- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution


Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
- Our Services
- Advertise With Us
- Explicit Success Scholars (E.S.S)
Explicit Success
Building Extraordinary Intellectuals & Success-driven Minds
20 Tips For Preparing An Effective Oral Presentation

Don’t mind the informal me, I just seem to love that ‘down-to-earthness’ – I personally believe that such disposition is a better facilitator of effective communication.
Without much ado, I am going to share with you some ideas on what I can safely call most people’s nightmare (next to examinations, of course) – An oral presentation.
Organizations and other platforms have also come to discover the essence of an effective oral presentation. How it can move an employee from a zero state of mind to an excited state of mind after a brief but powerful presentation.

Businesses are not left out too as it has become a core value that has to be portrayed to convince potential clients about a business idea.
Read this: How to manage your time effectively
Essentially, oral presentations are nothing to be scared of.
They add some kind of depth to the learning experience.
Not having this depth is what we should be scared of. Self-expression is just one of the core pillars of assessing how much and how well a student or presenter has assimilated the content of instructional material.
Overall, some of the most faced challenges associated with oral presentations are content and stage management which shall be discussed broadly here.
Whether you are a student, employee, professional or businessman , you sure need this skill to make a good impression.
Enjoy these tips, internalize them and start putting them into good practice. At the end of this write-up, you will discover the peculiar challenges of stage fright, how to deal with it and a few tidbits on presentation etiquette.

1. Know the content
Nothing breeds confidence like competence and nothing breeds competence like preparation . Being vast in and thoroughly familiar with whatever the subject of a presentation will, in no small way, reinforce your sense of having something genuinely interesting to offer.
With this in place, the presentation ceases to be a mere talk or some kind of recital. It indeed becomes an active engagement of the audience on a journey of discovery. All you need do is just visualize yourself as a tour guide or a curator in a museum.
All you need do is to relate antecedents, history, origins, facts, figures and aspects of the subject matter in such a way as to stimulate their imagination.
You lead the audience on, not exactly projecting yourself but helping them see what needs to be seen. You wouldn’t want to go to the stage and destroy the expectations of people eagerly waiting to listen to you.
2. Define the purpose of the presentation
A presentation isn’t just a list of random facts. It makes a specific point, just like laboratory reports or essays.
Without a clear purpose in mind, your presentation will most likely be a jumble of unorganized factual information, putting your audience in the dark about your true intent.
What is the most important message you want to convey to the audience? Consider this to be the idea or theme of your presentation.
Your presentation’s goal(s) could include, but are not restricted to, trying to inform, inspire, or persuade.
Remember that what you say as well as how you say it must be consistent with the presentation’s goal.
3. Be natural
The mistake a lot of presenters make is thinking that great presentations are all about big vocabulary and sophisticated terms.
May I indulge you in a different perspective – great presentations are all about presentations done in the most natural way. Be calm, relax and flow effortlessly .
Do your presentations like they are your daily routines. Help your audience feel like – “yes, I agree with what he is talking about”.
Rather than trying to charm the audience with a sophisticated style, be more committed to capturing their imagination through simple cues and vivid expressions.
There is a child in everyone, no matter how old. If possible, add a little humour here and there but try not to overdo it. Ensure you stay on track.
Read this: How to ask questions smartly
4. Invoke curiosity

This aspect is what makes your audience hooked until the end of your presentation. They want to know where you are headed. They can’t risk being distracted until you finish. All you need do is reawaken that curious infant in the brief moment of your presentation.
It is for this reason that presentations adopt visual aids and graphical tools. The world-famous PowerPoint computer application also goes hand in hand with projectors – large screens for a clearer, broader view.
Where else is such pervasive attention given to pictures and descriptive tools apart from a kindergarten? Such applications show that there is a childlike nature in every man. Invoke it!
Read: How To Celebrate Failure For Success
5. Get your audience involved
Get your audience involved in your presentation. Don’t stand behind a lectern all through, tale a brisk, confident walk and project your words into the minds of your audience. Don’t let the lectern come in between you and the audience.
Try to get your audience out of their seats, laughing, raising hands or even standing by your side to make an analysis. Getting your audience to laugh is not as difficult as you might think. For example, you might try, “Ladies and gentlemen, I was told to announce something very critical to the success of today’s event. Even though I don’t think it’s my place to begin my presentation with an announcement that has nothing to do with my topic.”
“Anyway, I’ve been asked to tell you that in the event that you laugh too hard, don’t cause a stampede or fart too loud.” 😆
Get free tips and tricks that will help you to achieve success faster 😉
6. Gesticulate
If you can request a cordless lavaliere mic, pls do, so that you can be as flexible with your hands as possible. A handheld mic might become tiring if your presentation takes a while.
Your audience will only remember 30% of what they hear & see but 70% of what they do will stick to them forever.
7. Project your words
Two things that can make your projection so vivid and impactful are a clear voice and clarity of communication. Try to emphasize the last sound of each word which will help you to sound very polished. This may sound odd to you when you start but eventually sound normal as you get used to it.
8. Take a pause

I cannot stress this enough. Take your time to pause! It kinda helps your audience to brainstorm, evaluate and re-evaluate. You shouldn’t say more than six to eight words at a time without a pause. As longer sentences reduce readability, longer spoken words also reduce absorption.
Use a full voice, then pause. Think of great speakers that utilized a full voice and paused. They did efficiently well. Such presentations drop some value within you.
9. Use acronyms
After you have written all the words on index cards, try to think of an acronym or Slang abbreviation that has every point you want to talk about. Use this strategy to keep your presentation in order.
For example, you may have written on a marriage/relationship index card – ask, support, kiss . Think of the first letter in each word and arrange them to ASK or any other word of your choice.
ASK will keep you on track this way:
A – Ask what he thinks
S – Support his opinion first
K – Kiss him when the discussion ends
You must have practised what you will say about each word beforehand. You will only use the acronym to keep track which the audience has no clue about. They will only think you are so perfect! If your oral presentation takes time and involves longer acronyms, you could keep your index card(s) on you just in case you get lost.
10. Give life to figures

The best way to do this is to put a ‘Point’ of mind-gripping information (pictures, graphs, a phrase or table, flow charts, diagrams or a statistic) on some slides and speaking to them.
While the audience is fixated on that slide, all you need do is try to make them see the aspects of the slides that are hidden. Hence, you help to make their imagination make up for the rest of the story.
Such information is alike in features such as introduction, plot build-up, themes climax/anticlimax, a hero and his trials/triumph and so on.
And like a good storyteller or the mythical Pied Piper, the story or the music as the case is, becomes the object of the audience’s attention. The presenter is merely an intermediary.

11. Face the object
Sure, it is not bad to feel weird for a moment. Gain your confidence back by becoming the audience for a moment.
Face the presentation with your hands towards the slide, board or what have you? Making this brief move takes a whole lot of burden off as you see that you do not have to be the audience’s object of attention for a while.
You can use this moment to stealthily move from your weak points to your strong points as you gain your confidence back .

Not all presentations have to be a serious one looking like a board meeting. It doesn’t have to be a brainstorming session to close a million-dollar deal. Smile if you can.
In fact, you should smile. It will reduce any pressure you might be feeling. You never know how powerful a smile can be until you smile at a confused child who looks at you and then returns the smile.
While you smile, make good eye contact with them and gesticulate as often as possible. This will create a good impression on your audience and make them connect with you easily.
Read this: Amazing facts about your handwriting
13. Intrigue them with stories

Whether it’s a story your grandfather told you or a story you learnt while growing up, people would love to listen. Stories are interesting ways to give your audience a light mood.
Who doesn’t like the taste of a little icing on the cake or peanuts in the chocolate? Just something a little bit different to ease the whole seriousness of the atmosphere.
Professional speakers are becoming professional storytellers , primarily stories about themselves or someone they know so well . If you can tell a story about each word or topic on your cards or slides, your speech will have a better flow.
14. Take corrections politely
One mistake people do is to try to show that they know better than their judges.
Judges, examiners, instructors or even a member of your audience can come into your presentation abruptly. Prepare your mind ahead for this and don’t fidget.
A simple “Noted, sir” “sorry, I skipped that” or “thanks for the feedback” would go a long way in determining your final presentation score.
Be courteous and mindful of harsh emotions as you face arguments or opposition. A wrong approach in dealing with this can ruin everything you have started. So be cool with everyone.
As a matter of fact, who you are and who the audience perceives you to be is a measure of the weight of your words.
Hence, it is safer to use universally acceptable codes of conduct and principles of etiquette that will put you in the good graces of the audience.
15. Define your target audience
The audience’s reaction is the only way to judge a good presentation. What do they currently know about your subject matter?
What are their perceptions about your subject matter: will they accept whatever you say, or will you have to persuade them to change their views? Do they have a good command of the English language?
An effective oral presentation requires much more than simply presenting your ideas or giving a presentation. It is all about clear communication and connecting with the audience.
Preparation is required to create that type of presentation. You must learn about your target audience to tailor your message.
If you’re talking to experts in your field, for example, you don’t have to explain all the terms you’re using but if you expect your audience to disagree with your assertions, it’s a great idea to provide additional illustrations and go into greater detail when presenting the evidence.
You can outline your presentation with your audience in mind to explain your main points and maintain a logical flow. The more you understand your target audience, the better you will be able to communicate with them.
16. P redict your audience’s thoughts and tell them
If you’re lucky enough to predict what is on their minds, you’ll get almost 100% attention from your audience. This lowers the barriers between you and them.
They’ll say “hey, he’s so clever hahaha”. Wow, you’re absolutely right! Tell them you know what they are thinking and answer a question they haven’t yet asked you.
17. Practice your presentation beforehand

You should start with yourself first. Talk to yourself, then move on to talking to a friend or small group of friends. When you build more confidence, start by speaking for free to become more professional.
You could begin by speaking to associations and clubs. Your audience may give you more networking opportunities when they enjoy your free presentations. There are business owners in your audience or people who work for businesses looking for speakers.
In fact, t here is much more to learn while you practise. By the time you become well-known, you can start charging a token or your prices can even become non-negotiable. 😉
18. Explore every possible detail about your subject matter
To prepare an effective oral presentation, you must thoroughly understand your subject matter, which means knowing far more than you will present.
There is no such thing as too much research. The more familiar you are with your content, the more settled and confident you will feel when presenting it to a group.
Take notes as you read about your topic. Then organize your notes for your presentation. The most straightforward structure is an outline.
In most cases, a concise outline will serve as a good template for presenting your topic. The introduction, body, and summary make up a concise outline.
- Introduction
In the introductory part, you must provide a concise context for your discussion. This is where you describe the problem or issue that the presentation will solve.
You want to immediately grab people’s attention, stimulate their interest, and get them pondering about your topic. That is what creating engaging content is all about.
The bulk of your presentation. It provides specific examples to back up your main point. This is where you add important facts, statistics, and details to your discourse.
Make certain that your material is presented articulately, with each point connected to another and clear progressions.
To summarize, highlight the previous points briefly. Use keywords from your introduction to restate your argument.
Take note of transitory phrases or words like “in summary.” Appreciate the audience for their time and, if the presentation format allows, gladly accept their questions.
A clear structure helps to support a clear and focused message, and it prevents you from jumping from concept to concept, which can make it difficult for your audience to grasp your presentation.
Having this in place, the presentation is no longer just a discussion. It truly becomes an active participation of the audience on a discovery journey. All you have to do is relate the subject’s antecedents, background, facts, statistics, and features in a way that stimulates their curiosity.
19. Use visual aids to supplement your content
It is easier to deliver an oral presentation when you employ visual aids. Visual aids, such as PowerPoint slides or printed handouts, provide structure to your presentation and assist the audience in comprehending the key points.
Since the majority of information is deemed and grasped visually, you may need to resolve this in your presentation by including a few visuals.
This would help the audience follow your discourse and possibly discuss a few of your points after the presentation is finished.
A good visual aid , as obvious as it may seem, must remain visual. Visuals can be bulleted lists or outlines, diagrams or figures, or pictures that depict crucial points that would be difficult to explain orally. Visual aids should be used to supplement, not compete with, your presentation. Use them only when they are necessary or beneficial.
20. Anticipate questions and prepare thoughtful answers in advance
A key component of preparing for an effective oral presentation is anticipating questions and creating thoughtful responses beforehand.
It demonstrates that you are knowledgeable about the subject and that you gave the subject some research. It also helps establish credibility and demonstrate your knowledge.
Additionally, it might assist you in remaining composed and assured throughout the presentation, especially if you are posed with unexpected questions. A few strategies for getting ready for questions are as follows:
- Researching your topic thoroughly: This will enable you to answer any questions that may come up about your subject matter.
- Identifying key points of confusion: Think about what aspects of your presentation may be most difficult for your audience to understand and prepare answers accordingly.
- Practicing your responses: Rehearse answering potential questions so you are more comfortable and confident when answering them during the presentation.
- Being open to feedback: Encourage your audience to ask questions and be open to feedback , even if it is critical. Take the opportunity to address any misconceptions or confusion that may have arisen during your presentation.
- Be prepared for the unexpected: Sometimes, the questions you get may be totally out of the blue, be prepared to answer those as well.
In summary, your oral presentation is highly related to your motion, posture, gesture, gesticulation, eye contact, pausing effect, response to applause and so on.
The evolving nature of education has seen many lecturers and teachers adopt oral examinations as an integral part of grading students’ performance.
That is apart from lines of study such as Medicine (Viva) and Law (mock trials) that already have oral-related content as a part of their continuous assessment.
It also affords the teacher the opportunity to do more than just teach but to also be a kind of ‘coach’ that nurtures not only the content but also the delivery of knowledge . As a teacher myself, I do subscribe to this method of teaching; after all, was it not Einstein that said – If you cannot explain it simply, then you do not understand it all.
In oral presentations, especially ones that adopt projected information, the words you speak are more important than the words you display.
However, the pictures you use are just as important as the words you speak. In no place is the saying truer – a picture is worth more than a thousand words.
Therefore, being in a position where you have to present your own perspective, with your own words and in your own style goes a long way in shaping your intellectual capabilities . It also builds self-confidence in those that eventually master it.
I wish you a hitch-free and mind-blowing experience in your next oral presentation. 😉 . Which of these tips has helped you tremendously?
Share with love!

Post Author: Ikeoluwa Ogedengbe
24 replies to “20 tips for preparing an effective oral presentation”.
Wonderful post! Putting these suggestions into practice will make anyone a ‘better’ presenter! Multiple thumbs up!
Sure, they will. Thanks for reading!
Thanks for this post, I believe it will help me gather more confidence in public speaking.
All the best in your next public speaking engagement, Josephine.
Love this post! I have a fear of public speaking so this checklist is so helpful! Thanks for sharing!
I’m glad you love it, Lissy.
Cool, just cool. I like it.
Thanks, Yeahme.
Thank you these are great tips! I have always had a lot of self confidence but always struggle with imposter syndrome so I get so nervous before public speaking!
Aww, I am sure these tips and a lot of practice will take the nervousness away.
This reminds me of my speech 101 class in college. I definitely with these tips — especially the one about knowing the content. Nothing prepares you more than knowing what you are talking about.
That’s absolutely right!
I used to work for a company that offered feedback for corporate leaders on presenting and I agree with everything you say. Bringing your personality into a presentation or speech can make a huge difference but it can take practice to get comfortable enough to bring that energy.
Yes, practice does a lot to make one perfect. Thanks for your input, Sarah.
This is a very helpful post. I wish I had read this when I was still a student. I didn’t like oral presentations and this could have given me a better perspective.
Awww, You may pass on the message to young students to ensure they get it right early.
Great read. Very helpful for my upcoming convention. Thanks for sharing.
I’m glad this helped. I wish you a splendid convention, Allison.
I precisely had to appreciate you once more. I do not know what I could possibly have followed in the absence of those thoughts provided by you on my field. Previously it was a very traumatic problem in my circumstances, however , discovering this professional fashion you managed the issue made me to jump with gladness. Now i am grateful for this information and even have high hopes you comprehend what a great job you have been carrying out instructing many people all through a blog. Most probably you have never come across all of us.
You’re welcome!
I truly enjoy looking through on this web site , it holds superb content .
You’re welcome
I just wanted to make a small note to say thanks to you for all of the fantastic ideas you are giving at this site. My time intensive internet research has at the end of the day been recognized with beneficial know-how to write about with my pals. I would believe that we readers are really endowed to exist in a really good community with very many outstanding individuals with good secrets. I feel somewhat fortunate to have come across your site and look forward to plenty of more fabulous minutes reading here. Thanks a lot again for everything.
Happy to help.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of new posts by email.
Discover more from Explicit Success
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.

24 Oral Presentations
Many academic courses require students to present information to their peers and teachers in a classroom setting. This is usually in the form of a short talk, often, but not always, accompanied by visual aids such as a power point. Students often become nervous at the idea of speaking in front of a group.
This chapter is divided under five headings to establish a quick reference guide for oral presentations.

A beginner, who may have little or no experience, should read each section in full.

