Project Discovery Adds New Evidence-Based Practices to Adapted Career Education Series
Education Associates , developer of Project Discovery, the hands-on career education and life skills curriculum for every learner, announces additions to its Adapted Career Education Series . The Adapted Series is the only hands-on curriculum specifically designed for students who have moderate to severe cognitive disabilities, including those with autism, to explore more than 100 entry-level jobs.
Building on its commitment to providing schools with resources to make a difference in the lives of their students, Education Associates partnered with Dr. Amy Spriggs, associate professor at the Department of Special Education, University of Kentucky, to evaluate the program and recommend ways to enhance the curriculum’s impact in the classroom. Guided by Spriggs’ expertise, additions to the Adapted Series include evidence-based practices to make the curriculum even more robust and appropriate for students with autism and other developmental disabilities.
“Individuals with disabilities are eight times less likely to be gainfully employed than those without disabilities,” said Spriggs. “The Adapted Series’ video modeling, real-life pictures and tools expose students to real-life experiences that promote independence, confidence and community.”
The updated version of the Adapted Series is now available to customers and includes the following new features:
· Video modeling of all activities to capture the critical aspects of each step within a process and provide a consistent method of presenting instruction.
· Systematic instructional procedures that offer a structured approach to teaching.
· Visual supports, such as visual schedules and real-life pictures, to enhance communication skills, behavior and independence.

Tech & Learning Newsletter
Tools and ideas to transform education. Sign up below.
· Data sheets for progress monitoring and performance evaluation of each step in an activity.
· Activities to support social communication and practice real world job skills using real tools.
· Behavior supports that are implemented in a predictable order to create an environment of known expectations for students with developmental disabilities.
“Our Adapted Series was developed by educators with more than 30 years of experience working with students with special needs,” said Tim Hagan, president at Education Associates. “It’s important to us that our program supports Universal Design for Learning components and addresses all the needs of individual students so they can learn in the ways that work best for them.”
To learn more about the Adapted Career Education Series, please visit educationassociates.com/adapted-series/ .
About Education Associates
Education Associates is the developer of Project Discovery, the leading comprehensive career education, job preparation and life skills programs for all learners, including those with special needs. Education Associates empowers educators and workforce development leaders to help all students realize their potential. Education Associates believes everyone can become "Job Ready and Life Ready" to live the vibrant, independent lives they deserve. To learn more, visit http://educationassociates.com .
PRODUCT SPOTLIGHT: LocknCharge FUYL Smart Locker System Simplifies Device Management for Schools
Colleges Are Using AI To Predict Student Success. These Predictions Are Often Wrong
How Implementing Coding, STEM, and Robotics Early Can Benefit Students
Most Popular
- 2 Colleges Are Using AI To Predict Student Success. These Predictions Are Often Wrong
- 3 How Implementing Coding, STEM, and Robotics Early Can Benefit Students
- 4 A New Book Argues Grades Are Failing Students. Here’s Why
- 5 Facing History and Ourselves: How to Use It to Teach
Career Education Research for Students with Autism and Developmental Disabilities
Introduction, main digest.
- Child Care (61.7% average student skills increase)
- Table Service (55.3% average student skills increase)
- Each beta site also demonstrated growth in job skill performance across all activities in the courses.
Call Us (208) 883-1144
Fax (208) 883-8062, 316 s jefferson st, moscow, id 83843.

MEET OUR PROVIDERS
W. rand walker, ph.d..
Dr. Rand Walker is the co-founder (along Dr. Tim Rehnberg) of Educational & Psychological Services (EPS) which was established in 1993. Dr. Walker has taught at both regional universities as clinical faculty and published in the areas of anxiety and advanced techniques in psychotherapy (including chapters in the Encyclopedia of Psychotherapy). Although all of the clinical staff are generalists (i.e. qualified to treat a broad range of issues and disorders) he has established a notable reputation for anxiety disorders as well as childhood disorders. He has a doctorate from the California School of Professional Psychology (now Alliant International University), a post-doctoral fellowship from Washington State University, and formal post-doctoral training in school psychology from the University of Idaho. Dr. Walker also founded the University of Idaho Child and Youth Study Center that provides assessments and consultations for children (at the Center of Disabilities and Human Development). He is also a musician playing guitar and singing with his group "Jon and Rand and Band."
Stephen A. Bergdahl, Ph.D.
Stephen Bergdahl, Ph.D. is a licensed clinical psychologist who provides psychotherapy in addition to a wide variety of educational and neurocognitive assessment services. He earned a Ph.D. and M.A. through the California School of Professional Psychology in Fresno, CA and published a dissertation titled The Mediating Effects of Spirituality Between Negative Life Events and Trauma-Based Symptoms, and he is published in the Journal of Traumatic Stress. Prior to professional psychological studies and practice, Dr. Bergdahl served for five years as a high school teacher in the biological sciences, including a pioneer neuroscience high school course. In addition to expertise in the psychological realm, Dr. Bergdahl is familiar with the education system and its demands for social, emotional, and learning disability assessment and support. He has a background in neurobiology from the University of California, Davis, and his current practice is informed by brain-based neurological research. Overall, he possesses a unique set of skills that make him effective as a psychotherapy and assessment clinician.
Angela Stone, Psy.D.
Angela holds a doctorate in Clinical Psychology from Central Michigan University. Both her graduate school program and her predoctoral internship site were accredited by the American Psychological Association. Her primary approach is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, but she is also trained in and implements additional treatment modalities, which incorporate best practices and focus on the best outcome for each client. She specializes in treating an array of anxiety disorders, depression, trauma, grief, and relationship issues. Dr. Stone has worked in both inpatient and outpatient settings since 1994 and works primarily with adults and adolescents who are 15 years of age and above. Angela believes in working in partnership with clients, utilizing their strengths to help them understand their challenges and achieve their goals.
