- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000

Interior of the Earth: Crust, Mantle and Core
Last updated on September 20, 2023 by ClearIAS Team

Table of Contents
What should you understand about the interior of the earth?
- It is not possible to know about the earth’s interior by direct observations because of the huge size and the changing nature of its interior composition.
- It is an almost impossible distance for the humans to reach till the centre of the earth (The earth’s radius is 6,370 km).
- Through mining and drilling operations we have been able to observe the earth’s interior directly only up to a depth of few kilometers.
- The rapid increase in temperature below the earth’s surface is mainly responsible for setting a limit to direct observations inside the earth.
- But still, through some direct and indirect sources, the scientists have a fair idea about how the earth’s interior look like.
Sources of Information about the interior of the earth
Direct sources:.
- Rocks from mining area
- Volcanic eruptions
Indirect Sources
- By analyzing the rate of change of temperature and pressure from the surface towards the interior.
- Meteors , as they belong to the same type of materials earth is made of.
- Gravitation , which is greater near poles and less at the equator.
- Gravity anomaly , which is the change in gravity value according to the mass of material, gives us information about the materials in the earth’s interior.
- Magnetic sources .
- Seismic Waves : the shadow zones of body waves ( Primary and secondary waves ) give us information about the state of materials in the interior.
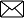
Structure of the earth’s interior
Structure of earth’s interior is fundamentally divided into three layers – crust, mantle and core .
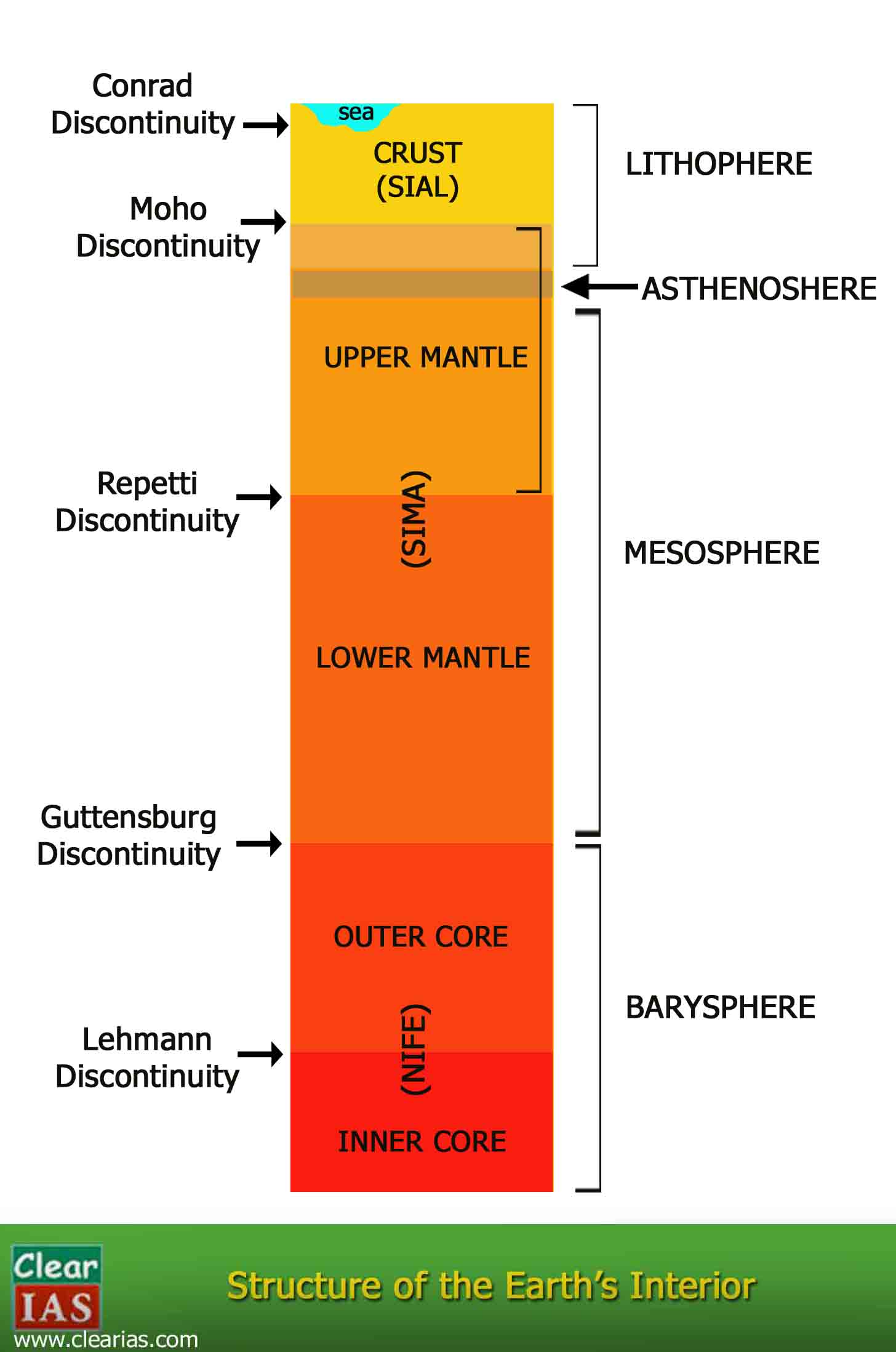
- It is the outermost solid part of the earth, normally about 8-40 kms thick.
- It is brittle in nature.
- Nearly 1% of the earth’s volume and 0.5% of earth’s mass are made of the crust.
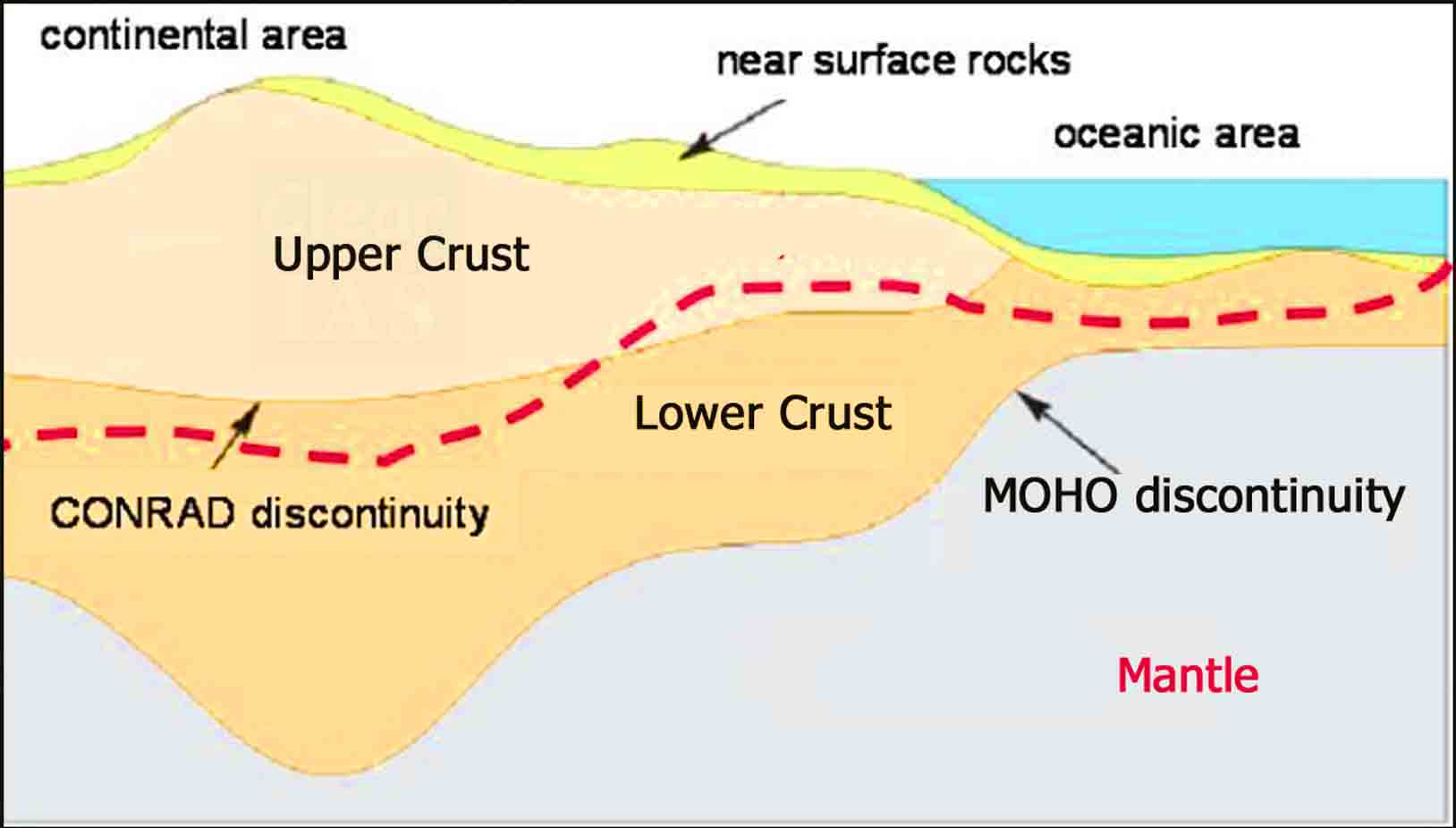
- The thickness of the crust under the oceanic and continental areas are different. Oceanic crust is thinner (about 5kms) as compared to the continental crust (about 30kms).
- Major constituent elements of crust are Silica (Si) and Aluminium (Al) and thus, it is often termed as SIAL (Sometimes SIAL is used to refer Lithosphere, which is the region comprising the crust and uppermost solid mantle, also).
- The mean density of the materials in the crust is 3g/cm3.
- The discontinuity between the hydrosphere and crust is termed as the Conrad Discontinuity.
- The portion of the interior beyond the crust is called as the mantle.
- The discontinuity between the crust and mantle is called as the Mohorovich Discontinuity or Moho discontinuity.
- The mantle is about 2900kms in thickness.
- Nearly 84% of the earth’s volume and 67% of the earth’s mass is occupied by the mantle.
- The major constituent elements of the mantle are Silicon and Magnesium and hence it is also termed as SIMA .
- The density of the layer is higher than the crust and varies from 3.3 – 5.4g/cm3.
- The uppermost solid part of the mantle and the entire crust constitute the Lithosphere .
- The asthenosphere (in between 80-200km) is a highly viscous, mechanically weak and ductile, deforming region of the upper mantle which lies just below the lithosphere.
- The asthenosphere is the main source of magma and it is the layer over which the lithospheric plates/ continental plates move ( plate tectonics ).
- The discontinuity between the upper mantle and the lower mantle is known as Repetti Discontinuity .
- The portion of the mantle which is just below the lithosphere and asthenosphere, but above the core is called as Mesosphere .
- It is the innermost layer surrounding the earth’s centre.
- The core is separated from the mantle by Guttenberg’s Discontinuity .
- It is composed mainly of iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni) and hence it is also called as NIFE .
- The core constitutes nearly 15% of earth’s volume and 32.5% of earth’s mass.
- The core is the densest layer of the earth with its density ranges between 9.5-14.5g/cm3.
- The Core consists of two sub-layers: the inner core and the outer core.
- The inner core is in solid state and the outer core is in the liquid state (or semi-liquid).
- The discontinuity between the upper core and the lower core is called as Lehmann Discontinuity.
- Barysphere is sometimes used to refer the core of the earth or sometimes the whole interior.
Temperature, Pressure and Density of the Earth’s Interior
Temperature.
- A rise in temperature with increase in depth is observed in mines and deep wells.
- These evidence along with molten lava erupted from the earth’s interior supports that the temperature increases towards the centre of the earth.
- The different observations show that the rate of increase of temperature is not uniform from the surface towards the earth’s centre. It is faster at some places and slower at other places.
- In the beginning, this rate of increase of temperature is at an average rate of 1 0 C for every 32m increase in depth.
- While in the upper 100kms, the increase in temperature is at the rate of 12 0 C per km and in the next 300kms, it is 20 0 C per km. But going further deep, this rate reduces to mere 10 0 C per km.
- Thus, it is assumed that the rate of increase of temperature beneath the surface is decreasing towards the centre (do not confuse rate of increase of temperature with increase of temperature. Temperature is always increasing from the earth’s surface towards the centre ).
- The temperature at the centre is estimated to lie somewhere between 3000 0 C and 5000 0 C, may be that much higher due to the chemical reactions under high-pressure conditions.
- Even in such a high temperature also, the materials at the centre of the earth are in solid state because of the heavy pressure of the overlying materials.
- Just like the temperature, the pressure is also increasing from the surface towards the centre of the earth.
- It is due to the huge weight of the overlying materials like rocks.
- It is estimated that in the deeper portions, the pressure is tremendously high which will be nearly 3 to 4 million times more than the pressure of the atmosphere at sea level.
- At high temperature, the materials beneath will melt towards the centre part of the earth but due to heavy pressure, these molten materials acquire the properties of a solid and are probably in a plastic state.
- Due to increase in pressure and presence of heavier materials like Nickel and Iron towards the centre, the density of earth’s layers also gets on increasing towards the centre .
- The average density of the layers gets on increasing from crust to core and it is nearly 14.5g/cm3 at the very centre.
Article by: Jijo Sudarsan

Top 10 Best-Selling ClearIAS Courses
Upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: unbeatable batch 2025 (online), rs.75000 rs.29000, upsc prelims marks booster + 2025 (online), rs.19999 rs.14999, upsc prelims test series (pts) 2025 (online), rs.9999 rs.4999, csat course 2025 (online), current affairs course 2025 (online), ncert foundation course (online), essay writing course for upsc cse (online), ethics course for upsc cse (online), upsc interview marks booster course (online), rs.9999 rs.4999.

