
Chapter 8: Making Academic Arguments

8.3 Types of Evidence in Academic Arguments
Robin Jeffrey and Yvonne Bruce
All academic writers use evidence to support their claims. However, different writing tasks in different fields require different types of evidence. Often, a combination of different types of evidence is required in order to adequately support and develop a point. Evidence is not simply “facts.” Evidence is not simply “quotes.”
Evidence is what a writer uses to support or defend his or her argument, and only valid and credible evidence is enough to make an argument strong.
For a review of what evidence means in terms of developing body paragraphs within an essay, you can refer back to Section 4.3 .
As you develop your research-supported essay, consider not only what types of evidence might support your ideas but also what types of evidence will be considered valid or credible according to the academic discipline or academic audience for which you are writing.
Evidence in the Humanities: Literature, Art, Film, Music, Philosophy
- Scholarly essays that analyze original works
- Details from an image, a film, or other work of art
- Passages from a musical composition
- Passages of text, including poetry
Evidence in the Humanities: History
- Primary Sources (photos, letters, maps, official documents, etc.)
- Other books or articles that interpret primary sources or other evidence.
Evidence in the Social Sciences: Psychology, Sociology, Political Science, Anthropology
- Books or articles that interpret data and results from other people’s original experiments or studies.
- Results from one’s own field research (including interviews, surveys, observations, etc.)
- Data from one’s own experiments
- Statistics derived from large studies
Evidence in the Sciences: Biology, Chemistry, Physics
- Data from the author of the paper’s own experiments
What remains consistent no matter the discipline in which you are writing, however, is that “evidence” NEVER speaks for itself—you must integrate it into your own argument or claim and demonstrate that the evidence supports your thesis. In addition, be alert to evidence that seems to contradict your claims or offers a counterargument to it: rebutting that counterargument can be powerful evidence for your claim. You can also make evidence that isn’t there an integral part of your argument, too. If you can’t find the evidence you think you need, ask yourself why it seems to be lacking, or if its absence adds a new dimension to your thinking about the topic. Remember, evidence is not the piling up of facts or quotes: evidence is only one component of a strong, well supported, well argued, and well written composition.
8.3 Types of Evidence in Academic Arguments by Robin Jeffrey and Yvonne Bruce is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.
- Current Students
- News & Press
- Exam Technique for In-Person Exams
- Revising for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Introduction to 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Before the 24 Hour Take Home Exam
- Exam Technique for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Structuring a Literature Review
- Writing Coursework under Time Constraints
- Reflective Writing
- Writing a Synopsis
- Structuring a Science Report
- Presentations
- How the University works out your degree award
- Accessing your assignment feedback via Canvas
- Inspera Digital Exams
- Writing Introductions and Conclusions
- Paragraphing
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting
- Proofreading
- Working with a Proofreader
- Writing Concisely
- The 1-Hour Writing Challenge
- Editing strategies
- Apostrophes
- Semi-colons
- Run-on sentences
- How to Improve your Grammar (native English)
- How to Improve your Grammar (non-native English)
- Independent Learning for Online Study
- Reflective Practice
- Academic Reading
- Strategic Reading Framework
- Note-taking Strategies
- Note-taking in Lectures
- Making Notes from Reading
- Using Evidence to Support your Argument
- Integrating Scholarship
- Managing Time and Motivation
- Dealing with Procrastination
- How to Paraphrase
- Quote or Paraphrase?
- How to Quote
- Referencing
- Responsible and Ethical use of AI
- Acknowledging use of AI
- Numeracy, Maths & Statistics
- Library Search
- Search Techniques
- Keeping up to date
- Evaluating Information
- Managing Information
- Understanding Artificial Intelligence
- Getting started with prompts
- Thinking Critically about AI
- Using Information generated by AI
- SensusAccess
- Develop Your Digital Skills
- Digital Tools to Help You Study

How to use your reading to support your points.
- Newcastle University
- Academic Skills Kit
- Study Skills
- Critical Thinking
All university research and scholarship is based on evidence, and your own assessed work as a student is no different. To convince your marker that you know what you’re talking about, you can’t just make a statement and expect them to accept it; you will need to provide robust evidence to justify your point, show how you have arrived at your conclusions and prove that it’s based on solid grounds. Everyone is entitled to their own opinion, and we are interested in your ideas, but you need to supply proof and show how it supports your statement, to persuade others of what you think. You might have seen this reflected in marking criteria, assignment guidelines or feedback that say you should ‘use evidence’, to ‘support your argument’ and ‘back up your point’.
What counts as evidence?
The most universal way to support a point is to provide a reference to a source which backs it up: either someone who agrees with you, or evidence that supports you. As your studies progress, this strategy may need to become more in depth, perhaps referencing multiple sources or commenting critically on them. One reference is good, but might be overly selective, ignoring contradictory or better sources. A carefully chosen reference from a highly regarded study or scholar is even better, and best of all is not one, but several sources which demonstrate a weight of evidence building up. More than three or four references starts to become a bit redundant though – the point is made!
What counts as acceptable evidence will vary depending on your subject. Arts and Humanities are based in more subjective argument and interpretation; Social Sciences often draw on qualitative and quantitative data, and Physical and Medical Sciences from empirical data. In some instances, your own personal experience can count as valid evidence, if you were writing a reflective assignment, for example, but it would not be appropriate if writing a report as it might not be representative, and cannot be verified by the reader.
Common knowledge
You don’t have to back up absolutely everything you say with evidence (or you’d soon run out of wordcount to advance your own point properly!). Some things are common knowledge. That could mean that a fact is just generally known by everyone, and not disputed or in doubt. This could include:
- facts such as London is the capital of the United Kingdom
- well documented dates such as the start of the First World War in 1914
- H 2 0 being the chemical formula for water
- things which everyone knows from their lived experience, such as the sky is blue.
Common knowledge could also mean a generally known fact in your specialist field of study, not necessarily known to lay people, but accepted as a basic, fundamental knowledge by everyone in your discipline. However, the higher your level of study, the more you can take specialist general knowledge for granted. A PhD student can be assumed to know the basics and not need to back them up, but a first year undergraduate might have to prove to their lecturer that they do understand what they are talking about, with a reference. If you aren’t sure if something is general knowledge or not, look at the texts you are reading and see if they include a reference to that fact or not. If not, it’s probably generally known. And you might need a reference to general knowledge that comes from outside your own subject.
Have I backed my point up?
To check if you’re supporting your own points with evidence, imagine that the reader is asking you after each statement that you make, ‘ how do you know that? How can you be sure of that? ’ If you have included something in your writing which robustly answers this question, then you’ve backed your point up. If not, think about what kind of evidence you could provide that would satisfy the reader.
You may not be able to find a citation that does exactly what you need it to do, but that doesn’t mean you can’t back your point up; a reference isn’t the only way to do this. You don’t have to find someone else who has said it first; you can make your own points in your own right too, if you support them. This becomes more true as you progress to higher stages of study. Think about your answer to the question, ‘How do I know that’, and what kind of evidence would best suit your purpose:
How do I know that?
- ‘I read it’. Then show the reader where you read it, with a reference
- ‘I worked it out based on something I read’ Then reference the data or opinion you based it on and explain how you built on that evidence with your reasoning.
- ‘I worked it all out myself’ Then show your reasoning in full.
- ‘I saw it in my own research’ Then show the reader your own supporting data or sources that you have collected with your analysis (this is more likely in a dissertation or research report or project where you have time to do your own research)
- ‘I don’t know – I just know! Don’t we all know that?’ Then this might be general knowledge (if you’re sure we all know that!)
All of these are valid ways to back up your own points, but some require you to do original research, which might be outside the scope of your assignment, or disproportionate to the importance of the point you’re making!
Using evidence to support your point
Sometimes it’s enough to include a reference at the end of your sentence, but at other times, you might need to do more than just add the evidence. Evidence doesn’t speak for itself, but often needs to be explained, analysed and interpreted so that the reader understands how it supports your point. You might feel that the reader can work it out for themselves, but it’s your job as the writer to do that work, not the reader. You might after all see it in different ways, and you want the reader to follow your reasoning and see it as you do. As you write or edit your draft, ask yourself:
- What does this evidence mean to you? How should the reader interpret it? Why is that interpretation the most convincing one?
- How does this evidence support your argument?
- To what extent does it support you? Are there any limitations or gaps you want to address or acknowledge?
- What are the implications of this evidence for your argument? “So what”?
Conflicting evidence
Sometimes we find evidence that actually contradicts what we want to say and our natural reaction might be to ignore it and hope that the reader isn’t aware of it. However, you can actually strengthen your work by acknowledging that conflicting evidence. Briefly explain why you think it is not as convincing or does not actually undermine your case, dismiss it and move on. This shows that you can critique your own work; you have considered various possibilities, actively looked for counterarguments, tested your thinking and have come to a carefully considered conclusion. Of course, if you can’t counter the conflicting evidence, then you might need to rethink your point!
What to do when you can't find evidence
Alternatively, you might not be able to find the evidence you need to support your claim. This might mean various things:
- that you need to broaden your search strategy (but set yourself a cut-off point so you don’t look for so long that you run out of time for the rest of your assignment)
- that what you assumed to be true isn’t quite right (in which case, you might need to do more reading and thinking)
- that no-one else has claimed or demonstrated this yet (which might be an opportunity to do some original thinking of your own, if you can evidence it and have time to research it).
Before you invest time in these options, consider how key the point is to your overall assignment. Is it essential or just a side issue?
Download this guide as a PDF
Using evidence to support your argument.
How to use your reading to support your points. **PDF Download**
Academic Skills Team
For more guidance on your learning, book a one-to-one tutorial with one of our tutors or visit our website for more activities and resources.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Types of Evidence in Academic Arguments
All academic writers use evidence to support their claims. However, different writing tasks in different fields require different types of evidence. Often, a combination of different types of evidence is required to support and develop a point adequately.
A writer uses evidence to support or defend his or her argument, and only valid and credible evidence is enough to make an argument strong.
Evidence is not simply “facts.” Evidence is not simply “quotes.”
As you develop your research-supported essay, consider not only what types of evidence might support your ideas but also what types of evidence will be considered valid or credible according to the academic discipline or academic audience for which you are writing.
Evidence in the Humanities: Literature, Art, Film, Music, Philosophy
- Scholarly essays that analyze original works
- Details from an image, a film, or other work of art
- Passages from a musical composition
- Passages of text, including poetry
Evidence in the Humanities: History
- Primary Sources (photos, letters, maps, official documents, etc.)
- Other books or articles that interpret primary sources or other evidence.
Evidence in the Social Sciences: Psychology, Sociology, Political Science, Anthropology
- Books or articles that interpret data and results from other people’s original experiments or studies.
- Results from one’s field research (including interviews, surveys, observations, etc.)
- Data from one’s experiments
- Statistics derived from large studies
Evidence in the Sciences: Biology, Chemistry, Physics
- Data from the author of the paper’s experiments
What remains consistent no matter the discipline in which you are writing, however, is that “evidence” NEVER speaks for itself—you must integrate it into your argument or claim and demonstrate that the evidence supports your thesis. In addition, be alert to evidence that seems to contradict your claims or offers a counterargument: rebutting that counterargument can be powerful evidence for your claim. You can also make evidence that isn’t there an integral part of your argument, too. If you can’t find the evidence you think you need, ask yourself why it seems to be lacking, or if its absence adds a new dimension to your thinking about the topic. Remember, evidence is not the piling up of facts or quotes: evidence is only one component of a strong, well supported, well-argued, and well-written composition.
Attributions
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
This page contains material from “About Writing: A Guide” by Robin Jeffrey, OpenOregon Educational Resources , Higher Education Coordination Commission: Office of Community Colleges and Workforce Development is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
This chapter has additions, edits, and organization by James Charles Devlin.
9.1 Types of Evidence in Academic Arguments Copyright © by James Charles Devlin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

