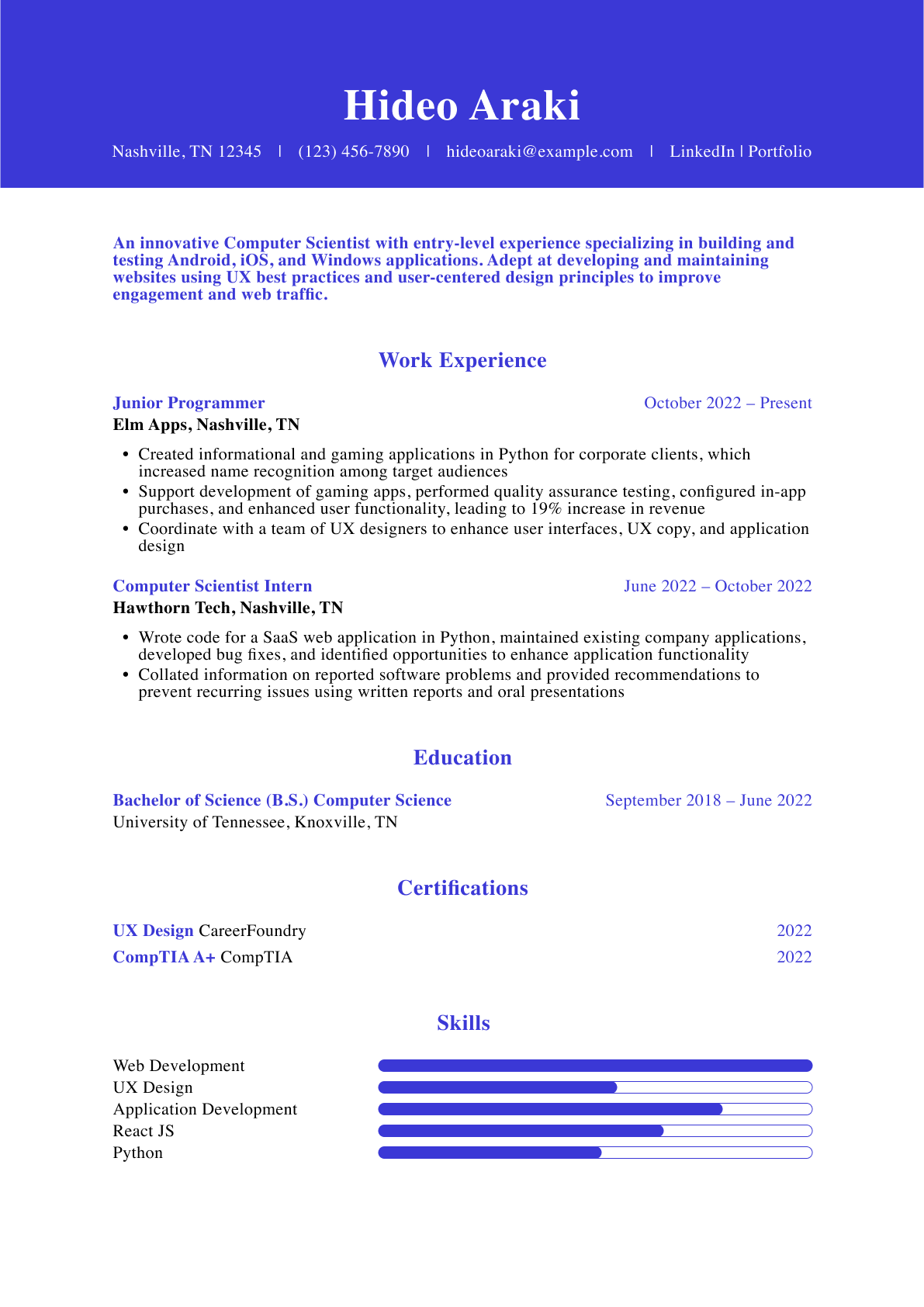
How to List Relevant Coursework On Resume [Tips & Examples!]

If you’re a college student, recent graduate, or entry-level professional, chances are you don’t have a lot of professional experience to list on your resume.
This, in turn, might make you feel insecure about your application, especially considering that the work experience section is among the most important section of a resume.
Well, listing your relevant coursework might just be the answer!
By listing the courses that are relevant to the job position or internship you’re applying for, you can show recruiters that while you don’t have much work experience, you have the right skills and knowledge for the job.
But what is the right way to list relevant coursework on your resume and is there a time when you shouldn’t list it all? And what exactly is relevant, to begin with?
In this article, we’re going to answer all those questions and more. Read on to learn:

When Is Relevant Coursework Necessary on a Resume?
- How to List Relevant Coursework on Your Resume in 3 Steps
7 Tips on Listing Relevant Coursework on Your Resume
Resume example with relevant coursework.
And more! Let’s dive right in.
What Makes Coursework Relevant?
Professional experience is one of the most important sections of a successful resume, but you first need to land a job to start building it.
Which begs the question, how can a recent graduate or entry-level professional prove they’ve got what it takes for an entry-level position with no, or minimal, professional experience ?
Well, this is where coursework comes in.
Together with academic projects and achievements, as well as extracurricular activities, listing relevant coursework can help students and entry-level professionals show they’ve got the necessary skills for the job despite not having the relevant professional experience.
The coursework you list on your resume should actually be related to the position you’re applying for.
For example, if you’re applying for a job as a graphic designer, listing your achievements in your World History class won’t really impress recruiters. If, on the other hand, you mention that you were top of your class in Design and Layout , you’ll be effectively showing recruiters that you have great potential as an up-and-coming graphic designer.
To sum things up, here are the top cases when relevant coursework is necessary on a resume:
- When you’re still a student
- When you’re applying with an entry-level resume
- When you’re applying for an internship
- When the coursework is directly related to the job position
If, on the other hand, you have 2+ years of work experience in the field, as well as the needed skill-set, coursework on your resume will only take up space and can be skipped entirely.
Checking the job description is another way of determining whether you should add relevant coursework to your resume. If, for example, the job description requires that you list your majors, GPA, diploma, or portfolio, chances are they’ll also be interested in your coursework, especially if it’s relevant to the position.
How to List Relevant Coursework on Your Resume in 3 Steps
So you’ve established that you should include relevant coursework on your resume. Now, you may be wondering where exactly to include it.
As a rule of thumb, coursework is listed under an applicant’s education history. Depending on whether you have any professional experience to list, the education section may come before or after the work experience section.
Here are the four best ways to add relevant coursework to your resume:
#1. Add a New Line in Your Education Section
Instead of creating a fresh section called “Relevant Coursework,” you’re better off just adding the courses to your education section.
As a student resume can be one-page max , this helps you to save up the space needed for other essential resume sections.
Here’s a practical example of what this looks like on the resume of a recent graduate applying for a high-school teaching position:
BA in World Literature
UC Berkeley
2012 - 2016
Relevant coursework: British Literature, American Literature, Medieval Literature, William Shakespeare, Language and Cognitive Development
#2. List Your Relevant Coursework in Bullet Points
To make your relevant coursework more visible and reader-friendly, list them in bullet points underneath your diploma title.
Here’s how the above Literature graduate’s resume would look like following this formatting:
Relevant Coursework:
- British Literature
- American Literature
- Medieval Literature
- William Shakespeare
- Language and Cognitive Development
#3. Explain How The Coursework is Relevant to the Position
Finally, if you want to take your relevant coursework resume section to the next level, add detailed explanations to your courses to support how they’re relevant to the position you’re applying for or how they helped develop your skill-set.
A recent study found that companies are suspending the use of degree completion as a proxy and instead now favor hiring on the basis of demonstrated skills and competencies . This means that your relevant coursework should aim to show exactly how it has helped you acquire the skills required for the position.
Here’s an example of how that would play out for a journalism student applying for an entry-level reporting job at a newspaper:
B.A. in Journalism and Mass Communication
Northwestern University, IL
2015 - 2018
- Writing and Reporting: Learned the ins and outs of news reporting through several practical assignments and exams.
- Media Ethics: Got introduced to the most essential ethical theories and decision-making strategies in journalism and wrote a paper on Ethical Journalism and Human Rights that got published in the Political Communication Journal.
- Gathering and Developing the News: Gained first-hand experience in interviewing, researching, newsgathering, and communicating with sources.
To make sure your coursework is as relevant as possible, check out the required skills in the job description. If you have taken classes that have helped you master those skills, then make sure to mention how by adding all the necessary details, as shown above.
Here are seven tips you should always keep in mind when listing coursework on your resume:
- Take advantage of keywords . When evaluating your resume, recruiters scan it to look for the keywords that were mentioned in the job description (e.g. skills, experiences, etc.). You can re-read the job ad and, where relevant, include these keywords in your coursework section.
- Tailor your resume to the job offer. In order for your coursework to add value to your resume, it really needs to be relevant. So, if you’re applying for a job that doesn’t take academic background into consideration or that’s completely unrelated to your major, you’re better off omitting coursework altogether and focusing on other important sections, such as your hard and soft skills.
- List online courses. If you’ve completed some online courses that are relevant to the position you’re applying for, feel free to also include them under relevant coursework.
- Add value through other academic achievements. Relevant coursework can say a lot about your potential, but recruiters will be even more easily convinced if you support it with other academic achievements, including your GPA, extracurricular activities, etc.
- Show how you’ve grown. When you’re explaining your relevant coursework in detail, you can include how you’ve grown by listing all the skills you acquired in the process. Those can be both soft skills, like communication and interpersonal skills, and hard skills like programming or doing extensive research.
- Change the relevant coursework as you progress. Many college students start working in their freshman year. If that’s the case with you, make sure to update your resume from year to year to reflect your academic journey and most recently acquired skills.
- Check for errors. A well-written, error-free resume shows that you’re attentive to detail and that you care to make a good impression.

Key Takeaways
And that’s a wrap! You now have all the necessary information to add relevant coursework to your resume effectively.
Before you start working on your resume, though, here’s a brief summary of the key points covered in this article:
- Listing relevant coursework on your resume is not mandatory but can be very helpful if you’re a student or an entry-level professional.
- If you have at least a year of professional experience, drop your relevant coursework and focus on tailoring your work experience and skills sections to the position.
- Relevant coursework typically goes under the education section. You can either give a general or a detailed summary of your coursework.
- You can make a separate relevant coursework section only if the job you’re applying for requires a strong academic record.
- Your coursework needs to be relevant to the position. This means you should leave them out of your resume if they have nothing to do with the role.

To provide a safer experience, the best content and great communication, we use cookies. Learn how we use them for non-authenticated users.
How To Include Your Relevant Coursework On A Resume
In This Guide:
How important is it to list relevant coursework on a resume as a college student, how can i include relevant coursework on a student resume, when to avoid coursework on resume, what other sections can you add that can have more impact than coursework, volunteer experience, extracurricular activities, passions/strengths/interests, relevant coursework on resume – takeaways.

