a well-organized outline. Identify key points, evidence, and arguments that you want to discuss and organize them into a well-written paper format. Your outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Start by introducing the text and your thesis statement. In the body paragraphs, discuss your main points and provide evidence from the text to support your argument. Use quotes and examples to illustrate your points. In conclusion, summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. In the following paragraphs, we'll delve deeper into writing each section with more details.
Actual Writing Process with a Response Paper Format
Now that you have completed the essential pre-writing steps, it's time to delve into the actual writing process of your paper. In this section of our comprehensive guide, we will explore how to start a response paper along with developing insightful body paragraphs and culminating in a powerful conclusion.
Engage the Reader In Your Introduction
The introduction is the first impression that your reader will have of your paper. It is important to make a good first impression, so you want to engage them right from the start. There are several ways to do this, such as providing context, using a hook, or starting with a rhetorical question.
For example, if you are writing a paper about the effects of social media on mental health, you might start with a hook like:
'Did you know that the average person spends over two hours a day on social media? That's more time than they spend exercising or socializing in person.'
When working with your paper, this hook immediately grabs the reader's attention and makes them interested in learning more about your topic.
Provide Context and Background Information
Once you have engaged the reader, it's important to provide context for the text you are analyzing. This includes information like the author's name, the title of the work, and the publication date. This information helps the reader understand the context of the text and why it is important.
For example, if you are analyzing a poem by Maya Angelou, you would want to provide some background information about her life and work. You might mention that she was a civil rights activist and a prolific writer and that the poem you are analyzing was written in 1969, during a time of great social and political upheaval in the United States.
Present Your Thesis Statement
Finally, it's important to present your thesis statement in the introduction. The thesis statement is the main argument of your paper, and it should be presented clearly and concisely so that the reader knows exactly what your paper is about.
For instance, if you are crafting a response paper example about the effects of social media on mental health, your thesis statement might be something like:
'This paper argues that excessive use of social media can have negative effects on mental health, including increased anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation.'
By presenting your thesis statement in the introduction, you are setting up the rest of your paper and giving the reader a roadmap for what to expect. This helps them stay focused and engaged throughout your paper.
Meanwhile, you can find out more about how to write an essay format and set the right referencing style for your assignment!
Crafting the Body
One key aspect of ensuring a well-structured and articulate paper is to utilize your typical response paper outline as a reliable roadmap. By following it, you can maintain focus, coherence, and logical flow throughout your response. Moreover, keep the following points in mind as you proceed with crafting the body of your response paper:
- Use evidence and examples from the text:
- Incorporate relevant quotes, statistics, or other evidence that supports your opinions and arguments.
- By using evidence from the text, you can strengthen your argument and demonstrate a deep understanding of the material.
- Analyze and interpret the text:
- Demonstrate your critical thinking skills by thoroughly analyzing and interpreting the text.
- Explain how the text relates to your thesis statement and overall argument.
- Provide a clear and concise response that showcases your knowledge and understanding of the material.
- Address counterarguments and alternative perspectives:
- Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to demonstrate your ability to consider different perspectives.
- Explain why your argument is stronger than the opposing viewpoint.
- Provide evidence to support your claim and solidify your stance.
Concluding Your Paper
In the conclusion of your response paper example, it is essential to consolidate your reactions, ideas, and arguments regarding the text. Summarize the key points discussed throughout your paper, drawing inferences whenever applicable.
When uncertain about how to write a conclusion for a research paper , the first important rule is to refrain from introducing new ideas or reiterating information already presented in the introduction of your paper. Instead, provide a concise and coherent summary that encapsulates the essence of your response, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Response Paper Example
To show you how to write a response paper effectively, our essay writer has provided an amazing example below. It will inspire you and help you on your own learning journey. Get ready to explore new ideas and expand your knowledge with our response paper sample.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on how to write a response paper, you have acquired the essential tools and knowledge to embark on your writing journey with confidence. With a firm grasp of pre-writing strategies, the art of crafting an engaging introduction, organizing a well-structured body, and understanding the significance of supporting arguments and addressing counter arguments with a good response paper example, you are poised to leave a lasting impression.
