How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals


How to write a speech that your audience remembers
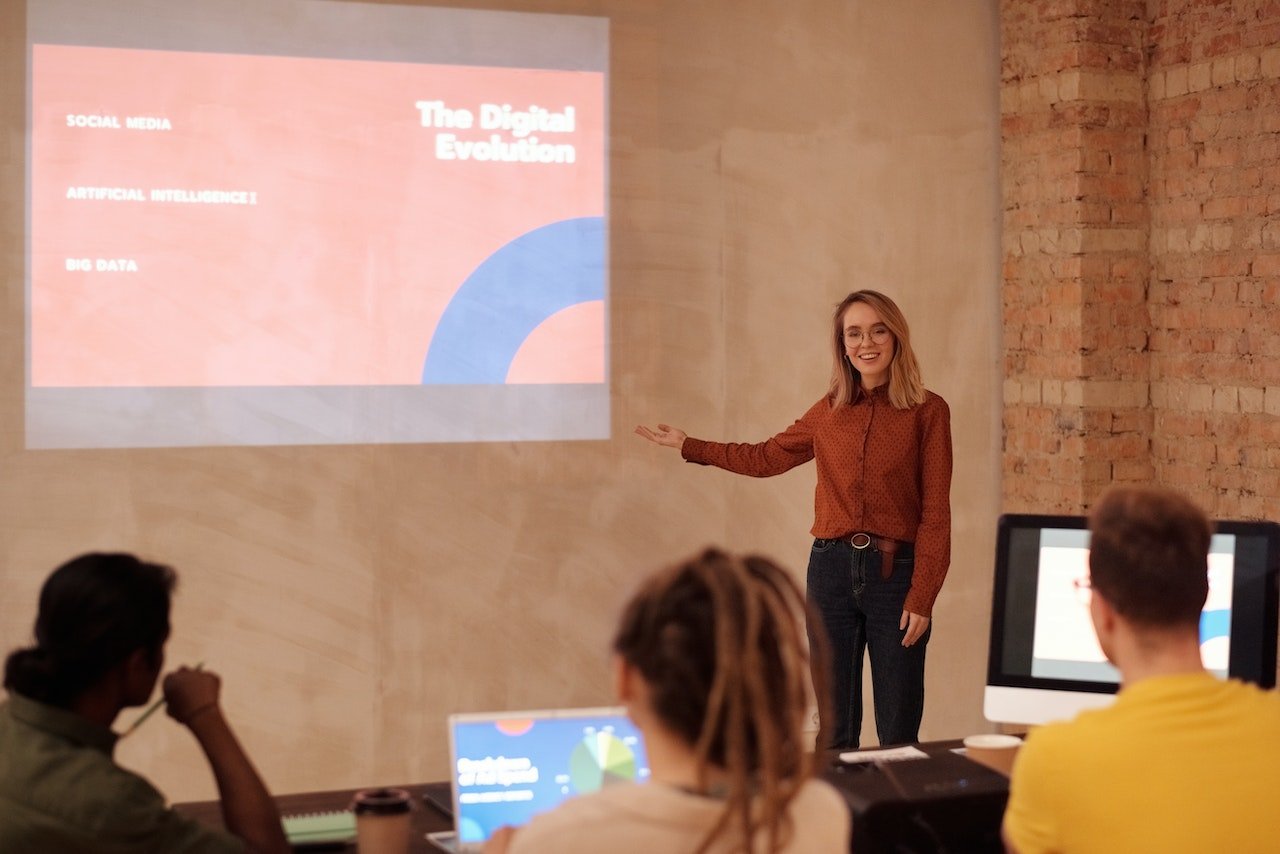

Whether in a work meeting or at an investor panel, you might give a speech at some point. And no matter how excited you are about the opportunity, the experience can be nerve-wracking .
But feeling butterflies doesn’t mean you can’t give a great speech. With the proper preparation and a clear outline, apprehensive public speakers and natural wordsmiths alike can write and present a compelling message. Here’s how to write a good speech you’ll be proud to deliver.
What is good speech writing?
Good speech writing is the art of crafting words and ideas into a compelling, coherent, and memorable message that resonates with the audience. Here are some key elements of great speech writing:
- It begins with clearly understanding the speech's purpose and the audience it seeks to engage.
- A well-written speech clearly conveys its central message, ensuring that the audience understands and retains the key points.
- It is structured thoughtfully, with a captivating opening, a well-organized body, and a conclusion that reinforces the main message.
- Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful and impactful spoken narrative.
What makes a good speech?
A great speech includes several key qualities, but three fundamental elements make a speech truly effective:
Clarity and purpose
Remembering the audience, cohesive structure.
While other important factors make a speech a home run, these three elements are essential for writing an effective speech.
The main elements of a good speech
The main elements of a speech typically include:
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your speech and grabs the audience's attention. It should include a hook or attention-grabbing opening, introduce the topic, and provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Opening/captivating statement: This is a strong statement that immediately engages the audience and creates curiosity about the speech topics.
- Thesis statement/central idea: The thesis statement or central idea is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of your speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience to understand what your speech is about.
- Body: The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main points or arguments. Each point is typically supported by evidence, examples, statistics, or anecdotes. The body should be organized logically and coherently, with smooth transitions between the main points.
- Supporting evidence: This includes facts, data, research findings, expert opinions, or personal stories that support and strengthen your main points. Well-chosen and credible evidence enhances the persuasive power of your speech.
- Transitions: Transitions are phrases or statements that connect different parts of your speech, guiding the audience from one idea to the next. Effective transitions signal the shifts in topics or ideas and help maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
- Counterarguments and rebuttals (if applicable): If your speech involves addressing opposing viewpoints or counterarguments, you should acknowledge and address them. Presenting counterarguments makes your speech more persuasive and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the final part of your speech and should bring your message to a satisfying close. Summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the audience with a memorable closing thought or call to action.
- Closing statement: This is the final statement that leaves a lasting impression and reinforces the main message of your speech. It can be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, a powerful quote, or a memorable anecdote.
- Delivery and presentation: How you deliver your speech is also an essential element to consider. Pay attention to your tone, body language, eye contact , voice modulation, and timing. Practice and rehearse your speech, and try using the 7-38-55 rule to ensure confident and effective delivery.
While the order and emphasis of these elements may vary depending on the type of speech and audience, these elements provide a framework for organizing and delivering a successful speech.

How to structure a good speech
You know what message you want to transmit, who you’re delivering it to, and even how you want to say it. But you need to know how to start, develop, and close a speech before writing it.
Think of a speech like an essay. It should have an introduction, conclusion, and body sections in between. This places ideas in a logical order that the audience can better understand and follow them. Learning how to make a speech with an outline gives your storytelling the scaffolding it needs to get its point across.
Here’s a general speech structure to guide your writing process:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
How to write a compelling speech opener
Some research shows that engaged audiences pay attention for only 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Other estimates are even lower, citing that people stop listening intently in fewer than 10 minutes . If you make a good first impression at the beginning of your speech, you have a better chance of interesting your audience through the middle when attention spans fade.
Implementing the INTRO model can help grab and keep your audience’s attention as soon as you start speaking. This acronym stands for interest, need, timing, roadmap, and objectives, and it represents the key points you should hit in an opening.
Here’s what to include for each of these points:
- Interest : Introduce yourself or your topic concisely and speak with confidence . Write a compelling opening statement using relevant data or an anecdote that the audience can relate to.
- Needs : The audience is listening to you because they have something to learn. If you’re pitching a new app idea to a panel of investors, those potential partners want to discover more about your product and what they can earn from it. Read the room and gently remind them of the purpose of your speech.
- Timing : When appropriate, let your audience know how long you’ll speak. This lets listeners set expectations and keep tabs on their own attention span. If a weary audience member knows you’ll talk for 40 minutes, they can better manage their energy as that time goes on.
- Routemap : Give a brief overview of the three main points you’ll cover in your speech. If an audience member’s attention starts to drop off and they miss a few sentences, they can more easily get their bearings if they know the general outline of the presentation.
- Objectives : Tell the audience what you hope to achieve, encouraging them to listen to the end for the payout.
Writing the middle of a speech
The body of your speech is the most information-dense section. Facts, visual aids, PowerPoints — all this information meets an audience with a waning attention span. Sticking to the speech structure gives your message focus and keeps you from going off track, making everything you say as useful as possible.
Limit the middle of your speech to three points, and support them with no more than three explanations. Following this model organizes your thoughts and prevents you from offering more information than the audience can retain.
Using this section of the speech to make your presentation interactive can add interest and engage your audience. Try including a video or demonstration to break the monotony. A quick poll or survey also keeps the audience on their toes.
Wrapping the speech up
To you, restating your points at the end can feel repetitive and dull. You’ve practiced countless times and heard it all before. But repetition aids memory and learning , helping your audience retain what you’ve told them. Use your speech’s conclusion to summarize the main points with a few short sentences.
Try to end on a memorable note, like posing a motivational quote or a thoughtful question the audience can contemplate once they leave. In proposal or pitch-style speeches, consider landing on a call to action (CTA) that invites your audience to take the next step.

How to write a good speech
If public speaking gives you the jitters, you’re not alone. Roughly 80% of the population feels nervous before giving a speech, and another 10% percent experiences intense anxiety and sometimes even panic.
The fear of failure can cause procrastination and can cause you to put off your speechwriting process until the last minute. Finding the right words takes time and preparation, and if you’re already feeling nervous, starting from a blank page might seem even harder.
But putting in the effort despite your stress is worth it. Presenting a speech you worked hard on fosters authenticity and connects you to the subject matter, which can help your audience understand your points better. Human connection is all about honesty and vulnerability, and if you want to connect to the people you’re speaking to, they should see that in you.
1. Identify your objectives and target audience
Before diving into the writing process, find healthy coping strategies to help you stop worrying . Then you can define your speech’s purpose, think about your target audience, and start identifying your objectives. Here are some questions to ask yourself and ground your thinking :
- What purpose do I want my speech to achieve?
- What would it mean to me if I achieved the speech’s purpose?
- What audience am I writing for?
- What do I know about my audience?
- What values do I want to transmit?
- If the audience remembers one take-home message, what should it be?
- What do I want my audience to feel, think, or do after I finish speaking?
- What parts of my message could be confusing and require further explanation?
2. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for tailoring your speech effectively. Consider the demographics of your audience, their interests, and their expectations. For instance, if you're addressing a group of healthcare professionals, you'll want to use medical terminology and data that resonate with them. Conversely, if your audience is a group of young students, you'd adjust your content to be more relatable to their experiences and interests.
3. Choose a clear message
Your message should be the central idea that you want your audience to take away from your speech. Let's say you're giving a speech on climate change. Your clear message might be something like, "Individual actions can make a significant impact on mitigating climate change." Throughout your speech, all your points and examples should support this central message, reinforcing it for your audience.
4. Structure your speech
Organizing your speech properly keeps your audience engaged and helps them follow your ideas. The introduction should grab your audience's attention and introduce the topic. For example, if you're discussing space exploration, you could start with a fascinating fact about a recent space mission. In the body, you'd present your main points logically, such as the history of space exploration, its scientific significance, and future prospects. Finally, in the conclusion, you'd summarize your key points and reiterate the importance of space exploration in advancing human knowledge.
5. Use engaging content for clarity
Engaging content includes stories, anecdotes, statistics, and examples that illustrate your main points. For instance, if you're giving a speech about the importance of reading, you might share a personal story about how a particular book changed your perspective. You could also include statistics on the benefits of reading, such as improved cognitive abilities and empathy.
6. Maintain clarity and simplicity
It's essential to communicate your ideas clearly. Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex language that might confuse your audience. For example, if you're discussing a medical breakthrough with a non-medical audience, explain complex terms in simple, understandable language.
7. Practice and rehearse
Practice is key to delivering a great speech. Rehearse multiple times to refine your delivery, timing, and tone. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to observe your body language and gestures. For instance, if you're giving a motivational speech, practice your gestures and expressions to convey enthusiasm and confidence.
8. Consider nonverbal communication
Your body language, tone of voice, and gestures should align with your message . If you're delivering a speech on leadership, maintain strong eye contact to convey authority and connection with your audience. A steady pace and varied tone can also enhance your speech's impact.
9. Engage your audience
Engaging your audience keeps them interested and attentive. Encourage interaction by asking thought-provoking questions or sharing relatable anecdotes. If you're giving a speech on teamwork, ask the audience to recall a time when teamwork led to a successful outcome, fostering engagement and connection.
10. Prepare for Q&A
Anticipate potential questions or objections your audience might have and prepare concise, well-informed responses. If you're delivering a speech on a controversial topic, such as healthcare reform, be ready to address common concerns, like the impact on healthcare costs or access to services, during the Q&A session.
By following these steps and incorporating examples that align with your specific speech topic and purpose, you can craft and deliver a compelling and impactful speech that resonates with your audience.

Tools for writing a great speech
There are several helpful tools available for speechwriting, both technological and communication-related. Here are a few examples:
- Word processing software: Tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or other word processors provide a user-friendly environment for writing and editing speeches. They offer features like spell-checking, grammar correction, formatting options, and easy revision tracking.
- Presentation software: Software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides is useful when creating visual aids to accompany your speech. These tools allow you to create engaging slideshows with text, images, charts, and videos to enhance your presentation.
- Speechwriting Templates: Online platforms or software offer pre-designed templates specifically for speechwriting. These templates provide guidance on structuring your speech and may include prompts for different sections like introductions, main points, and conclusions.
- Rhetorical devices and figures of speech: Rhetorical tools such as metaphors, similes, alliteration, and parallelism can add impact and persuasion to your speech. Resources like books, websites, or academic papers detailing various rhetorical devices can help you incorporate them effectively.
- Speechwriting apps: Mobile apps designed specifically for speechwriting can be helpful in organizing your thoughts, creating outlines, and composing a speech. These apps often provide features like voice recording, note-taking, and virtual prompts to keep you on track.
- Grammar and style checkers: Online tools or plugins like Grammarly or Hemingway Editor help improve the clarity and readability of your speech by checking for grammar, spelling, and style errors. They provide suggestions for sentence structure, word choice, and overall tone.
- Thesaurus and dictionary: Online or offline resources such as thesauruses and dictionaries help expand your vocabulary and find alternative words or phrases to express your ideas more effectively. They can also clarify meanings or provide context for unfamiliar terms.
- Online speechwriting communities: Joining online forums or communities focused on speechwriting can be beneficial for getting feedback, sharing ideas, and learning from experienced speechwriters. It's an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals and improve your public speaking skills through collaboration.
Remember, while these tools can assist in the speechwriting process, it's essential to use them thoughtfully and adapt them to your specific needs and style. The most important aspect of speechwriting remains the creativity, authenticity, and connection with your audience that you bring to your speech.

