An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings

Trending Articles
- Integrative plasma and fecal metabolomics identify functional metabolites in adenoma-colorectal cancer progression and as early diagnostic biomarkers. Sun Y, et al. Cancer Cell. 2024. PMID: 39137727
- Schwann cell-secreted PGE 2 promotes sensory neuron excitability during development. Kantarci H, et al. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39142281
- Macrophage-mediated myelin recycling fuels brain cancer malignancy. Kloosterman DJ, et al. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39137777
- The molecular architecture of the nuclear basket. Singh D, et al. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39127037
- CCL19-producing fibroblasts promote tertiary lymphoid structure formation enhancing anti-tumor IgG response in colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Zhang Y, et al. Cancer Cell. 2024. PMID: 39137726
Latest Literature
- Am Heart J (1)
- Am J Med (4)
- Ann Neurol (1)
- Arch Phys Med Rehabil (2)
- Clin Infect Dis (1)
- Gastroenterology (1)
- J Biol Chem (3)
- J Neurosci (4)
- Nat Commun (25)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 90
Impact of proton pump inhibitor use on clinical outcomes in East Asian patients receiving clopidogrel following drug-eluting stent implantation
Concomitant use of clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is common, but PPI may reduce the antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). We evaluate...
- View Full Text
Association of body shape phenotypes and body fat distribution indexes with inflammatory biomarkers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) and UK Biobank
The allometric body shape index (ABSI) and hip index (HI), as well as multi-trait body shape phenotypes, have not yet been compared in their associations with inflammatory markers. The aim of this study was to...
Overall and cause-specific mortality among patients diagnosed with gastric precancerous lesions in Sweden between 1979 and 2014: an observational cohort study
The Correa’s cascade, encompassing chronic non-atrophic gastritis, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and dysplasia, represents the well-recognized pathway for the development of non-cardia gastric can...
Trait impulsivity is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes incidence in adults over 8 years of follow-up: results from the NutriNet-Santé cohort
Type 2 diabetes is one of the most prevalent and preventable diseases worldwide and impulsivity, a psychological trait characterized by making quick decisions without forethought, has been suggested as a key f...
Chronic kidney disease: detect, diagnose, disclose—a UK primary care perspective of barriers and enablers to effective kidney care
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global public health problem with major human and economic consequences. Despite advances in clinical guidelines, classification systems and evidence-based treatments, CKD rem...
The impact of adverse childhood experiences on multimorbidity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) have been implicated in the aetiology of a range of health outcomes, including multimorbidity. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to identify, synthesise...
Vitamin B12 status and the risk of developing sepsis in patients with bacterial infection: a prospective observational cohort study
Data have shown that vitamin B12 has immunomodulatory effects via different pathways, which could influence the pathophysiology of sepsis. The objective of this study was to investigate whether vitamin B12 lev...
Differences in hypersensitivity reactions and gadolinium deposition disease/symptoms associated with gadolinium exposure to gadolinium-based contrast agents: new insights based on global databases VigiBase, FAERS, and IQVIA-MIDAS
Hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs) can occur unexpectedly and be life-threatening when gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are used. Gadolinium deposition disease (GDD) and symptoms associated with gadolin...
Influences of HPV disease perceptions, vaccine accessibility, and information exposure on social media on HPV vaccination uptake among 11,678 mothers with daughters aged 9–17 years in China: a cross-sectional study
Mothers play a crucial role in influencing their daughters’ HPV vaccination decisions. Addressing barriers to receiving HPV vaccination among mothers of girls may achieve two goals in one strike: increasing va...
Recent cervical cancer incidence, stage at diagnosis, and mortality trends in Puerto Rico, 2001–2019
Cervical cancer incidence is rising in Puerto Rico (PR). Whether the increase is real or reflective of increased diagnostic scrutiny remains unclear.
Daytime napping and the incidence of Parkinson’s disease: a prospective cohort study with Mendelian randomization
The causal relationship between daytime napping and the risk of Parkinson’s disease (PD) remains unclear, with prospective studies providing limited evidence. This study investigated the association between da...
Discrepancies between general and central obesity in arterial stiffness: observational studies and Mendelian randomization study
Obesity has been linked to arterial stiffness, while no consensus was reached on the association. We aimed to clarify the association of general and central obesity with arterial stiffness by combining observa...
One-year outcomes of a novel venous stent for symptomatic iliofemoral venous obstruction: prospective cohort study
A stent with characteristics of a hybrid design may have advantages in improving the patency of symptomatic iliofemoral vein obstruction. This study assessed the safety and effectiveness of the V-Mixtent Venou...
Unraveling the causality between gastroesophageal reflux disease and increased cancer risk: evidence from the UK Biobank and GWAS consortia
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition characterized by the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. Despite its widespread prevalence worldwide, the causal link between GERD and va...
Dilemma of commercial organ transplant in the Middle East
In recent years, the Middle East has witnessed a significant rise in commercial transplantation activities. This practice is driven by a multitude of factors including economic disparities, inadequate healthca...
Vitamin A carotenoids, but not retinoids, mediate the impact of a healthy diet on gut microbial diversity
Vitamin A is essential for physiological processes like vision and immunity. Vitamin A’s effect on gut microbiome composition, which affects absorption and metabolism of other vitamins, is still unknown. Here ...
Predicting disease recurrence in patients with endometriosis: an observational study
Despite surgical and pharmacological interventions, endometriosis can recur. Reliable information regarding risk of recurrence following a first diagnosis is scant. The aim of this study was to examine clinica...
History of childhood maltreatment associated with hospitalization or death due to COVID-19: a cohort study
Childhood maltreatment (CM) has been indicated in adverse health outcomes across the lifespan, including severe infection-related outcomes. Yet, data are scarce on the potential role of CM in severe COVID-19-r...
All-cause mortality and hospital admissions for nursing home residents during the COVID-19 pandemic: a Norwegian register-based cohort study
This paper investigates the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality and hospitalization among nursing home residents in Norway. While existing evidence shows that nursing home residents were overrep...
The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) as a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in US adults with diabetes or prediabetes: NHANES 1999–2018
The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) serves as a novel composite lipid indicator for atherosclerosis. However, the association between NHHR and mort...
Correction: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tuberculosis treatment outcomes in 49 high burden countries
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :312
Postoperative radiotherapy with docetaxel versus cisplatin for high-risk oral squamous cell carcinoma: a randomized phase II trial with exploratory analysis of ITGB1 as a potential predictive biomarker
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) causes significant mortality and morbidity worldwide. Surgical resection with adjuvant radiotherapy remains the standard treatment for locally advanced resectable OSCC. Resu...
The associations of chronic pain and 24-h movement behaviors with incident mental disorders: evidence from a large-scale cohort study
Chronic pain was associated with a higher risk of mental disorders (e.g., depression and anxiety). However, the role of 24-h movement behaviors in the association remains unclear.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tuberculosis treatment outcomes in 49 high burden countries
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted tuberculosis (TB) health services, including treatment support and access to drugs, as patients were not able to access health facilities. While the effect of this disruption on...
The Correction to this article has been published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :316
The impact of a digital guideline version on schizophrenia guideline knowledge: results from a multicenter cluster-randomized controlled trial
Clinical practice guidelines are crucial for enhancing healthcare quality and patient outcomes. Yet, their implementation remains inconsistent across various professions and disciplines. Previous findings on t...
Early detection of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma utilizing plasma cfDNA fragmentomics
Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC) is a prevalent gynecologic malignancy with a favorable prognosis if detected early. However, there is a lack of accurate and reliable early detection tests for UCEC....
Adults prenatally exposed to the Dutch Famine exhibit a metabolic signature associated with a broad spectrum of common diseases
Exposure to famine in the prenatal period is associated with an increased risk of metabolic disease, including obesity and type 2 diabetes. We employed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) metabolomic profiling to...
Development and validation of a patient-level model to predict dementia across a network of observational databases
A prediction model can be a useful tool to quantify the risk of a patient developing dementia in the next years and take risk-factor-targeted intervention. Numerous dementia prediction models have been develop...
An original study assessing biomarker success rate in breast cancer recurrence biomarker research
Breast cancer is the second most common cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Biomarker discovery has led to advances in understanding molecular phenotyping and thus has a great potential for precision manageme...
Short- and long-term impact of aspirin cessation in older adults: a target trial emulation
The net benefit of aspirin cessation in older adults remains uncertain. This study aimed to use observational data to emulate a randomized trial of aspirin cessation versus continuation in older adults without...
Unveiling the epigenetic impact of vegan vs. omnivorous diets on aging: insights from the Twins Nutrition Study (TwiNS)
Geroscience focuses on interventions to mitigate molecular changes associated with aging. Lifestyle modifications, medications, and social factors influence the aging process, yet the complex molecular mechani...
Correction: “The dream is that there’s one place you go”: a qualitative study of women’s experiences seeking care from Long COVID clinics in the USA
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :243
Comparative analysis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease burden between ages 20–54 and over 55 years: insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
To systematically analyze differences in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) burden between young and older adults.
Unraveling the metabolomic architecture of autism in a large Danish population-based cohort
The prevalence of autism in Denmark has been increasing, reaching 1.65% among 10-year-old children, and similar trends are seen elsewhere. Although there are several factors associated with autism, including g...
Early and long-term responses of intestinal microbiota and metabolites to 131 I treatment in differentiated thyroid cancer patients
Multiple high doses of 131 I therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) might disrupt the balance of gut microbiota and metabolites. This study aimed to investigate the alterations of intestinal ...
Is trofinetide a future treatment for Rett syndrome? A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a rare, life-threatening, genetic neurodevelopmental disorder. Treatment in RTT encounters many challenges. Trofinetide, a modified amino-terminal tripeptide of insulin-like growth facto...

Associations of sugar intake, high-sugar dietary pattern, and the risk of dementia: a prospective cohort study of 210,832 participants
Limited evidence demonstrated the potential relationship between dietary sugar intake and dementia. This association demands further clarification in a large-scale population.
Estimating the relative importance of epidemiological and behavioural parameters for epidemic mpox transmission: a modelling study
Many European countries experienced outbreaks of mpox in 2022, and there was an mpox outbreak in 2023 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. There were many apparent differences between these outbreaks and previ...
Evaluation of artificial intelligence-powered screening for sexually transmitted infections-related skin lesions using clinical images and metadata
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) pose a significant global public health challenge. Early diagnosis and treatment reduce STI transmission, but rely on recognising symptoms and care-seeking behaviour of t...
Foetal gluten immunogenic peptides during pregnancy: a new determinant on the coeliac exposome
The increasing incidence of coeliac disease is leading to a growing interest in active search for associated factors, even the intrauterine and early life. The exposome approach to disease encompasses a life c...
Gut microbiome in endometriosis: a cohort study on 1000 individuals
Endometriosis, defined as the presence of endometrial-like tissue outside of the uterus, is one of the most prevalent gynecological disorders. Although different theories have been proposed, its pathogenesis i...
The clinical value of artificial intelligence in assisting junior radiologists in thyroid ultrasound: a multicenter prospective study from real clinical practice
This study is to propose a clinically applicable 2-echelon (2e) diagnostic criteria for the analysis of thyroid nodules such that low-risk nodules are screened off while only suspicious or indeterminate ones a...
Correction: Olfactory bulb anomalies in KBG syndrome mouse model and patients
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :158
Correction: ABO and Rhesus blood groups and multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :206
Correction: Trends in cardiovascular risk factor prevalence, treatment, and control among US adolescents aged 12 to 19 years, 2001 to March 2020
The original article was published in BMC Medicine 2024 22 :245
Five years of change in adult twins: longitudinal changes of genetic and environmental influence on epigenetic clocks
Epigenetic clocks were known as promising biomarkers of aging, including original clocks trained by individual CpG sites and principal component (PC) clocks trained by PCs of CpG sites. The effects of genetic ...
Consistency, completeness and external validity of ethnicity recording in NHS primary care records: a cohort study in 25 million patients’ records at source using OpenSAFELY
Ethnicity is known to be an important correlate of health outcomes, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, where some ethnic groups were shown to be at higher risk of infection and adverse outcomes. The re...
The relationship between community food environment around schools and student meal participation: the role of school CEP participation status
Despite the many benefits of school meals, not all students participate. One reason students may not participate in school meals is because they instead purchase breakfast or lunch from food outlets located ar...
A longitudinal multi-centric cohort study assessing infant neurodevelopment delay among women with persistent postpartum depression in Nepal
Infant neurodevelopment in the first years after birth is determined by multiple factors, including parental care and maternal mental wellbeing. In this study, we aim to assess the impact of persistent materna...
Mining the interpretable prognostic features from pathological image of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using multi-modal deep learning
The advances in deep learning-based pathological image analysis have invoked tremendous insights into cancer prognostication. Still, lack of interpretability remains a significant barrier to clinical application.

