- PhD Interview Questions and Answers – 12 Things You May Be Asked

PhD Interview Questions and Answers
Written by Mark Bennett
Your PhD interview will be an important part of your postgraduate research application. This is your chance to meet your prospective department, discuss your project and show your potential as an academic researcher.
Of course, it’s also when that potential is going to be assessed.
You’ll need to show an awareness of what’s involved in a PhD project and prove that you have the right aspirations and approach to work on one for three (or more) years. You’ll also need to make it clear that this is the right university , department, research group or laboratory for you.
None of this has to be especially intimidating. Putting some thought into your project and your choice of institution can make answering PhD entrance interview questions quite simple.
On this page we’ve put together a list of the questions you might be asked at an interview. We’ve also explained why the university might be asking each question, and provided some tips on how to answer them
You won’t necessarily be asked all of these questions – and you almost certainly won’t be asked them in the order here. Some of them also overlap with each other. But they’re all topics that you should prepare to discuss at a PhD interview .
We’ve also included a selection of questions to ask during a PhD interview .
Let's get you PhD ready
Sign up to our weekly newsletter for the latest advice and guidance from our team of experts.
Interview questions about you
Your qualities as a researcher, team-member and individual are some of the most important factors in a university’s decision to accept you for a PhD.
Regardless of your subject area, you need to be the kind of person who can dedicate themselves to a three-year project. You also need to be able to work alongside other students and academics in a positive and successful research environment.
The interview is the best way for a university to assess this. Just as there’s more to doing a PhD than research and writing, there’s more to a prospective candidate than their academic record.
#1 Tell us about yourself…
This popular opener can feel like an awkwardly open ‘question’.
You’ll be prepared to explain your project, to say what a great fit it is for the university, perhaps even reference some current research. But how do you ‘answer’ an invitation to introduce yourself?
By introducing yourself.
Your interview panel isn’t trying to catch you out here. They’re offering an icebreaker to help ease you into the rest of the interview.
Obviously your response should be relevant to the occasion. But it doesn’t just have to be a presentation of your academic achievements, interests and goals (the interview will get to those in time!).
Say a little about your background, where you’re from and what your interests are. Don’t be afraid to relate these to your academic specialism and your choice of university.
If something specific inspired you to consider a PhD, mention it. If there’s something that’s attracted you to this city as well as the university, say so. (There’ll be plenty of time to talk up the institution and its research later).
- I’ve always been interested in discovering how things work, but my time as an undergraduate opened my eyes to the excitement and wider benefit of science. I had the chance to do some original research on my Masters and that’s inspired me to take up the challenge of a PhD. I’m also a keen hiker and amateur naturalist, so I’d love to combine my studies here with the chance to visit the local area.
- I was born in a house next to the local post-office. My first cat was called Timothy and he liked chasing string. At school my best friend was Kevin. My favourite colour is blue and my favourite flavour of ice-cream is raspberry ripple…
#2 What made you choose to do a PhD?
At some point in your interview your interviewers are going to want to know why you decided to do a doctorate.
This may seem like a simple question, but be wary of giving an overly simplistic answer. Just pointing out that you’re good at your subject and a PhD seemed like the logical next step won’t be enough – especially if there’s a funding decision to be made.
The panel is already satisfied that you’re academically capable and interested. You’ve demonstrated that by getting an interview (and turning up for it).
Now they want to assure themselves that you’ve got the motivation and drive to see you through three or more years of hard work on a PhD project.
- I’ve enjoyed my academic work so far, but I really feel I’ve got more to offer as an independent researcher. I’m also passionate about this subject and don’t feel enough attention has been paid to the questions I’m looking to address.
- I can’t think of anything to do with my Masters, but my current tutor says I’m clever enough for a PhD.
#3 What do you plan to do after you complete your PhD?
It might seem strange for your panel to ask about your post PhD plans. After all, those don’t have any really impact on your ability to do a PhD, do they? And graduation is at least three years away in any case; should you have thought that far ahead?
The answers to which are ‘yes’ and ‘of course you should.’
Universities want to make sure you’re doing a PhD for the right reasons (as above). Asking about your future plans is a great way to check this.
Students who ‘sleepwalk’ into a research project are much more likely to come unstuck or lose motivation when the going gets tough later on.
This doesn’t mean you have to have everything worked out, or that your ambitions have to be unique. If you're planning to apply for a post-doc after your PhD, say so. But demonstrate an understanding of academic career paths – and show that you’ve put some thought into alternatives.
It’s also the case that not everyone who gains a doctorate will go on to an academic job. Universities want to recruit PhD students responsibly and provide the kinds of skills and training they actually need.
So, don’t feel that you have to want to be a scholar to be accepted for a PhD. Research training can prepare you for a range of career paths . An appreciation of these will impress your interview panel. (Particularly if you’re applying for a professional doctorate ).
- I feel my PhD project can open up new lines of inquiry for this field and want to use it as the foundation for a fruitful research career. But, I’m also interested in the wider development opportunities included in this doctoral programme. I want to be an academic, but I’m happy to keep other options open.
- I expect someone will give me a job doing more research. That’s what PhDs do, right?
#4 What are your strengths and weaknesses?
A well-worn question, but a great opportunity to reflect on your abilities - as well as opportunities for further development during your PhD.
What your panel is really interested in is not so much what your strengths and weaknesses actually are , but your ability to identify them.
In practice, this means giving solid examples for strengths and showing how they relate to the PhD project you have in mind.
Don’t just say you’re a good time-keeper. Point out when you’ve had to be well organised and show that you understand the importance of self-directed study to a successful PhD.
When it comes to weaknesses, maintain the right balance.
A PhD interview probably isn’t the best time to wallow in existential self-doubt (unless you’re applying for a very specific topic in Philosophy). Equally though, answers like ‘my only downfall is excessive perfectionism’ can sound a bit contrived. If the panel is asking you about strengths and weaknesses, they want you to identify and reflect on both.
Be honest about the things you find challenging, but identify them as training needs and discuss how you expect to improve upon them as part of your PhD.
- I feel that I’m a good written communicator. My existing academic and professional work demonstrates an ability to put forward ideas clearly and concisely. I think this will help me manage the weight of information my PhD research needs to cover and the challenge of producing an effective thesis. But, I’m not always as organised as I’d like to be. I want to address this as part of my postgraduate training and hope to take advantage of classes and development opportunities early in my doctorate.
- My greatest strength is that I have no weaknesses! And my only weakness is that I have no strengths. Hang on...
#5 Are there any training needs you can identify ahead of your PhD?
This question (and its answer) can be part of an invitation to reflect on your strengths and weaknesses (as above).
But, you may be asked about training needs more specifically. This is likely if you’re applying to a more structured programme, within a Doctoral Training Partnership or similar.
Either way, this is a great opportunity to reflect on your aspirations as a researcher and show that you’ve read up on the project you’re applying to. If the university offers a series of training modules, mention them. Say what you hope to gain from them and how you think they’ll help you succeed in your PhD.
You might also want to refer to any discussion of your aims and aspirations with a doctorate. If you’re keeping an open mind about non-academic career paths, show an awareness of the transferrable skills this PhD can give you.
And don’t worry about revealing a few gaps in the core skills required by your discipline. A PhD is a training process, not a three-year exam.
- I’m really interested in communicating my research to a wider audience, but don’t know how best to go about doing this. I think the training module on public engagement will be a big help to me, both academically and more generally.
- I’m really bad at interviews. Do you have a class for that?
Interview questions about your PhD project
This is the university’s chance to further assess your suitability for an advertised PhD position, and the likely fit between your planned project and the expertise it has available.
It’s also your chance to expand on your research proposal and show that you have the skills, experience and understanding to complete a doctorate. For funded places (or other competitive projects), this is the time for you to prove that you are the best student for this PhD.
It’s a good idea to reference your research proposal (or other appropriate parts of your application) when answering these questions. But expand upon what the panel has already read. (And make sure there isn’t anything in that proposal that you aren’t confident enough to ‘back up’ in your interview!)
#6 Why this project?
The exact focus of this question will depend on whether you’re applying for an advertised PhD project (more common in Science, Engineering and Medicine) or proposing your own research within a department's PhD programme (more common in Arts, Humanities and some branches of the Social Sciences).
If you’re being considered for a pre-defined project, make sure you know it inside out. Say what it is that interests you about it. Compare it to similar projects (if appropriate) and explain your particular choice.
If you’re proposing your own project, this is your chance to show some passion and enthusiasm for it. Refer to your research proposal and take the opportunity to discuss and expand upon it.
In both cases you should point to some existing scholarship and show an awareness of the field you’ll be entering. You’ll also want to re-iterate what makes your project distinctive. After all, the PhD is defined as offering ‘an original contribution to knowledge.’
This doesn’t mean preparing a comprehensive list of key works or current research projects (that ‘literature review’ will be one of the first things you do on the actual PhD). At this stage the panel just wants to see that you understand your proposed project and are enthusiastic enough to see it through.
Depending on how the question is phrased, you may also discuss your choice of university at this stage – or explain why your previous work makes you a good fit for this particular PhD (see below).
- This PhD appeals to my existing research interests. But I’m also attracted by the opportunity to specialise and develop new expertise. Other projects didn’t seem to offer the same possibilities to pursue the questions that really interest me.
- To be honest, I’ll do anything if it’s funded.
#7 What makes you the right candidate for this PhD?
If you’re applying for a pre-defined PhD project , you’ll almost certainly be asked why you are the best candidate to undertake it (especially if there’s funding available).
Remember too that some of these projects aren’t automatically funded. Their financing can depend on the quality of the student they attract, so your panel will be very keen to make sure you’re going to be ‘Dr Right’.
You might still be asked about your suitability for a self-proposed PhD (in Arts or Humanities, for example). This is another way for your interviewers to assess those all-important motivation and commitment factors.
Whatever your situation, this is a good place to talk a bit about your previous work at undergraduate or Masters level. The panel already knows the grades you received, but now you have the chance to talk about what you actually did on those degrees. Show passion and give examples.
If an undergraduate module on gothic literature inspired you to propose a PhD on an under-researched aspect of eighteenth-century culture, say so. If your Masters has given you skills in exactly the kind of statistical analysis required by this doctorate, mention that.
- I’ve been interested in this topic since the final year of my undergraduate degree. This lead to my choice of Masters and helped me pick my dissertation topic, which I really enjoyed. I’m really excited to now go on and do some sustained research in this area as a PhD student.
- Well, I really like books…
#8 What difficulties do you expect to encounter during this project?
This is another fairly popular question topic. It might form part of a discussion of your strengths, weaknesses and training needs. Or you might be invited to speak more specifically about the challenges involved in your project.
The panel isn’t trying to catch you out here, so don’t be afraid to speak frankly. All projects involve their own potential pitfalls and complications.
Overcoming them will be part of completing a PhD; recognising them will show that you're ready to begin one.
Show that you’ve put some thought into the approach necessary for your research and the methodology you might use.
Don’t be afraid to identify problems you aren’t yet certain how to solve (the best way to organise some data, the authors to include in your initial survey of texts, etc) but suggest how you might go about investigating them.
This is also a good time to mention any training needs (if you haven’t already) and speak about how you plan to take advantage of development opportunities within your programme.
- I can see that some of the archival material I’ll need to examine for this project may be difficult to access. My first task will be to request permissions, arrange visits and develop a system for recording my findings. I’m hoping to undertake training in archival practices and seek advice from my supervisor as I develop these key skills early in my project.
- Yeah, I know a PhD is hard, but I’m just going to see how I get on.
#9 What would you like the impact of this project to be?
‘Impact’ is an increasingly important factor in academic work and this applies to PhD research too – especially if you’re funded.
Even if your panel doesn’t explicitly ask about impact, it’s a good idea to mention what you hope the wider outcome of your project might be. If you are asked this question – and are prepared for it – this is a great chance to get a leg up on the competition.
Impact essentially refers to the measurable effects of research outside academia. It’s a given that your PhD will have an effect on future work in your field. But universities are increasingly focussed on the benefits of their work beyond the ‘ivory tower’ of higher education and research.
This is particularly important if your project is funded. The money supporting your studies will probably have come from public revenues (via a Research Council studentship) or from a large charity or trust. Those organisations will want to make sure their investment is worthwhile.
Examples of impact differ a bit between fields.
If you’re in the Social Sciences you may already have some idea of the ‘outputs’ from your project. These could be educational workshops, policy guidance, etc.
If you’re in Science, Medicine or Engineering you’ll hope to provide economic benefits to industry or to healthcare.
Arts and Humanities PhDs can have impact too. Think about the ways in which you could take part in public engagement, such as teaching people about local history or archival resources. You could partner with local schools, or even media companies producing documentary work.
- I’m keen to share my passion for this subject with a wider audience. I’m hoping to maintain a public-facing blog documenting my research. I would also be keen to approach local schools and museums to discuss educational events.
- To be honest, I can’t really see how my work on medieval manuscript preservation has any benefit outside the university. I’d still like some funding though.
#10 How will you fund this project?
This question is obviously more likely in interviews for non-funded PhDs. (It would be somewhat strange for a university to ask you about funding for a project that carries a full studentship).
However, you might still be asked about contingency plans if funding falls through (particularly if funding hasn’t been secured at this stage) or if your project over-runs.
Self-funding students will obviously need to go into more detail here. It’s not the responsibility of your university to ask for a complete breakdown of your finances (or for you to provide one). Yet the panel will want to be sure that you understand the cost involved in doing a PhD and have some kind of plans in place.
It’s fine to say that you’ll be looking for extra funding and part-time work as you start the project. But make it clear that you’ll still have enough time to apply yourself to the actual research.
- I’ve shortlisted external funders and would be keen to investigate any small bursaries or other forms of support through the university. I’ve also made arrangements to work part-time, with the option to adjust this if my funding situation improves.
- I have no idea how I’m going to afford this. Are you sure I can’t have a scholarship?
Interview questions about your choice of university
Unsurprisingly, your interview panel will be interested to know why you’ve chosen their university for your PhD.
If proposing your own project you’ll be asked about the fit between your research aims and the expertise of the department you’d be entering.
If applying to a pre-defined PhD, you’ll be invited to explain why this laboratory or research group particularly appeals to you and what you yourself can contribute to them.
Preparing for these kinds of questions is actually quite easy. Read up on your prospective university, department and supervisors. Show that you’re aware of the kind of work they do and give examples.
Feel free to mention other aspects of the university that appeal to you – its reputation, its alumni, even its location – but keep the main focus on the fit between your work and their research environment.
#11 Why have you chosen to study a PhD at this university?
Whatever else your panel asks, you can be pretty sure a question about your choice of university and department will crop up at some point in a PhD interview.
Your answer gives you the opportunity to do several important things.
Most obviously you can talk about the university and its research. Explain why you’d like to study with these supervisors in particular, when you’ve used their work during your Bachelors degree or Masters (if relevant) and how you can contribute to their future projects.
This is also an opportunity to reiterate your awareness of the wider research context for your project. If other departments or laboratories are undertaking related work, mention that. Say what attracted you to this university in particular and what you hope to achieve as one of its students.
If your PhD is part of a structured Doctoral Programme (as is increasingly likely) you can touch on any training and development opportunities it includes. You may mention these elsewhere in your interview, but make sure to include them when speaking about the university’s appeal to you.
Finally, show an awareness of any relevant research facilities, resources or collections.
Does the university hold a unique archive? Suggest how it might support your investigations. Has the laboratory you’re working in been equipped with any new facilities? Show that you know about them and are interested in using them (as relevant).
Universities spend a lot of money on facilities and resources. They want students – particularly postgraduate researchers – who will make use of them.
- I’ve looked at lots of opportunities in this area. I feel that this project is the best of its kind, combining a unique research angle with a training programme that will meet my professional needs. I was already familiar with the work of my prospective supervisor and their research has greatly informed my own development as a scholar. I’m eager to combine my work with theirs and make use of the facilities the university has put together for this project.
- I did my Masters here and already have a flat in the city.
#12 What can you bring to this research group?
PhD candidates are more than just students. You’ll function, in many ways, as a junior academic working within a wider research environment.
You’ll network with other students and academics. You’ll probably teach undergraduates. You may even publish some of your research (independently, or alongside your supervisor).
This means that your potential contribution to a department or laboratory is, in many ways, just as important as what it can offer you.
If you’re asked a question about this, take the opportunity to sell yourself a little.
Talk about your experience (academic or professional) and outline your ambitions. Make it clear that you will provide a return on the time, money and resources that the university is considering investing in you.
- I’m eager to take advantage of the facilities and expertise this university has to offer. But I also want to contribute with my own expertise and enthusiasm. My previous work has given me the skills to make the most of the material involved in this project and I’m motivated to participate in new training. I’ll be proud to be a part of this department and would actively seek to represent it through my own publications and other research outputs.
- I have a Bachelors and a Masters in this subject so I’m quite clever.
What to ask in a PhD interview
Your PhD entrance interview will probably end with an invitation for you to ask your own questions of the panel. This part of the interview is as important as the answers you'll have already given.
Asking good questions demonstrates your motivation. It also shows that you’ve given some genuine consideration to the project and / or programme you’re applying to.
Don’t just ask questions ‘for effect’ though. This is your chance to find out more about the project you’ll be doing, the people you’ll be working with and the expectations of you as a PhD student.
Remember: you’re a good student, with lots of potential. You’re considering at least three years of hard work with this university. You need to know that you’ll get on with your supervisor, that your work will be appreciated and that there are good prospects for your project.
You’re here to be interviewed for a PhD, but nothing’s stopping you from doing a little interviewing of your own.
Here are a few good questions to considering asking at your PhD interview. They include ways to express enthusiasm for your project, as well as some useful inquiries to make for yourself:
What will the supervision arrangements be for the project?
This shows that you’re thinking practically and looking ahead to the process of actually doing the PhD. It’s also something you’ll probably want to check for yourself.
What kind of training and skills sessions are offered as part of the PhD programme?
This shows that you’re interested in the development opportunities that form part of a modern PhD. It’s also a good way to address any concerns you have about your own skills. Be careful though. Avoid asking simple questions about material that’s already covered in the PhD project description, or in the university’s postgraduate prospectus.
Will I have opportunities to teach / present / publish?
This is something else you’ll want to know for yourself, but it also demonstrates a practical approach to your PhD (and future career). A good PhD programme should offer some opportunity to teach or demonstrate towards the end of your project. Equally, you should be encouraged to communicate your research and supported in doing so.
How many other PhD students has this supervisor seen to completion?
Don’t be afraid to ask about previous students and what they’ve gone on to do. You may also want to know if you’ll be working with or alongside other students and what the arrangements for that will be.
Are there likely to be any changes to the funding arrangements for the project?
A good practical question. If you’re applying for a funded place, make sure you understand the terms of that funding (its duration, whether you can combine it with any other income, etc). If you’re currently self-funding, it won’t hurt to ask if the university anticipates having any support available for you in future.
Is the university or department likely to run any events or other associated projects during the period of my PhD?
This might not seem like an obvious question, but it’s worth asking. The university might be in the early stages of planning a major hosted conference, external partnership or outreach project. Asking about these shows a genuine interest in your university and its research and suggests that you’ll be the right sort of PhD student to help deliver them. Needless to say, these kinds of projects are also excellent opportunities to gain experience and build your CV.
Other questions will probably occur to you according to your specific circumstances and the nature of the project you’re applying to.
Focus on the things that would concern you as a student actually doing the PhD in question, but avoid trivial topics. Your panel will be happy to talk about library resources and lab facilities. They’ll be less keen to advise on the best local pubs or say how often the bus runs between campus and town.
Also try to avoid asking for information that’s readily available elsewhere. This suggests you haven’t done your research – which is never a good sign when applying to do research.
Still looking for that perfect PhD project?
While you're preparing for the interview stage of applications, it's a good idea to keep searching as many PhD projects are advertised throughout the year .
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
Mark bennett.
Mark joined FindAPhD to develop our first ever advice articles in 2013 and now serves as our Director of Audience & Editorial, making sure our websites and information are as useful as possible for people thinking about Masters and PhD study. He has a PhD in English Literature from the University of Sheffield, as well as Bachelors and Masters degrees from the University of Kent and the University of South Wales.
You may also like...

