
- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply


Building a Solid Internal Business Plan: Expert Guidance and Insights
An internal business plan is like a compass for your organization, guiding your team towards common goals and strategies. In this guide, we’ll break down each component of an internal business plan in simpler terms and share expert tips to help you create a plan that keeps your team on the same page.
Key Highlights
- An internal business plan is a roadmap that guides your team towards common goals and strategies.
- It helps align your team, make better decisions, and achieve success.
- Create a clear and concise plan with SMART goals, action steps, and communication strategies.
What is Internal Business Plan?
A business plan acts as a blueprint for your organization’s future, detailing its goals, strategies, and financial projections. An internal business plan takes this concept further, focusing specifically on aligning your team and ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in achieving your shared vision.
Differences Between Internal and External Business Plans:
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between internal and external business plans:
| Feature | Internal Business Plan | External Business Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To guide internal operations and decision-making | To secure funding, attract investors, or build partnerships |
| Target Audience | Employees, management, and stakeholders | Investors, lenders, and potential partners |
| Level of Detail | Highly detailed, including specific action plans, budget figures, and internal metrics | More general and concise, focusing on key strategies, financial projections, and market opportunities |
| Confidentiality | Usually treated as confidential and not shared outside the organization | May be publicly available and shared with third parties |
| Focus | Internal goals, operational efficiency, and team alignment | External perception, building confidence, and attracting resources |
What's the Purpose of an Internal Business Plan?
Think of an internal business plan as your team’s GPS for success. It’s all about getting everyone on the same page and heading toward the same goals. Unlike the fancy plans you show off to investors, this one is all about making sure your team knows where you’re headed and how to get there together.
Here's Why It Matters:
- Teamwork and Focus: It spells out what your gang is trying to achieve and gives everyone a clear focus on the mission.
- Smarter Choices: Helps everyone make better decisions by laying out the game plan. It's like having a playbook for your business moves.
- Using Resources Wisely: Shows where the money, people, and tech need to go, making sure everything's used just right.
- Making Everyone Accountable: Sets goals and ways to measure success so that everyone's accountable for their part.
- Happy Teams: When everyone knows what they're doing and why, it makes the team feel united and pumped up.
- Spotting Trouble Early: It's like having a radar for problems, so you can plan ahead and steer clear of disasters.
An internal business plan isn’t just a document—it’s your team’s guidebook, making sure everyone’s rowing in the same direction and making the right moves to reach those big goals.
Benefits of an Internal Business Plan:
- Improved Communication and Alignment: Creates a shared understanding of goals, strategies, and responsibilities within the organization.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Provides a data-driven foundation for strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
- Increased Accountability and Performance: Establishes key performance indicators (KPIs) and promotes accountability for achieving goals.
- Boosted Team Morale and Motivation: A clear roadmap fosters a sense of purpose and direction for team members.
- Improved Risk Management: Identifies potential challenges and facilitates the development of contingency plans.
Overall, an internal business plan serves as a vital tool for achieving organizational goals, fostering collaboration, and ensuring long-term success.
Checkout our free sample business plans now!
1. mission and vision: your organization's purpose (around 200 words).
Your mission defines why your organization exists, while your vision outlines what you aim to achieve in the future. Keep these statements clear and inspiring, as they set the direction for your entire team.
- Expert Tip 1: "Your mission and vision should motivate and unite your team. They're your organization's North Star." - Maria Rodriguez, Management Consultant.
2. Organizational Goals: What You Want to Achieve (Around 250 words)
Lay out your short-term and long-term goals. Make them specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). These goals give your team a sense of purpose and direction.
- Expert Tip 2: "Goals should be like checkpoints in a race - clear and achievable. They keep your team focused and motivated." - Mark Thompson, Organizational Strategist.
3. SWOT Analysis: Understanding Your Internal Landscape (Around 300 words)
Conduct a SWOT analysis to identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This helps your team understand your current position and potential challenges.
- Expert Tip 3: "SWOT analysis is like a diagnostic checkup. It helps you know where you're strong and where you need to improve." - Emily Turner, Business Analyst.
4. Key Strategies: How You'll Achieve Your Goals (Around 250 words)
Outline the strategies your organization will use to achieve its goals. These could include expanding to new markets, improving processes, or developing new products or services.
- Expert Tip 4: "Your strategies should align with your goals. They're the 'how' behind your 'what'." - David Reynolds, Strategy Consultant.
5. Action Plans: Who Does What (Around 350 words)
Break your strategies down into actionable steps. Assign responsibilities to specific team members, set deadlines, and define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress.
- Expert Tip 5: "Action plans turn ideas into actions. They make your strategies a reality." - Laura Martinez, Project Manager.
6. Budget and Resources: What You Need (Around 250 words)
Detail the budget and resources required to execute your action plans. This includes finances, manpower, technology, and any other resources necessary for success.
- Expert Tip 6: "Budgets ensure you have the resources to implement your plans. They're like a financial roadmap." - Susan James, Financial Analyst.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation: Keeping Things on Track (Around 300 words)
Explain how you’ll monitor progress and evaluate the success of your action plans. Regular assessments help your team stay on course and make adjustments as needed.
- Expert Tip 7: "Monitoring and evaluation ensure you're headed in the right direction. It's about continuous improvement." - John Stevens, Management Expert.
Hire our professional business plan writers now!
8. communication plan: keeping everyone informed (around 200 words).
Describe how you’ll communicate the plan to your team. Transparency and clear communication are crucial to ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Expert Tip 8: "A well-communicated plan fosters teamwork and alignment. It's the glue that holds your organization together." - Maria Rodriguez, Communication Specialist.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While crafting and implementing your internal business plan, be mindful of these common pitfalls:
- 1. Lack of Clarity and Specificity: Vague goals and objectives lead to confusion and hinder progress. Ensure your plan outlines SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals with clear action steps.
- 2. Ignoring Internal Analysis: Neglecting a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) leaves you blind to internal challenges and untapped potential. Conduct a thorough assessment to gain a realistic understanding of your organization's capabilities.
- 3. Unrealistic Budgeting: Overestimating resources or underestimating costs can derail your plan. Develop a realistic budget based on accurate data and forecasts to avoid financial constraints.
- 4. Inadequate Communication: Failing to communicate the plan effectively to your team leads to misalignment and inefficiency. Foster open communication channels and ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- 5. Rigid and Inflexible Approach: The business landscape is dynamic, so your plan should be adaptable. Be prepared to adjust your strategies and tactics as needed based on market changes, performance data, and feedback.
Tips to Overcome Challenges
- Seek feedback: Enlist the help of colleagues and stakeholders to review your plan and identify areas for improvement.
- Promote collaboration: Encourage open communication and brainstorming sessions to foster innovative ideas and solutions.
- Track progress regularly: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and identify areas needing adjustments.
- Be proactive: Anticipate potential challenges and develop contingency plans to minimize disruptions.
- Embrace flexibility: Be prepared to adapt your plan as needed based on evolving circumstances.
Measuring Success
Effective metrics for internal business plan success.
- Goal Achievement: Track progress towards achieving your defined SMART goals.
- Financial Performance: Monitor key financial metrics like revenue, profitability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Operational Efficiency: Measure improvements in efficiency through process metrics like cycle time and error rates.
- Team Performance: Evaluate team effectiveness by tracking KPIs like productivity, engagement, and satisfaction.
- Market Share and Growth: Monitor your market share and growth rate to assess your competitive position and market penetration.
Interpreting Data and Making Data-Driven Decisions:
- Analyze trends and patterns: Identify trends and patterns emerging from your data to understand the underlying drivers of success or failure.
- Investigate root causes: Delve deeper into the root causes behind performance data to pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Test and experiment: Utilize A/B testing and other experimental methods to validate your assumptions and optimize your strategies.
- Communicate data insights: Share key data insights with your team to promote transparency and inform decision-making.
- Make data-driven decisions: Base your strategic decisions on evidence and insights gleaned from your data analysis.
By implementing these tips and practices, you can avoid common pitfalls and effectively measure the success of your internal business plan. Remember, a successful plan requires continuous monitoring, feedback, and adaptation to ensure it remains relevant and effective in driving your organization towards its goals. Ready to write an internal business plan but don’t know what to do? Explore WiseBusinessPlans’ professional business plan writers to get started today!
What Must an Entrepreneur Do after Creating a Business Plan?
With your internal business plan finalized, it’s time to shift gears and focus on its execution. This crucial phase requires action, dedication, and strategic implementation to transform your vision into reality. Here’s what you, as an entrepreneur, must do after creating an internal business plan:
1. Secure Funding
- Assess your financial needs: Review your budget and determine the funding required to execute your plan. Explore various funding options, including personal savings, loans, grants, and angel investors.
- Craft a compelling pitch: Develop a concise and persuasive pitch deck that highlights your vision, market potential, and financial projections to attract investors.
- Build relationships with potential investors: Network with individuals and organizations interested in your industry and build relationships that can pave the way for funding opportunities.
2. Assemble Your Team
- Identify key roles: Determine the skills and expertise needed to implement your plan effectively.
- Recruit talented individuals: Find passionate and qualified individuals who share your vision and values, and build a cohesive and motivated team.
- Delegate and empower: Assign tasks and responsibilities based on individual strengths, fostering ownership and accountability within your team.
3. Execute Your Strategies
- Break down your plan into action steps: Divide your strategies into manageable tasks with clear deadlines.
- Implement best practices: Utilize proven strategies and methodologies aligned with your industry and goals.
- Monitor progress and adapt: Regularly track progress against your goals, identify areas needing improvement, and adapt your strategies as needed.
4. Foster Communication and Collaboration
- Communicate openly and transparently: Keep your team informed of progress, challenges, and decisions.
- Encourage feedback and input: Create an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns.
- Build trust and collaboration: Foster a collaborative culture that encourages teamwork and shared ownership of success.
5. Measure Performance and Analyze Data
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs): Identify specific metrics aligned with your goals and regularly track their progress.
- Analyze data and draw insights: Utilize data to identify trends, understand performance drivers, and make data-driven decisions.
- Continuously improve: Leverage data insights to identify areas for improvement and adapt your strategies to optimize performance.
By following these steps after crafting your internal business plan, leveraging a well-designed business plan template can further assist in effectively translating your vision into action, propelling your entrepreneurial journey towards success.
Hire our award-winning business plan writers now!
In summary, creating an internal business plan is about providing your team with a roadmap to success. By simplifying each section and focusing on clear communication, you’ll not only set your team on the right path but also promote unity and collaboration within your organization. Your internal business plan is your tool for achieving your mission and turning your vision into reality.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077


Join us on social
How to Create an Internal Business Plan for a New Company Initiative
It is important to put together a complete, comprehensive internal business plan for a few reasons.

Business plans for start-up companies have become mainstays in the business world. But more and more company initiatives and projects have begun to require business plans as a way of validating prudent investments and company spend as maturing businesses look for innovation within to drive future revenue growth. A time may come in a business or a division when you have a new idea or product you believe will equal big revenue for the company, but how do you convey your message to the larger organization? As the world turns towards innovation and technology to drive growth in this mature economy, creating an internal business plan is becoming more and more commonplace, if not a necessity.
If you have a good working relationship with your executive team, business ideas should not be popping up out of the blue. Instead, you should have a platform for discussion in either staff meetings or one-on-one sessions with the executives. However, it is important to put together a complete, comprehensive internal business plan for a few reasons:
- It shows that you have your stuff together and can be organized and methodical about your plan.
- You will need to evangelize your new plan quickly and succinctly throughout the organization, and a detailed business plan is the most effective way to disseminate information.
Here are a few suggestions for inclusion in your business to improve the probability of gaining approval:
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary may be the most important part of the internal business plan as it cements the audience’s first impression of the project. This may be the only page many executives have time to read and discuss, so make sure it tells the story in a summarized manner. Style, visualization, and financial accuracy are all important aspect of this page.
Questions to ask and answer include:
- What is the idea?
- Where did it come from?
- How much to you believe its worth?
- What is the duration of investment?
- What is the financial impact?
- What is the mechanism we need to enact and unlock this new revenue stream?
- How does this project tie into and/or complement the overall strategy for the business and any other growth initiatives? (It is important to see how this product or service will become an integral part of the organization for years to come and not a one-off fad or an ill-conceived idea.)
It is very important to lay out your marketing strategy, as this will be the main focus point for management in understanding how realistic it will be to achieve your results. First, you need to identify your target market, whether it be a specific demographic or fanbase or creating a new segment. You will need to be very specific about your methods of attracting your target customers and the message you are going to represent to the overall market. If you are tapping into a new market, how will you get your message out there? If you are stealing share or competing against another rival, what will be your differentiation to gain share?
Without the right combination of message and means of delivering the message, even truly superior new products may have trouble gaining traction in the marketplace. If you can show that you already have customers lined up ready to purchase your products or services, this makes your case more convincing.
Management Team
Executives want to support new projects and new ideas, but they need to be confident in the people you put in charge. If you, as the author of the internal business plan, will not be directly operating the new product or service, but someone else on your team will be the main contact, you want to make sure they are a good fit for the project.
The team structure has to go beyond just your normal, everyday team configuration. It must show how each team member’s background and accomplishments contribute essential elements needed to succeed with this new venture. The project may involve more than one department, so you will want to show that you put time and effort into determining the team and define the responsibilities of each member. Make sure that you have a diverse group of people that have the availability to dedicate time to the project with a good mix of senior and junior employees.
Financial Projections
As the executive team decides whether they are going to approve of the investment in this new product or service, they have to consider whether they are going to get a sufficient return on their investment. Not only do they have to consider ROI, but in many companies where resources are limited and staffing up can be a political nightmare, business units also have to consider opportunity costs or tradeoffs related to moving individuals and not having them concentrate on already productive and proven products and services.
The financial projections provide clues about how well thought out the new products and services are as well as their financial viability. The executive team will look for whether the team has presented a reasonable forecast for revenue and profit growth that is both aggressive, but realistic for the business unit. When they see projections that seem unattainable, the project immediately loses credibility. Executive teams also want to see whether the management team backed up the projections with sound assumptions based on hard data obtained from industry sources – or were the projections simply guesswork. Financial projections in a business plan do not need to be voluminous or excessively complex. However, they do need to be clear and reasonable while being exciting from a ROI standpoint.
Getting Support for Your Internal Business Plan
While you may include additional information in your business plan, it is important to keep it short and succinct. It is also important that you dedicate the correct resources to develop, publish, and present this business plan. Our team at 8020 Consulting has experience putting together business plans for project and initiatives. You can contact us to learn more .
If you’d like to learn more about internal momentum toward business goals, we invite you to download our operational review program guide . It offers insights into how to organize meetings and set roles to encourage organizational traction:

About the Author
Lester has over 15 years of professional finance experience in strategic planning, forecasting and budgeting, financial analysis, and business evaluation. Prior to joining 8020 Consulting, Lester was the Director of Business Planning and Analysis at Warner Bros. and had previously worked as a Senior Manager of Retail Analysis and Manager of Finance for The Walt Disney Company. Additionally, Lester has held positions at Thomson Reuters and Public Financial Management. In his career, Lester also operated as the Chief Financial Officer for a consumer goods start-up company, where he oversaw the Accounting, Finance, Operations and HR functions. Lester’s expertise centers around FP&A, budgeting and forecasting, financial modeling, cause of change analysis, consolidation, industry analysis, and project management. Lester holds a Bachelor of Arts in Economics from Stanford University, and an MBA in Corporate Strategy and Finance from The University of Michigan, Ross School of Business.
Join our mailing list.
Join our mailing list for exclusive content. No spam, just great insight.