For the intermediate learner, who has some experience with oral presentations, review the sections you feel you need work on.

The Purpose of an Oral Presentation
Generally, oral presentation is public speaking, either individually or as a group, the aim of which is to provide information, entertain, persuade the audience, or educate. In an academic setting, oral presentations are often assessable tasks with a marking criteria. Therefore, students are being evaluated on their capacity to speak and deliver relevant information within a set timeframe. An oral presentation differs from a speech in that it usually has visual aids and may involve audience interaction; ideas are both shown and explained . A speech, on the other hand, is a formal verbal discourse addressing an audience, without visual aids and audience participation.
Types of Oral Presentations
Individual presentation.
- Breathe and remember that everyone gets nervous when speaking in public. You are in control. You’ve got this!
- Know your content. The number one way to have a smooth presentation is to know what you want to say and how you want to say it. Write it down and rehearse it until you feel relaxed and confident and do not have to rely heavily on notes while speaking.
- Eliminate ‘umms’ and ‘ahhs’ from your oral presentation vocabulary. Speak slowly and clearly and pause when you need to. It is not a contest to see who can race through their presentation the fastest or fit the most content within the time limit. The average person speaks at a rate of 125 words per minute. Therefore, if you are required to speak for 10 minutes, you will need to write and practice 1250 words for speaking. Ensure you time yourself and get it right.
- Ensure you meet the requirements of the marking criteria, including non-verbal communication skills. Make good eye contact with the audience; watch your posture; don’t fidget.
- Know the language requirements. Check if you are permitted to use a more casual, conversational tone and first-person pronouns, or do you need to keep a more formal, academic tone?
Group Presentation
- All of the above applies, however you are working as part of a group. So how should you approach group work?
- Firstly, if you are not assigned to a group by your lecturer/tutor, choose people based on their availability and accessibility. If you cannot meet face-to-face you may schedule online meetings.
- Get to know each other. It’s easier to work with friends than strangers.
- Also consider everyone’s strengths and weaknesses. This will involve a discussion that will often lead to task or role allocations within the group, however, everyone should be carrying an equal level of the workload.
- Some group members may be more focused on getting the script written, with a different section for each team member to say. Others may be more experienced with the presentation software and skilled in editing and refining power point slides so they are appropriate for the presentation. Use one visual aid (one set of power point slides) for the whole group. Take turns presenting information and ideas.
- Be patient and tolerant with each other’s learning style and personality. Do not judge people in your group based on their personal appearance, sexual orientation, gender, age, or cultural background.
- Rehearse as a group, more than once. Keep rehearsing until you have seamless transitions between speakers. Ensure you thank the previous speaker and introduce the one following you. If you are rehearsing online, but have to present in-person, try to schedule some face-to-face time that will allow you to physically practice using the technology and classroom space of the campus.
- For further information on working as a group see:
Working as a group – my.UQ – University of Queensland
Writing Your Presentation
Approach the oral presentation task just as you would any other assignment. Review the available topics, do some background reading and research to ensure you can talk about the topic for the appropriate length of time and in an informed manner. Break the question down as demonstrated in Chapter 17 Breaking Down an Assignment. Where it differs from writing an essay is that the information in the written speech must align with the visual aid. Therefore, with each idea, concept or new information you write, think about how this might be visually displayed through minimal text and the occasional use of images. Proceed to write your ideas in full, but consider that not all information will end up on a power point slide. After all, it is you who are doing the presenting , not the power point. Your presentation skills are being evaluated; this may include a small percentage for the actual visual aid. This is also why it is important that EVERYONE has a turn at speaking during the presentation, as each person receives their own individual grade.
Using Visual Aids
A whole chapter could be written about the visual aids alone, therefore I will simply refer to the key points as noted by my.UQ
To keep your audience engaged and help them to remember what you have to say, you may want to use visual aids, such as slides.
When designing slides for your presentation, make sure:
- any text is brief, grammatically correct and easy to read. Use dot points and space between lines, plus large font size (18-20 point).
- Resist the temptation to use dark slides with a light-coloured font; it is hard on the eyes
- if images and graphs are used to support your main points, they should be non-intrusive on the written work
Images and Graphs
- Your audience will respond better to slides that deliver information quickly – images and graphs are a good way to do this. However, they are not always appropriate or necessary.
When choosing images, it’s important to find images that:
- support your presentation and aren’t just decorative
- are high quality, however, using large HD picture files can make the power point file too large overall for submission via Turnitin
- you have permission to use (Creative Commons license, royalty-free, own images, or purchased)
- suggested sites for free-to-use images: Openclipart – Clipping Culture ; Beautiful Free Images & Pictures | Unsplash ; Pxfuel – Royalty free stock photos free download ; When we share, everyone wins – Creative Commons
This is a general guide. The specific requirements for your course may be different. Make sure you read through any assignment requirements carefully and ask your lecturer or tutor if you’re unsure how to meet them.
Using Visual Aids Effectively
Too often, students make an impressive power point though do not understand how to use it effectively to enhance their presentation.
- Rehearse with the power point.
- Keep the slides synchronized with your presentation; change them at the appropriate time.
- Refer to the information on the slides. Point out details; comment on images; note facts such as data.
- Don’t let the power point just be something happening in the background while you speak.
- Write notes in your script to indicate when to change slides or which slide number the information applies to.
- Pace yourself so you are not spending a disproportionate amount of time on slides at the beginning of the presentation and racing through them at the end.
- Practice, practice, practice.
Nonverbal Communication
It is clear by the name that nonverbal communication are the ways that we communicate without speaking. Many people are already aware of this, however here are a few tips that relate specifically to oral presentations.
Being confident and looking confident are two different things. Fake it until you make it.
- Avoid slouching or leaning – standing up straight instantly gives you an air of confidence.
- Move! When you’re glued to one spot as a presenter, you’re not perceived as either confident or dynamic. Use the available space effectively, though do not exaggerate your natural movements so you look ridiculous.
- If you’re someone who “speaks with their hands”, resist the urge to constantly wave them around. They detract from your message. Occasional gestures are fine.
- Be animated, but don’t fidget. Ask someone to watch you rehearse and identify if you have any nervous, repetitive habits you may be unaware of, for example, constantly touching or ‘finger-combing’ your hair, rubbing your face.
- Avoid ‘voice fidgets’ also. If you needs to cough or clear your throat, do so once then take a drink of water.
- Avoid distractions. No phone turned on. Water available but off to one side.
- Keep your distance. Don’t hover over front-row audience members; this can be intimidating.
- Have a cheerful demeaner. You do not need to grin like a Cheshire cat throughout the presentation, yet your facial expression should be relaxed and welcoming.
- Maintain an engaging TONE in your voice. Sometimes it’s not what you’re saying that is putting your audience to sleep, it’s your monotonous tone. Vary your tone and pace.
- Don’t read your presentation – PRESENT it! Internalize your script so you can speak with confidence and only occasionally refer to your notes if needed.
- Lastly, make good eye contact with your audience members so they know you are talking with them, not at them. You’re having a conversation. Watch the link below for some great speaking tips, including eye contact.
Below is a video of some great tips about public speaking from Amy Wolff at TEDx Portland [1]
- Wolff. A. [The Oregonion]. (2016, April 9). 5 public speaking tips from TEDxPortland speaker coach [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JNOXZumCXNM&ab_channel=TheOregonian ↵
communication of thought by word
Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2021 by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Principedia

Ten Steps to Preparing an Effective Oral Presentation
- Determine the purpose of your presentation and identify your own objectives.
- Know your audience and what it knows.
- Define your topic.
- Arrange your material in a way that makes sense for your objectives.
- Compose your presentation.
- Create visual aids.
- Practice your presentation (don’t forget to time it!)
- Make necessary adjustments.
- Analyze the room where you’ll be giving your presentation (set-up, sight lines, equipment, etc.).
- Practice again.
- ← Answering Questions
- Novice v. Expert Problem Solvers →
Grand Valley State University
Search people & pages, office of undergraduate research and scholarship.
- Student Ambassadors
- Undergraduate Research Council
- What is Research?
- How to Get Started
- Programs & Grants
- Research/Creative Scholar Transcript Designation
- Student Spotlights
- Engaging Students
- Funding Opportunities
- Faculty Resources
- Outreach Presentation Request
- Chalk Art Symposium
- Undergraduate Research Fair
- Student Scholars Day
- Student Summer Scholars
- Events Calendar
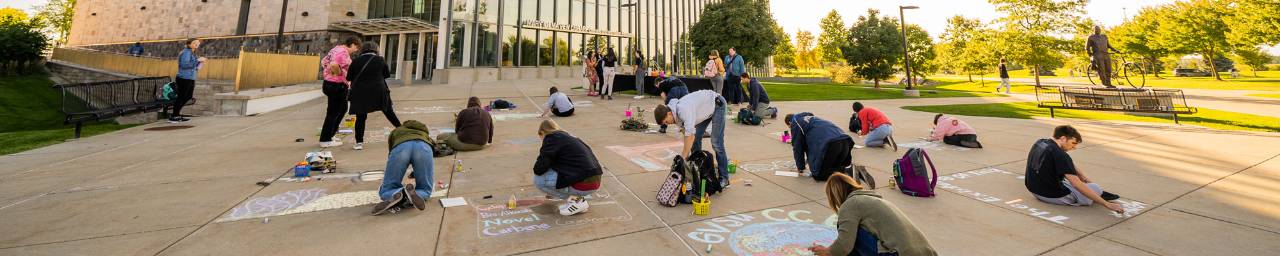
Students translate research from traditional posters and oral talks to the sidewalk at the first annual GVSU Chalk Art Symposium.
Oral Presentation Tips
An oral presentation is more than just reading a paper or set of slides to an audience. How you deliver your presentation is at least as important in effectively communicating your message as what you say. Use these guidelines to learn simple tools that help you prepare and present an effective presentation, and design PowerPoint slides that support and enhance your talk.
Preparing an Effective Presentation An effective presentation is more than just standing up and giving information. A presenter must consider how best to communicate the information to the audience. Use these tips to create a presentation that is both informative and interesting:
- Organize your thoughts. Start with an outline and develop good transitions between sections. Emphasize the real-world significance of your research.
- Have a strong opening. Why should the audience listen to you? One good way to get their attention is to start with a question, whether or not you expect an answer.
- Define terms early. If you are using terms that may be new to the audience, introduce them early in your presentation. Once an audience gets lost in unfamiliar terminology, it is extremely difficult to get them back on track.
- Finish with a bang. Find one or two sentences that sum up the importance of your research. How is the world better off as a result of what you have done?
- Design PowerPoint slides to introduce important information. Consider doing a presentation without PowerPoint. Then consider which points you cannot make without slides. Create only those slides that are necessary to improve your communication with the audience.
- Time yourself. Do not wait until the last minute to time your presentation. You only have 15 minutes to speak, so you want to know, as soon as possible, if you are close to that limit.
- Create effective notes for yourself. Have notes that you can read. Do not write out your entire talk; use an outline or other brief reminders of what you want to say. Make sure the text is large enough that you can read it from a distance.
- Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your presentation, the more comfortable you will be in front of an audience. Practice in front of a friend or two and ask for their feedback. Record yourself and listen to it critically. Make it better and do it again.
PowerPoint Tips Microsoft PowerPoint is a tremendous tool for presentations. It is also a tool that is sometimes not used effectively. If you are using PowerPoint, use these tips to enhance your presentation:
- Use a large font. As a general rule, avoid text smaller than 24 point.
- Use a clean typeface. Sans serif typefaces, such as Arial, are generally easier to read on a screen than serif typefaces, such as Times New Roman.
- Use bullet points, not complete sentences. The text on your slide provides an outline to what you are saying. If the entire text of your presentation is on your slides, there is no reason for the audience to listen to you. A common standard is the 6/7 rule: no more than six bulleted items per slide and no more than seven words per item.
- Use contrasting colors. Use a dark text on a light background or a light text on a dark background. Avoid combinations of colors that look similar. Avoid red/green combinations, as this is the most common form of color blindness.
- Use special effects sparingly. Using animations, cool transition effects, sounds and other special effects is an effective way to make sure the audience notices your slides. Unfortunately, that means that they are not listening to what you are saying. Use special effects only when they are necessary to make a point.
Presenting Effectively When you start your presentation, the audience will be interested in what you say. Use these tips to help keep them interested throughout your presentation:
- Be excited. You are talking about something exciting. If you remember to be excited, your audience will feel it and automatically become more interested.
- Speak with confidence. When you are speaking, you are the authority on your topic, but do not pretend that you know everything. If you do not know the answer to a question, admit it. Consider deferring the question to your mentor or offer to look into the matter further.
- Make eye contact with the audience. Your purpose is to communicate with your audience, and people listen more if they feel you are talking directly to them. As you speak, let your eyes settle on one person for several seconds before moving on to somebody else. You do not have to make eye contact with everybody, but make sure you connect with all areas of the audience equally.
- Avoid reading from the screen. First, if you are reading from the screen, you are not making eye contact with your audience. Second, if you put it on your slide, it is because you wanted them to read it, not you.
- Blank the screen when a slide is unnecessary. A slide that is not related to what you are speaking about can distract the audience. Pressing the letter B or the period key displays a black screen, which lets the audience concentrate solely on your words. Press the same key to restore the display.
- Use a pointer only when necessary. If you are using a laser pointer, remember to keep it off unless you need to highlight something on the screen.
- Explain your equations and graphs. When you display equations, explain them fully. Point out all constants and dependent and independent variables. With graphs, tell how they support your point. Explain the x- and y-axes and show how the graph progresses from left to right.
- Pause. Pauses bring audible structure to your presentation. They emphasize important information, make transitions obvious, and give the audience time to catch up between points and to read new slides. Pauses always feel much longer to speakers than to listeners. Practice counting silently to three (slowly) between points.
- Avoid filler words. Um, like, you know, and many others. To an audience, these are indications that you do not know what to say; you sound uncomfortable, so they start to feel uncomfortable as well. Speak slowly enough that you can collect your thoughts before moving ahead. If you really do not know what to say, pause silently until you do.
- Relax. I t is hard to relax when you are nervous, but your audience will be much more comfortable if you are too.
- Breathe. It is fine to be nervous. In fact, you should be all good presenters are nervous every time they are in front of an audience. The most effective way to keep your nerves in check aside from a lot of practice before hand is to remember to breathe deeply throughout your presentation.
- Acknowledge the people who supported your research. Be sure to thank the people who made your research possible, including your mentor, research team, collaborators, and other sources of funding and support.
Sharing your work can help you expand your network of contacts who share your research interests. For undergraduate researcher who intend to complete a graduate degree, presenting can be an invaluable experience. We recommend discussing your interest in sharing your research with your faculty advisor. They can help match your interests with the appropriate venue.
Office of Undergraduate Research and Scholarship Center for Undergraduate Scholar Engagement 230 Mary Idema Pew Library 1 Campus Drive Allendale , Michigan 49401
(616) 331-8100 ours@gvsu.edu
Monday - Friday 8:00 a.m. - 5:00 p.m.
Social Media
https://www.facebook.com/GVSU.OURS https://www.instagram.com/cuse_gvsu/ https://www.linkedin.com/groups/4644589/profile https://twitter.com/CUSE_GVSU https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCyjiHk8_L10kO2QIn9NcoFA
- GVSU is an AA/EO Institution
- Privacy Policy
- HEERF Funding
- Disclosures
- Copyright © 2024 GVSU
The 6 types of presentation (and why you need them)
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation , Public Speaking

We all have been exposed to different types of presentations right from school years.
Group presentations, lectures by teachers and professors, seminars, webinars or online presentations, e-learning, e-conferences, etc., are all different types of presentations that we come across in our daily lives.
But each of them work for different settings.
In this article, we will take a look at 6 such types of presentations and when and why you need them.
1. Informative Presentations
This is the most common type of presentation, be it in an educational setting or business or corporate setting.
The aim of an informative presentation is to give detailed information about a product, concept, or idea to a specific kind of audience.
They are often analytical or require a rational analysis of the data presented.
Training sessions or one-day workshops are good examples where this kind of presentation is used.
Here is an example of an informative presentation on public speaking and presentations.
Now, there are different situations where you can use informative presentations.
a) Reporting

Although a report is a written explanation of an event, it can also be verbal.
A perfect place to use informative presentations is news reporting , as it requires the presenter to present information systematically.
b) Briefing

