Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Matter in our Surroundings
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 1 matter in our surroundings, cbse case study questions class 9 science – matter in our surroundings, case study 1:, case study 2:, case study 3:.
i.) A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called

Case Study 4:
Case study 5:.
iv.) The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, ncert solutions class 6 english poorvi chapter 5 ila sachani: embroidering dreams with her feet, ncert solutions class 6 english poorvi chapter 5 the kites, ncert solutions class 6 english poorvi chapter 5 hamara bharat — incredible india, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 23 solutions রঙিন কার্ডের খেলা.
CBSE Expert

Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science PDF Download
Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions .

Case study questions are based on real or hypothetical scenarios that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply scientific concepts to solve problems or make informed decisions. They often present a detailed context, providing students with the opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter beyond basic recall.
Table of Contents
Class 9 Science: Case Study Questions
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on cbseexperts, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
Class 9 Science Syllabus
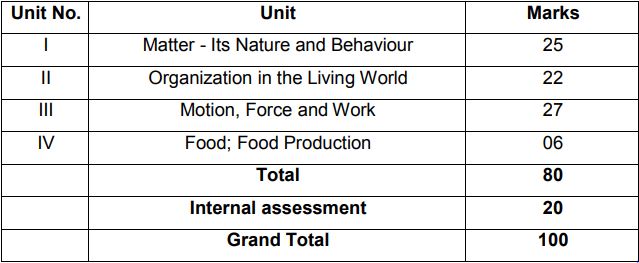
Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid, and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of statementing (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter: Elements, compounds, and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids, and suspensions. Physical and chemical changes (excluding separating the components of a mixture).
Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of Chemical Combination, Chemical formula of common compounds, Atomic and molecular masses.
Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, Valency, Atomic Number and Mass Number, Isotopes and Isobars.
Unit II: Organization in the Living World
Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Unit III: Motio n, Force, and Work
Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration.
Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy.
Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy (excluding commercial unit of Energy).
Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Unit IV: Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Books for Class 9 Science Exams

Benefits of Case Study Questions
- Enhancing Analytical Skills : Case study questions challenge students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. By engaging with these questions, students develop critical analytical skills that are essential for scientific thinking and problem-solving.
- Promoting Critical Thinking : Case study questions encourage students to think critically and evaluate different perspectives. They require students to reason, make logical deductions, and justify their answers with supporting evidence. This process helps in honing their critical thinking abilities, enabling them to approach problems from multiple angles.
- Encouraging Practical Application of Concepts : By presenting real-world or hypothetical situations, case study questions promote the application of scientific concepts in practical scenarios. This application-based approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter and helps students see the relevance of what they learn in the classroom to everyday life.
Case study questions of Class 9 Science provide students with an opportunity to apply their knowledge, enhance analytical skills, and think critically. By understanding the format, benefits, and effective strategies for answering case study questions, students can excel in this form of assessment. While challenges may arise, practicing time management, improving information extraction skills, and enhancing observation abilities will enable students to overcome these obstacles and perform well. Embracing case study questions as a valuable learning tool can contribute to a holistic understanding of scientific concepts and foster problem-solving abilities.
1. What is the purpose of case study questions in Class 9 Science?
Case study questions serve the purpose of evaluating a student’s understanding of scientific concepts, their ability to apply knowledge in real-life situations, and their analytical and critical thinking skills.
2. How can case study questions help improve analytical skills?
Case study questions require students to analyze complex scenarios, identify relevant information, and derive meaningful insights. Regular practice with such questions can significantly enhance analytical skills.
3. Are case study questions difficult to answer?
Case study questions can be challenging due to their comprehensive nature and the need for critical thinking. However, with practice and effective strategies, students can develop the skills necessary to answer them effectively.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions play a crucial role in the field of science education as they provide real-life scenarios for students to analyze, apply their knowledge, and develop problem-solving skills. This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science , covering various topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th SCIENCE Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions provide students with real-life scenarios that require critical thinking and application of scientific concepts. They help students understand the practical application of scientific principles and develop problem-solving skills in various scientific disciplines.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Tissues
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Sound
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
The above Case studies for Class 9 Science will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Benefits of Case Studies in Science Education
Case studies offer several advantages over traditional teaching methods. Here are some key benefits:
- Real-World Application : Case studies present authentic scenarios, enabling students to understand how scientific concepts are applied in real-life situations.
- Critical Thinking : Analyzing case studies requires students to think critically, make connections, and apply scientific knowledge to solve problems.
- Interdisciplinary Approach : Case studies often involve multiple scientific disciplines, fostering an interdisciplinary understanding of complex issues.
- Engagement and Active Learning : Case studies actively engage students in the learning process, promoting active participation, discussion, and collaboration.
- Skill Development : Case studies develop essential skills such as analytical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication of scientific concepts.
Importance of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions is crucial for Class 9 Science students to enhance their understanding and application of scientific concepts. Here’s why it is important:
- Application of Knowledge : Case studies allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to practical situations, bridging the gap between theory and real-world scenarios.
- Developing Analytical Skills : Analyzing case studies improves students’ ability to identify relevant information, make connections, and draw logical conclusions.
- Problem-Solving Skills : Case studies present complex problems that require students to think critically and develop effective problem-solving strategies.
- Enhanced Exam Performance : Practicing case study questions familiarizes students with the format and types of questions they may encounter in exams, leading to improved performance.
Subjects Covered in the Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
The case study questions for Class 9 Science cover the following subjects:
- Motion and Forces
- Light and Reflection
- Electricity
- Matter and Its Properties
- Atoms and Molecules
- Structure of the Atom
- Chemical Reactions
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Diversity in Living Organisms
- Natural Resources
Tips for Approaching Case Study Questions
To tackle case study questions effectively, consider the following tips:
- Read Carefully : Pay close attention to the details provided in the case study, as they hold crucial information for solving the problem.
- Analyze Methodically : Break down the problem into smaller components and analyze each part systematically.
- Apply Relevant Concepts : Identify the scientific principles relevant to the case study and apply them appropriately.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives : Explore different angles and viewpoints while proposing solutions, taking into account various scientific factors.
- Provide Justifications : Support your answers with scientific explanations and logical reasoning to strengthen your responses.
The Class 9 Science Case Study Questions provided in this article serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their scientific knowledge and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can develop a deeper understanding of scientific concepts and their practical applications. Embrace this opportunity to engage with real-world scenarios and strengthen your scientific acumen.
Q1: Are the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions aligned with the official curriculum?
Yes, the Class 9 Science Case Study Questions presented in this article are aligned with the official curriculum. They cover relevant topics and concepts that students need to study for their exams.
Q2: Can practicing case study questions alone guarantee success in Class 9 Science exams?
Practicing case study questions is an important part of exam preparation, but it should be complemented with a thorough understanding of the subject matter. It is advisable to study the concepts in detail, refer to textbooks, and engage in other learning activities to achieve success in exams.
Q3: Where I Can get Class 9 Science Case Study Questions ?
You can practice Class 9 Science Case Study Questions on schools.studyrate.in for free.
You Might Also Like
Class 9 science case study questions chapter 14 natural resources.

1569+ Class 9 Science MCQ Questions with Answers PDF Download
Class 9 science case study questions chapter 3 atoms and molecules, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- CBSE Class 9 Study Material
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Case Study Questions with Answers for Term 2 Exam 2022 (PDF)
Check important case study questions of cbse class 9 science to prepare for the cbse term 2 exam 2022. all these questions have been put together by subject experts..

CBSE Class 9 Term 2 Exam 2022: Important case based questions for CBSE Class 9 Science are provided here students to prepare for the upcoming Term 2 Exam 2022. All the questions provided below are curated by the subject experts. These questions are really helpful to revise important concepts and prepare the case study questions for the exam. Answers to all questions have been provided for reference. So, students should practice the chapter-wise questions to clearly understand the right way to attempt the case based questions. Download the chapter-wise questions in PDF.
Check some of the important case study questions below:
Q. Read the following and answer the questions :
A student was asked by his teacher to verify the law of conservation of mass in the laboratory. He prepared 5% aqueous solutions of NaCl and Na 2 SO 4 . He mixed 10 mL of both these solutions in a conical flask. He weighed the flask on a balance. He then stirred the flask with a rod and weighed it after sometime. There was no change in mass.
- Was the student able to verify the law of conservation of mass?
- If not, what was the mistake committed by him?
- In your opinion, what he should have done?
- What is the molar mass of Na 2 SO 4 ?
- No, he could not verify the law of conservation of mass in-spite of the fact that there was no change in mass.
- No chemical reaction takes place between NaCl and Na 2 SO 4 . This means that no reaction actually took place in the flask.
- He should have performed the experiment by using aqueous solutions of BaCl 2 and Na 2 SO 4 . A chemical reaction takes place in this case and a white precipitate of BaSO 4 is formed.
- Will the weight of the precipitate be the same as that of the reactants before mixing?
- If not, what she should have done?
- Which law of chemical combination does this support?
- State the law of conservation of mass.
- No, it will not be the same.
- She should have weighed the total contents of the beaker after the reaction and not the precipitate alone.
- It supports the law of conservation of mass.
- Mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- SSC MTS Exam Date 2024
- UGC NET Admit Card 2024
- Independence Day Questions and Answers 2024
- UGC NET City Intimation Slip 2024
- UP Police Constable Mock Test
- Independence Day Poems
- Independence Day Speech in Hindi
- Independence Day Drawing
- Independence Day Speech
- India Post GDS Cut Off
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 9
Latest Education News
Allahabad High Court Recruitment 2024 for Research Officer Posts, Apply Online
TS DSC Answer Key 2024 Out at tsdsc.aptonline.in: Download Teacher Response Sheet, Submit Objection
Har Ghar Tiranga Campaign 2024: Key Details, Objectives, Significance, Date
Brain Teaser: Think You Have a High IQ? Try Finding the 6 Hidden Words in 17 Seconds
IBPS Clerk Prelims Admit Card 2024 OUT at ibps.in: Download CRP Clerk IV Call Letter Here
Bastar University Result 2024 OUT at smkvbastar.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
SGBAU Result 2024 OUT at sgbau.ucanapply.com, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
भारत में किन लोगों को है गाड़ी पर तिरंगा लगाने की अनुमति, जानें
IBPS Clerk Admit Card 2024 Released: Check Direct Download Link at ibps.in
Find 3 differences between the cleaning lady pictures in 12 seconds!
UP Police Constable Exam City Slip, Admit Card 2024: यूपी पुलिस एग्जाम सिटी जल्द होने वाली है जारी, यहाँ से करें Download
SDM Full Form: Sub-Divisional Magistrate Functions, Role, Responsibility
Independence Day 2024 Quiz: Do you know these basic questions about India?
What Leads to the Formation of the Northern Aurora Lights? When will they be visible?
India's Journey to Becoming a Space Power Since Independence
UP Police Exam City Slip 2024 Soon at uppbpb.gov.in: Check UPPRPB Constable Admit Card Updates
Telangana NEET UG Counselling 2024 Registration Last Date Extended, Check Details Here
UPSC ESIC Nursing Officer Result 2024 Out at upsc.gov.in: Download Result PDF, What's Next
UPSC Chairman 2024: Preeti Sudan Takes Charge on Aug 1, Check Previous Chairman Names, Salary, Functions and Tenure
UPSC Mains Exam Date 2024 Out: Check Complete Timetable, Schedule
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings 2024-25
- Class 9 Important Question
- Chapter 1: Matter In Our Surroundings

CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter-1 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Chapter 1 of science in class 9 talks about matters of our surroundings. Many students consider science as a difficult and challenging subject as they face difficulty in understanding the concepts and theories of this subject. The best way to overcome this problem is to start practising Class 9 Science chapter 1 important questions. Solving these questions regularly will help the students to improve their skills on this subject. Thus, scoring good marks in the exams becomes easy for them. M atter in our surroundings class 9 important questions guides students in their preparation to make them efficient. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions | ||
Sl.No | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
1 | Chapter 1 | Matter in Our Surroundings |
2 | Chapter 2 |
|
3 | Chapter 3 |
|
4 | Chapter 4 |
|
5 | Chapter 5 |
|
6 | Chapter 6 |
|
7 | Chapter 7 |
|
8 | Chapter 8 |
|
9 | Chapter 9 |
|
10 | Chapter 10 |
|
11 | Chapter 11 |
|
12 | Chapter 12 |
|
13 | Chapter 13 |
|
14 | Chapter 14 |
|
15 | Chapter 15 |
|
Important Questions of Ch 1 Science Class 9 - Free PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions 1 Mark
1. Which of the following matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, the smell of perfume.
Ans: As we can define matter as any ‘physical substance’, hence almonds, air, chair, the smell of perfume, cold drink and smell can be considered as matter.
2. Convert the following temperature to a Celsius scale:
i) The temperature is 300 K.
Ans: When we use: K = 273 + ⁰C:
⁰C = K - 273
= 300 - 273
= 27⁰C
ii) The temperature is 573 K
⁰C = 573 - 273
= 300 ⁰C
3. What is the physical state of water at:
(a) A temperature of 250 ⁰C
Ans: The boiling point of water is 100 ⁰C, hence the physical state of water at 250⁰C will be gaseous.
(b) A temperature of 100 ⁰C
Ans: The boiling point of water is 100 ⁰C, hence at 100 ⁰C water is in the gaseous state.
4. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Ans: The reason behind the temperature of substance or matter remaining constant during a change of state is that during the change of state all of the heat or energy provided to particles of matter is utilized to take the particles of matter apart from each other.
5. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Ans: One method to liquefy atmospheric gases is to decrease the temperature and increase the pressure.
6. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles— water, sugar, and oxygen.
Ans: The order of increasing forces of attraction between the particles is as follows:
Oxygen< water< sugar.
7. What is the physical state of water at-
(a) A temperature of 25 ⁰C?
Ans: The physical state of water at 25 ⁰C is liquid.
(b) A temperature of ⁰C?
Ans: The physical state of water at ⁰C is solid.
(c) A temperature of 100⁰C?
Ans: The physical state of water at 100⁰C is gas.
8. If the humidity in the air increase then the rate of evaporation:
(a) decrease
(b) increase
(c) remain same
(d) both (b) and (a) depending upon the temperature
Ans: The correct option is (a) decrease.
9. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) boiling is a bulk phenomenon and evaporation is a surface phenomenon (b) boiling is a surface phenomenon and evaporation is a bulk phenomenon (c) boiling and evaporation both are a surface phenomenon
(d) boiling and surface both are bulk phenomenon
Ans: The correct option is (a) boiling is a bulk phenomenon and evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
10. If the temperature of a place is increase then evaporation:
(d) none of the above
Ans: The correct option is (b) increase.
11. Which of the following has the least inter atomic spacing?
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gases
(d) plasma
Ans: The correct option is (a), solid.
12. If you decrease the surface area and increase the temperature, then the rate of evaporation
(a) increase
(b) decrease
(d) may increase or decrease depending upon other factors
Ans: The correct option is (c), remain the same.
13. What will be the corresponding temperature in degree centigrade for 300 K:
(a) 30 ⁰C
(b) 300 ⁰C
(c) 27 ⁰C
(d) 673 ⁰C
Ans: The correct option is (c), 27 ⁰C.
14. Liquid to gas and gas to liquid changes are called:
(a) vaporization and condensation
(b) condensation and vaporization
(c) sublimation and condensation
(d) condensation and sublimation
Ans: The correct option will be (a), vaporization and condensation.
15. Physical state of water at is respectively
(a) liquid, solid, and gas
(b) solid, liquid, and gas
(c) solid, gas, and liquid
(d) gas, solid, and liquid
Ans: The correct option is (a), liquid, solid and gas.
Short Answer Questions 2 Marks
1. Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meters away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Ans: When it is a higher temperature the diffusion rate (movement) of particles will be very fast when compared to the diffusion rate of particles at a lower temperature and since the temperature of hot sizzling food is higher than cold food, the smell of hot sizzling food will be reaching us from several meters away.
2. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. (density = mass/volume).
Arrange the following in order of increasing density – air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron.
Ans: The correct order of increasing densities of the substances is as follows: Air < exhaust from chimneys< cotton< water< honey< chalk< iron.
3. Liquids generally have a lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Ans: Ice floats on the water since there is a large empty space inside the 3D structure of ice due to which it becomes less in weight as compared to water and can float on water.
4. Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Ans: In a desert cooler, when hot air enters through the straw mates it evaporates the water at a fast rate because the rate of evaporation is faster on a hot dry day. And because of the faster evaporation rate, it cools the air more conveniently than on a dry hot day.
5. How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Ans: Evaporation happens through the small pores on it causing a cooling effect, in an earthen pot. Therefore water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool during summer because of continuous evaporation.
6. Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Ans: As a perfume, petrol and perfume are volatile liquids, if put on our palm they will be absorbing heat from our palm and cause cooling.
7. Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Ans: When we use a saucer instead of a cup the surface for evaporation to occur will be increased resulting in faster evaporation of particles of tea or milk and allowing it to cool faster and taking a sip becomes easier.
8. What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Ans: We must wear the type of clothes which allow easy evaporation since evaporation causes cooling. And as the cotton absorbs sweat well and allows easy evaporation, we must prefer wearing cotton clothes in summer.
9. Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale.
a) The temperature is 293 K
Ans: When we use: ⁰C = K - 273
= 293 - 273
= 20 ⁰C
b) The temperature is 470 K
= 470 - 273
= 197 ⁰C
10. Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
a) The temperature is 25 ⁰C
Ans: When we use: K = ⁰C + 273
= 25 + 273
= 298 K
b)The temperature is 373 ⁰C
= 373 + 273
= 656 K
11. Give a reason for the following observations.
a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
Ans: Sublimation can be defined as the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage. Naphthalene balls will be having the property of sublimation because of which they directly vary from solid to gaseous state without a conversion into liquid. Hence, naphthalene balls will be vanishing with time leaving no solid.
b)We can get the smell of perfume sitting several meters away.
Ans: Volatile substances such as perfumes change from liquid state to gaseous state very fast which allows them to diffuse and mix up with the air particles to reach our nostrils. Therefore we get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
12. Give two reasons to justify -
a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
Ans: For a temperature of <0 ⁰Cwater is in solid-state, for 0⁰C → 100⁰C → water is in a liquid state and for temperature >100 ⁰C water is in a gaseous state. Since room temperature always lies between 0 ⁰C and 100 ⁰C and within this range the physical state of water is liquid so water is liquid at room temperature.
b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Ans: Since the room temperature is very less than the melting point of iron hence an almirah made up of iron will be a solid at room temperature.
13. Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Ans: Ice will be producing a more intense cooling effect as compared to water at 273 K because at 273 K ice will be absorbing latent heat of melting from the surroundings and will be getting converted into water. Therefore ice at 273 K is more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature.
14. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Ans: When the steam gets converted into boiling water it releases latent heat of water which results more severe burns when we compare it to boiling water.
15. What is evaporation? What are the factors affecting it?
Ans: Evaporation can be defined as the process of conversion of a substance from its liquid state to a gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point.
Evaporation will be dependant on the factor below:
a) Surface area
b) Temperature
c) Humidity
d) Wind speed
16. What happens when we apply pressure to the particles of matter?
Ans: Pressure can be defined as the force applied per cross-sectional area. Therefore when we apply pressure to the particles of matter, the force applied brings the particles closer to each other.
17. Define latent heat of vaporization and latent heat of fusion.
Ans: The heat energy required to change 1 kg of a substance from its liquid state to a gaseous state at atmospheric pressure without changing its temperature is known as latent heat of vaporization.
18. If the melting point of object A is high then what state do you expect it to be at room temperature?
Ans: The temperature at which a substance changes its state from solid to liquid is called its melting point. At a temperature below melting point, the substance will be in solid-state. Therefore, if the melting point of an object A is high then the object will be in solid-state.
19. What happens when the temperature of the solids increase?
Ans: When we increase the temperature of the solid, we are giving energy to it. That energy is utilized in increasing the kinetic energy of the particles and as a result, the speed of the particles is increased and they vibrate more freely. Once the particles overcome the force of attraction between them they start moving more freely.
20. When heat is being supplied to a solid, then what does the heat energy do to the particles of the solid?
Ans: The heat energy increases the kinetic energy of the particles which allows the particles to overcome the forces of attraction and start moving more freely and changing the state from solid to liquid.
21. Why is it that on increasing the wind speed the rate of evaporation increases?
Ans: If we increase the speed of the wind, then they will be blowing away with them. The water vapours in the air are blown away when the speed of wind is increased, making room for more water vapours and increasing the rate of evaporation.
22. Why do we say that evaporation is a surface phenomenon?
Ans: Only the particles at the surface of the liquid absorb energy and get converted into vapours, therefore evaporation is called a surface phenomenon.
Long Answer Questions 3 Marks
1. A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Ans: It is given that a diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. This is representing that the particles of water will be held together by weak forces of attraction between them and when any external force is applied the particles can be separated.
2. What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Ans: The particles of matter have the following characteristics:
i. The particles of matter are in continuous motion.
ii. There are gaps between the particles of matter.
iii. There is a force of attraction between the particles of matter which keeps them together.
3.
(a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter. Ans: Tabular differences in characteristics of matters are given below:
Solid | Liquid | Gas |
Particles of matter in solid state are rigid and incompressible. | Particles of matter in the liquid state are not rigid but are compressible to some extent. | Particles of matter in a gaseous state are not rigid at all and are more compressible than particles of solid or liquid. |
The particles will be having a definite shape and volume. | The particles have a definite volume but their shape is not defined. | The particles don’t have a definite shape or volume. |
The particles cannot flow. | The particles can easily flow from a higher level to lower level. | The particles can flow freely in all possible directions. |
Stone, wood, diamond, etc. are a few examples. | Water, cold drinks, milk, etc. are a few examples. | Smoke, oxygen, nitrogen etc. are some examples. |
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Rigidity → The property of matter to maintain its shape when external forces are applied to it is known as rigidity. Solids have this property.
Compressibility → The property of matter to allow compression when high pressure is applied to it is known as compressibility. Some Liquids and all gases have this property.
Fluidity → The property of matter to flow and change in its shape when external forces are applied to it is known as fluidity. Both liquids and gases have this property.
Filling a gas container → Gases are fluid in nature and are highly compressible which allows them to be filled within a vessel at high pressure. A large volume of gas can be filled in a container of less volume making it suitable and more cost-efficient for transportation.
Shape → Only solid objects have well-defined shapes while liquids can acquire any shape depending on the container they are kept in and gases don’t have any shape.
Kinetic energy → The particles of a matter are continuously in motion and thus have kinetic energy. As the particles in solids have the least movement, the kinetic energy of solids is the least. The particles of gases have the freest movements and hence they have the highest kinetic energy. The order of kinetic energies for different types of matters is: solid < liquid < gas
Density → Density of any substance can be explained as Mass per unit volume i.e. density = mass/volume.
4. Give reasons
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
Ans: The particles of gas have negligible attraction force between them because of which the particles move freely in all directions filling the whole container the gas is kept in.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Ans: The particles of gas move freely due to which they collide with the container walls continuously and randomly. Therefore the collision of particles on the container walls exerts pressure on the walls.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
Ans: Solids have rigid and fixed particles and have a definite shape and clear boundaries. Since a wooden table possesses all the qualities of a solid, it should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in the air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Ans: Since air is a gas and the forces of attraction between the particles of gas are very less which makes it easy to separate the particles with the help of an external force and hence we can easily move our hand in the air. Whereas in the case of solids the forces of attraction are very strong and we need a very high force to separate the particles of a solid and hence we need a karate expert for it.
5. Name A, B, C, D, E, and F in the following diagram showing changes in its state.
A is fusion or heating or melting.
B is vapourisation.
C is cooling or Condensation.
D is cooling or solidification.
E is sublimation.
F is solidification.
6. Are the three states of matter inter-convertible? How can they interconnect?
Ans: Yes, the three states of matter can be converted into each other.
The three states of matter are interconvertible as shown below:
a) By heating we can convert solids into liquids and by cooling we can convert liquids into solids.
b)We can convert liquids into gases by vaporization and we can convert gases to liquids by condensation.
c) Using sublimation we can convert solids into gases and vice versa and using condensation we can convert liquids into solids.
7. How does evaporation cause cooling?
Ans: During evaporation, the particles of a liquid absorb the heat from the surface and are converted into vapours utilizing the absorbed heat. This absorption of heat from the surface will be producing a cool surface.
8. Why should we wear cotton clothes in summer?
Ans: Since cotton is a good absorbent of water, it absorbs all the sweat from our body and allows easy and fast evaporation. The sweat absorbs heat from our body and evaporates which makes us feel cooler during a hot summer day. That is why we should wear cotton clothes in summer.
9. Differentiate between physical and chemical change?
Ans: The difference physical and chemical change is given below
Physical Change | Chemical Change |
i. Physical change is not permanent and can be reversed easily. ii. Physical change does not result in new substances. iii. There is no change in mass is a physical change. iv. The energy changes in a physical change are quite small. | i. Chemical change is permanent and cannot be reversed easily. ii. Chemical change produces new substances. iii. Change of mass is observed in a chemical change. iv. The changes in energy are large in a chemical change. |
10. A solution of H₂SO₄ is labeled 40%. The density of the solution is 1.3 gm/l. What is the concentration of the solution in %(m/v)?
Ans: The given concentration of the solution is 40%.
Therefore, 100 gm of the solution contains 40 g of H₂SO₄
Density = \[\frac{mass}{volume}\]
1.3gm/l = \[\frac{100 g}{volume}\]
Volume of the solution = \[\frac{100}{1.3}\]
= \[\frac{100}{1.3}\] ml
So, = \[\frac{100}{1.3}\] of the solution contains 40g of H₂SO₄
Therefore, 100 ml of solution will contain \[\frac{100 \times 40 \times 1.3}{100}\] g of H₂SO₄
= 52 g of H₂SO₄
Therefore, the concentration is 52% (m/v).
11. What is the state of inter particle distance inside a solid, liquid, and gas?
Ans: In a solid, the forces of attraction between the particles are very high and hence the particles of a solid will be very close to each other and the inter particle distance is the least.
In a liquid, the forces of attraction between the particles are very weak, and therefore the particles of a liquid will not be closely packed with each other and the inter-particle distance is large.
In a gas, the forces of attraction between the particles are almost negligible or extremely weak and therefore the particles of a gas are very loosely packed and are very far from each other and the inter particle distance is largest.
12. Why is it that to smell cold food, we have to go close but the smell of hot food reaches us several meters away?
Ans: When the particles are at higher temperature, their movements are fast and therefore they can travel up to several meters. Hence the hot food’s smell will be reaching us several meters away.
At lower temperatures, the movements of particles are not very fast and particles do not have enough kinetic energy to travel a distance of several meters. Therefore we have to go close to smell cold food.
13. Why is it that a wooden chair should be called a solid and not a liquid?
Ans: A wooden chair is a rigid object, the particles of a wooden chair are tightly packed with each other, the chair has a definite shape and the chair has negligible compressibility. Since a wooden chair possesses all the properties of a solid and not of a liquid, it should be called a solid, not a liquid.
14. Give an experiment to show that ammonium chloride undergoes sublimation.
Ans: Experiment for representing the sublimation of ammonium chloride (NHCl₄):
a) Take a crystal of ammonium chloride (NHCl₄) inside a china dish and an inverted funnel.
b) With the help of a burner, heat the ammonium chloride (NHCl₄) crystals.
c) When the ammonium chloride (NHCl₄) crystal is heated, vapours of (NHCl₄) and the Ammonium chloride (NHCl₄) which is solidified along the walls at the beaker’s upper end is observable.
d) This experiment shows that solid ammonium chloride (NHCl₄) undergoes solidification. It directly changes to vapour state from a solid state, it does not convert into liquid.