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
July 12, 2016 at 10:15 pm
sir i prefer reading offline …but ur notes on each issue attract me …I know that ir geography nots and history and economics are oriented from nce rts as i m reading them mercylessely.BT IS THIS SO WITH UR CULTURE NOTES ALSO
July 12, 2016 at 10:19 pm
sir plz say me in order that i will convince myself that after reading 9-12 ncerts …ramesh sigh ….gc leong……nitin singhania…..shankar ias…..vipin chandra or spectrum….my core syllablus will complete and no need to see ur notes as …..i have problem in vision …and cant use internet more.
October 1, 2016 at 12:30 am
Well written in point wise. Thank you sir. If possible can u plz lso upload the physiography of india as wel as other topics specific to indian geography. Thank you
December 6, 2016 at 10:19 am
Most of the aspects related to the topic covered point-wise and enable students to score good marks. Great effort.
March 17, 2017 at 8:56 pm
why it is important to study changes going around and inside earth crust? answer this question?
December 9, 2017 at 6:56 pm
Yes good question…..now listen few things ,what if some tragedy will happen and you don’t know about your room that where is the gate or which corner is the safest ,you simply land yourself into trouble knowing about that room completely will help you out …in the same way knowing about the interior of the earth is essential to explore it for the good reason
January 8, 2022 at 1:10 pm
My doubt is when pressure is inversely proportional to the temperature then how at the center or the inner most point tends to have high temperature with extremely high pressure.
April 25, 2017 at 10:48 am
Thanks very helpful… And not confusing
November 7, 2017 at 2:36 am
Very nice answer
January 10, 2018 at 12:17 pm
Sir this note is very helpful to me.Please upload note on plate techtonic theory.
February 28, 2018 at 10:37 pm
very helpful notes sir.
May 20, 2018 at 2:50 pm
Nice answer Thank you sir
July 5, 2018 at 8:19 pm
Very good effort every important topic is cover
August 24, 2018 at 5:44 pm
I like It becouse This note gives by perfect knowledge Thank you fo that.
December 15, 2018 at 8:26 pm
Ashu sir you gave a very clear example
March 16, 2019 at 3:58 pm
What are the problems found in the upper mantle and the transition zone??
June 5, 2019 at 3:07 pm
Alex chettayiii
June 22, 2019 at 8:26 pm
Sir according to ncert the volume percentage of crust is 0.5%,mantel is 16%,and core is 83% so how urs mantel 85% and core 25% will be correct
June 30, 2021 at 9:53 pm
Actually, the volume of Crust is 1%, Mantle is 85% and lastly, the core is 15%
August 25, 2019 at 12:40 pm
Sir how to make notes from ncert ….Before making notes how many
times should I read??
And also tell me about your’s macroupsc syllabus whether I would make make notes from each every single point sir….
August 28, 2019 at 8:58 pm
Thickness of Mantle is less than half of the radius of Earth but it accounts for 84% of total volume of earth and 68% mass. How? If thickness of mantle is less than core then how come volume of mantle is more i.e 84%. Can anyone explain the relation between thickness and volume
April 2, 2021 at 10:27 pm
Earth is a Sphere, core is at its center and surrounded by the mantle, so…though the thickness of the mantle is equal or bit less(not much) than the core , the volume of mantle is gonna be more (cuz core is at the center of the sphere and mantle is away from the center). (Hope it is cleared to u, but still if u need further help just mail me, i’ll try to help u out with a diagram. email id: [email protected] )
April 3, 2020 at 1:15 pm
Is it enough to clear the main… or is it only for prelims??
April 10, 2020 at 4:23 pm
Only for Prelims
July 18, 2020 at 12:43 pm
what are the chemical composition of crust,mantleand core
December 12, 2020 at 11:16 am
really helpful thanks.
January 16, 2021 at 8:09 pm
This comment is regarding “mesosphere” . I have read different books but could not find the word mesosphere for upper and lower mantle. I guess it is pyrosphere dominant in basalt. Please rectify me if m wrong. Thank u
March 5, 2022 at 8:43 am
Best explanation
September 26, 2022 at 11:47 pm
In the 1st pic, there should be lithosphere🙏 and very greatful to get notes from Clear IAS team. Thank you soo much.
November 12, 2022 at 3:31 pm
I thought that the continental crust is made of silica and aluminum making up the SIAL and oceanic crust rocks are mainly composed of silica and magnesium forming the SIMA. PLEASE CHECK ON THIS AND MAKE CLARIFICATIONS INSTEAD OF GENERALISING THEM AS SIAL. THE COMPOSITION OF ROCKS DIFFERS BETWEEN THE TWO LAYERS OF THE CRUST. PLEASE I DO WELCOME CORRECTIONS AS WELL. WE LEARN FROM EACH OTHER
August 13, 2023 at 9:08 am
oceanic crust is made of Silica and magnesium(SiMa) is write for crust layer
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
ClearIAS Programs: Admissions Open
Thank You 🙌
UPSC CSE 2025: Study Plan
Subscribe ClearIAS YouTube Channel

Get free study materials. Don’t miss ClearIAS updates.
Subscribe Now
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025

Cover the entire syllabus of UPSC CSE Prelims and Mains systematically.
Home — Essay Samples — Science — Earth Science — Earth’s Layers
The Layers of The Earth and Their Function
- Categories: Earth Earth Science
About this sample

Words: 362 |
Published: Jan 15, 2019
Words: 362 | Page: 1 | 2 min read
Works Cited
- Aldridge, M. (2015). Inside planet Earth. National Geographic Kids.
- Anderson, D. L. (2015). The interior of the Earth: an interdisciplinary perspective. Cambridge University Press.
- Bowring, S. A., Williams, I. S., & Compston, W. (1989). 238U–235U systematics in terrestrial uranium-bearing minerals. Science, 246(4934), 962-970.
- Christensen, U. R. (1996). The Earth's mantle: composition, structure, and evolution. Cambridge University Press.
- Duffy, T. S., Anderson, O. L., & Goncharov, A. F. (2001). Thermodynamics of mantle minerals—II. Phase equilibria. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 43(1), 65-124.
- Foulger, G. R. (2010). Plates vs. plumes: A geological controversy. Wiley-Blackwell.
- Jacobsen, S. B., & Garnero, E. J. (2010). A layered mantle transition zone in the northwest Pacific. Nature, 466(7307), 1062-1065.
- Riffenburgh, B. (2013). Encyclopedia of the Antarctic. Routledge.
- Rolf, T., & Snieder, R. (2013). The Earth's mantle: from seismic tomography to mineral physics. Cambridge University Press.
- Tanimoto, T., & Lay, T. (2000). The Earth's mantle. Nature, 405(6782), 633-634.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment Science

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1595 words
4 pages / 1699 words
1 pages / 608 words
1 pages / 528 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Earth Science
Earth is a beautiful planet and home to numerous species of animals, plants, and microorganisms. Despite its vastness and complexity, however, we have only begun to scratch the surface of its innate beauty and wonder. Throughout [...]
Science, the systematic study of the natural world, plays a vital role in our everyday lives. From the moment we wake up in the morning to the time we go to bed at night, we are surrounded by the wonders of science. It is [...]
Similarities Between Natural Sciences And HistoryIntroduction:Imagine walking through a vast library, with shelves upon shelves of books stretching out in every direction. On one side, you see volumes dedicated to the mysteries [...]
The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology that describes the dynamic transformations between the three primary rock types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. This cyclical process demonstrates how Earth's materials [...]
Basaltic magma - SiO2 45-55 wt%, high in Fe, Mg, Ca, low in K, NaAndesitic magma - SiO2 55-65 wt%, intermediate. in Fe, Mg, Ca, Na, KRhyolitic magma - SiO2 65-75%, low in Fe, Mg, Ca, high in K, NaTemperature of magmas is [...]
Carbon in its various forms has been known since ancient times in the form of soot, charcoal, graphite and diamonds. Its name is derived from a Latin word "carbo" which means "charcoal". Ancient cultures did not realize, of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Please wait...
Home » Articles » Interior of the earth
Interior Of The Earth: Complete Study Notes

Interior of the Earth: Geography is a vast subject and often creates hurdles for candidates. The Interior of the earth is an important topic for UPSC CSE preparation. Candidates need to have a depth knowledge to understand this topic properly. In this blog, we will provide you with the details of each aspect of the interior of the earth.
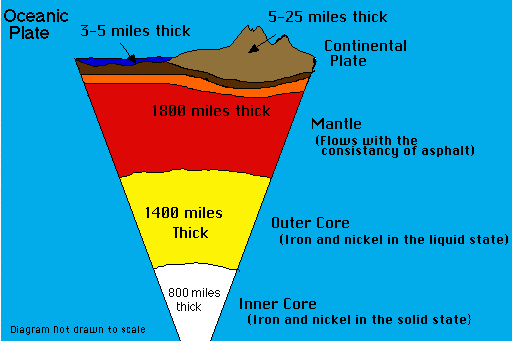
Earth has 3 major layers namely :
- Core (Outer Core & Inner Core)
Internal layers of the earth
The radius of the earth is 6,370 km. Thus, it is impossible to reach the center of the earth and find out about the composition. Also, this composition is changing in nature. The rapid increase in temperature is also one of the factors that put a limit to direct observation of the earth’s interior.
Sources of information are of two types: Direct & Indirect.
Some Direct Sources:
- Rocks (Mining)
- Volcanic Eruptions
Some Indirect Sources:
- Rate of change of temperature and pressure from the surface towards the interior
- Gravitation
- Gravity anomaly (gravity changes according to the mass of material thus giving us information about the materials in the earth’s interior).
- Meteors (they are made up of similar materials as earths)
- Seismic Waves (the shadow zones of body waves give us information about the state of materials in the interior)
- Earth’s hard outer layer is brittle in nature. It is less than 1% of Earth’s volume. The crust is made up of different types of rocks: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks.
- The crust is of two different types. One is the continental crust (under the land) and the other is the oceanic crust (under the ocean).
- The continental crust has an upper part called granitic rock and forms the continents. Silica and alumina (Sial) are their main constituents.
- The lower part has basaltic rock forming the Oceanic floor. Silica, iron, and magnesium (Sima) are its main constituents.
- The thickness of the crust varies from 5 to 70 kilometers. The continental crust is thicker, and the oceanic crust is thinner. The mean thickness of the oceanic crust is 5 km whereas that of the continental is around 30 km.
- The temperature of the crust increases with depth because of geothermal energy. Where the crust meets the mantle the temperatures can be between 200 °C (392 °F) to 400 °C (752 °F). The crust is the coldest among all layers because it is exposed to the atmosphere.
- The oldest oceanic basalt crust today is only about 200 million years. Most of the continental crust is much older. The oldest continental crustal rocks on Earth are cratons between 3.7 to 4.28 billion years old.
- The mantle is the mostly-solid bulk of Earth’s interior. The mantle lies between Earth’s dense , super-heated core and its thin outer layer, the crust . The mantle is about 2,900 kilometers (1,802 miles) thick and makes up a whopping 84% of Earth’s total volume.
- It is composed mainly of dense rocks rich in olivine.
- The rocks that makeup Earth’s mantle are mostly silicate s—a wide variety of compound s that share a silicon and oxygen structure. Common silicates found in the mantle include olivine, garnet, and pyroxene. The other major type of rock found in the mantle is magnesium oxide. Other mantle elements include iron, aluminum, calcium, sodium, and potassium.
- The temperature of the mantle varies greatly, from 1000° Celsius (1832° Fahrenheit) near its boundary with the crust, to 3700° Celsius (6692° Fahrenheit) near its boundary with the core. In the mantle, heat and pressure generally increase with depth.
- The transfer of heat and material in the mantle helps determine the landscape of Earth. Activity in the mantle drives plate tectonics , contributing to volcano es, seafloor spreading , earthquake s, and orogeny (mountain-building).
- The upper portion of the mantle is called the asthenosphere extending up to 400 km. It is the main source of magma and has a density higher than the crusts.
- Repetti discontinuity separates the outer and the inner mantle. The lower mantle extends beyond the asthenosphere. It is in a solid state.
- The Earth’s core is the central inner part of our planet. It has a solid inner core and a liquid outer core.
- The outer core of the Earth is a liquid layer about 2,260 kilometers thick. It is made of iron and nickel.
- Accounts for 16 percent of the earth’s volume.
- Core has the heaviest mineral materials of the highest density.
- Its outer boundary is 2,890 km (1,800 mi) beneath the Earth’s surface. The transition between the inner core and outer core is approximately 5,000 km (3,100 mi) beneath the Earth’s surface.
- The temperature of the outer core ranges from 4400 °C in the outer regions to 6100 °C near the inner core. Eddy currents in the nickel-iron fluid of the outer core are believed to influence the Earth’s magnetic field.
- The average magnetic field strength in the Earth’s outer core was measured to be 25 Gauss, 50 times stronger than the magnetic field at the surface
- Without the outer core, life on Earth would be very different. The convection of liquid metals in the outer core creates the Earth’s magnetic field. This magnetic field extends outward from the Earth for several thousand kilometers and creates a protective bubble around the Earth that deflects the Sun’s solar wind.
- The inner core of the Earth, as detected by seismology, is a solid sphere about 1,216 km (760 mi) in radius, or about 70% of that of the Moon. It is believed to be an iron-nickel alloy and may have a temperature similar to the Sun’s surface, approximately 5778 K (5505 °C).
- PFRDA Assistant Manager Notification 2024, Download PDF
- SSC GD Constable Notification 2025 Date Out, Download PDF
- SSC GD Cut Off 2025, Check Previous Year Cut Off
- RRB NTPC Full Form, Its History, Objective, & Reliability
- RRB NTPC Preparation Strategy 2024, Get 3 Months Study Plan

