AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

Free Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis , and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup or small business, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup or small business.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your small business and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan for your business plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.
6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
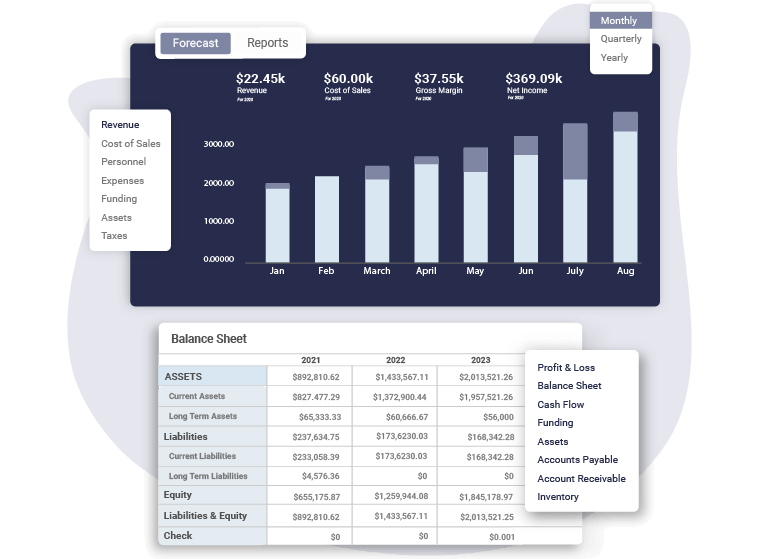
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
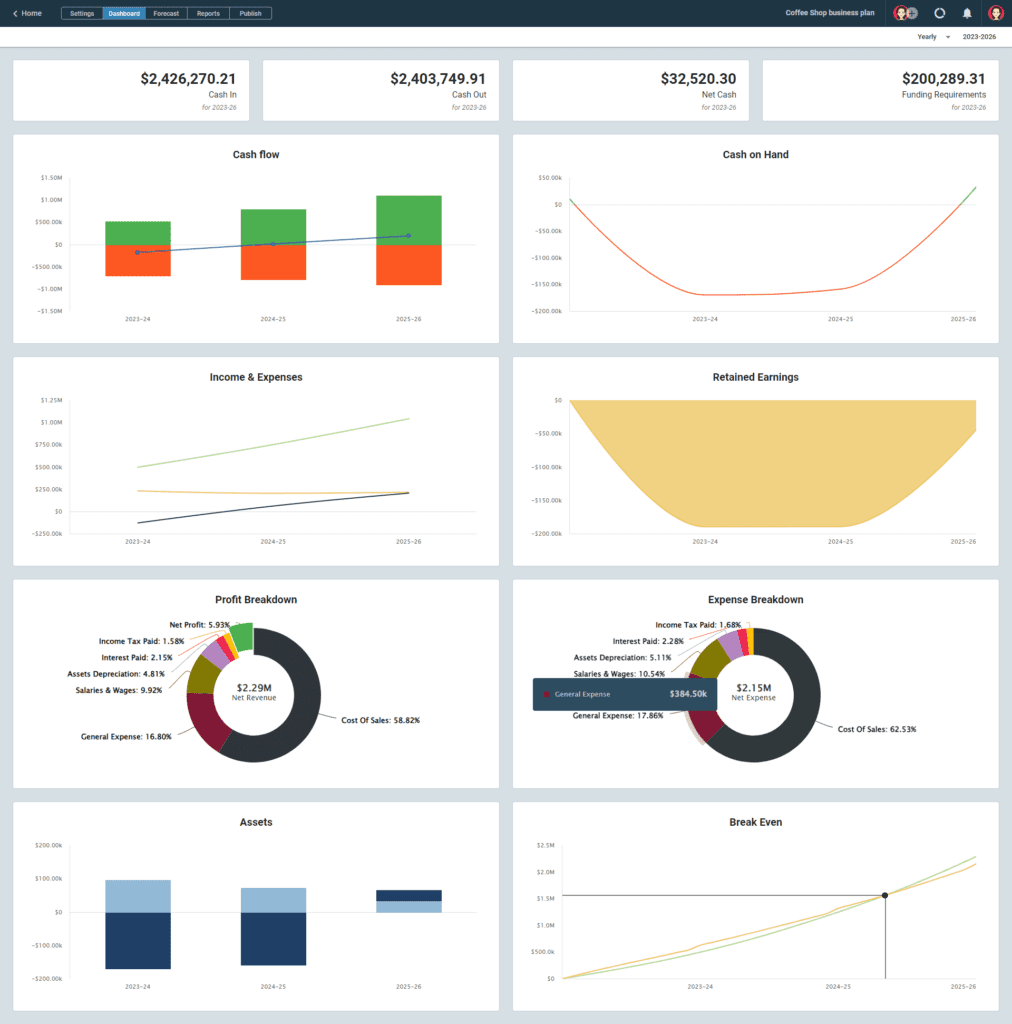
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan for your small business, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
Projected Balance Sheet
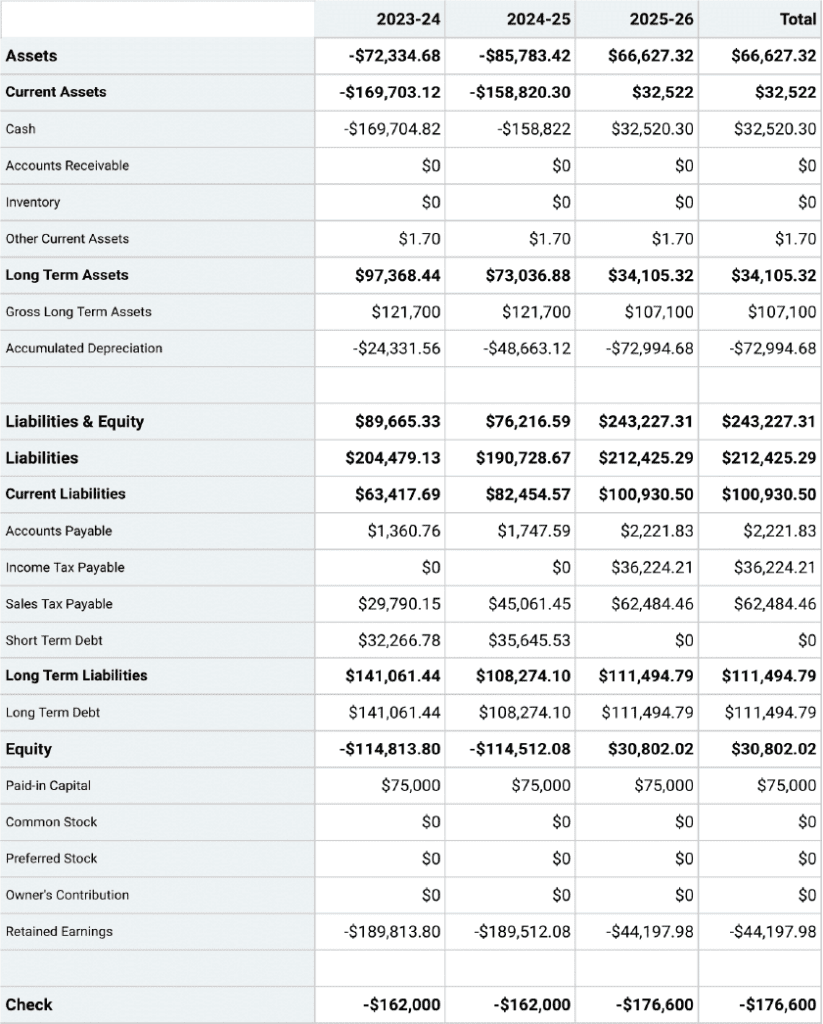
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
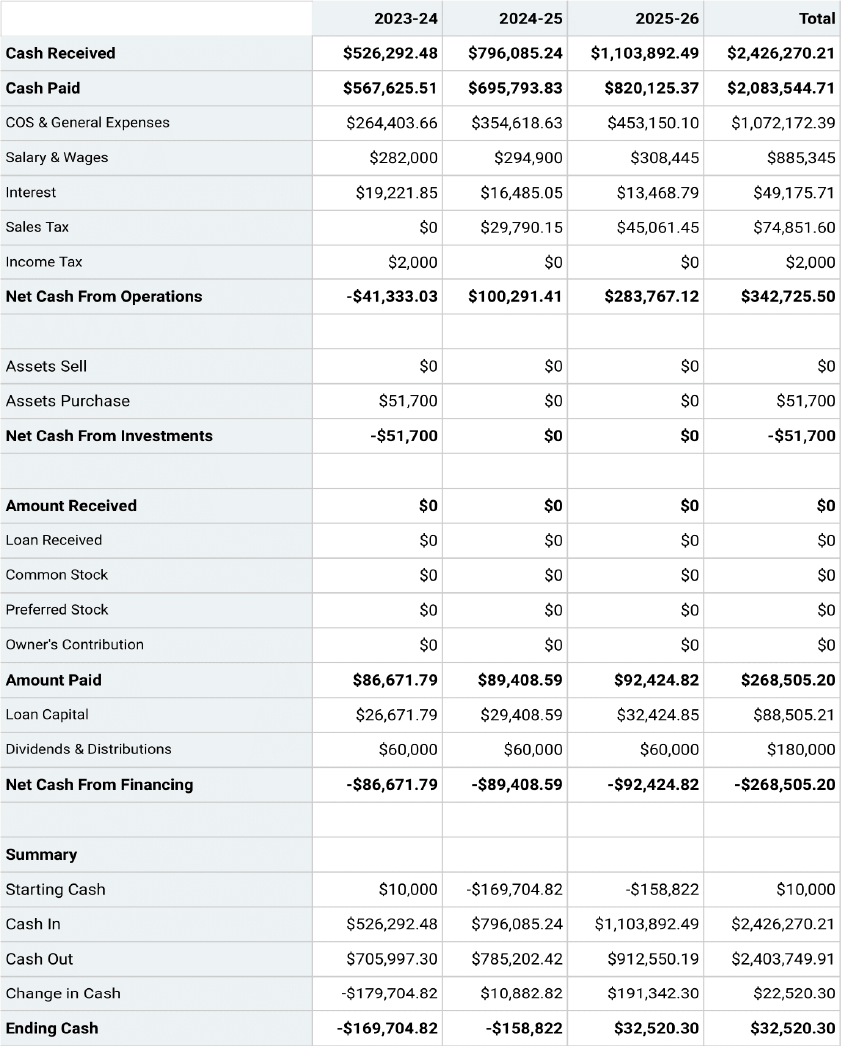
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
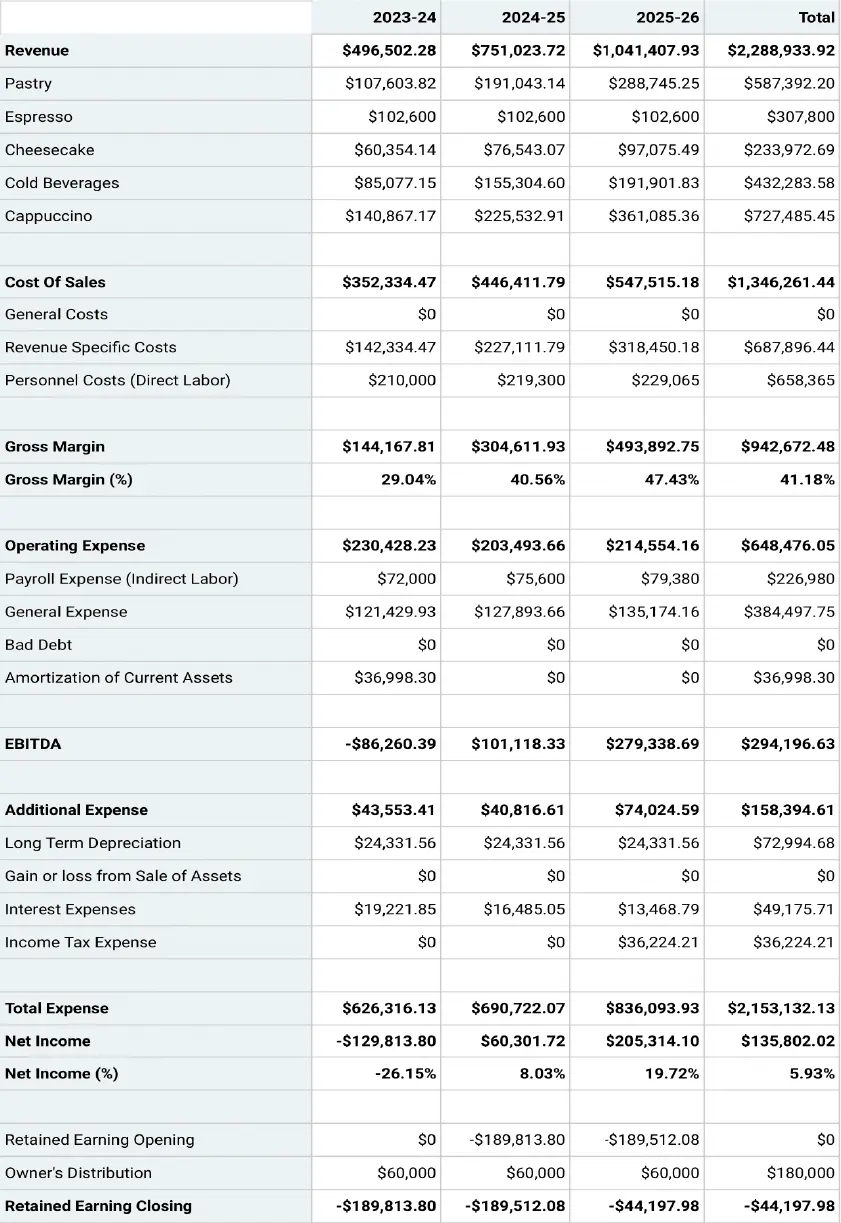
Break Even Analysis
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or small businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author
Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

How to Write a Financial Plan for a Business Plan

Noah Parsons
4 min. read
Updated July 11, 2024

Creating a financial plan for a business plan is often the most intimidating part for small business owners.
It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts.
Here is everything you need to include in your business plan’s financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid , and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan in business plans
A sound financial plan for a business plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, you’ll need to include a few additional pieces of information as part of your business plan’s financial plan example.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios.
While including these metrics in your financial plan for a business plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Key financial terms you should know
It’s not hard. Anybody who can run a business can understand these key financial terms. And every business owner and entrepreneur should know them.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- How to improve your financial plan
Your financial statements are the core part of your business plan’s financial plan that you’ll revisit most often. Instead of worrying about getting it perfect the first time, check out the following resources to learn how to improve your projections over time.
Common mistakes with business forecasts
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with startup financial projections. I read about 100 business plans per year, and I have this list of mistakes.
How to improve your financial projections
Learn how to improve your business financial projections by following these five basic guidelines.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan

How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Limited Time Offer:
Save Up to 25% on LivePlan today

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
How to Conduct a Strategic Financial Analysis for Your Business
Posted may 25, 2021 by noah parsons.