- Editorial Board
- Call for papers
- Editor’s choice
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Manuscript editing services
Annual Journal Metrics
Citation Impact 2023 Journal Impact Factor: 7.0 5-year Journal Impact Factor: 8.7 Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 2.000 SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 2.711 Speed 2023 Submission to first editorial decision (median days): 6 Submission to acceptance (median days): 145 Usage 2023 Downloads: 6,375,113 Altmetric mentions: 24,228
- More about our metrics
Announcements
medRxiv transfers
BMC Medicine is happy to consider manuscripts that have been, or will be, posted on a preprint server. Authors are able to submit their manuscripts directly from medRxiv , without having to re-upload files.
Registered reports
BMC Medicine is accepting Registered Reports. Find out more about this innovative format in our Submission Guidelines .
- Follow us on Twitter
BMC Medicine
ISSN: 1741-7015
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Research articles
Decompression alone or with fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis, intake of sugar sweetened beverages among children and adolescents, estimating the economic effect of harm associated with high risk prescribing of oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, personal protective effect of wearing surgical face masks in public spaces, learning implementation of a guideline based decision support system to improve hypertension treatment in primary care in china, intraosseous versus intravenous vascular access in upper extremity among adults with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, trends in long term vaping among adults in england, 2013-23, covid-19 infection and vaccination during first trimester and risk of congenital anomalies, lee silverman voice treatment versus nhs speech and language therapy versus control for dysarthria in people with parkinson’s disease, effectiveness of behavioural interventions with motivational interviewing on physical activity outcomes, trends in cardiovascular disease incidence among 22 million people in the uk over 20 years, colchicine in patients with acute ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack, sglt-2 inhibitors, glp-1 receptor agonists, and dpp-4 inhibitors and risk of hyperkalemia among people with type 2 diabetes, nab-paclitaxel, cisplatin, and capecitabine versus cisplatin and gemcitabine as first line chemotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, lateral episiotomy or in vacuum assisted delivery in nulliparous women, global burden of type 1 diabetes in adults aged 65 years and older, antiplatelet therapy after coronary artery bypass surgery, mailed feedback to primary care physicians on antibiotic prescribing, tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy as first line treatment for advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, epidural analgesia during labour and severe maternal morbidity, exposure to antibiotics during pregnancy or early infancy and risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, clinical and healthcare use outcomes after cessation of long term opioid treatment due to prescriber workforce exit, effect of the hpv vaccination programme on incidence of cervical cancer by socioeconomic deprivation in england, long acting progestogens vs combined oral contraceptive pill for preventing recurrence of endometriosis related pain, ultra-processed food consumption and all cause and cause specific mortality, comparative effectiveness of second line oral antidiabetic treatments among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, efficacy of psilocybin for treating symptoms of depression, reverse total shoulder replacement versus anatomical total shoulder replacement for osteoarthritis, effect of combination treatment with glp-1 receptor agonists and sglt-2 inhibitors on incidence of cardiovascular and serious renal events, prenatal opioid exposure and risk of neuropsychiatric disorders in children, temporal trends in lifetime risks of atrial fibrillation and its complications, antipsychotic use in people with dementia, predicting the risks of kidney failure and death in adults with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease, impact of large scale, multicomponent intervention to reduce proton pump inhibitor overuse, esketamine after childbirth for mothers with prenatal depression, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use and risk of thyroid cancer, use of progestogens and the risk of intracranial meningioma, delirium and incident dementia in hospital patients, derivation and external validation of a simple risk score for predicting severe acute kidney injury after intravenous cisplatin, quality and safety of artificial intelligence generated health information, large language models and the generation of health disinformation, 25 year trends in cancer incidence and mortality among adults in the uk, cervical pessary versus vaginal progesterone in women with a singleton pregnancy, comparison of prior authorization across insurers, diagnostic accuracy of magnetically guided capsule endoscopy with a detachable string for detecting oesophagogastric varices in adults with cirrhosis, ultra-processed food exposure and adverse health outcomes, added benefit and revenues of oncology drugs approved by the ema, exposure to air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular diseases, short term exposure to low level ambient fine particulate matter and natural cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory morbidity, optimal timing of influenza vaccination in young children, effect of exercise for depression, association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes, duration of cpr and outcomes for adults with in-hospital cardiac arrest, clinical effectiveness of an online physical and mental health rehabilitation programme for post-covid-19 condition, atypia detected during breast screening and subsequent development of cancer, publishers’ and journals’ instructions to authors on use of generative ai in academic and scientific publishing, effectiveness of glp-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes, neurological development in children born moderately or late preterm, invasive breast cancer and breast cancer death after non-screen detected ductal carcinoma in situ, all cause and cause specific mortality in obsessive-compulsive disorder, acute rehabilitation following traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation, perinatal depression and risk of mortality, undisclosed financial conflicts of interest in dsm-5-tr, effect of risk mitigation guidance opioid and stimulant dispensations on mortality and acute care visits, update to living systematic review on sars-cov-2 positivity in offspring and timing of mother-to-child transmission, perinatal depression and its health impact, christmas 2023: common healthcare related instruments subjected to magnetic attraction study, using autoregressive integrated moving average models for time series analysis of observational data, demand for morning after pill following new year holiday, christmas 2023: christmas recipes from the great british bake off, effect of a doctor working during the festive period on population health: experiment using doctor who episodes, christmas 2023: analysis of barbie medical and science career dolls, christmas 2023: effect of chair placement on physicians’ behavior and patients’ satisfaction, management of chronic pain secondary to temporomandibular disorders, christmas 2023: projecting complete redaction of clinical trial protocols, christmas 2023: a drug target for erectile dysfunction to help improve fertility, sexual activity, and wellbeing, christmas 2023: efficacy of cola ingestion for oesophageal food bolus impaction, conservative management versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy in adults with gallstone disease, social media use and health risk behaviours in young people, untreated cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 and cervical cancer, air pollution deaths attributable to fossil fuels, implementation of a high sensitivity cardiac troponin i assay and risk of myocardial infarction or death at five years, covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against post-covid-19 condition, association between patient-surgeon gender concordance and mortality after surgery, intravascular imaging guided versus coronary angiography guided percutaneous coronary intervention, treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men in primary care using a conservative intervention, autism intervention meta-analysis of early childhood studies, effectiveness of the live zoster vaccine during the 10 years following vaccination, effects of a multimodal intervention in primary care to reduce second line antibiotic prescriptions for urinary tract infections in women, pyrotinib versus placebo in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel in patients with her2 positive metastatic breast cancer, association of dcis size and margin status with risk of developing breast cancer post-treatment, racial differences in low value care among older patients in the us, pharmaceutical industry payments and delivery of low value cancer drugs, rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin in adults with coronary artery disease, clinical effectiveness of septoplasty versus medical management for nasal airways obstruction, ultrasound guided lavage with corticosteroid injection versus sham lavage with and without corticosteroid injection for calcific tendinopathy of shoulder, early versus delayed antihypertensive treatment in patients with acute ischaemic stroke, mortality risks associated with floods in 761 communities worldwide, interactive effects of ambient fine particulate matter and ozone on daily mortality in 372 cities, follow us on, content links.
- Collections
- Health in South Asia
- Women’s, children’s & adolescents’ health
- News and views
- BMJ Opinion
- Rapid responses
- Editorial staff
- BMJ in the USA
- BMJ in South Asia
- Submit your paper
- BMA members
- Subscribers
- Advertisers and sponsors
Explore BMJ
- Our company
- BMJ Careers
- BMJ Learning
- BMJ Masterclasses
- BMJ Journals
- BMJ Student
- Academic edition of The BMJ
- BMJ Best Practice
- The BMJ Awards
- Email alerts
- Activate subscription
Information

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

MEDLINE is the National Library of Medicine's (NLM) premier bibliographic database that contains references to journal articles in life sciences, with a concentration on biomedicine. See the MEDLINE Overview page for more information about MEDLINE.
MEDLINE content is searchable via PubMed and constitutes the primary component of PubMed, a literature database developed and maintained by the NLM National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
Last Reviewed: February 5, 2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Health Res Policy Syst

