- Faculty Issues

Mastering Out
By Colleen Flaherty
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.
Chelsea Corkins graduated Kansas State University in August 2013 with a joint undergraduate and master’s degree in biological and agricultural engineering. Later that month she headed to Virginia Tech for a Ph.D. program in biological systems engineering.
In many ways, Corkins thrived at Virginia Tech. She liked what she was learning, had friends and took on leadership roles that eventually led to her to being elected president of the Graduate Student Assembly. But doubts about pursuing a Ph.D. were creeping in. She wasn’t enthralled with research and looked forward to teaching undergraduates and maybe even high schoolers, not graduate students.
With the support of her dean, Karen dePauw, and several faculty teaching mentors, Corkins considered options beyond the Ph.D. -- including leaving with a master’s. Because she already had a master’s in her field, though, she changed tracks a bit. After taking some time off to work in an agricultural education program through Virginia Tech, she re-enrolled as a master’s student in agricultural leadership and community education.
Corkins graduated this year and is now working as a community engagement specialist in agricultural extension at the University of Missouri.
All told, Corkins took six years to get that second master's. But she doesn’t regret it -- or her choice to leave her Ph.D. program. She’s convinced that experiences she gained during and between her studies landed her the position she holds today.
“There is no required timeline for graduate school. And beginning a Ph.D. program should not require that you finish that program,” she said. “Many students are still very young and exploring what they like to do. You’re not signing your soul away when you sign up for a program. Those five or so years aren’t set in stone, and there’s a reason for that.”
She added, “You’re not indebted to anyone. It’s all part of the experience.”
That said, Corkins didn’t take her decision lightly, and says she could not have made it without the help of mentors. Without them, she might even have walked away from her time at Virginia Tech with no degree.
Others students complete their programs with few to no doubts. But Corkins said she still encourages current Ph.D. candidates to check in with themselves on a regular basis, starting early on. What are their career goals, have they changed of late and is a doctorate still compatible with them? How are students feeling about graduate school -- and life in general?
Corkins’s choice is one way to “master out” of a Ph.D. program, although she prefers the term “pivot.” More typically, “master out” is used to describe students who enroll in a Ph.D. program and exit with a master’s degree in that same field instead.
It’s unclear how often this happens. Over all, 50 percent of Ph.D. students don't finish their programs. But there is no national data on how many master out, as opposed to just leave, and institutions don’t typically track this path. But it probably happens more than we think. And those who have done it say it should be a more visible choice.
Beth Davey, a graduate student working at Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research in Australia, recently announced her decision to master out on Twitter. In a popular thread , she described a cycle of doubt about whether she wanted, needed or even deserved a Ph.D. Ultimately a friend’s decision to master out of a graduate program was the confirmation she needed that doing so was OK. That she would be OK.
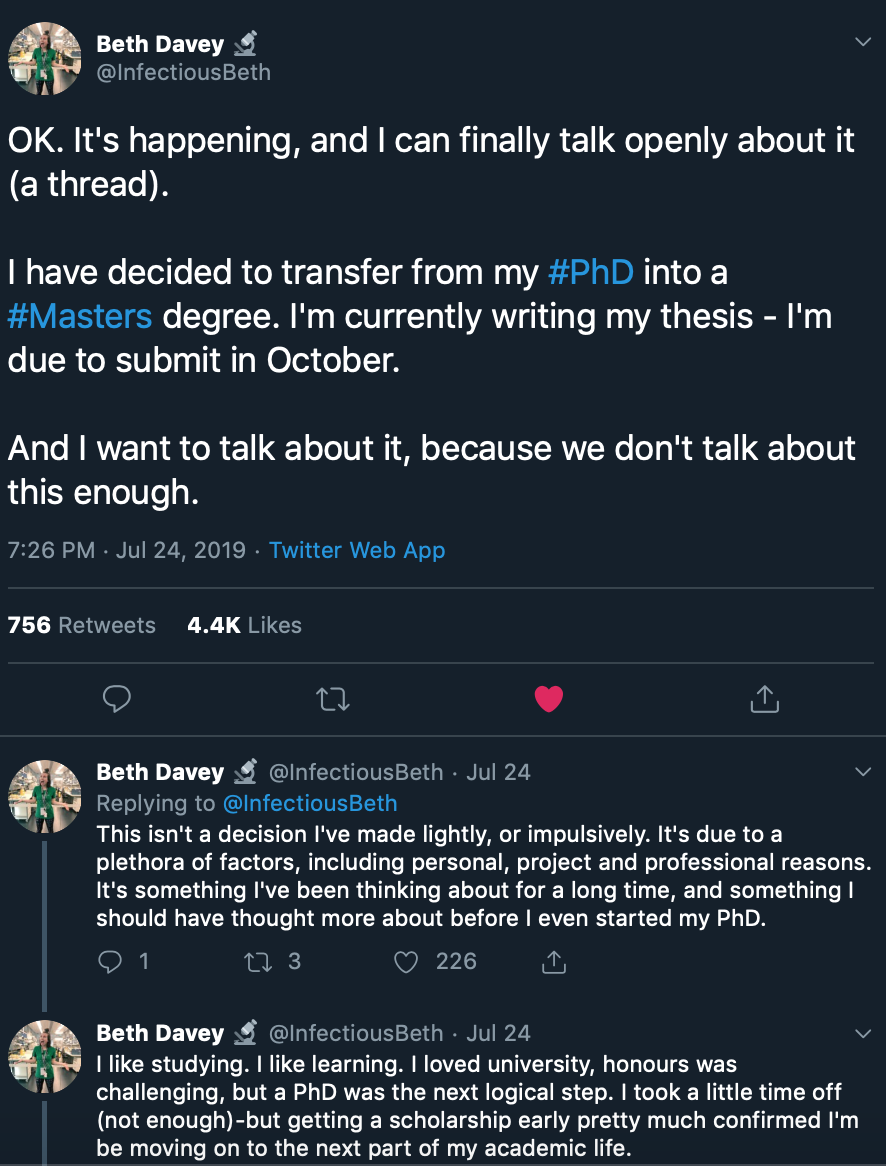
She added, “I also believe I rushed into my Ph.D., as it was the next logical step for me in academia, and I didn’t really know what else to do with my honors degree aside from a higher degree,” or working as a research assistant or technician, which she did for nine months.
Davey needs to finish her thesis to receive her master’s. She’s unsure about her exact career goals but hopeful she’ll be in a better place to contemplate them following graduation. Still, while she’s writing, she’s reaching out to her various networks and talking to people working in research, but not necessarily as researchers -- think project management, science communication and education. She also works at a science education center for K-12 students.
Suzanne Ortega, president of the Council of Graduate Schools, said there are multiple reasons that doctoral students leave with a master's, including family and life circumstances, “evolving career objectives, and a recognition that the master’s degree offers appealing options.”
Chris Golde, assistant director of career communities for doctoral students and postdoctoral fellows at Stanford University (and a columnist for Inside Higher Ed ), said a Ph.D. is a “very long commitment that’s not for everyone.” People can lose enthusiasm and “any number of things that happen in life can happen along the way.”
Still, students’ identities often became wrapped up in their Ph.D. goals, and some who might want to leave with a master’s don’t consider it (Golde doesn’t like the term "mastering out," either) because “any choice that’s not very visible is a harder one to make.”
Not a ‘Consolation Prize’
Yet Ortega said that exiting a doctoral program with a master’s degree “can be a very successful outcome, and one the higher education community should accept and support.” Regardless of why they leave, “students should know their degree is valued and can opens doors to additional career pathways and advancement.”
Jerry B. Weinberg, associate provost for research and dean of the Graduate School at Southern Illinois University at Edwardsville, said that the master’s degree is no longer the “consolation prize” for opting out of the doctoral track, but rather a “sought-after degree by employers in quite a few fields of practice.”
In many fields, such as natural science, technology, engineering, math and health care, he said, employers see the master’s degree as the “expected or preferred level of entry.” The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment in master’s-level occupations is projected to grow by almost 17 percent between 2016 and 2026, the fastest of any education level, Weinberg noted. And many recent employees without a master’s are returning to school as “a pathway to promotion and raises.”
Weinberg also said that Council of Graduate Schools data show how master’s degree applications and conferrals have increased continually over the last 10 years, with significant gains in the last five. About 84 percent of all graduate degrees conferred are at the master’s level, and institutions have changed the way they deliver programs to meet the needs of all students.
Instead of “mastering out,” Weinberg said it would be more accurate to say that students are mastering “in,” due to the increased demand.
Leonard Cassuto, professor of English at Fordham University who has written about and long advocated changing graduate education to focus on students, said a candidate’s decision to master out (or in) should never come as a total surprise to a department. Students should feel comfortable exploring their various degree and career options with their faculty mentors. And when they don’t, he said, the department has failed -- not the student.
Such conversations and decisions are better made earlier rather than later, Cassuto also said. It’s only natural for some students to decide, through a few years of graduate exploration, that a Ph.D. is not for them. But students leaving well into their research programs because that kind of work isn't for them also signals institutional failure, he said.
Centering Students
“Graduate education has centered on the Ph.D. since its inception, and that’s not necessarily a bad thing, as the Ph.D. can provide an organizing principle,” Cassuto said. “But as a professional institution, we haven’t done very much to think beyond the Ph.D., or people who don’t necessarily need it but are in graduate school anyway.”
In today’s academic job market and overall climate, in particular, he added, “no one can afford that kind of indifference.”
Golde, at Stanford, said students don’t necessarily need to share all their doubts with their faculty mentors and advisers, but rather explore them with someone. That’s why institutions need to develop infrastructures to support graduate students, including career centers and mental health facilities. Pre-existing anxiety and depression can make gradate school harder, she said, and can sometimes surface in graduate school.
Unfortunately, she said, many institutions are still playing catch-up when it comes to supporting graduate students in multiple ways, as they do undergraduates.
Master’s degrees are typically not conferred automatically. In Cassuto’s department, for example, Ph.D. students who enter without a master’s become eligible to get one after they pass their comps. But they have to formally request it from the graduate school.
At Stanford, Golde recommends that all Ph.D. students complete the paperwork and other necessary steps to get a master's for this reason -- what she joked was “credit for time served.”
At Virginia Tech, the master’s isn’t automatic, either. But dePauw, the dean who mentored Corkins, said the university accommodates students who decide they want to leave with a master’s instead of a Ph.D., such as by allowing them to stay on to complete any necessary requirements.
Some institutions, including Virginia Tech, have worked to provide the kind of infrastructure Golde mentioned and to promote cultural change. DePauw helped developed the Transformative Graduate Education initiative, which includes programs and courses that transcend departments and promote inclusion, interdisciplinarity and community. The campus also has a Graduate Life Center that houses courses, programs and events, administrative offices, and even graduate student apartments.
Still, dePauw said, there’s more work to be done to change graduate education and the way it influences students’ paths.
“Underlying some of these things is impostor syndrome and the personal angst and stress that goes on. Some people will kind of stick it out and persevere, but my philosophy about graduate education is that we should be thriving, not surviving,” she said. “We need to get these things out in the open and talk about them -- perfectionism and stress and work-life balance, and do more to make all of it easier. We have to change the culture of graduate education.”

How to Get Actionable AI Data at Your Institution
Chris Hausmann writes that colleges, divisions and departments need to be collecting their own data on students’ AI u

Share This Article
More from faculty issues.

The Academic Trumpists, Part 2
Scott McLemee concludes his review of David L. Swartz's study of pro-Trump academics.

How Do I Teach at a University That Wants Me in Jail?
Rosemary Admiral writes that her sense of belonging at her institution has been shattered.
The Academic Trumpists, Part 1
Scott McLemee reviews David L. Swartz’s study of the academics who support Donald Trump.
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Applying to graduate school
- Master’s vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences
Published on November 27, 2020 by Lauren Thomas . Revised on May 10, 2024.
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master’s and doctoral degrees:
- A master’s is a 1–2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers.
- A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3–7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research.
A master’s is also the necessary first step to a PhD. In the US, the master’s is built into PhD programs, while in most other countries, a separate master’s degree is required before applying for PhDs.
Master’s are far more common than PhDs. In the US, 24 million people have master’s or professional degrees, whereas only 4.5 million have doctorates.
Table of contents
Master’s vs phd at a glance, which is right for you, length of time required, career prospects, costs and salaries, application process, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about master's and phd degrees.
The table below shows the key differences between the two.
| Master’s | PhD | |
|---|---|---|
| Career prospects | Usually intended for a career outside of academia. | Prepares for a research career, ideally as a university professor. |
| Length of time | 1–2 years | 5–7 in the US (master’s degree included); 3–5 outside the US (after a separate master’s degree) |
| Structure | Mostly coursework, often with a semester-long or capstone project at the end. | 2 years of coursework (in the US), followed by 3–5 years of preparing a dissertation, which should make a significant original contribution to current knowledge. |
| Cost | Varies by country, university and program; usually higher upfront cost with limited financial aid available. | Tuition fees are usually waived and a living stipend provided in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. |
| Graduate salaries | Wage premium (compared to earnings with a high school education) is 23% on average. | Wage premium is 26% on average. |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
A PhD is right for you if:
- Your goal is to become a professor at a university or some other type of professional researcher.
- You love research and are passionate about discovering the answer to a particular question.
- You are willing to spend years pursuing your research even if you have to put up with a lot of dead ends and roadblocks.
A master’s degree is the better choice if any of the following apply:
- You want to continue studies in your field, but you’re not committed to a career as a professional researcher.
- You want to develop professional skills for a specific career.
- You are willing to pay a higher upfront cost if it means finishing with your degree (and thus being able to work) much faster.
- You want the option to study part-time while working.
The length of time required to complete a PhD or master’s degree varies. Unsurprisingly, PhDs take much longer, usually between 3–7 years. Master’s degrees are usually only 1–2 years.
Length of a master’s
Master’s degrees are usually 2 years, although 1-year master’s degrees also exist, mainly in the UK.
Most of the degree consists of classes and coursework, although many master’s programs include an intensive, semester-long master’s thesis or capstone project in which students bring together all they’ve learned to produce an original piece of work.
Length of a PhD
In the US, a PhD usually takes between 5 and 7 years to complete. The first 2 years are spent on coursework. Students, even those who choose to leave without finishing the program, usually receive a master’s degree at this point.
The next 3–5 years are spent preparing a dissertation —a lengthy piece of writing based on independent research, which aims to make a significant original contribution to one’s field.
Master’s degrees tend to prepare you for a career outside of academia, while PhDs are designed to lead to a career in research.
Careers for master’s graduates
There are two types of master’s degrees: terminal and research-intensive. The career prospects are different for each.
Terminal master’s degrees are intended to prepare students for careers outside of academia. Some degrees, known as professional degrees, specifically prepare students for particular professions; these include the Master of Public Policy (MPP), Master of Business Administration (MBA), Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT), Master of Fine Arts (MFA), and Master of Public Health (MPH) degrees.
Other master’s degrees, usually Master of Arts (MA) or Master of Sciences (MS or MSc) degrees, do not necessarily lead to a specific career, but are intended to be a final degree. Examples include an MS in Communications or MS in Data Analytics.
In research-intensive master’s programs, students take coursework intended to prepare them for writing an original piece of research known as the master’s thesis . Such programs are usually intended to prepare for further study in a doctoral program.
Careers for PhD graduates
As research degrees, PhDs are usually intended to lead to an academic career. A PhD can be thought of like an apprenticeship, where students learn from professional researchers (academics) how to produce their own research.
Most students aspire to become a university professor upon the completion of their degree. However, careers in academia are highly competitive, and the skills learned in a doctoral program often lend themselves well to other types of careers.
Some graduates who find they prefer teaching to producing research go on to be teachers at liberal arts colleges or even secondary schools. Others work in research-intensive careers in the government, private sector, or at think tanks.
Below are a few examples of specific fields and non-academic careers that are common destinations of graduates of those fields.
- Computer Science
- Lab Sciences
Many government jobs, including economists at a country’s central bank, are research-intensive and require a PhD. Think tanks also hire economists to carry out independent research.
In the private sector, economic consulting and technology firms frequently hire PhDs to solve real-world problems that require complex mathematical modeling.
Graduate students from the humanities are sometimes hired by museums, who can make use of their research and writing skills to curate exhibits and run public outreach.
Humanities PhDs are often well-suited to research and grant-writing roles at nonprofits. Since so much of research is funded by grants, PhD students often gain a lot of experience applying for them, which is a useful skill in the nonprofit sector.
There are a wide range of non-academic research jobs for lab scientists with doctorates in subjects like chemistry, biology, ecology and physics.
Many PhD graduates are hired by pharmaceutical companies that need to perform research to create and test their products. Government agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), also hire lab scientists to work on research projects.
Job prospects after graduation vary widely based on the field. In fields like management, computer science, statistics, and economics, there’s little underemployment—even graduates from less well-known programs can easily find jobs that pay well and use the skills they’ve gained from the PhD.
However, in other fields, particularly in the humanities, many PhD graduates have difficulty in the job market. Unfortunately, there are far more PhD graduates than assistant professor roles, so many instead take on part-time and low-paid roles as adjunct instructors. Even non-academic careers can sometimes be difficult for PhDs to move into, as they may be seen as “overqualified” or as lacking in relevant professional experience.
Because career options post-PhD vary so much, you should take the time to figure out what the career prospects are in your field. Doctoral programs often have detailed “placement” records online in which they list the career outcomes of their graduates immediately upon leaving the program. If you can’t find these records, contact the program and ask for them—placement information should play an important role in your choice of PhD program.
Although PhDs take far longer to complete, students often receive a living stipend in exchange for being a teaching or research assistant. Master’s degrees are shorter but less likely to be funded.
Both master’s degrees and PhDs lead to increased salaries upon graduation. While PhDs usually earn a bit more than those with a master’s degree, in some fields, the wages are identical, meaning that no financial benefit is gained from going on to a PhD.
Cost of a master’s
The upfront cost of a master’s degree is usually higher than a doctoral degree due to the lower amount of financial aid available. However, increased salaries also arrive faster than with a doctoral degree, because people graduate much earlier from a master’s program.
Some master’s students do receive stipends for their degrees, usually as compensation for being a teaching or research assistant. In addition, many people complete master’s degrees part time while working full-time, which allows them to fund their living costs as well as tuition.
The cost varies significantly by school and program. Public schools are usually cheaper than private ones. Some master’s degrees, such as MBAs, are notoriously expensive, but also result in much higher wages afterwards that make up for the high cost.
The master’s wage premium , or the extra amount that someone with a master’s degree makes than someone with just a high school diploma, is 23% on average. Many universities provide detailed statistics on the career and salary outcomes of their students. If they do not have this online, you should feel free to contact an administrator of the program and ask.
Cost of a PhD
PhDs, particularly outside the humanities, are usually (though not always) funded, meaning that tuition fees are fully waived and students receive a small living stipend. During the last 3–5 years of a PhD, after finishing their coursework (and sometimes before), students are usually expected to work as graduate instructors or research assistants in exchange for the stipend.
Sometimes students can apply for a fellowship (such as the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Program in the United States) that relieves them of any obligations to be a teaching or research assistant. Doctoral programs in the US tend to be better funded than in the rest of the world.
Sometimes, PhD degrees can be completed part-time, but this is rare. Students are usually expected to devote at least 40 hours a week to their research and work as teaching or research assistants.
The main cost of doctoral programs comes in the form of opportunity cost—all the years that students could be working a regular, full-time job, which usually pays much better than a graduate school stipend.
The average wage premium for PhDs is 26%, which is not much higher than the master’s degree premium.
In the US, the application process is similar for master’s and PhD programs. Both will generally ask for:
- At least one application essay, often called a personal statement or statement of purpose .
- Letters of recommendation .
- A resume or CV .
- Transcripts.
- Writing samples.
Applications for both types of programs also often require a standardized test. PhDs usually require the Graduate Record Examination (GRE), which tries to measure verbal reasoning, quantitative, critical thinking , and analytical writing skills. Many master’s programs require this test as well.
Applying for a master’s
Master’s degrees programs will often ask you to respond to specific essay prompts that may ask you to reflect upon not just your academic background, but also your personal character and future career ambitions.
Northwestern University’s Kellogg Business School requires Master’s of Business Administration (MBA) applicants write two essays, one about a recent time they demonstrated leadership and the second about their personal values.
Who you should ask for your letters of recommendation varies by program. If you are applying to a research-intensive master’s program, then you should choose former professors or research supervisors. For other programs, particularly business school, current work supervisors may be a better choice.
Some professional master’s programs require a specific test. For example, to apply to law school, you must take the Law School Admissions Test, or LSAT. For business school, you must take either the GRE or the Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT).
Applying for a PhD
When applying for a PhD, your resume should focus more on your research background—you should especially emphasize any publications you’ve authored or presentations that you’ve given.
Similarly, your statement of purpose should discuss research that you’ve participated in, whether as an assistant or the lead author. You should detail what exactly you did in projects you’ve contributed to, whether that’s conducting a literature review, coding regressions, or writing an entire article.
Your letters of recommendations should be from former professors or supervisors who can speak to your abilities and potential as a researcher. A good rule of thumb is to avoid asking for recommendations from anyone who does not themselves have a PhD.
If you want to know more about college essays , academic writing , and AI tools , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
College essays
- College essay examples
- College essay format
- College essay style
- College essay length
- Diversity essays
- Scholarship essays
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Avoiding repetition
- Literature review
- Conceptual framework
- Dissertation outline
- Thesis acknowledgements
- Burned or burnt
- Canceled or cancelled
- Dreamt or dreamed
- Gray or grey
- Theater vs theatre
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Thomas, L. (2024, May 09). Master's vs PhD | A Complete Guide to the Differences. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/graduate-school/masters-vs-phd/
Is this article helpful?