Please share your location to continue.
Check our help guide for more info.

- Human Resources
- Procurement

Writing an internal business plan
Beyond external, there are many internal reasons to write a business plan to support business success.

Related posts
- Business plan writing tips & advice for the avid entrepreneur
- How to write a business plan
- Business banking: Best banks and accounts for UK businesses
While all of the reasons for writing a business plan are usually described as external, such as landing investors or recruiting quality talent – there are plenty of reasons to make an internal business plan as well. Generally, such a plan is there to act as a roadmap for the company’s success; something to remind everyone of the joint vision they are working towards.
Business plan writing tips & advice for the avid entrepreneur
Why is a business plan important and who is it for, can a business plan improve your organisational performance, why make an internal business plan.
Generally, many large businesses utilise internal business plans to make sure that the overall company vision is not compromised and easily communicated to everyone. That sort of strategic direction is not easy to achieve solely by meetings and memos, especially if sprawling corporate structures are involved. Plus, the information laid out in such ways is always prone to change; which is why business plans are there to provide a more long-term, future-oriented set of values and motives.
Apart from that, as you will see in detail below; internal business plans are less focused on the financial aspect of running a business, at least when everything is functioning correctly in that regard. Instead, such plans are more often used to establish a set of metrics that the staff can use to see how hard they are working. Additionally, they are there to enable better performance management by upper management; ensuring that everyone realised what they need to do for their job performance not to suffer, and precisely what is expected of them in the workplace.
Overall, internal business plans allow for a higher degree of control and coordination among different levels of management and employees. Not only is communication vastly improved by the elimination of superfluous dilemmas; but the staff is also better able to voice their pleasure or concerns about where the company is going in the commercial and cultural sense. Such a plan is as much suited for staff empowerment as it is for better management .
Mission statement
If vision is about imagining and looking forward; your mission is very much about the present, and doing. In other words – you want to focus your mission statement on the practical, everyday actions that company employees can undertake to itch closer to the future forecast of the vision statement. So, make sure to lay out what kind of behaviours and actions must be done for your business to get where you want it to go.
For customer-oriented companies, the mission statement can also contain a succinct description of what the most average target consumer is for the company; something all employees will keep in mind. And then, tackle the public image of your company; what it is currently, what you want it to become, and what everyone needs to do to attain that image. That will bring a unique definition to your business in the eyes of the public, and give everyone a sense of clarity about what kind of collective they’re in.
If you want to bring even more clarity to your business, the only thing you can do is provide more specific desired outcomes for the future of your business. With that in mind, make sure to use your internal business plan to lay out a clear set of objectives for everyone who has access to it. Once you manage that, you will have a perfect guiding light to keep everyone involved headed in the proper direction.
Unlike the broader mission statement, your objectives should be less long-term and much more detail-oriented and specific. For example, you may want to choose a realistic revenue target and a reasonable date for hitting it. Then, think of what all of your employees need to do to manage this. And give them a set of objectives all of them are capable of understanding and working towards. Naturally, these must be in perfect alignment with your mission and vision, for the business plan to give a meaningful structure to your company culture .
Strategies are more general activities that your management must employ to reach the desired objectives. You want to make sure these are spelt out clearly, but they can be pretty broad in terms of scope. Remember – these will act as a bridge between your objectives and the practical actions that must be taken.
If you’re looking for examples, think in terms of detailed quarterly or monthly reviews, and better measurements of certain metrics to reach specific objectives. For example, most of your employees may need to work on revamping the quality control process at all production stages.
Action plans
Action plans are a part of the internal business plan; usually there to tie in a particular activity from a strategy with your set of objectives. Let’s clear this up a bit. Actions could mean the creation of a new product or a more modern marketing plan. It could also be the process of developing or investing in new systems. That is something you want to plan out annually and with strict deadlines.
Sustainability
Before you round out your internal business plan, there’s one crucial question you need to ask yourself. Namely, is your company capable of doing everything that this plan sets out to do? After all, with so many different management plans that are a part of this overall plan, it may all seem a bit overly ambitious. And while it sometimes just seems a bit confusing until everyone gets more comfortable with it; in many situations, an internal business plan may be too lofty to be realistic.
There’s no shame in making amendments to your internal business plan after it’s been circulated the company. After all, some things may prove to be not feasible after a couple of months. Or, an idea which seemed great to you, in the beginning, is now looking pretty outdated.
On the other hand, you don’t want to throw things out of the plan whenever they prove difficult to do; that’s also a recipe for disaster. Finding that middle ground between following an intricate, but realistic plan, and changing one that’s just not viable – that is something only a truly great manager is capable of.
Related topics
Related posts.

While there is no universal format for business plans; there are specific rules that anyone writing a business plan should...

To put it in the simplest possible terms - a business plan is a document, which details the purpose and...

Business plans are usually developed at the very start of a business to provide a clear road map or raise...

Copyright © 2013 – 2024 Entrepreneur Handbook Ltd. All rights reserved. Registered offices at 20-22 Wenlock Road, London, N1 7GU, UK.
- Human resources
- Start a business
Information
- Advertise with us
- Privacy policy
- Terms of use
Copyright © 2013 - 2024 Entrepreneur Handbook Ltd. All rights reserved. Registered offices at 20-22 Wenlock Road, London, N1 7GU, United Kingdom.
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Ultimate Guide To Crafting An Internal Business Plan

Every successful business starts with a clear plan, yet surprisingly, 70% of new ventures fail due to a lack of structured goals. Crafting an internal business plan isn’t just about financial forecasts and market analysis; it’s an essential roadmap for aligning your team. It’s the difference between haphazard progress and strategic growth.
The ultimate guide to crafting an internal business plan delves into tried-and-tested methodologies and innovative techniques. Borrowing insights from historic business triumphs and leveraging modern tools, it bridges the gap between theory and practical application. For instance, businesses with a solid internal plan tend to achieve 30% higher growth rates, according to various industry studies.
Ultimate Guide to Crafting an Internal Business Plan
Creating an internal business plan is more than just a good idea; it’s essential for guiding your company’s growth. It’s a roadmap that clarifies objectives and helps everyone stay on the same page. From identifying key goals to outlining specific strategies, an internal plan helps align your team’s efforts. It’s like having a GPS for your business journey. This guide will help you craft a plan that sets your business up for success.
Understanding the importance of a business plan is the first step. An effective plan includes various sections, like market analysis, financial projections, and operational strategies. Each section plays a vital role in shaping your business’s future. For instance, market analysis helps you understand customer needs and market trends. This information is crucial for making informed decisions.
The steps to developing an internal business plan start with setting clear goals. Next, you should perform a SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. After that, outline your marketing strategy and sales approach. Additionally, include detailed financial projections to predict future performance. These elements help create a comprehensive plan.
The benefits of having a well-crafted internal business plan are numerous. It not only helps in securing funding but also in tracking progress and measuring success. Companies with detailed plans are generally more profitable and robust. According to studies, businesses with plans grow 30% faster than those without. Therefore, investing time in creating your internal business plan can pay off significantly.
Importance of an Internal Business Plan
An internal business plan acts like a blueprint for your company. It guides day-to-day activities and helps with long-term planning. Without it, you might feel lost, like driving without a map. A clear plan helps you track progress and make necessary adjustments. It ensures everyone knows the goals and how to achieve them.
One major benefit is improved communication within the team. When everyone understands the plan, they can work together more efficiently. This collaboration leads to better problem-solving and innovation. Teams can come together to meet milestones and handle challenges. The plan also acts as a reference point for new hires.
Financial planning is another key aspect. An internal business plan includes detailed financial forecasts. These predictions help you manage cash flow and allocate resources wisely. They also prepare you for potential downturns. Knowing your financial standing allows for better decision-making.
Finally, having a solid internal business plan can attract investors. Investors look for businesses with clear strategies and solid plans. A well-documented plan shows you have thought through every aspect of your business. This increases your credibility and chances of securing funding. It shows you are serious and ready to grow.
Key Components of an Internal Business Plan
An effective internal business plan should include several key components. One of these is the executive summary, which gives a brief overview of your business. This section should grab attention and make people want to read more. It covers what your business does and its main objectives. This helps set the tone for the rest of the plan.
Another crucial component is the market analysis. This section involves researching your industry, target market, and competitors . It provides insights into what the market looks like and where your business fits in. Understanding these elements helps you identify opportunities and threats. It ensures your strategy aligns with market conditions.
Financial projections are also vital. They include forecasts for revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Income Statement
- Cash Flow Statement
- Balance Sheet
These projections help you plan for the future and manage resources effectively. They also make it easier to secure funding from investors.
Operational plans are another key component. This section details day-to-day business functions and management processes. It outlines how tasks will be completed and who will be responsible. This helps in organizing work and improving efficiency. It also ensures everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
Steps to Develop an Internal Business Plan
The first step is to define clear objectives. Know what you want to achieve with your business. Whether it’s increasing sales or expanding into new markets, having specific goals is crucial. These objectives will guide your entire planning process. Make sure they are measurable and achievable.
Next, conduct a SWOT analysis to identify your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This helps assess your current position in the market. Understanding these elements allows you to make informed decisions. It highlights areas for improvement and potential risks. Use the SWOT analysis to inform your strategy.
After that, focus on market research. Gather information about your industry, competitors, and customer needs. Use surveys, interviews, and publicly available data. This research will help you understand your target audience better. It also reveals market trends and opportunities.
The fourth step involves outlining your marketing strategy. Detail how you plan to attract and retain customers. This includes pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies. Make sure your marketing plan is aligned with your business objectives. Cover both online and offline tactics.
Then, develop financial projections. This includes forecasting your revenue, expenses, and profitability.
| Category | Projection |
|---|---|
| Revenue | $500,000 |
| Expenses | $300,000 |
| Profit | $200,000 |
These projections will help you manage your finances better. They are also critical for securing investments.
Finally, write the executive summary. Although it appears at the beginning of your plan, it’s best to write it last. This section summarizes the key points of your business plan. Make it engaging and concise. It should grab the reader’s attention and make them want to read more.
The Role of Market Analysis in Your Business Plan
Market analysis is a crucial part of any business plan. It helps you understand the landscape you are entering. Knowing your market trends, competitors, and customer needs is essential. This data provides the foundation for strategic decisions. It ensures your business is prepared for the challenges ahead.
One important aspect of market analysis is identifying your target audience. Knowing who your customers are will help you tailor your products and services to meet their needs. This involves segmenting the market into different groups. For example, you might categorize customers by age, gender, or purchasing habits. This helps in creating more effective marketing campaigns.
Understanding your competitors is equally important. A thorough competitor analysis will help you identify their strengths and weaknesses. This can reveal gaps in the market that your business can fill. It also helps you avoid potential pitfalls. Analyzing competitors gives you an edge, allowing you to strategize better.
Market analysis also involves studying current market trends. Keeping an eye on market trends helps you stay ahead of the curve. For instance, if there’s a growing demand for eco-friendly products, you can adjust your offerings accordingly. This helps in staying relevant and competitive. Adapting to market trends can also lead to new business opportunities.
Lastly, a detailed market analysis includes financial aspects. This involves understanding market size and growth rates.
| Year | Market Size (in billions) |
|---|---|
| 2022 | $1.2 |
| 2023 | $1.5 |
Knowing the financial health of the market helps in making investment decisions. It also aids in setting realistic business goals.
Financial Projections and Their Significance
Financial projections are a critical element in any business plan. They offer a forecast of your company’s future financial performance. These projections include estimates of income, expenses, and profitability. By predicting these financial outcomes, you can plan for growth and address potential challenges. They serve as a financial roadmap for your business.
One of the main benefits of financial projections is that they help in budgeting. Knowing your expected income and expenses allows for more precise financial planning. This ensures that you allocate resources efficiently. Having a clear budget helps avoid unexpected financial shortfalls. It also aids in making informed spending decisions.
Another significant aspect is their role in securing funding. Investors and lenders often require detailed financial projections. They need to know your business’s potential for profitability before providing funds. Accurate financial forecasts demonstrate your business acumen and preparedness. This improves your chances of securing the needed capital.
Financial projections also play a role in setting realistic business goals. By understanding your expected financial performance, you can set attainable objectives. This keeps the team focused and motivated. It also helps you measure progress over time. With clear financial targets, you can adjust strategies as needed.
Having detailed financial projections can also help anticipate market conditions. For instance, you might use these projections to forecast the impact of new market trends or economic shifts.
- Predicting revenue in different scenarios
- Planning for potential risks
- Adjusting strategies based on forecasts
This proactive approach can keep your business resilient. It prepares you to navigate both opportunities and challenges effectively.
How an Effective Internal Business Plan Enhances Your Business Growth
An effective internal business plan is crucial for driving growth. It provides a clear outline of your business strategies and goals. By having a detailed plan, you ensure everyone in the team knows their role. This alignment of efforts leads to more efficient operations. The clarity helps in achieving milestones timely.
Improved decision-making is another benefit. With data and projections at hand, you can make more informed choices. This reduces risks and maximizes opportunities for growth. For instance, knowing when to expand or when to cut costs becomes easier. An organized plan helps foresee potential pitfalls too.
An internal business plan also aids in performance tracking. You can set benchmarks and monitor progress against them. This makes it easy to identify areas needing improvement. Addressing these issues promptly keeps your growth trajectory on track. It provides a sense of direction for both management and staff.
Another way a strong plan boosts growth is by attracting investors. A well-documented business strategy piques investor interest. Detailed plans show you have thought through every aspect of your business. Investors are more likely to fund companies with solid plans.
| Component | Investor Interest (%) |
|---|---|
| Clear Objectives | 75 |
| Financial Projections | 65 |
| Market Analysis | 80 |
This ensures you have the necessary capital for expansion.
The structured approach also allows for better resource management. Knowing how resources are allocated ensures optimal usage.
- Avoids wastage of materials and time
- Keeps projects within budget limits
- Adds value to all operations involved
This efficiency contributes significantly to overall growth, making your business more robust.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about crafting an internal business plan. These insights will help you understand the various aspects involved in creating a comprehensive plan.
1. What is the main purpose of an internal business plan?
The primary purpose of an internal business plan is to serve as a strategic roadmap for a company. It aligns the team’s efforts towards common goals, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. This focus helps in optimizing resources and making informed decisions.
Additionally, it provides a framework for tracking progress and measuring success. By having clear objectives and detailed plans, businesses can adapt quickly to market changes. It’s essential for both short-term operations and long-term growth strategies.
2. How often should an internal business plan be updated?
An internal business plan should ideally be reviewed at least once a year. Regular updates ensure that the plan stays relevant amidst changing market conditions and evolving business priorities. However, if significant changes occur, such as new competition or shifts in customer behavior, it might require more frequent revisions.
A dynamic planning process allows for better adaptability and responsiveness. Updating your business plan regularly secures its effectiveness as a guiding tool for strategic decisions. Consistency in review cycles also promotes ongoing alignment across teams.
3. What key elements should be included in financial projections?
Financial projections in an internal business plan should cover revenue forecasts, expense estimates, and profit margins. Revenue forecasts predict sales based on current trends and Market analysis while expense estimates account for operational costs like salaries, rent, and utilities.
Additionally, profit margins indicate the potential profitability after all expenses are deducted from revenues. Detailed spreadsheets or tables help visualize these components clearly.. Accurate projections build confidence among stakeholders including investors and lenders by highlighting future financial health
4.How does market analysis contribute to a successful internal business plan?
Market analysis offers valuable insights into your industry landscape, helping identify opportunities and threats.Thereby giving clarity regarding consumer needs ,trends as well as competitor activities.Understanding these aspects ensures that you’ve tailored strategies effectively catering desired segment. Ensuring you stay competitive amidst constantly changing economic scenarios results highly beneficialfor increasing chances of sustainable growth moving forward .
This analysis involves identifying target audiences , estimating demand patterns/deviation over time . Also advises modifying approach/as needed keeping product line offerings updated / adequately distinguishable.This real-time information aids smarter resource allocation Moreover predicting eventual bottlenecks proficiently maximizing output reduces waste optimizing cost-cutting inefficient areas further improving down-line profitability altogether boosting overall enterprise value..prioritizing initiatives towards impactful innovations
Crafting an internal business plan is vital for any company’s success. It aligns team efforts, supports informed decision-making, and attracts investments. Regularly updating the plan ensures continued relevance in a changing market. This comprehensive approach secures business growth and sustainability.
Incorporating detailed financial projections and market analysis enhances the effectiveness of your plan. Employee involvement ensures practicality and boosts morale. With a solid internal business plan, your business is well-positioned to achieve its goals and navigate future challenges. Invest time in developing your plan, and the rewards will be substantial.