In today’s hiring landscape, your resume needs to quickly communicate all of your potential value to an employer. If you’re a student or recently graduated, your practical job experience may still be poor – but your coursework is probably rich.
So should you include the relevant classes you took on your resume? You can!
However, there are some factors you should consider before listing your coursework. You need to think about where you are in your career, what is the position you are applying for, and how relevant your education is to the job description.
Don’t get scared, it is not so much. Stay with us. This article will help you decide whether you need to include your relevant coursework.
You can also browse through our Resume Examples where you can see a perfect one for your dreamed position.
Upload & Check Your Resume
Drop your resume here or choose a file . PDF & DOCX only. Max 2MB file size.
If you are a student or have just graduated, it is possible that you don’t have enough professional experience to show. So a good way to demonstrate your expertise is by including your relevant coursework.
However, if you already have a year or more work experience, this section won’t be much of a help.
Then you should focus on the professional experience and achievements you’ve accomplished.
Even if you are a student or freshly graduated, there are jobs, for which relevant coursework won’t be helpful. For example a cashier or a waiter. If you are looking for these jobs, better emphasize on your technical skills and past experience.
If you’re applying for a job that emphasizes the importance of academic experience, like an internship or other education-focused position, it would be best to include a relevant coursework section on your resume.
Whether they are needed or not, look through the job description. This could help you understand what to write. If they’re looking for a certain diploma, certification, portfolio or GPA, these are indicators that you should include.
How much coursework you fit into your resume and where you include it depends on three factors:
- The number of relevant courses you’ve taken
- The detail you want to include
- The space you have
Most people include relevant coursework in the education section of their resumes.
To do this, just write “Relevant Coursework” beneath the degree name, and then use commas to separate the titles of the courses.
If you have enough space, you could also make a bullet list. This way it would be easier for the Recruiter to read.
Another way to write it is a separate section.
We, from Enhancv, have made that easy. Just go to our resume builder and make the most of it.
Write your relevant courses as a separate section if you want to include more than just the names of the classes. A perfect way to tell the Recruiter what you have learned through your studies when they are related to the job you are applying to.
Couple with academic achievements / GPA
If you don’t want to use a separate section, or you don’t have enough space for it, you can always couple them with your academic achievements or with your GPA.
Decide which to use in your resume, after you read the job description and see which is going to be more helpful to you to get that job.
If you have created a separate section for your coursework, just write the most important courses, depending on the job description.
Don’t put in all of your classes. It is going to take a lot of space and it would only distract the Recruiter.
If your coursework is crucial to the position consider putting it closer to the top of your resume.
If the class is necessary for the Hiring Managers don’t put it in the education section, because it could get lost along with all of the information.
Only list the names of your classes on your resume. Your university probably uses an internal system to number your courses, however, the employers wouldn’t know or care what the numbers mean.
If you have created a separate section for your coursework write just the most important courses, depending on the job description.
Don’t put all of your courses. It is going to take a lot of space and it would only distract the Recruiter.
Only list the name of your classes on your resume. Your university probably uses an internal system to number your courses, however, the employers won’t know or care what the numbers mean.
As we said earlier, coursework is a good way to show your educational achievements. However, there are times when it’s better not to include them.
If it’s been some time since you have been in school and the coursework is outdated, it might be best to leave the specifics off your resume.
What is more, keep an eye on the length of your resume. If you have just graduated or still a student, better make it no longer than one page. If there is no space for the related coursework, don’t include them if they are not specifically asked for in the job description.
Don’t include courses that are in no way relevant for the position.
If you have successfully finished a course in “Art History”, but you are applying to a position in a call center, don’t include it in your resume.
It will not help you to get the job you want and it will distract the Hiring Manager from your skills related to the position.
There are many other sections, which you can include if you have no experience. And sometimes, they could be much more important than the coursework.
According to Deloitte, 82% of hiring managers prefer applicants with volunteer experience.
They believe volunteer work makes you a good leader and strengthens your communication skills.
You should include your volunteer work when it is relevant to your professional development.
It can put you in good light and make you stand out among other applicants..
Check the great example from Avery Leclerq:
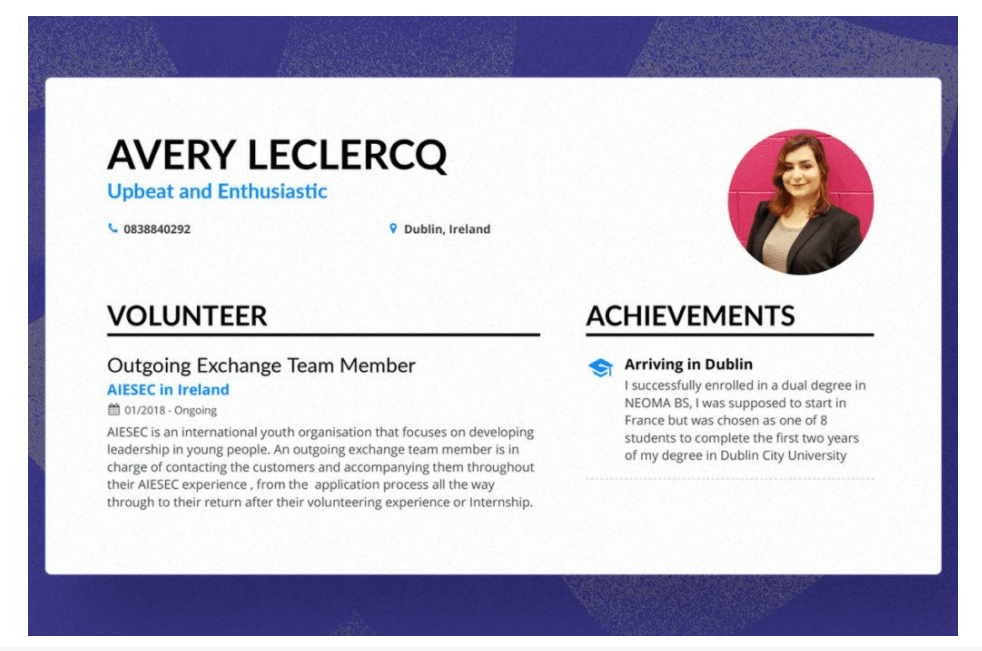
If you don’t have volunteer experience or it is not related to the position you are applying to, choose one of the sections below.
Focus the Hiring Manager’s attention on your experience outside of the university. It could be any extracurricular activity related to the position you are applying to.
For example, you could have been part of your local AIESEC team and participated in their initiatives.
Or you could have been part of a student organization or a club and made your university a better place to study in.
Adding this experience in your cover letter tells the Recruiter that you have developed yourself, your organizational skills, and you are motivated to help others.
Another way to make your resume look good without work experience is by adding activities and projects that are related somehow to the position you are applying for.
Even if they were university or academy projects, you have gained a lot while finishing them.
Recruiters will see that you’re a person who is dedicated to their career path and gains better skills and experience with side projects!
These can help you in identifying yourself and your own personality with the company’s culture fit profile.
Be sure to highlight your personality and unique qualities.
See this example:
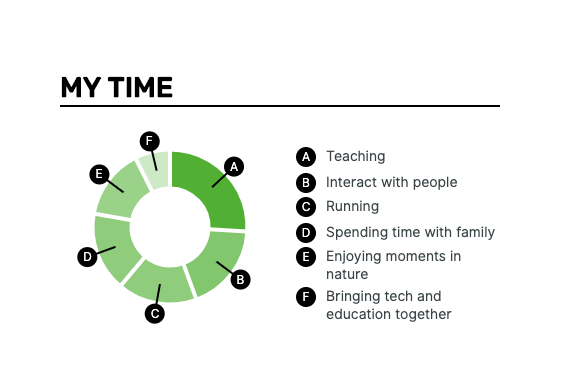
As it’s clear, the candidate is an outgoing, extroverted person who enjoys nature, tech and education.
It is a creative way to show your hobbies and interest. What is more, the Recruiter could make a conclusion just by seeing the pie chart and the distribution of time.
There is another section you can use – Passion. It can be used to enhance the effect of the hobbies and interests section.
Adding them is not mandatory, but might be valuable when your life passions are relevant to the job.
Whatever you choose to include, always make sure you present it in a way that sounds and looks professional.
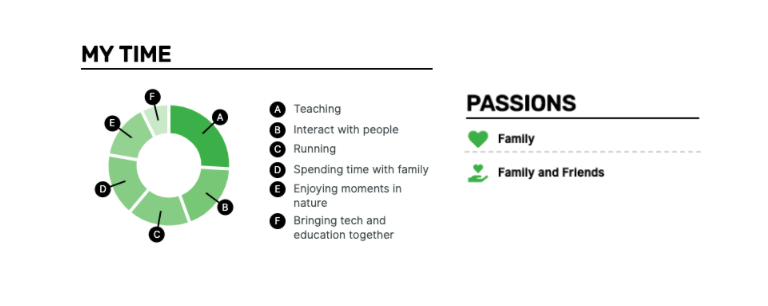
When both are included, they give a complete picture of who you are – not only in your work time.
That will significantly improve your chances of landing an interview, especially if you have a resume without job experience.
Here’s all you need to know about putting relevant coursework on a resume:
- It is not absolutely necessary to list relevant coursework in a resume;
- If you are a student or just graduated they could help you.
- If you have the experience, drop relevant coursework from your resume, and focus on your practical experience and skills.
- Use the education section to present the relevant coursework, you can separate them with commas or make a bullet-pointed list.
- Make a section only for your relevant coursework if the position you’re applying for requires a strong academic background;
- If it is not wanted by the job description, better drop it and focus on volunteer and extracurricular activities, hobbies, and interests relevant to the position.
Still not sure whether or not you should put relevant coursework on a resume? Or maybe it has helped you get your dream job? Write to us in the comments below!

- Resume Guides
How to Make A Great Resume Outline (Including Examples)
Marissa mayer: ''thank you for a great resume'', how to list address on a resume in 2024 – format, pro tips & examples, how to list publications on a resume: a guide for researchers, how long to hear back after an interview: 3 tips to win the waiting game, are there enough remote entry-level jobs here’s what 10 800 postings say.
- Create Resume
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Preferences
- Resume Examples
- Resume Templates
- AI Resume Builder
- Resume Summary Generator
- Resume Formats
- Resume Checker
- Resume Skills
- How to Write a Resume
- Modern Resume Templates
- Simple Resume Templates
- Cover Letter Builder
- Cover Letter Examples
- Cover Letter Templates
- Cover Letter Formats
- How to Write a Cover Letter
- Cover Letter Guides
- Job Interview Guides
- Job Interview Questions
- Career Resources
- Meet our customers
- Career resources
- English (UK)
- French (FR)
- German (DE)
- Spanish (ES)
- Swedish (SE)
© 2024 . All rights reserved.
Made with love by people who care.
How to List Relevant Coursework on a Resume

List Only Relevant Coursework that Matches the Job Description
You don’t need to use the official name of the course, feature academic projects to further highlight your coursework, include academic awards and your gpa, how to align your coursework with the job description.
Listing relevant coursework from your bachelor’s degree program on your resume can be advantageous for entry-level job seekers starting out within their industry. There are two ways to accomplish this. Including the coursework as bullet points within your education section is one approach. The other option is to create a whole new section that allows you to list your coursework separately and provide more insights into what you learned during your program. Throughout this guide, we’ll provide you with examples to help you showcase your coursework and land your first entry-level position.
Ideally, you should only list coursework relevant to the position you are applying for on your resume. For instance, if you’re seeking an accounting position, it wouldn’t make much sense to include an elective you completed in continental philosophy. As your job search begins, carefully analyze each posting before incorporating your coursework.
The more relevant details you’re able to incorporate into your resume, the more likely you’ll be to generate interviews during your search. Coursework can be beneficial for entry-level professionals, as it can sometimes be challenging to fill out your document with strong qualifications due to a lack of work history. Below, we’ll review an example of a job seeker looking for a mental health counseling role:
Bachelor of Science (B.S.), Psychology COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY, New York, NY September 2017 – May 2021
Coursework:
- Expressive Art Therapy
- Emotionally-Focused Therapy
- Psychotherapy
- Group & Family Counseling
Notice how in this first example, the job seeker is including both psychology and art courses in their education section. This might seem like a poor choice on the job seeker’s part, but in this situation, they’re actually demonstrating why they’re uniquely qualified for the position. Art therapy is a unique field within the mental health counseling space that utilizes a range of modalities and therapeutic approaches to help patients overcome trauma and cognitive disabilities. Showcasing their understanding of both art and psychology will show organizations that they have a dynamic skill set that can help them succeed within this niche clinical environment.
It’s important to understand that the names of courses vary significantly from university to university. If the official name of the course fails to convey what you were learning, you may want to use a relevant keyword as the course title instead. For instance, instead of “Intro Accounting 101”, you may want to use a title such as “Financial Accounting” instead. This will also help you to maintain compliance with Applicant Tracking System (ATS) requirements, as you can rename your courses to mirror high-impact keywords on the job description.
- Introduction to Developing Software 101
- Intro to Programming 102
- Advanced Computer Science 103
- Coding in the Modern Tech Landscape 103
- App Dev Capstone Course 104
Software Development Coursework
- Software Development Intro Course: Completed coursework on the fundamentals of software development, including the SDLC, application development, and JavaScript
- Python and JavaScript Programming: Completed a course on the use of Python and JavaScript for a variety of web development and software development projects
- Application Development Capstone : Completed a capstone course to build a functional mobile application in Python that enabled students to compare and contrast cost savings on used books and rentals versus new book prices
Notice how in the first example, the job seeker is using the exact names of the courses. Although “Coding in the Modern Tech Landscape” sounds like a good title, it doesn’t tell the hiring manager anything about what the student was learning during the course. In the second example, the candidate has changed the titles of the courses to better reflect the subject matter. They also provide fewer courses, and instead highlight more relevant details that match the position they’re applying for. This is a much more effective strategy for making a positive impression on the hiring manager and will greatly increase your chances of landing the interview.
If you’re going to list coursework on your resume, you should strongly consider building an academic projects section to provide deeper insights into your education experience and qualifications. It’s one thing to mention a Python class on your resume, but it’s another to showcase a project where you utilized this programming language to build a mobile application. Resumes with unique and compelling details are much more likely to grab the hiring manager’s attention, especially when applying for entry-level positions where the documents run the risk of appearing vague and generic. Below, you’ll find two examples to help you feature academic projects on your resume:
Academic Experience
Economics Projects, University of Syracuse, New York, NY September 2020 – May 2022
- Performed statistical analysis of financial trends within the housing market to create a predictive algorithm analyzing potential shifts based on a variety of economic factors, including foreclosures, housing market data, and projected household incomes
- Evaluated the risk and long-term ROI potential of a hypothetical start-up company by conducting a detailed analysis of the product use case, competitors, and market growth data
Web Development Projects, University of Michigan, Detroit, MI September 2020 – May 2022
- Designed and developed a web page featuring blogs, resources, and testimonials within the mobile gaming industry, including a platform for users to share insights
- Developed a mobile application to aid students in comparing and contrasting costs of used books and rentals across online stores and vendors, which included designing a feature to showcase cost savings of used books vs. new books in the university store
Another way to further enhance the impact of your coursework is by providing academic awards and recognitions on your resume. This will show hiring managers that you completed your coursework and excelled academically within your program. If your GPA is 3.6 or higher, you can also feel free to include it in your education section. If the number is lower, it may be better to omit it, as it won’t significantly impact your job application.
Bachelor of Science (B.S.), English TEMPLE UNIVERSITY, Philadelphia, PA, September 2017 – May 2021 GPA: 3.87/4.0
- President, Hyphen Literary Magazine, 2020-2021
- Recipient of the Temple English Award, 2021
- Dean’s List 2017-2021
- Magna Cum Laude
Bachelor of Science (B.S.) Computer Science UNIVERSITY OF SAN DIEGO, CA September 2017 – May 2021 GPA: 3.7/4.0
- President of the University Robotics Club, 2017-2021
- Dean’s List, 2018-2021
- Summa Cum Laude
The most important aspect of the resume-building process is tailoring your document toward individual job descriptions. Breaking into your target industry following graduation can often be challenging for entry-level job seekers. Other candidates may have hands-on experience that you lack, and to make a case for your candidacy, you’ll need to show hiring managers that you have the ideal qualifications to succeed in the role.
As you build out your resume, you should start by determining how your skill sets and education experience match the needs of the organization you’re applying to. Remember that it’s okay to alter the name of a course to convey key skill sets more clearly for the hiring manager, provided it’s an accurate representation of what you learned during the course. For instance, if a company is seeking a candidate who excels in financial planning and analysis (FP&A), it’s acceptable to feature this as a course instead of using a broad and vague title provided by the university.
By tailoring your coursework toward the job description, you’ll maximize your chances of generating interviews over the course of your job hunt.
Craft your perfect resume in minutes
Get 2x more interviews with Resume Builder. Access Pro Plan features for a limited time!