How often do you review your business numbers? If you look at the financial performance of your business at least once a month or perhaps even more frequently , you’re in good shape—and better off than most businesses.
Unfortunately, too many businesses review their books only every few months, and frankly, that’s not a great strategy. It gives those businesses fewer opportunities to see if things are going well or not. The more frequently you review your business finances, the more chances you have to find opportunities for growth .
But how do you approach reviewing your financials? What documents should you analyze? What exactly should you be looking for? Let’s try to answer those questions by introducing you to a process known as a strategic financial analysis.
What is a strategic financial analysis?
A strategic financial analysis is a review framework where you analyze performance, assess your goals, and make adjustments to your forecasts and strategy based on actual results. In short, this is where you connect the dots between your numbers and the actions that you’re taking. The intention is to identify any potential problems or opportunities within your financials and turn them into strategic steps for growth.
In some cases, this analysis may also include a deeper look at your business model, comparisons against your competitors , and even different forecast scenarios.
What financial statements should I review when conducting a strategic financial analysis?
When you’re reviewing your business financials, you’ll want to check these three key reports:
- Profit and loss (also known as an income statement)
- Balance sheet
Each report will tell you different things about your business. Put together, they’ll provide you with nearly everything you’ll want to know about your business performance. By the end, you should be able to bring your forecasts for these statements up to speed based on your actual results .
How to conduct a strategic financial analysis
Here are the five steps you’ll want to take when conducting a strategic analysis of your financial statements.
1. Compare your forecast to your actuals monthly
So, if you’re reviewing your business financials regularly, you’re off to a good start.
But to get even more value out of that financial review, you need to start comparing your actuals —how your business performed—to your forecast.
Ideally, compare your plan to what actually happens in a monthly meeting with your key staff. You’ll want to have your forecast handy as well as reports from your accounting software so you can compare the two and see if you’re on track.
If you’re using LivePlan, the software will do all of the number-crunching and comparison work for you—no spreadsheets required—and you’ll be able to compare everything in a simple financial dashboard .
2. Identify where you’re off track or exceeding projections
When you’re forecasting, you’re making educated guesses. This means that your actual financial performance in a given month will vary.
You’ll typically either be off track and performing worse than expected. On track and sitting fairly close to expectations. Or, outperforming your forecasts and exceeding expectations.
What does comparing my plan to my actual results do for me?
If you just review what happened in the past, you’ll get a good idea of what happened during the past month of your business. But, it’s difficult to know if your performance is good or bad if you’re not comparing your actual results against your plan.
- How do you know if you’re meeting your sales goals?
- Can you tell that you’re keeping your spending within your budget?
- Are you keeping as much cash in the bank as you need to?
Even more importantly, if you have plans to grow your business or make significant investments, you’ll want to know if it makes financial sense to spend the money. Should you invest now or should you wait for a better time? Should you open a second location or hold off?
By reviewing your plan and comparing it to your actual results, you’ll get a better sense of when you should look to expand, and when you should be reining things in. Make a mistake and invest in your business at the wrong time and you could create a cash flow crunch that could sink your business.
3. Review your Income statement (profit and loss or P&L)
Your income statement (also called profit and loss or P&L) documents your income and your expenses. When you compare this statement to your forecast, you’ll see if your sales are meeting your goals and if you’re keeping your expenses in line with your budget.
If you’re not sure what’s included in an income statement or what types of information you’ll find there, start with this guide to reading a profit and loss or income statement that will help orient you to each line item.
You can also download an income statement example to help you better visualize the information. For a more dynamic solution that displays actual results for completed periods right into your forecasted Profit and Loss statement, check out LivePlan’s LiveForecast feature . No more hours spent inputting accounting information. Just you spending more time digging into what is and isn’t working for your business.
When you’re ready to dive deeper and start your income statement analysis, use this income statement analysis guide for your monthly financial review. It walks you through typical questions that might come up as you’re doing your review. That way, you can use your findings to make better strategic decisions for the health and growth of your business.
4. Analyze your cash flow statement
Your cash flow statement will tell you exactly how cash moved into and out of your business. Comparing this statement to your cash flow forecast will tell you if you’re on track to grow your bank balance the way you had planned, and why you might be off track if things aren’t going the way you had hoped.
Check out this article on how to read a cash flow statement for a line-by-line explanation of how it works. And download our cash flow statement example PDF and Excel spreadsheet if you’re looking for a sample to work from as you review your own.
When you’re ready to start comparing your actual cash flow to your forecast, this guide to cash flow analysis will help you get started.
5. Review your balance sheet
Your balance sheet will give you a complete overview of your financial position. How much money are you owed and how much money do you owe? What assets does your business have? Your balance sheet analysis will help you understand if you’re collecting money from your customers at the right rate, and if you’re taking on more debt than planned.
If you’re new to balance sheet review, this article offers more insight on how a balance sheet is set up, and what you need to know about each line. You can also download a balance sheet example to help you visualize it better.
When you’re ready to do your monthly review, this balance sheet analysis guide will help you get started.
Look beyond your financials for more insights
Doing a monthly financial statement analysis—comparing your actuals to your plan or forecast—helps you keep a finger on the pulse of your business finances.
Additionally, it’s wise to look at industry benchmarks , financial shifts in your industry, and any other external factors that may be affecting your financial performance. Use your initial comparison to actual performance to jumpstart this market analysis and help you define the next steps.
When you identify a gap or variance between what you forecast and what actually happened, use that information to help you make strategic shifts in your business so you can quickly address challenges and take advantage of opportunities.
Editors’ note: This article was originally published in 2019 and updated for 2021.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Noah Parsons
Posted in growth & metrics, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

No products in the cart.
Crafting Your Business Plan Financials: A Step-by-Step Guide
This guide is my way of taking you by the hand (figuratively, of course) and walking you through the process of building your business plan financials. Whether you’re scribbling your first ever business plan on a napkin or revisiting an existing one to adapt to the ever-evolving market landscape, this guide is for you.
Key Takeaways
- Building business plan financials involves forecasting the three financial statements : income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- Financial projections should be based on market research and industry trends, as well as your unique business model and goals.
- Business plan financials are essential in securing funding, guiding decision-making, setting benchmarks, managing cash flow , and identifying risks and opportunities.
Understanding the Basics of Business Plan Financials
Diving into the world of business plan financials can feel a bit like stepping onto a dance floor for the first time. You know you need to move, but figuring out how to not step on your own feet (or anyone else’s) is the real challenge.
So, let’s break down the dance floor, shall we? Picture your business plan’s financial section as a trio of critical financial statements performing the most pivotal routine of the night, consisting of the Income Statement, the Balance Sheet, and the Cash Flow Statement.

- The Income Statement : Also known as the profit and loss statement , this is your financial performance’s highlight reel over a specific period. It tells you whether your business is hitting the high notes or if it’s time to change the tune. By tracking revenues, costs, and expenses, the Income Statement gives you a clear picture of your net profit or loss. Think of it as your business’s scorecard, showing you if you’re leading the dance or stepping on toes.
- The Balance Sheet : Imagine this as a snapshot capturing a moment in your business’s dance routine. It’s all about balance (hence the name). On one side, you have your assets—everything your business owns. On the other, liabilities and equity—everything your business owes plus the ownership interest. The Balance Sheet tells you exactly where you stand at any given moment, making sure you’re poised and ready for the next move.
- The Cash Flow Statement : If the Income Statement is about the performance and the Balance Sheet is about the pose, then the Cash Flow Statement is all about the movement. It tracks the cash coming in and going out of your business. This statement is your choreography, showing you if you’ve got the liquidity to keep dancing or if you’re about to trip over a lack of cash.
Why Do You Need Business Plan Financials?
Let’s dive into the different uses for those business plan financials, shall we?
Securing Funding : This one’s pretty straightforward. When you’re pitching to investors or applying for a loan, your financials are the proof in the pudding. They show that you’re not just all talk—you’ve got a plan that’s expected to bring in real money.
Guiding Decision-Making : Your financials are a compass in the wild terrain of business decisions. Want to know if you can afford to increase operating expenses, launch a new product, or expand into a new market? Your financials hold the answers.
Setting Benchmarks : Without benchmarks, how do you measure success? Your financials set clear goals for revenue, profit margins, and growth trajectories.
Cash Flow Management : Ah, cash flow projection —the lifeblood of any business. Your financials help you predict when money will be coming in and going out, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to keep the lights on.
Identifying Risks and Opportunities : By analyzing your financials, you can spot potential risks and opportunities before they become glaring issues or missed chances.
Step 1: Laying the Groundwork with Market Research
Understanding your market is akin to understanding the latest viral dance craze. You need to know who’s dancing, why they’re dancing, and what moves are most popular. In business terms, this means getting to grips with who your customers are, what needs or desires they have, and how your product or service fits into that picture. This is where market research comes into play.
How to Gather Data for Market Research:
- Start with Secondary Research : This is like the pre-party research before you hit the dance floor. Look into existing studies, industry reports, and market analysis that give you a bird’s-eye view of your sector. It’s cheaper (often free), quicker, and a great way to start outlining your market landscape. Websites like Statista and Pew Research are a great resource for secondary research.
- Dive into Primary Research : Now, it’s time to mingle at the party yourself. Surveys, interviews, and focus groups with potential customers will give you insights straight from the horse’s mouth. Yes, it’s more time-consuming and can be costlier, but the firsthand data you gather is worth its weight in gold.
- Analyze Your Competitors : Think of this as knowing who else is on the dance floor with you. Understanding their moves can help you find your unique rhythm. Look at their offerings, pricing strategies, and customer feedback. What are they doing well? Where are they stumbling? This insight is invaluable.
My Experience With Market Research
Let me take you back to the early days of my own business venture, when the concept of “market research” was as foreign to me as quantum physics. My team and I were launching a new financial tool designed to simplify budgeting for freelancers—a noble cause, but we were shooting in the dark with our sales forecast .
So, we hit the books (and the streets) for some hardcore market research. We surveyed freelancers about their budgeting woes, dove into forums where they vented their frustrations, and analyzed competitors who were only partially addressing these pain points. What we found was a goldmine of information that not only validated our product idea but also helped us pinpoint exactly how to position our tool in the market.
Armed with this data, we crafted our revenue projections not on wishful thinking but on solid, research-backed insights. And guess what? Our initial sales outperformed our projections by 20%. It was a clear testament to the power of laying the groundwork with thorough market research.
Step 2: Crafting Your Income Statement
Crafting your profit and loss statement is akin to writing the script for the blockbuster movie of your business’s financial performance. It’s where the rubber meets the road of financial statements, blending the drama of revenue streams with the gritty realism of expenses, all leading up to that climactic figure: your net income.
Breaking Down Revenue Streams
Let’s start our financial projections by casting our stars: the revenue streams. Identifying and projecting these is like mapping out the plot points of our story. For my own venture, it was a mix of predictable box office hits (fixed revenue from long-term contracts) and surprise indie darlings (variable sales from new markets).
The key here is diversity; relying on a single revenue stream is like betting your entire budget on a rookie director. Exciting, sure, but risky. By understanding and forecasting different sources of income, you’re setting the stage for a financial narrative that holds up against unexpected twists.
Fixed vs. Variable Expenses: The Supporting Cast
Next up, we have our supporting characters: fixed and variable costs. Fixed expenses are those steadfast sidekicks that stick with you through thick and thin—rent, salaries, and subscriptions.
They’re your base crew, essential but predictable. Variable expenses, on the other hand, are like those special effects in big action sequences—they fluctuate depending on the production’s scale (or, in our case, the business operations). Materials cost, commission fees, and shipping charges can vary, adding dynamism and a bit of unpredictability to our financial plot.
EBITDA, and Why It’s Your Friend

Now, let’s talk about a concept that might sound like the latest tech gadget but is actually one of your best allies: EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization). Imagine EBITDA as that veteran actor who brings depth and credibility to your movie.
It shows you how well your business is performing without getting bogged down by tax structures, financing decisions, or how much you’ve spent on those fancy ergonomic office chairs.
It is also a critical part of break even analysis. Break even analysis is like the climax of our financial story—it shows the point where your revenue and expenses are equal. It helps you determine how much you need to sell or how to adjust your costs to reach profitability.
Step 3: Building Your Balance Sheet
Think of your balance sheet as the ultimate snapshot of your business’s financial stability at any given moment. It’s like taking a selfie with your assets, liabilities, and equity—everything has to look just right.
Assets, Liabilities, and Equity: What Goes Where?
Imagine your business’s finances as a giant storage unit (stay with me here). On one side, you’ve got your assets—everything you own that has value. This includes cash in the bank, inventory, equipment, and even amounts owed to you by customers (receivables). These are like the treasures you’ve stored away, everything from the antique lamp (cash) to the boxes of unsold novels you swear will be collector’s items one day (inventory).
On the opposite side are your liabilities. Think of these as the IOUs taped to the door by your friends who’ve borrowed your stuff. These could be loans you need to pay back, money you owe to suppliers, or rent for the space your business occupies.
Balancing these two sides is your equity , which is essentially the net worth of your business. If you were to liquidate everything today—sell off all your treasures and pay back your friends—whatever cash you’re left holding is your equity. It’s what you truly “own” outright.
Maintaining a Healthy Balance Sheet Over Time
Here’s where things get personal. In the early days of my venture, our balance sheet was, to put it mildly, a bit of a fixer-upper. Our assets were like mismatched socks—present, but not exactly optimized. Meanwhile, our liabilities were like laundry piles—growing faster than we could manage. The turning point came when we started treating our balance sheet like our business’s health checkup, regularly reviewing and adjusting our financial strategies to ensure everything remained in healthy proportion.
We focused on bolstering our assets, not just by increasing sales but also by managing our receivables more effectively and making smart choices about what equipment to purchase or lease. Simultaneously, we worked on trimming down our liabilities, negotiating better terms with suppliers, and restructuring debt to more manageable levels.
Step 4: Forecasting Cash Flow
Forecasting cash flow—it’s like checking the weather before you head out on a road trip. You wouldn’t want to get caught in a storm without an umbrella, right? Similarly, in the world of finance and accounting, especially for us millennials hustling through our careers, understanding the ins and outs of cash flow is crucial for navigating the unpredictable journey of business operations without getting soaked.
Why Cash Flow is Your Business’s Weather Forecast

Cash flow is essentially the heartbeat of your business’s financial health—tracking the inflow and outflow of money. It’s what keeps the lights on, from paying your awesome team to ensuring the coffee machine (aka the real MVP) is always running. Without a keen eye on cash flow, even the most profitable business can find itself in a pinch when bills come due. It’s about timing, and just like you can’t download more time, you can’t magically create cash when you need it—unless you’ve planned ahead.
Step-by-Step Method for Creating a Cash Flow Forecast
- Start with the Basics : Gather data on all your cash inflows, like sales or accounts receivable , and outflows, including expenses, payroll, and loan payments. Think of it as setting up your playlist before the trip begins.
- Choose Your Time Frame : Decide if you’re mapping out the next month, quarter, or year. This is like deciding whether you’re road-tripping to the next town over or cross-country.
- Use Historical Data : Look back at past months or years to guide your predictions. It’s like knowing there’s always traffic at rush hour and planning your departure time accordingly.
- Factor in Seasonality : Just like packing an extra sweater for a chilly evening, remember that some months may have higher expenses or lower sales. Plan for these fluctuations.
- Keep It Updated : Your cash flow forecast isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it road map. Update it regularly with actual figures to stay on course. This is like checking your GPS for traffic updates in real-time.
My Great Cash Flow Mishap
Early in my career, I experienced what I affectionately call “The Great Cash Flow Mishap.” We were flying high, sales were up, and in my mind, we were invincible. I overlooked the importance of forecasting cash flow because, hey, money was coming in, right? Wrong. Sales being up didn’t mean cash in hand, thanks to generous payment terms we’d extended. When a large expense bill came due, we found ourselves in a financial thunderstorm without an umbrella.
It was a wake-up call. We scrambled, made it through, but learned a valuable lesson in the process: cash flow forecasting isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s essential. It’s the difference between sailing smoothly and getting caught in a downpour. Since then, I’ve treated cash flow forecasting like my financial weather app, always checking it to ensure we’re prepared for whatever financial weather lies ahead.
Step 5: Bringing It All Together for Financial Analysis
So, you’ve danced through the steps of laying down your financial groundwork, from market research all the way to cash flow forecasting. Now, it’s time for what I like to call the “big reveal” in our financial saga—financial analysis. Think of it as the season finale where all the plotlines converge, and you finally get to see the full picture of your business’s financial health. Exciting, right?
How to Use Your Financials to Calculate Key Ratios