And if you ever find yourself struggling to find inspiration or facing challenges with any aspect of your essays, order essay online and take advantage of the opportunity to seek assistance from our professional writing service team. By trusting us with your college essays and ordering a response paper, you can confidently navigate your academic journey!
Take the Stress Out of Writing Response Essays!
Our expert writers are ready to craft a tailored, insightful response essay example that meets your requirements.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Critical Response Essay

Students have to write different types of essays all the time. However, they face many problems when it comes to writing a critical response essay. Why is it so hard to manage? What are the main components of it? We will answer all these questions in our complete guide to help you learn how you can write this type of essays quickly and easily.
What Is a Critical Response Essay?
First things first – let’s find out what a critical response essay is and what components it includes.
It is an assignment that is based on your analytical skills. It implies the understanding of the primary source, such as literary work, movie or painting (its problematic, content, and significance), and the ability to perform critical thinking and reflect your opinion on the given subject.
The aim of critical response essay is to get familiarised with the subject, form your opinion (the agreement or disagreement with the author), reveal the problematic of the piece and support your claims with evidence from the primary source.
For example, your task might be to analyze the social structure in Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet.
How Is It Different From Other Essay Types?
Every essay you write has a very similar structure that consists of an introduction, the main body, and the conclusion. While this type is not an exception and is quite similar to an analytical essay , it still has differences. One of those is the fact that it contains two parts. The first part includes a quick summary of the analyzed work. The second part is a critique – a response to the author’s opinion, facts, examples, etc.
What Should You Pay Attention To?
Before we dive into the guide and the steps of crafting your critical essay, let’s take a look at some of the most common pitfalls that often occur during the writing process of a piece like this.
Not knowing what you are writing about.
This makes no sense, right? So, be sure to read the piece that your topic is based on and make sure you understand what it is about.
Not understanding what your task is.
Be attentive to the task and make sure you understand what is required from you. You would be surprised if you knew how many essays are written without even touching the main question or problematic.
Being in a hurry.
A lot of students start working on their essays at the very last moment and do it in haste. You can avoid a lot of mistakes if you are attentive, focused, and organized. If you have too little time to write a strong response essay yourself, you can always get the assistance of a professional writing service. This will help you to be on time with your assignment without sacrificing its quality.
And now let’s begin your journey of writing an essay.
Step 1. Examine the Primary Source
Before starting actually writing your critical essay, you need to get acquainted with the subject of your analysis. It might be an article, a book or any other type of text. Sometimes, this task is given for pieces of art, such as a painting or a movie.
So, the first step would be to gain as much information about the subject as possible. You might also search for some reviews or research papers on the subject. Be sure to examine the primary source thoroughly and read the complete text if it is a piece of writing.
Advice: make notes while you are working with your primary source. Highlight the main points that will build a basis for your analysis and which you can use to form your opinion on. Notes will also help you to structure your essay.
- Did you read the whole text or examined your primary source thoroughly?
- Did you find information on the topic of your assignment?
- Did you write down the key points that you are going to use for your essay?
Step 2. Analyze the Source and Your Notes
After you finished with your primary source, try to analyze and summarize all of your findings. Identify the problematic of the piece and find the appropriate notes that you have made to structure your future essay.
Formulate your opinion – are you agree or disagree with the author? Can you support your statements with evidence?
- Did you examine all the notes you have?
- Did you form your opinion on the subject?
- Did you find the arguments to support your main point?
- Did you succeed to define the strengths and weaknesses of the work?
Step 3. Write Your Essay
After you have all of the needed materials next to you, you can start working on the text of your essay.
- First of all, write a critical response essay rough draft.
- Reread your draft and make your edits.
- Proofread and edit your final version.
- Check for plagiarism, grammatical and punctuation errors.
- Write a Works Cited page or bibliography page (if required).
Now, we will look at each part of your essay in detail. Keep in mind that you have to follow the guidelines provided by your teacher or professor. Some critical response essay examples will come in handy at this step.
How to Write a Critical Response Introduction
Your introduction is the part where you have to provide your thesis statement. Once you have your opinion and your thoughts organized, it’s pretty easy to make them transform into a statement that all your essay will be built on. Express your agreement or disagreement with the author.