Understanding relevance of health research: considerations in the context of research impact assessment
Mark j. dobrow.
1 Institute of Health Policy, Management and Evaluation, Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, 155 College Street, 4th Floor, Toronto, ON M5T 3M6 Canada
Fiona A. Miller
2 Alberta Innovates - Health Solutions, Edmonton, Alberta Canada
Adalsteinn D. Brown
Associated data.
Not applicable. No datasets were generated or analysed during the development of the article.
With massive investment in health-related research, above and beyond investments in the management and delivery of healthcare and public health services, there has been increasing focus on the impact of health research to explore and explain the consequences of these investments and inform strategic planning. Relevance is reflected by increased attention to the usability and impact of health research, with research funders increasingly engaging in relevance assessment as an input to decision processes. Yet, it is unclear whether relevance is a synonym for or predictor of impact, a necessary condition or stage in achieving it, or a distinct aim of the research enterprise. The main aim of this paper is to improve our understanding of research relevance, with specific objectives to (1) unpack research relevance from both theoretical and practical perspectives, and (2) outline key considerations for its assessment.
Our approach involved the scholarly strategy of review and reflection. We prepared a draft paper based on an exploratory review of literature from various fields, and gained from detailed and insightful analysis and critique at a roundtable discussion with a group of key health research stakeholders. We also solicited review and feedback from a small sample of expert reviewers.
Conclusions
Research relevance seems increasingly important in justifying research investments and guiding strategic research planning. However, consideration of relevance has been largely tacit in the health research community, often depending on unexplained interpretations of value, fit and potential for impact. While research relevance seems a necessary condition for impact – a process or component of efforts to make rigorous research usable – ultimately, relevance stands apart from research impact. Careful and explicit consideration of research relevance is vital to gauge the overall value and impact of a wide range of individual and collective research efforts and investments. To improve understanding, this paper outlines four key considerations, including how research relevance assessments (1) orientate to, capture and compare research versus non-research sources, (2) consider both instrumental versus non-instrumental uses of research, (3) accommodate dynamic temporal-shifting perspectives on research, and (4) align with an intersubjective understanding of relevance.
Various levels of government in Canada collectively invest multiple billions of dollars in health-related research per annum, above and beyond investments in the management and delivery of healthcare and public health services. In recognition of this sizeable collective commitment, much work has focused on the impact of health research to explore and explain the consequences of these investments and inform strategic planning. Relevance is tacit in the increased attention to the usability and impact of health research. Additionally, research funders increasingly engage in relevance assessment as an input to decision processes; yet, it is unclear whether relevance is a synonym for or predictor of impact, a necessary condition or stage in achieving it, or a distinct aim of the research enterprise. Therefore, the main aim of this paper is to improve our understanding of research relevance as it relates to research quality and research impact, with specific objectives to (1) unpack research relevance from both theoretical and practical perspectives, and (2) outline key considerations for the assessment of research relevance.
Globally, there has been increasing critical assessment of the value of health research investments [ 1 – 3 ], with growing interest in research impact assessment (RIA) in the health sector [ 4 – 6 ]. RIA focuses on understanding how research activity can directly and indirectly advance knowledge, influence decision-making, and effect health and socio-economic outcomes, with a small but growing body of work seeking to develop better measures to evaluate (and ideally attribute) the returns on health research investments [ 6 ]. The Canadian Academy of Health Sciences (CAHS) released a comprehensive report on the subject in 2009 that presented a call for action, with a number of recommendations including establishing collaborative efforts among Canadian research funders to advance frameworks and sets of indicators and metrics for health research impact [ 4 ]. The CAHS impact framework [ 4 ], which drew on the Buxton and Hanney [ 7 ] ‘payback model’, among others, has provided a thoughtful starting point for considering the impact of health research in Canada. Subsequent work by Alberta Innovates – Health Solutions (AIHS) on a Research to Impact Framework (described in Graham et al. [ 8 ]) provides further insights on operationalising RIA frameworks for health research in Canada.
These initiatives are part of a broadly discussed shift in approaches to knowledge production, from an emphasis on investigator-initiated, curiosity driven work judged and guided by scientists, to expanded approaches to knowledge production, drawing on a wider set of actors and approaches, and emphasising relevance and usability. This shift from science produced by and for scientists to knowledge production that is “ socially distributed, application-oriented, trans-disciplinary, and subject to multiple accountabilities ” [ 9 ] has been characterised as a shift from ‘mode 1’ to ‘mode 2’ knowledge regimes. In the language of mode 2, interest in research ‘impact’ expresses a concern for application or consequence, and – in the economic language of return on investment – a concern that the yield is at least equal to the investment in the research itself. Extending this reasoning, interest in research ‘relevance’ may reflect a concern for accountability – linking research to the actor(s) for whom the research is performed and who will, ideally, put it to use.
In Canada, interest in research impact and relevance appears to have been felt most forcefully in the context of health services and policy research, which has long been encouraged to orient to the needs of policymakers, health system planners and related decision makers. More recently, there has been increased attention to ensuring that all forms of health research are ‘patient oriented’ – that is, that the research is prioritised, conducted and applied in ways that are accountable to this important end user. This call has been picked up on several fronts, including by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), which released its Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research (SPOR) in 2011. The SPOR vision “…is to demonstrably improve health outcomes and enhance patients’ health care experience through integration of evidence at all levels in the health care system ” [ 10 ]. In some respects, it represents a fundamental re-orientation for the primary funder of health research in Canada.
Though relevance is tacit in attention to research impact and the wider concern with mode 2 knowledge production, explicit attention to the meaning or measurement of research relevance is limited. The CAHS and AIHS frameworks, for example, acknowledge ‘relevance’ of health research but do not clearly define the term nor describe approaches for assessing it [ 4 , 8 ]. Rather, these frameworks emphasise the role of broad stakeholder engagement approaches and feedback mechanisms as methods for addressing relevance. For example, the AIHS framework notes the challenge of, and need to, move “ …beyond the collection of traditional scientific indicators […] to include measures of greater interest to the broader stakeholder community… ” [ 8 ] without stating explicitly how “ greater interest ” or related concepts such as relevance should be judged. As currently constructed, these RIA frameworks provide important advances in how we think about the impact of health research, but they were not intended to provide guidance specifically to the assessment of the relevance of health research.
Despite this lack of specific guidance on research relevance from a scholarly or measurement perspective, attention to it as a practical component of health research funding and organisation is evolving. There is, for example, growing use of ‘relevance assessment’ by research funders. The Canadian Health Services Research Foundation, in particular, was an innovator in incorporating relevance review into its applied research funding programmes, including promoting partnerships and knowledge translation (KT) with health system stakeholders [ 11 ]. Current applications for funding from the Institute of Gender and Health at CIHR go through ‘relevance review’ ( http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/45212.html ). Similarly, applications for Ontario’s Health System Research Fund are judged based on ‘internal review of relevance and impact’ ( http://www.health.gov.on.ca/en/pro/ministry/research/cihr.aspx ). However, given the lack of conceptual clarity on research relevance, and in particular, how relevance assessment aligns with and differs from impact assessment, there is a critical gap in our understanding that has implications for both its contemporary and ongoing application and our ability to make sound research investment decisions.
This work was commissioned by the Ontario SPOR SUPPORT (Support for People and Patient-Oriented Research and Trials) Unit (OSSU) – one of several units established at provincial and regional levels across Canada to work with CIHR in pursuing the SPOR. Like other research organisations, OSSU saw the need to consider the relevance of the research it supported, and it established both scientific and relevance advisory committees as part of its original governance structure [ 12 ], tasking the latter to “ …develop a measure, or small set of strategic measures, that serves to inspire the Ontario research, implementation, provider and patient communities to come together to make a difference for patients ” [ 12 ]. In the spirit of research and scholarship, OSSU then asked what exactly this commitment to research ‘relevance’ entailed.
Our approach to answering this question involved the scholarly strategy of review and reflection. As with the early investigations into research impact assessment, we were surprised to find so little reflexive attention to the topic within the health research community [ 13 ]. We prepared a draft paper based on an exploratory review of literature from various fields, and gained from detailed and insightful analysis and critique at a roundtable discussion with a small group of key health research stakeholders. We also solicited review and feedback from a small sample of expert reviewers.
The structure of our paper is as follows. First, to ‘unpack’ the concept of relevance, we review theoretical literature and then consider practical work both from within and outside the health sector, to ask what has been argued and concluded about the nature of relevance and its appropriate assessment. Next, we outline a series of forward-looking considerations for assessing research relevance and conclude with reflections on how research relevance assessment fits with evolving interest in RIA.
Unpacking relevance
Theoretical perspectives.
Before considering the relevance of health research, we need to step back and consider what we mean by the term ‘relevance’. A range of descriptors is often used to define relevance, including ‘pertinent to…’, ‘bearing upon…’, ‘connected with…’, or ‘appropriate to…’, ‘…the matter at hand’, as well as ‘germane’, ‘apropos’, ‘material’, ‘applicable’ and ‘satisfactory’. A large body of dedicated theoretical work on relevance, drawn from many fields and perspectives, such as computer science, information science, statistics/probability theory, artificial intelligence, cognitive science, epistemology, linguistics and jurisprudence [ 14 ], reflects its importance but also the challenge for establishing a common understanding of the term [ 14 , 15 ]. For example, Gärdenfors [ 16 ], in his discussion on the logic of relevance, noted that “ …relevance ought to be a central concept in the philosophy of science… ” given the position that “ …it is only relevant information that is of any importance… ” (p. 351). However, from a ‘research’ relevance perspective, the theoretical work on relevance has been linked to ‘information’, ‘evidence’, ‘reasoning’, ‘argument’ and ‘decision’ [ 15 – 18 ], each presenting variable framing that impedes practical definition or consistent comprehension of the term. Floridi [ 14 ] recently suggested that existing theories are “ …utterly useless when it comes to establish the actual relevance of some specific piece of information ” (p. 69), and goes on to advance a ‘subjectivist’ interpretation, with relevance judged by the questioner. While a subjectivist approach to relevance is intuitively appealing, its contribution to the assessment of research relevance presents particular challenges that we will discuss later in the paper.
Another approach to unpacking relevance is to consider the theoretical model behind the broad-based research strategies that have governed research investments and policies in high-income countries since the end of the Second World War. For the better part of the 20th century, a linear model was the dominant conceptual framework, whereby basic research was viewed as a necessary input for applied research, which then led to development and production [ 19 , 20 ]. In the late 1990s, an alternate thesis was introduced when Stokes proposed a new model for broad-based research strategy – known as Pasteur’s Quadrant – that highlighted the conceptual relationship between the ‘quest to understand’ and ‘practical needs’ [ 21 ]. While some research is clearly focused on advances in basic research (e.g. Niels Bohr’s foundational research on atomic structure and quantum theory), and some research is clearly focused on applied problems (e.g. Thomas Edison’s practical inventions), Stokes emphasised the potential for use-inspired basic research (e.g. Louis Pasteur’s foundational research on microbiology that addressed contemporaneous population health challenges). Pasteur’s Quadrant invokes consideration of ‘relevance’ with some commentators framing the two-by-two relationship as the relevance for advancement of basic knowledge and the relevance for immediate application [ 22 ]. Stokes’ model adds conceptual insight on the role of relevance when considering the value of research to society, however, it was not intended to specifically conceptualise the term and does not distinguish it from other related concepts such as research impact or value. Therefore, to provide further insights, we next consider relevance in practical settings.
Health sector perspectives
In the health sector, the idea that research should be ‘relevant’ is commonplace. Commitments to ‘knowledge translation’ and the ‘knowledge to action cycle’ [ 23 ] emphasise issues of relevance and provide considerable insight into approaches to ensuring research usability and use. At the same time, the health research community has given disproportionate attention to issues of research quality, with an emphasis on internal validity that may downplay external validity and suggest some tension between rigour and relevance. Thus, though the concept of relevance is of central importance to the health research enterprise, the failure to unpack it or explore it both theoretically and practically leaves room for misunderstanding and misapplication.
In the health sector, research relevance often arises as a practical question of the ‘fit’ between a body of knowledge or research approach and a specific field or issue (e.g. public health, primary healthcare, healthcare access, genomics, alternative healthcare, healthcare reform in rural areas). The results of two recent International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research task forces take this approach. The task forces developed questionnaires to assess the relevance and credibility of research other than randomised controlled trials (e.g. observational research, meta-network analysis) to inform healthcare decision-making [ 24 , 25 ]. Both make similar observations about relevance, reinforcing the subjectivist approach noted earlier, and can be summarised by the following statement by Berger et al. [ 24 ]:
“ Relevance addresses whether the results of the study/apply [sic] to the setting of interest to the decision maker. It addresses issues of external validity similar to the population, interventions, comparators, outcomes, and setting framework from evidence based medicine. There is no correct answer for relevance. Relevance is determined by each decision maker, and the relevance assessment determined by one decision maker will not necessarily apply to other decision makers. Individual studies may be designed with the perspective of particular decision makers in mind (e.g. payer or provider) ” (p.148, emphasis added).
Research relevance in health is also noted in discussion and debate regarding the value of qualitative research relative to the more established forms of quantitative health research. For example, Mays and Pope [ 26 ] suggest that qualitative research can be assessed “… by two broad criteria: validity and relevance ”. Their further discussion provides some insight into the several ways that research might be relevant, suggesting that:
“[r] esearch can be relevant when it either adds to knowledge or increases the confidence with which existing knowledge is regarded. Another important dimension of relevance is the extent to which findings can be generalised beyond the setting in which they were generated ” [ 27 ].
The work of Mays and Pope positions research relevance amidst the longstanding tension between internal and external validity. This tension reflects opposing foci on internal validity as the quality/rigour of research methodology and external validity as the applicability/transferability of research to other settings or contexts. While external validity is not the only measure of relevance – as research may remain relevant to some contexts even when not generalisable to others – it is an important component, and one that has not always attracted sufficient attention. For example, the Canadian health research community has focused considerable practical attention on internal validity as a critical component of evidence for clinical and health policy decisions. Evidence-based medicine, the Cochrane Collaboration, the Canadian and United States task forces on preventive healthcare/services and a long list of aligned groups have developed and established many tools to assess the quality of research evidence (e.g. GRADE [ 28 ]), with a predominant focus on issues of internal validity, and an emphasis on evidence hierarchies that is sometimes seen to be incompatible with ‘real world’ relevance. The relative lack of similar approaches or tools that focus on external validity in health research is notable, though movements to marshal evidence in support of sound public policy, such as the Campbell Collaboration, have attended to issues of external validity in other areas of health and social policy [ 29 ]. Further, there are emerging approaches and tools for documenting the external validity of health research and facilitating its use [ 30 ]. For example, WHO has supported the development of workbooks to contextualise health systems guidance for different contexts [ 31 ] and the field of local applicability and transferability of research has emerged to facilitate the adaptation of interventions from one setting to another, including the development of some well-documented tools like RE-AIM [ 32 ].
Alongside these emerging approaches and tools sits the established field of KT. KT has a strong history in Canada with a distinctive feature being a reliance on stakeholder engagement to support a commitment to improve research relevance. For example, the AIHS framework relies heavily on KT and stakeholder engagement approaches as part of its RIA, describing the mobilisation of knowledge through “ …a process of interactions, feedback, and engagement using a variety of mechanisms (e.g. collaborations, partnerships, networks, knowledge brokering) with relevant target audiences (i.e. actors and performers) across the health sector ” ([ 8 ] p. 362). Experience in stakeholder engagement, particularly with clinical, management and policy decision-makers, has become fairly extensive and there is now increased attention on engaging patients as core stakeholders in health research. If relevance is truly subjective, then KT efforts (including engagement, dissemination, promotion, communication) would appear to represent reasonable approaches for articulating, conveying and improving research relevance. However, if there are underlying elements of relevance that are more universal, then there is a risk that KT efforts – and subjectivist approaches to ensuring relevance – are akin to commercial marketing or communication strategies where the aim is to ‘sell’ more product and/or generate more influence that may not align with a more objective lens.
In sum, the health research community in Canada has a longstanding history of critically appraising research quality based on study design and research methodology, with greater emphasis on internal rather than external validity. As the same time, there is established expertise in KT, emphasising engagement with research users and adaptation to settings or contexts of use – approaches that may imply a subjectivist interpretation of relevance. Thus, while relevance is an important concept for the health research enterprise, its use is largely tacit and taken for granted.
Non-health sector perspectives
To unpack relevance further we consider some non-health sector perspectives that give attention to the term, often with formal definitions or taxonomies established. Examples include the legal, financial accounting, education and web search (information retrieval) sectors, each of which are briefly described below.
From a legal perspective, relevance has a specific meaning that relates to the admissibility of evidence in terms of its probative value (i.e. the extent to which evidence contributes to proving an important matter of fact) [ 33 ]. For example, a common objection to legal testimony or evidence is that it is ‘irrelevant’ [ 34 ]. Legal processes for considering the admissibility or legal-relevance of evidence are firmly established, requiring explicit declaration of evidentiary sources and direct consideration of that evidence as it relates both to a specific case and related historical precedents, something that is undeveloped in the health sector [ 35 ]. It is the formality, explicitness and retrospective nature of this process, which is directly associated with a specific case (or decision), that is characteristic of the consideration of relevance in the legal context.
Financial accounting provides another perspective on relevance. In this field, relevance is viewed as a fundamental component of generally accepted accounting principles. Relevance and materiality are emphasised such that accountants and auditors focus on financial information that meets the decision-making needs of users and is expected to affect their decisions. In financial accounting, ‘value relevance’ provides a more focused perspective on relevance, defined as “ …the ability of information disclosed by financial statements to capture and summarise firm value. Value relevance can be measured through the statistical relations between information presented by financial statements and stock market values or returns ” [ 36 ]. Similar to the legal perspective, the financial accounting perspective on relevance is set with a formal context, where the focal point (i.e. financial performance) is clear and principles (i.e. generally accepted accounting principles) and processes (i.e. financial reporting and auditing) are clearly established and monitored.
Education provides a slightly more expansive approach to operationalising relevance, given the more general aim of the enterprise. In the United States, the Glossary of Education Reform [ 37 ] notes that “ …the term relevance typically refers to learning experiences that are either directly applicable to the personal aspirations, interests, or cultural experiences of students (personal relevance) or that are connected in some way to real-world issues, problems, and contexts (life relevance) ”. They further state that “ personal relevance occurs when learning is connected to an individual student’s interests, aspirations, and life experiences ”, while “ life relevance occurs when learning is connected in some way to real-world issues, problems, and contexts outside of school ”. A similar framing of relevance in this context suggests that it “…extends the learning beyond the classroom by teaching students to apply what they are learning to real world situations ” [ 38 ]. While the education sector also makes numerous references to a ‘rigour and relevance’ dyad [ 39 ] in contrast to the dominance of the internal validity focus in healthcare, it is the prominent dual focus on ‘personal’ relevance (with its subjectivist orientation) and ‘life’ or ‘real world’ relevance (with its more universal orientation) that seems to most clearly define the education sector’s perspective on relevance.
One of the most intensive and competitive sectors focusing on relevance is the web search (or information retrieval) field. This includes dominant search engines such as Google and Bing, as well as a wide range of commercial and social media sites such as Amazon, eBay, Facebook and LinkedIn, that compete either directly or indirectly on their ability to identify relevant information in response to user queries. Therefore, the ability of these organisations to advance the theory and practice related to relevance is fundamental to their success. For example, Google was built upon the effectiveness of its search algorithm, which is in a constant state of evolution. Both explicit and implicit approaches to assess relevance are used to contribute to search algorithm refinements [ 40 ]. The explicit approach focuses on ‘relevance ratings’, whereby evaluators (e.g. human raters) are contracted to assess the degree of ‘helpfulness’ of search results paired to specific search queries [ 41 ]. The implicit approach to assess relevance monitors and aggregates search behaviour of millions of users who are likely unaware that their behaviour is being assessed. Google has more recently advanced ‘personalised relevance’, which uses past individual search behaviour to personalise/tailor future search results for the same individual. Pariser has critiqued this concept as “ the filter bubble ” [ 42 ], warning that Google’s intent to optimise search algorithms for personal relevance creates a “ …personal ecosystem of information… ” that limits the diversity of search results and promotes insularity. This personal relevance is situated within the pervasiveness of social media, which facilitates the advancement of ‘social relevance’. Personal and social relevance highlight two important orientations towards relevance – one built on increasingly detailed understanding of individual preferences and the other reflecting the growing power and increasing accessibility of crowd-sourced perspectives. Overall, web search has made important contributions to how we understand and operationalise relevance, including the use of increasingly sophisticated explicit and implicit feedback mechanisms and the ability to draw upon and analyse big data sets. Web search has also exposed the contrasting orientations of personal and social relevance that underscore the challenges of combining or integrating different relevance assessments.
These non-health sector perspectives on relevance highlight several considerations. First, they reinforce general findings that point to perspective, decision context, timeliness and precision of focus or ‘fit’ as key elements of relevance. Additionally, they highlight a few distinctive considerations. The formalistic contexts of financial accounting and law emphasise issues such as precedent and legitimacy, implying that relevance in a research sense might require the demonstration of some legitimate or credible association between research and its use or user, among other considerations. Further, the complex consumerist world of social media highlights some of the challenges of a purely subjectivist definition of relevance. Whereas the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research guidance takes a subjectivist stance in suggesting that, “[t] here is no correct answer for relevance ” [ 24 ], the “ filter bubble ” criticised by Pariser [ 42 ] suggests otherwise. Relevance solely to the personally-perceived interests of a research user is unlikely to adequately serve the collective commitments to health and health equity that are especially germane to the health research enterprise.
Forward-looking considerations for assessing the relevance of health research
To this point, we have endeavoured to unpack relevance from theoretical and practical perspectives. In light of these insights and in the context of persistent interest in research impact assessment and evolving interest in research relevance, we now turn to some specific forward-looking considerations for research relevance assessment (RRA).