This involves explaining both positive and negative aspects of a particular topic in a few words.
It is providing information quickly and effectively about an issue to influence decisions or to come to solutions.
Hence, the decision-making bodies of an organization can make use of this kind of presentation to save time and effectively come to conclusions.
c) Research
Informative presentations are often used to present research findings to a specific audience , as it involves reporting the findings and briefing it to the audience.
Hence, almost everywhere where research takes place, be it in an educational context or occupational , can make use of this kind of presentation.
Tips for giving informative presentations
- As there would be a lot of technical information and statistics, focus on the main points or agenda first and if you have more time, you can add them at the end
- Keep your presentation simple and clear . Avoid complex sentence structures and graphics
- Tell the outline of your presentation briefly in the introduction for a better flow
- Make sure that your presentation does not stretch for too long. 10-15 minutes is what your audience can concentrate on
- Restate your keyphrase at the end and briefly summarize all the important points of your presentation
Speech topics for an informative presentation
- Cropping techniques
- Organic Farming
- Corporate Farming
- Hydroponics
- Sustainable Agriculture, etc
- Climate change
- Environmental issues
- Eco-friendly ways of management
- Eco-politics
- Eco-feminism, etc
- Gender studies
- Gender and education
- Religious studies
- History of education
- Philosophy of education, etc
- Ethnic cultures
- Indigenous cultures
- Multiculturalism
- Popular culture
- Cultural trends, etc
- Business administration
- Business ethics
- Business models
- Promotion and marketing communications
- Finance, etc
2. Persuasive presentations
Persuasion is the art of motivating or convincing someone to act or make a change in their actions or thoughts.
If you are planning to give a persuasive presentation, and are looking for how to give a persuasive speech, check out our article on A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Persuasive Speech to gain in-depth knowledge about the art of giving persuasive presentations.
Persuasive presentations are also widely used form after informative presentations.
There are various circumstances where persuasive presentations can be used.
a) Policy-making

Government bodies make use of persuasion almost every time, be it the legislative or decision-making bodies, executive bodies, or even courts.
Even election campaigns involve using persuasive presentations as an instrument of their pre-determined goals of swaying the citizens.
For that matter, any executive or management body of an organization can make use of these kinds of presentations.
b) Value judgment

This kind involves answering the question “why” and supplementing it with possible benefits.
Most Ted talks and YouTube videos try to persuade the audience and fall into the persuasive presentation category.
Even religious heads use this as a means of persuading their believers to follow their belief system.
Deciding on a procedure or telling an audience the correct procedure of doing something is another situation.
An example of a persuasive presentation
Bailey parnell: is social media hurting your mental health.
This TED talk by Bailey Parnell is a good example of a persuasive presentation.
She starts strong by asking rhetorical questions that set the mood for her further points.
We can also see how the speaker is genuinely concerned regarding the issue, engaging the audience till the end.
Tips for giving a persuasive presentation
- Start your presentation with a relevant quote or statistics about your topic to establish credibility
- Tell personal anecdotes and examples wherever necessary to develop an emotional connection with your audience
- Deliver your presentation with passion and genuine interest to motivate your audience to think
- Answer the question “why” for better understanding and clarity in your presentation
- State your viewpoint clearly and clarify doubts if your audience seems to have any
Speech topics for persuasive presentations
- Is animal testing ethical?
- Should cosmetic surgery be banned?
- Can the death penalty be the only solution to the rising crime rates?
- Should the legal age be 18?
- Should immigration laws be revised?
- Why you should never add your parents on Facebook
- Guys are more interested in gossip than girls
- It is your major duty to annoy your parents
- You are not enjoying student life if you are not procrastinating
- Endless memes can be made on my life, etc
- Is taming wild and exotic animals ethical?
- The importance of emotional support animals
- Why are bunnies the perfect pet?
- Why do animals make the best companions?
- Why there is a need for patients to have emotional support animals, etc
- How and why there is a need to do business analysis before opening your business?
- Why small businesses are successful and more profitable?
- Why do sales and customer service departments need to be paid more?
- Why does the HR department need to be polite and understanding?
- Why should you not do business with a family member?
- How charity is a means of converting black money to white?
- Why is detaining people on the suspicion of terrorism justified?
- Should euthanasia be made legal?
- Should violent crime offenders be sentenced to death?
- Should foreigners be allowed to buy a property?
3. Demonstrative presentations
This involves demonstrating a process or the functioning of a product in a step-by-step fashion.
So, a master class on communication skills or making a product model is an example of a demonstrative presentation.
Usually, the audience is an active part of such presentations and these can work in any context where you want the audience to learn a new skill.
a) Instructions

This involves giving guidelines or steps of a process or work .
Teaching how to make a car model step-by-step is a good example where you can use this kind of informative presentation to guide your audience.
Another instance can be at the workplace , to train the employees or introduce them to a new product at work.
This type also works with demonstrating recipes and cooking workshops.
An example of demonstrative presentation
The easy guide on making just about any smoothie.
In this recipe demonstration, he tells his audience how many ingredients are involved and briefs them about the outline of his presentation at the start of his speech.
He also shows all steps in real-time so that the audience have a better understanding of the process and keeps them engaged.
Tips to give a demonstrative presentation
- Introduce your product and its function to your audience before telling them how to go about with the steps
- Explain the steps with diagrams or show them in real-time along with the audience
- Give equal time to every person in the audience for clearing doubts, if any
- Keep your introduction short. Not more than 5 minutes
- Discuss options or variations that the audience can try at the end of the presentation
Speech topics for demonstrative presentations
- How to administer CPR
- How to wrap a gift professionally
- How to budget your monthly income
- How to choose a car insurance
- How to restore a piece of antique furniture
4. Inspirational presentations
As the name suggests, this type of presentation involves inspiring others!
The main aim of an inspirational presentation is to motivate or move your audience and is also known as a motivational presentation.
Using techniques like storytelling, narrating personal anecdotes , or even humor work wonders as your audience develops an emotional connection to the message.
This TED talk by Luvvie Ajayi Jones is humorous but a lot more inspirational. Check it out!
Tips for giving an inspirational presentation
- Start with a question that will leave the audience thinking. Pause for some time and then begin with your presentation
- Develop a sense of connection by narrating personal incidents and experiences to grow empathy
- Have some main points that you want to emphasize on
- Make use of humor ! It instantly builds a connection with the listener
- Non-verbal elements like paralanguage, body language, speech modulations, tone, etc., makes a huge difference
Speech topics for an inspirational presentation
- Importance of diversity and inclusion
- Building mental resilience
- Need for change management
- Valuing small victories in life
- How procrastinating is your enemy
5. Business presentations
In the corporate world, presentations are the go-to solution to do anything: planning or strategizing, articulating company goals, screening candidates, status reports , and many more.
Let us take a dive into the different types of business presentations.
a) Sales presentation

Also known as sales pitches , sales presentations involve providing information about a product or a service to sell it.
It has a pre-defined strategy of initiating and closing the sales deal.
This can be done in person or nowadays, on the phone, or via e-communication .
b) Training sessions

Often employees have on-the-job training sessions that are aimed to increase the knowledge and skills of the employees.
This kind can also involve the audience to participate , like in demonstrative presentations.
c) Meetings

Meetings can be called for for different reasons and can be of different forms as well.
Conferences ( both video and in-person), board meetings, informal team meetings, daily reporting, etc., are all various contexts of meeting in a business setting.
d) E- presentations
E- presentations existed before the COVID pandemic as well but were used seldom.
But, with the ongoing pandemic, e-presentations or remote presentations have replaced all other types of presentations and will be with us for a while longer.
However, on the brighter side, it is an eco-friendly alternative to normal face-to-face kind of a set-up, and it also saves transportation and other costs !
e) Seminars

Seminars are widely used in the health sector , usually involving a panel of speakers on a topic. The audience is anywhere between 10 to 100.
It ends with a question and answers session , and the audience gets to take handouts with them.
f) One-on-one or 1:1

Interviews are usually one-on-one and involve presenting your achievements and capabilities to your prospective employer.
Apart from interviews, 1:1 meetings are also used in sales and marketing to crack a business deal.
Tips for giving business presentations
- Include key phrases and other important details on your slides and make them bold
- Avoid casual slangs and informal tone of speech
- If you are giving a sales presentation, explain your product or service in simple and clear words , and list the reasons why it is beneficial for your potential clients
- Make sure to be on time ! Delaying your audience will work against you and leave a bad impression on you and your company
- Know your material or content thoroughly to answer the questions asked by your audience
Speech topics for business presentations
- Implementing an Agile Project
- Introduction to data modeling
- Introduction to UML(Unified Modeling Language)
- Social Media strategies for a successful business
- Business writing for managers
6. Powerpoint presentations
PowerPoint presentations or PPTs are the most effective ones among all types of presentations simply because they are convenient and easy to understand .
They are available in different formats and are suitable to use in practically any type of presentation and context, be it business, educational, or for informal purposes.
There are various types of PowerPoint presentations that you can use depending on the context.
a) PPTs for general audience

- For general audiences, avoid using jargon terms
If you feel that you need to use them, provide the audience some background information about the field or topic being covered
- Avoid using more than 8 words per line, as anything more than that becomes difficult to remember
- Use bullets or a numbered list for better retention
- Try not to read from your PPT
- Give handouts or record your presentation in case anyone wants it
b) PPTs for teaching

- In this case, the PowerPoint is content-based
- Make sure that the words on the slides are visible
- Use bigger font and avoid fancy fonts
- Add relevant pictures and graphics to keep your audience engaged
- You can also add documentaries or relevant videos to aid in understanding
c) Repurpose PPTs
- This involves reinventing an earlier ppt or combining 1 or more than 1 PowerPoints
- Giving new touches to an earlier PPT or changing the format
- You can take any slide of your PPT and upload it on social media for growing your brand or business
- You can even convert your PPT into mp4 , i.e, video format
- You can even add voice and save the mp4 format, and you have a good marketing plan!
d) PechaKucha

- This type of PowerPoint presentation comes from the Japanese word PechaKucha meaning sound of a conversation or chit-chat
- This involves changing slides every 20 seconds
- There can be a maximum of 20 slides , which means your presentation lasts for only 6 minutes and 40 seconds
- The PPT mostly has graphics and fewer words
- This type of presentation is best suited for telling a story or a personal anecdote
e) Multimedia presentations

- This is the best kind of PPT to engage your audience
- It contains texts along with pictures, videos, infographics, music, illustrations, GIFs , and many more
- Add higher resolution images and videos , or even a 360-degree snapshot if you are in the sales and marketing industry
- Adding infographics such as charts and graphs makes the process of understanding easier and saves time
- Music in a PPT helps your audience to be relaxed, at the same time making them alert and engaged
Types of slides in a presentation
PowerPoint presentation slides are broadly classified into 3 categories: Text, Visual, and Mixed slides.
1. Text slides
As the name suggests, this category of slides involve words or texts.
You can format the text as plain sentences or pointers.
You may even arrange them all in a single slide or one line per slide.
The slide seen below is an example where every point is mentioned in a single slide.
2. Visual slides
This type of slide has visual elements such as images or videos , and are better known as conceptual slides since they are a better option than text slide to explain a particular concept.
You can use them at the start of the presentation to better visualize and grasp the meaning of the presentation.
The slide right below is a good example of a visual slide.

3. Mixed slides
Mixed slides combine the texts and visuals to give a comprehensive understanding of any concept or a speech.
Graphs and charts are the best examples of mixed slides.
Mixed slides have an advantage over the other slides; they keep your audience engaged, listening and participating more actively!
![oral presentation understanding Presentation Design: A Visual Guide to Creating Beautiful Slides [Free E-Book]](https://visme.co/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Say-It-Visually.jpg)
Types of Oral presentations
So far we came across 6 types of presentations, and they all share one common feature. They are all one of the types of oral presentations.
Oral presentations involve the use of verbal and non-verbal elements to deliver a speech to a particular or general audience.
All the types we discussed fall into these 4 broad categories:
1. Extemporaneous presentations
This type of presentation involves making short pointers or key phrases to aid while speaking.
You do not memorize, but organize the points and structure the speech way in advance.
Hence, on the day of your presentation, by just looking at the key points , you expand on them and move to the next point.
2. Impromptu presentations
Impromptu presentations are spoken without any preparation . It can be nerve-wracking for many, and hence not many are in favor of it.
There is a valid reason for their fear, as you have to make your speech as you say it!
However, those who are experts in their fields and are called upon to share a few words can easily give this type of presentation.
3. Manuscript presentations
The other extreme of the spectrum is manuscript presentations.
Here you have a script and you speak from it, word by word.
News anchors and show announcers usually engage in this type, since there are a lot of specific details that cannot be said wrong, and also, time constraints.
Usually, a prompter is used, from which the speaker speaks to their audience.
Nowadays, there are teleprompters , that are heavily used in the entertainment and media industry.
It is a digital screen that displays the contents, and the speaker speaks from it.
4. Memorized presentations
This type does not have any notes or cues , but you memorize or rote learn the whole speech.
School and some presentations at the workplace involve using this kind of presentation.
In most cases, we recommend not to memorise your speech in most cases. We’ve made a video on the same and how it could lead to you potentially blanking out on stage. Highly recommend you view this quick vid before choosing memorisation as a presentation path:
But, if you do choose it for whatever reason, since you are free from notes, you are free to focus on other aspects, such as body language and gestures.

Types of presentation styles
There are various presenting styles, but they do not work for all types of presentations.
Let us get familiar with them, and know which style works with which type.
a) The storyteller

This style of presentation involves the speaker narrating stories and engaging the audience emotionally .
This technique works best with persuasive and inspirational types of presentation.
So, how to tell a story in a presentation?
- Understand and know your audience : Knowing your audience will help you with how you will frame your story, at the same time gauging the relevance of your narrative
- Know your message : Be clear with what you want to convey through your story or how you are connecting the story with your actual presentation
- Try narrative a real-life story : Inspiring presenters often take their own stories or the stories of people whom they know as a supplement to their presentation. When the audience listens to your real-life examples, they become genuinely interested in your story
- Add visual aids : Using visual aids such as pictures, videos, multimedia, etc., increases the memory retention and engagement of your audience
- Use the “you” attitude : Tell the story keeping your audience in mind because ultimately they are going to be the receivers and hence, the story should be relevant and should include their point of view as well
Want more storytelling tactics? Mystery, characterisation and the final takeaway are some more key elements of a good story for your next presentation. We’ve gone deeper into this topic in this video if you would like to know more:
b) The Visual style

Most of us are visual learners, making visual information easy to understand and retain.
Visual aids like graphics, images, diagrams, key pointers or phrases , etc., are very useful when giving any type of presentation.
Some tips of presenting with visual style:
- Include only important pointers in your PowerPoint presentation and highlight or bold them
- Try including visuals that complement what you are saying and use them as a supplementary tool to aid in understanding your audience
- If you are giving a business presentation and want to include visuals, instead of plain texts, include graphics and charts to make information simpler to present and understand
- Avoid overly complex visuals as it will confuse the audience more
- Avoid using more than 6 lines per slide
c) Analytic style

If you have data records or statistical information to be presented, an analytic style will be more helpful.
It works best for Informative and Business types of presentations.
Tips to deliver in analytic style:
- Give handouts so that the audience is on track with your presentation and the information will be easier to comprehend
- Focus and speak on selected data as too much data statistics can be overwhelming for the audience
- You can make use of humor and personal anecdotes to keep the presentation interesting and engaging
- If you have too much data and are worried that you will not be able to explain it in the time frame given, avoid writing content of more than 2000 words
Quick tip: In case you have a PDF to present and want to edit the data points, there are multiple software programs that you can use to allow you to easily do this. Check out this list of the Best Free Recording Software Programs to know more.
d) The Connector

The connector style of presentation involves the speaker establishing a connection with the audience by pointing out similarities between them and the listeners.
This style works well with Sales and marketing presentations.
How to give a presentation using connector style?
- Have a Q & A round with the audience at the end of your presentation for clarifying any doubts and avoiding miscommunication
- Use audience polls at the start of your presentation to know your audience and tailor your speech accordingly
- Make use of body language and gestures for delivering your presentation effectively. If you are confused or want to know more about the aspects of how to use body and gestures, check out our article on To walk or stand still: How should you present when on stage?
- Ask questions to your audience at regular intervals for a better audience engagement
- Make use of multimedia sources to keep your audience engaged and entertained
Which type of presentation is best?
Although all the presentation types have their own bonuses and are suitable for certain circumstances, some are universal and can be used with a little bit of modification almost everywhere!
These are persuasive presentations!
You can use them in various settings; from political, business to educational.
Just remember to choose the right topic for the right audience, and a style that you think is the most suitable and you are good to go!
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
To conclude
We saw 6 types of presentation and understood it in detail.
We also gained some tips on how to make our presentation more engaging and also came across things to avoid as well.
We then explored the types of slides that you can use, and also the types of presenting orally.
We also gave you some tips and a few topic ideas that you can incorporate in your next speech!
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Presentations
How to Do an Oral Presentation
Last Updated: April 15, 2024
This article was co-authored by Vikas Agrawal . Vikas Agrawal is a Visual Content Marketing Expert & Entrepreneur, as well as the Founder of Full Service Creative Agency Infobrandz. With over 10 years of experience, he specializes in designing visually engaging content, such as infographics, videos, and e-books. He’s an expert in Making content marketing strategies and has contributed to and been featured in many publications including Forbes, Entrepreneur.com, and INC.com. This article has been viewed 49,591 times.
The power of words can control the thoughts, emotions and the decisions of others. Giving an oral presentation can be a challenge, but with the right plan and delivery, you can move an entire audience in your favor.
Researching Your Presentation

- If speaking about the effect of junk food on an adult’s mind, include the increase of serotonin, a happiness hormone. Then inform the audience how fast the hormone drastically depletes to give out worse feelings. This gives the perspective that even the advantages of junk food are outweighed by the negative effects.