Frank Hackett
Certified Professional Resume Writer (CPRW)
Frank Hackett is a professional resume writer and career consultant with over eight years of experience. As the lead editor at a boutique career consulting firm, Frank developed an innovative approach to resume writing that empowers job seekers to tell their professional stories. His approach involves creating accomplishment-driven documents that balance keyword optimization with personal branding. Frank is a Certified Professional Resume Writer (CPRW) with the Professional Association of Resume Writers and Career Coaches (PAWRCC).
Build a Resume to Enhance Your Career
- How to Land Your Dream Job Learn More
- How to Organize Your Job Search Learn More
- How to Include References in Your Job Search Learn More
- The Best Questions to Ask in a Job Interview Learn More
Essential Guides for Your Job Search
- How to Build the Perfect Computer Science Resume Learn More
- How to Build a Resume Learn More
- How Many Jobs Should You List on a Resume? Learn More
- How to Include Personal and Academic Projects on Your Resume Learn More
- Career Blog
Education in Progress on Your Resume: How to List it

As job markets become increasingly competitive, it’s essential to have an impressive resume that stands out from the crowd. One key element of a strong resume is education. Employers seek candidates who combine practical experience with a solid learning background. But what if you’re still pursuing your degree or professional development courses? How do you include that education in progress on your resume effectively? This article discusses the importance of education on a resume and provides practical tips on how to present ongoing education.
Importance of education in a resume
Listing your education on a resume is essential as it demonstrates your commitment to learning, a strong work ethic, and a desire to fill knowledge gaps that enhance your skills. Formal education, such as a bachelor’s or master’s degree, is crucial for some professions, while others demand additional training and certification.
Education information gives employers insight into your skills, which leads them to measure your potential for learning, reasoning, and critical thinking. Even if you don’t have completed education, highlighting the courses you’re currently taking or training you’re participating in can showcase your willingness to learn and your dedication to personal development.
How to present education in progress on a resume
If you’re still in school or taking courses, be sure to list the degree or certification you’re pursuing and include the expected date of completion. You can also provide details on relevant course work and academic achievements. If you’re taking courses for career development, mention the name of the course, the issuing institution, and the expected completion date. Remember to include any certifications you’ve earned from those courses or training programs.
Another way to showcase education in progress is to include the phrase “in progress,” “anticipated completion date,” or “expected graduation date” next to the corresponding certification or degree. These phrases help recruiters understand your current status in your academic journey.
The benefits of highlighting ongoing education on your resume
There are several advantages to highlighting education in progress on your resume. First, it demonstrates your commitment to your profession, your desire to learn, and your willingness to grow professionally. Additionally, it highlights the fact that you’re not resting on your past laurels.

Moreover, showing relevant courses and training programs can also help employers see that you have the necessary skills to handle the job’s requirements. This demonstrates that you have taken the initiative to develop those skills proactively.
Including relevant education in progress on your resume can enhance your credibility, and it’s an excellent strategy to differentiate yourself in a highly competitive job market. When done well, your resume can be your ticket to a more prosperous future.
Types of Education in Progress
If you’re still pursuing a new degree or certification, it’s important to list that information on your resume. Employers love to see that you’re working towards improving yourself and staying up-to-date in your field. Here are several types of education in progress that you may want to include:
Traditional College or University Degree
If you’re working towards a bachelor’s, master’s, or doctoral degree at a traditional college or university, make sure to list your degree, major, and expected graduation date. You can also include any relevant coursework or projects that highlight your skills and knowledge. Employers want to see that you have a clear plan for completing your degree and are committed to your education.
Online Courses and Certifications
In today’s digital age, many people are turning to online courses and certifications to further their education. This option is great for those who may not have the time or resources to attend a traditional college or university. List any online courses or certifications you are currently taking or plan to take in the near future. Be specific about the course or certification title, the date you expect to complete it, and any relevant skills or knowledge gained.
Boot Camp Programs
Boot camp programs are intensive, short-term educational courses designed to teach specific technical skills. If you’re enrolled in a boot camp program, make sure to list the program title, start and end dates, and any relevant projects or skills learned. Boot camps are highly focused on practical skills that are in demand by employers, so highlighting your participation in one can be a major selling point on your resume.
Apprenticeships and Internships
If you’re gaining practical experience through an apprenticeship or internship, it’s important to include this on your resume. List the company name, your position or title, the dates of your apprenticeship or internship, and any relevant projects or achievements. Employers love to see that you’ve gained real-world experience and are actively working towards developing your skills.
Education in progress can be a major asset on your resume. Whether you’re pursuing a traditional degree, taking online courses, participating in a boot camp, or gaining practical experience through an apprenticeship or internship, make sure to list these education endeavors to showcase your commitment to personal and professional growth.
Choosing the Right Section for Ongoing Education
The education section of a resume is a crucial aspect that indicates the level of education and academic achievements. However, ongoing education and training also play a critical role in demonstrating the candidate’s continuous learning and career growth.
When it comes to highlighting ongoing education on your resume, several sections can showcase your dedication to growth and development. Here are the four main sections that you can consider:
Education Section
The education section is the most common section to showcase ongoing education, as it is the primary place where academic qualifications are listed. This section should include your formal education, such as degree or diploma programs, and mention any ongoing studies, coursework, or current enrollment in a degree program.
If you’re currently pursuing a degree or certificate program, it’s essential to mention the program’s name, educational institution, start and anticipated completion date, and degree or certification name.

Certifications Section
Another section to consider including your ongoing education is the certification section. This section focuses on industry-specific certifications and credentials that demonstrate your skills and expertise. Listing your certifications highlights your commitment to your field and indicates that you’re up-to-date with current practices and trends.
If you’re pursuing additional certifications, list them in this section, and mention the certification body, date of completion, and certification name.
Professional Development Section
The professional development section is an excellent place to highlight any non-degree programs or courses that you’re currently enrolled in or completed. This section can include workshops, webinars, conferences, or training programs that you attend to enhance your skills and knowledge.
It’s essential to list these programs according to the level of relevance to your career goals and industry. Also, mention the event or program name, the institution or organization providing the learning experience, and the date of completion.
Relevant Experience Section
Lastly, you can incorporate your ongoing education and training by emphasizing the skills gained from your education and professional development sections in your relevant experience section. This section should include a summary of your work experience, skills, and accomplishments relevant to your career goals.
Emphasize how your continual learning and ongoing education contribute to your skill set and demonstrate your commitment to professional growth. For example, mention any responsibilities, tasks, or projects that showcase the skills acquired from your current and previous education and training experiences.
Carefully choosing the right section for ongoing education on your resume is crucial to reflect your career’s progression and dedication to growth and development. Consider all the above sections and highlight your ongoing education and learning commitment to the best of your ability.
Where to List Education in Progress on Your Resume
When it comes to listing education in progress on your resume, there are a few different options for placement. Depending on the details of your education and professional experience, you may want to consider one or more of the following methods:
Top of the Resume
One common option is to include any education in progress at the very top of your resume. This can be especially effective if your education is relevant to your desired job or career path. By highlighting your ongoing education right away, you can demonstrate your commitment to learning and professional development.
After Completed Education
Another option is to list any completed education first, followed by any education in progress. This may make the most sense if you’ve already achieved a degree or certification that is relevant to your field. By showing your completed education first, you can establish your qualifications and expertise before highlighting your ongoing education.
In the Professional Development Section
If you have a section on your resume that is specifically dedicated to professional development or continued education, you can include your education in progress there. This can be a great way to demonstrate your commitment to lifelong learning and staying up-to-date in your field.
In Description of Relevant Experience
Finally, if you have relevant experience that is directly tied to your ongoing education, you can mention your education in progress in the description of that experience. For example, if you’re currently pursuing a degree in marketing and you have hands-on experience working on marketing campaigns, you could mention your degree program in the bullet points describing your marketing experience. This can help to demonstrate how your education and experience are working together to make you a strong candidate for the job.
There is no one “right” way to list education in progress on your resume – you’ll need to consider your own background and goals in order to determine the best approach for you. By thinking carefully about where to include your education in progress, however, you can create a resume that showcases your skills, knowledge, and dedication to personal and professional growth.
How to Format Education in Progress
When you’re still in the process of completing your education, it’s important to format it correctly on your resume. Here are some key elements to include:
Name of the Program or Degree
Clearly state the name of the program or degree you’re pursuing. This will help recruiters and hiring managers understand your area of focus and level of expertise.
Institution or Provider
Include the name of the institution or provider where you are pursuing your education. This can help give insight into the rigor and quality of the program you’re taking.
Expected Completion Date
Indicate when you expect to complete your program or degree. This can be helpful for recruiters and hiring managers who are trying to assess your availability and qualifications.
Relevant Coursework and Projects
Highlight any relevant coursework or projects you’ve completed that relate to the field you’re pursuing. This can demonstrate not only your knowledge but also your initiative and ingenuity.
GPA or Grade Point Average
Include your GPA or grade point average if it is reasonably high. This can indicate that you’ve maintained good academic standing and that you are serious about your education.
Education in progress can be a valuable asset to include on your resume. By following these key formatting guidelines, you can help ensure that potential employers understand your qualifications and accomplishments in the best light possible.
How to Highlight Education in Progress in Your Work Experience
If you’re currently pursuing a degree or additional education while working, it’s important to showcase this ongoing education in your work experience section of your resume. Here are some techniques to effectively highlight your education in progress:
Including ongoing education in job titles
One way to display your education in progress is by adding it in your job titles. For example, if you’re currently pursuing a Masters in Marketing, you could list your job title as “Marketing Coordinator (Masters in Marketing in Progress)”. This will grab the employer’s attention and showcase your eagerness for continued learning and professional development.
Listing completed coursework in job descriptions
If you’re in the midst of completing your education, it can be helpful to list relevant coursework in your job descriptions. This not only highlights your education in progress, but it also demonstrates your knowledge and skills gained through your courses. For instance, if you’re applying for a job in finance and have completed several finance courses, mention them in your job description to show your expertise in that area.
Highlighting relevant projects
Finally, you can highlight your education in progress by showcasing relevant projects you’ve worked on that directly relate to your ongoing education. Choose projects that demonstrate the skills and knowledge you’ve gained through your coursework. Include a brief description of the project, your role, and how it showcases your education in progress.
By implementing these techniques, you can effectively highlight your education in progress in your work experience section of your resume. This not only shows your eagerness for continued learning, but also demonstrates to potential employers that you have value to bring to their organization.
Example of Listing Education in Progress
When it comes to your resume, it’s important to showcase your ongoing learning and development. Listing education in progress can demonstrate your dedication to self-improvement and an eagerness to stay up-to-date in your field. Here are some examples of how to list different types of education in progress on your resume.
Traditional Degrees in Progress
If you’re currently working towards a traditional degree, such as a bachelor’s or master’s, you can list it on your resume in a few different ways. One option is to simply include the degree program and expected graduation date under your education section. For example:
Bachelor of Science in Marketing, XYZ University Expected Graduation: May 2022
Alternatively, you can include any relevant coursework or special projects you’ve completed within the degree program, as well as any notable achievements. Here’s an example:
Bachelor of Science in Computer Science, ABC University
- Relevant coursework: Data Structures and Algorithms, Operating Systems, Database Systems
- Special project: Developed a chatbot using Python and TensorFlow
- Dean’s List (GPA above 3.5)
Online Courses and Certifications in Progress
With the rise of online learning, many people are pursuing courses and certifications outside of traditional degree programs. If you’re currently taking an online course or working towards a certification, you can list it on your resume like this:
Google Analytics Certification, Google In progress
Make sure to include the name of the course or certification, the organization offering it, and the fact that it’s in progress. If you’ve already completed some coursework or modules, you can mention that as well.
Boot Camp Programs in Progress
Boot camps are intensive programs that provide hands-on training in specific skills, such as coding, UX design, or digital marketing. If you’re currently enrolled in a boot camp program, you can list it on your resume like this:
Full Stack Web Development Boot Camp, Coding School Expected Completion: December 2021
Be sure to include the name of the program, the organization offering it, and the expected completion date.
Apprenticeships and Internships in Progress
If you’re gaining on-the-job experience through an apprenticeship or internship, you can list it on your resume to showcase your practical skills and industry-specific knowledge. Here’s an example:
Marketing Intern, Company X Expected Completion: August 2021
Include the title of your role, the company you’re interning with, and the expected completion date. You can also mention any specific projects or tasks you’ve worked on during your internship.
Listing education in progress on your resume can demonstrate your commitment to ongoing learning and development. Whether you’re pursuing a traditional degree, online certification, boot camp program, or on-the-job training, make sure to highlight your education and experience in a way that showcases your skills and expertise.
How Education in Progress Enhances Your Skills
Continuous learning is essential in today’s fast-paced world. It is not enough to have a degree, as the skills and knowledge required in most professions are constantly evolving. Therefore, it is paramount for individuals to seek out and take advantage of educational opportunities throughout their careers.
Acquiring new skills and knowledge through education in progress demonstrates initiative, curiosity, and resilience, all of which are highly valued by employers. Learning a new skill or gaining knowledge in a particular area shows that you are investing in yourself and your career development, making you a more valuable asset to any company.
Moreover, education in progress highlights your dedication and commitment to a specific field or profession. It is evidence of your willingness to take responsibility for your professional development and, in turn, demonstrates your motivation to succeed in your chosen career.
Education in progress enhances your skills by keeping you up to date with the latest industry trends and advancements. It also shows that you are constantly seeking to improve and learn, which can only be a benefit to you and any company you work for. Demonstrating motivation and commitment is crucial when looking for employment or career advancement, and education in progress is an excellent way to showcase these traits.
Listing your education in progress on your resume is a simple yet effective way to demonstrate your commitment to professional development and increase your employability. By continuing to learn and develop your skills, you increase your value to employers and set yourself up for long-term career success.
Tips for Presenting Education in Progress on Your Resume
When it comes to listing education in progress on your resume, there are a few key tips to keep in mind. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your education section sets you up for success and highlights your achievements and progress:
Emphasize achievements and progress: Rather than simply listing the courses you are currently taking, focus on the accomplishments and progress you’ve made thus far. This could include stellar grades, completed projects, or any other noteworthy achievements.
Avoid exaggeration and misrepresentation: While you want to highlight your accomplishments, it’s important to be truthful and avoid exaggerating or misrepresenting your education. This includes being honest about the courses you’ve taken and the grades you’ve earned.
Tailor the presentation to the position and industry: Depending on the position and industry you’re applying to, the way you present your education in progress may differ. For example, if you’re applying to a job in a highly technical field, you may want to include more specific details about the coursework you’ve completed. On the other hand, if you’re applying to a job in a more creative field, you may want to focus on the projects you’ve completed or the skills you’ve developed.
The key to presenting education in progress on your resume is to focus on your achievements and progress, while also being truthful and tailoring your presentation to the position and industry you’re applying to. By following these tips, you can create a compelling education section that helps you stand out from the competition.
Common Mistakes When Listing Education in Progress
When including ongoing education in your resume, there are some common mistakes to avoid. Here are three of the most significant:
1. Listing Too Many Programs
While it’s great to have a broad range of skills, listing too many ongoing education programs can give the impression that you’re indecisive or jack-of-all-trades. Instead of overwhelming your potential employer with many programs, focus on the ones that are the most relevant to the job or industry you’re applying for.
2. Disregarding Previous Education
Just because you’re still working on obtaining further education doesn’t mean that previous education has lost its value. It’s important to highlight previous educational experiences in your resume and show how they have prepared you for your current education.
3. Overemphasizing Ongoing Education
Of course, ongoing education is essential, but overemphasizing it can make it look like you don’t have any real-world job experience. Instead, find a balance between emphasizing your ongoing education while also drawing attention to your job experience.
By avoiding these common mistakes, your resume will showcase the value that your ongoing education brings to the table without losing sight of your previous experience.
Related Articles
- 40+ Modern Resume Templates to Stand Out
- Managing a Career Gap on Your Resume
- Intern Pharmacist Resume: Examples
- The Camp Counselor Resume Sample & Writing Tips
- Navigating Career Decisions: Tips for the Undecided
Rate this article
0 / 5. Reviews: 0