Lauren Thomas
Other students also liked, when to apply for graduate school | month-by-month timeline, how to write a statement of purpose | example, how to write a graduate school resume | template & example, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
PhD After Master’s: Your Next Academic Step
- June 15, 2024
- Office of Outreach and Relationships

Imagine standing at the crossroads of your postgraduate education, contemplating the next significant step in your academic progression. You’ve earned your master’s degree, gaining profound insights into your chosen field, yet there’s a calling to delve deeper. You dream of contributing novel research, answering unresolved questions, and elevating your expertise to the pinnacle of scholarly achievement. This is the moment many face when considering a PhD, a journey that promises not only academic advancement but also opportunities for profound professional growth and personal satisfaction.
Taking the leap from a master’s to a doctoral degree can seem daunting, but with the right resources and support, it becomes an attainable milestone. California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) have partnered to provide a seamless transition, combining CIU’s commitment to academic excellence and innovative online education with CSU’s affordable, competency-based learning model. This collaboration ensures that students have access to flexible online PhD programs designed to fit individual schedules and personalized support.
Key Takeaways
- PhD after a master’s degree signifies deeper research and specialization.
- Key factors to consider include long-term career goals and personal motivations.
- CIU and CSU partnership offers flexible online PhD programs.
- Doctoral residencies provide essential structure, training, and feedback.
- A successful PhD journey includes completing coursework and crafting a robust dissertation proposal.
Introduction to Pursuing a PhD After a Master’s
Embarking on a PhD journey following a master’s degree is a significant decision that can propel your educational trajectory and pave the way for career advancements. Evaluating this path involves considering both your intellectual pursuits and the long-term benefits to your professional development.
Understanding the Academic Path
Completing a PhD typically takes 3-4 years, during which students engage in advanced academic coursework and intense doctoral research. With most PhD students relying on a basic stipend, there’s often a need to balance financial considerations, such as missing out on pension contributions or full-time job benefits. A pivotal part of this academic trajectory is the commitment to both your research topic and your supervisor for the entire duration, ensuring alignment with your scholarly expertise and research interests.
Career Advantages and Personal Growth
Opting to pursue a PhD offers multiple career advantages and substantial personal growth. Engaging in doctoral research enhances your scholarly expertise, providing opportunities for specialized knowledge and leadership roles. Moreover, this path fosters the development of critical thinking and sophisticated problem-solving abilities, valuable skills in any professional context.
Research shows that high grades and advanced academic coursework are strong indicators of preparedness for a PhD program. Additionally, practical experience, such as research assistant roles or relevant volunteering, bolsters your application significantly. Aligning personal, academic, and professional experiences ensures readiness for this rigorous journey, making the educational trajectory smoother and more fulfilling.
California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) have partnered to facilitate this transition by offering flexible online PhD programs. CIU’s innovative online education and CSU’s commitment to affordable, competency-based learning provide a robust support system, making the pursuit of a PhD both accessible and efficient.
Advantages of Pursuing a PhD
Earning a PhD represents the highest level of academic achievement, providing unrivaled professional distinction and advanced research skills. Graduates are equipped to contribute significantly to their fields through innovative and independent research. This journey is not only about acquiring profound academic credentials but also about enhancing career opportunities.

The advantages of pursuing a PhD include both higher academic achievement and enhanced career prospects. While the time commitment is substantial—ranging from three to seven years—this investment pays off in various ways. Graduates are often regarded with prestigious qualifications that distinguish them within their professional circles, giving them a competitive edge in securing certain positions that might otherwise be out of reach.
Higher Academic Achievement
A PhD demands rigorous scholarly engagement and mastery of specialized subjects, often taking three to four years to complete. Students usually receive a basic stipend, easing financial burdens while navigating the intensive research requirements. By contributing original research to their field, doctoral candidates gain recognition and esteem, establishing a foundation for lifelong academic and professional success.
Enhanced Career Opportunities
In addition to heightened academic credentials, a PhD frequently leads to a substantial career advancement and an increase in earning potential. Studies show that doctorate holders often enjoy higher salaries compared to those with only a master’s degree across various fields. Moreover, the professional distinction afforded by a PhD can open doors to leadership roles, specialized research positions, and academia. Though initial salaries might start at an entry level if one leaves academia, the long-term benefits, including the potential for significant financial compensation, are considerable.
The collaboration between California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) exemplifies the seamless pathway from master’s to PhD. CIU’s innovative online education combined with CSU’s competency-based, affordable learning provides a robust structure supporting students’ journey towards achieving prestigious qualifications. This partnership ensures that students receive flexible, personalized support, facilitating efficient progress towards their doctoral degree.
Challenges of Pursuing a PhD
Pursuing a PhD is a significant commitment that comes with various challenges and demands, requiring careful consideration of multiple factors before embarking on this academic journey. A strong support system and a genuine passion for research are essential in navigating these difficulties.
Financial Considerations
One of the primary challenges is securing adequate funding for PhD studies. Students often rely on basic stipends, which necessitate financial modesty and can add to the overall academic stress. The costs don’t just include tuition fees, but also living expenses, which might require additional grants, scholarships, or even part-time employment. It’s critical to factor in the financial impact of not contributing to a pension or retirement fund during these years. Despite these expenses, completing a PhD can lead to higher earning potential in some fields, though this isn’t universally guaranteed, as many jobs do not require a PhD for success.
Emotional and Mental Challenges
The doctoral student life is often laden with periods of intense academic stress and personal sacrifice. Research setbacks, the pressure to publish, and maintaining self-motivation can take an emotional toll. According to statistics, 50 percent of Ph.D. students do not finish their programs, highlighting the need for strong emotional support networks. Institutions like California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) emphasize the importance of such support, providing resources aimed at mitigating these emotional and mental challenges.
Work-Life Balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is another significant challenge that PhD students face. Effective time management is essential to juggle academic responsibilities while also attending to personal life. Balancing research, coursework, and personal commitments demands strategic planning and prioritization. The collaboration between CIU and CSU offers flexibility through innovative online education and competency-based learning, which can help alleviate some of the pressures that come with managing doctoral studies alongside other life responsibilities.
Deciding the Right Time to Pursue a PhD
Choosing the optimal academic timing for pursuing a PhD is a crucial decision that affects your professional trajectory and long-term goals. Deciding whether to transition immediately from a master’s program or to gain practical career experience first can significantly influence your academic and professional journey.
Immediate Transition from Master’s
For those who opt for immediate transition, the advantage lies in maintaining the continuity of academic momentum. Bridging directly from a master’s program to a PhD allows for a seamless integration of acquired knowledge and advanced academic coursework. This path can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have clear research interests and a solid strategic education planning framework. Nonetheless, it’s vital to consider financial constraints, as most PhD students face stipends that could affect their ability to cover fees, rent, and other expenses.

Gaining Work Experience First
Conversely, gaining career experience prior to starting a PhD can provide valuable industry insights that enrich your research. Working as a research assistant or in a relevant job can help refine your professional trajectory and clarify if a PhD aligns with your long-term career aspirations. This period of career experience allows you to apply practical knowledge to academic research and may enhance your prospects for securing funding or choosing a supportive and knowledgeable PhD supervisor.
Considering these two pathways, it’s essential to align your decision with your strategic education planning and personal goals. Collaborations like the partnership between California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) offer tailored and flexible programs that can cater to diverse needs, ensuring a smooth transition regardless of the path you choose.
Choosing the Right PhD Program
Selecting the right PhD program is a crucial step in your academic journey. Your decision should encompass various criteria, such as aligning your research specialization with the projects offered and finding a supportive academic community. This process demands careful consideration of several factors, including the duration and nature of the program, available funding options, and potential mentorship in PhD studies.
Research Areas and Topics
One of the first steps in the doctoral program selection is identifying your research specialization. In STEM subjects, most advertised projects are predefined, offering a structured pathway for your doctoral research. However, if you are in the Arts, Humanities, or Social Sciences, self-proposed projects are more common and allow you to tailor your research more closely to your interests. Whether you opt for a predefined or self-proposed project, ensure that your chosen topic has the right scope for a doctorate, typically involving a commitment of about three to four years of full-time work.
Finding the Right Supervisor
Another critical aspect of your doctoral program selection is finding a supervisor whose expertise aligns with your research interests. Effective mentorship in PhD programs is fundamental to your academic success. Research potential supervisors thoroughly to understand their mentorship style and areas of expertise. A good match can significantly influence your progress and the overall doctoral journey.
California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) have partnered to simplify this process. CIU’s innovative online education and CSU’s focus on affordable, competency-based learning offer a seamless transition from a master’s to a PhD. Their collaboration provides flexible online programs with personalized support, making the journey to obtaining a doctoral degree both efficient and achievable.
California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) Partnership
The collaboration between California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) represents a significant milestone in the landscape of online doctoral programs. This unique academic alliance provides a seamless transition for students moving from a master’s program to a PhD.

Known for their innovative approaches to online education, CIU’s commitment to academic excellence merges ideally with CSU’s focus on affordable, competency-based learning. This CIU and CSU collaboration strives for the integration of online learning modalities, ensuring that doctoral candidates benefit from flexible academic structures and modern methodologies.
The partnership capitalizes on their combined strengths, streamlining the process for students aiming to achieve rigorous scholarship while maintaining a supportive learning environment. This collaboration fosters an academic setting that is both accessible and accommodating, meeting the diverse needs of today’s doctoral students.
By promoting the integration of online learning, CIU and CSU offer programs that not only cater to a broad range of academic interests but also provide personalized support tailored to individual student needs. This innovative partnership highlights the importance of flexibility and accessibility in advanced education, proving that high-quality doctoral education can be both rigorous and attainable.
Benefits of Online PhD Programs
Embarking on a virtual doctoral studies journey holds numerous advantages for aspiring scholars. With the collaboration between California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU), students benefit from a unique blend of flexibility and support in their academic pursuits.
Flexibility and Convenience
Online or distance learning PhD programs offer unparalleled flexibility, allowing students to seamlessly integrate their studies amidst busy work and personal schedules. These adaptable learning models enable candidates to continue working while pursuing their education, thus broadening their career horizons without sacrificing current professional engagements.
These programs span various fields—arts, humanities, natural sciences, social sciences, business, and communications—catering to a wide array of scholarly interests. Moreover, the ability to tailor learning experiences based on individual preferences and subject matter adds an extra layer of convenience and relevance.
Personalized Support
One of the significant online PhD advantages lies in the robust remote academic support systems these institutions provide. Virtual mentorship, access to digital resources, and personalized guidance help maintain a consistent academic momentum, ensuring students stay on track throughout their studies.
CIU and CSU emphasize the importance of specialized support structures, especially for subjects like physics, psychology, social work, and education, each requiring tailored online degree program tools. This partnership exemplifies the commitment to academic excellence through innovative support mechanisms, allowing students to efficiently navigate their doctoral journey.
The benefits of these programs extend beyond flexibility and support. Students save on travel expenses and related costs, benefiting from the same quality of instruction as their on-campus counterparts. Furthermore, online PhD programs provide ample opportunities for networking with professionals worldwide, enriching the academic experience and expanding career opportunities.
Competency-Based Learning at CSU
The Continents States University (CSU) excels in competency-based learning, prioritizing skill development and real-world knowledge application. With a strong emphasis on self-paced academics, CSU ensures that every student can tailor their education to their own speed and learning style, while retaining the rigor of traditional learning models.

Customized Learning Paths
CSU’s curriculum is designed with a skills-focused curriculum to meet the diverse needs of its students. Customized learning paths allow individuals to select courses and research projects that align with their professional goals and interests. For example, courses like EDRM 701 and EDRM 705 are crafted to provide a deep understanding of regression techniques and qualitative research methods, respectively.
Affordable Education
Affordability is a key factor in CSU’s mission. The university offers cost-effective degrees, minimizing financial barriers for students aiming to achieve higher education. Programs such as the online student affairs in higher education (SAHE) Master of Science degree provide comprehensive education in areas vital to student success, without the hefty price tag often associated with advanced degrees. Additionally, faculty members in the School of Education bring extensive practical experience, further enriching the tailored PhD programs available.
Preparing for the PhD Journey
Embarking on the PhD journey necessitates thorough doctoral preparation , beginning with a master’s degree in a related discipline as a prerequisite. While some programs may require additional coursework or pertinent research experience , it’s critical to identify key areas of interest and narrow down research topics that align with your career goals.
Successful research planning forms the cornerstone of your PhD journey. Prospective students must engage in extensive research planning to outline their projects, attending academic conferences, seminars, and workshops to expand networks and foster collaborations. Adding to those connections through research or teaching assistantships can provide financial support and invaluable experience.
Academic readiness encompasses both mental preparedness and establishing a work-life balance, crucial for managing stress and sustaining well-being throughout the typical three to four years of full-time study. Frequent milestones, such as initial project discussions, literature reviews, and thesis plan submissions, act as progress markers and help maintain focus.
The partnership between California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) offers a unique blend of successful PhD strategies . CIU, renowned for its innovative online education, and CSU, noted for its affordable and competency-based learning, provide flexible, online programs with personalized support. This collaboration ensures a seamless transition from a master’s to a PhD, helping students to navigate their academic pursuits efficiently.
As you prepare, cultivating the necessary skills, such as critical thinking and problem-solving, will be key. Establishing clear objectives and consistently engaging with academic milestones will ensure a successful navigation of the PhD landscape, ultimately paving the way for specialized job opportunities in academia or industry.
Managing the Transition from Master’s to PhD
Transitioning from a Master’s to a PhD program is a significant academic leap, necessitating effective academic transition strategies to ensure success. This process involves not only continuing to hone the critical skills developed during your Master’s studies but also extending your academic and professional networks.
Building on Master’s Skills
The substantive body of work required for a PhD, which typically encompasses around 80,000 words compared to the 20,000 words of a Master’s thesis, demands leveraging prior knowledge gained during your Master’s. This includes keen critical analysis, refined research methodologies, and advanced time management. Universities like California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) emphasize building on these foundational skills through their innovative and flexible online PhD programs.
Networking and Support Systems
Another vital aspect of transitioning from a Master’s to a PhD is creating professional connections that can provide a support system throughout your doctoral journey. Participating in networking events and support classes can help you establish a sense of community among first-year and later-stage PhD students, as well as build relationships with mentors, supervisors, and peers. Regular interactions with academic staff through research seminars and mentorship can significantly influence your PhD success, offering both guidance and motivation.
Partnerships like that of CIU and CSU further enhance this transition by providing personalized support systems and fostering environments conducive to both online and competency-based learning, ensuring that your shift to a PhD program is both smooth and efficient.
Finding the Right Support and Motivation
Embarking on a PhD journey can be both exhilarating and challenging, necessitating a robust support system. Recognizing the importance of this, California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) have collaborated to create a seamless transition from a master’s to a PhD program. CIU is known for its innovative online education and commitment to academic excellence, while CSU focuses on affordable, competency-based learning.
The mentorship in PhD programs plays a critical role in doctoral journey support. Mentors provide guidance, feedback, and academic encouragement crucial for maintaining intrinsic motivation. This support is essential given that a PhD typically spans 3-4 years and involves financial modesty with a basic stipend. External encouragement from supervisors, peers, and personal networks helps students navigate the financial costs, such as fees and living expenses, as well as the emotional strain that accompanies rigorous research commitments.
Moreover, intrinsic motivation is a key ingredient for enduring the demands of a PhD. Passion for the chosen topic and dedication to the research process can drive students through challenging phases. Internal drive, bolstered by external academic encouragement, ensures persistence and progress toward their ultimate goals. The CIU and CSU partnership provides personalized support tailored to the unique needs of each doctoral candidate, ensuring a balanced and supportive educational journey.
Potential Career Paths with a PhD
A PhD opens various pathways that extend beyond academia. Approximately 30% of PhD graduates remain in academic employment three years after completing their degree, involving roles such as postdoctoral researchers, lecturers, and professors (HEPI, 2020). These post-PhD careers in academia demand not only deep expertise but also a passion for teaching and mentorship.
Academic Careers
Academic employment typically involves a blend of teaching, research, and administrative responsibilities. Many PhD holders pursue postdoctoral research positions that offer a chance to further specialize their research. These roles, often lasting between 1 to 4 years, provide a stepping stone toward becoming a full-time faculty member at a university or a research institute. Approximately 70% of PhD holders in the Netherlands pursue careers outside academia, reflecting a growing trend towards non-academic job prospects driven by the evolving job market demands.
Industry Research Positions
PhD graduates are highly sought after in industry research and development roles, especially within sectors such as pharmaceuticals, data science, consultancy, industrial chemistry, aeronautics, finance, and software engineering (Bennett, 2022). The skills gained during doctoral research, including analytical thinking, autonomy, and teamwork, are invaluable assets in these industries. Unlike the shorter-term contracts typically associated with postdoc positions, industry roles often offer more financial stability and long-term career growth.
Other Professional Opportunities
Beyond academia and industry, PhD graduates can explore numerous non-academic job prospects. These include roles in the public, charity, and education sectors, as well as opportunities in entrepreneurship. Approximately 80% of postdoctoral researchers in the Netherlands pursue non-academic careers, leveraging their skills in policy advising, government research, or starting spin-off companies based on their research work. The Netherlands, for example, hosts a robust startup ecosystem, being one of the top 5 innovation leaders in Europe, thus providing ample resources for entrepreneurial ventures.
Real-Life Experiences and Testimonials
Embarking on a PhD journey is a monumental decision that significantly impacts your academic and personal life. The PhD graduate stories gathered from various interviews and personal accounts highlight both the challenges and rewards of this rigorous path.
For instance, many students receive a stipend of around $20,000 over 10 months, which is often considered below the living wage. Despite financial constraints, doctoral journey insights emphasize the invaluable experiences gained. One student, after hiking approximately 1,000 miles on the Appalachian Trail and nearly 2,000 miles on the Pacific Crest Trail, learned 12 significant lessons during the initial semester of their PhD program, navigating through massive reading lists that could reach 1,500 pages weekly.
The academic strain is considerable, with students producing heaps of articles, book reviews, and encyclopedia entries. Nevertheless, many PhD graduate stories confirm that the support from a close-knit cohort, typically consisting of around five students, and the mentorship from dedicated supervisors play pivotal roles in persevering through the program. For example, despite the prevalent occurrence of depression among grad students, the supportive graduate community and personalized academic environments provided by institutions like California Intercontinental University (CIU) and The Continents States University (CSU) enable students to manage stress and maintain motivation.
Katfriend #1 mentions that motivation is crucial, especially in Europe, where a PhD is often viewed as an advanced professional qualification. Meanwhile, Katfriend #2’s personal academic account reveals that self-discipline and focus facilitated the completion of their doctorate in just three years. Sabine Jacques reflects on the importance of having good supervisors and engaging in activities outside academia to combat loneliness, also pointing out the necessity of a genuine interest in one’s research topic.
Ultimately, these doctoral journey insights from various personal academic accounts offer invaluable guidance and inspiration. By understanding the diverse paths and outcomes achieved through the PhD process, prospective students can better prepare for their own academic endeavors.
The journey to achieving a PhD is a rigorous yet immensely enriching experience that prepares you for advanced academic and professional opportunities. This doctoral journey conclusion ties together the various facets of PhD pursuit, reflecting on how it serves as an investment in your future. Whether it’s enhancing your career prospects or fostering personal growth, the commitment to embark on this path truly defines academic advancement.
Programs like the Thesis Bootcamp illustrate the structured support available to PhD students. With a selection rate of about 26%, this program ensures a focused and competitive environment. The participants, over 400 in number, have demonstrated resilience and brilliance, an attribute noted among grad students. By generating a minimum of 5,000 words, and in some cases reaching up to 20,000 words, students showcase their dedication to scholarly achievement.
Pursuing your PhD through partnerships like that of California Intercontinental University and The Continents States University presents an even smoother transition from a master’s program. CIU’s innovative online education paired with CSU’s affordable, competency-based learning ensures you receive personalized support and flexibility. Such comprehensive programs align perfectly with the needs of modern PhD candidates, making this prestigious educational pursuit more accessible and manageable.
The decision to undertake this journey must be made with careful consideration of your individual goals, available support systems, and readiness for the immense commitment required. Reflecting on these factors ensures that your doctoral journey will be both rewarding and impactful, cementing your place in the realm of academic excellence and beyond.
Source Links
- https://capella.edu/blog/phd-doctorate/steps-in-getting-phd/
- https://talk.collegeconfidential.com/t/phd-after-bachelors-or-masters/1830586
- https://academicpositions.com/career-advice/master-s-first-or-straight-to-phd
- https://bitesizebio.com/11022/is-it-worth-doing-a-phd-after-a-masters/
- https://blog.accepted.com/applying-to-phd-programs-when-where-how-and-why/
- https://phdstudent.com/blogs/pros-and-cons-of-getting-a-master-s-before-a-doctorate-part-2/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/graduate-students-dilemma-should-i-do-phd-md-farhan-haque
- https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2019/08/05/why-mastering-out-phd-program-might-really-be-mastering
- https://www.findaphd.com/guides/finding-the-right-phd
- https://www.online-phd-programs.org/top-online-post-graduate-schools-west-coast
- https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/bitstream/1807/34067/1/Jeram_Sanjay_201211_PhD_thesis.pdf
- http://www.edugainoverseas.com/universities/partners/
- https://www.petersons.com/blog/online-phd-programs-become-an-expert-while-living-your-life/
- https://www.thechicagoschool.edu/insight/career-development/benefits-phd-programs-online/
- https://www.gcu.edu/blog/doctoral-journey/can-you-get-phd-online
- https://www.online.colostate.edu/degrees/olpc-phd/
- https://www.online.colostate.edu/degrees/student-affairs/
- https://kuscholarworks.ku.edu/bitstream/handle/1808/10023/Uden_ku_0099D_12036_DATA_1.pdf;s
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-prepare-phd-program-comprehensive-guide-nura-muhammad-sulaiman
- https://www.findaphd.com/guides/the-phd-journey
- https://blog.scrintal.com/10-essential-tips-for-considering-and-preparing-to-apply-for-a-phd-ddd8b3ba6461
- https://career-advice.jobs.ac.uk/studentship-advice/managing-the-transition-from-masters-to-phd-top-ten-tips/
- https://www.findaphd.com/blog/3347/using-a-masters-as-a-stepping-stone-towards-a-phd
- https://hellobio.com/blog/taking-positive-steps-towards-phd-success.html
- https://www.researchretold.com/career-paths-after-a-phd/
- https://www.academictransfer.com/en/blog/six-career-paths-for-phd-graduates/
- https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2020/01/29/phd-student-describes-what-hes-learned-about-grad-school-over-his-first-semester
- https://ipkitten.blogspot.com/2014/08/its-wonderful-phd-life-oh-wait-is-it.html
- https://thesiswhisperer.com/2019/07/17/a-5-step-program-for-finishing-your-phd-finally/
Related Posts

The Continents States University Achieves Candidacy Status for Accreditation by the International Accreditation Council for Business Education (IACBE)
Press Release St. Louis, MO, USA (August 2024) – The Continents States University is proud to announce that we have

The Continents States University Achieved IACBE Accreditation Candidacy
We’re proud to announce The Continents States University’s IACBE candidate for accreditation status. Our commitment to excellence in business education shines through this achievement.

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > Tips for Students > Master’s vs PhD — These are the Main Differences
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Master’s vs PhD — These are the Main Differences
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: October 31, 2019

The consideration between earning a master’s vs PhD is not always an easy choice. While many careers and personal aspirations may be complete with just an undergraduate degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s), a lot of people continue their higher education to obtain graduate degrees. These include a master’s and/or a PhD.
Neither a master’s degree nor a PhD is considered to be a walk in the park. Therefore, it’s useful to understand why you would earn either and then decide how far to go.

