

Assignment of Contract
Jump to section, what is an assignment of contract.
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the approved incoming party.
How Does Assignment of Contract Work?
An assignment of contract is simpler than you might think.
The process starts with an existing contract party who wishes to transfer their contractual obligations to a new party.
When this occurs, the existing contract party must first confirm that an assignment of contract is permissible under the legally binding agreement . Some contracts prohibit assignments of contract altogether, and some require the other parties of the agreement to agree to the transfer. However, the general rule is that contracts are freely assignable unless there is an explicit provision that says otherwise.
In other cases, some contracts allow an assignment of contract without any formal notification to other contract parties. If this is the case, once the existing contract party decides to reassign his duties, he must create a “Letter of Assignment ” to notify any other contract signers of the change.
The Letter of Assignment must include details about who is to take over the contractual obligations of the exiting party and when the transfer will take place. If the assignment is valid, the assignor is not required to obtain the consent or signature of the other parties to the original contract for the valid assignment to take place.
Check out this article to learn more about how assigning a contract works.
Contract Assignment Examples
Contract assignments are great tools for contract parties to use when they wish to transfer their commitments to a third party. Here are some examples of contract assignments to help you better understand them:
Anna signs a contract with a local trash company that entitles her to have her trash picked up twice a week. A year later, the trash company transferred her contract to a new trash service provider. This contract assignment effectively makes Anna’s contract now with the new service provider.
Hasina enters a contract with a national phone company for cell phone service. The company goes into bankruptcy and needs to close its doors but decides to transfer all current contracts to another provider who agrees to honor the same rates and level of service. The contract assignment is completed, and Hasina now has a contract with the new phone company as a result.
Here is an article where you can find out more about contract assignments.
Assignment of Contract in Real Estate
Assignment of contract is also used in real estate to make money without going the well-known routes of buying and flipping houses. When real estate LLC investors use an assignment of contract, they can make money off properties without ever actually buying them by instead opting to transfer real estate contracts .
This process is called real estate wholesaling.
Real Estate Wholesaling
Real estate wholesaling consists of locating deals on houses that you don’t plan to buy but instead plan to enter a contract to reassign the house to another buyer and pocket the profit.
The process is simple: real estate wholesalers negotiate purchase contracts with sellers. Then, they present these contracts to buyers who pay them an assignment fee for transferring the contract.
This process works because a real estate purchase agreement does not come with the obligation to buy a property. Instead, it sets forth certain purchasing parameters that must be fulfilled by the buyer of the property. In a nutshell, whoever signs the purchase contract has the right to buy the property, but those rights can usually be transferred by means of an assignment of contract.
This means that as long as the buyer who’s involved in the assignment of contract agrees with the purchasing terms, they can legally take over the contract.
But how do real estate wholesalers find these properties?
It is easier than you might think. Here are a few examples of ways that wholesalers find cheap houses to turn a profit on:
- Direct mailers
- Place newspaper ads
- Make posts in online forums
- Social media posts
The key to finding the perfect home for an assignment of contract is to locate sellers that are looking to get rid of their properties quickly. This might be a family who is looking to relocate for a job opportunity or someone who needs to make repairs on a home but can’t afford it. Either way, the quicker the wholesaler can close the deal, the better.
Once a property is located, wholesalers immediately go to work getting the details ironed out about how the sale will work. Transparency is key when it comes to wholesaling. This means that when a wholesaler intends to use an assignment of contract to transfer the rights to another person, they are always upfront about during the preliminary phases of the sale.
In addition to this practice just being good business, it makes sure the process goes as smoothly as possible later down the line. Wholesalers are clear in their intent and make sure buyers know that the contract could be transferred to another buyer before the closing date arrives.
After their offer is accepted and warranties are determined, wholesalers move to complete a title search . Title searches ensure that sellers have the right to enter into a purchase agreement on the property. They do this by searching for any outstanding tax payments, liens , or other roadblocks that could prevent the sale from going through.
Wholesalers also often work with experienced real estate lawyers who ensure that all of the legal paperwork is forthcoming and will stand up in court. Lawyers can also assist in the contract negotiation process if needed but often don’t come in until the final stages.
If the title search comes back clear and the real estate lawyer gives the green light, the wholesaler will immediately move to locate an entity to transfer the rights to buy.
One of the most attractive advantages of real estate wholesaling is that very little money is needed to get started. The process of finding a seller, negotiating a price, and performing a title search is an extremely cheap process that almost anyone can do.
On the other hand, it is not always a positive experience. It can be hard for wholesalers to find sellers who will agree to sell their homes for less than the market value. Even when they do, there is always a chance that the transferred buyer will back out of the sale, which leaves wholesalers obligated to either purchase the property themselves or scramble to find a new person to complete an assignment of contract with.
Learn more about assignment of contract in real estate by checking out this article .
Who Handles Assignment of Contract?
The best person to handle an assignment of contract is an attorney. Since these are detailed legal documents that deal with thousands of dollars, it is never a bad idea to have a professional on your side. If you need help with an assignment of contract or signing a business contract , post a project on ContractsCounsel. There, you can connect with attorneys who know everything there is to know about assignment of contract amendment and can walk you through the whole process.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Meet some of our Lawyers
I am a lawyer who helps small businesses, nonprofits, and startups with a wide variety of agreements, corporate formation, and corporate governance. I earned my BA from Tulane University and my JD from the University of Chicago Law School. Before starting my own practice, I worked at an international law firm in New York City. Outside of work, I am on the board of the nonprofit Seattle REconomy (which runs the NE Seattle and Shoreline tool libraries) and I enjoy gardening, baking bread, and outdoor activities with my spouse and two dogs.
Stirk Law is a law firm based in London that advises on dispute resolution, commercial and corporate arrangements, employment and private wealth. We are experts in our areas and experienced in advising on complex and high value matters in the UK and internationally. We have extensive onshore and offshore experience across a variety of areas such as the administration of trusts together with complex fraud and trust disputes. Our expertise includes the conduct of significant and high-value cases valued at up to in excess of £1 billion over a combined 40 years of legal practice in England, Jersey and Guernsey. As well as having a large international network, we work closely with a corporate investigations and risk advisory business based in London and Vienna. Together we can deliver a holistic service for cases involving fraud, dissipation of assets or other illegal activity.
Talin has over a decade of focused experience in business and international law. She is fiercely dedicated to her clients, thorough, detail-oriented, and gets the job done.
Results oriented business attorney focusing on the health care sector. Formerly worked in Biglaw doing large multi-million dollar mergers and acquisitions, financing, and outside corporate counsel. I brought my skillset to the small firm market, provide the highest level of professionalism and sophistication to smaller and startup companies.
Mr. LaRocco's focus is business law, corporate structuring, and contracts. He has a depth of experience working with entrepreneurs and startups, including some small public companies. As a result of his business background, he has not only acted as general counsel to companies, but has also been on the board of directors of several and been a business advisor and strategist. Some clients and projects I have recently done work for include hospitality consulting companies, web development/marketing agency, a governmental contractor, e-commerce consumer goods companies, an online apps, a music file-sharing company, a company that licenses its photos and graphic images, a video editing company, several SaaS companies, a merchant processing/services company, a financial services software company that earned a licensing and marketing contract with Thomson Reuters, manufacturing companies, and a real estate software company.
12 Year PQE Lawyer with wide experience in sports, media and tech.
Stan provides legal services to small to medium-sized clients in the New England region, and throughout the U.S. and abroad. His clients are involved in a variety of business sectors, including software development, e-commerce, investment management and advising, health care, manufacturing, biotechnology, telecommunications, retailing, and consulting and other services. Stan focuses on the unique needs of each of his clients, and seeks to establish long term relationships with them by providing timely, highly professional services and practical business judgment. Each client's objectives, business and management styles are carefully considered to help him provide more focused and relevant services. Stan also acts as an outsourced general counsel for some of his clients for the general management of their legal function, including the establishment of budgets, creation of internal compliance procedures, and the oversight of litigation or other outside legal services.
Find the best lawyer for your project

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
Need help with a Contract Agreement?
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
CONTRACT LAWYERS BY TOP CITIES
- Austin Contracts Lawyers
- Boston Contracts Lawyers
- Chicago Contracts Lawyers
- Dallas Contracts Lawyers
- Denver Contracts Lawyers
- Houston Contracts Lawyers
- Los Angeles Contracts Lawyers
- New York Contracts Lawyers
- Phoenix Contracts Lawyers
- San Diego Contracts Lawyers
- Tampa Contracts Lawyers
ASSIGNMENT OF CONTRACT LAWYERS BY CITY
- Austin Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Boston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Chicago Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Dallas Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Denver Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Houston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Los Angeles Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- New York Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Phoenix Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- San Diego Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Tampa Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
How It Works
Want to speak to someone.
Get in touch below and we will schedule a time to connect!
Find lawyers and attorneys by city
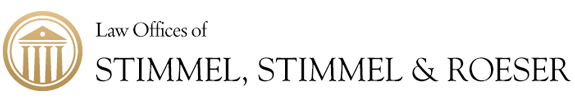
- assignments basic law
Assignments: The Basic Law
The assignment of a right or obligation is a common contractual event under the law and the right to assign (or prohibition against assignments) is found in the majority of agreements, leases and business structural documents created in the United States.
As with many terms commonly used, people are familiar with the term but often are not aware or fully aware of what the terms entail. The concept of assignment of rights and obligations is one of those simple concepts with wide ranging ramifications in the contractual and business context and the law imposes severe restrictions on the validity and effect of assignment in many instances. Clear contractual provisions concerning assignments and rights should be in every document and structure created and this article will outline why such drafting is essential for the creation of appropriate and effective contracts and structures.
The reader should first read the article on Limited Liability Entities in the United States and Contracts since the information in those articles will be assumed in this article.
Basic Definitions and Concepts:
An assignment is the transfer of rights held by one party called the “assignor” to another party called the “assignee.” The legal nature of the assignment and the contractual terms of the agreement between the parties determines some additional rights and liabilities that accompany the assignment. The assignment of rights under a contract usually completely transfers the rights to the assignee to receive the benefits accruing under the contract. Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court , 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950).
An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment in the underlying contract or lease. Where assignments are permitted, the assignor need not consult the other party to the contract but may merely assign the rights at that time. However, an assignment cannot have any adverse effect on the duties of the other party to the contract, nor can it diminish the chance of the other party receiving complete performance. The assignor normally remains liable unless there is an agreement to the contrary by the other party to the contract.
The effect of a valid assignment is to remove privity between the assignor and the obligor and create privity between the obligor and the assignee. Privity is usually defined as a direct and immediate contractual relationship. See Merchants case above.
Further, for the assignment to be effective in most jurisdictions, it must occur in the present. One does not normally assign a future right; the assignment vests immediate rights and obligations.
No specific language is required to create an assignment so long as the assignor makes clear his/her intent to assign identified contractual rights to the assignee. Since expensive litigation can erupt from ambiguous or vague language, obtaining the correct verbiage is vital. An agreement must manifest the intent to transfer rights and can either be oral or in writing and the rights assigned must be certain.
Note that an assignment of an interest is the transfer of some identifiable property, claim, or right from the assignor to the assignee. The assignment operates to transfer to the assignee all of the rights, title, or interest of the assignor in the thing assigned. A transfer of all rights, title, and interests conveys everything that the assignor owned in the thing assigned and the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor. Knott v. McDonald’s Corp ., 985 F. Supp. 1222 (N.D. Cal. 1997)
The parties must intend to effectuate an assignment at the time of the transfer, although no particular language or procedure is necessary. As long ago as the case of National Reserve Co. v. Metropolitan Trust Co ., 17 Cal. 2d 827 (Cal. 1941), the court held that in determining what rights or interests pass under an assignment, the intention of the parties as manifested in the instrument is controlling.
The intent of the parties to an assignment is a question of fact to be derived not only from the instrument executed by the parties but also from the surrounding circumstances. When there is no writing to evidence the intention to transfer some identifiable property, claim, or right, it is necessary to scrutinize the surrounding circumstances and parties’ acts to ascertain their intentions. Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998)
The general rule applicable to assignments of choses in action is that an assignment, unless there is a contract to the contrary, carries with it all securities held by the assignor as collateral to the claim and all rights incidental thereto and vests in the assignee the equitable title to such collateral securities and incidental rights. An unqualified assignment of a contract or chose in action, however, with no indication of the intent of the parties, vests in the assignee the assigned contract or chose and all rights and remedies incidental thereto.
More examples: In Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs ., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998), the court held that the assignee of a party to a subordination agreement is entitled to the benefits and is subject to the burdens of the agreement. In Florida E. C. R. Co. v. Eno , 99 Fla. 887 (Fla. 1930), the court held that the mere assignment of all sums due in and of itself creates no different or other liability of the owner to the assignee than that which existed from the owner to the assignor.
And note that even though an assignment vests in the assignee all rights, remedies, and contingent benefits which are incidental to the thing assigned, those which are personal to the assignor and for his sole benefit are not assigned. Rasp v. Hidden Valley Lake, Inc ., 519 N.E.2d 153, 158 (Ind. Ct. App. 1988). Thus, if the underlying agreement provides that a service can only be provided to X, X cannot assign that right to Y.
Novation Compared to Assignment:
Although the difference between a novation and an assignment may appear narrow, it is an essential one. “Novation is a act whereby one party transfers all its obligations and benefits under a contract to a third party.” In a novation, a third party successfully substitutes the original party as a party to the contract. “When a contract is novated, the other contracting party must be left in the same position he was in prior to the novation being made.”
A sublease is the transfer when a tenant retains some right of reentry onto the leased premises. However, if the tenant transfers the entire leasehold estate, retaining no right of reentry or other reversionary interest, then the transfer is an assignment. The assignor is normally also removed from liability to the landlord only if the landlord consents or allowed that right in the lease. In a sublease, the original tenant is not released from the obligations of the original lease.
Equitable Assignments:
An equitable assignment is one in which one has a future interest and is not valid at law but valid in a court of equity. In National Bank of Republic v. United Sec. Life Ins. & Trust Co. , 17 App. D.C. 112 (D.C. Cir. 1900), the court held that to constitute an equitable assignment of a chose in action, the following has to occur generally: anything said written or done, in pursuance of an agreement and for valuable consideration, or in consideration of an antecedent debt, to place a chose in action or fund out of the control of the owner, and appropriate it to or in favor of another person, amounts to an equitable assignment. Thus, an agreement, between a debtor and a creditor, that the debt shall be paid out of a specific fund going to the debtor may operate as an equitable assignment.
In Egyptian Navigation Co. v. Baker Invs. Corp. , 2008 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 30804 (S.D.N.Y. Apr. 14, 2008), the court stated that an equitable assignment occurs under English law when an assignor, with an intent to transfer his/her right to a chose in action, informs the assignee about the right so transferred.
An executory agreement or a declaration of trust are also equitable assignments if unenforceable as assignments by a court of law but enforceable by a court of equity exercising sound discretion according to the circumstances of the case. Since California combines courts of equity and courts of law, the same court would hear arguments as to whether an equitable assignment had occurred. Quite often, such relief is granted to avoid fraud or unjust enrichment.
Note that obtaining an assignment through fraudulent means invalidates the assignment. Fraud destroys the validity of everything into which it enters. It vitiates the most solemn contracts, documents, and even judgments. Walker v. Rich , 79 Cal. App. 139 (Cal. App. 1926). If an assignment is made with the fraudulent intent to delay, hinder, and defraud creditors, then it is void as fraudulent in fact. See our article on Transfers to Defraud Creditors .
But note that the motives that prompted an assignor to make the transfer will be considered as immaterial and will constitute no defense to an action by the assignee, if an assignment is considered as valid in all other respects.
Enforceability of Assignments:
Whether a right under a contract is capable of being transferred is determined by the law of the place where the contract was entered into. The validity and effect of an assignment is determined by the law of the place of assignment. The validity of an assignment of a contractual right is governed by the law of the state with the most significant relationship to the assignment and the parties.
In some jurisdictions, the traditional conflict of laws rules governing assignments has been rejected and the law of the place having the most significant contacts with the assignment applies. In Downs v. American Mut. Liability Ins. Co ., 14 N.Y.2d 266 (N.Y. 1964), a wife and her husband separated and the wife obtained a judgment of separation from the husband in New York. The judgment required the husband to pay a certain yearly sum to the wife. The husband assigned 50 percent of his future salary, wages, and earnings to the wife. The agreement authorized the employer to make such payments to the wife.
After the husband moved from New York, the wife learned that he was employed by an employer in Massachusetts. She sent the proper notice and demanded payment under the agreement. The employer refused and the wife brought an action for enforcement. The court observed that Massachusetts did not prohibit assignment of the husband’s wages. Moreover, Massachusetts law was not controlling because New York had the most significant relationship with the assignment. Therefore, the court ruled in favor of the wife.
Therefore, the validity of an assignment is determined by looking to the law of the forum with the most significant relationship to the assignment itself. To determine the applicable law of assignments, the court must look to the law of the state which is most significantly related to the principal issue before it.
Assignment of Contractual Rights:
Generally, the law allows the assignment of a contractual right unless the substitution of rights would materially change the duty of the obligor, materially increase the burden or risk imposed on the obligor by the contract, materially impair the chance of obtaining return performance, or materially reduce the value of the performance to the obligor. Restat 2d of Contracts, § 317(2)(a). This presumes that the underlying agreement is silent on the right to assign.
If the contract specifically precludes assignment, the contractual right is not assignable. Whether a contract is assignable is a matter of contractual intent and one must look to the language used by the parties to discern that intent.
In the absence of an express provision to the contrary, the rights and duties under a bilateral executory contract that does not involve personal skill, trust, or confidence may be assigned without the consent of the other party. But note that an assignment is invalid if it would materially alter the other party’s duties and responsibilities. Once an assignment is effective, the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor and assumes all of assignor’s rights. Hence, after a valid assignment, the assignor’s right to performance is extinguished, transferred to assignee, and the assignee possesses the same rights, benefits, and remedies assignor once possessed. Robert Lamb Hart Planners & Architects v. Evergreen, Ltd. , 787 F. Supp. 753 (S.D. Ohio 1992).
On the other hand, an assignee’s right against the obligor is subject to “all of the limitations of the assignor’s right, all defenses thereto, and all set-offs and counterclaims which would have been available against the assignor had there been no assignment, provided that these defenses and set-offs are based on facts existing at the time of the assignment.” See Robert Lamb , case, above.
The power of the contract to restrict assignment is broad. Usually, contractual provisions that restrict assignment of the contract without the consent of the obligor are valid and enforceable, even when there is statutory authorization for the assignment. The restriction of the power to assign is often ineffective unless the restriction is expressly and precisely stated. Anti-assignment clauses are effective only if they contain clear, unambiguous language of prohibition. Anti-assignment clauses protect only the obligor and do not affect the transaction between the assignee and assignor.
Usually, a prohibition against the assignment of a contract does not prevent an assignment of the right to receive payments due, unless circumstances indicate the contrary. Moreover, the contracting parties cannot, by a mere non-assignment provision, prevent the effectual alienation of the right to money which becomes due under the contract.
A contract provision prohibiting or restricting an assignment may be waived, or a party may so act as to be estopped from objecting to the assignment, such as by effectively ratifying the assignment. The power to void an assignment made in violation of an anti-assignment clause may be waived either before or after the assignment. See our article on Contracts.
Noncompete Clauses and Assignments:
Of critical import to most buyers of businesses is the ability to ensure that key employees of the business being purchased cannot start a competing company. Some states strictly limit such clauses, some do allow them. California does restrict noncompete clauses, only allowing them under certain circumstances. A common question in those states that do allow them is whether such rights can be assigned to a new party, such as the buyer of the buyer.
A covenant not to compete, also called a non-competitive clause, is a formal agreement prohibiting one party from performing similar work or business within a designated area for a specified amount of time. This type of clause is generally included in contracts between employer and employee and contracts between buyer and seller of a business.
Many workers sign a covenant not to compete as part of the paperwork required for employment. It may be a separate document similar to a non-disclosure agreement, or buried within a number of other clauses in a contract. A covenant not to compete is generally legal and enforceable, although there are some exceptions and restrictions.
Whenever a company recruits skilled employees, it invests a significant amount of time and training. For example, it often takes years before a research chemist or a design engineer develops a workable knowledge of a company’s product line, including trade secrets and highly sensitive information. Once an employee gains this knowledge and experience, however, all sorts of things can happen. The employee could work for the company until retirement, accept a better offer from a competing company or start up his or her own business.
A covenant not to compete may cover a number of potential issues between employers and former employees. Many companies spend years developing a local base of customers or clients. It is important that this customer base not fall into the hands of local competitors. When an employee signs a covenant not to compete, he or she usually agrees not to use insider knowledge of the company’s customer base to disadvantage the company. The covenant not to compete often defines a broad geographical area considered off-limits to former employees, possibly tens or hundreds of miles.
Another area of concern covered by a covenant not to compete is a potential ‘brain drain’. Some high-level former employees may seek to recruit others from the same company to create new competition. Retention of employees, especially those with unique skills or proprietary knowledge, is vital for most companies, so a covenant not to compete may spell out definite restrictions on the hiring or recruiting of employees.
A covenant not to compete may also define a specific amount of time before a former employee can seek employment in a similar field. Many companies offer a substantial severance package to make sure former employees are financially solvent until the terms of the covenant not to compete have been met.
Because the use of a covenant not to compete can be controversial, a handful of states, including California, have largely banned this type of contractual language. The legal enforcement of these agreements falls on individual states, and many have sided with the employee during arbitration or litigation. A covenant not to compete must be reasonable and specific, with defined time periods and coverage areas. If the agreement gives the company too much power over former employees or is ambiguous, state courts may declare it to be overbroad and therefore unenforceable. In such case, the employee would be free to pursue any employment opportunity, including working for a direct competitor or starting up a new company of his or her own.
It has been held that an employee’s covenant not to compete is assignable where one business is transferred to another, that a merger does not constitute an assignment of a covenant not to compete, and that a covenant not to compete is enforceable by a successor to the employer where the assignment does not create an added burden of employment or other disadvantage to the employee. However, in some states such as Hawaii, it has also been held that a covenant not to compete is not assignable and under various statutes for various reasons that such covenants are not enforceable against an employee by a successor to the employer. Hawaii v. Gannett Pac. Corp. , 99 F. Supp. 2d 1241 (D. Haw. 1999)
It is vital to obtain the relevant law of the applicable state before drafting or attempting to enforce assignment rights in this particular area.
Conclusion:
In the current business world of fast changing structures, agreements, employees and projects, the ability to assign rights and obligations is essential to allow flexibility and adjustment to new situations. Conversely, the ability to hold a contracting party into the deal may be essential for the future of a party. Thus, the law of assignments and the restriction on same is a critical aspect of every agreement and every structure. This basic provision is often glanced at by the contracting parties, or scribbled into the deal at the last minute but can easily become the most vital part of the transaction.
As an example, one client of ours came into the office outraged that his co venturer on a sizable exporting agreement, who had excellent connections in Brazil, had elected to pursue another venture instead and assigned the agreement to a party unknown to our client and without the business contacts our client considered vital. When we examined the handwritten agreement our client had drafted in a restaurant in Sao Paolo, we discovered there was no restriction on assignment whatsoever…our client had not even considered that right when drafting the agreement after a full day of work.
One choses who one does business with carefully…to ensure that one’s choice remains the party on the other side of the contract, one must master the ability to negotiate proper assignment provisions.
Founded in 1939, our law firm combines the ability to represent clients in domestic or international matters with the personal interaction with clients that is traditional to a long established law firm.
Read more about our firm
© 2024, Stimmel, Stimmel & Roeser, All rights reserved | Terms of Use | Site by Bay Design
(404) 738-5471