Beverage Manufacturing Start-up Financial Model
The beverage manufacturing industry is a dynamic and rapidly growing sector that caters to a diverse market ranging from soft drinks and juices to alc... read more
- Excel Model – $199.95 Version 5.2
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 5.2

Liquor Distillery Financial Plan Template
Distilleries, with their rich history of crafting spirits, have experienced a resurgence in popularity, driven by consumer interest in artisanal and l... read more
- Excel Version – $199.95 Version 5.4
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 5.4

Corporate Finance Toolkit – 25 Financial Models Excel Templates
The toolkit is an essential resource for any organization, providing a comprehensive collection of tools and templates designed to streamline financia... read more
- All Excel Model Templates – $249.00 Version 1
- PDF Demo & Excel Free Download – $0.00 Version 1

Taxi Company Business Financial Model
Embark on the road to success by starting your own Taxi Company Business. This comprehensive 10-year monthly Excel financial model template offers an ... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.5
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 1.5

Trucking Company Financial Model
Embrace the road ahead, where every mile traveled isn’t just a journey—it’s a commitment to keeping the gears of the global economy turning. Sta... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.2
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 1.2

Crypto Trading Platform – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model presenting an advanced 5-year financial plan of a Crypto Trading Platform allowing customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital curr... read more
- Excel Financial Model – $139.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Truck Rental Company Financial Model
This detailed 10-year monthly Excel template is specifically designed to formulate a business plan for a Truck Rental Business. It employs a thorough ... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 2.3
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 2.3

Kayak Boat Rental Business Model
Dive into the future of your kayak boat rental business with our cutting-edge 10-year monthly financial model, tailored to empower entrepreneurs and b... read more
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version .5

Event Organizer Business Model Template
Elevate your event planning business to new heights with our state-of-the-art Event Organizer Business Financial Model Template in Excel. The Excel sp... read more
- Event Organizer Template - Full Excel – $129.95 Version 1.4
- Event Organizer Template PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1.4

Gas / EV Charging Station 10-year Financial Forecasting Model
This model is adaptable and useful for a Gas Station, an EV Charging Station, or a combination of both types of Stations. The model is coherent, easy ... read more
- Full Open Excel – $50.00 Version 7
- PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 7
Gantt Chart Template: Intuitive and Innovative Planning Tool
Very simple to use, intuitive and innovative planning tool/Gantt Chart
- Gantt Chart Tool – $20.00 Version 1

Student Accommodation / Village Development Model – 20 years
This Student Accommodation 20-year Development Model (hold and lease) will produce 20 years of Three Statement Analysis, Re-valuations and the consequ... read more
- Excel Full Open – $50.00 Version 7
- PDF Explainer – $0.00 Version 7

Webinar Organizer Business Plan Template
Discover the key to financial success in your webinar ventures with our Webinar Organizer Business Plan Template. This webinar business template is an... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.4
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 1.4

Motorboat Rental Business Financial Model
Dive into the heart of financial planning with our Motorboat Rental Business Financial Model, designed to propel your venture into uncharted waters wi... read more

Paddle Boat Rental Business Model
The Paddle Boat Rental Business Financial Model is a pivotal tool for entrepreneurs venturing into the leisure and tourism industry. Crafted with prec... read more

Party Planning Business Financial Model
Introducing the Party Planning Business Financial Model – Your Ultimate Tool for Flawless Financial Management in Event Planning! In a highly person... read more
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 1.4

Tennis Court and Club Development – 10-year Financial Forecasting Model
Introducing our Tennis Courts and Club Financial Forecasting Model – your winning strategy for tennis court and club development. With unmatched coh... read more
- Full Open Excel – $49.00 Version 8
- PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 8

Business Plan on Two Pages
Simple but effective business plan template - on two pages.
- Business Plan Template – $32.00 Version 1

Gym and Fitness Club 10 year Financial Forecasting Model
Introducing our indispensable 10-Year Excel Financial Forecasting Model, a vital asset for gym and fitness club owners navigating the complexities of ... read more
- Full Open Excel – $40.00 Version 8
- PDF Explainer – $0.00 Version 8

Squash Court and Club Dynamic Financial Model 10 years
Introducing our Squash Courts and Club Financial Forecasting Model – a game-changer for aspiring squash enthusiasts and club developers. With unpara... read more
- Free PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 8

Self-Storage Park Development Model
This Self-Storage Park development model will produce 20 years of three-statement analysis and valuations. There is a sheet focused on the Investor An... read more
- Free PDF Explainer – $0.00 Version 7

Three Statement Financial Model Template
The three statement financial model template offers a fundamental Excel template designed to project the three key financial statements over the next ... read more
- Free Excel Version – $0.00 Version 1.1
McKinsey 7S Model Excel Template
Originating in the late 1970s by consultants at McKinsey & Company, the McKinsey 7S framework is a strategic management tool designed to align sev... read more
- Excel Template – $39.00 Version 1

Surfboard Rental Business Financial Model
Surfing is not just a sport—it's a lifestyle booming globally. With eco-tourism on the rise and outdoor adventures in high demand, now's the time to... read more
- Excel Version – $129.95 Version 1.1
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 1.1

Manpower Planning and Analysis Model
The Manpower Analysis Model was designed to equip HR managers and analysts with a tool to control the transition of a workforce from one year to anoth... read more
- Excel Model – $50.00 Version 7
- Model Manual – $0.00 Version 7

Brandy Distillery Business Financial Model
Discover the ultimate Brandy Distillery Business Financial Model, meticulously designed to provide 10-year comprehensive insights and strategies for y... read more

3-Statement Financial Model
3-year financial model that is specially designed for early-stage companies.
- 3-Statement-Excel-Model-with-5-year-Forecast.xlsx – $39.00 Version 1

E-Commerce Startup Company (5-year) Financial Forecast Model
By developing a detailed 5-year dynamic financial forecast model for a e-commerce startup, founders, investors, and stakeholders can gain insights int... read more
- Excel Model – $70.00 Version 1
- PDF Model – $0.00 Version 1

Cider Distillery Financial Model
With its longstanding tradition and swiftly growing global demand, the cider industry offers a lucrative opportunity for investors looking to tap into... read more
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 5.4
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
| Function | Audience | Type of Business Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Serve as a loose guide of objectives and timeline | Internal | Lean |
| Serve as a detailed, brass-tacks blueprint of business goals and timeline | Internal | Traditional |
| Serve as a strategic document with a narrative focus on organization-wide goals, priorities, and vision | Internal | Strategic |
| Earn a company loan or grant | External | Traditional (with focus on financial documents) |
| Attract investors or partners | External | Traditional/strategic (with focus on financials, as well as support departments, such as marketing, sales, product, etc.) |
| To test a business or startup idea | Internal | Lean |
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
7 Different Types of Business Plans Explained

11 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024

Business plans go by many names: Strategic plans, traditional plans , operational plans, feasibility plans, internal plans, growth plans, and more.
Different situations call for different types of plans.
But what makes each type of plan unique? And why should you consider one type over another?
In this article, we’ll uncover a quick process to find the right type of business plan, along with an overview of each option.
Let’s help you find the right planning format.
- What type of business plan do you need?
The short answer is… it depends.
Your current business stage, intended audience, and how you’ll use the plan will all impact what format works best.
Remember, just the act of planning will improve your chances of success . It’s important to land on an option that will support your needs. Don’t get too hung up on making the right choice and delay writing your plan.
So, how do you choose?
1. Know why you need a business plan
What are you creating a business plan for ? Are you pitching to potential investors? Applying for a loan? Trying to understand if your business idea is feasible?
You may need a business plan for one or multiple reasons. What you intend to do with it will inform what type of plan you need.
For example: A more robust and detailed plan may be necessary if you seek investment . But a shorter format could be more useful and less time-consuming if you’re just testing an idea.
2. Become familiar with your options
You don’t need to become a planning expert and understand every detail about every type of plan. You just need to know the basics:
- What makes this type of plan unique?
- What are its benefits?
- What are its drawbacks?
- Which types of businesses typically use it?
By taking the time to review, you’ll understand what you’re getting into and be more likely to complete your plan. Plus, you’ll come away with a document built with your use case(s) in mind—meaning you won’t have to restart to make it a valuable tool.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
3. Start small and grow
When choosing a business plan format, a good tactic is to opt for a shorter option and build from there. You’ll save time and effort and still come away with a working business plan.
Plus, you’ll better understand what further planning you may need to do. And you won’t be starting from scratch.
Read More: How to identify the right type of plan for your business
Again, the type of business plan you need fully depends on your situation and use case. But running through this quick exercise will help you narrow down your options.
Now let’s look at the common business plan types you can choose from.