Financial ratios might sound like something out of a high school math class you’d rather forget, but they’re actually pretty cool once you get to know them. They’re like the secret codes that unlock the mysteries of your business’s financial narrative. Here are a few key players:
- Profit Margin : Sales are great, but what’s left after expenses? This ratio tells you exactly that. It’s like checking how much gas is left in the tank after a long trip.
- Current Ratio : This one measures whether you have enough assets to cover your liabilities. Imagine you’re planning a big party (i.e., a major business move). Do you have enough snacks (assets) for all the guests (liabilities)?
- Debt to Equity Ratio : It shows the balance between the money you’ve borrowed and the money you’ve personally invested in your business. Think of it as the ratio between the contributions to the potluck from you and those from your friends.
Innovative Tools and Techniques for Financial Analysis
Gone are the days of poring over spreadsheets until your eyes cross. Today, we have an arsenal of innovative tools at our disposal that make financial analysis not just bearable but actually kind of fun:
- Cloud-Based Accounting Software : These platforms are like having a financial wizard by your side, automating many of the tedious tasks involved in financial analysis.
- Data Visualization Tools : Imagine turning your financial data into a vibrant art gallery. These tools help you visualize trends, patterns, and anomalies in your data, making complex information digestible at a glance.
- AI and Machine Learning : The new kids on the block, these technologies offer predictive insights based on your financial data, helping you make informed decisions about the future.
Step 6: Planning for the Future: Scenarios and Projections
Planning for the future in the fast-paced world of finance and accounting is a bit like trying to pack for a vacation without knowing the destination. Will it be sunny beaches or snowy mountains? In business, just as in travel, the key to being well-prepared lies in anticipating a range of scenarios. This approach doesn’t just cushion you against the unexpected; it equips you to navigate the twists and turns of the market with confidence and agility.
The Importance of Creating Financial Scenarios
Imagine you’re at a crossroads, each path leading to a different outcome for your business. One might lead to rapid growth if a new product takes off, another to steady progress as you expand your customer base, and yet another to a challenging period if the market takes a downturn. Creating financial scenarios is like mapping out each of these paths in advance, complete with signposts (financial indicators) that help you recognize which path you’re on and what you need to do to stay on course—or change direction if necessary.
This practice isn’t about predicting the future with crystal ball accuracy; it’s about being prepared for whatever comes your way. By considering various “what ifs” and planning for them, you transform uncertainty from a source of anxiety into a strategic advantage.
Practical Advice on Long-Term Financial Planning
- Start with a Solid Foundation : Your current financial statements are the launching pad for any long-term planning. Ensure they’re accurate and up-to-date.
- Identify Key Drivers : Understand what factors most significantly impact your business’s financial health—be it sales volume, pricing strategies, or cost controls—and model your scenarios around these drivers.
- Embrace Technology : Leverage financial planning software that allows you to create and compare different scenarios with ease. These tools can provide invaluable insights and save you a heap of time.
- Regular Reviews : The only constant in business is change. Regularly review and adjust your scenarios and projections to reflect new information and market conditions.
How “Planning for the Worst” Saved My Business
There was a time when my business faced what I fondly refer to as “the perfect storm”—a combination of market downturn, rising costs, and a major client backing out last minute. It was every entrepreneur’s nightmare. But here’s the twist: we weathered the storm, not by luck, but by preparation.
During sunnier days, we’d developed a “worst-case scenario” plan . It felt a bit like rehearsing for a play we never wanted to perform, but when the storm hit, that script became our survival guide. We knew exactly which costs to cut, how to streamline operations, and where we could find alternative revenue streams. It wasn’t easy, but that plan gave us the clarity and confidence to make tough decisions quickly.
That experience taught me a valuable lesson: optimism is a fantastic quality, but it’s preparation that truly makes us resilient. Planning for the worst doesn’t mean expecting it to happen; it means ensuring that no matter what comes your way, you’re ready to face it head-on.
Related Posts
- How To Get A Heavy Equipment Loan
- The Ultimate Guide to 50+ Financial Modeling Resources
- Your Flux Analysis Step-By-Step Survival Guide
- How To Do Account Reconciliation Without Pulling Your Hair Out
- Taking Vertical Analysis To The Next Level
- Your Unconventional Guide To Managing Working Capital
FP&A Leader | Digital Finance Advocate | Small Business Founder
Mike Dion brings a wealth of knowledge in business finance to his writing, drawing on his background as a Senior FP&A Leader. Over more than a decade of finance experience, Mike has added tens of millions of dollars to businesses from the Fortune 100 to startups and from Entertainment to Telecom. Mike received his Bachelor of Science in Finance and a Master of International Business from the University of Florida, laying a solid foundation for his career in finance and accounting. His work, featured in leading finance publications such as Seeking Alpha, serves as a resource for industry professionals seeking to navigate the complexities of corporate finance, small business finance, and finance software with ease.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Financial Analysis
The last article in a comprehensive series to help you craft the perfect business plan for your startup.

This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan .
Numbers tell the story. Bottom line results indicate the success or failure of any business.
Financial projections and estimates help entrepreneurs, lenders, and investors or lenders objectively evaluate a company's potential for success. If a business seeks outside funding, providing comprehensive financial reports and analysis is critical.
But most importantly, financial projections tell you whether your business has a chance of being viable--and if not let you know you have more work to do.
Most business plans include at least five basic reports or projections:
- Balance Sheet: Describes the company cash position including assets, liabilities, shareholders, and earnings retained to fund future operations or to serve as funding for expansion and growth. It indicates the financial health of a business.
- Income Statement: Also called a Profit and Loss statement, this report lists projected revenue and expenses. It shows whether a company will be profitable during a given time period.
- Cash Flow Statement: A projection of cash receipts and expense payments. It shows how and when cash will flow through the business; without cash, payments (including salaries) cannot be made.
- Operating Budget: A detailed breakdown of income and expenses; provides a guide for how the company will operate from a "dollars" point of view.
- Break-Even Analysis: A projection of the revenue required to cover all fixed and variable expenses. Shows when, under specific conditions, a business can expect to become profitable.
It's easy to find examples of all of the above. Even the most basic accounting software packages include templates and samples. You can also find templates in Excel and Google Docs. (A quick search like "google docs profit and loss statement" yields plenty of examples.)
Or you can work with an accountant to create the necessary financial projections and documents. Certainly feel free to do so... but I'd first recommend playing around with the reports yourself. While you don't need to be an accountant to run a business, you do need to understand your numbers... and the best way to understand your numbers is usually to actually work with your numbers.
But ultimately the tools you use to develop your numbers are not as important as whether those numbers are as accurate as possible--and whether those numbers help you decide whether to take the next step and put your business plan into action.
Then Financial Analysis can help you answer the most important business question: "Can we make a profit?"
Some business plans include less essential but potentially important information in an Appendix section. You may decide to include, as backup or additional information:
- Resumes of key leaders
- Additional descriptions of products and services
- Legal agreements
- Organizational charts
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Photographs of potential facilities, products, etc
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Additional financial documents or projections
Keep in mind creating an Appendix is usually only necessary if you're seeking financing or hoping to bring in partners or investors. Initially the people reading your business plan don't wish to plow through reams and reams of charts, numbers, and backup information. If one does want to dig deeper, fine--he or she can check out the documents in the Appendix.
That way your business plan can share your story clearly and concisely.
Otherwise, since you created your business plan... you should already have the backup.
And one last thing: always remember the goal of your business plan is to convince you that your idea makes sense--because it's your time, your money, and your effort on the line.
More in this series:
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Key Concepts
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: the Executive Summary
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Overview and Objectives
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Products and Services
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Market Opportunities
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Sales and Marketing
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Competitive Analysis
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Operations
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Management Team
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

How To Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
Building a financial projection as you write out your business plan can help you forecast how much money your business will bring in.

Planning for the future, whether it’s with growth in mind or just staying the course, is central to being a business owner. Part of this planning effort is making financial projections of sales, expenses, and—if all goes well—profits.
Even if your business is a startup that has yet to open its doors, you can still make projections. Here’s how to prepare your business plan financial projections, so your company will thrive.
What are business plan financial projections?
Business plan financial projections are a company’s estimates, or forecasts, of its financial performance at some point in the future. For existing businesses, draw on historical data to detail how your company expects metrics like revenue, expenses, profit, and cash flow to change over time.
Companies can create financial projections for any span of time, but typically they’re for between one and five years. Many companies revisit and amend these projections at least annually.
Creating financial projections is an important part of building a business plan . That’s because realistic estimates help company leaders set business goals, execute financial decisions, manage cash flow , identify areas for operational improvement, seek funding from investors, and more.
What are financial projections used for?
Financial forecasting serves as a useful tool for key stakeholders, both within and outside of the business. They often are used for:
Business planning
Accurate financial projections can help a company establish growth targets and other goals . They’re also used to determine whether ideas like a new product line are financially feasible. Future financial estimates are helpful tools for business contingency planning, which involves considering the monetary impact of adverse events and worst-case scenarios. They also provide a benchmark: If revenue is falling short of projections, for example, the company may need changes to keep business operations on track.
Projections may reveal potential problems—say, unexpected operating expenses that exceed cash inflows. A negative cash flow projection may suggest the business needs to secure funding through outside investments or bank loans, increase sales, improve margins, or cut costs.
When potential investors consider putting their money into a venture, they want a return on that investment. Business projections are a key tool they will use to make that decision. The projections can figure in establishing the valuation of your business, equity stakes, plans for an exit, and more. Investors may also use your projections to ensure that the business is meeting goals and benchmarks.
Loans or lines of credit
Lenders rely on financial projections to determine whether to extend a business loan to your company. They’ll want to see historical financial data like cash flow statements, your balance sheet , and other financial statements—but they’ll also look very closely at your multi-year financial projections. Good candidates can receive higher loan amounts with lower interest rates or more flexible payment plans.
Lenders may also use the estimated value of company assets to determine the collateral to secure the loan. Like investors, lenders typically refer to your projections over time to monitor progress and financial health.
What information is included in financial projections for a business?
Before sitting down to create projections, you’ll need to collect some data. Owners of an existing business can leverage three financial statements they likely already have: a balance sheet, an annual income statement , and a cash flow statement .
A new business, however, won’t have this historical data. So market research is crucial: Review competitors’ pricing strategies, scour research reports and market analysis , and scrutinize any other publicly available data that can help inform your projections. Beginning with conservative estimates and simple calculations can help you get started, and you can always add to the projections over time.
One business’s financial projections may be more detailed than another’s, but the forecasts typically rely on and include the following:
True to its name, a cash flow statement shows the money coming into and going out of the business over time: cash outflows and inflows. Cash flows fall into three main categories:
Income statement
Projected income statements, also known as projected profit and loss statements (P&Ls), forecast the company’s revenue and expenses for a given period.
Generally, this is a table with several line items for each category. Sales projections can include the sales forecast for each individual product or service (many companies break this down by month). Expenses are a similar setup: List your expected costs by category, including recurring expenses such as salaries and rent, as well as variable expenses for raw materials and transportation.
This exercise will also provide you with a net income projection, which is the difference between your revenue and expenses, including any taxes or interest payments. That number is a forecast of your profit or loss, hence why this document is often called a P&L.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet shows a snapshot of your company’s financial position at a specific point in time. Three important elements are included as balance sheet items:
- Assets. Assets are any tangible item of value that the company currently has on hand or will in the future, like cash, inventory, equipment, and accounts receivable. Intangible assets include copyrights, trademarks, patents and other intellectual property .
- Liabilities. Liabilities are anything that the company owes, including taxes, wages, accounts payable, dividends, and unearned revenue, such as customer payments for goods you haven’t yet delivered.
- Shareholder equity. The shareholder equity figure is derived by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. It reflects how much money, or capital, the company would have left over if the business paid all its liabilities at once or liquidated (this figure can be a negative number if liabilities exceed assets). Equity in business is the amount of capital that the owners and any other shareholders have tied up in the company.
They’re called balance sheets because assets always equal liabilities plus shareholder equity.
5 steps for creating financial projections for your business
- Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections
- Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis
- Forecast expenses
- Forecast sales
- Build financial projections
The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company:
1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections
The details of your projections may vary depending on their purpose. Are they for internal planning, pitching investors, or monitoring performance over time? Setting the time frame—monthly, quarterly, annually, or multi-year—will also inform the rest of the steps.
2. Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis
If available, gather historical financial statements, including balance sheets, cash flow statements, and annual income statements. New companies without this historical data may have to rely on market research, analyst reports, and industry benchmarks—all things that established companies also should use to support their assumptions.
3. Forecast expenses
Identify future spending based on direct costs of producing your goods and services ( cost of goods sold, or COGS) as well as operating expenses, including any recurring and one-time costs. Factor in expected changes in expenses, because this can evolve based on business growth, time in the market, and the launch of new products.
4. Forecast sales
Project sales for each revenue stream, broken down by month. These projections may be based on historical data or market research, and they should account for anticipated or likely changes in market demand and pricing.
5. Build financial projections
Now that you have projected expenses and revenue, you can plug that information into Shopify’s cash flow calculator and cash flow statement template . This information can also be used to forecast your income statement. In turn, these steps inform your calculations on the balance sheet, on which you’ll also account for any assets and liabilities .
Business plan financial projections FAQ
What are the main components of a financial projection in a business plan.
Generally speaking, most financial forecasts include projections for income, balance sheet, and cash flow.
What’s the difference between financial projection and financial forecast?
These two terms are often used interchangeably. Depending on the context, a financial forecast may refer to a more formal and detailed document—one that might include analysis and context for several financial metrics in a more complex financial model.
Do I need accounting or planning software for financial projections?
Not necessarily. Depending on factors like the age and size of your business, you may be able to prepare financial projections using a simple spreadsheet program. Large complicated businesses, however, usually use accounting software and other types of advanced data-management systems.
What are some limitations of financial projections?
Projections are by nature based on human assumptions and, of course, humans can’t truly predict the future—even with the aid of computers and software programs. Financial projections are, at best, estimates based on the information available at the time—not ironclad guarantees of future performance.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Sep 4, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
How To Conduct Financial Analysis for Your Company
Updated: July 22, 2024
Published: July 07, 2023
If someone were to ask you about your company’s financial strengths and weaknesses, could you give them a detailed answer?

As a founder, you need to know this type of information about your business. Understanding your financial performance is key to making better decisions about growth and investment plans.
The key to painting that picture lies in a process known as financial analysis.