Ultimate Checklist for Understanding Contract Assignment Rules
- February 28, 2024
- Moton Legal Group

In contracts, understanding assignment is key. Simply put, an assignment in contract law is when one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and responsibilities under a contract to another party (the assignee). This can include anything from leasing agreements to business operations. But why is this important? It’s because it allows for flexibility in business and personal dealings, a critical component in our world.
Here’s a quick rundown: – Contract Basics: The foundational agreements between parties. – Assignment Importance: Allowing the transfer of obligations and benefits to keep up with life’s changes.
Contracts are a staple in both personal and business worlds, acting as the backbone to many transactions and agreements encountered daily. Understanding the nuances, like assignments, can empower you to navigate these waters with confidence and ease. Whether you’re a business owner in the Southeast looking to expand or an individual managing personal agreements, grasp these basics, and you’re on the right path.
Understanding Contract Assignment
Contract Assignment sounds complicated, right? But, let’s break it down into simple terms. In contracts and legal agreements, knowing about assignment can save you a lot of headaches down the road. Whether you’re a business owner, a landlord, or just someone who deals with contracts, this is for you.
Legal Definition
At its core, contract assignment is about transferring rights or obligations under a contract from one party to another. Think of it as passing a baton in a relay race. The original party (the assignor) hands off their responsibilities or benefits to someone else (the assignee). But, there’s a twist – the race keeps going with the new runner without starting over.
Contract Law
In contract law, assignment comes into play in various ways. For example, if you’re a freelancer and you’ve agreed to complete a project but suddenly find yourself overbooked, you might assign that contract to another freelancer. This way, the job gets done, and your client is happy. However, not all contracts can be freely assigned. Some require the other party’s consent, and others can’t be assigned at all, especially if they involve personal skills or confidential trust.
Property Law
When it comes to property law, assignment often surfaces in landlord-tenant relationships. Say you’re renting a shop for your business, but you decide to move. If your lease allows it, you might assign your lease to another business. This means they take over your lease, stepping into your shoes, with all the rights and obligations that come with it.
The concept might seem straightforward, but there are important legal requirements and potential pitfalls to be aware of. For instance, an assignment could be prohibited by the contract itself, or it may significantly change the original deal’s terms in a way that’s not allowed. Plus, when you’re dealing with something that requires a unique skill set, like an artist or a consultant, those services typically can’t be passed on to someone else without agreement from all parties involved.
To navigate these complexities, understanding the fundamentals of assignment in contract law and property law is crucial. It ensures that when you’re ready to pass that baton, you’re doing it in a way that’s legal, effective, and doesn’t leave you tripping up before you reach the finish line.
The goal here is to make sure everyone involved understands what’s happening and agrees to it. That way, assignments can be a useful tool to manage your contracts and property agreements, keeping things moving smoothly even when changes come up.
For more detailed exploration on this topic, consider checking the comprehensive guide on Assignment (law)). This resource dives deeper into the nuances of contract assignment, offering insights and examples that can help clarify this complex area of law.
By grasping these basics, you’re well on your way to mastering the art of contract assignment. Whether you’re dealing with leases, business deals, or any agreement in between, knowing how to effectively assign a contract can be a game-changer.
Key Differences Between Assignment and Novation
When diving into contracts, two terms that often cause confusion are assignment and novation . While both deal with transferring obligations and rights under a contract, they are fundamentally different in several key aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in contract management or negotiation.
Rights Transfer
Assignment involves the transfer of benefits or rights from one party (the assignor) to another (the assignee). However, it’s important to note that only the benefits of the contract can be assigned, not the burdens. For instance, if someone has the right to receive payments under a contract, they can assign this right to someone else.
Novation , on the other hand, is more comprehensive. It involves transferring both the rights and obligations under a contract from one party to a new party. With novation, the original party is completely released from the contract, and a new contractual relationship is formed between the remaining and the new party. This is a key distinction because, in novation, all parties must agree to this new arrangement.
Obligations Transfer
Assignment doesn’t transfer the original party’s obligations under the contract. The assignor (the original party who had the rights under the contract) might still be liable if the assignee fails to fulfill the contract terms.
In contrast, novation transfers all obligations to the new party. Once a novation is complete, the new party takes over all rights and obligations, leaving the original party with no further legal liabilities or rights under the contract.
Written Agreement
While assignments can sometimes be informal or even verbal, novation almost always requires a written agreement. This is because novation affects more parties’ rights and obligations and has a more significant impact on the contractual relationship. A written agreement ensures that all parties are clear about the terms of the novation and their respective responsibilities.
In practice, the need for a written agreement in novation serves as a protection for all parties involved. It ensures that the transfer of obligations is clearly documented and legally enforceable.
For example, let’s say Alex agrees to paint Bailey’s house for $1,000. Later, Alex decides they can’t complete the job and wants Chris to take over. If Bailey agrees, they can sign a novation agreement where Chris agrees to paint the house under the same conditions. Alex is then relieved from the original contract, and Chris becomes responsible for completing the painting job.
Understanding the difference between assignment and novation is critical for anyone dealing with contracts. While both processes allow for the transfer of rights or obligations, they do so in different ways and with varying implications for all parties involved. Knowing when and how to use each can help ensure that your contractual relationships are managed effectively and legally sound.
For further in-depth information and real-life case examples on assignment in contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Next, we’ll delve into the legal requirements for a valid assignment, touching on express prohibition, material change, future rights, and the rare skill requirement. Understanding these will further equip you to navigate the complexities of contract assignments successfully.
Legal Requirements for a Valid Assignment
When dealing with assignment in contract law , it’s crucial to understand the legal backbone that supports a valid assignment. This ensures that the assignment stands up in a court of law if disputes arise. Let’s break down the must-know legal requirements: express prohibition, material change, future rights, and rare skill requirement.
Express Prohibition
The first stop on our checklist is to look for an express prohibition against assignment in the contract. This is a clause that outright states assignments are not allowed without the other party’s consent. If such language exists and you proceed with an assignment, you could be breaching the contract. Always read the fine print or have a legal expert review the contract for you.
Material Change
Next up is the material change requirement. The law states that an assignment cannot significantly alter the duties, increase the burdens, or impair the chances of the other party receiving due performance under the contract. For instance, if the contract involves personal services tailored to the specific party, assigning it to someone else might change the expected outcome, making such an assignment invalid.
Future Rights
Another important aspect is future rights . The rule here is straightforward: you can’t assign what you don’t have. This means that a promise to assign rights you may acquire in the future is generally not enforceable at present. An effective assignment requires that the rights exist at the time of the assignment.
Rare Skill Requirement
Lastly, let’s talk about the rare skill requirement . Some contracts are so specialized that they cannot be assigned to another party without compromising the contract’s integrity. This is often the case with contracts that rely on an individual’s unique skills or trust. Think of an artist commissioned for a portrait or a lawyer hired for their specialized legal expertise. In these scenarios, assignments are not feasible as they could severely impact the contract’s intended outcome.
Understanding these legal requirements is pivotal for navigating the complexities of assignment in contract law. By ensuring compliance with these principles, you can effectively manage contract assignments, safeguarding your interests and those of the other contracting party.
For anyone looking to delve deeper into the intricacies of contract law, you can explore detailed resources such as Assignment (law) on Wikipedia).
Moving forward, we’ll explore the common types of contract assignments, from landlord-tenant agreements to business contracts and intellectual property transfers. This will give you a clearer picture of how assignments work across different legal landscapes.
Common Types of Contract Assignments
When we dive into assignment in contract law , we find it touches nearly every aspect of our business and personal lives. Let’s simplify this complex topic by looking at some of the most common types of contract assignments you might encounter.
Landlord-Tenant Agreements
Imagine you’re renting a fantastic apartment but have to move because of a new job. Instead of breaking your lease, you can assign your lease to someone else. This means the new tenant takes over your lease, including rent payments and maintenance responsibilities. However, it’s crucial that the landlord agrees to this switch. If done right, it’s a win-win for everyone involved.