Glenn Vaughn, M.Ed. LCPC
Glenn Vaughn is a licensed clinical professional counselor. His undergraduate work was done at Westmont College, a private Christian liberal arts school in California. Post graduate work was through the University of Idaho and he is licensed in the State of Idaho. Mr. Vaughn considers himself a general practitioner with particular interests in couples counseling, EMDR, depression and anxiety. The ages of his clients range from seventeen to seventy-one years.
David Wait, M.D.
Dr. David Wait was born in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and is a graduate of Augustana College. He obtained his medical degree at the University of South Dakota School of Medicine. His residency was at the Psychiatric Research Institute and its affiliated University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in Little Rock. David has over 30 years' experience in psychiatry, with special interest in strengths and wellness-based treatment. He brings a valuable combination of extensive expertise and empathy in a practice that instills hope to people with mental health challenges while maximizing their strengths and personal growth. His approach is to empower patients to make and practice choices that lead to improved health and well-being, using an integrative model that recognizes that mental, physical, social, and spiritual health are one. Following residency training, Dr. Wait continued to work in research and program development as projects director for the Arkansas Mental Health Research and Training Institute, focusing on developing, researching, implementing, and then teaching novel strengths focused care for people with mental illness for the first 12 years of his career. Following this, Dr. Wait moved with his wife and 3 children to beautiful Coeur d'Alene, Idaho. He has been in clinical practice and leadership roles in the area since. In this work, Dr. Wait successfully helped people from all walks of life with a diverse range of emotional, psychiatric, and substance abuse challenges. Dr. Wait is board certified as a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, and a fellow of the American Psychiatric Association. He is licensed to practice medicine in Idaho and Washington.
Heather Lannigan, LCSW
Heather Lannigan is a Licensed Clinical Social Worker in both Idaho and Washington. She received her undergraduate degree at Washington State University and her Graduate degree from Eastern Washington University. Heather enjoys providing mental health counseling to people of all ages across their life span. While her primary therapy approach is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, she is also trained in other treatment modalities which help to aid people in their overall treatment goals. Living on the Palouse for the last 25 years has allowed Heather to raise her family and enjoy all this region has to offer.
Abby Lawton, M.Ed., Ed.S.
Abigail Lawton is a counselor focused on working with children and adolescents. She earned her Master of Education degree through Montana State University and then pursued a Master of Education Specialist degree through Eastern Washington University. Before professional psychological practice, Abigail was a school counselor and school psychologist and is very familiar with the education system. Abigail is passionate about educating youth on mental health and aiding them in developing the skills they need for success.
Fidget is a Labradoodle, bred and trained as a therapy dog to determine when and how she is needed. Her breeding combines the intelligence of a Poodle and the playful relational orientation of a Labrador Retriever. Her training, which began immediately after she was born, continued with consistent work by the breeder and one primary trainer, continuing on into the home and care of Glenn Vaughn and his wife, Karen. Fidget can typically be found at EPS with Glenn on Wednesdays and Thursdays, using her instincts to know whether she is needed or can just rest calmly. While she is an intuitive, gentle therapy dog, Fidget will always be accompanied by a therapist (most often Glenn) while in your company, at least until you get acquainted. If you have any thoughts or questions, please let us know. Fidget does not have to be in the room with you during therapy; other arrangements can be made during your session, and no feelings will be hurt. Fidget's role at EPS is that of a therapy dog, attuned to sense when she can provide assurance, companionship, and care.
Interested in our services? We’re here to help!

Our mission at EPS is to provide top quality psychological care, whether it is for mental health or educational needs.
Useful links, our newsletter, you need a helping hand with your project.
© EPS, PLLC Copyright. All Rights Reserved.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Prioritize With the MoSCoW Method

Do you need help prioritizing tasks when managing a project? There’s an acronym for that! It’s called the MoSCow method and it’s a great technique to help with prioritization.
What Is the MoSCoW Method?
The MoSCoW method is a technique that helps organizations prioritize what should be done first in a project. It is done in four steps that follow the acronym MoSCoW, which stands for must have, should have, could have and will not have. It’s used by anyone who needs to prioritize their work and is especially useful in project management.
