Cochrane Breast Cancer
Top 10 breast cancer topics needing a cochrane systematic review.

Deciding which research topics to focus on in medicine and health depends on many factors. These factors can include the currency of a topic, feedback from people providing or receiving care, and the priorities of funders.
In late 2019, the Cochrane Breast Cancer Group (part of Cochrane’s Cancer Network) conducted a formal priority-setting exercise to help decide which review topics were most needed in the Cochrane Library. The Group did this by circulating a survey listing 25 new or existing review topics to a diverse group of individuals who are part of the international breast cancer community. The survey asked individuals to rank their top 10 topics from the list. Read details about the aims and methods used for this priority-setting exercise, which adhered to the standards outlined in Cochrane’s priority setting guidance note .
What were the top 10 review topics?
|
|
|
1 | Omission of whole breast irradiation for postmenopausal women with early breast cancer | Can radiotherapy be safely omitted in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer? |
2 | Platinum-containing regimens for neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy in triple-negative breast cancer | What are the benefits and harms of adding platinum chemotherapy to standard therapy for people with triple-negative early breast cancer? |
3 | Overdiagnosis due to screening mammography for women aged 40 years and over | In women aged 40 years or older and at average risk, should they have a mammogram? |
4 | Post-mastectomy radiotherapy for women with early breast cancer and 1 to 3 positive lymph nodes | For women who have 1 to 3 positive axillary lymph nodes after mastectomy, does radiotherapy to the lymph nodes provide an additional benefit when compared to women who do not have radiotherapy to the lymph nodes? |
5 | Breast surgery for metastatic breast cancer | What are the benefits and harms of having breast surgery in addition to anti-cancer treatment when breast cancer has spread to another part of the body? |
6 | Partial breast irradiation for early breast cancer | Can radiotherapy delivered to part of the breast be as effective and safe as radiotherapy delivered to the whole breast for women who have had breast-conserving surgery? |
7 | Parenteral bone-active agents in adjuvant therapy | What are the benefits and harms of adding bisphosphonate or denosumab to standard anti-cancer treatment in women with early breast cancer? |
8 | Systemic therapies for preventing or treating aromatase inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal symptoms in early breast cancer | Can medications and supplements (such as complementary and alternative medicines) help to reduce the symptoms of aromatase inhibitor-induced muscle pain and stiffness compared to no therapy? |
9 | Non-hormonal interventions for hot flushes in women with a history of breast cancer | Can pharmacological agents (such as vitamin E, clonidine, gabapentin) and non-pharmacological therapies (such as meditation, aromatherapy, magnetic therapy) help to reduce the number of hot flushes compared to no therapy in women receiving endocrine therapy for breast cancer treatment, women experiencing menopause with a history of breast cancer or women experiencing menopause due to breast cancer treatment? |
10 | Hypofractionation radiation therapy for early breast cancer | Can fewer radiotherapy visits (by using a higher radiation dose at each visit) be as effective and safe as conventional radiotherapy treatments for women who have had breast-conserving surgery? |
Read about the ranking of the 25 new or existing review topics .
What is next?
Support to author teams For the top 10 topics, the Cochrane Breast Cancer Group will prioritise these topics during the editorial and peer-review process.
For all breast cancer review topics registered with Cochrane, the Cochrane Breast Cancer Group continues to work on these topics with author teams as these remain important topics. There will be no noticeable change in the support provided to author teams.
Future topics The Cochrane Breast Cancer Group is open to receiving new topic ideas. If you have suggestions for new topics that are not currently covered in the Cochrane Library, please send your idea to [email protected] .
Repeating this priority-setting exercise The priority-setting exercise may be repeated every 3 years, depending on resources.
Who responded to the survey?
The survey was circulated to over 800 individuals. Of the 199 people who responded, 90 people (45%) provided complete responses. The respondents were doctors (59%), researchers (18%) and people who had received treatment or currently receiving treatment for breast cancer (14%). Most respondents were from the UK, followed by the USA, Argentina, and India.
How did we calculate the ranking for each review topic?
The average ranking was calculated for each topic. This method is commonly used to determine ranking scores from surveys. This approach considers the number of counts for each ranking on a topic, the weighting of each rank (where a ranking of 1 gets the most weight) and the total number of counts.
[Cover image: foliage of the Yew tree. Taxanes, a class of chemotherapy drugs, were originally derived from the Yew tree]
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 108

Weakly-supervised deep learning models enable HER2-low prediction from H &E stained slides
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low breast cancer has emerged as a new subtype of tumor, for which novel antibody–drug conjugates have shown beneficial effects. Assessment of HER2 requires seve...
- View Full Text
Validation of an AI-based solution for breast cancer risk stratification using routine digital histopathology images
Stratipath Breast is a CE-IVD marked artificial intelligence-based solution for prognostic risk stratification of breast cancer patients into high- and low-risk groups, using haematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stain...
The SEMA3F-NRP1/NRP2 axis is a key factor in the acquisition of invasive traits in in situ breast ductal carcinoma
A better understanding of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is urgently needed to identify these preinvasive lesions as distinct clinical entities. Semaphorin 3F (SEMA3F) is a soluble axonal guidance molecule, a...
Association of Life’s Essential 8 cardiovascular health with breast cancer incidence and mortality according to genetic susceptibility of breast cancer: a prospective cohort study
Accumulating evidence suggests that cardiovascular diseases and breast cancer share a number of common risk factors, however, evidence on the association between cardiovascular health (CVH) and breast cancer i...
Micrometastases in axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer, post-neoadjuvant systemic therapy
The significance of minimal residual axillary disease, specifically micrometastases, following neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NST) remains largely unexplored. Our study aimed to elucidate the prognostic implica...
Development of a humanized anti-FABP4 monoclonal antibody for potential treatment of breast cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women diagnosed in the U.S. and worldwide. Obesity increases breast cancer risk without clear underlying molecular mechanisms. Our studies demonstrate that circulatin...
Genomic profiling and comparative analysis of male versus female metastatic breast cancer across subtypes
Male breast cancer (MaBC) has limited data on genomic alterations. We aimed to comprehensively describe and compare MaBC’s genomics with female breast cancer’s (FBC) across subtypes.
Downregulation of tRF-Cys-GCA-029 by hyperglycemia promotes tumorigenesis and glycolysis of diabetic breast cancer through upregulating PRKCG translation
Diabetes mellitus (DM) affects up to one-third of breast cancer (BC) patients. Patients with co-existing BC and DM (BC-DM) have worsened BC prognosis. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanisms orchestrating BC-DM...

Associations between quantitative measures of mammographic density and terminal ductal lobular unit involution in Chinese breast cancer patients
Higher mammographic density (MD), a radiological measure of the proportion of fibroglandular tissue in the breast, and lower terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) involution, a histological measure of the amount o...
Stromal lymphocytes are associated with upgrade of B3 breast lesions
Various histopathological, clinical and imaging parameters have been evaluated to identify a subset of women diagnosed with lesions with uncertain malignant potential (B3 or BIRADS 3/4A lesions) who could safe...
Epigallocatechin gallate and curcumin inhibit Bcl-2: a pharmacophore and docking based approach against cancer
The protein Bcl-2, well-known for its anti-apoptotic properties, has been implicated in cancer pathogenesis. Identifying the primary gene responsible for promoting improved cell survival and development has pr...
GNA13 suppresses proliferation of ER+ breast cancer cells via ERα dependent upregulation of the MYC oncogene
GNA13 (Gα13) is one of two alpha subunit members of the G12/13 family of heterotrimeric G-proteins which mediate signaling downstream of GPCRs. It is known to be essential for embryonic development and vasculogen...
Promoter profiles in plasma CfDNA exhibits a potential utility of predicting the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients
Gene expression profiles in breast tissue biopsies contain information related to chemotherapy efficacy. The promoter profiles in cell-free DNA (cfDNA) carrying gene expression information of the original tiss...
Androgen receptor-mediated pharmacogenomic expression quantitative trait loci: implications for breast cancer response to AR-targeting therapy
Endocrine therapy is the most important treatment modality of breast cancer patients whose tumors express the estrogen receptor α (ERα). The androgen receptor (AR) is also expressed in the vast majority (80–90...
Functions of methyltransferase-like 3 in breast cancer: pathogenesis, drug resistance, and therapeutic target
Breast cancer (BC) is a highly prevalent malignancy worldwide, with complex pathogenesis and treatment challenges. Research reveals that methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) is widely involved in the pathogenesis...
Effect of testosterone therapy on breast tissue composition and mammographic breast density in trans masculine individuals
The effect of gender-affirming testosterone therapy (TT) on breast cancer risk is unclear. This study investigated the association between TT and breast tissue composition and breast tissue density in trans ma...
Utilizing human cerebral organoids to model breast cancer brain metastasis in culture
Metastasis, the spread, and growth of malignant cells at secondary sites within a patient’s body, accounts for over 90% of cancer-related mortality. Breast cancer is the most common tumor type diagnosed and th...
A prospective study of HER3 expression pre and post neoadjuvant therapy of different breast cancer subtypes: implications for HER3 imaging therapy guidance
HER3, a member of the EGFR receptor family, plays a central role in driving oncogenic cell proliferation in breast cancer. Novel HER3 therapeutics are showing promising results while recently developed HER3 PE...
Atypical cell cycle regulation promotes mammary stem cell expansion during mammary development and tumourigenesis
The cell cycle of mammary stem cells must be tightly regulated to ensure normal homeostasis of the mammary gland to prevent abnormal proliferation and susceptibility to tumorigenesis. The atypical cell cycle r...
Circular RNA HSDL2 promotes breast cancer progression via miR-7978 ZNF704 axis and regulating hippo signaling pathway
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a new group of endogenous RNAs recently found to be involved in the development of various diseases, including their confirmed involvement in the progression of several types of ca...
Evaluating the immunologically “cold” tumor microenvironment after treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors utilizing PET imaging of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells in breast cancer mouse models
Immune-positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with tracers that target CD8 and granzyme B has shown promise in predicting the therapeutic response following immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) in immunologica...
TFAP2A downregulation mediates tumor-suppressive effect of miR-8072 in triple-negative breast cancer via inhibiting SNAI1 transcription
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) represents a highly aggressive subset of breast malignancies characterized by its challenging clinical management and unfavorable prognosis. While TFAP2A, a member of the A...
Association of early menarche with breast tumor molecular features and recurrence
Early menarche is an established risk factor for breast cancer but its molecular contribution to tumor biology and prognosis remains unclear.
Trends in chemotherapy use for early-stage breast cancer from 2006 to 2019
Little is known about how use of chemotherapy has evolved in breast cancer patients. We therefore describe chemotherapy patterns for women with stage I-IIIA breast cancer in the Optimal Breast Cancer Chemother...
In situ HER2 RNA expression as a predictor of pathologic complete response of HER2-positive breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy and anti-HER2 targeted treatment
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in situ hybridization (ISH) remain standard biomarkers for therapeutic decisions in human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancers (BCs); however, they are insuff...
Trastuzumab-functionalized bionic pyrotinib liposomes for targeted therapy of HER2-positive breast cancer
In this study, we prepared a bionic nanosystem of trastuzumab-functionalized SK-BR-3 cell membrane hybrid liposome-coated pyrotinib (Ptb-M-Lip-Her) for the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Transmissio...
An essential gene signature of breast cancer metastasis reveals targetable pathways
The differential gene expression profile of metastatic versus primary breast tumors represents an avenue for discovering new or underappreciated pathways underscoring processes of metastasis. However, as tumor...
Pre-treatment peripheral blood immunophenotyping and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in operable breast cancer
Tumor immune infiltration and peripheral blood immune signatures have prognostic and predictive value in breast cancer. Whether distinct peripheral blood immune phenotypes are associated with response to neoad...
Hypoxia-mediated repression of pyruvate carboxylase drives immunosuppression
Metabolic plasticity mediates breast cancer survival, growth, and immune evasion during metastasis. However, how tumor cell metabolism is influenced by and feeds back to regulate breast cancer progression are ...