Are you preparing for a PhD interview? Learn some of the do's and don'ts from our expert who has been through the process to help you ace yours.

Holly is officially coming to the end of her first year of PhD study. She talks to some other students to compare experiences and lessons learnt along the way.

Our guest blogger, Holly sat down with an expert on Imposter Syndrome to find out what it really is and how to tackle it.

A PhD is a great way to help you make a difference. We spoke to Josephine Agyeman-Duah about her PhD journey to improve outcomes for babies born preterm.

PhD Hard-talk is an online community for postgraduates and researchers to share their work and advice. We sat down to chat with the project founder, Noma Mguni to learn what PhD Hard-talk can do for you.

After winning our PhD Supervisor of the Year Award, we caught up with Clive Palmer to see how he got to where he is now and what life is like as a supervisor.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
9 things you should consider before embarking on a PhD
June 23, 2021 | 15 min read
By Andy Greenspon
The ideal research program you envision is not what it appears to be
Editor's Note: When Andy Greenspon wrote this article, he was a first-year student in Applied Physics at Harvard. Now he has completed his PhD. — Alison Bert, June 23, 2021
If you are planning to apply for a PhD program, you're probably getting advice from dozens of students, professors, administrators your parents and the Internet. Sometimes it's hard to know which advice to focus on and what will make the biggest difference in the long-run. So before you go back to daydreaming about the day you accept that Nobel Prize, here are nine things you should give serious thought to. One or more of these tips may save you from anguish and help you make better decisions as you embark on that path to a PhD.
1. Actively seek out information about PhD programs.
Depending on your undergraduate institution, there may be more or less support to guide you in selecting a PhD program – but there is generally much less than when you applied to college.
On the website of my physics department, I found a page written by one of my professors, which listed graduate school options in physics and engineering along with resources to consult. As far as I know, my career center did not send out much information about PhD programs. Only after applying to programs did I find out that my undergraduate website had a link providing general information applicable to most PhD programs. This is the kind of information that is available all over the Internet.
So don't wait for your career center or department to lay out a plan for you. Actively seek it out from your career center counselors, your professors, the Internet — and especially from alumni from your department who are in or graduated from your desired PhD program. First-hand experiences will almost always trump the knowledge you get second-hand.
2. A PhD program is not simply a continuation of your undergraduate program.
Many students don't internalize this idea until they have jumped head-first into a PhD program. The goal is not to complete an assigned set of courses as in an undergraduate program, but to develop significant and original research in your area of expertise. You will have required courses to take, especially if you do not have a master's degree yet, but these are designed merely to compliment your research and provide a broad and deep knowledge base to support you in your research endeavors.
At the end of your PhD program, you will be judged on your research, not on how well you did in your courses. Grades are not critical as long as you maintain the minimum GPA requirement, and you should not spend too much time on courses at the expense of research projects. Graduate courses tend to be designed to allow you to take away what you will find useful to your research more than to drill a rigid set of facts and techniques into your brain.
3. Take a break between your undergraduate education and a PhD program.
You are beginning your senior year of college, and your classmates are asking you if you are applying to graduate school. You think to yourself, "Well, I like studying this topic and the associated research, and I am going to need a PhD if I want to be a professor or do independent research, so I might as well get it done as soon as possible." But are you certain about the type of research you want to do? Do you know where you want to live for the next five years? Are you prepared to stay in an academic environment for nine years straight?
Many people burn out or end up trudging through their PhD program without a thought about what lies outside of or beyond it. A break of a year or two or even more may be necessary to gain perspective. If all you know is an academic environment, how can you compare it to anything else? Many people take a job for five or more years before going back to get their PhD. It is true though that the longer you stay out of school, the harder it is to go back to an academic environment with lower pay and a lack of set work hours. A one-year break will give you six months or so after graduation before PhD applications are due. A two-year gap might be ideal to provide time to identify your priorities in life and explore different areas of research without having school work or a thesis competing for your attention.
Getting research experience outside of a degree program can help focus your interests and give you a leg up on the competition when you finally decide to apply. It can also help you determine whether you will enjoy full-time research or if you might prefer an alternative career path that still incorporates science, for example, in policy, consulting or business — or a hybrid research job that combines scientific and non-scientific skills.
I will be forever grateful that I chose to do research in a non-academic environment for a year between my undergraduate and PhD programs. It gave me the chance to get a feel for doing nothing but research for a full year. Working at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in the Space Division, I was the manager of an optics lab, performing spectroscopic experiments on rocks and minerals placed in a vacuum chamber. While my boss determined the overall experimental design, I was able to make my own suggestions for experiments and use my own discretion in how to perform them. I presented this research at two national conferences as well — a first for me. I was also able to learn about other research being performed there, determine which projects excited me the most, and thus narrow down my criteria for a PhD program.
4. Your current area of study does not dictate what you have to study in graduate school.
You might be studying the function and regulation of membrane proteins or doing a computational analysis of the conductivity of different battery designs, but that doesn't mean your PhD project must revolve around similar projects. The transition between college or another research job to a PhD program is one of the main transitions in your life when it is perfectly acceptable to completely change research areas.
If you are doing computation, you may want to switch to lab-based work or vice versa. If you are working in biology but have always had an interest in photonics research, now is the time to try it out. You may find that you love the alternative research and devote your PhD to it, you might hate it and fall back on your previous area of study — or you may even discover a unique topic that incorporates both subjects.
One of the best aspects of the PhD program is that you can make the research your own. Remember, the answer to the question "Why are you doing this research?" should not be "Well, because it's what I've been working on for the past few years already."While my undergraduate research was in atomic physics, I easily transitioned into applied physics and materials science for my PhD program and was able to apply much of what I learned as an undergraduate to my current research. If you are moving from the sciences to a non-STEM field such as social sciences or humanities, this advice can still apply, though the transition is a bit more difficult and more of a permanent commitment.
5. Make sure the PhD program has a variety of research options, and learn about as many research groups as possible in your first year.
Even if you believe you are committed to one research area, you may find that five years of such work is not quite what you expected. As such, you should find a PhD program where the professors are not all working in the same narrowly focused research area. Make sure there are at least three professors working on an array of topics you could imagine yourself working on.
In many graduate programs, you are supposed to pick a research advisor before even starting. But such arrangements often do not work out, and you may be seeking a new advisor before you know it. That's why many programs give students one or two semesters to explore different research areas before choosing a permanent research advisor.
In your first year, you should explore the research of a diverse set of groups. After touring their labs, talking to the students, or sitting in on group meetings, you may find that this group is the right one for you.
In addition, consider the importance of who your research advisor will be. This will be the person you interact with regularly for five straight years and who will have a crucial influence on your research. Do you like their advising style? Does their personality mesh with yours? Can you get along? Of course, the research your advisor works on is critical, but if you have large disagreements at every meeting or do not get helpful advice on how to proceed with your research, you may not be able to succeed. At the very least, you must be able to handle your advisor's management of the lab and advising style if you are going to be productive in your work. The Harvard program I enrolled in has professors working on research spanning from nanophotonics to energy materials and biophysics, covering my wide range of interests. By spending time in labs and offices informally chatting with graduate students, I found an advisor whose personality and research interests meshed very well with me. Their genuine enthusiasm for this advisor and their excitement when talking about their research was the best input I could have received.
6. Location is more important than you think — but name recognition is not.
The first consideration in choosing a PhD program should be, "Is there research at this university that I am passionate about?" After all, you will have to study this topic in detail for four or more years. But when considering the location of a university, your first thought should not be, "I'm going to be in the lab all the time, so what does it matter if I'm by the beach, in a city, or in the middle of nowhere." Contrary to popular belief, you will have a life outside of the lab, and you will have to be able to live with it for four or more years. Unlike when you were an undergraduate, your social and extracurricular life will revolve less around the university community, so the environment of the surrounding area is important. Do you need a city atmosphere to be productive? Or is your ideal location surrounded by forests and mountains or by a beach? Is being close to your family important? Imagine what it will be like living in the area during the times you are not doing research; consider what activities will you do and how often will you want to visit family.
While many of the PhD programs that accepted me had research that truly excited me, the only place I could envision living for five or more years was Boston, as the city I grew up near and whose environment and culture I love, and to be close to my family.
While location is more important than you think, the reputation and prestige of the university is not. In graduate school, the reputation of the individual department you are joining — and sometimes even the specific research group you work in — are more important. There, you will develop research collaborations and professional connections that will be crucial during your program and beyond. When searching for a job after graduation, other scientists will look at your specific department, the people you have worked with and the research you have done.

At the Asgard Irish Pub in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Andy Greenspon talks with fellow graduate students from Harvard and MIT at an Ask for Evidence workshop organized by Sense About Science. He grew up near Boston and chose to go to graduate school there.
7. Those time management skills you developed in college? Develop them further.
After surviving college, you may think you have mastered the ability to squeeze in your coursework, extracurricular activities and even some sleep. In a PhD program, time management reaches a whole new level. You will not only have lectures to attend and homework to do. You will have to make time for your research, which will include spending extended periods of time in the lab, analyzing data, and scheduling time with other students to collaborate on research.
Also, you will most likely have to teach for a number of semesters, and you will want to attend any seminar that may be related to your research or that just peaks your interest. To top it all off, you will still want to do many of those extracurricular activities you did as an undergraduate. While in the abstract, it may seem simple enough to put this all into your calendar and stay organized, you will find quickly enough that the one hour you scheduled for a task might take two or three hours, putting you behind on everything else for the rest of the day or forcing you to cut other planned events. Be prepared for schedules to go awry, and be willing to sacrifice certain activities. For some, this might be sleep; for others, it might be an extracurricular activity or a few seminars they were hoping to attend. In short, don't panic when things don't go according to plan; anticipate possible delays and be ready to adapt.
8. Expect to learn research skills on the fly – or take advantage of the training your department or career center offers.
This may be the first time you will have to write fellowship or grant proposals, write scientific papers, attend conferences, present your research to others, or even peer-review scientific manuscripts. From my experience, very few college students or even PhD students receive formal training on how to perform any of these tasks. Usually people follow by example. But this is not always easy and can be quite aggravating sometimes. So seek out talks or interactive programs offered by your department or career center. The effort will be well worth it when you realize you've become quite adept at quickly and clearly explaining your research to others and at outlining scientific papers and grant proposals. Alternatively, ask a more experienced graduate student or your advisor for advice on these topics. In addition, be prepared for a learning curve when learning all the procedures and processes of the group you end up working in. There may be many new protocols to master, whether they involve synthesizing chemicals, growing bacterial cells, or aligning mirrors on an optical table. In addition, the group may use programming languages or data analysis software you are unfamiliar with. Don't get discouraged but plan to spend extra effort getting used to these procedures and systems. After working with them regularly, they will soon become second nature. When I first started my job at Johns Hopkins, I felt overwhelmed by all the intricacies of the experiment and definitely made a few mistakes, including breaking a number of optical elements. But by the end of my year there, I had written an updated protocol manual for the modifications I had made to the experimental procedures and was the "master" passing on my knowledge to the next person taking the job.
9. There are no real breaks.
In a stereotypical "9-to-5" job, when the workday is over or the weekend arrives, you can generally forget about your work. And a vacation provides an even longer respite. But in a PhD program, your schedule becomes "whenever you find time to get your work done." You might be in the lab during regular work hours or you might be working until 10 p.m. or later to finish an experiment. And the only time you might have available to analyze data might be at 1 a.m. Expect to work during part of the weekend, too. Graduate students do go on vacations but might still have to do some data analysis or a literature search while away.
As a PhD student, it might be hard to stop thinking about the next step in an experiment or that data sitting on your computer or that paper you were meaning to start. While I imagine some students can bifurcate their mind between graduate school life and everything else, that's quite hard for many of us to do. No matter what, my research lies somewhere in the back of my head. In short, your schedule is much more flexible as a PhD student, but as a result, you never truly take a break from your work.
While this may seem like a downer, remember that you should have passion for the research you work on (most of the time), so you should be excited to think up new experiments or different ways to consider that data you have collected. Even when I'm lying in bed about to fall asleep, I am sometimes ruminating about aspects of my experiment I could modify or what information I could do a literature search on to gain new insights. A PhD program is quite the commitment and rarely lives up to expectations – but it is well worth the time and effort you will spend for something that truly excites you.
Contributor
Andy greenspon.
6 Things I Learned from Being in a PhD Program
Being in a doctoral program brings its own share of challenges and rewards. Currently, I have completed almost two years in my PhD program. Looking back on my progress, I can proudly say that every challenge I encountered has helped me grow both academically and non-academically.
Here are six valuable lessons I learned from being in a PhD program and am still applying to my life:
Learn to Trust Yourself
This might sound simple, but for many people (especially graduate students), trusting yourself can be hard to do. There are moments where you might question your own capabilities and feel you are not up to par, but this is completely normal. Try to avoid dwelling on negative thoughts for long periods of time. The key in getting through a PhD program is to stay focused on your goals and to work on them every day. Making any kind of progress is crucial to getting things done. One thing that I do every day is write down what I am grateful for and what I want to achieve by the end of the day. By doing this, I feel more positive, and that positivity is reflected in everything I do.
Listen to Your Advisor
I admit I was extremely scared and felt vulnerable when I met my advisor for the first time. I was scared because I did not know what I had gotten myself into, and I felt inferior because my advisor, Dr. Middlestadt, is an expert in what she does. My field of study is health behavior and although I have a master’s degree in nutritional sciences, I quickly came to the realization that even though these two fields were related, they had different approaches. One of the things I love about doing my PhD is having a mentor who pushes me to my limits and makes me think critically when taking appropriate actions that are essential to my progress as a student.
Start Your Research as Early as You Can
After two months of being in the PhD program, I remember sitting in my apartment and asking myself, “Where should I start?” The words of my advisor immediately came to my mind: “Just start and try!” I believe that was a turning point in my life when I finally realized that any kind of research study is not perfect, and there is no right or wrong way to do it. Even if the idea might seem abstract in your mind, work on it, develop the idea, and implement it. I began collecting pilot data in the spring of 2016 and that summer, I was confident enough to go into the field and work on my study. I am currently analyzing my data and planning to take my qualifying exams in the next few months.
Engage in Opportunities Outside of Your School
Do not limit your knowledge to the realm of the school you are studying at and volunteer in your community . It took some time for me to network outside of school, but I eventually found the right opportunities. Talking to my professors and getting advice from the Office of Career Services helped me tremendously in networking with other people. Putting your knowledge and skills to practice in a real-world setting is a must in the health behavior field. Understanding health issues from the public’s perspective is eye-opening. Moreover, I was able to work with a multi-disciplinary team and learn from the rich experiences of my team members.
Stay in Touch With Friends and Family
I teach stress prevention to college students and one of the things I regularly preach and apply to my life is to nurture the relationships that matter. As an international student, no matter how busy I am, I always dedicate time to talk to my parents at least one to two hours every week. I am constantly in contact with my siblings and my best friend, Natacha. These people may be far in terms of distance, but not by heart. Aside from my family, I have a few close friends in Bloomington who I meet with and talk to on a regular basis. For example, my dear friend Debbie gives me the same kind of advice my mom would, and if I need help or find myself in a difficult situation, I know I can reach out to her.
Find and Maintain Hobbies you Enjoy
People who live in Bloomington can vouch for the harsh winter. One of the things I love doing is knitting and I keep myself occupied with other projects to stay warm. I try to exercise as much as I can and I enjoy gardening in the summer. I also spend a significant portion of my time cooking meals that remind me of my home country and my family. Being far from your country does not mean you cannot enjoy its flavors and spices!
One of the most important decisions I made in my life was to pursue my PhD and I do not regret it. I have had a productive journey and I know the skills and knowledge I am acquiring now will remain with me for the rest of my life. Being a doctoral student is a lot of hard work, but it is totally worth it!

You might also be interested in:

Bridging the Language Gap: Empowering Immigrant Professionals Through Contextualized English Programs
Sharif Krabti | September 9, 2024
Published in March 2024, the Department of Labor’s Bridging the Gap for New Americans report explores the barriers faced by internationally educated immigrants and refugees who seek to resume their careers in the United States. With our labor market increasingly in need of their skills and experience, the report highlights a key factor in workforce […]

Workforce Navigation Programs Fostering Inclusive Economies Across States
Sharif Krabti | September 3, 2024
In April, the U.S. Department of Labor released its Bridging the Gap for New Americans study of the barriers and opportunities facing internationally educated immigrants and refugees seeking to resume their careers in the United States. The study provides needed guidance for local, state, and federal stakeholders to further strengthen the inclusion of these workers […]

How States Are Opening Their Own Pathways to Occupational Licensure
In the United States, key regulated industries like education, engineering, and health care face significant labor shortages that are predicted to deepen in the coming years. Experts in the health care area alone project a shortfall of over 900,000 nurses by 2030 and up to 86,000 physicians by 2036 as the country’s population ages and […]

Mirriam’s Story: Achieving Goals with a WES Credential Evaluation
WES Staff | April 17, 2024
Today, Mirriam Mutemba Mbanga is a registered nurse at the Ministry of Health Zambia. But as a child, she dreamed of moving away from her home country. To hear about what motivates Mirriam, and how she hopes a WES credential evaluation will help her achieve her goals, keep reading. Reaching Milestones Inspired by her mother’s […]
We have updated our Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy . By using this website, you accept the new terms.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 06 November 2018
Twenty things I wish I’d known when I started my PhD
- Lucy A. Taylor 0
Lucy A. Taylor earned her zoology PhD from the University of Oxford, UK. She is now a postdoctoral researcher at Save the Elephants in Nairobi, Kenya, and a visiting researcher in the Department of Zoology at Oxford.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Starting a PhD can be tough. Looking back, there are many things I wish I’d known at the beginning. Here, I have curated a list of advice from current PhD students and postdoctoral researchers from the Department of Zoology at my institution, the University of Oxford, UK, to aid new graduate students.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-07332-x
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged. You can get in touch with the editor at [email protected].
Related Articles

What makes a good PhD student?
Make the most of PhDs

The grassroots organizations continuing the fight for Ukrainian science
Career Feature 11 SEP 24

How a struggling biotech company became a university ‘spin-in’
Career Q&A 10 SEP 24

The human costs of the research-assessment culture
Career Feature 09 SEP 24
My identity was stolen by a predatory conference
Correspondence 17 SEP 24

How can I publish open access when I can’t afford the fees?
Career Feature 02 SEP 24

Tales of a migratory marine biologist
Career Feature 28 AUG 24

Guide, don’t hide: reprogramming learning in the wake of AI
Career Guide 04 SEP 24

What I learnt from running a coding bootcamp
Career Column 21 AUG 24

The Taliban said women could study — three years on they still can’t
News 14 AUG 24
Associate or Full Professor Neuroimager Faculty Position - Mesulam Center (MCNADC)
Associate or Full Professor Tenure Track Faculty Position in Human Neuroimaging.
Chicago, Illinois
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine - Mesulam Center
Assistant Professor Tenure-Track Faculty Positions
Nashville, Tennessee
Vanderbilt University
Faculty Positions in Biology and Biological Engineering: Caltech, Pasadena, CA, United States
The Division of Biology and Biological Engineering (BBE) at Caltech is seeking new faculty in the area of Molecular Cell Biology.
Pasadena, California
California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
Assistant Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology
We seek applications for a tenure-track faculty position in the Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology.
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Harvard University - Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology
Husbandry Technician I
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
What is a PhD? Advice for PhD students
How long does it take to get a doctorate degree how do you get into grad school are you qualified to do a phd answers to these questions and more.
What is a PhD?
A PhD, which stands for “doctor of philosophy”, is the most advanced academic degree. It’s earned through extensive research on a specific topic, demonstrating expertise and contributing new knowledge to the field.
What does “PhD” mean?
The term “PhD” is often used as a synonym for any doctoral-level qualification. Doctorate degrees can often be split into two categories: MPhil and PhD.