15. What is distillation and fractional distillation? What is the basic property that separates the two methods?
Ans: The process of distillation is used for separating the components of a mixture containing two liquids, having different boiling points and both liquids boil without decomposition.
The process of fractional distillation is used for separating the components of a mixture containing more than two liquids having a boiling point difference of less than 25 K.
The basic property that separates these two methods is:
Using distillation we can separate only those components which have a significant difference in their boiling points. While fraction distillation is used when the difference in boiling points is less.
Many students don’t have a strong core knowledge on the subject of science and face difficulty in understanding the basics of the chapters. Due to which they lose a lot of marks in the final exams. To avoid these, students need to formulate a better preparation plan where they should give more emphasis to the practice of class 9th science chapter 1 important questions. Regular practice will help them to improve and be more confident about their own knowledge.
The questions that are included in chapter 1 science class 9 important questions are most likely to come in the exams. Thus, preparing the students better and efficient. Students can download the pdf of class 9 chapter 1 science important questions from the Vedantu site. This pdf is available for free. After downloading the pdf, students can refer to it at every stage of their preparation.
Important Question of Science Class 9 Chapter 1
Students will learn a lot of things from the chapter 'matters in our surroundings, let's discuss some of those things:
The matter is considered as a substance from which our cosmos is made of. Any substance with some mass, that takes volume and which can get comprehended by the senses is termed as a matter. There are a lot of exceptions in this case such as heat, light energy, electrical energy, sound energy, magnetism, vacuum, and shadow. This all is not considered a matter because they don't have mass and they don't take any place.
The substance 'matter' is believed to be composed of small constituent parts. Matters have minimal and minute units. Taking a glance on them is very difficult even with a high-power microscope.
To understand more simply, everything around you is made up of matter. Atoms and compounds of everything are made with small parts of matter. These atoms are responsible for building the things that we see and touch every day.
Characteristics of Matter
The different characteristics of matter are listed below:
The matter is a substance which is made up of small particles.
It is believed that the particles consist of intermolecular spaces between them.
The particles in the matter have a locomotive nature due to the kinetic energy inside them. When there is a surge in the temperature, the motion of particles intensifies.
The bits in the matter attract each other, but this reciprocal force of full becomes operational only when the particles are very close to each other. In solids, the particles are firmly held, which is why it is believed that they have a superior force of attraction. Whereas in gases, particles are loosely held; thus, they have a minimal force of attraction.
Nature of Matter
Depending upon the physical state of different materials or substances, the nature of matter is classified into three categories:
Solids are substances where the particles are held very close to each other due to a strong intermolecular force. The particles are so tightly held at their place that they can have only vibratory motions and nothing else. As the particles are tightly held, therefore solids have a definite shape and definite volume. Some examples of solids are wood, iron, glass, etc. Students while practising important question of science class 9 chapter 1 will learn more about this substance and that too in a straightforward way.
Those substances where the intermolecular forces are weak enough to allow the movement of particles are generally known as liquids. These particles are also closely held with each other, but they have more freedom of movement than the particles of solid. Liquids are substances with a definite volume but with no definite shape. These substances generally take the shape of the container in which they are stored. Some examples of liquid substances are milk, water, etc. To gain more detailed knowledge on this particular substance, students have to continue practising ch 1 science class 9 important questions without fail.
These types of substances have very weak intermolecular forces between their particles or molecules, so the molecules have the freedom to move. The distance between each particle in a gas is bigger if compared to the distance between particles in solids and gases. Gases do not have a fixed shape or a definite volume. These substances fully occupy the containers in which they are stored. Some examples of gases are air, hydrogen, oxygen, methane, etc. By practising important questions for class 9 science chapter 1 regularly, students can gain more knowledge on this particular substance.
These above three states of matter can be transformed from one form to the other just by changing the environment's temperature and pressure conditions. The composition of matter is also used to determine its nature. If a matter is composed of more than one particle, then it is considered as a mixture, but when it contains only one particle, then it is termed as a pure substance. Mixtures are further classified into homogeneous and heterogeneous categories. Pure substances can also get divided into elements and compounds.
All the information that you have read till now are some basics of the chapter 'Matter in our surroundings. But there is more to this chapter, and things will get complicated after getting inside the different topics of the chapter. Students find the theories of this chapter complicated and thus are incapable of scoring good marks, but by practising class 9 science chapter 1 important questions regularly, students can avoid fewer marks.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Important Questions
Some of the important questions that the students might face in the exams are as follows:
Mention the technique which is used for separating the substances from the mixture.
What is the difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture?
What do you understand by the term Matter?
State the different characteristics of matter.
What is the nature of matter? Explain in a brief way.
State the points which show that a physical Change is different from a chemical change.
What are the reasons which cause a matter to change its state from one form to another?
What do you understand by the term element?
What do we call a mixture of salt and sugar in our regular lives?
State the three states of matter based on the distance between the molecules.
State the process using which the seawater can get purified.
What are the properties of a solid?
State the properties of a liquid.
Mention the properties of a gas.
Which state of matter is related to Boyle's law.
CBSE Class 9 Chapter 1 MCQs
1. Due to which among the following phenomena, the water kept in the earthen pot becomes cool during summers?
Transpiration
Evaporation
2. Which of the following conditions will increase the evaporation of water?
Increase in temperature of the water
Decrease in temperature of the water
Less exposed surface area of water
Adding common salt to the water
3. Which of the following is the boiling point of water at sea level?
Answers: 1 (d), 2 (a) and 3 (c)
Benefits of Class 9th Science Chapter 1 Important Questions
Students who are facing problems in chapter 1 of class 9 are suggested to practice important questions of ch 1 science class 9 so that they can take advantage of this and prepare well. Some of the benefits of this list of questions are:
The questions are taken keeping in mind the syllabus and the format imposed by the CBSE board for class 9 students because any deviations from that can cost students a lot of marks.
The questions are selected under the guidance of some expert teachers who have years of experience in this field. They select questions according to the intellectual capability of the students.
The questions included in the list of chapter 1 science class 9 important questions are most likely to come in the exams, thus making students' preparation better and efficient.
The questions are given with solutions which are explained in a detailed manner.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 9
CBSE Class 9 Study Materials |
Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 |
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
In conclusion, the availability of important questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings is a valuable resource for students preparing for their examinations. These important questions cover key topics and concepts related to the chapter, helping students deepen their understanding of the properties of matter, changes of state, and the behavior of particles. Practicing some important questions, students can enhance their knowledge and improve their problem-solving skills. These questions encourage critical thinking and application of scientific principles, preparing students to answer exam questions effectively.
Engaging with these important questions enables students to consolidate their understanding of the chapter, identify areas where they need further clarification, and strengthen their grasp of the subject. They also serve as a valuable revision tool, helping students review and reinforce the concepts they have learned.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings 2024-25
1. Where can I find extra questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1- Matter in Our Surroundings?
There are several e-learning sites that provide more practice questions. On Vedantu, you may find the most frequently asked questions for each scientific chapter. Vedantu is a leading learning portal that offers all of the required exam preparation materials such as example papers, NCERT Answers, crucial questions, revision notes, and so on. Important questions for Chapter 1- Matter in Our Surroundings and other chapters, as well as solutions, are available on Vedantu's website for Class 9 CBSE students. Subject matter experts with sufficient expertise and experience in the topic prepare the replies. The key CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1 questions have been prepared in a PDF file for students to practice before examinations.
2. What are the two recently discovered states of matter?
Apart from the three-commonly known states of matter, there exist other two states of matter which are much talked about: Plasma and Bose-Einstein Condensate.
Plasma: Plasma state is the 4th state of matter which is an ionized gas. Plasma neither has a definite volume nor a definite shape. It can be defined as a gaseous substance into which sufficient energy is provided to free electrons from atoms or molecules and to allow both species i.e. ions or electrons to co-exist. Examples of plasma are Stars, lightning, etc. Plasma is also present inside the fluorescent lights.
Bose-Einstein Condensate: Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC) is a state of matter of a dilute gas of bosons (a boson is a particle that follows Bose-Einstein Statistics) cooled to a temperature very close to absolute zero. In simple words, BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density.
3. Can matter exist in all three states?
Indeed, materials may exist in all three states at the same time. At differing temperature and pressure circumstances, the three states of matter interconvert. In other words, pressure and temperature determine the state of a substance, i.e. whether it is solid, liquid, or gas. As water boils, it turns into vapour, and when it freezes at its freezing point, it turns into ice. It is critical to realise that the difference between different states of matter is caused by the location of component particles. As a result, these particles' characteristics can alter as a result of temperature and pressure.
4. What is the difference between boiling and evaporation?
Boiling is a bulk phenomenon whereas evaporation is a surface phenomenon. Particles from the bulk of the liquid change into vapour state in the process of boiling. However, in the process of evaporation, particles from the surface change into the vapour state by gaining enough energy from the atmosphere that weakens the force of attraction present into the liquid to change it into vapour form.
5. What is the significance of using Vedantu’s Important Questions for studying Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings of Class 9 Science?
Every crucial question from the Chapter- Matter in our Surroundings has been hand-picked by Vedantu's expert pros. Vedantu's Crucial Questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings of Class 9 Science has around 50 critical questions from the course. In tests, these questions are worth one to five points. Working through these questions will give you with the necessary chapter revision. It will also assist you in understanding how to develop optimal replies for various exam questions.
6. What are some important questions from Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings of Class 9 Science for exams?
Matter in Our Surroundings contains many important experiments, definitions, and reasoning questions that can be asked in the exams. Some of the examples of these questions are as follows:
Enlist the characteristics of particles of matter.
Suggest a method to liquefy gases.
Why is it that on increasing the wind speed the rate of evaporation increases?
Define latent heat of vaporization and latent heat of fusion.
For over 50 such important questions from this chapter, visit Vedantu .
7. Are the important questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings of Class 9 Science accessible offline?
Yes, the important questions for Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings of Class 9 Science are easily accessible offline by downloading its PDF file in the following simple steps.
Visit Vedantu and choose the subject and the chapter you want.
On the subsequent page, scroll down and look for the option to "Download PDF."
This will redirect you to a new page containing the link to download the required PDF promptly.
For an even smoother download process, install the Vedantu mobile app and access all the content easily from your phone.
8. How can you show that one crystal of potassium permanganate contains millions of tiny particles?
Dissolve two or three crystals of potassium permanganate and dissolve them in 100 ml of water. Take 10 ml of this solution and put it in another container with 90 ml of water. Take 10 ml of this new solution and again dissolve it in 90 ml of water. Dilute the solution six to eight times. You will find that water still remains coloured after much dilution. This proves that one crystal of potassium permanganate must contain millions of tiny particles that keep on dividing in the water.
9. How can evaporation cause cooling? Give examples.
As a liquid evaporates, its particles collect energy from the surrounding environment in order to recoup the energy lost during evaporation. As energy is taken from the surroundings, the surroundings get colder. In the summer, for example, people sprinkle water over the roofs of buildings to keep them cool. Our body's sweating system functions similarly. As we perspire on a hot day, our perspiration evaporates, which helps to lower our body temperature.
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (chemistry) Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 1 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Textbook Questions and Answers