- Traditional business plan
The traditional (or standard) business plan is an in-depth document covering every aspect of your business. It’s the most common plan type you’ll come across.
A traditional business plan is broken up into 10 sections:
- Executive summary
- Description of products and services
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Marketing and sales plan
- Business operations
- Key milestones and metrics
- Organization and management team
- Financial plan
- Appendix
Why use this type of plan?
A traditional business plan is best for anyone approaching specific business planning events—such as presenting a business plan to a bank or investor for funding.
A traditional plan can also be useful if you need to add more details around specific business areas.
For example: You start as a solopreneur and don’t immediately need to define your team structure. But eventually you hit a threshold where you need more staff in order to keep growing. A great way to explore which roles you need and how they will function is by fleshing out the organization and management section .
That’s the unseen value of a more detailed plan like this. While you can follow the structure outlined above and create an in-depth plan ready for funding, you can also choose which sections to prioritize.
Read More: How to write a traditional business plan
- One-page plan
The one-page business plan is a simplified (but just as useful) version of a traditional business plan. It follows the same structure, but is far easier to create. It can even be used as a pitch document.
Here’s how you’ll organize information when using a one-page plan:
- Value proposition
- Market need
- Your solution
- Competition
- Target market
- Sales and marketing
- Budget and sales goals
- Team summary
- Key partners
- Funding needs
A one-page plan is faster and easier to assemble than a traditional plan. You can write a one-page plan in as little as 30 minutes .
You’ll still cover the crucial details found in a traditional plan, but in a more manageable format.
So, if you’re exploring a business idea for the first time or updating your strategy—a one-page plan is ideal. You can review and update your entire plan in just a few minutes.
Applying for a loan with this type of plan probably wouldn’t make sense. Lenders typically want to see a more detailed plan to accurately assess potential risk.
However, it is a great option to send to investors.
“Investors these days are much less likely to look at a detailed plan,” says Palo Alto Software COO Noah Parsons. “An executive summary or one-page plan, pitch presentation, and financials are all a VC is likely to look at.”
Creating a more detailed plan is as much about being prepared as anything else. If you don’t dig into everything a traditional plan covers, you’ll struggle to land your pitch .
If you don’t intend to seek funding, a one-page plan is often all you need. The key is regularly revisiting it to stay on top of your business.
Let’s explore two unique processes to help you do that:
Read More: How to write a one-page business plan
Lean planning process
Lean planning is a process that uses your one-page plan as a testing tool. The goal is to create a plan and immediately put it into action to see if your ideas actually work. You’ll typically be focusing on one (or all) of the following areas:
- Strategy – What you will do
- Tactics – How you will do it
- Business Model – How you make money
- Schedule – Who is responsible and when will it happen
Why use this process?
Lean planning is best for businesses that need to move fast, test assumptions, revise, and get moving again. It’s short and simple, and meant to get everyone on the same page as quickly as possible.
That’s why it’s so popular for startups. They don’t necessarily need a detailed plan, since they’re mostly focused on determining whether or not they have a viable business idea .
The only drawback is that this planning process is built primarily around early-stage businesses. It can be a useful tool for established businesses looking to test a strategy, but it may not be as helpful for ongoing management.
Read More: The fundamentals of lean planning
Growth planning
Growth planning is a financials-focused planning process designed to help you make quick and strategic decisions.
Again, it starts with a one-page plan outlining your strategy, tactics, business model, and schedule. The next step is to create a working financial forecast that includes projected sales, expenses, and cash flows.
From there, you run your business.
As you go, track your actual financial performance and carve out time to compare it to your forecasts . If you spot any differences, these discrepancies may indicate problems or opportunities that call for adjusting your current strategy.
Growth planning combines the simplicity of the one-page plan and the speed of lean planning, with the power of financial forecasting.
This makes the process useful for every business stage and even allows you to skip to the forecasting step if you already have a plan.
With growth planning, you’ll:
- Regularly revisit your financials
- Better understand how your business operates
- Make quick and confident decisions
This process focuses on growing your business. If diving into your financials isn’t a priority right now, that’s okay. Start with a one-page plan instead, and revisit growth planning when you’re ready.
Read More: How to write a growth-oriented business plan
- Internal plan
Sometimes you just need a business plan that works as an internal management tool.
Something to help you:
- Set business goals
- Provide a high-level overview of operations
- Prepare to create budgets and financial projections
You don’t need an overly long and detailed business plan for this. Just a document that is easy to create, useful for developing or revisiting your strategy, and able to get everyone up to speed.
The internal plan is a great option if you’re not planning to present your plan to anyone outside your business. Especially if you’re an up-and-running business that may have created a plan previously. You might just need something simple for day-to-day use.
Read More: 8 steps to write a useful internal business plan
- 5-year business plan
Some investors or stakeholders may request a long-term plan stretching up to five years. They typically want to understand your vision for the future and see your long-term goals or milestones.
To be honest, creating a detailed long-term business plan is typically a waste of time. There are a few exceptions:
- A long-term plan is specifically asked for
- You want to outline your long-term vision
- Real estate development
- Medical product manufacturing
- Transportation, automotive, aviation, or aerospace development
The reality is, you can’t predict what will happen in the next month, let alone the next one, three, or five years.
So, when creating a long-term plan, don’t dig too deep into the details. Focus on establishing long-term goals , annual growth targets, and aspirational milestones you’d like to hit.
Then supplement these with a more focused one-page plan that actually describes your current business, which you can use in your business right now.
Read More: How to write a five-year business plan
- Nonprofit business plan
A nonprofit business plan is not too different from a traditional plan. You should still cover all of the sections I listed above to help you build a sustainable business.
The main differences in a nonprofit plan are tied to funding and awareness. You need to account for:
- Fundraising sources and activities.
- Alliances and partnerships.
- Promotion and outreach strategies.
You also need to set goals, track performance, and demonstrate that you have the right team to run a fiscally healthy organization. You’re just not pursuing profits, you’re trying to fulfill a mission. But you cannot serve your community if your organization isn’t financially stable.
If you can use your business plan to show that you’re a well-organized nonprofit organization, you are more likely to attract donors and convince investors to provide funding.
Read More: How to write a nonprofit business plan
Resources to help write your business plan
Don’t get too hung up on the type of business plan you choose. Remember, you can always start small and expand if you need to.
To help you do that, I recommend downloading our free one-page business plan template . It’s especially useful if you’re exploring an idea and need a quick way to document how your business will operate.
If you know you’ll pursue funding, download our free traditional business plan template . It’s already in an SBA-lender-approved format and provides detailed instructions for each section. And if you want to explore other options, check out our roundup of the 8 best business plan templates you can download for free.
Lastly, check out our library of over 550 sample business plans if you need inspiration. These can provide specific insight into what you should focus on in a given industry.
Remember, just by deciding to write a business plan, you are increasing your likelihood of success. Pick a format and start writing!
Types of business plans FAQ
Which type of planning should be done for a business?
The type of planning fully depends on your business stage and how you intend to use the plan. Generally, whatever format you choose should help you outline your strategy, business model, tactics, and timeline.
How many types of business plans are there?
There are seven common types of business plans, including: traditional, one-page, lean, growth, internal, 5-year, and nonprofit plans.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Plan writing resources
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

10 Min. Read
What Is a Balance Sheet? Definition, Formulas, and Example

6 Min. Read
11 Common Business Plan Mistakes You Should Avoid

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 28, 2024
Years ago, I had an idea to launch a line of region-specific board games. I knew there was a market for games that celebrated local culture and heritage. I was so excited about the concept and couldn't wait to get started.

But my idea never took off. Why? Because I didn‘t have a plan. I lacked direction, missed opportunities, and ultimately, the venture never got off the ground.

And that’s exactly why a business plan is important. It cements your vision, gives you clarity, and outlines your next step.
In this post, I‘ll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you’d need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan?
What is a business plan used for.
- Business Plan Template [Download Now]
Purposes of a Business Plan
What does a business plan need to include, types of business plans.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. It provides a detailed description of the business, including its products or services, target market, competitive landscape, and marketing and sales strategies. The plan also includes a financial section that forecasts revenue, expenses, and cash flow, as well as a funding request if the business is seeking investment.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]


5. Identifying Potential Problems
Business plans act as early warning systems that identify potential problems before they escalate into major obstacles.
How? When you conduct thorough market research, analyze competitor strategies, and evaluate financial projections, your plan pinpoints vulnerabilities and risks. This allows you to develop contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies.
This helps you prevent costly mistakes and shows investors and lenders you’re well-prepared and have considered various scenarios.
6. Attracts and Retains Talent
A well-articulated plan outlines your company's vision, mission, and values, showcasing a clear direction and purpose. People who want meaningful work that aligns with their ambitions will love this.
Also, it shows the company's potential for growth and stability. This instills confidence in employees and assures them of a secure future and opportunities for career advancement.
When you show growth potential and highlight a positive work culture, your business plan becomes a magnet for top talent.
7. Provides a Roadmap
A business plan provides a detailed roadmap for your company's future. It outlines your objectives, strategies, and the specific actions you need to achieve your goals.
When you define your path forward, a business plan helps you stay focused and on track, even when you face challenges or distractions. It’s a great reference tool that allows you to make smart decisions that align with your overall vision.
This way, having a comprehensive roadmap in the form of a business plan provides direction and clarity at every stage of your business journey.
8. Serves as a Marketing Tool
A business plan is not only an internal guide but also serves as a powerful marketing tool. Your business plan can showcase your company‘s strengths, unique value proposition, and growth potential when you’re looking for investors, partnerships, or new clients.
It provides a professional and polished overview of your business, which shows your commitment and strategic thinking to potential stakeholders.
Your business plan helps you attract the right people by clearly articulating your target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. In summary, it acts as a persuasive sales pitch.
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read.
The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement.
You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can.
This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

23 of My Favorite Free Marketing Newsletters
![the internal business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-flowchart-template-1-20240716-6679104-1.webp)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

18 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![the internal business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-1-20240625-3861486-1.webp)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![the internal business plan How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

- Business Plan
- Financial Model
- Feasibility Study
- Digital Marketing
- Template Shop

How to Write a Useful Internal Business Plan
You can use a business plan as an internal management tool to help you run your business. This doesn’t mean you have to write a full business plan for fundraising or pitching investors.
Keep your internal business plan simple so it’s easy to communicate. What’s the deal with internal business plans?
Your business plan keeps your team on track with your strategy, sets financial goals, and tracks performance so you can manage it better. This kind of document is easy to share across multiple channels, encourages employee engagement, and uncovers issues.
Make an internal business plan using a growth planning method . Using this method, business plans are simpler, shorter, and designed for internal communication.
Growth plans are great for internal business planning because they’re short, easy to update, and describe your business strategy succinctly. Basically, it’s an executive summary that should be analyzed, updated, and referenced consistently.
What’s the difference between an internal and an external business plan?
An internal business plan is a tool that helps you run your business better. It’s the best business plan for internal analysis, and it should be at the center of regular strategy meetings. New business ideas are often explored with internal business plans to see if they’re viable.
Internal business plans are usually for your partners and employees. In most cases, it’s just shared with people involved in your business on a day-to-day basis. Internal business plans are usually less formal since they’re aimed at business strategy and management. Business plans don’t include much of what external ones do.
In contrast, external business plans are for people outside your company. They’re typically part of the fundraising process and communicate your business strategies to lenders and investors. Business plans are also used when you’re buying or selling a company.
Since external business plans are meant to educate outsiders about your business, they usually include more info about the team behind your business, the business history, and milestones you’ve hit. It’s also more formal and usually a little longer than an internal business plan.
Why do you need a business plan?
Business Plan is the first document that an investor request. It contains all the plans that you execute in next five years. Mostly the investors are concern with how they will get their return. For this Marketing and Financial Plan section holds a very vital importance. Most business plan writers oversee those sections. For example, you show a great marketing strategy and when you read the financial plan section you see that the marketing budget is only $500 per month this would leave the investor in doubt.

1.Make a Business Plan
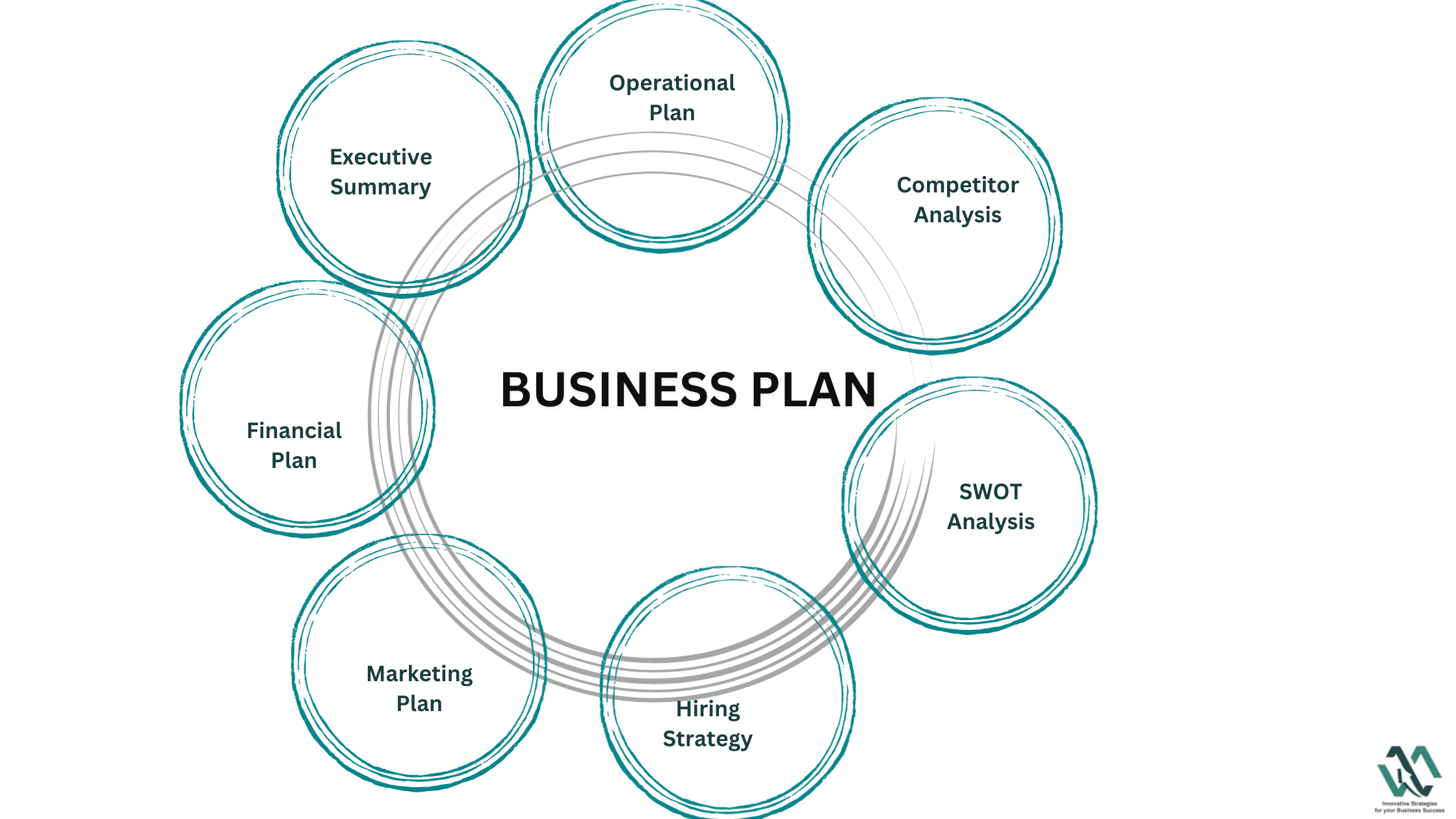
The key to a successful business is a solid strategy. Defining your strategy helps you stay focused as you grow. The world is full of opportunities. As a business owner, you need to know what your strategy is so you can evaluate whether or not an opportunity matches it.
There are also times when you’ll want to shift your strategy, but it has to be done thoughtfully. A business strategy gives you the guidance you need to steer your business to success.
2.Get everyone up to speed

Source:https://www.surfoffice.com/blog/teambuilding-statistics
Everybody on your team needs to be on the same page, especially when your team grows. Different people can have different visions of where your business is going. Different visions can make your business less efficient, because different goals make people work in different directions.
A good internal business plan keeps everyone on the same page and makes employee communication easier. It’s the document that defines your internal communications strategy and even your company culture. You’ll be able to engage your customers and grow your business more easily if you have a clear vision.
3.Performance and forecasts are key
Financial forecas t is the heart of any business pan. Most experts who creates business plan always starts with financial numbers. For this they usually prepare a financial model with assumptions related to that particular business mode l. The financial model if it contains market validation and competitor analysis it will result in a very accurate forecasted financial statemen t from which you can drive a financial metrics . Financial ratios gives a clear picture of the business and tells the startup owner what to do and write in the business plan. Sometimes the numbers are not favurrable this is a an alarming bell for the owner and then even before the start of the business he/she can take decision which could mitigate the risk of future loss. So therefore, the performance of any business can be judged from financial analysis which isan integral part of any startup.