What is financial analysis?
Financial analysis is the process of going over a company’s financial data to evaluate its performance in order to make informed business decisions. Founders and executives use financial analysis to assess performance and make strategic decisions, such as where to invest money to improve growth.
Externally, investors use financial analysis to make decisions about which companies are good investments. Potential lenders, such as banks, may also use financial analysis when they review loan applicants to assess your ability to pay back the money they lend.
Financial analysis is typically done by an external finance professional who reviews documents like the income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
How to do a financial analysis
1. collect your company’s financial statements.
Financial analysis helps you identify trends in your business’s performance. To get the best insights, compare your business performance over time.
Gather your recent financial statements, including your balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. Look at the last three to five years’ worth of data, which is enough to establish a trend while still focusing on your most recent (and relevant) performance.
Once you have all your documents, arrange them in chronological order.
.png)
Free Financial Planning Templates
Manage your business and personal finances with these five financial planning templates.
- Balance Sheet Template
- Profit & Loss Statement Template
- Financial Projection Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
2. Analyze balance sheets
Your balance sheets give you a snapshot of your company’s finances at a given point in time, such as the end of a fiscal year. On this sheet, you’ll see the value of your short- and long-term assets, debts, and owner’s equity.
Look at your balance sheets and consider the following questions:
- How much debt do you have compared to equity?
- Has your debt been increasing or decreasing over time?
- How liquid is the business? (i.e., how much of the business’s assets are short term?)
- How has the liquidity of the business changed over time?
3. Analyze income statements
Also known as a profit and loss (P&L) statement , the income statement provides insight into your company’s revenue , expenses, and profits.
Evaluate your income statements and look for trends in your:
- Gross revenue: Total amount of income generated by sales.
- Operating income: Revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). This tells you how much of your revenue remains after you account for operating expenses.
- Net profit (or loss): Revenue minus all expenses. This tells you how much money your company earned (or lost) after paying interest and taxes.
Startups can often take two to three years to become profitable . That’s why it’s helpful to track several financial metrics.
For example, you can have a net loss while still generating an operating profit. This means your core business is profitable, but you may still be paying off interest on the loans it took to get the business off the ground.
4. Analyze cash flow statements
Your cash flow statements give you insight into how money flows in and out of your business by looking at your expenses and which activities generate income.
Here are some steps to take in your cash flow analysis :
- Review cash flow for each activity (operating, investing, financing). Note whether cash flow is positive (the activity generates income) or negative (the activity loses money).
- Compare cash flow from each activity to see which generates the most income for your business.
- Review cash inflow and outflow over time to identify trends. Are they increasing or decreasing?
- Review total cash to see if it is increasing or decreasing over time.
5. Calculate relevant financial ratios
Calculate financial ratios to get a more detailed picture of your company’s profitability, liquidity, and overall operational efficiency. Here are some of the most common metrics to consider in a ratio analysis.

6. Summarize your findings
Put together all your findings. You can use the following prompts to help organize your analysis:
- What are my company’s financial strengths?
- What are my company’s financial weaknesses?
- How well did the company perform compared to previous financial projections?
- What are the possible explanations for my company’s strengths and weaknesses?
- What financial improvements do I want to make?
After you conduct your analysis, you’ll know where your business stands in terms of its finances and be able to have educated discussions with stakeholders and potential investors.
Furthermore, you’ll be able to use this knowledge to make more informed decisions about your business’s strategy.
Gaurav Nagani, CEO of help desk software company Desku.io, recommends conducting an analysis “before investing, at regular intervals, before making strategic decisions, and during difficult times.” This way, when you have to make impactful decisions, you’re doing so with a full picture of your company’s financial health.

Common types of financial analysis
There are several different types of financial analysis that you, or a financial professional, can use, depending on what you hope to glean.
Horizontal analysis
Horizontal analysis looks at a company’s performance over time by comparing financial statements over different periods, such as months, quarters, or years.
You can use it to identify growth trends and support financial forecasting , which is the process of using historical data to predict your company’s performance in the future.
Vertical analysis
Vertical analysis looks at a company’s financial performance relative to one metric, such as your total assets. In this case, all line items on the financial statements are expressed as a percentage of total assets. For example, you can use the debt-to-asset ratio, which looks at your total debt as a percentage of total assets.
Say your total debt is $4m and you have $10m in total assets. A vertical analysis would show your debts as 40% of total assets, which is what you get when you divide $4m by $10m.
Using vertical analysis makes it easy to see relationships between the metrics on different financial statements. It’s also helpful for comparing companies with one another for benchmarking.
Valuation is the process of using a company’s financial information to estimate the value of the business .
Investors often compare a company’s estimated value to its stock price to see if they want to buy shares. For startups, valuations are a necessary step to take before starting a priced fundraising round.
Growth Rates
Growth rates represent the percent change in a given metric over time, such as the percent change in net sales over four quarters. Analyzing growth rates can help forecast future performance for specific metrics.
Profitability
Analysts may use profitability ratios , which provide insight into how efficiently your company turns revenue into profit. The higher your profitability ratios, the more resources you’ll have to reinvest into the company’s growth or distribute to your shareholders.
Jeff Schmidt, vice president of financial modeling at Corporate Finance Institute, reminds entrepreneurs, “The point of analysis is to not focus on one method or another but consider the analysis in total and make the proper investment decision.”
Financial analysis example
One example of a financial analysis would be if a financial analyst calculated your company’s profitability ratios , which assess your company’s ability to make money, and leverage ratios , which measure your company’s ability to pay off its debts. Based on the results of the analysis, the analyst will decide if they want to recommend your company as a good investment.
Knowing how to do a financial analysis is a key skill for entrepreneurs because it helps you understand your company’s performance. You can use the insights you gain from financial analysis to make more informed decisions about your overall strategy.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![financial analysis for business plan What is Invoice Financing & How Does It Work? [+Pros & Cons]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/image2-Aug-29-2024-04-42-07-3493-PM.png)
What is Invoice Financing & How Does It Work? [+Pros & Cons]

Invoice vs. Receipt: What's the Difference? (+ When to Use Each)

Accounting 101: Accounting Basics for Beginners to Learn

What Is a Sales Invoice? How to Create One & Get Paid Fast

How To Conduct a Small-Business Valuation

A Guide to Managerial Accounting

What Is Goodwill in Accounting: An Explainer

A Quick Guide to GAAP Accounting for Your Business

How To Do Accounting for Your Startup: Steps, Tips, and Tools

Gross Revenue vs. Net Revenue: An Explainer
P&L Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Balance Sheet, and more.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
More From Forbes
Basics of a business plan financials section.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
A good business plan is an entrepreneur’s best friend. It’s an indispensable document, and every section matters, from the executive summary to the market analysis to the appendix; however, no section matters as much as the financials section. You’re in business to make money, after all, and your business plan has to clearly, numerically reflect a lucrative business pursuit, preferably with visuals, especially if you want funding.
The financials section of your business plan tells you and your potential investors, loan providers or partners whether your business idea makes economic sense. Without an impressive financials section, you’re looking at an uphill battle when it comes to scoring capital; underwhelming financials may indicate a need to make some revisions to your approach.
Basic Financials
So, how to build an impressive financials section? As with all things in small business, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach; it varies by business and field. But there are some general guidelines that can give you a clear idea of where to start and what kind of data you’ll need to gather.
You need to include at least three documents in the financials section of your business plan:
1. Income statement: Are you profitable?
2. Cash flow statement: How much cash do you have on hand?
3. Balance sheet: What’s your net worth?
There’s other financial information you can — and often should — add to your business plan, like sales forecasts and personnel plans. But the income statement, cash flow projections and balance sheet are the ones you can’t leave out.
Here's a brief run-down of the three major data sets.
Income Statement
Also called a profit/loss statement, here’s where your reader can see if your business is profitable. If you’re not operating the business yet, this will be a projected income statement, based on a well-informed analysis of your business’s first year.
The income statement is broken down by month and shows revenue (sales), expenses (costs of operating) and the resulting profit or loss for one fiscal year. (Revenue - expenses = profit/loss.)
Cash Flow Statements
Here’s where your reader can see how much money you’re going to need in the first year of operations. If you’re not yet up and running, you’ll only have projections.
For cash flow projections, you’ll predict the cash money that will flow into and out of your business in a particular month. You’ll need a year’s worth of monthly projections. If you’re already operating, also include cash flow statements for past months showing actual numbers.
Cash flow statements have three basic components: cash revenues, cash disbursements and reconciliation of revenues to disbursements. For each month, you start with your previous month’s balance, add revenues and subtract disbursements. The final balance becomes the opening balance for the following month.
Balance Sheet
Here’s where your reader sees your business’s net worth. It breaks down into monthly balance sheets and a final net worth at the end of the fiscal year. There are three parts to a balance sheet:
• Accounts receivable
• Inventory, equipment
• Real estate
2. Liabilities
• Accounts payable
• Loan debts
3. Equity: Total assets minus total liabilities (Assets = liabilities + equity.)
It’s good to offer readers an analysis of the three basic financial statements — how they fit together and what they mean for the future of your business. It doesn’t have to be in depth; focus is good. Just interpret the data from each statement, putting it in context and indicating what the reader should take away from the financials section of your business plan.
Other Financial Documents
These are the basics of your financials, but you’ll need to fill out the section with other data based on the specifics of your business and your capital needs. Other financial information you might provide includes:
• Sales forecast: Estimates of future sales volumes
• Personnel plan: Who you plan to recruit/hire and how much it will cost
• Breakeven analysis: Projected point at which your sales will match your expenses
• Financial history: Summary of your business finances from the start of operations to the present time
Make It Easy
A lot of this can be made easier with business planning software, which can not only guide you through the process and make sure you don’t leave anything else but may also generate graphs, charts and other visuals to accompany the data in your financials section. Those types of visuals are highly recommended because some readers will skim. Anything you can do to convey information in a glance imparts a benefit.
Revisit Monthly
Once in operation, don’t forget to go back into your financials every month to update your projections with actual numbers and then adjust any future projections accordingly. Regular updates will tell you if you’re on track with your predictions and hitting your goals, as well as whether you need to make adjustments. Don’t forget this part — when you’re starting out, planning really is your best friend.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
How to Develop a Small Business Financial Plan
By Andy Marker | April 29, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Financial planning is critical for any successful small business, but the process can be complicated. To help you get started, we’ve created a step-by-step guide and rounded up top tips from experts.
Included on this page, you’ll find what to include in a financial plan , steps to develop one , and a downloadable starter kit .
What Is a Small Business Financial Plan?
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth.

Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ideas. Craig Hewitt, Founder of Castos , shares that “creating a financial plan will show you if your business ideas are sustainable. A financial plan will show you where your business stands and help you make better decisions about resource allocation. It will also help you plan growth, survive cash flow shortages, and pitch to investors.”
Why Is It Important for a Small Business to Have a Financial Plan?
All small businesses should create a financial plan. This allows you to assess your business’s financial needs, recognize areas of opportunity, and project your growth over time. A strong financial plan is also a bonus for potential investors.

Mark Daoust , the President and CEO of Quiet Light Brokerage, Inc., explains why a financial plan is important for small businesses: “It can sometimes be difficult for business owners to evaluate their own progress, especially when starting a new company. A financial plan can be helpful in showing increased revenues, cash flow growth, and overall profit in quantifiable data. It's very encouraging for small business owners who are often working long hours and dealing with so many stressful decisions to know that they are on the right track.”
To learn more about other important considerations for a small business, peruse our list of free startup plan, budget, and cost templates .
What Does a Small Business Financial Plan Include?
All small businesses should include an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement in their financial plan. You may also include other documents, such as personnel plans, break-even points, and sales forecasts, depending on the business and industry.