What this handout is about
This handout will define what an argument is and explain why you need one in most of your academic essays.
Arguments are everywhere
You may be surprised to hear that the word “argument” does not have to be written anywhere in your assignment for it to be an important part of your task. In fact, making an argument—expressing a point of view on a subject and supporting it with evidence—is often the aim of academic writing. Your instructors may assume that you know this and thus may not explain the importance of arguments in class.
Most material you learn in college is or has been debated by someone, somewhere, at some time. Even when the material you read or hear is presented as a simple fact, it may actually be one person’s interpretation of a set of information. Instructors may call on you to examine that interpretation and defend it, refute it, or offer some new view of your own. In writing assignments, you will almost always need to do more than just summarize information that you have gathered or regurgitate facts that have been discussed in class. You will need to develop a point of view on or interpretation of that material and provide evidence for your position.
Consider an example. For nearly 2000 years, educated people in many Western cultures believed that bloodletting—deliberately causing a sick person to lose blood—was the most effective treatment for a variety of illnesses. The claim that bloodletting is beneficial to human health was not widely questioned until the 1800s, and some physicians continued to recommend bloodletting as late as the 1920s. Medical practices have now changed because some people began to doubt the effectiveness of bloodletting; these people argued against it and provided convincing evidence. Human knowledge grows out of such differences of opinion, and scholars like your instructors spend their lives engaged in debate over what claims may be counted as accurate in their fields. In their courses, they want you to engage in similar kinds of critical thinking and debate.
Argumentation is not just what your instructors do. We all use argumentation on a daily basis, and you probably already have some skill at crafting an argument. The more you improve your skills in this area, the better you will be at thinking critically, reasoning, making choices, and weighing evidence.
Making a claim
What is an argument? In academic writing, an argument is usually a main idea, often called a “claim” or “thesis statement,” backed up with evidence that supports the idea. In the majority of college papers, you will need to make some sort of claim and use evidence to support it, and your ability to do this well will separate your papers from those of students who see assignments as mere accumulations of fact and detail. In other words, gone are the happy days of being given a “topic” about which you can write anything. It is time to stake out a position and prove why it is a good position for a thinking person to hold. See our handout on thesis statements .
Claims can be as simple as “Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged,” with evidence such as, “In this experiment, protons and electrons acted in such and such a way.” Claims can also be as complex as “Genre is the most important element to the contract of expectations between filmmaker and audience,” using reasoning and evidence such as, “defying genre expectations can create a complete apocalypse of story form and content, leaving us stranded in a sort of genre-less abyss.” In either case, the rest of your paper will detail the reasoning and evidence that have led you to believe that your position is best.
When beginning to write a paper, ask yourself, “What is my point?” For example, the point of this handout is to help you become a better writer, and we are arguing that an important step in the process of writing effective arguments is understanding the concept of argumentation. If your papers do not have a main point, they cannot be arguing for anything. Asking yourself what your point is can help you avoid a mere “information dump.” Consider this: your instructors probably know a lot more than you do about your subject matter. Why, then, would you want to provide them with material they already know? Instructors are usually looking for two things:
- Proof that you understand the material
- A demonstration of your ability to use or apply the material in ways that go beyond what you have read or heard.
This second part can be done in many ways: you can critique the material, apply it to something else, or even just explain it in a different way. In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue.
Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as “Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.” Such a statement might capture your initial impressions of Wright as you have studied him in class; however, you need to look deeper and express specifically what caused that “greatness.” Your instructor will probably expect something more complicated, such as “Frank Lloyd Wright’s architecture combines elements of European modernism, Asian aesthetic form, and locally found materials to create a unique new style,” or “There are many strong similarities between Wright’s building designs and those of his mother, which suggests that he may have borrowed some of her ideas.” To develop your argument, you would then define your terms and prove your claim with evidence from Wright’s drawings and buildings and those of the other architects you mentioned.
Do not stop with having a point. You have to back up your point with evidence. The strength of your evidence, and your use of it, can make or break your argument. See our handout on evidence . You already have the natural inclination for this type of thinking, if not in an academic setting. Think about how you talked your parents into letting you borrow the family car. Did you present them with lots of instances of your past trustworthiness? Did you make them feel guilty because your friends’ parents all let them drive? Did you whine until they just wanted you to shut up? Did you look up statistics on teen driving and use them to show how you didn’t fit the dangerous-driver profile? These are all types of argumentation, and they exist in academia in similar forms.
Every field has slightly different requirements for acceptable evidence, so familiarize yourself with some arguments from within that field instead of just applying whatever evidence you like best. Pay attention to your textbooks and your instructor’s lectures. What types of argument and evidence are they using? The type of evidence that sways an English instructor may not work to convince a sociology instructor. Find out what counts as proof that something is true in that field. Is it statistics, a logical development of points, something from the object being discussed (art work, text, culture, or atom), the way something works, or some combination of more than one of these things?
Be consistent with your evidence. Unlike negotiating for the use of your parents’ car, a college paper is not the place for an all-out blitz of every type of argument. You can often use more than one type of evidence within a paper, but make sure that within each section you are providing the reader with evidence appropriate to each claim. So, if you start a paragraph or section with a statement like “Putting the student seating area closer to the basketball court will raise player performance,” do not follow with your evidence on how much more money the university could raise by letting more students go to games for free. Information about how fan support raises player morale, which then results in better play, would be a better follow-up. Your next section could offer clear reasons why undergraduates have as much or more right to attend an undergraduate event as wealthy alumni—but this information would not go in the same section as the fan support stuff. You cannot convince a confused person, so keep things tidy and ordered.
Counterargument
One way to strengthen your argument and show that you have a deep understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counterarguments or objections. By considering what someone who disagrees with your position might have to say about your argument, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not accepting your argument. Recall our discussion of student seating in the Dean Dome. To make the most effective argument possible, you should consider not only what students would say about seating but also what alumni who have paid a lot to get good seats might say.
You can generate counterarguments by asking yourself how someone who disagrees with you might respond to each of the points you’ve made or your position as a whole. If you can’t immediately imagine another position, here are some strategies to try:
- Do some research. It may seem to you that no one could possibly disagree with the position you are arguing, but someone probably has. For example, some people argue that a hotdog is a sandwich. If you are making an argument concerning, for example, the characteristics of an exceptional sandwich, you might want to see what some of these people have to say.
- Talk with a friend or with your teacher. Another person may be able to imagine counterarguments that haven’t occurred to you.
- Consider your conclusion or claim and the premises of your argument and imagine someone who denies each of them. For example, if you argued, “Cats make the best pets. This is because they are clean and independent,” you might imagine someone saying, “Cats do not make the best pets. They are dirty and needy.”
Once you have thought up some counterarguments, consider how you will respond to them—will you concede that your opponent has a point but explain why your audience should nonetheless accept your argument? Will you reject the counterargument and explain why it is mistaken? Either way, you will want to leave your reader with a sense that your argument is stronger than opposing arguments.
When you are summarizing opposing arguments, be charitable. Present each argument fairly and objectively, rather than trying to make it look foolish. You want to show that you have considered the many sides of the issue. If you simply attack or caricature your opponent (also referred to as presenting a “straw man”), you suggest that your argument is only capable of defeating an extremely weak adversary, which may undermine your argument rather than enhance it.
It is usually better to consider one or two serious counterarguments in some depth, rather than to give a long but superficial list of many different counterarguments and replies.
Be sure that your reply is consistent with your original argument. If considering a counterargument changes your position, you will need to go back and revise your original argument accordingly.
Audience is a very important consideration in argument. Take a look at our handout on audience . A lifetime of dealing with your family members has helped you figure out which arguments work best to persuade each of them. Maybe whining works with one parent, but the other will only accept cold, hard statistics. Your kid brother may listen only to the sound of money in his palm. It’s usually wise to think of your audience in an academic setting as someone who is perfectly smart but who doesn’t necessarily agree with you. You are not just expressing your opinion in an argument (“It’s true because I said so”), and in most cases your audience will know something about the subject at hand—so you will need sturdy proof. At the same time, do not think of your audience as capable of reading your mind. You have to come out and state both your claim and your evidence clearly. Do not assume that because the instructor knows the material, he or she understands what part of it you are using, what you think about it, and why you have taken the position you’ve chosen.
Critical reading
Critical reading is a big part of understanding argument. Although some of the material you read will be very persuasive, do not fall under the spell of the printed word as authority. Very few of your instructors think of the texts they assign as the last word on the subject. Remember that the author of every text has an agenda, something that he or she wants you to believe. This is OK—everything is written from someone’s perspective—but it’s a good thing to be aware of. For more information on objectivity and bias and on reading sources carefully, read our handouts on evaluating print sources and reading to write .
Take notes either in the margins of your source (if you are using a photocopy or your own book) or on a separate sheet as you read. Put away that highlighter! Simply highlighting a text is good for memorizing the main ideas in that text—it does not encourage critical reading. Part of your goal as a reader should be to put the author’s ideas in your own words. Then you can stop thinking of these ideas as facts and start thinking of them as arguments.
When you read, ask yourself questions like “What is the author trying to prove?” and “What is the author assuming I will agree with?” Do you agree with the author? Does the author adequately defend her argument? What kind of proof does she use? Is there something she leaves out that you would put in? Does putting it in hurt her argument? As you get used to reading critically, you will start to see the sometimes hidden agendas of other writers, and you can use this skill to improve your own ability to craft effective arguments.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Booth, Wayne C., Gregory G. Colomb, Joseph M. Williams, Joseph Bizup, and William T. FitzGerald. 2016. The Craft of Research , 4th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ede, Lisa. 2004. Work in Progress: A Guide to Academic Writing and Revising , 6th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Gage, John T. 2005. The Shape of Reason: Argumentative Writing in College , 4th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A., and John J. Ruszkiewicz. 2016. Everything’s an Argument , 7th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Write an A+ Argumentative Essay
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
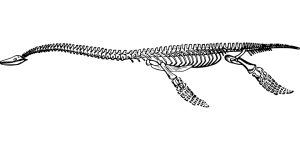
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Free Interview Course
Home > Blog > Essay Writing Guide – Using Evidence In Your Arguments
Essay Writing Guide – Using Evidence In Your Arguments