Relevance of research versus everything else
The first consideration for RRA is the acknowledgement that research is only one of many sources of insight to inform the needs or actions of research users. A research user is influenced by a wide range of political, legal, media, economic and other contextual information, interactions and experiences, as well as prevailing organisational governance, leadership, culture and values that all serve to complement (and often dominate) any insights that might be derived from research [ 43 ]. This reality implies that ‘relevance’ has a different meaning for researchers and research users. Researchers are typically interested in the relevance of a specific research product or activity for identifiable actions of (potentially) multiple research users; relevance is here judged relative to both the perceived needs of research users, and the extent and content of other related research. In contrast, research users are typically focused on identifying multiple relevant inputs to guide a specific action, only some of which may be research; relevance is here judged relative to both the research user’s needs and the form and content of the other inputs.
Given these distinct orientations to research relevance, RRA needs to be explicit about its comparative lens. Clear distinctions should be made between relevance based on the merits of the research product or activity (researcher lens) and relevance based on the relative value of research compared to other research and non-research sources (research user lens). RRA provides an opportunity to build more robust ways to characterise and assess the contribution of research to research users, including a more systematic and transparent articulation of anticipated research uses (akin to the Research Councils UK’s ‘Pathways to Impact’ [ 44 ] or descriptions of planned study design and methodological approach published in study protocols/registrations for randomised controlled trials or systematic reviews).
Beyond instrumental uses of research
The considerations noted above rely heavily on instrumental uses of research. Theoretically derived definitions of relevance, such as Floridi’s [ 14 ], tend to focus on the response to a specified question. This suggests a direct and tangible connection between research and its ‘use’. However, as Weiss [ 43 ] and others have observed, most types of research use are not instrumental, where use is documented and explicitly addresses a specific query or challenge for a research user. Rather, research use tends to be more conceptual, where use is indirect and evolves over time, or symbolic, where use may be politically or tactically motivated [ 43 ]. Research may also create externalities or unintended effects. For example, general research activity might support an engaged learning environment, interactive research relationships, and additional research-related discourse that provides benefits that are not attributable to any specific research product or activity. This has important ramifications for how research is funded and the role that relevance can play in that assessment. Ultimately, RRA needs to go beyond a singular understanding of research use as instrumental use, to develop better methods for capturing and assessing the relevance of the many non-instrumental uses of research.
The temporal factor
Another closely related consideration for RRA is the temporal context. Almost all research is conducted in a temporally defined period. Yet, while the quality of research is typically characterised by its methodology, which is a static feature typically not subject to temporal variation (e.g. the assessed quality of a randomised controlled trial should be consistent over time), relevance of research can be considered at any time (e.g. prior to the initiation of a research study or at different points in time post-completion) and is therefore subject to dynamic perceptions as they pertain to evolving action or decision contexts. Cohen [ 15 ] suggests that “ …relevance, like reasoning, has a prospective dimension as well as a retrospective one. It helps prediction as well as explanation ” (p. 182). The important insight is that, in contrast to research quality, the relevance of a specific research product can change over time, making assessment of research relevance more challenging.
This requires RRA to acknowledge the temporal factor and its associated implications for research relevance. At minimum, RRA should specify the temporal context as either pre-research (e.g. proposal/funding stage) or post-research (e.g. after research results have been produced). RRA at the pre-research stage focuses on proposed inputs and hypothetical outputs and outcomes, and may be more likely to overestimate instrumental research use and underestimate non-instrumental use. RRA at the post-research stage focuses mainly on the importance and value of actual outputs and tangible results, and may capture more non-instrumental research use. The pre-research stage is clearly aligned with research funding/investment processes, while the post-research stage can contribute to retrospective return-on-investment calculations and more general research impact assessment. However, employing this simple temporal categorisation should not lead us to lose sight of the dynamic, iterative nature of research relevance and the opportunity to assess it at interim and ongoing stages that captures re-interpretations or re-applications of research findings over time.
Moving from a subjective to an intersubjective understanding of relevance
An underlying theme in our review of relevance is subjectivity. Consider the broad scientific paradigms of positivism and interpretivism that are typically respectively aligned with research quality and research relevance. Research quality can be viewed as relating to characteristics or features that are assessed objectively, while research relevance may be seen as subjectively adjudicated. The subjective focus emphasises the variability of different perspectives and contexts and the suggestion that anyone can have a different take on the relevance of a specific research product or activity. For RRA, this reinforces a user-centred orientation to relevance assessment that privileges the judgment of the interrogator and raises the key question regarding who is positioned as the main arbiter of research relevance.
However, while relevance may never be characterised as universal, it could be argued that it is not purely subjective either. Rather, relevance may be more consistent with an intersubjective understanding that emphasises the extent of agreement or shared understanding among individual subjective perspectives representing a way to bridge the personal and the universal. The intersubjective view, while not presenting an objective approach to measuring relevance, does provide a road towards a meaningful and structured assessment of research relevance. It also emphasises the importance of representation in forging the intersubjective judgments that guide the research enterprise.
This paper has unpacked research relevance from different perspectives and outlined key considerations for its assessment. Alongside research impact assessment, research relevance seems increasingly important in justifying research investments and guiding strategic research planning. Indeed, judgments of ‘relevance’ are becoming a key component of the health research enterprise. However, consideration of relevance has been largely tacit in the health research community, often depending on unexplained interpretations of value, fit and potential for impact. Reviewing the various uses of relevance in health research, the concept is sometimes used as a synonym for research impact or positioned as a reliable predictor of later consequence. In many ways, research relevance seems a necessary condition for impact – a process or component of efforts to make rigorous research usable. However, relevance is not a necessary or sufficient condition to achieve impact. We expect that research that is relevant, and thus accountable to specific and legitimate users, will be impactful, but this may not necessarily be the case where other factors intervene. Additionally, we may expect that research that is impactful will be appropriately accountable – but again, this is not necessarily the case. Ultimately, relevance stands apart from research impact. Like rigour, relevance is a complementary but distinctive dimension of what it is that ensures ‘the good’ in health research.
While ‘relevance’ is ever-present, understanding of the concept in terms of health research is emergent and not well codified. To improve our understanding, this paper outlines four key considerations, including how research relevance assessments (1) orientate to, capture and compare research versus non-research sources, (2) consider both instrumental versus non-instrumental uses of research, (3) accommodate dynamic temporal-shifting perspectives on research, and (4) align with an intersubjective understanding of relevance. We believe careful and explicit consideration of research relevance, guided by transparent principles and processes is vital to gauge the overall value and impact of a wide range of individual and collective research efforts and investments. We hope this paper generates more discussion and debate to facilitate progress.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of participants of a roundtable discussion to gather feedback on an earlier version of this paper. Participants included Simon Denegri, National Director for Public Participation and Engagement in Research, National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) UK, and Chair of INVOLVE, UK; Lee Fairclough, Vice-President, Quality Improvement, Health Quality Ontario; Michael Hillmer, Director, Planning, Research and Analysis Branch, Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care; John McLaughlin, Chief Science Officer and Senior Scientist, Public Health Ontario; Allison Paprica, Director, Strategic Partnerships, ICES; Michael Schull, President and CEO, ICES; and Vasanthi Srinivasan, Executive Director, Ontario Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research (SPOR) SUPPORT Unit (OSSU). We also want to thank John Lavis of the McMaster Health Forum for his very helpful comments on an earlier draft. Though we owe these individuals and organisations many thanks for their insights and support, we alone are responsible for the final product.
This work was commissioned by the Ontario SPOR Support Unit (OSSU). The executive director of the OSSU was one of the participants in a roundtable discussion to gather feedback on an earlier version of this paper, but beyond that, the OSSU did not have any role in the design of the study, collection, analysis or interpretation of the data, or writing of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
Authors’ contributions.
ADB acquired funding for the study. MJD, FAM and ADB conceptualised the study. MJD, FAM, CF and ADB participated in the review and writing of the manuscript. MJD, FAM and ADB participated in the roundtable discussion. MJD, FAM and ADB reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript (CF passed away prior to submission of the manuscript).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
| AIHS | Alberta Innovates – Health Solutions |
| CAHS | Canadian Academy of Health Sciences |
| CHSRF | Canadian Health Services Research Foundation |
| CIHR | Canadian Institutes of Health Research |
| KT | knowledge translation |
| OSSU | Ontario SPOR SUPPORT Unit |
| RIA | research impact assessment |
| RRA | research relevance assessment |
| SPOR | Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research |
This article is dedicated to the memory of Dr Cy Frank, our co-author and esteemed colleague, whose untimely death occurred midway through development of this work. Among his many interests, Dr Frank was a champion for improving understanding of research impact assessment and provided many insights on the concept of research relevance, some of which we expand upon in this article. His many contributions to the health sector will live on, but he will be greatly missed.
Contributor Information
Mark J. Dobrow, Email: [email protected] .
Fiona A. Miller, Email: [email protected] .
Adalsteinn D. Brown, Email: [email protected] .
Medical Imaging
Uncover the latest and most impactful research in Medical Imaging. Explore pioneering discoveries, insightful ideas and new methods from leading researchers in the field.
Latest research
Presentation of mitral valve cleft with concurrent atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect detected by three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography: a case report.
- Azin Alizadehasl
- Ehsan Amini-Salehi
- Sara Nobakht
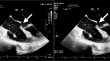
Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function in patients with iron deficiency anemia based on non-invasive left ventricular pressure–strain loops
- Xiaoyan Wang

Flow Matters: Optimizing Invasive Coronary Physiology to Improve Long-Term Outcomes
- Barry F. Uretsky
A novel robotic surgical assistant for total knee arthroplasty has a learning curve ranging from 6 to 14 cases and exhibits high accuracy in tibial bone cuts
- Nimit Thongpulsawad
- Chaiwat Achawakulthep
- Tawan Intiyanaravut

Machine Learning in Biliary Atresia: Taking a Cautious Step into the Future
- Rishi Bolia
Standardizing feeding strategies for preterm infants born greater than 1500 grams
- Ting Ting Fu
- Maame Arhin

Related journals

BMC Medical Imaging
BMC Medical Imagingis an open access journal publishing original peer-reviewed research articles in the development, evaluation, and use of imaging...

Current Cardiovascular Imaging Reports
Cardiovascular imaging technologies now play an expanded role in clinical practice. Beyond the diagnosis of a disease process, these techniques are...