More from ResumeHead

- EXPLORE Random Article
- Happiness Hub
How to Mention Relevant Coursework in a Resume
Last Updated: May 25, 2023 References
This article was co-authored by Amber Leima and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Amber Leima is a Resumé Consultant and the Founding Editor of Best Words Editing. She has two decades of experience helping people and companies express their unique value. Amber is a master at drawing out what matters from your personal story and promoting it to optimal effect, crafting beautifully clear resumés and on-point personal branding supported by thoughtfully-structured interview coaching. She holds Master’s and Bachelor’s degrees in English Literature from the University of Sussex, England. Her clients have been hired by their employers of choice, including Amazon, Meta, Microsoft, and PayPal. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 354,746 times.
Crafting a great resume isn’t easy! One of the many tricky parts is choosing what to add and what to leave out—for instance, should you list some relevant coursework? Adding coursework can be particularly important if you are a recent graduate and have little relevant work experience. If you determine that you should indeed add relevant coursework to your resume, it’s critical to ensure it is truly relevant to the position for which you are applying—and is listed in the right place with sensible formatting!
Selecting Coursework for Inclusion

- The general cut-off point is typically 5 years of relevant work experience: if you have less than this, add relevant coursework to your resume; if you have more than this, only add relevant coursework if it’s hyper-specific to the job or internship.
- Still not sure if you should add coursework to your resume? Ask yourself if you’ll rely on talking about coursework during an interview. In other words, do you have enough relevant work experience that you won’t need to mention your coursework during an interview? If the answer is “yes,” then you typically don’t need to add coursework to your resume.

- Remember: just because you’re not done with a course or degree doesn’t mean it’s irrelevant! Always list any in-progress coursework and note the planned completion date of the course or degree.
- List the courses by their actual title, not their course number or some nickname: for example, “United States History to 1877,” not “U.S. History 101” or “American History I.” This isn’t absolutely essential while brainstorming, but it makes things easier once it’s time to transfer coursework to your resume. [3] X Research source

- If, for example, you’re a communications major and are applying for a social media internship, any social media communication classes you’ve taken should be considered relevant. Or, if you’re applying for an HR job and have taken courses on finance and payroll as part of your human resources major, definitely include these if the position involves areas like compensation and benefits.

- For example, if you are applying for a position at an aerospace engineering firm, you should list your internship at an aerospace research facility. Or, if you are applying for a social media position at a marketing company, you might list volunteer experience as the social media director at a local festival.
Adding Coursework to Your Resume

- Suggested section title: Relevant Education and Coursework.
- For example, you may have earned a degree in English, but are now studying graphic design at your local college. If you are applying for a position at a graphic design firm, list this educational experience first, before your English degree.
Bachelor of Science in Genetic Engineering Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island Expected completion date: 05/2017

Bachelor of Science in Genetic Engineering Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island Expected completion date: 05/2017 Relevant coursework: Lab Testing & Reporting, Genetic Manipulation, Social Implications of Genetic Engineering.
Advanced Studies in Marketing and Advertising Hudson Community College, Hudson, New York Expected completion date: 05/2015

- It’s also not necessary to list your final GPA for a degree or course, as most employers will not notice the score. But if you graduated with high honors, such as summa cum laude or with honors , make a note of this in your resume.
Bachelor of Science in Anthropology, Graduated with Honors Concordia University, Montreal, Quebec Relevant Coursework: Advanced Topics in Social Anthropology, Research and Investigation, Advanced Studies in Ancient Cities.
Expert Q&A

- Even if your education and coursework listing feels a bit thin for the position, it’s important not to fabricate coursework on your resume. Your employer may ask you about this made-up coursework, putting you in a position where you must either come clean or be dishonest in your interview. [10] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://publichealth.gwu.edu/blogs/careers/2014/04/15/weekly-career-tip-including-relevant-coursework-on-a-resume/
- ↑ https://www.themuse.com/advice/how-to-and-how-not-to-list-education-on-your-resume
- ↑ Amber Leima. Resumé Consultant. Expert Interview. 18 March 2022.
- ↑ Alyson Garrido, PCC. Career Coach. Expert Interview. 24 January 2019.
- ↑ https://career.virginia.edu/blog/how-create-stem-resume-basics
- ↑ https://www.forbes.com/sites/dailymuse/2017/06/07/your-handy-answer-to-how-long-do-i-keep-my-graduation-year-on-my-resume/#3789e7ee6d2e
- ↑ https://www.payscale.com/career-news/2019/01/why-you-should-never-lie-on-a-resume-7-stories-of-people-who-got-caught
About this article

Referencing your coursework is a great way to show an employer the knowledge and experience you have in a particular field. If you've completed any coursework relevant to the job you're applying for, include it in your resume to show off your skills. To do this, list your coursework in your education section, underneath your degree. Write your degree or course first, then your university or college, followed by your graduation date or anticipated completion date. Then, underneath that, add the subheading “Relevant coursework,” and list 1-3 examples of relevant coursework. For more tips, including how to work out which coursework is most relevant to the job you’re applying for, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Franco Babah
Apr 24, 2017