Essay Writing Guide – Introduction
If you want to write a good essay, you need strong evidence to support your ideas. No matter how good your ideas are, you need to support them with evidence. Strong evidence is vital for achieving high grades in essay-based assessments. If you make a claim, you must always give evidence for it. In this essay writing guide, we’re going to take a look at how to incorporate evidence into your argument.
Essay Writing Guide – What is Evidence?
One dictionary defines evidence as follows:
“The available body of facts or information indicating whether a belief or proposition is true or valid.”
This means that evidence is material which can be used to support an argument, claim, belief, or proposition. For example, fossils and bones are evidence to support the accepted theory that dinosaurs once walked the earth.

Essay Writing Guide – Different Kinds of Evidence
The definition of evidence that we’ve given is quite broad. In essence, any kind of facts or information can be regarded as evidence. The thing to make note of is that not all evidence is good evidence! What determines whether evidence is good or bad will depend on the subject you’re writing an essay for. This is because different academic disciplines, such as History and English Literature, care more about different types of evidence. Let’s take a look at different kinds of evidence now.
- Sciences such as Physics, Biology, Chemistry and Psychology, value peer-reviewed results of scientific studies.This means that, when making scientific arguments, you need to find results from well-received studies to support your argument.
- In contrast, History accepts a wider range of kinds of evidence. Historical statistics are welcome, but historical interpretation is also important.Strong theories written by historians can be used to support your own argument.
- In a subject such as English Literature, evidence will usually come in the form of quotations. For example, you might be asked to discuss the themes of a play.
To support your argument, you should find relevant quotations from the play. Like History, interpretations are also accepted as evidence. Try to find writers in the field of literary criticism which present theories about the play, book, or poem that you’re writing about.
Essay Writing Guide – How to Use Evidence in an Essay
When writing an essay, it is essential that you provide evidence. As we’ve discussed, evidence takes many forms. Make sure your type of evidence is appropriate for the subject you’re writing about.
So, if you’re writing a Psychology essay, don’t fill it with historical interpretation. Hard facts are necessary to sell your hypothesis in a scientific essay. Likewise, don’t bring hard statistics into an English Literature essay. This subject is all about interpretation, and so scientific studies won’t be particularly useful.
Evidence is always used to support a point that you’re trying to make.
- So, you make your point first. This is the claim of your argument: “Dinosaurs walked the earth tens of millions of years ago.”
- Once you’ve made your point, move on to your evidence: “Fossils found in Central America show that creatures used to live there.”
- Then you need to link the evidence back to your point by explaining it: “We can use radiocarbon dating to estimate how old the fossils are. Some of these fossils are over a hundred million years old.”

Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Introducing Evidence
When incorporating evidence into an essay, you need to make sure it flows well. Try using some of these key phrases in your essay to help you introduce your evidence:
“The evidence clearly reveals…” “Analysis of the data suggests…” “This graph shows that…” “As shown by the information…” “This claim is supported by several authors, including…” “There seems to be a consensus regarding this…” “Popular opinion supports this idea…” “Popular opinion does not support this idea…” “Most experts agree…” “According to this study, we can deduce that…” “Over many years, this interpretation has developed…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Explaining Evidence
Once you’ve given your evidence, you need to be able explain it. Try using these phrases when explaining evidence in your essay:
“This means that…” “This evidence supports the claim that…” “This evidence supports this proposition because…” “It’s clear then, that this argument is supported by the evidence. This is because…” “If this evidence is true, then…” “This interpretation clearly supports the view that…” “This evidence suggests that…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Linking Evidence
Finally, you need to link your proposition, evidence, and explanation back to your main argument. Here are some phrases you can use to do this:
“Therefore, this analysis supports the central thesis of this essay…” “If followed to its logical conclusion, then this claim plays in favour of this essay’s core argument…” “The evidence and analysis presented here shows that…” “Due to this, it seems plausible that…” “In summary, it is shown that…” “While there are still many other ideas to consider, this proposition alone supports the view that…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Opposing Evidence
While most of the evidence you provide will support your argument, some essays will require you to examine counter-examples and evidence which opposes your central idea. So, make sure you clearly show that this evidence doesn’t damage your argument with the following phrases:
“While this evidence appears compelling, it doesn’t apply to these circumstances because…” “This counter-argument fails to acknowledge the following points: …” “While this is a popular counter-argument, it isn’t relevant to the focus of this essay, and therefore will not be discussed further.” “This claim relies on the premise that _____. The focus now will be to demonstrate that this premise is false.” “While this data appears to contradict the argument of this essay, this isn’t the case because…”
Essay Writing Guide – Key Phrases for Moving on to the Next Point
Eventually, you’ll need to move on to your next point. Here are some key phrases you can use to move from one point to another so that your essay flows better:
“Now that this claim has been suitably supported, the focus needs to shift to…” “The truth of this proposition has been clarified. Therefore, it is now appropriate to move to the next key argument in this essay: …” “This conclusion naturally leads to the next claim that…” “While this is compelling evidence, it is still not enough to logically reach the conclusion of this argument. It’s important to now discuss…” “While this theme is prominent in the text, others must also be considered, such as…” (Most relevant for English Literature essays)

Essay Writing Guide – Handy Phrases for Discussing Evidence
Finally, here are a few phrases that you can make use of to flesh out your arguments so that they read better:
“According to…” “Also…” “As well as…” “Based on…” “Clearly…” “Closely…” “Confirmed by…” “Evidently…” “For example…” “For instance…” “In addition…” “Therefore…” “This indicates that…” “This suggests…”
Essay Writing Guide – Conclusion
Whenever you make a new claim, support it with evidence. Evidence takes many different forms – find evidence that is appropriate to your subject or topic.
Start by introducing your argument. Then, give evidence. After that, explain your evidence. Finally, link your evidence back to your central argument.
Evidence is the fuel for your argument. Make sure you have enough of it to get you across the finish line!

Andy Bosworth
One thought on “ essay writing guide – using evidence in your arguments ”.
Clearly explained.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Free Aptitude Tests

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)

Table of Contents
We define an argumentative essay as a type of essay that presents arguments about both sides of an issue. The purpose is to convince the reader to accept a particular viewpoint or action. In an argumentative essay, the writer takes a stance on a controversial or debatable topic and supports their position with evidence, reasoning, and examples. The essay should also address counterarguments, demonstrating a thorough understanding of the topic.
What is an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay outline
- Types of argument claims
How to write an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay writing tips
- Good argumentative essay example
How to write a good thesis
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that presents a coherent and logical analysis of a specific topic. 1 The goal is to convince the reader to accept the writer’s point of view or opinion on a particular issue. Here are the key elements of an argumentative essay:
- Thesis Statement : The central claim or argument that the essay aims to prove.
- Introduction : Provides background information and introduces the thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph addresses a specific aspect of the argument, presents evidence, and may include counter arguments. Articulate your thesis statement better with Paperpal. Start writing now!
- Evidence : Supports the main argument with relevant facts, examples, statistics, or expert opinions.
- Counterarguments : Anticipates and addresses opposing viewpoints to strengthen the overall argument.
- Conclusion : Summarizes the main points, reinforces the thesis, and may suggest implications or actions.