- Balance Sheet: A balance sheet determines the difference between your liabilities and assets to determine your equity. “A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business’s financial position at a particular moment in time,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “It adds up everything your business owns and subtracts all debts — the difference reflects the net worth of the business, also referred to as equity .” Yüzbaşıoğlu explains that this statement consists of three parts: assets, liabilities, and equity. “Assets include your money in the bank, accounts receivable, inventories, and more. Liabilities can include your accounts payables, credit card balances, and loan repayments, for example. Equity for most small businesses is just the owner’s equity, but it could also include investors’ shares, retained earnings, or stock proceeds,” he says.
- Cash Flow Statement: A cash flow statement shows where the money is coming from and where it is going. For existing businesses, this will include bank statements that list deposits and expenditures. A new business may not have much cash flow information, but it can include all startup costs and funding sources. “A cash flow statement shows how much cash is generated and used during a given period of time. It documents all the money flowing in and out of your business,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Break-Even Analysis: A break-even analysis is a projection of how long it will take you to recoup your investments, such as expenses from startup costs or ongoing projects. In order to perform this analysis, Yüzbaşıoğlu explains, “You need to know the difference between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are the expenses that stay the same, regardless of how much you sell or don't sell. For example, expenses such as rent, wages, and accounting fees are typically fixed. Variable costs are the expenses that change in accordance with production or sales volume. “In other words, [a break-even analysis] determines the units of products or services you need to sell at least to cover your production costs. Generally, to calculate the break-even point in business, divide fixed costs by the gross profit margin. This produces a dollar figure that a company needs to break even,” Yüzbaşıoğlu shares.
- Personnel Plan: A personnel plan is an outline of various positions or departments that states what they do, why they are necessary, and how much they cost. This document is generally more useful for large businesses, or those that find themselves spending a large percentage of their budget on labor.
- Sales Forecast: A sales forecast can help determine how many sales and how much money you expect to make in a given time period. To learn more about various methods of predicting these figures, check out our guide to sales forecasting .
How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan
Writing a financial plan begins with collecting financial information from your small business. Create income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, and any other documents you need using that information. Then share those documents with relevant stakeholders.
“Creating a financial plan is key to any business and essential for success: It provides protection and an opportunity to grow,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “You can use [the financial plan] to make better-informed decisions about things like resource allocation on future projects and to help shape the success of your company.”
1. Create a Plan
Create a strategic business plan that includes your business strategy and goals, and define their financial impact. Your financial plan will inform decisions for every aspect of your business, so it is important to know what is important and what is at stake.
2. Gather Financial Information
Collect all of the available financial information about your business. Organize bank statements, loan information, sales numbers, inventory costs, payroll information, and any other income and expenses your business has incurred. If you have not already started to do so, regularly record all of this information and store it in an easily accessible place.
3. Create an Income Statement
Your income statement should display revenue, expenses, and profit for a given time period. Your revenue minus your expenses equals your profit or loss. Many businesses create a new statement yearly or quarterly, but small businesses with less cash flow may benefit from creating statements for shorter time frames.
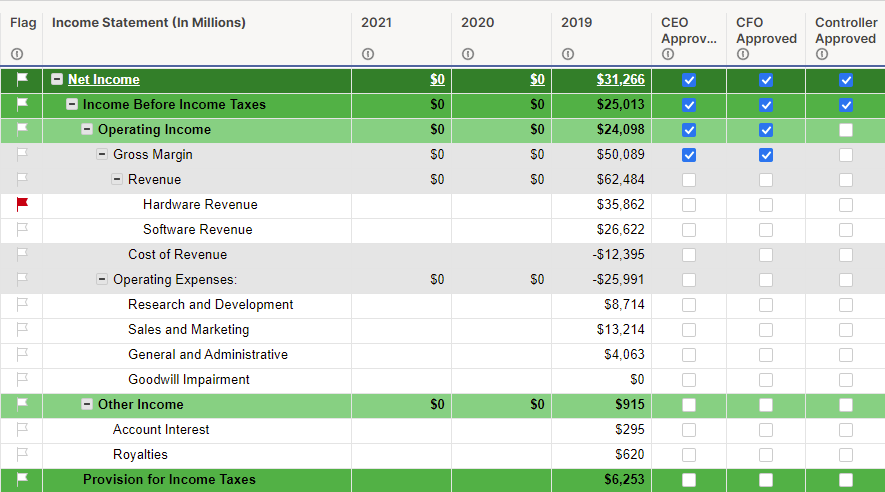
4. Create a Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a snapshot of your business’s financial status at a particular moment in time. You should update it on the same schedule as your income statement. To determine your equity, calculate all of your assets minus your liabilities.
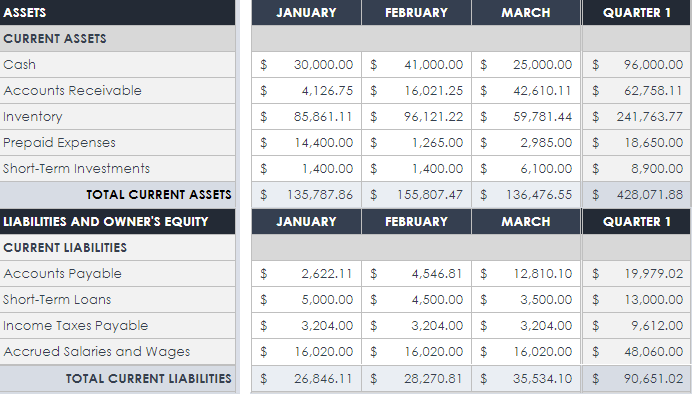
5. Create a Cash Flow Statement
As mentioned above, the cash flow statement shows all past and projected cash flow for your business. “Your cash flow statement needs to cover three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities,” suggests Hewitt. “Operating activities are the movement of cash from the sale or purchase of goods or services. Investing activities are the sale or purchase of long-term assets. Financing activities are transactions with creditors and investments.”
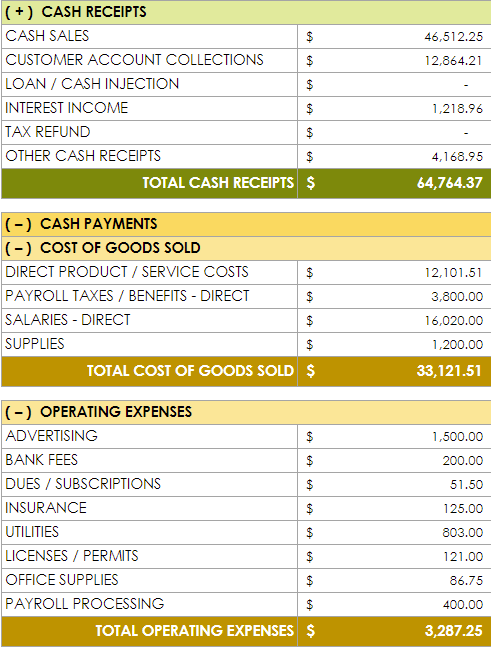
6. Create Other Documents as Needed
Depending on the age, size, and industry of your business, you may find it useful to include these other documents in your financial plan as well.
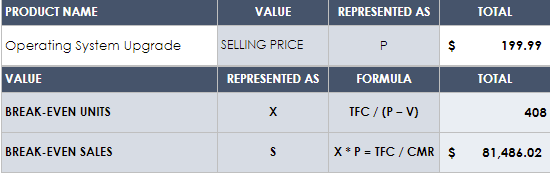
- Sales Forecast: Your sales forecast should reference sales numbers from your past to estimate sales numbers for your future. Sales forecasts may be more useful for established companies with historical numbers to compare to, but small businesses can use forecasts to set goals and break records month over month. “To make future financial projections, start with a sales forecast,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “Project your sales over the course of 12 months. After projecting sales, calculate your cost of sales (also called cost of goods or direct costs). This will let you calculate gross margin. Gross margin is sales less the cost of sales, and it's a useful number for comparing with different standard industry ratios.”
7. Save the Plan for Reference and Share as Needed
The most important part of a financial plan is sharing it with stakeholders. You can also use much of the same information in your financial plan to create a budget for your small business.