The most comprehensive online preparation portal for MBA, Banking and Government exams. Explore a range of mock tests and study material at www.oliveboard.in
Oliveboard Live Courses & Mock Test Series
- Monthly Current Affairs 2024
- Download RBI Grade B PYQ PDF
- Download IFSCA Grade A PYQs
- Download SEBI Grade A PYQs
- Attempt Free SSC CGL Mock Test 2024
- Attempt Free IBPS Mock Test 2024
- Attempt Free SSC CHSL Mock Test 2024
- Download Oliveboard App
- Follow Us on Google News for Latest Update
- Join Telegram Group for Latest Govt Jobs Update

Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Insights IAS Brochure |
- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru --> Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2025
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
- Insights IAS Brochure

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

- How to Study Art & Culture?
- What is Art and Culture? What is the difference between the two?
- Indus Civilization
- Evolution of rock-cut architecture in India
- Important rock-cut caves
- The contribution of Pallavas to Rock-cut architecture
- Comparision of art form found at Ellora and Mahabalipuram
- Buddhist Architecture
- Early Temples in India
- Basic form of Hindu temple
- Dravida style of temple architecture
- Nagara Style or North India Temple style
- Vesara style of temple architecture
- Characteristic features of Indo-Islamic form of architecture
- Styles of Islamic architecture in the Indian subcontinent
- Types of buildings in Islamic architecture in the Indian subcontinent
- Evolution of this form of architecture during the medieval period
- Modern Architecture
- Post-Independence architecture
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Bharhut Sculptures
- Sanchi Sculptures
- Gandhara School of Sculpture
- Mathura School of Sculpture
- Amaravati School of Sculpture
- Gupta Sculpture
- Medieval School of Sculpture
- Modern Indian Sculpture
- Pre Historic Painting
- Mural Paintings & Cave Paintings
- Pala School
- Mughal Paintings
- Bundi School of Painting
- Malwa School
- Mewar School
- Basohli School
- Kangra School
- Decanni School of Painting
- Madhubani Paintings or Mithila paintings
- Pattachitra
- Kalighat Painting
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Personalities Associated to Paintings
- Christianity
- Zoroastrianism
- Six Schools of Philosophy
- Lokayata / Charvaka
- Hindustani Music
- Carnatic Music
- Folk Music Tradition
- Modern Music
- Personalities associated with Music
- Bharatanatyam
- Mohiniattam
- Folk Dances
- Modern Dance in India
- Sanskrit Theatre
- Folk Theatre
- Modern Theatre
- Personalities associated with Theatre
- History of Puppetry
- String Puppetry
- Shadow Puppetry
- Rod Puppetry
- Glove Puppetry
- Indian Cinema and Circus
- Shankaracharya
- Ramanujacharya (1017-1137AD)
- Madhvacharya
- Vallabhacharya
- Kabir (1440-1510 AD)
- Guru Nanak (1469-1538 AD)
- Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
- Shankar Dev
- Purandaradasa
- Samard Ramdas
- Classical Languages
- Scheduled Languages
- Literature in Ancient India
- Buddhist and Jain Literature
- Tamil (Sangam) Literature
- Malayalam Literature
- Telugu Literature
- Medieval Literature
- Modern Literature
- Important characteristics of Fairs and Festivals of India
- Some of the major festivals that are celebrated in India
- Art & Crafts
- Ancient Science & Technology
- Medieval Science & Technology
- Famous Personalities in Science & Technology
- Tangible Cultural Heritage
- Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Heritage Sites
- Natural Heritage Sites
- Important Institutions
- Important programmes related to promotion and preservation of Indian heritage
- Ochre Colored Pottery (OCP)
- Black and Red Ware (BRW)
- Painted Grey-Ware (PGW)
- Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW)
- Origin of Martial arts in India
- Various forms of Martial arts in India
- Origin and Evolution of the Earth
- Geological History of the Earth
- Geological Time Scale
- Latitude and Longitude including important Parallels and Meridians
- Motions of the Earth and their effects
- Inclination of the Earth’s Axis and its effects
- Local and Standard Time and the International Date Line
- Eclipses – Solar, Lunar
- Layers of the Earth
- Temperature, Pressure and Density of the Earth’s Interior
- Sources of information for the study of Earth’s Interior
- Relevance of Seismology in studying the interior of the Earth
Importance of studying interior of the earth
- Formation of Rocks
- Different types of Rocks
- Rock to Soil formation
- Landform Development
- Continental Drift Theory
- Sea Floor Spreading
- Plate Tectonics Theory
- Formation of Second order relief
- How are Fold mountains formed?
- Types of folds
- Characteristics of fold mountains
- What are Block Mountains?
- What are faults?
- How are Block Mountains formed?
- Types of Block Mountains
- Characteristics of volcanic mountains
- Types of Volcanic Mountains
- Circum-erosional or Relict or Residual mountains
- Meaning & Definition
- How are Plateaus Formed?
- Classification of Plateaus based on location
- Types of Plateaus
- Some major Plateaus of the world
- Importance of Plateaus
- Different types of plains and their formation process
- Location of Plain Landforms
- Importance of Plains
- Other landforms
- Formation of Volcanoes
- Location of Volcanoes
- Reasons for Concentration of volcanoes along the Ring of Fire
- Extrusive Volcanic Landforms
- Intrusive Volcanic Landforms
- Effects of Volcanism
- Measures to mitigate volcanic disasters
- Introduction
- Causes of Earthquakes
- Distribution of Earthquakes
- Frequency of Earthquake Occurances
- Earthquake Waves
- Measuring Earthquakes
- Effects of Earthquakes
- Earthquake Hazard Zone Mapping
- Earthquake Swarms
- Reasons for the Earthquake proneness in India
- Earthquake Hazard Mitigation
- What is a fold?
- Geometry of a fold
- Classification of folds
- Fold mountains
- What is a fault?
- Fault Structure
- Fault Classifications
- Faulting Geometry
- Fault styles (types)
- Faults and Forces
- Effects of Faulting
- What is isostasy?
- Resulting Geological Processes from Isostasy
- Impact of weathering on its landscape
- Factors that Influence Weathering
- Types of weathering
- Significance of weathering
- Impact of anthropogenic activities on weathering
- How Weathering Is Different From Erosion?
- Agents of erosion
- Factors Impacting Erosion
- Positive Impact of Erosion on Human settlements
- Measures to control accelerated Erosion
- Fluvial erosional landforms
- Fluvial depositional landforms
- Erosional Landforms
- Depositional Features
- Karst topography
- Depositional features
- Erosional features
- Stages of Erosion process by wind
- Erosional landforms
- Transportation by Winds
- Depositional landforms
- Depositional Landforms
- Significance of Glaciers
- Structure, Composition of Atmosphere
- Weather & Climate
- Heat Budget
- Distribution of Temperature
- Temperature Inversion
- Pressure and Pressure belts
- Planetary Winds
- Periodic Winds
- Local Winds
- Precipitation-forms & Types, Distribution Of Rainfall
- Cyclones and Anticyclones
- World Climatic Regions
- Relief Features
- Bottom Reliefs of the Atlantic Ocean
- Bottom Reliefs of the Pacific Ocean
- Bottom Reliefs of the Indian Ocean
- Sources of Ocean heat
- Range of Ocean Temperature
- Distribution Patterns & Factors impacting distribution of temperature of Oceanic Water
- Horizontal Distribution of Temperature in Oceans
- Vertical Distribution of Temperature in Oceans
- What is Salinity?
- Why is salinity important?
- Factors determining ocean water salinity
- Distribution of Salinity
- Horizontal Distribution of Salinity
- Vertical Distribution of Salinity
- Regional distribution of water salinity across the oceans
- Anatomy of A Wave
- Wave Formation
- Tsunami Waves
- Suitable conditions for growth of coral reefs
- How reefs are made?
- Types of coral reef formations
- Location and Distribution of Coral Reefs
- Functions of coral reefs
- Importance of Coral reefs
- Threats to Coral reefs
- Coral bleaching
- Protection Measures of Coral Reefs
- Biogeography
- World Economic and Human Geography
- Important Places Mapping
Home » World Geography » Physical Geography of the World » Geomorphology » Interior Structure of the Earth » Importance of studying interior of the earth
- We rely on Earth for valuable resources such as soil, water, metals, industrial minerals, and energy, and we need to know how to find these resources and exploit them sustainably.
- We can study rocks and the fossils they contain to understand the evolution of our environment and the life within it.
- We can learn to minimize our risks from earthquakes, volcanoes, slope failures, and damaging storms.
- We can learn how and why Earth’s climate has changed in the past, and use that knowledge to understand both natural and human-caused climate change.
- We can recognize how our activities have altered the environment in many ways and the climate in increasingly serious ways, and how to avoid more severe changes in the future.
- We can use our knowledge of Earth to understand other planets in our solar system, as well as those around distant stars.

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology
Essay on Earth
500 words essay on earth.
The earth is the planet that we live on and it is the fifth-largest planet. It is positioned in third place from the Sun. This essay on earth will help you learn all about it in detail. Our earth is the only planet that can sustain humans and other living species. The vital substances such as air, water, and land make it possible.

All About Essay on Earth
The rocks make up the earth that has been around for billions of years. Similarly, water also makes up the earth. In fact, water covers 70% of the surface. It includes the oceans that you see, the rivers, the sea and more.
Thus, the remaining 30% is covered with land. The earth moves around the sun in an orbit and takes around 364 days plus 6 hours to complete one round around it. Thus, we refer to it as a year.
Just like revolution, the earth also rotates on its axis within 24 hours that we refer to as a solar day. When rotation is happening, some of the places on the planet face the sun while the others hide from it.
As a result, we get day and night. There are three layers on the earth which we know as the core, mantle and crust. The core is the centre of the earth that is usually very hot. Further, we have the crust that is the outer layer. Finally, between the core and crust, we have the mantle i.e. the middle part.
The layer that we live on is the outer one with the rocks. Earth is home to not just humans but millions of other plants and species. The water and air on the earth make it possible for life to sustain. As the earth is the only livable planet, we must protect it at all costs.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
There is No Planet B
The human impact on the planet earth is very dangerous. Through this essay on earth, we wish to make people aware of protecting the earth. There is no balance with nature as human activities are hampering the earth.
Needless to say, we are responsible for the climate crisis that is happening right now. Climate change is getting worse and we need to start getting serious about it. It has a direct impact on our food, air, education, water, and more.
The rising temperature and natural disasters are clear warning signs. Therefore, we need to come together to save the earth and leave a better planet for our future generations.
Being ignorant is not an option anymore. We must spread awareness about the crisis and take preventive measures to protect the earth. We must all plant more trees and avoid using non-biodegradable products.
Further, it is vital to choose sustainable options and use reusable alternatives. We must save the earth to save our future. There is no Planet B and we must start acting like it accordingly.
Conclusion of Essay on Earth
All in all, we must work together to plant more trees and avoid using plastic. It is also important to limit the use of non-renewable resources to give our future generations a better planet.
FAQ on Essay on Earth
Question 1: What is the earth for kids?
Answer 1: Earth is the third farthest planet from the sun. It is bright and bluish in appearance when we see it from outer space. Water covers 70% of the earth while land covers 30%. Moreover, the earth is the only planet that can sustain life.
Question 2: How can we protect the earth?
Answer 2: We can protect the earth by limiting the use of non-renewable resources. Further, we must not waste water and avoid using plastic.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Interior of the Earth - Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts - Notes, Videos & Tests
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Part of the course
| docs | 71 videos | 44 tests |
Interior of the Earth Study Material
| Revision Notes - Interior of the Earth Doc | 11 pages |

| Mind Map: Interior of the Earth Doc | 1 page |
| Earthquake: Causes and Types of Waves Video | 04:30 min |
| Interior of the Earth: Introduction Video | 11:50 min |
| NCERT Textbook - Interior of the Earth Doc | 9 pages |
| Interior of the Earth Video | 08:03 min |
| Volcanoes and Volcanic Landforms Video | 08:31 min |
| Types of Volcanoes Video | 04:42 min |
| Effects of Earthquake Video | 03:01 min |
| Short Question Answers : Interior of the Earth Doc | 5 pages |
| Long Question Answers : Interior of the Earth Doc | 7 pages |
| Important Questions: Interior of the Earth Doc | 13 pages |
NCERT Textbook of Interior of the Earth - Geography Class 11 | Free PDF
| NCERT Textbook - Interior of the Earth Doc 9 pages |
NCERT Solutions of Interior of the Earth - Geography Class 11
Videos for interior of the earth - geography class 11 | humanities/arts.
| Earthquake: Causes and Types of Waves Video 04:30 min |
| Interior of the Earth: Introduction Video 11:50 min |
| Interior of the Earth Video 08:03 min |
| Volcanoes and Volcanic Landforms Video 08:31 min |
| Types of Volcanoes Video 04:42 min |
| Effects of Earthquake Video 03:01 min |
Notes for Interior of the Earth - Geography Class 11 | Humanities/Arts
| Revision Notes - Interior of the Earth Doc 11 pages |
| Mind Map: Interior of the Earth Doc 1 pages |
| Short Question Answers : Interior of the Earth Doc 5 pages |
| Long Question Answers : Interior of the Earth Doc 7 pages |
| Important Questions: Interior of the Earth Doc 13 pages |
Online Test for Interior of the Earth - Geography Class 11 | Humanities/Arts
Extra questions for interior of the earth - geography class 11, other chapters in geography class 11 for humanities/arts.
| |
Top Courses for Humanities/Arts