Argumentative essay structure
Aristotelian, Rogerian, and Toulmin are three distinct approaches to argumentative essay structures, each with its principles and methods. 2 The choice depends on the purpose and nature of the topic. Here’s an overview of each type of argumentative essay format.
| ) | ||
| : Introduce the topic. Provide background information. Present the thesis statement or main argument. | : Introduce the issue. Provide background information. Establish a neutral and respectful tone. | : Introduce the issue. Provide background information. Present the claim or thesis. |
| : Provide context or background information. Set the stage for the argument. | : Describe opposing viewpoints without judgment. Show an understanding of the different perspectives. | : Clearly state the main argument or claim. |
| : Present the main argument with supporting evidence. Use logical reasoning. Address counterarguments and refute them. | : Present your thesis or main argument. Identify areas of common ground between opposing views. | : Provide evidence to support the claim. Include facts, examples, and statistics. |
| : Acknowledge opposing views. Provide counterarguments and evidence against them. | : Present your arguments while acknowledging opposing views. Emphasize shared values or goals. Seek compromise and understanding. | : Explain the reasoning that connects the evidence to the claim. Make the implicit assumptions explicit. |
| : Summarize the main points. Reassert the thesis. End with a strong concluding statement. | : Summarize areas of agreement. Reiterate the importance of finding common ground. End on a positive note. | : Provide additional support for the warrant. Offer further justification for the reasoning. |
| Address potential counterarguments. Provide evidence and reasoning to refute counterclaims. | ||
| Respond to counterarguments and reinforce the original claim. | ||
| Summarize the main points. Reinforce the strength of the argument. |
Have a looming deadline for your argumentative essay? Write 2x faster with Paperpal – Start now!
Argumentative essay outline
An argumentative essay presents a specific claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning. Here’s an outline for an argumentative essay, along with examples for each section: 3
1. Introduction :
- Hook : Start with a compelling statement, question, or anecdote to grab the reader’s attention.
Example: “Did you know that plastic pollution is threatening marine life at an alarming rate?”
- Background information : Provide brief context about the issue.
Example: “Plastic pollution has become a global environmental concern, with millions of tons of plastic waste entering our oceans yearly.”
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position.
Example: “We must take immediate action to reduce plastic usage and implement more sustainable alternatives to protect our marine ecosystem.”
2. Body Paragraphs :
- Topic sentence : Introduce the main idea of each paragraph.
Example: “The first step towards addressing the plastic pollution crisis is reducing single-use plastic consumption.”
- Evidence/Support : Provide evidence, facts, statistics, or examples that support your argument.
Example: “Research shows that plastic straws alone contribute to millions of tons of plastic waste annually, and many marine animals suffer from ingestion or entanglement.”
- Counterargument/Refutation : Acknowledge and refute opposing viewpoints.
Example: “Some argue that banning plastic straws is inconvenient for consumers, but the long-term environmental benefits far outweigh the temporary inconvenience.”
- Transition : Connect each paragraph to the next.
Example: “Having addressed the issue of single-use plastics, the focus must now shift to promoting sustainable alternatives.”
3. Counterargument Paragraph :
- Acknowledgement of opposing views : Recognize alternative perspectives on the issue.
Example: “While some may argue that individual actions cannot significantly impact global plastic pollution, the cumulative effect of collective efforts must be considered.”
- Counterargument and rebuttal : Present and refute the main counterargument.
Example: “However, individual actions, when multiplied across millions of people, can substantially reduce plastic waste. Small changes in behavior, such as using reusable bags and containers, can have a significant positive impact.”
4. Conclusion :
- Restatement of thesis : Summarize your main argument.
Example: “In conclusion, adopting sustainable practices and reducing single-use plastic is crucial for preserving our oceans and marine life.”
- Call to action : Encourage the reader to take specific steps or consider the argument’s implications.
Example: “It is our responsibility to make environmentally conscious choices and advocate for policies that prioritize the health of our planet. By collectively embracing sustainable alternatives, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier future.”

Types of argument claims
A claim is a statement or proposition a writer puts forward with evidence to persuade the reader. 4 Here are some common types of argument claims, along with examples:
- Fact Claims : These claims assert that something is true or false and can often be verified through evidence. Example: “Water boils at 100°C at sea level.”
- Value Claims : Value claims express judgments about the worth or morality of something, often based on personal beliefs or societal values. Example: “Organic farming is more ethical than conventional farming.”
- Policy Claims : Policy claims propose a course of action or argue for a specific policy, law, or regulation change. Example: “Schools should adopt a year-round education system to improve student learning outcomes.”
- Cause and Effect Claims : These claims argue that one event or condition leads to another, establishing a cause-and-effect relationship. Example: “Excessive use of social media is a leading cause of increased feelings of loneliness among young adults.”
- Definition Claims : Definition claims assert the meaning or classification of a concept or term. Example: “Artificial intelligence can be defined as machines exhibiting human-like cognitive functions.”
- Comparative Claims : Comparative claims assert that one thing is better or worse than another in certain respects. Example: “Online education is more cost-effective than traditional classroom learning.”
- Evaluation Claims : Evaluation claims assess the quality, significance, or effectiveness of something based on specific criteria. Example: “The new healthcare policy is more effective in providing affordable healthcare to all citizens.”
Understanding these argument claims can help writers construct more persuasive and well-supported arguments tailored to the specific nature of the claim.
If you’re wondering how to start an argumentative essay, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with the argumentative essay format and writing process.
- Choose a Topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or interested in. Ensure that the topic is debatable and has two or more sides.
- Define Your Position: Clearly state your stance on the issue. Consider opposing viewpoints and be ready to counter them.
- Conduct Research: Gather relevant information from credible sources, such as books, articles, and academic journals. Take notes on key points and supporting evidence.
- Create a Thesis Statement: Develop a concise and clear thesis statement that outlines your main argument. Convey your position on the issue and provide a roadmap for the essay.
- Outline Your Argumentative Essay: Organize your ideas logically by creating an outline. Include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis.
- Write the Introduction: Start with a hook to grab the reader’s attention (a quote, a question, a surprising fact). Provide background information on the topic. Present your thesis statement at the end of the introduction.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that relates to the thesis. Support your points with evidence and examples. Address counterarguments and refute them to strengthen your position. Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs.
- Address Counterarguments: Acknowledge and respond to opposing viewpoints. Anticipate objections and provide evidence to counter them.
- Write the Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your argumentative essay. Reinforce the significance of your argument. End with a call to action, a prediction, or a thought-provoking statement.
- Revise, Edit, and Share: Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency. Check for grammatical and spelling errors. Share your essay with peers, friends, or instructors for constructive feedback.
- Finalize Your Argumentative Essay: Make final edits based on feedback received. Ensure that your essay follows the required formatting and citation style.
Struggling to start your argumentative essay? Paperpal can help – try now!
Argumentative essay writing tips
Here are eight strategies to craft a compelling argumentative essay:
- Choose a Clear and Controversial Topic : Select a topic that sparks debate and has opposing viewpoints. A clear and controversial issue provides a solid foundation for a strong argument.
- Conduct Thorough Research : Gather relevant information from reputable sources to support your argument. Use a variety of sources, such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert opinions, to strengthen your position.
- Create a Strong Thesis Statement : Clearly articulate your main argument in a concise thesis statement. Your thesis should convey your stance on the issue and provide a roadmap for the reader to follow your argument.
- Develop a Logical Structure : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on a specific point of evidence that contributes to your overall argument. Ensure a logical flow from one point to the next.
- Provide Strong Evidence : Support your claims with solid evidence. Use facts, statistics, examples, and expert opinions to support your arguments. Be sure to cite your sources appropriately to maintain credibility.
- Address Counterarguments : Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counterarguments. Addressing and refuting alternative perspectives strengthens your essay and demonstrates a thorough understanding of the issue. Be mindful of maintaining a respectful tone even when discussing opposing views.
- Use Persuasive Language : Employ persuasive language to make your points effectively. Avoid emotional appeals without supporting evidence and strive for a respectful and professional tone.
- Craft a Compelling Conclusion : Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and leave a lasting impression in your conclusion. Encourage readers to consider the implications of your argument and potentially take action.