Did this article help you?
Irene Flores
Sep 6, 2017
Chetan Megha
Dec 31, 2016

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
How To List Relevant Coursework on Your Resume
Most students and recent graduates do not have a wealth of professional experience to list on a resume, so including relevant coursework can help potential employers get an idea of the skills and qualifications that you are currently developing. This article will cover what relevant coursework is as well as how and when to include it on your resume.
What is Relevant Coursework?
Relevant coursework refers to the classes and subjects that you studied in school which are useful for the position that you are applying for. For example, if you are applying to a marketing position and you have taken classes in psychology that focus on language, emotion, and motivation, that class would be considered relevant since the goal of marketing is to use language and emotion to motivate people to purchase goods and services.
Relevant coursework doesn’t only have to be strictly classes. You can also include academic projects like a thesis or dissertation as well as research that you have done. Online courses are also acceptable to list if they pertain to the job.
The courses and projects that you include must actually be relevant to the position that you are applying for. Don’t list your entire transcript - instead, choose the top 3-5 courses, projects, or subjects that are the most relevant.
If it’s not immediately clear why you are listing a course on your resume, consider including a brief description of the subject materials, projects you completed for the class, and/or how the class will help you perform in the position that you are applying for.
When To Include Relevant Coursework on Your Resume
Consider including relevant coursework on your resume if you are currently a student, you’ve recently graduated, you are applying to an internship , or you are applying to entry-level positions. Additionally, if you are applying to academic or other education-focused positions, it may be appropriate to include relevant courses and details about your studies.
Especially if you have taken AP, IB, or honors classes, listing relevant courses on your resume can show potential employers that you are intelligent, dedicated, and studious.
Finally, if the employer asks for details like a certain degree or diploma, your GPA, or a portfolio of past projects that you have completed, that can be a cue that they will be pleased to see your relevant coursework on your resume as well.
When Not To Include Relevant Coursework
If you have more than a year of professional work experience , you likely don’t need to include relevant coursework on your resume. If you have more than five years of work experience, you almost definitely do not need to include high school or college coursework. Employers will be focused more on your recent work experience than classes that you took many years ago.
Additionally, if you are applying for entry-level positions where school coursework isn’t particularly relevant at all (such as waitstaff jobs, outdoor recreation positions, etc.) then you may be better off focusing on hard and soft skills and certifications over schoolwork.
Selecting relevant coursework to advance your career
If you’re at the beginning (or even in the middle) of your college journey, it’s important to consider your future career as you select your course load. This will ensure you can list relevant coursework on a resume when it’s time for you to begin job hunting.
One way to do this is to research job titles you would like to have in the future and align the courses you select with the common skills listed in the job descriptions. If your school publishes a catalog, you may want to consult the course descriptions to figure out the skills you’ll gain from each course.
For example, someone who wants to go into marketing may take relevant courses in market research, consumer behavior, or emotional psychology. A person looking to be a graphic designer may need to take classes in typography, color theory, or UX design .
In some cases, your intended career will dictate the coursework you must take. For example, if you intend to be a certified public accountant, you may be required to take classes in auditing, tax concepts, business administration, and forensics. These classes are necessary to obtain certification and work as a CPA.
However, even in these cases, your schedule may still leave room for elective courses. If so, choose classes that will help you build relevant skills for your profession. For an accountant, those skills might be communication, critical thinking, and research strategies. Your related coursework, alongside your academic achievements, will help you stand out as a thoughtful, well-prepared candidate.
Make sure you use the resources available to you, such as academic and career counselors. These professionals have extensive experience helping people choose relevant classes that align with their career goals, and they can likely design an academic track to help you get where you want to be.
How To List Your Relevant Coursework
When crafting your job application, you don’t need a special relevant coursework resume section. Instead, you can incorporate this information into standard resume sections. If you’ve decided that it makes sense for you to include your relevant coursework on your resume, here’s how to do so:
Add Courses to Your Education Section
Naturally, it makes the most sense to add relevant coursework to the education section of your resume. You can add a subsection under each degree that you earned or school that you attended, or you can place your coursework at the bottom underneath all of your school details.
If you have little or no professional experience , place your education section first on your resume, just below your header and your resume objective . You may also wish to use a functional or skill-based resume format to highlight your skills. If you do have some relevant professional experience to list, place that at the top and your education section underneath.
Use either a comma-separated list, a simple bulleted list, or a bulleted list with some additional details for each course.
For example, here’s how to list coursework in a comma-separated list:
BA in Journalism
UC Davis, Davis, CA
Relevant Coursework: Ethical Journalism, Global Journalism, Technical Writing
You can also use a bulleted list, which can be helpful if you want to demonstrate proficiency in multiple fields:
Relevant Coursework: Journalism
- Ethical Journalism
- Global Journalism
- Editor of the weekly student newspaper
- Completed Research Internship with LA Times
Relevant Coursework: English
- Technical Writing
- Creative Writing
- Expository Writing
Finally, you may wish to include a short description of each course that reinforces its relevance to the job. When listing relevant coursework, you can include details about projects you completed in those classes. Here’s an example:
Relevant Coursework:
- Ethical Journalism - Learned principles and practices to ensure the accurate, complete, and fair exchange of information. Completed a hands-on project that included evaluating sources for real news stories to determine the accuracy of the reporting
- Global Journalism - Learned how to present news items with a global outlook and report on issues that affect the entire world
- Completed Research Internship with LA Times - Learned the basics of journalistic research and the processes involved in operating the largest metropolitan daily newspaper in the country
A comma-separated list will take up the least amount of precious space on your resume, but if your relevant coursework is the highlight of your resume and/or you have blank space to fill, you may wish to provide more detail about each course.
Tailor Your Relevant Coursework to Each Position
For every job you apply to, ensure that your resume lists only relevant coursework and projects that showcase job-related skills. Tailoring your entire resume to each position can help your application pass automated applicant tracking system ( ATS ) scans and get your resume into the hands of a human hiring manager. This can be achieved by using keywords and phrases from the job description as well as pertinent industry keywords throughout your resume to demonstrate that you have the qualifications , skills, and experience necessary for the job.
You can even tailor your education section and your relevant coursework to the job posting. Especially if you opt to use a detailed, bulleted list of relevant coursework, you can use the description of each course as an opportunity to include more keywords.
Start with the most relevant courses
Again, all the coursework that you include on your resume should be directly relevant to the position you are applying for. For example, if you’re applying for a job in the arts, you don’t need to give details about the math classes you took because they don’t represent relevant coursework. Resumes should always be customized for the position you want, and including unnecessary information prevents you from achieving that goal.
When listing courses, always start with the most relevant coursework first within your list. Most hiring managers will only spend a few seconds scanning your resume, so it’s crucial to put your most impressive and important details first.
Consider Adding Other Education Details
If you decide to include relevant coursework, you may wish to add other educational details and achievements as well to round out your academic background. For example, you might include your GPA (if it’s above a 3.5) and awards like honor roll, scholarships, dean’s list, being valedictorian/salutatorian, Latin honors (magna cum laude, etc.), and so forth. You can also include membership in school, national, or international honor societies, business or professional fraternities, and other groups or organizations.
Key Takeaways
Adding relevant coursework is a great way to beef up your resume if you do not have professional work experience to list, such as if you are currently a student, you’ve recently graduated, or you are applying to entry-level jobs. It can also be appropriate to include your coursework if you are applying for an academic-based position. If you do include your relevant coursework, ensure that it is, in fact, relevant - only include courses if they directly boost your ability to perform the job you are applying for.
Need help creating a resume to highlight your relevant coursework? Check out Jobseeker’s resume builder tool, which allows you to add your details and easily swap between resume templates , styles, colors, and more with just a few clicks. Then, download your polished, professional resume instantly and get started applying for jobs!
Get ahead of the competition
Make your job applications stand-out from other candidates.

The Ultimate Guide to Declaration in Resume

Best Font for Resume: Sizes, Styles, and Spacing

Highlighting Your Technical Skills for Resumes
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Resume and Cover Letter
- How to Put an Unfinished...
How to Put an Unfinished Degree on a Resume (with Examples)
7 min read · Updated on December 07, 2023

You went to college, but didn't finish – that's okay because you can still put it on your resume!
They say that a journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step. Sometimes you start down the road to a destination but don't complete the trip. That doesn't mean your progress is for nothing.
When it comes to college, even an unfinished degree may be something you'll want to let people know about. It doesn't matter whether circumstances prevented you from finishing, if you made a conscious decision to quit, or if you're going to finish it but just haven't yet. The steps you took in your academic career could be the thing that unlocks future employment doors.
But how do you put an unfinished degree on your resume? As it turns out, it's not difficult or something to be avoided. In this article, you'll find out when to include an unfinished degree on your resume plus some examples of how to write it.
Some college is often better than no college
All employers care about is whether you'll be able to do the job they have open. They'll want to see how your skills and knowledge align with the job description. This is of the utmost importance when writing your resume.
Consider the following:
Were any of the courses you took relevant to the job you're applying to?
Did you participate in, or complete, any major academic projects that would demonstrate the practical application of skills and knowledge?
Did you participate in any relevant clubs or extracurriculars that would pique a hiring manager's interest?
What type of independent study or research have you taken part in that would demonstrate initiative?
Do you have any certifications that improve your knowledge?
What skills did you acquire while you were at college? How are those relevant to the job you want?
Did you take on any leadership roles in college? Think about things like fraternities, sororities, and student government.
How does your professional network look? What did you do to build it up?
All of this is meant to shift your thinking so that you can focus on valuable experiences rather than your unfinished degree.
How to put an unfinished degree on your resume
Even though your focus should now be shifted from, “I didn't finish my degree, now what?” to “What skills and knowledge do I have that employers want?” you still have to include the fact that your degree is incomplete if you want to talk about it on your resume.
Adding a degree in progress on your resume
Sometimes, you'll run into an opportunity to apply for your dream job, but you haven't quite finished your degree yet. Pursuing your education shouldn't stop you from applying for the position you want. However, you want to be honest about the fact that your degree isn't complete yet.
At this point in your career, the Education section of your resume will look a bit like a Work History section, because you'll put more details about your degree and where you're getting it. At this point, because of your need to emphasize how your skills, knowledge, and coursework align with what's required in the job, you'll need to include those things on your resume. You also need to let a prospective employer know approximately when your degree will be complete.
Here's an example of how to include a degree that's still in progress on your resume:
Bachelor of Arts in Psychology | XYZ University | Expected completion: 12/2024
Relevant coursework: Introduction to Psychology, Psychology Research, Statistics, Psychology in the Workplace, Organizational Behavior, Coping Mechanisms, and Behavior Change.
GPA: 3.8/4.0
Internship: ABC School District, Teacher Support Program
PRO TIP: Only include your GPA if it's 3.5 or higher. We wrote a comprehensive article about when and if you should include your GPA on your resume. Click here to read it.
The inclusion of relevant coursework and an internship provides a great opportunity for you to inject relevant keywords into your resume. Those keywords will help your resume to be found by the applicant tracking systems that an astonishing number of employers use to weed out unqualified applicants.
Adding a degree you're not going to finish on your resume
Almost everyone has gone through a period of indecision regarding their degree plan. Some even change their major in college multiple times before landing on a path that suits them. Perhaps you've decided that college is no longer in your future or won't serve you very well in the career you've chosen to pursue.
It could still benefit you to add it to your resume. You could even include some details such as relevant coursework, if you need to get some keywords into your resume . As long as you keep the focus of your Education section on skills, achievements, and experiences gained during your time at school, an unfinished degree shouldn't make or break your candidacy for a job.
PRO TIP: Position yourself as someone with practical knowledge and a strong skill set to win that coveted interview offer.
Here's an example of how to add an unfinished degree that you're no longer pursuing to your resume:
Bachelor of Business Administration | XYZ University
Completed 80/120 credit hours, including finance, management, and marketing
Served as President of the Finance Club
Executed market analysis project that connected business with target market
In this example, you've shifted the focus away from the fact that the degree isn't finished. Instead, the reader – a hiring manager or recruiter – gains insight into your experiences, adding value to your application and demonstrating how you'll benefit the new team.
Don't forget the cover letter
The beauty of having a cover letter that complements your resume in situations when something needs to be explained can't be overstated. While your resume affords you some opportunity to dive into how your history aligns with the job opening, your cover letter lets you expand on the narrative to make it clearer.
Providing extra context in your cover letter to emphasize your skills can help you to stand out as a top candidate among the hundreds of other people applying for the same position.
Address the unfinished degree on your cover letter
You'll start a paragraph of your cover letter by quickly bringing up your unfinished degree. Talk about how a shift in your career focus has led you to change your mind on college. Emphasize that your desire for practical experience won out, as you felt that would be the best way to add value to future employers.
“I began my formal education working toward a Bachelor of Business Administration, but decided that it would serve future employers better if I had practical skills in marketing.”
Highlight skills you've acquired
Just like you did in your resume, talk about how your skills make you a great match for the job that the new company has available. Use verbiage from the job description to tailor your cover letter to the needs of the position.
“The coursework I finished, especially the courses in marketing and finance, has equipped me with a solid foundation in analysis and strategy planning that brings companies and consumers together to improve sales and profits.”
Mention achievements - employers love achievements!
Any time you can talk about something you've achieved, you show prospective employers value. By witnessing your past accomplishments, they get a real sense of what you can do for them.
“When I was the President of the Finance Club, I consistently found ways to automate manual processes to save time. One such process improvement reduced a 5-day turnaround to 2 days.”
Leverage your practical knowledge
Having an unfinished degree isn't the end of the world, as long as you can turn your educational experiences into a narrative that shows you're a determined individual with the right practical knowledge. In this sense, you're not someone with an incomplete degree, you're an engaging professional ready to make solid contributions to prospective employer teams.
Don't let an unfinished degree hold you back. Why not let us help you to craft a compelling resume that shifts the focus to your skills and achievements in a way that will land your resume at the top of the pile? Submit your resume now for a free resume review!
Recommended reading:
How to Create a Resume With No Education
What To Include in the Education Section of a Resume
Ask Amanda: What's the Best Way to List Education on a Resume?
Related Articles:
Do Hiring Managers Actually Read Cover Letters?
Why You Lose When You Lie on Your Resume: Learning From Mina Chang
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.
How to Write a Coursework

Coursework projects do not resemble essays, research papers, or dissertations. They are the combination of all three. Students spend less time writing coursework than on making a term paper, but this type of work requires more time and efforts than an ordinary essay - it is made of several essays. Thanks to our guide, each student can discover how to write coursework. If you are running out of time or lack experience to complete the specific coursework, we recommend using our coursework writing services to hire professional academic writers.
What is Coursework and Why Does It Matter?
Coursework definition: General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) coursework is a typical academic assignment, given in the course of study to evaluate the student’s knowledge, skills, and identify the final grade. Many students face this type of writing in the US colleges. One of the examples is a coursework UTD (The University of Texas at Dallas) - the requirements of this institution are strict, and many students fail to submit their papers and pass the corresponding courses.
Such type of assignment helps to have the ‘detective’ hat on: a student observes, examines, and evaluates the chosen topic using credible, up-to-date, and relevant sources. Working under controlled conditions is important. Participating in every school class will help to prepare good coursework by the end of the term. Take a look at the examples of what students of various profiles may face:
- English Composition - English coursework is an extended essay in most cases. A student has a right to pick the topic. The tutors provide their students with the list of recommended titles to choose from, sources to observe & analyze, and a format (e.g., a comparison between different relevant articles)
- Sciences - coursework for science is a complicated assignment. Such type of work appears in the form of a scientific paper to test what a writer investigates and reports independently.
- Geography - geography coursework is about collecting, reporting, and explaining information to reply to a certain geographical question or offer solutions to the problem. One idea is to explore the usage of a shopping mall or analyze the recent tornado. No matter whether you have to prepare a coursework Columbia or such paper for other educational institutions, keep in mind these differences!
Types of Coursework Explained
English Language coursework is the most common type of this assignment. At advanced GCE level, the student will be expected to write a couple of essays, totaling 3,000 words. Every assignment is 20 marks maximum.