For example, your thesis statement might be:
“Romeo and Juliet” by Shakespeare is a masterpiece that raises the problem of social inequality and classes differentiation which aggravates the drama culmination.
Advice: make sure you have evidence to support your thesis statement later in the text. Make your introduction in the form of a brief summary of the text and your statement. You need to introduce your reader to the topic and express your opinion on it.
- Did you embed your thesis statement?
- Is your thesis statement complete and suitable for the topic?
- Can you support your thesis statement with evidence?
- Did you summarize the analyzed subject?
- Did you start your introduction with a catchy sentence – a powerful statement, fact, quote or intriguing content?
- Did you include a transition sentence at the end of your introduction?
How to Write Critical Response Paragraphs
Explain each of your main points in separate body paragraphs. Structure your text so that the most strong statement with the following supporting evidence is placed first. Afterward, explain your other points and provide examples and evidence from the original text.
Remember that each of your statements should support your main idea – your thesis statement. Provide a claim at the beginning of the paragraph and then develop your idea in the following text. Support each of your claims with at least one quote from the primary source.
For example:
To distinguish the division between classes and express the contribution of each social class Shakespeare used different literary methods. For example, when a person from a lower class speaks, Shakespeare uses prose:
NURSE I saw the wound, I saw it with mine eyes (God save the mark!) here on his manly breast— A piteous corse, a bloody piteous corse, Pale, pale as ashes, all bedaubed in blood, All in gore blood. I swoonèd at the sight. (3.2.58-62)
At the same time upper-class characters speak in rhymed verse:
MONTAGUE But I can give thee more, For I will raise her statue in pure gold, That while Verona by that name is known, There shall no figure at such rate be set As that of true and faithful Juliet. (5.3.309-313)
- Did you support your thesis statement with claims?
- Do your claims appeal to critical response questions?
- Did you provide evidence for each claim?
How to Write Critical Response Conclusion
The best way to conclude your essay is to restate your thesis statement in different phrasing. Summarize all of your findings and repeat your opinion on the subject. A one- or two-paragraph conclusion is usually enough if not requested more.
We’ve also prepared some critical response essay topics for you:
- Explain the changes of the character throughout the novel: Frodo from Lord of the Rings /Dorian Gray from The Picture of Dorian Gray .
- Examine a setting and the atmosphere in the novel Gone with the Wind/Jane Eyre .
- Investigate the cultural or historical background in Romeo and Juliet/Macbeth .
- Describe the impact of the supporting character: Horatio in Hamlet /Renfield in Dracula .
- Describe the genre of the work and its influence on the mood of the piece: To Build a Fire/ For Whom the Bell Tolls.
This was our step-by-step guide to writing your perfect critical response essay. We hope our tips will be useful to you!
Related posts

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on February 4, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A good introduction paragraph is an essential part of any academic essay . It sets up your argument and tells the reader what to expect.
The main goals of an introduction are to:
- Catch your reader’s attention.
- Give background on your topic.
- Present your thesis statement —the central point of your essay.
This introduction example is taken from our interactive essay example on the history of Braille.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: hook your reader, step 2: give background information, step 3: present your thesis statement, step 4: map your essay’s structure, step 5: check and revise, more examples of essay introductions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Your first sentence sets the tone for the whole essay, so spend some time on writing an effective hook.
Avoid long, dense sentences—start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
The hook should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of the topic you’re writing about and why it’s interesting. Avoid overly broad claims or plain statements of fact.
Examples: Writing a good hook
Take a look at these examples of weak hooks and learn how to improve them.
- Braille was an extremely important invention.
- The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
The first sentence is a dry fact; the second sentence is more interesting, making a bold claim about exactly why the topic is important.
- The internet is defined as “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities.”
- The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education.
Avoid using a dictionary definition as your hook, especially if it’s an obvious term that everyone knows. The improved example here is still broad, but it gives us a much clearer sense of what the essay will be about.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is a famous book from the nineteenth century.
- Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement.