Business Contracts
In the business world, contract assignments are a daily occurrence. For example, if a company agrees to provide services but then realizes it’s overbooked, it can assign the contract to another company that can fulfill the obligations. This way, the project is completed on time, and the client remains happy. It’s a common practice that ensures flexibility and efficiency in business operations.

Intellectual Property
Intellectual property (IP) assignments are fascinating and complex. If an inventor creates a new product, they can assign their patent rights to a company in exchange for a lump sum or royalties. This transfer allows the company to produce and sell the invention, while the inventor benefits financially. However, it’s critical to note that with trademarks, the goodwill associated with the mark must also be transferred to maintain its value.
Understanding these types of assignments helps clarify the vast landscape of contract law. Whether it’s a cozy apartment, a crucial business deal, or a groundbreaking invention, assignments play a pivotal role in ensuring these transitions happen smoothly.
As we navigate through the realm of contract assignments, each type has its own set of rules and best practices. The key is to ensure all parties are on the same page and that the assignment is executed properly to avoid any legal pitfalls.
Diving deeper into the subject, next, we will explore how to execute a contract assignment effectively, ensuring all legal requirements are met and the process runs as smoothly as possible.
How to Execute a Contract Assignment Effectively
Executing a contract assignment effectively is crucial to ensure that all legal requirements are met and the process runs smoothly. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you navigate this process without any hiccups.
Written Consent
First and foremost, get written consent . This might seem like a no-brainer, but it’s surprising how often this step is overlooked. If the original contract requires the consent of the other party for an assignment to be valid, make sure you have this in black and white. Not just a handshake or a verbal agreement. This ensures clarity and avoids any ambiguity or disputes down the line.
Notice of Assignment
Next up, provide a notice of assignment to all relevant parties. This is not just common courtesy; it’s often a legal requirement. It informs all parties involved about the change in the assignment of rights or obligations under the contract. Think of it as updating your address with the post office; everyone needs to know where to send the mail now.
Privity of Estate
Understanding privity of estate is key in real estate transactions and leases. It refers to the legal relationship that exists between parties under a contract. When you assign a contract, the assignee steps into your shoes, but the original terms of the contract still apply. This means the assignee needs to be aware of and comply with the original agreement’s requirements.
Secondary Liability
Lastly, let’s talk about secondary liability . Just because you’ve assigned a contract doesn’t always mean you’re off the hook. In some cases, the original party (the assignor) may still hold some liability if the assignee fails to perform under the contract. It’s essential to understand the terms of your assignment agreement and whether it includes a release from liability for the assignor.
Executing a contract assignment effectively is all about dotting the I’s and crossing the T’s . By following these steps—securing written consent, issuing a notice of assignment, understanding privity of estate, and clarifying secondary liability—you’re setting yourself up for a seamless transition.
The goal is to ensure all parties are fully informed and agreeable to the changes being made. This not only helps in maintaining good relationships but also in avoiding potential legal issues down the line.
We’ll dive into some of the frequently asked questions about contract assignment to clear any lingering doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Contract Assignment
When navigating contracts, questions often arise, particularly about the concepts of assignment and novation. Let’s break these down into simpler terms.
What does assignment of a contract mean?
In the realm of assignment in contract law , think of assignment as passing the baton in a relay race. It’s where one party (the assignor) transfers their rights and benefits under a contract to another party (the assignee). However, unlike a relay race, the original party might still be on the hook for obligations unless the contract says otherwise. It’s like handing off the baton but still running alongside the new runner just in case.
Is an assignment legally binding?
Absolutely, an assignment is as binding as a pinky promise in the playground – but with legal muscle behind it. Once an assignment meets the necessary legal criteria (like not significantly changing the obligor’s duties or having express consent if required), it’s set in stone. This means both the assignee and the assignor must honor this transfer of rights or face potential legal actions. It’s a serious commitment, not just a casual exchange.
What is the difference between assignment and novation?
Now, this is where it gets a bit more intricate. If assignment is passing the baton, novation is forming a new team mid-race. It involves replacing an old obligation with a new one or adding a new party to take over an old one’s duties. Crucially, novation extinguishes the old contract and requires all original and new parties to agree. It’s a clean slate – the original party walks away, and the new party steps in, no strings attached.
While both assignment and novation change the playing field of a contract, novation requires a unanimous thumbs up from everyone involved, completely freeing the original party from their obligations. On the other hand, an assignment might leave the original party watching from the sidelines, ready to jump back in if needed.
Understanding these facets of assignment in contract law is crucial, whether you’re diving into a new agreement or navigating an existing one. Knowledge is power – especially when it comes to contracts.
As we wrap up these FAQs, the legal world of contracts is vast and sometimes complex, but breaking it down into bite-sized pieces can help demystify the process and empower you in your legal undertakings.
Here’s a helpful resource for further reading on the difference between assignment and cession.
Now, let’s continue on to the conclusion to tie all these insights together.
Navigating assignment in contract law can seem like a daunting task at first glance. However, with the right information and guidance, it becomes an invaluable tool in ensuring that your rights and obligations are protected and effectively managed in any contractual relationship.
At Moton Legal Group, we understand the intricacies of contract law and are dedicated to providing you with the expertise and support you need to navigate these waters. Whether you’re dealing with a straightforward contract assignment or facing more complex legal challenges, our team is here to help. We pride ourselves on our ability to demystify legal processes and make them accessible to everyone.
The key to successfully managing any contract assignment lies in understanding your rights, the obligations involved, and the potential impacts on all parties. It’s about ensuring that the assignment is executed in a way that is legally sound and aligns with your interests.
If you’re in need of assistance with a contract review, looking to understand more about how contract assignments work, or simply seeking legal advice on your contractual rights and responsibilities, Moton Legal Group is here for you. Our team of experienced attorneys is committed to providing the clarity, insight, and support you need to navigate the complexities of contract law with confidence.
For more information on how we can assist you with your contract review and other legal needs, visit our contract review service page .
In the constantly evolving landscape of contract law, having a trusted legal partner can make all the difference. Let Moton Legal Group be your guide, ensuring that your contractual dealings are handled with the utmost care, professionalism, and expertise. Together, we can navigate the complexities of contract law and secure the best possible outcomes for your legal matters.
Thank you for joining us on this journey through the fundamentals of assignment in contract law. We hope you found this information helpful and feel more empowered to handle your contractual affairs with confidence.
For more information Call :
Reach out now.
" * " indicates required fields
Recent Blog Posts:

In-Depth Guide to Personal Injury Compensation Process

Navigating the Legal Maze: Personal Injury Lawsuits Explained

Breaking Down Personal Injury Compensation: Amounts, Charts, and Estimates

Understanding Corporate Governance: Types and Structures

From Bills to Payouts: How Personal Injury Compensation Is Calculated

Corporate Tax Structures in the USA: What You Need to Know by Business Type

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 12 – Third-Party Rights
12.2 Assignment of Contract Rights
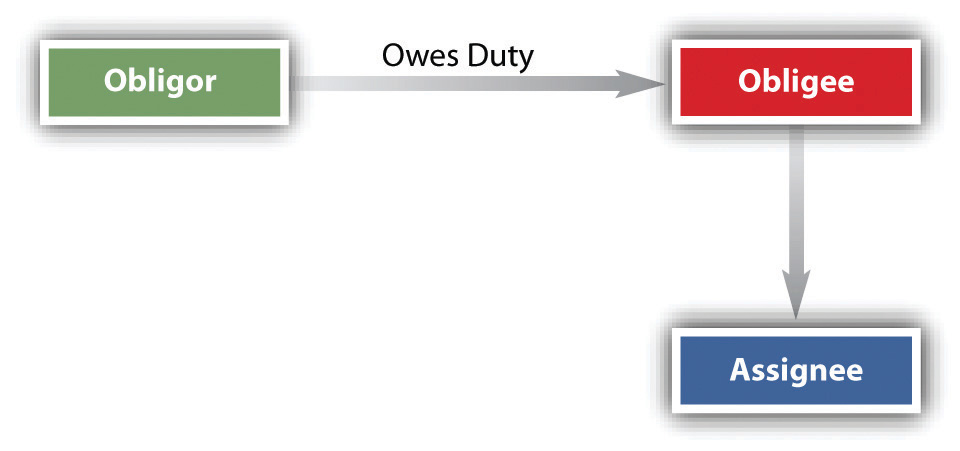
Contracts create rights and obligations between contracting parties. An assignment is the transfer of rights under a contract from one party (the assignor ) to another party (the assignee ). When a party assigns their rights under a contract, they are essentially transferring their ability to receive benefits or enforce terms of the contract to someone else. Stated another way, an assignment occurs when an obligee (one who has the right to receive a contract benefit) transfers a right to receive a contract benefit owed by the obligor (the one who has a duty to perform) to a third person ( assignee ); the obligee then becomes an assignor (one who makes an assignment). So, the party that makes the assignment is both an obligee and an assignor. The assignee acquires the right to receive the contractual obligations of the promisor, who is referred to as the obligor.
Generally, the assignor may assign any right unless (1) doing so would materially change the obligation of the obligor, materially burden him, increase his risk, or otherwise diminish the value to him of the original contract; (2) statute or public policy forbids the assignment; or (3) the contract itself precludes assignment. The common law of contracts and Articles 2 and 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) govern assignments. Assignments are a common occurrence in business, legal, and financial transactions.
Figure 12 .1 Assignment of Rights
Method of Assignment
Manifesting assent.
To effect an assignment , the assignor must make known his intention to transfer the rights to the third person. This intention must take place in the present – it cannot be a future intention. The assignor’s intention must be that the assignment is effective without need of any further action or any further manifestation of intention to make the assignment. Under the UCC, any assignments of rights in excess of $5,000 must be in writing, but otherwise, assignments can be oral and consideration is not required: the assignor could assign the right to the assignee for no exchange of money or any other consideration. For example, Mrs. Franklin has the right to receive $750 a month from the sale of a house she formerly owned; she assigns the right to receive the money to her son Jason, as a gift. The assignment is good, and need not be written.
Acceptance and Revocation
For the assignment to become effective, the assignee must manifest his acceptance under most circumstances. This is done automatically when, as is usually the case, the assignee has given consideration for the assignment (i.e., there is a contract between the assignor and the assignee in which the assignment is the assignor’s consideration), and then the assignment is not revocable without the assignee’s consent. Problems of acceptance normally arise only when the assignor intends the assignment as a gift. Then, for the assignment to be irrevocable, either the assignee must manifest his acceptance or the assignor must notify the assignee in writing of the assignment. Thus, if Mrs. Franklin assigns the $750 a month from the sale of her house to her son Jason as a gift, this assignment is valid, but revocable.
Notice to the obligor is not required, but an obligor who renders performance to the assignor without notice of the assignment (that performance of the contract is to be rendered now to the assignee) is discharged from their obligation within the contract. Obviously, the assignor cannot then keep the consideration he has received; he owes it to the assignee. But if notice is given to the obligor and she performs to the assignor anyway, the assignee can recover from either the obligor or the assignee, so the obligor could have to perform twice. Of course, an obligor who receives notice of the assignment from the assignee will want to be sure the assignment has really occurred. After all, anybody could waltz up to the obligor and say, “I’m the assignee of your contract with the bank. From now on, pay me the $500 a month, not the bank.” The obligor is entitled to verification of the assignment.
Effect of Assignment
An assignment of rights effectively makes the assignee “ stand in the shoes” of the assignor (the “shoe rule”). He gains all the rights against the obligor that the assignor had, but no more. An obligor who could avoid the assignor’s attempt to enforce the rights could avoid a similar attempt by the assignee. Suppose Dealer sells a car to Buyer on a contract where Buyer is to pay $300 per month and the car is warranted for 50,000 miles. If the car goes on the fritz before then and Dealer won’t fix it, Buyer could fix it for, say, $250 and deduct that $250 from the amount owed Dealer on the next installment. Now, if Dealer assigns the contract to Assignee, Assignee stands in Dealer’s shoes, and Buyer could likewise deduct the $250 from payment to Assignee.
The “shoe rule” does not apply to two types of assignments. First, it is inapplicable to the sale of a negotiable instrument to a holder in due course. Second, the rule may be waived: under the UCC and at common law, the obligor may agree in the original contract not to raise defenses against the assignee that could have been raised against the assignor. While a waiver of defenses makes the assignment more marketable from the assignee’s point of view, it is a situation fraught with peril to an obligor, who may sign a contract without understanding the full import of the waiver. Under the waiver rule, for example, a farmer who buys a tractor on credit and discovers later that it does not work would still be required to pay a credit company that purchased the contract; his defense that the merchandise was shoddy would be unavailing (he would, as used to be said, be “having to pay on a dead horse”).
For that reason, there are various rules that limit both the holder in due course and the waiver rule. Certain defenses, the so-called real defenses (infancy, duress, and fraud in the execution, among others), may always be asserted. Also, the waiver clause in the contract must have been presented in good faith, and if the assignee has actual notice of a defense that the buyer or lessee could raise, then the waiver is ineffective. Moreover, in consumer transactions, the UCC’s rule is subject to state laws that protect consumers (people buying things used primarily for personal, family, or household purposes), and many states, by statute or court decision, have made waivers of defenses ineffective in such consumer transactions . Federal Trade Commission regulations also affect the ability of many sellers to pass on rights to assignees free of defenses that buyers could raise against them. Because of these various limitations on the holder in due course and on waivers, the “shoe rule” will not govern in consumer transactions and, if there are real defenses or the assignee does not act in good faith, in business transactions as well.
Prohibited Assignments
The general rule—as previously noted—is that most contract rights are assignable, and the law favors freely assignable rights. There are five exceptions to this rule however.
Material Change in Duties of the Obligor
When an assignment has the effect of materially changing the duties that the obligor must perform, it is ineffective. Changing the party to whom the obligor must make a payment is not a material change of duty that will defeat an assignment, since that, of course, is the purpose behind most assignments. Nor will a minor change in the duties the obligor must perform defeat the assignment. But, some changes are significant enough to bar assignments.
Several residents in the town of Centerville sign up on an annual basis with the Centerville Times to receive their morning paper. A customer who is moving out of town may assign his right to receive the paper to someone else within the delivery route. As long as the assignee pays for the paper, the assignment is effective; the only relationship the obligor has to the assignee is a routine delivery in exchange for payment. But if the change involves assigning the right to receive the paper to someone that is outside of the delivery route, that change would be material, and the assignment could be invalid.
Assignment of Personal Rights
When it matters to the obligor who receives the benefit of his duty to perform under the contract, then the receipt of the benefit is a personal right that cannot be assigned. For example, a student seeking to earn pocket money during the school year signs up to do research work for a professor she admires and with whom she is friendly. The professor assigns the contract to one of his colleagues with whom the student does not get along. The assignment is ineffective because it matters to the student (the obligor) who the person of the assignee is. It is for this same reason that tenants usually cannot assign (sublet) their tenancies without the landlord’s permission because it matters to the landlord who the person is that is living in the landlord’s property.
Nassau Hotel Co. v. Barnett & Barse Corporation , 147 N.Y.S. 283 (1914)
MCLAUGHLIN, J.
Plaintiff owns a hotel at Long Beach, L. I., and on the 21st of November, 1912, it entered into a written agreement with the individual defendants Barnett and Barse to conduct the same for a period of years.…Shortly after this agreement was signed, Barnett and Barse organized the Barnett & Barse Corporation with a capital stock of $10,000, and then assigned the agreement to it. Immediately following the assignment, the corporation went into possession and assumed to carry out its terms. The plaintiff thereupon brought this action to cancel the agreement and to recover possession of the hotel and furniture therein, on the ground that the agreement was not assignable. [Summary judgment in favor of the plaintiff, defendant corporation appeals.]
The only question presented is whether the agreement was assignable. It provided, according to the allegations of the complaint, that the plaintiff leased the property to Barnett and Barse with all its equipment and furniture for a period of three years, with a privilege of five successive renewals of three years each. It expressly provided:
‘That said lessees…become responsible for the operation of the said hotel and for the upkeep and maintenance thereof and of all its furniture and equipment in accordance with the terms of this agreement and the said lessees shall have the exclusive possession, control and management thereof. * * * The said lessees hereby covenant and agree that they will operate the said hotel at all times in a first-class business-like manner, keep the same open for at least six (6) months of each year, * * *’ and ‘in lieu of rental the lessor and lessees hereby covenant and agree that the gross receipts of such operation shall be, as received, divided between the parties hereto as follows: (a) Nineteen per cent. (19%) to the lessor. * * * In the event of the failure of the lessees well and truly to perform the covenants and agreements herein contained,’ they should be liable in the sum of $50,000 as liquidated damages. That ‘in consideration and upon condition that the said lessees shall well and faithfully perform all the covenants and agreements by them to be performed without evasion or delay the said lessor for itself and its successors, covenants and agrees that the said lessees, their legal representatives and assigns may at all times during said term and the renewals thereof peaceably have and enjoy the said demised premises.’ And that ‘this agreement shall inure to the benefit of and bind the respective parties hereto, their personal representatives, successors and assigns.’
The complaint further alleges that the agreement was entered into by plaintiff in reliance upon the financial responsibility of Barnett and Barse, their personal character, and especially the experience of Barnett in conducting hotels; that, though he at first held a controlling interest in the Barnett & Barse Corporation, he has since sold all his stock to the defendant Barse, and has no interest in the corporation and no longer devotes any time or attention to the management or operation of the hotel.
…[C]learly…the agreement in question was personal to Barnett and Barse and could not be assigned by them without the plaintiff’s consent. By its terms the plaintiff not only entrusted them with the care and management of the hotel and its furnishings—valued, according to the allegations of the complaint, at more than $1,000,000—but agreed to accept as rental or compensation a percentage of the gross receipts. Obviously, the receipts depended to a large extent upon the management, and the care of the property upon the personal character and responsibility of the persons in possession. When the whole agreement is read, it is apparent that the plaintiff relied, in making it, upon the personal covenants of Barnett and Barse. They were financially responsible. As already said, Barnett had had a long and successful experience in managing hotels, which was undoubtedly an inducing cause for plaintiff’s making the agreement in question and for personally obligating them to carry out its terms.
It is suggested that because there is a clause in the agreement to the effect that it should ‘inure to the benefit of and bind the respective parties hereto, their personal representatives and assigns,’ that Barnett and Barse had a right to assign it to the corporation. But the intention of the parties is to be gathered, not from one clause, but from the entire instrument [Citation] and when it is thus read it clearly appears that Barnett and Barse were to personally carry out the terms of the agreement and did not have a right to assign it. This follows from the language used, which shows that a personal trust or confidence was reposed by the plaintiff in Barnett and Barse when the agreement was made.
In [Citation] it was said: “Rights arising out of contract cannot be transferred if they…involve a relation of personal confidence such that the party whose agreement conferred those rights must have intended them to be exercised only by him in whom he actually confided.”
This rule was applied in [Citation] the court holding that the plaintiff—the assignee—was not only technically, but substantially, a different entity from its predecessor, and that the defendant was not obliged to entrust its money collected on the sale of the presses to the responsibility of an entirely different corporation from that with which it had contracted, and that the contract could not be assigned to the plaintiff without the assent of the other party to it.
The reason which underlies the basis of the rule is that a party has the right to the benefit contemplated from the character, credit, and substance of him with whom he contracts, and in such case he is not bound to recognize…an assignment of the contract.
The order appealed from, therefore, is affirmed.
Case questions
- The corporation created to operate the hotel was apparently owned and operated by the same two men the plaintiff leased the hotel to in the first place. What objection would the plaintiff have to the corporate entity—actually, of course, a legal fiction—owning and operating the hotel?
- The defendants pointed to the clause about the contract inuring to the benefit of the parties “and assigns.” So the defendants assigned the contract. How could that not be allowed by the contract’s own terms?
- What is the controlling rule of law upon which the outcome here depends?
Assignment Forbidden by Statute or Public Policy
Various federal and state laws prohibit or regulate some contract assignments. For example, the assignment of future wages is regulated by state and federal law, such an attempt to try to effect such an assignment would not be valid. And even in the absence of statute, public policy might prohibit some assignments.
Contracts That Prohibit Assignment
A written contract may contain general language that prohibits assignment of rights or assignment of “the contract.” Both the Restatement and UCC Section 2-210(3) declare that in the absence of any contrary circumstances, a provision in the agreement that prohibits assigning “the contract” bars “only the delegation to the assignee of the assignor’s performance.” In other words, unless the contract specifically prohibits assignment of any of its terms, a party is free to assign anything except his or her own duties. Even if a contractual provision explicitly prohibits it, a right to damages for breach of the whole contract is assignable under UCC Section 2-210(2) in contracts for goods. Likewise, UCC Section 9-318(4) invalidates any contract provision that prohibits assigning sums already due or to become due. Indeed, in some states, at common law, a clause specifically prohibiting assignment will fail. For example, the buyer and the seller agree to the sale of land and to a provision barring assignment of the rights under the contract. The buyer pays the full price, but the seller refuses to convey. The buyer then assigns to her friend the right to obtain title to the land from the seller. The latter’s objection that the contract precludes such an assignment will fall on deaf ears in some states; the assignment is effective, and the friend may sue for the title. Bottom line, even though a contract may expressly state it cannot be assigned, that may not always be the case.
As we saw with integration clauses, if you are a Verizon Wireless ™ customer, you have agreed to their terms regarding assignment:
You cannot assign this Agreement or any of your rights or duties under it without our permission. However, we may assign this Agreement or any debt you owe us without notifying you.
Such assignment clauses can be found in many common contracts.
Rose v. Vulcan Materials Co. 194 S.E.2d 521 (N.C. 1973)
HUSKINS, J.
…Plaintiff [Rose], after leasing his quarry to J. E. Dooley and Son, Inc., promised not to engage in the rock-crushing business within an eight-mile radius of [the city of] Elkin for a period of ten years. In return for this promise, J. E. Dooley and Son, Inc., promised, among other things, to furnish plaintiff stone f.o.b. the quarry site at Cycle, North Carolina, at stipulated prices for ten years.…
By a contract effective 23 April 1960, Vulcan Materials Company, a corporation…, purchased the stone quarry operations and the assets and obligations of J. E. Dooley and Son, Inc.…[Vulcan sent Rose a letter, part of which read:]
Mr. Dooley brought to us this morning the contracts between you and his companies, copies of which are attached. This is to advise that Vulcan Materials Company assumes all phases of these contracts and intends to carry out the conditions of these contracts as they are stated.
In early 1961 Vulcan notified plaintiff that it would no longer sell stone to him at the prices set out in [the agreement between Rose and Dooley] and would thereafter charge plaintiff the same prices charged all of its other customers for stone. Commencing 11 May 1961, Vulcan raised stone prices to the plaintiff to a level in excess of the prices specified in [the Rose-Dooley agreement].
At the time Vulcan increased the prices of stone to amounts in excess of those specified in [the Rose-Dooley contract], plaintiff was engaged in his ready-mix cement business, using large quantities of stone, and had no other practical source of supply. Advising Vulcan that he intended to sue for breach of contract, he continued to purchase stone from Vulcan under protest.…
The total of these amounts over and above the prices specified in [the Rose-Dooley contract] is $25,231.57, [about $260,000 in 2024 dollars] and plaintiff seeks to recover said amount in this action.
The [Rose-Dooley] agreement was an executory bilateral contract under which plaintiff’s promise not to compete for ten years gained him a ten-year option to buy stone at specified prices. In most states, the assignee of an executory bilateral contract is not liable to anyone for the nonperformance of the assignor’s duties thereunder unless he expressly promises his assignor or the other contracting party to perform, or ‘assume,’ such duties.…These states refuse to imply a promise to perform the duties, but if the assignee expressly promises his assignor to perform, he is liable to the other contracting party on a third-party beneficiary theory. And, if the assignee makes such a promise directly to the other contracting party upon a consideration, of course he is liable to him thereon. [Citation]
A minority of states holds that the assignee of an executory bilateral contract under a general assignment becomes not only assignee of the rights of the assignor but also delegatee of his duties; and that, absent a showing of contrary intent, the assignee impliedly promises the assignor that he will perform the duties so delegated. This rule is expressed in Restatement, Contracts, s 164 (1932) as follows:
(1) Where a party under a bilateral contract which is at the time wholly or partially executory on both sides purports to assign the whole contract, his action is interpreted, in the absence of circumstances showing a contrary intention, as an assignment of the assignor’s rights under the contract and a delegation of the performance of the assignor’s duties.
(2) Acceptance by the assignee of such an assignment is interpreted, in the absence of circumstances showing a contrary intention, as both an assent to become an assignee of the assignor’s rights and as a promise to the assignor to assume the performance of the assignor’s duties.’ (emphasis added)
We…adopt the Restatement rule and expressly hold that the assignee under a general assignment of an executory bilateral contract, in the absence of circumstances showing a contrary intention, becomes the delegatee of his assignor’s duties and impliedly promises his assignor that he will perform such duties.
The rule we adopt and reaffirm here is regarded as the more reasonable view by legal scholars and textwriters. Professor Grismore says:
It is submitted that the acceptance of an assignment in this form does presumptively import a tacit promise on the part of the assignee to assume the burdens of the contract, and that this presumption should prevail in the absence of the clear showing of a contrary intention. The presumption seems reasonable in view of the evident expectation of the parties. The assignment on its face indicates an intent to do more than simply to transfer the benefits assured by the contract. It purports to transfer the contract as a whole, and since the contract is made up of both benefits and burdens both must be intended to be included.…Grismore, Is the Assignee of a Contract Liable for the Nonperformance of Delegated Duties? 18 Mich.L.Rev. 284 (1920).
In addition, with respect to transactions governed by the Uniform Commercial Code, an assignment of a contract in general terms is a delegation of performance of the duties of the assignor, and its acceptance by the assignee constitutes a promise by him to perform those duties. Our holding in this case maintains a desirable uniformity in the field of contract liability.
We further hold that the other party to the original contract may sue the assignee as a third-party beneficiary of his promise of performance which he impliedly makes to his assignor, under the rule above laid down, by accepting the general assignment. Younce v. Lumber Co. , [Citation] (1908), holds that where the assignee makes an express promise of performance to his assignor, the other contracting party may sue him for breach thereof. We see no reason why the same result should not obtain where the assignee breaches his promise of performance implied under the rule of Restatement s 164. ‘That the assignee is liable at the suit of the third party where he expressly assumes and promises to perform delegated duties has already been decided in a few cases (citing Younce). If an express promise will support such an action it is difficult to see why a tacit promise should not have the same effect.’ Grismore, supra. Parenthetically, we note that such is the rule under the Uniform Commercial Code, [2-210].
We now apply the foregoing principles to the case at hand. The contract of 23 April 1960, between defendant and J. E. Dooley and Son, Inc., under which, as stipulated by the parties, ‘the defendant purchased the assets and obligations of J. E. Dooley and Son, Inc.,’ was a general assignment of all the assets and obligations of J. E. Dooley and Son, Inc., including those under [the Rose-Dooley contract]. When defendant accepted such assignment it thereby became delegatee of its assignor’s duties under it and impliedly promised to perform such duties.
When defendant later failed to perform such duties by refusing to continue sales of stone to plaintiff at the prices specified in [the Rose-Dooley contract], it breached its implied promise of performance and plaintiff was entitled to bring suit thereon as a third-party beneficiary.
The decision…is reversed with directions that the case be certified to the Superior Court of Forsyth County for reinstatement of the judgment of the trial court in accordance with this opinion.
- Why did Rose need the crushed rock from the quarry he originally leased to Dooley?
- What argument did Vulcan make as to why it should not be liable to sell crushed rock to Rose at the price set out in the Rose-Dooley contract?
- What rule did the court here announce in deciding that Vulcan was required to sell rock at the price set out in the Rose-Dooley contract? That is, what is the controlling rule of law in this case?
Future Contracts
The law distinguishes between assigning future rights under an existing contract and assigning rights that will arise from a future contract. Rights contingent on a future event can be assigned in exactly the same manner as existing rights, as long as the contingent rights are already incorporated in a contract. Ben has a long-standing deal with his neighbor, Mrs. Robinson, to keep the latter’s walk clear of snow at twenty dollars a snowfall. Ben is saving his money for a new printer, but when he is eighty dollars shy of the purchase price, he becomes impatient and cajoles a friend into loaning him the balance. In return, Ben assigns his friend the earnings from the next four snowfalls. The assignment is effective. However, a right that will arise from a future contract cannot be the subject of a present assignment.
Partial Assignments
An assignor may assign part of a contractual right, but only if the obligor can perform that part of his contractual obligation separately from the remainder of his obligation. Assignment of part of a payment due is always enforceable. However, if the obligor objects, neither the assignor nor the assignee may sue him unless both are party to the suit. Mrs. Robinson owes Ben one hundred dollars. Ben assigns fifty dollars of that sum to his friend. Mrs. Robinson is perplexed by this assignment and refuses to pay until the situation is explained to her satisfaction. The friend brings suit against Mrs. Robinson. The court cannot hear the case unless Ben is also a party to the suit. This ensures all parties to the dispute are present at once and avoids multiple lawsuits.
Successive Assignments
It may happen that an assignor assigns the same interest twice. With certain exceptions, the first assignee takes precedence over any subsequent assignee. One obvious exception is when the first assignment is ineffective or revocable. A subsequent assignment has the effect of revoking a prior assignment that is ineffective or revocable. Another exception: if in good faith the subsequent assignee gives consideration for the assignment and has no knowledge of the prior assignment, he takes precedence whenever he obtains payment from, performance from, or a judgment against the obligor, or whenever he receives some tangible evidence from the assignor that the right has been assigned (e.g., a bank deposit book or an insurance policy).
Some states follow the different English rule: the first assignee to give notice to the obligor has priority, regardless of the order in which the assignments were made. Furthermore, if the assignment falls within the filing requirements of UCC Article 9 the first assignee to file will prevail.
Figure 1 2 .2 Successive Assignments
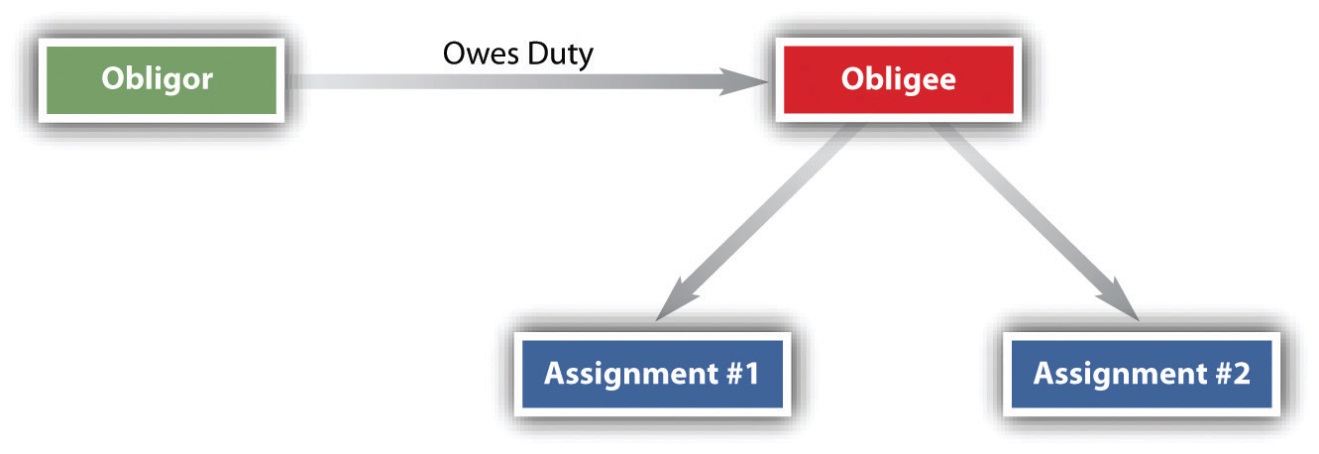
Assignor’s Warranties
An assignor has legal responsibilities in making assignments. Unless the contract explicitly states to the contrary, a person who assigns a right for value makes certain assignor’s warranties to the assignee: that he will not upset the assignment, that he has the right to make it, and that there are no defenses that will defeat it. However, the assignor does not guarantee payment; assignment does not by itself amount to a warranty that the obligor is solvent or will perform as agreed in the original contract. Mrs. Robinson owes Ben fifty dollars. Ben assigns this sum to his friend. Before the friend collects, Ben releases Mrs. Robinson from her obligation. The friend may sue Ben for the fifty dollars. Or again, if Ben represents to his friend that Mrs. Robinson owes him (Ben) fifty dollars and assigns his friend that amount, but in fact Mrs. Robinson does not owe Ben that much, then Ben has breached his assignor’s warranty. The assignor’s warranties may be express or implied.
Video on Assignment
Check your Understanding
the transfer of rights under a contract from one party to another party
the party who transfers their rights to another
a person to whom a property right is transferred
one to whom an obligation is made
one who makes and has an obligation
a legal relationship, created by law or contract, in which a person or business owes something to another
relevant and significant
Business Law I - Interactive Copyright © 2024 by Melanie Morris is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Primary tabs
Assignment is a legal term whereby an individual, the “assignor,” transfers rights, property, or other benefits to another known as the “ assignee .” This concept is used in both contract and property law. The term can refer to either the act of transfer or the rights /property/benefits being transferred.
Contract Law
Under contract law, assignment of a contract is both: (1) an assignment of rights; and (2) a delegation of duties , in the absence of evidence otherwise. For example, if A contracts with B to teach B guitar for $50, A can assign this contract to C. That is, this assignment is both: (1) an assignment of A’s rights under the contract to the $50; and (2) a delegation of A’s duty to teach guitar to C. In this example, A is both the “assignor” and the “delegee” who d elegates the duties to another (C), C is known as the “ obligor ” who must perform the obligations to the assignee , and B is the “ assignee ” who is owed duties and is liable to the “ obligor ”.
(1) Assignment of Rights/Duties Under Contract Law
There are a few notable rules regarding assignments under contract law. First, if an individual has not yet secured the contract to perform duties to another, he/she cannot assign his/her future right to an assignee . That is, if A has not yet contracted with B to teach B guitar, A cannot assign his/her rights to C. Second, rights cannot be assigned when they materially change the obligor ’s duty and rights. Third, the obligor can sue the assignee directly if the assignee does not pay him/her. Following the previous example, this means that C ( obligor ) can sue B ( assignee ) if C teaches guitar to B, but B does not pay C $50 in return.
(2) Delegation of Duties
If the promised performance requires a rare genius or skill, then the delegee cannot delegate it to the obligor. It can only be delegated if the promised performance is more commonplace. Further, an obligee can sue if the assignee does not perform. However, the delegee is secondarily liable unless there has been an express release of the delegee. That is, if B does want C to teach guitar but C refuses to, then B can sue C. If C still refuses to perform, then B can compel A to fulfill the duties under secondary liability.
Lastly, a related concept is novation , which is when a new obligor substitutes and releases an old obligor. If novation occurs, then the original obligor’s duties are wiped out. However, novation requires an original obligee’s consent .
Property Law
Under property law, assignment typically arises in landlord-tenant situations. For example, A might be renting from landlord B but wants to another party (C) to take over the property. In this scenario, A might be able to choose between assigning and subleasing the property to C. If assigning , A would be giving C the entire balance of the term, with no reversion to anyone whereas if subleasing , A would be giving C for a limited period of the remaining term. Significantly, under assignment C would have privity of estate with the landlord while under a sublease, C would not.
[Last updated in May of 2020 by the Wex Definitions Team ]
- business law
- landlord & tenant
- property & real estate law
- trusts, inheritances & estates
- wex definitions
Assignment Clauses: Transferring Contractual Rights and Obligations
Transferring contractual rights and obligations is a complex area of law that many find confusing.
This article will clearly explain assignment clauses, which allow the transfer of contractual rights and duties to third parties.
You'll learn the mechanics of how assignment works, the procedures and pitfalls to watch out for when assigning obligations, and practical guidance for drafting effective assignment provisions in your contracts.
Introduction to Assignment Clauses in Contracts
Assignment clauses allow parties to a contract to transfer their contractual rights and obligations to a third party. They provide a contractual basis for the assignment, detailing the terms and conditions under which it can occur.
Understanding the Contractual Basis of Assignment Clauses
Assignment clauses establish the permission and framework for transferring rights and duties under a contract. Key points:
- They provide the contractual grounds enabling assignments of a party's rights or delegation of their duties.
- Clauses outline requirements and restrictions , such as needing consent from the counterparty.
- They define the scope of transfer , clarifying what can and can't be assigned/delegated.
- Stipulate terms and conditions of assignment, like rights of original parties post-transfer.
The Role of Assignment Clauses in Transferring Contractual Rights and Obligations
Assignment clauses facilitate the transfer of rights and duties under a contract:
- Enable flexibility - Parties can assign rights/duties to meet changing needs.
- Allow monetization - Rights under lucrative contracts can be sold.
- Improve creditworthiness - Income streams can be used as collateral.
- Permit specialization - Duties can be delegated to more capable third parties.
Well-drafted clauses enhance commercial usefulness of contracts while protecting original parties.
General Rule and Restrictions on Assignment
The default legal position allows assignment of rights without consent, but duties cannot be delegated without counterparty consent. However, clauses often override defaults:
- Commonly require consent for assigning rights.
- May prohibit assignment outright in some/all cases.
- Can stipulate conditions enabling assignments e.g. credit checks.
- Override restrictions by expressly permitting assignments without consent.
Assignment vs. Novation: Distinguishing the Mechanisms for Transferring Contractual Obligations
Assignment transfers rights/duties without changing the contract. Novation replaces a contract with a new one:
- Under assignment , original contractual terms continue unchanged. Under novation , old contract is discharged and replaced.
- In assignment, rights/duties transfer separately. In novation, all rights/duties transfer together by replacing entire contract.
- With assignment, original party may retain duties/rights. With novation, original party's involvement ends entirely.
So novation discharges original contract, while assignment preserves existing terms.
Can contract rights legally be transferred by an assignment?
Yes, contract rights can legally be transferred from one party to another through a process called assignment. This allows the original party, known as the assignor, to transfer rights, obligations, benefits or property to another party, known as the assignee.
There are some key things to know about legally transferring contract rights via an assignment:
General Rule : Unless the contract states otherwise, either party to a contract typically has the power to assign their rights to a third party. This general rule allows free assignability.
Prior Written Consent : Many contracts contain clauses requiring the counterparty's prior written consent before assignment is allowed. This restricts free assignability.
Continuing Obligations : When assigning rights, any continuing obligations under the contract must also be transferred to the assignee unless otherwise agreed. The assignor's obligations will generally terminate.
Novation : Assignment only transfers rights/obligations to the assignee. The original counterparty still remains a party to the contract. Novation is required to substitute the assignee entirely for the assignor.
So in summary, contractual rights can legally be assigned from one party to another with some limitations. Any restrictions on assignment freedom should be clearly spelled out in the contract language itself. Proper novation procedures may also be required for a complete transfer.
What is the assignment of rights and obligations clause?
An assignment clause allows one party to a contract (the assignor) to transfer the rights and obligations under the contract to a third party (the assignee). This transfers all rights and obligations to the new party.
Some key things to know about assignment clauses:
The assignor can only transfer rights and benefits, not burdens or liabilities. The original party still bears responsibilities.
Assignments usually require consent from the other original contracting party. Often the contract specifies the assignor must obtain prior written consent before assigning.
Rights refers to the right to enforce performance of obligations. Obligations refers to the responsibility to perform duties under the contract.
An assignment does not discharge the assignor of obligations unless there is a novation. The assignor remains liable in case the assignee defaults.
Certain rights and obligations can be specified to not transfer. These are called non-assignable rights and survive assignment.
So in summary, an assignment clause permits a contractual transfer of rights and obligations to a new party, with some limitations around consent, novation, non-assignable rights, etc. It is an important clause governing changes in parties bound by the contract.