An analytical essay : Evaluate, compare, & contrast 3 different sources of data interconnected by a common theme; written /spoken / multimedia content. Discuss different uses for targeting various audiences. Learn more on our blog.
Original essay with a supportive commentary : A student will have to come up with a single piece of media writing in the observed modes (written, spoken, or multimodal). Add a supporting piece with details about the aspects of English language. English Language & Literature coursework is a bit different. The basic requirements are the same, and the parts are:
An analytical study : Sharing an analysis of the chosen piece and its relation to the related content. It will show how well the writer understands the original piece. Tutors grade such works based on the:
- Use of the proper terminology and the coherence of the written words;
- Understanding & evaluation of the way a structure, form, and language create the written & spoken word;
- Opportunity to observe relationships between various pieces of writing.
Creative writing & commentary : Produce a creative piece that imitates the style of the assessed text. Share comments to backup your understanding. The goal is to show the knowledge, prove the competence, and use appropriate language skills in communicating with the target audience. You will also need a relevant coursework resume (review) in both cases. Keep on reading to learn how to write coursework of A level.
How to Write a Coursework: Guide for Students
Several factors may lead to the coursework being disqualified. It is a serious matter! The risk factors include:
- Plagiarism - it is the worst thing that could happen to any type of academic assignment. Lots of relevant information is available on the world wide web today, and the tutors are strict about the issue of plagiarism. Write everything in your own words! If you decide to insert the quotes from the sources, apply the suggested citation format and develop a list of references. Sign the declaration claiming it is your original project. If you're unsure about how to approach this, seeking professional help by choosing to write my coursework can be a wise decision.
- Word count - do not ignore the specific requirements concerning the length of the coursework. Specify if the footnotes, appendices, & references are included in the word count.
- Topics - go through the list of available themes. If there is an examination planned on the specific topic, try to pick another idea for the coursework.
- Tutor’s assistance - do not ignore the help of your instructor, ask them to provide guidance on what to write. Ask the questions to learn more details, but keep in mind they can go through the 1st draft once and just offer some general recommendations.
Choosing a Topic for Your Project
Dedicate enough time to this extra important question. Select the field of your interest if it is possible to relate it to the course. That is the golden rule of choosing a coursework topic - keep in mind the rest of the hints:
- Analyze the offered list of topics or develop yours
- Pick a topic from the area of your expertise related to the studied subject
- Select the topic you are interested in
- Choose the topic you’ve started to observe in the past
- Check how much relevant, up-to-date information is available on the Internet about each of the topics
- Pick what you can measure, change, & control (they call it a ‘fair test’)
- Use the ideas of previous researchers and students
- Do not choose a topic with a vast scope - you risk struggling to research it correctly
10 Good Coursework Topics
- Non-traditional Forms of Poetry with TC Tolbert
- Documentary Foundations: Usage of Oral Histories with Beth Alvarado
- Traditional Forms of Poetry
- Hermit Crabs: Type of Fiction
- Writing the Autobiographical Poem
- Creative Non-Fiction on the Examples of New Journalists
- Authors without Borders
- Writing the Sticky Stuff
- Socially Engaged Literary Arts
- Common Vocabulary
Research & Data Collection
Research is an integral part of coursework. Have you written research papers before? If yes, you will find it easier to select proper primary & secondary sources and gather the necessary information (evidence to support the main point - thesis). Depending on the required paper format, cite & reference the following sources:
- Books & e-Books
Base the project on a specific hypothesis. The research must start with minimum one hypothesis. The research stage for some topics may consist of visiting websites to collect information. Leave another time for collecting the data as it is the heart of the research. Three methods of data collection are known:
- Direct personal investigation : The one an author does individually (using literature and findings from previous studies);
- Interview/Questionnaire : The researcher should gather the data from the respondents asking questions regarding required data;
- Discussion with community leaders : Community leaders are approached to fetch information for the necessary data.
In case a student works on a scientific experiment, they should pay attention to planning the analysis with the help of rigorous scientific methods (keeping in mind the Health & Safety precautions you take). Review background information and theories. Take notes to express what you expect to occur to compare & contrast it to what happened in real life. In the write-up stage, one has to evaluate and present the findings.

Writing a Coursework Outline
The writing process follows the research. Do not start it without preparing an action plan and scheduling the work - a paper pin for English coursework is based on an extended essay . An outline will look different for the science coursework projects. The goal of creating a plan is to prevent a writer from being disorganized and waffling.

Let us explain coursework outline on the specific example - a project on the global pursuit of lower costs and the role of human rights.
Start with the brief introduction explaining why it might be a topic of interest for many people. Mention those vast corporations like Wal-Mart abuse human rights by choosing and using child labor in the factories.
Provide an overview of the problem . Define human rights and costs. Pick the definitions from the official dictionaries and cite them properly when inserting in the text. Try to explain the terms in your own words.
Develop a body of the coursework , start with the case for & against ethical business practices. Using evidence and examples, list the arguments supporting ethical business practices and another side of the coin. Include a business case for ethical practices after the opening body paragraph.
Move to discussing ethical responsibilities ; explain why business organizations should care about the ethical aspects of their activities. After three sections of the body, one can conclude the paper. It can be a good idea to share a fact or statistics stressing the importance of research problem in the essay conclusion. End up with the reference list that may look this way:
- Klein N (2000) No Logo (Flamingo, London)
- Marcousé I, Gillespie A, Martin B, Surridge M and Wall N (2003) Business Studies 2e (Hodder Arnold, Oxon)
- Royal Dutch Shell (2006) 4th Quarter Financial Report at (site example)

Additional Elements
Supporting materials and pictures are a must! The sciences & geography projects require tables, charts, graphs, and other types of images to illustrate the complicated topic. Not only should you add the pictures - it is essential to interpret and reference each of them. A separate part of the coursework where the student list and explains every visual element is Appendix , and it is an optional part. The presence of appendix increases the chances to earn an A+.
How to Write an Introduction for Coursework?
Most of the students underestimate the role of introduction & conclusion when it comes to writing an essay. An eye-catchy introduction is a key to success. The primary purposes of a coursework introduction are:
- To grab the reader’s attention
- To introduce the topic
- To explain the research importance
- To come up with a compelling thesis statement
The opening paragraph shows the depth of the writer’s acquaintance with the topic. Look at the expert tips below. They will help to learn how to write a coursework introduction to make the tutor want to read your entire paper.
What Is an Introduction?
The introduction of GCSE coursework is the opening paragraph that aims to interpret the central questions and purposes of the entire paper. It should have several elements to be effective. Those are:
- A hook sentence
- Background information
- Problem significance
- Solid thesis statement
Advice from our Experienced Writer
How to write an introduction to coursework? The quality of this part predetermines paper’s success. Look at some common mistakes writers do while working on the coursework introduction - try to prevent them!
Ignoring the prompt. Many students tend to neglect the tutor’s instructions. It is critical to read the prompt several times, highlight the main points, research question, rules, and grading rubric details.
Missing a plan. The prompt does not always say to develop a coursework outline. Without a plan for every separate section, it is impossible to write a flawless piece step-by-step. No matter whether you have to write a term paper, research paper, dissertation, or C3 coursework, get ready with the detailed plan. Once you understand how to write an introduction, it will be easier to develop the rest of the paper.
For those who need a helping hand in ensuring their work meets all the standards and deadlines, don't hesitate to buy coursework from trusted professionals.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
Coursework: Requirements for an A+ Paper
- Icon Calendar 5 July 2024
- Icon Page 4102 words
- Icon Clock 19 min read
Academic writing is an essential activity in higher education and comes in various forms. Basically, one of these forms is coursework writing, where instructors assess students’ levels of understanding of a course during a semester. Unlike other papers, coursework assignments evaluate students’ understanding of a particular course and not just a topic in a class. Besides, various forms of coursework writing include essays, term papers, theses, dissertations, report projects, and others. Hence, people need to learn what is a coursework assignment and how to write such a paper effectively.
General Aspects
College and university students undertake different kinds of academic exercises, with writing projects taking a significant portion of their grades. Basically, one of these exercises is the writing of a coursework paper, an assignment they submit at the end of their semester. This kind of work also assesses students’ understanding of a particular field of study within a single semester. In turn, instructors rarely require someone to write a paper for things they learned during a previous semester. Therefore, coursework entails completing various writing assignments, such as essays, research projects, experiments, and presentations that assess a student’s understanding and application of a subject material.
What Is a Coursework and Its Purpose
According to its definition, coursework is an academic project assignment that students are required to undertake as part of their educational curriculum and which they must submit before a final closure of an entire semester. The primary purpose of writing a coursework assignment is to evaluate learners’ levels of knowledge and skills acquisition, meaning such a project contributes to their final grades (Godfrey, 2022). Ideally, coursework is what students learn during a semester, and such an assignment is meant to measure how well they have understood a subject matter. Moreover, individuals use reliable and relevant sources to study, examine, and evaluate a chosen coursework topic (Haines, 2021). As such, this task is very similar to other academic assignments, such as essays, research papers, reports, thesis writing, dissertations, and other types of papers . In terms of pages and words, the length of a coursework assignment depends on academic levels, subjects, institution’s requirements, and its nature and scope, while general guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 6-10 pages
- Words: 1,500-2,500 words
- Length: 10-16 pages
- Words: 2,500-4,000 words
University (Undergraduate)
- Length: 16-24 pages
- Words: 4,000-6,000 words
Master’s
- Length: 24-32 pages
- Words: 6,000-8,000 words
- Length: 32-52 pages or more (depending on the complexity and depth of the research)
- Words: 8,000-13,000 words or more