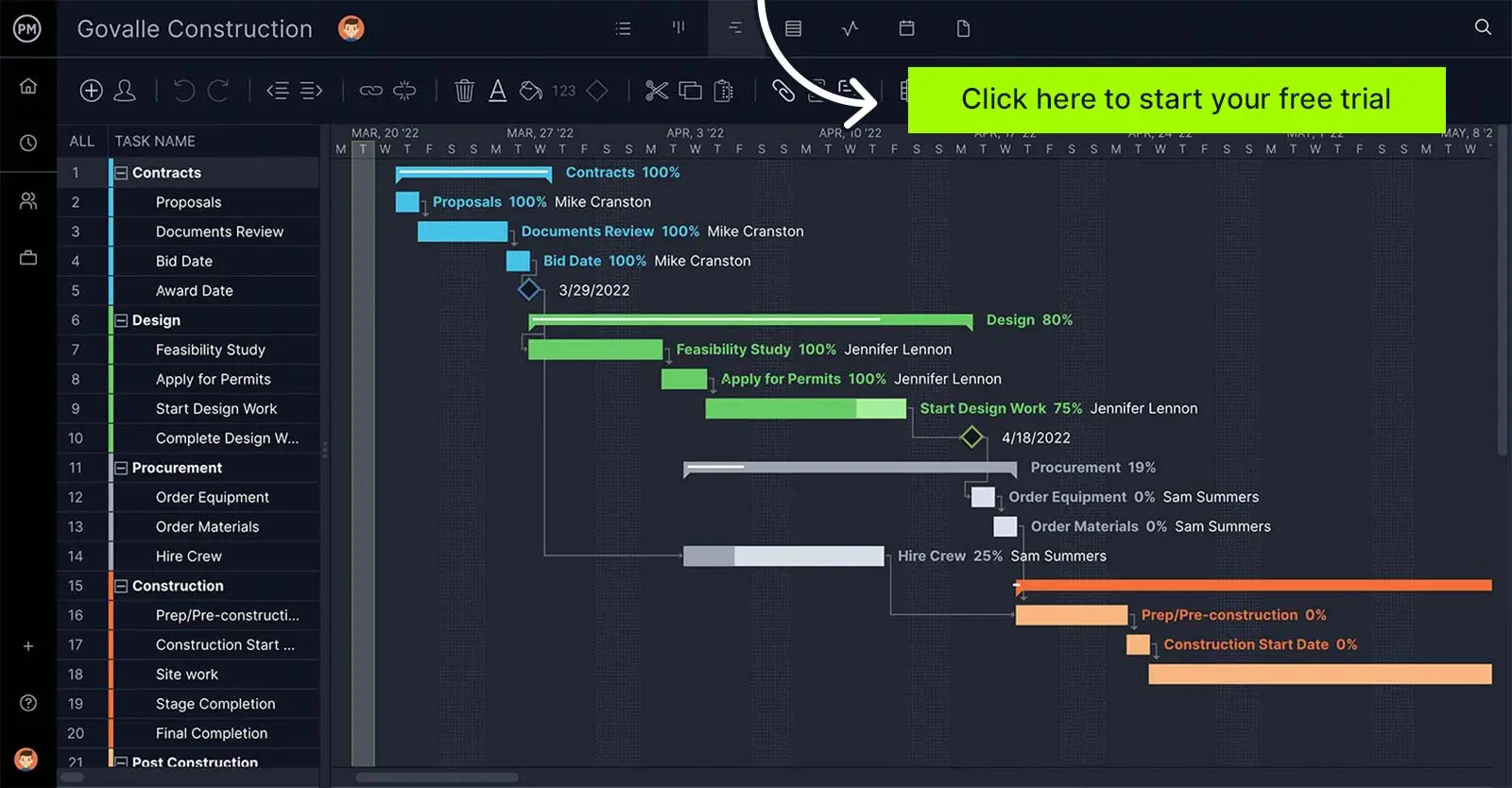
The MoSCoW method can help when project planning. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that can take the results of your MoSCow method and organize them into a project plan. Our powerful Gantt charts organize tasks, link all four task dependencies to avoid delays and can set a baseline to capture the project plan and compare it to the actual progress to ensure you stay on schedule. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
MoSCoW Prioritization Categories
Managing a project is often about managing what you will – and won’t! – get done in the given project timeline . When there are no priorities set, projects can quickly become free-for-alls, with the loudest voices in the room getting their work prioritized over others, often not for the benefit of the project or the organization.
But there’s a different approach. It’s called the MoSCoW method for defining and managing requirements and tasks in a project . Here is a list to clarify what those requirements are:
Must-Have Requirements (M)
Another way to refer to this is as the minimum usable subset (MUS) or what the project must deliver. In other words, the project must deliver these on the target date for the project to remain on track. No delay is acceptable. It is either going to take the project off track, it’s unsafe or even illegal not to have this done by the time given in the project’s business case .
A way to understand if you’re dealing with a MUS is by asking yourself, “What happens if this isn’t met?” If the answer is, “The project fails ,” then you have a MUS. Any workaround that can be devised to continue with the project and not jeopardize its success, means this isn’t a MUS.
Should-Have Requirements (S)
This type of requirement is almost as important as a MUS, but it’s not vital to the success of the project. In other words, the project doesn’t depend on this requirement. You might not want to leave it out, as it could have a great impact on the project, but in the end, it can be done without causing any irreparable harm. Again, leaving out this requirement means a lot of work (finding a solution, changing stakeholders’ expectations, maybe experiencing some inefficiency), but the project can go on.
Could-Have Requirements (C)
The difference between a should-have requirement and a could-have requirement is simply by figuring out the degree of pain that would be caused by not meeting it. That is, how will it impact the business value of the project, how many people would be affected, etc. Therefore, a could-have requirement is something you’d like but is less important than a should-have requirement. There will be an impact if it’s left out of the project, but less than the impact of a should-have requirement.
What We Will Not Have This Time (W)
Here is where you can collect those requirements that are not feasible for a specific release. Maybe next time, but the project remains strong without them. This is a great way to avoid project scope creep . Once initiatives are placed in the not-have-time category, teams know that they’re not a priority for this go-around and can place them on the back burner and out of their mind. This allows them to focus more sharply on those requirements that are important to the project.
What Is the MoSCoW Method Used For?
The MoSCow method can be of use to anyone who has work and needs to prioritize that work to know what’s essential and what can be ignored. It’s mostly used in product development, software development and project management. In project management that helps determine which tasks, requirements, products and user stories (in agile projects) the team needs to prioritize.
How to Implement the MoSCoW Method in 3 Steps
The MoSCoW method is a valuable tool, but only if you know how to use it. Here are three steps that will help you use the MoSCoW method when prioritizing your project.
1. Gather Project Requirements
Start by identifying all project requirements . Just make a giant list and be as thorough as possible. You don’t want to leave out anything that might prove essential to the project.
2. Prioritize Project Requirements
Now go through that list and attach a letter to each, according to the MoSCoW method of M for must-have, S for should have, C could have and W for what you won’t have. This allows you to prioritize the work and know what can be put aside to focus on what’s important.
3. Track the Completion of Project Deliverables
Now that you’ve classified your requirements, you can carry out the work in a timely manner. Tracking that work ensures that you don’t miss any deadlines and that all high-priority requirements will be met.
Benefits of the MoSCoW Method
The clear benefit of using the MoSCoW method is that it provides a means to prioritize work and know what is essential to the project and what can be ignored if time and cost prevent one from completing every requirement. But there are more advantages of the MoSCoW method, some of which we list below.