Photo by Good Free Photos on Unsplash
Definitions: master’s vs phd.
Bost a master’s and PhD are defined as postgraduate degrees, but they require different commitments and styles of learning.
1. Master’s Degree:
Mostly all master’s degrees will require the completion of an undergraduate bachelor’s degree to enroll. They generally all share the same common requirement for a thesis or dissertation to graduate.
Earning a master’s degree through a taught program will result in the completion of a Master of Art (MA), Master of Science (MS), or Master of Philosophy (MPhil). For those who earn their master’s degree through research, they will earn a Master of Research (Mre), in a tailored field of study. There are also degree-specific master’s programs like Master of Business Administration (MBA) and Master of Education (M.Ed).
After earning a master’s degree, the next step is a PhD, which entails both working and performing research at an institution. A PhD is an abbreviation for “Doctor of Philosophy.” It is the highest academic degree one can achieve. As such, it is a time-consuming pursuit that requires a lot of studying and research.
You may be wondering, “Do you need a master’s to get a PhD?”
Technically, the answer is not always. Some students skip a master’s and go straight for their PhD, but they may lack research experience. While it could save money, the transition between a bachelor’s and a PhD is incredibly sharp. It may be harder to complete a PhD without the experience from a master’s.
Yet, some institutions may allow for the possibility to earn both your master’s and PhD in conjunction with one another. This will alleviate the transition between skipping a master’s and going straight to earning a PhD.
Should You Get a Master’s or PhD?
There are many considerations to factor when deciding between a master’s of PhD. For starters, it’s useful to consider the amount of time it will take, the cost, and the benefits and disadvantages of each. It is also of utmost importance to explore your own personal goals and reasons for wanting a graduate degree.
If your desired career of choice requires a PhD, like becoming a university professor, then you have your answer. If you want to start a business and benefit by networking while in school, a Master of Business Administration (MBA) could be a good idea. Consider what you want to pursue as a career and find out the requirements first.
Another useful thing to note is that a master’s degree can be used for a shift in careers. For example, if you attended college and earned a bachelor’s degree in humanities, but now you want to pursue science, you can still earn your master’s degree in a scientific discipline. On the other hand, a PhD is tailored to your field of study and specialty, so it will require that you are sure of your direction when you first earn your master’s degree.
Length of Time
A typical master’s degree program takes about two years full-time. However, there are accelerated programs that can be completed in just a year or so.
A PhD, in general, requires five to six years of studying, teaching, and research. However, it may even take some students up to eight or nine years to graduate. With this significant investment in time, it’s necessary to know if a PhD is right for you before starting.
The cost of both programs varies by institution and enrollment status of part-time versus full-time. However, since a PhD takes longer to complete, it will end up costing more. With that said, if you look into your return on investment, a PhD could end up yielding a higher salary, and therefore end up “costing less.”
Additionally, there is also the possibility of being paid to complete your PhD. Some students may receive an academic stipend, a university fellowship or apprenticeship or a reduced fee to earn their PhD while completing research (or teaching) at an institution. It’s also possible to get financial aid through a scholarship or grant.
As tuition rates continue to rise, it’s useful to look into alternative institutions for affordable education. For example, the University of the People offers a tuition-free master’s program in Business Administration and Education. This means you can study 100% online and graduate for less than the cost of most programs.
Weighing the Benefits
When comparing the two degree types, here are some benefits of each:
- Career-oriented
- Can open the door for more job opportunities
- Costs less than a PhD
- Takes less time than a PhD
- Helps you stand out from those with only an undergraduate degree
- You can perform research in your field of choice
- You become an expert in your field
- The prefix Dr. is added to your name
- You can teach in academia at the highest level
Required Commitment and Reasons to Pursue
Both a master’s and a PhD require a huge amount of hard work and utter commitment. You must be dedicated and motivated to complete either degree. Since most careers only may require a bachelor’s degree, having a master’s or PhD will set you apart from the competition. However, this should not be the sole reason to pursue either.
You may be wondering why would you earn either degree. Here’s a look at some motivational factors:
Reasons to Study for a Master’s
- Your career requires it (see next section)
- You want to advance your subject knowledge
- You want to experience graduate school and network with peers
Reasons to Study for a PhD
- You want to contribute new research to your field of choice
- Your career requires a PhD
- You want to earn the title of Dr.

Photo by Online Marketing on Unsplash
Required degrees by career.
Most people are motivated to pursue higher education because their desired careers require they do so. Here, we will break down those fields that require the completion of a master’s degree as it’s high on the list of reasons why to get one.
- Education Administration: To work as an administrator in an educational institution, you need to hold an advanced degree. A Master’s in Education (M.Ed) will provide you with the necessary knowledge and required skills to succeed in the field.
- Executive Level Business: A Master’s in Business (MBA) will not only place you ahead of the competition to land high-level positions in the field of business, but it can also be the jumping off point for becoming your own boss.
- Environmental Science: With issues in climate change and technological advancement, careers in Environmental Science are growing. As with most scientific careers, it requires a master’s degree where you will learn Applied Ecology, Environmental Policy, Environmental Chemistry, and more.
- Mental Health: To become a licensed practitioner and assist in mental health counseling, you will continue your education through a master’s degree in the field.
- Physical Therapy: Employers of physical therapists often prefer them to obtain a master’s degree in the discipline as the field is highly specialized.
Of course, some careers require a PhD. These careers are easy to spot because they have the prefix Dr. in front of them or the suffix like J.D. (Juris Doctor). To become a lawyer, doctor of medicine, veterinary medicine or psychologist/psychiatrist, you must obtain a PhD in the respective field.
Salary Differences Between Master’s and Ph.D. Graduates
According to a study performed by the Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce , the overall evidence shows that the higher the degree you have, the higher your salary potential. However, the differences vary by subject level and field.
In general, the expected lifetime earnings of those with each degree level is as follows:
- High School Diploma: $973,000
- Bachelor’s Degree: $1.3 million
- Master’s Degree: $2.7 million
- Doctorate Degree: $3.3 million
The Bottom Line
Aside from the financial cost and length of time, the opportunity to earn a master’s and a doctorate degree can offer several benefits.
However, it is an undertaking that requires a lot of dedication and motivation on behalf of the student. As such, it’s important to perform research on your desired career’s requirements, as well as your personal interest in pursuing either a Phd vs master’s.
In this article
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
What Comes After a Master's Degree?
Know Your Graduate School Options Beyond a Master's
- Choosing a Graduate Program
- Tips & Advice
- Admissions Essays
- Recommendation Letters
- Medical School Admissions
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
- M.A., Developmental Psychology, Fordham University
After receiving your master's degree, there are still more options to study in graduate school, including an additional master's degree, doctorate programs (Ph.D., Ed.D., and others) and certificate programs to consider. These degree and certificate programs all vary in level, time to complete, and more.
Additional Master's Degrees
If you have already earned a master's degree and wish to continue your studies, you might consider a second master's degree. Since master's degrees tend to be specialized degrees, as you grow within your career you may find that a new specialty is required or that two specialties will make you an even more desirable candidate when job hunting. In education, for example, many teachers earn a Master's of Arts in Teaching degree but may return to the classroom to study for a degree in the field in which they are teaching, such as English or mathematics. They may also wish to pursue a degree in organizational leadership, especially if they are looking to grow into an administrative role in the school.
Master's degrees generally take two, sometimes three, years to complete (after earning a bachelor's degree), but pursuing a second degree in a similar discipline might allow you to carry over some credits and complete the program sooner. There are also some accelerated master's programs that can earn you a degree in less than a year; just be prepared for a lot of hard work. All master's programs entail coursework and exams , and, depending on the field, possibly an internship or other applied experience (for example, in some fields of psychology ). Whether a thesis is required to obtain a master's degree depends on the program. Some programs require a written thesis; others offer an option between a thesis and a comprehensive exam . Some programs provide capstone courses, which are usually semester-long courses that provide a comprehensive overview of everything learned within the program and ask students to complete several small thesis statements to demonstrate mastery.
A meaningful way in which master's programs differ from many, but not all, doctoral programs is in the level of financial aid available to students. Most programs do not offer as much assistance to master's students as they do for doctoral students, and so students often pay most if not all of their tuition. Many top institutions even offer full scholarships for doctoral students, but a doctoral program is usually a much more comprehensive and time-consuming educational program, requiring a full-time commitment, versus the possibility of working your full-time job while going for a master's degree.
The value of the master's degree varies by field. In some areas such as business, a master's is the unstated norm and necessary for advancement. Other fields do not require advanced degrees for career advancement. In some cases, a master's degree may hold advantages over a doctoral degree. For example, a master's degree in social work (MSW) may be more cost-effective than a doctoral degree, given the time and funds required to earn the degree and the pay differential. The admission offices at the schools you're applying to can often help you determine which program is best for you.
Ph.D. and Other Doctoral Degrees
A doctoral degree is a more advanced degree and takes more time (often a great deal more time). Depending on the program, a Ph.D. could take four to eight years to complete. Typically, a Ph.D. in North American programs entails two to three years of coursework and a dissertation — an independent research project designed to uncover new knowledge in your field that must be of publishable quality. A dissertation can take a year or more to complete, with most averaging about 18 months. Some fields, like applied psychology, may also require an internship of one year or more.
Most doctorate programs offer various forms of financial aid , from assistantships to scholarships to loans. The availability and types of support vary by discipline (e.g., those in which faculty conduct research sponsored by large grants are more likely to hire students in exchange for tuition) and by the institution. Students in some doctoral programs also earn master's degrees along the way.
Certificate Programs
Certificates can usually be earned in less than a year and are often significantly less expensive than going after additional degrees. If you're wondering what should come after your master's degree and you're not sure if a doctoral program is right for you, this could be the way to go. Certificates range in scope greatly and can allow you to hyperfocus on the areas in which you wish to excel. Some schools even offer certificate programs that are of a masters degree caliber, so you can walk away better prepared for your career and without breaking the bank. Employers who offer tuition assistance may look favorably on a less expensive certificate program as well.
Which Is the Best?
There is no easy answer. It depends on your interests, field, motivation, and career goals. Read more about your field and consult faculty advisers to learn more about which option best fits your career goals. Some final considerations are as follows:
- What types of jobs do a master's degree, doctoral degree, and certificate holders have? Do they differ? How?
- How much will each degree cost? How much will you earn after obtaining each degree? Is the outcome worth the cost? What can you afford?
- How much time do you have to invest in additional schooling?
- Are you interested enough to pursue many years of schooling?
- Will earning a doctoral degree offer a substantial benefit in your employment and advancement opportunities?
Only you know which is the right degree for you. Take your time and ask questions, then carefully weigh what you learn about each, its opportunities, as well as your own needs, interests, and competencies. What comes after a master's degree is up to you.
- What Does It Take to Earn a Master's Degree?
- Degree Requirements for Therapists
- The Meaning and Significance of a PsyD
- How to Decide Between a Ph.D. or Psy.D. in Psychology
- Should I Seek the MSW, PhD or DSW for a Career in Social Work?
- Can You Change Fields from Undergrad to Grad?
- 6 Tips Applying to Grad School for a Different Major
- What to Expect in an Online Graduate Class
- Grad School Online Education Advantages and Disadvantages
- Best Dental Schools in the U.S.
- Top 10 Best Veterinary Schools in the U.S.
- 3 Considerations in Selecting a Graduate Program
- How to Choose Between Grad Schools
- A Doctor of Philosophy or Doctorate
- A Note About Masters and Doctoral Comprehensive Exams
- What is Grad School Like?
- Skip to main content
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Apply Apply
- Follow Us

Demystifying Graduate Degrees: Comparing Master’s vs. Doctorate

You want a graduate degree — to continue exploring your passions, make discoveries or advance your career — but how do you turn that decision into a plan?
It starts with understanding the difference between a master’s and a PhD in your field. They differ in length, intensity, curriculum and career paths, so you’ll also need a clear idea of why you want to pursue a graduate degree to determine which one you should get.
What Is a Master’s Degree?
If you’ve completed your undergraduate degree, it might be time to ask, “What’s next?”
That’s where Master’s degrees can come in.
Whether you want to specialize in a particular area or get advanced skills in your profession, a master’s degree can help you get there in 1-2 years.
The most common types of master's degrees include:
- Master of Arts (MA),
- Master of Science (MS),
- Master of Business Administration (MBA),
- Master of Education (MEd),
- and Master of Fine Arts (MFA).
What do you learn in a master’s program?
The short answer? A lot.
Master’s degree programs are designed to build on the foundational knowledge gained during your undergraduate studies, and the curriculum focuses on advanced knowledge and skills in a particular field.
Here’s what you can expect to encounter in a master’s program:
Advanced coursework: Master's programs provide advanced courses that build upon the foundational knowledge gained during your undergraduate studies. These courses delve deeper into specific topics within your field and often explore the latest research and developments.
Specialization: One of the primary goals of a master's program is to allow you to specialize in a particular area. Whether pursuing a Master of Arts, Master of Science, or a professional degree like an MBA, you can focus your studies on a specific subfield or concentration within your discipline.
Research and analysis: Many master's programs require you to engage in research projects and analytical work. This could involve conducting independent research under the guidance of a faculty advisor or participating in group research projects with fellow students. Through these research experiences, you’ll develop critical thinking and analytical skills, learn how to gather and evaluate relevant data and draw meaningful conclusions.
Practical applications and internships: Some master's programs incorporate practical training opportunities like internships, practicums, or field experiences; hands-on experiences allow you to apply the knowledge and skills gained in the classroom to real-world settings.
Collaboration and networking: A Master's program is a rich collaboration and networking environment. Collaborative projects, group discussions, and professional events allow you to exchange ideas and build connections within your field, often leading to long-lasting professional relationships and potential career opportunities.
Thesis project: Outside of building skills like project management, problem-solving, project management, and effective communication, thesis projects in master's degree programs serve as a cornerstone for building advanced skills, expanding professional networks, and contributing to the body of knowledge in your respective field.
Why get a master’s degree?
Career advancement: One primary advantage of getting a master’s degree is an edge in the job market. Employers value the specialized knowledge and advanced skills that come with a master’s degree, opening up new and exciting career opportunities. The cherry on top? Individuals with a master’s degree often earn more than those without an advanced degree — you can take that to the bank, especially if you set yourself up for financial success during your studies. Flexibility: Another aspect to consider is the flexibility that a master’s degree offers. Many programs offer part-time or online options, allowing you to balance your studies with work or other commitments. This flexibility can be particularly helpful if you’re already established in your career but want to gain additional qualifications. Growth opportunities: Depending on your field, a master’s degree can be a stepping stone toward a PhD or other doctoral programs. It gives you a solid foundation in research methods and academic rigor — a boon if you want to pursue a career in academia or conduct advanced research.
What is a Doctoral Degree or PhD?
A doctoral degree is a terminal degree — it represents the pinnacle of academic achievement and is the most advanced degree you can attain. Doctoral students want to become authorities in their chosen fields and develop the skills to conduct independent and original research.
Doctoral programs usually span 3-6 years of full-time study, during which students complete advanced coursework, pass comprehensive examinations, engage in extensive research and ultimately produce a dissertation that contributes new knowledge to the field.
There are several types of doctoral degrees based on different academic and professional aspirations, including:
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD),
- Doctor of Education (EdD),
- And Doctor of Psychology (PsyD), among others.
What do you learn in a doctoral program?
When you successfully defend your dissertation and complete your degree, you also become an expert in your field — but it doesn’t happen overnight. Here's what you can expect to encounter in a doctoral program:
Advanced research: If you’re looking for a hard emphasis on research, a doctoral program is the place to be. Over several years, PhD students engage in extensive research activities — including conducting independent research, producing scholarly publications, and contributing to the knowledge base of their field through original research contributions.
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks: PhDs are an incredible opportunity to deepen your understanding of theoretical and conceptual frameworks in your field of study. You'll critically analyze existing theories, evaluate their applicability, and develop your theoretical frameworks to advance knowledge and understanding in your chosen area of research.
Advanced methodological training: Because a dissertation is an original research project, you’ll gain advanced training in research methodologies and data analysis techniques, like designing robust research studies, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing valid and reliable conclusions from your research findings.
Critical thinking and intellectual independence: Both academia and industry employers highly value independent thinkers and workers. Doctoral programs foster critical thinking and intellectual independence by challenging you to evaluate existing research, identify gaps in knowledge, and propose innovative research ideas. Teaching and Mentoring Experience: Being a teacher or mentor is a great opportunity to share your hard-earned knowledge, and universities agree. Doctoral programs often provide opportunities to teach and mentor undergraduate students, develop effective pedagogical skills, and contribute to the academic community.
Dissertation project: Your dissertation is the culmination of years of hard work within your field. By enrolling in a doctoral program, you’re also given the chance to participate in a significant and original research endeavor that demonstrates the expertise you’ve worked so hard to cultivate.
Why Get a Doctorate?
Having a doctorate doesn’t just open doors; it can kick them down. A doctorate might be right for you if you’re looking for a door to these things:
Expertise and specialization: Doctoral degrees can be a labor of love. They help you delve deeper into a specific subject area, gaining expertise and specialization.
Research opportunities: Extensive research training, opportunities for conducting original research, and contributing new knowledge to the academic community — these three things make a doctorate coveted by students, universities, and employers.
Salary potential and career advancement: In some fields, having a doctorate can lead to higher earning potential and increased salary opportunities. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , doctoral degree holders made an average of $1,885 per week in 2020, while master’s degree holders made an average of $1,545 per week.
Contribution to society: Doctoral research often addresses pressing societal issues, contributing to advancements in technology, healthcare, education, and other areas for the benefit of society — for many students, contributing to the greater good is just as rewarding as career advancement or personal development.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
You might have heard “thesis” and “dissertation” used interchangeably, but they’re not quite the same. Here are the general distinctions to consider:
- A thesis is usually associated with a master's degree program. Students undertake a research project in the final stage of their degree.
- It typically involves conducting original research or analyzing existing research to answer a specific research question.
- The length of a thesis varies based on the field and program requirements, but it’s usually shorter than a dissertation.
Dissertation:
- A dissertation is typically associated with a doctoral degree program. It is an extensive, in-depth research project that marks the culmination of a doctoral program.
- in-depth exploration of a research topic
- comprehensive literature review
- methodology section
- data collection and analysis
- substantive discussion of findings and conclusions.
- Dissertations are usually longer than theses and may take several years to complete.
- Once you’ve completed your dissertation, you participate in a formal defense of the research, where you’ll present your findings to a committee of experts in the field.
Key Differences: Master's vs. PhD
| Feature: | Master's Degree: | Doctoral Degree: |
| Time Commitment | 1-2 years | 4-6+ years |
| Research | More focused on providing an advanced understanding of established knowledge within a field | Emphasis on creating new knowledge through original research |
| Capstone | Thesis | Dissertation |
| Admission Requirements | Less stringent | May require additional materials like recommendation letters, writing samples, and examples of previous research |
| Career Advancement | Often more geared toward professional practice in various industries | Designed to prepare students for careers in academic research |
Deciding Between Master's vs. PhD Programs
“Should I get a master’s degree or a PhD?”
Answering that question can be exciting — and a bit intimidating. You must consider long-term career objectives, personal interests, and the time you can commit. Plus, the level of specialization you wish to achieve based on your career path is also a factor. Typically, a PhD is a prerequisite for those aspiring to research careers in academia, while professional roles in various industries may require only a master's degree.
It’s still worth noting that students have the option of completing a master's degree first and then, based on their experiences and career aspirations, deciding whether to pursue a PhD.
Find the right graduate degree at SMU
A graduate degree is a big investment, so investing in the right program is important.
SMU offers a diverse array of master's and PhD programs tailored to align with your unique interests and career goals, and personalized support, from the applicant to the graduate, is always available.
Whether you're interested in pursuing a PhD in Chemistry or are almost finished with your MBA, we can help you find the right advanced degree.
This could just be the beginning of your journey. Get a closer look at applying to graduate programs of your choice with our guide, How to Get a PhD: A Guide to Choosing and Applying to PhD Programs .

Learn More About
Doctoral degrees at SMU, and how you can choose the right program and thrive in it, in our Guide to Getting a PhD.

Request more
Information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information
Published On
More articles, recommended articles for you, why an organizational psychology master’s pays off.
Understanding what motivates employees and how to create thriving workplaces is key for today's...
Is a Master’s in Economics Worth It?
If you’re contemplating a career in economics, you might be wondering if a master’s degree in the...
Is a Master's in Education Worth It for Teachers?
If you’re considering returning to the student side of the classroom and pursuing a graduate degree...
Browse articles by topic
Subscribe to.
- Meet the Mentors
- Get Involved
- Get the T-Shirt
- Life Science Marketing
- Community Marketing
- Custom Marketing
Join Us Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.
- Genomics & Epigenetics
- DNA / RNA Manipulation and Analysis
- Protein Expression & Analysis
- PCR & Real-time PCR
- Flow Cytometry
- Microscopy & Imaging
- Cells and Model Organisms
- Analytical Chemistry and Chromatography Techniques
- Chemistry for Biologists
- Basic Lab Skills & Know-how
- Equipment Mastery & Hacks
- Managing the Scientific Literature
- Career Development and Networking
- Dealing with Fellow Scientists
- Getting Funded
- Lab Statistics & Math
- Organization & Productivity
- Personal Development
- PhD Survival
- Soft Skills & Tools
- Software & Online Tools
- Survive & Thrive
- Taming the Literature
- Writing, Publishing & Presenting
Is it Worth Doing a PhD After a Master’s?
Thinking of doing a PhD? Here are some essential considerations from a PhD graduate to help you decide whether or not getting a PhD is worth it.
Published April 24, 2024

I am a PhD qualified research professional with a strong background in Translational Medicine and Biomedical research. This has involved carrying out research into a variety of diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory lung disease, cancer and cardiovascular disease and drug allergy/hypersensitivity. I gained experience in laboratory and research management and now work in medical education regulation.