Importance of Interior of the Earth Humanities/Arts
Interior of the earth notes free pdf download, important questions for interior of the earth, interior of the earth practice questions.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

- Classroom Programme
- Interview Guidance
- Online Programme
- Drishti Store
- My Bookmarks
- My Progress
- Change Password
- From The Editor's Desk
- How To Use The New Website
- Help Centre
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
- Mains Practice Questions
- Filter By :
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Indian Society
Mains practice questions is now being continued in Be Mains Ready program with a dedicated syllabus coverage for Mains 2019. To join this program, click here "Be Mains Ready program"
Q. Discuss the internal structure of the Earth and comment on S and P-waves shadow zones with suitable diagrams.
- Start the answer by briefly mentioning the interior of earth.
- Discuss the differentiation of layers of earth and role of seismic waves in the study of the interior of earth.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
On the basis of seismic investigations, the earth can be divided into three major layers: crust, mantle, core.
Differentiation of layers of Earth
- The upper layer which is less dense and granitic in character, is known as "sial", while the lower layer which is basaltic in character is known as "sima".
- It extends down to 30 or 40 kilometer beneath continents and to about 10 km beneath ocean basins
- The boundary between these is at about 700 km depth.
- The upper mantle contains a most important zone called the "asthenosphere". It is located at depths between 50 to 100 km.
- This zone provides lava for volcanic eruptions.
- The outer core is composed of iron mixed with nickel and trace amounts of lighter elements.
- The outer core is not under enough pressure to be solid, so it is liquid even though it has a composition similar to the inner core.
Role of Seismic Waves in Study of Interior of Earth
The study of the passage of seismic waves through the earth has helped in knowing the structure of the earth's interior and in defining the physical properties of various layers. For example:
- The "outer core" was discovered when it was found that P-waves were bent inwards thereby producing a "shadow zone" at the surface.
- Since the S-waves do not pass through the outer core, it is concluded that it may be in the liquid state.

Seismic waves travel different velocities depending on the nature of the layer in which they are travelling. Thus they not only indicate the position of each layer but also give clues as to its composition.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Earth’s interior- Layers of the earth
Table of Contents
Introduction
In this article, we will discuss the earth’s interior and the internal layers of the earth.
The surface of the earth is an outcome of the processes operating in the interior of the earth. Both exogenic and endogenic forces are constantly shaping the landscape of Earth. It is fascinating to know how scientists have gathered information about the different layers of the Earth.
The radius of the earth is about 6370km. Till now, no one can reach the centre of the earth. Most of our knowledge about the earth’s interior is based on the estimates and inferences. However, the study of seismic waves has contributed immensely to our understanding of the different layers of the earth. For instance, the velocity and the path travelled by the waves provide the authenticity of the physical conditions prevailing inside the earth.
Sources of information about the layers of the earth
Direct sources.
- Deep oceanic drilling projects.
- Volcanic eruption.
Indirect sources
- Temperature and pressure increase with the increasing distance from the surface towards the Earth’s interior.
- The density of the material.
- Gravitational Anomaly .
- Seismic activities.
Based on the physical conditions, the earth can be divided into three layers. That are crust, mantle and core. These layers are further subdivided based on their properties.

Layers of the earth
- It is the uppermost and the thinnest layer of the earth.
- The average thickness of the crust is about 35 km.
- Moreover, the crust can be further divided into the Continental crust and Oceanic crust.
Continental crust
- In terms of structure, composition, density and thickness, the continental crust differs from the oceanic crust.
- It is composed of granitic and andesitic rocks .
- The continental crust is rich in Feldspar mineral .
- Moreover, the density of the continental crust is about 2.6gm/cm3.
- The average thickness is about 40km.
- However, under the mountainous regions, the thickness reaches up to 100 Km.
Oceanic crust
- The oceanic crust is made up of the Basalt.
- It is rich in ferro-magnesia.
- Its density is about 3 gm/cm 3.
- The Conrad discontinuity divides the continental crust and the oceanic crust.
Moho discontinuity
The moho discontinuity separates the crust and mantle.
- The mantle extends from the base of the crust at a depth of 2900km.
- It comprises about 80% of the earth’s total volume.
- Mantle contain Iron, magnesium and calcium.
- Because of increasing temperature and pressure inside the earth, it is hotter and denser than the crust.
- At the depth of about 670km, the mantle is divided into upper and the lower mantle.
Upper mantle
- It comprises of Peridotite and Gabbro and Plagioclase minerals .
- The average density of the upper mantle is about 4.5 gm/cm3.
- The average temperature of this layer is about 1100 C ⁰.
- The Repetti Discontinuity separates the upper mantle from the lower mantle.
- Due to Repetti discontinuity, there is a sharp increase in the velocity of the seismic waves.
- The upper mantle is heterogeneous in terms of density and composition.
- The thickness of the uppermost part of this stratum is about 80-100 km.
- The uppermost part of the upper mantle is as rigid as the crust.
- Both crust and upper mantle constitute the Lithosphere.
Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere is that part of the layer of earth which is below the Lithosphere. It extends at a depth of 100 km to 400 km from the lithosphere. Due to the high temperature, this region is partially molten. Here the velocity of seismic wave slowdowns abruptly. This region is called Low-velocity region. Also, it is rich in Peridotite . Moreover, this region is popularly known as the Magma Chamber .
Lower mantle
- The lower mantle extends at a depth of 670 km to 2900km.
- The average density of this region is about 6.5gm/cm 3 .
- It is composed of Olivine , Plagioclase and Orthoclase minerals.
- Guttenberg Discontinuity separates the lower mantle and the upper core of the earth.

At the depth of 2900 km to 6371 km, lies the core of the earth. Because of metallic composition, its density is nearly twice as the mantle. It comprises of 15% to 16% of the total volume of the earth. The core is divided into two regions called the outer core and the inner core.
- It extends between 2900 km to 5150 km.
- The density of the outer core is about 10gm/cm 3 .
- It mainly consists of Iron and Nickle (about 85%).
- The outer core is always in the molten state.
- Lehman Discontinuity separates the outer core and the inner-core.
- The inner-core extends between 5150 km to 6371 km.
- The average density of the inner core is about 13gm/cm3.
- Despite the high temperature, the inner-core is always in the solid-state due to very high pressure prevailing in this region.
- The temperature of the inner core is about 6000 C⁰.
Frequently asked Questions-
The asthenosphere is part of which layer.
The asthenosphere is the part of Upper mantle layer of the earth.
Layers which are solid?
The crust and the inner core.
What is the location of Conrad discontinuity?
The location of Conrad discontinuity is between the oceanic crust and the continental crust.

What is the location of Moho discontinuity?
The location of Moho discontinuity is between the crust and the mantle layer of the earth.
Location of Repetti discontinuity?
The Repettis discontinuity is located between the upper and the lower mantle. The sharp increase in the velocity of the seismic wave is indicative of the existence of this discontinuity.
What is the location of Guttenburg discontinuity?
Between the lower mantle and outer core of the earth. Here, the velocity of P( primary) waves decreases abruptly. On the other hand, the S (Secondary) waves disappear beyond this discontinuity.
What is the location of Lehman discontinuity?
It is located between the outer and the inner core of the earth. The increase in the velocity of P waves shows the existence of this discontinuity.
Which layer of the Earth has thermal convectional currents?
The thermal convectional currents are common in the Mantle layer of the earth.
- How did the theory of plate tectonics evolve over time?
- 7 Criticisms of Continental Drift Theory by Alfred Wegener
- Malthus theory of population: critical analysis & relevance
- Major Types of Clouds formation and their Characteristics
- Get Detailed Bpsc syllabus 2022-23
3 thoughts on “Earth’s interior- Layers of the earth”
Pingback: Bpsc geography optional syllabus 2022 updated | geography4u
I’ve been watching the USGS, for the last 37 years. I keep seeing the depth of earthquakes listed. Over the last couple years. I became interested in the depts of EQ’s wondering just how deep they are. This page help provide better understanding of the depths of EQ’s and exactly what layers of the earth’s surface are being reached. Thank you for whoever researched this and whomever posted this.
Thank you for your valuable feedback
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
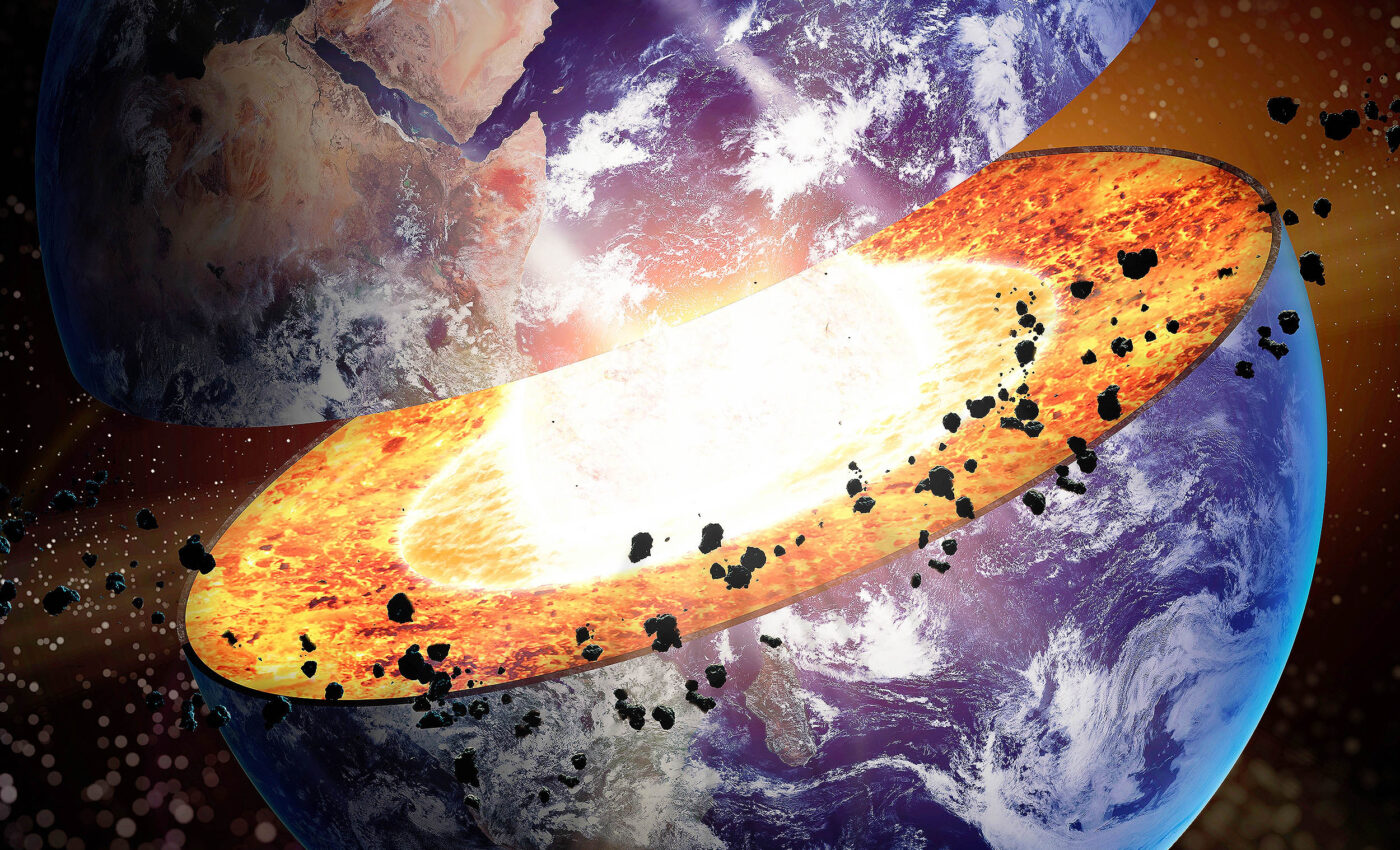