Download your Study Abroad Guide for FREE!
An MPhil is similar to a PhD as it includes a research element (which is usually shorter and less in-depth than a PhD thesis, and often more akin to a dissertation undertaken at undergraduate or master’s level).
MPhil students focus more on interpreting existing knowledge and theory and critically evaluating other people’s work rather than producing their own research. The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries.
A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as “candidates”, to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
PhD requirements vary significantly among countries and institutions. The PhD, once completed, grants the successful candidate the title of “doctor of philosophy”, also called PhD or DPhil.
What is a professional doctorate?
A professional doctorate is a kind of degree that helps people become experts in their fields. Instead of focusing mainly on theory and research like a regular PhD, a professional doctorate is all about practical skills and knowledge.
This kind of doctorate is great for students who want to get better at their jobs in areas like teaching, healthcare, business, law or psychology. The courses and projects in these programmes are designed to tackle real problems you might face at work.
For example, you might have heard of the doctor of education (EdD), doctor of business administration (DBA), doctor of psychology (PsyD) or doctor of nursing practice (DNP). These programmes combine learning, hands-on projects and sometimes a thesis paper or essay to show you’re skilled at solving on-the-job challenges.
How long does it take to study a PhD?
The time required to complete a PhD can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, a full-time PhD programme takes around three to six years to finish. However, it’s important to take into account individual circumstances and the nature of the research involved.
1. Full-time vs. part-time: If you’re studying full-time, dedicating most of your time to your studies, it usually takes about three to four years to complete a PhD. However, studying part-time while managing other commitments might extend the duration. Part-time PhDs can take around six to eight years, and sometimes even longer.
2. Nature of research: The complexity of your research proposal can influence the time required. Certain research questions may involve intricate experiments, extensive data collection or in-depth analysis, potentially leading to a longer completion timeline.
3. Field of study: The subject area you’re researching can also affect the necessary time. Some fields, such as sciences or engineering, might involve more hands-on work, while theoretical subjects might require more time for literature review and analysis.
4. Supervision and support: The guidance and availability of your academic supervisor can affect the pace of your research progress. Regular meetings and effective communication can help keep your studies on track.
5. Thesis writing: While the research phase is crucial, the stage of writing your thesis is equally significant. Organising and presenting your research findings in a clear and cohesive manner can take several months.
6. External commitments: Personal commitments, such as work, family or health-related factors, can influence your study time. Some students need to balance these alongside their PhD studies, potentially extending the duration.
7. External Funding: The availability of funding can also affect your study duration. Some funding might be linked to specific project timelines or research objectives.
So, although a PhD usually takes between three and six years of full-time study, with potential variations based on research complexity, enrolment as part-time or full-time, field of study and personal circumstances. It’s vital to have a realistic understanding of these factors when planning your PhD journey.
How long is a PhD in the UK?
In the UK, the length of a PhD programme typically ranges from three to four years of full-time study. As explained above, there are many factors to consider.
How long is a PhD in the US?
Similarly to the UK, in the United States, the duration of a PhD programme can vary widely depending on the field of study, research topic and individual circumstances. On average, a full-time PhD programme in the US typically takes between five and six years to complete.
Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US?
PhD programmes generally take longer to complete in the US than in the UK due to various factors in the education systems and programme structures of each country:
1. Programme structure: UK PhD programmes often emphasise early, focused research from the first year, leading to shorter completion times. In contrast, US programmes commonly include more initial coursework in your first and second year and broader foundational training, which can extend the overall duration.
2. Course work requirements: Many US PhD programmes require a lot of course work, which can lengthen the time needed to finish. UK programmes tend to have fewer or no course work demands, allowing students to concentrate primarily on research skills.
3. Research funding: In the UK, PhD funding is often awarded with specific timeframes in mind, motivating completion of the research degree in the agreed duration. In the US, funding approaches can vary, requiring students to secure funding from multiple sources, potentially affecting their progress and completion time.
4. Teaching responsibilities: Some US PhD students take on teaching roles as part of their funding, dividing their time and potentially prolonging their studies.
5. Research approach: Differences in research methodologies and project scopes can affect the time needed for data collection, experimentation and analysis.
6. Academic culture: The US education system values a well-rounded education, including coursework and comprehensive exams. This can extend the time before full-time research begins. UK PhD programmes often prioritise independent research early on.
7. Part-time and work commitments: US PhD candidates might have more flexibility for part-time work or other commitments, which can affect research progress.
8. Dissertation requirements: US PhD programmes generally include a longer and more comprehensive dissertation, involving more chapters and a broader exploration of the research topic.
These variations in programme structures, funding models and academic cultures contribute to the differing completion times between the two countries.
What qualifications do you need for a PhD?
To be eligible for a PhD programme, certain educational qualifications are generally expected by universities. These qualifications serve as indicators of your readiness to engage in advanced research and contribute to the academic community.
First, an undergraduate or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field is typically the most common requirement. This degree provides you with a foundational understanding of the subject and introduces you to basic research methodologies. It serves as a starting point for your academic journey.
Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme?
In addition to an undergraduate degree, many PhD programmes also require candidates to hold postgraduate or master’s degrees, often in fields related to the intended PhD research. A master’s degree offers a deeper exploration of the subject matter and enhances your research skills. Possessing a master’s degree signifies a higher level of expertise and specialisation.
The combination of both undergraduate and postgraduate degrees demonstrates a solid academic background. This background is crucial before you engage in doctoral study because pursuing a PhD involves more than just knowledge; it requires advanced research abilities, critical thinking and the capacity to provide an original contribution and new insights into the chosen field of study.
While these qualifications are usually requested, there are exceptions. Some institutions offer direct-entry programmes that encompass bachelor’s, master’s and PhD degrees in a streamlined structure. This approach is often seen in scientific and engineering disciplines rather than humanities.
In exceptional cases, outstanding performance during undergraduate studies, coupled with a well-defined research proposal, might lead to direct entry into a PhD programme without requiring a master’s degree.
Admission requirements can vary between universities and programmes. Some institutions might have more flexible prerequisites, while others could have more stringent criteria. Make sure that you thoroughly research all admission requirements of the PhD programmes you’re interested in to ensure you provide the right information.
Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries?
PhD entry requirements in Canada and Australia can be somewhat similar to those in the UK and the US, but there are also some differences. Just like in the UK and the US, having a bachelor’s degree followed by a master’s degree is a common way to qualify for a PhD in Canada and Australia. However, the exact rules can vary, such as how much research experience you need or the grades you should have.
In Canada and Australia, as in the UK and the US, international students usually need to show their English language skills through tests like IELTS or TOEFL. And, like in other places, you might need to give a research proposal to explain what you want to study for your PhD.
But remember, even though there are some similarities, each country has its own rules.
PhD diary: Preparing for a PhD Nine things to know before doing a PhD Women in STEM: undertaking PhD research in cancer Studying for a part-time PhD: the challenges and the benefits Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student? Looking for PhD tips? Why not check Twitter PhD diary: Where do I begin? How to do a PhD on a budget
How much does it cost to study a PhD?
The cost of pursuing a PhD can vary significantly between international and home (domestic) students, and it depends on the country, university and programme you choose.
United Kingdom (UK)
Home students in the UK often pay lower tuition fees compared with international students. Home students might also have access to government funding or subsidised tuition rates.
International students typically pay higher tuition fees, which can vary widely depending on the university and programme. Fees can range from around £10,000 to £25,000 or more per year.
United States (US)
PhD programme costs in the US can be quite high, especially for international students. Public universities often have lower tuition rates for in-state residents compared with out-of-state residents and international students.
Private universities in the US generally have higher tuition fees, and international students might be charged higher rates than domestic students.
Canadian universities often charge higher tuition fees for international students compared with domestic students.
Some universities offer funding packages that include tuition waivers and stipends for both domestic and international doctoral students.
In Australia, domestic students (Australian citizens and permanent residents) usually pay lower tuition fees than international students.
International students in Australia might have higher tuition fees, and costs can vary based on the university and programme.
Apart from tuition fees, other aspects play a role in the overall financial consideration:
PhD studentship: Many universities offer PhD studentships that provide financial support to research students, covering both tuition fees and a stipend for living expenses.
Stipend and housing: Stipends are designed to cover living expenses. Stipend amounts can vary depending on the university and location. If you’re studying in London in the UK, stipends might be higher to account for the higher living costs in the city. Some universities also offer subsidised or affordable housing options for doctoral students.
Tuition and stipend packages: Some PhD programmes provide funding packages that include both tuition waivers and stipends. These packages are to help relieve the financial burden on students during their doctoral studies.
Research the financial support options provided by the universities you’re interested in to make an informed decision about the cost of your PhD journey.
What funding options are available for PhD candidates?
PhD candidates have various funding options available to support their studies and research journeys. Some of these options include:
PhD scholarships: Scholarships are a common form of financial aid for PhD candidates. They are awarded based on academic merit, research potential or other specific criteria. Scholarships can cover tuition fees and provide a stipend for living expenses.
Bursaries: Bursaries are another form of financial assistance offered to students, including PhD candidates, based on financial need. They can help cover tuition fees or provide additional financial support.
In the UK, specific funding options are available:
Regional consortium: Some regions have research consortiums that offer funding opportunities for doctoral candidates. These collaborations can provide financial support for research projects aligned with specific regional needs.
UK research institute: Research councils in the UK often offer stipends to PhD candidates. These stipends cover living expenses and support research work.
University-based studentship: Many UK universities offer studentships. You can read more about these above.
In the USA, there are also funding options available:
Research assistantships (RAs): Many universities offer research assistantships where PhD candidates work on research projects under the guidance of faculty members. In exchange, they receive stipends and often have their tuition waived.
Teaching assistantships (TA): Teaching assistantships involve assisting professors in teaching undergraduate courses. In return, PhD candidates receive stipends and sometimes tuition remission.
Fellowships: Fellowships are competitive awards that provide financial support for PhD candidates. They can come from universities, government agencies, private foundations and other institutions. Fellowships can cover tuition, provide stipends and offer research or travel funds.
Graduate assistantships: Graduate assistantships include a range of roles, from research and teaching to administrative support. These positions often come with stipends and sometimes include tuition benefits.
External grants and fellowships: PhD candidates can apply for grants and fellowships from external organisations and foundations that support research careers in specific fields. Examples include the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Fulbright Programme.
Employer sponsorship: In some cases, employers might sponsor employees to pursue PhDs, especially if the research aligns with the company’s interests.
You can read about the current available scholarships for international students of all education levels on our website .
What does a PhD Involve?
How does a PhD work?
A PhD includes thorough academic research and significant contributions to your chosen field of study. The timeline for completing a PhD can significantly vary based on the country, college or university you attend and the specific subject you study.
The duration of a PhD programme can vary based on factors such as the institution’s requirements and the academic discipline you’re pursuing. For instance, the timeline for a PhD in a science-related field might differ from that of a humanities discipline.
UK PhD timeline example
Looking at a typical PhD degree in a London higher education institution, we can consider this example timeline.
In the initial year of your PhD, you’ll collaborate closely with your designated academic supervisor. This collaboration involves refining and solidifying your research proposal, which lays the foundation for your entire doctoral journey.
This is also the time to establish a comprehensive plan, complete with well-defined milestones and deadlines. A crucial aspect of this year is conducting an extensive literature review, immersing yourself in existing academic works to understand the landscape of your chosen research area. It’s important to make sure that your research idea is original and distinct from prior studies.
As you begin the second year, you’ll actively collect data and gather information related to your research topic. Simultaneously, you’ll initiate the process of crafting your thesis. This involves combining your research findings and analysis into sections of your thesis document.
This is also the phase where you might have opportunities to share your research insights at academic meetings, conferences or workshops. Depending on the programme, you might even engage in teaching activities. Some PhD candidates also begin contributing to academic journals or books, showcasing their findings to a broader audience.
The third year of a PhD programme often marks the final stage of your research efforts. This is when you dedicate substantial time to writing and finalising your complete thesis. Once your thesis is completed to the highest standard, you’ll submit it for thorough evaluation.
A significant milestone in the third year is the viva voce, an oral examination where you’ll defend your thesis before a panel of experts in your field. The viva voce is an opportunity to showcase your deep understanding of your research and defend your findings.
Why should you do a PhD?
For many people, acquiring a doctorate degree is the pinnacle of academic achievement, the culmination of years of commitment to higher education.
However, the act of pursuing a PhD can be a complex, frustrating, expensive and time-consuming exercise. But with the right preparation, some sound advice and a thorough understanding of the task at hand, your years as a doctoral student can be some of the most rewarding of your life.
People choose to work towards a doctorate for many reasons. If you are looking to pursue an academic position, such as university lecturer or researcher, then a PhD is usually required.
Many people obtain a PhD as part of a partnership with an employer, particularly in scientific fields such as engineering, where their research can prove useful for companies.
In some cases, however, PhDs are simply down to an individual’s love of a subject and their desire to learn more about their field.
What are some benefits of studying a PhD?
Pursuing a PhD can have many benefits that extend beyond academic achievement, encompassing personal growth, professional advancement and meaningful contributions to knowledge.
One of the most notable benefits of a PhD is the potential for tenure in academia. Attaining tenure provides a level of job security that allows you to delve into long-term research projects and make enduring contributions to your field. It signifies a stage where you can explore innovative ideas and pursue in-depth research, fostering your academic legacy.
While not obligatory, the opportunity to collaborate on research projects with your supervisor is another valuable aspect of a PhD pursuit. These collaborations might even come with financial compensation, offering real-world experience, skill development and practical applications of your research. Engaging in such collaborations can enrich your research portfolio and refine your research methodologies.
A pivotal aspect of a PhD journey is the chance to publish your original research findings. By disseminating your work in academic journals or presenting it at conferences, you contribute to the expansion of knowledge within your field. These publications establish your expertise and reputation among peers and researchers worldwide, leaving a lasting impact.
The pursuit of a PhD can provide a unique platform to build a diverse network of colleagues, mentors and collaborators. Engaging with fellow researchers, attending conferences and participating in academic events offer opportunities to make valuable connections. This network can lead to collaborations, expose you to a spectrum of perspectives and pave the way for future research endeavours.
What is a PhD thesis? And what is a PhD viva?
A PhD thesis will be produced with help from an academic supervisor, usually one with expertise in your particular field of study. This thesis is the backbone of a PhD, and is the candidate’s opportunity to communicate their original research to others in their field (and a wider audience). PhD students also have to explain their research project and defend their thesis in front of a panel of academics. This part of the process is often the most challenging, since writing a thesis is a major part of many undergraduate or master’s degrees, but having to defend it from criticism in real time is arguably more daunting. This questioning is known as a “viva”, and examiners will pay particular attention to a PhD’s weaknesses either in terms of methodology or findings. Candidates will be expected to have a strong understanding of their subject areas and be able to justify specific elements of their research quickly and succinctly.
In rare cases, students going for a PhD may instead be awarded an MPhil if the academic standard of their work is not considered fully up to par but still strong enough to be deserving of a qualification.
Can you do a PhD part time?
Many PhD and MPhil candidates choose to pursue their qualification part time, in order to allow time to work and earn while studying. This is especially true of older students, who might be returning to academia after working for a few years.
When applying, you should always speak to the admissions team at your university to ensure this is possible and then continue to work with your supervisor to balance all your commitments.
Can I do a PhD through distance learning?
This is something else that you will need to check with your university. Some institutions offer this option, depending on the nature of your research.
You will need to be clear how many times you will need to travel to your university to meet with your supervisor throughout your PhD.
Your PhD supervisor
Choosing the right PhD supervisor is essential if you want to get the most out of your PhD. Do your research into the faculty at the institution and ensure that you meet with your proposed supervisor (either virtually or in person) before fully committing.
You need to know that not only do they have the right expertise and understanding of your research but also that your personalities won’t clash throughout your PhD.
Remember, to complete your PhD, you will need a strong support network in place, and your supervisor is a key part of that network.
Coping with PhD stress
If you do decide to embark on a doctorate, you may well encounter stress and anxiety. The work involved is often carried out alone, the hours can be long and many students can suffer from the pressure they feel is on their shoulders.
Ensuring that you check in regularly with your emotions and your workload is crucial to avoid burnout. If you have other commitments, such as a job or a family, then learning to balance these can feel overwhelming at times.
Give yourself regular breaks, speak to your supervisor and ensure that you know what university resources and support systems are available to you in case you need to access them.
Post-doctorate: what happens after you finish your PhD?
Many PhD graduates pursue a career in academia, while others will work in industry. Some might take time out, if they can afford to, to recover from the efforts of PhD study.
Whatever you choose to do, undertaking a PhD is a huge task that can open up a range of doors professionally. Just remember to take some time out to celebrate your achievement.
How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential?
How much does a professor with a PhD make a year?
Professors with PhDs can earn different amounts depending on where they work and their experience. In the UK, a professor might make around £50,000 to £100,000 or more each year. In the US, it's between about $60,000 and $200,000 or even higher. The exact salary depends on things like the place they work, if they have tenure, and what they teach.
How much does a PhD add to salary?
Having a PhD can make your salary higher than if you had a lower degree. But exactly how much more you earn can change. On average, people with PhDs earn more than those with bachelor’s or master’s degrees. The increase in salary is influenced by many things, such as the job you do, where you work and what field you’re in.
In fields such as research, healthcare, technology and finance, your knowledge and skills from your PhD can potentially help you secure a higher salary position.
In the end, having a PhD can boost your earning potential and open doors to well-paying jobs, including professorships and special roles in different areas. But the exact effect on your salary is influenced by many things, so ensure you weigh the cost against the benefit.
How to choose a PhD programme?
Choosing a PhD programme involves defining your research interest, researching supervisors and programme reputation, evaluating funding options, reviewing programme structure, considering available resources, assessing networking opportunities, factoring in location and career outcomes, visiting the campus if possible and trusting your instincts.
How can I find available PhD programmes?
You can find available PhD programmes by visiting university websites, using online directories such as “FindAPhD”, checking professional associations, networking with professors and students, following universities on social media, attending career fairs and conferences, contacting universities directly and exploring research institutes’ websites.
How to apply for a PhD programme?
To apply for a PhD programme:
Research and select universities aligned with your interests.
Contact potential supervisors, sharing your proposal, CV and references.
Prepare application materials: research proposal, CV, recommendation letters and a writing sample.
Ensure you meet academic and language-proficiency requirements.
Complete an online application through the university’s portal.
Pay any required application fees.
Write a statement of purpose explaining your motivations.
Provide official transcripts of your academic records.
Submit standardised test scores if needed.
Some programmes may require an interview.
The admissions committee reviews applications and decides.
Apply for scholarships or assistantships.
Upon acceptance, review and respond to the offer letter.
Plan travel, accommodation and logistics accordingly.
Remember to research and follow each university’s specific application guidelines and deadlines.
How to apply for a PhD as an international student?
Many stages of the PhD application process are the same for international students as domestic students. However, there are sometimes some additional steps:
International students should apply for a student visa.
Take language proficiency tests such as TOEFL or IELTS if required.
Provide certificates if needed to validate your previous degrees.
Show evidence of sufficient funds for tuition and living expenses.
Check if you need health insurance for your chosen destination.
Translate and authenticate academic transcripts if necessary.
Attend orientation sessions for cultural adaptation.
Apply for university housing or explore off-campus options.
Familiarise yourself with international student support services.
Ben Osborne, the postgraduate student recruitment manager at the University of Sussex explains in detail how to apply for a PhD in the UK .
Giulia Evolvi, a lecturer in media and communication at Erasmus University, Rotterdam explains how to apply for a PhD in the US .
Finally, Samiul Hossain explores the question Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student?
Q. What is a PhD? A. A PhD is the highest level of academic degree awarded by universities, involving in-depth research and a substantial thesis.
Q. What does “PhD” mean? A. “PhD” stands for doctor of philosophy, recognising expertise in a field.
Q. What is a professional doctorate? A. A professional doctorate emphasises practical application in fields such as education or healthcare.
Q. How long does it take to study a PhD? A. It takes between three and six years to study a full-time PhD programme.
Q. How long is a PhD in the UK? A. It takes around three to four years to study a full-time UK PhD.
Q. How long is a PhD in the US? A. It takes approximately five to six years to complete a full-time US PhD.
Q. Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US? A. US programmes often include more course work and broader training.
Q. What qualifications do you need for a PhD? A. You usually need an undergraduate degree as a minimum requirement, although a master’s might be preferred.
Q. Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme? A. Master’s degrees are preferred but not always required.
Q. Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries? A. Entry requirements are similar in many countries, but there may be additional requirements. Make sure to check the university website for specific details.
Q. How much does it cost to study a PhD? A. The cost of PhD programmes vary by country and university.
Q. What funding options are available for PhD candidates? A. Scholarships, assistantships, fellowships, grants, stipends are all funding options for PhD candidates.
Q. What does a PhD involve? A. PhDs involve research, seminars, thesis, literature review, data analysis and a PhD viva.
Q. Why should you do a PhD? A. There are many reasons to study a PhD including personal growth, research skills, contributions to academia and professional development.
Q. What are some benefits of studying a PhD? A. Benefits of graduating with a PhD include achieving tenure, collaborations with colleagues, publication of your work, and networking opportunities.
Q. What is a PhD thesis? A. A PhD thesis is a comprehensive document that showcases the original research conducted by a PhD candidate.
Q. What is a PhD viva? A. A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce or oral examination, is the final evaluation of a PhD candidate’s research and thesis where the panel asks questions, engages in discussions and assesses the depth of the candidate’s understanding and expertise.
Q. Can you do a PhD part-time? A. Yes, part-time options are available for PhDs.
Q. Can I do a PhD through distance learning? A. Some universities offer online PhDs; you can find out more on their websites.
Q. How to choose a PhD programme? A. You can find PhD programmes through research, by contacting faculty, checking resources and considering location.
Q. How can I find available PhD programme? A. You can find available PhD programmes on university sites, through directories and by networking.
Q. How to apply for a PhD programme A. To apply for a PhD programme, research suitable universities and programmes, get in touch with potential supervisors, gather required documents like transcripts and reference letters, complete the online application, pay any necessary fees and submit a statement of purpose and research proposal. If needed, meet language-proficiency criteria and attend interviews. After acceptance, explore funding choices, confirm your spot and get ready for the programme’s start.
Q. How to apply for a PhD as an international student A. To apply for a PhD as an international student, follow similar steps to domestic students, but you need to include securing a student visa and passing language requirements.
Q. What is a PhD dropout rate? A. The dropout rate from PhDs varies but is approximately 30-40 per cent.
Q. How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential? A. A PhD can boost earning potential, especially in research, technology, healthcare and academia. Impact varies by job, industry and location. Experience, skills and demand also influence salary.
Q. How to address a person with a PhD? A. When addressing someone with a PhD, it’s respectful to use “Dr”, followed by their last name, whether they have a PhD in an academic field or a professional doctorate. For instance, “Dr. Smith”.
Q. Is there a difference between a PhD and a doctorate? A. The terms “PhD” and “doctorate” are often used interchangeably, though a PhD is a specific type of doctorate focused on original research. A doctorate can refer more broadly to any doctoral-level degree, including professional doctorates with practical applications.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and an MD? A. A PhD is a doctor of philosophy, awarded for academic research, while an MD is a doctor of medicine, focusing on medical practice. They lead to different career paths and involve distinct areas of study.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and a professional doctorate? A. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree, while a professional doctorate emphasises applying research to practical fields such as education or business. PhDs often involve original research, while professional doctorates focus on real-world application.
Q. What is the difference between UK and US PhDs? A. The difference between UK and US PhDs lies mainly in structure and duration. UK PhDs often have shorter durations and a stronger emphasis on independent research from an early stage. US PhDs typically include more initial coursework and broader foundational training before full-time research begins.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD student and a candidate? A. A PhD student is actively studying and researching in a doctoral programme, while a PhD candidate has completed programme requirements except for the dissertation and is close to completion.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an EdD? A. A PhD and an EdD (doctor of education) differ in focus. A PhD emphasises research and academic contributions, while an EdD focuses on applying research to practical educational issues.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a DBA? A. A PhD and a DBA (doctor of business administration) differ in purpose. A PhD emphasises theoretical research and academia, while a DBA is practice-oriented, aimed at solving real business problems.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a PsyD? A. A PhD and a PsyD (doctor of psychology) differ in emphasis. A PhD focuses on research and academia, while a PsyD emphasises clinical practice and applying psychological knowledge.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an LLD? A. A PhD and an LLD (doctor of laws or Legum doctor) are distinct. A PhD is awarded in various disciplines, while an LLD is usually an honorary degree for significant contributions to law.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an MD-PhD? A. A PhD and an MD-PhD differ. An MD-PhD is a dual degree combining medical training (MD) with research training (PhD).
Q. What is the Cambridge PhD? A. A Cambridge PhD involves original research guided by a supervisor, resulting in a thesis. It’s offered at the University of Cambridge .
Q. What is the Oxford DPhil? A. An Oxford DPhil is equivalent to a PhD and involves independent research leading to a thesis. The term “DPhil” is unique to the University of Oxford .
Q. What is the PhD programme acceptance rate? A. PhD acceptance rates vary by university, field and competition. Prestigious universities and competitive fields often have lower acceptance rates.
Q. What is a PhD supervisor? A. A PhD supervisor guides and supports a student’s research journey, providing expertise and feedback.
Q. What is a PhD panel? A. A PhD panel evaluates a candidate’s research, thesis and oral defence. It consists of experts in the field.
Q. What is a PhD stipend? A. A PhD stipend is a regular payment supporting living expenses during research, often tied to teaching or research assistant roles.
Q. What is a PhD progression assessment? A. A PhD progression assessment evaluates a student’s progress, often confirming their continuation in the programme.
Q. What is a PhD defence? A. A PhD defence, or viva, is the final oral examination where a candidate presents and defends their research findings and thesis before experts.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Pursuing a PhD in neuroscience
Luis Humberto Eudave Ramos