Is it worth doing a PhD? It’s a long, financially modest commitment requiring self-motivation, but it can offer career advantages and personal growth. Not all careers require a PhD, so explore alternatives first. Choose your topic and supervisor wisely, and don’t do one for the sake of it.
Listen to one of our scientific editorial team members read this article. Click here to access more audio articles or subscribe.
Is it worth doing a PhD? This is a question that probably plagues every research student at some point in their career.
The decision to pursue a PhD after getting your Master’s degree is a difficult one. A PhD is a huge undertaking emotionally, mentally, and financially.
Considerations That Are True for Everyone Wanting to Do a PhD
It takes 3–4 years to complete, during which you are on a pretty basic stipend (OK, you’re poor).
You also need the ability to continually motivate yourself through the times when your experiments are not working (most of the time).
Oh, and you might not see as much of your friends and family as you would like, especially when you’re writing up your thesis.
People pursue PhDs for a variety of reasons: some know from the start that they want to run labs at a university, some feel pressured to go for the top degree in their field, some see it as a natural progression after receiving their Master’s, and some continue in academia because they just don’t know what to do next.
For all, it is a highly personal decision, but one that shouldn’t be taken lightly.
During my undergraduate degree, I had the opportunity to work in a research laboratory as part of a summer vacation scholarship.
The PhD student supervising me on a day-to-day basis gave me a really useful piece of advice: don’t do a Master’s or a PhD just for the sake of doing one . She encouraged me to thoroughly explore my options and not to merely drift into a postgraduate course just because I didn’t know what else to do.
So, is it worth you doing a PhD? The following questions might help you to decide.
1. Is it Worth Doing a PhD to Pursue Your Chosen Career Path?
Not every job requires a PhD for you to be successful. In fact, many do not. If you are not planning to stay in academia long-term, then a PhD may be of no additional benefit to you. Picture the type of job you would like to have once you are finished with your education; our handy article lists some options .
Having a PhD might give you an edge over other candidates and help you secure a position, even if a PhD is not required for a particular job. However, it can also work against you, potentially making you overqualified and less likely to get the job.
Have a career discussion with as many people as possible to get different opinions and viewpoints. Try to talk to people who have chosen a variety of career paths. Also, talk to people who have done or are doing a PhD; their experience and insight can be invaluable.
2. Have You Explored Other Options?
For example, like gaining experience in industry or working in a laboratory as a research assistant or technician ?
It’s hard to make a clear-headed decision when you are caught up in the middle of things. Sometimes it is better to take a step back and pursue an option without making a multi-year commitment.
Working as a research assistant in an academic laboratory for a year or so is a great way to figure out if you enjoy working in the academic environment and, more specifically, within a particular laboratory. This kind of experience should confirm if doing a PhD is right for you.
3. Have you Found a Supervisor and a Topic?
Remember that you’ll be committing to both the topic and the supervisor for 3-4 years!
A good PhD supervisor is worth their weight in gold, and finding a good mentor should be a priority. Furthermore, you need to be passionate about your research topic to motivate you during the tremendously tough times. Make sure you work on something you care about.
4. Do You Have Support from Family and Friends?
Talk to your support network, i.e. your friends and family. They are the ones you will rely on heavily while doing the PhD for emotional support (parents may also be a source of financial support).
If you are looking for further advice, make sure you check out our article with pointers for PhD students . Are you sure that a PhD is the right move for you? Search for PhDs in Biological and Medical Sciences to find the right PhD to suit you.

5. Can You Afford to Do a PhD?
Doing a PhD can be costly. There may be fees, and you’ll need to be able to live, so factor in rent, food, and bills too. Depending on where you live and plan on studying, you may be able to get a grant or stipend to help cover the costs.
If you are considering working on the side, note that this might not be feasible. Often PhD work is more than a full-time job, leaving you little room to earn on the side. That said, there might be options for paid work as part of your PhD—for example, as a teaching assistant (remember those helpful people during your lab practical? They were probably PhD students!).
In addition, you need to factor in what you’ll be missing out on compared with entering the workforce – you’ll most likely not be contributing to a pension or retirement fund or other benefits of a full-time job (e.g., health care).
You also need to consider that if you plan on leaving academia after a PhD, you may still be on an ‘entry-level’ salary and, therefore, several years behind where you could have been if you had not done a PhD.
Q. What are some common emotional or mental challenges that PhD students might face throughout their studies, beyond the practical considerations discussed in the article? A. Common emotional or mental challenges experienced by PhD students encompass more than just the practical aspects outlined in the article. These challenges may include feelings of isolation, imposter syndrome, burnout from intense workloads, and the pressure to produce original research amidst setbacks and failures. Q. How does the perceived value of a PhD differ across various industries or academic disciplines, and how might this impact an individual’s decision to pursue advanced research? A. The perceived value of a PhD varies significantly across different industries and academic fields. While some sectors highly prioritize advanced degrees for career advancement, others may place more emphasis on practical experience or specialized skills. Understanding this variability is crucial if you’re deciding whether to do a PhD, as it directly influences their career prospects and potential pathways post-graduation. Q. Can you provide more detail on the financial assistance options available for PhD students, such as scholarships or grants, and how these might alleviate the financial strain mentioned in the article? A. Financial assistance for PhD students can come in various forms, including: • Scholarships. • Grants. • Teaching assistantships. • Research assistantships. • Part-time jobs. These resources play a vital role in alleviating the financial burden associated with pursuing a PhD, such as tuition fees and living expenses. Exploring these options and understanding their availability can significantly impact a student’s decision-making process regarding the feasibility of undertaking doctoral studies.
Deciding Whether to Do a PhD In Summary
That’s my personal advice on deciding whether to do a PhD. In short, you’ll be financially poorer off in the short term, and completing a PhD can be incredibly straining.
However, if you want to pursue a career in academia, it’s basically a requirement. Plus, you will learn practical skills, make lifelong friends, and have a higher earning potential in some fields.
Did you fund yourself during your PhD, and if so, how? Did you find your experience of completing one rewarding, taxing, or both? Let us know in the comments section below.
Originally published November 13, 2013. Reviewed and updated in December 2020 and March 2024.
Share this article:
More 'Career Development and Networking' articles

What to Do If You Want to Become a Freelance Writer
A lot of people today are drawn to freelancing and want to become a freelance writer. There are great benefits when you work from home (like doing work in your pajamas) or wherever you feel most comfortable. The appeal is even greater when you count in that you make your own hours and you are…

Careers for Scientists – Business Development Manager
Looking for a new direction in your career? This is the latest in our new series of articles that focus on careers for scientists. When we started this series, we thought you’d be interested in finding out about who does what behind the scenes at Bitesize Bio, and how we got here. I interviewed our…

Nine Tips for Clinicians Starting a Scientific Career
There are many examples of the impact of physician-scientists on translational research. Dr Barry Marshall swallowed a steaming culture of Helicobacter pylori which eventually resulted in antibiotics curing peptic ulcer disease. However, the process of training these individuals is as effortless as training fish to ride bicycles. Our journeys into the laboratory have been equally…

6 Common Fears When Entering the Lab and How to Deal With Them
The prospect of walking into the lab for the first time to do some ‘real’ research is hugely exciting. Ambitious thoughts fill your mind about what a brilliant research scientist you are about to become, making that all-important difference and saving the world. That is, until you step over the threshold and The Fear overcomes…

How to Make Your Resume Impress
Now that you know who you are trying to impress with your resume, it’s time to focus on how it looks and reads. Remember,.this is NOT the venue to display your creativity. They key is to keep it simple and clear. Follow a simple format that is easy to read – remember that your audience…

Making a Good Impression – How to Successfully Network at a Conference
For many, myself included, the idea of attending a large conference and talking to hundreds of new people can be terrifying. Often times there are people in attendance you may want to collaborate with, or that you see as possible future employers, and you really don’t want to make a bad first impression. Luckily, there…
Become a better scientist in just 3 steps at a time.
Every week, our team condenses the best hard-won wisdom from our mentors’ webinars, podcasts, articles, eBooks, and more and delivers it directly to your inbox.
Don’t delay! Sign up now
Newsletters
- Technical Skills
- More Skills
- Microscopy Focus
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
Copyright © Science Squared – all rights reserved
10 Things Every Molecular Biologist Should Know

The eBook with top tips from our Researcher community.
- The Difference Between Masters and PhD Study
Written by Sarah Hastings-Woodhouse
The main difference between a Masters and a PhD is the purpose of each degree. A Masters degree involves expanding your understanding of existing scholarship in a particular subject area. The purpose of PhD study, on the other hand, is to make an original contribution to your field.
So, the biggest adjustment to expect as you progress from Masters to PhD study is a higher degree of independence (and responsibility). Beyond widening your expertise and improving your research skills, you’ll be expected to break new academic ground.
But exactly how will your academic life change as you make the leap from Masters student to PhD candidate? In this guide, we’ll provide a quick overview of how PhD and Masters study compare, including applications, course structure, assessment and more.
| Area | Masters | PhD |
|---|---|---|
| Length (full-time) | 1-2 years | 3-5 years |
| Grading | Four levels (Disstiction, Merit, Pass or Fail) | Pass, Resubmit or Fail |
| Course structure | Multiple graded modules | Designed by you and your supervisor |
| Purpose | To gain an advanced understanding of a research field | To develop the scholarship of a research field |
Applications
If you’ve already completed an undergraduate and a Masters degree, you might consider yourself something of a university applications veteran. How different can applying for a PhD really be?
There are quite a few similarities between the Masters and the PhD application process. Both will tend to require:
- A personal statement
- Your academic transcript
- Details of at least two referees
As at Masters level, you’ll submit each application directly to your chosen institution, usually through the university’s own applications portal.
The process of applying for a predesigned PhD will more closely resemble that of applying for a Masters. But if you’re planning on designing a self-proposed project , you’ll be in slightly more unfamiliar territory. Rather than responding to an advertised PhD project in your application, you’ll essentially be writing that project specification yourself in the form of your research proposal .
An academic CV is only occasionally required for a Masters application, but almost always required for a PhD application. Its purpose is to summarise your professional and academic experience, in order to demonstrate that you’re well-qualified to complete the project.
It’s useful to think of applying for a PhD as similar to applying for a job. While an application for a taught programme (such as a Masters) involves communicating why you want to study the course and how you feel it will aid your academic and professional development, the focus of a PhD application should be what you can do for the institution. Remember that, if successful, you’ll become a valued member of an academic department, and that those reviewing your application are your prospective colleagues!
Applying for a PhD also requires an extra step that you won’t have encountered at Master’s level – contacting prospective supervisors . It’s often preferable to complete this stage before you submit your final application (though this can vary from institution to institution). Reaching out to supervisors can be an intimidating and confusing process, especially since you won’t have had to do anything similar for previous applications. Our handy list of dos and don’ts will help ensure you’re familiar with all the relevant etiquette before you click send!
Applying for a PhD
Want to know how to apply for a PhD in more detail? Have a read of our step-by-step doctoral application guide.
The MPhil to PhD upgrade
As we’ve said, the main difference between a Masters and a PhD is that the latter requires you to contribute original material to your field. This might be a daunting prospect, but luckily the first phase of a PhD usually acts as something of a ‘transitional’ period which should help you adapt to the demands of doctoral study.
In the UK, most PhD students are initially registered for a Master of Philosophy (MPhil) degree, before being ' upgraded ’ to the status of full PhD candidate (this will occur after 9-18 months for full time students, or after 15-24 months for part-time students).
This first stage of your PhD will largely be spent writing up your upgrade report . The largest component of this will usually be a literature review . You’ll likely have written a literature review as part of your Masters dissertation , so this part shouldn’t be too unfamiliar. You’ll need to demonstrate a comprehensive and critical understanding of existing scholarship in your field and situate your own research within this wider academic context.
This time round, however, you’ll need to illustrate how your research will contribute something new to the field. Don’t panic, though – now isn’t the time to present any original findings in detail (save that for your final thesis). You just need to identify a gap in the academic market and indicate how you plan to fill it.
The rest of the upgrade report should illustrate how you plan to progress with your project. You will be required to include a research question, planned methodology and a rough timetable of future work. Sometimes, you’ll also submit a sample of work you’ve already done towards your thesis.
You’ll then complete an oral presentation known as the PhD upgrade viva . It’s uncommon to ‘fail’ a PhD upgrade, though you may be asked to repeat the process if there is any concern about your progress. The important thing to remember is that you won’t progress to the status of full PhD candidate until the department is satisfied that you’re ready to (and you’ll often be given a couple of shots at demonstrating this).
Course structure
The most obvious difference between a Masters and a PhD in terms of overarching course structure is length. Whereas a Masters is completed in 1-2 years, a PhD will usually take 3-4 years (if studied full-time) or 5-6 years (if studied part-time).
3-4 years may sound like a long time, but by the end of a PhD you’ll not only researched, written and defended your thesis but also amassed significant additional experience. This might include:
- Publishing papers
- Presenting at academic conferences
- Administration within your department
Despite having longer to complete it, you can expect to work at a similar level of intensity for your PhD as you did for you Masters – and to undertake a much wider variety of activities in the process.
At undergraduate and Masters level, you’ll have grown used to each year of study being structured similarly. While the complexity of material will increase as the course progresses, each academic year will have followed a similar format (a series of taught modules culminating in assessment through examination or coursework).
A PhD, by contrast, moves through a series of phases. In your first year, you’ll usually write up a comprehensive overview of existing scholarship in your field in the form of a literature review and draw up a plan for the completion of your project. Your second year will typically be dedicated to completing the bulk of your research , before you write up your final dissertation over your third and fourth years. You can find out more about each stage in our guide to the PhD journey .
PhD candidates aren’t assessed in the same way as Masters and undergraduate students – so yes, you can wave goodbye to regular coursework and exams! You’ll only be formally ‘examined’ at two points during your programme – your PhD upgrade viva (as explained above), and your final viva voce , in which you’ll defend your final thesis in an oral examination.
This doesn’t mean it will be a complete free-for-all between these two milestones, however. Most universities will monitor your progress to make sure that you are continuing to meet the standards of the department year-on-year.
It’s common for PhD candidates to be monitored through progression reviews (which are generally annual for full-time students). You may have to submit a report outlining how your thesis has progressed to date and what your plan is for the following year, as well as any training or other university work (such as teaching) you have undertaken. If the department feels that you haven’t made sufficient progress, you may be required to register for a lower award, or to leave the university altogether.
At Masters level, you’ll have been given a grade out of 100 for each examination or piece of coursework (if in the UK) and graduated with a degree classification ranging from a Distinction to a Fail. At PhD level you won’t be ‘graded’ as such – it’s better to think of your viva examinations and progression reviews as a series of checkpoints that you’ll need to pass in order to earn your doctorate.
Ultimately, the outcome of your final viva will either be that you are awarded a PhD or that you are not (or that you might be after you’ve made some tweaks – see our full guide to viva voce results ). There’s no such thing as a ‘good’ or ‘bad’ PhD in the same way that you can receive different classifications of Masters degree.
Hopefully this guide has given you some idea of how PhD and Masters study compare, and helped you feel a little less apprehensive about making the leap!
To find out more about PhD study, have a browse of the many detailed guides in our advice section .
Ready to do a PhD?
Search our project listings to find out what you could be studying.
Want More Updates & Advice?

What happens during a typical PhD, and when? We've summarised the main milestones of a doctoral research journey.

The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to know about the PhD dissertation.

This page will give you an idea of what to expect from your routine as a PhD student, explaining how your daily life will look at you progress through a doctoral degree.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a PhD in the USA.

Postgraduate students in the UK are not eligible for the same funding as undergraduates or the free-hours entitlement for workers. So, what childcare support are postgraduate students eligible for?

The UK education system is divided into levels. This guide is your one-stop overview into what these levels are and what they mean for postgraduate students.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

Can I do a PhD after masters? How long does it take to get a PhD / Doctorate
A common question that many graduate students have is whether they can pursue a PhD after completing their master’s degree.
The answer is yes, it is possible to continue your academic career by obtaining a doctoral degree in your field of study.
There are several factors that need to be considered before embarking on this path.
This article will provide an overview of the key factors students should consider when deciding whether to pursue a PhD after completing their master’s degree.
Should I get my PhD after my masters? What about industry?
Deciding whether to pursue a PhD immediately after a master’s degree or enter the workforce first depends on personal goals, interests, and circumstances.
A PhD typically requires around five years of self-directed effort, similar to starting a business. If passionate about research, it might be best to begin right away.
Working in industry before pursuing a PhD can lead to habits that may not benefit academia and can take longer to adjust back to a scholarly environment.
Long-term relationships are essential in academia, and aggressive industry tactics might not be well-received.
Starting a PhD earlier allows for more time to produce research and establish a successful career, particularly for those considering a long-term academic path.
PhD pursuit offers flexibility in research topics and projects, enabling exploration across various subjects and building connections with professionals from different fields. This leads to unique opportunities and experiences that may not be available when working for a single company.
Considering factors like personal goals and readiness for the workload and demands of a PhD program is crucial.
Weigh the potential benefits of advancing education against the time, cost, and personal demands of a doctoral program. If a PhD aligns with one’s career aspirations and personal goals, it may be a worthwhile pursuit.
However, if the investment required outweighs the potential benefits, it might not be the best choice.
It’s always possible to try a PhD program for a year or two and then make a more informed decision based on individual experiences.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD or Doctorate? Time to complete everything
Leading up to getting a PhD there are many qualifications you need to get. Here is the amount of time a typical US Doctorate can take to achieve including all of the previous qualifications. It can take up to 13 years to complete
| Bachelor’s Degree | 4 years (typical) | 4 years |
| Master’s Degree (optional) | 2 years (typical) | 6 years |
| PhD Coursework | 3 years (average) | 9 years |
| PhD Comprehensive Exams | 1-2 semesters | 9.5 years |
| PhD Dissertation: This is a key component of the years of study involved in a doctorate degree. Research | 3 years (average) | 12.5 years |
| PhD Dissertation Defense | 1-2 semesters | 13 years |
The length of time to complete a PhD varies depending on several factors.
On average, in the US it takes about six years, with three years dedicated to coursework and another three years for the dissertation project.
Factors that can influence the duration include:
- prerequisites of the program,
- program format,
- the student’s motivation,
- prior knowledge,
- Personal circumstances, such as being an international student, can influence the time it takes to complete the doctoral program.
- Funding and scholarship stipend can significantly affect the years of study and the time it takes to earn a doctorate degree.
- field of study,
- dissertation topic,
- Support of the graduate advisor can be a crucial factor in minimizing the time it takes to complete a doctorate degree.
The range can be as short as three years or as long as seven to eight years , depending on the individual and the circumstances.
Do you need a master’s for a PhD? A shorter career path that doesn’t take so long.
In certain fields, such as clinical psychology, it is possible to pursue a PhD without obtaining a master’s degree first.
To do so, one must demonstrate a strong academic and research background, as well as a commitment to the field.
Here are the most important attributes if you are thinking about going straight into a PhD without a master’s:
- Strong academic and research background: Ensure that you have excelled in your coursework and maintained a high GPA.
- Undergraduate research experience: Engage in research projects during your undergraduate studies, preferably with a thesis component.
- Clinical exposure (if applicable): Gain relevant experience in the field to showcase your practical knowledge and commitment.
- Leadership experience: Participate in activities that demonstrate your ability to lead and work effectively within a team, as this can be advantageous in the years of study required to earn a doctorate degree.
- Interpersonal skills: Develop strong communication and collaboration skills, which are essential for success in a PhD program.
- Clear determination: Express your dedication to pursuing a PhD directly from your undergraduate studies, highlighting your commitment to the field and how quickly you aim to earn a doctorate.
- Assess your certainty: Be sure that you are confident in your goals and prepared to invest the necessary effort to be competitive without a master’s degree.
By satisfying these requirements, you can better assess your eligibility to apply for a PhD without a master’s degree and potentially save time and money in the process.
Earn a Doctorate without a Masters – How Does It Work?
Obtaining a PhD without a master’s degree is not a common path, but it is possible under certain circumstances.
Typically, a PhD candidate has an undergraduate degree with high grades, a master’s degree, and relevant research skills.
However, there are exceptions where individuals have successfully transitioned from their undergraduate studies directly to a PhD program.
One such scenario involves having a strong rapport with a potential PhD supervisor, perhaps from your undergraduate program, which can significantly reduce the time it takes to earn a doctorate.
This relationship can help compensate for the lack of a master’s degree, but it’s not a guarantee.
Another example is being an exceptional student with a first-class undergraduate degree and a dissertation closely aligned with the advertised PhD project.
Demonstrating an outstanding attitude and performance during your undergraduate project may give you an edge over other applicants.
In applied PhDs, practical experience can also be beneficial, particularly if it includes valuable contacts in the field.
For instance, if your PhD is related to professional sports and you have numerous connections within the industry, it may facilitate recruitment and collaboration, enhancing your chances of acceptance.
However, as with the other examples, this is not a sure-fire way to secure a position.
While securing a PhD without a master’s degree is challenging, it is not impossible.
The best approach is to pursue a master’s degree, as it will better prepare you for a PhD program. – Dr Andy Stapleton
Nonetheless, if you are determined to bypass the master’s route, perseverance and strategic networking can potentially lead to success.
What after Masters: MPhil or Doctorate Degree?
After completing a Master’s degree, you may be considering whether to pursue an MPhil or a PhD.
Here are the differences between the two:
| Level | Intermediate research degree | Highest academic research degree |
| Objective | Develop research skills | Produce independent research contributing to the field |
| Duration | 1-2 years (full-time) | Typically take 3-7 years (full-time or part-time). |
| Scope | Smaller in scale and depth | Broader scope and deeper engagement |
| Research Focus | Less complex topics | More complex topics |
| Supervision | Supervised research | Supervised research with more independence |
| Training | Limited | Research workshops, writing classes, group work, interdisciplinary modules |
| Career Impact | Good for research-oriented positions | Greater career advancement in academia and research |
| Dissertation | Smaller in scale and less comprehensive | Larger, more comprehensive, and novel research project |
A PhD, being the highest academic title awarded for independent research, offers a broader scope and deeper engagement with complex topics than an MA or MPhil.
It can be thought of as an apprenticeship in planning and conducting your research.
The program duration ranges from three to seven years, depending on whether you choose to study full-time or part-time.
Entry is competitive, as candidates must demonstrate a strong track record of academic success.
PhD students attend research workshops, writing classes, and work in groups to explore each other’s studies.
They have opportunities to discuss their research across the university, in graduate school, and other classes, which can be particularly beneficial for an international student. A PhD involves a multi-year project based on independent research, with support from supervisors and training that contributes to the chosen field of study.
It’s essential to have a clear idea of the topic you want to explore in-depth and the methods you plan to employ before applying for a PhD program.
Doing a PhD can be both intellectually and emotionally demanding.
However, working in a department with dedicated and talented staff, excellent supervisors, ongoing training, and support from fellow students can make the experience enjoyable and rewarding.
It is crucial to choose the right supervisor and have a good working relationship with them, as this can significantly impact your PhD journey and the time it takes to complete it.
Wrapping up PhD programs after a masters – how long does it take to complete?
Pursuing a PhD after a master’s degree is a common path for those looking to advance in academia or research-intensive careers.
While obtaining a PhD requires a significant commitment of time and resources, it can lead to prestigious positions or high-paying jobs. It is crucial to consider personal goals, interests, and the job prospects in the field before enrolling in a doctoral program.
For those considering a PhD without a master’s degree, it is essential to demonstrate a strong academic and research background and commit to the field.
The decision between an MPhil and a PhD depends on the desired scope, depth, and career impact of the research. Ultimately, individuals should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the time it takes, cost, and personal demands of a doctoral program before making a decision.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