According to investopedia most business fail due to lack of financial planning. And half of the businesses in US fails in first year. Let us suppose if the have financial planning they would have mitigate the risk of loss. If you ask any financial or business expert they would always tell you the importance of finance.
Business Plan writing tips
The internal business plan is simple and direct. Instead of long paragraphs and lengthy explanations, make it simple and bulleted. Don’t forget, the plan is for you, so make it something you’ll use often and update regularly. One-page business plans are easy to keep current and use, compared to long documents.
Here’s what you need to include:
1.The value proposition
This is a one-sentence summary of your business. Who do you serve and what value do you provide? In this section, you can share your mission statement – it’s a reminder to your team about what you’re all about.
2.What you can do about it
Your products and services are usually easy to describe. You’ll define the problem your company solves for your customers in this section. Defining the problems you help your customers solve will keep you focused as you explore new revenue streams.
3.Market and competition
Determining your target customers is just as important as defining your customers’ problems. It helps make sure your marketing campaigns are targeted and your team knows who you’re trying to reach. Track what alternatives your customers might consider and why they might choose a competitor over you.
4.Marketing channels and campaigns
You should define how you’re going to sell your products and services and how you’re going to reach customers in your internal business plan. You can use your internal business plan to guide your expansion into new markets.
5.Projection of financials
Make sure your team knows how much to expect in terms of sales and expenses. Besides that, cash flow forecasts can help you decide when to raise additional funding or open a line of credit.
6. Achievements
Each milestone defines your team’s key goals and objectives. Setting a few key goals for the upcoming months isn’t about setting day-to-day tasks. With milestones, you’ll keep your team focused.
7. Teamwork
The internal business planning section can be skipped if your team isn’t growing. Consider your key team growth areas if hiring and adding staff is a key part of your business strategy.
Looking for a great business plan ?
Most business owners don’t know what they need to convince investors. They think they need a business plan. The business plan doesn’t mean you write strategies in it. It just means you follow old traditional ways of writing one. You should always start with a financial plan . Once the numbers are approved, you can start writing the business plan. You have good content, but your presentation isn’t great. Therefore, you need a business plan template too. Myinvestorchoice.com has it all. Financials with deep research and analysis, a business plan based on target market, and then a presentation . Please download our brochure below
You can design your own website. The easiest way to make sure your website can accomplish all of these goals is to hire a pro. You’ll have more time to run and grow your business.
Please download your brochure for your business plan below – Myinvestorchoice is ranked the number 1 Agency on Upwork for preparing business plans
https://Www.Waste-Ndc.pro/community/profile/tressa79906983/
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details. https://Www.Waste-Ndc.pro/community/profile/tressa79906983/
Your explanations of email marketing key performance indicators (KPIs) have been clear.
buy sendgrid smtp
The tips on influencer marketing were highly valuable.
Fahad Sarwar
The article on increasing email sign-ups was very insightful.
https://ukrain-Forum.biz.ua
You made some really good points there. I looked on the web to learn mpre about the issue and found most individuals will goo along with your views on thiks site. https://ukrain-Forum.biz.ua
Thank you if you have any questions email me at [email protected]
Backlink Website List
Ensure your website's authority and increase organic traffic with these updated resources for SEO backlink websites 2024.
Utilize these resources to enhance your website's SEO performance effectively.
Post a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Leave a Reply
Email address
Website Url
Save my name, and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

Duty the obligations of business will frequently occur that pleasure have too repudiated annoyances endures accepted.
Free Consultation
Get in touch.
Sheikh Zayed Road, Al-Moosa Tower 1, Office 604, 7th Floor, Dubai, UAE
Information
- Case Studies
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Are you still unsure about purchasing the service or do you need more convincing? If so, please fill out this form and one of our experts will contact you to schedule a meeting. He will explain to you during the meeting how to prepare investor-ready documents, such as forecasted financial statements, business plans, pitch decks, business proposals, and feasibility studies. We will keep your personal information private and will not share it with any third parties.
No products in the cart.
Click one of our contacts below to chat on WhatsApp

Social Chat is free, download and try it now here!
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
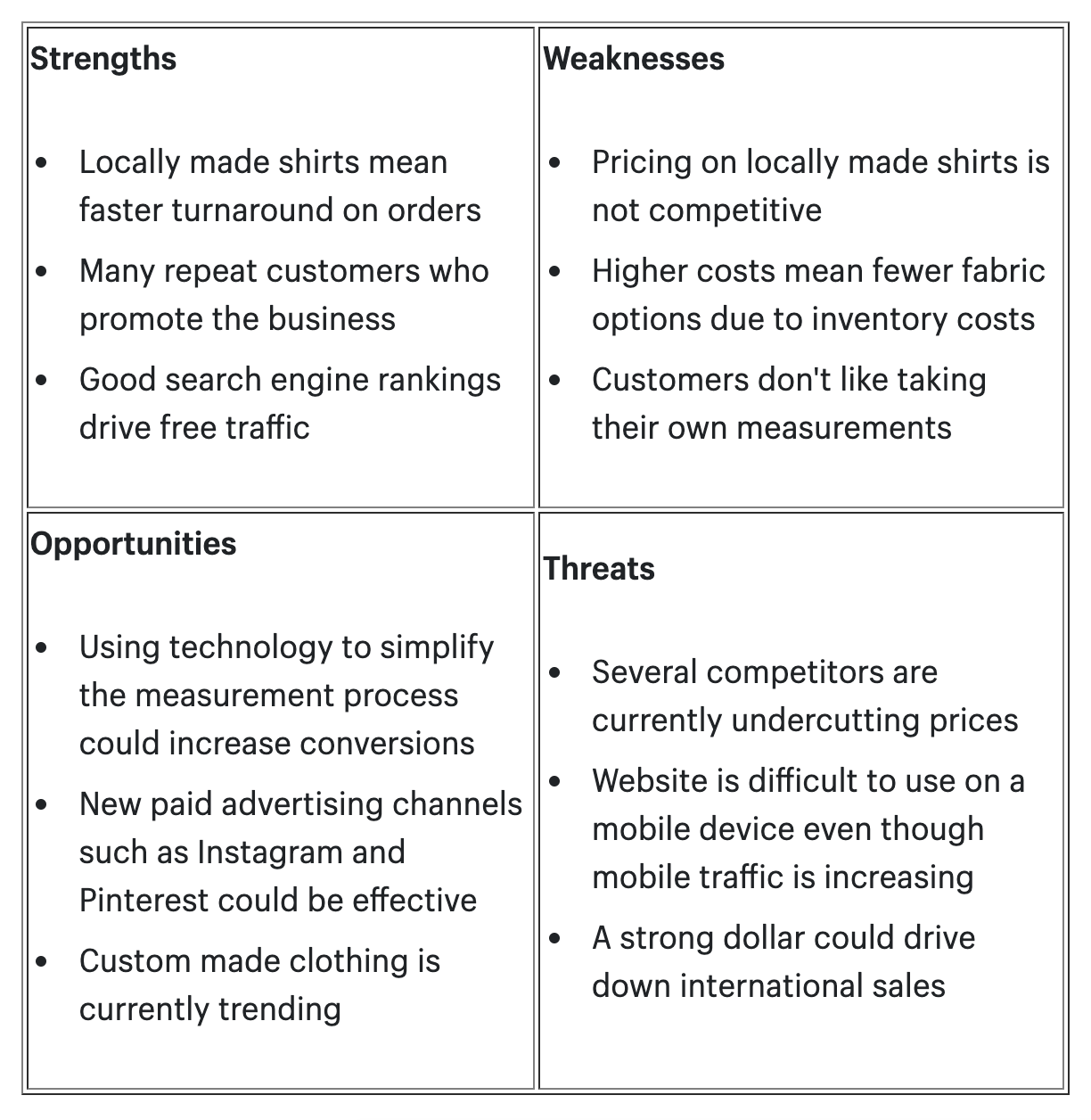
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
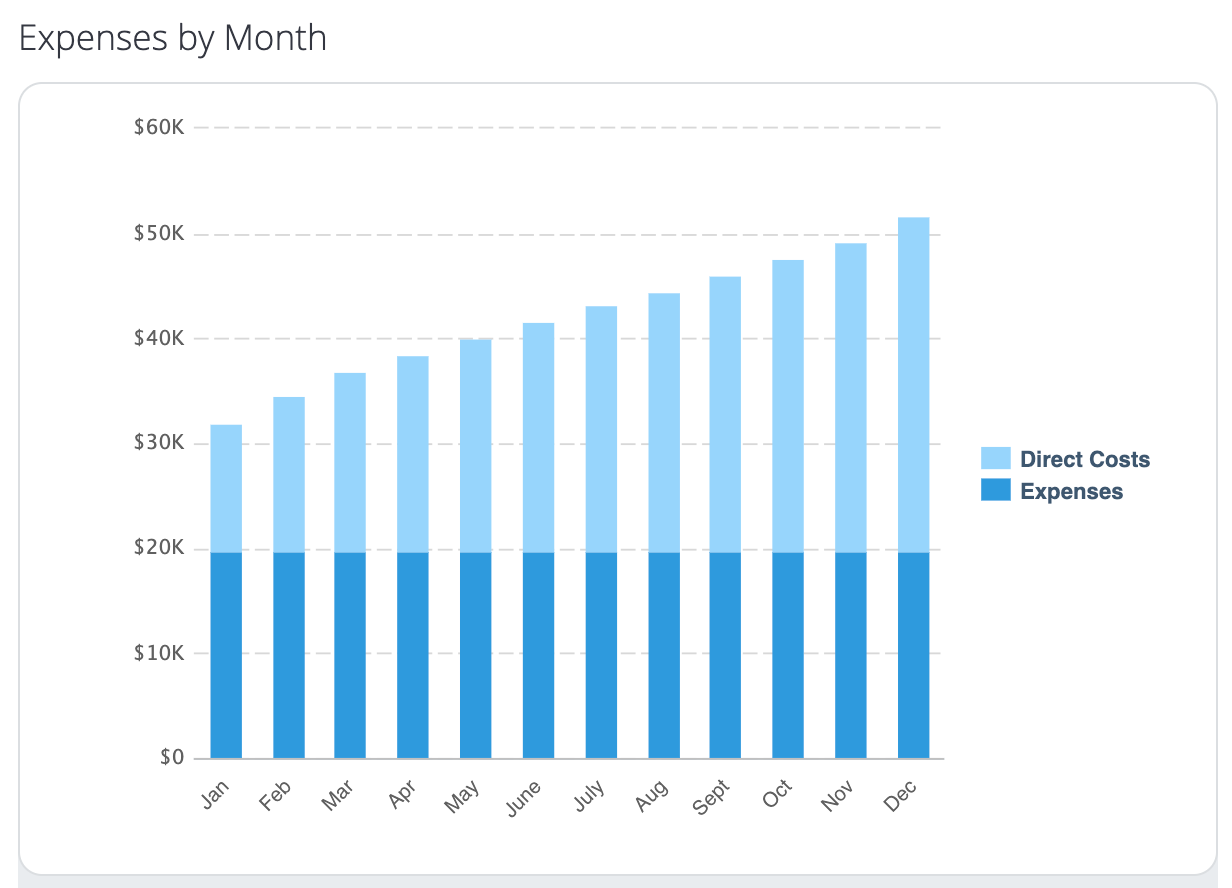
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
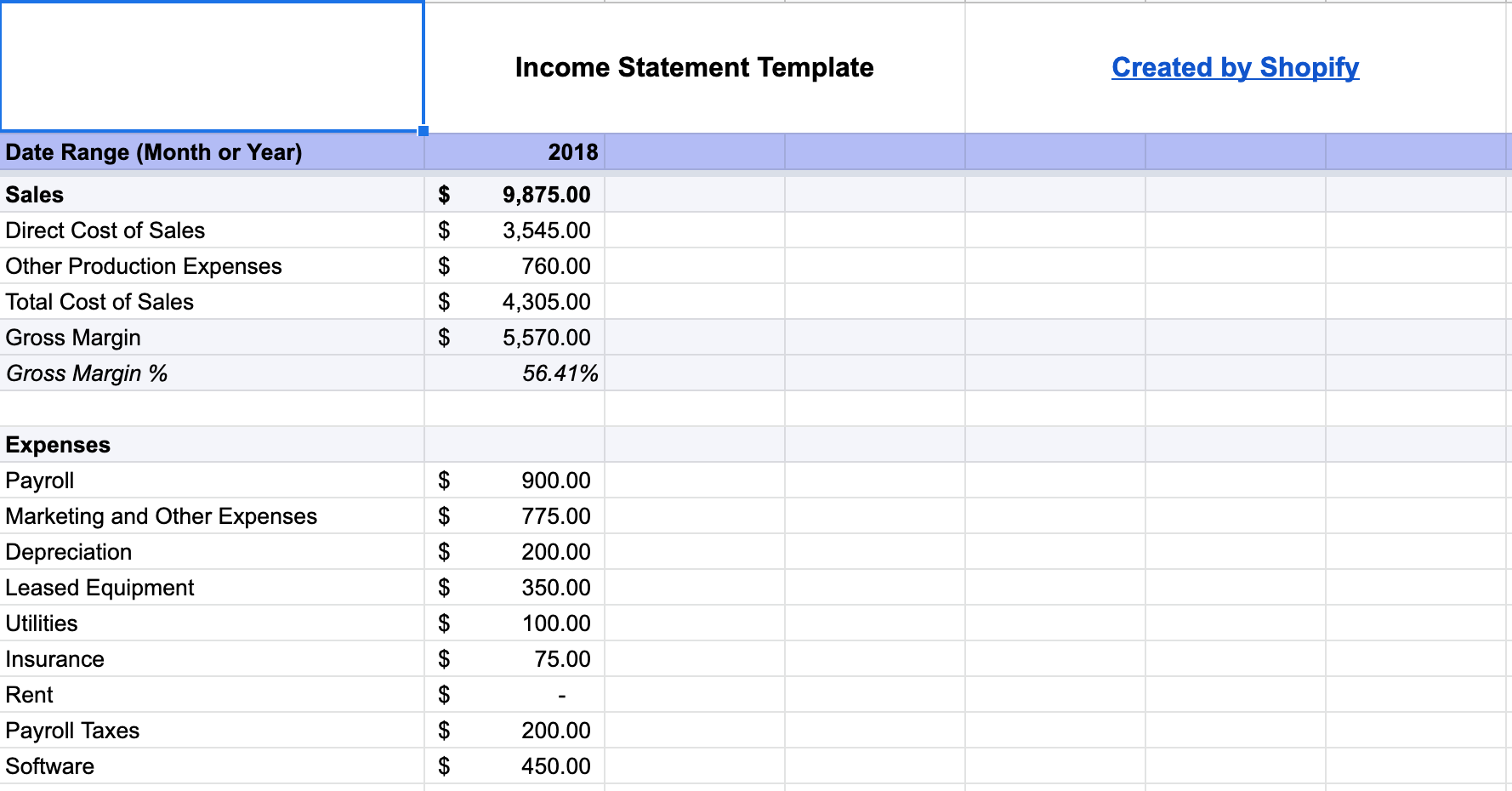
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 12, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Starting a business
Why internal business plans are essential to have
Internal business plans are essential for the success of any business. An internal business plan is similar to an external business plan in its overall structure. However, external business plans are designed to secure funding for a business and are presented to banks, investors, and other lending institutions. They contain high levels of detail about financial projections, customer demographics, growth strategies, and much more.
Internal Business Plan Must-Haves
Final thoughts.
Internal business plans touch on many of the same points, but all the number crunching isn’t totally necessary. Your company’s internal business plan should be structured more as a reference document for employees. It’s different from an employee handbook because it’s not a procedural manual on work expectations.
An internal business plan is more of a guide on how the company will work together to achieve its goals. Your internal business plan should be an iterative document, meaning it changes and evolves as your company grows. It’s crucial to revisit these types of business plans frequently to ensure that it’s living up to its design. If not, changes must either be made to the internal business plan itself or the goals it’s trying to help achieve must be adjusted to become more attainable.
Internal Business plans can have dozens of sections covering whatever topics you feel are vital for your company. However, here are some areas that are commonly covered in almost every internal business plan.
Mission and Vision Statements
Mission and vision statements are found in both external and internal business plans and many other company documents. The vision statement is the ultimate reason you have a business, and the mission statement is the actionable strategy it takes to be successful.
Specific and Attainable Goals
Business productivity can be measured by evaluating the goals outlined in your internal business plan. These goals should be clear, measurable, and broken down into different business segments. For example, what are your long-term marketing goals, and what are the short-term benchmarks your company must reach to achieve them? This is a prime example of why you must revisit internal business plans regularly. Each set of goals for every business segment should execute your mission and vision statements.
The strategies portion of your internal business plan lists out a specific method to achieve the goals mentioned above and benchmarks. You should formulate customized strategies for every business segment. Although some goals may be the same, no two segment’s methods should be the same. For instance, your company’s sales strategy will not be the same as your customer service department. However, they may share goals like “a streamlined and overall enjoyable customer experience.”
Systems and Processes
The systems and processes section of your internal business plan supports both the business goals and the strategy. Suppose you have hard-lined expectations of your leadership or other employees. It should be specified here. You could, for example, clarify that employee reviews by management will take place bi-annually.
This section can also list every role at the company and its scope of work. Internal operating systems and how departments should interact should also be made clear in this section. Much of this information would also be found in an employee handbook, but you can explain why a system or process exists in the internal business plan.
You can create many different business plans for your business, but an internal business plan is a cornerstone for how your company operates. Your internal business plan is a living document and should be reviewed regularly to ensure your company stays true to its original purpose. It’s essential to ensuring that things within the business stay consistent.
Suppose you find that your business isn’t living up to its goals in the internal plan. In that case, it’s better to examine why it’s not performing and try to fix that instead of drastically altering the original plan. It should be a barometer of success, and if you constantly change the plan, you have no standards to go by.
Factors such as changes in ownership, external market factors, and other business mergers or partnerships can be reasons for altering an internal business plan. However, the most successful companies always try to keep their initial vision and mission statements intact.
Editors’ Recommendations
- Why branding matters when starting a restaurant
- What Uber’s resurrection teaches us about adversity as a startup
- Tips for starting a successful ice cream truck business
- Start your own business with these 5 devices
- 5 must-haves for the professional violinist
- Business plans