What are assignments of contracts and what rights and obligations do they confer?
An assignment of contract allows one party to a contract to transfer their contractual rights and obligations to a third party. This transfers the benefits and burdens of the contract to the new party.
The key things to know about assigning contracts are:
The party wishing to assign the contract must get prior written consent from the other contracting party before assigning their rights and obligations.
Once assigned, the new party takes on all the rights and obligations under the contract. They step into the shoes of the original party.
The original party may still be liable under the contract if the new party doesn't fulfil the obligations. This depends on the specifics of the assignment agreement.
Certain rights and obligations can be drafted to not transfer through assignments. These include confidentiality clauses, non-compete clauses, etc.
So in summary, assigning a contract transfers a party's contractual rights and obligations to a new third party with the prior consent of the counterparty. The new party assumes those rights and obligations going forward.
What is the assignment of contractual obligations?
The assignment of contractual obligations refers to the transfer of rights and duties associated with a contract from one party (the assignor) to another (the assignee). This allows the original party to the contract to essentially hand over their place in the agreement to a new party.
There are a few key things to know about assigning contracts:
The assignor must obtain consent from the other contracting party before assigning the contract. This is usually done through a prior written consent clause in the original agreement.
All rights and obligations under the contract transfer to the assignee. They step into the shoes of the assignor and take on those responsibilities.
The assignment does not terminate the contract. The agreement remains intact and binding upon the new assignee.
Certain service contracts may limit or prohibit assignment altogether if duties rely heavily on the identity, skills, or qualifications of the contracting parties.
Overall, assignment clauses allow for the flexible transfer of contractual rights and duties to new parties over the course of a contract term. However, consent and notification requirements should be strictly followed to ensure a smooth transition.
sbb-itb-e93bf99
The mechanics of assignment: transferring contractual rights, assignment of all rights: the scope and extent.
An assignment clause allows a party to a contract (the assignor) to transfer all or some of their rights under the contract to a third party (the assignee). The clause typically specifies the scope of rights that can be assigned.
For example, an assignment clause may state that the assignor has the right to assign "all of its rights and obligations under this Agreement". This broad language enables the assignor to transfer their entire bundle of contractual rights - including payment rights, intellectual property rights, access rights etc. - to the assignee.
On the other hand, a narrower assignment clause may limit transferrable rights to specific obligations, like payment collection. Defining the breadth of assignable rights is important for both parties to understand what can or cannot be transferred to a third party under the contract.
Prior Written Consent for Assignment: When and Why It's Necessary
Many assignment clauses require the assignor to obtain the other party's prior written consent before assigning contractual rights. This consent requirement enables the non-assigning party to vet and approve the assignee to ensure they can fulfill the contract satisfactorily.
Requiring prior written consent prevents unauthorized transfers that could allow an unsuitable third party to acquire rights without the other party's endorsement. For example, a software company may want to review a proposed assignee's technical capabilities before consenting for them to be assigned a complex software license.
However, prior consent requirements can deter free transferability of contractual rights. Consequently, the assignment clause may specify certain conditions where no consent is necessary for assignment - like transfers to corporate affiliates or subsidiaries.
The Impact of Assignment on Parties' Rights and Obligations
When an authorized assignment occurs, the assignor transfers all relevant rights and obligations defined in the assignment clause to the assignee. The assignee legally assumes those rights and duties previously held by the assignor.
Consequently, the assignee gains the contractual rights to any outstanding payments owed to the assignor by the other contracting party. The assignee can then collect those payments directly.
Moreover, the assignor remains obligated to complete any duties under the contract not transferred to the assignee. For complex contracts, an accompanying assignment and assumption agreement clearly delineates each party's specific ongoing rights and obligations after assignment.
Executing an Assignment and Assumption Agreement
Properly executing an assignment of contractual rights involves signing an assignment and assumption agreement that contractually transfers those rights from the assignor to the assignee.
Key steps include:
The assignor and assignee mutually agree to the proposed assignment in writing
All parties sign an assignment and assumption agreement detailing the rights and duties transferred from the assignor to the assignee
The other contracting party provides prior written consent to the assignment, if required under the contract
The executed agreement is properly delivered to the concerned parties
An assignment and assumption agreement clarifies each party's rights and obligations going forward. Recording the agreement provides legal documentation of the transfer should any dispute arise.
Following proper protocols for executing assignment agreements helps ensure smooth transitions of contractual rights between parties.
Assigning Contractual Obligations: Procedures and Pitfalls
Transferring contractual obligations from one party to another can be complex. Here are some key considerations when assigning obligations to ensure a smooth transition.
NOVATION: A Distinct Path for Transferring Contractual Obligations
Novation provides an alternative route to assign obligations, discharging the existing contract and creating a new one between the transferee and the other party. This requires consent from all involved. Novation releases the transferor from future liability, while assignment may not.
Agent May Assign: Delegating Duties and Responsibilities
An agent authorized to make contracts on behalf of another can delegate duties and responsibilities to a new agent, but only if the contract expressly permits it. The new agent assumes all delegated obligations. The original agent remains liable if the new agent fails to perform.
Continuing Rights and Obligations After Assignment
Some rights and duties may survive assignment. For example, confidentiality obligations often continue post-assignment. And if payment obligations transfer but breach later, the harmed party can still seek recourse from the original obligor.
The Requirement for Consent of the Other Party in Obligation Transfers
Generally, the other contract party must consent before obligations transfer to a new entity. Consent protects parties from being bound to unknown or unsuitable new obligors. If obligations shift without consent, the other party can sue for breach.
In summary, assigning obligations requires care to avoid legal pitfalls. Following proper procedures will ensure smooth transfers and prevent disputes. Key considerations include limitations on delegation, gaining consent, and managing continuing duties.
Termination of Rights and Obligations: Assignment Clauses and Contract Endings
Understanding termination of rights and obligations upon assignment.
When a party assigns their rights or obligations under a contract to a third party, it can impact when and how the contract terminates. Generally, an assignment itself does not automatically terminate the contract. However, many contracts include provisions detailing when rights and obligations will terminate, and these may be affected by an assignment.
For example, some contracts state that if a party assigns the agreement without consent, it constitutes a breach allowing the non-assigning party to terminate. Other agreements may specify certain rights and duties end upon assignment while others survive. Analyzing termination and survival clauses closely is key to understanding the interplay with assignments.
Survival of Rights and Obligations: What Persists Post-Assignment
Even after an assignment, some contractual rights and duties may continue rather than terminating entirely. Common examples include confidentiality, non-compete clauses, warranties, and indemnification. The contract may state these obligations survive assignment and continue to bind the original party or the assignee post-transfer.
When drafting assignment agreements, clearly specifying which rights and responsibilities will remain with the assignor versus shifting to the assignee is crucial. Without clarity, disputes may arise over who bears ongoing duties after an assignment. Careful contract wording can prevent this.
Assignment Subject to Clause: Ensuring Compliance with Existing Terms
Most contracts contain language stipulating assignment is "subject to terms and conditions herein." This means any assignment must comply with all clauses governing transferability per the original agreement. These generally include provisions requiring consent, restricting assignment, or allowing assignment only to approved entities.
Attempting to assign a contract while violating its internal clauses risks breach. Parties looking to assign must carefully analyze the original terms first, then structure the assignment to align. This maintains compliance and prevents disputes over nonconformant assignments.
The Effect of Assignment on Termination Triggers
Beyond endings stipulated in termination clauses, contracts may list events triggering optional or automatic termination. Common examples include bankruptcy, corporate dissolution, and change in control. Assigning a contract can impact these provisions.
For instance, an acquisition causing a change in control could enable the non-assigning party to terminate. Or assignment during bankruptcy proceedings could alter the application of related termination triggers. Understanding these interdependencies ensures parties can assess the full scope of assignment's effects.
Practical Guidelines for Assignment Clauses
How to secure the right to assignment: practical steps.
To secure the contractual right to assignment, parties should take the following key steps:
Explicitly state in the contract that each party has the right to assign all or part of the agreement. This establishes the baseline right to assign.
Specify any required consents needed for assignment, such as written consent from the non-assigning party. This clarifies the parameters around exercising the right.
Indicate when consent is not required , for instance, assignment to a subsidiary or affiliate. This carves out permissions.
Note any partial assignments that are allowed or prohibited. This prevents confusion on splitting up rights.
Outline notice procedures for informing the other party of an assignment. This enables proper communication.
Following these practical steps will ensure all parties understand and secure the rights around assignment.
Assignment Clauses: Binding Upon Successors and Assigns
Assignment clauses can bind both a party's successors and assigns to the contract terms through careful drafting. Here are two key methods:
Explicitly state the contract is "binding upon and inures to the benefit of the parties permitted successors and assigns." This directly binds them.
Include successors and assigns in the definition of the "parties", then note rights and obligations are "binding on the parties." This indirectly binds them.
However, successors have no obligations under the contract until they assume those obligations through a formal assumption agreement. So while they may be bound, explicit assignment and assumption is key.
Drafting an Assignment Clause: Essential Elements and Considerations
When drafting an assignment clause, four key elements require consideration:
Right to Assign - Define which rights can and cannot be assigned under the agreement. Be as explicit as possible.
Required Consents - Note any consents from the non-assigning party required to assign the rights. Detail notification procedures.
Binding Effect - State if successors and assigns will be bound by the terms. Specify any assumption procedures.
Exceptions - Carve out any scenario such as assignment to affiliates where consent is not needed.
Additionally, parties should align on governing laws, partial assignments, and continuing obligations in case of termination. Covering these elements will lead to a robust assignment clause.
Negotiating Assignment Clauses: Balancing Flexibility and Control
When negotiating assignment clauses, parties are balancing two competing interests - the assignor wants flexibility, while the assignee wants control. Here are two strategies to achieve both:
Consent Parameters - The assignee may request full consent rights over assignments. A compromise is only requiring consent in specified reasonable situations.
Notice Procedures - The assignor may not want burdensome consent procedures. A compromise is consent when given reasonable advance notice.
Additionally, limiting assignments to list of approved entities, requiring assumption agreements, or excluding select rights from assignment can provide more control.
Carefully negotiating these aspects can lead to clauses that provide flexibility while still giving parties oversight over assignments.
Conclusion: Embracing Assignment Clauses in Contractual Agreements
Summarizing the importance of assignment clauses.
Assignment clauses play a pivotal role in modern contractual agreements by enabling the transfer of contractual rights and obligations between parties. They provide flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances over the course of a contract. Key takeaways regarding the importance of assignment clauses include:
They facilitate transactions like mergers, acquisitions, or sales of business assets by transferring contracts to new owners. This promotes business growth and development.
They allow the original contracting party to bring in a more capable or specialized assignee to fulfill the contract. This optimizes contract performance.
They give parties an "exit strategy" to extract themselves from unwanted contracts through assignment. This mitigates risk.
They enable the continuation of contracts even when the original parties undergo significant corporate changes. This promotes stability.
In summary, embracing well-drafted assignment clauses generates significant strategic advantages for all contracting parties.
Reflecting on the Benefits and Risks of Transferring Rights and Obligations
The transfer of contractual rights and obligations certainly can yield major benefits, but also carries notable risks requiring careful evaluation, such as:
Potential Benefits
- Access specialized expertise or capabilities from assignee
- Flexibility to change course as circumstances evolve
- Facilitate major transactions and corporate changes
Potential Risks
- Breach of confidentiality by assignee
- Lack of consent from counterparty for assignment
- Assignee lacks competence to fulfill obligations
Ultimately, with proper risk assessment and mitigation, the benefits will generally outweigh the risks. But all parties must approach the transfer thoughtfully.
Ensuring Clarity and Compliance: Final Thoughts on Assignment Provisions
When drafting assignment clauses, clarity regarding rights, risks, and responsibilities is paramount. Key considerations include:
- Specifying any rights or obligations excluded from assignment
- Requiring prior written consent of counterparties for assignment
- Addressing legal and regulatory compliance issues
- Mitigating risks like confidentiality breaches or lack of competence
With well-crafted assignment provisions that address these areas, businesses can harness the flexibility and strategic power of contractual transfers with greater confidence and reduced risk.
Related posts
- Novation: Legal Concept Explained