5 tips for writing a speech
Behind every great speech is an excellent idea and a speaker who refined it. But a successful speech is about more than the initial words on the page, and there are a few more things you can do to help it land.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech:
1. Structure first, write second
If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first. This can also help you identify unclear points or moments that disrupt your flow.
2. Do your homework
Data strengthens your argument with a scientific edge. Research your topic with an eye for attention-grabbing statistics, or look for findings you can use to support each point. If you’re pitching a product or service, pull information from company metrics that demonstrate past or potential successes.
Audience members will likely have questions, so learn all talking points inside and out. If you tell investors that your product will provide 12% returns, for example, come prepared with projections that support that statement.
3. Sound like yourself
Memorable speakers have distinct voices. Think of Martin Luther King Jr’s urgent, inspiring timbre or Oprah’s empathetic, personal tone . Establish your voice — one that aligns with your personality and values — and stick with it. If you’re a motivational speaker, keep your tone upbeat to inspire your audience . If you’re the CEO of a startup, try sounding assured but approachable.
4. Practice
As you practice a speech, you become more confident , gain a better handle on the material, and learn the outline so well that unexpected questions are less likely to trip you up. Practice in front of a colleague or friend for honest feedback about what you could change, and speak in front of the mirror to tweak your nonverbal communication and body language .
5. Remember to breathe
When you’re stressed, you breathe more rapidly . It can be challenging to talk normally when you can’t regulate your breath. Before your presentation, try some mindful breathing exercises so that when the day comes, you already have strategies that will calm you down and remain present . This can also help you control your voice and avoid speaking too quickly.
How to ghostwrite a great speech for someone else
Ghostwriting a speech requires a unique set of skills, as you're essentially writing a piece that will be delivered by someone else. Here are some tips on how to effectively ghostwrite a speech:
- Understand the speaker's voice and style : Begin by thoroughly understanding the speaker's personality, speaking style, and preferences. This includes their tone, humor, and any personal anecdotes they may want to include.
- Interview the speaker : Have a detailed conversation with the speaker to gather information about their speech's purpose, target audience, key messages, and any specific points they want to emphasize. Ask for personal stories or examples they may want to include.
- Research thoroughly : Research the topic to ensure you have a strong foundation of knowledge. This helps you craft a well-informed and credible speech.
- Create an outline : Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval.
- Write in the speaker's voice : While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style. Use language and phrasing that feel natural to them. If they have a particular way of expressing ideas, incorporate that into the speech.
- Craft a captivating opening : Begin the speech with a compelling opening that grabs the audience's attention. This could be a relevant quote, an interesting fact, a personal anecdote, or a thought-provoking question.
- Organize content logically : Ensure the speech flows logically, with each point building on the previous one. Use transitions to guide the audience from one idea to the next smoothly.
- Incorporate engaging stories and examples : Include anecdotes, stories, and real-life examples that illustrate key points and make the speech relatable and memorable.
- Edit and revise : Edit the speech carefully for clarity, grammar, and coherence. Ensure the speech is the right length and aligns with the speaker's time constraints.
- Seek feedback : Share drafts of the speech with the speaker for their feedback and revisions. They may have specific changes or additions they'd like to make.
- Practice delivery : If possible, work with the speaker on their delivery. Practice the speech together, allowing the speaker to become familiar with the content and your writing style.
- Maintain confidentiality : As a ghostwriter, it's essential to respect the confidentiality and anonymity of the work. Do not disclose that you wrote the speech unless you have the speaker's permission to do so.
- Be flexible : Be open to making changes and revisions as per the speaker's preferences. Your goal is to make them look good and effectively convey their message.
- Meet deadlines : Stick to agreed-upon deadlines for drafts and revisions. Punctuality and reliability are essential in ghostwriting.
- Provide support : Support the speaker during their preparation and rehearsal process. This can include helping with cue cards, speech notes, or any other materials they need.
Remember that successful ghostwriting is about capturing the essence of the speaker while delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Collaboration, communication, and adaptability are key to achieving this.
Give your best speech yet
Learn how to make a speech that’ll hold an audience’s attention by structuring your thoughts and practicing frequently. Put the effort into writing and preparing your content, and aim to improve your breathing, eye contact , and body language as you practice. The more you work on your speech, the more confident you’ll become.
The energy you invest in writing an effective speech will help your audience remember and connect to every concept. Remember: some life-changing philosophies have come from good speeches, so give your words a chance to resonate with others. You might even change their thinking.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
Use a personal SWOT analysis to discover your strengths and weaknesses
How to not be nervous for a presentation — 13 tips that work (really), is being ego driven damaging your career being purpose-driven is better, put out-of-office messages to work for you when you’re away, what’s a vocation 8 tips for finding yours, how to send a reminder email that’s professional and effective, setting goals for 2024 to ring in the new year right, create a networking plan in 7 easy steps, how long should you stay in a job this guide will help you figure it out, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, 18 effective strategies to improve your communication skills, 8 tips to improve your public speaking skills, the importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, anxious about meetings learn how to run a meeting with these 10 tips, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, 6 presentation skills and how to improve them, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Speech Crafting →
The Definitive Guide on Structuring a Speech and Presentation

So, you have an important presentation coming up which requires you to not only write up a speech but also present it.
You’re probably nervous, as most people are when it comes to public speaking, which is natural.
A good way to feel confident before and during your presentation is to ensure that you are well-prepared on the content you will be presenting.
To help you prepare , you can research and learn more about your subject, practice your presentation in front of friends or family or even in front of a mirror.
While practicing , factor in the time you’ve been allocated to give your presentation, which will allow you to keep time without rushing through your presentation . This will help you avoid leaving key points out.
Additionally, you should ensure that you are audible and well understood . So, if you are a fast speaker like me, you should try slowing down .
Nerves aside, you probably are a good speaker who writes good content. However, not having your speech structured properly may make it hard for your audience to not only understand each point you are trying to put across but also the gist of your whole speech.
A well-structured speech not only prevents your audience from getting lost but also assists your audience in understanding your message.
Without a proper structure, your speech will have no sense of direction, which will leave your audience scattered on the main points you would like to put across.
Note: Research has shown that audiences tend to retain structured information 40% more precisely than unstructured information.
To begin with, you first need to draw up a speech outline .

How to Structure a Speech to Get Your Message Across Clearly
Presentation outline.
A speech outline is a general description of what your speech will be about.
The General Speech Outline is most commonly used.
This is made up of the introduction, the main body and the conclusion.
- The Introduction
This tells your audience who you are and what you are to talk about. This is where you grab your audience’s attention.
- The Main Body
This is where you begin making your arguments. To make it easier for your audience to follow what you’re talking about, you should divide your arguments into easy-to-understand and short points.
To help the audience understand your point, think up a good analogy or give a real story that they can use to relate to the points you’ve put across.
If your speech relies on data that helps emphasize your key points, then include the data to add more weight.
Pro-Tip: Ensure your data has been sourced from credible source s.
- The Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize everything that you’ve talked about in your speech and ties it up in a bow that is easy to recall. So ensure it’s memorable!
Now that your outline is drawn up, next, you should focus on the type of structure you will be using to write up your speech.

The Common Characteristics of a Good Speech Structure
Choosing the structure that you will use for your presentation may present a challenge, as you may be conflicted on the right structure for you. To help with this, you need to ask yourself:
- What is the objective of your presentation?
- Who is your audience?
- What is your audience most interested in?
- What are the key points your audience should recall after your presentation?
Taking these factors into consideration will allow you to structure your speech in a way that puts your main points across, helps the audience follow along throughout your presentation and also helps them remember the most important bits.
There are various types of speech structures, which include:
- Problem-Solution Structure
This type of structure is good for presentations that require you to influence the audiences’ thoughts on an issue.
This approach may need you to appeal to your audience both emotionally and logically.

- Demonstration Structure
This structure is particularly useful when your presentation requires a lot of demonstrations .
For instance, if your speech focuses on a specific product, this particular structure allows you to explain why the commodity is not only valuable but also necessary.
This may be followed up by how the product can solve various issues which can be better explained through a demonstration .
Now, we do a deep dive into a typical speech structure, highlighting its flow, which should incorporate the speech outline you’d already drawn up.
1. First things first, say hi.
Ever heard of a speaker who came up to the stage and without a greeting or an introduction began with their presentation? Well, me neither.

(Unless you are in a speech contest where time is very limited. But even then, the contest Toastmaster would have introduced you.)
Before you begin your presentation, introduce yourself to your audience, highlighting your relevant expertise. Your introduction need not be very detailed or long but it helps establish rapport (a connection) between you and the audience.
This is where you show exactly why you are worth listening to, through your words.
2. Introduction
Under the introduction, you will be talking about the purpose and subject of your presentation. There will be no point to this if the audience is uninterested in your subject matter.
Therefore, your objective is to not only talk about the aforementioned points but also gain your audience’s confidence, attention and interest, while also connecting with them.

To help filter down your presentation, you should:
- Introduce your topic and explain the topic area
- Mention the challenges or issues that you will be exploring in this area
- Talk about the purpose of your presentation; this is the basis of your presentation.
- Give a statement of what you hope the outcome of your presentation will be
- Demonstrate using a preview how your presentation has been organized .
Additionally, you should also;
- Specify or give a general estimate of how long your presentation will take.
- Communicate whether you’d prefer to answer any questions the audience may have in an allotted time frame or throughout your presentation.
- Let the audience know whether handouts on your presentation will be provided or whether they should take notes (if applicable).
It should be noted though that how you structure your introduction may sometimes be dependent on the amount of time you’ve been allotted for your presentation.
Related: How to Start Your Speech to Engage the Audience
3. The Main Body
Here, you will be delving into details, talking about the topics you’d introduced in your introduction.
To ensure your audience doesn’t get lost as you discuss your presentation in detail, you should divide what you will be talking about into different topics.
This will allow you to talk about each topic in its entirety before moving onto the next, thus making it easier for your audience to not only understand your key points but keep up with the presentation.

Pro-Tip: Providing a mini-summary of what you have discussed under each topic before moving on to the next helps the audience distinguish the main points from the details and understand the key points better.
4. The Conclusion
Some speakers often make the mistake of not concluding their presentations with purpose, which leaves their messages unreinforced.
Presentations usually have a specific objective in mind that they plan to attain. While your presentation may have gone well, you need to reinforce your message in your conclusion.
To do this, you need to:
- Indicate that you are nearing the end of your presentation
- Rehash your topic and aim of your presentation
- Summarize your main points
- Give an enlightening call-to-action
- Proceed to the final section of your presentation
Pro-Tip: Always make sure that you make the closing statement for your presentation after the Q&A session. This is because audiences are likely to remember the last thing they hear.
Related: How to End a Speech With a Bang (And be Remembered)
5. Question and Answer Time
This depends on whether you had allotted a time frame where the audience would be allowed to ask questions concerning your presentation. If you had not, then this is a perfect time to invite questions from the audience.

To do so, you should begin by thanking your audience for their time and for participating (if there was a Q&A session throughout the presentation).
While it’s totally fine to make the Q&A session a part of your presentation, focusing on your topics of discussion and letting the session come at the end of your talk allows the audience time to fully grasp your content, is recommended.
Conclusion: On Building a Speech Structure
We’ve discussed the various types of structures you can use to make your presentation as good as you would like it to be. While presentation structures may be different, there are a few factors that may affect the structure of your presentation.
These include:
- If your talk is restricted by time constraints
- How much interaction you’d like from your audience
- If the audience is knowledgeable on the subject of your discussion.
- Whether you need visual assistance or need to give demonstrations
- The setting in which you will give your presentation
In summary, structuring your presentation in a simple and logical way that allows your audience to keep up with your talk is not only important but beneficial. As they say, the proof of the pudding is in the eating, so go out and put into practice the suggestions above!

- Find a Club
- Start a Club
- Toggle Search

How to Build a Speech
Structure, stories, and word choice are all key to crafting a compelling presentation..
By Ruth Nasrullah
There was a time when flowery, dense language was the standard for public speaking—18th-century North America, for instance. Here is the beginning of George Washington’s 1796 farewell speech:
The period for a new election of a citizen to administer the executive government of the United States being not far distant, and the time actually arrived when your thoughts must be employed in designating the person who is to be clothed with that important trust, it appears to me proper, especially as it may conduce to a more distinct expression ...
And that excerpt is far from the conclusion of just that first sentence. Imagine using language like that in a Toastmasters meeting!
Analyze why the opening of this august speech wouldn’t work today and two major problems quickly become apparent. First, it could have been cut down at least by half; and second, even after 20 seconds, the audience still doesn’t know much about the speaker’s purpose.
Fortunately for modern-day speakers, the Toastmasters educational program emphasizes the skill of speechwriting. Here are a few guidelines to mastering the art and technique of writing speeches.
My Kingdom for a Subject!
Need a speech topic? First identify your purpose. What do you want to do? Inform? Persuade? Inspire? Educate? Next, home in on a subject. You can select something most people can relate to—or most people in your audience can relate to—or something arcane that will require a little bit of research.
Step three: Start brainstorming.
What about your Ultimate Frisbee team? Your cat’s finicky ways? Your child’s piano recital? Your childhood dream of becoming president and what became of it? Holiday traditions in your country or region? Vanilla or chocolate? Cake or pie?
A word of caution: It may go without saying, but when it comes to controversial topics such as religion or politics, make sure you know the club policies governing such subjects—and the audience’s sensibilities.
Elena Paweta, DTM, is a member of Poland’s First Toastmasters club, based in Warsaw. She is also an organizer of TEDx events , programs in local communities that feature a diversity of speakers across several disciplines who address a variety of subjects. This gives her particular insight into crafting and refining speech topics.
“As we advance and become more experienced and confident, we can cover topics that may influence others,” Paweta says. “We can use this amazing tool [public speaking] to change people’s lives for the better.”