Why study a PhD in English literature?
John Francis Davies


8 habits to help you get through your PhD
Shabana Khan
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
- Graduate School
How to Answer, “Why Do You Want to Do a PhD?”

When applying for graduate school, your “why do you want to do a PhD?” answer to this common question will be something you want to prepare in advance: doctorate admissions can be pretty competitive, which is why acing your interview is key to securing that acceptance. If you are wondering how to get into grad school , preparing yourself early can allow for enough time to perfect all aspects of your application.
This article includes helpful samples of answers to this notorious interview question, explores why it is asked, and provides some tips for planning out your future response. We also cover the benefits of graduate school interview preparation for improving your chances of getting into your dream PhD program and achieving your goals.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free initial consultation here <<
Listen to the blog!
Article Contents 10 min read
“why do you want to do a phd” sample answers.
Sample Answer 1 (academic/career/literary research focus)
I am interested in a PhD at your institution because I wish to further my literary research and become a professor at the university level. My plan is to be a top scholar of 19th-century and Victorian literature. I first became acquainted with the period during my bachelor’s degree when one of my favorite professors encouraged me to study the portrayal of gender and sexuality in works of that period, specifically through the writings of the Brontë sisters. I became fascinated with how concepts of masculinity, femininity, and androgyny interact in their writing and how they subvert conventions of the gothic genre to represent female rage against oppression by men. That interest led to the completion of my master’s degree at McGill University, where I wrote a major research paper on the subject. Something I want to further discuss in my published work is how this concept transforms as it appears in novels of the 20 th -century and contemporary literature. The ultimate goal is to further ingratiate myself within current scholarship in the field. I also know the value of a good teacher, and I want to be able to inspire a future generation of students, just as my professors inspired me.
Sample Answer 2 (personal growth/curiosity focus)
Planning out my future was not always easy for me. Growing up, I did not have a clue where to start. I was a few semesters into my undergraduate degree before I figured out what I actually wanted to study. I then left my economics and finance majors behind and started a psychology program, which is when I originally became interested in the impact of social media on mental health, whether it be positive or negative. Social media was steadily growing in popularity at the time and is now a staple in our personal and professional lives. It has been an interesting experience to watch this shift occur right in front of my eyes as I completed my bachelor’s and eventually my master’s degree. I never had to look very hard to find what to focus my attention on because there were always new studies coming out about the effects of smartphones and social media apps. This is a field that is frequently changing and presenting new developments. For me, there is something really fascinating about that aspect of our digital world. I want to do this doctorate degree as a culmination of my education in this area now that it feels like I have finally found my calling.
This question, like the “tell me about yourself” PhD interview question , may be frustrating to encounter, as it can be considered broad or redundant. However, when a graduate program director asks this question, they want to get down to the nitty-gritty of who you are and why you are here in front of them. Another way of wording this question would be: What is your motivation for applying to graduate school? Not many people wake up one day and randomly apply to a PhD program on a whim. Therefore, the department you are applying to wants to find out more aspects of your personality and reasoning beyond the contents of your graduate school resume or grad school career goals statement . They want to see what kind of student, instructor, professor, scholar, or colleague you will be. Graduate programs are usually not very large, so they want a sense of who they will be working with for the next few years.
Of course, you can touch upon your past experiences studying or otherwise if it is relevant to what you are currently pursuing, but the overall purpose of your interview is to give them more information about you than what they already know. Answering this question illustrates how concise you can be and how you speak about yourself or your interests. It tests your self-awareness as you are planning to take on an advanced degree at the doctorate level. Your response will also depend on whatever program or field you are applying to. Someone applying for a doctoral program in the sciences may have different components to bring up in their answer than a psychology or humanities applicant.
Even after applying to graduate school, you may still be wondering should you pursue a master’s or PhD , but this could be because you have not yet narrowed down your reasons for doing one. When constructing your response, you will need to reflect on your personal reasons for going forward with a PhD. You want your answers in your interview to be genuine and truly reflective of your interests in their program. It is possible that your reasoning stems from a combination of multiple different places. Here are some of the more common reasons that PhD applicants pursue further education that may resonate with your story:
1. Boosting Academic and Career Prospects
You may have an interest in further developing your career opportunities, whether they are inside or outside of academia. To become a lecturer or a professor at the university level, a doctoral degree is usually required for most disciplines. Many people want to take that extra step to build upon their master’s degree and become a notable expert in their field. Completing a PhD can be the catalyst for learning how to find a job in academia . Feeling the desire to explore that possibility or strive toward that path is a perfectly acceptable reason for completing a PhD. Even if you do not have aspirations to become a professor, a PhD could lead to viable options outside of academia. A doctorate degree could simply be about opening as many doors as possible, which is necessary to succeed in any job market.
2. Achieving Personal Development
Many potential PhD applicants want to fulfill a personal goal when completing their degree. It is your degree after all, so it is normal for your reasons to lead back to you and your wishes. Nobody is expecting you to be completing this degree for anyone else. It may be a life-changing experience for you as a whole, even if it is not directly linked to your studies. There are other aspects to going to school that are not immediately apparent. A PhD program is also a way to learn new skills, meet new people, and move to a new place, perhaps. You will have the opportunity to expand your network and give yourself every opportunity to succeed. Ask yourself: what can you accomplish personally with this PhD that you cannot without it? Your eventual response in an interview could mention specific resolutions that come with acquiring your doctorate degree. A PhD can act as validation for the years of study you have behind you or can give you a greater sense of pride in your academic abilities.
3. Fulfilling Curiosity
When you apply to a doctoral program, you have probably thought about specific subjects you want to consider. While you can wait to figure out exactly how to find a PhD topic until after you get accepted, you should already have a basic idea of what you want to pursue and be ready to discuss it when asked about it in an interview. When you apply to an advanced degree, you are not expected to know everything, even though it may seem so. Where you find inspiration to learn is key to your motivations as you embark on this new journey. Each individual applicant comes in the door with their own story and rationale for pursuing a PhD. You could be inspired by a particular scholar, era, or world issue. Give your interviewer the larger picture as to why a PhD is necessary for you. Whatever you are curious about will make you stand out from other applicants who have similar backgrounds. Making sure to explain that these objectives require a PhD is also very important to proving your candidacy to a program director.
4. Advancing Research
Springboarding off of curiosity, research is how scientific innovation is published to the masses. It is the physical manifestation of your curiosity and transforms an idea into reality. Students often use graduate education as a means to publicize their work. Many ground-breaking studies begin within university walls. A PhD could be the vehicle that helps you pursue worthwhile research that can ultimately have a greater impact on your field of study as well as the world at large. Before you apply, you should ideally jot down some research questions or objectives you plan to explore, either during or after completing your PhD. Writing a research interest statement could also help in this regard. These interests could wholly motivate you to pursue a PhD first and foremost. For instance, if your wish is to positively effect the environment and develop research that could combat climate change, the resources of an academic institution can help further develop that goal.
5. Training Before Further Education
In certain cases, a PhD could add layers to a student’s training before attempting another educational pursuit, such as medical school. For instance, prospective medical students often ask themselves, “Do I need a graduate degree to gain admission to medical school?” because they want to strengthen their application with a doctorate degree in the sciences or another relevant field. A PhD before medical school could also result in an impressive research resume for the applicant and provide them further motivation for becoming a doctor. There are also programs that combine both degrees, such as MD-PhD programs , that focus primarily on research and scientific innovation rather than clinical work. Many prospective medical students apply to PhD programs to explore every option at their disposal and create a solid foundation of research before officially applying to medical school.
Interview questions may need the most thought in terms of how you respond to them. Some of the most common and difficult graduate school interview questions are often the simplest in scope. Here are a few tips for how to structure and create a proper answer as to why you want to do a PhD:
1. Research, Research, Research
Research is not only what your PhD will lead to but also a crucial portion of preparing for it. Learn everything you can about the programs you are applying to, what academic opportunities they might lead to, and what careers they lend themselves to. It is also never too early to look into some thesis writing services for when you may eventually need them. Researching programs will give you a better grasp on why you are applying to a specific school when you are eventually asked the question. With less information about the school or its program, there is less of a chance you will be able to fully articulate why you should further your studies there.
2. Brainstorm Your Response
The first thing to do is to brainstorm all the reasons you want to complete a doctorate degree. Get a piece of paper or blank document and start to take note of everything that comes to mind. These can be specific reasons, potential research topics, programs you are interested in, the city you will move to, or anything else that could motivate you to complete your PhD. You could also use what you may have already written for a PhD motivation letter as a base for what you want to touch upon. Once complete, parse through what is most important for your response and discard the rest.
3. Have a Beginning, Middle, and End
In terms of structure, you will want to create a mini narrative that captures the interviewer’s interest. It should be detailed and unique to you without being overblown. Make sure that your answer flows, is concise, and does not go over two minutes, as you could risk losing the interviewer’s attention. You might want to mention your prior studies or academic research first, then what sparked your interest in doing a PhD, and then perhaps end with a little tidbit as to why you are attracted to that school’s program specifically.
4. Use Bullet Points
While you should always be thinking about how to structure your response to achieve the best result, it is important to avoid memorizing a script or simply listing the items on your CV for graduate school . This could wind up making you sound robotic and rehearsed, which may leave a lukewarm impression on an admissions officer or interviewer. It is a little tedious to consider, but you want the response to flow logically without seeming too prepared. Planning out your answer in bullet points will allow you to stick to what information you want to convey while still answering the question in a natural way.
Self-reflection is important when applying to any academic program. A question that requires you to dig deep, such as “Why do you want to do a PhD?” may cause anxiety. PhD interviews in particular can be intimidating if you are not ready or feel lost about where to start preparing. Thankfully, there are resources for you to receive aid should you need it. Reading tips for applying to graduate school will get you into the right mindset to begin preparing for your PhD. It could also inspire you to put more effort into perfecting your application.
Meanwhile, seeking graduate school application help from a professional is a sure-fire way to alleviate the stress associated with pursuing a doctoral degree. There is no shame in asking for a helping hand as you make important decisions about your academic future. You can only succeed if you give yourself the room to do so.
Interviewers tend to ask this question to get to know more about your personality and motivations when applying to their program. It is also a way to further explore what your interests are and how you express yourself when talking about them.
One of the most important things to remember when answering this question is to be genuine and focus on accurately articulating what your true motivations are. Surely, you applied to the PhD program for multiple reasons, so try and relay those to the interviewer as clearly as you can.
Yes and no. Your response to this question will be similar to what is already in your statement of purpose. Your statement is also an assessment of your writing skills, especially depending on the program you are applying to. Do not differentiate too much until it is a completely different answer. This could make your response come off as disingenuous.
The answer to this question should ideally be about a minute or 90 seconds long. A response under a minute is probably a little too short. Two minutes is the absolute maximum length. You could risk losing the attention of the interviewer if it surpasses that timeframe. Moreover, this will not be the only question you will have to answer, so show respect for the interviewer’s time by keeping your responses brief and to the point.
Be careful not to neglect your particular motivation for applying by going off topic. You also do not have to touch on every single accomplishment on your CV unless they are relevant. Mentioning your master’s degree or other larger accomplishments could be worthwhile, but be sure to think about the future and why specifically you want to complete a PhD.
PhD interview and postdoc interview questions can touch on many different topics. You will surely encounter both personal questions as well as field-related ones. These will make up a large chunk of what will be discussed during the interview.
You can, but unless they are well-versed in graduate school admissions, their feedback might not be as useful to you. To truly see an improvement in your interview skills, you should receive feedback that is tailored and personalized to you from someone who is aware of what graduate school interviewers are looking for, such as a grad school advisor .
Your best bet is a grad school advisor who is an admissions expert specifically trained to help students navigate the complex process of applying to graduate school programs. Advisors who are especially knowledgeable about doctorate programs can also be called PhD consultants . These individuals can help you with all aspects of graduate school applications, including interview preparation, editing application documents, and more.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
- EN Action Another action
- Free Counselling
Thanks for visiting TopUniversities.com today! So that we can show you the most relevant information, please select the option that most closely relates to you.
- Looking for undergraduate studies
- Looking for postgraduate studies
- Student but not looking for further education at the moment
- Parent or Guardian
- University administrator
- Professional
Thanks for sending your response.
Your input will help us improve your experience. You can close this popup to continue using the website or choose an option below to register in or login.
Already have an account? Sign in
Why a PhD is Worth it!
Staff Writer
Share this Page
Table of contents
- Introduction
Join the knowledge economy
Diverse range of research roles, transferable skills, gain some 'gravitas'.
Considering a PhD ? It could be the best decision you ever make, both in terms of your career and personal development . Here's why...
Okay, let's start with the arguments against. First: who wants a PhD degree when you can earn a six-figure salary with an MBA or a professional degree in much less time? Imagine watching your friends drive off to work in their expensive cars while you're still stuck in the library or lab.
Let’s accept it, doing a PhD can be intellectually challenging, physically tiring and emotionally draining. So, why should anyone do a PhD? And is it worth the effort?
To begin with, PhDs are an essential part of the knowledge economy. Completing a PhD is all about creating fresh knowledge, discovering new things and developing new skills.
It is a degree meant for those who seek greater depth of knowledge in a specific area. With a PhD, ‘one can make a difference’, says Professor Paul KH Tam, Pro Vice Chancellor and Vice President (Research), University of Hong Kong. “A PhD is about pursuing knowledge for the passion of acquiring knowledge. If one is fortunate, one’s discovery/invention may even change society,” he adds.
Although academia is considered to be the most obvious path for any PhD holder, the degree also paves way to a career in industries centered on research and innovation.
“In developing countries, where there is a gap in higher-education sector, but where government as well as society realize and pursue a policy to develop knowledge-based economy, there is an across the board need for increased PhDs both in academia and in industry,” says Prof Tam.
He adds that PhDs are required for the discovery of new drugs to satisfy the health needs of an ageing population, to continue making communication technology (iPhone, iPad) as one of the major driving forces of economic activities in modern society and to develop the understanding of humanities as society faces the challenges of coping with the side-effects of science and technology.
“Areas with high demand for very specialized and high level research skills demand PhDs. In the current economy, these areas may be biotechnology, information systems and medical and environmental engineering.
"That said, a PhD in liberal arts discipline is likely to be a passport to employment in any number of areas from media to political advising to independent research work,” says Dr Emmaline Bexley, Melbourne Graduate School of Education, University of Melbourne, Australia.
Sectors such as manufacturing, scientific research and development, health and social work and business activities all welcome PhD holders.
Besides this, a PhD degree helps you develop valuable transferrable skills, which are held dear by the employers. The very nature of the degree teaches candidates to be team players, problem solvers, have great presentation and communication skills apart from having an analytical mind and perseverance.
“Employers value the transferrable skills which PhD candidates bring to the table and they take on PhD holders from a variety of disciplines. The process of doing a PhD is often recognized as a training in creativity, critical inquiry, negotiation skills, professionalism and confidence,” says Dr Nathalie Mather-L’Huillier, Postgraduate Recruitment and Admissions Manager (Research), University of Edinburgh.
Dr Harry Kelly, Chemistry Operations Manager, GlaxoSmithKline, says that many view a PhD as an excellent means to acquire theoretical as well as practical skills. He says, “Together with high levels of innovation, creativity and ability to solve complex problems…PhD…enhances transferable skills such as communication skills and the ability to work in a team, both of which are critical to the achievement of our drug discovery programmes.”
Testimonials