Good argumentative essay example
Let’s consider a sample of argumentative essay on how social media enhances connectivity:
In the digital age, social media has emerged as a powerful tool that transcends geographical boundaries, connecting individuals from diverse backgrounds and providing a platform for an array of voices to be heard. While critics argue that social media fosters division and amplifies negativity, it is essential to recognize the positive aspects of this digital revolution and how it enhances connectivity by providing a platform for diverse voices to flourish. One of the primary benefits of social media is its ability to facilitate instant communication and connection across the globe. Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram break down geographical barriers, enabling people to establish and maintain relationships regardless of physical location and fostering a sense of global community. Furthermore, social media has transformed how people stay connected with friends and family. Whether separated by miles or time zones, social media ensures that relationships remain dynamic and relevant, contributing to a more interconnected world. Moreover, social media has played a pivotal role in giving voice to social justice movements and marginalized communities. Movements such as #BlackLivesMatter, #MeToo, and #ClimateStrike have gained momentum through social media, allowing individuals to share their stories and advocate for change on a global scale. This digital activism can shape public opinion and hold institutions accountable. Social media platforms provide a dynamic space for open dialogue and discourse. Users can engage in discussions, share information, and challenge each other’s perspectives, fostering a culture of critical thinking. This open exchange of ideas contributes to a more informed and enlightened society where individuals can broaden their horizons and develop a nuanced understanding of complex issues. While criticisms of social media abound, it is crucial to recognize its positive impact on connectivity and the amplification of diverse voices. Social media transcends physical and cultural barriers, connecting people across the globe and providing a platform for marginalized voices to be heard. By fostering open dialogue and facilitating the exchange of ideas, social media contributes to a more interconnected and empowered society. Embracing the positive aspects of social media allows us to harness its potential for positive change and collective growth.
- Clearly Define Your Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement is the core of your argumentative essay. Clearly articulate your main argument or position on the issue. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Provide Strong Supporting Evidence: Back up your thesis with solid evidence from reliable sources and examples. This can include facts, statistics, expert opinions, anecdotes, or real-life examples. Make sure your evidence is relevant to your argument, as it impacts the overall persuasiveness of your thesis.
- Anticipate Counterarguments and Address Them: Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to strengthen credibility. This also shows that you engage critically with the topic rather than presenting a one-sided argument.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Writing a winning argumentative essay not only showcases your ability to critically analyze a topic but also demonstrates your skill in persuasively presenting your stance backed by evidence. Achieving this level of writing excellence can be time-consuming. This is where Paperpal, your AI academic writing assistant, steps in to revolutionize the way you approach argumentative essays. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Paperpal to write your essay:
Upgrade your essays with Paperpal
- Sign Up or Log In: Begin by creating an account or logging into paperpal.com .
- Navigate to Paperpal Copilot: Once logged in, proceed to the Templates section from the side navigation bar.
- Generate an essay outline: Under Templates, click on the ‘Outline’ tab and choose ‘Essay’ from the options and provide your topic to generate an outline.
- Develop your essay: Use this structured outline as a guide to flesh out your essay. If you encounter any roadblocks, click on Brainstorm and get subject-specific assistance, ensuring you stay on track.
- Refine your writing: To elevate the academic tone of your essay, select a paragraph and use the ‘Make Academic’ feature under the ‘Rewrite’ tab, ensuring your argumentative essay resonates with an academic audience.
- Final Touches: Make your argumentative essay submission ready with Paperpal’s language, grammar, consistency and plagiarism checks, and improve your chances of acceptance.
Paperpal not only simplifies the essay writing process but also ensures your argumentative essay is persuasive, well-structured, and academically rigorous. Sign up today and transform how you write argumentative essays.
The length of an argumentative essay can vary, but it typically falls within the range of 1,000 to 2,500 words. However, the specific requirements may depend on the guidelines provided.
You might write an argumentative essay when: 1. You want to convince others of the validity of your position. 2. There is a controversial or debatable issue that requires discussion. 3. You need to present evidence and logical reasoning to support your claims. 4. You want to explore and critically analyze different perspectives on a topic.
Argumentative Essay: Purpose : An argumentative essay aims to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a specific point of view or argument. Structure : It follows a clear structure with an introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, counterarguments and refutations, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is formal and relies on logical reasoning, evidence, and critical analysis. Narrative/Descriptive Essay: Purpose : These aim to tell a story or describe an experience, while a descriptive essay focuses on creating a vivid picture of a person, place, or thing. Structure : They may have a more flexible structure. They often include an engaging introduction, a well-developed body that builds the story or description, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is more personal and expressive to evoke emotions or provide sensory details.
- Gladd, J. (2020). Tips for Writing Academic Persuasive Essays. Write What Matters .
- Nimehchisalem, V. (2018). Pyramid of argumentation: Towards an integrated model for teaching and assessing ESL writing. Language & Communication , 5 (2), 185-200.
- Press, B. (2022). Argumentative Essays: A Step-by-Step Guide . Broadview Press.
- Rieke, R. D., Sillars, M. O., & Peterson, T. R. (2005). Argumentation and critical decision making . Pearson/Allyn & Bacon.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
- How to Write a Hypothesis? Types and Examples
Make Your Research Paper Error-Free with Paperpal’s Online Spell Checker
The do’s & don’ts of using generative ai tools ethically in academia, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers....
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
Using evidence.
Like a lawyer in a jury trial, a writer must convince her audience of the validity of her argument by using evidence effectively. As a writer, you must also use evidence to persuade your readers to accept your claims. But how do you use evidence to your advantage? By leading your reader through your reasoning.
The types of evidence you use change from discipline to discipline--you might use quotations from a poem or a literary critic, for example, in a literature paper; you might use data from an experiment in a lab report.
The process of putting together your argument is called analysis --it interprets evidence in order to support, test, and/or refine a claim . The chief claim in an analytical essay is called the thesis . A thesis provides the controlling idea for a paper and should be original (that is, not completely obvious), assertive, and arguable. A strong thesis also requires solid evidence to support and develop it because without evidence, a claim is merely an unsubstantiated idea or opinion.
This Web page will cover these basic issues (you can click or scroll down to a particular topic):
- Incorporating evidence effectively.
- Integrating quotations smoothly.
- Citing your sources.
Incorporating Evidence Into Your Essay
When should you incorporate evidence.
Once you have formulated your claim, your thesis (see the WTS pamphlet, " How to Write a Thesis Statement ," for ideas and tips), you should use evidence to help strengthen your thesis and any assertion you make that relates to your thesis. Here are some ways to work evidence into your writing:
- Offer evidence that agrees with your stance up to a point, then add to it with ideas of your own.
- Present evidence that contradicts your stance, and then argue against (refute) that evidence and therefore strengthen your position.
- Use sources against each other, as if they were experts on a panel discussing your proposition.
- Use quotations to support your assertion, not merely to state or restate your claim.
Weak and Strong Uses of Evidence
In order to use evidence effectively, you need to integrate it smoothly into your essay by following this pattern:
- State your claim.
- Give your evidence, remembering to relate it to the claim.
- Comment on the evidence to show how it supports the claim.
To see the differences between strong and weak uses of evidence, here are two paragraphs.
Weak use of evidence
Today, we are too self-centered. Most families no longer sit down to eat together, preferring instead to eat on the go while rushing to the next appointment (Gleick 148). Everything is about what we want.
This is a weak example of evidence because the evidence is not related to the claim. What does the claim about self-centeredness have to do with families eating together? The writer doesn't explain the connection.
The same evidence can be used to support the same claim, but only with the addition of a clear connection between claim and evidence, and some analysis of the evidence cited.
Stronger use of evidence
Today, Americans are too self-centered. Even our families don't matter as much anymore as they once did. Other people and activities take precedence. In fact, the evidence shows that most American families no longer eat together, preferring instead to eat on the go while rushing to the next appointment (Gleick 148). Sit-down meals are a time to share and connect with others; however, that connection has become less valued, as families begin to prize individual activities over shared time, promoting self-centeredness over group identity.
This is a far better example, as the evidence is more smoothly integrated into the text, the link between the claim and the evidence is strengthened, and the evidence itself is analyzed to provide support for the claim.
Using Quotations: A Special Type of Evidence
One effective way to support your claim is to use quotations. However, because quotations involve someone else's words, you need to take special care to integrate this kind of evidence into your essay. Here are two examples using quotations, one less effective and one more so.
Ineffective Use of Quotation
Today, we are too self-centered. "We are consumers-on-the-run . . . the very notion of the family meal as a sit-down occasion is vanishing. Adults and children alike eat . . . on the way to their next activity" (Gleick 148). Everything is about what we want.
This example is ineffective because the quotation is not integrated with the writer's ideas. Notice how the writer has dropped the quotation into the paragraph without making any connection between it and the claim. Furthermore, she has not discussed the quotation's significance, which makes it difficult for the reader to see the relationship between the evidence and the writer's point.
A More Effective Use of Quotation
Today, Americans are too self-centered. Even our families don't matter as much any more as they once did. Other people and activities take precedence, as James Gleick says in his book, Faster . "We are consumers-on-the-run . . . the very notion of the family meal as a sit-down occasion is vanishing. Adults and children alike eat . . . on the way to their next activity" (148). Sit-down meals are a time to share and connect with others; however, that connection has become less valued, as families begin to prize individual activities over shared time, promoting self-centeredness over group identity.
The second example is more effective because it follows the guidelines for incorporating evidence into an essay. Notice, too, that it uses a lead-in phrase (". . . as James Gleick says in his book, Faster ") to introduce the direct quotation. This lead-in phrase helps to integrate the quotation with the writer's ideas. Also notice that the writer discusses and comments upon the quotation immediately afterwards, which allows the reader to see the quotation's connection to the writer's point.
REMEMBER: Discussing the significance of your evidence develops and expands your paper!
Citing Your Sources
Evidence appears in essays in the form of quotations and paraphrasing. Both forms of evidence must be cited in your text. Citing evidence means distinguishing other writers' information from your own ideas and giving credit to your sources. There are plenty of general ways to do citations. Note both the lead-in phrases and the punctuation (except the brackets) in the following examples:
Quoting: According to Source X, "[direct quotation]" ([date or page #]).
Paraphrasing: Although Source Z argues that [his/her point in your own words], a better way to view the issue is [your own point] ([citation]).
Summarizing: In her book, Source P's main points are Q, R, and S [citation].
Your job during the course of your essay is to persuade your readers that your claims are feasible and are the most effective way of interpreting the evidence.
Questions to Ask Yourself When Revising Your Paper
- Have I offered my reader evidence to substantiate each assertion I make in my paper?
- Do I thoroughly explain why/how my evidence backs up my ideas?
- Do I avoid generalizing in my paper by specifically explaining how my evidence is representative?
- Do I provide evidence that not only confirms but also qualifies my paper's main claims?
- Do I use evidence to test and evolve my ideas, rather than to just confirm them?
- Do I cite my sources thoroughly and correctly?
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels
The Argument: Types of Evidence
Argumentation and evidence.
In most papers, the writer’s aim is to find a topic and make a claim about it. This claim is better known as the writer's argument.
With it, the writer attempts to win the reader over to his/her view of the topic, or, at the very least, to show the reader a new perspective about the subject discussed. If the writer is going to make some headway with an argument, however, he/she must be able to give evidence to support the claims the paper will make. There are three main categories of evidence that are essential to gain the audience's confidence in the writer's assertions. These categories are Fact, Judgment, and Testimony.
This page explores the types of evidence used in argumentation. See also the page on logic and argumentation .
Facts are among the best tools to involve the reader in the argument. Since facts are indisputable, the writer automatically wins the reader’s mutual agreement by utilizing them. A statement declaring, "On January 28, 1986, the shuttle Challenger exploded upon lift-off," must be accepted by the reader, since it is a historical certainty. Facts are used primarily to get the reader to stand on the writer's plane of reasoning. For instance, if a writer wanted to argue that smoking is a detriment to your health, he/she would begin by citing factual information about the large number of people who die every year from smoke-related diseases. This would then force the reader to agree with the writer on at least one point.
Facts, however, cannot carry the entire argument. It is necessary for the writer to utilize Judgments as well. These are assumptions that the writer makes about his/her subject after carefully considering the facts. For example, a writer could start by presenting certain facts about the knowledge that scientists had regarding the condition of the Challenger prior to takeoff. From these facts, the writer concludes that the disaster could have been avoided if a few scientists been willing to speak up about some unsettling findings. This would be a judgment on the writer's part. There is nothing in the history books or newspapers that can prove this assumption to be true. The success or failure of the entire argument rests on whether or not the writer can utilize adequate reasoning in coming to the right judgments.
The final type of evidence used in writing a convincing argument is Testimony. There are two types of testimony: 1) the account of an eyewitness, and 2) the judgment of an expert who has had the chance to examine and interpret the facts. Both of these lend validity to an argument. The eyewitness can supply important facts for the writer to use, and the expert can provide valuable judgments in order to give strength to the argument. For instance, in the case of the Space Shuttle Challenger, the writer might use the testimony of one of the personnel who was present at NASA meetings before the launch. The writer might also use an astrophysicist’s opinion about whether or not evidence existed before takeoff that the Shuttle was not safe to launch.
However, the writer must exercise caution when employing these two types of testimony in his or her paper. Eyewitness accounts cannot always be reliable; no one person has an objective view of an event. Also, an expert’s opinion is not beyond dispute; another expert in the same field of study may find faulty reasoning in the first expert’s judgment. Also, the writer must be careful not to use an expert in one field to make a judgment about a subject in another. Imagine the absurdity of computer genius Bill Gates making an official statement on archeology.
Internet Resources
>> Dartmouth Logic and Argumentation Guide
Copyright © 2009 Wheaton College Writing Center
Definition and Examples of Evidence in Argument
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In argument, evidence refers to facts, documentation or testimony used to strengthen a claim, support an argument or reach a conclusion.
The evidence isn't the same as proof. "Whereas evidence allows for professional judgment, the proof is absolute and incontestable," said Denis Hayes in "Learning and Teaching in Primary Schools."
Observations About Evidence
- "Without evidence to support them, any statements you make in your writing have little or no value; they're simply opinions, and 10 people may have 10 different opinions, none of which is more valid than the others unless there is clear and potent evidence to support it." Neil Murray, "Writing Essays in English Language and Linguistics ," 2012
- "When conducting empirical research, the researcher's primary responsibility is to provide evidence to support his or her claim about the relationship between the variables described in the research hypothesis. T]he researcher must collect data that will convince us of the accuracy of his or her predictions." Bart L. Weathington et al., "Research Methods for the Behavioral and Social Sciences," 2010
Making Connections
David Rosenwasser and Jill Stephen comment on making connections that leave out the steps that lead to them in 2009's "Writing Analytically."
"A common assumption about evidence is that is is 'the stuff that proves I'm right.' Although this way of thinking about evidence is not wrong, it is much too limited. Corroboration (proving the validity of a claim) is one of the functions of evidence, but not the only one. Writing well means sharing your thought process with your readers, telling them why you believe the evidence means what you say it does.
"Writers who think that evidence speaks for itself often do very little with their evidence except put it next to their claims: 'The party was terrible: There was no alcohol' -- or, alternatively, 'The party was great: There was no alcohol.' Just juxtaposing the evidence with the claim leaves out the thinking that connects them, thereby implying that the logic of the connection is obvious.
"But even for readers prone to agreeing with a given claim, simply pointing to the evidence is not enough."
Qualitative and Quantitative Evidence
Julie M. Farrar defines two kinds of evidence in "Evidence: Encyclopedia of Rhetoric and Composition ," from 2006.
"The mere presence of information does not constitute evidence; the informative statements must be accepted as evidence by an audience and believed by it to be relevant to the claim at issue. Evidence can be generally classified as qualitative and quantitative. The former emphasizes explanation and description, appearing continuous rather than discrete, while the latter offers measurement and prediction. Both kinds of information require interpretation, for at no time do the facts speak for themselves."
Opening the Door
In "Evidence: Practice Under the Rules" from 1999, Christopher B. Mueller and Laird C. Kirkpatrick discuss evidence as it relates to trial law.
"The more far-reaching effect of introducing evidence [in a trial] is to pave the way for other parties to introduce evidence, question witnesses and offer argument on the subject in attempts to rebut or confine the initial evidence. In the customary phrase, the party who offers evidence on a point is said to have 'opened the door,' meaning that the other side may now make countermoves to answer or rebut the initial evidence, 'fighting fire with fire.'"
Dubious Evidence
In "Not on the Doctor’s Checklist, but Touch Matters" from 2010 in The New York Times, Danielle Ofri discusses findings called evidence that isn't actually valid.
"[I]s there any research to show that a physical exam -- in a healthy person -- is of any benefit? Despite a long and storied tradition, a physical exam is more a habit than a clinically proven method of picking up the disease in asymptomatic people. There is scant evidence to suggest that routinely listening to every healthy person’s lungs or pressing on every normal person’s liver will find a disease that wasn’t suggested by the patient’s history. For a healthy person, an 'abnormal finding' on a physical exam is more likely to be a false positive than a real sign of illness."
Other Examples of Dubious Evidence
- "America must not ignore the threat gathering against us. Facing clear evidence of peril, we cannot wait for the final proof, the smoking gun that could come in the form of a mushroom cloud." President George W. Bush, in justifying the invasion of Iraq in 2003
- "We have it. The smoking gun. The evidence. The potential weapon of mass destruction we have been looking for as our pretext of invading Iraq. There's just one problem: it's in North Korea." Jon Stewart, "The Daily Show," 2005
- Usage and Examples of a Rebuttal
- Data Definition and Examples in Argument
- What Does It Mean to Make a Claim During an Argument?
- What is a Logical Fallacy?
- Premise Definition and Examples in Arguments
- What Is a Hasty Generalization?
- Stacking the Deck Logical Fallacy
- What Is Confirmation Bias?
- Techne (Rhetoric)
- paralogism (rhetoric and logic)
- Backing (argument)
- Socratic Dialogue (Argumentation)
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Stipulative Definitions in English
- Rhetorical Move
- expeditio (elimination)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Organizing Your Argument