Deceptively Simple: The Structure
Ramona J. Smith is the 2018 World Champion of Public Speaking. Watch her winning speech and you’ll get a clue to what helps make it great: a solid, simple outline. She enters the stage and crouches down in a boxer’s stance, throwing punches in the air. She explains that we may get knocked down in life, but if we persevere we will be “still standing,” a phrase she repeats throughout, for emphasis. She then goes on to describe three events in her life that she had to fight through (extending the metaphor) and expands on each.
And how does she conclude the speech? With the phrase she offered in the beginning: “still standing.” It’s simple, yet so powerful.
To supplement that structure, Smith makes the speech come alive with vocal variety, exuberant body language (shadowboxing), and even a prop (a towel thrown to the ground).
Smith, President of the Cy-Fair Super Speakers Club in Cypress, Texas, says the key to writing a great speech is to keep it simple. “I start with the skeleton, then start to throw meat on the bones,” she says.
World Champion Ramona J. Smith says the key to writing a great speech is to keep it simple. "I start with the skeleton, then start to throw meat on the bones."
She writes speeches in three parts—introduction, body, and conclusion. In the body she identifies three points, just as in her championship speech. “Then I flesh out those three points, add transitions between each and then a call to action between the third point and the conclusion.”
Smith has another key piece of advice: Call on fellow Toastmasters for help. “Look in your club for writers,” she says. “There’s an English teacher or writer in every club—see if they can help you.”
Act Out—But in a Good Way
Toastmaster Wayne Lebowitz, a retired jeweler from Somerville, Massachusetts, always knew he wanted to be an actor. Although he ultimately found his career in the family business, he brings theatrical sensibilities to public speaking.
Writing a speech is like writing a script, he says. Start with an attention-grabbing device. For instance:
“How many of you have hunted a bear? Okay, I see by the lack of hands raised that none of you have. Let me tell you about bear hunting.” Using the bear motif, he demonstrates another approach: “I just found out that there are only three bears left in Somerville, Massachusetts. That’s three more than I thought we had.”
Lebowitz emphasizes that people remember stories. “I realize when I give a speech, I’ve got to entertain them. Otherwise, whatever my message is, it’s lost.”
He suggests the same format that Ramona J. Smith uses. “The body of your speech should consist of three bullet points,” he says. “And have a story to back up each point.” Lebowitz recommends closing the speech by reiterating those bullet points and tying together the closing and opening.
At a recent meeting of his club, Somerville Toastmasters, the first speaker gave a speech about a work situation by providing three points in the beginning, then elaborating on them, and returning to them again at the end. Because she used vocal variety and good details, the simple structure worked.
“Show, don’t tell” is advice often offered to writers whose work needs a little spark. The concept can also apply to speechwriting. Paint a picture for your audience with the language you use.
Jing Humphreys, DTM, a member of the Earlybirds Club in Butler, Pennsylvania, is a believer in the power of word choice.
“I like vivid word descriptions,” she says. “Like you can feel it happening in front of you because of the choice of words the speaker uses.”
Need a speech topic? First identify your purpose. What do you want to do? Inform? Persuade? Inspire? Educate?
Despite working in a highly technical field where there isn’t as much room for creativity with language, outside of work she is a proponent of conjuring up dramatic images to move the audience. (Example: “a big, vast ocean so clear you can almost see the bottom of it.”) This is also the message she imparts as a mentor and an evaluator: To tell a story, use powerful imagery, and don’t be afraid to provoke strong feelings in your audience.
“I just evaluated one of my club members,” she says. “I told him ‘Scare me and then save me.’ The audience needs to know why am I listening to you—why is this important to me?”
Don’t forget that you need to know your audience. If the venue is in a country with a nuanced culture and/or a culture that has significant differences from your own, make sure you’ve done your homework so you avoid potentially offensive gaffes. If you want to add jokes, try them out on others first to be sure your humor isn’t tone-deaf .
Include the Visual
Visual aids can be a powerful addition, and in some cases a necessary one, to a presentation. Technical presentations generally require the speaker to provide graphics, charts, schematics, etc., in order to fully explain the topic. Non-technical presentations, too, can gain a boost from props or visual aids.
Check that all your references are correct. Did Queen Elizabeth really give the Gettysburg Address or was your mind wandering when you wrote that?
A word about PowerPoint: Don’t read from the slides. The slides should supplement your words. In most cases, you can use words for the narrative, and the projector screen for ideas that are best conveyed graphically. The words you speak and the images you show should complement each other.
I am not a fan of PowerPoint, so when I did the “Get Comfortable With Visual Aids” project in Toastmasters’ old Competent Communication manual, I opted for a wig mannequin and demonstrated different ways Muslim women wear head scarves. It gave me the opportunity to personalize my speech and present something tangible, and it supported my discussion of why Muslim women wear head scarves.
Not So Fast!
Transitional statements help the audience easily follow you from one section of your speech to the next, or from one idea to another.
There is a wide range of transitions that serve different functions. Some keep the audience focused on the topic or time frame you are discussing; some provide examples of a particular subject area, reinforcing a point and introducing examples seamlessly. Here are just a few common transitions:
1. To tie your introduction to your first point in the body of the speech:
• Let me give you an example ...
• To get started, let’s examine ...
• First, I’m going to discuss ...
2. To move from one point within the body to the next:
• In the same way, this item tends to melt in the heat ...
• Let me show you something equally troubling ...
• This is similar to the kind of speech we’re studying ...
3. To begin the conclusion to your speech:
• All in all, this educational journey was …
• Looking back, I’m glad that I …
• To sum up, these three reasons are why …
If your speech feels or sounds awkward as you move through the main points, lead the listener with transitions, like those listed above. When in doubt, try reading that section aloud to someone else; if they are unclear about the connection between two ideas or two statements, look for a proper transition.
The Final Steps
Always do a final review of your writing before turning your attention to rehearsing. A few essential areas to look over:
- Double-check your grammar and pronunciation. This may seem like a no-brainer, but don’t assume you have it right. A great classic reference book to aid with this is The Elements of Grammar by Margaret Shertzer. Many other useful books—and grammar-related websites—exist as well, including The Elements of Style by William Strunk Jr. and E.B. White, Write Right! by Jan Venolia, grammarbook.com , and www.quickanddirtytips.com/grammar-girl .
- Examine your writing for continuity of theme; make sure you aren’t wandering from your main point. Remove or revise anything that takes your speech off track.
- Make sure everything makes logical sense. Sometimes you get so deep into your subject that you mention ideas only you can understand.
- Check that all your references are correct . Did Queen Elizabeth really give the Gettysburg Address or was your mind wandering when you wrote that?
- Don’t go overboard with quotes. They can be used to enhance a speech, but make sure the quote you use is pithy, brief, and very relevant. Be sure you’re citing the correct author of the quote (pro tip: Look somewhere besides social media to verify the source).
When you’ve done all you can do to polish the writing of your speech, you will feel confident and ready. The Toastmasters guidelines for speechwriting will prepare you well.
Share this article
Related articles.

Speechwriting
Speechwriting 101
Expert speechwriters weigh in on the basics of crafting a speech.
Mitch Mirkin

Communication
5 Easy Tips for Crafting a Speech
Start with the two basic concepts of construction and content.
Judith T. Krauthamer

Presentation Skills
5 Great Ways to Begin a Speech
Learn to hook your audience in 10 seconds.
Anne Barab, DTM, AS
Listen for Lessons on Crafting a Speech
In this ToastCaster podcast , Greg Gazin speaks with Toastmaster Freddi Dogterom, DTM, AS, from Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. Dogterom, a professional speaker with more than 20 years of experience, offers up lessons on crafting your speech or presentation. Click the play button below to listen to this episode.
Learn more about the award-winning publication.
About magazine.
Discover more about the award-winning publication.
Magazine FAQ
Answers to your common magazine questions.
Submissions
How to submit an article query, photo, or story idea.
Meet the editorial team.