Lasofoxifene as a potential treatment for aromatase inhibitor-resistant ER-positive breast cancer
Breast cancers treated with aromatase inhibitors (AIs) can develop AI resistance, which is often driven by estrogen receptor-alpha (ERα/ ESR1 ) activating mutations, as well as by ER-independent signaling pathways....
NSUN2/YBX1 promotes the progression of breast cancer by enhancing HGH1 mRNA stability through m 5 C methylation
RNA m 5 C methylation has been extensively implicated in the occurrence and development of tumors. As the main methyltransferase, NSUN2 plays a crucial regulatory role across diverse tumor types. However, the preci...
Inflammation at diagnosis and cognitive impairment two years later in breast cancer patients from the Canto-Cog study
Inflammation could be related to cancer-related cognitive impairment (CRCI) and might be used as a predictive marker of long-term CRCI. We evaluated associations between inflammatory markers assessed at diagno...
Increased expression of REG3A promotes tumorigenic behavior in triple negative breast cancer cells
Identifying new targets in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains critical. REG3A (regenerating islet-derived protein 3 A), a calcium-dependent lectin protein, was thoroughly investigated for its express...
Alpha-6 integrin deletion delays the formation of Brca1/p53-deficient basal-like breast tumors by restricting luminal progenitor cell expansion
The aberrant amplification of mammary luminal progenitors is at the origin of basal-like breast cancers associated with BRCA1 mutations. Integrins mediate cell–matrix adhesion and transmit mechanical and chemi...
Deep learning-based risk stratification of preoperative breast biopsies using digital whole slide images
Nottingham histological grade (NHG) is a well established prognostic factor in breast cancer histopathology but has a high inter-assessor variability with many tumours being classified as intermediate grade, N...
Unraveling malignant phenotype of peritumoral tissue: transcriptomic insights into early-stage breast cancer
Early-stage invasive ductal carcinoma displays high survival rates due to early detection and treatments. However, there is still a chance of relapse of 3–15% after treatment. The aim of this study was to unco...
Reproductive characteristics, menopausal status, race and ethnicity, and risk of breast cancer subtypes defined by ER, PR and HER2 status: the Breast Cancer Etiology in Minorities study
Associations between reproductive factors and risk of breast cancer differ by subtype defined by joint estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and HER2 expression status. Racial and ethnic differen...
EDI3 knockdown in ER-HER2+ breast cancer cells reduces tumor burden and improves survival in two mouse models of experimental metastasis
Despite progress understanding the mechanisms underlying tumor spread, metastasis remains a clinical challenge. We identified the choline-producing glycerophosphodiesterase, EDI3 and reported its association w...
Elevated expression of wildtype RhoC promotes ErbB2- and Pik3ca- induced mammary tumor formation
Copy number gains in genes coding for Rho activating exchange factors as well as losses affecting genes coding for RhoGAP proteins are common in breast cancer (BC), suggesting that elevated Rho signaling may p...
Optimising the diagnostic accuracy of First post-contrAst SubtracTed breast MRI (FAST MRI) through interpretation-training: a multicentre e-learning study, mapping the learning curve of NHS Breast Screening Programme (NHSBSP) mammogram readers using an enriched dataset
Abbreviated breast MRI (FAST MRI) is being introduced into clinical practice to screen women with mammographically dense breasts or with a personal history of breast cancer. This study aimed to optimise diagno...
Breast cancer patients enrolled in the Swiss mammography screening program “donna” demonstrate prolonged survival
We compared the survival rates of women with breast cancer (BC) detected within versus outside the mammography screening program (MSP) “donna”.
Correction: NSABP FB-10: a phase Ib/II trial evaluating ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) with neratinib in women with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer
The original article was published in Breast Cancer Research 2024 26 :69
Deep learning of mammogram images to reduce unnecessary breast biopsies: a preliminary study
Patients with a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4 mammogram are currently recommended for biopsy. However, 70–80% of the biopsies are negative/benign. In this study, we developed a deep lear...
Reporting on patient’s body mass index (BMI) in recent clinical trials for patients with breast cancer: a systematic review
The proportion of patients with breast cancer and obesity is increasing. While the therapeutic landscape of breast cancer has been expanding, we lack knowledge about the potential differential efficacy of most...
Infrared laser moxibustion for cancer-related fatigue in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial
Cancer-related fatigue (CRF) is a pervasive, persistent, and distressing symptom experienced by cancer patients, for which few treatments are available. We investigated the efficacy and safety of infrared lase...
Association of area- and volumetric-mammographic density and breast cancer risk in women of Asian descent: a case control study
Mammographic density (MD) has been shown to be a strong and independent risk factor for breast cancer in women of European and Asian descent. However, the majority of Asian studies to date have used BI-RADS a...
Fusogenic vesicular stomatitis virus combined with natural killer T cell immunotherapy controls metastatic breast cancer
Metastatic breast cancer is a leading cause of cancer death in woman. Current treatment options are often associated with adverse side effects and poor outcomes, demonstrating the need for effective new treatm...
Enhancing pathological complete response prediction in breast cancer: the role of dynamic characterization of DCE-MRI and its association with tumor heterogeneity
Early prediction of pathological complete response (pCR) is important for deciding appropriate treatment strategies for patients. In this study, we aimed to quantify the dynamic characteristics of dynamic cont...
Proteogenomic characterization of difficult-to-treat breast cancer with tumor cells enriched through laser microdissection
Breast cancer (BC) is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death among women globally. Despite advances, there is considerable variation in clinical outcomes for patients with non...
CD163 + macrophages in the triple-negative breast tumor microenvironment are associated with improved survival in the Women’s Circle of Health Study and the Women’s Circle of Health Follow-Up Study
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are a prominent immune subpopulation in the tumor microenvironment that could potentially serve as therapeutic targets for breast cancer. Thus, it is important to characteri...
- Editorial Board
- Manuscript editing services
- Instructions for Editors
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Collections
- Follow us on Twitter
Annual Journal Metrics
Citation Impact 2023 Journal Impact Factor: 6.1 5-year Journal Impact Factor: 7.1 Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 1.865 SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 2.578 Speed 2023 Submission to first editorial decision (median days): 14 Submission to acceptance (median days): 129 Usage 2023 Downloads: 2,432,781 Altmetric mentions: 1,561
- More about our metrics
Breast Cancer Research
ISSN: 1465-542X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Breast cancer: a review of the literature
Affiliation.
- 1 Texas Life Insurance Company, 900 Washington Avenue, Waco, TX 76701, USA.
- PMID: 14733031
This article presents a comprehensive review of the Breast Cancer literature examining epidemiology, diagnosis, pathology, "benign" breast disease, breast carcinoma in situ syndromes, staging, and post-treatment surveillance among many topics. Breast cancer remains the most commonly occurring cancer in women. Breast cancer detection, treatment, and prevention are prominent issues in public health and medical practice. Background information on developments in these arenas is provided so that medical directors can continue to update their approach to the assessment of breast cancer risk.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Lobular carcinoma in situ: current concepts and controversies. Schnitt SJ, Morrow M. Schnitt SJ, et al. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1999 Aug;16(3):209-23. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10490198 Review.
- Risk of invasive breast carcinoma among women diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ and lobular carcinoma in situ, 1988-2001. Li CI, Malone KE, Saltzman BS, Daling JR. Li CI, et al. Cancer. 2006 May 15;106(10):2104-12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21864. Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16604564
- Lobular carcinoma in situ and intraductal carcinoma of the breast. Rosen PP. Rosen PP. Monogr Pathol. 1984;(25):59-105. Monogr Pathol. 1984. PMID: 6330539 Review. No abstract available.
- Lobular neoplasia. Long term risk of breast cancer and relation to other factors. Bodian CA, Perzin KH, Lattes R. Bodian CA, et al. Cancer. 1996 Sep 1;78(5):1024-34. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960901)78:5 3.0.CO;2-4. Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8780540
- Noninvasive breast cancer: Part 2. Lobular carcinoma in situ--incidence, presentation, guidelines to treatment. Swain SM. Swain SM. Oncology (Williston Park). 1989 Mar;3(3):35-40; discussion 40, 42, 44 passim. Oncology (Williston Park). 1989. PMID: 2561881 Review.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed potential regulatory biomarkers and repurposable drugs for breast cancer treatment. Shornale Akter M, Uddin MH, Atikur Rahman S, Hossain MA, Ashik MAR, Zaman NN, Faruk O, Hossain MS, Parvin A, Rahman MH. Shornale Akter M, et al. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 May;7(5):e2009. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2009. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38717954 Free PMC article.
- Chemoinformatics and machine learning techniques to identify novel inhibitors of the lemur tyrosine kinase-3 receptor involved in breast cancer. Alrumaihi F. Alrumaihi F. Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 4;11:1366763. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1366763. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38638686 Free PMC article.
- Stage Shifting by Modifying the Determinants of Breast Cancer Stage at Diagnosis: A Simulation Study. Pokharel G, Wang Q, Khan M, Robson PJ, Shack L, Kopciuk KA. Pokharel G, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;16(6):1201. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061201. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539535 Free PMC article.
- Chromium and lead levels and alteration in DDPH inhibition in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Pakmanesh F, Mahjoub S, Neamati N, Moslemi D. Pakmanesh F, et al. Caspian J Intern Med. 2023 Summer;14(3):553-559. doi: 10.22088/cjim.14.3.533. Caspian J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37520864 Free PMC article.
- Human arginase I: a potential broad-spectrum anti-cancer agent. Anakha J, Prasad YR, Sharma N, Pande AH. Anakha J, et al. 3 Biotech. 2023 May;13(5):159. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03590-3. Epub 2023 May 3. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37152001 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
- Genetic Alliance
- MedlinePlus Health Information
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Breast Cancer Research Results and Study Updates
See Advances in Breast Cancer Research for an overview of recent findings and progress, plus ongoing projects supported by NCI.
Drs. Ruth Pfeiffer and Peter Kraft of NCI’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics discuss how breast cancer risk assessment tools are created and how people can use them to understand and manage their risk.
Some people with no evidence of cancer in nearby lymph nodes after presurgical chemotherapy can skip radiation to that area without increasing the risk of the cancer returning, a clinical trial found. But some experts caution that more details are needed.
For women in their 70s and older, the risk of overdiagnosis with routine screening mammography is substantial, a new study suggests. The findings highlight the need for conversations between older women and their health care providers about the potential benefits and harms of continuing screening mammography.
Many young women who are diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer want to become pregnant in the future. New research suggests that these women may be able to pause their hormone therapy for up to 2 years as they try to get pregnant without raising the risk of a recurrence in the short term.
For younger women with advanced breast cancer, the combination of ribociclib (Kisqali) and hormone therapy was much better at shrinking metastatic tumors than standard chemotherapy treatments, results from an NCI-funded clinical trial show.
In a large clinical trial, a condensed course of radiation therapy was as effective and safe as a longer standard course for those with higher-risk early-stage breast cancer who had a lumpectomy. This shorter radiation course makes treatment less of a burden for patients.
Adding the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to chemotherapy can help some patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer live longer. In the KEYNOTE-355 trial, overall survival improved among patients whose tumors had high levels of the PD-L1 protein.
People with metastatic breast cancer whose tumors had low levels of HER2 protein lived longer after treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu) than those treated with standard chemotherapy, results of the DESTINY-Breast04 clinical trial show.
NCI researchers have shown that an experimental form of immunotherapy that uses an individual’s own tumor-fighting immune cells could potentially be used to treat people with metastatic breast cancer who have exhausted all other treatment options.
Most breast cancer risk tools were developed with data mainly from White women and don’t work as well for Black women. A new tool that estimates risk for Black women may help identify those who might benefit from earlier screening, enabling earlier diagnosis and treatment.
In people with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, the targeted drug trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu) markedly lengthened progression-free survival compared with trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcycla), new study results show.
In a large clinical trial, women with HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer treated with ribociclib (Kisqali) and letrozole (Femara) as their initial treatment lived approximately 1 year longer than women treated with letrozole only.
Women with early-stage breast cancer who had one or both breasts surgically removed (a unilateral or bilateral mastectomy) had lower scores on a quality-of-life survey than women who had breast-conserving surgery, a new study has found.
For women undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer, meeting the national physical activity guidelines may help alleviate cognitive issues, a new study suggests. The benefits may be even greater for patients who were physically active before treatment.