Intext Questions
Question 1: Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer: Chair, air, almonds, and cold-drink are matters.
Explanation: Things that occupy space and have some mass are called matter. Since chair, air, almonds and cold-drink occupy some space and have some mass, so these are matter.
Question 2: Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer: The smell of hot sizzling food reaches severed meters away, as the particles of hot food have more kinetic energy and hence the rate of diffusion is more than the particles of cold food.
Smell of anything comes because of gases emanating from the given thing. The smell reaches to us because of diffusion of gas. The rate of diffusion increases with increase in temperature. This happens because of higher kinetic energy due to higher temperature. That is why smell of hot sizzling food reaches to us from several feet. On the other hand, the kinetic energy of gases emanating from cold food is low because of lower temperature. Due to this, we need to move closer to a cold food to take its smell.
Question 3: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. This shows that the particles of water have intermolecular space and has less force of attraction.
Question 4: What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Answer: The characteristics of particles of matter are:
- Particles of matter have spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of mater attract each other.
Question 1: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density − air, exhaust from chimney, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron.
Answer: The given substances in the increasing order of their densities can be represented as:
Air < Exhaust from chimney < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
Explanation: Air is the mixture of gases. Chimney exhaust is also a mixture of gases; along with some heavier particles, such as ash. This makes the density of chimney exhaust more than air. Cotton is a porous solid and which has lot of air trapped within pores. This makes its volume more than water. Therefore, it is less dense than water.
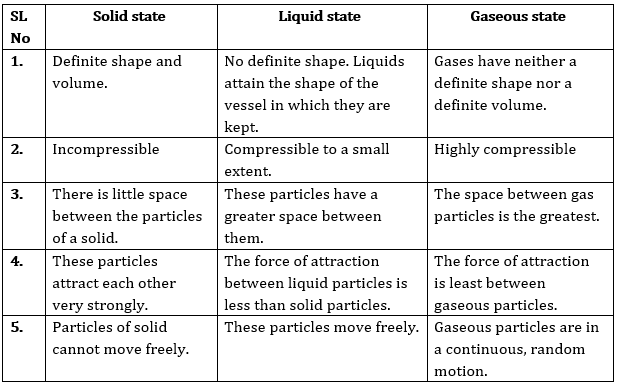
Question 2: (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter. (b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Answer: (a) The differences in the characteristics of states of matter are given in the following table.
The difference in the characteristics of the three states of matter.
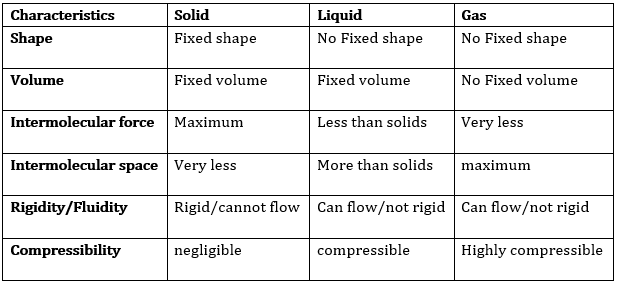
(b) Rigidity: The greatest force of attraction between particles and close packing of particles make solids rigid. Rigidity is one of the unique properties of solids. Because of rigidity, a solid can resist from getting distorted. Because of rigidity a solid has definite shape and volume. Rigidity is negligible in fluid and gas.
Compressibility: Compressibility is one of the most important characteristics of gas. Because of lot of space between particles, a gas can be compressed to a great extent.
Liquid and solid cannot be compressed because of the least space between their particles.
Fluidity: The ability to flow is called fluidity. The less force of attraction and more space between particles make liquid and gas to flow. That’s why liquid and gas are called fluid.
Filling of a gas container: Liquids do not fill a gas container completely, while gases fill the gas container completely in which it is kept. This is because the particles of gas can move in all the directions.
Shape: Solids have fixed shape. Liquid and gas take the shape of the container in which they are kept. This happens because of less force of attraction and more kinetic energy between particles of liquids and negligible force of attraction and highest kinetic energy between particles of gas.
Kinetic energy: The kinetic energy of particles of solid is the minimum. They only vibrate at their fixed position. The kinetic energy of particles of liquid is more than that of solid. But they can slide above one another. The kinetic energy of particles of gas is the maximum.
Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. The density of solid is highest, of liquid is less than solid and of gas is minimum.
Question 3: Give reasons: (a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept. (b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container. (c) A wooden table should be called a solid. (d) We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Answer: (a) There is little attraction between particles of gas. Thus, gas particles move freely in all directions. Therefore, gas completely fills the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) Because of negligible force of attraction between particles of gas, the particles of gas have the highest kinetic energy. These properties enable the particles of gas to move in all directions and hit the walls of container from all sides. Because of this a gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container in which it is kept.
(c) A wooden table has a definite shape and volume. It is very rigid and cannot be compressed i.e., it has the characteristics of a solid. Hence, a wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) Particles of air have large spaces between them. On the other hand, wood has little space between its particles. Also, it is rigid. For this reason, we can easily move our hands in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Since, air is gas, so its particles are loosely packed and there is negligible force of attraction between its particles. Because of that we can easily move our hand in air. But wood is a solid, so the force of attraction between its particles is greatest. The particles of wooden block are closely packed. That’s why we cannot move our hand through a solid block of wood. However, a karate expert can exert required pressure to break the great force of attraction of the particles of a solid wooden block.
Question 4: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer: During freezing of water, some space between the particles of water is left vacant with some air trapped between them. These empty spaces having air in them makes the density of ice; lower than that of water. That’s why ice floats on water.
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures into the Celsius scale. (a) 300 K (b) 573 K
Answer: (a) 300 K = (300 − 273)°C = 27°C (b) 573 K = (573 − 273)°C = 300°C
Question 2: What is the physical state of water at (a) 250°C (b) 100°C
Answer: (a) Water at 250°C exists in gaseous state.
(b) At 100°C, water can exist in both liquid and gaseous form. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of vaporization, water starts changing from liquid state to gaseous state.
Question 3: For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer: During a change of state, the temperature remains constant. This is because all the heat supplied to increase the temperature is utilized (as latent heat) in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. Therefore, this heat does not contribute in increasing the temperature of the substance.
Question 4: Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer: Atmospheric gas is liquefied by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature.
PAGE NO. 10
Question 1: Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer: Desert cooler works on the basis of evaporation. In hot and dry days the moisture level is very low in atmosphere which increases the rate of evaporation. Because of faster evaporation, cooler works well. That’s why desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day.
When a liquid evaporates, the particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surroundings to compensate the loss of energy during evaporation. This makes the surroundings cool.
In a desert cooler, the water inside it is made to evaporate. This leads to absorption of energy from the surroundings, thereby cooling the surroundings. Again, we know that evaporation depends on the amount of water vapour present in air (humidity). If the amount of water vapour present in air is less, then evaporation is more. On a hot dry day, the amount of water vapour present in air is less. Thus, water present inside the desert cooler evaporates more, thereby cooling the surroundings more. That is why a desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day.
Question 2: How does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summers?
Answer: Water from porous wall of earthen pot evaporates continuously, which lowers the temperature of water kept in the earthen pot. In summer moisture level is very low in the atmosphere, which increases the rate of evaporation as evaporation is inversely proportional to the moisture level in atmosphere. That is why in summer water kept in earthen pot becomes cool.
Question 3: Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer: When we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on our palm, it evaporates. During evaporation, particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surrounding or the surface of the palm to compensate for the loss of energy, making the surroundings cool. Hence, our palm feels cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it.
Question 4: Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
Answer: When hot tea or milk is kept in a saucer, the liquid is exposed over a larger surface area as compared to in case of the liquid being kept in a cup. The larger surface area enables the faster cooling. That’s why we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than from a cup.
Question 5: What type of clothes should we wear in summers?
Answer: In summer, it is preferred to wear light-coloured cotton clothes because light colour reflects heat and cotton materials have pores that absorb sweat, facilitating their evaporation hence causing a cooling effect in the skin.
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures into the Celsius scale. (a) 293 K (b) 470 K
Answer: Temperature in Celsius scale = Temperature in Kelvin scale – 273
(a) 293K= (293 – 273)°C = 20°C
(b) 470K= (470 – 273)°C = 197°C
Question 2: Convert the following temperatures into the Kelvin scale. (a) 25°C (b) 373°C
Answer: Temperature in Kelvin scale = Temperature in Celsius scale + 273
(a) 25°C = (25+273)K = 298K
(b) 373°C = (373+273)K = 646K
Question 3: Give reasons for the following observations. (a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid. (b) We can get the smell of perfume while sitting several metres away.
Answer: (a) At room temperature, naphthalene balls undergo sublimation wherein they directly get converted from a solid to a gaseous state without having to undergo the intermediate state, i.e., the liquid state.
(b) Perfumes vaporize very fast and its vapours diffuse into air easily. That is why we can smell perfume sitting several meters away.
Question 4: Arrange the following in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer: Oxygen < Water < Sugar.
Explanation: Oxygen is a gas, thus force of attraction is negligible between particles. Water is a liquid, thus force of attraction between particles is more than liquid and less than solid. Sugar is a solid, thus force of attraction between particles is greatest.
Question 5: What is the physical state of water at — (a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C?
Answer: (a) At 25°C – water is in liquid state. (b) At 0°C – water is in solid state. (c) At 100°C – water is in transition state, i.e. in liquid and gas both.
Question 6: Give two reasons to justify: (a) water at room temperature is a liquid. (b) an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer: (a) At room temperature (25 °C), water is a liquid because it has the following characteristic of liquid:
(i) Water has definite volume, but not definite shape as it takes the shape of the container in which it is kept. (ii) Water flows at room temperature.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature because: (i) It has definite shape. (ii) It has definite volume.
Question 7: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer: At 273K ice requires more latent heat to melt into water, while water at 273K requires less latent heat; to come to the room temperature. So, ice at 273 K is more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature.
Question 8: What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer: Steam produces more severe burns than boiling water. This is because steam has more energy than boiling water, present in it in the form of latent heat of vaporization.
Question 9: Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state:
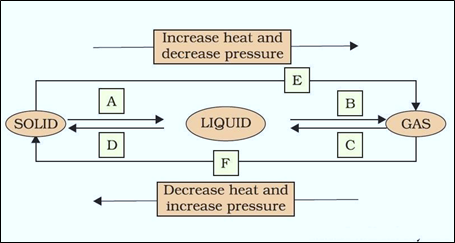
Answer: A: Melting (or) fusion (or) liquefaction B: Evaporation (or) vaporization C: Condensation D: Solidification E: Sublimation F: Sublimation
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 1.1 | Physical Nature of Matter |
| 1.2 | Characteristics of Particles of Matter |
| 1.3 | States of Matter |
| 1.4 | Can Matter Change its Shape? |
| 1.5 | Evaporation |
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Science Chapter 1
October 2, 2019 by Sastry CBSE
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Is there any similarity in materials? Answer: Yes, all materials possess mass and occupy space.
Question 2. When 50 g of sugar is dissolved in 100 mL of water, there is no increase in volume. What characteristic of matter is illustrated by this observation? Answer: This observation indicates that particles of water have spaces between them into which sugar particles fit.
Question 3. What happens when an inflated air balloon is pricked with a pin? Name the property of the gaseous state exhibited by this observation. Answer: The balloon bursts and diffusion takes place.
Question 4. Name the process which occurs when a drop of dettol is added to water. Answer: When dettol is added to water, diffusion takes place.
Question 5. To which physical state of matter do the following statements apply? (i) Incompressible, no fixed shape (ii) Compressible, no definite volume Answer: (i) Liquid (ii) Gas
Question 6. Name the state of matter in which: (i) Layers of particles can slip and slide over one another easily. (ii) Particles just move around randomly because of very weak force of attraction. Answer: (i) Liquid state, (ii) Gaseous state.
Question 7. Define density and give its SI unit. Answer: Density of a substance is defined as the mass per unit volume. Its SI unit is kgm -3 .
Question 8. In which of the following, the particles have highest forces of attraction? Water, NaCl (solid), ice or, wax. Answer: NaCl (solid) has particles with the highest forces of attraction.
Question 9. Why do the gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container than the solids? Answer: In gases, the particles move randomly at high speed and they collide with each other and with the walls of the container.
Question 10. Which of the following diffuses faster? Water vapour, wax or, ethyl alcohol. Answer: Water vapour
Question 11. Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice cold water? Answer: The water vapour present in the air comes in contact with cold surface of the glass, loses its energy and gets converted into droplets of water.
Question 12. Can materials exist in all the three states? Answer: Yes, materials can exist in all the three states under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
Question 13. Kinetic energy of particles of water in three vessels A, B and C are E A , E B and E C respectively and E A > E B > E C . Arrange the temperatures, T A , T B and T C of water in the three vessels in increasing order. Answer: T C < T B < T A , the kinetic energy of particles is greater at higher temperature.
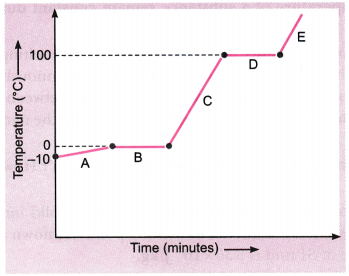

Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-I
Question 1. When a crystal of potassium permanganate is placed in a beaker containing water, its purple colour spreads throughout the water. What do you conclude from this observation about the nature of potassium permanganate and water? Answer: When we place few crystals of potassium permanganate in a beaker containing water, we get two distinct layers—colourless water at the top and pink colour at the bottom. After few minutes, pink colour spreads and whole solution turns pink due to diffusion. Since potassium permanganate is a solid substance, it does not possess so much space. Water molecules due to liquid state, collide with solid particles and intermix due to sufficient space between molecules.
Question 2. Why do solids have a regular geometrical shape? Answer: In solids, the particles have highly ordered arrangement because the intermolecular forces between the particles are very strong. Therefore, solids have a regular geometrical shape.
Question 3. Why are gases compressible but not liquids? Answer: Gases are compressible because the intermolecular space is very large in gases, whereas liquids are not compressible because in liquids, the intermolecular space is less.
Question 4. Can a rubber band change its shape on stretching? Is it a solid? Answer: Yes, a rubber band changes shape under force and regains the same shape when the force is removed. It breaks on applying excessive force. Yes, it is a solid.
Question 5. Why steam at 100°C is better for heating purposes than water at 100°C? Answer: Steam at 100°C is better for heating purposes than water at 100°C because the energy of 1 kg of steam at 100°C is 22.6 × 10 5 joule which is more than that of 1 kg of water at the same temperature.
Question 6. Give two ways in which melting points and boiling points can be useful. Answer:
- To check whether the substance is pure or not.
- To identify and characterise the substance.
Question 7. Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment. [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C, but steam has more energy because of latent heat of vaporisation.
Question 8. Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during its melting point or boiling point? [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: The temperature of a substance remains constant at its melting and boiling points until all the substance melts or boils because, the heat supplied is continuously used up in changing the state of the substance by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. This heat energy absorbed without showing any rise in temperature is given the name latent heat of fusion/latent heat of vaporisation.
Question 9. What do you understand by the term ‘latent heat of fusion’? How much is the latent heat of fusion of ice? Answer: The amount of heat that is required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure without any change in temperature at its melting point, is known as latent heat of fusion. The latent heat of fusion of ice in SI unit is 3.35 × 10 5 J/kg.
Question 10. Which gas is called dry ice? Why? Answer: Solid CO 2 is known as dry ice. This is because it directly gets converted into gaseous state without passing through liquid state on decreasing the pressure to 1 atmosphere.
Question 12. Why do the doctors advise to put strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person having high fever? Answer: When a person has fever, his body temperature becomes more than the normal body temperature. If we put strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person suffering from high fever, the water evaporates taking heat from the body. Thus, moist strips will lower his body temperature.
Question 14. Why do wet clothes dry quickly in the sun than in the shade? Answer: The temperature in the sunny area is higher than in the shade and evaporation takes place at a faster rate at high temperature. Hence, wet clothes dry quickly in the sun.
Question 15. Why do trees acquire more leaves during summer? Answer: During summer the temperature is generally very high. In order to keep cool, a tree must transpire (transpiration is a phenomenon of evaporation of water from the leaves) more to keep itself cool. More transpiration requires more leaves. Hence, a tree acquires more leaves during summer.
Question 16. Why do we feel comfortable under a fan when we are perspiring? Answer: The sweat is readily evaporated from the body by the air from the fan. As a result, we feel comfortable under a fan.
Question 17. Why do people sprinkle water on the roof after a hot sunny day? Answer: Water sprinkled on the roof evaporates by taking the large latent heat of vaporisation from the ground. This makes the place cool and comfortable.
Question 18. It is a hot summer day, Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes respectively. Who do you think would be more comfortable and why? [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: Priyanshi would be more comfortable because cotton is a good absorber than nylon. It absorbs sweat from the body and provides large surface area for evaporation which causes cooling effect. As a result, body feels cool and comfortable.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-II
Question 1. Substance ‘A’ has high compressibility and can be easily liquefied. It can take up the shape of any container. Predict the nature of the substance. Enlist four properties of this state of matter. Answer: ‘A’ is a gas. Properties of gases:
- They do not have fixed shape and fixed volume.
- They have large interparticle space.
- They have least forces of attraction between the molecules.
- They are highly compressible.
Question 2. Suggest an activity to show that the rate of diffusion of liquids decreases with increase in density of the liquid. Answer:
- Take two beakers filled with water.
- Put a drop of blue ink slowly along the sides of the first beaker and honey in the same way in another beaker.
- Leave it undisturbed.
- We observe that honey diffuses slowly as compared to ink.
This experiment shows that lesser the density, faster the rate of diffusion.
Question 3. Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion
- Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water.
- Spreading of virus on sneezing.
- Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt.
- Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
- Preserving pickles in salt.
- Spreading of smell of cake being baked throughout the house.
- Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration. [NCERT Exemplar]
Question 4. Explain what happens to the molecular motion and energy of 1 kg of water at 273 K when it is changed into ice at same temperature. How is the latent heat of fusion related to the energy exchange that takes place during this change of state? Answer:
- Molecular motion decreases as water gets converted into ice.
- Latent heat of solidification is given off.
Latent heat of solidification is equal to latent heat of fusion.
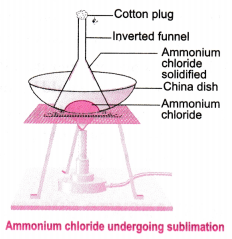
- Take crystals of ammonium chloride in a china dish.
- Put the china dish on a tripod stand with wire gauze.
- Put an inverted funnel on the china dish and insert a cotton plug in the stem of the funnel.
- Heat the china dish on a low flame.
- In the inside of the funnel white deposits of ammonium chloride is seen which directly converts into gaseous state and then solidifies.
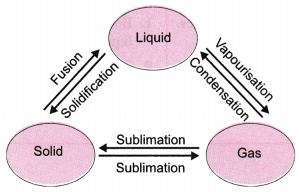
Question 8. Explain how the rate of evaporation of a liquid is affected with:
- Increase in temperature of the liquid.
- Decrease in exposed surface area.
- Increase in moisture in the surrounding air.
- Increase in wind speed.
- Rate of evaporation increases with rise in temperature.
- Evaporation is less when exposed surface area decreases.
- Less evaporation if moisture content is high in the air.
- Rate of evaporation increases if wind speed increases.
Question 9. You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster? [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: Conditions that can increase the rate of evaporation of water are:
- An increase in the surface area by spreading the shirt.
- An increase in the temperature by putting the shirt under the sun.
- Increase in the wind speed by spreading it under the fan.
Question 10. How does evaporation differ from boiling? Answer:
| 1. Evaporation takes place at all temperatures. | 1. Boiling takes place only at the boiling point of the liquid. |
| 2. Temperature changes during evaporation. | 2. The temperature does not change during boiling. |
| 3. It is a very slow process. | 3. It is a fast process. |
| 4. Evaporation takes place only at the surface of the liquid. | 4. Boiling takes place in the entire body of the liquid. |
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1. Describe the continuous motion of particles of matter with the help of an activity. Answer: (a) To demonstrate motion of particles in air:
- Place few lighted incense sticks in a corner of a room.
- Move about the room and smell the fragrance of the incense sticks.
The fragrance produced due to burning of incense sticks is due to movement of vapours produced rapidly in all directions.
(b) To demonstrate motion of particles of solid matter:
- Drop a crystal of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate into a glass of hot water.
- Do not stir the solution and allow the crystals to settle at the bottom.
- The colour of the solid is seen spreading slowly. This is because the solid particles diffuse in the water.
- In a beaker take some water and insert a thermometer in it with the help of a clamp.
- Put the beaker on a tripod stand and heat the apparatus with the help of kerosene burner slowly.
- Observe what happens to water.
- You will observe a steady stream of bubbles. This temperature is the boiling point of water.
Determination of melting point of ice:
- Take crushed ice in a beaker and insert a thermometer in the beaker by hanging it from the clamp of the stand in such a way that the bulb of the thermometer is completely inside the ice.
- Wait for some time and keep recording the temperature after small intervals of time.
- Note down the temperature when ice just starts melting.
- Let the bulb of the thermometer remain in mixture of ice and water for some more time and keep recording the temperature. This temperature is the melting point of ice.