Speechwriting
9 Structure and Organization
Writing a Speech That Audiences Can Grasp
In this chapter . . .
For a speech to be effective, the material must be presented in a way that makes it not only engaging but easy for the audience to follow. Having a clear structure and a well-organized speech makes this possible. In this chapter we cover the elements of a well-structured speech, using transitions to connect each element, and patterns for organizing the order of your main points.
Have you had this experience? You have an instructor who is easy to take notes from because they help you see the main ideas and give you cues as to what is most important to write down and study for the test. On the other hand, you might have an instructor who tells interesting stories, says provocative things, and leads engaging discussions, but you have a tough time following where the instruction is going. If you’ve experienced either of these, you already know that structure and the organized presentation of material makes a big difference for listening and learning. The structure is like a house, which has essential parts like a roof, walls, windows, and doors. Organization is like the placement of rooms within the house, arranged for a logical and easy flow.
This chapter will teach you about creating a speech through an outlining process that involves structure and organization. In the earlier chapter Ways of Delivering Speeches , you learned about several different modes of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, and manuscript. Each of these suggests a different kind of speech document. An impromptu speech will have a very minimal document or none at all. An extemporaneous delivery requires a very thorough outline, and a manuscript delivery requires a fully written speech text. Here’s a crucial point to understand: Whether you plan to deliver extemporaneously or from a fully written text. The process of outlining is crucial. A manuscript is simply a thorough outline into which all the words have been written.
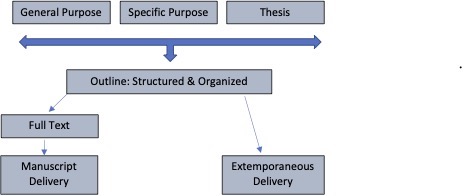
Four Elements of a Structured Speech
A well-structured speech has four distinct elements: introduction, body, connective statements, and conclusion. While this sounds simple, each of these elements has sub-elements and nuances that are important to understand. Introductions and conclusions are complex enough to warrant their own chapter and will be discussed in depth further on.
Introduction and Conclusion
The importance of a good introduction cannot be overstated. The clearer and more thorough the introduction, the more likely your audience will listen to the rest of the speech and not “turn off.” An introduction, which typically occupies 10-15% of your entire speech, serves many functions including getting the audience’s attention, establishing your credibility, stating your thesis, and previewing your main points.
Like an introduction, speech conclusions are essential. They serve the function of reiterating the key points of your speech and leave the audience with something to remember.
The elements of introductions and conclusions will be discussed in the following chapter. The remainder of this chapter is devoted to the body of the speech and its connectors.
The Body of a Speech
The body of a speech is comprised of several distinct groups of related information or arguments. A proper group is one where a) the group can be described in a single clear sentence, and b) there’s a logical relationship between everything within it. We call that describing sentence a main point . Speeches typically have several main points, all logically related to the thesis/central idea of the speech. Main points are followed by explanation, elaboration, and supporting evidence that are called sub-points .
Main Points
A main point in a speech is a complete sentence that states the topic for information that is logically grouped together. In a writing course, you may have learned about writing a paragraph topic sentence. This is typically the first sentence of a paragraph and states the topic of the paragraph. Speechwriting is similar. Whether you’re composing an essay with a paragraph topic sentences or a drafting a speech with main points, everything in the section attached to the main point should logically pertain to it. If not, then the information belongs under a different main point. Let’s look at an example of three main points:
General Purpose: To persuade
Specific Purpose: To motivate my classmates in English 101 to participate in a study abroad program.
Thesis: A semester-long study abroad experience produces lifelong benefits by teaching you about another culture, developing your language skills, and enhancing your future career prospects.
Main point #1: A study abroad experience allows you to acquire firsthand experience of another culture through classes, extra-curricular activities, and social connections.
Main point #2: You’ll turbocharge your acquisition of second language skills through an immersive experience living with a family.
Main point #3: A study abroad experience on your resume shows that you have acquired the kind of language and cultural skills that appeal to employers in many sectors.
Notice that each main point is expressed in a complete sentence, not merely #1 Culture; #2 Language; #3 Career. One-word signals are useless as a cue for speaking. Additionally, students are often tempted to write main points as directions to themselves, “Talk about the health department” or “Mention the solution.” This isn’t helpful for you, either. Better: “The health department provides many services for low-income residents” says something we can all understand.
Finally, the important thing to understand about speechwriting is that listeners have limits as to how many categories of information they can keep in mind. The number of main points that can be addressed in any speech is determined by the time allotted for a speech but is also affected by the fact that speeches are limited in their ability to convey substantial amounts of information. For a speech of five to seven minutes, three or four main points are usually enough. More than that would be difficult to manage—for both speaker and audience.
Obviously, creating your main points isn’t the end of the story. Each main point requires additional information or reinforcement. We call these sub-points. Sub-points provide explanation, detail, elaboration, and/or supporting evidence. Consider main point #1 in the previous example, now with sub-points:
Sub-point A: How a country thinks about education is a window into the life of that culture. While on a study abroad program, you’ll typically take 3-5 classes at foreign universities, usually with local professors. This not only provides new learning, but it opens your eyes to different modes of education.
Sub-point B: Learning about a culture isn’t limited to the classroom. Study abroad programs include many extra-curricular activities that introduce you to art, food, music, sports, and other everyday elements of a country’s culture. These vary depending on the program and there’s something for everyone! The website gooverseas.com provides information on hundreds of programs.
Sub-point C: The opportunity to socialize with peers in other countries is one of most attractive elements of studying abroad. You may form friendships that will last a lifetime. “I have made valuable connections in a country I hope to return to someday” according to a blog post by Rachel Smith, a student at the University of Kansas. [1]
Notice that each of these sub-points pertains to the main point. The sub-points contribute to the main point by providing explanation, detail, elaboration, and/or supporting evidence. Now imagine you had a fourth sub-point:
Sub-point D: And while doing all that socializing, you’ll really improve your language skills.
Does that sub-point belong to main point #1? Or should it be grouped with main point#2 or main point #3?
Connective Statements
Connectives or “connective statements” are broad terms that encompass several types of statements or phrases. They are designed to help “connect” parts of your speech to make it easier for audience members to follow. Connectives are tools that add to the planned redundancy, and they are methods for helping the audience listen, retain information, and follow your structure. In fact, it’s one thing to have a well-organized speech. It’s another for the audience to be able to “consume” or understand that organization.
Connectives in general perform several functions:
- Remind the audience of what has come before
- Remind the audience of the central focus or purpose of the speech
- Forecast what is coming next
- Help the audience have a sense of context in the speech—where are we?
- Explain the logical connection between the previous main idea(s) and next one or previous sub-points and the next one
- Explain your own mental processes in arranging the material as you have
- Keep the audience’s attention through repetition and a sense of movement
Connective statement can include “internal summaries,” “internal previews” “signposts” and “bridging or transition statements.” Each of these helps connect the main ideas of your speech for the audience, but they have different emphases and are useful for different types of speeches.
Types of connectives and examples
Internal summaries emphasize what has come before and remind the audience of what has been covered.
“So far I have shown how the designers of King Tut’s burial tomb used the antechamber to scare away intruders and the second chamber to prepare royal visitors for the experience of seeing the sarcophagus.”
Internal previews let your audience know what is coming up next in the speech and what to expect regarding the content of your speech.
“In this next part of the presentation I will share with you what the truly secret and valuable part of the King Tut’s pyramid: his burial chamber and the treasury.”
Signposts emphasize physical movement through the speech content and let the audience know exactly where they are. Signposting can be as simple as “First,” “Next,” “Lastly” or numbers such as “First,” “Second,” Third,” and “Fourth.” Signposting is meant to be a brief way to let your audience know where they are in the speech. It may help to think of these like the mile markers you see along interstates that tell you where you’re and how many more miles you will travel until you reach your destination.
“The second aspect of baking chocolate chip cookies is to combine your ingredients in the recommended way.”
Bridging or transition statements emphasize moving the audience psychologically to the next step.
“I have mentioned two huge disadvantages to students who don’t have extracurricular music programs. Let me ask: Is that what we want for our students? If not, what can we do about it?”
They can also serve to connect seemingly disconnected (but related) material, most commonly between your main points.
“After looking at how the Cherokee Indians of the North Georgia mountain region were politically important until the 1840s and the Trail of Tears, we can compare their experience with that of the Indians of Central Georgia who did not assimilate in the same way as the Cherokee.”
At a minimum, a bridge or transition statement is saying, “Now that we have looked at (talked about, etc.) X, let’s look at Y.”
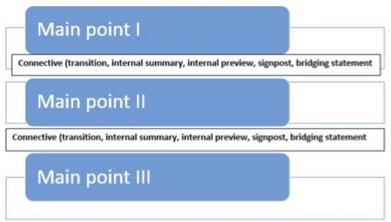
There’s no standard format for connectives. However, there are a few pieces of advice to keep in mind about them:
First, connectives are for connecting main points. They are not for providing evidence, statistics, stories, examples, or new factual information for the supporting points of the main ideas of the speech.
Second, while connectives in essay writing can be relatively short—a word or phrase, in public speaking, connectives need to be a sentence or two. When you first start preparing and practicing connectives, you may feel that you’re being too obvious with them, and they are “clunky.” Some connectives may seem to be hitting the audience over the head with them like a hammer. While it’s possible to overdo connectives, it’s less likely than you would think. The audience will appreciate them, and as you listen to your classmates’ speeches, you’ll become aware of when they are present and when they are absent.
Lack of connectives results in hard-to-follow speeches where the information seems to come up unexpectedly or the speaker seems to jump to something new without warning or clarification.
Finally, you’ll also want to vary your connectives and not use the same one all the time. Remember that there are several types of connectives.
Patterns of Organization
At the beginning of this chapter, you read the analogy that a speech structure is like a house and organization is like the arrangement of the rooms. So far, we have talked about structure. The introduction, body, main point, sub-point, connectives—these are the house. But what about the arrangement of the rooms? How will you put your main points in a logical order?
There are some standard ways of organizing the body of a speech. These are called “patterns of organization.” In each of the examples below, you’ll see how the specific purpose gives shape to the organization of the speech and how each one exemplifies one of the six main organizational patterns.
Please note that these are simple, basic outlines for example purposes. The actual content of the speech outline or manuscript will be much further developed.
Chronological Pattern
Specific Purpose: To describe to my classmates the four stages of rehabilitation in addiction recovery.
Main Points:
- The first stage is acknowledging the problem and entering treatment.
- The second stage is early abstinence, a difficult period in the rehabilitation facility.
- The third stage is maintaining abstinence after release from the rehab facility.
- The fourth stage is advanced recovery after a period of several years.
The example above uses what is termed the chronological pattern of organization . Chronological always refers to time order. Organizing your main points chronologically is usually appropriate for process speeches (how-to speeches) or for informational speeches that emphasize how something developed from beginning to end. Since the specific purpose in the example above is about stages, it’s necessary to put the four stages in the right order. It would make no sense to put the fourth stage second and the third stage first.
Chronological time can be long or short. If you were giving a speech about the history of the Civil Rights Movement, that period would cover several decades; if you were giving a speech about the process of changing the oil in a car, that process takes less than an hour. Whether the time is long or short, it’s best to avoid a simple, chronological list of steps or facts. A better strategy is to put the information into three to five groups so that the audience has a framework. It would be easy in the case of the Civil Rights Movement to list the many events that happened over more than two decades, but that could be overwhelming for the audience. Instead, your chronological “grouping” might be:
- The movement saw African Americans struggling for legal recognition before the landmark 1954 Brown v. Board of Education decision.
- The movement was galvanized and motivated by the 1955-1956 Montgomery Bus Boycott.
- The movement saw its goals met in the Civil Rights Act of 1965.
In this way, the chronological organization isn’t an overwhelming list of events. It focuses the audience on three events that pushed the Civil Rights movement forward.
Spatial Pattern
You can see that chronological is a highly-used organizational structure, since one of the ways our minds work is through time-orientation—past, present, future. Another common thought process is movement in space or direction, which is called the spatial pattern . For example:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the three regional cooking styles of Italy.
- In the mountainous region of the North, the food emphasizes cheese and meat.
- In the middle region of Tuscany, the cuisine emphasizes grains and olives.
- In the southern region and Sicily, the diet is based on fish and seafood.
In this example, the content is moving from northern to southern Italy, as the word “regional” would indicate. For a more localized example:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the layout of the White House.
- The East Wing includes the entrance ways and offices for the First Lady.
- The most well-known part of the White House is the West Wing.
- The residential part of the White House is on the second floor. (The emphasis here is the movement a tour would go through.)
For an even more localized example:
Specific Purpose: To describe to my Anatomy and Physiology class the three layers of the human skin.
- The outer layer is the epidermis, which is the outermost barrier of protection.
- The second layer beneath is the dermis.
- The third layer closest to the bone is the hypodermis, made of fat and connective tissue.
Topical / Parts of the Whole Pattern
The topical organizational pattern is probably the most all-purpose, in that many speech topics could use it. Many subjects will have main points that naturally divide into “types of,” “kinds of,” “sorts of,” or “categories of.” Other subjects naturally divide into “parts of the whole.” However, as mentioned previously, you want to keep your categories simple, clear, distinct, and at five or fewer.
Specific Purpose: To explain to my first-year students the concept of SMART goals.
- SMART goals are specific and clear.
- SMART goals are measurable.
- SMART goals are attainable or achievable.
- SMART goals are relevant and worth doing.
- SMART goals are time-bound and doable within a time period.
Specific Purpose: To explain the four characteristics of quality diamonds.
- Valuable diamonds have the characteristic of cut.
- Valuable diamonds have the characteristic of carat.
- Valuable diamonds have the characteristic of color.
- Valuable diamonds have the characteristic of clarity.
Specific Purpose: To describe to my audience the four main chambers of a human heart.
- The first chamber in the blood flow is the right atrium.
- The second chamber in the blood flow is the right ventricle.
- The third chamber in the blood flow is the left atrium.
- The fourth chamber in the blood flow and then out to the body is the left ventricle.
At this point in discussing organizational patterns and looking at these examples, two points should be made about them and about speech organization in general:
First, you might look at the example about the chambers of the heart and say, “But couldn’t that be chronological, too, since that’s the order of the blood flow procedure?” Yes, it could. There will be times when a specific purpose could work with two different organizational patterns. In this case, it’s just a matter of emphasis. This speech emphasizes the anatomy of the heart, and the organization is “parts of the whole.” If the speech’s specific purpose were “To explain to my classmates the flow of blood through the chambers of the heart,” the organizational pattern would emphasize chronological, altering the pattern.
Another principle of organization to think about when using topical organization is “climax” organization. That means putting your strongest argument or most important point last when applicable. For example:
Specific purpose: To defend before my classmates the proposition that capital punishment should be abolished in the United States.
- Capital punishment does not save money for the justice system.
- Capital punishment does not deter crime in the United States historically.
- Capital punishment has resulted in many unjust executions.
In most people’s minds, “unjust executions” is a bigger reason to end a practice than the cost, since an unjust execution means the loss of an innocent life and a violation of our principles. If you believe Main Point III is the strongest argument of the three, putting it last builds up to a climax.
Cause & Effect Pattern
If the specific purpose mentions words such as “causes,” “origins,” “roots of,” “foundations,” “basis,” “grounds,” or “source,” it’s a causal order; if it mentions words such as “effects,” “results,” “outcomes,” “consequences,” or “products,” it’s effect order. If it mentions both, it would of course be cause/effect order. This example shows a cause/effect pattern:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the causes and effects of schizophrenia.
- Schizophrenia has genetic, social, and environmental causes.
- Schizophrenia has educational, relational, and medical effects.
Problem-Solution Pattern
The principle behind the problem-solution pattern is that if you explain a problem to an audience, you shouldn’t leave them hanging without solutions. Problems are discussed for understanding and to do something about them. This is why the problem-solution pattern is often used for speeches that have the objective of persuading an audience to take action.
When you want to persuade someone to act, the first reason is usually that something needs fixing. Let’s say you want the members of the school board to provide more funds for music at the three local high schools in your county. What is missing because music or arts are not funded? What is the problem ?
Specific Purpose: To persuade the members of the school board to take action to support the music program at the school.
- Students who don’t have extracurricular music in their lives have lower SAT scores.
- Schools that don’t have extracurricular music programs have more gang violence and juvenile delinquency.
- $120,000 would go to bands.
- $80,000 would go to choral programs.
Of course, this is a simple outline, and you would need to provide evidence to support the arguments, but it shows how the problem-solution pattern works.
Psychologically, it makes more sense to use problem-solution rather than solution-problem. The audience will be more motivated to listen if you address needs, deficiencies, or problems in their lives rather than giving them solutions first.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
A variation of the problem-solution pattern, and one that sometimes requires more in-depth exploration of an issue, is the “problem-cause-solution” pattern. If you were giving a speech on the future extinction of certain animal species, it would be insufficient to just explain that numbers of species are about to become extinct. Your second point would logically have to explain the cause behind this happening. Is it due to climate change, some type of pollution, encroachment on habitats, disease, or some other reason? In many cases, you can’t really solve a problem without first identifying what caused the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the age to obtain a driver’s license in the state of Georgia should be raised to 18.
- There’s a problem in this country with young drivers getting into serious automobile accidents leading to many preventable deaths.
- One of the primary causes of this is younger drivers’ inability to remain focused and make good decisions due to incomplete brain development.
- One solution that will help reduce the number of young drivers involved in accidents would be to raise the age for obtaining a driver’s license to 18.
Some Additional Principles of Speech Organization
It’s possible that you may use more than one of these organizational patterns within a single speech. You should also note that in all the examples to this point (which have been kept simple for the purpose of explanation), each main point is relatively equal in emphasis; therefore, the time spent on each should be equal as well. You would not want your first main point to be 30 seconds long, the second one to be 90 seconds, and the third 3 minutes. For example:
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the rules of baseball.
- Baseball has rules about equipment.
- Baseball has rules about the numbers of players.
- Baseball has rules about play.
Main Point #2 isn’t really equal in size to the other two. There’s a great deal you could say about equipment and even more about the rules of playing baseball, but the number of players would take you about ten seconds to say. If Main Point #2 were “Baseball has rules about the positions on the field,” that would make more sense and be closer in level of importance to the other two.
The organization of your speech may not be the most interesting part to think about, but without it, great ideas will seem jumbled and confusing to your audience. Even more, good connectives will ensure your audience can follow you and understand the logical connections you’re making with your main ideas. Finally, because your audience will understand you better and perceive you as organized, you’ll gain more credibility as a speaker if you’re organized. A side benefit to learning to be an organized public speaker is that your writing skills will improve, specifically your organization and sentence structure.
Roberto is thinking about giving an informative speech on the status of HIV-AIDS currently in the U.S. He has different ideas about how to approach the speech. Here are his four main thoughts:
- pharmaceutical companies making drugs available in the developing world
- changes in attitudes toward HIV-AIDS and HIV-AIDS patients over the last three decades
- how HIV affects the body of a patient
- major breakthroughs in HIV-AIDS treatment
Assuming all these subjects would be researchable and appropriate for the audience, write specific purpose statements for each. What organizational patterns would he probably use for each specific purpose?
Media Attributions
- Speech Structure Flow © Mechele Leon is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Connectives
- https://blog-college.ku.edu/tag/study-abroad-stories/ ↵
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Write a Speech to Engage your Audience
February 19, 2021 - Dom Barnard
In order to write a speech, you need to think about your audience, the required length, and the purpose or topic. This is true whether you are writing a wedding speech, conference presentation, investor pitch, or any other type of speech.
Being a great speech writer can help you get a promotion, motivate people, sell a business idea, persuade others and much more – it’s an essential skill in the modern world. In this article, we cover key tips for writing a speech.
Initial planning – Why? Who? What?
You should invest time strategically considering the speech. This will help you decide on the key message and content about your topic. Here are some points to consider.
- What do I want to achieve?
- When I achieve this, what will that do for me?
- Why am I speaking?
- What is the purpose of this speech?
- Who are the audience and who do they represent?
- Who do I represent?
- What do I know about them? (culture, language, level of expertise)
- How much influence do they have?
- What is the main message and key points?
- What specific action is implied?
- What level of information should I include?
- What is important to them?
Popular speech structure
You need to catch the audience attention early, very early (see section below). Deliver a memorable beginning, a clear middle and structured ending.
Popular speech structure:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
Secondary Point (Optional: supports main)
Tertiary Point (Optional: supports secondary and main)
Attention span of your audience
Research shows that attention span is greatest at the beginning of a speech, reduces considerably during the middle of your speech and picks up again towards the end when your audience know you about to finish.
Don’t try to put too many ideas into your speech. Research shows that people remember very little from speeches, so just give them one or two ideas to hang onto.

These two articles explain audience attention span in more detail, and how to write a speech to extend it:
- How many minutes is the audience’s attention span?
- What to do when you’re losing your audience
Speech introduction
Make sure your opening few seconds are memorable as this is when your audience will make up their minds about you. Use a bold sentence to grab their attention, works best with numbers reinforcing your point.
An example sentence might be – “After this speech, I’m confident 50% of you will go out and buy a VR headset.” Follow these tips on how to write a speech intro:
Remember the INTRO model
This is more focused on presentations but sections can be applied broadly to other general speeches.
1. Interest
You: Introduce yourself confidently and clearly Audience: Why should I listen to you?
You: Remind the audience the reasons for this speech Audience: What’s in it for me?
You: State length of speech at beginning, “Over the next 15 minutes” Audience: How long until I can get a coffee?
4. Routemap
You: State the main points, “Today I’m going to cover 4 main points” Audience: Which sections of the speech are important to me?
5. Objectives
You: Clearly state the objective, “By the end of this speech, I would like to…” Audience: So that’s what you want from me today…
Example: Great speech opening
This speech opening is by Jamie Oliver, giving a TED talk on teaching every child about food.
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead through the food that they eat. My name’s Jamie Oliver. I’m 34 years old. I’m from Essex in England and for the last seven years I’ve worked fairly tirelessly to save lives in my own way. I’m not a doctor; I’m a chef, I don’t have expensive equipment or medicine. I use information, education. I profoundly believe that the power of food has a primal place in our homes that binds us to the best bits of life. We have an awful, awful reality right now. America, you’re at the top of your game. This is one of the most unhealthy countries in the world.