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How can I effectively present my argument?
In order for your argument to be persuasive, it must use an organizational structure that the audience perceives as both logical and easy to parse. Three argumentative methods —the Toulmin Method , Classical Method , and Rogerian Method — give guidance for how to organize the points in an argument.
Note that these are only three of the most popular models for organizing an argument. Alternatives exist. Be sure to consult your instructor and/or defer to your assignment’s directions if you’re unsure which to use (if any).
Toulmin Method
The Toulmin Method is a formula that allows writers to build a sturdy logical foundation for their arguments. First proposed by author Stephen Toulmin in The Uses of Argument (1958), the Toulmin Method emphasizes building a thorough support structure for each of an argument's key claims.
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows:
Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument.
Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
Warrant (Bridge): In this section, you explain why or how your data supports the claim. As a result, the underlying assumption that you build your argument on is grounded in reason.
Backing (Foundation): Here, you provide any additional logic or reasoning that may be necessary to support the warrant.
Counterclaim: You should anticipate a counterclaim that negates the main points in your argument. Don't avoid arguments that oppose your own. Instead, become familiar with the opposing perspective. If you respond to counterclaims, you appear unbiased (and, therefore, you earn the respect of your readers). You may even want to include several counterclaims to show that you have thoroughly researched the topic.
Rebuttal: In this section, you incorporate your own evidence that disagrees with the counterclaim. It is essential to include a thorough warrant or bridge to strengthen your essay’s argument. If you present data to your audience without explaining how it supports your thesis, your readers may not make a connection between the two, or they may draw different conclusions.
Example of the Toulmin Method:
Claim: Hybrid cars are an effective strategy to fight pollution.
Data1: Driving a private car is a typical citizen's most air-polluting activity.
Warrant 1: Due to the fact that cars are the largest source of private (as opposed to industrial) air pollution, switching to hybrid cars should have an impact on fighting pollution.
Data 2: Each vehicle produced is going to stay on the road for roughly 12 to 15 years.
Warrant 2: Cars generally have a long lifespan, meaning that the decision to switch to a hybrid car will make a long-term impact on pollution levels.
Data 3: Hybrid cars combine a gasoline engine with a battery-powered electric motor.
Warrant 3: The combination of these technologies produces less pollution.
Counterclaim: Instead of focusing on cars, which still encourages an inefficient culture of driving even as it cuts down on pollution, the nation should focus on building and encouraging the use of mass transit systems.
Rebuttal: While mass transit is an idea that should be encouraged, it is not feasible in many rural and suburban areas, or for people who must commute to work. Thus, hybrid cars are a better solution for much of the nation's population.
Rogerian Method
The Rogerian Method (named for, but not developed by, influential American psychotherapist Carl R. Rogers) is a popular method for controversial issues. This strategy seeks to find a common ground between parties by making the audience understand perspectives that stretch beyond (or even run counter to) the writer’s position. Moreso than other methods, it places an emphasis on reiterating an opponent's argument to his or her satisfaction. The persuasive power of the Rogerian Method lies in its ability to define the terms of the argument in such a way that:
- your position seems like a reasonable compromise.
- you seem compassionate and empathetic.
The basic format of the Rogerian Method is as follows:
Introduction: Introduce the issue to the audience, striving to remain as objective as possible.
Opposing View : Explain the other side’s position in an unbiased way. When you discuss the counterargument without judgement, the opposing side can see how you do not directly dismiss perspectives which conflict with your stance.
Statement of Validity (Understanding): This section discusses how you acknowledge how the other side’s points can be valid under certain circumstances. You identify how and why their perspective makes sense in a specific context, but still present your own argument.
Statement of Your Position: By this point, you have demonstrated that you understand the other side’s viewpoint. In this section, you explain your own stance.
Statement of Contexts : Explore scenarios in which your position has merit. When you explain how your argument is most appropriate for certain contexts, the reader can recognize that you acknowledge the multiple ways to view the complex issue.
Statement of Benefits: You should conclude by explaining to the opposing side why they would benefit from accepting your position. By explaining the advantages of your argument, you close on a positive note without completely dismissing the other side’s perspective.
Example of the Rogerian Method:
Introduction: The issue of whether children should wear school uniforms is subject to some debate.
Opposing View: Some parents think that requiring children to wear uniforms is best.
Statement of Validity (Understanding): Those parents who support uniforms argue that, when all students wear the same uniform, the students can develop a unified sense of school pride and inclusiveness.
Statement of Your Position : Students should not be required to wear school uniforms. Mandatory uniforms would forbid choices that allow students to be creative and express themselves through clothing.
Statement of Contexts: However, even if uniforms might hypothetically promote inclusivity, in most real-life contexts, administrators can use uniform policies to enforce conformity. Students should have the option to explore their identity through clothing without the fear of being ostracized.
Statement of Benefits: Though both sides seek to promote students' best interests, students should not be required to wear school uniforms. By giving students freedom over their choice, students can explore their self-identity by choosing how to present themselves to their peers.
Classical Method
The Classical Method of structuring an argument is another common way to organize your points. Originally devised by the Greek philosopher Aristotle (and then later developed by Roman thinkers like Cicero and Quintilian), classical arguments tend to focus on issues of definition and the careful application of evidence. Thus, the underlying assumption of classical argumentation is that, when all parties understand the issue perfectly, the correct course of action will be clear.
The basic format of the Classical Method is as follows:
Introduction (Exordium): Introduce the issue and explain its significance. You should also establish your credibility and the topic’s legitimacy.
Statement of Background (Narratio): Present vital contextual or historical information to the audience to further their understanding of the issue. By doing so, you provide the reader with a working knowledge about the topic independent of your own stance.
Proposition (Propositio): After you provide the reader with contextual knowledge, you are ready to state your claims which relate to the information you have provided previously. This section outlines your major points for the reader.
Proof (Confirmatio): You should explain your reasons and evidence to the reader. Be sure to thoroughly justify your reasons. In this section, if necessary, you can provide supplementary evidence and subpoints.
Refutation (Refuatio): In this section, you address anticipated counterarguments that disagree with your thesis. Though you acknowledge the other side’s perspective, it is important to prove why your stance is more logical.
Conclusion (Peroratio): You should summarize your main points. The conclusion also caters to the reader’s emotions and values. The use of pathos here makes the reader more inclined to consider your argument.
Example of the Classical Method:
Introduction (Exordium): Millions of workers are paid a set hourly wage nationwide. The federal minimum wage is standardized to protect workers from being paid too little. Research points to many viewpoints on how much to pay these workers. Some families cannot afford to support their households on the current wages provided for performing a minimum wage job .
Statement of Background (Narratio): Currently, millions of American workers struggle to make ends meet on a minimum wage. This puts a strain on workers’ personal and professional lives. Some work multiple jobs to provide for their families.
Proposition (Propositio): The current federal minimum wage should be increased to better accommodate millions of overworked Americans. By raising the minimum wage, workers can spend more time cultivating their livelihoods.
Proof (Confirmatio): According to the United States Department of Labor, 80.4 million Americans work for an hourly wage, but nearly 1.3 million receive wages less than the federal minimum. The pay raise will alleviate the stress of these workers. Their lives would benefit from this raise because it affects multiple areas of their lives.
Refutation (Refuatio): There is some evidence that raising the federal wage might increase the cost of living. However, other evidence contradicts this or suggests that the increase would not be great. Additionally, worries about a cost of living increase must be balanced with the benefits of providing necessary funds to millions of hardworking Americans.
Conclusion (Peroratio): If the federal minimum wage was raised, many workers could alleviate some of their financial burdens. As a result, their emotional wellbeing would improve overall. Though some argue that the cost of living could increase, the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Legal Matters
- Contracts and Legal Agreements
How to Introduce Evidence in an Essay
Last Updated: May 5, 2024
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. This article has been viewed 243,861 times.
When well integrated into your argument, evidence helps prove that you've done your research and thought critically about your topic. But what's the best way to introduce evidence so it feels seamless and has the highest impact? There are actually quite a few effective strategies you can use, and we've rounded up the best ones for you here. Try some of the tips below to introduce evidence in your essay and make a persuasive argument.
Things You Should Know
- "According to..."
- "The text says..."
- "Researchers have learned..."
- "For example..."
- "[Author's name] writes..."
Setting up the Evidence