- Masters vs PhD – Differences Explained
- Types of Doctorates
The decision of whether or not to pursue a Masters or PhD (or both) after you complete your undergraduate studies is not necessarily a straightforward one. Both are postgraduate degrees but are different in terms of the academic experience and the career paths taken afterwards.
In short, a Masters degree involves a year of study, primarily through taught lectures and a final dissertation research project, whilst a PhD (also referred to as a doctorate degree) is a three-year commitment of independent research on a specific subject.
There’s more to it than that, however – read on for more information.
What Is a Masters Degree?
A Masters degree is the next level of education after the completion of an undergraduate degree, commonly known as a Bachelors.
These degree levels are often referred to in terms of cycles so that a Bachelor’s is a first-cycle degree, a Masters is a second-cycle and finally, a PhD is the third-cycle of higher education (and the highest).
Masters degrees demand an intense period of study, usually centred around a core series of lectures and taught modules, coupled with coursework assignments and exams, followed by the completion of a contained research project usually taking students 3-4 months to complete.
These types of degrees are attractive to recent graduates who want to delve deeper into their specific field of study, gaining some research experience and more specialised knowledge beyond what an undergraduate degree can offer.
Equally, some pursue a Masters degree program in a subject that is only tangentially related to their Bachelors degree, helping them gain a broader depth of knowledge.
These degrees also serve as a significant stepping stone for those already in employment who want to progress their current career development and earn a higher salary. They can also be an excellent method for helping in changing careers completely by learning new skills and subject knowledge.
What Is a PhD Degree?
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest academic degree that can be awarded and is the third and final cycle in the progression of higher education.
A doctoral degree is earned on the basis of producing a significant, independent and novel body of work (a Thesis) that contributes new knowledge to a particular research topic.
These are research degrees that are a significant investment of a candidate’s time, resources and energy and are all but a pre-requisite for anyone considering a career in academia, such as eventually becoming a professor.
There are some exceptions to this, such as those with a medical background who may earn an MD (Doctor of Medicine), which is the equivalent of a PhD.
Doctoral degrees can also have a significant positive impact on career development outside of academia, especially in fields such as engineering, business and finance that have a high demand for highly qualified and capable people.
A graduate student engaged in PhD study is commonly known as a PhD student, PhD candidate or doctoral student.
What are the Benefits of a Masters Degree?
There are several reasons one might consider doing a Masters degree rather than a PhD in their graduate education. These include:
- It takes approximately a third of the time to do compared to a doctorate degree and costs less too.
- It’s a good way to differentiate yourself from those that hold only an undergraduate degree without having to commit to a substantial research degree.
- The end goal is more career-focused as opposed to research-focused. For example, it is practically an ‘easier’ route to changing or progressing your career if that aligns with your professional goals.
What are the Benefits of Doing a PhD?
You may continue on into a doctoral program after a Masters or you may even dive straight in after completing your undergraduate studies. So, what are the advantages of completing this third-cycle?
- You’ll have developed a wealth of transferable skills at graduate school, such as effective communication of complex concepts, multi-tasking time-management and the ability to adapt to and solve unexpected problems.
- A doctorate helps to establish you as an expert within your chosen subject area; your work will hopefully have furthered the knowledge in this.
- It will open up career paths and teaching positions within academia that may otherwise be very difficult to get a hold in (although these career paths will still be very competitive).
- You can add the title ‘Dr’ in front of your name!
Which Degree Is More Impactful: A Masters or a PhD?
On paper, the answer should be clear: A doctorate degree is the highest degree you can earn, so has more impact than a Masters, which in turn has more impact than a Bachelors.
The reality is that the size of the impact (if any) really depends on the subject area and the career path you choose (if the measure of impact is how it positively improves your career prospects, that is).
For someone with aspirations of becoming a professor, a PhD will be of greater value than a Masters alone.
Equally, it’s also possible that someone with a PhD entering a different field or one that doesn’t require a PhD may find that their degree has no bearing on their career or in some cases may even be seen as a ‘negative’ with a concern of the person being ‘over-qualified’ for a position. There are many scenarios in which professional experience would be more valuable to an employer than a doctorate degree.
Check out the links below to our interviews with Prof. Debby Cotton and Dr Nikolay Nikolov to read their experiences of when a going through a PhD program has had a clear benefit (Prof. Cotton) and when it hasn’t been helpful (Dr Nikolov).

Do You Need to Have a Masters to do a PhD?
This really depends on the university, department and sometimes even the project and supervisor.
From a purely application process perspective, some institutions may formally require you to hold a Masters degree relevant to the subject of the PhD project before you can enter their doctoral program.
In another scenario, most universities are unlikely to accept candidates that were awarded below a 2:1 (in the UK) in their undergraduate degree but may consider someone who has ‘made up’ for this with a high-grade Masters.
Lastly, some universities now offer PhD programmes that incorporate an additional year of study in which you would complete a Masters degree before carrying directly on into a PhD project. As you’d expect, even if a university doesn’t formally require you to hold one, a Masters degree can help separate you from other applicants in being accepted on the project.
Check out our detailed guide to doing a PhD without a Master’s .
Why Do a Masters before Your PhD?
Even if you don’t need to have one, it could still be beneficial to begin your postgraduate study by doing a Masters first before you embark on your doctorate journey.
As mentioned previously it’ll help you stand out from applicants that don’t have one, but beyond that, it’ll give you a taster of what research life could be like, especially if you stay at the same university and department for your PhD.
The one-year commitment (in the UK at least) of carrying out a Masters first, and in particular your research project, will help you better understand if this is truly something you want to commit the next three or more years to.
You’ll learn some of the skills of independent research, from performing detailed literature searches to more complex, analytical writing.
At the end of it, you should be in a stronger position to consider your options and decide about whether to continue into a PhD at graduate school.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Masters Degree?
In the UK, a full-time Masters degrees take students one calendar year to complete: The programme of study usually starts in September, the final research project the following April and final project viva around August. Part-time degrees are usually double the time.
How Long Does It Take to Get a PhD?
In the UK, most PhD projects take 3-4 years to complete , as reflected by the majority of funded projects offering stipends to cover living expenses of about 3.5 years.
For many reasons, projects may end up taking longer to complete, however. This might be because of difficulties in collecting enough data, or if the project is being done part-time.
Which One is More Expensive to Do?
As you’d expect, as a PhD takes three times as long to complete as a Masters degree, it will cost you more to do as far as university fees are concerned.
Another thing to consider is that many PhD projects come with some level of funding equivalent to a low salary, which may cover the cost of tuition fees and living expenses, whilst it is usually more difficult to obtain funding for Masters study.
Conversely, a Masters graduate may progress into a higher (versus PhD funding) salary sooner whilst a PhD student will endure three years of a comparatively low income.
A Masters vs a PhD: Conclusion
If you’re considering continue further graduate study after your undergraduate degree, the question of doing a Masters vs a PhD is likely to come up. They are both considered an advanced degree, each with their own advantages.
There are benefits to doing either of these graduate programs or even both of them; your decision here can be easier if you have an idea of the career you want to follow or if you know you have a love for research!
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Should I Pursue A Master’s or A Ph.D.?

The first step in deciding on the right graduate program for you is to figure out which degree will best serve you—a master’s or a doctor of philosophy (Ph.D.). Here are a few factors to consider.
What are your career goals?
- Professional master’s: A good choice if you want to develop a particular skill set in order to practice a particular profession. This type of degree provides coursework focused on learning and practicing skills.
- Research master’s: A good fit if you want to gain expertise in a discipline and know how to teach it. A research master’s typically includes a research project or thesis and comprehensive exams in addition to coursework and provides experience in research and scholarship.
- Ph.D. (doctor of philosophy): Consider this option if your goal is to ground yourself in a body of research and develop the ability to add to that body of knowledge. Ph.D. study includes a major research project in addition to coursework, and a Ph.D. is the highest scholastic degree awarded by American universities. Contrary to common perception, career paths for Ph.D. graduates are quite varied, not just limited to academia. Ph.D. training helps you hones skills such as writing, research, teaching, data analysis, communicating complex topics—all of which can translate into many sectors, including industry, government, nonprofit, and entrepreneurship.
See career data for Duke graduate programs' alumni
How much time do you have to pursue a graduate degree?
Master’s degrees typically take two years to complete, while Ph.D. programs generally take five to seven years ( see Duke programs' time-to-degree ). That is a significant difference in commitment and opportunity costs. It might also play a key role in deciding which factors take higher priority as you evaluate a program. How does the length of the program fit with your career and family plans? How important is the surrounding community if you are going to be there for seven years instead of two? How long are you able or willing to go on a limited income while in graduate school?
How much can you afford to pay for a graduate degree?
Consider your personal financial situation (e.g., how much savings and student loans do you have), as well as how much financial aid you can get. Master’s and Ph.D. programs differ greatly in the amount of financial aid available. Ph.D. programs tend to offer significantly more financial support than master’s programs (but often will have research or teaching requirements).
A typical Ph.D. financial aid package usually includes coverage of tuition and fees, a living stipend, and some level of support for health insurance for a set number of years. For instance, Duke’s standard Ph.D. package covers tuition, mandatory fees, and a stipend for five years, as well as health insurance premiums for six years.
Within an institution, the level of financial support often differs across programs, so be sure to ask your specific program about the financial aid it offers. There are also many national organizations that provide competitive fellowships and scholarships for graduate students.
Know which degree you want to pursue? Here are some key things to look for in a program .
Get the Reddit app
This subreddit is for discussing academic life, and for asking questions directed towards people involved in academia, (both science and humanities).
Any PhD holders(or knew someone) that did masters AFTER doing their PhD?
I was thinking of following this path. What do you think? What was your reason?
Like for example I wanna take a PhD in molecular biology/ omics and take masters in let's say... uhm... statistics. Is this possible?
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Varsity Athletes
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
This website uses cookies to ensure the best user experience. Privacy & Cookies Notice Accept Cookies
Manage My Cookies
Manage Cookie Preferences
| NECESSARY COOKIES These cookies are essential to enable the services to provide the requested feature, such as remembering you have logged in. | ALWAYS ACTIVE |
| Accept | Reject | |
| PERFORMANCE AND ANALYTIC COOKIES These cookies are used to collect information on how users interact with Chicago Booth websites allowing us to improve the user experience and optimize our site where needed based on these interactions. All information these cookies collect is aggregated and therefore anonymous. | |
| FUNCTIONAL COOKIES These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages or by us. | |
| TARGETING OR ADVERTISING COOKIES These cookies collect information about your browsing habits to make advertising relevant to you and your interests. The cookies will remember the website you have visited, and this information is shared with other parties such as advertising technology service providers and advertisers. | |
| SOCIAL MEDIA COOKIES These cookies are used when you share information using a social media sharing button or “like” button on our websites, or you link your account or engage with our content on or through a social media site. The social network will record that you have done this. This information may be linked to targeting/advertising activities. |
Confirm My Selections
Request Information from Booth
- Booth Stories
- The Chicago Approach
- Innovation History
- Faculty Impact
- A Global Footprint
- Our Commitment to Diversity and Inclusion
- Our Collaborative Community
- Lifelong Learning
- Leadership Impact
- A Lifetime of Career Advancement
- Leadership Stories

Specialized Masters Applications Now Open
Take the first step toward jump-starting your future career in business by applying to one of our specialized masters programs..
- By Booth Staff
- July 18, 2024
- Share This Page
Chicago Booth’s specialized masters programs serve as a great next step for current seniors in undergrad or recent graduates who are looking to pursue a career in business.
Booth’s Master in Management (MiM) is a 10-month program for recent college graduates who did not earn a bachelor of business administration degree. As a MiM student, you’ll have the opportunity to build upon the critical thinking skills you gathered in college while gaining foundational business expertise needed to thrive in the business world.
Booth’s Master in Finance (MiF) is a 15-month program that targets recent college graduates with a quantitative background. As a MiF student, you have the opportunity to build upon your quant skills in order to secure roles in asset management, investment banking, or fintech.
Both programs offer a pathway to kick off your career in business with confidence. If you are interested in taking the next step toward positioning yourself for successful progression in the business world, we invite you to look at the information listed below as you begin preparing your application:
Specialized Masters Requirements
As part of the application process for both programs, you are required to submit your essays, two letters of recommendation, transcript(s), and standardized test score(s). We also require you to have graduated from or be on track to graduate with an undergraduate degree. We encourage you to check out our full list of application requirements for MiM and MiF as you start crafting your application.
*We accept the GMAT and GRE. There is no preference on which exam you should take.
Essay Prompts
Essay One: How will the Booth Master in Finance/Management help you achieve your immediate and long-term career goals? (Maximum 300 words.)
Essay Two: Graduate finance/management education is as much about personal growth as it is about professional development. We’d like to learn more about you outside of the classroom and work environments. Use this opportunity to tell us something about who you are. (Maximum 400 words.)
* Our Master in Finance Program requires candidates to submit a video essay component at the time of application as well.
Application Deadlines
Master in Management Program:
- Round One: October 10, 2024
- Round Two: January 9, 2025
- Round Three: March 6, 2025
- Round Four: May 1, 2025
Master in Finance Program:
- One Deadline: January 9, 2025
Don’t just dream about what you want your future to look like; build toward your dream career with Chicago Booth by pursuing one of our specialized masters programs. As you begin the admissions process, we encourage you to stay engaged with us ( MiM or MiF ) and reach out to us via email if you have any questions.
Start Your Application Today
Apply now start your application today, related topics.
- Master in Finance
- Master in Management
More Stories from Chicago Booth
Influencing the future of finance.
In this Q&A, incoming student Rohan Mathur shares what drew him to Booth’s Master in Finance Program and how it will support his career goals.
Chicago Booth Creates New Master in Management Degree
Beginning in fall 2024, this new program brings Booth’s transformational business education to ambitious recent college graduates.
- Early Career
Empowering Entrepreneurship with Crypto
Through the more stable cryptocurrency Akoin, Lynn Liss, ’01, hopes to bring new opportunities to entrepreneurs throughout Africa.
- Financial Inclusion
Booth News & Events to Your Inbox
Stay informed with Booth's newsletter, event notifications, and regular updates featuring faculty research and stories of leadership and impact.
YOUR PRIVACY We want to demonstrate our commitment to your privacy. Please review Chicago Booth's privacy notice , which provides information explaining how and why we collect particular information when you visit our website.
You are now signed up to receive news, event notifications, and stories from Chicago Booth. Thank you for taking this step to hear more about our community!
Stay informed with Booth's newsletter to receive event notifications and updates featuring faculty research and stories of leadership and impact.
There appears to be a technical issue with your browser
This issue is preventing our website from loading properly. Please review the following troubleshooting tips or contact us at [email protected] .
The Top International Relations Schools
Create an FP account to save articles to read later.
ALREADY AN FP SUBSCRIBER? LOGIN
- World Brief
- Editors’ Picks
- Africa Brief
- China Brief
- Latin America Brief
- South Asia Brief
- Situation Report
- Flash Points
- War in Ukraine
- Israel and Hamas
- U.S.-China competition
- U.S. election 2024
- Biden's foreign policy
- Trade and economics
- Artificial intelligence
- Asia & the Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
How Trump and Harris Compare on Economic Policy
Could civil war erupt in america, ones and tooze, foreign policy live.