Writing Your Script

- Make sure to begin each argument with a clear description of the content such as. "The result of eating junk food has increased negative emotions such as depression, anxiety and low self-esteem". This gives the audience a quick outlook of what the argument is about. Always remember to state how the argument relates and supports the topic question.

- If necessary, this is where you could include, "My name is ___ and I will be speaking about the effect on junk food on our minds." Then you include a brief out view of each argument you will be speaking about. Do not include any information about your arguments in the introduction.

- Some example concluding sentences include, "The entire process of the mind, changed by a simple bite of a cookie. Our entire body's control system, defined by our choices of food. The definite truth. You are what you eat."
Practicing and Performing

- Taking the effort to memorize your script allows you to keep eye contact with the audience and brings confidence to your speech. Reading from an entire script can easily cause you to lose your place and stutter. Also make sure they are the same size and only put important key words or those that are hard to remember. This allows you to easily flip through and read off the cue cards.

What Is The Best Way To Start a Presentation?
Expert Q&A
- Research persuasive language techniques. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Watch online speeches to get an idea of how to tone your presentation. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Color code each sentence on your cue cards to never lose track. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.princeton.edu/~archss/webpdfs08/BaharMartonosi.pdf
- ↑ https://education.seattlepi.com/give-good-speech-presentations-college-1147.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Henry Williams
Mar 20, 2016
Did this article help you?
Pavithra Arthi
Feb 14, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Lippincott Open Access

How to deliver an oral presentation
Georgina wellstead.
a Lister Hospital, East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust
Katharine Whitehurst
b Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital
Buket Gundogan
c University College London
d Guy's St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Delivering an oral presentation in conferences and meetings can seem daunting. However, if delivered effectively, it can be an invaluable opportunity to showcase your work in front of peers as well as receive feedback on your project. In this “How to” article, we demonstrate how one can plan and successfully deliver an engaging oral presentation.
Giving an oral presentation at a scientific conference is an almost inevitable task at some point during your medical career. The prospect of presenting your original work to colleagues and peers, however, may be intimidating, and it can be difficult to know how to approach it. Nonetheless, it is important to remember that although daunting, an oral presentation is one of the best ways to get your work out there, and so should be looked upon as an exciting and invaluable opportunity.
Slide content
Although things may vary slightly depending on the type of research you are presenting, the typical structure is as follows:
- Opening slide (title of study, authors, institutions, and date)
- Methodology
- Discussion (including strengths and weaknesses of the study)
Conclusions
Picking out only the most important findings to include in your presentation is key and will keep it concise and easy to follow. This in turn will keep your viewers engaged, and more likely to understand and remember your presentation.
Psychological analysis of PowerPoint presentations, finds that 8 psychological principles are often violated 1 . One of these was the limited capacity of working memory, which can hold 4 units of information at any 1 time in most circumstances. Hence, too many points or concepts on a slide could be detrimental to the presenter’s desire to give information.
You can also help keep your audience engaged with images, which you can talk around, rather than lots of text. Video can also be useful, for example, a surgical procedure. However, be warned that IT can let you down when you need it most and you need to have a backup plan if the video fails. It’s worth coming to the venue early and testing it and resolving issues beforehand with the AV support staff if speaking at a conference.
Slide design and layout
It is important not to clutter your slides with too much text or too many pictures. An easy way to do this is by using the 5×5 rule. This means using no more than 5 bullet points per slide, with no more than 5 words per bullet point. It is also good to break up the text-heavy slides with ones including diagrams or graphs. This can also help to convey your results in a more visual and easy-to-understand way.
It is best to keep the slide design simple, as busy backgrounds and loud color schemes are distracting. Ensure that you use a uniform font and stick to the same color scheme throughout. As a general rule, a light-colored background with dark-colored text is easier to read than light-colored text on a dark-colored background. If you can use an image instead of text, this is even better.
A systematic review study of expert opinion papers demonstrates several key recommendations on how to effectively deliver medical research presentations 2 . These include:
- Keeping your slides simple
- Knowing your audience (pitching to the right level)
- Making eye contact
- Rehearsing the presentation
- Do not read from the slides
- Limiting the number of lines per slide
- Sticking to the allotted time
You should practice your presentation before the conference, making sure that you stick to the allocated time given to you. Oral presentations are usually short (around 8–10 min maximum), and it is, therefore, easy to go under or over time if you have not rehearsed. Aiming to spend around 1 minute per slide is usually a good guide. It is useful to present to your colleagues and seniors, allowing them to ask you questions afterwards so that you can be prepared for the sort of questions you may get asked at the conference. Knowing your research inside out and reading around the subject is advisable, as there may be experts watching you at the conference with more challenging questions! Make sure you re-read your paper the day before, or on the day of the conference to refresh your memory.
It is useful to bring along handouts of your presentation for those who may be interested. Rather than printing out miniature versions of your power point slides, it is better to condense your findings into a brief word document. Not only will this be easier to read, but you will also save a lot of paper by doing this!
Delivering the presentation
Having rehearsed your presentation beforehand, the most important thing to do when you get to the conference is to keep calm and be confident. Remember that you know your own research better than anyone else in the room! Be sure to take some deep breaths and speak at an appropriate pace and volume, making good eye contact with your viewers. If there is a microphone, don’t keep turning away from it as the audience will get frustrated if your voice keeps cutting in and out. Gesturing and using pointers when appropriate can be a really useful tool, and will enable you to emphasize your important findings.
Presenting tips
- Do not hide behind the computer. Come out to the center or side and present there.
- Maintain eye contact with the audience, especially the judges.
- Remember to pause every so often.
- Don’t clutter your presentation with verbal noise such as “umm,” “like,” or “so.” You will look more slick if you avoid this.
- Rhetorical questions once in a while can be useful in maintaining the audience’s attention.
When reaching the end of your presentation, you should slow down in order to clearly convey your key points. Using phases such as “in summary” and “to conclude” often prompts those who have drifted off slightly during your presentation start paying attention again, so it is a critical time to make sure that your work is understood and remembered. Leaving up your conclusions/summary slide for a short while after stopping speaking will give the audience time to digest the information. Conclude by acknowledging any fellow authors or assistants before thanking the audience for their attention and inviting any questions (as long as you have left sufficient time).
If asked a question, firstly thank the audience member, then repeat what they have asked to the rest of the listeners in case they didn’t hear the first time. Keep your answers short and succinct, and if unsure say that the questioner has raised a good point and that you will have to look into it further. Having someone else in the audience write down the question is useful for this.
The key points to remember when preparing for an oral presentation are:
- Keep your slides simple and concise using the 5×5 rule and images.
- When appropriate; rehearse timings; prepare answers to questions; speak slowly and use gestures/ pointers where appropriate; make eye contact with the audience; emphasize your key points at the end; make acknowledgments and thank the audience; invite questions and be confident but not arrogant.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest with regard to the content of this report.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Published online 8 June 2017

- Joyner Library
- Laupus Health Sciences Library
- Music Library
- Digital Collections
- Special Collections
- North Carolina Collection
- Teaching Resources
- The ScholarShip Institutional Repository
- Country Doctor Museum
Presentations: Oral Presentations
- Poster Design
- Poster Content
- Poster Presentation
- Oral Presentations
- Printing & Archiving
Oral Presentations Purpose
An Oral Research Presentation is meant to showcase your research findings. A successful oral research presentation should: communicate the importance of your research; clearly state your findings and the analysis of those findings; prompt discussion between researcher and audience. Below you will find information on how to create and give a successful oral presentation.
Creating an Effective Presentation
Who has a harder job the speaker? Or, the audience?
Most people think speaker has the hardest job during an oral presentation, because they are having to stand up in a room full of people and give a presentation. However, if the speaker is not engaging and if the material is way outside of the audiences knowledge level, the audience can have a difficult job as well. Below you will find some tips on how to be an effective presenter and how to engage with your audience.
Organization of a Presentation
Introduction/Beginning
How are you going to begin? How are you going to get the attention of your audience? You need to take the time and think about how you are going to get started!
Here are some ways you could start:
- Ask the audience a question
- make a statement
- show them something
No matter how you start your presentation it needs to relate to your research and capture the audiences attention.
Preview what you are going to discuss . Audiences do not like to be manipulated or tricked. Tell the audience exactly what you are going to discuss, this will help them follow along. *Do not say you are going to cover three points and then try to cover 8 points.
At the end of your introduction, the audience should feel like they know exactly what you are going to discuss and exactly how you are going to get there.
Body/Middle
Conclusion/End
Delivery and Communication
Eye Contact
Making eye contact is a great way to engage with your audience. Eye contact should be no longer than 2-3 seconds per person. Eye contact for much longer than that can begin to make the audience member feel uncomfortable.
Smiling lets attendees know you are happy to be there and that you are excited to talk with them about your project.
We all know that body language says a lot, so here are some things you should remember when giving your presentation.
- Stand with both feet on the floor, not with one foot crossed over the other.
- Do not stand with your hands in your pockets, or with your arms crossed.
- Stand tall with confidence and own your space (remember you are the expert).
Abbreviated Notes
Having a written set of notes or key points that you want to address can help prevent you from reading the poster.
Speak Clearly
Sometimes when we get nervous we begin to talk fast and blur our words. It is important that you make sure every word is distinct and clear. A great way to practice your speech is to say tongue twisters.
Ten tiny tots tottered toward the shore
Literally literary. Literally literary. Literally literary.
Sally soon saw that she should sew some sheets.
Avoid Fillers
Occasionally we pick up fillers that we are not aware of, such as um, like, well, etc. One way to get rid of fillers is to have a friend listen to your speech and every time you say a "filler" have that friend tap you on the arm or say your name. This will bring the filler to light, then you can practice avoiding that filler.
Manage Anxiety
Many people get nervous when they are about to speak to a crowd of people. Below are ways that you can manage your anxiety levels.
- Practice, Practice, Practice - the more prepared you are the less nervous you will be.
- Recognize that anxiety is just a big shot of adrenalin.
- Take deep breaths before your presentation to calm you down.
Components of an Oral Research Presentation
Introduction
The introduction section of your oral presentation should consist of 3 main parts.
Part 1: Existing facts
In order to give audience members the "full picture", you first need to provide them with information about past research. What facts already exist? What is already known about your research area?
Part 2: Shortcomings
Once you have highlighted past research and existing facts. You now need to address what is left to be known, or what shortcomings exist within the current information. This should set the groundwork for your experiment. Keep in mind, how does your research fill these gaps or help address these questions?
Part 3: Purpose or Hypothesis
After you have addressed past/current research and have identified shortcomings/gaps, it is now time to address your research. During this portion of the introduction you need to tell viewers why you are conducting your research experiement/study, and what you hope to accomplish by doing so.
In this section you should share with your audience how you went about collecting and analyzing your data
Should include:
- Participants: Who or what was in the study?
- Materials/ measurements: what did you measure?
- Procedures: How did you do the study?
- Data-analysis: What analysis were conducted?
This section contains FACTS – with no opinion, commentary or interpretation. Graphs, charts and images can be used to display data in a clear and organized way.
Keep in mind when making figures:
- Make sure axis, treatments, and data sets are clearly labeled
- Strive for simplicity, especially in figure titles.
- Know when to use what kind of graph
- Be careful with colors.
Interpretation and commentary takes place here. This section should give a clear summary of your findings.
You should:
- Address the positive and negative aspects of you research
- Discuss how and if your research question was answered.
- Highlight the novel and important findings
- Speculate on what could be occurring in your system
Future Research
- State your goals
- Include information about why you believe research should go in the direction you are proposing
- Discuss briefly how you plan to implement the research goals, if you chose to do so.
Why include References?
- It allows viewers to locate the material that you used, and can help viewers expand their knowledge of your research topic.
- Indicates that you have conducted a thorough review of the literature and conducted your research from an informed perspective.
- Guards you against intellectual theft. Ideas are considered intellectual property failure to cite someone's ideas can have serious consequences.
Acknowledgements
This section is used to thank the people, programs and funding agencies that allowed you to perform your research.
Questions
Allow for about 2-3 minutes at the end of your presentation for questions.
It is important to be prepared.
- Know why you conducted the study
- Be prepared to answer questions about why you chose a specific methodology
If you DO NOT know the answer to a question
Visual Aids
PowerPoints and other visual aids can be used to support what you are presenting about.
Power Point Slides and other visual aids can help support your presentation, however there are some things you should consider:
- Do not overdo it . One big mistake that presenters make is they have a slide for every single item they want to say. One way you can avoid this is by writing your presentation in Word first, instead of making a Power Point Presentation. By doing this you can type exactly what you want to say, and once your presentation is complete, you can create Power Point slides that help support your presentation.
Formula for number of visual aids : Length of presentation divided by 2 plus 1
example: 12 minute presentation should have no more than 7 slides.
- Does it add interest?
- Does it prove?
- Does it clarify?
- Do not read the text . Most people can read, and if they have the option of reading material themselves versus listen to you read it, they are going to read it themselves and then your voice becomes an annoyance. Also, when you are reading the text you are probably not engaging with the audience.
- No more than 4-6 lines on a slide and no more than 4-6 words in a line.
- People should be able to read your slide in 6 seconds.
- << Previous: Poster Presentation
- Next: Printing & Archiving >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 9:02 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ecu.edu/c.php?g=637469
Search form

Search This Site
Recipient Directory
- Getting Started
- Policies for Grants
- Double Hoo Award
- Harrison Undergraduate Research Awards
- Kenan Award
- University Undergraduate Award for Arts Projects
- URN Conference Grants
- USOAR Program
- UVA Summer Programs
- Other Opportunities
- Faculty Support
- USOAR Mentor
- Presentation Format Details
- Information For Mentors
Oral Presentation Tips
- Poster Presentations
- Research Journals
How To Make an Oral Presentation of Your Research
You’ve been working on your research for months, and now that it’s finished, or almost there, you need to make an oral presentation. Perhaps you are applying to attend the ACC Meeting of the Minds undergraduate research conference. Maybe you would like to participate in the Undergraduate Research Symposium in the spring semester here at UVA. Here are some tips to help you bring order to the ideas swirling in your head—and communicate the key points about your research to an audience.
Timing. Find out how long your talk should be. As you decide what to present, keep in mind that a ten-minute talk is very different from a 45-minute lecture. If you only have ten minutes, you’ll need to focus on the most important points. With more time, you’ll still need to focus on those points, but you’ll be able to present additional supporting detail. Time yourself giving your talk, and make cuts if you need to. It is fine to end a bit early. Going overtime shows your lack of preparation.
Audience. Find out what sort of audience will listen to your talk. Specialists in your field will bring a different sort of understanding to your presentation from a general audience; you may be able to use certain technical terms without defining them, but always beware of jargon and acronyms. With a general audience, you need to ask yourself what educated people not in your field will know, define any terms that may be unfamiliar to them, and make an effort to explain the significance of your research in terms the listeners are likely to understand.
Content. Students often think they need to explain every single thing they know or be perceived as knowing too little. This is not true. Giving a talk is a great opportunity to think about the big picture rather than focusing on details. This can be hard if you are immersed in the specifics of your project.
Step back for a moment to before you became the expert on your particular topic. What piqued your interest? Why did you start asking the questions you asked? Now step into the future. When you look back on this research, what will you remember as the most interesting or compelling thing you learned? Were there surprises?
Now you are ready to ask yourself: What are the points I want to convey? What do I want the audience to learn? When audience members remember my talk the following day, what main point do I want them to remember?
- introduce yourself;
- present your research question and why it matters;
- describe how you conducted your research,
- explain what you found out and what it means; and
- conclude with a summary of your main points.
Depending on your topic, you may need to provide background information so that the audience understands the significance of your inquiry. Be judicious in the amount of information you give, and do not let this discussion get you off track. Once you’ve provided sufficient background, bring the focus back to your research by reminding the audience of your research question.
Do not even think of opening PowerPoint until you have organized your ideas and decided on your main points. If you need guidance, see below for a sample oral presentation outline.
PowerPoint. You should treat PowerPoint as a useful tool. You can use it to incorporate images into your presentation , to emphasize important points , and to guide your audience in following your argument . You should not use it for anything else.
This means:
Don’t present too much information on the slides. The audience cannot read a long section of text and simultaneously listen to you speak about it. If you really must provide a long quotation, then highlight the words and phrases you want to emphasize, and read the quote out loud, slowly, so the audience can absorb it.
Do explain to your audience what each chart or graph indicates. Use charts and graphs to convey information clearly, not simply to show that you did the work.
Don’t spend extra time on making a fancy PowerPoint presentation with moving images and graphics unless they are vital for communicating your ideas.
Do be prepared to give your talk even if technology fails. If your charts don’t look quite right on the screen, or you forget your flash drive, or there’s a power outage, or half the audience can’t see the screen, you should still be able to make an effective presentation. (Bring a printout to speak from, just in case any of these disasters befalls you.)
Tone. It is best to approach your prepared talk as a somewhat formal occasion. Treat your audience—and your topic—with respect. Even if you know everyone in the room, introduce yourself. Don’t address audience members as “you guys.” Dress neatly. Most of all, share your enthusiasm for your subject.
Practice speaking slowly and clearly. If you want to emphasize an important point, repeat it. Practice speaking slowly and clearly.
You don’t need to read your talk, and in fact you should avoid doing so. But you should speak it out loud enough times that you know when there are points that tend to trip you up, where you might have a tendency to throw in something new and get off track, and whether some of your transitions are not smooth enough.
And, of course, time yourself. Make cuts if you need to.
Practice again.
Sample Oral Presentation Outline
Introduction Hello, my name is ____. I am a ___-year student at the University of Virginia majoring in ____. I’m going to talk to you today about my research on _____.
Context of research
- I had the opportunity to join Professor ____’s lab, where the research focus is____.
- This is research for my Distinguished Majors thesis….
- I got interested in this area because ….
Research question and significance
- I wanted to find out _______[insert your research question].
- This is an important question because _____. OR This question interested me because ______.
Research methods/design
- I thought the best way to answer this question would be by ______.
- I chose this method because….
Research activity Here’s what I did: _______.
Results Here’s what I found out: ______.
Significance of results/where this research might lead
- This result matters because….
- Now that I’ve learned this, I see that some other questions to ask are….
Conclusion/Summary of main points I set out to answer ______ [research question] by _______ [research methods]. And I discovered that ______ [brief statement of results]. This was interesting because _____ [significance]/This will help us understand ____.<
Acknowledgments
- I am grateful to my advisor, Professor _____, for her guidance.…
- My work was supported by a _____ award. OR I’d like to thank the ____ Family for their generosity.
Questions I would be happy to take your questions.