Maintenance and Support Clauses in Service Agreements

What is a Revenue Expense?

Resistance To Change In Accounting Firms And How To Overcome It
Unlock the talent your business deserves.
Hire Accounting and Finance Professionals from South America.
- Start Interviewing For Free

Choose Your Legal Category:
- Online Law Library
- Bankruptcy Law
- Business Law
- Civil Law
- Criminal Law
- Employment Law
- Family Law
- Finance Law
- Government Law
- Immigration Law
- Insurance Law
- Intellectual Property Law
- Personal Injury Law
- Products & Services Law
- Real Estate Law
- Wills, Trusts & Estates Law
- Attorney Referral Services
- Top 10 Most Popular Articles
- Legal Dictionary
- How It Works - Clients
- Legal Center
- About LegalMatch
- Consumer Satisfaction
- Editorial Policy
- Attorneys Market Your Law Practice Attorney Login Schedule a Demo Now Did LegalMatch Call You Recently? How It Works - Attorneys Attorney Resources Attorney Success Stories Attorney Success Story Videos Compare Legal Marketing Services Cases Heatmap View Cases
- Find a Lawyer
- Legal Topics
- Contract Law
- When Can a Party Assign Contractual Rights to...
When Can a Party Assign Contractual Rights to Another Party?
(This may not be the same place you live)
What is a Contract?
An agreement between two private parties creates mutual legal obligations. A contract can be either oral or written. However, oral contracts are more challenging to enforce and should be avoided, if possible.
A contract that involves a significant amount of money (over $500) must be written in order to be valid. Every aspect of life involves contracts. To ensure you have a valid contract, you must understand the rules governing them.
All valid contracts must include the following elements to be enforced:
- An offer (I will pay you $1,000 for 1,000 cupcakes);
- And acceptance of the offer presented with (Another person accepts $1,000 for 1,000 cupcakes);
- A promise to perform (Other person says they will perform);
- A valuable consideration ($1,000);
- A time or an event when the performance must be made (1,000 cupcakes exactly two weeks from now);
- Terms and conditions for the performance (The cupcakes must be chocolate and have vanilla frosting); and
- Performance (The 1,000 cupcakes are delivered, and the person is paid $1,000).
On top of that, the courts will not enforce certain contracts unless they are in writing. These contracts fall under the Statute of Frauds and must be in writing. Examples include marriage contracts, contracts not to be performed within one year, interest on land contracts, and the decedent’s debt guarantees.
When dealing with a contract issue, it is important to consider the local laws since state statutes govern most contracts.
What are the Required Elements for a Contract?
What is considered a breach of a contract, what are there different types of contracts, what is a contract assignment, does a contract assignment need to be in writing, do i need a lawyer for help with contract assignments.
Any contract must contain five elements. A contract must have a legal purpose and cannot be used for illegal purposes. Contracting to commit a crime (such as hiring a hitman). In addition, there must be a mutual agreement between the parties. In order for this to occur, one party must have made an offer to another party for acceptance. The signing of a contract, for instance, indicates that the parties are in agreement and on the same page.
Some offers may not have an expiration period , so the offer remains open for a “reasonable” time. Offers can also be revoked until acceptance occurs. Acceptance usually means agreeing to the terms of the offer, and if there is any change to the terms in the acceptance, it would be considered a counteroffer. States differ on this, and it would be ideal to consider the regulations in your local jurisdiction.
Third, consideration is key in order for the contract to be valid. Both parties agree to provide something of value in exchange for a benefit. The consideration can take the form of a car, money, or even manual labor. It must be something of real value.
Gifts and promises differ as well. It is not considered a contract if someone gives you a handbag or if they promise to give you a handbag but don’t; there is still no contract. A contract exists, however, when a friend promises you a handbag in exchange for completing a task. I will buy you a handbag if you clean my gutters.
Fourth, the parties must be legally competent . Minors and the mentally impaired cannot validly contract. Additionally, the party must be of a sound mind while contracting and without the influence of drugs or alcohol. Lastly, all parties must agree based on their own will. Contracts will be void if there is a mistake, duress, or fraud by one or more parties.
The contract is breached if either party fails to fulfill its legal obligations. The other party will suffer economic losses if one party violates the contract. As an example, if you hired a construction company to complete a project on time and that company failed to meet the deadline, then you will most likely suffer financial losses.
There are several options available to compensate for those losses. You can either sue for damages, demand specific performance , or terminate the contract. In the end, the court will decide the outcome and the amount of compensation.
A unilateral contract involves a promise in exchange for specific performance. In a bilateral contract, one promise is exchanged for another promise.
Other types of contracts include:
- Express contracts usually specify orally or in writing the exact terms of the contract;
- Conditional contracts are based upon the completion of a condition;
- Joint and several contracts have multiple parties involved;
- Implied contracts where courts find that a contract exists based on the situation;
- Unconscionable contracts put one party at a greater advantage than another one and are considered unjust;
- Adhesion contracts are considered to give one party more bargaining power than another and therefore result in a “take it or leave it” situation;
- Option contracts allow you to enter into another contract with another party at a later time; and
- Fixed-price contracts involve a buyer and a seller that agree to pay a fixed price for a project.
Keeping in mind that contracts come in all shapes and sizes is something we deal with every day. Contact a local lawyer if you are unsure what type of contract to which you are a party.
A contract assignment occurs when one party in a contract transfers or “assigns” their contract rights to another party. For instance, suppose that party X contracts with party Y, stating that Y will build their house. X can then assign their rights to the building to another party (Z) if they choose to do so. Here, X is called the “assignor,” while Z is called the “assignee.”
Contractual rights may be assigned to another party at any time unless:
- The contract prohibits the assignment of contractual rights
- The assignment would fundamentally change certain duties or risks involved in the contract
- The assignment has to do with future rights derived from a future, non-existent contract
- The assignment is legally prohibited by law
Aside from these situations, contract assignments are allowed and frequently occur in many situations. This is especially common in contracts involving sub-contracts and building projects.
An oral agreement is usually sufficient for a contract assignment to be valid. The original party (the obligor) does not need to be informed of the assignment. In any contract situation, it’s best if the agreement is reduced to writing and signed by all parties. By doing this, everyone will be on the same page, and a record of interactions can be maintained in case of a lawsuit.
Contract rights often contain many terms, which can get more complex when other parties enter the picture. You may need to hire a contract lawyer for advice and guidance if you have any questions, concerns, or disputes involving contract assignments.
A qualified lawyer can assist with drafting documents, reviewing agreements, and other tasks. Furthermore, your lawyer can represent you in court if you need to file a legal claim. An issue that involves a large amount of money or evidence that the contract is invalid can easily get out of hand.
Save Time and Money - Speak With a Lawyer Right Away
- Buy one 30-minute consultation call or subscribe for unlimited calls
- Subscription includes access to unlimited consultation calls at a reduced price
- Receive quick expert feedback or review your DIY legal documents
- Have peace of mind without a long wait or industry standard retainer
- Get the right guidance - Schedule a call with a lawyer today!
Need a Contract Lawyer in your Area?
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Ty McDuffey
LegalMatch Legal Writer
Updating Author
Ty began working at LegalMatch in November 2021. Ty holds a Professional Writing Degree from Missouri State University with a minor in Economics. Ty received his Juris Doctorate from the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Law in May of 2021. Before joining LegalMatch, Ty worked as a law clerk and freelance writer. Ty is a native of Lake of the Ozarks, Missouri, and currently resides in Kansas City. Read More

Jose Rivera, J.D.
Managing Editor
Original Author
Related Articles
- What Are Contractual Rights?
- When a Party to a Contract Makes a Unilateral Mistake
- Unilateral Mistake Examples
- Retainer Fee Contracts
- What is a Non-disclosure Agreement
- Breach of a Confidentiality Agreement
- Non-Disclosure Agreement Violation
- Lawyers for Contracts: Contract Dispute Attorney Near Me
- Contract Mistake Lawyers
- Contract Error Lawsuits
- Breach of Real Estate Contract
- Fraud in Contract Law
- Contract Coercion
- Legally Binding Contracts
- Contract Violation Lawyers
- Binding Agreement
- Duty to Read a Contract
- What are Employment Contracts?
- Resolving Contract Conflicts
- State Employment Contracts
- Land Contract Agreements
- Installment Contract
- What is a Land Contract?
- What is a Service Contract?
- Service-Level Agreement Disputes
- Contract Obligations
- Legal Contracts
- Indemnity Clause Law
- Indemnification
- Warranty Contract Lawyers
Discover the Trustworthy LegalMatch Advantage
- No fee to present your case
- Choose from lawyers in your area
- A 100% confidential service
How does LegalMatch work?
Law Library Disclaimer

16 people have successfully posted their cases

How does it work?
1. choose this template.
Start by clicking on "Fill out the template"
2. Complete the document
Answer a few questions and your document is created automatically.
3. Save - Print
Your document is ready! You will receive it in Word and PDF formats. You will be able to modify it.
Contract Assignment Agreement
Rating: 4.8 - 105 votes
This Contract Assignment Agreement document is used to transfer rights and responsibilities under an original contract from one Party, known as the Assignor, to another, known as the Assignee. The Assignor who was a Party to the original contract can use this document to assign their rights under the original contract to the Assignee, as well as delegating their duties under the original contract to that Assignee. For example, a nanny who as contracted with a family to watch their children but is no longer able to due to a move could assign their rights and responsibilities under the original service contract to a new childcare provider.
How to use this document
Prior to using this document, the original contract is consulted to be sure that an assignment is not prohibited and that any necessary permissions from the other Party to the original contract, known as the Obligor, have been obtained. Once this has been done, the document can be used. The Agreement contains important information such as the identities of all parties to the Agreement, the expiration date (if any) of the original contract, whether the original contract requires the Obligor's consent before assigning rights and, if so, the form of consent that the Assignor obtained and when, and which state's laws will govern the interpretation of the Agreement.
If the Agreement involves the transfer of land from one Party to another , the document will include information about where the property is located, as well as space for the document to be recorded in the county's official records, and a notary page customized for the land's location so that the document can be notarized.
Once the document has been completed, it is signed, dated, and copies are given to all concerned parties , including the Assignor, the Assignee, and the Obligor. If the Agreement concerns the transfer of land, the Agreement is then notarized and taken to be recorded so that there is an official record that the property was transferred.
Applicable law
The assignment of contracts that involve the provision of services is governed by common law in the " Second Restatement of Contracts " (the "Restatement"). The Restatement is a non-binding authority in all of U.S common law in the area of contracts and commercial transactions. Though the Restatement is non-binding, it is frequently cited by courts in explaining their reasoning in interpreting contractual disputes.
The assignment of contracts for sale of goods is governed by the Uniform Commercial Code (the "UCC") in § 2-209 Modification, Rescission and Waiver .
How to modify the template
You fill out a form. The document is created before your eyes as you respond to the questions.
At the end, you receive it in Word and PDF formats. You can modify it and reuse it.
Contract Assignment Agreement - FREE - Sample, template
Country: United States
General Business Documents - Other downloadable templates of legal documents
- Amendment to Agreement
- Loan Agreement
- Loan Agreement Modification
- Release of Loan Agreement
- Non-Compete Agreement
- Partnership Dissolution Agreement
- Notice of Withdrawal from Partnership
- Power Of Attorney
- Debt Acknowledgment Form
- Meeting Minutes
- Request to Alter Contract
- Release Agreement
- Guaranty Agreement
- Joint Venture Agreement
- Debt Settlement Agreement
- Breach of Contract Notice
- Corporate Proxy
- Mutual Rescission and Release Agreement
- Notice for Non-Renewal of Contract
- Meeting Notice
- Other downloadable templates of legal documents