Summer 2024 Issue
Print Archive
FP Analytics
- In-depth Special Reports
- Issue Briefs
- Power Maps and Interactive Microsites
- FP Simulations & PeaceGames
- Graphics Database
Catalysts for Change
Webinar: how to create a successful podcast, fp @ unga79, ai for healthy cities, her power @ unga79.
By submitting your email, you agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use and to receive email correspondence from us. You may opt out at any time.
Your guide to the most important world stories of the day
Essential analysis of the stories shaping geopolitics on the continent
The latest news, analysis, and data from the country each week
Weekly update on what’s driving U.S. national security policy
Evening roundup with our editors’ favorite stories of the day
One-stop digest of politics, economics, and culture
Weekly update on developments in India and its neighbors
A curated selection of our very best long reads
The Top International Relations Schools of 2024, Ranked
An insider’s guide to the world’s best programs—for both policy and academic careers.
The Teaching, Research, and International Policy (TRIP) Project at William & Mary’s Global Research Institute has long partnered with Foreign Policy to create a reputational ranking of academic programs in international relations. Over the past two decades, our process has remained simple and consistent: We ask IR professionals what they think are the five best places to study for an undergraduate, terminal master’s, and doctoral degree.
In our most recent survey on the topic, conducted from October 2022 to January 2023, we received responses from 979 IR scholars across the United States, 294 staff affiliated with U.S. think tanks, and 291 policymakers who worked in the U.S. government during the George W. Bush, Obama, and Trump administrations. For the first time, we also asked respondents which Ph.D. programs are best for a student interested in a policy career, rather than an academic one. As the number of tenure-track positions in universities declines and the demand for expertise within the policy community increases , this question is more relevant today than ever before.
JUMP TO CATEGORY
- UNDERGRADUATE
- Ph.D., ACADEMIC
- Ph.D., POLICY
Undergraduate Programs
| International Relations Faculty | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | School | Percentage |
| 1 | Princeton University | 48.37 |
| 2 | Harvard University | 46.65 |
| 3 | Georgetown University | 43.59 |
| 4 | Stanford University | 42.83 |
| 5 | Columbia University | 29.83 |
| 6 | University of Chicago | 23.33 |
| 7 | Yale University | 17.4 |
| 8 | American University | 15.49 |
| 9 | George Washington University | 14.91 |
| 10 | Dartmouth College | 14.72 |
| 11 | University of California, San Diego | 11.85 |
| 12 | University of California, Berkeley | 10.52 |
| 13 | University of Michigan | 10.33 |
| 14 | Johns Hopkins University | 10.13 |
| 14 | Tufts University | 10.13 |
| 16 | William & Mary | 9.56 |
| 17 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 8.22 |
| 18 | University of Pennsylvania | 5.93 |
| 19 | Brown University | 5.35 |
| 20 | Swarthmore College | 4.02 |
| 20 | University of Denver | 4.02 |
| 22 | Ohio State University | 3.82 |
| 22 | University of California, Los Angeles | 3.82 |
| 24 | Cornell University | 3.63 |
| 25 | University of Virginia | 3.44 |
| 26 | New York University | 3.25 |
| 26 | University of Notre Dame | 3.25 |
| 26 | University of Southern California | 3.25 |
| 29 | Duke University | 3.06 |
| 29 | Williams College | 3.06 |
| 31 | University of Texas at Austin | 2.87 |
| 32 | Middlebury College | 2.29 |
| 33 | Brigham Young University | 2.1 |
| 34 | University of Minnesota, Twin Cities | 1.91 |
| 34 | Wellesley College | 1.91 |
| 36 | University of Wisconsin, Madison | 1.72 |
| 37 | Boston University | 1.53 |
| 38 | Indiana University, Bloomington | 1.34 |
| 38 | Pomona College | 1.34 |
| 38 | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill | 1.34 |
| 41 | Boston College | 1.15 |
| 41 | Macalester College | 1.15 |
| 41 | Syracuse University | 1.15 |
| 41 | Vanderbilt University | 1.15 |
| 41 | Washington University in St. Louis | 1.15 |
| 46 | Carleton College | 0.96 |
| 46 | Pennsylvania State University | 0.96 |
| 46 | University of California, Santa Barbara | 0.96 |
| 46 | University of Rochester | 0.96 |
| 46 | University of Washington | 0.96 |
| 51 | Amherst College | 0.76 |
| 51 | Claremont McKenna College | 0.76 |
| 51 | Emory University | 0.76 |
| 51 | Rice University | 0.76 |
| 51 | Rutgers University, New Brunswick | 0.76 |
| 51 | Seton Hall University | 0.76 |
| 51 | Texas A&M University | 0.76 |
| 51 | University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee | 0.76 |
| 51 | Vassar College | 0.76 |
| 60 | Colgate University | 0.57 |
| 60 | Florida International University | 0.57 |
| 60 | Hobart and William Smith Colleges | 0.57 |
| 60 | Northwestern University | 0.57 |
| 60 | Oberlin College and Conservatory | 0.57 |
| 60 | United States Military Academy, West Point | 0.57 |
| 60 | University of California, Irvine | 0.57 |
| 60 | University of Georgia | 0.57 |
| 60 | University of Maryland, College Park | 0.57 |
| 60 | Virginia Tech | 0.57 |
| 70 | Arizona State University | 0.38 |
| 70 | Baylor University | 0.38 |
| 70 | Bowdoin College | 0.38 |
| 70 | Davidson College | 0.38 |
| 70 | Eckerd College | 0.38 |
| 70 | Elon University | 0.38 |
| 70 | Hillsdale College | 0.38 |
| 70 | Michigan State University | 0.38 |
| 70 | Occidental College | 0.38 |
| 70 | St. John's College | 0.38 |
| 70 | The New School | 0.38 |
| 70 | University of Florida | 0.38 |
| 70 | University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign | 0.38 |
| 83 | Assumption University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Barnard College | 0.19 |
| 83 | California State University, Chico | 0.19 |
| 83 | Carnegie Mellon University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Colby College | 0.19 |
| 83 | College of Wooster | 0.19 |
| 83 | Dickinson College | 0.19 |
| 83 | George Mason University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Georgia Institute of Technology | 0.19 |
| 83 | Ithaca College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Kalamazoo College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Kennesaw State University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Lafayette College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Lewis & Clark | 0.19 |
| 83 | Mount Holyoke College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Northeastern University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Pepperdine University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Purdue University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Reed College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Rhodes College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Roger Williams University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Sam Houston State University | 0.19 |
| 83 | St. Thomas Aquinas College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Temple University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Texas Christian University | 0.19 |
| 83 | The Citadel, the Military College of South Carolina | 0.19 |
| 83 | Evergreen State College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Troy University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Truman State University | 0.19 |
| 83 | United States Naval Academy | 0.19 |
| 83 | University at Albany, State University of New York | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of California, Davis | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of California, San Francisco | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of California, Santa Cruz | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Colorado, Boulder | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Hawaii, Manoa | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Iowa | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Massachusetts, Amherst | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Mississippi | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Pittsburgh | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Puget Sound | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Toledo | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Utah | 0.19 |
| 83 | University of Vermont | 0.19 |
| 83 | Ursinus College | 0.19 |
| 83 | Virginia Commonwealth University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Virginia Military Institute | 0.19 |
| 83 | Washington and Lee University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Webster University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Wesleyan University | 0.19 |
| 83 | Wright State University | 0.19 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown University | 70.39 |
| 2 | Harvard University | 61.18 |
| 3 | Princeton University | 42.11 |
| 4 | Stanford University | 38.82 |
| 5 | Johns Hopkins University | 30.92 |
| 6 | Yale University | 28.95 |
| 7 | Tufts University | 27.63 |
| 8 | George Washington University | 25 |
| 9 | Columbia University | 22.37 |
| 10 | American University | 11.18 |
| 10 | University of Chicago | 11.18 |
| 12 | University of California, Berkeley | 8.55 |
| 13 | University of Virginia | 6.58 |
| 14 | William & Mary | 4.61 |
| 15 | University of Michigan, Ann Arbor | 3.95 |
| 15 | University of Texas at Austin | 3.95 |
| 17 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 3.29 |
| 18 | Brown University | 2.63 |
| 18 | New York University | 2.63 |
| 18 | University of Pennsylvania | 2.63 |
| 18 | Williams College | 2.63 |
| 22 | Cornell University | 1.97 |
| 22 | Dartmouth College | 1.97 |
| 22 | Duke University | 1.97 |
| 22 | Middlebury College | 1.97 |
| 22 | Syracuse University | 1.97 |
| 22 | Texas A&M University | 1.97 |
| 22 | United States Military Academy, West Point | 1.97 |
| 22 | University of California, Los Angeles | 1.97 |
| 30 | Liberty University | 1.32 |
| 30 | Pomona College | 1.32 |
| 30 | United States Naval Academy | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of California, San Diego | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Colorado, Boulder | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Denver | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Notre Dame | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Southern California | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Washington | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Wisconsin, Madison | 1.32 |
| 40 | Adams State University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Arizona State University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Brigham Young University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Carleton College | 0.66 |
| 40 | Colorado State University | 0.66 |
| 40 | George Mason University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Marine Corps University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Mercyhurst University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Missouri State University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Regent University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Rice University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Sarah Lawrence College | 0.66 |
| 40 | Seton Hall University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Swarthmore College | 0.66 |
| 40 | Catholic University of America | 0.66 |
| 40 | The Citadel, the Military College of South Carolina | 0.66 |
| 40 | Tulane University | 0.66 |
| 40 | United States Air Force Academy | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of California, Santa Barbara | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of Houston | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of Massachusetts, Amherst | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of Missouri | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of Nebraska, Lincoln | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill | 0.66 |
| 40 | University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee | 0.66 |
| 40 | Ursinus College | 0.66 |
| 40 | Utah Valley University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Vanderbilt University | 0.66 |
| 40 | Virginia Military Institute | 0.66 |
| 40 | Washington and Lee University | 0.66 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown University | 65.12 |
| 2 | Harvard University | 64.34 |
| 3 | Princeton University | 47.29 |
| 4 | Stanford University | 44.19 |
| 5 | Columbia University | 40.31 |
| 6 | Yale University | 29.46 |
| 7 | Johns Hopkins University | 27.13 |
| 8 | George Washington University | 21.71 |
| 9 | Tufts University | 16.28 |
| 10 | University of Chicago | 14.73 |
| 11 | American University | 6.98 |
| 11 | University of California, Berkeley | 6.98 |
| 13 | University of California, San Diego | 6.2 |
| 14 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 5.43 |
| 15 | Cornell University | 3.88 |
| 15 | University of Pennsylvania | 3.88 |
| 15 | William & Mary | 3.88 |
| 15 | Williams College | 3.88 |
| 19 | Dartmouth College | 3.1 |
| 20 | Brown University | 2.33 |
| 20 | New York University | 2.33 |
| 20 | University of Michigan | 2.33 |
| 20 | University of Virginia | 2.33 |
| 24 | Duke University | 1.55 |
| 24 | Northwestern University | 1.55 |
| 24 | Swarthmore College | 1.55 |
| 24 | Texas A&M University | 1.55 |
| 24 | University of California, Davis | 1.55 |
| 24 | University of California, Los Angeles | 1.55 |
| 24 | University of Denver | 1.55 |
| 24 | University of Southern California | 1.55 |
| 24 | University of Washington | 1.55 |
| 33 | Barclay College | 0.78 |
| 33 | Brigham Young University | 0.78 |
| 33 | Carleton College | 0.78 |
| 33 | Carnegie Mellon University | 0.78 |
| 33 | George Mason University | 0.78 |
| 33 | Indiana University, Bloomington | 0.78 |
| 33 | Middlebury College | 0.78 |
| 33 | Pomona College | 0.78 |
| 33 | SUNY, Geneseo | 0.78 |
| 33 | Syracuse University | 0.78 |
| 33 | Ohio State University | 0.78 |
| 33 | Tulane University | 0.78 |
| 33 | United States Naval Academy | 0.78 |
| 33 | University of Central Florida | 0.78 |
| 33 | University of Hawaii, Manoa | 0.78 |
| 33 | University of Maryland College Park | 0.78 |
| 33 | University of Massachusetts, Amherst | 0.78 |
| 33 | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill | 0.78 |
| 33 | University of Texas at Austin | 0.78 |
| 33 | Washington University in St. Louis | 0.78 |
| 33 | Wellesley College | 0.78 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown University | 75.34 |
| 2 | Johns Hopkins University | 59.03 |
| 3 | Harvard University | 52.23 |
| 4 | Columbia University | 39.61 |
| 5 | Princeton University | 34.37 |
| 6 | George Washington University | 33.2 |
| 7 | Tufts University | 32.04 |
| 8 | American University | 22.52 |
| 9 | London School of Economics and Political Science | 13.59 |
| 10 | University of Chicago | 12.04 |
| 11 | Stanford University | 8.16 |
| 12 | University of Denver | 7.77 |
| 13 | Yale University | 6.41 |
| 14 | University of California, San Diego | 4.66 |
| 15 | Sciences Po | 4.27 |
| 16 | Syracuse University | 4.08 |
| 17 | University of Oxford | 3.69 |
| 18 | Texas A&M University | 3.11 |
| 19 | University of Texas at Austin | 2.72 |
| 20 | Geneva Graduate Institute | 2.33 |
| 21 | King's College London | 2.14 |
| 21 | University of Cambridge | 2.14 |
| 21 | University of Michigan | 2.14 |
| 24 | New York University | 1.75 |
| 25 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 1.55 |
| 25 | University of California, Berkeley | 1.55 |
| 27 | University of Pittsburgh | 1.36 |
| 28 | Duke University | 1.17 |
| 28 | Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey | 1.17 |
| 30 | Cornell University | 0.97 |
| 30 | Seton Hall University | 0.97 |
| 30 | University of Notre Dame | 0.97 |
| 30 | University of Pennsylvania | 0.97 |
| 30 | University of Toronto | 0.97 |
| 30 | University of Virginia | 0.97 |
| 36 | Leiden University | 0.78 |
| 36 | Ohio State University | 0.78 |
| 38 | Boston University | 0.58 |
| 38 | George Mason University | 0.58 |
| 38 | The New School | 0.58 |
| 38 | Pennsylvania State University | 0.58 |
| 38 | University of London | 0.58 |
| 38 | University of Maryland, College Park | 0.58 |
| 44 | Aberystwyth University | 0.39 |
| 44 | Australian National University | 0.39 |
| 44 | Brown University | 0.39 |
| 44 | Dartmouth College | 0.39 |
| 44 | Georgia Institute of Technology | 0.39 |
| 44 | Hertie School of Governance | 0.39 |
| 44 | University of British Columbia | 0.39 |
| 44 | University of California, Los Angeles | 0.39 |
| 44 | University of Georgia | 0.39 |
| 44 | Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne University | 0.39 |
| 44 | University of St. Andrews | 0.39 |
| 44 | University of Sussex | 0.39 |
| 44 | University of Washington | 0.39 |
| 44 | Uppsala University | 0.39 |
| 58 | Albright College | 0.19 |
| 58 | Angelo State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Arizona State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Barcelona Institute of International Studies | 0.19 |
| 58 | Baylor University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Berlin Polytechnic | 0.19 |
| 58 | Carleton College | 0.19 |
| 58 | Carleton University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Carnegie Mellon University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Central European University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Clark University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Erasmus University Rotterdam | 0.19 |
| 58 | Florida International University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Geneva School of Diplomacy and International Relations | 0.19 |
| 58 | Hillsdale College | 0.19 |
| 58 | Indiana University, Bloomington | 0.19 |
| 58 | Institute of World Politics | 0.19 |
| 58 | Kennesaw State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Michigan State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Nanyang Technological University | 0.19 |
| 58 | National University of Singapore | 0.19 |
| 58 | Naval Postgraduate School | 0.19 |
| 58 | North Carolina State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Northeastern University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Old Dominion University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Paris Nanterre University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Peking University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Pomona College | 0.19 |
| 58 | Royal Holloway, University of London | 0.19 |
| 58 | Rutgers University, New Brunswick | 0.19 |
| 58 | Sam Houston State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | St. Thomas Aquinas College | 0.19 |
| 58 | Catholic University of America | 0.19 |
| 58 | The Citadel, the Military College of South Carolina | 0.19 |
| 58 | Troy University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Schwarzman College at Tsinghua University | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Arizona | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Baltimore | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of California, Irvine | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of California, Santa Barbara | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Colorado, Denver | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Florida | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Hawaii, Manoa | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Hong Kong | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Kent | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Kentucky | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Minnesota, Twin Cities | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of South Carolina, Columbia | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Sydney | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Warwick | 0.19 |
| 58 | University of Wisconsin, Madison | 0.19 |
| 58 | Virginia Tech | 0.19 |
| 58 | Washington University in St. Louis | 0.19 |
| 58 | Webster University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Western Michigan University | 0.19 |
| 58 | William & Mary | 0.19 |
| 58 | World Trade Institute University of Bern | 0.19 |
| 58 | Wright State University | 0.19 |
| 58 | Yonsei University | 0.19 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown University | 67.39 |
| 2 | Johns Hopkins University | 61.59 |
| 3 | Harvard University | 58.7 |
| 4 | Tufts University | 39.13 |
| 5 | Princeton University | 34.78 |
| 6 | Columbia University | 26.81 |
| 7 | London School of Economics and Political Science | 20.29 |
| 8 | George Washington University | 17.39 |
| 9 | Stanford University | 14.49 |
| 10 | American University | 12.32 |
| 10 | Yale University | 12.32 |
| 12 | University of Oxford | 11.59 |
| 13 | University of Chicago | 5.8 |
| 14 | Sciences Po | 4.35 |
| 15 | King's College London | 3.62 |
| 16 | National War College | 2.9 |
| 16 | University of California, Berkeley | 2.9 |
| 18 | National Defense University | 2.17 |
| 18 | University of Cambridge | 2.17 |
| 18 | University of Denver | 2.17 |
| 18 | University of Pennsylvania | 2.17 |
| 18 | University of Texas at Austin | 2.17 |
| 18 | University of Virginia | 2.17 |
| 24 | Duke University | 1.45 |
| 24 | George Mason University | 1.45 |
| 24 | Liberty University | 1.45 |
| 24 | Naval Postgraduate School | 1.45 |
| 24 | Schwarzman College at Tsinghua University | 1.45 |
| 24 | University of Michigan | 1.45 |
| 24 | University of Pittsburgh | 1.45 |
| 24 | William & Mary | 1.45 |
| 32 | Air War College | 0.72 |
| 32 | Arizona State University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Australian National University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Catholic University, Leuven | 0.72 |
| 32 | Cornell University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Florida International University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Iowa State University of Science and Technology | 0.72 |
| 32 | Leiden University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 0.72 |
| 32 | Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey | 0.72 |
| 32 | Missouri State University | 0.72 |
| 32 | National University of Singapore | 0.72 |
| 32 | Naval War College | 0.72 |
| 32 | Seton Hall University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Syracuse University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Texas A&M University | 0.72 |
| 32 | Tulane University | 0.72 |
| 32 | United States Military Academy, West Point | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of California, San Diego | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of Colorado, Boulder | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of Kentucky | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of London | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of Massachusetts, Amherst | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of Notre Dame | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of South Carolina, Columbia | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of St. Andrews | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of Sussex | 0.72 |
| 32 | University of Sydney | 0.72 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown University | 73.17 |
| 2 | Johns Hopkins University | 65.85 |
| 3 | Harvard University | 52.03 |
| 4 | Columbia University | 42.28 |
| 5 | Tufts University | 39.84 |
| 6 | Princeton University | 38.21 |
| 7 | George Washington University | 21.14 |
| 8 | London School of Economics and Political Science | 17.07 |
| 9 | University of Oxford | 16.26 |
| 10 | Stanford University | 13.01 |
| 11 | Yale University | 8.94 |
| 12 | American University | 8.13 |
| 13 | Sciences Po | 6.5 |
| 13 | University of California, San Diego | 6.5 |
| 15 | University of Chicago | 5.69 |
| 16 | King's College London | 3.25 |
| 16 | New York University | 3.25 |
| 16 | University of California, Berkeley | 3.25 |
| 19 | University of Cambridge | 2.44 |
| 20 | Geneva Graduate Institute | 1.63 |
| 20 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 1.63 |
| 20 | National University of Singapore | 1.63 |
| 20 | Texas A&M University | 1.63 |
| 20 | University of London | 1.63 |
| 20 | University of Michigan | 1.63 |
| 20 | University of Texas at Austin | 1.63 |
| 20 | University of Virginia | 1.63 |
| 28 | Australian National University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Central European University | 0.81 |
| 28 | College of Europe, Belgium | 0.81 |
| 28 | Cornell University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Duke University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Institute of World Politics | 0.81 |
| 28 | Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey | 0.81 |
| 28 | National Defense University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Naval Postgraduate School | 0.81 |
| 28 | Northwestern University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Pace University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Pepperdine University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Sophia University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Syracuse University | 0.81 |
| 28 | Tulane University | 0.81 |
| 28 | University College London | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of California, Davis | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of Denver | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of Edinburgh | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of Pennsylvania | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of St. Andrews | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of Sussex | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of Tokyo | 0.81 |
| 28 | University of Washington | 0.81 |
| 28 | William & Mary | 0.81 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harvard University | 64.65 |
| 2 | Princeton University | 60.3 |
| 3 | Stanford University | 59.36 |
| 4 | Columbia University | 38 |
| 5 | University of Chicago | 27.6 |
| 6 | Yale University | 27.03 |
| 7 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 20.04 |
| 7 | University of California, San Diego | 20.04 |
| 9 | University of Michigan | 17.58 |
| 10 | University of California, Berkeley | 17.01 |
| 11 | University of Oxford | 12.85 |
| 12 | Georgetown University | 11.53 |
| 13 | London School of Economics and Political Science | 7.94 |
| 14 | Cornell University | 6.24 |
| 15 | Johns Hopkins University | 6.05 |
| 16 | University of Cambridge | 5.86 |
| 17 | Ohio State University | 5.48 |
| 18 | University of Pennsylvania | 5.29 |
| 19 | George Washington University | 4.91 |
| 19 | New York University | 4.91 |
| 21 | American University | 4.16 |
| 22 | University of California, Los Angeles | 3.78 |
| 23 | Duke University | 2.65 |
| 24 | Tufts University | 1.89 |
| 24 | University of Minnesota, Twin Cities | 1.89 |
| 26 | University of Texas at Austin | 1.7 |
| 27 | Emory University | 1.51 |
| 27 | University of Rochester | 1.51 |
| 27 | University of Toronto | 1.51 |
| 30 | Brown University | 1.32 |
| 30 | Pennsylvania State University | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Virginia | 1.32 |
| 30 | University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee | 1.32 |
| 34 | Geneva Graduate Institute | 0.95 |
| 34 | Rice University | 0.95 |
| 34 | Sciences Po | 0.95 |
| 34 | University of Denver | 0.95 |
| 34 | University of Iowa | 0.95 |
| 34 | University of Southern California | 0.95 |
| 34 | Washington University in St. Louis | 0.95 |
| 41 | Aberystwyth University | 0.76 |
| 41 | Northwestern University | 0.76 |
| 41 | University of Amsterdam | 0.76 |
| 41 | University of Maryland, College Park | 0.76 |
| 41 | University of St. Andrews | 0.76 |
| 41 | University of Wisconsin, Madison | 0.76 |
| 47 | Australian National University | 0.57 |
| 47 | Baylor University | 0.57 |
| 47 | University of Georgia | 0.57 |
| 47 | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill | 0.57 |
| 47 | University of North Texas | 0.57 |
| 47 | University of Notre Dame | 0.57 |
| 47 | Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne University | 0.57 |
| 47 | Uppsala University | 0.57 |
| 55 | Boston College | 0.38 |
| 55 | Dartmouth College | 0.38 |
| 55 | Florida International University | 0.38 |
| 55 | George Mason University | 0.38 |
| 55 | Indiana University, Bloomington | 0.38 |
| 55 | Michigan State University | 0.38 |
| 55 | Queen's University, Canada | 0.38 |
| 55 | University of Arizona | 0.38 |
| 55 | University of Essex | 0.38 |
| 55 | University of London | 0.38 |
| 55 | University of Sussex | 0.38 |
| 55 | University of Warwick | 0.38 |
| 55 | University of Washington | 0.38 |
| 55 | Vanderbilt University | 0.38 |
| 55 | York University | 0.38 |
| 70 | Charles University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Corvinus University of Budapest | 0.19 |
| 70 | ETH Zurich | 0.19 |
| 70 | Eastern Illinois University | 0.19 |
| 70 | European University Institute | 0.19 |
| 70 | Free University of Berlin | 0.19 |
| 70 | Geneva School of Diplomacy and International Relations | 0.19 |
| 70 | Hebrew University of Jerusalem | 0.19 |
| 70 | Hillsdale College | 0.19 |
| 70 | Jagiellonian University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Kennesaw State University | 0.19 |
| 70 | King's College London | 0.19 |
| 70 | Koc University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Leiden University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Lund University | 0.19 |
| 70 | McGill University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey | 0.19 |
| 70 | National University of Singapore | 0.19 |
| 70 | Old Dominion University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Paris Nanterre University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Syracuse University | 0.19 |
| 70 | Texas A&M University | 0.19 |
| 70 | The New School | 0.19 |
| 70 | University College Cork | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Bologna | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of California, Irvine | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Connecticut | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Copenhagen | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Edinburgh | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Hawaii, Manoa | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Mississippi | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Nebraska, Lincoln | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Oklahoma | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Ottawa | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Pittsburgh | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Queensland | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of São Paulo | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Utah | 0.19 |
| 70 | University of Zaragoza | 0.19 |
| 70 | Virginia Tech | 0.19 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harvard University | 85.53 |
| 2 | Stanford University | 56.58 |
| 3 | Princeton University | 51.32 |
| 4 | Yale University | 42.11 |
| 5 | University of Oxford | 34.21 |
| 6 | Georgetown University | 31.58 |
| 7 | Columbia University | 27.63 |
| 8 | Johns Hopkins University | 25 |
| 9 | University of Chicago | 19.74 |
| 10 | London School of Economics and Political Science | 17.11 |
| 11 | University of California, Berkeley | 13.16 |
| 12 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 11.84 |
| 12 | University of Cambridge | 11.84 |
| 14 | Tufts University | 7.89 |
| 15 | George Washington University | 5.26 |
| 16 | American University | 3.95 |
| 16 | Duke University | 3.95 |
| 16 | University of Michigan | 3.95 |
| 19 | King's College London | 2.63 |
| 19 | New York University | 2.63 |
| 19 | Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne University | 2.63 |
| 22 | Dartmouth College | 1.32 |
| 22 | Sciences Po | 1.32 |
| 22 | University of California, Los Angeles | 1.32 |
| 22 | University of Denver | 1.32 |
| 22 | University of Notre Dame | 1.32 |
| 22 | University of Pennsylvania | 1.32 |
| 22 | University of Texas at Austin | 1.32 |
| Rank | School | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harvard University | 77.08 |
| 2 | Princeton University | 55.21 |
| 2 | Stanford University | 55.21 |
| 4 | Columbia University | 46.88 |
| 5 | Yale University | 33.33 |
| 6 | University of Oxford | 25 |
| 7 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology | 23.96 |
| 8 | Georgetown University | 22.92 |
| 9 | University of Chicago | 19.79 |
| 10 | Johns Hopkins University | 16.67 |
| 11 | University of California, Berkeley | 13.54 |
| 12 | Tufts University | 11.46 |
| 13 | University of Cambridge | 8.33 |
| 14 | University of California, San Diego | 7.29 |
| 14 | University of Michigan | 7.29 |
| 16 | London School of Economics and Political Science | 6.25 |
| 17 | Sciences Po | 5.21 |
| 18 | George Washington University | 4.17 |
| 19 | Cornell University | 3.12 |
| 20 | American University | 2.08 |
| 20 | Duke University | 2.08 |
| 20 | Ohio State University | 2.08 |
| 20 | University of California, Los Angeles | 2.08 |
| 24 | Australian National University | 1.04 |
| 24 | King's College London | 1.04 |
| 24 | National University of Singapore | 1.04 |
| 24 | New York University | 1.04 |
| 24 | Northwestern University | 1.04 |
| 24 | Pennsylvania State University | 1.04 |
| 24 | University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign | 1.04 |
| 24 | University of London | 1.04 |
| 24 | University of Pennsylvania | 1.04 |
| 24 | University of St. Andrews | 1.04 |
| 24 | University of Virginia | 1.04 |
| 24 | University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee | 1.04 |
These results should look familiar to those who follow national undergraduate rankings. Ivy League schools, Stanford University, the University of Chicago, and a few large public universities were favored across the board. But a handful of outliers punched well above their weight: Georgetown University, American University, George Washington University, Tufts University, and William & Mary all placed much higher here compared with their rankings in U.S. News & World Report , widely considered the most influential college ranking in the United States. In fact, Georgetown stands out as the top undergraduate choice among policymakers and think tank staff.
Advertisement
Master’s Programs
For master’s students hoping to pursue a policy career, all three groups we surveyed expressed a preference for programs on the East Coast. Only a few schools located west of the Rocky Mountains made the top 20 in each list. Respondents also highlighted several options outside the United States in the top 20: IR faculty included four international programs, while policymakers included five—all located in Europe—and think tankers included eight, one of which is in Asia.
Ph.D. Programs for Academics
IR faculty members’ rankings of Ph.D. programs have proved remarkably stable over the years. Between our 2017 survey and our most recent one, no top 15 program has moved more than one spot in either direction; in fact, most held the same rank. Additionally, policymakers and think tank staff appeared to value academic Ph.D. programs located in Washington, D.C., and outside the United States much more than U.S.-based IR scholars did.
Ph.D. Programs for Policymakers
When asked about doctoral students pursuing a policy career, all three groups we surveyed showed a preference for institutions with strong connections to Washington. Schools such as George Washington University, Georgetown University, and American University are ranked higher for students pursuing policy careers than for those hoping to enter academia. Conversely, institutions such as the University of Chicago and Massachusetts Institute of Technology are ranked lower for policy careers than academic ones. This shift highlights the importance of proximity to policy centers and the availability of practical engagement opportunities in shaping perceptions of a program’s value for a policy-oriented career in IR.
Advice to Prospective Students
Prospective students would do well to explore the specific features of various programs rather than focusing solely on a broad reputational ranking, which tells us little about a program’s regional, functional, or methodological strengths. For example, both academic and policymaker respondents who specialize in international political economy and/or trade policy ranked the London School of Economics master’s program higher than respondents who focus on security policy. Similarly, academics who specialize in the study of Latin America ranked the University of California, Berkeley Ph.D. program higher for an academic career than their non-Latin Americanist colleagues.
Still, prospective students should keep in mind that reputation matters. Although reputation may be an imperfect indicator of quality, it is a strong indicator of perceived quality within the field. A program’s standing can have conscious and unconscious effects on graduate school admissions committees, scholarship committees, and hiring managers in the public, private, and higher education sectors. For this reason, our ranking provides a systematic measure of these perceptions to assist prospective students in making informed choices as they plan for their future.