Question 4. Discuss the various factors which affect the rate of evaporation. Latent heat of evaporation of two liquids A and B is 100 J/kg and 150 J/kg respectively. Which one can produce more cooling effect and why? Answer: Factors affecting the rate of evaporation:
- Surface area: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in surface area.
- Temperature: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in temperature.
- Humidity: The rate of evaporation decreases with increase in humidity.
- Wind speed: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in wind speed.
- Nature of the liquid: The volatile compounds evaporate faster than less volatile compounds (liquids).
B will produce more cooling effect because it will absorb more heat from the surroundings for evaporation.
Question 5. Comment on the following statements: (a) Evaporation causes cooling. (b) Rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with increase in humidity. (c) Sponge though compressible is a solid. (d) Ice is solid at 0°C, while water is liquid at room temperature. (e) Sugar crystals dissolve faster in hot water than cold water. [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (a) Evaporation produces cooling as the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings and change into vapour, thereby producing a cooling effect. (b) Air around us cannot hold more than a definite amount of water vapour at a given temperature which is known as humidity. So, if the air is already rich in water vapour, it will not take up more water; therefore, rate of evaporation of water will decrease. (c) A sponge has minute holes in which air is trapped. Also the material is not rigid. When we press it, the air is expelled out and we are able to compress it. But it is a solid because it has definite shape and volume and does not change its shape unless compressed. (d) Ice is solid at 0°C because it has a definite volume and definite shape due to strong intermolecular forces. Water is liquid at room temperature because it has definite volume and no definite shape due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction. (e) Sugar crystals dissolve faster in hot water than cold water because hot water molecules have more kinetic energy. Due to this, they strike faster on the particles of sugar than cold water molecules. As a result, hot water will dissolve them faster than cold water.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
Question 2. ‘A small volume of water in a kettle can fill a kitchen with steam’. Explain why. Answer: The liquid form of water converts into gaseous form in steam. Its particles move very rapidly in all the directions and fill the kitchen as gases completely fills the vessel.
Question 3. A sample of water under study was found to boil at 102°C at normal temperature and pressure. Is the water pure? Will this water freeze at 0°C? Comment. [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: Its freezing point will be below 0°C due to the presence of a non-volatile impurity in it.
Question 4. You are given the following substances with their melting and boiling points.
| X | -219 | -183 |
| Y | 119 | 445 |
| Z | – 15 | 78 |
Identify the physical states of X, Y and Z at room temperature (30°C). Answer: ‘X’ is gas at room temperature. ‘Y’ is solid at room temperature. ‘Z’ is liquid at room temperature.
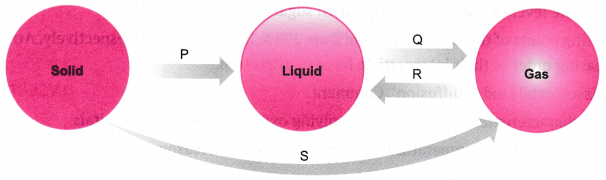
Question 7. Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations. [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: In case of ice, the water molecules have low energy while in case of steam the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of water molecules in steam is transformed as heat and may cause burns. On the other hand, in case of ice, the water molecules take energy from the body and thus, give a cooling effect.
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
myCBSEguide
- Entrance Exam
- Competitive Exams
- ICSE & ISC
- Teacher Exams
- UP Board
- Uttarakhand Board
- Bihar Board
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Haryana Board
- Jharkhand Board
- MP Board
- Rajasthan Board
- Courses
- Test Generator
- Homework Help
- News & Updates