Helps Ensure Stakeholder Satisfaction
Stakeholders have a vested interest in the project and the project should satisfy their expectations . The MoSCoW method helps manage stakeholders by getting them to all agree on the prioritization of requirements and, therefore, helps to resolve any conflicts that might arise over the execution of those requirements.
It’s Easy to Understand and Implement
Using the MoSCoW method identifies the priority of project requirements. This information can then be disseminated to the project team so it’s clear to everyone what must be done. Now the team understands what’s prioritized and can implement those requirements first.
Helps Teams Cut Unnecessary Costs
The MoSCoW method allows everyone on the project team to know what they have to get done first, which increases revenue by decreasing operational costs, improving productivity and increasing customer satisfaction.
Moscow Method Example
Leadership guru Susanne Madsen leads this training video on how to use the MoSCoW Method to prioritize your requirements in a project.

How ProjectManager Helps You Prioritize
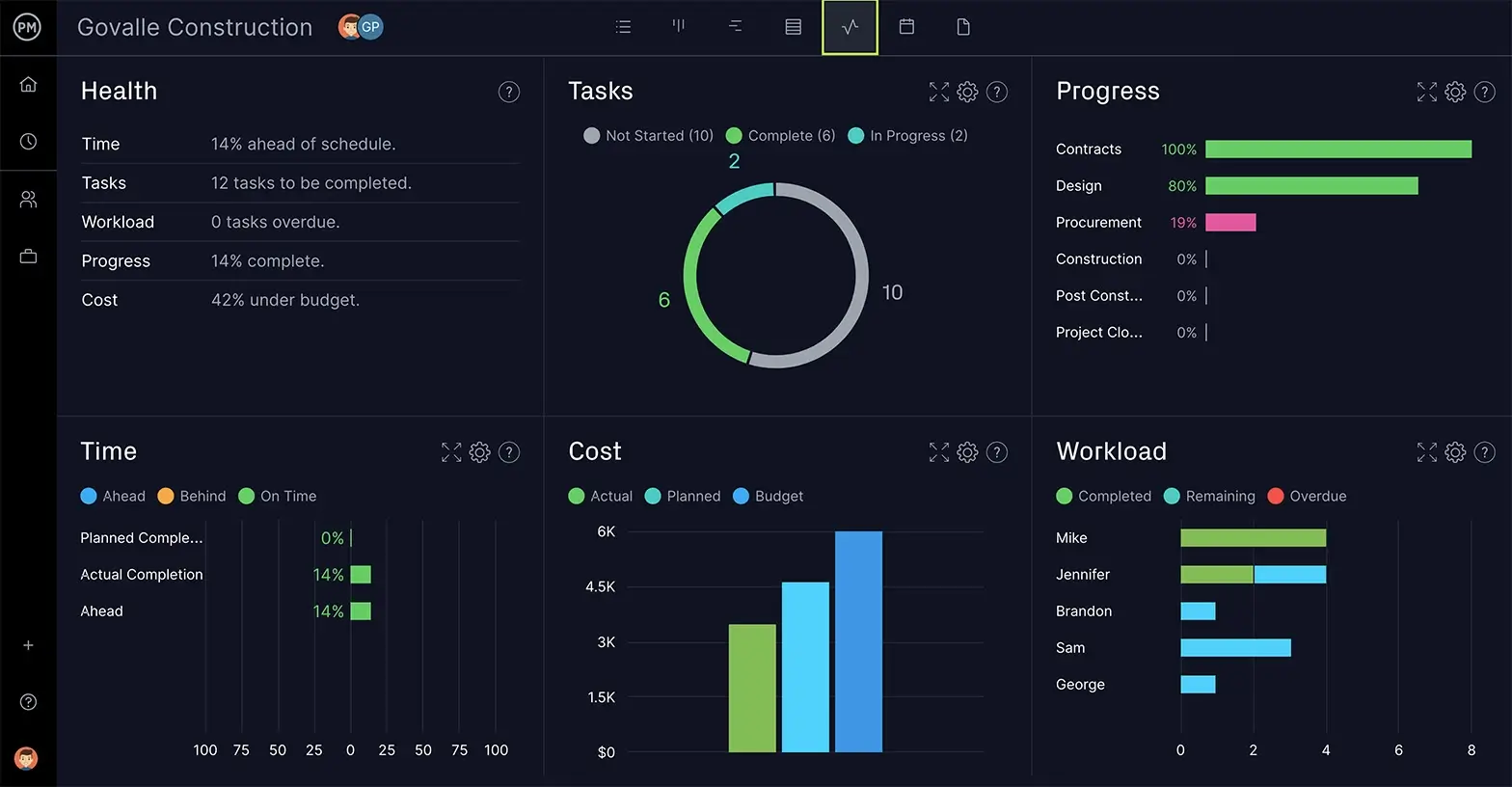
ProjectManager is online project management software that can make sure your requirements are being met throughout the life cycle of the project. Because our software gives you real-time data, you’re able to meet your priorities.
Our real-time dashboard shows real-time data that is displayed over six different project metrics. These numbers are crunched and illustrated in colorful, easy-to-read graphs and charts that keep project managers keenly assessed on the progress of their priorities.
Workflow is also visualized with kanban boards that keep teams focused on their priorities. Online Gantt charts can link dependencies and teams can collaborate at the task level, adding comments, documents and images.
There’s so much more that ProjectManager offers. To get a full picture of what we can do to help you better manage your next project, try our free 30-day trial today.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.

The University of Chicago The Law School
Innovation clinic—significant achievements for 2023-24.