Sacituzumab govitecan (Trodelvy) now has regular FDA approval for people with locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The update follows last year’s accelerated approval of the drug for people with TNBC.
For some people with ER-positive breast cancer, a new imaging test may help guide decisions about receiving hormone therapy, according to a new study. The test can show whether estrogen receptors in tumors are active and responsive to estrogen.
The test, which helps guide treatment decisions, was not as good at predicting the risk of death from breast cancer for Black patients as for White patients, a new study has found. The findings highlight the need for greater racial diversity in research studies.
The drug abemaciclib (Verzenio) may be a new treatment option for people with the most common type of breast cancer, with new study findings suggesting that it can reduce the risk of the cancer returning.
Fertility preservation for young women with breast cancer doesn’t increase their risk of dying in the ensuing decades, a new study affirmed. Experts said the findings support routinely offering fertility preservation to patients who want it.
Some postmenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer may not benefit from chemotherapy and can safely forgo the treatment, according to clinical trial results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
A heart-related event, like a heart attack, may make breast cancer grow faster, a new study suggests. In mice, heart attacks accelerated breast tumor growth and human studies linked cardiac events with breast cancer recurrence, researchers reported.
FDA has approved sacituzumab govitecan (Trodelvy) for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Under the approval, patients must have already undergone at least two prior treatment regimens.
Women with high-risk breast cancer who engaged in regular exercise before their cancer diagnosis and after treatment were less likely to have their cancer return or to die compared with women who were inactive, a recent study found.
Researchers have developed a “microscaled” approach to analyze the proteins and genetic changes (proteogenomics) of a tumor that uses tissue from a core needle biopsy. The analyses can provide important information that may help guide treatment.
Tucatinib improved survival for women in the HER2CLIMB trial, including some whose cancer had spread to the brain. Trastuzumab deruxtecan improved survival and shrank many tumors in the DESTINY-Breast01 trial, which led to its accelerated approval.
A TAILORx analysis shows women with early-stage breast cancer and high recurrence scores on the Oncotype DX who received chemotherapy with hormone therapy had better long-term outcomes than what would be expected from hormone therapy alone.
Men with breast cancer may be more likely to die of the disease than women, particularly during the first 5 years after diagnosis, a new study suggests. The higher likelihood of death was linked in part to undertreatment and later diagnosis.
In a survey of nearly 600 breast cancer survivors, researchers found that the cost of care factored into the decisions the women made about what type of surgery to get. Many women also reported never discussing costs with their physicians.
FDA has expanded the approved use of the drug ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), also called T-DM1, to include adjuvant treatment in some women with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.
Many women diagnosed with ovarian and breast cancer are not undergoing tests for inherited genetic mutations that can provide important information to help guide decisions about treatment and longer-term cancer screening, a new study has found.
FDA has approved atezolizumab (Tecentriq) in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of some women with advanced triple-negative breast cancer. This is the first FDA-approved regimen for breast cancer to include immunotherapy.
The build-up of connective tissue around some types of cancer can act as a barrier to immunotherapy. A new study uses a bone marrow transplant drug, plerixafor, to break down this barrier and improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in animal models of breast cancer.
A new study in mice shows that disrupting the relationship between breast cancer cells that spread to bone and normal cells surrounding them makes the cancer cells sensitive to treatment.
In women with early-stage breast cancer, two clinical trials have shown that both whole- and partial-breast radiation therapy are effective at preventing the cancer from returning after breast-conserving surgery.
Researchers are testing a topical-gel form of the drug tamoxifen to see if it can help prevent breast cancer as effectively as the oral form of the drug but with fewer side effects.
Findings from a clinical study and a mouse study may shed light on genetic risk factors for developing cancer-related cognitive problems in older breast cancer survivors. The results suggest a gene associated with Alzheimer’s disease may play a role.
Arsenic trioxide and retinoic acid work together to target the master regulator protein Pin1, a new study shows. In cancer cell lines and mice, the drug combination slowed the growth of triple-negative breast cancer tumors.
FDA has expanded the approved uses of ribociclib (Kisqali) for women with advanced breast cancer, including new uses in pre- and postmenopausal women. It’s the first approval under a new FDA program to speed the review of cancer drugs.
Using a liquid biopsy to test for tumor cells circulating in blood, researchers found that, in women with breast cancer, the presence of these cells could identify women at risk of their cancer returning years later.
Findings from the TAILORx clinical trial show chemotherapy does not benefit most women with early breast cancer. The new data, released at the 2018 ASCO annual meeting, will help inform treatment decisions for many women with early-stage breast cancer.
Do cancer study participants want to receive their genetic test results? A recent study involving women with a history of breast cancer tested an approach for returning genetic research results and evaluated the impact those results had on the women.
Researchers compared the risk of death for women with breast cancer who had low skeletal muscle mass, or sarcopenia, at the time of their cancer diagnosis and women who had adequate muscle mass.
Some people who have been treated for breast cancer or lymphoma have a higher risk of developing congestive heart failure than people who haven’t had cancer, results from a new study show.
FDA has approved the CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) as a first-line treatment in some women with advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Under the approval, the drug must be used in combination with an aromatase inhibitor.
A new study in mice raises the possibility that using microscopic, oxygen-carrying bubbles may improve the effectiveness of radiation therapy in the treatment of breast cancer.
The drug olaparib (Lynparza®) is the first treatment approved by the Food and Drug Administration for patients with metastatic breast cancer who have inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes.
Joint pain caused by aromatase inhibitors in postmenopausal women with breast cancer can cause some women to stop taking the drugs. Reducing their symptoms may translate into better adherence to therapy.
DigitalCommons@UNMC
Home > Eppley Institute > Theses & Dissertations
Theses & Dissertations: Cancer Research
Theses/dissertations from 2024 2024.
Novel Spirocyclic Dimer (SpiD3) Displays Potent Preclinical Effects in Hematological Malignancies , Alexandria Eiken
Chemotherapy-Induced Modulation of Tumor Antigen Presentation , Alaina C. Larson
Understanding the role of MASTL in colon homeostasis and colitis-associated cancer development , Kristina Pravoverov
Dying Right: Supporting Anti-Cancer Therapy Through Immunogenic Cell Death , Elizabeth Schmitz
Therapeutic Effects of BET Protein Inhibition in B-cell Malignancies and Beyond , Audrey L. Smith
Targeting KSR1 to inhibit stemness and therapy resistance , Heidi M. Vieira
Identifying the Molecular Determinants of Lung Metastatic Adaptation in Prostate Cancer , Grace M. Waldron
Identification of Mitotic Phosphatases and Cyclin K as Novel Molecular Targets in Pancreatic Cancer , Yi Xiao
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
Development of Combination Therapy Strategies to Treat Cancer Using Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors , Nicholas Mullen
Overcoming Resistance Mechanisms to CDK4/6 Inhibitor Treatment Using CDK6-Selective PROTAC , Sarah Truong
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Omics Analysis in Cancer and Development , Emalie J. Clement
Investigating the Role of Splenic Macrophages in Pancreatic Cancer , Daisy V. Gonzalez
Polymeric Chloroquine in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Therapy , Rubayat Islam Khan
Evaluating Targets and Therapeutics for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer , Shelby M. Knoche
Characterization of 1,1-Diarylethylene FOXM1 Inhibitors Against High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma Cells , Cassie Liu
Novel Mechanisms of Protein Kinase C α Regulation and Function , Xinyue Li
SOX2 Dosage Governs Tumor Cell Identity and Proliferation , Ethan P. Metz
Post-Transcriptional Control of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Ras-Driven Colorectal Cancers , Chaitra Rao
Use of Machine Learning Algorithms and Highly Multiplexed Immunohistochemistry to Perform In-Depth Characterization of Primary Pancreatic Tumors and Metastatic Sites , Krysten Vance
Characterization of Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Immunosuppressed Patient , Megan E. Wackel
Visceral adipose tissue remodeling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cachexia: the role of activin A signaling , Pauline Xu
Phos-Tag-Based Screens Identify Novel Therapeutic Targets in Ovarian Cancer and Pancreatic Cancer , Renya Zeng
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
Functional Characterization of Cancer-Associated DNA Polymerase ε Variants , Stephanie R. Barbari
Pancreatic Cancer: Novel Therapy, Research Tools, and Educational Outreach , Ayrianne J. Crawford
Apixaban to Prevent Thrombosis in Adult Patients Treated With Asparaginase , Krishna Gundabolu
Molecular Investigation into the Biologic and Prognostic Elements of Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma with Regulators of Tumor Microenvironment Signaling Explored in Model Systems , Tyler Herek
Utilizing Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras to Target the Transcriptional Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 9 and 12 , Hannah King
Insights into Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis and Metastasis Using a Bedside-to-Bench Approach , Marissa Lobl
Development of a MUC16-Targeted Near-Infrared Antibody Probe for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery of Pancreatic Cancer , Madeline T. Olson
FGFR4 glycosylation and processing in cholangiocarcinoma promote cancer signaling , Andrew J. Phillips
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Cooperativity of CCNE1 and FOXM1 in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer , Lucy Elge
Characterizing the critical role of metabolic and redox homeostasis in colorectal cancer , Danielle Frodyma
Genomic and Transcriptomic Alterations in Metabolic Regulators and Implications for Anti-tumoral Immune Response , Ryan J. King
Dimers of Isatin Derived Spirocyclic NF-κB Inhibitor Exhibit Potent Anticancer Activity by Inducing UPR Mediated Apoptosis , Smit Kour
From Development to Therapy: A Panoramic Approach to Further Our Understanding of Cancer , Brittany Poelaert
The Cellular Origin and Molecular Drivers of Claudin-Low Mammary Cancer , Patrick D. Raedler
Mitochondrial Metabolism as a Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer , Simon Shin
Development of Fluorescent Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Intraoperative Tumor Detection , Nicholas E. Wojtynek
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
The role of E3 ubiquitin ligase FBXO9 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis , R. Willow Hynes-Smith
BRCA1 & CTDP1 BRCT Domainomics in the DNA Damage Response , Kimiko L. Krieger
Targeted Inhibition of Histone Deacetyltransferases for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy , Richard Laschanzky
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Class I Molecule Components and Amyloid Precursor-Like Protein 2 (APLP2): Roles in Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration , Bailee Sliker
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
FOXM1 Expression and Contribution to Genomic Instability and Chemoresistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer , Carter J. Barger
Overcoming TCF4-Driven BCR Signaling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma , Keenan Hartert
Functional Role of Protein Kinase C Alpha in Endometrial Carcinogenesis , Alice Hsu
Functional Signature Ontology-Based Identification and Validation of Novel Therapeutic Targets and Natural Products for the Treatment of Cancer , Beth Neilsen
Elucidating the Roles of Lunatic Fringe in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma , Prathamesh Patil
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Metabolic Reprogramming of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells in Response to Chronic Low pH Stress , Jaime Abrego
Understanding the Relationship between TGF-Beta and IGF-1R Signaling in Colorectal Cancer , Katie L. Bailey
The Role of EHD2 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis and Progression , Timothy A. Bielecki
Perturbing anti-apoptotic proteins to develop novel cancer therapies , Jacob Contreras
Role of Ezrin in Colorectal Cancer Cell Survival Regulation , Premila Leiphrakpam
Evaluation of Aminopyrazole Analogs as Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors for Colorectal Cancer Therapy , Caroline Robb
Identifying the Role of Janus Kinase 1 in Mammary Gland Development and Breast Cancer , Barbara Swenson
DNMT3A Haploinsufficiency Provokes Hematologic Malignancy of B-Lymphoid, T-Lymphoid, and Myeloid Lineage in Mice , Garland Michael Upchurch
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
EHD1 As a Positive Regulator of Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 Receptor , Luke R. Cypher
Inflammation- and Cancer-Associated Neurolymphatic Remodeling and Cachexia in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma , Darci M. Fink
Role of CBL-family Ubiquitin Ligases as Critical Negative Regulators of T Cell Activation and Functions , Benjamin Goetz
Exploration into the Functional Impact of MUC1 on the Formation and Regulation of Transcriptional Complexes Containing AP-1 and p53 , Ryan L. Hanson
DNA Polymerase Zeta-Dependent Mutagenesis: Molecular Specificity, Extent of Error-Prone Synthesis, and the Role of dNTP Pools , Olga V. Kochenova
Defining the Role of Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation in the Regulation of Gap Junction Proteins , Hanjun Li
Molecular Mechanisms Regulating MYC and PGC1β Expression in Colon Cancer , Jamie L. McCall
Pancreatic Cancer Invasion of the Lymphatic Vasculature and Contributions of the Tumor Microenvironment: Roles for E-selectin and CXCR4 , Maria M. Steele
Altered Levels of SOX2, and Its Associated Protein Musashi2, Disrupt Critical Cell Functions in Cancer and Embryonic Stem Cells , Erin L. Wuebben

Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Characterization and target identification of non-toxic IKKβ inhibitors for anticancer therapy , Elizabeth Blowers
Effectors of Ras and KSR1 dependent colon tumorigenesis , Binita Das
Characterization of cancer-associated DNA polymerase delta variants , Tony M. Mertz
A Role for EHD Family Endocytic Regulators in Endothelial Biology , Alexandra E. J. Moffitt
Biochemical pathways regulating mammary epithelial cell homeostasis and differentiation , Chandrani Mukhopadhyay
EPACs: epigenetic regulators that affect cell survival in cancer. , Catherine Murari
Role of the C-terminus of the Catalytic Subunit of Translesion Synthesis Polymerase ζ (Zeta) in UV-induced Mutagensis , Hollie M. Siebler
LGR5 Activates TGFbeta Signaling and Suppresses Metastasis in Colon Cancer , Xiaolin Zhou
LGR5 Activates TGFβ Signaling and Suppresses Metastasis in Colon Cancer , Xiaolin Zhou
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Genetic dissection of the role of CBL-family ubiquitin ligases and their associated adapters in epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis , Gulzar Ahmad
Strategies for the identification of chemical probes to study signaling pathways , Jamie Leigh Arnst
Defining the mechanism of signaling through the C-terminus of MUC1 , Roger B. Brown
Targeting telomerase in human pancreatic cancer cells , Katrina Burchett
The identification of KSR1-like molecules in ras-addicted colorectal cancer cells , Drew Gehring
Mechanisms of regulation of AID APOBEC deaminases activity and protection of the genome from promiscuous deamination , Artem Georgievich Lada
Characterization of the DNA-biding properties of human telomeric proteins , Amanda Lakamp-Hawley
Studies on MUC1, p120-catenin, Kaiso: coordinate role of mucins, cell adhesion molecules and cell cycle players in pancreatic cancer , Xiang Liu
Epac interaction with the TGFbeta PKA pathway to regulate cell survival in colon cancer , Meghan Lynn Mendick
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
Deconvolution of the phosphorylation patterns of replication protein A by the DNA damage response to breaks , Kerry D. Brader
Modeling malignant breast cancer occurrence and survival in black and white women , Michael Gleason
The role of dna methyltransferases in myc-induced lymphomagenesis , Ryan A. Hlady
Design and development of inhibitors of CBL (TKB)-protein interactions , Eric A. Kumar
Pancreatic cancer-associated miRNAs : expression, regulation and function , Ashley M. Mohr
Mechanistic studies of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) , Xiaming Pang
Novel roles for JAK2/STAT5 signaling in mammary gland development, cancer, and immune dysregulation , Jeffrey Wayne Schmidt
Optimization of therapeutics against lethal pancreatic cancer , Joshua J. Souchek
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
Immune-based novel diagnostic mechanisms for pancreatic cancer , Michael J. Baine
Sox2 associated proteins are essential for cell fate , Jesse Lee Cox
KSR2 regulates cellular proliferation, transformation, and metabolism , Mario R. Fernandez
Discovery of a novel signaling cross-talk between TPX2 and the aurora kinases during mitosis , Jyoti Iyer
Regulation of metabolism by KSR proteins , Paula Jean Klutho
The role of ERK 1/2 signaling in the dna damage-induced G2 , Ryan Kolb
Regulation of the Bcl-2 family network during apoptosis induced by different stimuli , Hernando Lopez
Studies on the role of cullin3 in mitosis , Saili Moghe
Characteristics of amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (APLP2) in pancreatic cancer and Ewing's sarcoma , Haley Louise Capek Peters
Structural and biophysical analysis of a human inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase polymorphism , Peter David Simone
- Eppley Institute Website
- McGoogan Library
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
Author Corner
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Your Account
Manage your account, subscriptions and profile.
MyKomen Health
ShareForCures
In Your Community
In Your Community
View resources and events in your local community.
Change your location:

Susan G. Komen®
One moment can change everything.
Breast Cancer Research Table Topics
Established and probable risk factors.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| and inherited gene mutations and cancer risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mammography
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
Early and locally advanced breast cancer.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inflammatory breast cancer (non-metastatic)
Metastatic breast cancer.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Updated 05/03/24
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Effective Tips and Topic Ideas for Literature Review on Breast Cancer
Are you a first-year medical student who has to hand in a thesis or dissertation to graduate?
Then don’t wait till the third year to start the work. Start searching for the right topic today. Breast cancer is one of the most concerning diseases in the world.
Although there are awareness campaigns and sessions organized all over the world, this subject still needs further research and study to minimize, if not eliminate, the number of affecters.
This makes it the perfect theme for your medical thesis.
Below mentioned are some ideas for topics in the field of breast cancer
But before we move on to that, let’s have a look at what cancer actually is.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a disease caused by abnormal uncontrolled cell growth in the body. There are two properties that make cancer cells malignant. They have uncontrolled growth and they are metastasis (which means that they spread from one part of the body to another).
For A Literature Review on Breast Cancer
Students can cover this topic from several points of view. You can cover the disease from the doctor’s point of view or students’. You can conduct study on the prevention, incidence, or cure of the research. Another interesting aspect is the psychological mind frame of the patients. You can also conduct your study on the many problems that the patients have to go through like strained family relations, social acceptance, and economic problems.
Some Ideas for Topics:
- Involvement of different receptors in breast cancer metastasis
- Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival
- Identification of the breast cancer susceptibility gene
- Relationship of human breast cancer and ovarian cancer
- Lymphatic mapping for breast cancer
- Prospective identification of tumor-causing breast cancer cells
- Reproductive factors and breast cancer
- Effect of psychosocial treatment on survival of patients with metastatic breast cancer
- Relationship between breast cancer and hormone-replacement therapy
- How coping mediates the effect of optimism on distress: a study of women with early-stage breast cancer
- Breast cancer knowledge &self-care practices of women
- Follow-up care after a diagnosis of breast cancer – patient’s perspectives
Basically, for writing a breast cancer literature review you need to include related terminology in your literature review to make it narrower. While searching for the right topic on this theme, you need to make sure that your research topic is supported with relevant articles that will help in the study.
Before taking the topic to your supervisor, make sure that it is supported by articles that have been published in authentic journals. You also need to make sure that your research topic will not become obsolete in the near future and that the scope of the research is just right. It should be wide enough to be significant but should be narrow enough to be covered within the designated time frame.
Paid Topic Mini Proposal (500 Words)
You will get the topics first and then the mini proposal which includes:
- An explanation why we choose this topic.
- 2-3 research questions.
- Key literature resources identification.
- Suitable methodology including raw sample size and data collection method
- View a Sample of Service
Note: After submitting your order please must check your email [inbox/spam] folders for order confirmation and login details. If the email goes in spam please mark not as spam to avoid any communication gap between us.
Get An Expert Dissertation Writing Help To Achieve Good Grades
By placing an order with us, you can get;
- Writer consultation before payment to ensure your work is in safe hands.
- Free topic if you don't have one
- Draft submissions to check the quality of the work as per supervisor's feedback
- Free revisions
- Complete privacy
- Plagiarism Free work
- Guaranteed 2:1 (With help of your supervisor's feedback)
- 2 Instalments plan
- Special discounts
Other Posts
- 45 Human Rights Dissertation Topics Ideas & Examples February 7, 2020 -->
- 49 Risk Management Dissertation Topics Ideas & examples February 27, 2020 -->
- 49 Waste Management Dissertation Topics Ideas February 27, 2020 -->
- 53 Best Dissertation topics on domestic violence & Examples November 30, 2021 -->
- 53 Sports Dissertation Topics and examples in 2023 March 17, 2020 -->
- 56 Best Critical Care Nursing Research Topics ideas with examples November 18, 2021 -->
- 57 Best Ecommerce Research Topics Ideas and Examples November 30, 2021 -->
- 57 Best Forensic Science Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 17, 2020 -->
- 57 Best Real Estate Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 16, 2020 -->
- 57+ Best Health and Social Care Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 16, 2020 -->
- 59 Anthropology Dissertation Topics Ideas & Examples March 17, 2020 -->
- 62 Ideas for English Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 13, 2020 -->
- 63 Graphic Design Dissertation Topics Ideas February 7, 2020 -->
- 63+ Best Communications dissertation Topics in 2023 March 11, 2020 -->
- 87 Dementia dissertation topics in nursing November 18, 2021 -->
- 99 Microfinance Dissertation Topics Ideas & Examples February 26, 2020 -->
- Animation Topics for Writing a Perfect Animation Dissertation February 4, 2020 -->
- Best 29 Music Dissertation Topics Ideas & Examples February 26, 2020 -->
- Best 35 Cultural Studies Dissertation Topics March 13, 2020 -->
- Best 39 Photography Dissertation Topics and Ideas in 2023 February 26, 2020 -->
- Best 49 Social Policy Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 16, 2020 -->
- Best 49 Sports Psychology Dissertation Topics Ideas February 27, 2020 -->
- Best 53+ Geography Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 17, 2020 -->
- Best 59 Engineering Dissertation Topics Ideas and Examples February 6, 2020 -->
- Best 59 Networking Dissertation Topics Ideas & Examples February 26, 2020 -->
- Best Art dissertation Topics and ideas in 2023 March 11, 2020 -->
- Best Construction Dissertation Topics, Ideas, and Samples March 13, 2020 -->
- Best Environmental Science Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 16, 2020 -->
- Best Film Studies Dissertation Topics in 2023 March 16, 2020 -->
- Best French Dissertation Topics and Ideas 2023 April 1, 2020 -->
WhatsApp and Get 35% off promo code now!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.22(5); 2021 Nov
Influence of cultural practices on breast cancer risks, stage at presentation and outcome in a multi-ethnic developing country
Norlia abdullah.
1 Department of Surgery, University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, 56000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Norazlina Mohamed
2 Department of Pharmacology, University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, 56000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Associated Data
Not applicable.
Malaysia is a developing country made up of three main ethnicities: Malay, Chinese and Indian. There are significant ethnic differences with regard to the type of daily food and cooking methods, contraception, breast-feeding preferences, confinement period and care, postmenopausal intake and influence of the traditional healer. Breast cancer is the most common cancer among Malaysian women across all three ethnicities. However, the National Cancer Registry and local medical centres have documented ethnic differences in breast cancer risk (Chinese, 40.7 per 100,000; Indian, 38.1 per 100,000; Malay, 31.5 per 100,000), peak age (youngest in the Malays), stage at presentation (largest percentage at advanced stage among the Malays) and survival (poorest survival rate among the Malays). The Malays have several practices that are protective against breast cancer compared with the Chinese. However, the Malays have strong beliefs in the traditional healer, which contribute to the delay in getting treatment, causing a poor outcome and a low survival rate. The highest BRCA1 and 2 genetic mutation incidence is amongst the Chinese, but the Malays have the largest triple-negative breast cancer rates. These factors may also contribute to the statistical breast cancer data.
1. Introduction
Worldwide, breast cancer is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer when statistics for both sexes are combined. For women, breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of mortality ( 1 ). In Asia, the most common cancer types in women are breast, lung, cervical, colorectal and stomach cancer. The mortality-to-incidence ratios are the highest in lung, liver and stomach cancer, and the lowest in colorectal, breast and prostate cancer ( 2 ). In 2012, there were 639,824 cases of breast cancer recorded in Asian countries, with 228,926 deaths. Malaysia recorded 5,410 cases of breast cancer, with 2,572 deaths, in 2012 ( 3 ). Based on Malaysia's 2016 National Cancer Registry, a total of 21,634 cases of female breast cancer were diagnosed over a period of 4 years between 2012 and 2016 compared with 18,206 cases in the 2007–2011 report. Breast cancer is the most common cancer and has accounted for 34.1% of all cancer cases among women in Malaysia. The age-standardised rate was increased from 31.1 per 100,000 population in 2007–2011 to 34.1 between 2012 and 2016 ( 4 ).
Malaysia is a developing country made up of three main ethnicities: Malay, Chinese and Indian. Multi-ethnicity in Malaysia started after the establishment of the Straits Settlements in Penang, Malacca and Singapore, and later on, the acquisition of the Malay territories by the British. These British colonizers brought in a number of labourers from China and India to work on the land ( 5 ). The Chinese migrants were placed to work in tin mines, whilst the Indian population laboured in the rubber plantations.
With regard to the breast cancer incidence rate among the three major ethnic groups, the incidence is highest among the Chinese (40.7 per 100,000 individuals) followed by the Indians (38.1 per 100,000 individuals) and the Malays (31.5 per 100,000 individuals). The overall lifetime risk is 1 in 22 for the Chinese, 1 in 23 for the Indians and 1 in 30 for the Malays ( 4 ). The Malays have been observed to be significantly younger at the time of cancer presentation (average, 50 years old) compared with the Chinese (average, 57 years old) and Indians (average 56 years old). The Malays also have a more advanced stage at diagnosis compared with the other two ethnic groups ( 6 ). The Malay ethnicity was observed to be a poor prognostic factor in breast cancer, conferring 1.5 times the risk of death compared with the Chinese ethnicity ( 7 ). Similarly, it was noted that the Malays had a lower survival rate of 39.7% compared with 48.2% in the Chinese and 47.2% in the Indians ( 8 ). These Malay women presented with the more advanced stages compared with the women of the other two ethnicities, and had the worst survival rate ( 9 , 10 ). Singapore, which is a multi-ethnic country similar to Malaysia, also reported a similar breast cancer incidence rate that was higher among Chinese women compared with that among the Malays and Indians ( 11 ). Table I shows the statistics of breast cancer among the different ethnic groups.
Statistics of breast cancer and genetic mutations among the different ethnic groups in Malaysia.
| Statistic | Malay | Chinese | Indian | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence (per 100,000) in a 5-year period | ( ) | |||
| 2007-2011 | 27.2 | 41.5 | 37.1 | |
| 2012-2016 | 31.5 | 40.7 | 38.1 | |
| Overall lifetime risk | 1 in 30 | 1 in 22 | 1 in 23 | ( ) |
| Age at presentation, years | 50 | 57 | 56 | ( ) |
| 46 | 51 | 53 | ( ) | |
| Metastatic disease at presentation, % | 14.2 | 9.2 | 11.9 | ( ) |
| 16 | 9 | 4 | ( ) | |
| Median tumour size at diagnosis, mm | 35 | 25 | 30 | ( ) |
| Oestrogen receptor-positive tumours, % | 52.5 | 58.1 | 52.5 | ( ) |
| Oestrogen receptor-negative tumours, % | 47.5 | 41.9 | 47.5 | ( ) |
| High-grade tumours, % | 44.7 | 39.4 | 43.9 | ( ) |
| Malaysian 5-year survival rate, % | 39.7 | 48.2 | 47.2 | ( ) |
| Malaysian average survival time, years | 6.41 | 7.10 | 6.45 | ( ) |
| Malaysian-Singapore 5-year survival rate, % | 58.5 | 75.8 | 68 | ( ) |
| BRCA1 and 2 mutations, % | 23.5 | 63.1 | 11.8 | ( ) |
Although there has been ethnic integration, and the occurrence of marriages between ethnicities, each group has largely retained its own unique culture and way of life. In Malaysia, the statistical data combines the Malays with the smaller indigenous groups to form the Bumiputera group. The Malays (Bumiputera) now make up 69.6% of the population, the Chinese 22.6% and the Indians 6.8%, with the remaining percentage being constituted from the other ethnic minorities. The total population now stands at 32.6 million people ( 12 )
According to a review of the literature, to the best of our knowledge, there has been only one paper discussing the possible causes or correlation between the lifestyle and culture of the three ethnicities in Malaysia and breast cancer risk ( 13 ). However, this paper lacks references for a number of the points that were raised. A large part of this paper discussed the general lifestyles that had led to Malaysian women developing cancer as a whole, but did not compare the practices between the different ethnicities, as the title had suggested.
The present review comprehensively analyses different cultural practices and how they may have affected the risk, stage at presentation and outcome of women with breast cancer in Malaysia, a multi-ethnic developing country. The significant ethnic differences appear to be in the type of daily food and cooking methods, contraception, fertility rates, breast-feeding practices, confinement period and care, postmenopausal intake and influence of the traditional healer, which are all discussed.
2. Dietary habits
As in most cases, dietary practices play a big role with regard to health. The three ethnic races in Malaysia have their preferences in food preparation. The Malays and the Indians use a lot of turmeric or curcumin in their routine cooking, consisting of curries and other spicy gravies. Curcumin is a polyphenol from the plant Curcuma longa . Although not a phyto-oestrogen, it has been shown to inhibit the proliferation of various breast cancer cell lines and also to induce the apoptosis of breast cancer cells ( 14 ). Curcumin has also been found to minimise the risk of metastases in breast cancer by downregulating the inflammatory cytokines C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 and 2 via nuclear factor-κB, an inflammation- and cell survival-related transcription factor ( 15 ).
The typical Chinese diet does not include turmeric. Instead, a lot of soya (soy) products, consisting of soya sauce, bean curd and soya-bean drink, are used. Soya beans fall in the isoflavones category of phyto-oestrogens. In a dose-response meta-analysis report, each increment of 10 mg/day soy isoflavone was associated with a 3% decreased breast cancer risk ( 16 ). Phyto-oestrogens are very weak mimickers of natural oestrogens, with an affinity for oestrogen receptors of 1,000-10,000 times lower than oestradiol ( 17 ). There are two types of oestrogen receptors (ERs), ER-α and ER-β. Stimulation of ER-α causes an increase in tumour growth, but stimulation of ER-β causes tumour regression. Oestradiol has equal affinity for both types of ERs. Tamoxifen has double the affinity for ER-β compared with that for ER-α. However, phyto-oestrogens have five times greater affinity for ER-β compared with that for ER-α ( 18 ). A bi-phasic behaviour of isoflavones has also been observed in vitro , whereby a low dose stimulated the growth of MCF-7 cells (ER-positive breast cancer cell line), but not MDA-MB cells (ER-negative breast cancer cell line). At high doses, isoflavones inhibit the growth of both ER-positive and -negative cell lines ( 19 , 20 ). Another important Chinese cooking ingredient is sesame, which is consumed as seeds and as sesame oil ( 21 ). Sesame seeds contain a lignan, which is also a type of phyto-oestrogen. However, its chemical compound, enterolactone, is metabolized in the gut and may have limited effects on humans ( 17 ).
In another study, a low dietary fibre intake was associated with higher risks of developing breast cancer ( 22 ). In a nutrient-wide association study, it was reported that a high intake of fibre and fruits was associated with a lower breast cancer risk ( 23 ). It was found that the total consumption of vegetables and fruits differ amongst the different ethnic groups in Malaysia. The Malays have the highest consumption, followed by the Chinese and the Indians ( 24 ), and this may influence breast cancer risk in these ethnic groups.
In Malaysia, alcohol consumption is significantly higher among males compared with females. Among the three ethnic groups, binge drinking was recorded to be highest in the Indians (54%), followed by the Chinese at 39% and the Malays at 8% ( 25 ). The Malay women, who are Muslims, do not consume alcohol as it is forbidden in Islam. Some Chinese women consume alcohol on social occasions and some Indian women in the estates consume illicit alcohol (samsu) ( 26 ). Frequent and high consumption of alcohol are risk factors for breast cancer, as shown in a study among premenopausal women in Japan ( 27 ). Similarly, one report identified alcohol as one of the environmental factors related to cancer ( 28 ). Due to the differences in alcohol consumption among the ethnic groups, breast cancer risk and incidence may also differ.
3. Confinement diet
Across the three ethnicities, the confinement period is traditionally regarded important in order to protect the well-being of the woman, as it allows the body to recuperate and recover from childbirth. At the time, certain dietary practices are observed. ‘Hot foods’ are recommended. ‘Hot foods’ refer to spicy food, with the effect of making the one eating it sweat easily. The Malay confinement period lasts 44 days in which the new mother would be required to wear a special corset ( bengkung ) ( 29 ). Firstly, two large rectangle pieces of cloth are sewn together with a central compartment filled with spices; this is placed over the front of the belly. Next, a long plain piece of cloth is wrapped snugly around the body, over the spice-filled piece, starting from the upper down to the lower abdomen. The new mother would undergo whole body massage daily. Warm compression from heated stones would be placed on the abdominal wall for several minutes at a time, daily, over 3–7 days; this is similar to the application of a hot water bottle. The confinement diet consists of not only young tubers of turmeric, but also its young shoots. Other foods consist of the snake-head fish (ikan haruan), anchovies, meat, ginger, black pepper and a herb locally known as Kacip Fatimah [ Labisia pumila (LP )]. This herb has been found to have cytotoxic activity against the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line ( 30 , 31 ), prostate cancer cell lines ( 32 , 33 ) and melanoma cells ( 34 ). It has also been found to have anti-fungal and anti-inflammatory properties ( 30 ), including bronchodilatory properties ( 35 ).
The confinement period for Chinese women is a month. The confinement diet consists of large amounts of ginger and sesame, as well as special brews in the form of rice wine in which chicken and pork trotters had been simmered. Some women are also given additional drinks such as Dom Pérignon, a French wine, which is highly regarded by the Chinese to be good for women during confinement ( 21 ).
During the confinement period, Chinese women are also given Ginseng ( Panax ginseng ) and Dong Quai or Tong Kuei ( Angelica sinensis ). Traditionally known as ‘female ginseng’, Dong Quai is often given to women at other times too. Amongst its indicated properties are the improvement of fertility and libido, and the treatment of dysmenorrhoea and premenstrual syndrome ( 21 ). Amato et al ( 36 ) showed that, in vitro , Dong Quai and Ginseng increased breast cancer cell line multiplication by 16 and 27 times, respectively. However, recent studies ( 37 , 38 ) have shown conflicting findings. Dong Quai did not exert significant stimulatory effects on breast cancer in both an in vivo breast tumour xenograft-bearing nude mouse model and in an in vitro human breast cancer cell line. However, precaution is required if Dong Quai is to be used in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients due to its ability to induce oestrogen receptor-α expression and its tumorigenic potential via promotion of cancer stem cell activity in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer ( 39 , 40 ). Ginseng has also been shown to inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cell lines in a time- and dose-dependent manner by activating the apoptotic pathway ( 41 ).
Similar to the Chinese, the Indian women undergo a confinement of 30 days. However, their diet is very different from that of Chinese women. Indian women avoid ‘cooling foods’ such as cucumber, murungai ( Moringa oleifera ) fruits and grapes, but are encouraged to consume more spices such as black pepper, cardamon, aniseed, turmeric and ginger ( 42 ). In a study conducted in Singapore, Indian women were also observed to increase their consumption of garlic ( 43 ). A high consumption of garlic has been shown to have an inverse association with breast cancer, as reported in a study conducted among women aged 39–70 years in Puerto Rico ( 44 ).
4. Fertility rate
The fertility rates of the three ethnicities differ, with the highest amongst Malay women and the lowest among Chinese women ( 12 ). There is a close association between breast cancer and parity, whereby increased parity or fertility lessens breast cancer risk ( 28 ).
In 2014, it was found that 52% of Malaysian women practiced family planning consisting of both non-modern and modern methods. The most favoured modern contraception was the oral contraceptive pill (OCP) at 13.2% usage ( 45 ). Contraceptive practices also differed between the ethnicities, with the pill being used the most by Chinese women (45.6%), followed by the Indian (32.2%) and Malay (28.2%) women ( 46 ). Use of the OCP has been shown to increase breast cancer risk ( 28 ).
5. Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is beneficial to both the mother and the child. For the mother, there is an association with a decreased breast cancer risk if the baby is breastfed for >6 months ( 28 ). Local data have shown that a higher percentage of Malays tend to breastfeed longer compared with the percentage of Chinese ( 47 ). In one study, it was determined that Chinese women who were working, from a high income family and with male infants were less likely to breastfeed their baby ( 48 ). In a study that analysed a group of 682 women (Malays, 60.9%; Chinese, 18.7%; and Indians, 16%), it was found that exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months was practised by 52.5% of the Malays, 15.6% of the Chinese and 35.8% of the Indians ( 49 ).
6. Postmenopausal diet
Similar to during the confinement period, LP is also commonly taken by Malay women postmenopause. The menopause is associated with several symptoms and mental health changes (vasomotor symptoms and cognitive function), as well as changes in physiological systems and functions (cardiovascular and bone health) ( 50 ). In rats who were given LP and oestrogen, the collagen fibres that held the adipocytes together became fragmented causing lipolysis. This showed that there is a possible role for LP in preventing postmenopausal obesity ( 51 ). Additionally, a study by Fazliana et al ( 52 ) showed that the plant caused an increase in the production of leptin, leading to weight loss and improvement in insulin sensitivity. Nadia et al ( 53 ) demonstrated the anti-oxidative role of LP, and Abdul Kadir et al ( 54 ) found it to lower serum triglyceride levels. High triglyceride levels have been shown to be associated with coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women ( 55 , 56 ).
A study comparing LP with premarin, one of the medications used for hormone replacement therapy, showed that LP did not prevent the loss of bone mass ( 57 ). However, another study in animal models showed it to be comparable to premarin in preventing osteoporotic fractures in oestrogen-deficient states ( 58 ). A pilot study on women administered LP extracts demonstrated no increase in mammographic density ( 59 ). This is important, as an increase in mammographic density would make interpretation more difficult and has been shown to increase breast cancer risk ( 60 , 61 ).
Just like in Chinese women during the confinement period, Chinese postmenopausal women take Dong Quai to treat vasomotor symptoms ( 21 ). As shown by Amato et al ( 36 ), these menopausal women now have an added risk of developing breast cancer due to this consumption.
7. Traditional healer
According to the Malay culture, the traditional healer or medicine man, known as a ‘bomoh’, is much respected in society. This is especially so among the rural population ( 62 ). Often, the services of the healer is sought after for numerous illnesses in both children and adults. These include physical illnesses, spiritual illnesses and those believed to be related to sorcery or black-magic. Even family related issues like infidelity, separation, divorce or the search for a life partner often involve seeking the advice of the healer.
In Malaysia, the highest users of traditional and complementary treatment are the Sabah Natives, followed by the Malays ( 63 ). Among all patients with breast cancer, there are several reasons for seeking traditional healers, including recommendations from family members and friends, sanction from family, perceived benefit and compatibility, healer credibility, and reservation towards Western medicine and system delays ( 64 ).
For physical lesions, one of the common taboos conveyed by these healers is contact of the affected body part with metal objects. Those who follow these orders would not come to hospital, as often a biopsy would need to be taken, which would involve the use of metal needles. When the treatment from a particular healer did not work or the illness did not go away, a second or third bomoh would be consulted. Only after failing these treatments, which could lead to a delay of 6 to 12 months, would these women present themselves to a hospital. This accounts for the late diagnosis at stages 3 or 4 for Malay women with breast cancer. As expected, these women with more advanced diseases have poorer outcomes. Among the three ethnicities, the Malay women are the worst affected in this regard ( 8 – 10 ).
8. Genetic mutations
Genetic research performed by Thirthagiri et al ( 65 ) discovered that Chinese women had the highest incidence of BRCA1 and 2 mutations at 63.1%, followed by Malay women at 23.1% and Indian women at 11.8%. Among the Chinese women, there was an equal proportion of BRCA1 and 2 mutations. There was more BRCA2 mutations among the Malays. These mutations led to early onset breast cancer (age ≤40 years). A total of 27 deleterious mutations were detected (14 in BRCA1 and 13 in BRCA2), and 47 variants of uncertain clinical significance were identified (16 in BRCA1 and 31 in BRCA2). This study may significantly contribute to the current statistical evidence on incidence of breast cancer by ethnicity.
9. Cumulative overall survival
The cumulative overall survival of Malaysian and Singaporean women ( 9 ) was demonstrated in a full model adjusted for socio-demographic factors, tumour characteristics and treatment ( Fig. 1 ). The findings showed that the cumulative overall survival rate was lowest for Malay women. This data was also supported by results from other previous studies ( 8 , 10 ).