Instead of just stating a fact that the reader already knows, the improved hook here tells us about the mainstream interpretation of the book, implying that this essay will offer a different interpretation.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Next, give your reader the context they need to understand your topic and argument. Depending on the subject of your essay, this might include:
- Historical, geographical, or social context
- An outline of the debate you’re addressing
- A summary of relevant theories or research about the topic
- Definitions of key terms
The information here should be broad but clearly focused and relevant to your argument. Don’t give too much detail—you can mention points that you will return to later, but save your evidence and interpretation for the main body of the essay.
How much space you need for background depends on your topic and the scope of your essay. In our Braille example, we take a few sentences to introduce the topic and sketch the social context that the essay will address:
Now it’s time to narrow your focus and show exactly what you want to say about the topic. This is your thesis statement —a sentence or two that sums up your overall argument.
This is the most important part of your introduction. A good thesis isn’t just a statement of fact, but a claim that requires evidence and explanation.
The goal is to clearly convey your own position in a debate or your central point about a topic.
Particularly in longer essays, it’s helpful to end the introduction by signposting what will be covered in each part. Keep it concise and give your reader a clear sense of the direction your argument will take.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you research and write, your argument might change focus or direction as you learn more.
For this reason, it’s often a good idea to wait until later in the writing process before you write the introduction paragraph—it can even be the very last thing you write.
When you’ve finished writing the essay body and conclusion , you should return to the introduction and check that it matches the content of the essay.
It’s especially important to make sure your thesis statement accurately represents what you do in the essay. If your argument has gone in a different direction than planned, tweak your thesis statement to match what you actually say.
To polish your writing, you can use something like a paraphrasing tool .
You can use the checklist below to make sure your introduction does everything it’s supposed to.
Checklist: Essay introduction
My first sentence is engaging and relevant.
I have introduced the topic with necessary background information.
I have defined any important terms.
My thesis statement clearly presents my main point or argument.
Everything in the introduction is relevant to the main body of the essay.
You have a strong introduction - now make sure the rest of your essay is just as good.
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This introduction to an argumentative essay sets up the debate about the internet and education, and then clearly states the position the essay will argue for.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
This introduction to a short expository essay leads into the topic (the invention of the printing press) and states the main point the essay will explain (the effect of this invention on European society).
In many ways, the invention of the printing press marked the end of the Middle Ages. The medieval period in Europe is often remembered as a time of intellectual and political stagnation. Prior to the Renaissance, the average person had very limited access to books and was unlikely to be literate. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century allowed for much less restricted circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
This introduction to a literary analysis essay , about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , starts by describing a simplistic popular view of the story, and then states how the author will give a more complex analysis of the text’s literary devices.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale. Arguably the first science fiction novel, its plot can be read as a warning about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, and in popular culture representations of the character as a “mad scientist”, Victor Frankenstein represents the callous, arrogant ambition of modern science. However, far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to gradually transform our impression of Frankenstein, portraying him in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Introduction | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 23, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to conclude an essay | interactive example, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
COMMENTS
1. Identify the main topic or issue you will be responding to. 2. State your position or stance on the topic clearly and concisely. 3. Provide a brief preview of the key points or arguments you will present in your essay to support your thesis. Remember, your thesis statement should be specific, focused, and debatable.
5 Responses. Your reaction will be one or more of the following: Agreement/disagreement with the ideas in the text. Reaction to how the ideas in the text relate to your own experience. Reaction to how ideas in the text relate to other things you've read. Your analysis of the author and audience. Your evaluation of how this text tries to ...
A good response paper template will make it easier for a reader to separate your point of view from author's opinion. The essay is often divided into these sections: introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs. Below is an example of a response essay outline template: Introduction. Briefly introduce the topic of the response paper
1. Introduction. The introductory paragraph in a critical response essay consists of two primary sections: a summary of an article and a thesis statement. Firstly, a summary of an article consists of the text's central argument and the purpose of the presentation of the argument (Davies, 2022).
Get an outline of the process for how to write a response essay from the prewriting to the final piece. See all the different steps in action to make writing a response essay a breeze. ... It provides an overview of the opinions you plan to convey. For example, if your response to a song was horrible, state that in your thesis along with the ...