EJNMMI Reports
EJNMMI Reportsis the inclusive science journal of the EJNMMI journal family. It is a peer-reviewed open access journal, following international...
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Heart disease is rampant in parts of the rural South. Researchers are hitting the road to learn why
Darrell Dixon holds a photo of him and his dad, Darrell Dixon Sr., at his home in Hernando, Miss., on August 11, 2024. (Millicent Dixon via AP)
A medical trailer, being used to test rural residents’ heart and lung function as part of a study to determine why the rates of heart and lung disease are so much higher in the rural South, is seen, May 8, 2024, in Napoleonville, La. (Sean Coady/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute via AP)
A billboard for a new study about why heart and lung disease is so much higher in the rural South is seen in Napoleonville, La., on May 8, 2024. (Sean Coady/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute via AP)
- Copy Link copied
Darrell Dixon’s father was just 25 when he had a major heart attack in the rural Mississippi Delta. By his early 40s, a series of additional attacks had left his heart muscle too weak to pump enough blood to his body. He died in 2013 at the age of 49.
“It was a big jolt for our family,” Dixon, 36, recalled. “For myself, personally, it also got me thinking about heredity. I just wondered whether I was next.”
The death spurred Dixon to get involved in an unusual and ambitious new health study.
Public health experts from some of the nation’s leading research institutions have deployed a massive medical trailer to rural parts of the South to test and survey thousands of local residents. The goal: to understand why the rates of heart and lung disease are dramatically higher there than in other parts of the U.S.
“This rural health disadvantage, it doesn’t matter whether you’re white or Black, it hurts you,” said Dr. Vasan Ramachandran, a leader of the project who used to oversee the Framingham Heart Study — the nation’s longest-running study of heart disease. “No race is spared, although people of color fare worse.”
The researchers aim to test the heart and lung function of roughly 4,600 residents of 10 counties and parishes in Alabama, Kentucky, Louisiana and Mississippi while collecting information about their environments, health history and lifestyles. They are also giving participants a fitness tracker and plan to survey them repeatedly for years to check for any major medical events.
Ramachandran, now dean of the University of Texas School of Public Health in San Antonio, said rural populations in the U.S. rarely receive such personal, long-term attention from epidemiologists. More than a dozen institutions are helping with the study, including Johns Hopkins University, the University of California, Berkeley, and Duke University.
The 52-foot-long (16-meter-long), 27-ton trailer is outfitted with instruments that examine calcium in the arteries, the structure of the heart, lung capacity and other, more common health indicators such as blood pressure and weight. The initial exam can take more than three hours.
“They’re reaching out and going out into the community in ways that I have not seen before,” said Lynn Spruill, the mayor of Starkville, Mississippi, in Oktibbeha County, where the trailer arrived in 2022 and medical staff tested more than 700 people.
Studies and data from U.S. health officials show rural populations in the U.S. are unhealthier and have lower life expectancy than Americans in urban areas. The health disparity is even greater in the South, where mortality rates from heart disease — the leading cause of death in the U.S. — for people 35 and older are more than twice the national average in some rural communities. Lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, which the study is also examining, are also more prevalent in the South.
Researchers have multiple theories for the disparity. Hospital closures and physician shortages have left many rural residents with limited access to care. Healthy food, fitness opportunities and public transit are often scarcer. Poverty rates are higher, and fewer people receive health coverage through their employers. In the rural South, poverty rates and the share of people without health insurance are even greater.
Smoking cigarettes is a major cause of heart disease, and at least 20% of adults smoked in Alabama, Kentucky, Louisiana and Mississippi , according to 2019 data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Obesity is another factor. In 2022, self-reported height and weight put between 38% and 40% of adults in the four states in the obese body mass index category.
By closely examining local residents and their environments, the rural study seeks clearer answers about what’s driving the additional health burden in the South. Researchers also want to understand what makes some rural counties there much healthier than others.
“We’re interested in both the risk, but also the resilience piece of it,” said Lindsay Pool, an epidemiologist with the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, which has awarded more than $40 million for the study.
To accomplish that goal, researchers are also visiting rural areas with low risk for heart and lung disease in three of the states — Louisiana, Mississippi and Kentucky — despite similar demographics.
Oktibbeha County, home to Mississippi State University, in the eastern part of Mississippi near the Alabama border, is the low-risk location. The researchers are contrasting it with Panola County in northern Mississippi about 60 miles (97 kilometers) south of Memphis, Tennessee.
Both counties have poverty rates that exceed 20% and a similar and sizeable share of people under 65 without health insurance. But between 2019 and 2021, the death rate from heart disease for those 35 and over was 647 per 100,000 people in Panola County compared to 395 per 100,000 in Oktibbeha County, according to CDC data .
In more urban Rankin County, Mississippi, part of the Jackson metro area, the figure was 331. The U.S. average over the same period was 326.
Dixon, who works in Panola County for a regional development organization and serves as a consultant for the heart and lung study, helped recruit more than 600 Panola County residents for the project. Heart conditions are so prevalent there that it’s common to hear people discussing their medications and side effects at local shops and churches, he said.
Dixon’s father, Darrell Dixon Sr., lived in Clarksdale, about 40 miles (64 kilometers) west of Panola County. He long suffered from high blood pressure and had a strong family history of heart disease.
He had an additional major heart attack after an inmate he had grown close to as chaplain of the Mississippi State Penitentiary was executed, Dixon said, and then spent the last years of his life in and out of the hospital with congestive heart failure.
“He really suffered,” Dixon said. He hopes the study will shed light on any unseen environmental factors that may have played a role in his dad’s death and raise awareness among local residents about “how to live better.”
The trailer is now in Louisiana’s northeastern Franklin Parish, where the death rate from heart disease between 2019 and 2021 was a whopping 859 per 100,000 people for those 35 and over, according to the CDC data. About 200 miles (322 kilometers) south in New Orleans, it was 340.
The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute plans to extend the study to 2031, and researchers hope to examine all the participants in person again.
“The longer you can follow people, the more you can understand disease development and progression,” Pool, the epidemiologist, said.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Collection 29 March 2022
2021 Top 25 Health Sciences Articles
We are pleased to share with you the 25 most downloaded Nature Communications articles* in health sciences published in 2021. (Please note we have a separate collection on the Top 25 COVID-19 papers .) Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an international community.
Browse all Top 25 subject area collections here .
*Data obtained from SN Insights (based on Digital Science's Dimensions) and normalised to account for articles published later in the year.
Research highlights

Association of sleep duration in middle and old age with incidence of dementia
Sleep dysregulation has been linked to dementia, but it is unknown whether sleep duration earlier in life is associated with dementia risk. Here, the authors show higher dementia risk associated with short sleep duration (six hours or less) in a longitudinal study of middle and older age adults.
- Séverine Sabia
- Aurore Fayosse
- Archana Singh-Manoux
Longitudinal analysis of blood markers reveals progressive loss of resilience and predicts human lifespan limit
Aging is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases and functional decline. Here, the authors investigate the fluctuations of physiological indices along aging trajectories and observed a characteristic decrease in the organism state recovery rate.
- Timothy V. Pyrkov
- Konstantin Avchaciov
- Peter O. Fedichev
Restoration of energy homeostasis by SIRT6 extends healthy lifespan
Aging is associated with increased frailty and disrupted energy homeostasis. Here, the authors show that SIRT6 overexpression extends the lifespan of male and female mice and demonstrate that SIRT6 optimizes energy homeostasis in old age, which delays frailty and preserves healthy aging.
- A. Roichman
- S. Elhanati
- H. Y. Cohen
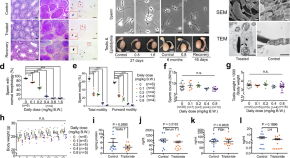
Triptonide is a reversible non-hormonal male contraceptive agent in mice and non-human primates
No male contraceptive pills are currently available. Here, the authors use triptonide, a compound derived from a Chinese plant, to deform sperm so that they cannot move properly, thereby causing reversible infertility in male mice and monkeys.
- Zongliang Chang
- Weibing Qin
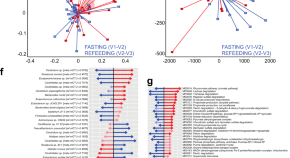
Fasting alters the gut microbiome reducing blood pressure and body weight in metabolic syndrome patients
Nutritional modification including fasting has been shown to reduce cardiometabolic risk linked to western diet. Here the authors show implementation of fasting resulted in alterations to the intestinal microbiota, and circulating immune cells, improving blood pressure and body weight in patients with metabolic syndrome.
- András Maifeld
- Hendrik Bartolomaeus
- Sofia K. Forslund
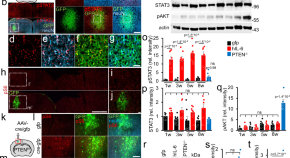
Transneuronal delivery of hyper-interleukin-6 enables functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury in mice
The CNS has limited ability to regenerate following injury, Here, the authors show that a single injection of AAV-hyper-interleukin-6 in the sensory motor cortex results in corticospinal and raphe spinal tracts regeneration in the injured spinal cord as well as functional recovery in mice.
- Marco Leibinger
- Charlotte Zeitler
- Dietmar Fischer
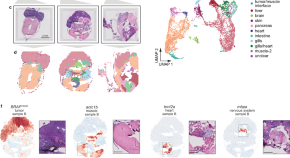
Spatially resolved transcriptomics reveals the architecture of the tumor-microenvironment interface
During tumor progression, cancer cells contact different neighboring cell types, but it is unclear how these interactions affect cancer cell behavior. Here, the authors use spatially resolved transcriptomics and single-cell RNA-seq to study the role of cilia at the tumormicroenvironment interface.
- Miranda V. Hunter
- Reuben Moncada
- Richard M. White
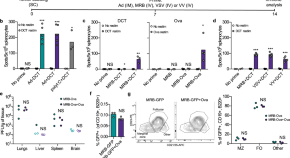
Adjuvant oncolytic virotherapy for personalized anti-cancer vaccination
Viruses expressing tumour antigens can prime and boost anti-tumour immunity but the efficiency of this approach depends on the capacity of the virus to infect the host. Here, the authors show that vaccination with oncolytic viruses co-administered with tumour antigenic peptides is as efficient as antigen-engineered oncolytic viruses.
- K. Geoffroy
- M.-C. Bourgeois-Daigneault
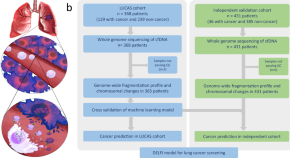
Detection and characterization of lung cancer using cell-free DNA fragmentomes
DNA from tumour cells can be detected in the blood of cancer patients. Here, the authors show that cell free DNA fragmentation patterns can identify lung cancer patients and when this information is further interrogated it can be used to predict lung cancer histological subtype.
- Dimitrios Mathios
- Jakob Sidenius Johansen
- Victor E. Velculescu
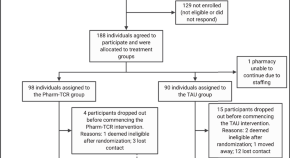
A randomized controlled trial of pharmacist-led therapeutic carbohydrate and energy restriction in type 2 diabetes
Community pharmacists are accessible healthcare providers with expertise in medication management. Here the authors show that a low-carbohydrate, low-energy diet implemented by community pharmacists reduced diabetes medication use and improved glucose control in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Cody Durrer
- Sean McKelvey
- Jonathan P. Little