"CUHK’s MBA programme provided me with the stepping stone into a larger sports Asian market wherein I could leverage the large alumni network to make the right connections for relevant discussions and learning."
Read my story
Abhinav Singh Bhal Chinese University of Hong Kong graduate

"I have so many wonderful memories of my MBA and I think, for me, the biggest thing that I've taken away was not what I learned in the classroom but the relationships, the friendships, the community that I'm now part of."
Alex Pitt QS scholarship recipient

"The best part of my degree is getting to know more about how important my job as an architect is: the hidden roles I play, that every beautiful feature has significance, and that even the smallest details are well thought out."
Rayyan Sultan Said Al-Harthy University of Nizwa student

"An MBA at EAHM is superior due to the nature of the Academy’s academic and industry strength. The subject matter, the curriculum structure and the access to opportunities within the hospitality industry is remarkable."
Sharihan Al Mashary Emirates Academy of Hospitality Management graduate
Doing a PhD is not as much about ‘patience or persistence’ as much it is about ‘quality and preparation’ according to Professor Richard Anthony Strugnell, Pro Vice Chancellor (Graduate Research), The University of Melbourne.
That is why those who earn the degree are held in high esteem. It wouldn't be wrong to say that a PhD degree gives gravitas to one’s social standing. “In society, a PhD in any field still stands for something,” says Professor Thomas Vogel, Pro Rector for Doctoral Studies, ETH Zurich.
However, it is also a degree to be pursued by only those who are truly driven to do something original, create a new knowledge base and be prepared to discover the unknown. “One of the hardest things to do in the world in educational terms is the PhD, but the rewards are amazing. The self-fulfilment and satisfaction you achieve from it pushes you to go through all the hard work and toil,” says Prof Andrew George, Head of Graduate School, Imperial College London.
But he also adds, “You should only do a PhD if you are really interested in it, not if you can’t think of doing anything better.” Point taken!
- More about the benefits of completing a PhD >
saved this article
Recommended articles Last year

The AI research combatting the online spread of false information
Advice for international students currently in Ukraine
QS World University Rankings by Subject 2021: Release summary page
Discover top-ranked universities.
universities
events every year
Sign up to continue reading
Ask me about universities, programs, or rankings!

Our chatbot is here to guide you.
QS SearchBot

- Common PhD Interview Questions
- Applying to a PhD
In this guide, we’ll share 11 common PhD interview questions and our suggestions on how to answer them.
A PhD interview is an essential step in securing a doctorate position. This is because it enables the prospective supervisor to get to know you better and determine whether you’d be a good fit for the project. Equally, it provides you with the opportunity to learn more about the project and what the university offers. Although being asked to attend an interview by the admissions committee can be daunting, it’s actually a positive sign. It means that based on your application and academic qualification, the academic department believes you have the potential to make a good PhD student for the position.
Whilst most questions you’ll be asked during your PhD interview will focus on your proposed research project, a handful of generic questions will almost certainly be asked. To give yourself the best chance of succeeding in the interview, we highly recommend that you prepare answers to these generic questions beforehand.
Without further delay, here are 11 common PhD interview questions and tips on how you should answer them.
1. Tell Us About Yourself
It comes at no surprise that this common ice-breaker question is at the top of our list. This question will likely be asked to help you calm your initial nerves and settle into your interview. As this is a warm-up question, aim to give the interviewer a general overview about yourself as opposed to a detailed breakdown. To achieve this, structure your answer into three sections:

- Academic History : start with a summary of your academic background – where and what have you studied? What grades did you achieve?
- Research Topic : go onto explain your research interest in your chosen topic – what do you like about it? Do you intend to pursue a career related to it upon obtaining your degree?
- Why a PhD : Finish with why you want to undertake a PhD – do you want to make a contribution to science? Do you want to get a job in academia?
2. Why Do You Want to Do A PhD?
Although you may have touched on this in your answer to the above, your interviews will want to know more of the detail if they ask this question as a direct followup.
Though it may appear obvious, the interviewer is specifically interested in discovering your personal motivations for undertaking a PhD . Too often, students answer this question by listing the benefits of a PhD. Not only will the interviewer already know the benefits of a PhD, but a generic answer also won’t help you stand out among the other applicants.
To answer this question and leave a lasting impact, try to include an academic or personal experience that has strengthened your passion for research. As well as this, outline what your career aspirations are and explain how the proposed PhD will help you achieve them. The key to selling yourself here is to let the interviewer know how passionate you are about the project without having to say it.
3. Why Did You Choose This Project?
This is your chance to show that you have researched the University, supervisor and project.
First, talk about the project. Is there a particular aspect that you’re interested in? If so, mention it. This will show that you’re engaged in the topic and already have a basic understanding of the field. Besides this, a great way to show that you’ve really looked into the research topic would be to discuss a certain part of the methodology the project could adopt.
Next, talk about the University – there may be several universities offering similar projects, but what makes this one stand out? Is it their resources? Is it the prospective supervisor’s research group? Is it their previous involvement in previous influential studies? Again, show that you’ve adequately researched the University and clearly understand what makes it unique.
Finally, you can mention if your decision to apply to their university has been influenced by the expertise of the proposed supervisor. Given that the supervisor will be highly knowledgeable in the research topic you’re applying to, it’s possible they may have contributed to some significant findings in it. If so, it’s acceptable to acknowledge this by mentioning how you would like the opportunity to work under their guidance. However, be careful not to overdo. Although you may be sincere in your answer, it can go against you if your supervisor feels like you’re trying to flatter him. To avoid giving this impression, focus on how his or her expertise will help you develop into a competent researcher.
4. Why Should We Choose You?
A very blunt question, but your PhD supervisor will want to make sure you’re the best candidate for the position. This is especially true given they’ll be responsible for supporting you over the next few years. Therefore, the primary aim of your answer will be to reassure them you have the skills and experience required to undertake a doctoral study. To achieve this, identify the critical knowledge and skills required for the project and discuss how you meet each of these. Follow up each justification with a short, relevant example to help give your answers more impact.
When asked this question, some students tend to just summarise their academic CV and cover letter . This isn’t an effective way to answer the question as you’re telling the supervisor information they already know about you. It’s fine to reiterate a few key points, however, try to delve deeper into what you can offer going forward as opposed to what you’ve achieved in the past. As part of your answer, identify the soft skills which will be imperative to the doctorate and state how you have each of these. These can include skills such as effective communication, great time management, problem-solving, adaptability and high work ethic.
5. How Did You Come up With This Project?
If you’ve developed your own research proposal , then expect to have to defend it as part of your interview. You should have a thorough understanding of what the current gaps in knowledge are surrounding your research topic and how these could limit the findings of your study. Besides this, you’ll want to show that you’re clear on what the key aims and objectives of your project are and appreciate how they could contribute to your field of research. This last point is essential in convincing the interviewers this project is a worthy pursuit. What makes your project groundbreaking and worth dedicating several years to?
The interviewer wants to know if you have thought out all aspects of your project and so will likely scrutinise the finer details of your proposal. Therefore, be ready to outline the literature you’ve read and discuss how you evaluated different methodologies before suggesting your current one.
If you want an edge over other students, you can also produce a high-level plan, similar to the one below (but with more detail), which outlines the different phases of your research project. This can include stages such as the literature review, undertaking experiments, producing your thesis and preparing for your viva voce. Although they won’t expect your plan to be fully accurate, especially given how dynamic research projects can be, it will show your positive attitude towards being imitative and taking responsibility for your project.
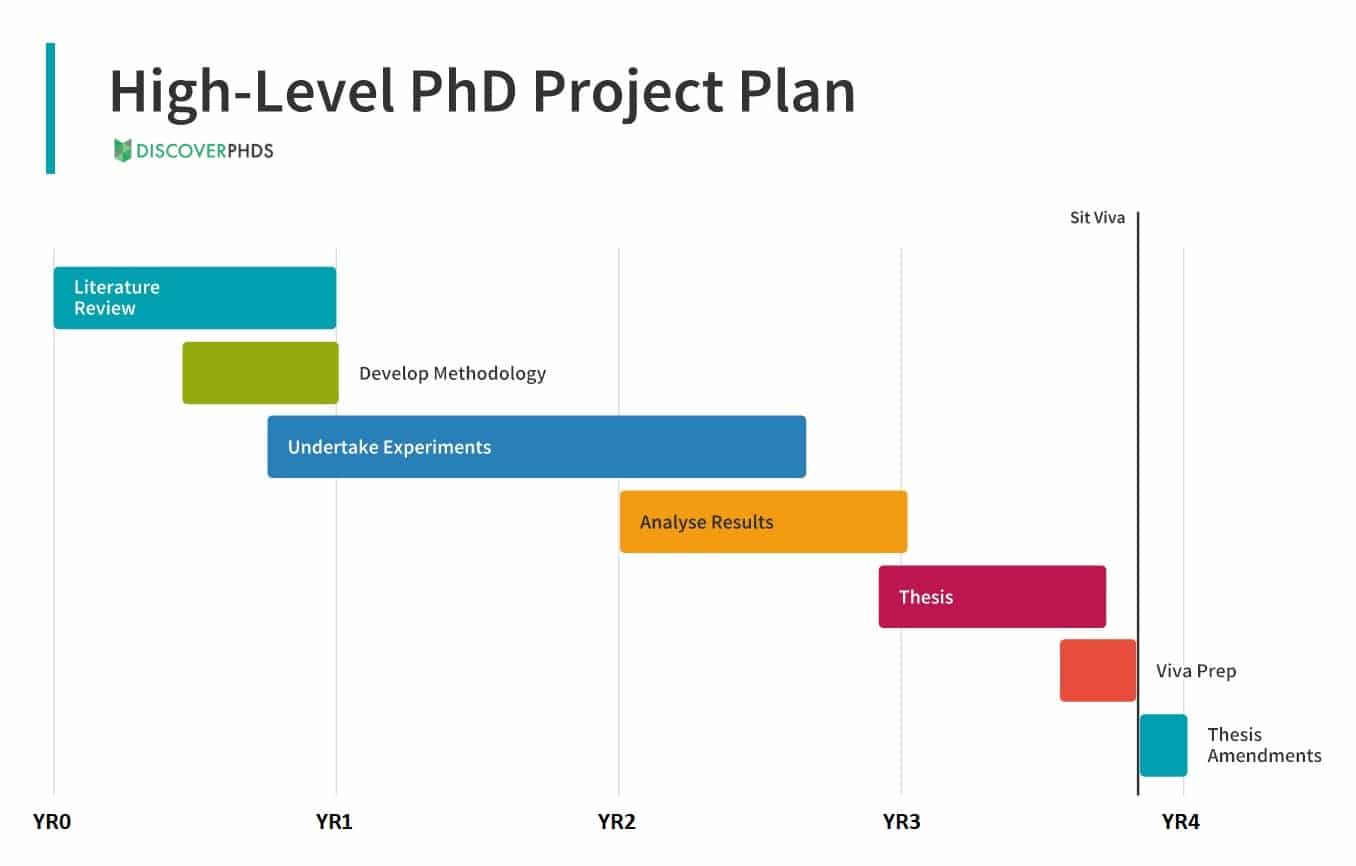
6. What Challenges Are You Expecting to Encounter in This Project?
A common PhD interview question students struggle with is “What difficulties do you think you will face?” This purpose of this question is to check how much you’ve thought about the project. Students who provide a poor answer generally do so as they think admitting to any potential difficulties may make them seem incompetent. This couldn’t be any further from the truth.
Identifying potential difficulties shows the interviewers you’ve given serious thought to the project. This reassures the supervisor that should you run into difficulties during the research, you’re not only capable of identifying them but also mature enough to do so. Not highlighting potential difficulties, whether it’s due to a lack of confidence or understanding the project, suggests your project will be vulnerable to problems which could go amiss.
When answering this question, try to follow up on each potential difficulty with how you intend to address it. This can include measures such as making use of internal development opportunities, enrolling onto external training courses or signing up to specific research master classes.
7. What Are Your Strengths and Weaknesses?
This is a standard question for most interviews, and a PhD interview is no different.
Pick strengths that compliment your PhD programme. For example, if applying to a Physics or Engineering PhD, mentioning you have good attention to detail would be highly beneficial given the amount of data analysis involved. Try to support each of your claims with a relevant example. Using the above case as an example, you could discuss how as part of your Bachelor’s or Master’s dissertation project, your high attention to detail allowed you to streamline some of your experiments or identify potential problems with your data.
Likewise, try to discuss a weakness that won’t be detrimental to your research project. An example of something you would want to avoid would be “I have a tendency to put the hard tasks off until the end until I know I should really start working on them to not miss any deadlines“. Although this may seem like a harmless response, it will seriously concern the interview panel. This is because a model student will need to be consistent in their efforts to meet the challenging workload, even in times of difficulty. As before, follow up your weakness with a plan on how you intend to address it. For example, if you state your weakness as public speaking, a suitable follow up would be to discuss how you would like to work on it by presenting your research to undergraduate students and attending seminars.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
8. Can You Describe a Time You Encountered a Problem or Challenge and How You Approached It?
A key trait of all successful researchers is the ability to overcome problems independently. Given that even a minor problem can derail a research project, it’s important for your project supervisor to know whether you can adequately address them.
Despite what your example may me, try to cover the below three aspects as part of your answer:
- Identification – How did you identify the problem? Was a check you had in place triggered or did you stumble upon it naturally?
- Deconstruction – How did you break the problem down? Did you identify any assumptions or limitations which could have been associated with it? If so, how?
- Overcoming – How did you identify the solution? If you had several solutions, how did you determine the most sensible one? What did you learn from it?
Your example doesn’t need to relate directly to the research programme you’re applying to, however, it should be kept academic if possible. For example, you could discuss a challenge you encountered during your undergraduate dissertation project, such as limited literature on your research topic or inaccurate experiment results.
The key point to remember here is that a supervisor is there to supervise, not to fix all your problems. Not only will they not have the time do to this, but it will directly go against the ethical requirement of ensuring your work is yours and yours alone.
9. What Are Your Career Aspirations?