Earth has a vast interior ocean, 400-miles under our feet, that creates 'ringwoodite' gems
Thanks to the discovery of a mineral called ringwoodite, a team of scientists made a surprising discovery that could change how we think about Earth’s water reserves
The researchers found strong evidence that huge amounts of water — comparable to several oceans — are hidden deep within the Earth’s mantle beneath the United States.
The discovery, made by geophysicist Steve Jacobsen from Northwestern University and seismologist Brandon Schmandt from the University of New Mexico , may represent the planet’s largest water reservoir.
Rethinking Earth’s water cycle
Published in the journal Science , their findings shed light on the Earth’s formation, composition, and the amount of water trapped in mantle rock.
“Geological processes on the Earth’s surface, such as earthquakes or erupting volcanoes, are an expression of what is going on inside the Earth, out of our sight,” explained Jacobsen, a co-author of the paper.
“I think we are finally seeing evidence for a whole-Earth water cycle , which may help explain the vast amount of liquid water on the surface of our habitable planet. Scientists have been looking for this missing deep water for decades,” Jacobsen continued.
Earth’s mantle has remarkable secrets
Scientists have long speculated about the existence of water trapped in the Earth’s mantle , located between the lower and upper mantle at depths of 250 to 410 miles.
Jacobsen and Schmandt are the first to provide direct evidence of water in this “transition zone” on a regional scale, extending across most of the interior of the United States.
“Melting of rock at this depth is remarkable because most melting in the mantle occurs much shallower, in the upper 50 miles,” said Schmandt, a co-author of the paper.
“If there is a substantial amount of H2O in the transition zone , then some melting should take place in areas where there is flow into the lower mantle, and that is consistent with what we found.”
Liquid, ice, vapor and a fourth form of water
The water discovered in the mantle is not in a form familiar to us – it is not liquid, ice, or vapor. Instead, it is trapped inside the molecular structure of the minerals in the mantle rock.
The immense pressure created by 250 miles of solid rock, along with temperatures above 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit, causes water molecules to split and form hydroxyl radicals (OH) that can be bound into a mineral’s crystal structure.
“Whether or not this unique sample is representative of the Earth’s interior composition is not known, however,” Jacobsen said. “Now we have found evidence for extensive melting beneath North America at the same depths corresponding to the dehydration of ringwoodite, which is exactly what has been happening in my experiments.”
Following the ringwoodite
Ringwoodite, a high-pressure mineral with a captivating blue hue, was named after the Australian geologist Alfred Ringwood, forms deep within the Earth’s mantle at depths between 410 and 660 kilometers (250-410 miles). What makes ringwoodite truly remarkable is its ability to store water within its crystal structure.
Synthesizing ringwoodite in the lab
Jacobsen has been synthesizing ringwoodite, a sapphire-like blue mineral, in his Northwestern lab by reacting the green mineral olivine with water at high-pressure conditions. He found that more than one percent of the weight of ringwoodite’s crystal structure can consist of water.
Under the immense pressures and temperatures found in the mantle’s transition zone, water molecules split into hydroxyl radicals (OH), which can then be incorporated into ringwoodite’s structure. This mineral acts like a sponge, soaking up water and storing it in the deep Earth .
“There is something very special about the crystal structure of ringwoodite that allows it to attract hydrogen and trap water. This mineral can contain a lot of water under conditions of the deep mantle,” Jacobsen noted.
Ringwoodite implications for Earth
The presence of water-rich ringwoodite in the Earth’s mantle has implications for our understanding of the planet’s formation and its potential for habitability.
As scientists continue to study this intriguing mineral, they may uncover new insights into the role of water in the Earth’s deep interior and its influence on the geologic processes that shape our world.
Ringwoodite’s ability to store and transport water within the mantle could also have implications for the search for life on other planets, as the presence of water is considered a key factor in the development and sustainability of life as we know it.
Detecting magma beneath North America
Using seismic waves, Schmandt detected the presence of magma beneath North America, which aligned with Jacobsen’s findings of partial melt when subjecting synthesized ringwoodite to conditions around 400 miles below the Earth’s surface.
Additionally, seismic studies have detected regions of partial melting in the mantle’s transition zone, which could be attributed to the release of water from ringwoodite as it transforms into other minerals at greater depths.
“Seismic data from the USArray are giving us a clearer picture than ever before of the Earth’s internal structure beneath North America,” Schmandt explained. “The melting we see appears to be driven by subduction — the downwelling of mantle material from the surface.”
Process of dehydration melting
The melting detected by the researchers is called dehydration melting.
When ringwoodite in the transition zone moves deeper into the lower mantle, it forms a higher-pressure mineral called silicate perovskite , which cannot absorb water. This causes the rock at the boundary between the transition zone and lower mantle to partially melt.
“When a rock with a lot of H2O moves from the transition zone to the lower mantle it needs to get rid of the H2O somehow, so it melts a little bit,” Schmandt said. “This is called dehydration melting.”
“Once the water is released, much of it may become trapped there in the transition zone,” Jacobsen added.
How ringwoodite was accidentally discovered
The international team of scientists responsible for this remarkable find was led by Graham Pearson, Canada Excellence Research Chair in Arctic Resources at the University of Alberta .
Analysis of the mineral sample revealed that it contains a significant amount of water — 1.5 per cent of its weight — a finding that proved to have far-reaching implications for our understanding of the Earth’s interior and its dynamic nature.
Elusive ringwoodite
Ringwoodite, a form of the mineral peridot, is believed to exist in large quantities under high pressures in the transition zone between the Earth’s upper and lower mantle.
While ringwoodite has been found in meteorites, no terrestrial sample had ever been discovered before Graham Pearson came along. Due to the extreme depths at which it is formed, this elusive mineral is inaccessible for direct fieldwork.
Contribution of artisan miners in Brazil
The ringwoodite sample was found in 2008 in the Juina area of Mato Grosso, Brazil, where artisan miners unearthed a diamond from shallow river gravels.
The diamond, which had been brought to the Earth’s surface by a deeply derived volcanic rock known as kimberlite, contained the ringwoodite inclusion.
Pearson’s team had been searching for another mineral when they purchased the three-millimeter-wide, dirty-looking, commercially worthless brown diamond.
The ringwoodite itself, invisible to the naked eye and buried beneath the surface, was fortunately discovered by Pearson’s graduate student, John McNeill, in 2009.
“It’s so small, this inclusion, it’s extremely difficult to find, never mind work on,” Pearson said, “so it was a bit of a piece of luck, this discovery, as are many scientific discoveries.”
Confirming the Find
The sample underwent years of rigorous analysis using Raman and infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction before it was officially confirmed as ringwoodite.
The critical water measurements were performed at Pearson’s Arctic Resources Geochemistry Laboratory at the University of Alberta, which forms part of the world-renowned Canadian Centre for Isotopic Microanalysis , also home to the world’s largest academic diamond research group.
Implications for Earth’s Dynamics
For Pearson, one of the world’s leading authorities in the study of deep Earth diamond host rocks, this discovery proved to be the most significant of his career.
It confirmed about 50 years of theoretical and experimental work by geophysicists, seismologists, and other scientists trying to understand the makeup of the Earth’s interior.
“One of the reasons the Earth is such a dynamic planet is the presence of some water in its interior,” Pearson said. “Water changes everything about the way a planet works.”
Ringwoodite, Earth’s water cycle, and the future
In summary, the crucial discovery of a vast water reservoir deep within the Earth’s mantle by Steve Jacobsen and Brandon Schmandt has revolutionized our understanding of the planet’s formation, composition, and water cycle.
As researchers continued to explore the complex processes occurring far beneath the Earth’s surface, their ringwoodite findings provided a new understanding of the delicate balance that makes our planet habitable.
The presence of this hidden ocean, trapped within the crystals of mantle rock, serves as a testament to the incredible forces at work within the Earth and the countless mysteries that still lie beneath our feet.
With each new revelation, we move closer to unraveling the secrets of our planet’s past, present, and future, and to appreciating the remarkable world we call home.
The full study was published in the journal Science and the journal Nature
—–
Like what you read? Subscribe to our newsletter for engaging articles, exclusive content, and the latest updates.
Check us out on EarthSnap , a free app brought to you by Eric Ralls and Earth.com.

MCQs and Answers
Engineering interview questions, Mcqs, Objective Questions,Class Notes,Seminor topics,Lab Viva Pdf free download. CIVIL | Mechanical | CSE | EEE | ECE | IT | Chemical Online Quiz Tests for Freshers.
[PDF Notes] Short essay on the Interior of the Earth
The exact knowledge about the interior of the earth still remains an enigma. Yet knowledge of the structure, composition and the processes going on within it would certainly help scientists answer questions regarding crystal motion, earthquakes, the volcanic eruptions and the origins of the continents and of the earth itself.
To quote Monk house, “The condition of the interior of the earth is for the most part outside the province of the geographer, “its study belongs to the geophysicist. Nevertheless, certain facts are relevant in order to help the understanding of surface features.”
The uncertainties of the earth’s interior are due to the fact it is at such a great distance (6400 km) from the surface of the earth that makes it practically out of bounds for direct observation.
As the earth gradually solidified, heavier elements slowly sank towards the center, and lighter elements slowly moved upward to the surface concentrating in the earth’s crust.
Earth’s interior is arranged roughly in concentric layers, each one distinct either in chemical composition or temperature, with heat radiating outward from the centre by conduction and then by physical convection in the more plastic levels nearer the surface.
It is interesting to know as to how scientists gathered knowledge about these layers and what the characteristics of each of these layers are.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
English Compositions
Short Essay on Our Planet Earth [100, 200, 400 words] With PDF
Earth is the only planet that sustains life and ecosystems. In this lesson, you will learn to write essays in three different sets on the planet earth to help you in preparing for your upcoming examinations.