A metabolome atlas of the aging mouse brain
Metabolites play an important role in physiology, yet the complexity of the metabolome and its interaction with disease and aging is poorly understood. Here the authors present a comprehensive atlas of the mouse brain metabolome and how it changes during aging.
- Oliver Fiehn
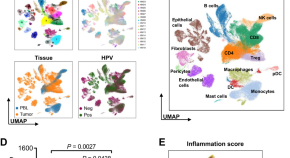
Investigating immune and non-immune cell interactions in head and neck tumors by single-cell RNA sequencing
The tumor microenvironment (TME) has an important role in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) progression. Here, using single-cell RNA sequencing and multiplexed imaging, the authors report the cellular complexity of the TME in patients with HNSCC, exploring inflammatory status, stromal heterogeneity and immune checkpoint receptor-ligand interactions.
- Cornelius H. L. Kürten
- Aditi Kulkarni
- Robert L. Ferris
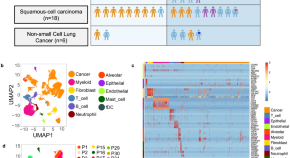
Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Comprehensive profiles of tumour and microenvironment are critical to understand heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Here, the authors profile 42 late-stage NSCLC patients with single-cell RNA-seq, revealing immune landscapes that are associated with cancer subtype or heterogeneity.
- Fengying Wu
- Caicun Zhou
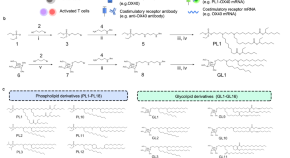
Biomimetic nanoparticles deliver mRNAs encoding costimulatory receptors and enhance T cell mediated cancer immunotherapy
Antibodies targeting OX40 or CD137, two T cell costimulatory receptors, have been shown to improve antitumor immunity. Here the authors design a phospholipid-derived nanoparticle to deliver OX40 or CD137 mRNA to T cells in vivo, improving efficacy of anti-OX40 and anti-CD137 antibody therapy in preclinical tumor models.
- Xinfu Zhang
- Yizhou Dong
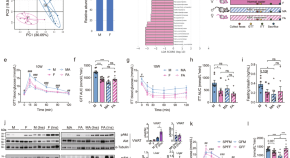
Sexual dimorphism in glucose metabolism is shaped by androgen-driven gut microbiome
Male sex is a risk factor for impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes. Here the authors identify that androgen modulates the gut microbiome, which drives insulin resistance and contributes to sexual dimorphism in glucose metabolism in mice.
- Weiqing Wang
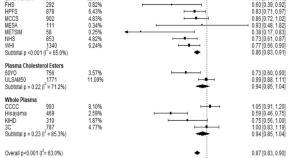
Blood n-3 fatty acid levels and total and cause-specific mortality from 17 prospective studies
Associations between of omega-3 fatty acids and mortality are not clear. Here the authors report that, based on a pooled analysis of 17 prospective cohort studies, higher blood omega-3 fatty acid levels correlate with lower risk of all-cause mortality.
- William S. Harris
- Nathan L. Tintle
- The Fatty Acids and Outcomes Research Consortium (FORCE)
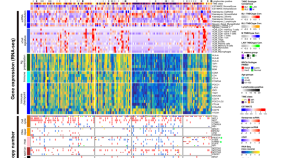
Multi-omics analysis identifies therapeutic vulnerabilities in triple-negative breast cancer subtypes
Triple negative breast cancer can be divided into additional subtypes. Here, using omics analyses, the authors show that in the mesenchymal subtype expression of MHC-1 is repressed and that this can be restored by using drugs that target subunits of the epigenetic modifier PRC2.
- Brian D. Lehmann
- Antonio Colaprico
- X. Steven Chen
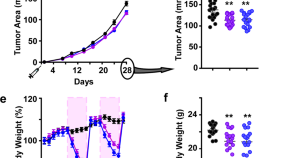
Daily caloric restriction limits tumor growth more effectively than caloric cycling regardless of dietary composition
Caloric restriction (CR) has been shown as an effective intervention to reduce tumorigenesis, but alternative less stringent dietary interventions have also been considered. Here, the authors show that in a murine model of breast cancer CR has a larger effect on preventing tumorigenesis and metastasis compared to periodic caloric cycling.
- Laura C. D. Pomatto-Watson
- Monica Bodogai
- Rafael de Cabo
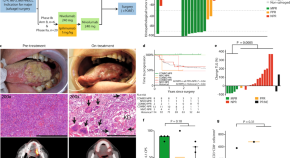
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab induces major pathological responses in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Immune checkpoint blockade has become standard care for patients with recurrent metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Here the authors present the results of a non-randomized phase Ib/IIa trial, reporting safety and efficacy of neoadjuvant nivolumab monotherapy and nivolumab plus ipilimumab prior to standard-of-care surgery in patients with HNSCC. .
- Joris L. Vos
- Joris B. W. Elbers
- Charlotte L. Zuur
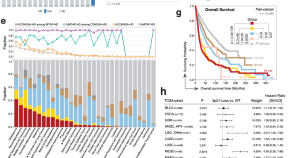
9p21 loss confers a cold tumor immune microenvironment and primary resistance to immune checkpoint therapy
The molecular mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint therapy remain elusive. Here, the authors perform immunogenomic analysis of TCGA data and data from clinical trials for antiPD-1/PD-L1 therapy and highlight the association of 9p21 loss with a cold tumor microenvironment and resistance to therapy.
- Guangchun Han
- Guoliang Yang
- Linghua Wang
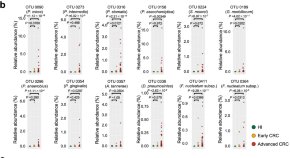
Gut bacteria identified in colorectal cancer patients promote tumourigenesis via butyrate secretion
Several bacteria in the gut microbiota have been associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) but it is not completely clear whether they have a role in tumourigenesis. Here, the authors show enrichment of 12 bacterial taxa in two cohorts of CRC patients and that two Porphyromonas species accelerate CRC onset through butyrate secretion.
- Shintaro Okumura
- Yusuke Konishi
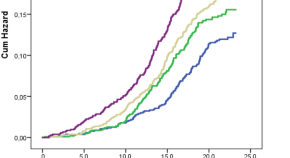
Elevated circulating follistatin associates with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes
Follistatin promotes in type 2 diabetes (T2D) pathogenesis in model animals and is elevated in patients with T2D. Here the authors report that plasma follistatin associates with increased risk of incident T2D in two longitudinal cohorts, and show that follistatin regulates insulin-induced suppression lipolysis in cultured human adipocytes.
- Chuanyan Wu
- Yang De Marinis
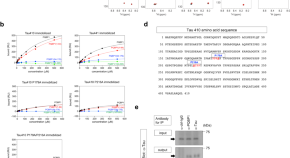
Tau activates microglia via the PQBP1-cGAS-STING pathway to promote brain inflammation
Brain inflammation generally accelerates neurodegeneration but the mechanisms of this are not fully characterised. Here the authors show that PQBP1 in microglia is important for sensing extrinsic Tau 3 R/4 R proteins and triggers an innate immune response through cGAS and STING resulting in cognitive impairment.
- Hiroki Shiwaku
- Hitoshi Okazawa
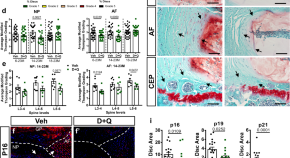
Long-term treatment with senolytic drugs Dasatinib and Quercetin ameliorates age-dependent intervertebral disc degeneration in mice
Intervertebral disc degeneration is a leading cause of chronic back pain and disability. Here the authors show that long term treatment with senolytic compounds Dasatinib and Quercetin reduces disc senescence burden and ameliorates age-dependent degeneration in mice.
- Emanuel J. Novais
- Victoria A. Tran
- Makarand V. Risbud
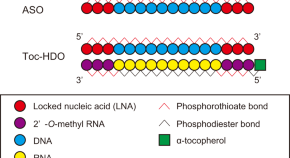
DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide technology for regulating lymphocytes in vivo
Using gene silencing to regulate lymphocyte function is a promising therapeutic approach for autommunity, inflammation and cancer. Here the authors use a heteroduplex oligonucleotide for improved potency, efficacy and longer retention times.
- Masaki Ohyagi
- Tetsuya Nagata
- Takanori Yokota
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 30, Number 10—October 2024
One Health Investigation into Mpox and Pets, United States
Suggested citation for this article
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) is zoonotic and capable of infecting many mammal species. However, whether common companion animals are susceptible to MPXV infection is unclear. During July 2022–March 2023, we collected animal and environmental swab samples within homes of confirmed human mpox case-patients and tested for MPXV and human DNA by PCR. We also used ELISA for orthopoxvirus antibody detection. Overall, 12% (22/191) of animal and 25% (14/56) of environmental swab samples from 4 households, including samples from 4 dogs and 1 cat, were positive for MPXV DNA, but we did not detect viable MPXV or orthopoxvirus antibodies. Among MPXV PCR-positive swab samples, 82% from animals and 93% the environment amplified human DNA with a statistically significant correlation in observed cycle threshold values. Our findings demonstrate likely DNA contamination from the human mpox cases. Despite the high likelihood for exposure, however, we found no indications that companion animals were infected with MPXV.
Before 2022, the primary mode for monkeypox virus (MPXV) transmission was known to be zoonotic, and only limited human-to-human transmission was documented ( 1 , 2 ). Human MPXV infections resulting in mpox disease were hypothesized to be the result of direct or potentially indirect contact with infected wild mammals in Central and Western Africa ( 3 , 4 ). Our understanding of the potential for human-to-human spread of MPXV considerably broadened in the spring of 2022 ( 5 , 6 ). During that time, variant of clade II MPXV (clade IIb) was found in to be transmitted via direct contact among human populations and spreading primarily through sexual networks outside of mpox endemic regions ( 5 , 6 ).
Given the zoonotic origin and reported broad host-range of MPXV, efforts to understand and limit potential human-to-animal transmission are ongoing ( 4 , 7 ). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides guidance that persons with mpox stop or avoid contact with animals and that animals should be kept away from potentially infectious lesion material, objects, or surfaces ( 8 ). Mpox patients are generally urged by public health agencies to isolate at home unless hospitalization is clinically necessary ( 9 , 10 ). A person with mpox is considered infectious throughout their illness and until lesions have fully healed with new skin underneath; therefore, public health officials recommend that mpox patients isolating at home take proper infection control measures to prevent spread of infectious particles throughout the home ( 11 – 13 ). Unless infected persons take measures to completely isolate or reduce transmission potential, companion animals in close contact with mpox patients and their environments could be at higher risk for MPXV exposure than other mammal species, warranting special concern and investigation.
As of July 2024, no cases of MPXV infection or mpox disease had been confirmed in common domestic animals, such as dogs and cats, during the current global outbreak or any past outbreaks. One study in July 2022 described a 4-year-old dog in France that had been living and co-sleeping with 2 mpox case-patients ( 14 ). In that study, MPXV DNA was identified in swab samples from the dog’s skin and surface of mucosal lesions and in anal and oral swab samples ( 14 ). However, follow-up investigations suggested that the animal was not infected with MPXV ( 15 ). A similar case was documented in Brazil in August 2022, when a 5-month-old dog had lesions that were MPXV-positive by quantitative PCR ( 16 ). Whether viral DNA detection was a result of MPXV infection in those animals or the result of environmental contamination due to close contact with infected humans is unclear. We conducted a One Health investigation in the United States to assess the susceptibility of companion animals to mpox and the risk for reverse-zoonotic transmission within households.
Methods and Materials
Study population.
The CDC Muti-National Mpox Response’s One Health Team worked in collaboration with state and local jurisdictions to investigate the susceptibility of companion animals to MPXV infection. As part of that effort, CDC and state public health investigators collected blood samples from companion animals and swab specimens from companion animals and animal-associated objects. CDC tested swab and serum specimens via real-time PCR, orthopoxvirus (OPXV) serology, and viral culture. All animals tested were companion animals in a residence of a person with probable or confirmed mpox while the person was infectious. Animal sampling occurred within 21 days of any direct contact with the ill person before the person recovered ( Table 1 ).
During July 2022–March 2023, we conducted sample collection in the District of Columbia, Virginia, Minnesota, and Tennessee, USA. After the initial sampling timepoint, we attempted follow-up sampling from all households 3–4 months later to collect animal serum samples and assess postexposure or postinfection immune responses.
Questionnaire and Consent
State and local public health personnel from the District of Columbia, Virginia, Minnesota, and Tennessee assisted with the study by interviewing mpox cases in their jurisdictions and requesting their voluntary participation in the study. After a person gave verbal consent to participate, they were provided with a survey questionnaire and consent forms. The questionnaire ascertained details and a timeline of the human case, the animal’s health condition, general household information, types of contact between the person with mpox and the animal or animals in the household, and information about wild or domestic animals in and around the household. This project was reviewed by CDC clearance, cleared for human subjects, and determined to be nonresearch public health surveillance that did not require submission to the CDC institutional review board (project no. 0900f3eb81f79d72).
Swab Sample Collection
We performed all animal handling and sampling procedures in accordance with the approved CDC Institutional Animal Care Use Committee protocol (no. DOTMULX3183), in collaboration with state public health agencies, and with written consent of the animal’s owner. We collected a standardized set of polyester swab (Puritan, https://www.puritanmedproducts.com ) samples from the animal’s dorsum fur, ventral abdomen, oral cavity, and anorectal area under supervision of the owner. We sampled animal lesions, if present. We also collected animal-associated environmental (AAE) specimens from objects and surfaces often used by the animal.
Sample Processing and PCR
We processed swab samples by using the swab extraction tube system (SETS; Roche, https://www.roche.com ) with 400 μL of phosphate-buffered saline; after DNA extraction, we tested all samples for MPXV DNA by real-time PCR using an MPXV clade II–specific assay ( 17 ). In addition, we tested samples for human DNA by using the RNase-P PCR assay, which is used as an endogenous control when testing human specimens ( 18 ). We calculated Pearson correlation coefficients to assess the relationship between cycle threshold (Ct) values of MPXV clade II PCR–positive (Ct values < 37) and RNase-P reactive (Ct values <40) samples.
Viral Culture
We tested all PCR-positive swab samples for viable virus via cell culture by adding an aliquot of swab eluate to BSC-40 cell monolayers in T-25 flasks. We used an inoculation volume of 50 μL + 25 μL, depending on available eluate volume. We incubated flasks at 35.5°C in an atmosphere of 6% CO 2 in Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium ( 19 ). We incubated and observed flasks < 14 days or until ≈100% of monolayer showed cytopathic effect, following methods and media supplements described previously ( 11 ). To control the overgrowth of bacteria or fungi in T-25 flasks, we added penicillin/streptomycin, amphotericin B, and gentamicin to the cell culture medium. If we detected any bacterial or fungal contamination, we performed 4 cycles of medium replacement to wash the monolayers and repeated this process as needed to prevent overgrowth.
Blood Collection and Serologic Testing
We attempted blood collection from all cooperative animals for which the owner provided consent. We collected < 3 mL of blood from 20/34 animals during initial sampling and 21/25 animals during follow-up sampling. We cleaned the external venipuncture site with 90% ethanol and used a syringe or vacutainer needle for blood collection. For dogs and 1 rabbit, we collected blood via the cephalic or lateral saphenous veins. For cats, we collected blood via the jugular or medial saphenous veins. We stored and transported blood tubes at 4°C–20°C before centrifugation, after which we transferred serum into 2-mL cryotubes and stored at temperatures of at least –20°C until laboratory testing. We conducted a modified ELISA on all serum samples to determine presence of OPXV IgG antibodies, as previously described ( 20 , 21 ). We tested serum samples at a dilution of 1:100 by using microtiter plates coated with purified vaccinia virus (Dryvax strain) and using the A/G protein as the secondary antibody at a 1:10,000 concentration and developed plates for 25 minutes.
Data Analysis
When referring to animal swab samples, we defined prevalence as the proportion of total swabs collected from each animal from which we detected either MPXV DNA or RNase-P (RNP) by PCR. When referring to AAE samples, we defined prevalence as the proportion of total swabs collected from the AAE samples within that animal’s household that were MPXV-positive or RNP-positive. We also referred to detection of RNase-P via PCR as presence of human DNA.
For each animal, we calculated the duration of exposure, defined as cumulative number of days before sampling that an infectious owner had direct contact with the animal, including durations where direct contact was not reported but the animal was still sharing a common space with a person with mpox. Duration of exposure represented the total period that infectious lesion material (crusts or exudates) or other infectious particles were potentially shed or transferred within the home, to which the animal potentially had contact, either directly or via fomites.
We investigated factors reported in questionnaires that could affect animal MPXV exposure ( Table 1 ). Those factors included whether the owner was symptomatic during time of sampling (coded SXDS); the degree of animal outdoor activity (coded AOA), which we stratified by none (no outdoor activity), walks (periodic or frequent supervised walks outside), and yard (allowed in yard or outside unsupervised frequently or for prolonged periods); co-sleeping with the animal while the owner was infectious (coded CSI); and a score comprised of the sum of all reported interaction types between animals and humans that involved direct contact (coded DIS), which included cuddling, hugging, petting, kissing, co-sleeping, sharing food, and grooming ( Table 1 ).
We compared bivariate correlation coefficients among variables compiled from questionnaire data or diagnostic testing. We used SPSS Statistics 27 (IBM, https://www.ibm.com ) to compute Pearson correlation coefficients. We performed 2-tailed tests of significance and considered p values of < 0.05 or < 0.01 statistically significant, as applicable.
Overall, we sampled 34 individual companion animals from 21 households: 24 domestic dogs, 9 domestic cats, and 1 domestic rabbit ( Table 2 ). The age of the animals ranged from 4 months to 16 years; 22 were male and 12 were female. All but 1 household had a single human mpox case; the other household had 2 cases. We collected a total of 191 swab specimens from animals and 56 AAE specimens. If excess blood was available, we opportunistically tested select blood specimens via PCR, including 10 whole blood specimens preserved in EDTA and 1 blood clot. At examination, we observed skin lesions in 6 dogs and 1 cat, and lesion features and locations varied.
PCR for Animal Samples
Samples collected from 5 individual animals (4 dogs, 1 cat) from 4 households were MPXV-positive; 2 of the dogs shared a household. Total animal swab MPXV positivity was 12% (22/191); 21 MPXV-positive swabs were from dogs, and 1 was from a cat ( Table 3 ). All MPXV-positive animals also had > 1 sample with an RNP-positive test result. Ct values of MPXV-positive samples were 25.2–36.7 (mean 34.5). Results of specific sample types collected were 29% (4/14) for skin lesions, 16% (6/37) for ventral skin or fur, 12% (4/33) for dorsal fur, 11% (4/35) for periocular area, 8% (3/36) for anorectal area, and 3% (1/36) for oral.