- You can use 1-2 sentences to set up the evidence, if needed, but usually more concise you are, the better.

- For example, you may make an argument like, “Desire is a complicated, confusing emotion that causes pain to others.”
- Or you may make an assertion like, “The treatment of addiction must consider root cause issues like mental health and poor living conditions.”

- For example, you may write, “The novel explores the theme of adolescent love and desire.”
- Or you may write, “Many studies show that addiction is a mental health issue.”
Putting in the Evidence

- For example, you may use an introductory clause like, “According to Anne Carson…”, "In the following chart...," “The author states…," "The survey shows...." or “The study argues…”
- Place a comma after the introductory clause if you are using a quote. For example, “According to Anne Carson, ‘Desire is no light thing" or "The study notes, 'levels of addiction rise as levels of poverty and homelessness also rise.'"
- A list of introductory clauses can be found here: https://student.unsw.edu.au/introducing-quotations-and-paraphrases .

- For example, you may write, “In the novel, Carson is never shy about how her characters express desire for each other: ‘When they made love/ Geryon liked to touch in slow succession each of the bones of Herakles' back…’”
- Or you may write, "The study charts the rise in addiction levels, concluding: 'There is a higher level of addiction in specific areas of the United States.'"

- For example, you may write, “Carson views events as inevitable, as man moving through time like “a harpoon,” much like the fates of her characters.”
- Or you may write, "The chart indicates the rising levels of addiction in young people, an "epidemic" that shows no sign of slowing down."

- For example, you may write in the first mention, “In Anne Carson’s The Autobiography of Red , the color red signifies desire, love, and monstrosity.” Or you may write, "In the study Addiction Rates conducted by the Harvard Review...".
- After the first mention, you can write, “Carson states…” or “The study explores…”.
- If you are citing the author’s name in-text as part of your citation style, you do not need to note their name in the text. You can just use the quote and then place the citation at the end.

- If you are paraphrasing a source, you may still use quotation marks around any text you are lifting directly from the source.

- For example, you may write, “In the novel, the characters express desire for each other: ‘When they made love/ Geryon liked to touch in slow succession each of the bones of Herakles' back (Carson, 48).”
- Or you may write, "Based on the data in the graph below, the study shows the 'intersection between opioid addiction and income' (Branson, 10)."
- If you are using footnotes or endnotes, make sure you use the appropriate citation for each piece of evidence you place in your essay.

- You may also mention the title of the work or source you are paraphrasing or summarizing and the author's name in the paraphrase or summary.
- For example, you may write a paraphrase like, "As noted in various studies, the correlation between addiction and mental illness is often ignored by medical health professionals (Deder, 10)."
- Or you may write a summary like, " The Autobiography of Red is an exploration of desire and love between strange beings, what critics have called a hybrid work that combines ancient meter with modern language (Zambreno, 15)."

- The only time you should place 2 pieces of evidence together is when you want to directly compare 2 short quotes (each less than 1 line long).
- Your analysis should then include a complete compare and contrast of the 2 quotes to show you have thought critically about them both.
Analyzing the Evidence

- For example, you may write, “In the novel, Carson is never shy about how her characters express desire for each other: ‘When they made love/ Geryon liked to touch in slow succession each of the bones of Herakles' back (Carson, 48). The connection between Geryon and Herakles is intimate and gentle, a love that connects the two characters in a physical and emotional way.”
- Or you may write, "In the study Addiction Rates conducted by the Harvard Review, the data shows a 50% rise in addiction levels in specific areas across the United States. The study illustrates a clear connection between addiction levels and communities where income falls below the poverty line and there is a housing shortage or crisis."

- For example, you may write, “Carson’s treatment of the relationship between Geryon and Herakles can be linked back to her approach to desire as a whole in the novel, which acts as both a catalyst and an impediment for her characters.”
- Or you may write, "The survey conducted by Dr. Paula Bronson, accompanied by a detailed academic dissertation, supports the argument that addiction is not a stand alone issue that can be addressed in isolation."