Additionally, be sure to conduct regular reviews, as things will inevitably change. “My best tip for small businesses when creating a financial plan is to schedule reviews. Once you have your plan in place, it is essential that you review it often and compare how well the strategy fits with the actual monthly expenses. This will help you adjust your plan accordingly and prepare for the year ahead,” suggests Janet Patterson, Loan and Finance Expert at Highway Title Loans.
Small Business Financial Plan Example
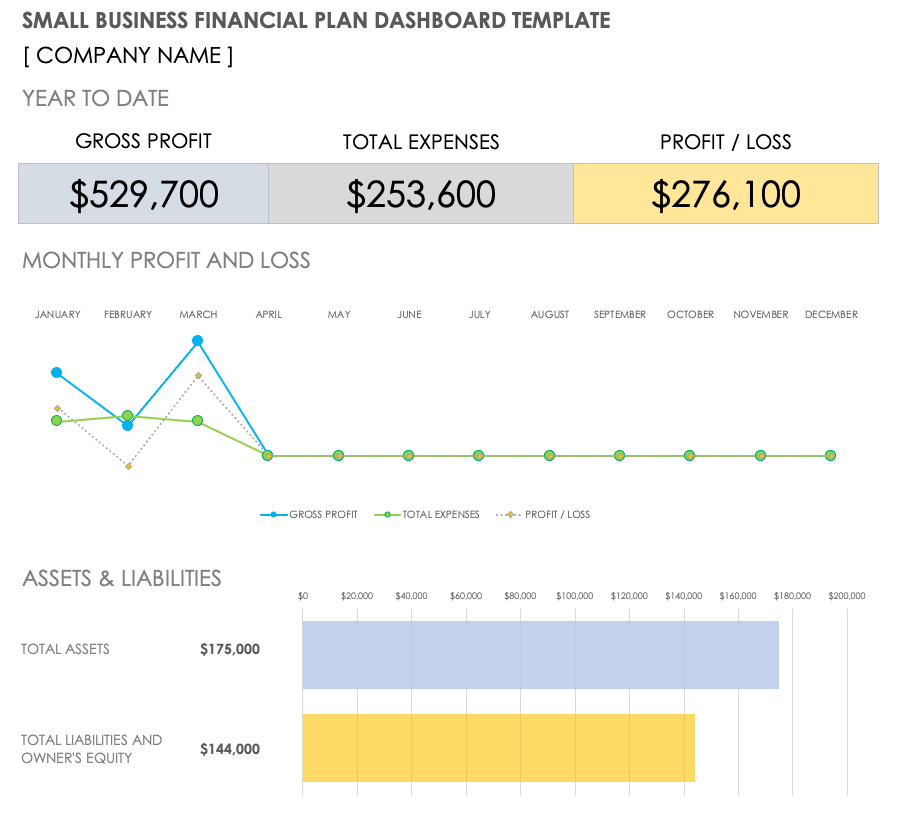
Download Small Business Financial Plan Example Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Here is an example of what a completed small business financial plan dashboard might look like. Once you have completed your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements, use a template to create visual graphs to display the information to make it easier to read and share. In this example, this small business plots its income and cash flow statements quarterly, but you may find it valuable to update yours more often.
Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
Download Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
We’ve created this small business financial plan starter kit to help you get organized and complete your financial plan. In this kit, you will find a fully customizable income statement template, a balance sheet template, a cash flow statement template, and a dashboard template to display results. We have also included templates for break-even analysis, a personnel plan, and sales forecasts to meet your ongoing financial planning needs.
Small Business Income Statement Template
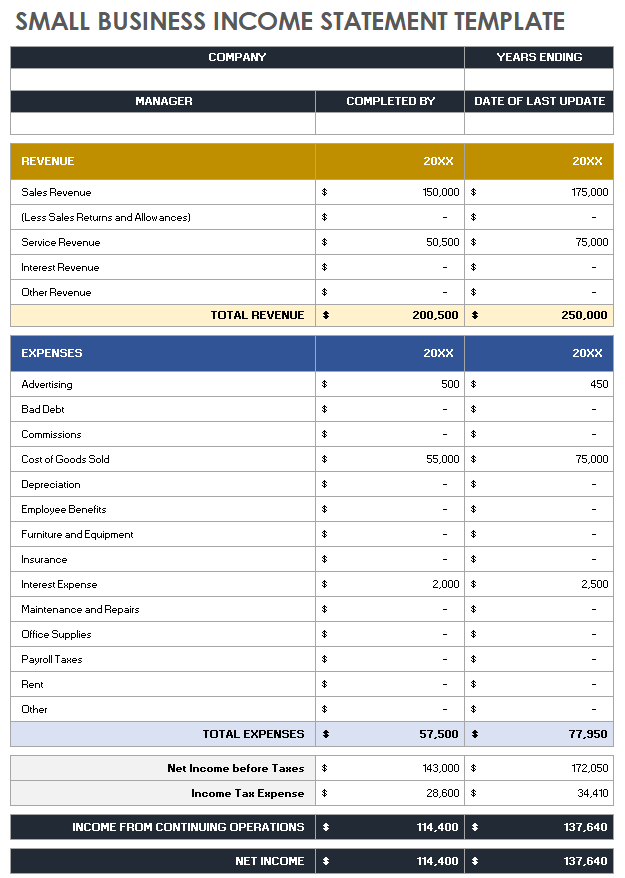
Download Small Business Income Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business income statement template to input your income information and track your growth over time. This template is filled to track by the year, but you can also track by months or quarters. The template is fully customizable to suit your business needs.
Small Business Balance Sheet Template
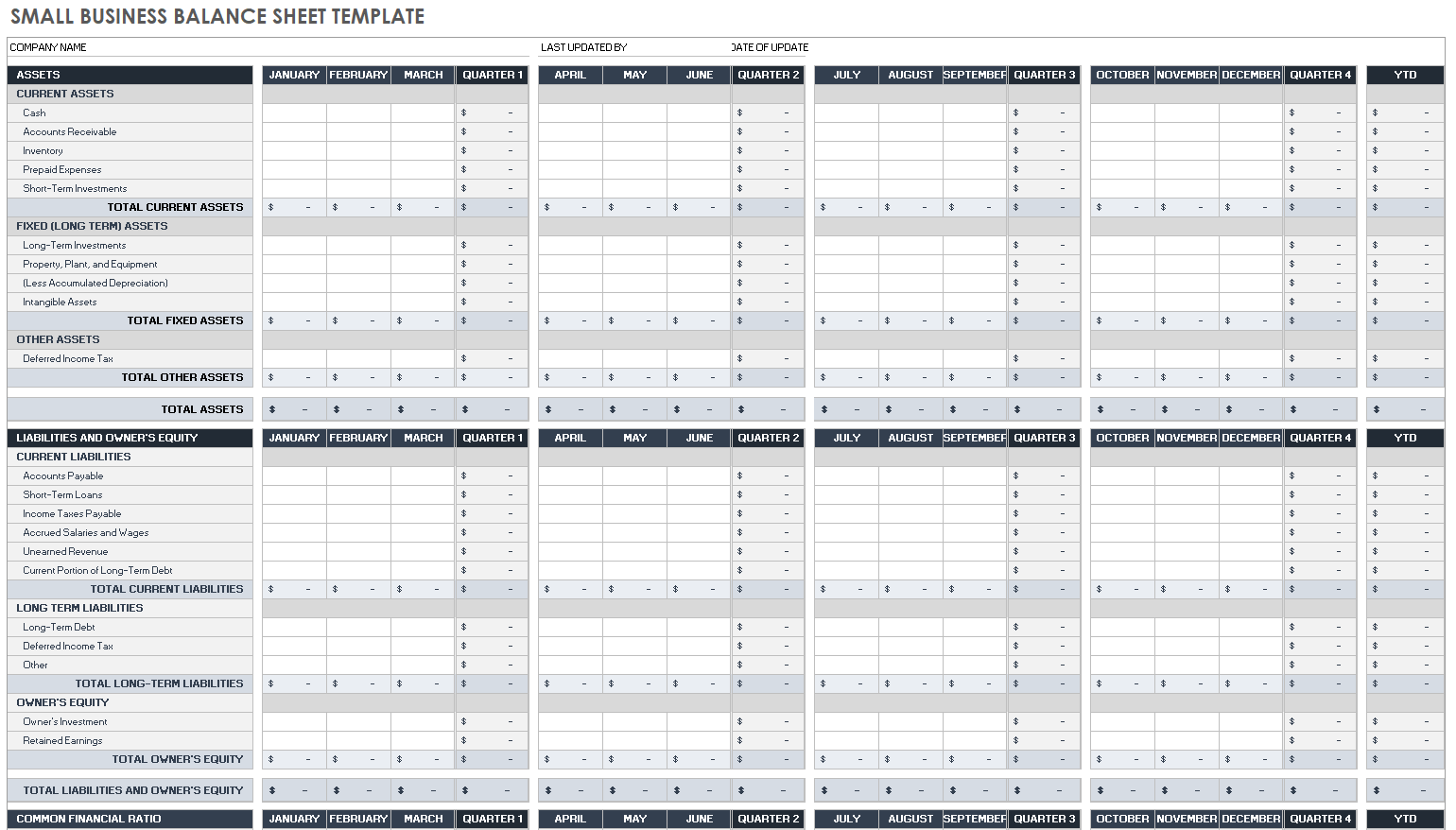
Download Small Business Balance Sheet Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This customizable balance sheet template was created with small businesses in mind. Use it to create a snapshot of your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity quarter over quarter.
Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template
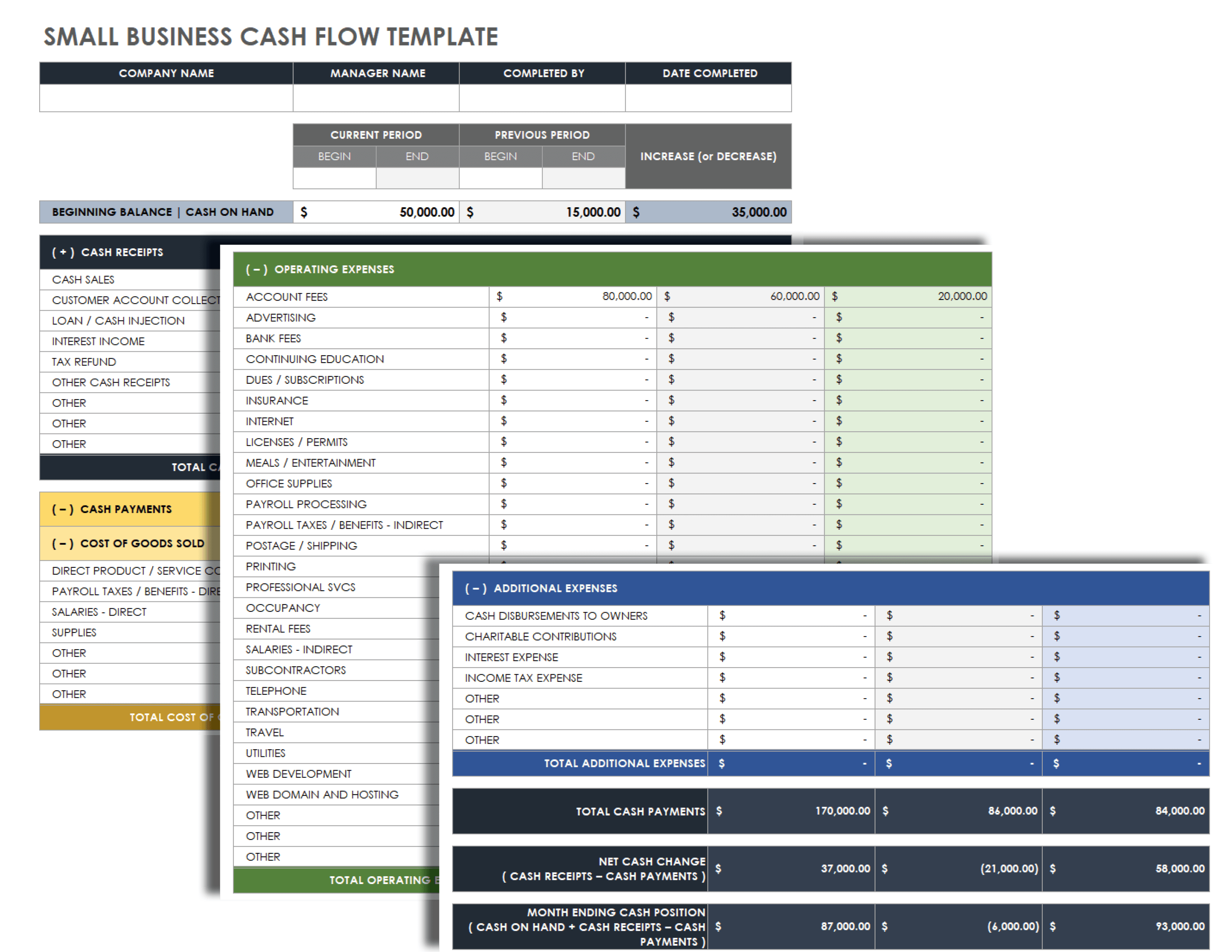
Download Small Business Cash Flow Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable cash flow statement template to stay organized when documenting your cash flow. Note the time frame and input all of your financial data in the appropriate cell. With this information, the template will automatically generate your total cash payments, net cash change, and ending cash position.
Break-Even Analysis Template
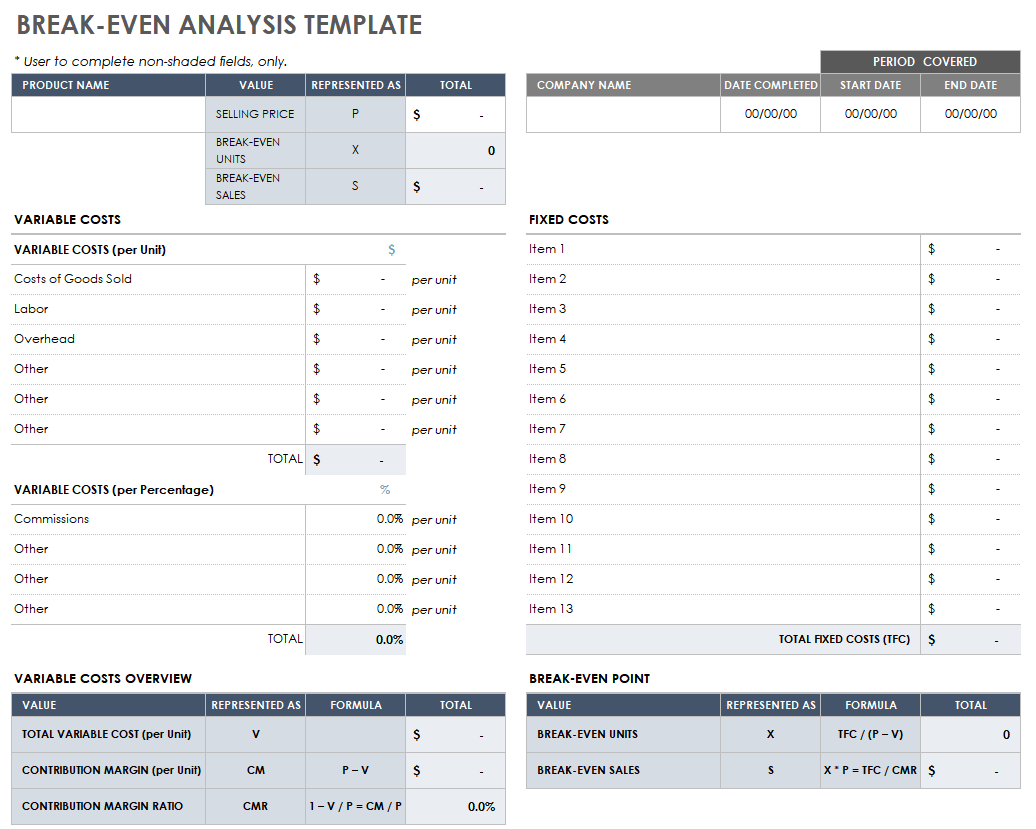
Download Break-Even Analysis Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This powerful template can help you determine the point at which you will break even on product investment. Input the sale price of the product, as well as its various associated costs, and this template will display the number of units needed to break even on your initial costs.
Personnel Plan Template
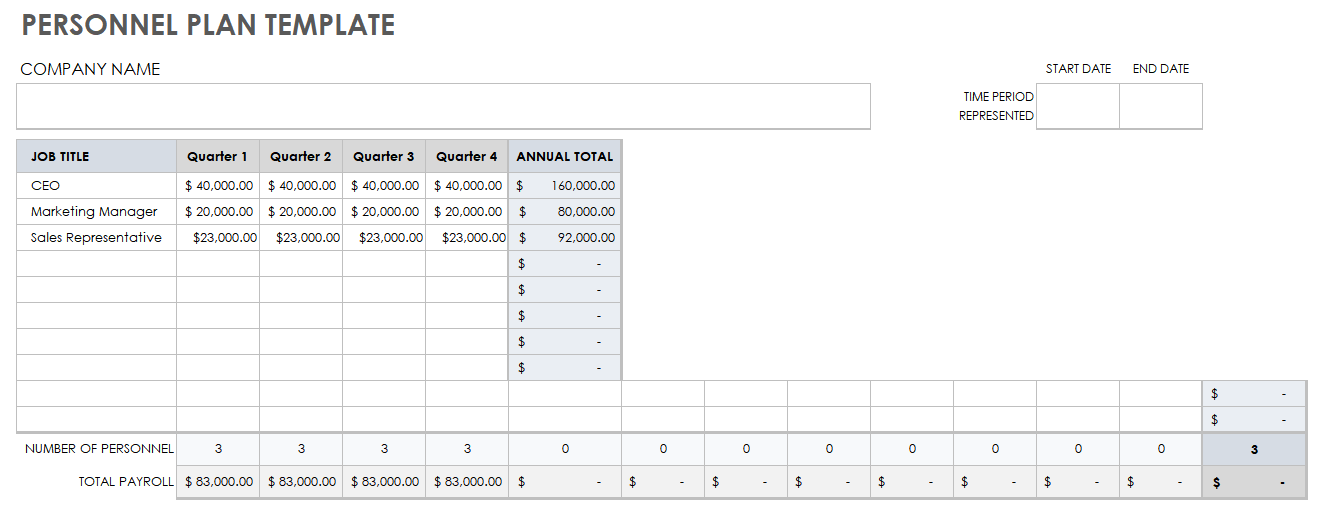
Download Personnel Plan Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this simple personnel plan template to help organize and define the monetary cost of the various roles or departments within your company. This template will generate a labor cost total that you can use to compare roles and determine whether you need to make cuts or identify areas for growth.
Sales Forecast Template
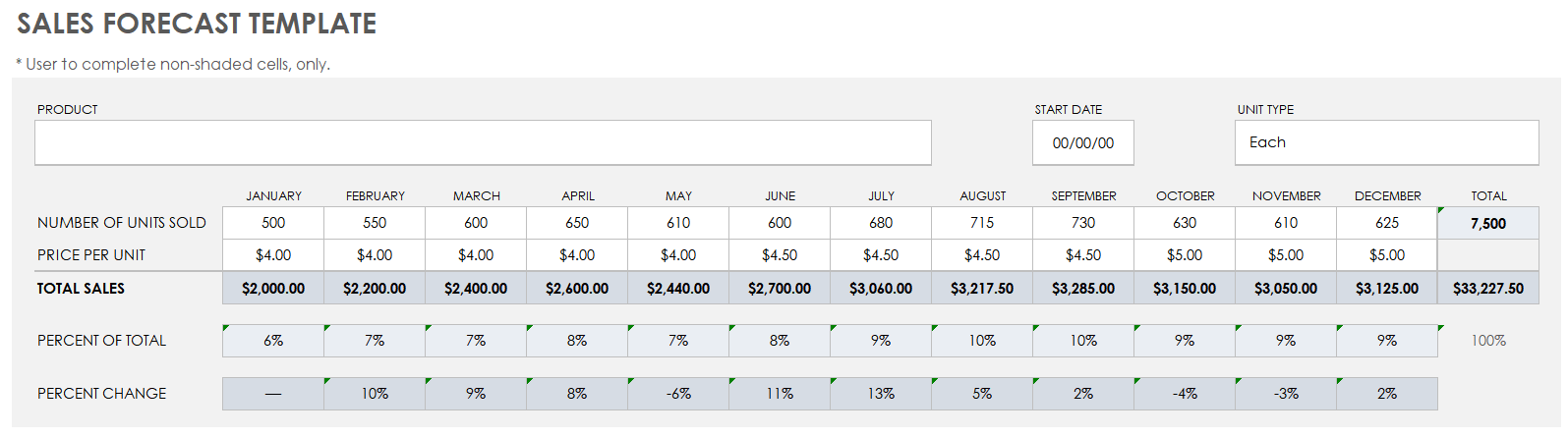
Download Sales Forecast Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable template to forecast your sales month over month and determine the percentage changes. You can use this template to set goals and track sales history as well.
Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template
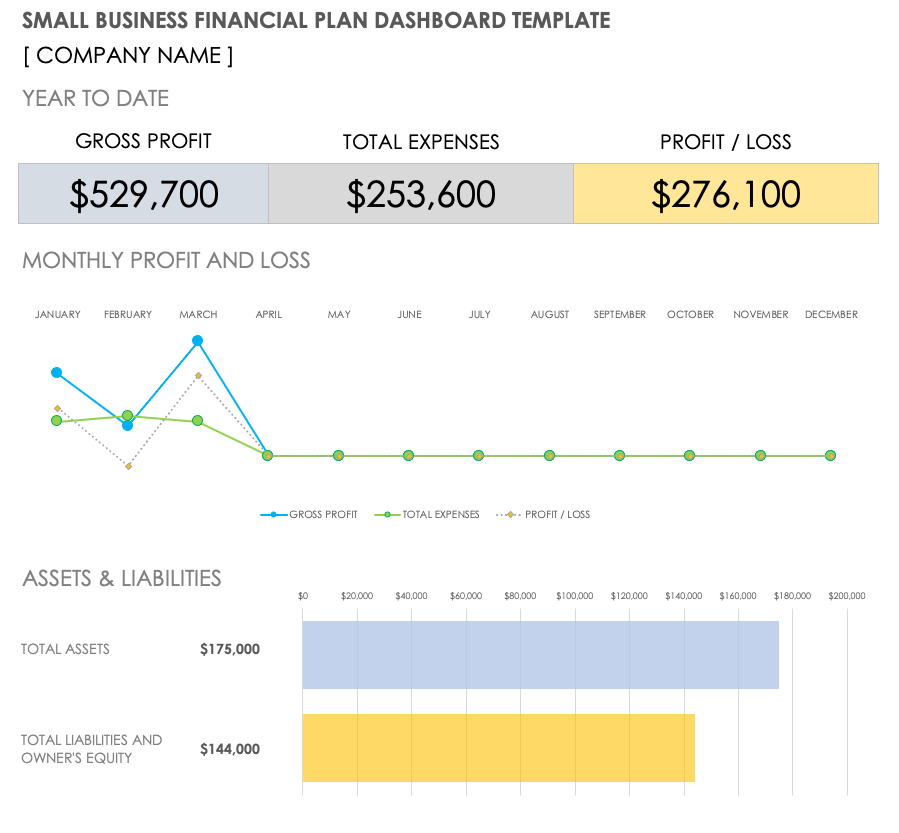
Download Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This dashboard template provides a visual example of a small business financial plan. It presents the information from your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in a graphical form that is easy to read and share.
Tips for Completing a Financial Plan for a Small Business
You can simplify the development of your small business financial plan in many ways, from outlining your goals to considering where you may need help. We’ve outlined a few tips from our experts below:

- Outline Your Business Goals: Before you create a financial plan, outline your business goals. This will help you determine where money is being well spent to achieve those goals and where it may not be. “Before applying for financing or investment, list the expected business goals for the next three to five years. You can ask a certified public accountant for help in this regard,” says Thé. The U.S. Small Business Administration or a local small business development center can also help you to understand the local market and important factors for business success. For more help, check out our quick how-to guide on writing a business plan .
- Make Sure You Have the Right Permits and Insurance: One of the best ways to keep your financial plan on track is to anticipate large expenditures. Double- and triple-check that you have the permits and insurances you need so that you do not incur any fines or surprise expenses down the line. “If you own your own business, you're no longer able to count on your employer for your insurance needs. It's important to have a plan for how you're going to pay for this additional expense and make sure that you know what specific insurance you need to cover your business,” suggests Daost.
- Separate Personal Goals from Business Goals: Be as unbiased as possible when creating and laying out your business’s financial goals. Your financial and prestige goals as a business owner may be loftier than what your business can currently achieve in the present. Inflating sales forecasts or income numbers will only come back to bite you in the end.
- Consider Hiring Help: You don’t know what you don’t know, but fortunately, many financial experts are ready to help you. “Hiring financial advisors can help you make sound financial decisions for your business and create a financial roadmap to follow. Many businesses fail in the first few years due to poor planning, which leads to costly mistakes. Having a financial advisor can help keep your business alive, make a profit, and thrive,” says Hewitt.
- Include Less Obvious Expenses: No income or expense is too small to consider — it all matters when you are creating your financial plan. “I wish I had known that you’re supposed to incorporate anticipated internal hidden expenses in the plan as well,” Patterson shares. “I formulated my first financial plan myself and didn’t have enough knowledge back then. Hence, I missed out on essential expenses, like office maintenance, that are less common.”
Do Small Business Owners Need a Financial Planner?
Not all small business owners need a designated financial planner, but you should understand the documents and information that make up a financial plan. If you do not hire an advisor, you must be informed about your own finances.
Small business owners tend to wear many hats, but Powell says, “it depends on the organization of the owner and their experience with the financial side of operating businesses.” Hiring a financial advisor can take some tasks off your plate and save you time to focus on the many other details that need your attention. Financial planners are experts in their field and may have more intimate knowledge of market trends and changing tax information that can end up saving you money in the long run.
Yüzbaşıoğlu adds, “Small business owners can greatly benefit from working with a financial advisor. A successful small business often requires more than just the skills of an entrepreneur; a financial advisor can help the company effectively manage risks and maximize opportunities.”
For more examples of the tasks a financial planner might be able to help with, check through our list of free financial planning templates .
Drive Small Business Success with Financial Planning in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.
- Business Planning
Business Plan Financial Projections
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Financial projections are forecasted analyses of your business’ future that include income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements. We have found them to be an crucial part of your business plan for the following reasons:
- They can help prove or disprove the viability of your business idea. For example, if your initial projections show your company will never make a sizable profit, your venture might not be feasible. Or, in such a case, you might figure out ways to raise prices, enter new markets, or streamline operations to make it profitable.
- Financial projections give investors and lenders an idea of how well your business is likely to do in the future. They can give lenders the confidence that you’ll be able to comfortably repay their loan with interest. And for equity investors, your projections can give them faith that you’ll earn them a solid return on investment. In both cases, your projections can help you secure the funding you need to launch or grow your business.
- Financial projections help you track your progress over time and ensure your business is on track to meet its goals. For example, if your financial projections show you should generate $500,000 in sales during the year, but you are not on track to accomplish that, you’ll know you need to take corrective action to achieve your goal.
Below you’ll learn more about the key components of financial projections and how to complete and include them in your business plan.
What Are Business Plan Financial Projections?
Financial projections are an estimate of your company’s future financial performance through financial forecasting. They are typically used by businesses to secure funding, but can also be useful for internal decision-making and planning purposes. There are three main financial statements that you will need to include in your business plan financial projections:
1. Income Statement Projection
The income statement projection is a forecast of your company’s future revenues and expenses. It should include line items for each type of income and expense, as well as a total at the end.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your projection:
- Revenue: Your revenue projection should break down your expected sales by product or service, as well as by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Expenses: Your expense projection should include a breakdown of your expected costs by category, such as marketing, salaries, and rent. Again, it is important to be realistic in your estimates.
- Net Income: The net income projection is the difference between your revenue and expenses. This number tells you how much profit your company is expected to make.
Sample Income Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
2. Cash Flow Statement & Projection
The cash flow statement and projection are a forecast of your company’s future cash inflows and outflows. It is important to include a cash flow projection in your business plan, as it will give investors and lenders an idea of your company’s ability to generate cash.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your cash flow projection:
- The cash flow statement shows a breakdown of your expected cash inflows and outflows by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Cash inflows should include items such as sales revenue, interest income, and capital gains. Cash outflows should include items such as salaries, rent, and marketing expenses.
- It is important to track your company’s cash flow over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy cash flow is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Cash Flow Statements
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
3. Balance Sheet Projection
The balance sheet projection is a forecast of your company’s future financial position. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
A projection should include a breakdown of your company’s assets and liabilities by category. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
It is important to track your company’s financial position over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy balance is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
How to Create Financial Projections
Creating financial projections for your business plan can be a daunting task, but it’s important to put together accurate and realistic financial projections in order to give your business the best chance for success.
Cost Assumptions
When you create financial projections, it is important to be realistic about the costs your business will incur, using historical financial data can help with this. You will need to make assumptions about the cost of goods sold, operational costs, and capital expenditures.
It is important to track your company’s expenses over time to ensure that it is staying within its budget. A healthy bottom line is necessary for a successful business.
Capital Expenditures, Funding, Tax, and Balance Sheet Items
You will also need to make assumptions about capital expenditures, funding, tax, and balance sheet items. These assumptions will help you to create a realistic financial picture of your business.
Capital Expenditures
When projecting your company’s capital expenditures, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type of equipment or property your business will purchase. You will also need to estimate the cost of the purchase.
When projecting your company’s funding needs, you will need to make a number of assumptions about where the money will come from. This might include assumptions about bank loans, venture capital, or angel investors.
When projecting your company’s tax liability, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the tax rates that will apply to your business. You will also need to estimate the amount of taxes your company will owe.
Balance Sheet Items
When projecting your company’s balance, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type and amount of debt your business will have. You will also need to estimate the value of your company’s assets and liabilities.
Financial Projection Scenarios
Write two financial scenarios when creating your financial projections, a best-case scenario, and a worst-case scenario. Use your list of assumptions to come up with realistic numbers for each scenario.
Presuming that you have already generated a list of assumptions, the creation of best and worst-case scenarios should be relatively simple. For each assumption, generate a high and low estimate. For example, if you are assuming that your company will have $100,000 in revenue, your high estimate might be $120,000 and your low estimate might be $80,000.
Once you have generated high and low estimates for all of your assumptions, you can create two scenarios: a best case scenario and a worst-case scenario. Simply plug the high estimates into your financial projections for the best-case scenario and the low estimates into your financial projections for the worst-case scenario.
Conduct a Ratio Analysis
A ratio analysis is a useful tool that can be used to evaluate a company’s financial health. Ratios can be used to compare a company’s performance to its industry average or to its own historical performance.
There are a number of different ratios that can be used in ratio analysis. Some of the more popular ones include the following:
- Gross margin ratio
- Operating margin ratio
- Return on assets (ROA)
- Return on equity (ROE)
To conduct a ratio analysis, you will need financial statements for your company and for its competitors. You will also need industry average ratios. These can be found in industry reports or on financial websites.
Once you have the necessary information, you can calculate the ratios for your company and compare them to the industry averages or to your own historical performance. If your company’s ratios are significantly different from the industry averages, it might be indicative of a problem.
Be Realistic
When creating your financial projections, it is important to be realistic. Your projections should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future financial performance will be. This includes projected operating income, a projected income statement, and a profit and loss statement.
Your goal should be to create a realistic set of financial projections that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Sales Forecast
One of the most important aspects of your financial projections is your sales forecast. Your sales forecast should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future sales will be.
Your sales forecast should be realistic and achievable. Do not try to “game” the system by creating an overly optimistic or pessimistic forecast. Your goal should be to create a realistic sales forecast that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Creating a sales forecast is not an exact science, but there are a number of methods that can be used to generate realistic estimates. Some common methods include market analysis, competitor analysis, and customer surveys.
Create Multi-Year Financial Projections
When creating financial projections, it is important to generate projections for multiple years. This will give you a better sense of how your company’s financial performance is likely to change over time.
It is also important to remember that your financial projections are just that: projections. They are based on a number of assumptions and are not guaranteed to be accurate. As such, you should review and update your projections on a regular basis to ensure that they remain relevant.
Creating financial projections is an important part of any business plan. However, it’s important to remember that these projections are just estimates. They are not guarantees of future success.
Business Plan Financial Projections FAQs
What is a business plan financial projection.
A business plan financial projection is a forecast of your company's future financial performance. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
What are annual income statements?
The Annual income statement is a financial document and a financial model that summarize a company's revenues and expenses over the course of a fiscal year. They provide a snapshot of a company's financial health and performance and can be used to track trends and make comparisons with other businesses.
What are the necessary financial statements?
The necessary financial statements for a business plan are an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
How do I create financial projections?
You can create financial projections by making a list of assumptions, creating two scenarios (best case and worst case), conducting a ratio analysis, and being realistic.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Financial Statement Analysis
- How It Works
Types of Financial Statements
Financial performance.
- Financial Statement Analysis FAQs
- Corporate Finance
- Financial statements: Balance, income, cash flow, and equity
Financial Statement Analysis: How It’s Done, by Statement Type
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Katrina Ávila Munichiello is an experienced editor, writer, fact-checker, and proofreader with more than fourteen years of experience working with print and online publications.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KatrinaAvilaMunichiellophoto-9d116d50f0874b61887d2d214d440889.jpg)
What Is Financial Statement Analysis?
Financial statement analysis is the process of analyzing a company’s financial statements for decision-making purposes. External stakeholders use it to understand the overall health of an organization and to evaluate financial performance and business value. Internal constituents use it as a monitoring tool for managing the finances.
Key Takeaways
- Financial statement analysis is used by internal and external stakeholders to evaluate business performance and value.
- Financial accounting calls for all companies to create a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which form the basis for financial statement analysis.
- Horizontal, vertical, and ratio analysis are three techniques that analysts use when analyzing financial statements.
Jiaqi Zhou / Investopedia
How to Analyze Financial Statements
The financial statements of a company record important financial data on every aspect of a business’s activities. As such, they can be evaluated on the basis of past, current, and projected performance.
In general, financial statements are centered around generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) in the United States. These principles require a company to create and maintain three main financial statements: the balance sheet, the income statement, and the cash flow statement. Public companies have stricter standards for financial statement reporting. Public companies must follow GAAP, which requires accrual accounting. Private companies have greater flexibility in their financial statement preparation and have the option to use either accrual or cash accounting.
Several techniques are commonly used as part of financial statement analysis. Three of the most important techniques are horizontal analysis , vertical analysis , and ratio analysis . Horizontal analysis compares data horizontally, by analyzing values of line items across two or more years. Vertical analysis looks at the vertical effects that line items have on other parts of the business and the business’s proportions. Ratio analysis uses important ratio metrics to calculate statistical relationships.
Companies use the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to manage the operations of their business and to provide transparency to their stakeholders. All three statements are interconnected and create different views of a company’s activities and performance.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a report of a company’s financial worth in terms of book value. It is broken into three parts to include a company’s assets , liabilities , and shareholder equity . Short-term assets such as cash and accounts receivable can tell a lot about a company’s operational efficiency; liabilities include the company’s expense arrangements and the debt capital it is paying off; and shareholder equity includes details on equity capital investments and retained earnings from periodic net income. The balance sheet must balance assets and liabilities to equal shareholder equity. This figure is considered a company’s book value and serves as an important performance metric that increases or decreases with the financial activities of a company.
Income Statement
The income statement breaks down the revenue that a company earns against the expenses involved in its business to provide a bottom line, meaning the net profit or loss. The income statement is broken into three parts that help to analyze business efficiency at three different points. It begins with revenue and the direct costs associated with revenue to identify gross profit . It then moves to operating profit , which subtracts indirect expenses like marketing costs, general costs, and depreciation. Finally, after deducting interest and taxes, the net income is reached.
Basic analysis of the income statement usually involves the calculation of gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, which each divide profit by revenue. Profit margin helps to show where company costs are low or high at different points of the operations.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement provides an overview of the company’s cash flows from operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Net income is carried over to the cash flow statement, where it is included as the top line item for operating activities. Like its title, investing activities include cash flows involved with firm-wide investments. The financing activities section includes cash flow from both debt and equity financing. The bottom line shows how much cash a company has available.
Free Cash Flow and Other Valuation Statements
Companies and analysts also use free cash flow statements and other valuation statements to analyze the value of a company . Free cash flow statements arrive at a net present value by discounting the free cash flow that a company is estimated to generate over time. Private companies may keep a valuation statement as they progress toward potentially going public.
Financial statements are maintained by companies daily and used internally for business management. In general, both internal and external stakeholders use the same corporate finance methodologies for maintaining business activities and evaluating overall financial performance .
When doing comprehensive financial statement analysis, analysts typically use multiple years of data to facilitate horizontal analysis. Each financial statement is also analyzed with vertical analysis to understand how different categories of the statement are influencing results. Finally, ratio analysis can be used to isolate some performance metrics in each statement and bring together data points across statements collectively.
Below is a breakdown of some of the most common ratio metrics:
- Balance sheet : This includes asset turnover, quick ratio, receivables turnover, days to sales, debt to assets, and debt to equity.
- Income statement : This includes gross profit margin, operating profit margin, net profit margin, tax ratio efficiency, and interest coverage.
- Cash flow : This includes cash and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) . These metrics may be shown on a per-share basis.
- Comprehensive : This includes return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE) , along with DuPont analysis .
What are the advantages of financial statement analysis?
The main point of financial statement analysis is to evaluate a company’s performance or value through a company’s balance sheet, income statement, or statement of cash flows. By using a number of techniques, such as horizontal, vertical, or ratio analysis, investors may develop a more nuanced picture of a company’s financial profile.
What are the different types of financial statement analysis?
Most often, analysts will use three main techniques for analyzing a company’s financial statements.
First, horizontal analysis involves comparing historical data. Usually, the purpose of horizontal analysis is to detect growth trends across different time periods.
Second, vertical analysis compares items on a financial statement in relation to each other. For instance, an expense item could be expressed as a percentage of company sales.
Finally, ratio analysis, a central part of fundamental equity analysis, compares line-item data. Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, earnings per share, or dividend yield are examples of ratio analysis.
What is an example of financial statement analysis?
An analyst may first look at a number of ratios on a company’s income statement to determine how efficiently it generates profits and shareholder value. For instance, gross profit margin will show the difference between revenues and the cost of goods sold. If the company has a higher gross profit margin than its competitors, this may indicate a positive sign for the company. At the same time, the analyst may observe that the gross profit margin has been increasing over nine fiscal periods, applying a horizontal analysis to the company’s operating trends.
Congressional Research Service. “ Cash Versus Accrual Basis of Accounting: An Introduction ,” Page 3 (Page 7 of PDF).
Internal Revenue Service. “ Publication 538 (01/2022), Accounting Periods and Methods: Methods You Can Use. ”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TermDefinitions_Incomestatementcopy-ac02efd513b44addb6f05224b38af19c.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Writing a Business Plan—Financial Projections
Spell out your financial forecast in dollars and sense
Creating financial projections for your startup is both an art and a science. Although investors want to see cold, hard numbers, it can be difficult to predict your financial performance three years down the road, especially if you are still raising seed money. Regardless, short- and medium-term financial projections are a required part of your business plan if you want serious attention from investors.
The financial section of your business plan should include a sales forecast , expenses budget , cash flow statement , balance sheet , and a profit and loss statement . Be sure to follow the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) set forth by the Financial Accounting Standards Board , a private-sector organization responsible for setting financial accounting and reporting standards in the U.S. If financial reporting is new territory for you, have an accountant review your projections.
Sales Forecast
As a startup business, you do not have past results to review, which can make forecasting sales difficult. It can be done, though, if you have a good understanding of the market you are entering and industry trends as a whole. In fact, sales forecasts based on a solid understanding of industry and market trends will show potential investors that you've done your homework and your forecast is more than just guesswork.
In practical terms, your forecast should be broken down by monthly sales with entries showing which units are being sold, their price points, and how many you expect to sell. When getting into the second year of your business plan and beyond, it's acceptable to reduce the forecast to quarterly sales. In fact, that's the case for most items in your business plan.
Expenses Budget
What you're selling has to cost something, and this budget is where you need to show your expenses. These include the cost to your business of the units being sold in addition to overhead. It's a good idea to break down your expenses by fixed costs and variable costs. For example, certain expenses will be the same or close to the same every month, including rent, insurance, and others. Some costs likely will vary month by month such as advertising or seasonal sales help.
Cash Flow Statement
As with your sales forecast, cash flow statements for a startup require doing some homework since you do not have historical data to use as a reference. This statement, in short, breaks down how much cash is coming into your business on a monthly basis vs. how much is going out. By using your sales forecasts and your expenses budget, you can estimate your cash flow intelligently.
Keep in mind that revenue often will trail sales, depending on the type of business you are operating. For example, if you have contracts with clients, they may not be paying for items they purchase until the month following delivery. Some clients may carry balances 60 or 90 days beyond delivery. You need to account for this lag when calculating exactly when you expect to see your revenue.
Profit and Loss Statement
Your P&L statement should take the information from your sales projections, expenses budget, and cash flow statement to project how much you expect in profits or losses through the three years included in your business plan. You should have a figure for each individual year as well as a figure for the full three-year period.
Balance Sheet
You provide a breakdown of all of your assets and liabilities in the balances sheet. Many of these assets and liabilities are items that go beyond monthly sales and expenses. For example, any property, equipment, or unsold inventory you own is an asset with a value that can be assigned to it. The same goes for outstanding invoices owed to you that have not been paid. Even though you don't have the cash in hand, you can count those invoices as assets. The amount you owe on a business loan or the amount you owe others on invoices you've not paid would count as liabilities. The balance is the difference between the value of everything you own vs. the value of everything you owe.
Break-Even Projection
If you've done a good job projecting your sales and expenses and inputting the numbers into a spreadsheet, you should be able to identify a date when your business breaks even—in other words, the date when you become profitable, with more money coming in than going out. As a startup business, this is not expected to happen overnight, but potential investors want to see that you have a date in mind and that you can support that projection with the numbers you've supplied in the financial section of your business plan.
Additional Tips
When putting together your financial projections, keep some general tips in mind:
- Get comfortable with spreadsheet software if you aren't already. It is the starting point for all financial projections and offers flexibility, allowing you to quickly change assumptions or weigh alternative scenarios. Microsoft Excel is the most common, and chances are you already have it on your computer. You can also buy special software packages to help with financial projections.
- Prepare a five-year projection . Don’t include this one in the business plan, since the further into the future you project, the harder it is to predict. However, have the projection available in case an investor asks for it.
- Offer two scenarios only . Investors will want to see a best-case and worst-case scenario, but don’t inundate your business plan with myriad medium-case scenarios. They likely will just cause confusion.
- Be reasonable and clear . As mentioned before, financial forecasting is as much art as science. You’ll have to assume certain things, such as your revenue growth, how your raw material and administrative costs will grow, and how effective you’ll be at collecting on accounts receivable. It’s best to be realistic in your projections as you try to recruit investors. If your industry is going through a contraction period and you’re projecting revenue growth of 20 percent a month, expect investors to see red flags.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, business plan financials: 3 statements to include.
The finance section of your business plan is essential to securing investors and determining whether your idea is even viable. Here's what to include.