Short Essay on Our Planet Earth in 100 Words
Earth is a rare planet since it is the only one that can support life. On Earth, life is possible for various reasons, the most essential of which are the availability of water and the presence of oxygen. Earth is a member of the Solar System. The Earth, along with the other seven planets, orbits the Sun.
One spin takes approximately twenty-four hours, and one revolution takes 365 days and four hours. Day and night, as well as the changing of seasons, occurs due to rotation and revolution. However, we have jeopardized our planet by our sheer ignorance and negligence. We must practise conservation of resources and look after mother earth while we have time.
Short Essay on Our Planet Earth in 200 Words
Earth is a blue planet that is special from the rest of the planets because it is the only one to sustain life. The availability of water and oxygen are two of the most crucial factors that make life possible on Earth. The Earth rotates around the Sun, along with seven other planets in the solar system. It takes 24 hours to complete one rotation, and approximately 365 days and 4 hours to complete one revolution. Day and night, as well as changing seasons, are all conceivable due to these two movements.
However, we are wasting and taking advantage of the natural resources that have been bestowed upon us. Overuse and exploitation of all-natural resources produce pollution to such an alarming degree that life on Earth is on the verge of extinction. The depletion of the ozone layer has resulted in global warming. The melting of glaciers has resulted in rising temperatures.
Many animals have become extinct or are endangered. To protect the environment, we must work together. Conversation, resource reduction, reuse, and recycling will take us a long way toward restoring the natural ecosystem. We are as unique as our home planet. We have superior intelligence, which we must employ for the benefit of all living beings. The Earth is our natural home, and we must create a place that is as good as, if not better than, paradise.
Short Essay on Our Planet Earth in 400 Words
Earth is a unique planet as it is the only planet that sustains life. Life is possible on Earth because of many reasons, and the most important among them is the availability of water and oxygen. Earth is a part of the family of the Sun. It belongs to the Solar System.
Earth, along with seven other planets, revolves around the Sun. It takes roughly twenty-four hours to complete one rotation and 365 days and 4 hours to complete one revolution. Rotation and revolution make day and night and change of seasons simultaneously possible. The five seasons we experience in one revolution are Spring, Summer, Monsoon, Autumn, and Winter.
However, we are misusing resources and exploiting the natural gifts that have been so heavily endowed upon us. Overuse and misuse of all the natural resources are causing pollution to such an extent that it has become alarming to the point of destruction. The most common form of pollution caused upon the earth by us is Air Pollution, Land Pollution, Water Pollution, and Noise Pollution.
This, in turn, had resulted in Ozone Layer Depletion and Global Warming. Due to ozone layer depletion, there harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun are reaching the earth. It, in turn, is melting glaciers and causing a rise in temperature every year. Many animals have either extinct or are endangered due to human activities.
Some extinct animals worldwide are Sabre-toothed Cat, Woolly Mammoth, Dodo, Great Auk, Stellers Sea Cow, Tasmanian Tiger, Passenger Pigeon, Pyrenean Ibex. The extinct animals in the Indian subcontinent are the Indian Cheetah, pink-headed duck, northern Sumatran rhinoceros, and Sunderban dwarf rhinoceros.
The endangered animals that are in need of our immediate attention in India are Royal Bengal Tiger, Snow leopard, Red panda, Indian rhinoceros, Nilgiri tahr, Asiatic lion, Ganges river dolphin, Gharial and Hangul, among others. We have exploited fossil fuels to such an extent that now we run the risk of using them completely. We must switch to alternative sources of energy that are nature friendly. Solar power, windmills, hydra power should be used more often, and deforestation must be made illegal worldwide.
We must come together to preserve the natural environment. Conversation, reduction, reuse and recycling of the resources will take us a long way in rebuilding the natural habitat. We are as unique as our planet earth. We have higher intelligence, and we must use it for the well-being of all living organisms. The Earth is our natural abode, and we must make a place as close to Paradise, if not better.
Hopefully, after going through this lesson, you have a holistic idea about our planet Earth. I have tried to cover every aspect that makes it unique and the reasons to practise conversation of natural resources. If you still have any doubts regarding this session, kindly let me know through the comment section below. To read more such essays on many important topics, keep browsing our website.
Join us on Telegram to get the latest updates on our upcoming sessions. Thank you, see you again soon.
Satellite images show Ukraine's expanding attacks inside Russia
Ukraine’s daring incursion into Russia has been backed by an expanding campaign of aerial attacks on strategic targets — from bridges in the Kursk region , where its ground forces have pressed their surprise assault, to an air base and an oil depot set ablaze deep inside Russian territory.
Kyiv has touted these attacks and its use of U.S. weapons in videos proudly shared on social media. NBC News has geolocated some of those videos, and analyzed satellite images to track the campaign.
‘As many problems as possible’
Last Friday and then on Sunday, Ukraine’s air force shared videos purporting to show at least two strategic bridges blown up over the Seim River in Russia’s southern Kursk border region , which Ukrainian troops invaded in a daring assault more than two weeks ago.
The claims were supported by satellite imagery showing at least one destroyed span near the town of Glushkovo. The destruction of the bridges over the river could isolate Russian forces in the area hoping to halt the Ukrainian advance.
Ukraine initially practiced a strict informational silence about the surprise Kursk operation, which has overturned the status quo of the 2 1/2-year war. But that has since changed, and this week, Ukraine has been advertising its attacks inside Russia.
Having targeted the permanent bridges, Ukraine’s military shared a video Wednesday saying its special forces were using the U.S.-manufactured high-mobility artillery rocket system (HIMARS) to destroy pontoon bridges and engineering equipment in the Kursk region as well — a first official acknowledgement that Kyiv was using Western weapons in the Kursk offensive.Pontoon bridges are temporary structures that militaries often build to maintain critical supply lines when permanent structures are damaged or destroyed.
NBC News was able to geolocate a segment of the video to a bend on the Seim River several miles from Glushkovo, where a bridge span was hit earlier. NBC News was not able to verify whether the video shows the destruction of a pontoon bridge or when it was shot.
Another video shared Thursday by the country’s air force chief, Lt. Gen. Mykola Oleshchuk, claimed to show Ukraine’s use of guided aerial bombs to destroy two “bridge crossings” in Kursk this week. NBC News also geolocated part of that video to an area close to Glushkovo.
The abundance of videos shared by Kyiv in recent days could signal its intention to project confidence over its ability to strike targets and stoke unease inside Russia.“We must all understand that to drive the occupier from our land, we must create as many problems for the Russian state as possible on its own territory,” President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said Thursday .
And those problems are surely accumulating for the Kremlin.
A diesel depot in the town of Proletarsk in Russia’s southern Rostov region, which borders Ukraine, has been ablaze for days after it was hit by Ukrainian drones on Sunday. More than 500 firefighters have been battling the fire, which at one point spread to over 100,000 square feet, according to Russian state media.
Ukraine claimed responsibility for hitting the depot, which its army’s general staff said stored oil products used to supply the Russian army. Regional Gov. Vasily Golubev blamed the fire — which he said was affecting “warehouses” in Proletarsk, without specifying that a strategic depot was involved — on falling drone debris.
Satellite images captured on Monday, the day after the alleged attack, show flames and thick clouds of black smoke billowing from the depot. Other satellite images showed the blaze still burning on Thursday.
Another case of Ukraine reaching deeper into Russia this week involved an airfield in the southern Volgograd region.A dramatic video geolocated by NBC News on Thursday showed huge plumes of smoke filling the sky above the air base as explosions are heard in the background.
The region’s governor, Andrei Bocharov, confirmed a fire broke out at a Defense Ministry facility after a drone attack, without specifying the nature of the facility. A Ukrainian security source told NBC News that its military attacked the region’s Marinovka air base, targeting warehouses storing antitank weapons and fuel.
While it’s hard to discern details of the damage to the air base from the satellite imagery, large swaths of what appears to be burned-out land can be seen in the image taken after the alleged attack.
In the latest attack later Thursday, a railway ferry with fuel tanks on board was hit in a port in the southern region of Krasnodar, across from the occupied Crimean Peninsula.Russian officials blamed Kyiv, but Ukraine has so far not claimed responsibility.
Krasnodar Gov. Veniamin Kondratyev said the ferry sank as a result of the hit and the resulting fire, adding that booms had been deployed in the water to prevent the spread of fuel. Local emergency officials said one crew member remained missing and 17 were rescued.
The attacks this week and the ongoing incursion appear to have surprised not only Moscow, but also Ukraine’s Western partners.Yet Washington has maintained so far that it has no issue with Kyiv’s use of its weapons.
Responding to the statement from Ukraine’s military that the U.S.-supplied HIMARS were used in Kursk this week, Pentagon spokesperson Lt. Col. Charlie Dietz told NBC News the weapons are being employed from within Ukraine, as far as Washington can tell, and it has not seen them being moved to Kursk or inside Russia.
“Back in May, we gave Ukraine permission to use U.S.-provided munitions, with the exception of ATACMS, to defend themselves against Russian troops north of the border, and that is what Ukraine has said they are doing,” Dietz said.
Max Butterworth is a Photo Editor for NBC News based in London.
Yuliya Talmazan is a reporter for NBC News Digital, based in London.
Matthew Mulligan is a reporter for the NBC News Social Newsgathering team based in London.
Marin Scott is an Associate Reporter on the Social Newsgathering team.

Inside quietest place on Earth where you can hear your blood pumping and eyes blinking

The quietest place on Earth is so silent you can hear yourself blinking.
The record is held by the anechoic test chamber at Orfield Laboratories in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, where an ambient sound level of -24.9 dBA (decibels A-weighted) was recorded.
Visitors to the room, which is specially designed to suppress sound, have reported being able to hear blood moving through their veins, hearing their eyelids closing as they blink, and feeling sick and disorientated.
The Orfield Labs room first broke the record in 2004 with a background noise reading of -9.4 dBA.
Did you know? “The Quietest Place on Earth” is the anechoic chamber at Orfield Laboratories Inc. in #Minneapolis pic.twitter.com/Fsk7E2pPW2 — realPRO (@realPROmpls) February 13, 2015
Even lower sound levels of -13 dBA were recorded there in 2012 after some improvements, but the room lost its record for a little while in 2015, when an anechoic chamber at Microsoft Headquarters in Washington, USA, recorded levels of -20.35 dBA.
Orfield Labs took the record back again in 2021 and has held it ever since.
The room supresses 99.99% of sound thanks to its 3.3-foot-thick fibreglass acoustic wedges, as well as the double walls of insulated steel and a foot of concrete.
Company founder, Steven Orfield, told MailOnline : “When it’s quiet, ears will adapt. The quieter the room, the more things you hear. You'll hear your heart beating, sometimes you can hear your lungs, hear your stomach gurgling loudly.
“In the anechoic chamber, you become the sound.”
The chamber is used primarily for product testing and research.
An anechoic chamber is a room designed to completely absorb reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. This is the difference between bursting a ballon outside and inside a anechoic chamber https://t.co/idYuaOHwzn [full video by dydxlnx: https://t.co/tvGVQbK4wr ] pic.twitter.com/xwIpoeHv78 — Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) January 17, 2022
The lab has been used by motorcycle maker Harley-Davidson to make their bikes quieter while retaining their signature sound and by washing machine manufacturer Whirlpool to develop metaphors for what sounds should sound like.
Steven explained: “We record products and people listen to them based on semantic terms, like ‘expensive’, ‘low quality’. We measure their feelings and associations.”
He himself once said that after spending 30 minutes inside the chamber, he could hear the mechanical valve inside his heart working very loudly.
Header image: Alamy
If you like watching records being broken you should check out our Records Weekly series on YouTube…
‘In Pursuit’: The Power of Epistemic Humility
Elizabeth H. Bradley and Jonathon S. Kahn ask if the breakdown of dialogue on campus is in part a reflection of how we teach.
By Elizabeth H. Bradley and Jonathon S. Kahn
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

Olena Zagoruyko/iStock/Getty Images Plus
A new academic year is set to begin after what was one of the most tumultuous years on college campuses since the Vietnam War–era protests. Depending on one’s perspective, higher education institutions have emerged as sites of protest against a disturbing foreign conflict rife with humanitarian crises; they have been dangerous hotbeds of radicalism threatening Jewish community members; or they have been testing grounds for the limits of free speech in the 21st century. From our vantage point, as the president and a faculty member at a small liberal arts college, all can be true, and it is precisely the legitimacy of multiple perspectives that has made life on campus this past year so difficult and demanding.
We can’t sugarcoat it, because we live it: The breakdown of dialogue on college campuses is real. The irony that liberal arts institutions of higher education are struggling to navigate diverse perspectives is not lost on us. Institutions of higher education insist that navigating differences is core to their work. Mission statements aplenty claim that being able to engage multiple viewpoints represents a central educational value. That so many colleges and universities are grappling with their most basic and central educational commitments should give pause.
It pushes us to ask a question that has largely gone unasked: Is a breakdown in how we now educate partially to blame for the current breakdown on campuses? In other words, is it us?
Most Popular
- Professor finds way to see if students used AI to cheat
- Open-access expansion threatens academic publishing industry
- Six ways to promote belonging among college students
Current tumult has obscured a crucial organizing tenet of higher education: to be always in pursuit of greater understanding. It is cliché, perhaps. But in these toughest of days, we found ourselves thinking about the deeper implications of being “in pursuit.” To pursue understanding is to conceive of knowledge building as requiring continuous seeking, revising and questioning. Such an approach to learning is desperately needed today not only because it fosters curiosity (which it does) but also because it staves off absolutist impulses to deride and silence others’ views, impulses we have seen firsthand.
Consider, for example, a tremendously difficult class one of us co-taught on the history of blackface performances and minstrel practices during the early part of the 20th century at what was then our all-women’s college. Since the course dealt with deeply racist practices, the understandable desire to singularly condemn the college’s history was palpable. Indeed, at the start of the class, many students, most of whom were white, described their motivations for taking the class primarily in terms of exposing the college’s racist past. “Critique” was the language they spoke, which they took to mean uncovering the college’s blameworthy history, denouncing the practices they were studying and confirming their own absolutes about race and hypocrisy at elite institutions more broadly. They described their attachment to the institution as tenuous. It was clear that, to their thinking, college was a place to have an educational experience and receive a degree, while the notion that they might develop a sense of fidelity or obligation to a college with a racist history, or develop a complex understanding of a condemned practice, was an anathema.
But something different happened. What unfolded over the course of the semester was an exercise in the pursuit of understanding. If the students began the course convinced about the racist motivations of their counterparts in the early 20th century, their research complicated those assumptions. They learned that all-women performances of blackface at that time were quite rare, and so what was happening on campus then represented something distinct. Their inquiries led them to consider the transition from 19th-century Victorian models of white womanhood to newer formulations in the early 20th century that came to be known as first-wave feminism. They began to ask: Is it possible that these blackface performances contributed to this transition? Did commitments to feminism and gender equality at that time actually reinforce persistent racial inequalities? How is it possible that these young women could have genuinely believed they were pursuing a form of self-liberation through racist tropes and performances?
Their answers to these questions went in many directions, and none of them excused the racism of this time. But instead of vilifying these earlier students and refusing to understand perspectives different from their own, our students began to see their predecessors as flawed and complicated with multiple motivations; these included a daring to do what men were doing in an attempt to articulate their own desires for equality. Again, our students did not excuse these practices or the women who participated in them as much as they began to understand their behavior as sitting in a complex network of forces, a condition that may very well mark the human experience. Crucially in the final sets of class meetings, the students began to wonder about themselves as similarly flawed and circumscribed by social forces of which they may not be fully aware.
The effects of this insight on the students’ relationships to the institution were significant. They began to see the college in the early 20th century as a context in which young white women, many of whom were from the middle classes, were struggling to craft a self during a tumultuous time of changing norms. The parallels became obvious. The students began to understand that they too sit in cross-pressured contexts in which they are haltingly and fallibly trying to make sense of themselves in their own turbulent times.
We do not want to overstate the effects of the class; however, the experience gave students a profound encounter with the power of epistemic humility, an acknowledgement of the necessity of curiosity, nuance, uncertainty and multiple perspectives needed for building knowledge. That encounter expanded the students’ capacity to understand—and even have empathy for—a broader range of experiences and perspectives, a necessary condition for engaging the pluralism possible on a college campus.
The question facing higher education today is how to build these types of experiences. The good news is that this doesn’t require fancy lab equipment or other expensive infrastructure. It does require three basic elements—instructors committed to giving their students an experience of novel inquiry, primary sources and time. When faculty make clear that the entire purpose of the class is for students to figure out what they think, students begin to understand the power of question asking. From there, any question—from the teacher, their classmates and themselves—feels exploratory and enticing.
Primary sources—original documents or images—are vital because they cry out for multiple interpretations, functioning like a ball-and-socket joint around which students’ thoughts, ideas and questions can begin to turn. Critically, all this takes time. Students need time to trust that the instructor genuinely wants them to go on a journey of their own. And the meanings of images and texts surface slowly, yielding only to the student’s patience and persistence to ask questions from multiple perspectives.
At the end of the 19th century, William James insisted that education required “the habit of always seeing an alternative, of not taking the usual for granted, of making conventionalities fluid again, of imagining foreign states of mind.” In the 20th century, W. E. B. Du Bois worried about the dangers of education reinforcing “the overwhelming sense of the I, and the consequent forgetting of the Thou.” And in the 21st century, the feminist literary theorist Rita Felski asks , “Why—even as we extol multiplicity, difference, hybridity … are we so hyperarticulate about our adversaries?”
Editors’ Picks
- Academic Publishers Threatened By Open-Access Expansion
- New Sweet Briar Policy Bars Transgender Students
- Supreme Court Keeps Debt-Relief Plan Blocked for Now
All three circle around the same idea. To be always in the pursuit of greater understanding is to confess that we have more to learn. It is to conceive of education as a process of relationship building between our own perspectives and experiences not our own. Without this, our relationships with those with different experiences risk becoming brittle and unsustainable. Unable to contain a community’s multitudes, we resort to excising—canceling—those whom we cannot countenance. The pursuit of understanding requires the opposite.
Today’s campuses need to develop and be given greater latitude for this version of learning. We know from experience that this process is messy, and we need to allow for that messiness, knowing that exploration, mistakes and missteps are all part of learning. We must resist the temptation to drop the “in pursuit” and focus only on the “understanding,” as if learning amounts to nothing more than the dogmatic piling up of facts.
The pursuit of understanding emphasizes the dynamics of learning, which necessarily expands our abilities to comprehend a broad range of perspectives and experiences. Most importantly, the pursuit of understanding pushes us to ask what sort of human each of us wants to be in relation to others. Our future together relies on being forever in pursuit.
Elizabeth H. Bradley is the president of Vassar College and a professor of science, technology and society, and of political science. She is deeply engaged with research on the performance and quality of higher education institutions in the U.S. Jonathon S. Kahn is a professor of religion and the former director of engaged pluralism at Vassar College. He works at the intersection of race, religious ethics and politics.