- For example, you may write, “The value of love between two people is not romanticized, but it is still considered essential, similar to the feeling of belonging, another key theme in the novel.”
- Or you may write, "There is clearly a need to reassess the current thinking around addiction and mental illness so the health and sciences community can better study these pressing issues."
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Tristen Bonacci. Licensed English Teacher. Expert Interview. 21 December 2021.
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/quoliterature/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evidence/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/using-evidence.html
About This Article

Before you introduce evidence into your essay, begin the paragraph with a topic sentence. This sentence should give the reader an overview of the point you’ll be arguing or making with the evidence. When you get to citing the evidence, begin the sentence with a clause like, “The study finds” or “According to Anne Carson.” You can also include a short quotation in the middle of a sentence without introducing it with a clause. Remember to introduce the author’s first and last name when you use the evidence for the first time. Afterwards, you can just mention their last name. Once you’ve presented the evidence, take time to explain in your own words how it backs up the point you’re making. For tips on how to reference your evidence correctly, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Apr 15, 2022
Did this article help you?

Mar 2, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

6 tips for writing an opinion essay that will sway even the worst critics
Choose a juicy topic and give evidence to craft a compelling argument

Latest Articles
Are blueberries really blue how nature plays tricks on you, hong kong’s first mid-autumn drone show, festive events aim to boost tourism, hong kong teacher accused of sexually assaulting 16-year-old girl, hong kong blind union: 60 years of supporting city’s visually impaired, the lens: china schools’ recycling scheme raises questions about equity and sustainability, deep dive: hongkongers earning less money as unemployment rises.

Writing an effective opinion essay requires a clear stance, solid reasoning and compelling evidence.
Whether you are arguing for or against a hot-button issue, these six tips can help you craft a strong and persuasive piece.
With practice, you can effectively advocate for your viewpoint on any issue.
1. Choose a juicy topic
If you have the option to pick your topic, find a controversial issue that people have strong feelings about. It could be a current event, a social policy, or an ethical dilemma.
You can use topics such as the ethics of gene editing and designer babies, the pros and cons of vaccine mandates and the impact of social media on teen mental health.
The spicier, the better. No one wants to read about something boring.
2. Take a clear position
Don’t be wishy-washy. Be direct when you state your opinion. Make it clear where you stand and why you believe you are right. You can say, “I firmly believe that gene editing technology should be heavily regulated to prevent abuse.” Don’t be afraid to state your view with confidence. Your goal is to persuade the reader to see things from your perspective.
9 back-to-school idioms to help you pass English with flying colours
3. Bring the evidence
You cannot have the attitude that you are right just because you say so. Support your claims with solid proof, such as statistics, expert testimony, historical precedents, logical reasoning or personal anecdotes.
For instance, if you are writing about why teens should not be allowed to use social media in school, you can include data on the increased rates of anxiety, depression and cyberbullying among teens with high social media use. The more substantial your evidence, the more convincing your argument will be. Don’t forget to cite your sources.
4. Address counterarguments
Acknowledge that there are two sides to every story. Outline the key counterarguments, then explain why your position is still more valid or compelling. To illustrate, “Critics argue that the regulation of gene editing will stifle scientific progress, but the risks of unchecked development far outweigh these concerns.” This shows you have considered the full scope of the issue.
5. Use a logical structure
Guide your readers through your reasoning step-by-step. Start with an introduction that hooks the reader and lays out your thesis. Build your case in the body with smooth transitions between ideas, then wrap it all up in the conclusion. Keep it organised and easy to follow.
6. Write with passion and clarity
Don’t be afraid to let your unique voice shine through. Use vivid language, rhetorical devices, and an authoritative tone to make your argument feel compelling.
For example, compare these two sentences – “Social media has had a negative impact on teenagers” and “The epidemic of social media addiction has corrupted the mental well-being of the next generation”.
The second sentence uses more vivid, emotive language to convey the writer’s passionate stance on this issue. This creates a much more persuasive and authoritative tone than the dry, matter-of-fact phrasing of the first sentence.
At the same time, keep your points concise so your argument is easy for the reader to follow. Don’t use 10 words when five will do.
- entertainment
- journalism resources
- latest reports
- learning resources
- college & uni life
- career advice
trending topics
Types of evidence in argumentative essay
Sometimes the best evidence for your argument is a hard fact or visual essayshark discount of a typs. If you are working on a project for a class, look carefully at the assignment prompt. Literacy Center Ideas. Mueller and Laird C. Learn about Easel. And are some types of evidence better than others? Realtors use the same type of analogical evidence when determining the value of a home. It will also offer links to additional resources. Click to order now. This argument essay is designed to help you out in a quick fix OR to teach in-depth rhetorical analysis. What are some examples of ineffective evidence? Great for distance learning, the slides are designed to lead your students with models and supports through the entire process!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Books, journals, websites, newspapers, magazines, and documentary films are some of the most common sources of evidence for academic writing. Our handout on evaluating print sources will help you choose your print sources wisely, and the library has a tutorial on evaluating both print sources and websites. A librarian can help you find sources ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Evidence is not simply "facts." Evidence is not simply "quotes." Evidence is what a writer uses to support or defend his or her argument, and only valid and credible evidence is enough to make an argument strong. For a review of what evidence means in terms of developing body paragraphs within an essay, you can refer back to Section 4.3.
Argumentative Writing and Using Evidence, Spring 2022. 4 of 5. Evidence: A study of New York middle schools found that by extending school lunches to all students, regardless of family income, test scores increased by 0.083 standard deviations in math and 0.059 in English Language Arts for non-poor students, and, though smaller, statistically ...
Using Evidence to Support your Argument. All university research and scholarship is based on evidence, and your own assessed work as a student is no different. To convince your marker that you know what you're talking about, you can't just make a statement and expect them to accept it; you will need to provide robust evidence to justify ...
As you develop your research-supported essay, consider not only what types of evidence might support your ideas but also what types of evidence will be considered valid or credible according to the academic discipline or academic audience for which you are writing. Evidence in the Humanities: Literature, Art, Film, Music, Philosophy.
An argumentative essay is a piece of writing that uses factual evidence and logical support to convince the reader of a certain way of thinking. Although many types of essays aim at persuading the reader to believe a specific point of view, argumentative essays rely heavily on hard evidence, drawing on other studies and sources to prove their argument is best.
In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue. Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as "Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.". Such a statement might capture your initial ...
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
When incorporating evidence into an essay, you need to make sure it flows well. Try using some of these key phrases in your essay to help you introduce your evidence: "The evidence clearly reveals…". "Analysis of the data suggests…". "This graph shows that…". "As shown by the information…". "This claim is supported by ...
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that presents a coherent and logical analysis of a specific topic. 1 The goal is to convince the reader to accept the writer's point of view or opinion on a particular issue. Here are the key elements of an argumentative essay: Thesis Statement: The central claim or argument that the essay aims to ...
The process of putting together your argument is called analysis--it interprets evidence in order to support, test, and/or refine a claim. The chief claim in an analytical essay is called the thesis. A thesis provides the controlling idea for a paper and should be original (that is, not completely obvious), assertive, and arguable.
Arguments. An argument is a claim about a topic that is supported by reasons and evidence. Many academic assignments ask you to make an argument, even though the word "argument" never appears in the directions. For example, if you're writing or giving a persuasive speech about solar power, you might try to convince your audience that the ...
The final type of evidence used in writing a convincing argument is Testimony. There are two types of testimony: 1) the account of an eyewitness, and 2) the judgment of an expert who has had the chance to examine and interpret the facts. Both of these lend validity to an argument. The eyewitness can supply important facts for the writer to use ...
The 4 parts of an argumentative essay are the claim, counterclaim, reasoning, and evidence. The claim is the author's argument that they are attempting to prove in the essay.
In argument, evidence refers to facts, documentation or testimony used to strengthen a claim, support an argument or reach a conclusion. The evidence isn't the same as proof. "Whereas evidence allows for professional judgment, the proof is absolute and incontestable," said Denis Hayes in "Learning and Teaching in Primary Schools."
An argumentative essay is a piece of writing that uses logical evidence and empirical data to convince readers of a particular position on a topic. Because of its reliance on structure and planning, the first step in writing one is often drafting a solid argumentative essay outline.
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows: Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument. Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
Setting up the Evidence. Download Article. 1. Set up the evidence in the first sentence of the paragraph. The first sentence in the paragraph or section of your essay is called the topic sentence. It should let the reader know what is going to be discussed in the paragraph or section. If the paragraph is one of many in the body of your essay ...
In an argumentative essay, your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning. In an expository essay, you'll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn't have to include a strong opinion in this case ...
An argumentative essay is a type of research paper that requires you to investigate a given topic or theme, among other things. We guide you through writing one with examples. ... There's definitely room for personal thought and interpretation, but you mostly want to focus on your argument and evidence. Your argumentative essay will usually ...
Writing an effective opinion essay requires a clear stance, solid reasoning and compelling evidence. Whether you are arguing for or against a hot-button issue, these six tips can help you craft a ...
17. How is an inductive argument structured? An inductive argument begins with specific evidence and moves to a generalized conclusion that accounts for the evidence. 18. How is a deductive argument structured? starts with a general truth or assumption and moves to provide evidence or support. Revising an essay Discuss the steps to revise an ...
Types of evidence in argumentative essay Brown v. You could also include evidence that there is a variety of other activities available for people to participate in, such as museums and sports. Now you know that there are are 6 types of evidence in writing: Anecdotal evidence, Statistical evidence, Testimonial evidence, Textual evidence, Analogical evidence, amd Logical evidence.