Crafting Effective Patent Assignment Contracts
Crafting effective patent assignment contracts requires a meticulously drafted agreement that clearly outlines the scope of assignment, allocates patent rights, and specifies obligations and representations. A well-defined scope of assignment prevents ambiguity, while identifying and allocating patent rights facilitates a smooth transfer of ownership. Effective dispute resolution mechanisms and confidentiality provisions safeguard the assignor's interests. Ensuring enforceability and validity is crucial, and statutory compliance with patent laws and regulations is vital. By carefully addressing these key components, parties can establish a comprehensive and enforceable patent assignment contract that protects their intellectual property rights and business interests, and unlocks the full potential of their innovative discoveries.
Table of Contents
Defining the Scope of Assignment
Typically, a patent assignment contract explicitly defines the scope of assignment to clarify which patent rights are being transferred and to what extent. This clarity is vital in establishing assignment boundaries, facilitating that all parties involved understand the scope of the transfer. By defining the scope, the contract sets out the specific patent rights being assigned, including the type of patent, patent applications, and any related know-how. Scope limitations are also vital, as they determine the extent of the transfer, including geographic limitations, field-of-use restrictions, and exclusivity provisions. A well-defined scope of assignment prevents ambiguity and potential disputes, allowing the assignor and assignee to navigate the transfer with confidence. By clearly outlining the scope of assignment, the contract provides a solid foundation for the transfer of patent rights, facilitating a smooth and efficient transaction.
Identifying and Allocating Rights
Beyond clarifying the scope of assignment, a patent assignment contract must also explicitly identify and allocate the specific patent rights being transferred, thereby providing a clear understanding of the rights and obligations of the assignor and assignee. This involves specifying the exact patent rights being assigned, including the patent numbers, filing dates, and jurisdictions. The contract should also clearly define the rights holders, including the assignor and assignee, and their respective responsibilities and obligations.
A thorough risk evaluation is vital to identify potential pitfalls and allocate risks accordingly. This includes evaluating the potential risks associated with the assigned patent rights, such as litigation risks, invalidation risks, and infringement risks. By conducting a thorough risk evaluation, the parties can negotiate and allocate these risks in a manner that is fair and reasonable. The contract should also address issues related to patent maintenance, including the payment of maintenance fees and the responsibility for responding to office actions. By carefully identifying and allocating patent rights, the parties can facilitate a smooth transfer of ownership and minimize potential disputes.
Obligations and Representations
In patent assignment contracts, the assignor's key obligations, representations, and warranties are vital components that allocate risk and safeguard the assignee's interests are protected. These provisions establish the assignor's commitments and assurances regarding the patent's ownership, validity, and infringement status, among other aspects. By specifying these obligations, representations, and warranties, the parties can clarify their responsibilities and liabilities, thereby mitigating potential disputes and facilitating a smoother transfer of patent rights.
Assignor's Key Obligations
Typically, an assignor's key obligations in a patent assignment contract include a range of warranties, representations, and covenants that provide assurance to the assignee regarding the assigned patent rights. These obligations are vital in establishing the assignor's liability and providing the assignee's confidence in the transaction. One of the primary obligations is to act in good faith, implying that the assignor will not engage in any fraudulent or deceptive behavior that may compromise the validity or value of the assigned patent rights. The assignor is also expected to disclose all relevant information about the patent, including any existing licenses, encumbrances, or potential disputes. In addition, the assignor may be required to cooperate with the assignee in any future proceedings related to the patent, such as litigation or prosecution. By fulfilling these obligations, the assignor demonstrates its commitment to the transaction and minimizes the risk of assignor liability. Effective drafting of these obligations is vital to a smooth and successful patent assignment.
Representations and Warranties
Representations and warranties form a critical component of patent assignment contracts, as they enable the assignee to rely on the assignor's assertions regarding the validity, ownership, and encumbrance status of the assigned patent rights. These provisions allocate risk between the parties, providing the assignee with a level of comfort that the assigned patent rights are free from encumbrances and that the assignor has the right to assign them. The assignor's representations and warranties typically cover key aspects such as the patent's validity, ownership, and freedom from liens or encumbrances. The assignor may also provide risk disclosures, highlighting potential issues or uncertainties associated with the assigned patent rights. In the event of a warranty breach, the assignee may be entitled to seek indemnification or other remedies. Well-drafted representations and warranties can help mitigate the risk of warranty breaches and facilitate a smoother transaction. By carefully negotiating and drafting these provisions, parties can allocate risk and promote a successful patent assignment.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Effective dispute resolution mechanisms are built into patent assignment contracts to resolve conflicts arising from contractual ambiguities, performance failures, or disagreements over intellectual property rights. These mechanisms guarantee that disputes are addressed efficiently, reducing the risk of litigation and preserving the parties' business relationship.
In crafting a dispute resolution mechanism, parties may opt for arbitration, which provides a binding decision on the dispute. To mitigate the costs associated with arbitration, parties may agree on a cap for arbitration fees. This approach helps to contain costs and encourages parties to negotiate a settlement. Alternatively, parties may choose mediation strategies, which facilitate negotiation and settlement through a neutral third-party mediator . Mediation is often a cost-effective and efficient means of resolving disputes, as it encourages open communication and cooperation between parties. By incorporating these dispute resolution mechanisms into the patent assignment contract, parties can minimize the risk of disputes and facilitate a smooth transaction.
Protecting Confidential Information
A patent assignment contract's confidentiality provisions safeguard the assignor's valuable trade secrets and proprietary information, protecting the assignor's intellectual property and business competitiveness. These provisions are vital, as they shield the assignor's sensitive information during or after the agreement's term. To provide thorough protection, the contract should include non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) that outline the scope of confidential information, the assignee's obligations, and the consequences of breaching confidentiality.
Implementing information firewalls is another vital aspect of protecting confidential information . This involves restricting access to sensitive information to only those individuals who need it to perform their duties, thereby minimizing the risk of unauthorized disclosure. The contract should specify the protocols for handling and storing confidential information, as well as the procedures for reporting and addressing any breaches. By incorporating robust confidentiality provisions and information firewalls, patent assignment contracts can effectively shield the assignor's valuable trade secrets and proprietary information, thereby pledging that the assignee does not disclose or misuse such confidential information during or after the agreement's term.
Ensuring Enforceability and Validity
In addition to safeguarding confidential information, a well-drafted patent assignment contract must also verify that its terms are legally binding and enforceable, thereby securing the assignor's rights and interests are protected throughout the agreement's duration. To validate enforceability and validity, it is vital to address jurisdictional issues by specifying the governing law and dispute resolution mechanisms. This clarity prevents potential conflicts and ambiguities that may arise from differing legal interpretations.
Furthermore, statutory compliance is vital to validate the assignment contract. The contract must conform to relevant patent laws, regulations, and guidelines, including those related to patent ownership, assignment, and recordation. Non-compliance may lead to the contract being deemed invalid or unenforceable, compromising the assignor's rights and interests. By carefully considering these factors, parties can create a robust patent assignment contract that withstands legal scrutiny, providing a solid foundation for their business transactions. By doing so, they can confirm that their intellectual property rights are adequately protected and their commercial objectives are achieved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can patent assignment contracts be electronically signed and still be valid?.
Yes, patent assignment contracts can be electronically signed and remain valid, as digital signatures and electronic authentication methods, such as PKI and biometric verification, provide a secure and legally recognized means of authentication.
What Happens if the Assignor Goes Bankrupt After Signing the Contract?
In the event of assignor bankruptcy, the assignee's rights may be jeopardized. To mitigate this risk, it is crucial to prioritize asset protection measures, such as perfecting security interests, to safeguard continued patent ownership and rights.
Can Patent Assignment Contracts Be Amended or Updated Later?
Patent assignment contracts can be amended or updated later, but only with mutual consent of all parties involved, as any changes may have significant legal implications, necessitating careful review and negotiation to guarantee validity and enforceability.
Do Patent Assignment Contracts Need to Be Notarized or Witnessed?
Regarding legal formalities, patent assignment contracts typically do not require notarization or witnessing, as the signature requirements are often satisfied by the parties' written consent, although local laws or organizational policies may dictate otherwise.
Can a Patent Assignment Contract Be Terminated or Cancelled?
A patent assignment contract can be terminated or cancelled due to breach consequences, allowing parties to seek judicial review and potentially rescind the agreement, but only if contractual provisions or applicable laws permit such cancellation.
- Help and information
- Comparative
- Constitutional & Administrative
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Environment
- Equity & Trusts
- Competition
- Human Rights & Immigration
- Intellectual Property
- International Criminal
- International Environmental
- Private International
- Public International
- IT & Communications
- Jurisprudence & Philosophy of Law
- Legal Practice Course
- English Legal System (ELS)
- Legal Skills & Practice
- Medical & Healthcare
- Study & Revision
- Business and Government
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter

Cheshire, Fifoot, and Furmston's Law of Contract (17th edn)
- Preface to the Seventeenth Edition
- New to this Edition
- Table of Cases
- Table of Statutes
- Table of Statutory Instruments
- Table of European Union Legislation
- 1. Historical Introduction
- 2. Some Factors Affecting Modern Contract Law
- 3. The Phenomena of Agreement
- 4. Consideration
- 5. Intention to Create Legal Relations
- 6. The Contents of the Contract
- 7. Unenforceable Contracts
- 9. Misrepresentation, Duress, and Undue Influence
- 10. Contracts Rendered Void by Statute
- 11. Contracts Illegal by Statute or at Common Law
- 12. Contracts Void at Common Law on Grounds of Public Policy
- 13. Capacity of Parties
- 14. Privity of Contract
- 15. Privity of Contract Under the Law of Agency
- 16. The Voluntary Assignment of Contractual Rights and Liabilities
- 17. The Involuntary Assignment of Contractual Rights and Liabilities
- 18. Performance and Breach
- 19. Discharge by Agreement
- 20. Discharge Under the Doctrine of Frustration
- 21. Remedies for Breach of Contract
p. 629 16. The Voluntary Assignment of Contractual Rights and Liabilities
- M P Furmston M P Furmston Late Bencher of Gray's Inn, Emeritus Professor of Law at University of Bristol and Singapore Management University, and Professor of Law at Sunway
- https://doi.org/10.1093/he/9780198747383.003.0016
- Published in print: 06 April 2017
- Published online: September 2017
This chapter discusses the assignment of contractual rights and liabilities. It covers the assignability of contractual rights; rules that govern assignments, whether statutory or equitable; novation distinguished from assignment; and negotiability distinguished from assignability.
- contract law
- contractual rights
- negotiability
- assignability
You do not currently have access to this chapter
Please sign in to access the full content.
Access to the full content requires a subscription
Printed from Oxford Law Trove. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 28 August 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [81.177.182.154]
- 81.177.182.154
Characters remaining 500 /500
Construction of the Contract of Assignment in Private Law: Genesis and Development ( Pp. 75-81)
Related articles, journal indexing.

- Astros, Jason Heyward Agree To Deal
- Pirates To Move Oneil Cruz To Center Field
- Blake Snell, Jordan Montgomery Discuss Relationship With Scott Boras
- Nationals Promote Dylan Crews
- Cardinals Place Willson Contreras On 15-Day IL Due To Finger Fracture
- Giants, Matt Chapman Have “Had Conversations” About Potential Extension
- Hoops Rumors
- Pro Football Rumors
- Pro Hockey Rumors
MLB Trade Rumors
Angels Designate Mike Baumann For Assignment
By Anthony Franco | August 23, 2024 at 4:29pm CDT
The Angels announced that they have selected the contract of righty reliever Ryan Zeferjahn . In a corresponding roster move, fellow reliever Mike Baumann has been designated for assignment.
Baumann has ridden the DFA carousel throughout the season. The righty is out of options, so teams need to continue taking him off the 40-man roster if they nudge him out of the bullpen. No club has successfully gotten Baumann through waivers. He has gone from the Orioles to the Mariners, Giants and Halos via DFA resolutions throughout the year.
The 28-year-old hasn’t pitched especially well at any of those stops. He owns a cumulative 5.24 ERA through 44 2/3 innings. The Jacksonville product’s 19.5% strikeout percentage, 10.2% walk rate and 1.61 home runs per nine are all subpar. A few teams have nevertheless been intrigued by his still above-average velocity (96.4 MPH on the fastball) and last year’s decent results. He’s a season removed from a 3.76 ERA across 64 2/3 innings with Baltimore.
Baumann will land back on waivers in the next couple days. Any claiming team would need to keep him in the MLB bullpen. He surpassed the two-year service threshold this season and will play on a pre-arbitration salary for another year.
Zeferjahn, a University of Kansas product, steps into the vacated bullpen spot. The 6’5″ righty is a former third-round pick of the Red Sox. Command issues quickly pushed him to the bullpen, where Zeferjahn has shown strikeout stuff. He has fanned more than 28% of opponents in his five-year minor league career. That’s up to nearly 31% this season between the top two minor league levels. Zeferjahn carries a 3.33 earned run average across 46 innings on the season.
The Angels acquired him as part of a four-player return for reliever Luis García at the deadline. Three of them — Zeferjahn, outfielder Matthew Lugo and first baseman Niko Kavadas — were in the high minors at the time. Kavadas debuted last week. Los Angeles would have needed to add Zeferjahn to the 40-man this offseason to keep him out of the Rule 5 draft. They’ll give him his first big league opportunity a few weeks earlier than that as he tries to carve out a middle relief role going into next season.
22 Comments
What’s your thoughts on zeferjahn red Sox fans?
Big hit in Rocket City
Funny, they’re bringing up all these pitchers, while we’re all sitting here waiting for Moore to be called up. I’ll stand on my record that I’m ok with Moore staying down as long as he needs to. there’s no rush.
Baumann wasn’t long for the team, so this is fine. Lets see what Super Hans can do.
@kellin they need to see who they have for the bullpen next year surprised Reyes hasn’t been called up. Moore is kinda slumping but he’s still doing better than schanuel when they called him up, hasn’t made a error, and they could use a 2nd baseman. Unless they want to go for the 1st overall pick since the whitesox can’t get it.
@Rexhudler86 who’s Reyes? I’m not aware of a Reyes in the Angels org since Gerardo Reyes who’s now with the A’s.
I meant Torres
As pitchers adjust, Moore is beginning to struggle – he’s striking out in roughly a third of plate appearances at AA, and his swing decisions are becoming more suspect. Too aggressive, and he’s fighting the umps too frequently.
They may call him up anyway, but he’s not a finished product by any means, and needs a little maturity on a few levels.
@turksteeth yeah he still has better stats than schanuel, but I agree about the pitchers figuring him out. Working with both Washington’s til the end of the season shouldn’t hurt, and let him earn the spot in spring training.
@rex Just ignore the trolls (referring to post below). If you don’t feed them, they’ll go away.

I just want to congratulate the Angels and their inept organization for extending the GM on the very day they fell into last place!!! Way to go!!! Oakland is no longer Jokeland!!!
That’s because Oakland doesn’t have a MLB team anymore
Same could be said of the Pacific Coast League Angels.
@theylive thanks for your pointless comment.
@Rex Only pointless to a fan unconscious of where his team is and the direction you’re going in. It was shameful to extend Minasian because rewarding ineptitude creates more of the same.
LIVE – You think Minasian is the problem. He’s not. Pay attention.
Agreed, Baumann wasn’t a long term offer.
Zeferjahn might be. Might not. Might as well get a look at him.
Makes sense they cut Baumann. They allowed him ten appearances and he put 20 men on in nine and a third innings. Quick taste, and the taste was bitter.
Trivia question: How many teams have NOT DFAd Mike Baumann this year?
And how many of them will do so in the next 5 weeks?
Would Baumann break a record if he were to make it to the Majors with a fifth team this season? I can think of a bunch of guys who have played for four teams in a season but never five.
Niko Kavadas is a monster.
Love this game. Baumann. 10-1 last year. Undefeated this year. Can’t hold down a job .. and I get it. Ohhh, the war stories he’ll have for the grandkids.