Advancing a Global Affairs Career
The intersection of large-scale challenges and technological advancements demands a broader range of knowledge and skills from international relations professionals. Learn about the impact this is having on employment trends in the latest FP Graduate School Guide .
To learn how your academic institution can be part of the FP Guides, contact Director of Academic Partnerships: Sherri Greeves, [email protected] .
Irene Entringer García Blanes is a senior project manager for the Teaching, Research, and International Policy Project at William & Mary. Twitter: @EntringerIrene
Susan Peterson is the Wendy and Emery Reves professor of government and international relations at William & Mary.
Michael J. Tierney is the George and Mary Hylton professor of international relations and director of the Global Research Institute at William & Mary. Twitter: @MikeTierneyIR
Join the Conversation
Commenting on this and other recent articles is just one benefit of a Foreign Policy subscription.
Already a subscriber? Log In .
Subscribe Subscribe
View Comments
Join the conversation on this and other recent Foreign Policy articles when you subscribe now.
Not your account? Log out
Please follow our comment guidelines , stay on topic, and be civil, courteous, and respectful of others’ beliefs.
Change your username:
I agree to abide by FP’s comment guidelines . (Required)
Confirm your username to get started.
The default username below has been generated using the first name and last initial on your FP subscriber account. Usernames may be updated at any time and must not contain inappropriate or offensive language.
More from Foreign Policy
Harris and walz can remake u.s. foreign policy.
The VP pick may help Harris reinvest in diplomacy—and abandon America’s reflex for military interventionism.
The Two Biggest Global Trends Are at War
World leaders will have to learn to navigate the contradictions of the new world order.
Ukraine’s Invasion of Russia Could Bring a Quicker End to the War
One aim of the surprise breakthrough may be for Kyiv to gain leverage in negotiations.
Tim Walz Has Always Been Consistent on China
What the olympics mean to china, m. night shyamalan pulls off the ultimate twist, the world cup is coming to america—and heading for disaster, does israel’s conflict with hezbollah have an endgame, america’s middle east defense rests on aircraft carriers, icj opinion on israeli settlements, explained, hamas refuses to attend upcoming cease-fire, hostage talks, new women leaders, same old international politics.
Sign up for World Brief
FP’s flagship evening newsletter guiding you through the most important world stories of the day, written by Alexandra Sharp . Delivered weekdays.
- Preparing to Apply
- How to Apply
- After Applying
- Why Penn State?
- Military and Veteran Students
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Degree Programs
- Academic Dates and Deadlines
- Policies for Students
- Theses and Dissertations
- Integrated Undergraduate-Graduate Plans
- Commencement
- Planning Your Finances
- External Funding Opportunities
- Information for Graduate Assistants
- Student Recognition Awards
- Funding FAQ
- Professional Development
- New Students
- From the Dean
- Advising and Mentoring Tips
- Academic Support
- Student Support FAQs
- Addressing Concerns
- Well-Being Resources
- Office of Graduate Educational Equity Programs (OGEEP)
- J. Jeffrey and Ann Marie Fox Graduate School Open House
- Programs and Initiatives
- McNair Scholars Program
- Summer Research Opportunities Program (SROP)
- Resources and Partners
- Office of the Vice Provost for Graduate Education and Dean
- Vision, Mission, and Strategic Plan
- By the Numbers
- Contact the J. Jeffrey and Ann Marie Fox Graduate School
- Resource Library
This dialog contains the full navigation menu for gradschool.psu.edu.
J. Jeffrey and Ann Marie Fox Graduate School at Penn State
- Student Support
Information For
- Alumni and Friends
- Veterans and Military Service Members
Helpful Links
- Graduate Education Policies
- Graduate Bulletin
- Student Teaching Certificate
- Graduate Exhibition
- Three Minute Thesis
- Accelerate to Industry
For Faculty and Staff
- Graduate Council
- Graduate Education Resource Portal

Social Media
From the faqs.
Email your adjusted information to [email protected] .
Legal Statements
- Non-Discrimination
- Equal Opportunity
- Accessibility
- The Pennsylvania State University © 2024
- Arnold School of Public Health
- Location Location
- Contact Contact
- Colleges and Schools
- 2024 News Archive
Physical therapy graduate to serve U.S. military soldiers and veterans

August 12, 2024 | Erin Bluvas, [email protected]
Growing up in Canada, Lemir Lira felt like he got to travel the world without even leaving his hometown. “Toronto was such a diverse and multicultural city that exposed me to different foods, music and customs,” he says.
After studying psychology at York University, Lira moved back to Houston, Texas, where he was born. He spent a couple years working with youth in underserved communities before enlisting in the U.S. Army.
Following Basic Training and Airborne School, Lira found himself stationed at Ft. Liberty in North Carolina. He also found himself afflicted by some minor orthopedic injuries and setbacks.
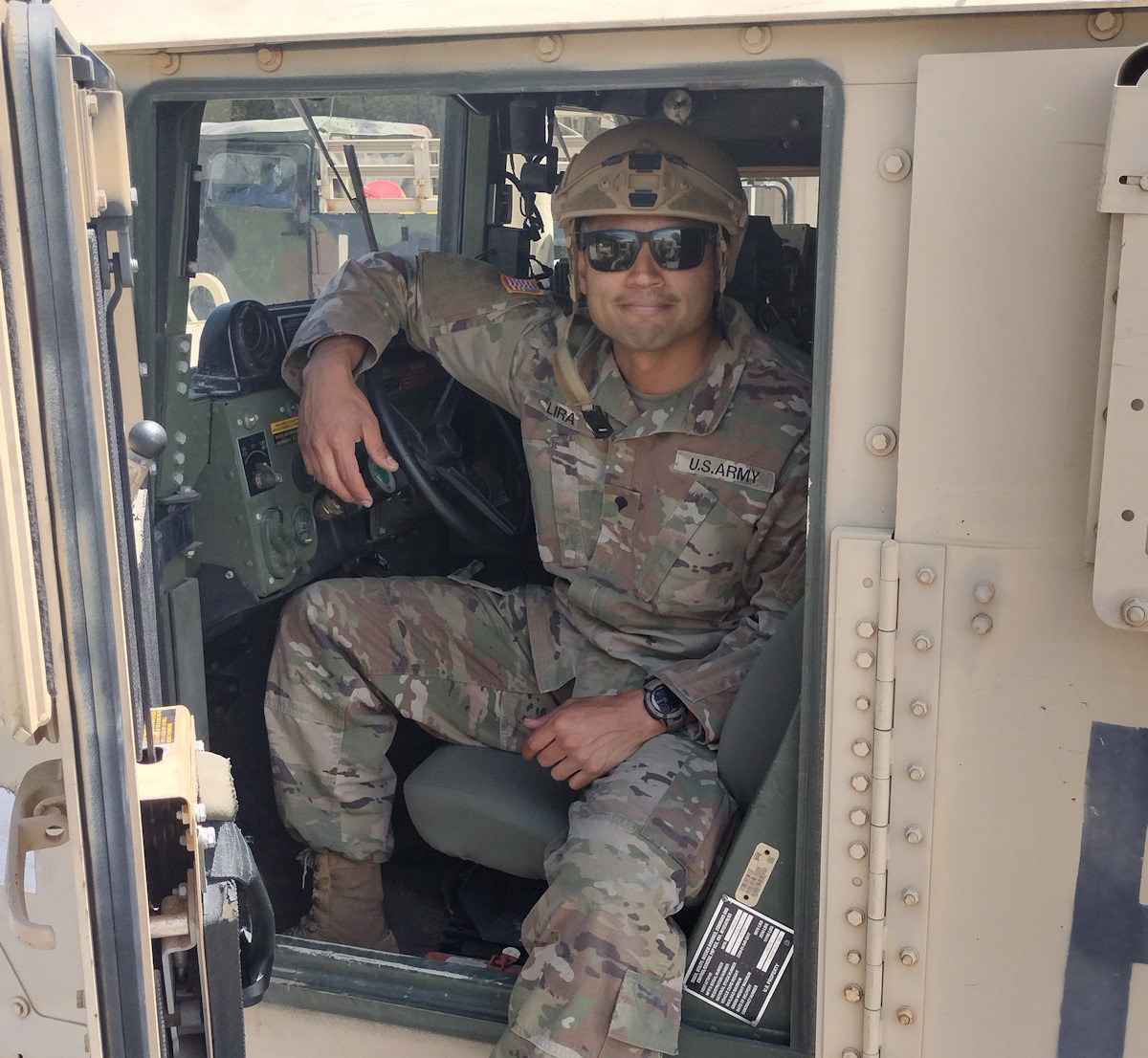

“This is where my exposure to physical therapy in the military setting began, and I had my ‘lightbulb’ moment realizing I could combine my two passions of continuing military service with the pursuit of a career in health care,” Lira says. “I had a new mission: to serve my fellow soldiers as a physical therapist when they were at their most vulnerable.”
While continuing his military service – first as a paratrooper with the U.S. Army National Guard and then as an infantry sniper with the SC Army National Guard – he began looking into Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) programs. The Department of Exercise Science ’s research-oriented curriculum and its warm and welcoming staff put the Arnold School at the top of his list.
“I was very happy to hear that USC is known to be a very military-friendly institution, which allowed me to balance being a member of the SC Army National Guard while simultaneously juggling my academic studies,” Lira adds. “I was very lucky to be provided the opportunity to select clinical sites that best aligned with my goal of serving military veterans and active-duty service members.”
Rotating among sites like Shaw Air Force Base and the William Jennings Bryan Dorn Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Lira says he received outstanding mentorship from all his clinical instructors. He particularly connected with Matthew Geary , Cathy Arnot and Alicia Flach .
I was very lucky to be provided the opportunity to select clinical sites that best aligned with my goal of serving military veterans and active-duty service members.
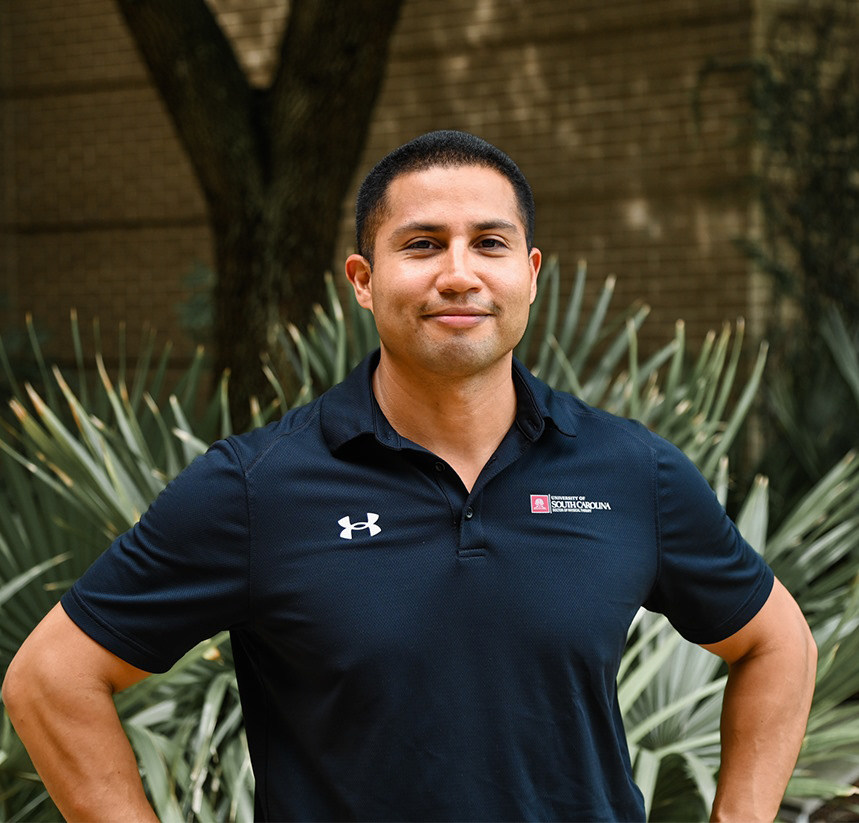

“I cannot give enough thanks to my amazing program clinical director, Dr. Geary, who always made himself available to meet and discuss clinical site placements that best aligned with my future career goals,” Lira says. “I had a marvelous research supervisor, Dr. Arnot, who put my mind at ease when working on our final program research project. Lastly, I was very fortunate to have been paired with a faculty mentor, Dr. Flach, who continues to inspire me today to break barriers and advocate for our patients and the PT profession.”
After graduating this month, Lira plans to specialize in orthopedics and become a Physical Therapy Officer in the U.S. Army to serve the military members who sacrifice so much and work tirelessly to keep the country safe. He’ll miss the gorgeous campus, the capital city’s vibrant food scene and strolls along the Congaree River.
“My experience at USC’s Columbia campus has been amazing from beginning to end, and the DPT program was designed with the student in mind,” says Lira, who appreciated the small class sizes and mentorship from faculty and upper-class members from day one. “I know that my degree and time spent at USC has best prepared me to serve soldiers by instilling in me the importance of seeking the most current evidence-based PT practices.”
Find Out More
The Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program prepares top-tier physical therapists to diagnose and treat individuals of all ages that have health-related conditions that limit their abilities to move through an individualized, high-quality, and high-value clinical program rooted in exceptional, evidence-based client care.

Meet Our Class of 2024
The Arnold School is proud of our 2024 graduates, who will go on to change the world locally and globally. Learn about some of the other outstanding individuals who completed one of our 34 programs this year.
Challenge the conventional. Create the exceptional. No Limits.

College Sports | Kellam High graduate Kemari Copeland is…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
Evening Edition
- William & Mary
- Virginia Tech
- Other Colleges
- Sports Columnists
College Sports
College sports | kellam high graduate kemari copeland is delighted to play defense for virginia tech after winding route.

The road Copeland took to become a Hokie — that included a few more bumps and detours than what might be considered standard.
“I’m a person that for whatever I do and set my mind to, I just have to do it,” said Copeland, a Kellam High graduate who transferred last December to Virginia Tech and is projected to be part of the rotation on a deep and experienced defensive line. “Coming here was one of my dreams. I always wanted to play (for) Virginia Tech, and if this is what I had to do to get here, then I would do it.”
Copeland had to do plenty. When he suits up later this month for the Hokies’ season opener at Vanderbilt, he will be representing his third team in as many seasons.
The recruiting interest in Copeland, who was rated the No. 28 senior in Hampton Roads by The Virginian-Pilot after the 2021 season, came mostly from FCS schools such as VMI, Fordham and William & Mary. At the FBS level, offers came from Army, Navy and Marshall.
The 6-foot-3, 280-pound defensive lineman ultimately opted for Army and headed to West Point a few months later. The 2022 season went well for Copeland, who appeared in seven games as a freshman, including the Cadets’ 20-17 win over Navy to conclude the year.
While he saw limited action that first season, Copeland said he realized that football could be part of his life beyond college. The small taste of Division I football convinced him that there could be a professional career ahead for him. But that can be a problem when you play for Army, which in almost all cases requires graduates to fulfill their military commitments.
“I knew I wanted to play Power Five football,” he said during Virginia Tech’s preseason media day. “I felt personally I could get a better chance to get to the league here than I would at Army.”
So shortly after the season ended, Copeland informed his coaches that he wanted to move on to a school that could help improve his chances of an NFL career. It took some time to convince anyone that this was a good idea.
“It was definitely hard,” Copeland said. “The coaching staff was hard on me (when I told them). They called my parents — both my mom and my dad. Oh my. … My parents come from military families. They were hard on me and said don’t do it.
“But I feel as a man, sometimes you have to make (hard) decisions about your life.”
Copeland held his ground and resigned his commission. However, there were more barriers ahead.
While he hoped to land at another Division I school when he entered the transfer portal at the end of the 2022 season, he said transcript issues left the junior-college route as his only option. But it wasn’t a dead end. Iowa Western Community College, located near the Iowa-Nebraska border and more than 1,300 miles from Virginia Beach, was one of the best.

The attention came early. Iowa Western’s spring game was attended by several college scouts. Offers started to come long before Copeland played his first official game for the Reivers.
“As far as (playing) JUCO, it was a lot of fun.,” said Copeland, who said he was offered by schools such as Tennessee, Auburn, Texas A&M and Oregon State. “Coming from Army and then going to JUCO, it made it a lot easier because of how hard Army was. JUCO was definitely easier than that. It was hard being out there in Iowa. I’m from Virginia Beach, so being all that way out there was hard, but I had to do it if I was going to make it to the next level.”
Copeland helped Iowa Western to a 12-1 record and a spot in the NJCAA Division I football championship game, where the Reivers beat East Mississippi 61-14. More importantly, he was contacted late midway through the regular season by a coach who used to visit him when he was in high school — Virginia Tech defensive line coach J.C. Price.
Those visits came when Price was working as an assistant for Marshall, one of the schools that offered Copeland when he was in high school.
“I remember in October, Coach Price called me, and I was like ‘What! Virginia Tech? I might be able to go home now!’” he said. “Once he called me, I knew it was the school for me. It was also a sigh of relief. Because with the current process, coaches call you 24-7, and I was still trying to focus on football and stuff.”
Price said Copeland’s decision to spend his sophomore year in the Midwest probably led to some “late-night conversations with himself,” but Price said he also saw someone who still had the same personality qualities from high school but had matured and had found his place on the football field.
“I knew he was going to be a D-lineman way back then, even though he was playing ‘Mike’ linebacker back at Kellam,” Price said. “It’s been great to see this thing come full circle for him. He always wanted to be here, and it shows to never give up on a dream, keep working, and no matter what obstacle they put in front of you, just keep fighting.”
Copeland said his time with the Hokies so far has gone fast, but that’s because he has enjoyed his experiences. That includes the spring practices, where the action on the field was sometimes overshadowed by who was watching on the sidelines.
“Seeing guys like (former Hokies quarterback) Mike Vick … and being in the same spotlight as him now is something I have to get used to,” Copeland said. “It’s been crazy seeing guys like Tremaine Edmunds. I came on a visit here, and we went to the locker room at halftime and he was in there. I was like ‘this guy is as big as heck.’ Being in the same vicinity as these guys is a blessing.”
More in College Sports

SUBSCRIBER ONLY
Nations pride rules in arlington million at colonial downs.