Cumulative overall survival by ethnicity in 5,264 South East Asian women with breast cancer. From Nirmala Boo-pathy ( 9 ), doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030995.g001.
10. Comparison between three ethnic groups
Chinese women who have the lowest fertility rate, highest OCP use, poorest breast feeding practices and highest alcohol intake are associated with increased breast cancer risks. Soya seems to be associated with decreased cellular proliferation in vitro . However, a diet rich in soya alone, as one beneficial factor, would not be able to overcome all the other negative lifestyle practices. With the added factor of having the highest incidence of BRCA1 and 2 genetic mutations amongst the three ethnicities, it is not unexpected that Chinese women have the highest risk of breast cancer.
In comparison, Malay women have the highest fertility rate, lowest OCP usage, best breast feeding practices, no alcohol consumption and the intake of a herb (Kacip Fatimah) with in vitro cytotoxic properties. All of these are in favour of lowering breast cancer risks. The setback among this group is a strong belief in the traditional healer, which causes late presentation to hospitals and poor survival outcomes.
The practices observed by Indian women come between those practiced by the Chinese and the Malays, which put them second highest in terms of breast cancer risk. Table II summarizes the differences in cultural practices among the three ethnic groups and the influence on breast cancer risk.
Cultural practices of the three major ethnic groups in Malaysia and breast cancer risks.
| A, Dietary habits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Practice | Breast cancer risk |
| Malay | Turmeric/curcumin consumption | Reduced risk: Curcumin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of breast cancer cell lines ( ) |
| High consumption of vegetables and fruits | Reduced risk: High dietary fibre reduces breast cancer risk in a study of Malaysians compared with controls ( ) Women, aged 25 to 70 years, followed-up for 15 years, in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study showed that high fibre intake reduced breast cancer risk ( ) | |
| Chinese | Soy product consumption | Reduced risk: A meta-analysis of Chinese women (aged 30–79 years) followed up for 10 years and other studies in Asia and Western countries found that an increase in soy intake reduced breast cancer risk ( ) |
| Alcohol consumption | Increased risk: Alcohol consumption is a risk factor for breast cancer in premenopausal women ( ) | |
| Indian | Turmeric/curcumin consumption | Reduced risk: As aforementioned ( ) |
| Alcohol consumption | Increased risk: As aforementioned ( ) | |
| Malay | Turmeric/curcumin consumption | Reduced risk: As aforementioned ( ) |
| Kacip Fatimah ( consumption | Reduced risk: Cytotoxic activity against the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line ( , ) | |
| Chinese | Alcohol consumption | Increased risk: As aforementioned ( ) |
| Ginseng and Dong Quai ( ) consumption | Conflicting reports: Recent studies showed that Dong Quai did not induce breast cancer but caution use in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients, while ginseng inhibits growth of breast cancer cell lines ( , ) | |
| Indian | Turmeric/curcumin | Reduced risk: As aforementioned ( ) |
| Malay | Highest parity rate, lowest usage of OCP | Reduced risk: Increased parity lessens breast cancer risks ( ) |
| Chinese | Lowest parity rate, highest usage of OCP | Increased risk: Use of OCP increase breast cancer risk ( ) |
| Indian | Parity and usage of OCP ranking between that of the Malays and the Chinese | Medium risk |
| Malay | Most practiced | Reduced risk: Decrease breast cancer risk if breastfeeding for >6 months ( ) |
| Chinese | Least practiced | Increased risk: No breast feeding protective effect against breast cancer ( ) |
| Indian | In between the Malays & the Chinese | Reduced risk: Decrease breast cancer risk if breastfeeding for >6 months ( ) |
| Malay | Kacip Fatimah ( consumption | Reduced risk: As aforementioned ( , ) |
| Chinese | Dong Quai ( ) consumption | Conflicting reports: As aforementioned ( ) |
| Indian | Data not available | Data not available |
| Malay | Strong belief | Increased risk: These women had the worst outcome ( – ) |
| Chinese | No strong belief | No increased risk |
| Indian | No strong belief | No increased risk |
A large part of the aforementioned herbal research showed findings from in vitro studies and animal models, with limited studies in humans. Although this is a commendable start, further clinical trials need to be completed in order to produce more robust data to facilitate the use of such herbs in the clinical setting. From the current data, LP appears a safer option than hormone replacement therapy, which is associated with elevated breast cancer risks according to the Women's Health Initiative study, plus increased risks of stroke and thromboembolic diseases ( 66 ).
The peak age of breast cancer in Malay women is lower compared with that in Chinese and Indian women ( 6 , 9 ). This may be related to the different cancer subtypes among the ethnic groups. The luminal A subtype occurs significantly more frequently in the Chinese than in the Malays. However, the percentage of triple-negative subtype cases is significantly higher in the Malays than in the Chinese ( 67 ). Triple-negative breast cancer has been associated with a younger age at the time of diagnosis and a more advanced disease stage ( 68 ). However, when Asians as a whole are considered, the peak age of breast cancer incidence is between 40 and 50 years old, as opposed to between 60 and 70 years old in Western countries ( 69 ). Biological, genetic and the environmental factors may contribute to these differences.
11. Conclusion
Based on the data presented, the three ethnicities have distinct cultural practices that may influence breast cancer occurrence. The lowest incidence of breast cancer in the Malays may be attributable to their lifestyle and cultural practices. However, the Malays present with the disease at an advanced stage and have a low survival rate. It is hoped that the three ethnicities will learn from each other and adjust their cultural practices. This would mean continuing the beneficial praticises and abandoning the detrimental ones. This is a challenging task and may take a longer time, as often traditional changes occur more easily with a newer generation. Some individuals may have sensitive sentiments attached to their cultural practices and will oppose changes. The government and non-government organisations would need to work together to educate the public to increase their breast cancer awareness and advocate the best lifestyle practices. This would be the best way forward in an attempt to decrease the incidence of breast cancer and improve the outcome at a national level as Malaysia strives forward to become a developed country in the future. Besides Malaysia, the aforementioned information may be beneficial to Asians worldwide who share a similar lifestyle and diet.
Acknowledgements
Availability of data and materials, authors' contributions.
NA conceptualized the study and prepared the original and final drafts. NM reviewed and edited the article. All authors have read and approved the manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Patient consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Unexpected expression and function of fcεri in immortalized breast cancer cells: a cautionary null study.