- Presentation
Oral presentation skill: what it is and how to develop it
- May 1, 2022

In each private and professional environment, effective communication is a fundamental skill. Among the various types of communication, oral shows stand out as an effective capability of conveying information, ideas, and opinions. Whether in academic, business, or social environments, the potential to deliver a compelling oral presentation can notably affect how your message is received. This article will discover what is oral presentation skills, the purpose of oral presentation, how to use them effectively, and when to use them in Presentation design services.

Table of Contents
What are Oral Presentation Skills?
Oral presentation skills refer to the ability to convey information and ideas through spoken words, body language, and visual aids in a structured and engaging manner. It involves organizing thoughts, tailoring content to the audience, and delivering the message confidently and clearly.
These skills encompass verbal and non-verbal communication techniques, ensuring your message is understood, remembered, and impactful.
The Purpose of Oral Presentation
These are the main purpose of Oral presentation skills:
1-Inform and Educate:
Oral presentations are an advantageous tool for disseminating know-how and information. Whether it is a business proposal, research finding, or an academic seminar, the main purpose is to inform and instruct the target market about the subject matter.
2-Persuade and Influence:
In a professional context, oral presentations are frequently used to persuade and affect stakeholders, customers, or colleagues. It could be a sales pitch, a project proposal, or a motivational talk to inspire action or change.
3-Showcase Skills:
Presentations can also showcase your expertise and proficiency in a particular field. A well-delivered presentation can leave a lasting impression and enhance credibility and reputation.

The different types of oral presentations
Luckily, there are different types of oral presentations. The type you give will depend on what’s needed in the situation! For example, an informative speech is typically used to educate your audience about something specific while a persuasive one tries convincing people around them that they should do/believe so-and it doesn’t matter if this works because both have their own purposes behind them anyway.
How to Use Oral Presentation Skills Effectively?
Here are some tips to improve your oral presentation skills effectively:
Know Your Audience:
Tailor your presentation to your audience’s needs, interests, and knowledge level. Understand their expectations and adjust your content accordingly to ensure maximum engagement.
Structure Your Presentation:
Organize your content into a clear and logical structure. Typically, a presentation consists of an introduction, main points with supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Ensure smooth transitions between sections to maintain flow.
Engaging Visuals:
Utilize visuals such as slides, videos, or props to complement your verbal message. Visual aids can enhance understanding and retention but avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information.
Practice and Rehearse:
Practice your presentation multiple times to become familiar with the content and delivery. Rehearsing also helps reduce nervousness and build confidence in communicating effectively.
Eye Contact and Body Language:
Maintain eye contact with the audience and use positive body language to create a connection. Gestures, facial expressions, and posture can convey confidence and enthusiasm, enhancing the impact of your message.
How to develop your oral presentation skills
To improve your oral presentation skills, be prepared and know the material inside out. Additionally, practice makes perfect! It’s helpful to pay attention not just to what you’re saying but also to how YOU are sounding–that is assuming people will actually listen anyway (which they won’t).
Eye contact can help engage an audience as well by making them feel like their opinion matters or that this person truly wants input from every single individual present at any given time during a speech/presentation session…all while smiling confidently with pride because these techniques work wonders even on oneself.
When do you need to Use Oral Presentation Skills?
1-academic settings:.
Students often use oral presentations to share research findings, present projects, or defend their theses. Mastering these skills boosts grades and prepares students for future professional endeavors.
2-Public Speaking Engagements:
Speaking at conferences, seminars, workshops, or occasions allows sharing knowledge, network, and construct recognition as a professional in your field.
3-Social and Personal Life :
Strong oral presentation capabilities are precious in daily life, whether or not speaking at family gatherings, handing over a toast at a wedding, or sharing thoughts in a neighborhood meeting.
4-Social and Personal Life:
Strong oral presentation skills are valuable in everyday life, whether speaking at family gatherings, delivering a toast at a wedding, or sharing ideas in a community meeting.

Tips for delivering an effective oral presentation
Here are a few tips to help you deliver an effective oral presentation. First, start off by grabbing your audience’s attention with an interesting opening sentence or phrase; keep them interested in what comes after that! And remember not everyone will understand all the jargon used during a technical conversation so try keeping things clear and simple – even if it means sacrificing some depth knowledge (which isn’t always bad!).
Practice makes perfect – the more you present, the better you’ll get!
Presentations are a common occurrence in today’s business world. Whether you’re giving an oral presentation to your team or pitching for investors, being able to communicate effectively and inspire lively will set clients’ minds at ease when they hear from YOU! Here is some advice on how best to approach this essential skill: Maintain eye contact with every person who speaks during yours as well as their own reactions; don’t get distracted by anything around them (including other people) because it can cause hesitation which makes someone else more comfortable speaking up instead – even if what was said wasn’t exactly relevant towards our current topic discussion., Use gestures often so everyone understands where certain points lie within the overall message.
Based on your current knowledge about what is Oral presentation skills, you are aware that they are valuable in today’s fast-paced and interconnected world. Mastering these skills allows you to communicate your ideas effectively, influence others positively, and showcase your expertise. You can become a confident and impactful communicator in any setting by understanding the purpose, honing the techniques, and recognizing when to employ oral presentation skills. So, embrace the challenge, practice, and watch as your ability to connect and inspire others soars to new heights.
What are the 5 Ps of oral presentation?
The 5Ps of Oral presentation are planning, preparation, practice, performance, and passion, which can guide you to a successful presentation.
What is the difference between public speaking and oral presentation?
The main factor of public speaking is the involvement with the live audience. However oral presentations can be carried out with or without a live audience.

- Graphic Design , UI-UX
How to Become a Motion Graphic Designer?

A Brief Overview of Lean UX

UX Strategy and Its Components
you'r more than welcome
7 days a week, 9:30 AM – 5:30 PM
contact info
[email protected] +971581974748
- LB07129, Jebel Ali Freezone, Dubai, UAE
Got a Project?
We’re a team of creatives who are excited about unique ideas and help companies to create amazing identity by offering wide range of digital services
© 2021 All rights reserved.
Be the first one who knows about updates!
enter your email address 📩
Welcome to the club 🎉.
From now on, Temis will inform you of its most valuable content and offers. You can also subscribe to this list at the moment. We will also protect your privacy

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
16 Oral Presentations
Chapter attribution.
David McMurrey and Cassandra Race
Oral Presentations
A common assignment in technical writing courses—not to mention in the workplace—is to prepare and deliver an oral presentation, a task most of us would be happy to avoid. However, while employers look for coursework and experience in preparing written documents, they also look for experience in oral presentations as well. Look back at the first chapter. Remember how important interpersonal communication skills are in the workplace.
The following was written for a standard face-to-face classroom setting. If you are taking an online technical writing course, oral reports can be sent in as “scripts,” or audio versions can be transmitted live or recorded. In any case, students may evaluate each other’s oral reports by filling out a form like the one provided at the end of this chapter or responding through the discussion board.
If you can believe the research, most people would rather have root canal surgery without novocaine than stand up in front of a group and speak. It truly is one of the great stressors. But with some help from the resources that follow, you can be a champion presenter.
For additional information on oral presentations and public speaking in general, see Effective Presentations . This is part of an online tutorial series provided by Kansas University Medical Center. This section has many resources that will be helpful to you.
Topic and Situation for the Oral Presentation
For the oral report in a technical writing course, imagine that you are formally handing over your final written report to the people with whom you set up the hypothetical contract or agreement. For example, imagine that you had contracted with a software company to write its user guide. Once you had completed it, you’d have a meeting with chief officers to formally deliver the guide. You’d spend some time orienting them to the guide, showing them how it is organized and written, and discussing some of its highlights. Your goal is to get them acquainted with the guide and to prompt them for any concerns or questions. (Your class will gladly pretend to be whoever you tell them to be during your talk.)
As you can see, you shouldn’t have to do any research to prepare for this assignment—just plan the details of your talk and get at least one visual ready. If you have a report topic that you’d prefer not to present orally, discuss other possibilities with your instructor. Here are some brainstorming possibilities in case you want to present something else:
- Informative purpose: An oral report can be primarily informative. For example, as a member of a committee involved in a project to relocate the plant, your job might be to give an oral report on the condition of the building and grounds at one of the sites proposed for purchase. Or, you might be required to go before the city council and report on the success of the new city-sponsored recycling project.
- Instructional purpose: An oral report can be instructional. Your task might be to train new employees to use certain equipment or to perform certain routine tasks.
- Persuasive purpose: An oral report can be persuasive. You might want to convince members of local civic organizations to support a city-wide recycling program. You might appear before the city council to persuade its members to reserve certain city-owned lands for park areas, softball and baseball parks, or community gardens.
- Topics: You can start by thinking of a technical subject, for example, solar panels, microprocessors, drip irrigation, or laser surgery. For your oral report, think of a subject you’d be interested in talking about, but find a reason why an audience would want to hear your oral report.
- Place or situation: You can find topics for oral reports or make more detailed plans for them by thinking about the place or the situation in which your oral report might naturally be given: at a neighborhood association? at the parent–teachers’ association meeting? at a church meeting? at the gardening club? at a city council meeting? at a meeting of the board of directors or high-level executives of a company? Thinking about an oral report this way makes you focus on the audience, their reasons for listening to you, and their interests and background. As in all technical writing situations, identifying and understanding your audience is of the utmost importance.
Content and Requirements for the Oral Presentation
The focus for your oral presentation is clear, understandable presentation; well-organized, well-planned, well-timed discussion. You don’t need to be Mr. or Ms. Slick-Operator—just present the essentials of what you have to say in a calm, organized, well-planned manner.
When you give your oral presentation, we’ll all be listening for the same things. Use the following as a requirements list, as a way of focusing your preparations:
- Situation : Plan to explain to the class what the situation of your oral report is, who you are, and who they should imagine they are. Make sure that there is a clean break between this brief explanation and the beginning of your actual oral report.
- Timing : Make sure your oral report lasts no longer than the time allotted. Your instructor will work out some signals to indicate when the mark is approaching, has arrived, or has passed.
- Indicate the purpose of your oral report
- give an overview of its contents
- find some way to interest the audience
- Visuals : Use at least one visual—preferably slides using presentation software (such as Powerpoint) or transparencies for the overhead projector. Flip charts and objects for display are okay, but avoid scribbling stuff on the chalkboard or whiteboard or relying strictly on handouts. Make sure you discuss key elements of your visuals. Don’t just throw them up there and ignore them. Point out things about them; explain them to the audience.
- Explanation : Plan to explain any technical aspect of your topic clearly and understandably. Don’t race through complex, technical stuff—slow down and explain it carefully so that we understand it.
- Transitions : Use “verbal headings”—by now, you’ve gotten used to using headings in your written work. There is a corollary in oral reports. With these, you give your audience a very clear signal you are moving from one topic or part of your talk to the next Your presentation visual can signal your headings.
- Planning : Plan your report in advance and practice it so that it is organized. Make sure that listeners know what you are talking about and why, which part of the talk you are in, and what’s coming next. Overviews and verbal headings greatly contribute to this sense of organization.
- summarize (go back over high points of what you’ve discussed)
- conclude (state some logical conclusion based on what you have presented)
- provide some last thought (end with some final interesting point but general enough not to require elaboration)
- or some combination of these three
- Questions : And certainly, you’ll want to prompt the audience for questions and concerns.
- Timing (again) : As mentioned above, be sure your oral report is carefully timed. Some ideas on how to work within an allotted time frame are presented in the next section.
Preparing for the Oral Presentation
Pick the method of preparing for the talk that best suits your comfort level with public speaking and with your topic. However, plan to do ample preparation and rehearsal—some people assume that they can just jump up there and ad-lib for so many minutes and be relaxed and informal. It doesn’t often work that way—drawing a mental blank is the more common experience. A well-delivered presentation is the result of a lot of work and a lot of practice.
Here are the obvious possibilities for preparation and delivery:
- Write a script, practice it; keep it around for quick-reference during your talk.
- Set up an outline of your talk; practice with it, bring it for reference.
- Set up cue cards, practice with them, and use them during your talk.
- Write a script and read from it.
Of course, the extemporaneous or impromptu methods are also out there for the brave and the adventurous. However, please bear in mind that up to 25 people will be listening to you—you owe them a good presentation, one that is clear, understandable, well-planned, organized, and on target with your purpose and audience.
It doesn’t matter which method you use to prepare for the talk, but you want to make sure that you know your material. The head-down style of reading your report directly from a script has problems. There is little or no eye contact or interaction with the audience. The delivery tends toward a dull, boring monotone that either puts listeners off or is hard to understand. And, most of us cannot stand to have reports read to us!
For many reasons, most people get nervous when they have to give oral presentations. Being well prepared is your best defense against the nerves. Try to remember that your classmates and instructor are a very forgiving, supportive group. You don’t have to be a slick entertainer—just be clear, organized, and understandable. The nerves will wear off someday, the more oral presenting you do. In the meantime, breathe deeply and enjoy.
The following is an example of an introduction to an oral presentation. Use it as a guide for planning your own.
Oral Presentation: Enhancement of the Recycling Program
Valerie and I represent the Austin Coalition for Recycling, a group that was founded in the late 1960s, partly in response to rising utility bills and partly out of a concern for the environment and its resources. High utility bills not only hurt each of us in our pocketbooks but also hurt the quality of life of our city as a whole.
We are all particularly proud of what a fine city we live in and what wonderful citizen involvement there is herein a whole range of civic activities. These things make our city special and ought to be the force that enables us to make a recycling program an integral part of the city’s waste management program. Backed by the City, a new powerful recycling program will contribute enormously to keeping Austin the wonderful place it is.
Valerie and I want to talk to you about how recycling works currently, how it will work once integrated with the city’s waste management program, how this integration will benefit our city, and what you can do to support this plan.
Delivering an Oral Presentation
When you give an oral report, focus on common problem areas such as these:
- Timing —Make sure you keep within the time limit. Finishing more than a minute under the time limit is also a problem. Rehearse, rehearse, rehearse until you get the timing just right.
- Volume —Obviously, you must be sure to speak loud enough so that all of your audience can hear you. You might find some way to practice speaking a little louder in the days before the oral presentation.
- Pacing, speed —Sometimes, oral presentators who are nervous talk too fast. All that adrenaline causes them to speed through their talk, making it hard for the audience to follow. In general, it helps listeners understand you better if you speak a bit more slowly and deliberately than you do in normal conversation. Slow down, take it easy, be clear…and breathe.
- Gestures and posture —Watch out for nervous hands flying all over the place. This too can be distracting—and a bit comical. At the same time, don’t turn yourself into a mannequin. Plan to keep your hands clasped together or holding onto the podium and only occasionally making some gesture. Definitely keep your hands out of your pockets or waistband. As for posture, avoid slouching at the podium or leaning against the wall. Stand up straight, and keep your head up.
- Verbal crutches —Watch out for too much “uh,” “you know,” “okay” and other kinds of nervous verbal habits. Instead of saying “uh” or “you know” every three seconds, just don’t say anything at all. In the days before your oral presentation, practice speaking without these verbal crutches. The silence that replaces them is not a bad thing—it gives listeners time to process what you are saying.
The following is an example of how topic headings can make your presentation easy for your listeners to follow.
Excerpt from an oral report
As you can see from the preceding, our fairly average-size city produces a surprisingly large amount of solid waste. What is the cost of getting rid of it? I can tell you from the start that it is not cheap…
The next sentence indicates that the speaker is moving on to a new topic (“cost”).
[discussion of the costs of disposal]
…Not only are the costs of getting rid of our garbage high, as I have shown, but it’s getting harder and harder for city officials to find areas in which to get rid of it. The geographical problems in disposal…
Planning and Preparing Visuals for the Oral Presentation
Prepare at least one visual for this report. Here are some ideas for the “medium” to use for your visuals:
- Presentation software slides —Projecting images (“slides”) using software such as Powerpoint has become the standard, even though maligned by some. One common problem with the construction of these slides is cramming too much information on individual slides. A quick search on terms like Powerpoint presentation will enable you to read about creating these slides and designing them intelligently. Of course, the room in which you use these slides has to have a computer projector.
- Transparencies for overhead projector —The overhead projector used with transparencies seems to have been relegated to antiquity—but not entirely. If you have to use this method, you will design your visual on a sheet of blank paper, then photocopy it, and create a transparency of it.
- Posterboard-size charts —Another possibility is to get some poster board and draw and letter what you want your audience to see. Of course, it’s not easy making charts look neat and professional.
- Handouts —You can run off copies of what you want your listeners to see and hand them out before or during your talk. This option is even less effective than the first two because you can’t point to what you want your listeners to see and because handouts distract listeners’ attention away from you. Still, for certain visual needs, handouts are the only choice. Keep in mind that if you are not well prepared, the handouts become a place for your distracted audience to doodle.
- Objects —If you need to demonstrate certain procedures, you may need to bring in actual physical objects. Rehearse what you are going to do with these objects; sometimes they can take up a lot more time than you expect.
Avoid just scribbling your visual on the chalkboard or whiteboard. Whatever you scribble can be neatly prepared and made into a presentation slide, transparency, or posterboard-size chart. Take some time to make your visuals look sharp and professional—do your best to ensure that they are legible to the entire audience.
As for the content of your visuals, consider these ideas:
- Drawing or diagram of key objects —If you describe or refer to any objects during your talk, try to get visuals of them so that you can point to different components or features.
- Tables, charts, graphs —If you discuss statistical data, present it in some form or table, chart, or graph. Many members of your audience may be less comfortable “hearing” such data as opposed to seeing it.
- Outline of your talk, report, or both —If you are at a loss for visuals to use in your oral presentation, or if your presentation is complex, have an outline of it that you can show at various points during your talk.
- Key terms and definitions —A good idea for visuals (especially when you can’t think of any others) is to set up a two-column list of key terms you use during your oral presentation with their definitions in the second column.
- Key concepts or points —Similarly, you can list your key points and show them in visuals. (Outlines, key terms, and main points are all good, legitimate ways of incorporating visuals into oral presentations when you can’t think of any others.)
During your actual oral report, make sure to discuss your visuals, refer to them, guide your listeners through the key points in your visuals. It’s a big problem just to throw a visual up on the screen and never even refer to it.
As you prepare your visuals, look at resources that will help you. There are many rules for using PowerPoint, down to the font size and how many words to put on a single slide, but you will have to choose the style that best suits your subject and your presentation style.
The two videos that follow will provide some pointers. As you watch them, make some notes to help you remember what you learn from them. The first one is funny: Life After Death by PowerPoint by Don McMillan, an engineer turned comedian.
Life After Death by PowerPoint
You may also have heard about the presentation skills of Steve Jobs. The video that follows is the introduction of the I-Phone…and as you watch, take notes on how Jobs sets up his talk and his visuals. Observe how he connects with the audience…and then see if you can work some of his strategies into your own presentation skills. This is a long video…you don’t need to watch it all but do take enough time to form some good impressions.
Steve Jobs iPhone Presentation
An Introduction to Technical Communication Copyright © by sherenahuntsman is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