| Section | Content |
|---|---|
| Title Page | Includes a specific title of a coursework project, student’s name, instructor’s name, course name, and date. |
| Table of Contents | Outlines all the sections and subsections with page numbers. |
| Abstract/Executive Summary | Presents a brief summary of an entire paper, including main objectives, methods, results, and conclusions. Typically, its length is about 150-250 words. |
| Introduction | Introduces an assigned topic, provides background information, states a research question or thesis, and outlines a primary purpose and objectives of an entire coursework. |
| Literature Review | Reviews relevant literature, highlighting key theories, concepts, and studies related to a picked topic. |
| Methodology | Describes research methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data and includes details about a study design, participants, instruments, and procedures. |
| Results | Presents key findings of a particular research or analysis and includes tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate these results. |
| Discussion | Interprets obtained results, discussing their implications, significance, and relevance to a research question or thesis, addresses any limitations, and suggests areas for future research. |
| Conclusion | Summarizes central findings and arguments, reiterates a study’s significance, and provides a final thought or call to action. |
| List of References | Provides all the sources cited in a whole coursework and formatted according to a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian). |
| Appendices | Includes any additional material, such as raw data, detailed calculations, or supplementary information, that supports a main text but is too lengthy to include in its main sections. |
Note: Some sections of a coursework paper can be added, deleted, or combined with each other, and it depends on specific college instructions. However, a typical structure of coursework covers a title page, table of contents, abstract/executive summary, introduction with a thesis or research question, literature review, methods, results, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices.
Differences With Other Papers
In any course of their classes, students write different types of papers, including essays, research papers, and reports. Basically, the major difference between coursework writing and these papers is that it assesses people’ understanding of what they have discovered throughout a semester (Couch, 2021). In contrast, essays and other papers assess learners’ understanding of a specific topic, concept, result, or theory. Moreover, students may need to address an issue in their project they might have covered in an essay assignment sometime during a previous semester. As such, a coursework assignment is broader in scope than other papers.
Expectations
Like essays and other papers, a coursework assignment varies from one area of study to another. For example, there is a coursework for the English subject and another for the sciences (Godfrey, 2022). Therefore, individuals are expected to complete their coursework assignments according to their instructor’s or department’s instructions. In most cases, this expectation includes presenting an assignment in an essay format, where they select a title of their choice. Depending on a specific subject, some assignments expect students to collect, examine, infer, and report data when answering a specific question (Haines, 2021). Finally, in college, coursework refers to writing assignments, projects, and tasks students must complete as part of their academic curriculum to demonstrate their understanding and application of a subject material.
When it comes to a grading aspect of academic assignments, instructors look at how well a student has attended to all the requirements and expectations. For instance, these requirements include writing about a choice of themes or text excerpts in a given format (Haines, 2021). In essence, people must use a good approach they believe is likely to give them a higher grade, meaning a technique that helps them to answer a specific question methodically, logically, and critically by using relevant information. In essence, these are three dimensions for grading a coursework assignment (Couch, 2021). As such, to write a coursework paper effectively, one should conduct thorough research, follow a clear and organized structure, adhere to given guidelines, and proofread a final document to ensure accuracy and coherence.
Steps on How to Write a Coursework Paper
Like an essay, a coursework assignment takes a particular structure. Basically, students should understand core components and make sure they address them in their academic writing (Bjorn et al., 2022). In this case, the most significant issue for writers is to ensure a logical flow of ideas. Moreover, developing a thesis statement is essential to provide high-quality essays with a guideline on focal issues. Primarily, these issues are class concepts and theories a person has learned in a specific course during a semester (Godfrey, 2022). As a result, to write coursework, students thoroughly research their topics, create detailed outlines, adhere to specified formats, draft their content clearly and concisely, and proofread their papers for any mistakes.
Step 1: Preparation
Planning or preparation is the first step in writing a coursework paper. For instance, an essence of any form of academic writing is to measure a person’s level of understanding about a particular area of study (Haines, 2021). To start coursework, students begin by carefully reviewing assignment guidelines, conducting preliminary research to understand their assigned topics, and outlining main points and structure of their papers. Since such an project measures what a student has learned in a given course, it is paramount for each person to prepare well when executing an assignment. Here, learners have to choose a topic that they are comfortable with, one that they are passionate about. Additionally, they should generate ideas about their coursework by deciding what is relevant and what is not. In principle, a typical reasoning that guides this decision is a particular expectation outlined in assignment instructions (Godfrey, 2022). Lastly, people should understand their audience – consumers of their work or readers. Like any other assignment, a target audience is course instructors. Hence, writers should ensure their class projects satisfy a curiosity of readers. In turn, some examples of sentence starters for beginning a coursework paper include:
- In recent years, the topic of [subject] has gained a significant attention due to its direct impact on [related field/issue], while this coursework aims to explore … .
- The origins of [subject] can be traced back to [year/era], when [important event/person] first introduced a particular concept of … .
- Understanding [subject] is crucial for [reason/field], as it offers more insights into [related concept or application], and this paper seeks to examine … .
- Currently, [subject] is experiencing a period of rapid development, with new research and advancements being made in areas, such as … .
- By exploring a research question: [research question], this paper aims to examine [purpose of the study] … .
- While much has been written about [subject], there remains a significant knowledge gap in a current literature regarding [specific aspect], which this paper will investigate … .
- During my studies/experience in [related field], I observed [specific phenomenon], which prompted me to investigate [subject] more thoroughly … .
- According to recent statistics, [relevant statistic] highlights the importance of [subject], which this coursework will explore … .
- As [author/expert] once said, ‘[relevant quote],’ this statement underscores a real significance of [subject], which will be a particular focus of this paper in … .
- This coursework is based on a particular hypothesis that [hypothesis statement], and this comprehensive analysis and research will seek to prove/disprove … .
Step 2: Setting Up
After preparation, people should set up the stage for coursework writing. Basically, a first preoccupation is to find sources relevant to an assignment prompt – those that are more likely to provide enough evidence and support needed claims. As scholars review credible sources, they should take notes to provide a strong argumentation in their projects (Walter & Stouck, 2020). Then, another activity involves deciding on a coursework outline, which should help to answer an assignment prompt logically and critically. Lastly, learners should create an annotated bibliography, a summary of each source they intend to use as a valid basis for their arguments in an entire document.
Step 3: Writing a First Draft
After preparing and setting up the stage, students should start writing a first version of their coursework assignment. In this case, armed with notes taken during a review of reliable sources and an outline they have created, people should start with a first draft, where they develop a thesis statement. Basing all opinions and arguments on a thesis, writers should answer an assignment prompt methodically, logically, and critically. For example, a coursework statement is a concise declaration of a main objective or thesis that an entire project aims to explore and demonstrate (Godfrey, 2022). Moreover, a thesis statement should ‘hook’ a target audience and make them interested in reading a substantial part of a paper – a body. In essence, a body section is where students use all the evidence they have gathered about an assigned topic, while a thesis informs a target audience of what individuals have focused on in their papers. As a result, any coursework paper adopts a typical outline, as indicated below:
- Table of Contents
- Abstract or Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Body Paragraph(s)
- Reference List
- Appendices (Optional)
Step 4: Wrapping It Up
It is normal for a writer to make mistakes when writing an academic document. For example, these mistakes include inconsistent arguments, irrelevant content, punctuation errors, and countless grammatical mistakes (Haines, 2021). Therefore, after completing a first draft, writers should read it through, at least twice, to identify these mistakes and correct them. Basically, common processes of correction include revising and editing a written paper. Regarding revisions, students should give their work to a friend or mentor to read it through. In their feedback, these individuals are likely to point out areas where authors should make corrections for their papers to be logical and interesting to read. Concerning editing a complete document, people should proofread their work to ensure it is free of spelling mistakes, punctuation errors, and other grammatical mishaps.
Step 5: Developing Body Paragraphs
A body paragraph of any academic text, including a coursework assignment, utilizes several features to make a whole paper logical. Basically, the first feature is writing a topic sentence that opens up each paragraph (Couch, 2021). In principle, a primary purpose of this feature is to strengthen a central idea captured in a thesis statement. Then, the rest of a single paragraph structure backs up this claim using evidence gathered from different sources. In turn, another feature is a concluding sentence, which closes each paragraph (Godfrey, 2022). As such, a main goal of this aspect is to connect a topic sentence with a thesis statement. Finally, another feature is transition words and phrases that help readers to sense a logical flow of ideas throughout a whole paper. In short, writers use transitions within and between paragraphs to create a logical flow of information and ideas.
Step 6: Referencing Format and Peer Reviewing
Besides ensuring an entire paper is written methodically and logically, authors should see it meets the highest academic writing standards. In this regard, they should ensure it follows a particular format – APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian. In most cases, an assignment prompt dictates a specific format learners should use. Moreover, a particular referencing manual informs about a typical structure of a whole paper and its format of citations. In turn, another essential activity that students should perform is to commit a complete document to peer review. Here, authors give coursework papers to distinguished scholars, such as a professor or classmate, to assess an overall validity and quality of information used, including sources.
Step 7: Writing a Final Draft
After subjecting a first draft to vigorous scrutiny through revisions, editions, and peer review, people should start writing a final draft of a coursework paper. Basically, this draft should be thoroughly polished, meaning it should be free of spelling, punctuation, and grammatical mistakes, as well as inconsistent arguments and irrelevant sentences (Lawrence, 2020). Moreover, it should indicate an effective use of transitions in paper’s body paragraphs. In short, a final draft is an improved version of a first draft because writers have revised and edited it and incorporated feedback from a friend, mentor, or professor. However, they still need to read through a final draft, at least once, to ensure it is perfect before submission to a grading department. In turn, if someone notes several mistakes, it means another revision is necessary. Hence, a student’s focus should be a correct content, organization of ideas, style of writing, and format.
Types of Coursework
Given that coursework assignments test students’ levels of understanding about a course’s content in a given semester, it means such a project takes several writing forms. For example, these documents include a term paper, a Master’s thesis, a dissertation, or a report project (Godfrey, 2022). Ideally, such a composition is an essential requirement for a student to complete an entire course successfully. It also means such a project is essential to be awarded a degree. Moreover, the only difference between these types of coursework assignments is that they take a different approach to examining and analyzing a course’s content, with each subject taking a unique approach. In turn, common types of coursework projects include:
| Type | Content |
|---|---|
| Essay | A written document that talks about a specific topic or argument and requires analysis and critical thinking. |
| Research Paper | An in-depth study on a specific topic that involves gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data and evidence from various credible sources. |
| Laboratory Report | A detailed account of an experiment, including methodology, results, and analysis of findings. |
| Case Study | An examination of a particular instance or event, analyzing it in detail to draw conclusions or lessons. |
| Project | A comprehensive task that often includes research, design, and implementation, resulting in a final product or presentation. |
| Presentation | An oral or visual display of research or knowledge on a particular topic, using PowerPoint slides or other visual aids. |
| Portfolio | A collection of work samples that demonstrate skills, competencies, and achievements over a period of time. |
| Dissertation/Thesis | An extensive and original piece of research conducted independently, and such a paper is required for completing a degree program. |
| Annotated Bibliography | A list of found sources with brief descriptions and evaluations of each, and such an assignment is used as a preparatory step for a research project. |
| Creative Work | A project that involves creating original content, such as a piece of art, literature, or a multimedia presentation. |
Writing Techniques
The dream of every student is to pass any assessment and attain a higher grade. In a coursework assignment, learners can utilize different techniques to ensure they attain higher grades after assessments (Haines, 2021). As indicated earlier about a grading aspect of coursework, writers should use an approach they believe answers an assignment prompt methodically, logically, and critically. As a result, every technique they use must allow them to answer a specific question in a way that satisfies these three grading dimensions.
Compare and Contrast
A compare and contrast essay technique is about analyzing two subjects, ideas, concepts, or theories by comparing them, contrasting them, or doing both. Basically, a primary purpose of answering a coursework assignment through this writing approach is that students must not state obvious things (Couch, 2021). Instead, they need to shed light on subtle differences or unexpected similarities between subjects, ideas, concepts, or theories.
Cause and Effect
A cause and effect essay technique allows writers to develop their paper’s body by analyzing possible reasons for and consequences of a decision, action, or event. When organizing a paragraph, students adopt a structure that allows them to arrange defined causes and effects in a chronological or reverse chronological order (Godfrey, 2022). Alternatively, authors can present their arguments through emphasis, starting from least important to most important aspects, or vice versa.
Investigation
An investigation technique involves undertaking an in-depth examination of a topic, idea, concept, or theory. Basically, this technique’s primary goal is to demonstrate that students have gained a thorough knowledge of a specific subject, which is indicated in their methodical, logical, and critical analysis and presentation of information. In esense, ensuring research findings are interpreted and presented in an organized manner throughout a research paper is critical (Walter & Stouck, 2020). Ultimately, such a technique enables writers to demonstrate their articulate understanding of various viewpoints about a particular issue under investigation.
How to Present Strong Arguments
For an academic paper to capture an audience’s attention and interest, students must not only develop a thesis statement but also ensure they use strong arguments to back up a central idea in a main statement. Basically, the “they say, I say” technique is the simplest method to present arguments properly (Couch, 2021). In this regard, the information that a person uses in answering a coursework assignment prompt should be free of plagiarism and cite all sources properly. Then, another way to ensure an entire writing is persuasive is to confirm that authors have attained a required word count limit without counting footnotes, endnotes, references, and appendices (Haines, 2021). Ideally, selecting a topic that one is comfortable with and passionate about enables an overall writing to be high-quality in terms of argumentation. Besides, students should discuss alternatives with their mentor or instructor. Finally, a thesis statement should not be complicated.
Scope of Research
Students make different kinds of mistakes when writing academic texts. For example, a common mistake in coursework writing involves a scope, where students fail to focus on one area of a particular topic and instead try to be broad in their argumentation (Godfrey, 2022). In principle, they may waste space talking about irrelevant material, leaving them with little space to write about a core idea. As such, an effective solution to this problem is to develop a thesis statement that sets out a paper’s specific agenda. In doing so, authors can realize every time they go off-topic.
Colloquialism
By considering colloquialisms, students may use a language that is not standard for academic writing. Essentially, this problem is particularly common with learners who become excited about a specific topic and try to express their ideas creatively (Haines, 2021). Moreover, a whole project shifts from being evidence-based to a document about an author’s opinion. In turn, a particular solution to such a problem is to pick a topic that is exciting and critically discussed in an existing literature. As a result, students can identify several sources that discuss their assigned topics to use as bases for evidence of their claims and arguments about their central themes.
Common Mistakes
- Lack of Clarity in Thesis Statement: Failing to clearly define a main argument or purpose of an entire paper can lead to a lack of focus throughout a coursework project.
- Insufficient Research: Relying on too few sources or not consulting credible and up-to-date references can weaken an overall quality and depth of an analysis.
- Poor Organization: Not following a logical writing structure can make a paper difficult to follow due to an inadequate flow of ideas.
- Overuse of Quotations: Excessively quoting sources rather than paraphrasing or synthesizing information can make a whole paper seem unoriginal and reduce an author’s voice.
- Ignoring Formatting Guidelines: Not adhering to a required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian) or formatting instructions can result in a loss of marks.
- Lack of Proofreading: Submitting a paper with grammatical errors, typos, and spelling mistakes can undermine an overall professionalism and readability of a project.
- Inadequate Analysis: Simply describing sources without critically analyzing or interpreting the information can lead to writing a biased paper.
- Failure to Address a Prompt: Straying from an assigned topic or not fully addressing a coursework prompt can result in an irrelevant or incomplete paper.
- Plagiarism: Copying text without proper citing attribution, even unintentionally, can lead to serious academic consequences.
- Weak Conclusion: Ending a coursework paper without a clear closure or failing to adequately summarize key findings and implications can leave any reader unsatisfied.
Coursework vs. Research Paper
Ideally, an outline of a coursework assignment is similar to that of a research paper. In this case, an abstract serves as a brief overview of a research paper and informs readers of writer’s focal points. More importantly, such an outline has a body, where writers use different paragraphs to make an argument about a specific topic. In turn, each of the paragraphs begins with a topic sentence and ends with a concluding sentence. Like research papers, body paragraphs of a coursework assignment serve to cement writer’s claims and arguments, which are linked to a thesis statement.
Students should master following tips when it comes to writing a coursework assignment:
- Choose an exciting topic and stick to it. Basically, students come across tons of exciting information about their topic. However, to avoid going off-script, they should focus on their core subject and avoid a particular temptation of using data that may prove irrelevant.
- Use evidence (quotes and statistics) selectively. In principle, relevancy is a significant indicator of a high-grade paper. As such, where authors are not going to refer to some data directly because it adds no value to their argument, they should avoid dwelling on it in their paper.
- Cite sources correctly. When citing sources, writers should note format standards in use – APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian – as each has a unique approach.
- Revise, edit, and proofread a complete paper. High-quality coursework writing should be free of inconsistent arguments, irrelevant sentences, and spelling, punctuation, and grammatical mistakes.
A coursework project is among writing assignments that students in colleges and universities undertake in preparation for their degree. Unlike other papers, this assignment assesses learners’ understanding of what they have learned in a course in a given semester. As such, students must complete and submit it before a semester comes to closure. Finally, different types of coursework include essays, term papers, theses, dissertations, and report projects.
Bjorn, G. A., Quaynor, L., & Burgasser, A. J. (2022). Reading research for writing: Co-constructing core skills using primary literature. Impacting Education: Journal on Transforming Professional Practice , 7 (1), 47–58. https://doi.org/10.5195/ie.2022.237
Couch, D. (2021). Your guide to college writing . Chemeketa Press.
Godfrey, J. (2022). Writing for university . Bloomsbury Academic.
Haines, C. (2021). Assessing students’ written work marking essays and reports . Routledge.
Lawrence, T. S. (2020). Writing a research paper. International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics , 106 (4), 674–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.12.005
Walter, L., & Stouck, J. (2020). Writing the literature review: Graduate student experiences. The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning , 11 (1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.5206/cjsotl-rcacea.2020.1.8295
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Court Case in MLA 9: A Simple Guide With Examples
- Icon Calendar 7 August 2020
- Icon Page 1829 words