1. Introduction
2. materials and methods, 2.1. cell lines, 2.2. antibodies, 2.3. chloroacetate esterase staining (cae), 2.4. immunofluorescence, 2.5. flow cytometry, 2.5.1. fcεri flow cytometry, 2.5.2. ca 2+ flux assay, 2.6. polymerase chain reaction (pcr), 2.6.1. rna extraction, 2.6.2. cdna synthesis, 2.6.4. gel electrophoresis, 2.7. immunoblotting, 2.8. il-6 elisa, 2.9. r-2 genomic data search, 3.1. cae staining, 3.2. fluorescence, fcεri in 4t1 tumors in vivo, 3.3. anti-fcεriα expression in vitro, 3.4. ca 2+ flux assay, 3.6. il-6 elisa, 3.7. r2 genomics, 4. discussion, 5. conclusions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, acknowledgments, conflicts of interest.
- How Common Is Breast Cancer? Breast Cancer Statistics ; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-cancer.html (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Aponte-López, A.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M.; Cortes-Muñoz, D.; Muñoz-Cruz, S. Mast Cell, the Neglected Member of the Tumor Microenvironment: Role in Breast Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2018 , 2018 , 2584243-11. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Rasé, V.J.; Hayward, R.; Haughian, J.M.; Pullen, N.A. T h 17, T h 22, and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Population Dynamics and Response to IL-6 in 4T1 Mammary Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022 , 23 , 10299. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Lyons, D.O.; Plewes, M.R.; Pullen, N.A. Soluble transforming growth factor beta-1 enhances murine mast cell release of Interleukin 6 in IgE-independent and Interleukin 13 in IgE-dependent settings in vitro. PLoS ONE 2018 , 13 , e0207704. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Varanasi, S.K.; Kaech, S.M.; Bui, J.D. SnapShot: Cancer immunoediting. Cell 2022 , 185 , 4038–4038.e1. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ganeshan, K.; Johnston, L.K.; Bryce, P.J. TGF-β1 limits the onset of innate lung inflammation by promoting mast cell-derived IL-6. J. Immunol. 2013 , 190 , 5731–5738. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Terada, T. Stromal mast cells and nerve fibers in various chronic liver diseases: Relevance to hepatic fibrosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999 , 94 , 1923–1932. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Terada, T. Mast cell subpopulations in chronic inflammatory hepatobiliary diseases. Liver 2000 , 20 , 152–156. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mangan, P.R.; Harrington, L.E.; O’Quinn, D.B.; Helms, W.S.; Bullard, D.C.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.D.; Wahl, S.M.; Schoeb, T.R.; Weaver, C.T. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature 2006 , 441 , 231–234. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006 , 441 , 235–238. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kirshenbaum, A.S.; Akin, C.; Wu, Y.; Rottem, M.; Goff, J.P.; Beaven, M.A.; Rao, V.K.; Metcalfe, D.D. Characterization of novel stem cell factor responsive human mast cell lines LAD 1 and 2 established from a patient with mast cell sarcoma/leukemia; activation following aggregation of FceRI or FcgRI. Leuk. Res. 2003 , 27 , 677–682. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Haughian, J.M.; Pinto, M.P.; Harrell, J.C.; Bliesner, B.S.; Joensuu, K.M.; Dye, W.W.; Sartorius, C.A.; Tan, A.C.; Heikkilä, P.; Perou, C.M.; et al. Maintenance of hormone responsiveness in luminal breast cancers by suppression of notch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012 , 109 , 2742–2747. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Lyons, D. Regulators of Mast Cell Activation; Scholarship & Creative Works @ Digital UNC. 2023. Available online: https://digscholarship.unco.edu/dissertations/960/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Protocol—Cell Surface Flow Cytometry Staining Protocol. Available online: https://www.biolegend.com/fr-ch/protocols/cell-surface-flow-cytometry-staining-protocol (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Vita, A.A.; Pullen, N.A. Exploring the mechanism of berberine-mediated T fh cell immunosuppression. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022 , 105 , 154343. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Belitskaya-Levy. R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform [Dataset]. In Expression Data from Breast Samples of Postmenopausal Women ; 2023; Available online: https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Russo. R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform [Dataset]. In Defining the Genomic Signature of the Parous Breast ; 2023; Available online: https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Russo. R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform [Dataset]. In Genomic Signature of Parity in the Breast of Premenopausal Women ; 2023; Available online: https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Gruvberger-Saal. R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform [Dataset]. In Clinical Associations of ESR2 (Estrogen Receptor Beta; ERÎ2) Expression across Thousands of Primary Breast Tumors ; 2022; Available online: https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Brown. R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform [Dataset]. In Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Identify Novel Subtypes and Targets of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer ; 2016; Available online: https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Sinn. R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform [Dataset]. In A Robust 18-Gene Predictor for Sensitivity to Endocrine Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer ; 2019; Available online: https://hgserver1.amc.nl/cgi-bin/r2/main.cgi (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Nagata, Y.; Suzuki, R. FcεRI: A Master Regulator of Mast Cell Functions. Cells 2022 , 11 , 622. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Fonseca, J.E.; Santos, M.J.; Canhao, H.; Choi, E. Interleukin-6 as a key player in systemic inflammation and joint destruction. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009 , 8 , 538–542. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chaudhury, A.; Howe, P.H. The tale of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) signaling: A soigné enigma. IUBMB Life 2009 , 61 , 929–939. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gruber, B.L.; Marchese, M.J.; Kew, R.R. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 mediates mast cell chemotaxis. J. Immunol. 1994 , 152 , 5860–5867. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kyritsi, K.; Kennedy, L.; Meadows, V.; Hargrove, L.; Demieville, J.; Pham, L.; Sybenga, A.; Kundu, D.; Cerritos, K.; Meng, F.; et al. Retracted: Mast Cells Induce Ductular Reaction Mimicking Liver Injury in Mice Through Mast Cell-Derived Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Signaling. Hepatology 2021 , 73 , 2397–2410. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Helby, J.; Bojesen, S.E.; Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G. IgE and risk of cancer in 37 747 individuals from the general population. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2015 , 26 , 1784–1790. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Singer, J.; Achatz-Straussberger, G.; Bentley-Lukschal, A.; Fazekas-Singer, J.; Achatz, G.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. AllergoOncology: High innate IgE levels are decisive for the survival of cancer-bearing mice. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019 , 12 , 100044. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, G.; Jianzhong, C.; Zheng, Y. Decreased Level of IgE is Associated with Breast Cancer and Allergic Diseases. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016 , 22 , 587–597. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- McCraw, A.J.; Chauhan, J.; Bax, H.J.; Stavraka, C.; Osborn, G.; Grandits, M.; López-Abente, J.; Josephs, D.H.; Spicer, J.; Wagner, G.K.; et al. Insights from IgE Immune Surveillance in Allergy and Cancer for Anti-Tumour IgE Treatments. Cancers 2021 , 13 , 4460. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gomez, G. Current Strategies to Inhibit High Affinity FcεRI-Mediated Signaling for the Treatment of Allergic Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019 , 10 , 175. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A. Why Most Published Research Findings Are False. PLoS Med. 2005 , 2 , e124. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Joober, R.; Schmitz, N.; Annable, L.; Boksa, P. Publication bias: What are the challenges and can they be overcome? J. Psychiatry Neurosci. JPN 2012 , 37 , 149–152. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Primer Name | 5′-3′ Sequence | Primer Length |
|---|---|---|
| FceRIa-F | ACTGTACGGGCAAAGTGTGG | 81 |
| FceRIa-R | ACTTCTCACGCGGAGCTTTT | 81 |
| FceRIb-F | CCTCCAGTGCACCTGACATT | 149 |
| FceRIb-R | ATGTCCGCCATGTCTGCTTT | 149 |
| FceRIg-F | GCCGTGATCTTGTTCTTGCTC | 78 |
| FceRIg-R | GCCTTTCGGACCTGGATCTT | 78 |
| Author Name | Tissue Type | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|
| Belitskaya-Levy | Postmenopausal Normal Breast | 107 |
| Russo | Nulli-parous Normal Breast | 113 |
| Russo | Full-term Pregnancy Normal Breast | 109 |
| Gruvberger-Saal | Primary Tumor Breast | 3207 |
| Brown | TNBC Tumor Breast | 198 |
| Sinn | Tumor Breast Metastatic | 1108 |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Ashbaugh, A.M.; Lyons, D.O.; Keyser, C.M.; Pullen, N.A. Unexpected Expression and Function of FcεRI in Immortalized Breast Cancer Cells: A Cautionary Null Study. Cells 2024 , 13 , 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161399
Ashbaugh AM, Lyons DO, Keyser CM, Pullen NA. Unexpected Expression and Function of FcεRI in Immortalized Breast Cancer Cells: A Cautionary Null Study. Cells . 2024; 13(16):1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161399
Ashbaugh, Alexandria M., David O. Lyons, Carianna M. Keyser, and Nicholas A. Pullen. 2024. "Unexpected Expression and Function of FcεRI in Immortalized Breast Cancer Cells: A Cautionary Null Study" Cells 13, no. 16: 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161399
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
August 22, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Novel AI algorithm assists in breast cancer screening
by University of Eastern Finland
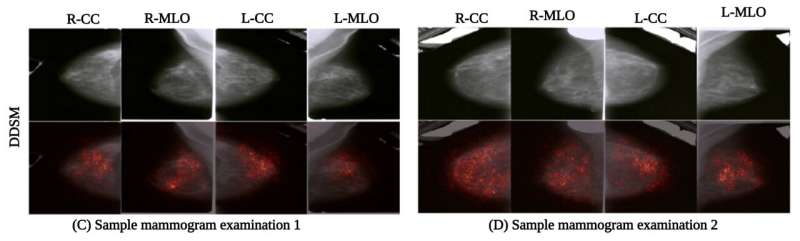
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have developed a novel artificial intelligence-based algorithm, MV-DEFEAT, to improve mammogram density assessment. This development holds promise for transforming radiological practices by enabling more precise diagnoses. The study is published in IEEE Access .
High breast tissue density is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, and breast tissue density can be estimated from mammograms. The accurate assessment of mammograms is crucial for effective breast cancer screening, yet challenges such as variability in radiological evaluations and a global shortage of radiologists complicate these efforts.
The MV-DEFEAT algorithm aims to address these issues by incorporating deep learning techniques that evaluate multiple mammogram views at the same time for mammogram density assessment, mirroring the decision-making process of radiologists.
The research team involved with AI in cancer research consists of Doctoral Researcher Gudhe Raju, Professor Arto Mannermaa and Senior Researcher Hamid Behravan.
In the present study, they employed an innovative multi-view deep evidential fusion approach. Their method leverages elements of the Dempster-Shafer evidential theory and subjective logic to assess mammogram images from multiple views, thus providing a more comprehensive analysis.
MV-DEFEAT showed remarkable improvements over existing approaches. It demonstrates a significant improvement in mammogram screening accuracy by automatically and reliably quantifying the density and distribution of dense breast tissue within mammograms.
For instance, in the public VinDr-Mammo dataset which consists of over 10,000 mammograms, the algorithm has achieved an impressive 50.78% improvement in distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors over the existing multi-view approach.
Interestingly, the algorithm's effectiveness persisted across different datasets, reflecting its robust performance to adapt to diverse patient demographics.
The study utilized extensive data from four open-source datasets, enhancing the algorithm's applicability and accuracy across different populations. Such capabilities underline the importance of AI-based approaches in medical diagnostics.
Furthermore, while MV-DEFEAT significantly aids in breast cancer screening, the team at the University of Eastern Finland emphasizes the need for continued refinement and validation of the algorithm to ensure its reliability and efficacy in clinical settings .
These promising results pave the way for the use of AI in enhancing diagnostic processes, potentially leading to earlier detection and better patient outcomes in breast cancer care.
"To fully integrate AI like MV-DEFEAT into clinical practice , it is crucial to build trust among health care professionals through rigorous testing and validation. Indeed, our next steps involve further validation studies to establish MV-DEFEAT as a reliable tool for breast cancer diagnostics in Finland," says Doctoral Researcher Raju Gudhe of the University of Eastern Finland.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Study identifies metabolic switch essential for generation of memory T cells and anti-tumor immunity
19 hours ago