Chesapeake Post 280 SEALs are eliminated from American Legion region baseball tournament

Down the Line: Peninsula native Curt Newsome steps down as Emory & Henry football coach to focus on fighting cancer

College Sports | William & Mary offensive tackle Charles Grant doing “Good Works” on his way to the NFL
Trending nationally.
- Metal detectors cause long lines and delays on first day of school in Florida
- 2 ex-Los Angeles County deputies accused of raid to try and extort $37 million from Chinese national
- The US Navy’s warship production is in its worst state in 25 years. What’s behind it?
- In experiments, San Diego researchers gave cash to low-income people. Here’s what they learned.
- Let us now praise famous bluesmen: Buddy Guy is retiring at age 88
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
I wasted six years of my life getting a PhD degree. What should I do, and how will I survive?
I struggled with low self confidence throughout my bachelors, masters and PhD in chemical engineering. After spending two years in Masters and six years in getting a PhD degree, I am lost at what I can do with my life.
Initially, my plan was to be in academia. Though I love doing research, I don't see that as a possibility anymore.
I did not do well in my PhD. I have only two first-author journal publications in ~2.5 impact factor journals. I did not acquire significant skills. I am bad at programming, and I have a 3.7 GPA. I did not learn to drive or learn any foreign language. I did not improve my health or developed a new hobby. I even did not spend time on having a relationship. In short, I have done nothing over the past six years.
My PhD supervisor has given me a postdoc position. And I feel extremely inadequate. I feel that I won't be able to do anything after my postdoc year, and I will just be a burden and disappointment to my parents.
I am an international student living in the US.
I don't know what I should do. What should I do?
- career-path
- academic-life
- early-career
- emotional-responses
- 190 I think your only issue is one of self esteem. I suggest you find a counsellor and discuss where you are and how you feel. Don't let imposter syndrome lead to depression. Your advisor can give you professional advice, but you should also seek personal advice. The future is brighter than you think. – Buffy Commented Dec 7, 2019 at 16:30
- 7 Is the work fun though? – smcs Commented Dec 9, 2019 at 9:52
- 1 Is there anything in your past that is unresolved? I suspect your low self confidence stems from something else and not the PhD itself. For example you mention lack of relationship, so I suspect you have a non-existent sex life. Are you exercising and eating right? All of those things need to be in order for you to be happy doing a PhD. Otherwise all you'll have is a PhD which is empty and meaningless. – sashang Commented Dec 9, 2019 at 23:45
- 3 ‘I have only two publications …’ to me, who has a grand total of zero from both the PhD project that fell short of its desired outcome and my first two years of postdoc in which the ‘basically already finished, just this’ project turned out almost impossible, this is quite a violet slap in the face. – Jan Commented Dec 10, 2019 at 2:33
- 1 Seek counselling! The problems you describe have very little to do with academia, but very much with you. This website cannot provide adequate counselling in that regard (although some of the answers of course hit very relevant points). – user2705196 Commented Dec 10, 2019 at 18:21
9 Answers 9
It looks to me like you did not do so badly as you think. Two publications and 3.7 GPA are not so bad. It might depend on the field, it might not be the best ever, but I have seen much worse. If your supervisor offered you a postdoc position after having you for 6 years as a PhD student, it means that they consider your work useful.
You might be suffering from impostor syndrome . Do read the question and the answers in that link and see if you identify.
If you are not sure now, you have plenty of time during your postdoc year to decide whether you want to continue in academia or get a job in industry. The pros and cons of both options have been discussed extensively, as a quick Google search for "industry vs academia" shows. I personally agree with this source .
And, in most cases, the answer to "I have wasted X years of my life because I did not do Y and Z" is "do not look at the past and do Y and Z now". Especially when, as in your case, Y and Z can be done at any stage in your career life, such as learning languages, programming or driving.
- 27 Also, the field is chemistry, where the PhD is basically required for an entry level position in industry, so that is certainly not a waste of time. – Simon Richter Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 13:29
- 13 @SimonRichter Actually, the field is engineering (chemical engineering) where a BSc is enough for entry level jobs industry. – Cell Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 16:52
- 2 Get a job in industry. The great part is, that at the end of the project/delivery/month, work is done and completed. At least for me, I never considered the results in science 'done'; also pace is probably faster, so you will get getting quite a few achievements under your belt quickly (since you are smart). – lalala Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 19:03
- 3 @Cell Where I've worked, a PhD is automatically hired into a position that it would take ~5 years to get promoted to from entry-level with BSc, and the PhD can offer more job opportunities and security in the right industry. If OP goes into industry, the last six years could be well worth it! – Sam Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 19:45
- 1 @Sam That's nice, but I never said getting a PhD is a bad idea. I was only correcting the previous poster. With that being said, unless you plan on doing novel research, a PhD may make you overqualified for many jobs that can be done by a BASc, or MEng. You also didn't say what your field is. – Cell Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 20:20
To be honest, I'm tempted to agree with Buffy. It sounds like the biggest issue you have might actually be the one you identified at the start of your post - low self-confidence. Studying for a PhD, and working in academia in general, has a tendency to have that effect on people - you're far from alone.
If I were you, I'd be tempted to take stock of my overall life situation at this point, perhaps with some input from the people around me, and try to get an objective view of how things really are - they may not actually be as bad as you think.
For example, here are some plus points:
You finished a PhD. That's already a huge deal - lots of people don't even start a PhD, and of those who do, a proportion never finish. Of those who finish, lots of people feel like they didn't change the world with their PhD, and that's fine - most people don't, and that's not required. You've got the rest of your life to worry about that, if you want to, and it's not required even then. It's ok to just live and be happy sometimes.
You've got a postdoc position lined up, if you want to stay in academia. Your supervisor wants you to stay, which means you probably did something right during your PhD. Maybe your PhD didn't actually go as badly as you think.
If you've just finished your PhD, it's quite likely (in the absence of other evidence to the contrary, which I don't have) that you're still relatively young. That means you've got time on your side - there's still a whole lot of life ahead of you in which to do all the things you want to do (learning to drive, learning a foreign language, improving your health, developing your hobbies, having a relationship, ...). It sounds like you're unhappy that you haven't been doing those things, which means you'd probably be happier if you started doing them. Pick one and go start on it right now - hopefully you'll feel better (it's generally worked for me, when I've been feeling down). Starting on one of them sounds like much more fun than carrying on feeling fed up about not doing them, at any rate.
Best of luck!
p.s. For what it's worth, the fact that you've got a list of things you wish you'd been doing, and are unhappy that you haven't been doing them, is a good sign - there's an easy fix for that, which is go do some of them. That's much better than not having a list of things, and sitting there having existential angst and wondering whether life is pointless :)
- The postdoc is with my PhD advisor. I don't think that's an achievement. Probably my advisor felt pity on me and gave me the position. – Abhik Tandon Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 0:57
- 45 @AbhikTandon: Bear in mind that your advisor has something to lose from keeping you if you're truly not delivering (there's an opportunity cost - they could look for someone better). If they're keeping you, it's safe to assume you're at least above bar. Some advisors are kind, but few are so kind that they'll use their scarce funding to renew someone who has no possibility of being useful to them in any way. Advisors who pity you buy you a beer, gently tell you the truth, and help you find a job elsewhere; they don't generally commit £30k or more just to cheer you up. – Stuart Golodetz Commented Dec 8, 2019 at 1:45
- 4 @AbhikTandon Do consider that a PostDoc position often involves mentoring or teaching junior students, grading work, running tutorials, et cetera. Given that your PhD advisor is judged and graded not just on their research, but also on their teaching methods/standards, it's a role they quite literally cannot afford to give out of pity. You not being "up to standard" would put their job on the line! (That said, finding a hobby - preferably something more physically active than mentally, such as a martial art, to contrast with work - for a couple of evenings a week is a good idea.) – Chronocidal Commented Dec 9, 2019 at 8:41
- the highest possible academic degree that one can achieve
- a job in the field
- a life in a developed country
You're faring really well.
This is not to say that what you're feeling isn't real. It is real, and there is a problem. It's just that the problem is not what you have, but who you are. What you have is a highly successful life, at the same time, you are depressed and miserable.
You don't need more things, you have it all. No Nature publication will take you out of your dark place. You need to learn to enjoy life and accept yourself.
I know the last sentence is useless in itself, because it only tells you what you need, but not how to do it. Unfortunately, that's about as far as a stranger on the internet can get you. Speak to friends, speak to a psychologist, speak to anyone willing to listen, speak to yourself and try to figure out where does this need for accomplishments comes from, so you can move on.
- Technically I believe a DSc is a higher academic degree - but that usually comes at the end of a distinguished academic degree. – Martin Bonner supports Monica Commented Dec 10, 2019 at 16:06
- 1 @MartinBonnersupportsMonica DSc is not universally higher than PhD. In some countries DSc is just what a PhD in biology/physics is called, while in other countries DSc is just honorary, while other countries don't use PhD at all and have only DSc, which are seen as the equivalent of PhD, in countries that have PhD. – Andrei Commented Dec 10, 2019 at 17:51
You need to talk to someone – be that a counsellor (as @Buffy has suggested in the comments), a family member, a friend, or even (depending on your relationship) your supervisor. It does sound like a good part (if not most!) of the problem you describe may stem from impostor syndrome, and if that's the case, then it will be crucial to have others as a sounding board, to help put things into perspective. I have never known anyone in academia who didn't struggle at some point, somehow. Academia is tough, research is hard and failures are inevitable.
You mention you love doing research. Considering that you have also successfully turned that research into publications, it rather sounds like you do have what it takes to succeed. (Again, to put things into perspective, in my field it is normal for PhD students to graduate with 0–1 publications, and the impact factor of what's considered the leading journal is about 2.3. Different fields are different, yes. But you have definitely not failed.)
The other things you mention seem more minor to me. You say you are bad at programming. But you can always improve – programming, if anything, is one of those things where practice makes perfect. You mention you have neglected your health, hobbies and interpersonal relationships. But this is not uncommon: these things happen to many people who pursue a PhD, in various ways, and it is not too late to do something about them now. You say you have done nothing over the past 6 years. This cannot be literally true (you have earned a PhD, an enormous undertaking), but even if it were, the thing to do now would be to start doing those things you have neglected in the past.
But please do consider talking to someone. Having to verbalize your own thoughts and feelings is an excellent way of beginning to understand your thoughts and feelings, and of starting to see a solution.
Get your frame of reference right.
Achieving a PhD puts you in the 5% highest educated part of the population. That's quite significant. But you're comparing yourself to the smartest people in your direct environment - an environment set up try to get together all the smartest people.
If you don't manage to be in the top 1%, surely being in the top 5% is still something to feel pretty happy with?
They are marathon runners on arrival.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xSZlSaPJAdQ
Do they look well? Can you imagine, how bad feeling could it be, being there, after 42km of running?
But believe me: it is uncomparably better to be there, than for us, watching them on the youtube .
Don't do any irrecoverable mistake now! Wait, at least some months, more ideally some years! Take some longer leave, if you can (probably you can), and do nothing! Only think.
For example, now you can learn to drive. Ask anybody having a driving license, but no Phd, would they switch to the other.
I know what it's like to feel like you "haven't been living" for years. Six years of my life disappeared by my being extremely sick.
I have 5 years of unemployment in my résumé, an unfinished PhD, a tiny professional network, and ongoing health problems which make many things impossible. But I'm living again.
Some people have been in prison for 10 years. Some have escaped war-torn countries. Some have recovered from drugs or alcoholism. It's very hard when you suddenly awaken from a world of constraints into a world of choices, seemingly at a huge disadvantage from others within it. (I am not saying you've got it easier than they do. I'm saying you have this in common.)
Some of them go on to do amazing things. They have a moment that will define their life, and they work and work and work and work to a level that others can't imagine, and do something great for the benefit of their fellow man.
Others are just happy to be alive, happy to have gotten away from a bad place. Nothing wrong with that.
The most important thing in life is not success or respect or glory. It is to make choices that keep you out of misery. Anything more is a bonus.
But asking the question you're asking proves you are ready to change your life.
Maybe you could go to your home country or a country in poverty, where your skills and knowledge could make a bigger difference. Remember you don't need to use your degree at all; you could enter a completely different field. It's better to do it by choice than by necessity. Doing a variety of menial jobs of different sorts can be really enriching, since you see life from so many angles.
Doing a PhD doesn't just teach you about your topic; it teaches you about being thorough, exploring the state of the art, problem-solving, organisational skills, and so on. These make you very valuable if you use them well.
I know what I want to create. And I know what's stopping me is not my 6 missing years; it's my unwillingness to confront my weaknesses (like networking and time management.) Now I'm confronting these things, and I'm surprised at my success.
Go get 'em.
Two first-authored papers is not bad, I seen a lot of people getting phd for way less and still being full of themselves. You are doing good.
You don't think you did well during your PhD, but you stuck with it anyways. That sounds like a lot of PhD students. But, it also sounds like students that stuck with something, b/c their parents were back-seat driving their futures.
As others have said, your self-esteem issues stem from something. Something makes you feel inadequate all the time, and makes you compare yourself to others all the time.
Usually, that starts from overbearing parents constantly comparing you to other kids, chastising you for not being as good as some top-tier, stellar performer in your same grade or field, etc.
My dad did that to me my whole life. I was expected to get good grades. When I got them, I didn't get a "good job!" or anything. But, if I got bad grades, I got punished. As I got older, my dad would constantly compare me and my siblings against each other and to other kids his coworkers had. "So-n-so's kid is doing XYZ." (to insinuate it's better then what I was planning on doing, or was doing).
Even when I was an adult, my dad was trying to back-seat drive my career with "advice" that wasn't so much him trying to do what was best for me, but what was best for my career. He never took me, as a person, into consideration when giving advice.
What I realized over time (chatting with my dad extensively) was that he made decisions in his career... he gave up moving up the ladder or managerial positions, because he decided to start a family. He took a back-seat position at his job where he kept his head down and kept his mouth shut so he could keep earning an income and not rock the boat while supporting his family. He made one major career shift up the ladder to get more money, and in retrospect it was an awful decision that uprooted the family and set in motion events that pretty much tore the family apart.
What I realized as I got older was that he was trying to coach me to have the career he wished he could have; he was trying to guide his dream job vicariously through me.
He would push it in ways by either telling me exactly things he thought I should do, or package it as "I was chatting with kids at the gym and giving them advice, and this one kids doing XYZ" (again, to insinuate this "one kid" was doing something better then I was).
I got sick of it.
So, I stopped chatting with him about work, school, etc. When he'd ask or press, I simply told him that I was only going to speak with him like a member of the family, not someone I was seeking career counseling from.
I eventually had a blow-up with him, because I was tired of him trying to back-seat drive my life while I was watching his life implode around him with issues he wasn't staying on top of during a situation that basically forced me to take control of his responsibilities when he ended up in the hospital.
What I learned was ... just ignore him.
In 20 years time, my dad won't be around any more. But, god-willing.. I will.
In 20 years time, will I be happy if I had followed my dad's advice and done this and that? No. I'd be miserable, because he was pushing me to go in directions that were making me miserable.
So, why bother listening to him? Why bother trying to please him?
In 20 years time I can follow his advice and be miserable while he's dead, or I can ignore it and be happy while he's also dead.
Ultimately, I have to figure out what makes me happy, though.
But, when you have someone constantly telling you that you're not doing good enough, you need to do better, you're not doing as well as so-n-so over there, you should be heading in a certain direction, you need to do it all before a certain BS time limit... you know what, you eventually turn into a hot mess that thinks very little of yourself b/c you constantly have a devil on your shoulder that never thinks what you're doing is good enough.
Tell that person (or those people) to go screw off.
Since you're international.. and you're in a STEM field.. and you went through a PhD even though it sounds like you didn't really want to .. I'm going to assume you're Indian.
You need to have a moment of clarity where you decide to be your own person and stop having your family tell you what you need to do and where you need to go in life.
That can be hard if your family is paying the bills.
But, I may be making assumptions, but your story sounds almost identical to a ton of other folks I rubbed elbows with in college... all of them Indian. They were taking STEM when really they wanted to do liberal arts or whatever they were passionate about. Their family pushed them into an "lucrative career", b/c it's all about the money and status with them.
I had a couple of Indian folks tell me they had a massive weight lifted off their shoulders when they told their family to stuff themselves. They were dating people locally, and one was wanting to marry the girl he was dating. One guy dropped his STEM and went into art which is what he really wanted to do (and he was an AMAZING artist).
Ultimately, you have to figure out what makes you happy, and stop listening to folks constantly running you down and telling you you're not good enough.
I rented a room from a gay couple, and one of the guys had a degree in aeronautic engineering. You know what he did for a living? He was the director of a high school band. His parents pushed him to do engineering, b/c he was in the closet and just kept his nose down and did what they said. When he finally got older, he got tired of them, and came out of the closet and pursued what really made him happy: music.
People have to have that moment.
So, you're asking how you'll survive over here? I think you really need to ask yourself what will make you happy. And, you need to start ignoring folks that are running you down.
With a PhD in Chemistry, you don't have to be a great programmer. There are companies that will hire you to figure out some chemistry, and team you up with Comp Sci or Info Sys folks that will do all the coding and stuff for reports, data science, etc.
If you don't like what you have a PhD in, then go figure out what you do like. Maybe you like working on motorcycles or scuba diving or whatever.. find a way to make a career out of it.
It's better to live a modest life that makes you happy, even at the expense of others, then to be rich and f'ing miserable b/c you decided to make everyone else happy.. usually folks that won't be alive in 20 years time.. which just leaves you miserable while they're dead.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged career-path postdocs academic-life early-career emotional-responses ..
- Featured on Meta
- Introducing an accessibility dashboard and some upcoming changes to display...
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- What tool has a ring on the end of a threaded handle shaft?
- Permutations of the natural numbers with a common conditionally convergent series
- Earliest example of space travel involving interdimensional 'shortcuts'
- She's a black belt in judo
- Counting them 100 years later
- Why is the completely dark disk of the Moon visible on a new moon if the lunar orbit is at an angle to the Earth’s?
- Traveling to Canada from another country as a greencard holder
- What is the Mac OS equilivent of linux's `hostname -I`?
- Using elastic-net only for feature selection
- Direct limits in homotopy category
- Special generating sets of the additive group of rational numbers
- Would a manned Mars landing be possible with Apollo-era technology?
- A property of tamely ramified extensions
- section numbers in PDF outline
- How do I use "batcat" to colorize the output of the "--help" and "-h" options of commands?
- What is the meaning of 'in the note'?
- Why is consciousness confined?
- Suntne viva entia quae spirant per suam pellem (et non pulmone) "animalia"?
- Is the word ekklesia ever used to describe unbelievers?
- Can light be somehow confined to create a kugelblitz?
- Safe App Development - general questions
- Can't find this type of matrix in any index. It's the Jacobian of a non linear ODE system, and each row has only two row-specific values.
- What counts as a pet?
- How to deal with a boss that is using non-related arguments in a dissent?

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A Masters takes 1 (UK) to 2 (rest of Europe) years, while a PhD takes at least 3 (UK, 4 years limit) to potentially 6+ years. - In addition, it can be easier for people to do a part time Masters than a part time PhD to extend their knowledge. It also avoids the repetition of the introduction from an undergraduate degree.
3,763 2 12 21. I agree with all of this, and I'd also like to add that even though some programs do not award a terminal Master's degree after the 2nd year of the PhD program, the accomplishment is still implied, and pursuing a Master's in the same field would be unusual and, in rare cases, interpreted as an effort to avoid competing on the job ...
Corkins's choice is one way to "master out" of a Ph.D. program, although she prefers the term "pivot.". More typically, "master out" is used to describe students who enroll in a Ph.D. program and exit with a master's degree in that same field instead. It's unclear how often this happens.
The strategy worked. The summer after she obtained her Ph.D., she became a scientific adviser and clerk at a law firm, working during the day and going to law school at night. Managing work and school was intense, and going to school part time meant that she finished her degree in 4 years instead of the usual three.
The two most common types of graduate degrees are master's and doctoral degrees: A master's is a 1-2 year degree that can prepare you for a multitude of careers. A PhD, or doctoral degree, takes 3-7 years to complete (depending on the country) and prepares you for a career in academic research. A master's is also the necessary first ...
It's not just for the next 3-5 years that you need for a PhD. If you do a PhD, after you graduate, you'll need to find a job. If you get a job now, you'll already have a job. If you do well you might even command a higher salary in 5 years' time compared to entering the market as a fresh PhD.
The substantive body of work required for a PhD, which typically encompasses around 80,000 words compared to the 20,000 words of a Master's thesis, demands leveraging prior knowledge gained during your Master's. This includes keen critical analysis, refined research methodologies, and advanced time management.
2. PhD: After earning a master's degree, the next step is a PhD, which entails both working and performing research at an institution. A PhD is an abbreviation for "Doctor of Philosophy.". It is the highest academic degree one can achieve. As such, it is a time-consuming pursuit that requires a lot of studying and research.
After receiving your master's degree, there are still more options to study in graduate school, including an additional master's degree, doctorate programs (Ph.D., Ed.D., and others) and certificate programs to consider. These degree and certificate programs all vary in level, time to complete, and more.
Having a Ph.D. means you are not only a general master of the field but that you also have a specific study that you understand completely. Students with master's degrees have mastery in a subject, but a Ph.D. takes this mastery further. Such mastery can help you become a leading member of academia or the author of a book on the subject.
Summary. An Integrated Masters with a PhD (iPhD) is a four-year postgraduate level programme that combines a one-year Masters course with a three-year PhD course. They allow students to familiarise themselves with their chosen topic, research methods and academic writing techniques before embarking on their own independent research project.
In some fields, having a doctorate can lead to higher earning potential and increased salary opportunities. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, doctoral degree holders made an average of $1,885 per week in 2020, while master's degree holders made an average of $1,545 per week. Contribution to society:
The decision to pursue a PhD after getting your Master's degree is a difficult one. A PhD is a huge undertaking emotionally, mentally, and financially. Considerations That Are True for Everyone Wanting to Do a PhD. It takes 3-4 years to complete, during which you are on a pretty basic stipend (OK, you're poor).
The most obvious difference between a Masters and a PhD in terms of overarching course structure is length. Whereas a Masters is completed in 1-2 years, a PhD will usually take 3-4 years (if studied full-time) or 5-6 years (if studied part-time). 3-4 years may sound like a long time, but by the end of a PhD you'll not only researched, written ...
Deciding whether to pursue a PhD immediately after a master's degree or enter the workforce first depends on personal goals, interests, and circumstances. A PhD typically requires around five years of self-directed effort, similar to starting a business. If passionate about research, it might be best to begin right away.
A Masters degree is the next level of education after the completion of an undergraduate degree, commonly known as a Bachelors. These degree levels are often referred to in terms of cycles so that a Bachelor's is a first-cycle degree, a Masters is a second-cycle and finally, a PhD is the third-cycle of higher education (and the highest).
Ph.D. study includes a major research project in addition to coursework, and a Ph.D. is the highest scholastic degree awarded by American universities. Contrary to common perception, career paths for Ph.D. graduates are quite varied, not just limited to academia. Ph.D. training helps you hones skills such as writing, research, teaching, data ...
As we mentioned earlier, having a master's can boost your employability. This is often the case when it comes to graduate schemes. While there are some graduate schemes that accept grads with 2:2s, a lot will specify that they're only open to those with a 2:1 and above OR a postgraduate degree. Particularly if you received a 2:2 at uni, a ...
PhD in Microbiology did Masters in Financial Management. PhD in Engineering did Masters in Applied Math. PhD in Mathematics did a Masters in Management. And if you want a semi-famous person, Michael Griffin, former NASA director, did not only one, but FOUR Masters after his PhD.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master's and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic ...
Mar 23, 2014 at 8:06. yes, but does people with masters degree complete their PhD's sooner.. - Ank. Mar 23, 2014 at 8:15. 6. Yes, you will probably complete the PhD a bit sooner. You'll have more research experience, and if continuing your research on the same or similar project, you'll already have experience in the field.
Specialized Masters Requirements. As part of the application process for both programs, you are required to submit your essays, two letters of recommendation, transcript(s), and standardized test score(s). We also require you to have graduated from or be on track to graduate with an undergraduate degree.
For master's students hoping to pursue a policy career, all three groups we surveyed expressed a preference for programs on the East Coast. Only a few schools located west of the Rocky Mountains ...
Kern Graduate Building University Park, PA 16802 Contact the Fox Graduate School
A lecturer at Sydney's Macquarie University, her research interests include breaking, street dance and hip-hop culture, while her PhD thesis focused on the intersection of gender and Sydney's ...
"One con to purchasing a house as a new graduate may include having to relocate for a new job shortly after purchasing," Charnet says. It can be harder to sell a home than to cancel a rental ...
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
After graduating this month, Lemir Lira plans to specialize in orthopedics and become a Physical Therapy Officer in the U.S. Army to serve the military members who sacrifice so much and work tirelessly to keep the country safe. ... Physical therapy graduate to serve U.S. military soldiers and veterans Posted on: August 12, 2024; Updated on ...
The recruiting interest in Copeland, who was rated the No. 28 senior in Hampton Roads by The Virginian-Pilot after the 2021 season, came mostly from FCS schools such as VMI, Fordham and William ...
I struggled with low self confidence throughout my bachelors, masters and PhD in chemical engineering. After spending two years in Masters and six years in getting a PhD degree, I am lost at what I can do with my life. Initially, my plan was to be in academia. Though I love doing research, I don't see that as a possibility anymore.