Your interviewers will want to see that you’ve considered what you will do after completing your PhD. This is to help them determine what your motivations are and to confirm that you want to enrol onto a PhD for the right reasons. It’s clear that anyone who has thought through their decision will have a long-term plan in mind, even if it’s a handful of well-considered options.
Don’t feel like your answer needs to relate to academia. One of the many benefits of a PhD degree is that it can lead to a variety of career paths. By being open with your true intentions, they can better determine what support and training you’ll require from them.
Despite your long-term goals, research into this and know the route you’d like to take post-PhD. A good understanding of your career plans and how to get there will go a long way in conveying your commitment to the project.
10. How Will You Fund This Project?
The interviewing panel will ask about this if your project is self-funded or conditionally funded (e.g. competitive funding schemes where funding is not guaranteed).
You don’t need to provide a complete breakdown of your savings, nor would they expect you to. The primary concern the interviewers want to address is that you’re fully aware of the costs associated with undertaking a PhD . If you intend to apply for external funding or take on a part-time job, mention this. In doing so, make sure you stress that you will base your part-time work around your PhD and not the other way around. The interviewers want to reassure themselves that you will make your research your top priority throughout the course of your degree.
11. Do You Have Any Questions for Us?
This interview is not only for the supervisors to evaluate you but also for you to evaluate them, the PhD project and University.
Although you will have already researched the position at length, ensure you ask questions when offered to do so. Asking questions will show that you’re engaged and are an individual who likes to make informed decisions. Not asking questions, or not asking well thought-out ones, will send the wrong message.
If you’re wondering what makes a great question, a quick internet search for “What questions should I ask at a PhD Interview?” show’s you’re not alone. Some examples of great questions to ask in a PhD interview are:
- Are there any major developments or partnerships planned for the department? – Although this won’t always be the case, the department may be planning to upgrade its research facilities or partner with another leading institution. Asking about this shows you’re genuinely enthusiastic about undertaking influential research.
- What are the supervision arrangements? – This is a great way to find out if your expectations match that of your potential supervisors. This can include aspects such as how often the two of you will meet and what level of support they intend to provide.
- Will there be any opportunities for teaching within the department? – If you intend to pursue an academic career after completing your research, this will be a brilliant way to show them you’re committed to your long-term plans. Even if you plan on following a different career path, asking will let you know whether there is any opportunity to earn whilst you study.
- What opportunities will I have for presenting my research? – This shows you intend to be an active member within your research field. This won’t be great only for your development but will help the university increase its research network and reputation in the wider community.
Other PhD Interview Tips and Advice to Help You Prepare
- Format – The format of the PhD interview varies depending on the University. If you’re unsure of what format your upcoming interview will follow, get in touch with the department you will interview with. They should be able to give you an idea about what to expect and how long it will typically last. This knowledge will prove invaluable when preparing for a PhD interview.
- Video interview – Some interviews will be conducted as either a phone interview or a skype interview. This is especially true if you’re an international student still within your home country. If so, conduct your interview in a place with a reliable internet connection and a clean backdrop.
- Attendance – Usually, your interview will comprise the primary and secondary supervisor. However, sometimes your interview panel can comprise non-technical staff or the Head of Department.
- Presentation – You may be asked to prepare a PhD interview presentation if you’re proposing your own research topic . If you’re requested to do this, keep it brief, use at least 80% of the time they permit and base it around your research proposal.
- Paperwork – Bring two to three copies of your application form, and if applicable, your research proposal. Although in most cases your interviewers would have bought their own copy, it’s better to be on the safe side.
- Etiquette – If you’re unsure of what to wear to a PhD interview, a good general rule of thumb is to wear what you would to a formal job interview. In other words, keep it formal. Additionally, learn how to pronounce the names of the interviewers and any other staff members you may mention beforehand.
- Practice – There’s a lot of truth in the old saying ‘practice makes perfect’. You will want to practise as many PhD interview questions as you can. Don’t just limit yourself to the ones discussed on here. Find as many PhD questions as you can and prepare draft answers for all of them. In fact, you don’t even need to limit yourself to questions specifically for PhD students. There are many out there that, although written for generic academic interviews or the job market, will be applicable to you. If you find yourself short on resources, try searching for ‘tell us a time when you…’ in google as these will provide great scenario-based questions you can practise with.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Our Culture
- Open and FAIR Data
- Research projects
- Publications
- Cellular Genomics
- Decoding Biodiversity
- Delivering Sustainable Wheat
- Earlham Biofoundry
- Transformative Genomics
- Scientific Groups Our groups work at the forefront of life science, technology development, and innovation.
- High-Performance Sequencing Dedicated and efficient high-throughput genomics led by experts in sequencing and bioinformatics.
- Single-cell and Spatial Analysis Platforms to support single- or multi-cell analysis, from cell isolation, to library preparation, sequencing and analysis.
- Earlham Biofoundry Providing expertise in synthetic biology approaches and access to laboratory automation
- Tools and resources Explore our software and datasets which enable the bioscience community to do better science.
- Cloud Computing Infrastructure for Data-intensive Bioscience
- Web Hosting for Sites, Tools and Web Services
- Earlham Enterprises Ltd
- Events Calendar Browse through our upcoming and past events.
- About our training High-quality, specialist training and development for the research community.
- Year in industry Supporting undergraduate students to develop skills and experience for future career development.
- Internships and opportunities Opportunities for the next generation of scientists to develop their skills and knowledge in the life sciences.
- Immersive visitors A bespoke, structured training programme, engaging with the faculty, expertise and facilities at the Earlham Institute.
- News Catch up on our latest news and browse the press archive.
- Articles Explore our science and impact around the world through engaging stories.
- Impact Stories Find out how we are contributing to the major challenges of our time.
- Impact Through Policy Advocacy Engaging across the political spectrum to exchange knowledge and inform public policy.
- Public engagement and outreach Communicating our research to inspire and engage learning.
- Communications at EI We work across digital, multimedia, creative design and public relations to communicate our research.
- Our Vision and Mission
- Inclusivity, diversity, equality and accessibility
- Scientific Advisory Board
- Our Management Team
- Operations Division
- Careers overview
- Postgraduate Studies
- Group leaders
- Fellowships
- Life at Earlham Institute
- Living in Norfolk

10 things you need to know before starting a PhD degree
So you want to do a PhD degree, huh? Here we've got everything you need to know about getting started.
So you want to do a PhD degree, huh? Are you sure about that? It’s not going to be an easy decision, so I’ve put together a list of 10 things you need to know before starting a PhD degree. Oh, and don’t panic!
I have recently graduated from the University of Manchester with a PhD in Plant Sciences after four difficult, but enjoyable, years. During those four years, I often felt slightly lost – and there was more than one occasion on which I didn’t even want to imagine writing up my thesis in fear of delving into fits of panic.
On reflection, I realise that – to quote a colleague – commencing my PhD was like “jumping in the deep end with your eyes closed.” If only I’d known to take a deep breath.
1. Are you sure you want to do a PhD degree?
Let’s be under no false impressions, completing a PhD isn’t easy. There will be times when you feel like Wile E Coyote chasing after the Roadrunner – a little bit out of your depth a lot of the time. It’s four years of your life, so make sure it is what you really want to do.
If you want to pursue a career in science, a PhD isn’t always necessary.
It is possible to make great inroads into industry without a doctoral degree. That said, a PhD can also be a very useful qualification with many transferable skills to add to your CV.
By the time you’ll have finished, you can include essentials such as time management, organisational skills, prioritising workloads, attention to detail, writing skills, presenting to an audience – and most importantly – resilience, to name but a few.
2. Choose your project, and supervisor, wisely.
This is very important.
Time after time, our experienced scientists at EI, including Erik Van-Den-Bergh (and I agree) say, “ make sure you’re extremely passionate about exactly that subject. ” When I saw the PhD opening that I eventually was offered, I remember being demonstrably ecstatic about the project before I’d even started it.
I was always interested in calcium signalling and organised a meeting with my potential supervisor immediately, which (to quote Billy Connolly) I leapt into in a mood of gay abandon.
Not only does this help you to keep engaged with your project even through the painstakingly slow times, it also greatly enhances your ability to sell yourself in an interview. If you can show passion and enthusiasm about the project and the science then you’ll be that one step ahead of other candidates – which is all the more important now that many studentships are competitive.
You have to be the best out of many, often exceptional candidates.
However, as important as it is to be passionate about your project, make sure that the person who will be supervising you is worthy.
Does your potential supervisor have a prolific track record of publishing work? What is the community of scientists like in the lab you may be working in? Are there experienced post-doctoral scientists working in the lab? Who will your advisor be? Is your supervisor an expert in the field you are interested in? Is the work you will be doing ground-breaking and novel, or is it quite niche?
There is nothing more frustrating – and I know many PhD degree students with this problem – than having a supervisor who is rarely there to talk to, shows little interest in your work, and cannot help when you are struggling in the third year of your project and some guidance would be much appreciated.
Personally, and I was very lucky to have this, I think it’s incredibly useful to have two supervisors. My PhD degree was split between the University of Manchester and the Marine Biological Association in Plymouth. Between my supervisors, I had two people with expertise in different fields, who could give me some fantastic advice from different perspectives. This also meant that I had two people to check through my thesis chapters and provide useful comments on my drafts.

Make sure you are passionate about your subject before taking it to PhD level. And by passionate I mean really passionate.
For a start, you will most likely have to write a literature review in your first three months, which if done well will form the main bulk of your thesis introduction and will save you a lot of stress and strain when it comes to writing up.
At the end of your first year, you will have to write a continuation report, which is your proof that you deserve to carry on to the end of your three or four years. This doesn’t leave much time for lab work, which means time management is incredibly important. If you think you’ll be able to swan in at 11 and leave at 3, think again.
Fundamentally, never, ever rest on your laurels! As tempting as it may be to slack-off slightly in the second year of your four year PhD, don’t.
4. Be organised.
This is a no-brainer but still, it’s worth a mention. Take an hour on a Monday morning to come up with a list of short-term and long-term goals. You’ll probably have to present your work at regular lab meetings, so it’s always worth knowing what has to be done (lest you look a pillock in front of the lab when there’s nothing to show for your last two weeks.)
It’s always good to have a timeline of what will be done when. If you have a PCR, maybe you can squeeze in another experiment, read a few papers, start writing the introduction to your thesis, or even start collecting the data you already have into figures.
The more good use you make of your time, the easier it’ll be to finish your PhD in the long run. Plus, it’s lovely to sit back and look at actual graphs, rather than worry about having enough to put into a paper. Once you’ve typed up your data, you’ll realise you’ve done far more than you had anticipated and the next step forward will be entirely more apparent.
5. Embrace change – don’t get bogged down in the details.
Felix Shaw – one of our bioinformatics researchers at EI – put it best when he said, “ it felt like I was running into brick walls all the way through [my PhD]… you’d run into a brick wall, surmount it, only to run straight into another. ”
You’ll find that, often, experiments don’t work. What might seem like a great idea could turn out to be as bad as choosing to bat first on a fresh wicket on the first day of the third Ashes test at Edgbaston. (Yeah, we don't know what that means either - Ed).
Resilience is key while completing your PhD. Be open to change and embrace the chance to experiment in different ways. You might even end up with a thesis chapter including all of your failures, which at the very least is something interesting to discuss during your viva voce .
6. Learn how to build, and use, your network.
As a PhD student, you are a complete novice in the world of science and most things in the lab will be – if not new to you – not exquisitely familiar. This matters not, if you take advantage of the people around you.
Firstly, there are lab technicians and research assistants, who have probably been using the technique you are learning for years and years. They are incredibly experienced at a number of techniques and are often very happy to help show you how things are done.
There are postdocs and other PhD students, too. Not only can they help you with day-to-day experiments, they can offer a unique perspective on how something is done and will probably have a handy back-catalogue of fancy new techniques to try.
There are also a bunch of PIs, not limited to your own, who are great to talk to. These people run labs of their own, have different ideas, and might even give you a job once you’ve completed your PhD.
Don’t limit yourself to the labs directly around you, however. There are a massive number of science conferences going on all around the world. Some of them, such as the Society of Biology Conference, take place every year at a similar time in different locations, attracting many of the leaders in their respective fields.
If you are terrified by the prospect of speaking at a full-blown science conference and having your work questioned by genuine skeptics, there are also many student-led conferences which will help you dangle your fresh toes in the murky waters of presenting your work.
One such conference, the Second Student Bioinformatics Symposium, which took place at Earlham Institute in October 2016, was a great place for candidates to share their projects with peers, who are often much more friendly than veteran researchers with 30 year careers to their name when it comes to the questions at the end of your talk.
Another great reason to attend conferences, of course, is the social-side too – make the most of this. You never know who you might meet and connect with over a few drinks once the talks are over and the party commences.
7. Keep your options open.
You should be aware that for every 200 PhD students, only 7 will get a permanent academic post , so it’s incredibly unlikely that you’ll become a Professor – and even if you make PI, it probably won’t be until your mid-forties.
You may also, despite having commenced along the academic path, decide that actually, working in a lab environment isn’t for you. Most PhD graduates, eventually, will not pursue an academic career, but move on to a wide range of other vocations.
It might be that Science Communication is more up your street. This was certainly the case for me – and I made sure that I took part in as many public engagement events as possible while completing my PhD. Most Universities have an active public engagement profile, while organisations such as STEM can provide you with ample opportunities to interact with schools and the general public.
You might also consider entrepreneurship as a route away from academia, which might still allow you to use your expert scientific knowledge. There are a variety of competitions and workshops available to those with a business mind, a strong example being Biotechnology YES.
I, for example, took part in the Thought for Food Challenge, through which I have been able to attend events around the world and meet a vast array of like-minded individuals. Many of the participants from the challenge have gone on to set up successful businesses and have even found jobs as a result of the competition.

8. Balance.
Remember that you still have a life outside of your PhD degree – and that this can be one of the greatest opportunities to make amazing friends from around the world.
A science institute is usually home to the brightest students from a variety of countries and can provide a chance to experience a delightful range of different people and cultures. Don’t just stick to the people in your lab, go to events for postgraduate students and meet people from all over campus.
There are usually academic happy hours happening on Fridays after work where you can buy cheap beer, or some lucky institutions even have their own bar. At Norwich Research Park, we not only have the Rec Centre, along with bar, swimming pool, calcetto, samba classes, archery, and a range of other activities, but there are also biweekly “Postdoc pub clubs” which are very fun to join on a Tuesday evening.
Maintain your hobbies and keep up with friends outside of your PhD and you’ll probably find it’s not that gruelling a process after all.
Plus, the people you meet and become friends with might be able to help you out – or at least be able to offer a sympathetic shoulder.

9. Practical advice.
If, after reading all of this, you’re still going to march forth and claim your doctorhood, then this section should be rather useful.
Firstly, make sure your data is backed up. It’s amazing how many people don’t do this and you’d be bonkers not to. Keep your work saved on a shared drive, so that if your computer decides to spontaneously combust upon pressing the return key, you won’t have lost all of your precious work – or have to go through every one of your lab books and type it all up again.
Secondly, don’t leave your bag in the pub with your half-written thesis in it. I did this, the bag was fine, I was in a state of terror for at least half an hour before the kind person at Weatherspoons located said bag.
Thirdly, read. Read broadly, read anything and everything that’s closely related to your project – or completely unrelated. It’s sometimes amazing where you might find a stroke of inspiration, a new technique you hadn’t thought of … or even in idea of where you might like to go next.
Finally, ask questions – all of the time. No matter how stupid it might sound in your head, everyone’s probably been asked it before, and if you don’t ask, you don’t get.
You’ll probably look far less stupid if you just ask the person standing next to you how the gradient PCR function works on your thermal cycler rather than standing there randomly prodding buttons and looking flustered, anyway.
10. Savour the positives.
At the end of all of this, it has to be said that doing a PhD is absolutely brilliant. There’s no other time in your life that you’ll be this free to pursue your very own project and work almost completely independently. By the time you come to the end of your PhD, you will be the leading expert in the world on something. A real expert! Until the next PhD student comes along …
Related reading.

A PhD, is it worth it? Just ask our students

The realities of doing a PhD

My advice for PhD students? See what bites

COVID and my PhD: to lockdown and back

How does a PhD work and how to find the right one

Building the confidence to take on a PhD
PhD life, 10 things we learned in our first six months