How not to open your speech
Avoid the following opening comments:
- “ Apologies, I’m a little nervous about speaking ” – no need to make the audience aware of this, it will make them focus on how nervous you are instead of what you are saying
- “ I’ve got the graveyard shift ” – you are telling people not to expect much
- “ I’m what stands between you and lunch ” – even if people weren’t thinking it, after this comment, all they are thinking of is when will you finish so they can eat
- “ We are running late, so I’ll do my best to explain… ” – instead of this, state how long your speech will take so that people know when they will be leaving
Middle of the speech
The body of your speech is where the majority of the information is. The audience has been introduced to the subject and reasons for the speech. Now you need to present your arguments and examples, data, illustrations backing up your key message.
How to write a speech body can be difficult, the best way to build this section is to write down three points you are trying to convey in your speech, your main, secondary and tertiary points. Then write down three descriptions clarifying each of these points. The descriptions should be simple, memorable and meaningful.
The middle of your speech is where the audience start losing attention. Keep this in mind and ensure your message is clear. Use images, jokes and rhetoric questions to keep the audience engaged.
Don’t overwhelm your audience with many points. It is much more valuable to make a small number of points well, than to have too many points which aren’t made satisfactorily.

Obama and his speeches
Obama’s speeches are well prepared with a focus on powerful words “A change is brought about because ordinary people do extraordinary things“. His speeches use simple language and quotes from famous speeches his listeners can relate to.
For additional trademark Obama techniques, check out How Barack Obama prepares his speeches.
How to end a speech
Similar to the opening, your closing statements should be impactful, re-stating the key message of your speech. We advise learning your ending few lines word for word. The ending is an opportunity to:
- Leave the audience with a lasting impression of your speech
- Summarise the main points
- Provide further ideas and discussion points for the audience to take away with them
- Thank the audience for taking the time to listen
Methods to end your speech
Quotation Close – use a famous quote to get the audience’s attention and create a link to your speech.
Bookend Close – refer back to an opening statement and repeat it or add a few extra words to elaborate on it.
Open Question – ask the audience a provocative question or a call to action to perform some task on the back of your speech.
For additional tips on how to write a speech, in particular how to close your speech, read:
- 5 great ways to end a speech
- 10 ways to end your speech with a bang
- Presentations: language expert – signposting
Ideas for ending a speech
- Key message
- Refer to opening impact statement
- Objectives met
- Call to action
- End on an Up
Step-by-step process for writing a speech
Here’s how to write your speech from concept to completion.
- Outline your speech’s structure. What are the main ideas for each section?
- Write out the main ideas in your outline. Don’t worry about making it perfect – just write as much of it down as you can
- Edit and polish what you’ve written until you have a good first draft of your speech
- Now you need to practice and memorize your speech . The more you practice, the more you’ll figure out which sections need changing. You’ll also get an idea of length and if you need to extend / shorten it.
- Update your speech, practice some more, and revise your speech until it has a great flow and you feel comfortable with it.
Classic speech transcripts
One of the best ways for learning how to write a speech is reading other well written ones. Here are a list of famous speeches to read and learn from:
- Bill Gates TED Talk Transcript from 2015: Warns of Pandemics, Epidemics
- Facebook COO Sheryl Sandberg Commencement Speech at Harvard 2014
- Ronald Reagan Memorial Day Speech Transcript 1984
- I Have Been to the Mountaintop Speech Transcript – Martin Luther King Jr.
Writing a speech
Topic outline.
The purpose of a speech is often to inform or persuade an audience.
Speeches are usually written to be spoken directly to an audience and can be used to entertain, influencing the listeners that the viewpoint of the speaker is correct.
Speeches can also be used to encourage the audience to take action or to change their behaviour in some way; for example, to join a particular school club or society, or to recycle more.
The ways you use language and vocabulary when writing the words of a speech will depend on the audience and the purpose you are writing for; for example, in a speech to a group of teachers and parents giving your views on a recent proposal, formal language is most appropriate.
- think about the audience that the speech is for – are you giving your speech to a group of people you know, or do not know, or a mixture of both? If you know your audience well, you may be able to relax a little, but a speech is still a formal kind of talk and would usually not include slang
- whether your audience are likely to disagree with what you say – you will need to consider any possible objections and deal with them. Use language carefully to make objections seem less significant; for example, using phrases like ‘A few people may still think, however’
- the reason you are giving this speech and how you feel about this topic – try to imagine the words of your speech as you would speak them out loud. Your tone of voice must match your message, so choose words that appeal to the emotions of your listeners. Focus on what you want your audience to know and feel by the end of your speech
- how to engage your listeners – f or example, you might use inclusive words or phrases like ‘we’, ‘all of us’ and ‘our’ to make your listeners feel that you are all on the same side.
- Plan where you want to finish your speech and how you will get there before you start writing – t h e structure of a speech is usually in three parts. For example:
- An opening that grabs your audience's attention and makes the overall topic of your speech clear – for example, pose a question to the audience where you can predict the answer.
- A well-structured, supported and developed argument – for example, to support your argument you might use real life examples or anecdotes.
- A powerful conclusion – for example, group your final words or ideas in threes to help make them memorable or end with a thought- provoking question or image and thank your audience for listening.
- Organise your ideas into paragraphs as appropriate – this will help you to develop and support your points convincingly, to build your argument and/or offer a full explanation of a particular point of view.
- S how the connectio ns between ideas in sentences and paragraphs – where a new point or idea follows on from what you have already said you might use linking words or phrases such as, ‘in addition’, ‘likewise’ or ‘similarly’.
- Select activity Example of a speech Example of a speech
- Select activity Resource Resource
Oratory Club
Public Speaking Helpline

How to Structure a Speech?
To structure a speech, start with a clear opening, support your main points with evidence, and conclude with a strong ending. By following this structure, you will engage your audience and deliver a compelling message that sticks in their minds.
Now, let’s dive into the details and explore how to structure a speech effectively. A well-structured speech is like a road map that guides both the speaker and the audience. It ensures that your ideas flow logically and your message resonates with your listeners.
Whether you’re presenting in a corporate setting, giving a TED talk, or speaking at a social event, a solid speech structure is crucial for success. We will discuss the essential elements of structuring a speech that captures attention, conveys your message effectively, and leaves a lasting impact. So, let’s get started with the opening of your speech.
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Table of Contents
In order to structure a speech effectively, it is essential to follow these six guidelines. By avoiding overused words, keeping sentences concise, utilizing a range of phrases, and maintaining a human-like tone, your speech will engage and captivate your audience.
Remember to adhere to these guidelines for an impactful and well-structured speech.
Understand Your Audience
Develop a clear structure, craft a strong opening, organize your main points, deliver a memorable conclusion.

Credit: m.youtube.com

Credit: www.tes.com
Frequently Asked Questions For How To Structure A Speech?
What are the 5 sections of a speech.
The 5 sections of a speech are introduction, body, main points, supporting details, and conclusion.
What Are The 7 Steps To Writing A Speech?
The 7 steps to writing a speech are as follows: 1. Determine your topic and purpose. 2. Conduct thorough research and gather relevant information. 3. Create an outline or structure for your speech. 4. Write a compelling introduction to grab your audience’s attention.
5. Develop clear main points and supporting arguments or evidence. 6. Craft a memorable conclusion that reinforces your main message. 7. Practice and revise your speech to ensure clarity and effective delivery.
What Are The 5 Major Steps In Speech Writing?
The 5 major steps in speech writing include: 1. Research the topic thoroughly to gather relevant information. 2. Organize the speech by creating an outline or structure. 3. Write a compelling introduction to grab the audience’s attention. 4. Develop the body of the speech with logical points and supporting evidence.
5. Conclude with a memorable closing statement that leaves a lasting impression.
What Are The 5 Ways To Organize A Speech?
The five ways to organize a speech include: chronological order, spatial order, topical order, problem-solution order, and cause-effect order.
How Do You Structure A Speech?
To structure a speech effectively, start with a strong introduction, followed by clear main points, and end with a memorable conclusion.
An effective speech structure is crucial for engaging and captivating your audience. By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you can create a well-organized and impactful speech. Remember to start with a strong introduction, use clear transitions between main points, and end with a powerful conclusion.
Practice and confident delivery will help you deliver a memorable speech that resonates with your audience.
Similar Posts

Why Should You Consider the Context of Your Communication?
To effectively communicate, it is crucial to consider the context of your communication. This helps ensure the message is understood and received accurately. By considering the context, you can tailor your communication to suit the specific situation and audience, leading to better engagement and outcomes. Taking into account the context allows you to be mindful…

How to Improve Your Communication Skills Instantly?
To improve your communication skills instantly, practice active listening and use clear and concise language. Effective communication is essential for building positive relationships and achieving success in both personal and professional settings. By honing your communication skills, you can convey your ideas more effectively, understand others better, and enhance your overall communication experience. We will…

How to Cut off Communication With Someone You Love
To cut off communication with someone you love, identify the reason and release your emotions. Don’t react, start small, keep a journal, meditate, be patient, and look forward. Acknowledge the truth, identify needs, accept what the love meant, look to the future, prioritize other relationships, spend time on yourself, give yourself space, and understand it…

How to Practice Communication Skills Alone?
To practice communication skills alone, you can practice in front of a mirror, which allows you to observe your body language and gain a new perspective on your delivery. This technique helps you become more aware of how your audience will perceive your speech and can enhance your overall communication skills. It’s a convenient and…
Effective Conversation Skills
Effective conversation skills are crucial for successful communication and building strong relationships. With clear and concise communication, individuals can convey their thoughts, ideas, and emotions effectively. Developing these skills involves active listening, empathy, and the ability to articulate thoughts clearly. Additionally, maintaining good eye contact and using appropriate body language are essential for effective communication….
Communications Vs Public Relations: Get To Know Which Is Right For You?
Are you curious about the difference between communications and public relations? You’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll explore these two fields and uncover their unique characteristics. So, let’s dive in and discover the exciting world of communications and public relations! When it comes to communications, it’s all about conveying information effectively…
Writing Center Speech Structure
Section navigation, a guide to basic speech structure.
“A Speech is not an essay up on its hind legs!”
T he biggest difference between preparing a speech and preparing an essay is the audience. The essay’s audience—a reader—takes in the written ideas through the eyes. A public presentations’ audience, however, understands the speaker’s ideas by seeing, hearing and “feeling” the speaker by using their eyes, ears and heart. If an essay’s ideas aren’t clear, its audience can read the words over and over again. When speaking in front of a live audience, however, you only have one shot at getting your point across.
Good news! You can get your point across in one shot with structure.
I like to think of a speech as a journey that you and your audience take together. You don’t want to lose your audience, so plan for a clear beginning (introduction), middle (body) and end (conclusion).
FIRST: Decide where you’re going. Where are you taking your audience? We call this your PURPOSE, and speakers often begin their planning by writing a purpose statement .
Purpose statements are ambitious, active and audience focused.
Here are some examples:
- My purpose is to teach my audience three ways they can turn data into clear, useful charts.
- My purpose is to persuade my audience to vote for this new idea because it’s affordable, quick to implement and will have long-lasting positive impact.
- My purpose is to inspire my audience by sharing research that may predict sustainable life on Mars.
A purpose statement is critical in speech planning because:
- It keeps you “one sentence clear.” You know where you’re headed with the audience.
- It basically writes the body of your speech for you. (three ways to turn data into charts; vote because it’s affordable, quick and lasting; the two to three ways my research might predict sustainability on Mars...)
- It gives you a way to evaluate how successful you were after your presentation. Ask yourself: Did I achieve my purpose?
Now that you have your purpose statement, you can write your Introduction, right? WRONG!
Begin writing your speech by outlining the body of the speech first. Then write the introduction. You can’t introduce what you haven’t written yet, so begin with the body of the speech first.
Ultimately, the outline of your speech will have an introduction, a body and a conclusion.
Introduction
- Engage the audience. Start with a story, a startling statement, statistic, or a question that grabs your audience’s attention. The best presentations begin by answering “why...” In other words, why you are excited about your research or speech topic, and most important, why the audience should care. Watch Simon Sinek’s TED talk for inspiration.
- Focus the presentation. Now that your audience knows why they should care, state your thesis or goal. Let your audience know what they’ll learn.
- Preview the presentation’s structure, content or approach to let the audience know how the presentation will unfold.
Organize your talk logically and clearly around 2-3 main points or arguments. For each major section of your presentation, follow the “4 S Structure” 1 :
- Signpost the point (“First, I’m going to point out the problem with...” My second argument is that...” “Now let me explain my methodology.”)
- State the point clearly and succinctly
- Support the point with data, cases, description, relevant studies, etc.
- Summarize the point
Then make a clear transition to the next major section.
Summarize and re-focus. Review key points or arguments. Restate the thesis.
- Close. Create a closing statement. Nodding back to the introduction can alert the audience that the speech has come to an end and provides a satisfying sense of final closure. Avoid using “Thank you” as your conclusion. Wait until the audience applauds. Then, thank them for that.
Audience Questions
1. Adapted from Joyce Ferguson, “Speaking Across the Curriculum at UNCG,” in Communication Across the UNCG Curriculum: A Guide for Faculty, ed. Karen Meyers, University of North Carolina—Greensboro, 2002.
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- Blogging Aloud
- About me/contact
- How to outline a speech
Sample speech outline template
Get a printable. Learn how to outline a speech effectively.
By: Susan Dugdale
There's a printable sample speech outline template below for you to download, and use.
Why? Because a well-completed outline becomes the backbone of your speech. You'll use it to guide you logically, and carefully, through ALL the aspects you need to consider before you actually write the speech itself.
It will help you clarify what material you want to cover to fit your audience, and speech purpose, as well as help to effectively organize it.

What you'll find on this page:
- t he reasons for using a speech outline
- how to outline a speech : the 4 essentials steps involved in writing an outline - detailed sequential help, with examples, covering: 1. choosing a topic, 2. audience analysis, 3. choosing the best organizational pattern to fit your speech purpose, 4. what to put in each part of your speech: introduction, body and conclusion
- a printable speech outline template to download
- links to 2 completed examples of speech outlines (a demonstration and a persuasive speech. Both with printable outlines to download.)
- a link to 7 completed examples of impromptu speech outlines , each with printable speech outline templates
- links to more resources for preparing an effective speech
Why bother writing a speech outline?
Because completing a speech outline is the first vital step toward preparing a successful speech.