Outline. Introduction (1-2 paragraphs): grab the reader's attention and state your subject and purpose. Body (3 or more paragraphs): Summarize the article you read in 1-2 paragraphs. Give three or more responses to the article with evidence to back them up. Responses include answering the following: What do you think about the ideas in the ...
It's a response to a piece of media, such as a book, event, article, movie, or podcast. How is a reaction essay structured? A reaction essay follows the same structure as other types of essays. Here is an example of a five-paragraph reaction essay outline: Introduction paragraph. Body paragraph. Body paragraph. Body paragraph. Conclusion ...
An introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion are the most important parts of a response essay. The introduction should give background information about the text and include a that shows the writer's opinion about the text. The writer's from the text in the body paragraphs. The conclusion should restate the main points and give a ...
A response essay consists of 5-7 paragraphs: an introduction- a summary paragraph of the article; a response- 3 or more body paragraphs responding to the author; a conclusion- a concluding paragraph summing up your thoughts. Outline the essay your want to write. Use the structure of the response essay to determine the order of each paragraph.
Write the Introduction. The introduction of a response paper sets the tone for the entire essay and is crucial for capturing the reader's interest. It should be engaging, informative, and clearly state the purpose of your paper. Engage the Reader. Begin the introductory paragraph with a compelling hook: a thought-provoking question, a striking fact, or a brief anecdote related to the text.
A summary/response essay may, at first, seem like a simplistic exercise for a college course. But the truth is that most academic writing requires us to successfully accomplish at least two tasks: summarizing what others have said and presenting what you have to say. Because of this, summarizing and responding are core skills that every writer ...
Record your thoughts. Develop a thesis. Write an outline. Construct your essay. It may be helpful to imagine yourself watching a movie review as you're preparing your outline. You will use the same framework for your response paper: a summary of the work with several of your own thoughts and assessments mixed in.
Group together similar ideas and then delve deeper. Make sure that your paragraph flows. Do not just cobble together a list of statements or quotes. Make sure that each point follows and adds to the previous point. Make sure you give priority to the narrative devices. Do not just add irrelevant details in order to pad the paragraph; or if there ...
Summary Writing Steps. A summary is telling the main ideas of the article in your own words. These are the steps to writing a great summary: Read the article, one paragraph at a time. For each paragraph, underline the main idea sentence (topic sentence). If you can't underline the book, write that sentence on your computer or a piece of paper.
Response Essay Examples. 75 samples. A response essay is a sub-genre of critical writing. It describes your impressions from a book, movie, art, music, research paper, or any other creation. Its distinctive feature is the unlimited subjectivity allowing you to express whatever emotions the analyzed object has evoked.
Sample: Effective Response #1. The article could have been much more convincing if the author didn't begin most of his back-up arguments with "I", it gave the article a complaining and ranting tone, when an argument is explained like "a real course creates intellectual joy, at least in some.
Introduction. Paragraph 1: The first part of the introduction which needs to be vivid, catchy and reflect the point you are about to make. Paragraph 2: Provide a context to your response essay: details about the source-text and the author and what the main points in the article are. Body.
Learn how to write a summary and a response to an essay, with examples of organizational formats and tips for persuasive arguments. Find out how to cite the author, the title, and the main ideas of the essay.
Sample response paper "Typography and Identity" in PDF with margin notes. Sample response paper "Typography and Identity" accessible version with notes in parentheses. This page titled 5.7: Sample Response Essays is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anna Mills ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources ...
A critical response essay should contain these sections: Introduction; Summary; Analysis; Response; Conclusion; The introduction and conclusion should exist as separate paragraphs within the essay.
Carefully Read and Analyze the Text. The first step in response paper creation is to carefully read and analyze the text. This involves more than just reading the words on the page; it requires critical thinking and analysis. As you read, pay attention to the author's tone, style, and use of language.
Step 1. Examine the Primary Source. Before starting actually writing your critical essay, you need to get acquainted with the subject of your analysis. It might be an article, a book or any other type of text. Sometimes, this task is given for pieces of art, such as a painting or a movie. So, the first step would be to gain as much information ...
Learn how to write an effective introduction paragraph for your academic essay with this guide. It covers the four steps of hooking your reader, giving background information, presenting your thesis statement and mapping your essay structure.