The Power of Strong Oral and Written Communication Skills
Learn how to improve your oral and written communication skills by expressing ideas clearly, fostering understanding, and connecting with others.
Oral and written communication skills are essential components of effective interaction, involving both verbal and written forms of conveying information and ideas.
Oral communication skills encompass the ability to express thoughts, opinions, and information through spoken words, while written communication skills involve conveying messages, instructions, or thoughts using written language.
Both oral and written communication skills play a pivotal role in expressing ideas clearly, fostering understanding, and connecting with others across different contexts.
Importance of Effective Communication in Various Aspects of Life
Effective communication skills are paramount in personal, professional, and academic spheres. In the workplace, clear oral and written communication enables employees to articulate ideas, collaborate with colleagues, and present their thoughts convincingly to employers or clients.
Written communication skills are crucial for crafting professional documents such as emails, reports, and cover letters. In academic settings, effective communication aids students in presenting research, participating in discussions, and writing papers.
Moreover, in everyday life, strong communication skills foster better relationships, facilitate successful interactions, and contribute to overall clarity and understanding in various interactions.

The Importance of Oral Communication Skills
Effective verbal communication in personal relationships.
Building Strong Connections with Others: Oral communication skills are instrumental in establishing meaningful relationships. Through effective verbal communication, individuals can share thoughts, emotions, and experiences, fostering deeper connections and understanding with family, friends, and acquaintances.
Open and honest conversations enable individuals to connect on a personal level and build trust, enhancing the quality of relationships.
Resolving Conflicts and Misunderstandings: Strong verbal communication skills are essential for addressing conflicts and resolving misunderstandings.
The ability to express oneself clearly, actively listen, and provide constructive feedback aids in navigating difficult conversations. Individuals with strong oral communication skills can discuss concerns, clarify misunderstandings, and find mutually agreeable solutions, contributing to healthier and more harmonious relationships.
Professional Benefits of Strong Oral Communication
Effective Teamwork and Collaboration: In the professional realm, effective verbal communication skills are crucial for successful teamwork and collaboration.
The ability to communicate ideas, provide feedback, and actively participate in discussions contributes to a productive work environment. Teams that communicate well can exchange insights, pool talents, and achieve common goals efficiently.
Improved Public Speaking and Presentation Skills: Strong oral communication skills enhance public speaking and presentation abilities. Professionals who can convey information persuasively and engage their audience effectively make impactful presentations.
Whether delivering a pitch, leading a meeting, or presenting to a large audience, strong verbal communication skills instill confidence and captivate listeners, leaving a lasting impression.
Developing Verbal Communication Skills
Active listening techniques: .
Active listening is a foundational skill for improving oral communication. This technique involves fully engaging with the speaker, giving them your undivided attention, and understanding their message beyond just words.
By maintaining eye contact, nodding, and asking clarifying questions, you demonstrate your genuine interest and comprehension. Active listening helps foster better connections, minimizes misunderstandings, and allows you to respond thoughtfully.
Enhancing Non-Verbal Communication:
Non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions, gestures, and body language, play a significant role in conveying messages during oral communication. Developing awareness of your non-verbal cues and aligning them with your spoken words enhances your overall communication effectiveness. Positive non-verbal communication signals attentiveness, openness, and confidence, helping you build rapport and establish credibility.
Practicing Effective Speaking and Clarity of Expression:
Practicing effective speaking involves expressing ideas clearly, concisely, and confidently. Focus on articulation, pronunciation, and tone to ensure your words are understood. Using appropriate vocabulary and structuring your sentences coherently adds to your communication clarity.
Regular practice through discussions, presentations, and even role-playing scenarios can help you refine your speaking skills and overcome any hesitations or stumbling blocks in verbal communication.
The Importance of Written Communication Skills
Written communication in the workplace:.
Effective written communication is essential in professional settings for several reasons. Clear and concise emails and memos ensure that information is conveyed accurately without confusion.
Professional written reports and documentation contribute to organized and well-documented project management, decision-making, and compliance with industry standards. Strong written communication skills not only reflect your competence but also facilitate seamless communication within the team and with stakeholders.
Personal Benefits of Strong Written Communication:
Developing strong written communication skills has personal benefits beyond the workplace. It enhances your organization and critical thinking abilities as you structure your thoughts logically and coherently.
Expressing thoughts and ideas effectively in writing allows you to communicate with clarity and precision. This skill is valuable for both formal and informal contexts, from crafting persuasive essays to sharing ideas on social media. Strengthening your written communication skills empowers you to convey your messages with impact and engage with a broader audience.
Developing Written Communication Skills
Understanding the Purpose and Audience: Developing strong written communication skills involves considering the purpose and audience of your writing. Identifying why you are writing and who your target audience is helps tailor your message appropriately.
Whether it's a formal report, an email to colleagues, or a social media post, knowing your purpose guides your content and tone. For example, writing an informative report for a professional audience requires a different approach than composing a casual email to friends. Understanding your purpose and audience ensures that your written communication is relevant, engaging, and effective.
Organization and Structure in Writing: Effective writing requires proper organization and structure to present ideas coherently. Start with an introduction that captures the reader's attention and outlines the main points.
Organize the body of your writing logically, presenting ideas in a sequence that flows smoothly. Each paragraph should focus on a single idea, and transitions should link your points seamlessly.
Conclude with a summary that reinforces your main message or provides a call to action. Well-organized writing guides readers through your content and makes it easier to comprehend and remember.
Effective Use of Grammar, Punctuation, and Vocabulary: Grammatical accuracy, proper punctuation, and varied vocabulary are crucial for clear and effective written communication.
Grammatical errors and awkward phrasing can detract from your message, leading to confusion or misinterpretation. Correct punctuation enhances the clarity and readability of your writing.
Additionally, using a diverse range of vocabulary improves the richness and precision of your content. Regularly reviewing grammar rules, practicing proofreading, and expanding your vocabulary are essential steps in enhancing your written communication skills.
Integrating Oral and Written Communication Skills
Bridging the gap between oral and written communication:.
Integrating both oral and written communication skills is essential for effective communication in various contexts. While oral communication allows for immediate interaction and engagement, written communication provides a lasting record and reference.
Bridging the gap between these skills involves recognizing their complementary nature. For instance, articulating ideas clearly in writing helps structure your thoughts and can serve as a foundation for confident verbal communication.
Similarly, the ability to express yourself eloquently in speech can translate to persuasive writing. By honing both oral and written communication skills, individuals can convey their ideas comprehensively and adapt to diverse communication scenarios.
The Impact of Effective Communication Skills on Overall Success:
Proficiency in both oral and written communication is a cornerstone of overall success. In professional settings, strong communication skills enhance collaboration, leadership, and the ability to influence others positively.
Employers often seek candidates with excellent communication skills, as these skills contribute to effective teamwork, client relationships, and project management. Moreover, these skills extend to personal life, fostering better relationships and facilitating efficient interactions in everyday situations.
Mastering effective communication, whether oral or written, empowers individuals to navigate challenges, convey their ideas persuasively, and achieve their goals with confidence.
In today's interconnected world, oral and written communication skills hold immense value. The ability to convey ideas effectively through spoken and written words is pivotal in personal, academic, and professional spheres.
Strong oral communication skills enable meaningful interactions, resolving conflicts, and fostering connections. Meanwhile, proficient written communication skills allow for clear documentation, organized thought expression, and impactful written reports.
The journey towards mastering oral and written communication skills is ongoing. Continuously refining these skills offers numerous benefits, enhancing career prospects, building strong relationships, and contributing to personal growth.
Embrace opportunities to enhance your communication abilities, whether by practicing active listening, refining your writing style, or engaging in public speaking.
By prioritizing the development of these skills, you empower yourself to effectively navigate various communication scenarios, enrich your interactions, and contribute positively to your personal and professional life.
Introducing Dive: The Perfect AI Companion for 2023
Dive is your ultimate AI assistant for supercharging your meetings. Dive seamlessly integrates with popular video conferencing platforms, revolutionizing your meeting experience.
With automated task allocation, real-time transcription , and insightful analytics, Dive ensures your meetings are efficient, engaging, and result-driven. Elevate collaboration and productivity with Dive and make every meeting count.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus, mi quis viverra ornare, eros dolor interdum nulla, ut commodo diam libero vitae erat. Aenean faucibus nibh et justo cursus id rutrum lorem imperdiet. Nunc ut sem vitae risus tristique posuere.
Enjoyed this read?
Stay up to date with the latest remote work insights from our research lab

September 13, 2023

June 13, 2023
Related Articles

How to Write a Perfect Meeting Purpose Statement?

The Perfect Guide to Fast and Efficient Meetings

The Best Way to Start a Meeting

A Guide to Safety Committee Meetings
Dive into your best meetings today!
Free forever plan
No credit card required
Cancel anytime