How to Cite a Dissertation or Thesis in Chicago/Turabian With Examples
- Icon Calendar 5 August 2020
- Icon Page 2196 words
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Entering Class Profile
- Education & CV
- GMAT & GRE
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Letters of Recommendation
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Fields of Study
- Student Life
Typically, students take four courses per quarter until the course requirements are completed. Students typically complete all coursework in 2-3 years.
You’ll be required to complete a minimum of courses both in your chosen field and in various other disciplines. Depending on your chosen field, you may take as much as 50% of your coursework outside Stanford GSB. For example, it’s not unusual for students to enroll in a significant number of courses in the Departments of Economics, Engineering, and Sociology .
Because Stanford GSB is close to the center of the university and follows the university calendar , taking courses in other departments is convenient. Your advisor can help you choose such courses.
If you find you’re lacking any prerequisites, you may need to undertake additional preparation before or during your first year to ensure you’re on track to complete all requirements in a timely fashion. If you’ve completed commensurate coursework elsewhere (e.g., at a comparable doctoral program), you may request a waiver for certain coursework.
Stanford University
Specific requirements by field of study.
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Get Involved
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Reading Materials
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
There are currently road test cancellations or DMV offices closed for in-person services. See our “ Cancellations, Closings and Delays ” page for more information.
Complete Pre-Licensing Requirements
Practice driving.
You must have supervised driving practice and follow the restrictions for learner permit holders .
If you have a Class DJ or MJ learner permit, you must have a minimum of 50 hours of supervised practice driving that includes at least 15 hours of driving after sunset before you take a road test. You must bring to the road test a completed Certification of Supervised Driving (MV-262) (PDF) signed by your parent or guardian.
If you are under the age of 18, you must wait at least six months from the date you received your learner permit to schedule your road test.
Driving Schools
Once you have a learner permit, you must have supervised driving practice. One way to achieve the recommended amount of supervised driving practice is to take driving lessons at a licensed driving school.
Find a Driving School Near You
Next Section
Take a Pre-Licensing Course
The Pre-Licensing Course , also known as the 5-Hour Course, is a DMV-approved, standardized course that provides the knowledge you will need as a new driver. The course covers many important topics, including:
- driving within the highway transportation system
- driver habits and skills
- feelings, attitudes, and risk-taking
- alcohol, other drugs, and driving
All new drivers must the Pre-Licensing Course before taking a DMV road test and applying for a license unless they complete a 48-hour Driver Education Program through their local high school or college.
Find a Pre-Licensing Course
Related Information
Related documents, mv-262: certificate of supervised driving (pdf).
Every driver license applicant who is 16 or 17 years old at the time of the road test, and who has a junior learner permit, must present this certification to the DMV license examiner at the time of the road test. The certification must be signed by a parent or guardian.
Become an Organ Donor
Enroll in the Donate Life Registry to become an organ donor
Translation Services
This page is available in other languages
- Siloy is watching
- INQUIRER.net
- RADYO INQUIRER
LTO-7: Drivers can now complete theoretical driving course online
CEBU CITY, Philippines – Drivers in Central Visayas can soon expect a more flexible approach to obtaining their theoretical driving course certifications.
The Land Transportation Office here (LTO-7) will roll out an Online Theoretical Driving Course (OTDC) by the end of 2024, which aims to offer a modern, tech-driven alternative to traditional in-person classes.
In a recent press release, the LTO announced that the new OTDC would allow applicants to complete their driver education at their convenience, accommodating busy schedules and providing the flexibility to study from home or any preferred location.
“The public will now have the option to enroll in LTO-accredited driving schools offering Online TDC, which will accommodate busy schedules,” said LTO 7 Regional Director Glen Galario.
How to get a new driver’s license
How to renew your driver’s license with 10 or more but less than 40 demerits
According to Galario, this development aligns with President Ferdinand “Bongbong” Marcos Jr.’s push to digitalize government services and aims to streamline the licensing process in the region.
He explained that the online course is designed to cater to both professionals and students, facilitating easier integration of driver education into their daily routines.
LTO-7 is currently reviewing applications from driving schools seeking accreditation to offer the OTDC and will provide updates on accredited providers and enrollment procedures on the LTO website.
The OTDC will consist of a 15-hour module required for obtaining a Student Permit.
As of June 2024, LTO-7 has issued 8,185 Theoretical Driving Course certificates through its Malasakit on Wheels – EPatrol Mobile Service program, representing 88 percent of the total certificates issued in 2023.
Subscribe to our daily newsletter
By providing an email address. I agree to the Terms of Use and acknowledge that I have read the Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The comments uploaded on this site do not necessarily represent or reflect the views of management and owner of Cebudailynews. We reserve the right to exclude comments that we deem to be inconsistent with our editorial standards.
Latest News
Dela rosa intends to seek sc clarification if icc issues arrest warrant, p64 food budget per day not enough according to psa, dynamic herb cebu fc lands in group h of afc champions league two, p64-a-day threshold is insulting and saddening, says sen. hontiveros, cabc’s ‘1st mortabond cup’ promises action-packed, level-playing field hoop wars , featured stories, young math whiz in cebu uses amazing talent to find dad, dbm: mid-year bonus included in gov’t workers’ pay hike, p5m for cebu city residents wanting to start a small business, japan ‘megaquake’ warning lifted, people told to ‘go back to normal’, baby and mother die after giving birth on cebu city sidewalk.
Subscribe to our regional newsletter
- Environment
© 2024 Cebu Daily News - All Rights Reserved
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. By continuing, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. To find out more, please click this link.

COMMENTS
When your coursework is not really relevant to the position you seek. Including irrelevant coursework could actually distract from your important skills and experiences. Situations in which coursework was completed so long ago that the information is no longer useful. For instance, many technology-related courses can lose their value over time.
1. Use a single-column format. The single-column format looks similar to the education section on your resume, simply displaying your relevant coursework in list form. For example, a candidate applying for a journalism job might include the following: Relevant Editorial Coursework. Ethical Journalism.
Example of relevant coursework in an education section. Most people include coursework in the education section of their resumes. If you want to expand your education section, write "Relevant Coursework" under your degree name, and then use commas to separate the names of the courses. For example:
UCLA, Los Angeles, CA. Relevant Coursework: Language and Cognitive Development, Psychology of Emotion, Psychological Statistics, Cognitive Linguistics. If you add the relevant courses to a resume in this way, you'll have plenty of room for including other academic achievements on your resume. 2.
As you can see, this comma-separated list focuses on classes you've taken that office managers love to see on an admin assistant resume. It's short, to the point, and gives them only relevant information. 2. Relevant Coursework Resume Example—High School Graduate Seeking Customer Service Job.
Relevant coursework: British Literature, American Literature, Medieval Literature, William Shakespeare, Language and Cognitive Development. #2. List Your Relevant Coursework in Bullet Points. To make your relevant coursework more visible and reader-friendly, list them in bullet points underneath your diploma title.
If you want to include any online courses you have taken on your resume, you can use the following steps to incorporate this training: 1. Focus on relevant coursework. When deciding whether to include online courses on your resume, you must first determine their relevance. You may need to edit your list depending on the jobs you are applying to ...
The relevant coursework section is an optional entry-level resume section that includes coursework you've completed related to the job you're applying for. It can include projects, academic achievements, extracurriculars and volunteer experience. If you're a student or have just graduated, relevant coursework is a good way to demonstrate your ...
The number of relevant courses you've taken. The detail you want to include. The space you have. Most people include relevant coursework in the education section of their resumes. To do this, just write "Relevant Coursework" beneath the degree name, and then use commas to separate the titles of the courses.
List Only Relevant Coursework that Matches the Job Description . Ideally, you should only list coursework relevant to the position you are applying for on your resume. For instance, if you're seeking an accounting position, it wouldn't make much sense to include an elective you completed in continental philosophy.
Listing completed coursework in job descriptions. If you're in the midst of completing your education, it can be helpful to list relevant coursework in your job descriptions. This not only highlights your education in progress, but it also demonstrates your knowledge and skills gained through your courses. For instance, if you're applying ...
Remember: just because you're not done with a course or degree doesn't mean it's irrelevant! Always list any in-progress coursework and note the planned completion date of the course or degree. 3. List 5-10 potentially job-relevant courses for each of your degrees. At this point, define "relevant" very broadly!
Here's an example of how to list unfinished college on your resume if it's highly relevant to the job: UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN - Ann Arbor, Michigan. 2018-2020, GPA: 3.8/4.0. Completed 75 credits towards a B.A. in Environmental Studies with a specialization in Urban Planning.
Completed Research Internship with LA Times; Relevant Coursework: English. Technical Writing; Creative Writing; Expository Writing; Finally, you may wish to include a short description of each course that reinforces its relevance to the job. When listing relevant coursework, you can include details about projects you completed in those classes.
Under your education heading, list each of the institutions you attended, along with the dates and the degrees earned. Underneath these subheadings, you can list your individual courses in a bulleted list. Alternatively, you can add a relevant coursework subheading and list your classes, separated by commas. 3.
On your resume, you can make a section called 'Relevant Coursework' and list any specific classes that are useful for the job you're applying to. For instance, if you are applying for a finance internship, list any business or finance courses you completed. In this section, you could also include any meaningful research experiences you had.
At this point, because of your need to emphasize how your skills, knowledge, and coursework align with what's required in the job, you'll need to include those things on your resume. You also need to let a prospective employer know approximately when your degree will be complete. ... Completed 80/120 credit hours, including finance, management ...
Many students face this type of writing in the US colleges. One of the examples is a coursework UTD (The University of Texas at Dallas) - the requirements of this institution are strict, and many students fail to submit their papers and pass the corresponding courses. Such type of assignment helps to have the 'detective' hat on: a student ...
Coursework is practical work or studies completed by a student in partial fulfilment of training or degree. Coursework includes projects, fieldwork, design studies, extensive college essays, and other activities. The type of work required varies on the course. It is mostly a part of the learning process and a step towards preparing students to ...
Coursework was removed from UK GCSE courses and replaced by "Controlled Assessment", much of which must be completed under exam conditions, without teacher assistance and with access to resources tightly controlled in order to reduce the possibility of cheating. [2] However, this too has been largely removed and replaced by mainly exam-based assessment as part of a general GCSE reform.
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Completed 64 credit hours toward a BS in computer science, 2018 - 2020. You should include related coursework and any other academic information, such as honors and certificates. Some colleges offer micro-credentials and other certificate programs that can boost the education section of your resume.
Like essays and other papers, a coursework assignment varies from one area of study to another. For example, there is a coursework for the English subject and another for the sciences (Godfrey, 2022). Therefore, individuals are expected to complete their coursework assignments according to their instructor's or department's instructions.
Coursework. Typically, students take four courses per quarter until the course requirements are completed. Students typically complete all coursework in 2-3 years. You'll be required to complete a minimum of courses both in your chosen field and in various other disciplines. Depending on your chosen field, you may take as much as 50% of your ...
The Pre-Licensing Course, also known as the 5-Hour Course, is a DMV-approved, standardized course that provides the knowledge you will need as a new driver. The course covers many important topics, including: driving within the highway transportation system; driver habits and skills; feelings, attitudes, and risk-taking; alcohol, other drugs ...
Complete a Motorcycle Safety Course approved by the Motorcycle Safety Foundation. Gather the following items and mail to the address on the application: A completed out-of-state driver license application (an application must be completed for a new Class M driver license) Motorcycle Safety Course (MSB-8 or MSB-8R) completion certificate.
The Land Transportation Office here (LTO-7) will roll out an Online Theoretical Driving Course (OTDC) by the end of 2024, which aims to offer a modern, tech-driven alternative to traditional in ...
The Wyndham Championship was completed at 8:06 a.m. Matt Kuchar makes par at No. 18 and finishes T12. — PGA TOUR Communications (@PGATOURComms) August 12, 2024 But Kuchar's decision may have ...
Understand the concept of CAT 2025 Complete 1 Year Blueprint with CAT & Other MBA Entrance Tests course curated by Karishma Vanvani on Unacademy. The Verbal Ability and RC course is delivered in Hinglish. ... Complete Course on Para Completion for CAT 2024. Shabana . Starts on 2nd Sep. Hinglish. Other Management Exams. Course on Critical ...
Open champions Gary Player and John Daly have also issued pleas to the R&A, while the course, itself, has declared that 2027, the next blank spot on the Open schedule, would be perfect.
Xherdan Shaqiri has rejoined Basel on a three-year contract following his departure from Chicago Fire. 32-year-old Shaqiri and the Chicago Fire confirmed they had mutually agreed to terminate the ...