It is often overlooked in a misguided attempt to get on with what is considered the real work: writing the speech, or the words you're going to say.
Despite what many people think, time spent completing an outline is not wasted. Instead, it helps you save it. A nd sidestep any anxiety caused by inadequate preparation.
The process might appear daunting and horrifically time consuming but prepare a speech outline all the same.☺
What you'll learn about speech structure, matching content to your speech purpose and your audience's needs will pay you back over and over again. I promise you, having an outline will make giving a speech easier and less stressful.
How to best use this page
Read the page all the way through to familiarize yourself with the terms and the process. When you're done, click the link at the foot of the page to download and print the blank sample speech outline template for your own use.
How to outline a speech: 4 essential steps
The process of outlining a speech is broken down into 4 essential steps.
(Click a heading to find out more about each one)
- deciding on your topic
- considering the audience and refining your topic to suit them
- deciding on the purpose of the speech
- choosing an organizational method to support your speech purpose
- opening greeting and attention getter
- defining your thesis statement (a summary of what your speech is about)
- establishing your credibility
- an overview and the benefit to the audience
- transition or link between introduction and body
- main ideas with supporting ideas
- examples and details
- summary of main points
- closer or call to action
Remember this old saying?
First: tell them what you're going to tell them. Second: tell them. Third: tell them what you told them.
A simple, or basic, speech outline follows that advice.
- 'Tell them what you're going to tell them' becomes your introduction
- 'Tell them' forms the body
- 'Tell them what you told them' is your conclusion
Step 1 - Preparation for writing a speech outline
You need to complete this step before you do anything else. It is made up of five smaller steps, each of them an important part of the overall process. The decisions you make at this point will have a major impact on the final outcome of your speech.
By the time you are finished step 1 you will have:
- decided on your topic
- analyzed your audience
- refined your topic to meet the needs of your audience
- decided on the specific purpose of your speech
- chosen the best fitting of six organizational patterns to use - one matching your purpose and your material

Start with choosing a topic
The place to begin is deciding what you are going to talk about.
For example, if you are a realtor (real estate agent) who has been asked to talk to a suburban community group residential real estate seems like a good logical topic to pick.
(If you don't have a topic in mind, go to speech topics . You'll find 100s of them ordered by speech type and theme.)
Put yourself to one side & focus on your audience
However, before you make a final decision considering more closely who will be listening to you makes better sense than assuming whatever you come up with will be right!
How do you really know what aspects of your topic are best suited to meet your audience's needs? Or what would be of real benefit for them to hear about?
The scope of the topic 'residential real estate' is huge.
Your speech could cover any number of sub-topics like: financial advice for first home buyers, how to thoroughly check a house before purchase, the rise of mortgagee default sales, the collapse of property development schemes, how to purchase properties for makeovers...
Analyze your audience
So before you settle on the exact topic of your speech analyze your audience .
Without analysis you are 'guessing' what would be interesting and relevant for them to hear.
Refine your topic
Using what you found out about your audience, decide on an aspect of your topic that will be of benefit to them and the angle you will take on it. Take care with this. One size does not fit all!
For example a speech on housing affordability which includes a step by step plan toward buying a first home will likely interest an audience of youngish, (late 20s- early 40s), people with steady professional incomes.
But for another audience, (e.g. one that is older, less financially secure, or younger and not ready to consider settling yet...), it could be completely inappropriate.
Minimize the risk of getting it wrong by finding out as much as you can about your audience.
Deciding on the purpose of your speech
What is the purpose of this speech? Why are you giving it?
Is it to persuade or inform? Is it to demonstrate, entertain, or welcome? Or is it a combination of these?
What do you want your speech to achieve? Is there a particular action you want people to take as a result of listening to you?
Your answers to all of these questions will dictate what organizational pattern you'll use for your speech, its content and tone.
Return to Top
Choosing an organizational pattern or method

There are 6 basic organizational patterns or methods of arranging the body (main points) of your material. Choose the one most appropriate for your need.
1. Cause - Effect
Because event 'A' happened, event 'B' occurred.
- Because the driver was speeding, they crashed the car.
- Because of the earthquake, the city was destroyed.
- Because the minimum wage is low, families can not afford good health care.
2. Problem - Solution
The problem is 'X'. The answer is 'Y'.
- The problem is unaffordable housing. The solution is community funded housing complexes.
- The problem is unemployment. The solution is meaningful, sustainable education and employment programs.
- The problem is poor food choices. The solution is practical community outreach programs to teach people about nutrition, food buying, storage and preparation, along side living wages, educational and employment programs.
This pattern suits a broad topic which can be broken down into naturally occurring sub-topics.
- The broad topic is 'Vocal Variety'. Its sub-topics include rate of speech, use of pausing, voice tone, volume, articulation...
- The broad topic is 'Organizational speech patterns'. Sub-topics could be problem-solution, cause- effect, logical...
- The broad topic is 'Residential real estate'. Its sub-topics could include houses for first-home buyers, how to apply for a mortgage, how to select the right neighborhood to buy in, the impact of high-density housing...
4. Spatial or geographic
Use this pattern for topics dealing with physical spaces.
- The 10 most popular tourist attractions in New Zealand.
- The European migration patterns of the 19th century.
- The population shift from country to town in USA.
5. Time or chronological/sequential
These are either historical topics or demonstration speeches. The foundation of both is an ordered sequence of events.
For example:
- The history of women's suffrage in USA, the abolition of slavery
- How to bake a cake, how to mend a puncture in a bicycle tire, or how to knot a tie
6. Advantage - disadvantage
Use this pattern to examine the range of positive and negative aspects of an idea or event.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of private schooling?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of lowering the voting age?
- What is good about supporting local industry? What is negative about supporting local industry?
Step Two - Outlining the introduction

The 5 parts of preparing an introduction
1. greeting & attention getter.
How are you going to greet your audience, grab their attention and compel them to listen?
You could use a rhetorical question, a startling statistic, a quotation or a humorous one-liner. To be effective it must be related to your topic and apt for your audience.
- Rhetorical question How many of you really are more afraid of public speaking than death?
- A startling statistic Apparently in USA 75% of the population experiences public speaking anxiety. Some just a little. And some a lot.
- A quotation Mark Twain famously said, there are only two types of speakers in the world: the nervous and the liars.
- Humorous Speaker of United States House of Representatives, Nancy Pelosi set a record for the longest speech on the House floor: 8 hours and 7 minutes. Relax. I only plan on taking 15 minutes of your valuable time. * * Be careful with humor. It will only work if it's appropriate; that is fitting for the occasion, and understood by the majority of your audience. For more about Nancy's record: Nancy Pelosi's all-day marathon speech sets record as longest continuous speech since at least 1909.
For more on effective speech openings see: How to write a speech introduction - 12 of the best ways to start a speech
2. Thesis statement
This is a short summary of your speech topic and your point of view or angle.
Example:
Green politics is no longer a fanciful fringe fad. It is a necessity.
3. Credibility
This segment establishes your right to speak on the topic. It cites your qualification or expertise.
Using myself as an example, I can speak about preparing speeches because I've written many over the past twenty or so years. Prior to becoming a professional speech writer , I taught high school level English and drama and I also belonged to the global public speaking club Toastmasters for a long time.
4. Summative overview
This is a brief outline of the main points you are going to cover.
Today I am going to share with you three effective ways to lessen public speaking fear.
The first and second cover aspects of preparation: writing and rehearsal or practice: actually doing the work, rather than being frightened of it. ☺ The third is about the benefits of public speaking.
5. Benefit(s)
What's in your speech for your audience? Why will they want to hear what you've got to tell them? Be specific. Tell them.
When you make a decision to speak up in public you also gain: confidence, the ability to take on leadership roles, a growing collection of presentation skills like story telling, how to use your voice, the ability to use props well, how to listen, how to craft a speech to meet the needs of specific audiences... In short, you release the potential to become a bigger and better you * .
( * For more see 14 benefits of public speaking .)
Step Three - Outlining the body of your speech
This is the heart of your speech, the place where you lay out what you want to share with your audience.
Generally three main ideas, along with supporting examples, work more effectively than four or five or more. If you have a number of them to choose from, go with your three strongest points. And if one of your final three is noticeably weaker sandwich it between the other two.
If you intend to use visual aids (slides showing graphs, tables or images), or actual props, mark them in too.

Note: If you're unsure about the exact nature of links or transitions and how they work or what they are, you'll find more about them, with examples, on my page how to write a speech
- Main Idea 3 - Supporting ideas - Details and examples - Visuals or props - Transition to...
Step Four - Outlining the conclusion of your speech
There are four parts to preparing an effective conclusion to your speech. Use them to draw together and summarize all the material from your introduction and the body of your speech, and end with a clincher!

- Summary of main ideas These are the main points you covered in the body of your speech.
- Re-statement of thesis statement Use the statement from your introduction to reinforce your message.
- Re-statement of benefit to audience Remind the audience of the benefits they'll receive through carrying out whatever your propose. Again this comes from your introduction.
- Closer, Clincher or Call to Action This is your final sentence. To ensure your speech ends with a bang rather than a whimper check out this page on how to end a speech memorably. You'll find options and examples.
Get your printable sample speech outline template
This is a simple four page PDF of all four steps and their sub- headings with spaces for you to write your notes. Click to download and print your sample speech outline now.

2 completed examples of speech outlines
Use these links to go to a fully completed:
- demonstration speech outline example on how to leave an effective voice mail message (with a free printable sequential demonstration speech outline template)
- persuasive speech topic outline example on overcoming public speaking fear using Monroe's Motivated Sequence (with a free printable MMS persuasive speech outline template)
Example impromptu speech outline patterns
Impromptu speech outline patterns - seven different structural formats, each with completed examples and a free blank printable outline for you to download and use.

Other resources for preparing successful speeches
Planning and writing, rehearsing a speech.
Once you're done with planning, completing your sample speech outline and writing find out how to rehearse. A speech is a live performance. Rehearsal helps you expose and iron out glitches before you find them out the hard way - in front of your audience.
Speech evaluation
And if your speech is being assessed check out this standard speech evaluation form to see what aspects are likely to be judged and how a rating scale works.
- Return to the top
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
Structuring a Speech Right: 7 Simple Tips
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

We’re not all Obamas and Martin Luther Kings. Even though we’d like to think we would kill it on stage, let’s not kid ourselves; coming up with a line like “Give me liberty, or give me death!” was not made up on the spot.
A good speech has to have the right structure. A speech structure encompasses 3 main components: the introduction, body, and conclusion. Following a structure allows you to integrate multiple elements into your speech while still keeping the purpose intact.
Of course, speeches take time to write. They’re not done in a spur of the moment. Even improv speeches aren’t actually improv speeches. Up until the time leading up to a speech, thoughts about how to start, how to grab attention, and how to end will constantly float through your mind.
The best way to avoid becoming a jumbling mess on stage is to take the time to sit down and come up with a structure to your speech.
It may be evident depending on what type of topic you want to approach, or it can take weeks to decide what structure best suits your statement. So how exactly do you decide what structure is best for your case?
Here are 7 simple tips on structuring a speech right.
1. Create an Outline for your Speech
Just like a letter or a report, a speech has a basic outline. You may have learned this in your English class but just in case were here to refresh your memory.
Every address contains 3 parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion.
To better understand how to form each section let us break down this speech delivered by Julian Treasure on “How to speak so that people want to listen.”
Introduction
The introduction in the example: “The human voice. It’s the instrument we all play. It’s the most powerful sound in the world, probably the only one that can start a war or say, “I love you.” And yet many people have the experience that when they speak, people don’t listen to them. Why is that? How can we speak powerfully to make a change in the world? “
Analysis : Julian Treasure immediately introduces the focus of his speech: How to speak powerfully. He highlights the significance of talking, a common problem regarding speaking, and poses a question that his speech will address.
This introduction is concise and to the point. Using a problem-solution strategy he effectively introduces the audience to his topic.
Your opening line is your chance to grab the attention of your audience and will determine how impactful your speech will be. Here are some ideas you could use to write your opening line:
- Ask a provoking question
- Open with a shocking fact or statistic
- Start with a personal story that is connected to your topic
- Make your audience do a simple short activity with you
If you have a hard time coming up with a good opening line, here is an article on 50 Speech Opening Lines (& How to Create Your Own) l The Ultimate Guide that will help you come up with a memorable and influential introduction.
Thesis Statement
The thesis statement in the example: If you speak powerfully, people will want to listen consciously.
Analysis: The speaker bases his whole speech on this one sentence and effectively weaves his speech around it.
Your thesis statement will decide what you’re gonna focus on and what your talk will revolve around. Your entire speech structure will be woven around your thesis statement.
4 Questions to Help you Form your Thesis Statement
Before deciding your thesis statement ask yourself these questions:
- Why have you chosen the topic?
- What is your take-home message? What have you learned, and why do you feel it is relevant?
- Is the purpose of your topic to inform, convince or entertain your audience?
- What do you want the audience to take away from this speech?
The body is like the main course of a speech. This part is where you deliver all the information you’ve learned. This is where you need to incorporate 3 things:
Primary Idea
The primary idea in the example: To give the audience tips on how to improve their speaking.
Decide the main idea of your speech. Once you have formed your thesis statement writing about the main idea of your speech becomes a piece of cake.
The sub-topics in the example: The seven deadly sins of speaking, foundations of speech and the toolbox of speech.
Breaking down your speech will make it easier for the audience to follow.
Under your central idea, what are some specific areas you want to highlight? If you are delivering an informative speech then it might be better to divide your main category into sub-categories to avoid overwhelming your audience.
Supporting Evidence
The supporting evidence in the example: The speaker demonstrates the importance of tone in speaking by enacting the different types of inflections on stage, proving his point effectively.
Similarly, to add credibility to your subtopics, you need to use examples to prove why your topic is essential.
Depending upon the context, you could enact a scene either by yourself, using a prop or with the help of a volunteer, talk about a personal experience, or use statistics to support your statement.
Great is the art of beginning, but greater is the art of ending. Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
The closing line in the example: “What would the world be like if we were creating sound consciously, and consuming sound consciously, and designing all our environment consciously for sound? That would be a world that does sound beautiful, and one where understanding would be the norm, and that is an idea worth spreading.”
Analysis: The speaker summarises the goal of his speech and provokes the audience to think about the power of speaking and listening using rhetorical questions.
Tie your speech and make it concise. If your purpose was to inspire the audience to change, you could ask the audience to do something on the spot.
For example, before concluding his speech, Julain Treasure asks his audience to perform some vocal exercises with him, giving the audience a chance to learn something new.
Here’s a small tip: If the address is followed by a question-and-answer session or a small activity like filling a form, then deliver a small summary before it.
In our example, Julian Treasure first asks the audience to perform the exercise with him and then delivers his closing line reinforcing his main statement one last time.
The proper closing line will succeed in making your audience feel inspired and motivated. To get some ideas on what type of closing lines might best suit your speech, here is an article you can read on 50 Speech Closing Lines (& How to Create Your Own) | The Ultimate Guide
2. Know your Audience