The Innovation Clinic continued its track record of success during the 2023-2024 school year, facing unprecedented demand for our pro bono services as our reputation for providing high caliber transactional and regulatory representation spread. The overwhelming number of assistance requests we received from the University of Chicago, City of Chicago, and even national startup and venture capital communities enabled our students to cherry-pick the most interesting, pedagogically valuable assignments offered to them. Our focus on serving startups, rather than all small- to medium-sized businesses, and our specialization in the needs and considerations that these companies have, which differ substantially from the needs of more traditional small businesses, has proven to be a strong differentiator for the program both in terms of business development and prospective and current student interest, as has our further focus on tackling idiosyncratic, complex regulatory challenges for first-of-their kind startups. We are also beginning to enjoy more long-term relationships with clients who repeatedly engage us for multiple projects over the course of a year or more as their legal needs develop.
This year’s twelve students completed over twenty projects and represented clients in a very broad range of industries: mental health and wellbeing, content creation, medical education, biotech and drug discovery, chemistry, food and beverage, art, personal finance, renewable energy, fintech, consumer products and services, artificial intelligence (“AI”), and others. The matters that the students handled gave them an unparalleled view into the emerging companies and venture capital space, at a level of complexity and agency that most junior lawyers will not experience until several years into their careers.
Representative Engagements
While the Innovation Clinic’s engagements are highly confidential and cannot be described in detail, a high-level description of a representative sample of projects undertaken by the Innovation Clinic this year includes:
Transactional/Commercial Work
- A previous client developing a symptom-tracking wellness app for chronic disease sufferers engaged the Innovation Clinic again, this time to restructure its cap table by moving one founder’s interest in the company to a foreign holding company and subjecting the holding company to appropriate protections in favor of the startup.
- Another client with whom the Innovation Clinic had already worked several times engaged us for several new projects, including (1) restructuring their cap table and issuing equity to an additional, new founder, (2) drafting several different forms of license agreements that the company could use when generating content for the platform, covering situations in which the company would license existing content from other providers, jointly develop new content together with contractors or specialists that would then be jointly owned by all creators, or commission contractors to make content solely owned by the company, (3) drafting simple agreements for future equity (“Safes”) for the company to use in its seed stage fundraising round, and (4) drafting terms of service and a privacy policy for the platform.
- Yet another repeat client, an internet platform that supports independent artists by creating short films featuring the artists to promote their work and facilitates sales of the artists’ art through its platform, retained us this year to draft a form of independent contractor agreement that could be used when the company hires artists to be featured in content that the company’s Fortune 500 brand partners commission from the company, and to create capsule art collections that could be sold by these Fortune 500 brand partners in conjunction with the content promotion.
- We worked with a platform using AI to accelerate the Investigational New Drug (IND) approval and application process to draft a form of license agreement for use with its customers and an NDA for prospective investors.
- A novel personal finance platform for young, high-earning individuals engaged the Innovation Clinic to form an entity for the platform, including helping the founders to negotiate a deal among them with respect to roles and equity, terms that the equity would be subject to, and other post-incorporation matters, as well as to draft terms of service and a privacy policy for the platform.
- Students also formed an entity for a biotech therapeutics company founded by University of Chicago faculty members and an AI-powered legal billing management platform founded by University of Chicago students.
- A founder the Innovation Clinic had represented in connection with one venture engaged us on behalf of his other venture team to draft an equity incentive plan for the company as well as other required implementing documentation. His venture with which we previously worked also engaged us this year to draft Safes to be used with over twenty investors in a seed financing round.
More information regarding other types of transactional projects that we typically take on can be found here .
Regulatory Research and Advice
- A team of Innovation Clinic students invested a substantial portion of our regulatory time this year performing highly detailed and complicated research into public utilities laws of several states to advise a groundbreaking renewable energy technology company as to how its product might be regulated in these states and its clearest path to market. This project involved a review of not only the relevant state statutes but also an analysis of the interplay between state and federal statutes as it relates to public utilities law, the administrative codes of the relevant state executive branch agencies, and binding and non-binding administrative orders, decisions and guidance from such agencies in other contexts that could shed light on how such states would regulate this never-before-seen product that their laws clearly never contemplated could exist. The highly varied approach to utilities regulation in all states examined led to a nuanced set of analysis and recommendations for the client.
- In another significant research project, a separate team of Innovation Clinic students undertook a comprehensive review of all settlement orders and court decisions related to actions brought by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau for violations of the prohibition on unfair, deceptive, or abusive acts and practices under the Consumer Financial Protection Act, as well as selected relevant settlement orders, court decisions, and other formal and informal guidance documents related to actions brought by the Federal Trade Commission for violations of the prohibition on unfair or deceptive acts or practices under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, to assemble a playbook for a fintech company regarding compliance. This playbook, which distilled very complicated, voluminous legal decisions and concepts into a series of bullet points with clear, easy-to-follow rules and best practices, designed to be distributed to non-lawyers in many different facets of this business, covered all aspects of operations that could subject a company like this one to liability under the laws examined, including with respect to asset purchase transactions, marketing and consumer onboarding, usage of certain terms of art in advertising, disclosure requirements, fee structures, communications with customers, legal documentation requirements, customer service and support, debt collection practices, arrangements with third parties who act on the company’s behalf, and more.
Miscellaneous
- Last year’s students built upon the Innovation Clinic’s progress in shaping the rules promulgated by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (“FinCEN”) pursuant to the Corporate Transparency Act to create a client alert summarizing the final rule, its impact on startups, and what startups need to know in order to comply. When FinCEN issued additional guidance with respect to that final rule and changed portions of the final rule including timelines for compliance, this year’s students updated the alert, then distributed it to current and former clients to notify them of the need to comply. The final bulletin is available here .