- Dashboard
- Mobile App (Android)
- Browse Courses
- New & Updates
- Join Us
- Login
- Register
No products in the cart.
Class 9 Science NCERT Notes, Sample Papers & Tests
Get the best grades with the help of myCBSEguide where you can access Class 9 Science question papers, revision notes, important questions, NCERT & Exemplar Solutions, and learning videos.
- CBSE Syllabus
CBSE Sample Papers
Cbse last year papers, user submitted papers, case study questions, mock tests, matter in our surrounding, is matter around us pure, atoms and molecules, structure of the atoms, cell - basic unit of life, forces and laws of motion, gravitation, work and energy, improvement in food resources.
- CBSE Test Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
CBSE Important Questions
Other useful resourses, online tests, learning videos.
At the secondary stage, students are required to understand abstraction and have quantitative reasoning. At this stage, they are introduced to the idea of atoms and molecules being the building blocks of matter. Students come across new experiments and theories, like Newton’s law of gravitation. Student-friendly myCBSEguide app brings to you a complete course for Class 9 Science.
CBSE Class 9 Science Study Material
The best content available for the CBSE course is available on the myCBSEguide mobile app. Our Class 9 Science course includes sample question papers, chapter-based NCERT solutions, revision notes, exemplar solutions, test papers, and learning videos. Our NCERT solutions are available for free download in PDF format, others comprise premium content. The curriculum of Class 9 Science is designed to provide a number of opportunities for the students to engage with the processes of Science like observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulation, plotting graphs, etc. Therefore, students need to have a robust preparation right from this level to have a stronger foundational knowledge for higher education in the subject of science. Here you will find the Class 9 Science CBSE Syllabus, Sample Papers, Last Year Papers (school-based), expert-made Case Study Questions, and Mock Tests. One can use these to plan their preparation.
CBSE Class 9 Science Syllabus
A syllabus is one such thing that is subject to get updated as and when the requirement is. The secondary science syllabus has been designed around seven broad themes. They are as follows:
- The World of The Living
- How Things Work
- Moving Things
- People and Ideas
- Natural Phenomenon and Natural Resources
Students must be super sure about the syllabus and the chapters it includes so that their preparation goes in the right direction. Check the topic details for the Class 9 Science syllabus 2022-23 on this link. The units along with the marks allotted have been reflected in the table given below.
| Unit No. | Unit | Marks |
| I | Matter - Its Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| II | Organization in the Living World | 22 |
| III | Motion, Force and Work | 27 |
| IV | Food; Food Production | 06 |
| TOTAL | 80 | |
|
| Internal Assessment | 20 |
| TOTAL | 100 | |
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
The importance of NCERT solutions in the CBSE curriculum is known to all. In fact, for all the CBSE subjects, the chapter-end textbook questions have a special position and should not be overlooked at any cost. You can access to Class 9 NCERT Solutions on our students dashboard for all the subjects. The best part is it is available for free and teachers can use them to generate question papers as well.
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter-wise Solutions
- Atoms and Molecules part 1
- Diversity in Living Organisms part 2
- Forces and Laws of Motion part 1
- Gravitation part 2
- Improvement in Food Resources part 1
- Is Matter around Us Pure part 1
To access the NCERT solutions for other chapters, click on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science .
CBE Class 9 Science Revision Notes
Revision Notes have the crux of a chapter, which assures having command over a condensed knowledge of all the important points included in the chapter. On myCBSEguide, you get quick revision notes for all the subjects. You can check our Class 9 Science Revision Notes which will be very helpful for having an overall view of a particular chapter in no time.
The link to the Revision Notes of some of the Class 9 Science Chapters is listed below:
- Diversity in Living Organisms class 9 Notes Science
- Motion class 9 Notes Science
- Forces and Laws of Motion class 9 Notes Science
- Gravitation class 9 Notes Science
- Work and Energy class 9 Notes Science
- Sound class 9 Notes Science
CBSE Class 9 Science Sample Papers & Test Papers
There is no official sample paper for class 9 issued by the CBSE. Taking a cue from class 10 sample papers, we at myCBSEguide prepare such model question papers in all the subjects for class 9. Having good practice with sample papers is absolutely necessary if you aim to score really well in your papers. Here you get to download the Class 9 Science Sample Papers 2022-23 . Be it a school final examination or board sample papers are helpful for both. It not only makes the students more sure but also enables make the best use of their time.
Apart from sample papers, there is a provision for class 9 science test papers, which can be used by students and teachers equally to keep a tab on small targets. Our online tests and mock tests for class 9 science can be used to learn in a play way method.
CBSE Class 09 Science Case Study Questions
To promote competency-based education, CBSE has included new kinds of questions to test the analytical skills of the students. These are the case study questions in which the students require to identify the problems in the given real-life scenario and find solutions in their own way. You can get the best of the case study questions on myCBSEguide .
For the secondary level, the case study questions for science usually are given in the form of a passage having a diagram or a graph based on which a few subjective or objective questions are asked. It is obvious that the level of difficulty of these case study questions changes with the class. Hence, we bring the case study questions according to the different levels of difficulty. The Class 9 case study questions are designed to engage the students in critical thinking thing and apply problem-solving techniques. Check out Class 9 Case Study Questions for sample questions.
Students who aim to perform well and pass with flying colours must download the myCBSEguide app and prepare with the help of the materials provided here.
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions. You can find …
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
NCERT textbook solutions for class 9 are now available in the myCBSEguide App for free. Students can download and access the latest NCERT book chapter-end questions and answers from the myCBSEguide App and student dashboard. We offer NCERT questions and solutions for class 9 Social Science, Science, Mathematics, English Language …
CBSE Class 9 Science Syllabus 2022-23
CBSE Class 9 Science Syllabus 2022-23 includes Matter- Its Nature and Behaviour, Organization in the Living World, Motion, Force and Work, Food Production etc for the session 2022 – 2023. Here is the detailed syllabus. To download class 9 Science CBSE latest sample question papers for the 2023 exams, please …
CBSE Term-1 MCQ Sample Papers 2021-22
CBSE will ask only MCQs in Term-1 Examination this year. The board will hold this first term exam in Nov-Dec 2021. As CBSE has already cleared that 1st term exam will carry 90 minutes, now it’s time to start preparation. Students can download CBSE Term-1 MCQ Sample Papers from myCBSEguide …
CBSE to Conduct Two Term Exams in 2021-22
CBSE has issued a circular on 5th July 2021 regarding the Special Scheme of Assessment for Board Examination Classes X and XII for the Session 2021-22. Here is the complete text of the circular. COVID 19 pandemic caused almost all CBSE schools to function in a virtual mode for the …
CBSE Reduced Syllabus by 30% for Session 2020-21
CBSE, New Delhi has reduced the syllabus for classes 9 to 12 by 30%. The CBSE Revised Syllabus 2020-21 is available in CBSE official website and myCBSEguide mobile app. Here is the complete circular regarding CBSE Revised Syllabus 2020-21: CBSE Reduced the Syllabus The prevailing health emergency in the country …
Report Card in myCBSEguide App
The new update of myCBSEguide App includes Report Card feature for students. This will help students to monitor their progress. Report Card is also a very useful tool for parents to check the performance of the student. What is Report Card in myCBSEguide App? Report Card is a tool in …
Multiple Choice Questions for CBSE Class 10 and 12
The new curriculum issued by CBSE, New Delhi includes objective type questions along with Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ). Now CBSE will ask around 20% questions based on objective type questions. myCBSEguide App has more than one lakh MCQ from class 3 to 12 in almost all major subjects. MCQ questions …
JSTSE Previous Year Papers 2009 to 2019
Download JSTSE previous year papers from the year 2009 to 2019 in PDF format for free from myCBSEguide App and website. JSTSE (Junior Science Talent Search Examination) JSTSE Previous Year Question Papers are now available in myCBSEguide App for free. JSTSE past 10 year question papers and solutions are also …
CBSE Syllabus for Class 9 Science 2019-20
CBSE Syllabus of Class 9 Science 2019-20 Science allows us to understand the interactions between various chemicals and our bodies to make medicine, to transfer electrons through wires and into light bulbs so we can see without sunlight. We could survive without science, but life would be more difficult. The …