Multiple sclerosis appears to protect against Alzheimer's disease
Aug 23, 2024

Good sleep habits important for overweight adults, study suggests

Mediterranean diet supplement can affect epigenetics associated with healthy aging

New method for quantifying boredom in the body during temporary stress

Cancer researchers develop new method that uses internal clock inside tumor cells to optimize therapies

Strength training activates cellular waste disposal, interdisciplinary research reveals

Being a 'weekend warrior' could be as good for brain health as exercising throughout the week
Simple blood test for Alzheimer's disease could change how the disease is detected and diagnosed

Chlamydia can settle in the intestine, organoid experiments reveal
Related stories.

How new FDA rules on breast density could affect mammogram results
Aug 20, 2024
What is a mammogram, and why are they important?
Oct 24, 2022
Consumer Health: Are you due for a mammogram?
Oct 18, 2021

Mayo Clinic Minute: Determining if you have dense breasts
Oct 21, 2021

Age, race impact AI performance on digital mammograms, study finds
May 21, 2024
Study shows combining AI models improves breast cancer risk assessment
Aug 29, 2023
Recommended for you

AI platform enhances lung cancer diagnosis accuracy

Detective algorithm predicts best drugs for genetic disorders and cancer
Aug 22, 2024

Novel PET/CT technique accurately detects neuroblastoma in children with short scan time and no anesthesia
Aug 21, 2024
Can AI pick IVF embryos as well as a human? First randomized controlled trial shows promise

Generative AI can not yet reliably read and extract information from clinical notes in medical records, finds study
Aug 19, 2024

Worldwide machine learning contest advances wearable tech for Parkinson's disease
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
‘Boy Meets World’ Star Danielle Fishel Reveals Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Fishel shared her diagnosis while also issuing an important public service announcement.

Danielle Fishel is opening up about her recent health scare—a breast cancer diagnosis.
During the Aug. 19 episode of her Pod Meets World podcast, Fishel shared with her co-hosts, fellow Boy Meets World castmates Rider Strong and Will Friedle , that she was recently diagnosed with breast cancer.
“I was recently diagnosed with DCIS, which stands for ductal carcinoma in situ, which is a form of breast cancer,” the 43-year-old disclosed.
“It is very, very, very early. It’s technically stage zero. To be specific—just because I like too much information all the time—I was diagnosed with high-grade DCIS with micro-invasion.”
Fishel assured fans that she was “going to be fine” and planned to have surgery to remove the cancer before undergoing a series of follow-up treatments.
“I’ve had to make a lot of decisions over the last couple of days,” she said, before adding that she initially planned on only telling her inner circle. She thought she’d prefer to “suffer in silence” and “suck it up,” only sharing with others after she’d beaten it.
Fishel, who first only told her husband, Jensen Karp —with whom she shares sons Adler , 5, and Keaton , 2—along with her parents and brother, said she decided to share her experience with listeners to encourage them to get mammograms regularly.
“The more people I talk to, the more people have had their own experiences—either being diagnosed with cancer themselves or knowing a family member who’s been diagnosed with cancer—and the world of resources and experiences that can be shared by sharing it, and things that can be learned.”
“The only reason I caught this cancer when it is still stage zero is because the day I got my text message that my yearly mammogram was due, I made the appointment,” Fishel shared.
Acknowledging just how easy it is to let preventative and routine check-ups slip by, Fishel pleaded with fans to hear her message.
“It would be so easy to say, ‘I don’t have time for that. I went to my mammogram last year; I was fine last year, I don’t need to go again this year. What are the chances? It’s gonna be fine; I was fine last year.’ And I didn’t. Instead, I was like, ‘Yeah, it’s time—gotta make that appointment,’ and they found it so, so, so early that I’m going to be fine,” she said.
“If it’s time for your appointment, if you’ve never had an appointment before, get in there. If you have to find out that you have cancer, find out when it’s at stage 0, if possible.”
Strong and Friedle both rallied around their friend and longtime colleague.
“It’s mind-boggling. Right now, my wife and I know four people—four friends—who are dealing with breast cancer,” said Strong, also encouraging fans to “get checked.”
“And for men, too—prostate exams and colonoscopies—these are all things that are super important, so don’t put them off,” Friedle added.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
What were the top 10 review topics? Rank. Topic in Cochrane format. Topic question in lay terms. 1. Omission of whole breast irradiation for postmenopausal women with early breast cancer. Can radiotherapy be safely omitted in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer? 2. Platinum-containing regimens for neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy in ...
Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. "Breast cancer and hormone replacement therapy: collaborative reanalysis of data from 51 epidemiological studies of 52 705 women with breast cancer and 108 411 women without breast cancer.". The Lancet 350.9084 (1997): 1047-1059. 1657.
Breast cancer is currently one of the most prevalently diagnosed cancers and the 5th cause of cancer-related deaths with an estimated number of 2.3 million new cases worldwide according to ... Korde L.A. Genetics of breast cancer: A topic in evolution. Ann. Oncol. 2015; 26:1291-1299. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv022. [PMC free article] ...
Breast cancer (BC) is a highly prevalent malignancy worldwide, with complex pathogenesis and treatment challenges. Research reveals that methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) is widely involved in the pathogenesis... Dongqiong Xiao, Mingfu Zhang, Yi Qu and Xiaojuan Su. Breast Cancer Research 2024 26 :110.
knowledge and beliefs about breast cancer (Hall, Pfriemer, & Wimberley, 2007). A higher proportion of Hispanic/Latino women experience a lower quality of life (QoL) than women from other racial groups; an observation that is associated with late-stage breast cancer diagnosis in Hispanic/Latino women (Graves et al., 2012). Such lower
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in women in the world. Breast cancer patients account for as much as 36% of oncological patients. An estimated 2.089 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer in 2018 [, ]. The incidence of this malignant tumor is increasing in all regions of the world, but the highest incidence occurs in ...
Collectively, this work contributes novel findings about the breast cancer immune microenvironment that may aid in precision medicine approaches for breast cancer prevention and intervention, and highlights the importance of diversity in impactful and equitable clinical research. Date of publication. 2022; Keyword. Pathology; breast cancer ...
Mammography can detect breast cancer at the asymptomatic phase with around 85% sensitivity and around 95% specificity (19). Since 2009 the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends breast cancer screening with biennial mammograms for women age 50 to 74 years old (18, 20).
Dr. Melissa Goldsmith College of Nursing Abstract. Purpose: The purpose of this thesis is to develop best-practice recommendations for nurses and. o use when caring for patient. have the BRCA gene mutations. kground: The BRCA gene mutations greatly increase a woman's risk of dev. loping cancerin her life.
This article presents a comprehensive review of the Breast Cancer literature examining epidemiology, diagnosis, pathology, "benign" breast disease, breast carcinoma in situ syndromes, staging, and post-treatment surveillance among many topics. Breast cancer remains the most commonly occurring cancer in women. Breast cancer detection, treatment ...
Diet and breast cancer - A recent study connected eating the Mediterranean Diet to lower risk. And previous research has pointed to carotenoids - the family of orange- and red-colored phytonutrients in such foods as carrots and tomatoes - linking to lower risk of breast cancers. Carotenoid-rich foods and the Mediterranean Diet are packed ...
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), comprised predominantly of the basal-like (BBC) and claudin-low (CLBC) intrinsic subtypes, is a proliferative, invasive disease that accounts for 15-20% of breast cancer cases. Unlike with other breast cancer subtypes, TNBC treatment modalities are generally limited to surgery, radiation, and cytotoxic ...
With the exponential increase in new cases coupled with an increased mortality rate, cancer has ranked as the second most prevalent cause of death in the world. Early detection is paramount for suitable diagnosis and effective treatment of different kinds of cancers, but this is limited to the accuracy and sensitivity of available diagnostic imaging methods. Breast cancer is the most widely ...
Breast Cancer information for young women -A project for Terveysnetti Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women, after skin cancer. It is most commonly diagnosed in women aged 55 to 64. It is estimated that around 1.67 million new cases of breast cancer occurred among women worldwide in 2012 (most
Posted: January 20, 2023. Many young women who are diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer want to become pregnant in the future. New research suggests that these women may be able to pause their hormone therapy for up to 2 years as they try to get pregnant without raising the risk of a recurrence in the short term.
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 PDF. Deconvolution of the phosphorylation patterns of replication protein A by the DNA damage response to breaks, Kerry D. Brader. PDF. Modeling malignant breast cancer occurrence and survival in black and white women, Michael Gleason. PDF. The role of dna methyltransferases in myc-induced lymphomagenesis, Ryan A ...
Create a spot-on reference in APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, and other styles. Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Breast cancer, mastectomy, nursing care.'. Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button.
breast[Porter, 1998] ridding the body of this excess of black bile involved venesection, purgation, cupping, leaching, enemas and bizarre diets (many "alternative" treatments of breast cancer to this day are in fact a form of neo-galenism). In the mid 19th Century the humoral theory of breast cancer was overturned by a mechanistic model which
Treatment for inflammatory breast cancer and overall survival. CDK4/6 inhibitors and treatment for metastatic breast cancer. Elacestrant (Orserdu) and treatment for metastatic breast cancer. PI3 kinase inhibitors and AKT inhibitors for metastatic breast cancer treatment. Trastuzumab (Herceptin) and treatment for metastatic breast cancer.
Objective: The aim of this study was to perform a bibliometric analysis of the 100 most cited articles related to breast cancer. Materials and Methods: The research was done on the Web of Science (WOS) database. Only research articles were included in the study. Results were obtained by typing the term "breast cancer" in the WOS Search box.
The core project in this thesis is the translational study PGSNPS, which aimed to investigate the pharmacogenetics of breast cancer chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting. Blood or saliva samples were collected from over 2300 patients, who were recruited during a 4 year period. The trial design was adapted to a GWAS approach.
Some Ideas for Topics: Involvement of different receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival. Identification of the breast cancer susceptibility gene. Relationship of human breast cancer and ovarian cancer. Lymphatic mapping for breast cancer. Prospective identification of tumor-causing breast ...
A study led by investigators at the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found that Manuka honey could potentially be an alternative, natural option for breast cancer prevention and ...
Dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy can improve survival for patients with high-risk breast cancer, according to a team of researchers that includes the Karolinska Institutet. The international ...
Return to work two years after a breast cancer diagnosis is associated with higher cognitive speed performance before and after treatment, according to a study published online Aug. 19 in JAMA ...
Based on Malaysia's 2016 National Cancer Registry, a total of 21,634 cases of female breast cancer were diagnosed over a period of 4 years between 2012 and 2016 compared with 18,206 cases in the 2007-2011 report. Breast cancer is the most common cancer and has accounted for 34.1% of all cancer cases among women in Malaysia.
A new study found that Manuka honey could potentially be an alternative, natural option for breast cancer prevention and treatment -- particularly for estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer ...
The high-affinity IgE receptor, FcεRI, is typically associated with type 2 effectors such as mast cells (MC). The relatively unique expression profile of FcεRI and accumulating evidence from pre-clinical and clinical settings, such as MC interactions with tumors, have led us to study MCs as a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Our work identified MCs interacting with tumor cells ...
High breast tissue density is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, and breast tissue density can be estimated from mammograms. The accurate assessment of mammograms is crucial for ...
Image Credit: Getty Images. Danielle Fishel is opening up about her recent health scare—a breast cancer diagnosis.. During the Aug. 19 episode of her Pod Meets World podcast, Fishel shared with ...