80+ Sections
Built in Canada, India, Israel, Italy, Colombia, and USA.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
In the social and behavioral sciences, an oral presentation assignment involves an individual student or group of students verbally addressing an audience on a specific research-based topic, often utilizing slides to help audience members understand and retain what they both see and hear. The purpose is to inform, report, and explain the significance of research findings, and your critical analysis of those findings, within a specific period of time, often in the form of a reasoned and persuasive argument. Oral presentations are assigned to assess a student’s ability to organize and communicate relevant information effectively to a particular audience. Giving an oral presentation is considered an important learning skill because the ability to speak persuasively in front of an audience is transferable to most professional workplace settings.
Oral Presentations. Learning Co-Op. University of Wollongong, Australia; Oral Presentations. Undergraduate Research Office, Michigan State University; Oral Presentations. Presentations Research Guide, East Carolina University Libraries; Tsang, Art. “Enhancing Learners’ Awareness of Oral Presentation (Delivery) Skills in the Context of Self-regulated Learning.” Active Learning in Higher Education 21 (2020): 39-50.
Preparing for Your Oral Presentation
In some classes, writing the research paper is only part of what is required in reporting the results your work. Your professor may also require you to give an oral presentation about your study. Here are some things to think about before you are scheduled to give a presentation.
1. What should I say?
If your professor hasn't explicitly stated what the content of your presentation should focus on, think about what you want to achieve and what you consider to be the most important things that members of the audience should know about your research. Think about the following: Do I want to inform my audience, inspire them to think about my research, or convince them of a particular point of view? These questions will help frame how to approach your presentation topic.
2. Oral communication is different from written communication
Your audience has just one chance to hear your talk; they can't "re-read" your words if they get confused. Focus on being clear, particularly if the audience can't ask questions during the talk. There are two well-known ways to communicate your points effectively, often applied in combination. The first is the K.I.S.S. method [Keep It Simple Stupid]. Focus your presentation on getting two to three key points across. The second approach is to repeat key insights: tell them what you're going to tell them [forecast], tell them [explain], and then tell them what you just told them [summarize].
3. Think about your audience
Yes, you want to demonstrate to your professor that you have conducted a good study. But professors often ask students to give an oral presentation to practice the art of communicating and to learn to speak clearly and audibly about yourself and your research. Questions to think about include: What background knowledge do they have about my topic? Does the audience have any particular interests? How am I going to involve them in my presentation?
4. Create effective notes
If you don't have notes to refer to as you speak, you run the risk of forgetting something important. Also, having no notes increases the chance you'll lose your train of thought and begin relying on reading from the presentation slides. Think about the best ways to create notes that can be easily referred to as you speak. This is important! Nothing is more distracting to an audience than the speaker fumbling around with notes as they try to speak. It gives the impression of being disorganized and unprepared.
NOTE: A good strategy is to have a page of notes for each slide so that the act of referring to a new page helps remind you to move to the next slide. This also creates a natural pause that allows your audience to contemplate what you just presented.
Strategies for creating effective notes for yourself include the following:
- Choose a large, readable font [at least 18 point in Ariel ]; avoid using fancy text fonts or cursive text.
- Use bold text, underlining, or different-colored text to highlight elements of your speech that you want to emphasize. Don't over do it, though. Only highlight the most important elements of your presentation.
- Leave adequate space on your notes to jot down additional thoughts or observations before and during your presentation. This is also helpful when writing down your thoughts in response to a question or to remember a multi-part question [remember to have a pen with you when you give your presentation].
- Place a cue in the text of your notes to indicate when to move to the next slide, to click on a link, or to take some other action, such as, linking to a video. If appropriate, include a cue in your notes if there is a point during your presentation when you want the audience to refer to a handout.
- Spell out challenging words phonetically and practice saying them ahead of time. This is particularly important for accurately pronouncing people’s names, technical or scientific terminology, words in a foreign language, or any unfamiliar words.
Creating and Using Overheads. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kelly, Christine. Mastering the Art of Presenting. Inside Higher Education Career Advice; Giving an Oral Presentation. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Lucas, Stephen. The Art of Public Speaking . 12th edition. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2015; Peery, Angela B. Creating Effective Presentations: Staff Development with Impact . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield Education, 2011; Peoples, Deborah Carter. Guidelines for Oral Presentations. Ohio Wesleyan University Libraries; Perret, Nellie. Oral Presentations. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Speeches. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Storz, Carl et al. Oral Presentation Skills. Institut national de télécommunications, EVRY FRANCE.
Organizing the Content
In the process of organizing the content of your presentation, begin by thinking about what you want to achieve and how are you going to involve your audience in the presentation.
- Brainstorm your topic and write a rough outline. Don’t get carried away—remember you have a limited amount of time for your presentation.
- Organize your material and draft what you want to say [see below].
- Summarize your draft into key points to write on your presentation slides and/or note cards and/or handout.
- Prepare your visual aids.
- Rehearse your presentation and practice getting the presentation completed within the time limit given by your professor. Ask a friend to listen and time you.
GENERAL OUTLINE
I. Introduction [may be written last]
- Capture your listeners’ attention . Begin with a question, an amusing story, a provocative statement, a personal story, or anything that will engage your audience and make them think. For example, "As a first-gen student, my hardest adjustment to college was the amount of papers I had to write...."
- State your purpose . For example, "I’m going to talk about..."; "This morning I want to explain…."
- Present an outline of your talk . For example, “I will concentrate on the following points: First of all…Then…This will lead to…And finally…"
II. The Body
- Present your main points one by one in a logical order .
- Pause at the end of each point . Give people time to take notes, or time to think about what you are saying.
- Make it clear when you move to another point . For example, “The next point is that...”; “Of course, we must not forget that...”; “However, it's important to realize that....”
- Use clear examples to illustrate your points and/or key findings .
- If appropriate, consider using visual aids to make your presentation more interesting [e.g., a map, chart, picture, link to a video, etc.].
III. The Conclusion
- Leave your audience with a clear summary of everything that you have covered.
- Summarize the main points again . For example, use phrases like: "So, in conclusion..."; "To recap the main issues...," "In summary, it is important to realize...."
- Restate the purpose of your talk, and say that you have achieved your aim : "My intention was ..., and it should now be clear that...."
- Don't let the talk just fizzle out . Make it obvious that you have reached the end of the presentation.
- Thank the audience, and invite questions : "Thank you. Are there any questions?"
NOTE: When asking your audience if anyone has any questions, give people time to contemplate what you have said and to formulate a question. It may seem like an awkward pause to wait ten seconds or so for someone to raise their hand, but it's frustrating to have a question come to mind but be cutoff because the presenter rushed to end the talk.
ANOTHER NOTE: If your last slide includes any contact information or other important information, leave it up long enough to ensure audience members have time to write the information down. Nothing is more frustrating to an audience member than wanting to jot something down, but the presenter closes the slides immediately after finishing.
Creating and Using Overheads. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Giving an Oral Presentation. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Lucas, Stephen. The Art of Public Speaking . 12th ed. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2015; Peery, Angela B. Creating Effective Presentations: Staff Development with Impact . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield Education, 2011; Peoples, Deborah Carter. Guidelines for Oral Presentations. Ohio Wesleyan University Libraries; Perret, Nellie. Oral Presentations. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Speeches. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Storz, Carl et al. Oral Presentation Skills. Institut national de télécommunications, EVRY FRANCE.
Delivering Your Presentation
When delivering your presentation, keep in mind the following points to help you remain focused and ensure that everything goes as planned.
Pay Attention to Language!
- Keep it simple . The aim is to communicate, not to show off your vocabulary. Using complex words or phrases increases the chance of stumbling over a word and losing your train of thought.
- Emphasize the key points . Make sure people realize which are the key points of your study. Repeat them using different phrasing to help the audience remember them.
- Check the pronunciation of difficult, unusual, or foreign words beforehand . Keep it simple, but if you have to use unfamiliar words, write them out phonetically in your notes and practice saying them. This is particularly important when pronouncing proper names. Give the definition of words that are unusual or are being used in a particular context [e.g., "By using the term affective response, I am referring to..."].
Use Your Voice to Communicate Clearly
- Speak loud enough for everyone in the room to hear you . Projecting your voice may feel uncomfortably loud at first, but if people can't hear you, they won't try to listen. However, moderate your voice if you are talking in front of a microphone.
- Speak slowly and clearly . Don’t rush! Speaking fast makes it harder for people to understand you and signals being nervous.
- Avoid the use of "fillers." Linguists refer to utterances such as um, ah, you know, and like as fillers. They occur most often during transitions from one idea to another and, if expressed too much, are distracting to an audience. The better you know your presentation, the better you can control these verbal tics.
- Vary your voice quality . If you always use the same volume and pitch [for example, all loud, or all soft, or in a monotone] during your presentation, your audience will stop listening. Use a higher pitch and volume in your voice when you begin a new point or when emphasizing the transition to a new point.
- Speakers with accents need to slow down [so do most others]. Non-native speakers often speak English faster than we slow-mouthed native speakers, usually because most non-English languages flow more quickly than English. Slowing down helps the audience to comprehend what you are saying.
- Slow down for key points . These are also moments in your presentation to consider using body language, such as hand gestures or leaving the podium to point to a slide, to help emphasize key points.
- Use pauses . Don't be afraid of short periods of silence. They give you a chance to gather your thoughts, and your audience an opportunity to think about what you've just said.
Also Use Your Body Language to Communicate!
- Stand straight and comfortably . Do not slouch or shuffle about. If you appear bored or uninterested in what your talking about, the audience will emulate this as well. Wear something comfortable. This is not the time to wear an itchy wool sweater or new high heel shoes for the first time.
- Hold your head up . Look around and make eye contact with people in the audience [or at least pretend to]. Do not just look at your professor or your notes the whole time! Looking up at your your audience brings them into the conversation. If you don't include the audience, they won't listen to you.
- When you are talking to your friends, you naturally use your hands, your facial expression, and your body to add to your communication . Do it in your presentation as well. It will make things far more interesting for the audience.
- Don't turn your back on the audience and don't fidget! Neither moving around nor standing still is wrong. Practice either to make yourself comfortable. Even when pointing to a slide, don't turn your back; stand at the side and turn your head towards the audience as you speak.
- Keep your hands out of your pocket . This is a natural habit when speaking. One hand in your pocket gives the impression of being relaxed, but both hands in pockets looks too casual and should be avoided.
Interact with the Audience
- Be aware of how your audience is reacting to your presentation . Are they interested or bored? If they look confused, stop and ask them [e.g., "Is anything I've covered so far unclear?"]. Stop and explain a point again if needed.
- Check after highlighting key points to ask if the audience is still with you . "Does that make sense?"; "Is that clear?" Don't do this often during the presentation but, if the audience looks disengaged, interrupting your talk to ask a quick question can re-focus their attention even if no one answers.
- Do not apologize for anything . If you believe something will be hard to read or understand, don't use it. If you apologize for feeling awkward and nervous, you'll only succeed in drawing attention to the fact you are feeling awkward and nervous and your audience will begin looking for this, rather than focusing on what you are saying.
- Be open to questions . If someone asks a question in the middle of your talk, answer it. If it disrupts your train of thought momentarily, that's ok because your audience will understand. Questions show that the audience is listening with interest and, therefore, should not be regarded as an attack on you, but as a collaborative search for deeper understanding. However, don't engage in an extended conversation with an audience member or the rest of the audience will begin to feel left out. If an audience member persists, kindly tell them that the issue can be addressed after you've completed the rest of your presentation and note to them that their issue may be addressed later in your presentation [it may not be, but at least saying so allows you to move on].
- Be ready to get the discussion going after your presentation . Professors often want a brief discussion to take place after a presentation. Just in case nobody has anything to say or no one asks any questions, be prepared to ask your audience some provocative questions or bring up key issues for discussion.
Amirian, Seyed Mohammad Reza and Elaheh Tavakoli. “Academic Oral Presentation Self-Efficacy: A Cross-Sectional Interdisciplinary Comparative Study.” Higher Education Research and Development 35 (December 2016): 1095-1110; Balistreri, William F. “Giving an Effective Presentation.” Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 35 (July 2002): 1-4; Creating and Using Overheads. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Enfield, N. J. How We Talk: The Inner Workings of Conversation . New York: Basic Books, 2017; Giving an Oral Presentation. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Lucas, Stephen. The Art of Public Speaking . 12th ed. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2015; Peery, Angela B. Creating Effective Presentations: Staff Development with Impact . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield Education, 2011; Peoples, Deborah Carter. Guidelines for Oral Presentations. Ohio Wesleyan University Libraries; Perret, Nellie. Oral Presentations. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Speeches. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Storz, Carl et al. Oral Presentation Skills. Institut national de télécommunications, EVRY FRANCE.
Speaking Tip
Your First Words are Your Most Important Words!
Your introduction should begin with something that grabs the attention of your audience, such as, an interesting statistic, a brief narrative or story, or a bold assertion, and then clearly tell the audience in a well-crafted sentence what you plan to accomplish in your presentation. Your introductory statement should be constructed so as to invite the audience to pay close attention to your message and to give the audience a clear sense of the direction in which you are about to take them.
Lucas, Stephen. The Art of Public Speaking . 12th edition. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2015.
Another Speaking Tip
Talk to Your Audience, Don't Read to Them!
A presentation is not the same as reading a prepared speech or essay. If you read your presentation as if it were an essay, your audience will probably understand very little about what you say and will lose their concentration quickly. Use notes, cue cards, or presentation slides as prompts that highlight key points, and speak to your audience . Include everyone by looking at them and maintaining regular eye-contact [but don't stare or glare at people]. Limit reading text to quotes or to specific points you want to emphasize.
- << Previous: Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Next: Group Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

PDS Biotech Announces Abstract Accepted for Oral Presentation at 2024 ASTRO Annual Meeting
PRINCETON, N.J., Aug. 08, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- PDS Biotechnology Corporation (Nasdaq: PDSB) (“PDS Biotech” or the “Company”), a late-stage immunotherapy company focused on transforming how the immune system targets and kills cancers and the development of infectious disease vaccines, today announced that updated data from the IMMUNOCERV Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating Versamune ® HPV (formerly PDS0101) with chemoradiation to treat locally advanced cervical cancer will be presented during an oral presentation at the 2024 ASTRO Annual Meeting being held in Washington, DC, and virtually September 29 through October 2, 2024.
Details of the presentation are as follows:
Date: Tuesday, October 1, 2024, 2:50-3:00 p.m. ET Session title: SS 34 - GYN 2: Strategies and Innovations of Clinical Trials in Gynecologic Cancers Presentation title: 298 - IMMUNOCERV Phase II Trial Combining the HPV-Specific T Cell Immunotherapy PDS0101 with Chemoradiation for Treatment of Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Presenting author: Adam Grippin, M.D., Ph.D., The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
About PDS Biotechnology PDS Biotechnology is a late-stage immunotherapy company focused on transforming how the immune system targets and kills cancers and the development of infectious disease vaccines. The Company plans to initiate a pivotal clinical trial in 2024 to advance its lead program in advanced HPV16-positive head and neck squamous cell cancers. PDS Biotech’s lead investigational targeted immunotherapy Versamune ® HPV is being developed in combination with a standard-of-care immune checkpoint inhibitor, and also in a triple combination including PDS01ADC, an IL-12 fused antibody drug conjugate (ADC), and a standard-of-care immune checkpoint inhibitor.
For more information, please visit www.pdsbiotech.com .
Forward Looking Statements This communication contains forward-looking statements (including within the meaning of Section 21E of the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and Section 27A of the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended) concerning PDS Biotechnology Corporation (the “Company”) and other matters. These statements may discuss goals, intentions and expectations as to future plans, trends, events, results of operations or financial condition, or otherwise, based on current beliefs of the Company’s management, as well as assumptions made by, and information currently available to, management. Forward-looking statements generally include statements that are predictive in nature and depend upon or refer to future events or conditions, and include words such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “would,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “likely,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “intend,” “forecast,” “guidance”, “outlook” and other similar expressions among others. Forward-looking statements are based on current beliefs and assumptions that are subject to risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance. Actual results could differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statement as a result of various factors, including, without limitation: the Company’s ability to protect its intellectual property rights; the Company’s anticipated capital requirements, including the Company’s anticipated cash runway and the Company’s current expectations regarding its plans for future equity financings; the Company’s dependence on additional financing to fund its operations and complete the development and commercialization of its product candidates, and the risks that raising such additional capital may restrict the Company’s operations or require the Company to relinquish rights to the Company’s technologies or product candidates; the Company’s limited operating history in the Company’s current line of business, which makes it difficult to evaluate the Company’s prospects, the Company’s business plan or the likelihood of the Company’s successful implementation of such business plan; the timing for the Company or its partners to initiate the planned clinical trials for PDS01ADC, PDS0101, PDS0203 and other Versamune ® and Infectimune ® based product candidates; the future success of such trials; the successful implementation of the Company’s research and development programs and collaborations, including any collaboration studies concerning PDS01ADC, PDS0101, PDS0203 and other Versamune ® and Infectimune ® based product candidates and the Company’s interpretation of the results and findings of such programs and collaborations and whether such results are sufficient to support the future success of the Company’s product candidates; the success, timing and cost of the Company’s ongoing clinical trials and anticipated clinical trials for the Company’s current product candidates, including statements regarding the timing of initiation, pace of enrollment and completion of the trials (including the Company’s ability to fully fund its disclosed clinical trials, which assumes no material changes to the Company’s currently projected expenses), futility analyses, presentations at conferences and data reported in an abstract, and receipt of interim or preliminary results (including, without limitation, any preclinical results or data), which are not necessarily indicative of the final results of the Company’s ongoing clinical trials; any Company statements about its understanding of product candidates mechanisms of action and interpretation of preclinical and early clinical results from its clinical development programs and any collaboration studies; the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern; and other factors, including legislative, regulatory, political and economic developments not within the Company’s control. The foregoing review of important factors that could cause actual events to differ from expectations should not be construed as exhaustive and should be read in conjunction with statements that are included herein and elsewhere, including the other risks, uncertainties, and other factors described under “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and elsewhere in the documents we file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The forward-looking statements are made only as of the date of this press release and, except as required by applicable law, the Company undertakes no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statement, or to make any other forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Versamune ® and Infectimune ® are registered trademarks of PDS Biotechnology Corporation.
Investor Contact: Mike Moyer LifeSci Advisors Phone +1 (617) 308-4306 Email: [email protected]
Media Contact: Gina Mangiaracina 6 Degrees Phone +1 (917) 797-7904 Email: [email protected]

- PDS Biotechnology -stock
- News for PDS Biotechnology
PDS Biotech Announces Abstract Accepted for Oral Presentation at 2024 ASTRO Annual Meeting
PRINCETON, N.J., Aug. 08, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- PDS Biotechnology Corporation (Nasdaq: PDSB) (“PDS Biotech” or the “Company”), a late-stage immunotherapy company focused on transforming how the immune system targets and kills cancers and the development of infectious disease vaccines, today announced that updated data from the IMMUNOCERV Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating Versamune ® HPV (formerly PDS0101) with chemoradiation to treat locally advanced cervical cancer will be presented during an oral presentation at the 2024 ASTRO Annual Meeting being held in Washington, DC, and virtually September 29 through October 2, 2024.
Details of the presentation are as follows:
Date: Tuesday, October 1, 2024, 2:50-3:00 p.m. ET Session title: SS 34 - GYN 2: Strategies and Innovations of Clinical Trials in Gynecologic Cancers Presentation title: 298 - IMMUNOCERV Phase II Trial Combining the HPV-Specific T Cell Immunotherapy PDS0101 with Chemoradiation for Treatment of Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Presenting author: Adam Grippin, M.D., Ph.D., The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
About PDS Biotechnology PDS Biotechnology is a late-stage immunotherapy company focused on transforming how the immune system targets and kills cancers and the development of infectious disease vaccines. The Company plans to initiate a pivotal clinical trial in 2024 to advance its lead program in advanced HPV16-positive head and neck squamous cell cancers. PDS Biotech’s lead investigational targeted immunotherapy Versamune ® HPV is being developed in combination with a standard-of-care immune checkpoint inhibitor, and also in a triple combination including PDS01ADC, an IL-12 fused antibody drug conjugate (ADC), and a standard-of-care immune checkpoint inhibitor.
For more information, please visit www.pdsbiotech.com.
Forward Looking Statements This communication contains forward-looking statements (including within the meaning of Section 21E of the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and Section 27A of the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended) concerning PDS Biotechnology Corporation (the “Company”) and other matters. These statements may discuss goals, intentions and expectations as to future plans, trends, events, results of operations or financial condition, or otherwise, based on current beliefs of the Company’s management, as well as assumptions made by, and information currently available to, management. Forward-looking statements generally include statements that are predictive in nature and depend upon or refer to future events or conditions, and include words such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “would,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “likely,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “intend,” “forecast,” “guidance”, “outlook” and other similar expressions among others. Forward-looking statements are based on current beliefs and assumptions that are subject to risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance. Actual results could differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statement as a result of various factors, including, without limitation: the Company’s ability to protect its intellectual property rights; the Company’s anticipated capital requirements, including the Company’s anticipated cash runway and the Company’s current expectations regarding its plans for future equity financings; the Company’s dependence on additional financing to fund its operations and complete the development and commercialization of its product candidates, and the risks that raising such additional capital may restrict the Company’s operations or require the Company to relinquish rights to the Company’s technologies or product candidates; the Company’s limited operating history in the Company’s current line of business, which makes it difficult to evaluate the Company’s prospects, the Company’s business plan or the likelihood of the Company’s successful implementation of such business plan; the timing for the Company or its partners to initiate the planned clinical trials for PDS01ADC, PDS0101, PDS0203 and other Versamune ® and Infectimune ® based product candidates; the future success of such trials; the successful implementation of the Company’s research and development programs and collaborations, including any collaboration studies concerning PDS01ADC, PDS0101, PDS0203 and other Versamune ® and Infectimune ® based product candidates and the Company’s interpretation of the results and findings of such programs and collaborations and whether such results are sufficient to support the future success of the Company’s product candidates; the success, timing and cost of the Company’s ongoing clinical trials and anticipated clinical trials for the Company’s current product candidates, including statements regarding the timing of initiation, pace of enrollment and completion of the trials (including the Company’s ability to fully fund its disclosed clinical trials, which assumes no material changes to the Company’s currently projected expenses), futility analyses, presentations at conferences and data reported in an abstract, and receipt of interim or preliminary results (including, without limitation, any preclinical results or data), which are not necessarily indicative of the final results of the Company’s ongoing clinical trials; any Company statements about its understanding of product candidates mechanisms of action and interpretation of preclinical and early clinical results from its clinical development programs and any collaboration studies; the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern; and other factors, including legislative, regulatory, political and economic developments not within the Company’s control. The foregoing review of important factors that could cause actual events to differ from expectations should not be construed as exhaustive and should be read in conjunction with statements that are included herein and elsewhere, including the other risks, uncertainties, and other factors described under “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and elsewhere in the documents we file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The forward-looking statements are made only as of the date of this press release and, except as required by applicable law, the Company undertakes no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statement, or to make any other forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Versamune ® and Infectimune ® are registered trademarks of PDS Biotechnology Corporation.
Investor Contact: Mike Moyer LifeSci Advisors Phone +1 (617) 308-4306 Email: [email protected]
Media Contact: Gina Mangiaracina 6 Degrees Phone +1 (917) 797-7904 Email: [email protected]