Among animal MPXV-positive specimens, 82% were RNP-positive, whereas 25% of the MPXV DNA–negative specimens were RNP-positive ( Table 3 ). Ct values of MPXV-positive specimens that were RNP-positive positively correlated (p<0.01). In animal specimens, 18% (4/22) were MPXV-positive and RNP-negative, and positive Ct values (range 35.3–36.1) were near the upper limit of detection (Ct 37) for the assay. We did not detect MPXV DNA in any of the blood specimens tested via MPXV PCR. In addition, MPXV DNA prevalence in animal samples alone and when combined with AAE specimens significantly correlated with RNP prevalence in those same samples (p<0.05).
We collected AAE specimens from 20/21 households, predominately from animal beds or bedding, toys, and food and water dishes. Among households, 29% (6/21) were positive for MPXV DNA, as were 25% (14/56) of collected specimens, 93% (13/14) of which were positive for MPXV and RNP ( Table 3 ). In those same samples, AAE MPXV DNA prevalence positively correlated with human DNA prevalence (p<0.05). Of the 4 households with MPXV-positive animal swab specimens, all had MPXV-positive AAE swabs with Ct values of 29.9–35.9 (mean 32.8). For AAE specimens that were MPXV- and RNP-positive, the MPXV and RNase-P Ct values were significantly correlated (p<0.01). Of all AAE specimens, 66% (37/56) were RNP-positive, of which 82% (9/11) of specimens with Ct values <37 were in the 4 households with MPXV-positive AAE and animal swab samples.
Viral Culture and Serology
We attempted viral culture from all specimens with Ct values < 36 (n = 31), and all were negative with no signs of cytopathic effect. Three specimens from 2 dogs had bacterial contamination causing destruction of monolayer by day 6 or 7 postinfection, despite mitigating steps or retesting, and the harvested culture media tested negative by MPXV-specific PCR. In addition, all initial (n = 20) and follow-up (n = 22) serum specimens collected were ELISA-negative, and we detected no OPXV IgG. For 1 dog that had samples with the lowest MPXV Ct values, we collected 2 follow-up samples 2 months apart. Of the 5 animals that had MPXV-positive swab specimens, 3 did not have blood sampled at the initial timepoint due to noncompliance or aggression, and 3 were not available at the postexposure sampling timepoint.
Questionnaire Analysis
In total, 32% (11/34) of animals had preexisting health issues and 5 animals had preexisting skin lesions. In addition to the 5 animals with skin lesions that developed before owner symptom onset (all sampled), 2 additional animals had lesions that developed after owner symptom onset. We observed and sampled those lesions during the initial sampling visit, and 1 animal had skin and fur, periocular, and anorectal specimens that were PCR-positive for MPXV DNA, but we did not detect MPXV DNA from the lesion specimen, and serology results also were negative.
In total, 33% (7/21) of households reported no contact change with their animals. Reported types of changes in animal interactions included reducing frequency of interactions (9/21), stopping interactions (8/21), use of PPE during interactions (6/21), and relocating or isolating the animal (4/21); 1 household reported relegating animal care to uninfected persons outside the household. However, all but 1 household reported > 1 type of direct contact activity with each animal after the MPXV-positive human in the household had symptoms develop ( Table 1 ).
Households comprised apartments (n = 11) or single-family homes (n = 10), and approximate size range was 500–3,500 ft 2 ( Table 1 ). We observed a significant negative correlation between household size and prevalence of either MPXV (p<0.05) or human DNA (p<0.01) in animal samples and human DNA prevalence in environmental samples (p<0.01). Apart from human DNA prevalence, household size, and environmental MPXV prevalence, we observed no other statistically significant relationships for other variables potentially influencing prevalence of MPXV DNA in animal samples.
CDC advises that persons with mpox should avoid contact with animals, including pets, until lesions have fully healed to prevent potential virus spillback. That recommendation is because of uncertainty regarding susceptibility of companion animals to MPXV ( 9 ). If MPXV-infected persons cannot avoid contact with pets within the household, practicing appropriate infection control will prevent further exposure potential. In most households we visited, recommended quarantine and infection control procedures were not consistently followed.
Despite MPXV-positive swab specimens detected on the skin or fur of dogs and cats and in associated environmental samples, no dogs or cats with live virus or antibodies detected have been reported globally. In 2 cases outside of the United States in which MPXV DNA was detected in dogs ( 14 , 16 ), apart from apparent skin lesions, no other signs of infection were reported in the animals, including virus cultured from samples or OPXV antibodies detected by serology after additional investigation ( 15 ).
In our household study, skin lesions in 7 animals were the only observable clinical features that were potentially consistent with mpox disease. However, 5 animals exhibited lesions before owner symptom onset, and the 2 animals with skin lesions that were observed after owner symptom onset were negative for MPXV by PCR. Only 1 animal had MPXV-positive lesions sampled, a dog with lesion swab samples collected from a grouping of 3 large lesions on its rear leg, and the average Ct value of samples was 25.2. After further testing to consider potential DNA contamination from the owner, that sample also had the lowest average RNase-P Ct value (29.3) of all samples tested. In addition, that dog’s lesions were reported to have formed before symptom onset in the owner, culture attempts from that and all other samples were negative, and OPXV antibodies were not detected during any timepoint tested. Therefore, after reviewing all the data, we did not consider this animal a confirmed mpox case.
All animals with MPXV-positive samples in this study also had RNP-positive specimens collected, indicating the presence of human DNA. The statistically significant correlation of MPXV- and RNP-positive samples, MPXV PCR results showing high Ct values indicating low viral DNA loads, and the lack of viable virus or antibodies in the collected samples strongly suggest that observed lesions or scabs in these animals were not the result of MPXV infection. In addition, from our knowledge of MPXV pathology, an MPXV lesion would most likely produce high viral loads and at levels higher than for other sample types ( 22 ).
As reported in other household environmental sampling studies, MPXV DNA can be widely detected in indoor or household settings ( 11 , 12 , 23 – 25 ). In this study, we found that households with smaller shared spaces were significantly correlated with both MPXV and human DNA prevalence, suggesting that the risk for MPXV exposure could be higher in smaller living quarters. Given the capability of MPXV DNA to disseminate within the household of a person with mpox, and after consideration of the PCR results detailed here, persons with mpox, not the companion animals, likely were the source of the MPXV DNA we detected in the household.
The potential for contamination from either direct contact with a person with mpox or indirect exposure to materials containing MPXV DNA should be considered when interpreting results of PCR testing from companion animals. In addition, case definitions should consider potential extraneous contamination and require more than a PCR-positive result from an animal to be considered a confirmed animal mpox case ( 26 ). Contamination should also be considered as a reason for a positive PCR result and false positive results in humans with nonspecific lesions who have potentially had contact with an mpox case-patient.
MPXV infection in companion animals, if they are suitable hosts, is uncharacterized; clinical signs, viral shedding, and duration of infectious period are unknown. Thus, although unlikely, given the limits of our sampling design, it is possible that an infected animal escaped detection in our study. However, the overall PCR and serologic evidence best fits the hypothesis that the MPXV DNA detected in animal samples submitted for PCR testing is a result of DNA contamination from the infected human within the household.
More work is needed to determine the susceptibility of companion animals to clade-IIb MPXV. Thus, CDC still recommends that companion animal owners with mpox limit their interactions with their pets while infectious, particularly if they are sharing smaller living spaces. That precautionary measure is recommended until more information is available about the susceptibility of common mammalian companion animal species to mpox.
In conclusion, no strong evidence yet exists to suggest that common companion animals, such as dogs or cats, are susceptible to infection with clade IIb MPXV. Given high likelihood for exposure among most of these animals, the paucity of evidence indicating infection might indicate resistance to infection. Nonetheless, to prevent further viral spread and potential evolution and establishment of new endemic areas, during public health emergencies caused by emerging zoonotic diseases, responders should apply a One Health approach to investigate potential spillback of human infections to animals, including pets.
Mr. Morgan is a biologist in the Poxvirus and Rabies Branch, Division of High Consequence Pathogens and Pathology, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. His research interests include the virus-host interactions of orthopoxviruses and lyssaviruses in the environment.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Epidemiology, Laboratory and Testing, and STLT (State, Tribal, Local, or Territorial) Task Forces of the CDC 2022 Multinational Mpox Response and the CDC Poxvirus and Rabies Branch, Division of High Consequence Pathogens and Pathology, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases. We also acknowledge additional persons and entities who assisted with this study, including the Minnesota Department of Health, including Patrice Vandelinde, Victoria Lappi, and Anna Strain; the Virginia Department of Health, including Kenneth Gordon, Christina Chommanard, Luisa Angel Cortes, Clarissa Bonnefond, Lisa Engle, and Cynthia Rieken; the Tennessee Department of Health and Agriculture, including Jane Yackley, Dilani Goonewardene, and Whitnie Smartt; and DC Department of Health, including Sarah Gillani, Will Still, and Karla Miletti. In addition, we acknowledge, Casey Barton-Behravesh, Yoshinori Nakazawa, Modupe Osinubi, Ashutosh Wadhwa, and Ariel Caudle for their assistance.
All funding for this study was provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 2022 Multinational Mpox Response (CDC Mpox Response). The CDC Mpox Response provided technical review and oversight of this manuscript before publication. This study and report were also supported in part by an appointment to the Applied Epidemiology Fellowship Program, administered by the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) and funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (cooperative agreement no. 1NU38OT000297-03-00).
- Nolen LD , Osadebe L , Katomba J , Likofata J , Mukadi D , Monroe B , et al. Extended human-to-human transmission during a monkeypox outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg Infect Dis . 2016 ; 22 : 1014 – 21 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Durski KN , McCollum AM , Nakazawa Y , Petersen BW , Reynolds MG , Briand S , et al. Emergence of Monkeypox - West and Central Africa, 1970-2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2018 ; 67 : 306 – 10 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Reynolds MG , Doty JB , McCollum AM , Olson VA , Nakazawa Y . Monkeypox re-emergence in Africa: a call to expand the concept and practice of One Health. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther . 2019 ; 17 : 129 – 39 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Reynolds MG , Guagliardo SAJ , Nakazawa YJ , Doty JB , Mauldin MR . Understanding orthopoxvirus host range and evolution: from the enigmatic to the usual suspects. Curr Opin Virol . 2018 ; 28 : 108 – 15 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Sah R , Abdelaal A , Reda A , Katamesh BE , Manirambona E , Abdelmonem H , et al. Monkeypox and its possible sexual transmission: where are we now with its evidence? Pathogens . 2022 ; 11 : 924 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Low N , Bachmann LH , Ogoina D , McDonald R , Ipekci AM , Quilter LAS , et al. Mpox virus and transmission through sexual contact: Defining the research agenda. PLoS Med . 2023 ; 20 : e1004163 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- McQuiston JH , Braden CR , Bowen MD , McCollum AM , McDonald R , Carnes N , et al. The CDC domestic mpox response—United States, 2022–2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2023 ; 72 : 547 – 52 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Mpox in the home [ cited 2023 Dec 8 ]. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/veterinarian/mpox-in-animals.html
- Adler H , Gould S , Hine P , Snell LB , Wong W , Houlihan CF , et al. ; NHS England High Consequence Infectious Diseases (Airborne) Network . Clinical features and management of human monkeypox: a retrospective observational study in the UK. Lancet Infect Dis . 2022 ; 22 : 1153 – 62 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Minhaj FS , Ogale YP , Whitehill F , Schultz J , Foote M , Davidson W , et al. ; Monkeypox Response Team 2022 . Monkeypox Response Team 2022. Monkeypox outbreak—nine states, May 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2022 ; 71 : 764 – 9 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Morgan CN , Whitehill F , Doty JB , Schulte J , Matheny A , Stringer J , et al. Environmental persistence of monkeypox virus on surfaces in household of person with travel-associated infection, Dallas, Texas, USA, 2021. Emerg Infect Dis . 2022 ; 28 : 1982 – 9 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Pfeiffer JA , Collingwood A , Rider LE , Minhaj FS , Matheny AM , Kling C , et al. High-contact object and surface contamination in a household of persons with monkeypox virus infection—Utah, June 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep . 2022 ; 71 : 1092 – 4 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Mpox: isolation and infection control at home [ cited 2023 Jan 21 ]. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/clinicians/infection-control-home.html
- Seang S , Burrel S , Todesco E , Leducq V , Monsel G , Le Pluart D , et al. Evidence of human-to-dog transmission of monkeypox virus. Lancet . 2022 ; 400 : 658 – 9 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- The French Agency for Food . Monkeypox: what is the risk of spreading to pets? [in French] [ cited 2022 Dec 16 ]. https://www.anses.fr/fr/content/variole-du-singe-quel-risque-de-diffusion-aux-animaux-de-compagnie
- Brazilian Ministry of Health . Ministry of Health is notified of the first case of monkeypox in a domestic animal [in Portuguese] [ cited 2022 Dec 3 ]. https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/2022/agosto/ministerio-da-saude-e-notificado-do-primeiro-caso-de-variola-dos-macacos-em-animal
- Li Y , Zhao H , Wilkins K , Hughes C , Damon IK . Real-time PCR assays for the specific detection of monkeypox virus West African and Congo Basin strain DNA. J Virol Methods . 2010 ; 169 : 223 – 7 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Test procedure: monkeypox virus generic real-time PCR test [ cited 2023 Oct 7 ]. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/pdf/PCR-Diagnostic-Protocol-508.pdf
- Hughes CM , Liu L , Davidson WB , Radford KW , Wilkins K , Monroe B , et al. A tale of two viruses: coinfections of monkeypox and varicella zoster virus in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Am J Trop Med Hyg . 2020 ; 104 : 604 – 11 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Karem KL , Reynolds M , Braden Z , Lou G , Bernard N , Patton J , et al. characterization of acute-phase humoral immunity to monkeypox: use of immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of monkeypox infection during the 2003 North American outbreak. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol . 2005 ; 12 : 867 – 72 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Hutson CL , Olson VA , Carroll DS , Abel JA , Hughes CM , Braden ZH , et al. A prairie dog animal model of systemic orthopoxvirus disease using West African and Congo Basin strains of monkeypox virus. J Gen Virol . 2009 ; 90 : 323 – 33 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Kim H , Kwon R , Lee H , Lee SW , Rahmati M , Koyanagi A , et al. Viral load dynamics and shedding kinetics of mpox infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Travel Med . 2023 ; 30 : taad111 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Gould S , Atkinson B , Onianwa O , Spencer A , Furneaux J , Grieves J , et al. ; NHS England Airborne High Consequence Infectious Diseases Network . Air and surface sampling for monkeypox virus in a UK hospital: an observational study. Lancet Microbe . 2022 ; 3 : e904 – 11 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Nörz D , Pfefferle S , Brehm TT , Franke G , Grewe I , Knobling B , et al. Evidence of surface contamination in hospital rooms occupied by patients infected with monkeypox, Germany, June 2022. Euro Surveill . 2022 ; 27 : 2200477 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Atkinson B , Burton C , Pottage T , Thompson K-A , Ngabo D , Crook A , et al. Infection-competent monkeypox virus contamination identified in domestic settings following an imported case of monkeypox into the UK. Environ Microbiol . 2022 ; 24 : 4561 – 9 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Interim CDC case definition for animal cases of monkeypox [ cited 2023 Mar 14 ]. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/veterinarian/animal-officials.html#case-def
- Table 1 . Summary of variables coded from household and questionnaire data used in a One Health investigation into mpox and pets, United States
- Table 2 . Animal and environment sampling and diagnostic testing data from a One Health investigation into mpox and pets, United States
- Table 3 . PCR results of for monkeypox virus clade II and RNase-P DNA assays from swab samples of companion animals and animal-associated objects and surfaces during a One Health investigation into mpox...
Suggested citation for this article : Morgan CN, Wendling NM, Baird N, Kling C, Lopez L, Navarra T, et al. One Health investigation into mpox and pets, United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Oct [ date cited ]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid3010.240632
DOI: 10.3201/eid3010.240632
Original Publication Date: August 14, 2024
Table of Contents – Volume 30, Number 10—October 2024
| EID Search Options |
|---|
| – Search articles by author and/or keyword. |
| – Search articles by the topic country. |
| – Search articles by article type and issue. |
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Jeffrey B. Doty, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 4055 Tudor Center Dr, Anchorage, Alaska 99508, USA
Comment submitted successfully, thank you for your feedback.
There was an unexpected error. Message not sent.
Metric Details
Article views: 1.
Data is collected weekly and does not include downloads and attachments. View data is from .
What is the Altmetric Attention Score?
The Altmetric Attention Score for a research output provides an indicator of the amount of attention that it has received. The score is derived from an automated algorithm, and represents a weighted count of the amount of attention Altmetric picked up for a research output.