- In furtherance of that work, additional Innovation Clinic students this year analyzed the impact of the final rule not just on the Innovation Clinic’s clients but also its impact on the Innovation Clinic, and how the Innovation Clinic should change its practices to ensure compliance and minimize risk to the Innovation Clinic. This also involved putting together a comprehensive filing guide for companies that are ready to file their certificates of incorporation to show them procedurally how to do so and explain the choices they must make during the filing process, so that the Innovation Clinic would not be involved in directing or controlling the filings and thus would not be considered a “company applicant” on any client’s Corporate Transparency Act filings with FinCEN.
- The Innovation Clinic also began producing thought leadership pieces regarding AI, leveraging our distinct and uniquely University of Chicago expertise in structuring early-stage companies and analyzing complex regulatory issues with a law and economics lens to add our voice to those speaking on this important topic. One student wrote about whether non-profits are really the most desirable form of entity for mitigating risks associated with AI development, and another team of students prepared an analysis of the EU’s AI Act, comparing it to the Executive Order on AI from President Biden, and recommended a path forward for an AI regulatory environment in the United States. Both pieces can be found here , with more to come!
Innovation Trek
Thanks to another generous gift from Douglas Clark, ’89, and managing partner of Wilson, Sonsini, Goodrich & Rosati, we were able to operationalize the second Innovation Trek over Spring Break 2024. The Innovation Trek provides University of Chicago Law School students with a rare opportunity to explore the innovation and venture capital ecosystem in its epicenter, Silicon Valley. The program enables participating students to learn from business and legal experts in a variety of different industries and roles within the ecosystem to see how the law and economics principles that students learn about in the classroom play out in the real world, and facilitates meaningful connections between alumni, students, and other speakers who are leaders in their fields. This year, we took twenty-three students (as opposed to twelve during the first Trek) and expanded the offering to include not just Innovation Clinic students but also interested students from our JD/MBA Program and Doctoroff Business Leadership Program. We also enjoyed four jam-packed days in Silicon Valley, expanding the trip from the two and a half days that we spent in the Bay Area during our 2022 Trek.
The substantive sessions of the Trek were varied and impactful, and enabled in no small part thanks to substantial contributions from numerous alumni of the Law School. Students were fortunate to visit Coinbase’s Mountain View headquarters to learn from legal leaders at the company on all things Coinbase, crypto, and in-house, Plug & Play Tech Center’s Sunnyvale location to learn more about its investment thesis and accelerator programming, and Google’s Moonshot Factory, X, where we heard from lawyers at a number of different Alphabet companies about their lives as in-house counsel and the varied roles that in-house lawyers can have. We were also hosted by Wilson, Sonsini, Goodrich & Rosati and Fenwick & West LLP where we held sessions featuring lawyers from those firms, alumni from within and outside of those firms, and non-lawyer industry experts on topics such as artificial intelligence, climate tech and renewables, intellectual property, biotech, investing in Silicon Valley, and growth stage companies, and general advice on career trajectories and strategies. We further held a young alumni roundtable, where our students got to speak with alumni who graduated in the past five years for intimate, candid discussions about life as junior associates. In total, our students heard from more than forty speakers, including over twenty University of Chicago alumni from various divisions.
The Trek didn’t stop with education, though. Throughout the week students also had the opportunity to network with speakers to learn more from them outside the confines of panel presentations and to grow their networks. We had a networking dinner with Kirkland & Ellis, a closing dinner with all Trek participants, and for the first time hosted an event for admitted students, Trek participants, and alumni to come together to share experiences and recruit the next generation of Law School students. Several speakers and students stayed in touch following the Trek, and this resulted not just in meaningful relationships but also in employment for some students who attended.
More information on the purposes of the Trek is available here , the full itinerary is available here , and one student participant’s story describing her reflections on and descriptions of her experience on the Trek is available here .
The Innovation Clinic is grateful to all of its clients for continuing to provide its students with challenging, high-quality legal work, and to the many alumni who engage with us for providing an irreplaceable client pipeline and for sharing their time and energy with our students. Our clients are breaking the mold and bringing innovations to market that will improve the lives of people around the world in numerous ways. We are glad to aid in their success in any way that we can. We look forward to another productive year in 2024-2025!
- Integrations
- Learning Center
MoSCoW Prioritization
What is moscow prioritization.
MoSCoW prioritization, also known as the MoSCoW method or MoSCoW analysis, is a popular prioritization technique for managing requirements.
The acronym MoSCoW represents four categories of initiatives: must-have, should-have, could-have, and won’t-have, or will not have right now. Some companies also use the “W” in MoSCoW to mean “wish.”
What is the History of the MoSCoW Method?
Software development expert Dai Clegg created the MoSCoW method while working at Oracle. He designed the framework to help his team prioritize tasks during development work on product releases.
You can find a detailed account of using MoSCoW prioritization in the Dynamic System Development Method (DSDM) handbook . But because MoSCoW can prioritize tasks within any time-boxed project, teams have adapted the method for a broad range of uses.
How Does MoSCoW Prioritization Work?
Before running a MoSCoW analysis, a few things need to happen. First, key stakeholders and the product team need to get aligned on objectives and prioritization factors. Then, all participants must agree on which initiatives to prioritize.
At this point, your team should also discuss how they will settle any disagreements in prioritization. If you can establish how to resolve disputes before they come up, you can help prevent those disagreements from holding up progress.
Finally, you’ll also want to reach a consensus on what percentage of resources you’d like to allocate to each category.
With the groundwork complete, you may begin determining which category is most appropriate for each initiative. But, first, let’s further break down each category in the MoSCoW method.
Start prioritizing your roadmap
Moscow prioritization categories.

1. Must-have initiatives
As the name suggests, this category consists of initiatives that are “musts” for your team. They represent non-negotiable needs for the project, product, or release in question. For example, if you’re releasing a healthcare application, a must-have initiative may be security functionalities that help maintain compliance.
The “must-have” category requires the team to complete a mandatory task. If you’re unsure about whether something belongs in this category, ask yourself the following.