A Leadership Position We Aren’t Prepared For
Faculty members who run a lab have a research job and a leadership job, but they are often only trained for one of th
Share This Article
More from views.

In Defense of the AAUP’s Statement on Boycotts
John K. Wilson opposes academic boycotts but supports the AAUP’s controversial new statement nevertheless.

A Model for Advancing Institutional Effectiveness via Undergraduate Research
To help scale traditional faculty/student models of undergraduate research engagement, institutional leaders can cons

Where Progressive Illiberalism Reigns
Litigation stemming from antisemitism on campuses shows that colleges must revive their commitments to freedom and to
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
- Physics Concept Questions And Answers
- Interior Of Earth Questions
Interior of Earth Questions
The interior of the Earth is made up of three parts: crust, mantle, and core. The inner core is found to be in a solid state, and the outer core is in a liquid state. The outermost layer of Earth is called the crust. The crust is relatively cold, thin, and brittle. The next layer is the mantle. It has a density higher than the crust portion with 10 to 200 km thickness.
Read more: Interior of Earth
Important Interior of Earth Questions with Answers
1. The mantle occupies _____ of the Earth.
Answer: c) 84%
Explanation: Earth’s mantle occupies 84% of space.
2. How is the interior of the Earth classified?
The interior of the Earth is classified into crust, mantle, and core.
3. The outermost solid part of the Earth is known as ______.
- None of the options
Explanation: Crust is the outermost layer of the Earth.
4. State true or false: The asthenosphere is the lower portion of the mantle.
Answer: b) FALSE
Explanation: The upper portion of the mantle is known as the asthenosphere.
5. Why is the term ‘SIAL’ used to refer to the crust and lithosphere?
Since the major constituent minerals of the crust are silica (Si) and aluminium (Al), it is referred to as SIAL.
6. Which among the following is made of solid rocks?
Answer: b) Mantle
Explanation: The mantle is made up of solid rocks and is hot.
7. Why is the core also known as the “nife” layer?
The core is called the “nife” layer since it is composed of heavy materials like nickel (Ni) and iron (Fe).
8. In which state is the core of the Earth?
- Both solid and liquid
Answer: d) Both solid and liquid
Explanation: The outer core is in a liquid state, and the inner core is in solid state.
9. The uppermost part of the mantle and crust are called the _______.
- Hydrosphere
- Lithosphere
Answer: c) Lithosphere
Explanation: The crust and the uppermost part of the mantle are known as the lithosphere.
10. Mantle has a density ______ the crust portion.
- Higher than
Answer: b) Higher than
Explanation: The density of the mantle is comparatively higher than the crust.
Watch the video below to understand the composition of each layer

Practice Questions
- What are the various layers of the Earth?
- How is the interior of Earth classified?
- List the properties of the crust.
- List three properties of the mantle.
- What is meant by the core of the Earth, and how is it classified?
| Related links | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PHYSICS Related Links | |
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Boeing’s No Good, Never-Ending Tailspin Might Take NASA With It

By Clive Irving
Mr. Irving is an investigative journalist who has covered aviation and aerospace for more than 30 years.
Fifty-five years ago, when humans first walked on the moon, the Apollo 11 astronauts left Earth through the massive power of the Saturn V rocket. The greatest punch came from the rocket’s first stage, which provided 7.5 million pounds of thrust. The awesome spectacle of that first stage was thanks to the work by engineers at Boeing.
Fast forward to the present day, and here is a new spectacle in space provided by Boeing. It’s not awesome.
Two astronauts, Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore, arrived at the International Space Station on June 6 , expecting to stay for just over a week. Now they won’t be heading back to Earth until February. Their ride was on the Boeing Starliner spacecraft, now deemed by NASA to be too risky for the return trip because of a host of troublesome technical glitches.
NASA spin doctors object to headlines declaring that the astronauts are “stranded” or “stuck” in space, pointing out correctly that they are not in jeopardy.
But make no mistake: This is a fiasco. And not just because of the strain it puts on Ms. Williams and Mr. Wilmore and their families. Boeing’s engineering woes extend beyond Starliner; they threaten NASA’s bigger goals of going back to the moon through its Artemis program, for which Boeing has become an essential partner. I was told that a number of retired astronauts are increasingly troubled by Boeing’s performance. This loss in confidence helps put the entire Artemis program into a new state of uncertainty.
Consider the fact that on Aug. 7, Steve Stich, the manager for NASA’s commercial crew program, used the term “multiple failure” to describe the possible concerns he and his team were contemplating about the spacecraft’s propulsion system.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

News | August 17, 2023
Super blue moons: your questions answered.
By Tracy Vogel and Ernie Wright

A trifecta of labels is being applied to the Moon of Aug. 30-31, 2023. It’s a full moon , a supermoon , and finally a blue moon. You may hear it referred to as a super blue moon as a result. It sounds exciting, but what does that really mean? We’ve got you covered.
What is a supermoon?
The Moon travels around our planet in an elliptical orbit, or an elongated circle, with Earth closer to one side of the ellipse. Each month, the Moon passes through the point closest to Earth (perigee) and the point farthest from Earth (apogee). When the Moon is at or near its closest point to Earth at the same time as it is full, it is called a “supermoon.” During this event, because the full moon is a little bit closer to us than usual , it appears especially large and bright in the sky.
Because the Moon’s orbit wobbles and differs depending on where the Sun and Earth are in their orbits, the exact distance of these closest and furthest points varies. But the Moon can look up to 14 percent bigger at perigee than apogee.
OK, so what is a blue moon?
A blue moon is the term for when we see the full moon twice in a single month. The Moon's cycle is 29.5 days, so just a bit shorter than the average length of a calendar month. Eventually that gap results in a full moon happening at the beginning of a month with enough days still remaining for another full cycle ― so a second full moon in the same month. In other words, a full moon that happens on the 1st or 2nd of a month will probably be followed by a second full moon on the 30th or 31st. This happens every two to three years.
People sometimes refer to two types of blue moons: monthly and seasonal. This upcoming moon is a monthly blue moon. Seasonal blue moons occur when there are four full moons in a single season (spring, summer, fall and winter) instead of the usual three.
Will the Moon be blue?
No, that’s just the term for two full moons in a month.
Is the Moon ever blue?
On rare occasions, tiny particles in the air ― typically of smoke or dust ― can scatter away red wavelengths of light, causing the Moon to appear blue.
Will this Moon be bigger and more “super?”
You probably won’t notice a big difference in size. When the Moon is closest to Earth (a “supermoon”), it can look up to 14 percent bigger than when it’s farthest from Earth. This is similar to the size difference between a quarter and a nickel. Because the Moon will be close to us in its orbit, it will appear a bit brighter than usual.
Not-So-Super Moon vs. Supermoon
Credit: nasa’s scientific visualization studio, do blue moons and supermoons always occur together.
No. The term “supermoon” is used to describe a full Moon that occurs within a day or so of perigee, so they happen three to four times a year. About 25 percent of all full moons are supermoons, but only 3 percent of full moons are blue moons. The time between super blue moons is quite irregular ― it can be as much as 20 years ― but in general, 10 years is the average. The next super blue moons will occur in a pair, in January and March 2037.
So if it’s not blue and not super-sized, is this worth checking out?
Hey, it’s always a good time to look at the Moon! Try our Daily Moon Guide to see if you can locate some of our recommended daily Moon sights.
Related Stories
You Might Also Like


Local News | A look inside Lincoln Park’s brand new animal…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Things to Do
- Classifieds
SUBSCRIBER ONLY
Local news | a look inside lincoln park’s brand new animal shelter.

Gloria Bonora's dog died on Sunday, Aug. 25. On Tuesday, Aug. 27, Bonora sat in a pastel blue room at the new Lincoln Park Animal Shelter, filling out papers to adopt Rapunzel, a German Shepherd who'd been with the shelter for about a month.
Subscribe to continue reading this article.
Already subscribed to login in, click here., more in local news.

Crime and Public Safety | Man who targeted police in shootout with child in house sentenced on numerous felonies

Crime and Public Safety | Riverview resident sentenced after wrong-way crash kills woman, pregnant woman’s baby

Michigan News | Out-of-state crews help restore power services throughout Michigan

Things To Do | River Rouge Days to return Sept. 6, 7, 8
Columbia Entrepreneurs Changing the Beauty Business
From moisturizer to pimple patches, alumni are using their cosmetics smarts to tap into a multibillion-dollar industry.
Earth Therapeutics
Bringing K-beauty innovation to essential spa products
John Kang ’88CC, ’91LAW had virtually zero experience with skin care when he began selling loofah sponges to Bed Bath & Beyond under the name Earth Therapeutics in 1993. He certainly didn’t see himself becoming a leading beauty entrepreneur. But after quitting his budding law career to focus on the brand (an offshoot of his parents’ importing business), the two-time Columbia graduate found an unexpected calling. “This was a total accident,” Kang says. “There wasn’t a lot of intention at the time, but here I am over thirty years later.”
Today, Earth Therapeutics sells not only sponges but a variety of home-spa items, from hand cream to hair towels to “anti-stress” pillow mist. The brand, a mainstay of Ulta Beauty, Walmart, and other mass retailers, is especially known for its natural foot-care products. “I like to think I came out with the first foot lotion,” says Kang, the company’s president and CEO. “When I designed it twenty-five years ago, people were like, who the heck is going to buy foot lotion? But it turned out to be one of our absolute bestsellers.”
Since launching that first moisturizing foot cream, Kang and his team have introduced an array of other pedicure products. “My personal favorites are the Sole Scrubber foot-wash mat used together with the foamy foot shampoo,” says Julia Kang-Reeves ’94GSAS, Kang’s sister. Kang-Reeves, who earned a master’s degree in classics from Columbia before joining the family business, currently serves as Earth Therapeutics’ marketing director.
As the Long Island–based company has evolved, Kang and his team have remained focused on the utilitarian nature of their beauty brand. “When I first started out, a lot of the products out there were based more on color and fragrance,” says Kang. “I didn’t want to do that. A product has to do what it says it’s going to do: if it claims to heal cracked and dry feet, it’s got to do that. How it looks and smells is secondary.”
In recent years, Earth Therapeutics has integrated more Korean innovations into its product line, whether through ingredients (seaweed, milkweed) or accessories (sheet masks, under-eye patches). “Korean beauty is all about the ingredients: using less-harsh chemicals with an emphasis on healing,” says Kang, who, along with Kang-Reeves, was born in South Korea. “We’re focusing now on the K-beauty segment of foot care with cutting-edge products like foot masks.”
Kang-Reeves echoes the brand’s ingredient-driven philosophy in her marketing and promotes Earth Therapeutics as high-quality but affordable and appropriate for a wide range of customers. “Over the past few years, beauty has become even more of a red-hot industry, fueled by trends and the influencer frenzy,” she says. “But Earth Therapeutics is about more than beauty. We’re a wellness brand offering reliable products for the entire body, yoked together by an ethic of quality self-care for all.”