What’s the third year of a PhD like? Tips for navigating your PhD

PhD by experience
- Scientific Groups
- High-Performance Sequencing
- Single-cell and Spatial Analysis
- Tools and resources
- Events Calendar
- About our training
- Year in industry
- Internships and opportunities
- Immersive visitors
- Impact Stories
- Impact Through Policy Advocacy
- Public engagement and outreach
- Communications at EI
What is a PhD?
There’s a lot of mystery surrounding the PhD. Although most people have a vague understanding of what it is, there are a lot of misconceptions about what doing one actually entails. How long does a PhD actually take? Do you have to be a super genius to do one? This article will clear up the confusion and answer some common questions.
First of all, what does PhD stand for?
PhD is an abbreviation of Philosophiae doctor which is Latin for “doctor of philosophy”. All PhD are “doctors of philosophy” regardless of whether the degree is in physics, biology, anthropology or actual philosophy.
So, what is a PhD?
In the simplest terms, it’s the highest academic degree. It is earned by spending three or more years doing original, independent research to produce a thesis which is orally defended.
What does a PhD entail?
A PhD is first and foremost a research degree so the majority of your time will be spent researching. What exactly this looks like depends on the field you’re studying. You may be in a library, or running experiments in a lab, or in the field. Regardless of where you research, you will be regularly meeting with your supervisor to check your progress. Your supervisor will also give you feedback and help you work through any problems you may encounter. They will also provide encouragement and support as you progress through your PhD.
As a doctoral student, you may also have to complete a certain level of graduate-level courses or take exams to demonstrate your knowledge of certain subjects in your field. You will also be expected to participate in other vital aspects of academic life such as teaching, attending and presenting at conferences, grant writing, and publishing in academic journals.
The final step is the PhD defence. The after submitting your written thesis to your committee, they will set a date for your defence. The defence is an oral exam where you show your mastery of the subject area by explaining, discussing, and defending your thesis to a committee of internal and external examiners. The examiners also ask the candidate questions about their dissertation and the field more generally. If the defence is successful, the candidate is awarded their degree and the title of “Doctor”.
How long does it take to earn a PhD?
It can take anywhere from three to six years depending on the country you study in. European PhDs tend to be shorter as candidates begin working on their research projects right away, while American PhDs are longer and require couple years of coursework and exams before the candidate begins their research.
What qualifications do you need to do a PhD?
Drive, determination, and curiosity first of all! On a more practical side, excellent grades, strong letters of recommendation, and the appropriate qualifications. In most parts of Europe, a Master’s degree is a must for PhD applicants, while many American programs allow students to apply for a PhD straight from their undergraduate degree. You can read more about the requirements and PhD application process here .
How much will it cost?
It’s difficult to say how much a PhD will cost as it is so dependant on where you are from, where you study, and what you study. Some PhD are fully funded, such as those at the top American schools, while others are funded through university scholarships or national grants. In some parts of Europe, PhD students are paid nationally-legislated salaries. Occasionally PhD candidates do have to take out personal loans to fund their studies. You can find out more about what funding is available for PhD students from the posting itself, the departmental website, or the university’s graduate school website.
What can I do with a PhD?
A PhD is an essential qualification for a career in academia or research. It is the first step to becoming a lecturer or professor or a scientist at a university or research institute. However, not all PhDs choose to continue on in academia. The advanced research skills you learn during a PhD are advantageous in a variety of diverse fields such as pharmaceuticals, finance, law, journalism, and tech.
Discover related jobs
Discover similar employers
Accelerate your academic career
How to Be a Career-Minded PhD Student
At the start of your PhD the job market might be the furthest thing from...
Practical Advice for Moving to Germany to Study or Research
Everything you need to know about moving to Germany to research or study...
Major PhD Fellowships
Looking for a way to fund your PhD? Here are several full and partial sc...
What Should I Call My Professor?
Should you refer to them as “Professor”, “Doctor” or something else? The...
Preparing for Your PhD Defence
Here are some tips to help you beat the nerves and rock your defence.
Top 10 PhD Interview Questions
While you cannot predict the exact questions you will be asked, certain ...
Jobs by field
- Programming Languages 180
- Machine Learning 172
- Electrical Engineering 172
- Artificial Intelligence 159
- Molecular Biology 141
- Electronics 130
- Cell Biology 130
- Materials Engineering 122
- Computational Sciences 113
- Genetics 101
Jobs by type
- Postdoc 319
- Assistant / Associate Professor 175
- Professor 118
- Researcher 114
- Lecturer / Senior Lecturer 76
- Tenure Track 65
- Engineer 61
- Management / Leadership 51
- Research assistant 41
Jobs by country
- Belgium 228
- The Netherlands 161
- Germany 117
- Morocco 106
- Finland 103
- Switzerland 98
- Luxembourg 74
Jobs by employer
- Mohammed VI Polytechnic Unive... 106
- KU Leuven 85
- University of Luxembourg 72
- Eindhoven University of Techn... 62
- Ghent University 43
- ETH Zürich 43
- Silicon Austria Labs (SAL) 35
- KTH Royal Institute of Techno... 35
- University of Twente 28
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Can PhDs legitimately claim to be doctors?
I’ve frequently heard people claim that individuals who hold PhDs are not “real” doctors. These people assert that only physicians can rightfully claim this title, and that it’s inappropriate for PhD-holders to use this term. For some reason, many also think that the MD is much more difficult to attain than a PhD for example in computer science.
So - should Ph.D.s Be Referred To As ‘Doctor?
Ps: currently i am a PhD student and don't know why the question is being devoted!
- 25 The answer is "Yes". – Michael Commented Mar 27, 2017 at 15:07
- 1 Yes they can legitimately claim that, just not that they are medical doctors (or doctors in any other field they are no doctor in). – skymningen Commented Mar 27, 2017 at 15:07
- 2 The people I know who say this (of themselves) are usually being somewhat sarcastic and say this as a form of irony . – Dave L Renfro Commented Mar 27, 2017 at 16:30
- 2 This is possibly country dependent, but for Germany this is utterly wrong: "many also think that the MD is much more difficult to attain than a PhD" - Medical doctors get the equivalent of a "paper doctorate" thrown after them so they can be called "doctor" as part of their degree, while "real doctors" have to start a doctorate and carry out rigorous research to obtain the degree/academic title. Now other countries may handle this very differently and there this statement may or may not be true. – DetlevCM Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 6:45
- 3 One of my former colleagues long ago told me: "The only time I call myself Dr Friedman is when I make a reservation at a restaurant." – GEdgar Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 14:28
7 Answers 7
In the modern USA the title of doctor is valid for both medical doctors and holders of PhDs in the US, but particular customs may vary by institution. The general rule of thumb for etiquette is to refer to someone however they wish to be referred to. If you have a PhD that insists they be referred to as doctor it would be very impolite to not do so. Likewise if you have an MD who insists that you do not use their title it would be similarly impolite.
In situations where it is important to avoid confusion it is common to spell it out explicitly. Rather than using the honorific use the explicit degree, for example it is very common for email signatures to look like:
John Doe, Ph.D. in Computer Science
Dr. John Doe
Similarly, an MD would tend to say:
Jane Doe, MD, Cardiologist
Jane Doe, MD, Ph.D., Cardiology
I suspect that your question has another component, which is essentially whether or not it is "fair" for a Ph.D. holder to refer to themselves as doctor. This requires an assumption that the MD is more challenging to attain than a Ph.D., and that calling oneself a doctor is somehow illegitimately taking the status of a medical doctor. Let me just say that the people who have earned these degrees are generally less concerned about this than those who have not, and that the title someone puts after their name doesn't tell you very much about their individual ability, dedication, or experience.
One of the original meanings for the word "doctor" is teacher or scholar. It literally is derived from the Latin verb docēre which means to teach. As such, a medical doctor is literally a teacher or scholar of medicine. A Computer Science doctor is a teacher or scholar of computer science. The title "Dr" is just a recognition of level of knowledge that a person has obtained in a giving field through recognized academic challenges.
In France the situation is somewhat complex. The overall answer is "yes". But hear me out.
Let me first spell out the theory. It is important to make the distinction between the diploma , the degree , and the title .
- At the end of a " doctorat " (PhD), you are awarded a PhD diploma , which confers you the university degree of doctor. For this you must write a research thesis . This is the fourth and highest university degree. (The other three degrees are, in order, baccalauréat = high school degree, licence = bachelor, and master , none of which grant a title).
- At the end of studies of medicine, you are awarded a State diploma of "doctor of medicine" (MD). However, this diploma does not confer the university degree of doctor. To obtain the diploma, you must write a "practice thesis" ( thèse d'exercice ), which is not at all like a PhD thesis (no requirement of originality, lasts a much smaller time – writing a bibliographical survey is sufficient to obtain it for example). This means that someone who "only" has a diploma of doctor must do an actual PhD in medicine before teaching in university, or doing medical research, and write an actual research thesis. (Hence some people are "double doctors", a title I just made up.)
On a PhD diploma it is explicitly written "The national diploma of doctor is awarded to XXX and confers the degree of doctor , to enjoy the associated rights and prerogatives". The part in italics is not written on diplomas for medical doctors.
Both diplomas give you the title of "doctor". By law, only these diplomas give you the right of using this title. So yes, certainly, a PhD holder has the right to be called " docteur ". MD too. But no one else.
In fact, there is a famous story here. Someone got a " chargé de recherche " ("scientist") position at CNRS. This is somewhat prestigious in French academia, and very competitive. It is essentially a rank of "research-only associate professor". Then he wrote an article in a magazine, signing his name "Docteur XXX". A regional journal called him out on him, saying he was not a real doctor, but only a "mere scientist" (an inane statement once you know that a PhD is required to get this "scientist" position * ). This eventually went to the approximate equivalent of the Supreme Court ( Cour de cassation ), and the regional journal was condemned for defamation of character in 2009. You can read more about it here (in French). In 2013, the law was changed to explicitly state that PhD holders have the right to call themselves and be called "doctor" in professional settings.
So unless you want to get sued and lose (and we don't do plea deals here), you better call PhD holders "doctor" if they ask for it in France.
Now there is the practice. As you know, in theory, practice and theory are the same, but in practice, they differ :)
In ordinary situations, only medical doctors are called "docteur" . It is extremely rare for PhD holders to actually use the title, and then, only in writing (usually in very formal documents). I cannot recall ever hearing someone call a PhD holder "docteur", while I have heard it numerous times for medical doctors. I have a PhD since a few months ago, and only foreigners have called me "doctor". On doors, on faculty directories, on websites... nobody ever write "Dr X". It just doesn't happen.
So it is extremely unlikely that someone would insist that you call them "docteur" if they are not a medical doctor. (In fact even for a medical doctor it would be in bad taste for them to ask... anyway.) But if they do ask, you should oblige.
* Honesty makes me want to amend this a little. The French name for the position, " chargé de recherches ", literally means "someone who has been tasked with research". It sounds a bit bad, because it makes it sound like the person in question is a mere subordinate who does as they are told and nothing else. As I said, it's actually a permanent, research-only position, and a very competitive one at that. It's the same kind of deal as "assistant professor", who are not the assistant of anyone nowadays but still have this somewhat bad-sounding title. (In the private sector, someone with the level of responsibility of an assistant professor would certainly have a grandiose title like "Team manager"... but I digress.)
- Very informative and quite different from the US. And congratulations on your new degree. Here you would likely be called "Doc" by your students. – Buffy Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 12:11
- @Buffy Thanks! (To be fair I've had it since November but I'm still happy about it :) ). The students just call me "Sir". On the other hand, the use of "professor" is much more relaxed, and I was sometimes called the "exercise session professor" when I was basically a TA, and should have been called " chargé de TD " = "someone tasked with exercise sessions"... Even though the actual title of "professor" is theoretically reserved for full professors. – user9646 Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 12:13
For Germany the situation should be as follows, IANAL.
If you have your PhD degree from any university as listed in the Carnegie list (find the list here: https://carnegieclassifications.iu.edu/ ), then generally you can use the Dr. prefix instead of the PhD abbreviation.
(See FAQ item #18 here: https://www.berlin.de/sen/wissenschaft/studium/abschluesse-und-titelfuehrung/haeufige-fragen/ )
This should generalize in my opinion to the whole country.
I would like to refer to a dictionary to answer https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/doctor
The word doctor (in English) can refer to
A physician; a member of the medical profession; one who is trained and licensed to heal the sick or injured. The final examination and qualification may award a doctor degree in which case the post-nominal letters are D.O., DPM, M.D., DMD, DDS, DPT, DC, Pharm.D., in the US or MBBS in the UK. quotations ▼ If you still feel unwell tomorrow, see your doctor. A person who has attained a doctorate, such as a Ph.D. or Th.D. or one of many other terminal degrees conferred by a college or university.
Outside of academic circles, the former is the commonly used definition, so without context, "doctor" will be understood as "physician". And thus a PhD who isn't a physician appears to be a "doctor (PhD) who isn't a doctor (physician)" and this contradiction is commonly refered to as "not a real doctor" or "not that kind of doctor".
So I would say referring to a PhD as doctor is technically correct (and might be unambiguous with some context as in "doctor in computer science") but without context you do risk being misunderstood.
For languages other than English I don't have a good overview, but the same overload of meanings occurs e.g. in German ("Herr Doktor" is probably a male physician) while in Italian it is common to refer to your self as "dottore" after the master already (and then afaik the upper case / lower case spelling disambiguates the master from the PhD).
I've encountered this argument before. Remember, It's not as if the term 'doctor' is protected. Two cases in point:
- A two year law degree is called a 'juris doctor'. Newly minted JDs will be quick to remind you that they, too, are doctors.
- In parts of the U.K., calling a surgeon a 'doctor' is an insult, as historically the surgeons were barbers (who'd 'doctor you up'), because barbers had the sharp tools necessary for surgery. Many U.K. Surgeons go by 'Mr.'
My advice - relying on titles is pointless. Use your intellectual prowess to impress.
If all else fails, insist you go by 'Professor'....or if in or from Germany, 'Professor Doktor'.
- 7 All PhDs are Doctors (specifically, of Philosophy). Not all PhDs are Professors. – Bryan Krause ♦ Commented Mar 28, 2017 at 22:26
- 4 Actually in some parts of the world the term doctor is protected. Germany is famous for it -- even people with PhDs from outside Germanu can't just call themselves Dr. Related to that a juris doctor is normally a post-graduate degree, but they don't call themselves doctors based on historical laws that once forbid lawyers from advertising (and so claiming to be a doctor was consider to promotional). Surgeons as I understand it normally complete medical school and become Dr , then when they complete there further training at a surgical college, they become Mister – Frames Catherine White Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 7:11
- @LyndonWhite Yes, but only in the UK. – Azor Ahai -him- Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 17:47
- @LyndonWhite if the university is on the Carnegie list, you can call yourself Dr. in Germany with a Ph. D. from a US university. – stephanmg Commented Feb 3, 2021 at 14:31
Only Ph.D holders must be referred to as doctors. Physicians have only bachelors degrees, although the medical degree was divided into two stages in the U.S universities, still, Physicians only have bachelors degree. Doctors are researchers who have finished their dissertations and became scholars in their fields. Physicians don’t write a dissertation and all what they do is to “treat” people from illness, not to “teach” students in universities. Note: The word “Doctor” is a latin word that means “I teach”, and it has nothing to do with treatment or medicine.
- 2 That is country specific - in the European programs I'm familiar with, the physicians' degree is at least Master equivalent (not bachelor) and it is hard to find physicians who don't stay a little longer to write a dissertation and earn the "Dr. med". – pseyfert Commented Aug 23, 2018 at 6:32
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged phd ..
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
Hot Network Questions
- Is the forced detention of adult students by private universities legal?
- A function to convert numbers from scientific notation to plain decimal
- crontab schedule on Alpine Linux runs on days it's not supposed to run on
- '05 Scion tC, bought used. 145k miles , unknown if spark plugs were ever changed. Should I change 'em?
- Movie from the fifties where aliens look human but wear sunglasses to hide that they have no irises (color) in their eyes - only whites!
- Smoking on a hotel room's balcony in Greece
- Can All Truths Be Scientifically Verified?
- What was the newest chess piece
- Seeking a Text-Based Version of Paul Dirac's 1926 Paper on Quantum Mechanics
- Sum of the individual kinetic energies of the particles which make the system the same as the K.E. of the center of mass? What's bad in my reasoning?
- How to narrow hotel map down to Old Town of Cologne, Germany
- Help with understanding a rigid geometry proof
- What was the document that Paul and Chloe signed with Sabrina?
- Could a Gamma Ray Burst knock a Space Mirror out of orbit?
- Would a scientific theory of everything be falsifiable?
- Are these colored sets closed under multiplication?
- How to react to a rejection based on a single one-line negative review?
- Grothendieck topoi as a constructive property
- Can I use a Forward Transformer in a Flyback Converter Circuit?
- Alice splits the bill not too generously with Bob
- Cutting a curve through a thick timber without waste
- Class and macro with same name from different libraries
- Can turbo trainers be easily damaged when instaling a cassette?
- What is an apologetic to confront Schellenberg's non-resistant divine hiddenness argument?
The best answers to “Why do you want to do a PhD?”

If you are interviewing for a PhD position, chances are high that you will be asked about your motivation to do a PhD. And sometimes, simple questions are the hardest to answer. Therefore, it is smart to prepare an excellent response to this question in advance.
Creating your unique answer to “Why do you want to do a PhD?”
While this diversity is a good thing, the lack of clarity on what a good answer to the question “Why do you want to do a PhD?” constitutes, makes it particularly daunting.
A convincing response during a PhD application interview increases your chance of securing the position: it clarifies your ambition and can leave a memorable impression.
Write down everything that comes to your mind. Your notes could include words like “ curiosity” , and short sentences such as “ to be able to become a professor in the future” but also honest reflections such as “ I want to be able to call myself Dr”.
The following categories are some of the best to frame your unique answer to the question:
Doing a PhD to satisfy your scientific curiosity
There are different ways to emphasise your scientific curiosity. For instance, you could explain how a specific topic caught your interest. For example by reading the work of a specific scholar, following a course, or listening to a talk.
Doing a PhD because of your societal or environmental ambitions
Many people connect their answers to “Why do you want to do a PhD?” to societal or environmental ambitions. And for a reason: These answers can be very powerful!
You can, for instance, tell a short personal story about why you find something important. Did you have a life-changing experience? Or do you maybe know someone who has been affected by a societal shortcoming?
Doing a PhD for self-development
On the contrary, openness and a drive to improve yourself and learn new skills are highly valued by PhD supervisors. Thus, self-development can be another good framework for your answer.
Doing a PhD to improve your (academic) career prospects
Ambitions to work within academia are more straightforward to explain. For example, in most cases, you simply need a PhD to secure a lecturer position or professorship.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, key quotes to motivate and drive academic success, how to select a journal for publication as a phd student, related articles, are summer schools for master’s students worth it, 100 things to do before university starts, writing a successful academic cv (and a free template), why do you deserve a scholarship 10 outstanding justifications.
Exploding pagers belonging to Hezbollah kill at least 8 and injure more than 2,700 in Lebanon
The militant group Hezbollah said Tuesday that pagers belonging to its members had blown up across Lebanon , killing at least eight people and injuring more than 2,700, according to the country’s Health Ministry.
Iran-backed Hezbollah pinned the blame for the widespread and seemingly simultaneous blasts on Israel, without providing evidence. Israel did not immediately respond to requests for comment on the accusations and the explosions.
More than 200 people were in critical condition, the public health minister, Dr. Firas Abiad, told reporters. According to The Associated Press and Al Jazeera , officials updated the death toll after Abiad's news conference.
During the emergency, Lebanese officials ordered the public to avoid using handheld communication devices.
Mojtaba Amani, Iran’s ambassador to Lebanon, was among the injured, according to the country’s embassy. In a post on X , it described his injuries as “superficial" and added that he was in a good condition.
Hezbollah said in its a statement that explosions killed "a girl and two brothers."
It added that the blasts came from pagers belonging to “employees in various Hezbollah units and institutions.”
One of those killed was Muhammad Mahdi, the son of Ali Ammar, a Hezbollah member of Parliament, according to the National News Agency, which is state-run.
Hezbollah says it has handed out pagers to members, many of whom stopped using cellphones out of fear that Israel could use them to track and monitor them.
“The ministry requests all citizens who own wireless communication devices to stay away from them until the truth of what is happening is revealed,” the Health Ministry said, according to NNA.
It was unclear whether the explosions were part of a coordinated attack, which would represent a significant security breach for Hezbollah.
Matt Miller, a State Department spokesperson, told reporters at a briefing that the U.S. hadn't been aware of the "incident" in advance and was "gathering information" about the detonations.
Lebanon's Red Cross said it deployed 130 ambulances to respond to explosion injuries, with 170 more vehicles on standby. The country's civil emergency authority urged people to donate blood at hospitals "as soon as possible," state news reported.
Reuters reported that dozens of Hezbollah members were seriously wounded in Lebanon’s south and in the southern suburbs of the capital, Beirut.
A Reuters journalist saw 10 Hezbollah members bleeding from wounds in the Beirut suburb of Dahiyeh, the agency said. It was unclear how many civilians were affected.
By late Tuesday afternoon local time, no one had taken responsibility for the explosions, some of which appeared to have been captured on closed-circuit TV video and shared on social media.