Student Subscription
Unlock the exclusive content designed for the toppers, more courses.

Admission Test

Mathematics

Social Science

English Lang & Lit. (184)

Download myCBSEguide App
All courses.
- Entrance Exams
- Competative Exams
- Teachers Exams
- Uttrakand Board
- Bihar Board
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Haryana Board
- Jharkhand Board
- Rajasthan Board
Other Websites
- Examin8.com
CBSE Courses
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 09
- CBSE Class 08
- CBSE Class 07
- CBSE Class 06
- CBSE Class 05
- CBSE Class 04
- CBSE Class 03
- CBSE Class 02
- CBSE Class 01
- CBSE MCQ Tests
- CBSE 10 Year Papers
NCERT Solutions
- Submit Your Papers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 09
- NCERT Solutions for Class 08
- NCERT Solutions for Class 07
- NCERT Solutions for Class 06
- NCERT Solutions for Class 05
- NCERT Solutions for Class 04
- NCERT Solutions for Class 03
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 09 Sample Papers
- CBSE Results | CBSE Datesheet
Please Wait..

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Category: Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Case study questions for class 9 science chapter 15 improvement in food resources, case study questions for class 9 science chapter 14 natural resources, case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 9 force and laws of motion, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 8 motion, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 7 diversity in living organisms, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 6 tissues, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 2 is matter around us pure, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 5 the fundamental unit of life, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 13 why do we fall ill, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 11 work and energy, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 10 gravitation, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 4 structure of atom, case study and passage based questions for class 9 science chapter 3 atoms and molecules.

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
If NCERT website is not working properly in your device kindly clear your browser cache, cookies, temp files and retry click to know more.
- Skip to main content |
- Skip to navigation |
- Screen Reader Access |
- Text Size: A- | A | A+
- Site View: A A

Textbooks PDF (I-XII)
| |




IMAGES
COMMENTS
Q14: List all the factors which affects the rate of evaporation. A14: The factors affecting the rate of evaporation are: (a) an increase in surface area. (b) an increase in temperature. (c) an increase in wind speed. (d) a decrease in humidity. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 science.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Matter in our Surroundings Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies ...
b) Dissolution, combustion, sublimation, and oxidation. c) Fermentation, photosynthesis, respiration, and digestion. d) Oxidation, reduction, precipitation, and ionization. Answer: a) Evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 ...
Class 9 science case study question 1. Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as fuel these days in vehicles.
Question 1: There are three states of matter - solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries, and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility. Solids have a tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force. Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they ...
Q2: When solid changes into vapours, the process is called. (a) Evaporation. (b) Boiling. (c) Sublimation. (d) Vapourisation. Ans: (c) Sublimation is the process by which a solid changes directly into a gas without passing through the liquid state. Q3: A substance melts at 5°C and boils at 150°C.
by experts. Download PDF Case Study Questions of Class 9 Science to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams Exam 2023-24. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions. Case study questions are based on real or ...
This article aims to present a comprehensive collection of case study questions for Class 9 Science, covering various topics and concepts. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th. CBSE Class 9 Science Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in ...
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Extra Questions Solved. I. Multiple Choice Questions in Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Choose the correct option: 1. Evaporation of a liquid occurs at. (a) boiling point. (b) a fixed temperature. (c) temperature lower than boiling point.
9. Define latent heat of fusion. Answer: Latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at its melting point. 10. Define sublimation. Answer: Sublimation is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through liquid state and vice-versa. 11.
CBSE Class 9 Science Sample Paper with Solutions for Term 2 Exam 2022. Check some of the important case study questions below: Q. Read the following and answer the questions: A student was asked ...
The questions that are included in chapter 1 science class 9 important questions are most likely to come in the exams. Thus, preparing the students better and efficient. Students can download the pdf of class 9 chapter 1 science important questions from the Vedantu site. This pdf is available for free.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Here we are providing case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound. Students are suggested to go through each and every case study questions for better understanding of the chapter. Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1:
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings is an important study material from the standpoint of your CBSE Class 9 Science examination. Detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry provided here will help you understand the fundamental concepts taught in the chapter.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skills) Question 1. The diagram below shows burning of an oil lamp. Draw the arrangement of particles of position 'X' and 'Y' when the lamp is burning. Question 2. 'A small volume of water in a kettle can fill a kitchen with steam'.
The CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science - Pdf is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 9 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Here you will find the Class 9 Science CBSE Syllabus, Sample Papers, Last Year Papers (school-based), expert-made Case Study Questions, and Mock Tests. One can use these to plan their preparation. CBSE Class 9 Science Syllabus. A syllabus is one such thing that is subject to get updated as and when the requirement is.
Q2: Read the following information and answer the questions based on information and related studied concepts. Substance - 1. is brittle. Substance - 2. melts at 5°C and boils at 150°C. Substance - 3. has high melting point of 800°C. Substance - 4. has melting point -169°C and boiling point -104°C.
Maths Case-Study Qs. Maths Case-Study Qs. VIEW ALL. TopperLearning offers an online platform to access case studies for CBSE Class 9 students. Explore your analytical and problem-solving skills by solving case studies with our expert guidance. Get started today!
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings; An Imperial Capital - Vijayanagara Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 12 History Chapter 7; India's External Relations Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 12 Political Science Chapter 11
The NCERT Exemplar Solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding is provided here for the benefit of the students. Studying the NCERT Exemplar Solution will give you in-depth knowledge of the concepts discussed in the chapter. NCERT Exemplar questions are designed in such a way that students can learn all the basic and ...
NCERT, Sri Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi-110016. [email protected]. +91 8800440559
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 maths. In this article, you will find case study ...
Reading Time: 7 minutes Last Updated on August 2, 2024 by XAM CONTENT. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board.
1. ________ phenomena would increase on raising the temperature. 2. The property of flow is unique to fluids. ______ is the correct statement. 3. What is the boiling point of water at sea level? Access NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 here . Important Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings are given here.
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 maths. In this article, you will find case study ...
Document Description: Case Study Based Questions: Friction for Class 8 2024 is part of Science Class 8 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Study Based Questions: Friction have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Case Study Based Questions: Friction covers topics like Case Study and Case Study Based Questions: Friction Example, for Class 8 2024 Exam.