Kid needs a haircut. Thinks he’s Josh Hader
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Please login to leave a reply.
Log in Register
- Feeds by Team
- Commenting Policy
- Privacy Policy
MLB Trade Rumors is not affiliated with Major League Baseball, MLB or MLB.com

Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Okert designated for release or assignment, Twins select contract of Scott Blewett

Minnesota Twins pitcher Steven Okert, second right, stands on the mound with teammates as pitching coach Pete Maki, right, approaches during the sixth inning of a baseball game against the Los Angeles Dodgers, Monday, April 8, 2024, in Minneapolis. (AP Photo/Abbie Parr)
The Minnesota Twins announced Saturday that a contract was selected for Scott Blewett from Triple-A St. Paul.
Blewett, a right-handed pitcher, will be making his second stint with the Twins this season after appearing in one game earlier this month on August 12.
There, against the Kansas City Royals, Blewett pitched for one scoreless inning with one strikeout.
He has appeared in 38 games for the Saints this season, going 5-2 with a 3.79 ERA, one save, 17 walks and 54 strikeouts. To make room for Blewett, the Twins have designated left-handed pitcher Steven Okert for release or assignment. Okert made 44 appearances with one start for the Twins this season, going 3-2 with a 5.09 ERA, one save, seven holds, 16 walks and 33 strikeouts.
- SI SWIMSUIT
- SI SPORTSBOOK
Thunder 4 More: OKC's Isaiah Hartenstein Set to Prove his Contract Value Right
Chase gemes | 10 hours ago.

- Oklahoma City Thunder
On Saturday, July 6, a history-making player walked into Paycom Center as an official part of the Oklahoma City Thunder for the first time.
Former New York Knicks center Isaiah Hartenstein inked the largest free agent contract in Thunder history, granting him a three-year/$87 million contract. It was a pretty penny to offer, but he was a player Oklahoma City had its eyes set on bringing to its frontcourt rotation.
Leaving New York wasn't an easy decision for Hartenstein to make. He enjoyed the culture surrounding his former team and was thankful to get a significant role in head coach Tom Thibodeau's rotation during his two seasons there. But presented with the opportunity to join the previous No. 1 seed in the Western Conference on an immense contract, it was tough to pass on.
"From afar," Hartenstein began, "I always saw how the culture was, especially since they've been in OKC. The style of play I think really fits me. I'm a high-IQ player ... (and) I think I'm one of the best passers in the NBA."
Signing Hartenstein made perfect sense for the Thunder. It lacked a true backup center behind Chet Holmgren that could retain a similar defensive impact last season, along with a rebounding issue across the board. He's exactly the type of player that can help solve those issues, and because of that, it seems to be worth the uncommonly high bidding price.
The 26-year-old has witnessed Oklahoma City's culture grow on the sidelines for a number of years, as Holmgren, Shai Gilgeous-Alexander and Jalen Williams — amongst others — have catapulted from a team on the outside looking into a legitimate championship contender in a matter of a couple of seasons. Seeing that develop so rapidly created some natural excitement around potentially joining the team, which certainly factored in his decision.
"I think every time you see them go on the court, there's a certain competitiveness always to them," Hartenstein said. "They're very excited for each other, and I think in the NBA you don't have that a lot where no matter who's doing good, the whole team is excited for each other."
Hartenstein comes in as the third-oldest player on the Thunder roster, but he'll fit right into the environment in its locker room. Even though most of the team is on the younger side, they've played far more like a veteran group than anything. There's a natural maturity that isn't commonly seen with other young teams, and he only adds to that.
"Age-wise they're young, but I feel like the approach they have to the game makes them very mature," Hartenstein said. I take this game very serious ... so that was really exciting to me."
Within Oklahoma City's lineup, Hartenstein is expected to serve in a bench capacity for most of the season. When Holmgren stepped off the court it struggled to fill in his production effectively, so it needs him to predominately play behind. However, lineups with both centers playing alongside each other will certainly be experimented with throughout the season, especially against bigger matchups.
The defense and rebounding areas of Hartenstein's game are already noticed as key strengths, but he'll also have an opportunity to develop his offense this year. Head coach Mark Daigneault wants him to be a proactive piece offensively by getting the ball in his hands, playmaking in the post and even shooting the ball more, which will just add another layer to the Thunder's system.
High expectations are naturally going to come with a franchise record-setting contract. Many players throughout the seasons have come and left Oklahoma City, so to be No. 1 is a large pedestal to be placed on. There's no doubt he'll be an integral piece for this season — and probably the next two — he just has to play to those standards.
Back in the days of Russell Westbrook, Kevin Durant and James Harden, Hartenstein loved following the Thunder while in Germany. Lots of time has passed since, but he's found his way to that very team as the biggest free agent in its history. That's quite the journey, isn't it?
"It's an honor," Hartenstein said.
Want to join the discussion? Like Thunder on SI on Facebook and follow us on Twitter to stay up to date on all the latest Thunder news. You can also meet the team behind the coverage.

CHASE GEMES
Chase is a sophomore at the University of Missouri - Columbia studying journalism. He is sports editor for Mizzou’s student newspaper, The Maneater.
Follow chasegemes
Jump to navigation

- EU Documents
- Investment Treaties
- Recent Literature
- Newsletters
Moscow Convention for the Protection of Investors’ Rights
- Copyright 2015 italaw
- Top of Page
Yankees designate Tonkin for assignment, four months after claiming him from Mets

New York Yankees relief pitcher Michael Tonkin delivers during the baseball game against the Philadelphia Phillies, Monday, July 29, 2024, in Philadelphia. (Chris Szagola/AP)
Assignment Contract Law: Everything You Need to Know
Assignment contract law occurs when a party assigns their contractual rights to a third party. 3 min read updated on January 01, 2024
Assignment contract law occurs when a party assigns their contractual rights to a third party. The benefit that the issuing party would have received from the contract is now assigned to the third party. The party appointing their rights is referred to as the assignor, while the party obtaining the rights is the assignee.
Assignment Contract
In an assignment contract, the assignor prefers that the assignee reverses roles and assumes the contractual rights and obligations as stated in the contract. Before this can occur, all parties in the original contract must be notified. The obligor is the party that's culpable for carrying out the duties included in the contract.
To simplify the concept, the assignment contract is a second agreement created by the assignor that transfers the benefit from the obligor to the assignee. In other words, the benefit won't go to the assignor, but instead to the assignee. The assignment contract will most likely be the second agreement between the assignee and obligor, as it should be in addition to the original contract. Important detailed information should be included, such as:
- Name of party members
- Rights to be appointed
- Other additional clauses
When Is Assignment Contract Needed?
Generally speaking, assignment contracts can be both written and oral. However, it is recommended that the contract is written in the following circumstances:
- Valuable services or property is involved
- The rights and duties being exchanged contain highly technical or complex terms
- The transfer of physical land or property is occurring
- There is no history between any of the parties involved
- If there is any future intention of assigning the responsibility of the contract to another business or person
- You're accepting contracts or responsibilities owned by a third party
Normally, the obligor doesn't need to be notified of an assignment of contract rights. However, the obligor is responsible for alerting the other parties if they plan on appointing another party to complete their duties or responsibilities.
What if an Assignment Contract Is Violated?
When an assignment contract is breached, the assignee may sue the obligor for a breach of contract or defective performance.
Determining specific liability may depend on the many components of the contract. To prevent confusion, it is recommended that clauses are built into the assignment contract that identify the responsibilities and liabilities of all parties involved.
How Assignments Work
The specific language used in the contract will determine how the assignment plays out. For example, one contract may prohibit assignment, while another contract may require that all parties involved agree to it before proceeding. Remember, an assignment of contract does not necessarily alleviate an assignor from all liability. Many contracts include an assurance clause guaranteeing performance. In other words, the initial parties to the contract guarantee the assignee will achieve the desired goal.
When Assignments Will Not Be Enforced
The following situations indicate when an assignment of a contract is not enforced:
- The contract specifically prohibits assignment
- The assignment drastically changes the expected outcome
- The assignment is against public policy or illegal
Delegation vs. Assignment
Occasionally, one party in a contract will desire to pass on or delegate their responsibility to a third party without creating an assignment contract. Some duties are so specific in nature that they cannot be delegated. Adding a clause in the contract to prevent a party from delegating their responsibilities and duties is highly recommended.
Three Steps to Follow if You Want to Assign a Contract
There are three main steps to take if you're looking to assign a contract:
- Make sure the current contract does not contain an anti-assignment clause
- Officially execute the assignment by transferring the parties' obligations and rights
- Notify the obligor of the changes made
Once the obligor is notified, the assignor will effectively be relieved of liability.
Anti-Assignment Clauses
If you'd prefer not to allow the party you're doing business with to assign a contract, you may be able to prevent this from occurring by clearly stating anti-assignment clauses in the original contract. The three most common anti-assignment clauses are:
- Consent required for assignment
- Consent not needed for new owners or affiliates
- Consent not unreasonably withheld
Based on these three clauses, no party in the contract is allowed to delegate or assign any obligations or rights without prior written consent from the other parties. Any delegation or assignment in violation of this passage shall be deemed void. It is not possible to write an anti-assignment clause that goes against an assignment that is issued or ordered by a court.
If you need help with assignment contract law, you can post your job on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Assignment of Rights and Obligations Under a Contract
- Legal Assignment
- Assignment Law
- Assignment of Rights Example
- Assignment Of Contracts
- What Is the Definition of Assigns
- Consent to Assignment
- Delegation vs Assignment
- Assignment Legal Definition
- Partial Assignment of Contract

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Assignment of rights changes the foundational terms of the agreement. The assignment is illegal in some way. If assignment of contract takes place, but the contract actually prohibits it, the assignment will automatically be voided. When a transfer of contract rights will somehow change the basics of the contract, assignment cannot happen.
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the ...
Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court, 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950). An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment ...
An assignment of contract occurs when one party to an existing contract (the "assignor") hands off the contract's obligations and benefits to another party (the "assignee"). Ideally, the assignor wants the assignee to step into their shoes and assume all of their contractual obligations and rights. In order to do that, the other party to the ...
Assignments, on the other hand, involve the transfer of rights. If the parties in our previous example had created a novation, Rob would be entirely accountable to Dave and John would be clear of responsibility. A novation replaces the earliest party with a new party. Contract Assignment. An Assignment Agreement can also be called a Contract ...
As long as you're free to assign the contract, prepare and enter into the assignment, which is basically an agreement transferring your rights and obligations. Notify the obligor, or the non-transferring party. After you assign contract rights to the assignee, notify the other party that was the original contractor, also known as the obligor.
In a contract assignment, one of the two parties to a contract may transfer their right to the other's performance to a third party. This is known as "contract assignment.". Generally, all rights under a contract may be assigned. A provision in the contract that states the contract may not be assigned usually refers to the delegation of ...
Legal Definition. At its core, contract assignment is about transferring rights or obligations under a contract from one party to another. Think of it as passing a baton in a relay race. The original party (the assignor) hands off their responsibilities or benefits to someone else (the assignee).
The Concept of a Contract Assignment. Contracts create rights and duties. By an assignment, an obligee (one who has the right to receive a contract benefit) transfers a right to receive a contract benefit owed by the obligor (the one who has a duty to perform) to a third person (assignee); the obligee then becomes an assignor (one who makes an assignment).
A written contract may contain general language that prohibits assignment of rights or assignment of "the contract." Both the Restatement and UCC Section 2-210(3) declare that in the absence of any contrary circumstances, a provision in the agreement that prohibits assigning "the contract" bars "only the delegation to the assignee of ...
A contract assignment agreement may be created in cases involving a contract assignment. An assignment is where the recipient of products, services, or other rights transfers (assigns) their rights to another party. The party transferring their rights is the assignor, while the party performing the services is dubbed the obligor.
assignment. Assignment is a legal term whereby an individual, the "assignor," transfers rights, property, or other benefits to another known as the " assignee .". This concept is used in both contract and property law. The term can refer to either the act of transfer or the rights /property/benefits being transferred.
The Mechanics of Assignment: Transferring Contractual Rights Assignment of All Rights: The Scope and Extent. An assignment clause allows a party to a contract (the assignor) to transfer all or some of their rights under the contract to a third party (the assignee). The clause typically specifies the scope of rights that can be assigned.
The assignment of a contract can substantially alter the allocation of rights and duties among the parties, potentially leading to a redefinition of their contractual relationships. This shift can have significant implications for the contractual boundaries, as the assignee may assume new rights and obligations that were previously held by the ...
Contractual rights may be assigned to another party at any time unless: The contract prohibits the assignment of contractual rights. The assignment would fundamentally change certain duties or risks involved in the contract. The assignment has to do with future rights derived from a future, non-existent contract.
4.8 - 105 votes. Download a basic template (FREE) Create a customized document ($24.99) This Contract Assignment Agreement document is used to transfer rights and responsibilities under an original contract from one Party, known as the Assignor, to another, known as the Assignee. The Assignor who was a Party to the original contract can use ...
Crafting effective patent assignment contracts requires a meticulously drafted agreement that clearly outlines the scope of assignment, allocates patent rights, and specifies obligations and representations. A well-defined scope of assignment prevents ambiguity, while identifying and allocating patent rights facilitates a smooth transfer of ...
This chapter discusses the assignment of contractual rights and liabilities. It covers the assignability of contractual rights; rules that govern assignments, whether statutory or equitable; novation distinguished from assignment; and negotiability distinguished from assignability.
The White Sox announced Tuesday that they've designated right-handed reliever John Brebbia for assignment and optioned third baseman Bryan Ramos to Triple-A Charlotte. Their roster spots will go ...
Kostina O.V., Mikhailichenko I.A., (2021), CONSTRUCTION OF THE CONTRACT OF ASSIGNMENT IN PRIVATE LAW: GENESIS AND DEVELOPMENT. Economic Problems and Legal Practice, 6 => 75-81.
The Angels announced that they have selected the contract of righty reliever Ryan Zeferjahn. In a corresponding roster move, fellow reliever Mike Baumann has been designated for assignment.
The Minnesota Twins announced Saturday that a contract was selected for Scott Blewett from Triple-A St. Paul. Blewett, a right-handed pitcher, will be making his second stint with the Twins this ...
In an assignment contract, the assignor prefers that the assignee reverses roles and assumes the contractual rights and obligations as stated in the contract. Before this can occur, all parties to the original contract must be notified. Contracts create duties and rights. An obligor is the party who is legally or contractually obliged to ...
The new contract comes after a credible strike threat compelled the snack giant to return to the bargaining table and come to terms on a fair agreement. "This contract is a powerful testament to the strength of our rank-and-file members, who made clear they were ready to fight for the fair pay and benefits they deserve," said Josh Graves ...
Subscribe for Updates. 2834. 2835
High expectations are naturally going to come with a franchise record-setting contract. Many players throughout the seasons have come and left Oklahoma City, so to be No. 1 is a large pedestal to ...
Interpretation of Article 11 of Moscow Convention on the Protection of Investor Rights Summary Judgment of the Economic Court of the Commonwealth of Independent States (Russian) View case details 2834
The New York Yankees shuffled their bullpen Sunday, designating Michael Tonkin for assignment and selecting the contract of Phil Bickford from Triple-A Scranton/Wilkes-Barre.
In an assignment contract, the assignor prefers that the assignee reverses roles and assumes the contractual rights and obligations as stated in the contract. Before this can occur, all parties in the original contract must be notified. The obligor is the party that's culpable for carrying out the duties included in the contract.
Since July 1, 2024, we have disabled all ads to improve your reading experience. This commitment costs us $10,000 a month. Your support can help us fill the gap.