In a second statement, Hezbollah said it had reviewed “all the facts” and information and held Israel responsible for the explosions, which occurred a day after Israel announced a new war objective , fueling fears of a new military offensive in Lebanon.
Lebanon’s foreign ministry condemned what it called an “Israeli cyber attack,” adding that it would submit a complaint about the detonations to the U.N. Security Council.
“This dangerous and deliberate Israeli escalation is accompanied by Israeli threats to expand the scope of the war towards Lebanon on a large scale, and the intransigence of Israeli positions calling for more bloodshed, destruction and devastation,” it said in a statement.
Former CIA Director John Brennan told NBC News that he believes the pagers had some kind of explosive in the hardware based in part on the scale and simultaneous nature of the attack. He speculated that the pagers were at some point intercepted and switched "for the ones that Hezbollah thought were going to be benign."
"All suspicion has to rest on Israel for being the responsible party," Brennan said.
He added that he believed Israel's intention was to send a message to Hezbollah of its capabilities to get to the militia inside Lebanon.
Israel has warned the U.S., its closest ally, that “military action” would most likely be the only way to address mounting hostilities with Hezbollah.
Late Monday, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s office announced that his security Cabinet had updated its list of war objectives to include the safe return of residents who have been displaced from their homes near the northern border because of months of fighting with Hezbollah.
“Israel will continue to act to implement this objective,” the prime minister’s office said.
Thousands of people have been displaced on both sides of the Israel-Lebanon border since Israel began an offensive in Gaza following the Hamas-led Oct. 7 terrorist attacks. Hezbollah has vowed to continue attacks until Israel’s assault on Gaza ends.
Israeli tensions with Hezbollah, a powerful militia and political party that formed in 1986 and rose to power after Israel invaded southern Lebanon in pursuit of Palestine Liberation Organization fighters, spiraled during the war in Gaza.
Last month, Israel struck Lebanon with what it said were pre-emptive strikes to prevent plans by Hezbollah to launch a widespread assault across the countries' shared border.
The attacks came weeks after Israel assassinated a top Hezbollah commander, Fouad Shukur . Hezbollah sought revenge by launching a drone attack on Israel's Glilot base, which is near Tel Aviv.
International diplomats, particularly those from the U.S. and France, have been working for months to de-escalate the conflict between Hezbollah and Israel in an effort to contain the war in Gaza.
Chantal Da Silva reports on world news for NBC News Digital and is based in London.
Doha Madani is a senior breaking news reporter for NBC News. Pronouns: she/her.
Raf Sanchez is a foreign correspondent for NBC News.
Watch CBS News
What's known about Ryan Wesley Routh, Trump assassination attempt suspect arrested in Florida
By Kerry Breen , Anna Schecter
Updated on: September 17, 2024 / 5:12 PM EDT / CBS News
A picture is emerging of Ryan Wesley Routh, the suspect who officials say pointed a high-powered rifle from the tree line of a Florida golf course where former President Donald Trump was golfing Sunday afternoon. The FBI and U.S. Secret Service are investigating the incident, which the FBI said "appears to be an attempted assassination of former President Trump."
Routh, 58, appeared in federal court Monday morning on two charges, possession of a firearm by a convicted felon and possession of a firearm with an obliterated serial number. If convicted of both charges, he would face a maximum of 20 years in prison.
Routh was armed with an AK-47-style rifle and was allegedly 300-500 yards away from Trump when a member of the former president's Secret Service detail spotted his rifle in the tree line, according to Palm Beach County Sheriff Ric Bradshaw. (In an affidavit filed the following day, an FBI special agent described the weapon as "a loaded SKS-style, 7.62x39 caliber rifle with a scope.")
The suspect was a few holes ahead of where the president was golfing at the Trump International Golf Course in West Palm Beach, officials said. The Secret Service said Monday that the suspect did not have a line of sight to Trump.
The Secret Service says the agent opened fire at the suspect, who "did not fire or get off any shots at our agent," according to acting director Ronald Rowe.
Bradshaw said a witness then saw a man jump out of the bushes and flee in a black Nissan SUV. Officials got the license plate number, and the car was pulled over about 50 miles north of the golf course on I-95. The driver was detained and identified as the suspect.

Law enforcement found the rifle, a scope, two backpacks with ceramic tile and a GoPro camera in the bushes at the scene, officials said. They said DNA evidence was recovered and is being tested.
According to an affidavit from an FBI agent, data obtained from Routh's cellphone service provider showed that his phone was in the vicinity of the area along the Trump International tree line for about 12 hours before the encounter, from approximately 1:59 a.m. to approximately 1:31 p.m. Sunday.
On Tuesday, agents with the FBI and Homeland Security Investigations raided Routh's home on the Hawaiian island of Oahu. A CBS News crew counted at least eight federal agents inside the home. Sarah Rice, an FBI spokesperson on scene, described the federal activity as "court authorized."
As the investigation continues, here's what we know about the suspect:
A decades-long criminal history
Routh told a judge Monday he's employed and makes about $3,000 a month, but he didn't provide details about his job. He said he didn't have any assets. During Monday's hearing, it was determined that he qualified for a public defender.
His most recent address is listed in Hawaii, but he spent most of his life in North Carolina, according to property records. Routh owned Camp Box Honolulu, a shed-building company, according to his LinkedIn profile. The account also says that he studied at North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University and graduated in 1998.
Records show Routh's issues with the law go back to the 1990s and include lesser charges of writing bad checks. But in 2002 he was charged with possession of a weapon of mass destruction, a felony, according to North Carolina Department of Corrections records. In another incident, he was charged with misdemeanors, including a hit-and-run offense, resisting arrest, and a concealed weapons violation, the records show.
But his son, Oren Routh, told CBS News his father wasn't violent, and he said he was "definitely surprised" by the latest allegations.
"He's a good person and has been a hard worker his whole life. He's a great man and good dad, non-violent, and was never abusive. I was definitely surprised this happened. He taught us to work hard and be good people. I haven't known him to own guns or ever hurt anyone in any way, always tried to help his community in any and every way possible," Oren Routh said.
Suspect criticized Trump online
Routh voted Democratic in the 2024 primary election in North Carolina, and he voted in person, according to the North Carolina State Board of Elections. He appears to be registered as an unaffiliated voter.
His account on X, formerly known as Twitter, has now been suspended, and it included a number of posts about Trump.
"@realDonaldTrump While you were my choice in 2106, I and the world hoped that president Trump would be different and better than the candidate, but we all were greatly disappointment and it seems you are getting worse and devolving," he wrote in a June 2020 post. "I will be glad when you gone."
He also referenced the July 13 assassination attempt on Trump in multiple posts, suggesting that President Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris should visit the injured and attend the funeral of the Pennsylvania rally-goer who was killed.
A Facebook account under Routh's name was no longer online on Sunday evening.
Passionate support for Ukraine
A CBS News review of Routh's social media shows his pro-Ukraine views seeped into his public statements as well. Routh was passionate about supporting Ukraine, even traveling overseas in hopes of fighting in the country's war against Russia in 2022.
"I am coming to Ukraine from Hawaii to fight for your kids and families and democracy.. I will come and die for you," he wrote on X. In a post on LinkedIn, he shared a photo of himself in Kyiv, Ukraine's capital.
But things didn't appear to work out quite as he expected. In an interview with Newsweek Romania in 2022, he said, "My initial goal was to come fight … but I'm 56, so initially they were like, I have no military experience, so they were like, you're not an ideal candidate. So they said, not right this minute. So plan B was to come here to Kyiv and promote getting more people here."
"This is about good versus evil," he told the outlet in a video interview.

He urged people, even those who didn't have military skills, to take up arms for Ukraine, and offered to help connect them with military units. He was interviewed by several news organizations, including The New York Times and Semafor , in 2023.
He told Semafor that he had not been able to convince the Ukrainian Defense Ministry "to issue one single visa" for the soldiers. It's not clear whether he was actually ever in contact with the ministry about his proposal.
Ukraine's Defense Intelligence Unit International Legion said in a statement Monday that Routh never served with them and "has no relation to the unit."
Routh spoke with CBS News about his Ukraine ambitions
CBS News senior foreign correspondent Holly Williams immediately recognized Routh's name when she woke up in London on Monday to the news of his arrest. She'd been in contact with him for more than a year in the early stages of the war in Ukraine, which she's covered extensively.
It was one of the fliers he helped post around Kyiv, offering to help other foreigners get deployed with Ukrainian battalions, that initially caught Williams' eye and prompted her to get in touch with him.
They spoke at least once on the phone, and texted frequently. Routh put Williams in touch with several foreign fighters and she said he seemed very genuine and passionate about supporting Ukraine in its battle to fend off Russia's invasion.
But Williams said Routh, at times, seemed fairly naïve, including when he spoke of his ambition to help bring thousands of Afghan and Syrian fighters into Ukraine to join the war effort.
The last time Williams heard from Routh was November 2023, when he said he was back in Hawaii.
Pat Milton and Manuel Bojorquez contributed to this report.
- Donald Trump
Kerry Breen is a news editor at CBSNews.com. A graduate of New York University's Arthur L. Carter School of Journalism, she previously worked at NBC News' TODAY Digital. She covers current events, breaking news and issues including substance use.
More from CBS News

Trump touts World Liberty Financial crypto exchange, but questions remain

Biden administration asks Congress to surge Secret Service funding

Texas's Abbott declares Venezuelan gang a terrorist group

Springfield, Ohio, schools ramp up security after false claims, bomb threats
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Is 'University doctorate' a correct way to describe someone who has done a PhD. at a particular university?
The term 'University graduate'(For e.g. Stanford graduate) is ambiguous in the sense that it does not indicate if the concerned individual has an undergraduate, post-graduate or a PhD. degree from the university.
So, I wanted to know whether the above ambiguity can be eliminated by describing the individual as University undergraduate, University graduate and University doctorate to indicate completion of undergraduate, graduate and doctorate degrees at the university.
If A has done a PhD. from Stanford University, Can we call A as a Stanford doctorate?
- expressions
- A is a doctor, not a doctorate. A doctor has a doctorate, and you can say it's a Stanford doctorate. – michael.hor257k Commented Sep 1, 2017 at 10:26
- For instance, The phrase - 'Jon, a Stanford doctor', has a connotation of a medical doctor than someone having done PhD. from Stanford. – Sendhilkumar Alalasundaram Commented Sep 1, 2017 at 12:22
2 Answers 2
I've heard people described as "a PhD", particularly in an American context.
For example: "She's a Stanford PhD", or "I'm a PhD".
A few usages found with Google:
https://irevolutions.org/2011/10/05/its-official-im-a-phd/
[ https://www.reddit.com/r/explainlikeimaphd/]
- yes, this is a good suggestion. But I am also interested in understanding if there is any semantic/syntactic impropriety in using 'A is a University doctorate' to refer to a someone who has done a PhD from the university. – Sendhilkumar Alalasundaram Commented Sep 1, 2017 at 12:24
- 'A is a University doctorate' seems strange to me. Maybe better: 'A holds a University doctorate' or 'A has been awarded a University doctorate'. I agree that "doctorate" is the degree, not the person; so we should not say that a person is a doctorate. – GEdgar Commented Sep 1, 2017 at 13:12
- The doctorate is the degree; the doctor is the person who receives the degree. All doctorates are equivalent, so University PhD isn't used. If you do use it, you are implying pragmatically that a PhD from University is either much better or much inferior to the norm. So be careful you understand the context. – John Lawler Commented Sep 1, 2017 at 15:00
I wanted to know whether the above ambiguity can be eliminated by describing the individual as University undergraduate, University graduate and University doctorate to indicate completion of undergraduate, graduate and doctorate degrees at the university.
No. You can't do this. First of all, "undergraduate" means someone who hasn't yet obtained their Bachelor's degree. So it would be quite wrong to use the word "undergraduate" to indicate completion of their degree.
Actually, the OED defines "bachelor" as meaning someone who has obtained their Bachelor's degree but not their Master's. ("One who has taken the first or lowest degree at a university, who is not yet a master of the Arts" - OED.) However, you can't in practice go around calling such people "bachelors". It's too ambiguous, because the word "bachelor" has other meanings, and you won't be widely understood. Nor (even disregarding the polysemy) would "Stanford bachelor" necessarily mean someone who had obtained their degree from Stanford. It could equally mean someone who's obtained a degree (possibly from elsewhere) and who now lives in Stanford or studies at Stanford.
Nor can you use the word "graduate" to mean that the person has completed a postgraduate degree. A university graduate is someone who has completed any university degree. It doesn't need to be a postgraduate degree. Someone with a Bachelor's degree is a graduate; so is someone with a Master's; and so is someone with a doctorate.
Your Answer
Sign up or log in, post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged expressions or ask your own question .
- Featured on Meta
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
Hot Network Questions
- What was the newest chess piece
- Cutting a curve through a thick timber without waste
- Use the lower of two voltages when one is active
- A function to convert numbers from scientific notation to plain decimal
- My team is not responsive to group messages and other group initiatives. What should be the appropriate solution?
- Movie from the fifties where aliens look human but wear sunglasses to hide that they have no irises (color) in their eyes - only whites!
- Grid-based pathfinding for a lot of agents: how to implement "Tight-Following"?
- Was the total glaciation of the world, a.k.a. snowball earth, due to Bok space clouds?
- Ki Savo: Idols of Wood and Stone
- How can I assign a heredoc to a variable in a way that's portable across Unix and Mac?
- What was the document that Paul and Chloe signed with Sabrina?
- Help with understanding a rigid geometry proof
- What does "either" refer to in "We don't have to run to phone booths anymore, either"?
- Why does fdisk create a 512B partition when I enter +256K?
- Determining Entropy in PHP
- Fear of getting injured in Judo
- Why is 'это' neuter in this expression?
- Would a scientific theory of everything be falsifiable?
- Are these colored sets closed under multiplication?
- Grothendieck topoi as a constructive property
- Would Dicyanoacetylene Make a Good Flamethrower Fuel?
- On Concordant Readings in Titrations
- Cartoon Network (Pakistan or India) show around 2007 or 2009 featuring a brother and sister who fight but later become allies
- Seeking a Text-Based Version of Paul Dirac's 1926 Paper on Quantum Mechanics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The "tell me about yourself" PhD interview question seems like something you do not need to prepare for or think about. But ignoring the importance of this interview question imperils your candidacy, since admissions committees scrutinize this part of the interview as much as other elements of your application, like your grad school statement of purpose, research resume, or statement of ...
Be honest about the things you find challenging, but identify them as training needs and discuss how you expect to improve upon them as part of your PhD. Do answer: I feel that I'm a good written communicator. My existing academic and professional work demonstrates an ability to put forward ideas clearly and concisely.
9. There are no real breaks. In a stereotypical "9-to-5" job, when the workday is over or the weekend arrives, you can generally forget about your work. And a vacation provides an even longer respite. But in a PhD program, your schedule becomes "whenever you find time to get your work done."
Here are six valuable lessons I learned from being in a PhD program and am still applying to my life: Learn to Trust Yourself. This might sound simple, but for many people (especially graduate students), trusting yourself can be hard to do. There are moments where you might question your own capabilities and feel you are not up to par, but this ...
20. Enjoy your PhD! It can be tough, and there will be days when you wish you had a 'normal' job, but PhDs are full of wonderful experiences and give you the opportunity to work on something ...
The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries. A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as "candidates", to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
Some of the most common and difficult graduate school interview questions are often the simplest in scope. Here are a few tips for how to structure and create a proper answer as to why you want to do a PhD: 1. Research, Research, Research. Research is not only what your PhD will lead to but also a crucial portion of preparing for it.
Completing a PhD is all about creating fresh knowledge, discovering new things and developing new skills. It is a degree meant for those who seek greater depth of knowledge in a specific area. With a PhD, 'one can make a difference', says Professor Paul KH Tam, Pro Vice Chancellor and Vice President (Research), University of Hong Kong.
Common PhD Interview Questions. In this guide, we'll share 11 common PhD interview questions and our suggestions on how to answer them. A PhD interview is an essential step in securing a doctorate position. This is because it enables the prospective supervisor to get to know you better and determine whether you'd be a good fit for the project.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor in philosophia) [1] is a terminal degree, that usually denotes the highest level of academic achievement in a given discipline and is awarded following a course of graduate study and original research.The name of the degree is most often abbreviated PhD (or, at times, as Ph.D. in North America), pronounced as three ...
Take your time there is no rush. Quality over quantity. A good presentation of bad results > bad presentation with good results. Don t take your failures personnaly. Research is hard and doesn't care about your feelings. Communicate with your PI but don't forget you are the only expert of your subject.
Here are ten common PhD interview questions. 1. Tell us about yourself. This is a popular opener for just about any type of interview. It's meant to be an easy icebreaker, but that doesn't mean there isn't a wrong answer. Make sure to your response is relevant to the context of a PhD interview. Talk about your academic background ...
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say ...
5. Embrace change - don't get bogged down in the details. Felix Shaw - one of our bioinformatics researchers at EI - put it best when he said, " it felt like I was running into brick walls all the way through [my PhD]… you'd run into a brick wall, surmount it, only to run straight into another. It's true.
A PhD is an essential qualification for a career in academia or research. It is the first step to becoming a lecturer or professor or a scientist at a university or research institute. However, not all PhDs choose to continue on in academia. The advanced research skills you learn during a PhD are advantageous in a variety of diverse fields such ...
Doctorate, or doctoral, is an umbrella term for many degrees — PhD among them — at the height of the academic ladder. Doctorate degrees fall under two categories, and here is where the confusion often lies. The first category, Research (also referred to as Academic) includes, among others: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)**.
Some analysts say instead that some sort of supply chain attack, which involved the pagers being tampered with during their manufacture or in transit, was more likely.
A PhD is a Doctor of Philosophy. In answer to the question, "Is a PhD a doctor," the answer is yes. Both a PhD and a professional doctorate like an EdD earn you the title of "doctor.". But there are differences between the types of doctoral degrees. Learn more about a PhD vs. a professional doctorate below.
This is possibly country dependent, but for Germany this is utterly wrong: "many also think that the MD is much more difficult to attain than a PhD" - Medical doctors get the equivalent of a "paper doctorate" thrown after them so they can be called "doctor" as part of their degree, while "real doctors" have to start a doctorate and carry out rigorous research to obtain the degree/academic title.
Doing a PhD to improve your (academic) career prospects. Another legitimate reason for wanting to do a PhD is your professional goals. These goals can involve a career within academia, or outside of academia. (Both have valid advantages and disadvantages.)
Ryan Wesley Routh put his enmity toward Donald Trump - the man he once supported but then dismissed as an "idiot," a "buffoon" and a "fool" - at the center of a rambling and ...
Secret Service agents fired on a man with a rifle who had been hiding for hours in the wooded edge of a Trump golf club in Florida, officials said. Former President Donald J. Trump was unhurt.
One way we measure safety is by testing how well our model continues to follow its safety rules if a user tries to bypass them (known as "jailbreaking"). On one of our hardest jailbreaking tests, GPT-4o scored 22 (on a scale of 0-100) while our o1-preview model scored 84. You can read more about this in the system card and our research post.
The militant group Hezbollah said Tuesday that pagers belonging to its members had blown up across Lebanon, killing at least eight and injuring more than 2,700, according to the country's Health ...
If you decide to uncock your wrists and get that clubhead going really fast before your lower body does anything, that's a speed killer," says MacKenzie, who helped Matt Fitzpatrick add distance ...
A picture is emerging of Ryan Wesley Routh, the suspect who officials say pointed a high-powered rifle from the tree line of a Florida golf course where former President Donald Trump was golfing ...
The doctorate is the degree; the doctor is the person who receives the degree. All doctorates are equivalent, so University PhD isn't used. If you do use it, you are implying pragmatically that a PhD from University is either much better or much inferior to the norm. So be careful you understand the context. -