Your speech is for the audience, so having prior knowledge of what kind of audience you are speaking to, be it in terms of demography, age, gender, or occupation, all influence how you will structure your speech.
Suppose your address is for the purpose of entertainment, to inform, or to commemorate an important event. In that case, your audience’s demographics will be diverse, so your content must be relatable and appeal to these diverse groups.
In addition to using search engines, here are some sites you can make use of to gather information on your topic that will help refine and make your content more relatable:
However, if your speech is for the purpose of persuasion or to promote, then there are specific steps you can take to curate and refine your content to suit your audience.
In addition to using the previously mentioned sites, you can carry out the following:
- Conduct surveys
- Use Google Analytics to analyze customer base and traffic to your website
- Research competition and their marketing strategies
- Observe trends
3. Choose a Speech Pattern to Structure your Speech
Now that you have a basic outline of your speech, you have an idea of what you want to say and what message you wish to impart.
Now you have to build your topic into something comprehensible and logical. You have to make it appealing to the audience and engaging.
Your speech should be focused on your case, easy to follow and understand, and should align with your audience’s interests.
There are multiple styles you can use to structure your speech. Following a tone will help organize your speech and make it transition smoothly while sticking to a theme. Adopting the right pattern is a crucial step to structuring your speech.
Chronological
As the name suggests, a chronological pattern follows a specific sequence of events organized by the time or date they occurred.
Indeed, using this pattern will make it easier for you to deliver your speech and more accessible for the audience to follow.
A perfect example of a chronological speech pattern is the speech delivered by Martin Luther King Jr., titled “I have a dream”
Summary: He highlights an event of the past (the Emancipation Proclamation), talks about the present scenario (racial discrimination), and finally sends off the audience with his ambitions and dreams for the future.
If every person would gain this perspective, it would change us [all]. Dror Benshetrit
Spatial means something that occupies or is related to space. A spatial speech pattern quite literally incorporates the spatial aspects of what you are going to talk about.
For example, talking about the layout of a building you would start by saying, “ The building has one entrance and one exit, on the ground floor there are 3 rooms and on the second floor… “
Spatial patterns are used when your central idea is derived from an object or specific location. They will enable you to delve into the properties and relations of objects and form connections between them.
For instance, Damaris Hollingsworth, an architect, highlights her growth that has been influenced by buildings.
Summary: Here, she describes a building, its layout, and how it influenced her growth. Her main point, which is “architecture can influence social behavior and connections,” is derived from different styles of architecture that she has encountered.
A topical speech pattern is suitable when the topic you have chosen contains several subtopics that you might want to talk about.
A topical design organizes your speech into several categories allowing you to delve deeper into your topic while still providing a sense of flow.
Most suitable for speeches that are informative in nature, you can choose a general statement, then make subcategories that go into the specifics of your account and provide support for your general idea.
Although not necessary, usually organizing your speech by topics and delivering them in chronological order makes your address become more organized and makes it easier to smoothly transition from one case to the next.
Take this speech by Louise Evans as an example.
Summary: Her main topic is on how to master communication. However, she further divides her subject into 5 subcategories allowing her to explain the barriers that prevent effective communication, talks about her personal experiences, and makes it easy for the audience to follow.
Compare and contrast

Using the compare and contrast pattern gives you a segue to support your claims while showcasing the advantages it has over another object(s).
To use a compare and contrast pattern, in-depth research needs to be conducted on what two objects you will compare, like their properties, how similar they are, and what differences they have.
An easy way to form your speech using this pattern is to first draw up a Venn diagram of the two topics you want to compare. This will help you track what similarities you want to draw up and what differences you want to highlight.
To effectively use this pattern, you could take the two objects in question and compare and contrast them in different aspects, such as how they appear or behave in a specific environment related to the main topic.
Example: Comparing the real-time responses of Siri and Alexa.
Aspects you could cover:
- Rate of response time
- Accuracy of the responses
- Suitability of the responses
This is a common pattern seen in speeches targeted to introduce or market products, and in debate speeches. Compare and contrast patterns allow speakers to highlight their idea while providing the audience with the whole perspective.
Cause and Effect
The cause and effect pattern simply talks about an event or a series of events and the effect it has produced as a result.
This pattern is effective as you focus on various aspects of your speech, allowing you to analyze events responsible for the cause and dissect the implications that the reason has produced.
In simple words, you explain the action and analyze the reaction.
In this informative speech delivered by Ruairi Robertson, he cleverly incorporates cause and effect to elucidate the mechanisms of the body.
Summary: He talks about the events that led to an increase in antibiotics. Because of this, there was an increase in gastrointestinal disorders and brain health, which led us to understand the importance of food in health.
Keep in mind, You don’t need to follow only one pattern. You could use a combination of patterns depending on your preference.
Without a pattern, your speech will not have logic and structure and makes it difficult for anyone to follow. An unstructured talk is like trying to align a circle to a triangle. No one sees the point, and it becomes exhausting to listen to.
4. Don’t Shy Away from Repetition

It goes without saying that your audience is bound to lose parts or zone out from time to time. Holding the attention of a room is tough, and it becomes more daunting when your audience is more extensive.
Statistics show that the average attention span for an audience is 5 to 10 minutes, so it is almost impossible to expect your audience to remember everything from a speech.
However, the main aim of your address is to highlight the importance of your central idea, so try to repeat your thesis statement from time to time by paraphrasing it.
For example, take the commencement speech delivered by Mary Schmich , famously known for its opening line, “Wear sunscreen.”
The idea of her speech is to push the youth to embrace their present, and she drives in this point using simple lines like “enjoy the power and beauty of your youth” and “don’t worry about the future.”
5. Work on your Transitions
Transition helps make your address attain fluency. To keep your audience hooked, you have to master the journey from point A to B to C and so forth.
Take this speech delivered by Shashi Tharoor as an example where he talks about the importance of a well-formed mind.
Summary: He explains the problems of the education system using 4 E’s: Expansion, Equity, Excellence and Employability. These are excerpts taken from the speech showing how he transitions from one E to the next:
“… So expansion has taken place. We’ve also had to fight for the second E of Equity. ..”
“.. .in getting those two things more or less right, I dont know how well we did on the third E, which is the E of Excellence. “
“… and that ties into the fourth E that I’ve added to this catechism: Employability .”
Speech patterns contribute significantly to the smooth transitions of a speech. If you’re looking for ways to transition from one part to the next, there are a list of transitional devices you can make use of.
6. Revise and Edit

Now that you know what will essentially go into your speech and have decided a pattern to follow, the final step is to revise.
Revision involves reading through your speech and editing it, correcting any mistakes, be it grammatical or spelling.
These are some questions that need to be ticked off:
- Have you focused on your central idea?
- Do you have enough supporting ideas and evidence?
- Have you established credibility?
- Have you offered enough for the audience to take away?
7. Identify the gaps

In-depth research will always pull up shortcomings of your particular topic.
There will more often than not be something that has not been considered, and this will help you provide a unique spin on your perspective.
Make a note of the flaws and gaps of your topic. This will help you write a speech that has clarity and logically convey your ideas. It also adds to your credibility as a speaker who is objective and willing to accept all aspects of your speech.
Writing a speech takes time and effort. Right from choosing the topic up till deciding your closing line can take weeks to write.
Followed by rounds of editing and revision, structuring a speech is no easy feat. However, just following these 7 simple tips will ease your workload and certainly make sure you nail structuring your speech the right way.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
We apologize for any inconvenience as we update our site to a new look.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Grammar: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
Definitions and examples of basic sentence elements.
The Mastering the Mechanics webinar series also describes required sentence elements and varying sentence types. Please see these archived webinars for more information.
Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font = prepositional phrase
Independent clause : An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence. It contains a subject and a verb and is a complete idea.
- I like spaghetti .
- He reads many books .
Dependent clause : A dependent clause is not a complete sentence. It must be attached to an independent clause to become complete. This is also known as a subordinate clause.
- Although I like spaghetti,…
- Because he reads many books,…
Subject : A person, animal, place, thing, or concept that does an action. Determine the subject in a sentence by asking the question “Who or what?”
- I like spaghetti.
- He reads many books.
Verb : Expresses what the person, animal, place, thing, or concept does. Determine the verb in a sentence by asking the question “What was the action or what happened?”
- The movie is good. (The be verb is also sometimes referred to as a copula or a linking verb. It links the subject, in this case "the movie," to the complement or the predicate of the sentence, in this case, "good.")
Object : A person, animal, place, thing, or concept that receives the action. Determine the object in a sentence by asking the question “The subject did what?” or “To whom?/For whom?”
Prepositional Phrase : A phrase that begins with a preposition (i.e., in, at for, behind, until, after, of, during) and modifies a word in the sentence. A prepositional phrase answers one of many questions. Here are a few examples: “Where? When? In what way?”
- I like spaghetti for dinner .
- He reads many books in the library .
English Sentence Structure
The following statements are true about sentences in English:
- H e obtained his degree.
- He obtained his degree .
- Smith he obtained his degree.
- He obtained his degree.
- He (subject) obtained (verb) his degree (object).
Simple Sentences
A simple sentence contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. However, it contains only one independent clause.
Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font =prepositional phrase
Here are a few examples:
- She wrote .
- She completed her literature review .
- He organized his sources by theme .
- They studied APA rules for many hours .
Compound Sentences
A compound sentence contains at least two independent clauses. These two independent clauses can be combined with a comma and a coordinating conjunction or with a semicolon .
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma or semicolon = pink, regular font ; coordinating conjunction = green, underlined
- She completed her literature review , and she created her reference list .
- He organized his sources by theme ; then, he updated his reference list .
- They studied APA rules for many hours , but they realized there was still much to learn .
Using some compound sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
Complex Sentences
A complex sentence contains at least one independent clause and at least one dependent clause. Dependent clauses can refer to the subject (who, which) the sequence/time (since, while), or the causal elements (because, if) of the independent clause.
If a sentence begins with a dependent clause, note the comma after this clause. If, on the other hand, the sentence begins with an independent clause, there is not a comma separating the two clauses.
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma = pink, regular font ; dependent clause = blue, italics
- Note the comma in this sentence because it begins with a dependent clause.
- Note that there is no comma in this sentence because it begins with an independent clause.
- Using some complex sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
Compound-Complex Sentences
Sentence types can also be combined. A compound-complex sentence contains at least two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
Key: independent clause = yellow, bold ; comma or semicolon = pink, regular font ; coordinating conjunction = green, underlined ; dependent clause = blue, italics
- She completed her literature review , but she still needs to work on her methods section even though she finished her methods course last semester .
- Although he organized his sources by theme , he decided to arrange them chronologically , and he carefully followed the MEAL plan for organization .
- T hey studied APA rules for many hours , and they decided that writing in APA made sense because it was clear, concise, and objective .
- Using some complex-compound sentences in writing allows for more sentence variety .
- Pay close attention to comma usage in complex-compound sentences so that the reader is easily able to follow the intended meaning.
Sentence Structure Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Structuring Sentences: Types of Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Simple Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Compound Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Complex Sentences (video transcript)
- Structuring Sentences: Combining Sentences (video transcript)
- Common Error: Unclear Subjects (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Punctuation as Symbols (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Commas (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Periods (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Semicolons (video transcript)
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Main Parts of Speech
- Next Page: Run-On Sentences and Sentence Fragments
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Log In 0 The website uses cookies for functionality and the collection of anonymised analytics data. We do not set cookies for marketing or advertising purposes. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies and our privacy policy . We're sorry, but you cannot use our site without agreeing to our cookie usage and privacy policy . You can change your mind and continue to use our site by clicking the button below. This confirms that you accept our cookie usage and privacy policy.
Free English Lessons
Parts of speech in english – video.
Download PDF

In this lesson, you can learn about parts of speech in English.
How many parts of speech are there in english can you name them, and explain what they do, understanding parts of speech —nouns, verbs, adjectives, and so on—can help you to understand english sentence structure and how english grammar works., in this class, you’ll learn the basic information about parts of speech, you’ll see some ways that parts of speech can be more complicated than you might expect, and you’ll have several chances to practice, quiz: parts of speech in english.
Now test your understanding of the different parts of speech by trying this quiz. There are 20 questions, which get harder as you go through it!
When you have finished, click ‘View Questions’ to see all the correct answers and read the explanations. There are links to further study resources in the explanations.
Quiz Summary
0 of 20 Questions completed
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 20 Questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 ) 0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
| Average score | |
| Your score |
- Not categorized 0%
Well done! You’ve finished!
That’s an excellent score and this quiz is extremely difficult! Congratulations!
A perfect score on an incredibly difficult quiz! Congratulations!
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
1 . Question
For the first five questions, answer true or false.
True or false: a word can be different parts of speech depending on its function and meaning in the sentence.
Review part three of the lesson if you need help with this one.
2 . Question
True or false: a noun can be a word or a phrase.
3 . Question
True or false: if a word can be a noun, it can only be a noun.
4 . Question
True or false: when analysing parts of speech, you don’t need to think about what the sentence means.
5 . Question
True or false: articles (‘the’, ‘a’), demonstratives (‘this’, ‘that’), quantifiers (‘some’, ‘few’) and possessive adjectives (‘your’, ‘their’) are all determiners.
Remember that determiners specify the noun you’re referring to. Do all these words do this?
6 . Question
For the next five questions, choose the part of speech described.
What part of speech can be an action or a state?
- Interjections
- Conjunctions
‘Run’ is an action and ‘understand’ is a state.
7 . Question
What part of speech can describe verbs, adjectives, adverbs or whole sentences?
- Prepositions
8 . Question
What part of speech represents or replaces nouns?
9 . Question
What part of speech expresses an emotion or can be used to react to something?
10 . Question
Which part of speech doesn’t indicate something about a noun?
- Determiners
11 . Question
For the next five questions, match the words in the sentence with the parts of speech.
“He slept badly.”
Sort elements
12 . Question
Match the words in the sentence with the parts of speech.
“She has bought a second-hand car.”
- noun phrase
This time, you’re not analysing each word but the function of word groups and phrases in the sentence.
13 . Question
“Um, can you stop making so much noise, please?”
- ‘um’ and ‘please’
- 'can' and 'stop'
- 'you'
- 'making so much noise'
14 . Question
“Is this your bag or mine?”
- conjunction
- (possessive) pronoun
15 . Question
“Hey! Give his new watch back to him.”
- interjection
- preposition
16 . Question
For the last five questions, tick all the words that are correct.
Which words can be nouns?
You need to choose three answers.
17 . Question
Which words can be adverbs?
Only one word here is not an adverb.
18 . Question
Which words can be determiners?
This time there are two correct answers.
19 . Question
Which words can be more than one part of speech?
Two answers are correct; one of the others doesn’t even exist!
20 . Question
Which words are conjunctions?
- nevertheless
This is a deliberately difficult question to end with! A conjunction must be followed by a noun (or noun phrase) and then a verb, with no commas.
So, first question: how many parts of speech are there?
Well, we did a Google search, and many of the top results said ‘eight’. So there must be eight parts of speech in English.
Wrong! There are nine.
So, what are they?
1. Guide to Parts of Speech in English
Number one: nouns. Nouns can be things, animals, or people, like doctor, pencil, tree or cat.
Nouns can also be ideas or abstract things, like idea, happiness, time or money.