PDS Biotechnology News MORE
Related Stocks
- See us on twitter
ASTRO 2024 "Best of Physics": Oral Presentation
October 2, 2024
"Multi-Contrast MRI Acceleration with K-Space Progressive Learning and Image-Space Self-to-Peer Aggregation" by Xiaohan Xing, Lequan Yu, Lingting Zhu, Lei Xing, Lianli Liu has been selected as the Best of Physics for this year's ASTRO annual meeting. It will be presented in the oral scientific session "Best of Physics."

Xiaohan Xing, Postdoctoral Scholar

Lianli Liu, Clinical Assistant Professor
- October 2, 2024 Multi-Contrast MRI Acceleration with K-Space Progressive Learning and Image-Space Self-to-Peer Aggregation
- July 23, 2024 AI Foundation Model (FM)
- July 22, 2024 Cynthia Chuang Honored as AAPM Fellow 2024
- July 6, 2024 Large Language Model-Augmented Target Delineation in Radiation Therapy
- June 7, 2024 Medical Physics Impact Award
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- Advisory Committees
- Advisory Committee Calendar
- September 9, 2024: Meeting of the Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting Announcement - 09/09/2024
Advisory Committee Meeting | In Person
Event Title September 9, 2024: Meeting of the Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting Announcement September 9, 2024
What is an advisory committee.
Advisory committees provide independent expert advice to the FDA on broad scientific topics or on certain products to help the agency make sound decisions based on the available science. Advisory committees make non-binding recommendations to the FDA, which generally follows the recommendations but is not legally bound to do so. Please see, " Advisory Committees Give FDA Critical Advice and the Public a Voice ," for more information.
Center: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research
Location: The public may attend the meeting at the FDA White Oak Campus, 10903 New Hampshire Ave., Bldg. 31 Conference Center, the Great Room (Rm. 1503), Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002. The public will also have the option to participate, and the advisory committee meeting will be heard, viewed, captioned, and recorded through an online teleconferencing and/or video conferencing platform.
The Committee will discuss new drug application 213972, for oral sulopenem etzadroxil/probenecid tablets consisting of 500 milligrams (mg) sulopenem etzadroxil and 500 mg probenecid, submitted by Iterum Therapeutics US Ltd., for the proposed indication of treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections caused by designated susceptible bacteria in adult women 18 years of age and older.
Meeting Materials
FDA intends to make background material and the link to the live webcast available to the public no later than two (2) business days before the meeting in the Event Materials section of this web page. If FDA is unable to post the background material on its website prior to the meeting, the background material will be made publicly available at the location of the advisory committee meeting and on FDA’s website at the time of the advisory committee meeting. The meeting presentations will also be heard, viewed, captioned, and recorded through an online teleconferencing and/or video conferencing platform. The online presentation of materials will include slide presentations with audio and video components in a manner that most closely resembles an in-person advisory committee meeting.
Public Participation Information
Interested persons may present data, information, or views, orally or in writing, on issues pending before the Committee.
FDA is establishing a docket for public comment on this meeting. The docket number is FDA-2024-N-3538 . The docket will close on September 6, 2024. Submit either electronic or written comments on this public meeting by September 6, 2024. Please note that late, untimely filed comments will not be considered. Electronic comments must be submitted on or before September 6, 2024. The https://www.regulations.gov electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern Time at the end of September 6, 2024. Comments received by mail/hand delivery/courier (for written/paper submissions) will be considered timely if they are postmarked or the delivery service acceptance receipt is on or before that date.
Comments received on or before August 29, 2024 will be provided to the Committee. Comments received after that date will be taken into consideration by FDA. In the event that the meeting is cancelled, FDA will continue to evaluate any relevant applications or information, and consider any comments submitted to the docket, as appropriate. You may submit comments as follows:
Electronic Submissions
Submit electronic comments in the following way:
- Federal eRulemaking Portal: https://www.regulations.gov . Follow the instructions for submitting comments. Comments submitted electronically, including attachments, to https://www.regulations.gov will be posted to the docket unchanged. Because your comment will be made public, you are solely responsible for ensuring that your comment does not include any confidential information that you or a third party may not wish to be posted, such as medical information, your or anyone else’s Social Security number, or confidential business information, such as a manufacturing process. Please note that if you include your name, contact information, or other information that identifies you in the body of your comments, that information will be posted on https://www.regulations.gov .
- If you want to submit a comment with confidential information that you do not wish to be made available to the public, submit the comment as a written/paper submission and in the manner detailed (see “Written/Paper Submissions” and “Instructions”).
Written/Paper Submissions
Submit written/paper submissions as follows:
- Mail/Hand delivery/Courier (for written/paper submissions): Dockets Management Staff (HFA-305), Food and Drug Administration, 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061, Rockville, MD 20852.
- For written/paper comments submitted to the Dockets Management Staff, FDA will post your comment, as well as any attachments, except for information submitted, marked and identified, as confidential, if submitted as detailed in “Instructions.”
Instructions: All submissions received must include the Docket No. FDA-2024-N-3538 for “Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee; Notice of Meeting; Establishment of a Public Docket; Request for Comments--New Drug Application 213972 for Sulopenem Etzadroxil/Probenecid Tablets.” Received comments, those filed in a timely manner, will be placed in the docket and, except for those submitted as “Confidential Submissions,” publicly viewable at https://www.regulations.gov or at the Dockets Management Staff between 9 a.m. and 4 p.m., Monday through Friday, 240-402-7500.
- Confidential Submissions--To submit a comment with confidential information that you do not wish to be made publicly available, submit your comments only as a written/paper submission. You should submit two copies total. One copy will include the information you claim to be confidential with a heading or cover note that states “THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION.” FDA will review this copy, including the claimed confidential information, in its consideration of comments. The second copy, which will have the claimed confidential information redacted/blacked out, will be available for public viewing and posted on https://www.regulations.gov . Submit both copies to the Dockets Management Staff. If you do not wish your name and contact information be made publicly available, you can provide this information on the cover sheet and not in the body of your comments and you must identify the information as “confidential.” Any information marked as “confidential” will not be disclosed except in accordance with 21 CFR 10.20 and other applicable disclosure law. For more information about FDA’s posting of comments to public dockets, see 80 FR 56469, September 18, 2015, or access the information at: https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2015-09-18/pdf/2015-23389.pdf .
Docket: For access to the docket to read background documents or the electronic and written/paper comments received, go to https://www.regulations.gov and insert the docket number, found in brackets in the heading of this document, into the “Search” box and follow the prompts and/or go to the Dockets Management Staff, 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061, Rockville, MD 20852, 240-402-7500.
Oral Presentations
Oral presentations from the public will be scheduled between approximately between 1:45 p.m. to 2:45 p.m. Eastern Time. Those individuals interested in making formal oral presentations should notify the contact person and submit a brief statement of the general nature of the evidence or arguments they wish to present, the names and addresses of proposed participants, whether they would like to present online or in-person, and an indication of the approximate time requested to make their presentation on or before August 21, 2024.
Time allotted for each presentation may be limited. If the number of registrants requesting to speak is greater than can be reasonably accommodated during the scheduled open public hearing session, FDA may conduct a lottery to determine the speakers for the scheduled open public hearing session. Similarly, room for interested persons to participate in-person may be limited. If the number of registrants requesting to speak in-person during the open public hearing is greater than can be reasonably accommodated in the venue for the in-person portion of the advisory committee meeting, FDA may conduct a lottery to determine the speakers who will be invited to participate in-person. The contact person will notify interested persons regarding their request to speak by August 22, 2024.
Webcast Information
CDER plans to provide a free of charge, live webcast of the upcoming advisory committee meeting. If there are instances where the webcast transmission is not successful, staff will work to re-establish the transmission as soon as possible. Further information regarding the webcast, including the web address for the webcast, will be made available no later than two (2) business days before the meeting in the Event Materials section of this web page.
CDER plans to post archived webcasts after the meeting, however, in cases where transmission was not successful, archived webcasts will not be available.
Contact Information
- LaToya Bonner, PharmD Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue WO31-2417 Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 Phone: 240-402-2507 Email: [email protected]
- FDA Advisory Committee Information Line 1-800-741-8138 (301-443-0572 in the Washington DC area) Please call the Information Line for up-to-date information on this hearing.
- For press inquiries, please contact the Office of Media Affairs at Email: [email protected] or 301–796–4540
A notice in the Federal Register about last minute modifications that impact a previously announced advisory committee meeting cannot always be published quickly enough to provide timely notice. Therefore, you should always check the agency’s website or call the committee’s Designated Federal Officer (see Contact Information) to learn about possible modifications before coming to the meeting.
Persons attending FDA’s advisory committee meetings are advised that the agency is not responsible for providing access to electrical outlets. FDA welcomes the attendance of the public at its advisory committee meetings and will make every effort to accommodate persons with disabilities. If you require accommodations due to a disability, please contact the committee’s Designated Federal Officer (see Contact Information) at least 7 days in advance of the meeting.
Answers to commonly asked questions including information regarding special accommodations due to a disability may be accessed at: Common Questions and Answers about FDA Advisory Committee Meetings .
FDA is committed to the orderly conduct of its advisory committee meetings. Please visit our Web site at Public Conduct During FDA Advisory Committee Meetings for procedures on public conduct during advisory committee meetings.
Notice of this meeting is given under the Federal Advisory Committee Act (5 U.S.C. app.2).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new ...
Oral Presentations. Or. l Presen. ations1. PlanningOral presentations are one of the most common assignments i. college courses. Scholars, professionals, and students in all fields desire to disseminate the new knowledge they produce, and this is often accomplished by delivering oral presentations in class, at conferences, in public lectures, or i.
20. Anticipate questions and prepare thoughtful answers in advance. A key component of preparing for an effective oral presentation is anticipating questions and creating thoughtful responses beforehand. It demonstrates that you are knowledgeable about the subject and that you gave the subject some research.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
The Purpose of an Oral Presentation. Generally, oral presentation is public speaking, either individually or as a group, the aim of which is to provide information, entertain, persuade the audience, or educate. In an academic setting, oral presentations are often assessable tasks with a marking criteria. Therefore, students are being evaluated ...
Define your topic. Arrange your material in a way that makes sense for your objectives. Compose your presentation. Create visual aids. Practice your presentation (don't forget to time it!) Make necessary adjustments. Analyze the room where you'll be giving your presentation (set-up, sight lines, equipment, etc.). Practice again.
Tip #2: Use simple language that is easy for people to follow. The words you select, and how you use them, will make a big difference in how well people hear—and remember—what you tell them. This is especially true in oral presentations. "When we write sentences for people to read, we can add more complexities.
An oral presentation is more than just reading a paper or set of slides to an audience. How you deliver your presentation is at least as important in effectively communicating your message as what you say. Use these guidelines to learn simple tools that help you prepare and present an effective presentation, and design PowerPoint slides that ...
They are all one of the types of oral presentations. Oral presentations involve the use of verbal and non-verbal elements to deliver a speech to a particular or general audience. All the types we discussed fall into these 4 broad categories: 1. Extemporaneous presentations. This type of presentation involves making short pointers or key phrases ...
1. Prepare your cue cards. Do not paste your entire script on to the cue cards. Key words are your best friend in an oral presentation. Only having certain key words on your script allows you to easily track your train of words and gives you the opportunity to focus on your audience.
An easy way to do this is by using the 5×5 rule. This means using no more than 5 bullet points per slide, with no more than 5 words per bullet point. It is also good to break up the text-heavy slides with ones including diagrams or graphs. This can also help to convey your results in a more visual and easy-to-understand way.
Giving an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam can be quite scary, but we're here to help you. Watch two students giving presentations and then read the tips carefully. ... Check your understanding: grouping - useful phrases. Worksheets and downloads. Oral presentation - planning sheet 199.44 KB. Oral presentation - tips 257.4 KB.
Oral Presentations Purpose. An Oral Research Presentation is meant to showcase your research findings. A successful oral research presentation should: communicate the importance of your research; clearly state your findings and the analysis of those findings; prompt discussion between researcher and audience. Below you will find information on ...
present your research question and why it matters; describe how you conducted your research, explain what you found out and what it means; and. conclude with a summary of your main points. Depending on your topic, you may need to provide background information so that the audience understands the significance of your inquiry.
Oral presentation skills refer to the ability to convey information and ideas through spoken words, body language, and visual aids in a structured and engaging manner. It involves organizing thoughts, tailoring content to the audience, and delivering the message confidently and clearly. These skills encompass verbal and non-verbal communication ...
This guide will highlight some of the basics of giving a good oral presentation, dissecting it into three simple parts: preparation, presentation and feedback. Preparation: • Two repetitive actions underpin this phase: preparation and practice! • First prepare, then practice, then do the same again a few more times!
What is an oral presentation? An oral presentation is a formal, research-based presentation of your work. Presentations happen in a range of different places. For instance, if you work at a company that assigns people to teams to collaborate on projects, your project team might give an oral presentation of your progress on a particular project.
As in all technical writing situations, identifying and understanding your audience is of the utmost importance. Content and Requirements for the Oral Presentation. The focus for your oral presentation is clear, understandable presentation; well-organized, well-planned, well-timed discussion. You don't need to be Mr. or Ms. Slick-Operator ...
In today's interconnected world, oral and written communication skills hold immense value. The ability to convey ideas effectively through spoken and written words is pivotal in personal, academic, and professional spheres. Strong oral communication skills enable meaningful interactions, resolving conflicts, and fostering connections.
In the social and behavioral sciences, an oral presentation assignment involves an individual student or group of students verbally addressing an audience on a specific research-based topic, often utilizing slides to help audience members understand and retain what they both see and hear. The purpose is to inform, report, and explain the significance of research findings, and your critical ...
PRINCETON, N.J., Aug. 08, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- PDS Biotechnology Corporation (Nasdaq: PDSB) ("PDS Biotech" or the "Company"), a late-stage immunotherapy company focused on transforming how the immune system targets and kills cancers and the development of infectious disease vaccines, today announced that updated data from the ...
Presentation title: 298 - IMMUNOCERV Phase II Trial Combining the HPV-Specific T Cell Immunotherapy PDS0101 with Chemoradiation for Treatment of Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Presenting author ...
ASTRO 2024 "Best of Physics": Oral Presentation October 2, 2024 "Multi-Contrast MRI Acceleration with K-Space Progressive Learning and Image-Space Self-to-Peer Aggregation" by Xiaohan Xing, Lequan Yu, Lingting Zhu, Lei Xing, Lianli Liu has been selected as the Best of Physics for this year's ASTRO annual meeting. It will be presented in the ...
Oral Presentations. Oral presentations from the public will be scheduled between approximately between 1:45 p.m. to 2:45 p.m. Eastern Time. Those individuals interested in making formal oral ...