If the product won’t work without an initiative, or the release becomes useless without it, the initiative is most likely a “must-have.”
2. Should-have initiatives
Should-have initiatives are just a step below must-haves. They are essential to the product, project, or release, but they are not vital. If left out, the product or project still functions. However, the initiatives may add significant value.
“Should-have” initiatives are different from “must-have” initiatives in that they can get scheduled for a future release without impacting the current one. For example, performance improvements, minor bug fixes, or new functionality may be “should-have” initiatives. Without them, the product still works.
3. Could-have initiatives
Another way of describing “could-have” initiatives is nice-to-haves. “Could-have” initiatives are not necessary to the core function of the product. However, compared with “should-have” initiatives, they have a much smaller impact on the outcome if left out.
So, initiatives placed in the “could-have” category are often the first to be deprioritized if a project in the “should-have” or “must-have” category ends up larger than expected.
4. Will not have (this time)
One benefit of the MoSCoW method is that it places several initiatives in the “will-not-have” category. The category can manage expectations about what the team will not include in a specific release (or another timeframe you’re prioritizing).
Placing initiatives in the “will-not-have” category is one way to help prevent scope creep . If initiatives are in this category, the team knows they are not a priority for this specific time frame.
Some initiatives in the “will-not-have” group will be prioritized in the future, while others are not likely to happen. Some teams decide to differentiate between those by creating a subcategory within this group.
How Can Development Teams Use MoSCoW?
Although Dai Clegg developed the approach to help prioritize tasks around his team’s limited time, the MoSCoW method also works when a development team faces limitations other than time. For example:
Prioritize based on budgetary constraints.
What if a development team’s limiting factor is not a deadline but a tight budget imposed by the company? Working with the product managers, the team can use MoSCoW first to decide on the initiatives that represent must-haves and the should-haves. Then, using the development department’s budget as the guide, the team can figure out which items they can complete.
Prioritize based on the team’s skillsets.
A cross-functional product team might also find itself constrained by the experience and expertise of its developers. If the product roadmap calls for functionality the team does not have the skills to build, this limiting factor will play into scoring those items in their MoSCoW analysis.
Prioritize based on competing needs at the company.
Cross-functional teams can also find themselves constrained by other company priorities. The team wants to make progress on a new product release, but the executive staff has created tight deadlines for further releases in the same timeframe. In this case, the team can use MoSCoW to determine which aspects of their desired release represent must-haves and temporarily backlog everything else.
What Are the Drawbacks of MoSCoW Prioritization?
Although many product and development teams have prioritized MoSCoW, the approach has potential pitfalls. Here are a few examples.
1. An inconsistent scoring process can lead to tasks placed in the wrong categories.
One common criticism against MoSCoW is that it does not include an objective methodology for ranking initiatives against each other. Your team will need to bring this methodology to your analysis. The MoSCoW approach works only to ensure that your team applies a consistent scoring system for all initiatives.
Pro tip: One proven method is weighted scoring, where your team measures each initiative on your backlog against a standard set of cost and benefit criteria. You can use the weighted scoring approach in ProductPlan’s roadmap app .
2. Not including all relevant stakeholders can lead to items placed in the wrong categories.
To know which of your team’s initiatives represent must-haves for your product and which are merely should-haves, you will need as much context as possible.
For example, you might need someone from your sales team to let you know how important (or unimportant) prospective buyers view a proposed new feature.
One pitfall of the MoSCoW method is that you could make poor decisions about where to slot each initiative unless your team receives input from all relevant stakeholders.
3. Team bias for (or against) initiatives can undermine MoSCoW’s effectiveness.
Because MoSCoW does not include an objective scoring method, your team members can fall victim to their own opinions about certain initiatives.
One risk of using MoSCoW prioritization is that a team can mistakenly think MoSCoW itself represents an objective way of measuring the items on their list. They discuss an initiative, agree that it is a “should have,” and move on to the next.
But your team will also need an objective and consistent framework for ranking all initiatives. That is the only way to minimize your team’s biases in favor of items or against them.
When Do You Use the MoSCoW Method for Prioritization?
MoSCoW prioritization is effective for teams that want to include representatives from the whole organization in their process. You can capture a broader perspective by involving participants from various functional departments.
Another reason you may want to use MoSCoW prioritization is it allows your team to determine how much effort goes into each category. Therefore, you can ensure you’re delivering a good variety of initiatives in each release.
What Are Best Practices for Using MoSCoW Prioritization?
If you’re considering giving MoSCoW prioritization a try, here are a few steps to keep in mind. Incorporating these into your process will help your team gain more value from the MoSCoW method.
1. Choose an objective ranking or scoring system.
Remember, MoSCoW helps your team group items into the appropriate buckets—from must-have items down to your longer-term wish list. But MoSCoW itself doesn’t help you determine which item belongs in which category.
You will need a separate ranking methodology. You can choose from many, such as:
- Weighted scoring
- Value vs. complexity
- Buy-a-feature
- Opportunity scoring
For help finding the best scoring methodology for your team, check out ProductPlan’s article: 7 strategies to choose the best features for your product .
2. Seek input from all key stakeholders.
To make sure you’re placing each initiative into the right bucket—must-have, should-have, could-have, or won’t-have—your team needs context.
At the beginning of your MoSCoW method, your team should consider which stakeholders can provide valuable context and insights. Sales? Customer success? The executive staff? Product managers in another area of your business? Include them in your initiative scoring process if you think they can help you see opportunities or threats your team might miss.
3. Share your MoSCoW process across your organization.
MoSCoW gives your team a tangible way to show your organization prioritizing initiatives for your products or projects.
The method can help you build company-wide consensus for your work, or at least help you show stakeholders why you made the decisions you did.
Communicating your team’s prioritization strategy also helps you set expectations across the business. When they see your methodology for choosing one initiative over another, stakeholders in other departments will understand that your team has thought through and weighed all decisions you’ve made.