Giving clean, gentle skin care a celebrity glow-up
It’s a problem familiar to many: dry, blemish-prone skin often made worse by creams and serums — even the expensive ones. For those with sensitive skin, finding the right cosmetic products can be a challenge. The Outset , a New York City–based beauty startup founded by two sensitive-skin sufferers, Kate Foster Lengyel ’11BUS and actress Scarlett Johansson, aims to help solve this dilemma by making skin care cleaner, simpler, and less irritating.
“Sensitive skin is reactive,” says Lengyel, a veteran of the cosmetics and fashion industries with an MBA from Columbia. “It’s often the result of having a disrupted skin barrier, which is what keeps in moisture. Stress on that barrier can come from too many products, too many harsh active ingredients, or allergens like fragrance, gluten, or nuts. We’re trying to remove as many sources of irritation as possible with a less-is-more approach.”
Since launching in 2021, The Outset has captured the attention of skin-care enthusiasts for its gentle ingredients and cruelty-free testing approach. “The secret sauce is our approach to hydration,” explains Lengyel. “We use a proprietary botanical complex called Hyaluroset sourced from the seeds of cassia flower that’s been proven to outperform hyaluronic acid.” Earlier this year, the company introduced a mineral-based sunscreen called Hydrasheer. “That was really important for me, because I have a half-inch scar on my forehead from skin cancer,” says Lengyel. “Plus, 80 percent of our skin’s aging comes from UV exposure, but only 29 percent of people are wearing SPF every day.”
Lengyel, who started her career in beauty marketing at Victoria’s Secret over twenty years ago, has had a front-row seat to the cosmetics industry’s evolution. “There used to be a top-down approach of big brands dictating the trends, and now it’s the consumer voice doing that,” she says. The Outset, whose products are sold by Sephora, Goop, and other retailers, taps into today’s digital-consumption habits through TikTok (500,000+ followers) and Instagram (300,000+ followers) and oversees an online platform of superfans who the company calls “Skinsiders.”
While The Outset undoubtedly benefits from Johansson’s star power, Lengyel believes that the quality of products is what primarily drives loyalty and growth. “We operate with a ‘Startup 101’ mentality that I learned at Columbia Business School,” she says. “The brand has to be able to stand on its own; it has to deliver on and exceed expectations with or without Scarlett’s attachment. There’s a demand now for ‘better-for-you’ products, and we pride ourselves on clean ingredients that are efficacious, safe, and a joy to use.”
Hero Cosmetics
Popularizing pimple patches in the United States
Ju Rhyu ’08BUS was an expat living in South Korea when a common skin problem inspired a dramatic career move. It was 2013, and “I was breaking out, and I didn’t know why,” says Rhyu, who was then working for Samsung. “Maybe it was the different environment or different lifestyle stress, but it was really frustrating.” Around that time, she had begun noticing an odd skin-care trend on the streets of Seoul: people wearing small, round stickers on their faces to treat pimples. “I bought some and was blown away by how well they worked,” says Rhyu. “I have sensitive skin, so a lot of creams and ointments would turn my skin red, flaky, and dry. The patches did not do that.”

Rhyu, who grew up in a Korean-American household in Seattle, wondered why such a simple and effective zit solution hadn’t gained traction stateside (“Why was I learning about this now and not when I was a teenager?” she recalls thinking). So the Columbia Business School alumna came up with an innovative idea: marketing the popular Korean product in the United States under her own American brand.
In 2017, Rhyu officially cofounded Hero Cosmetics , a skin-care company known for its Mighty Patch stickers. “They’re made with hydrocolloid, which is a fluid-absorbing gel,” says Rhyu. Although hydrocolloid adhesives have existed in the US for many years, they’ve historically been used on wounds, not acne. “When applied to an inflamed pimple, they absorb the gunk and promote fast recovery,” Rhyu explains. Since introducing the original Mighty Patch through Amazon, Hero has added stickers specifically for daytime and overnight use, for dark spots and early-stage blemishes, and for the chin, nose, and forehead. The brand also produces cleanser, moisturizer, and other products designed to promote clearer skin.
Hero was acquired in 2022 by consumer-goods giant Church & Dwight for $630 million, and its products can be found at retailers like Target, CVS, and Ulta Beauty. The brand is also expanding internationally; its growth, Rhyu says, has a lot to do with its appeal to adults with mild or moderate acne, like her. “Hero is talking to an ignored audience,” says Rhyu, who in addition to running the New York City–based company as CEO, supports other entrepreneurs as an angel investor. “Traditionally, acne products have been for teens and folks with more serious acne. The formulas are quite harsh and focused on drying the skin. Hero offers something for anyone and everyone who has that occasional breakout and wants control over their skin.”
13 More Alumni Beauty Brands
AbsoluteJOI skin care, founded by Anne C. Beal ’93PH
AMP Beauty cosmetics retailer, cofounded by Angel Lenise Pyles ’11JRN
Delvaux hairstyling clay, founded by Filipe Delvaux ’22SPS
Emilie Heathe makeup and nail polish, founded by Emily H. Rudman ’14BUS
Glow Recipe skin care, cofounded by Christine Chang ’10GSAS
IT Cosmetics makeup and skin care, founded by Jamie Kern Lima ’04BUS
Olfactory NYC custom fragrances, founded by Joseph Vittoria ’21BUS
Peach & Lily skin care, founded by Alicia Yoon ’04CC
Prakti skin care, founded by Pritika Swarup ’21GS
RéVive skin care, CEO Elana Drell-Szyfer ’91CC
Shespoke custom lipsticks, cofounded by Kelsey Groome ’19BUS
Soko Glam cosmetics retailer, cofounded by Dave Cho ’15BUS
Sundays nail polish, founded by Amy Ling Lin ’16BUS
This article appears in the Fall 2024 print edition of Columbia Magazine with the title "The Business of Beauty."
More From Alumni

The Best Spots for Birding in NYC
Birder Angela Co ’05GSAPP recommends five avian hotspots around the city

Inside Gotham Chopra’s Religion of Sports
The documentary filmmaker argues that the world of sports is a faith like any other

7 Columbia Coffee Entrepreneurs You Should Know
Alumni-owned coffee shops and roasters are energizing communities through cold brew, cappuccinos, cortados, and more
Stay Connected.
Sign up for our newsletter.
General Data Protection Regulation
Columbia University Privacy Notice

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The core constitutes nearly 15% of earth's volume and 32.5% of earth's mass. The core is the densest layer of the earth with its density ranges between 9.5-14.5g/cm3. The Core consists of two sub-layers: the inner core and the outer core. The inner core is in solid state and the outer core is in the liquid state (or semi-liquid).
Interior of the Earth. The crust, the mantle, and the core are the three layers that make up the earth. The core only forms 15 per cent of the Earth's volume, whereas the mantle occupies 84 per cent. The remaining 1 per cent is made up of the crust. From the picture, we see that at the centre of the Earth lies the core, then there is the ...
The interior of the earth can reveal the nature of lithosphere. A knowledge of earth's interior is essential for understanding plate tectonics. Hence, this lesson is about the interior of the ...
Aptitude And Foundational Values For Civil Services: History, Evolution & Challenge. Diving into the heart of the Earth in "Unveiling Earth's Hidden Layers." Discovering the mysteries of the planet's interior, its diverse layers, and their role in shaping the world as we know it.
At the very surface of the Earth is the crust, the topmost layer, made mostly out of solid rocks. It also is made up of iron, oxygen, silicon, magnesium and aluminium. It is the thinnest layer out of all the layers. The crust is the deepest in areas where there are mountains. It can be 43 miles thick in those areas.
The Mantle. The mantle is the mostly-solid bulk of Earth's interior. The mantle lies between Earth's dense, super-heated core and its thin outer layer, the crust. The mantle is about 2,900 kilometers (1,802 miles) thick and makes up a whopping 84% of Earth's total volume.
Importance of studying interior of the earth. We rely on Earth for valuable resources such as soil, water, metals, industrial minerals, and energy, and we need to know how to find these resources and exploit them sustainably. We can study rocks and the fossils they contain to understand the evolution of our environment and the life within it ...
500 Words Essay On Earth. The earth is the planet that we live on and it is the fifth-largest planet. It is positioned in third place from the Sun. This essay on earth will help you learn all about it in detail. Our earth is the only planet that can sustain humans and other living species. The vital substances such as air, water, and land make ...
The earth's radius is about 6,378 km. No one can reach the centre of the earth and make observations or collect samples of the material. Under such conditions, you may wonder how scientists tell us about the earth's interior and the type of materials that exist at such depths. Most of our knowledge about the interior of
Enhance your skills with practice papers tailored for Interior of the Earth, question paper analysis, and language proficiency. Access the best books, sample papers, and study material specifically designed for Interior of the Earth to ensure effective preparation. Stay informed about the Humanities/Arts exam date and official website updates.
Start the answer by briefly mentioning the interior of earth. Discuss the differentiation of layers of earth and role of seismic waves in the study of the interior of earth. Conclude Suitably. Introduction. On the basis of seismic investigations, the earth can be divided into three major layers: crust, mantle, core. Body. Differentiation of ...
In this article, we will discuss the earth's interior and the internal layers of the earth. The surface of the earth is an outcome of the processes operating in the interior of the earth. Both exogenic and endogenic forces are constantly shaping the landscape of Earth. It is fascinating to know how scientists have gathered information about ...
"One of the reasons the Earth is such a dynamic planet is the presence of some water in its interior," Pearson said. "Water changes everything about the way a planet works." Ringwoodite, Earth's water cycle, and the future. In summary, the crucial discovery of a vast water reservoir deep within the Earth's mantle by Steve Jacobsen ...
The solid part of the Earth consist of solid rocks and soil. The Earths surface is the geosphere. The hydrosphere makes up all of the water on Earth's surface. The Earth is divided into three layers the crust, mantle, and the core. The crust is very brittle and this is why it was easy for Mount St. Helen to blow it to pieces.
It is interesting to know as to how scientists gathered knowledge about these layers and what the characteristics of each of these layers are. engineer May 26, 2024 Class Notes PPT. [PDF Notes] Short essay on the Interior of the EarthThe exact knowledge about the interior of the earth still remains an enigma. Yet knowledge of the structure ...
Earth scientists are working to determine the course of future lava flows in Iceland's southwestern corner one bucketful at a time.
Earth is a member of the Solar System. The Earth, along with the other seven planets, orbits the Sun. One spin takes approximately twenty-four hours, and one revolution takes 365 days and four hours. Day and night, as well as the changing of seasons, occurs due to rotation and revolution. However, we have jeopardized our planet by our sheer ...
Butch Wilmore, top, and Suni Williams, inside the International Space Station, on July 2, 2024. ... will journey back to Earth without a crew, likely sometime in early September, according to NASA
Essay Sample Content Preview: Earth's Interior. Name. Professor. Date. Earth's interior. Planets are structured into distinct layers. The layers appear in the order of densities of the materials making up these layers. The densest materials form the innermost layers while the least dense form the outermost layer.
Ukraine's daring incursion into Russia has been backed by an expanding campaign of aerial attacks on strategic targets — from bridges in the Kursk region where its ground forces have pressed ...
The quietest place on Earth is so silent you can hear yourself blinking.. The record is held by the anechoic test chamber at Orfield Laboratories in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, where an ambient sound level of -24.9 dBA (decibels A-weighted) was recorded.. Visitors to the room, which is specially designed to suppress sound, have reported being able to hear blood moving through their veins ...
Two ways that Scientist may study and find the interior of the Earth are with Meteorites and Magnetic Fields. The scientist may use meteorites to discover the interior of the Earth's earlier solar system by studying the meteorites that arrived on the Earth. The scientist might use magnetic fields by the science advances which involves measuring ...
Elizabeth H. Bradley and Jonathon S. Kahn ask if the breakdown of dialogue on campus is in part a reflection of how we teach. A new academic year is set to begin after what was one of the most tumultuous years on college campuses since the Vietnam War-era protests. Depending on one's perspective, higher education institutions have emerged as sites of protest against a disturbing foreign ...
The interior of the Earth is classified into crust, mantle, and core. 3. The outermost solid part of the Earth is known as ______. Answer: c) Explanation: Crust is the outermost layer of the Earth. 4. State true or false: The asthenosphere is the lower portion of the mantle. Answer: b) FALSE.
Studying the earth's interior can help us to understand earthquakes, volcanoes, plate tectonics and more about the inner earth's natural processes. In general the earth's interior has been sorted by Gravity. Heavier elements like iron tend to sink toward the center or core of the earth. Lighter materials, the silicates, oxygen compounds and ...
Guest Essay. Boeing's No Good, Never-Ending Tailspin Might Take NASA With It. Aug. 28, 2024 ... Long after Ms. Williams and Mr. Wilmore make it back to Earth, there will still be the Boeing ...
Citizen scientists spotted an object zipping through the Milky Way at more than 1 million miles an hour, and a new study shows it could be a rare hypervelocity star.
You probably won't notice a big difference in size. When the Moon is closest to Earth (a "supermoon"), it can look up to 14 percent bigger than when it's farthest from Earth. This is similar to the size difference between a quarter and a nickel. Because the Moon will be close to us in its orbit, it will appear a bit brighter than usual.
Gloria Bonora's dog died on Sunday, Aug. 25. On Tuesday, Aug. 27, Bonora sat in a pastel blue room at the new Lincoln Park Animal Shelter, filling out papers to adopt Rapunzel, a German Sheph…
Earth Therapeutics Bringing K-beauty innovation to essential spa products. From moisturizer to pimple patches, alumni are using their cosmetics smarts to tap into a multibillion-dollar industry. ... Inside Gotham Chopra's Religion of Sports. The documentary filmmaker argues that the world of sports is a faith like any other. 7 Columbia Coffee ...