When starting a cafe kitchen, it’s important to have all the essentials stocked for an optimal work space. The right products can streamline kitchen tasks and improve the overall success of your cafe. Start with the basics and continue investing in your kitchen tools as your cafe grows–it makes running a business practical and sustainable.
Well-stocked essentials, combined with smart kitchen prep, can make each day go smoothly and ensure that the quality of your food is consistent and up to standard.
When starting a beauty salon, having the right tools is important. Before you open, making sure that your beauty salon is well-stocked will set you up for success. More importantly, it’s vital to invest in high-quality tools that take manicures, pedicures, and beauty treatments to the next level. Combined with great skills, tools elevate a client’s experience and make it likelier for them to return. Give your salon the tools it deserves and start your business on the right foot. It can be easy, effortless, and simple.
From nail clippers to nail files, take the time to look for high-quality tools that take manicures, pedicures, and beauty treatments to the next level. Your clients will feel the difference, and you’ll enjoy using quality tools when you’re on the job.
- Business Guides
You went to cosmetology school, and you wonder what you should do now? You should create your own salon business. You want to provide customers the chance to have a haircut, wax their eyebrows, and give them the chance to feel beautiful. You understand that it takes time and effort for people to take care of their hair and shape their eyebrows. You need the tools to start your salon and provide beauty assistants to your customers whether it is waxing, clipping nails, or cutting their hair. You have the experience to give your customers the chance that they want to feel a completely different person.
You believe in self-care. You want to provide the self-care that your customers need. You understand by living in a modern world it is hard to dedicate time to take of yourself physically due to personal situations and work hours. That is why you created a business that provides the self-care needs for your customers. You want to give them a positive change to their appearance and give them a boost of confidence. You want to give your customers the chance to love themselves and to love their bodies. Your business will provide customers the chance of having self-love and high self-esteem.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marketing-plan-ff4bce0e2c52493f909e631039c8f4ca.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

The Business Planning Process: 6 Steps To Creating a New Plan
In this article, we will define and explain the basic business planning process to help your business move in the right direction.
What is Business Planning?
Business planning is the process whereby an organization’s leaders figure out the best roadmap for growth and document their plan for success.
The business planning process includes diagnosing the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses, improving its efficiency, working out how it will compete against rival firms in the future, and setting milestones for progress so they can be measured.
The process includes writing a new business plan. What is a business plan? It is a written document that provides an outline and resources needed to achieve success. Whether you are writing your plan from scratch, from a simple business plan template , or working with an experienced business plan consultant or writer, business planning for startups, small businesses, and existing companies is the same.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
The best business planning process is to use our business plan template to streamline the creation of your plan: Download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template and finish your business plan & financial model in hours.
The Better Business Planning Process
The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows:
- Do Your Research
- Calculate Your Financial Forecast
- Draft Your Plan
- Revise & Proofread
- Nail the Business Plan Presentation
We’ve provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
1. Do Your Research
Conduct detailed research into the industry, target market, existing customer base, competitors, and costs of the business begins the process. Consider each new step a new project that requires project planning and execution. You may ask yourself the following questions:
- What are your business goals?
- What is the current state of your business?
- What are the current industry trends?
- What is your competition doing?
There are a variety of resources needed, ranging from databases and articles to direct interviews with other entrepreneurs, potential customers, or industry experts. The information gathered during this process should be documented and organized carefully, including the source as there is a need to cite sources within your business plan.
You may also want to complete a SWOT Analysis for your own business to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and potential risks as this will help you develop your strategies to highlight your competitive advantage.
2. Strategize
Now, you will use the research to determine the best strategy for your business. You may choose to develop new strategies or refine existing strategies that have demonstrated success in the industry. Pulling the best practices of the industry provides a foundation, but then you should expand on the different activities that focus on your competitive advantage.
This step of the planning process may include formulating a vision for the company’s future, which can be done by conducting intensive customer interviews and understanding their motivations for purchasing goods and services of interest. Dig deeper into decisions on an appropriate marketing plan, operational processes to execute your plan, and human resources required for the first five years of the company’s life.
3. Calculate Your Financial Forecast
All of the activities you choose for your strategy come at some cost and, hopefully, lead to some revenues. Sketch out the financial situation by looking at whether you can expect revenues to cover all costs and leave room for profit in the long run.
Begin to insert your financial assumptions and startup costs into a financial model which can produce a first-year cash flow statement for you, giving you the best sense of the cash you will need on hand to fund your early operations.
A full set of financial statements provides the details about the company’s operations and performance, including its expenses and profits by accounting period (quarterly or year-to-date). Financial statements also provide a snapshot of the company’s current financial position, including its assets and liabilities.
This is one of the most valued aspects of any business plan as it provides a straightforward summary of what a company does with its money, or how it grows from initial investment to become profitable.
4. Draft Your Plan
With financials more or less settled and a strategy decided, it is time to draft through the narrative of each component of your business plan . With the background work you have completed, the drafting itself should be a relatively painless process.
If you have trouble writing convincing prose, this is a time to seek the help of an experienced business plan writer who can put together the plan from this point.
5. Revise & Proofread
Revisit the entire plan to look for any ideas or wording that may be confusing, redundant, or irrelevant to the points you are making within the plan. You may want to work with other management team members in your business who are familiar with the company’s operations or marketing plan in order to fine-tune the plan.
Finally, proofread thoroughly for spelling, grammar, and formatting, enlisting the help of others to act as additional sets of eyes. You may begin to experience burnout from working on the plan for so long and have a need to set it aside for a bit to look at it again with fresh eyes.
6. Nail the Business Plan Presentation
The presentation of the business plan should succinctly highlight the key points outlined above and include additional material that would be helpful to potential investors such as financial information, resumes of key employees, or samples of marketing materials. It can also be beneficial to provide a report on past sales or financial performance and what the business has done to bring it back into positive territory.
Business Planning Process Conclusion
Every entrepreneur dreams of the day their business becomes wildly successful.
But what does that really mean? How do you know whether your idea is worth pursuing?
And how do you stay motivated when things are not going as planned? The answers to these questions can be found in your business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs make better decisions and avoid common pitfalls along the way.
Business plans are dynamic documents that can be revised and presented to different audiences throughout the course of a company’s life. For example, a business may have one plan for its initial investment proposal, another which focuses more on milestones and objectives for the first several years in existence, and yet one more which is used specifically when raising funds.
Business plans are a critical first step for any company looking to attract investors or receive grant money, as they allow a new organization to better convey its potential and business goals to those able to provide financial resources.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
The Different Types of Business Plans

Free Business Plan Template
- June 29, 2023
Different situations call for different business plans.
Whether you want to acquire funds, analyze market risks, introduce a new product, or simply need a roadmap for business operations— a specifically tailored business plan is essential for different business purposes.
Identifying the type of business plan you require is quintessential so that you create a document fit for your business needs.
In this blog post, we will introduce you to the 7 different types of business plans and help you understand which suits your business needs the best.
Ready to get started? Let’s dive right in.
Types of business plans
Businesses in different business situations call for different business plans.
To understand different types of business plans, we will categorize them based on audience, scope, and purpose to instill better clarity in your minds.
Let us understand these in detail to help you choose your ideal business plan.
Based on audience
Business plans are broadly categorized into two types based on the type of audience they cater to.
1. Internal business plans
As the name suggests, an internal business plan is solely for the people inside the company. These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc.
Internal business plans focus primarily on the company’s goals, operations, finances, and personnel and define the strategies to achieve their goals.
2. External business plans
On the contrary, external business plans are intended for people outside the company, such as investors, banks, partners, etc.
These plans usually contain detailed information about the company’s background, finances, market share, and business strategies.
Based on scope
Similarly, business plans are classified into two types based on their size and the depth of information they encompass.
1. Standard business plan
A standard plan or traditional business plan is a professional document offering a comprehensive understanding of your business idea. It serves as a step-by-step guide to launching your business and offers a roadmap to operate it efficiently.
A standard plan follows a structured format and usually includes components such as
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Products and services
- Marketing and sales plan
- Operations plan
- Financial plan
- Funding demand
Most entrepreneurs follow this structure to write a business plan and add depth to the sections that hold significant value to them.
Best for: Startups and businesses that require a detailed roadmap or operate in highly volatile markets. These plans are also used for getting funding approvals.
2. Lean business plans
A lean plan, also known as a startup business plan, is a condensed version of the standard business plan including highlights and summaries of all its sections.
Such plans empower entrepreneurs to kickstart their business endeavors with a minimum viable product and build it gradually by gathering real market feedback.
Lean business plans are crafted with brevity and outline your strategies, revenue model, tactics, and timeline.
- Strategies: How will you reach your goals
- Tactics: What are the KPIs to evaluate your performance
- Revenue model: How will you make money
- Timeline: Who will accomplish the tasks
Drafting such plans is not only easier, it is considered to be more efficient compared to a standard plan.
Best for: Entrepreneurs who want to quickly launch their business in a hot-moving market.
Based on purpose
Every business plan tends to solve a specific purpose. Let’s understand 7 different types of business plans based on different purposes.
1. One-page business plan
One-page business plans offer a snapshot of your entire business idea in one page. Such plans follow the same structure as traditional plans, however, they are much more concise and crisp.
One-page plans are simplified versions of detailed business plans and can be placed together in less than 10 minutes.
They are quite useful when you want to convey essential information in a brief document without missing out on important points.
Best for: One-page business plan is best suited for startups and small businesses that require rapid adjustments and quick implementation.
2. Growth business plan
A growth business plan combines the crispness of one-page business plans and the detailing of financial forecasts to enable prompt decision-making.
Such plans are quite handy when you want to upscale or grow your business without writing a full-fledged detailed business plan.
Businesses can compare their forecasts with the actuals, identify the discrepancies in the current strategy, and adjust it to ensure maximum growth when they have a clear demonstration of financials.
To prepare your growth business plan, outline the target market, business strategies, and a business model as you do in your one-page plans. And additionally, also include detailed financial projections for sales, cash flow, and revenue to help individuals make data-driven decisions.
Best for: A growth plan is best for businesses entering new markets, launching new products, scaling operations, or practicing a growth planning process.
3. Strategic business plan
Strategic business plans highlight your strategic objectives, define your business strategies, and outline a roadmap to take you there. It covers the nitty-gritty about your company’s goals, mission objectives, and long-term vision.
Such plans are extremely efficient in communicating your goals to internal teams and stakeholders, while ensuring everyone is on the same page as you.
Best for: Businesses and startups planning long-term growth and nonprofits aiming to increase their impact.
4. Feasibility business plan
A feasibility business plan is specifically designed to test the viability of a new product or business expansion in a new market. As opposed to a detailed business plan, such plans focus on two primary matters:
- Determining the existence of a market
- Determining the profits of the initiative
This type of business plan usually excludes all the other sections included in usual business plans. Instead, it concentrates mainly on the scope of a new initiative, its profitability, market analysis, competition, and associated financial implications.
It is mostly crafted for internal management and ends with recommendations on whether the decision to enter a new market or introduce a new product or service is viable or not.
Best for: Established businesses and early-stage startups to assess the viability of a specific product, market, or business idea before allocating significant resources.
5. Operational business plan
Operational plans are specific documents outlining processes and procedures of day-to-day business activities. Such plans focus on operational aspects of the business such as logistics, inventory, supply chain, production, and resource allocation.
A well-mapped operational plan serves as a guidebook for internal team and management. It streamlines the workflow, establishes SOPs, and offers a clear understanding of who will perform what tasks and what resources will be required.
There is no strict format outlining the contents of such a plan. The plan just needs to be clear, communicative, and viable enough to implement practically.
Best for: Established businesses to manage operations and resource allocation and startups to establish standard clear processes.
6. Nonprofit business plan
Nonprofit business plans are suited for businesses that operate for a charitable or social cause. Such plans are quite similar to traditional plans, however, they include an additional section where you explain the impact your non-profit organization will make in society.
Like a traditional plan, you will highlight the business concept, outline the market research, set the business goals, determine your business and promotional strategies, and demonstrate your team.
Additionally, you will include a section demonstrating the financial sustainability of the nonprofit venture. This is essential to attract donors, grants, and investors for your nonprofit business.
Best for: Nonprofit startups planning to secure funding and grants from financial institutions.
7. What-If business plan
What-if business plans are contingency plans used to draft strategies for the worst-case scenarios. This plan is usually less formal unless a funding request is included.
Such planning allows you to test and study the impact of different hypothetical situations related to the market, environment, competition, and legal regulations on your business.
Best for: Businesses in highly volatile markets and companies practicing crisis management. Also suited when considering mergers, price hikes, or undertaking any major business decision.
And those are some of the many different types of business plans you can have for your business. Wondering which one your business needs? Let us make your choice easier.
Choosing the right type of business plan
Here are the 2 criteria that will help in determining the right plan for your business.
The first step to choosing a business plan is to understand the purpose and objective of writing a business plan. For instance, your objective could be to acquire funds, guide an internal team, create a strategic roadmap, expand into a new geographic market, or prepare for contingencies.
Align your objective with the purpose of specific business plans and see which one suits you the best.
2. Scope of business
The scope and complexity of your business play a crucial role in determining the type of business plan you require. Take into account factors like products and service offerings, the scale of the business, and the business complexity to make a choice.
Even the stage of your business, depending on whether it is a startup or an established business, will influence this decision.
Start preparing your business plan with Upmetrics
You now have a proper understanding of the different types of business. If you’re not sure which one to pick, let us help you.
Our business planning software helps create stellar business plans and saves you the pain of writing one from scratch.
You can either choose a business plan sample and follow its step-by-step instructions to prepare your functional and actionable business plan.
Don’t have enough time to write the entire thing from scratch? Go ahead with our AI business plan generator ; it will quickly generate the entire plan for you..
Simply enter your business details, answer a few questions, and see your plan coming together in front of your eyes in less than 15 minutes.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 most common sections of a business plan.
The 8 common components of a successful business plan include
- Management team
Which type of business plan is right for me?
The answer entirely depends upon what you want to achieve with your business plan. Apart from that the scope, nature, and complexity of your business will determine the type of business plan you need.
Do I need a business plan to start a business?
A business plan is highly recommended before you kickstart your business endeavor. It builds a solid foundation for your business idea and offers a roadmap to achieve your strategic and business objectives. A well-drafted business proposal increases the chances of your business venture succeeding.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning


- Global (EN)
- Albania (en)
- Algeria (fr)
- Argentina (es)
- Armenia (en)
- Australia (en)
- Austria (de)
- Austria (en)
- Azerbaijan (en)
- Bahamas (en)
- Bahrain (en)
- Bangladesh (en)
- Barbados (en)
- Belgium (en)
- Belgium (nl)
- Bermuda (en)
- Bosnia and Herzegovina (en)
- Brasil (pt)
- Brazil (en)
- British Virgin Islands (en)
- Bulgaria (en)
- Cambodia (en)
- Cameroon (fr)
- Canada (en)
- Canada (fr)
- Cayman Islands (en)
- Channel Islands (en)
- Colombia (es)
- Costa Rica (es)
- Croatia (en)
- Cyprus (en)
- Czech Republic (cs)
- Czech Republic (en)
- DR Congo (fr)
- Denmark (da)
- Denmark (en)
- Ecuador (es)
- Estonia (en)
- Estonia (et)
- Finland (fi)
- France (fr)
- Georgia (en)
- Germany (de)
- Germany (en)
- Gibraltar (en)
- Greece (el)
- Greece (en)
- Hong Kong SAR (en)
- Hungary (en)
- Hungary (hu)
- Iceland (is)
- Indonesia (en)
- Ireland (en)
- Isle of Man (en)
- Israel (en)
- Ivory Coast (fr)
- Jamaica (en)
- Jordan (en)
- Kazakhstan (en)
- Kazakhstan (kk)
- Kazakhstan (ru)
- Kuwait (en)
- Latvia (en)
- Latvia (lv)
- Lebanon (en)
- Lithuania (en)
- Lithuania (lt)
- Luxembourg (en)
- Macau SAR (en)
- Malaysia (en)
- Mauritius (en)
- Mexico (es)
- Moldova (en)
- Monaco (en)
- Monaco (fr)
- Mongolia (en)
- Montenegro (en)
- Mozambique (en)
- Myanmar (en)
- Namibia (en)
- Netherlands (en)
- Netherlands (nl)
- New Zealand (en)
- Nigeria (en)
- North Macedonia (en)
- Norway (nb)
- Pakistan (en)
- Panama (es)
- Philippines (en)
- Poland (en)
- Poland (pl)
- Portugal (en)
- Portugal (pt)
- Romania (en)
- Romania (ro)
- Saudi Arabia (en)
- Serbia (en)
- Singapore (en)
- Slovakia (en)
- Slovakia (sk)
- Slovenia (en)
- South Africa (en)
- Sri Lanka (en)
- Sweden (sv)
- Switzerland (de)
- Switzerland (en)
- Switzerland (fr)
- Taiwan (en)
- Taiwan (zh)
- Thailand (en)
- Trinidad and Tobago (en)
- Tunisia (en)
- Tunisia (fr)
- Turkey (en)
- Turkey (tr)
- Ukraine (en)
- Ukraine (ru)
- Ukraine (uk)
- United Arab Emirates (en)
- United Kingdom (en)
- United States (en)
- Uruguay (es)
- Uzbekistan (en)
- Uzbekistan (ru)
- Venezuela (es)
- Vietnam (en)
- Vietnam (vi)
- Zambia (en)
- Zimbabwe (en)
- Financial Reporting View
- Women's Leadership
- Corporate Finance
- Board Leadership
- Executive Education
Fresh thinking and actionable insights that address critical issues your organization faces.
- Insights by Industry
- Insights by Topic
KPMG's multi-disciplinary approach and deep, practical industry knowledge help clients meet challenges and respond to opportunities.
- Advisory Services
- Audit Services
- Tax Services
Services to meet your business goals
Technology Alliances
KPMG has market-leading alliances with many of the world's leading software and services vendors.
Helping clients meet their business challenges begins with an in-depth understanding of the industries in which they work. That’s why KPMG LLP established its industry-driven structure. In fact, KPMG LLP was the first of the Big Four firms to organize itself along the same industry lines as clients.
- Our Industries
How We Work
We bring together passionate problem-solvers, innovative technologies, and full-service capabilities to create opportunity with every insight.
- What sets us apart
Careers & Culture
What is culture? Culture is how we do things around here. It is the combination of a predominant mindset, actions (both big and small) that we all commit to every day, and the underlying processes, programs and systems supporting how work gets done.
Relevant Results
Sorry, there are no results matching your search., how hr supports a winning performance improvement plan.
Find ways to increase the speed and efficiency of daily HR processes.

Strategy and C-suite leaders are seeking to optimize today’s ways of working while navigating the rapid pace of social, technological, and consumer changes. The human resources (HR) function is no exception.
One of the most effective tactics: implement processes to empower human capital leaders to make continuous improvements that eliminate redundancies, reduce costs, and increase margins. This focus on the human capital function should be part of a larger transformation to become a culture of Continuous Performance Improvement (CPI) across the organization. With a culture of CPI, everyone in the organization focuses on increasing productivity and efficiency in existing processes—even if those processes already represent improvement over prior approaches.
To be sure, there is no single method for driving CPI amid disruption. KPMG recommends that Strategy and other C-suite leaders apply a wide lens and a balanced approach. The best way to optimize results isn’t a focus solely on costs or solely on growth. Instead, balance both goals.
Applying CPI to your human resources function
Talent is crucial to establishing and maintaining a competitive advantage. Organizations that attract, engage, develop, and retain top talent through modern and meaningful experiences tend to drive the most productivity increases, efficiency gains, and, ultimately, cost savings from lower turnover. This in turn optimizes and maximizes the potential of their workforce and helps chart an effective path for future growth.
Failing to optimize a workforce through human capital programs—developing succession plans and specialist career pathways, for example—can result in negative cost impacts and long-term repercussions.
To avoid that fate, forward-looking companies are going all in on addressing employee experience. Indeed, in a recent KPMG survey of 300 chief HR officers (CHROs), 61 percent said they need to alter their employee value proposition (EVP) in response to the external labor market. The respondents told us that some of the most important parts of the EVP when attracting, developing, and retaining talent are culture (50 percent), company values and purpose (47 percent), fair pay (34 percent), and offering flexible working (33 percent).
At the same time, leaders are actively exploring the potential value of generative AI. Workforce transformation—through immediate worker role augmentation—is at the center of that exploration. The HR function is key to advancing in the journey, which starts with addressing four workforce considerations:

- Identifying capabilities, roles, and enablers
- Addressing risk and compliance
- Activating role augmentation
- Capturing value
Getting to an optimized state means more services and more digital capabilities underpinning it all. HR organizations need to deliver that experience in a highly cost effective and positive way that inspires people to continuously seek ways to improve how they work and adapt to change.
KPMG recommends a CPI approach, grounded in data and metrics, which can help improve EVP. It also better enables employees to focus on value-added activities—including the shift to GenAI-enabled work. For example, payroll processing cycle times could be shortened by modernizing the organization’s timekeeping solutions, which then frees up managers to focus on operational outcomes.
When employees call in for HR help versus leveraging a self-service option, a tangible impact to their experience is the time required to get a response and handle follow-ups, as well as the quality of the resolution. A CPI-minded organization conducts continuous reviews of whether the right systems, shared services, offshoring, or outsourcing model is in place to derive cost efficiencies while improving response and cycle times for its key services to the business.
Explore more
Popular category topics

4 Ways to Drive More Performance Improvement Value
How organizations can use ongoing performance improvement to enhance speed and efficiency in daily processes for more productive outcomes

3 Must-Haves to continuously improve performance
How organizations can use ongoing performance improvement to enhance speed and efficiency in daily processes

Enhance Risk Effectiveness by Improving Performance
How continuous performance improvement can enhance corporate regulatory compliance and mitigate risk exposure

The ROI from continually improving performance
Unlocking efficiency and value: the strategic advantage of embedding continuous performance improvement (CPI) in your organization.
KPMG. Make the Difference
As a trusted collaborator, we work closely with clients throughout the entire CPI journey. Using our extensive industry knowledge and experience, we employ an integrated, cross-functional approach to effectively optimize performance, digitize processes, and drive growth even against economic volatility and rapid market shifts.
Subscribe to receive Elevate Perspectives alerts
Elevate Perspectives: A knowledge center to fortify your transformation efforts with essential perspectives.
Learn how KPMG can help uncover opportunities to decrease costs, increase efficiency, and create value through continuous performance improvement.