If any stakeholders have an issue with one of your decisions, they will understand that they can’t simply complain—they’ll need to present you with evidence to alter your course of action.
Related Terms
2×2 prioritization matrix / Eisenhower matrix / DACI decision-making framework / ICE scoring model / RICE scoring model
Prioritizing your roadmap using our guide
Talk to an expert.
Schedule a few minutes with us to share more about your product roadmapping goals and we'll tailor a demo to show you how easy it is to build strategic roadmaps, align behind customer needs, prioritize, and measure success.
Share on Mastodon

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Project Discovery and Achieve Life Skills programs developed by Education Associates help students learn about their career interests and gain entry-level job skills in key career areas. Using an applied, hands-on approach to career exploration, Project Discovery helps students with disabilities to become Job Ready and increases their ...
The Education Associates Project Discovery Special Education Transition System is a nationally-validated curriculum to help administrators and teachers accomplish many of these tasks required by NCLB and IDEA. This comprehensive curriculum is a hands-on approach that provides middle and high school special needs students with
Career Exploration Learn Real Skills by Using Real Job Tools. Learners will explore, practice and learn real job skills with real job tools to be Job Ready. Meeting all students where they are. Differentiated instruction for beginning, immediate and advanced learners. 0 % Average Increase in Greenhouse Test Scores - Jefferson County, AL Want to learn […]
Project Discovery is an approved K-12 career and life skills curriculum to prepare students with special needs and those who are at risk of dropping out of s...
arketable Skills in Pursuit of PurposeHands-on training series to prepare learners grades 10-12 and ages 18-21+ for entry-level empl. yment by developing marketable skills.Competency-based, day-by-day detailed lessons skillfu. ly prepare students for the workplace. Participants learn job-related skills, life skills.
Education Associates, developer of Project Discovery, the hands-on career education and life skills curriculum for every learner, announces additions to its Adapted Career Education Series.The Adapted Series is the only hands-on curriculum specifically designed for students who have moderate to severe cognitive disabilities, including those with autism, to explore more than 100 entry-level jobs.
The Project Discovery and Achieve Life Skills programs developed by Education Associates help students learn about their career interests and gain entry-level job skills in key career areas. Using an applied, hands-on approach to career exploration, Project Discovery helps students with disabilities to become Job Ready and increases their ...
The Project Discovery and Achieve Life Skills programs developed by Education Associates help students learn about their career interests and gain entry-level job skills in key career areas. Using an applied, hands-on approach to career exploration, Project Discovery helps students with disabilities to become Job
Project Discovery provides Effective, hands-on career education using real tools to perform real jobs for all students. Career Awareness: Introduction to career pathways Career Exploration: Over 100 career choices to help students find their future. Adapted: Opening career doors for students with autism and other significant challenges
Project Discovery's Life and Work Skills Solutions prepare students to be workforce ready. This year U.S. schools, job coaches, vocational rehabilitation counselors and transition coordinators are working hard to comply with the new Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA) Pre-Employment Transition Services (Pre-ETS) mandates. Education Associates has designed a new WIOA Solution ...
Author: Education Associates Inc. Published: 2016/10/14 - Updated: 2021/04/30 Contents: Summary - Introduction - Main - Related. Synopsis: Project Discovery is a hands-on career education curriculum with systematic instruction and video modeling. Videos that model behavior, like those in Project Discovery, are particularly effective to elicit ...
Who We Help. Project Discovery students come from economically disadvantaged families. Yet year after year, our students outperform their socioeconomic peers. In fact, Project discovery students graduate from high school on time and go on to college at a rate higher that than the general population of Virginia.
Project Discovery combines a nationally recognized curriculum of workshops that improve study skills, time management, and financial planning with assistance to students and parents applying for both admissions and financial aid. Project Discovery also takes students to college campuses where they can meet with financial aid and admissions ...
David Wait, M.D. Dr. David Wait was born in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and is a graduate of Augustana College. He obtained his medical degree at the University of South Dakota School of Medicine. His residency was at the Psychiatric Research Institute and its affiliated University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in Little Rock.
Take the next step in your Job Ready Life Ready Journey.
Here are three steps that will help you use the MoSCoW method when prioritizing your project. 1. Gather Project Requirements. Start by identifying all project requirements. Just make a giant list and be as thorough as possible. You don't want to leave out anything that might prove essential to the project. 2.
Key Points. The MoSCoW method is a simple and highly useful approach that enables you to prioritize project tasks as critical and non-critical. MoSCoW stands for: Must - These are tasks that you must complete for the project to be considered a success. Should - These are critical activities that are less urgent than Must tasks.
General The Innovation Clinic continued its track record of success during the 2023-2024 school year, facing unprecedented demand for our pro bono services as our reputation for providing high caliber transactional and regulatory representation spread. The overwhelming number of assistance requests we received from the University of Chicago, City of Chicago, and even national startup and ...
Project Discovery; Achieve Life Skills; Digital Badge Credentials; Professional Development; Why Us. Why Us; Proven Results; Resources! Resources! Find The Funds; Videos; Customers; Let's Talk! Place An Order; Let's talk. PLACE AN ORDER. Get Started Today! Take the next step in your Job Ready Life Ready Journey.
MoSCoW prioritization, also known as the MoSCoW method or MoSCoW analysis, is a popular prioritization technique for managing requirements. The acronym MoSCoW represents four categories of initiatives: must-have, should-have, could-have, and won't-have, or will not have right now. Some companies also use the "W" in MoSCoW to mean "wish.".
Project Discovery and Achieve Life Skills solutions support activities as defined by IDEA, Carl D. Perkins, and the Adult Education & Family Literacy Act. In addition our curriculum specifically supports programs to address learning loss , evidence-based summer enrichment and comprehensive after-school programs - all elements that can be ...