Number two: verbs. Verbs can be actions, like do, run, fly or win.
Verbs can also describe states, like be, love, believe or understand.
Number three: adjectives. Adjectives describe nouns. For example: red, big, metal, or beautiful.
Number four: adverbs . Adverbs can describe verbs, meaning they describe how someone does something. For example, quickly, loudly, angrily or well.
Adverbs can also describe adjectives, other adverbs, or even whole sentences. For example, very is an adverb which can describe an adjective— very slow —or another adverb— very slowly.
Unfortunately or sometimes are adverbs which can be used to add information to a whole sentence.
For example:
- Unfortunately, they missed the train and were late to their own wedding!
- Sometimes, I wish I’d made different choices in life.
So, adverbs are a little more complicated. Here’s a good way to remember it: adjectives and adverbs both describe other words. They are both used to add information to something else.
Adjectives describe nouns, and adverbs describe everything else: verbs, adjectives, adverbs and whole sentences.
Number five: pronouns.
Pronouns replace or represent nouns. For example, I, you, she or they are pronouns which represent different people.
You use pronouns to avoid repeating the same word, or to refer to something when it’s obvious what you mean.
- How was the weather there?
There is a pronoun which refers to a place. If you’ve already mentioned the place you’re talking about, you don’t need to say it again.
Another example:
- Give me two, please.
Two is a pronoun which refers to a quantity of something which has already been mentioned. The person you’re talking to already knows what you’re talking about.
Number six: prepositions.
Prepositions usually go before a noun or noun phrase. What’s their job?
Prepositions can do two basic things: first, they can add an idea of time, place, or movement to a noun. For example:
- on Wednesday
- in the corner
- towards the door
Secondly, prepositions can connect other words to a noun, or a pronoun.
For example, think about the verb depend on. The preposition on connects the verb depend to the object of the verb. For example:
- It depends on the cost.
Usually, the noun or noun phrase goes after the preposition.
However, sometimes the preposition can link to a noun (or pronoun) earlier in the sentence. For example:
- What does it depend on?
Here, on links to the pronoun what.
Number seven: conjunctions.
Conjunctions connect two things. A conjunction can connect two words:
- I like cake and ice-cream.
A conjunction can connect two phrases:
- Do you want to go now or wait till this afternoon?
You can also use a conjunction to connect two clauses:
- Although I’ve been trying to learn for years, I’m still really bad at drawing.
Number eight: determiners
Determiners go before a noun. They include words like a, the, this or that, which help to specify which noun you’re talking about.
Words like my, your, his, her, etc. are also determiners. They specify which noun you’re talking about by saying who something belongs to.
Determiners can also tell you how many of something there are. Look at three examples:
- ten bananas
- some people
- both of my brothers
The words ten, some and both are determiners.
Number nine: interjections
Interjections are different, because they aren’t normally part of a sentence.
Interjections are words or phrases which show how you feel. For example:

So, now you know about the nine parts of speech in English.
2. Practice with Parts of Speech in English
Let’s practice! Look at three sentences. Each sentence has five words.
- They told me about it.
- Look in the big cupboard.
- Put it there, but carefully.
Can you identify which part of speech each word is? Pause the video and think about your answers.
How did you do? Could you identify the parts of speech correctly?
Let’s look at one more.
- I’m staying in this evening.
What part of speech are these words? Think about it.
So, I is a pronoun, am is a verb, and staying is also a verb.
What about in? Did you say it’s a preposition?
It’s not a preposition; it’s an adverb.
How does this work? We had the word in in one of the sentences you saw before, and it was a preposition.
So, what’s going on?
3. The Same Word Can be More than One Part of Speech
Some words can only be one thing.
For example, the words independence or hair can only be nouns.
Believe and destroy can only be verbs.
However, many words can be more than one part of speech.
There are two things happening here.
First, a word can be two different things, which have the same written form and the same pronunciation.
Think about the word win. Is it a noun or a verb?
It can be both.
- I’m sure they’ll win the game this weekend.
- We’ll be hoping for a win in the big game this weekend.
Many words are like this. Another example: red can be an adjective or a noun.
- What do you think about this red for the kitchen?
- I like that red top she was wearing.
This is very common: very often, a word with one written form can be two (or more) different parts of speech.
We told you there are two things happening here; what’s the other?
Sometimes, a word can be different parts of speech depending on its function in the sentence.
Look at two sentences:
- I have a few photos of my grandparents.
- Sure, you can have a few.
Here’s a question: what part of speech is few in these sentences?
In the first sentence, few is a determiner; in the second, it’s a pronoun.
Can you explain why this is?
Think about what few does in these two sentences.
In the first sentence, few adds a quantity to the noun photos. It tells us how many photos you have. This makes it a determiner.
In the second sentence, few replaces a noun. You don’t know which noun it replaces, but in context, you would understand what the person meant.
Maybe it was ‘a few biscuits’, or ‘a few pieces of paper.’
We don’t know! But, you do know that few replaces a noun, which makes it a pronoun.
Another example is the sentence we saw before:
Prepositions go with nouns, and connect nouns to other words in the sentence. In here doesn’t go with a noun, so it can’t be a preposition.
Learn more with this Oxford Online English lesson on adverbs – to, in, at .
In here means ‘at home’, and it adds information to the verb stay. What kind of words add information to verbs?
Adverbs! So, in is an adverb.
Wait a minute, did we ever finish explaining what parts of speech are in this sentence?
You’re right! We didn’t. Let’s do it now. You need to say what parts of speech the words this evening are.
Can you do it?
Maybe you said that this is a determiner, and evening is a noun. That’s technically correct, but it’s not the best answer.
The best answer is that this evening is an adverb.
How do you explain that?
4. Compound Parts of Speech in English
Until now, you’ve seen single words, and how single words can be nouns, verbs, etc.
However, when you’re thinking about parts of speech, you can’t just think about single words. Phrases can also be nouns, verbs, adjectives, and so on.
Let’s do an example:
- Add a small spoonful of brown sugar, then turn the heat down and stir the mixture gently.
Think about the first part of this sentence: add a small spoonful of brown sugar.
What parts of speech do we have here?
Of course, you can go through it word by word. You can say, add is a verb, a is a determiner, small is an adjective and so on.
But, is that the most useful way of looking at it?
It makes more sense to see this as a verb— add —and a noun— a small spoonful of brown sugar.
The noun is made up of several parts of speech: determiners, adjectives, prepositions and nouns, but together they have one meaning. These words refer to one thing.
You can analyse a sentence in several different layers. So, you can see a small spoonful of brown sugar as six individual words, or one noun phrase.
You could also see it as three parts: a determiner— a small spoonful —a preposition— of —and a noun— brown sugar.
Confused? We understand! You want to know the answer. You want to know which way is ‘correct’.
There isn’t one ‘correct’ way to see this. There are different perspectives.
A better question is: which perspective makes more sense?
In this sentence, a small spoonful of brown sugar refers to one thing in the world. So it makes sense to think of it as one part of speech in the sentence.
What about the second part of the sentence? How would you analyse the parts of speech?
As you saw before, there isn’t one right answer, but here’s a suggestion.
The sentence contains a conjunction— then —and then two verb phrases linked with the conjunction and.
This makes sense because the sentence is telling you to do two things: turn the heat down and stir the mixture gently.
So, it makes sense to see turn the heat down as one part of speech, because it’s telling you do to one thing.
Let’s put these ideas together.
First, when you think about parts of speech, you can’t just memorise information. You have to look at each sentence individually, and think about what each word is doing.
Secondly, always think about what the sentence means in the real world. Sentences aren’t abstract things; they refer to real people, real things and real actions.
There is always more than one way to analyse the parts of speech in a sentence: choose the way that makes sense based on what the sentence is telling you about real life!
Let’s do a more challenging practice exercise so you can see these ideas in action.
5. More Challenging Practice with English Parts of Speech
Look at three sentences:
- Amazing! It’s way better than I ever thought it would be.
- She was an amazing clinician , who came up with many innovative ways to treat patients.
- I don’t believe it!
How would you analyse the parts of speech in these sentences? Think about the ideas we talked about in the last section. Does it make sense to break the sentences into individual words, or is it better to group words into phrases?
Pause the video and think about your ideas.
You can pause the video again to look at these in more detail.
Notice how the same word can be different parts of speech in different sentences. For example, amazing is an interjection in one sentence, and an adjective in another.
Notice also the different layers of analysis. For example, look at the phrase many innovative ways. You can see this as one noun phrase, or as a determiner plus a noun phrase, or as three individual parts: a determiner, an adjective and a noun.
Which is correct? They all are! Choose the perspective which makes more sense to you.
Thanks for watching!
We Offer Video Licensing and Production
Use our videos in your own materials or corporate training, videos edited to your specifications, scripts written to reflect your training needs, bulk pricing available.
Interested?
More English Lessons
English grammar lessons.

- Facebook 153
- Odnoklassniki icon Odnoklassniki 0
- VKontakte 0
- Pinterest 0
- LinkedIn 29

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Step 4: Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your speech the more you'll discover which sections need reworked, which transitions should be improved, and which sentences are hard to say. You'll also find out how you're doing on length. Step 5: Update, practice, and revise your speech until it has a great flow and you feel ...
Writer, Daniel Pink, put it well when he said: Give the speech a beginning, a middle and an end. You don't have to take the audience by the hand and walk them through each step. And you don't have to proceed chronologically. But having that structure in your head will give your speech a shape.
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Learning how to write a speech requires a keen awareness of how to tailor your rhetoric to a given issue and specific audience. Check out our essential speech-writing guidelines to learn how to craft an effective message that resonates with your audience.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech: 1. Structure first, write second. If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first.
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
Introduce your topic and explain the topic area. Mention the challenges or issues that you will be exploring in this area. Talk about the purpose of your presentation; this is the basis of your presentation. Give a statement of what you hope the outcome of your presentation will be.
In this video, we'll walk you through how to write a speech by showing you the different structures you can use! Watch more of our video lessons at http://ww...
To supplement that structure, Smith makes the speech come alive with vocal variety, exuberant body language (shadowboxing), and even a prop (a towel thrown to the ground). Smith, President of the Cy-Fair Super Speakers Club in Cypress, Texas, says the key to writing a great speech is to keep it simple.
The structure is like a house, which has essential parts like a roof, walls, windows, and doors. Organization is like the placement of rooms within the house, arranged for a logical and easy flow. This chapter will teach you about creating a speech through an outlining process that involves structure and organization.
Writing a speech can be a daunting task, especially if you want to engage your audience and deliver your message effectively. In this blog post, you'll learn how to write a speech that follows a clear structure, uses persuasive techniques, and incorporates storytelling elements. You'll also get tips on how to practice your speech with VirtualSpeech, an online platform that provides AI-powered ...
Plan where you want to finish your speech and how you will get there before you start writing - t h e structure of a speech is usually in three parts. For example: An opening that grabs your audience's attention and makes the overall topic of your speech clear - for example, pose a question to the audience where you can predict the answer.
The 5 major steps in speech writing include: 1. Research the topic thoroughly to gather relevant information. 2. Organize the speech by creating an outline or structure. 3. Write a compelling introduction to grab the audience's attention. 4. Develop the body of the speech with logical points and supporting evidence. 5.
"A Speech is not an essay up on its hind legs!" T he biggest difference between preparing a speech and preparing an essay is the audience. The essay's audience—a reader—takes in the written ideas through the eyes. A public presentations' audience, however, understands the speaker's ideas by seeing, hearing and "feeling" the speaker by using their eyes, ears and heart.
how to outline a speech: the 4 essentials steps involved in writing an outline - detailed sequential help, with examples, covering: 1. choosing a topic, 2. audience analysis, 3. choosing the best organizational pattern to fit your speech purpose, 4. what to put in each part of your speech: introduction, body and conclusion. a printable speech ...
Here are 7 simple tips on structuring a speech right. 1. Create an Outline for your Speech. Just like a letter or a report, a speech has a basic outline. You may have learned this in your English class but just in case were here to refresh your memory. Every address contains 3 parts: the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Learn how to structure the introduction, body and conclusion of a speech.Want more resources like this? ... Learn how to structure the introduction, body and conclusion of a speech.Want more ...
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
Organizing speeches serves two important functions. First, organization helps improve clarity of thought in a systematic way. Second, organization increases the likelihood that the speech will be effective. Audiences are unlikely to understand disorganized speeches and even less likely to think that disorganized speakers are reliable or credible.
A simple sentence contains a subject and a verb, and it may also have an object and modifiers. However, it contains only one independent clause. Key: Yellow, bold = subject; green underline = verb, blue, italics = object, pink, regular font =prepositional phrase. Here are a few examples:
3. Structure your speech. To structure your speech and make it easy for your audience to understand your point, split it into three sections: Introduction, main body, and conclusion. In each section you're trying to achieve a different aim: In the Introduction, your aim is to tell your audience who you are and what you're talking about ...
Just like y is sometimes a vowel and sometimes a consonant, there are words that are sometimes one part of speech and other times another. Here are a few examples: "I went to work " (noun). "I work in the garden" (verb). "She paints very well " (adverb). "They are finally well now, after weeks of illness" (adjective).
True or false: a word can be different parts of speech depending on its function and meaning in the sentence. 1. True. 2. False. True or false: a noun can be a word or a phrase. True or false: if a word can be a noun, it can only be a noun. True or false: when analysing parts of speech, you don't need to think about what the sentence means.