By submitting, you agree that KPMG LLP may process any personal information you provide pursuant to KPMG LLP's Privacy Statement .
Thank you for contacting KPMG. We will respond to you as soon as possible.
Contact KPMG
Job seekers
Visit our careers section or search our jobs database.
Use the RFP submission form to detail the services KPMG can help assist you with.
Office locations
International hotline
You can confidentially report concerns to the KPMG International hotline
Press contacts
Do you need to speak with our Press Office? Here's how to get in touch.
More From Forbes
The 5 digital supply chain challenges every business should plan for before their next fiscal year.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Nirav Patel is President and CEO, Bristlecone , leading the way in supply chain transformation and digital resilience.
Supply chains are complicated, typically consisting of a number of complex factors and a large network of players. Adding to the everyday challenges supply chain professionals face, disruption has become the norm in the global marketplace and customer expectations are on the rise. In order to be productive and successful, businesses have to operate seamlessly with their teams, providers, partners, customers and other stakeholders. Doing so requires navigating and mitigating supply chain challenges in ways that not only improve their efficiency but also deliver exceptional customer experiences.
There are a number of key challenges driving today’s supply chain trends. Here are the 5 supply chain challenges every business must plan for before the coming fiscal year.
Fragmented Data Across Network Nodes And Limited Visibility
Data fragmentation, i.e., the scattering of an organization’s data stored in a variety of disparate sources, creates a number of challenges, namely limited visibility. Fragmented data makes it difficult, sometimes nearly impossible, to protect and manage digital assets. It also creates enormous challenges toward gaining a comprehensive view of available data and the global visibility required for analytics and crucial decision making. In many cases, the enormity of the data in storage means it is too large for traditional systems to process, the speed at which new data is amassed adds to the challenge and the variety of data types means greater complexity in processing. Plus, data fragmentation is costly.
The solution is the consolidation and structuring of all data sources via suitable data system structure and design, thereby turning fragmented data into an indispensable asset. Viable solutions—data warehouse or data lake—with the help of AI supported by machine learning can enable effective data mining, increased visibility and enhanced analytics. With data fragmentation addressed, businesses can readily identify challenges as well as opportunities.
A Multitude Of Internal And External Risks, Including Global Events
In today’s global economy, internal and external risks abound. The last few years have created a new era—one of unpredictability—which promises to affect supply chains now and well into the future. Global events, like the pandemic with its continually emerging variants, resulted in new border restrictions with more red tape as well as shortages of both materials and labor and ever-increasing costs. In addition, calls for environmentally sustainable practices put added pressure on an already strained supply chain.
Preparedness is the key to meeting ever-evolving global challenges, and digital transformation can help by connecting systems and enhancing communication and visibility across the entire organization. The implementation of new, innovative practices means data can be leveraged for agility in decision making to increase resiliency in light of major disruptions and build solutions to complex challenges.
Constantly Changing Buying Behavior and High Expectations
Rapid fluctuations in demand and buying behavior and higher-than-ever customer expectations require supply chain improvements not only in speed of delivery but also in overall quality and service. Even so, the supply chain industry continues to face greater disruption. Speed and quality are now on equal footing with price from a consumer perspective. And alongside consumer demands for speed and quality come safety regulations and a variety of compliance regulations, which vary from place to place. To top it all off, environmentalism and sustainability are in high demand by today’s consumers.
Digitization can help businesses face these challenges by focusing on automation and business intelligence and supporting supply chain processes. Automation speeds up processes, decreases manual efforts, reduces human error and allows team members to focus on areas where human expertise is most valuable.
Tug Of War: Business Process Control Vs. Collaboration
Business process control, the checks and balances, as well as the analysis of business processes, allow for not only problem-solving but problem prevention and should go hand-in-hand with collaboration rather than be in a continuous tug of war for overall control. Business control ensures that everyone understands company procedures and goals and, when partnered with collaboration, allows for higher performance, greater efficiency, faster responses to disruptions and better solutions to challenges.
Shifting from the ongoing tug-of-war between business process control and collaboration to one in which both processes coexist promises greater success with sound decision-making and forward-thinking actions that together mean better overall supply chain performance and productivity.
Reactionary Step-Change / Single Variable Improvements
Continuous improvement is needed for optimized supply chain processes. The past few years have been filled with reactionary change—making changes to move forward based on current and evolving circumstances. While reactionary change is sometimes required, it can lead to unwanted compromise to company goals. Intentional changes look at the big picture and prepare for future changes, aligning with the values and goals of the organization. In either scenario, step-change improvements can ensure operations continue at the level the company expects.
Small incremental improvements can act as a cycle for ongoing refinement where changes are relatively simple and value-driven with minimal risk. Step-change improvements require greater reconfiguration of processes to improve systems, such as implementing new competencies or enhancing workflow. Larger changes require re-engineering, which transforms an organization. While small refinements and large re-engineering are both common in supply chain transformation, step-change improvements work as complementary practices to drive overall performance.
Ongoing supply chain challenges can be resolved by digital supply chain solutions that ensure visibility, information exchange, effective data aggregation, collaboration, analytics, automation, innovative practices and step-change improvements. We must work toward having digitization and humanization working together to solve these challenges. Companies that see digitization as not an end-all solution in itself but as an extension of the capabilities employees can provide will buffer themselves against future disruption and limit their future challenges—ultimately leading to an antifragile supply chain that thrives on change.
Forbes Technology Council is an invitation-only community for world-class CIOs, CTOs and technology executives. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
Employer-offered educational assistance programs can help pay for college
More in news.
- Topics in the news
- News releases
- Multimedia center
- Tax relief in disaster situations
- Inflation Reduction Act
- Taxpayer First Act
- Tax scams and consumer alerts
- The tax gap
- Fact sheets
- IRS Tax Tips
- e-News subscriptions
- IRS guidance
- Media contacts
- IRS statements and announcements
IRS Tax Tip 2024-68. Aug. 7, 2024
An educational assistance program is an employer’s written plan PDF to provide employees with undergraduate or graduate-level educational assistance. These programs allow employers to pay student loan debt and other education expenses tax-free.
Eligible expenses
Educational assistance programs can help pay for:
- Tuition and other fees
- Qualified education loans
Loan payments
These programs can be used to pay principal and interest on an employee's qualified education loans.
The option is available only for payments made after March 27, 2020. Under current law, this option will be available until Dec. 31, 2025.
Payments made directly to the lender and those made to the employee qualify under these programs. By law, tax-free benefits under an educational assistance program are limited to $5,250 per employee per year. Normally, assistance provided above that level is taxable as wages.
For other requirements, see Publication 15-B, Employer's Tax Guide to Fringe Benefits . Chapter 10 in Publication 970, Tax Benefits for Education , provides details on what qualifies as a student loan.
More information
- Frequently asked questions about educational assistance programs
Subscribe to IRS Tax Tips
JPMorgan Chase is giving its employees an AI assistant powered by ChatGPT maker OpenAI

JPMorgan Chase has rolled out a generative artificial intelligence assistant to tens of thousands of its employees in recent weeks, the initial phase of a broader plan to inject the technology throughout the sprawling financial giant.
The program, called LLM Suite, is already available to more than 60,000 employees, helping them with tasks like writing emails and reports. The software is expected to eventually be as ubiquitous within the bank as the videoconferencing program Zoom, people with knowledge of the plans told CNBC.
Rather than developing its own AI models, JPMorgan designed LLM Suite to be a portal that allows users to tap external large language models — the complex programs underpinning generative AI tools — and launched it with ChatGPT maker OpenAI’s LLM, said the people.
“Ultimately, we’d like to be able to move pretty fluidly across models depending on the use cases,” Teresa Heitsenrether , JPMorgan’s chief data and analytics officer, said in an interview. “The plan is not to be beholden to any one model provider.”
The move by JPMorgan, the largest U.S. bank by assets, shows how quickly generative AI has swept through American corporations since the arrival of ChatGPT in late 2022. Rival bank Morgan Stanley has already released a pair of OpenAI-powered tools for its financial advisors. And consumer tech giant Apple said in June that it was integrating OpenAI models into the operating system of hundreds of millions of its consumer devices, vastly expanding its reach.
The technology — hailed by some as the “ Cognitive Revolution ” in which tasks formerly done by knowledge workers will be automated — could be as important as the advent of electricity , the printing press and the internet, JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon said in April.
It will likely “augment virtually every job” at the bank, Dimon said. JPMorgan had about 313,000 employees as of June.
ChatGPT ban
The bank is giving employees what is essentially OpenAI’s ChatGPT in a JPMorgan-approved wrapper more than a year after it restricted employees from using ChatGPT. That’s because JPMorgan didn’t want to expose its data to external providers, Heitsenrether said.
“Since our data is a key differentiator, we don’t want it being used to train the model,” she said. “We’ve implemented it in a way that we can leverage the model while still keeping our data protected.”
The bank has introduced LLM Suite broadly across the company, with groups using it in JPMorgan’s consumer division, investment bank, and asset and wealth management business, the people said. It can help employees with writing, summarizing lengthy documents, problem solving using Excel, and generating ideas.
But getting it on employees’ desktops is just the first step, according to Heitsenrether, who was promoted in 2023 to lead the bank’s adoption of the red-hot technology.
“You have to teach people how to do prompt engineering that is relevant for their domain to show them what it can actually do,” Heitsenrether said. “The more people get deep into it and unlock what it’s good at and what it’s not, the more we’re starting to see the ideas really flourishing.”
The bank’s engineers can also use LLM Suite to incorporate functions from external AI models directly into their programs, she said.
'Exponentially bigger'
JPMorgan has been working on traditional AI and machine learning for more than a decade, but the arrival of ChatGPT forced it to pivot.
Traditional, or narrow, AI performs specific tasks involving pattern recognition, like making predictions based on historical data. Generative AI is more advanced, however, and trains models on vast data sets with the goal of pattern creation, which is how human-sounding text or realistic images are formed.
The number of uses for generative AI are “exponentially bigger” than previous technology because of how flexible LLMs are, Heitsenrether said.
The bank is testing many cases for both forms of AI and has already put a few into production.
JPMorgan is using generative AI to create marketing content for social media channels, map out itineraries for clients of the travel agency it acquired in 2022 and summarize meetings for financial advisors, she said.
The consumer bank uses AI to determine where to place new branches and ATMs by ingesting satellite images and in call centers to help service personnel quickly find answers, Heitsenrether said.
In the firm’s global-payments business, which moves more than $8 trillion around the world daily, AI helps prevent hundreds of millions of dollars in fraud, she said.
But the bank is being more cautious with generative AI that directly touches upon the individual customer because of the risk that a chatbot gives bad information, Heitsenrether said.
Ultimately, the generative AI field may develop into “five or six big foundational models” that dominate the market, she said.
The bank is testing LLMs from U.S. tech giants as well as open source models to onboard to its portal next, said the people, who declined to be identified speaking about the bank’s AI strategy.
Friend or foe?
Heitsenrether charted out three stages for the evolution of generative AI at JPMorgan.
The first is simply making the models available to workers; the second involves adding proprietary JPMorgan data to help boost employee productivity, which is the stage that has just begun at the company.
The third is a larger leap that would unlock far greater productivity gains, which is when generative AI is powerful enough to operate as autonomous agents that perform complex multistep tasks. That would make rank-and-file employees more like managers with AI assistants at their command.
The technology will likely empower some workers while displacing others, changing the composition of the industry in ways that are hard to predict.
Banking jobs are the most prone to automation of all industries, including technology, health care and retail, according to consulting firm Accenture . AI could boost the sector’s profits by $170 billion in just four years, Citigroup analysts said.
People should consider generative AI “like an assistant that takes away the more mundane things that we would all like to not do, where it can just give you the answer without grinding through the spreadsheets,” Heitsenrether said.
“You can focus on the higher-value work,” she said.
— CNBC’s Leslie Picker contributed to this report.
More from CNBC:
- Stellantis laying off 2,450 plant workers due to discontinuation of Ram ‘Classic’ pickup truck
- Trump Media reports $16 million loss for quarter as revenue falls
- Wealthy investors find opportunities in stock market sell-offs

IMAGES
COMMENTS
You'll keep your team focused on the most important objectives by setting milestones. 8. Your team. If your team isn't growing, you can skip this section for internal business planning. But, if a key part of your business strategy is to hire and add important team members, identify your key team growth areas.
A business plan acts as a blueprint for your organization's future, detailing its goals, strategies, and financial projections. An internal business plan takes this concept further, focusing specifically on aligning your team and ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in achieving your shared vision.
The internal business plan can be considered an argumentative document since it is a powerful tool for convincing the board members to approve a plan of action. It does so by providing a clear and compelling vision for the organization's future. In a well-crafted internal business plan, the need for action can be demonstrated. ...
The Executive Summary may be the most important part of the internal business plan as it cements the audience's first impression of the project. This may be the only page many executives have time to read and discuss, so make sure it tells the story in a summarized manner. Style, visualization, and financial accuracy are all important aspect ...
Action plans. Action plans are a part of the internal business plan; usually there to tie in a particular activity from a strategy with your set of objectives. Let's clear this up a bit. Actions could mean the creation of a new product or a more modern marketing plan. It could also be the process of developing or investing in new systems.
Crafting an internal business plan is vital for any company's success. It aligns team efforts, supports informed decision-making, and attracts investments. Regularly updating the plan ensures continued relevance in a changing market. This comprehensive approach secures business growth and sustainability.
An internal business plan is a tool designed to help you and make running your company simpler. It is the best business plan for internal analysis and ought to be the main topic of discussion at ...
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
A simple, step-by-step guide to writing a compelling business plan with real-world examples and a free downloadable template. ... If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don't necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary ...
Maybe it's investing in new equipment or developing new systems. Plan it out for the year and have a deadline that it has to be completed by. If it's something that gets repeated, make sure it ...
The internal plan is a great option if you're not planning to present your plan to anyone outside your business. Especially if you're an up-and-running business that may have created a plan previously. You might just need something simple for day-to-day use. Read More: 8 steps to write a useful internal business plan. 5-year business plan
3. Internal Business Plan. Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively. Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include: Department-specific budgets. Target demographic ...
Creating an internal business plan is a strategic move for any company. It helps align everyone within the organization towards common goals. Let's explore a simple 8-step process to build an…
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Business Plan writing tips. The internal business plan is simple and direct. Instead of long paragraphs and lengthy explanations, make it simple and bulleted. Don't forget, the plan is for you, so make it something you'll use often and update regularly. One-page business plans are easy to keep current and use, compared to long documents.
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
An internal business plan is the tool used to communicate these goals in a clear, effective, and calculated manner. External business plans serve the purpose of raising capital. Banks constantly visit with small businesses desiring a loan to finance a new project.
An internal business plan is an extension of your overall business plan. It is usually an annual plan that is further divided into quarterly plans to help existing businesses with their operations and goals. Since it is a process, we at Global-SIBE Consult prefer to call it "internal business planning". It is a strategic process that you ...
By Steven Johnson September 5, 2021. Internal business plans are essential for the success of any business. An internal business plan is similar to an external business plan in its overall structure. However, external business plans are designed to secure funding for a business and are presented to banks, investors, and other lending institutions.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
The business planning process includes diagnosing the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, improving its efficiency, working out how it will compete against rival firms in the future, and setting milestones for progress so they can be measured. ... This is one of the most valued aspects of any business plan as it provides a ...
A business plan can be internal or external. The trait refers to the plan's audience: An internal plan is just for people inside your business, and typically a specific subset of people inside ...
These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc. Internal business plans focus primarily on the company's goals, operations, finances, and personnel and define the strategies to achieve their goals. 2. External business plans. On the contrary, external business plans are intended for people outside the ...
Ask three types of questions: 1. Business performance. Sample question: How did the business unit perform against the goals and objectives established in the last strategic plan?. 2. Reasons for not meeting the target. Sample question: What internal and/or external factors prevented you from achieving business goals?. 3. Tactics to overcome challenges
But there's disagreement on that among scientists. "A cheek swab wouldn't allow you to reach a robust conclusion on someone's sex and potential advantage in sport," says Prof Williams.
Services to meet your business goals. ... How HR supports a winning performance improvement plan. Find ways to increase the speed and efficiency of daily HR processes. Continuous performance improvement is about increasing productivity and efficiency in existing processes—doing things faster, better, and with less labor where possible. ...
Here are the 5 supply chain challenges every business must plan for before the coming fiscal year. ... In today's global economy, internal and external risks abound. The last few years have ...
IRS Tax Tip 2024-68. Aug. 7, 2024 An educational assistance program is an employer's written plan PDF to provide employees with undergraduate or graduate-level educational assistance. These programs allow employers to pay student loan debt and other education expenses tax-free.
Proposed Fiscal Year 2025 Internal Audit Plan I. Executive Summary: Staff seeks approval of the Fiscal Year (FY) 2025 internal audit plan. II. Discussion: Texas Government Code section 2102.008 provides that a state agency's annual audit plan developed by the internal auditor must be approved by the agency's governing board.
JPMorgan Chase has rolled out a generative artificial intelligence assistant to tens of thousands of its employees in recent weeks, the initial phase of a broader plan to inject the technology ...