Sticky H2O: Innovative adhesion research in Pa. unveils surprising properties of water

Their research began as a study on how animals interact with surfaces in nature, but their latest findings challenge one of our most fundamental suppositions about surface adhesion.
Ali Dhinojwala, W. Gerald Austen Endowed Chair and H.A. Morton Professor at Akron University, with his team of University of Pittsburgh’s Tevis Jacobs, University of Friedberg’s Lars Pastewka and Anirudha Sumant of the Argonne National Laboratory wanted to examine nature’s solutions to the problem of adhesion. What allows a gecko to run up a wall? How does a spider walk along its sticky silk?
The traditional view of adhesion is that water impedes the process — it would be laughable to try to put a Band-Aid on in the shower. But Dhinojwala says that when the team took a closer look at the interactions of wet and rough surfaces, the answer wasn’t so simple. Although the water made it more difficult to push two surfaces together, in some instances, the presence of water made it significantly harder to pull the two surfaces apart.
“That's where the surprise was — that when we look at the contact and we look at the adhesion, we see that there is 50% of that area still covered with water. So intuition would say, ‘hey, look, 50% of the area is covered with water. Adhesion should be low.’” Dhinojwala said. “But we started observing that when we pull them off, we actually get four to five times more adhesion than what we were expecting.”
Start your morning with today's news on Pittsburgh and Pennsylvania.
The team is still narrowing down the exact reason why water can enhance adhesion under certain conditions, but associate professor and Whiteford Faculty Fellow at the University of Pittsburgh Tevis Jacobs says it all has to do with the scales of roughness.
After the surfaces were chemically prepared at the Argonne National Laboratory in Illinois, Jacobs’ group characterized their roughness down to the atomic scale at the University of Pittsburgh. There are large variations in classifying roughness — small-, intermediate- and large-scale bumps on the surface that are in charge of different properties.
“You're going for a hike, right? There's bumpiness that are the pebbles on the ground, there's bumpiness that are the boulders, and then there's bumpiness that are the mountains,” Jacobs said. “You can imagine two places that have the same pebble scale roughness, but, you know, one is the Swiss Alps and one is Kansas.”
When it comes to adhesion, the large- and intermediate-scale roughness — the mountains and the boulders — control the drainage of water that typically gets in the way of adhering two objects together. The very small scale, however, can control the retention of water in tiny nano-pockets that prevent the surfaces from pulling apart.
Jacobs says that these findings open up new possibilities for improving underwater adhesion, challenging old ideas that we should always squeeze out as much water as possible in order to treat underwater adhesion the same way we treat dry adhesion.
“You can't just say, ‘rougher is better underwater’ or ‘smoother is better underwater,’” Jacobs said. “It unlocks this whole new pathway to optimizing surfaces where, yes, you want drainage at some scales — at larger scales — but you actually might not want drainage at the very small scales.”
The team plans to continue looking into applications of these new findings, but the research could have a significant impact on the biomedical industry in the form of bandages, health monitoring sensors on moist skin, advanced adhesives that could replace sutures and other fluid transfer technologies like syringes and o-rings.
While they have their work cut out for them exploring proposed explanations for the behavior of trapped water and developing practical applications for their findings, Jacobs says these kinds of unexpected developments are great catalysts for more exciting work.
“In my opinion, the best science is not, ‘Here's the answer,’” he said. “It's, ‘Wow! Here's a bunch of new interesting questions.’”
After years of data collection and research and six months of writing, Dhinojwala’s team published their full findings in the multidisciplinary journal Science Advances on Aug. 7.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
PubMed® comprises more than 37 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
Harvard Medical School has created a large department dedicated to developing and teaching young scientists about the emerging field of computational medicine. This field uses new mathematical techniques to make sense of the thousands of numbers generated in experiments measuring various molecules. Analyzing such "big data" was once ...
Find breakthrough research in BMC Medicine, an open access journal with 7.0 Impact Factor, and 6 days to first decision. Open for submissions! BMC Medicine ...
Medical research articles from across Nature Portfolio. Medical research involves research in a wide range of fields, such as biology, chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology with the goal of ...
Original research studies that can improve decision making in clinical medicine, public health, health care policy, medical education, or biomedical research.
An integrated data and sample repository for clinical, cellular and multi-omics research from diverse spaceflight missions known as Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA) is presented.
Explore the index of articles published by the New England Journal of Medicine, from original research to videos in clinical medicine and more.
K.J. Moise, Jr. and OthersN Engl J Med 2024;391:526-537. In a trial involving 13 pregnancies at high risk for early-onset severe hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, nipocalimab increased ...
PMC is a free archive of biomedical and life sciences literature from PubMed. Search, browse and access full-text articles from journals and books.
MEDLINE is the National Library of Medicine's (NLM) premier bibliographic database that contains references to journal articles in life sciences, with a concentration on biomedicine. See the MEDLINE Overview page for more information about MEDLINE.
To celebrate the end of our 25th anniversary year, we asked thought leaders and experts in the field to answer one question: What will shape the next 25 years of medical research?
After an earlier publication dealing with aspects of study design, the present article deals with study types in primary and secondary research. The article focuses on study types in primary research. A special article will be devoted to study types in secondary research, such as meta-analyses and reviews.
Articles Investigating the effect of enhanced cleaning and disinfection of shared medical equipment on health-care-associated infections in Australia (CLEEN): a stepped-wedge, cluster randomised, controlled trial The Lancet Infectious Diseases Published: August 13, 2024 Katrina Browne Nicole M White Philip L Russo Allen C Cheng Andrew J Stewardson
Statistical Methods in Medical Research is a highly ranked, peer reviewed scholarly journal and is the leading vehicle for articles in all the main areas of medical statistics and therefore an essential reference for all medical statisticians. It is … | View full journal description.
With massive investment in health-related research, above and beyond investments in the management and delivery of healthcare and public health services, there has been increasing focus on the impact of health research to explore and explain the consequences ...
The editors announce a new Perspective series exploring key ethical questions facing medicine today; the hope is that medical ethics can keep pace with the evolution — and revolutions — in ...
Official Publication of the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS) Archives of Medical Research publishes original peer-reviewed medical research in an attempt to bridge the gaps created by medical specialization. Contributions are grouped into three main categories - biomedical, clinical, ….
Read the latest articles of Archives of Medical Research at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
When asked about the purpose of medical research most people would hopefully reply: to advance knowledge for the good of society; to improve the health of people worldwide; or to find better ways to treat and prevent disease. The reality is different. The research environment, with its different players, is now much less conducive to thinking ...
Read the latest Research articles in Medical research from Scientific Reports
Find the latest research papers and news in Medical Imaging. Read stories and opinions from top researchers in our research community.
Rapidly advancing biomedical and electronic technologies, ongoing health disparities, and new online educational modalities are all changing medicine and medical education. As medical training continues to evolve, research is increasingly critical to help improve it, but medical education research can pose unique ethical challenges.
Read the latest articles from The New England Journal of Medicine on various topics, such as thyroiditis, hip pain, low back pain, and more.
Public health experts from some of the nation's leading research universities have deployed a massive medical trailer to rural parts of the South as part of an ambitious and unusual new health study.
The Born This Way Foundation empowers youth advocates to champion a sense of community and innovation to drive change for youth mental health. These programmes and others that are emerging are providing a blueprint for youth involvement that sees young people as co-designers and leaders in mental health services, research, and development.
Browse the 25 most downloaded Nature Communications articles in health sciences published in 2021.
Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released. Volume 30, Number 10—October 2024 Research One Health Investigation into Mpox and Pets, United States
Health, Science & Tech. Sticky H2O: Innovative adhesion research in Pa. unveils surprising properties of water ... Their research began as a study on how animals interact with surfaces in nature ...
It is hoped the declaration of mpox as a public health emergency will lead to research, funding, and the introduction of other international public health measures being accelerated.