If your business plan is the blueprint of how to run your company, the financials section is the key to making it happen. The finance section of your business plan is essential to determining whether your idea is even viable in the long term. It’s also necessary to convince investors of this viability and subsequently secure the type and amount of funding you need. Here’s what to include in your business plan financials.
[Read: How to Write a One-Page Business Plan ]
What are business plan financials?
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you’ll need to plan for your business’s future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any funding requests in this part of your business plan.
Business plan financials are vital because they allow you to budget for existing or future expenses, as well as forecast your business’s future finances. A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Sections to include in your business plan financials
Here are the three statements to include in the finance section of your business plan:
Profit and loss statement
A profit and loss statement , also known as an income statement, identifies your business’s revenue (profit) and expenses (loss). This document describes your company’s overall financial health in a given time period. While profit and loss statements are typically prepared quarterly, you will need to do so at least annually before filing your business tax return with the IRS.
Common items to include on a profit and loss statement :
- Revenue: total sales and refunds, including any money gained from selling property or equipment.
- Expenditures: total expenses.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): the cost of making products, including materials and time.
- Gross margin: revenue minus COGS.
- Operational expenditures (OPEX): the cost of running your business, including paying employees, rent, equipment and travel expenses.
- Depreciation: any loss of value over time, such as with equipment.
- Earnings before tax (EBT): revenue minus COGS, OPEX, interest, loan payments and depreciation.
- Profit: revenue minus all of your expenses.
Businesses that have not yet started should provide projected income statements in their financials section. Currently operational businesses should include past and present income statements, in addition to any future projections.
[Read: Top Small Business Planning Strategies ]
A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your company’s finances, allowing you to keep track of earnings and expenses. It includes what your business owns (assets) versus what it owes (liabilities), as well as how much your business is currently worth (equity).
On the assets side of your balance sheet, you will have three subsections: current assets, fixed assets and other assets. Current assets include cash or its equivalent value, while fixed assets refer to long-term investments like equipment or buildings. Any assets that do not fall within these categories, such as patents and copyrights, can be classified as other assets.
On the liabilities side of your balance sheet, include a total of what your business owes. These can be broken down into two parts: current liabilities (amounts to be paid within a year) and long-term liabilities (amounts due for longer than a year, including mortgages and employee benefits).
Once you’ve calculated your assets and liabilities, you can determine your business’s net worth, also known as equity. This can be calculated by subtracting what you owe from what you own, or assets minus liabilities.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement shows the exact amount of money coming into your business (inflow) and going out of it (outflow). Each cost incurred or amount earned should be documented on its own line, and categorized into one of the following three categories: operating activities, investment activities and financing activities. These three categories can all have inflow and outflow activities.
Operating activities involve any ongoing expenses necessary for day-to-day operations; these are likely to make up the majority of your cash flow statement. Investment activities, on the other hand, cover any long-term payments that are needed to start and run your business. Finally, financing activities include the money you’ve used to fund your business venture, including transactions with creditors or funders.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
Join us on October 8, 2024! Tune in at 12:30 p.m. ET for expert tips from top business leaders and Olympic gold medalist Dominique Dawes. Plus, access our exclusive evening program, where we’ll announce the CO—100 Top Business! - Register Now!
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us October 8, 2024
Unlock today’s biggest trends with expert tips and inspiring stories from Olympic gold medalist Dominique Dawes! Don’t miss our exclusive evening program and CO—100 Top Business announcement!

RSVP Now for the CO—100 Small Business Forum!
Discover today’s biggest AI and social media marketing trends with top business experts! Get inspired by Dominique Dawes’ entrepreneurial journey and enjoy free access to our exclusive evening program, featuring the CO—100 Top Business reveal. Register now!
More tips for your startup
How to choose a legal entity for your startup, how to choose the right business entity: sole proprietorship, 5 steps to use social media to launch your business.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.

Working together, we can reimagine medicine to improve and extend people’s lives.
Financial Planning & Analysis lead
About the role.
Major accountabilities:
Key contributor to the Leadership Therapeutic Areas (“TA”) assigned
- Critical member of the TA Management Team – helps to formulate strategies, guides investment, and implement actions that help to gain market share and increase profitability.
- Setting the tone for good financial practices within the BU
- Maintenance of the TA’s relationship with the local CPO finance team and specifically with the CCFO
2. Leader of Financial Planning
- Lead the Budget, Latest Estimation and Latest Outlook processes and discussions; integrate and coordinate financial processes with the Marketing planning processes at the local level
- Well thought-out and high-quality plans with transparency of assumptions and analyses of risks and opportunities
- Coordinated with all members of the TA management team (e.g., marketing, sales, medical)
- Also coordinated with the CPO (e.g., allocations, or on universal assumptions such as inflation rates)
- Challenging all contributors (including TA Head) to the budget/LE on the underlying assumptions to Budget/LE; pushing back on the team when appropriate
- Attention to forecasting accuracy for both sales and expenses (monthly)
- Participation in the long-term planning of the business through the Strategic Planning process
- Assisting in preparation of Budget/LE presentations for Regional Team
- Work closely with the local Marketing, Sales, Medical and Market Access teams sharing responsibility of formulating business strategies, guide investment and resource allocation, monitoring commitment, implement actions, shared approval responsibility.
3. Analysis/Reporting of Financial Performance
- Full ownership of and responsibility for all aspects of the IMI BU P&L.
- Analysis of Sales and Market Share (including trending of data) to provide IMI management with insights into the business, early detection of risks/opportunities vs. plan, etc.
- Analysis and understanding of the commercial aspects of the business, e.g., discounts per channel, per customer and per brand. Benchmark selected key indicators with other Novartis businesses and/or other international companies
- Analysis and control of operational expenses, incl. analysis of variations to the authorized budgets / LEs.
- Managing the headcount analysis and control
- Review and follow-up as needed on: aging of receivables (DSOs), surpluses or deficits of product inventories (stock-in-trade), IMI’s impact on overall CPO working capital and/or country asset limits, and payables to vendors
- Evaluation of the BU’s Risks and Opportunities, including a latest outlook for the month/quarter/year; also identification and implementation of gap closing actions.
- Communication of unexpected events affecting performance, or impacting key assumptions, in a transparent and timely manner.
- Preparation of regular, comprehensive performance reports (including Business Review documents and monthly Executive Summary Reports) to the Regional Office on timely basis
4. Analysis of Business Proposals/investments.
- Financial evaluation of business proposals or projects for the assigned TAs. (e.g., Field Force expansion, launching of a new product or indication).
- Financial evaluation of Marketing investments and allocation of funds among potential projects to maximize return for the assigned TAs. Use of appropriate analytical tools as necessary.
- Ad hoc analyses as may be necessary.
5. Strategic Planning
Prepare for IMI portfolio by managing the sensitivity of the external relationships including government and distributors where the market has a number of healthcare, and funding systems and the pricing for these new models will have a significant positive/negative implication on the Gulf (GCC) countries.
6. Management Cash Flow
- Lead the Budget, Latest Estimation and Latest Outlook processes and discussions
- Achieving the MCF%
- Explain MCF variances, opportunities, and challenges through budget and financial forecasts for use in Global and Regional.
- Application of general Balance Sheet and Cash Flow knowledge in support of the business
- Identify and utilize best practices in FP&A and disseminate them within the Organization.
- Ensure the IMI is compliant with internal control standards, reporting requirements, accounting guidance, and be observant for any potential CoC issues
- Assist with audits where required, and where follow-up is needed ensure compliance with / implementation of the agreed-to action plans.
- Assist with development / implementation of planning and analysis tools and/or systems
- Perform assigned NFCM controls with high quality and on a timely manner
- Ensure Saudi talent development and succession planning to meet the Saudization milestones; coach, guide and mentor FP&A associate within the country, including upscaling capabilities.
- Lead successful and efficient interaction with Distributors and Customers.
- Collaborate with Internal Audit and FCCR team to ensure consistent financial data reporting processes and results.
- Lead the Monthly Local and Regional Business Review.
- In the absent of the FRA team in the country, FP&A Lead plays major roll to ensure all the monthly reporting are meeting local expectations.
- Support FRA team in the monthly cross charge for Novartis AG (NCC changes).
- Support the FRA team in the monthly closing.
- Accompaniment throughout the institutional tender process. Ensures quick turnaround of ad-hoc analysis, providing accurate information / analysis required for timely decision-making.
- Proactively carry out value added analyses on financial data, supporting and testing information provided by Global, Regional and Local financial officers. Assist with the development of detailed budget and financial forecasts for use in Global and Regional, as well as Country, Business Franchise, and Business Unit planning.
- Proactively interface with financial officers in other Country organizations to obtain financial best practices and in market data results, benchmarking country results and methods against ones from other markets.
- Drive continuous learning within the Country by performing post implementation financial analyses on past initiatives and sharing results across the organization Ensure consistency and interoperability between different financial reporting systems.
- Support CCFO to coordinate with cooperate tax department to resolve all tax related issues and assist to resolve all financial queries and statement analysis.
- Providing leadership, direction and management of the finance and accounting team
- Providing strategic recommendations to the CPO leadership members
- Establishing and developing relations with senior management and external partners and stakeholders.
Ideal Background
- Degree educated in Business Administration, Financial management, Accountant, Industrial Engineer or Life Sciences. Desirable degrees: MBA, Chartered/Certified Accountant.
- Fluency in English is prerequisite, while knowledge of Arabic and would be an advantage.
- Significant (7-10 years) experience in budgeting and/or controlling positions or within pharmaceuticals industry.
- Experience designing and operating financial reporting and forecasting systems
- Excellent analytical ability.
- Strong written and oral communication skills, and ability to clearly present financial data in reports distributed to Regional and Global officers.
Why Novartis: Helping people with disease and their families takes more than innovative science. It takes a community of smart, passionate people like you. Collaborating, supporting and inspiring each other. Combining to achieve breakthroughs that change patients’ lives. Ready to create a brighter future together? https://www.novartis.com/about/strategy/people-and-culture
Join our Novartis Network: Not the right Novartis role for you? Sign up to our talent community to stay connected and learn about suitable career opportunities as soon as they come up: https://talentnetwork.novartis.com/network
Benefits and Rewards: Read our handbook to learn about all the ways we’ll help you thrive personally and professionally: https://www.novartis.com/careers/benefits-rewards
Novartis is committed to building an outstanding, inclusive work environment and diverse teams' representative of the patients and communities we serve.

- Enterprise Solutions
- Talent Solutions
- Case Studies
- State of Independence
- Guides & Research
- Meet Our Team
Press enter to see results
5 Steps to Kickstart Your 2025 Business Planning

- Strategic planning for the year ahead is important for self-employed professionals.
- Planning ahead can help you navigate challenges and position your business for optimal growth.
- Create a roadmap for success in the coming year with these five steps.
Proactive planning is the cornerstone of any successful business, especially in today’s rapidly changing market. For self-employed professionals, taking the time to strategically plan for the year ahead is not just advisable—it’s essential. Early planning can be the difference between surviving and thriving in 2025. With a well-thought-out plan, you can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and position your independent business for sustained growth.
Below, we explore five steps to kickstart your 2025 business planning. From assessing your current performance to developing a strategic growth plan, these steps will help you create a roadmap for success in the coming year
Step 1: Assess Your Current Business Performance
Before planning for 2025, start by evaluating how your business performed in 2024. This assessment will give you a clear understanding of where you stand and what areas need improvement. Two helpful ways to do this are to conduct a review of your highs and lows from the previous year and perform a SWOT analysis. Here’s how:
Review 2024 achievements and shortfalls: Start by analyzing what worked well and what didn’t. Look at key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue growth, client retention, and profitability. Did you meet your financial targets? How satisfied are your clients? Identifying your achievements and shortfalls will provide valuable insights into areas where you can build on your successes or make necessary adjustments.
Conduct a SWOT analysis: Next, perform a SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. A SWOT analysis can be a helpful way to understand where your business is positioned and how to plan for the year ahead. For example, if you’ve identified a new market opportunity, your 2025 plan can focus on capturing that market. Conversely, recognizing a potential threat, such as an emerging competitor, will allow you to strategize accordingly.
Positioning Your Small Business for the Future of Work
Step 2: Define Clear Financial Goals for 2025
Financial goals are the foundation of your business plan. Without clear objectives, it’s challenging to measure success or allocate resources effectively. To define financial goals for the coming year, set revenue and profit targets, and budget for growth.
Establish realistic revenue goals based on past performance and current market trends. Consider factors like seasonal fluctuations, economic conditions, and industry developments. In addition to revenue targets, set specific profit margins and cash flow objectives to ensure your business remains profitable and financially stable.
Remember, growth requires investment, so it’s essential to create a budget that supports your expansion plans. Allocate funds for costs such as marketing and technology upgrades, but also plan for both fixed and variable costs. Remember to account for contingencies—unexpected expenses can derail even the best-laid plans if not anticipated.
Gross Margin vs Net Margin: Definitions and How to Calculate
Step 3: Conduct Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Understanding the market landscape for your area of expertise is vital for staying ahead of the curve in 2025. Conducting thorough research and analysis will help you make informed decisions and capitalize on new opportunities. Stay informed about emerging trends in your industry that could impact your business in 2025. Use tools like industry reports, market research surveys, and customer feedback to gather insights. Keeping up with trends will allow you to anticipate changes and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Another helpful step is to assess your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. What are they doing well, and where are they falling short? Understanding your competitive position is crucial for identifying opportunities to differentiate your business. Whether it’s through superior customer service, innovative products, or more efficient operations, knowing where you stand will help you carve out a stronger market presence.
8 Tips to Make Your Small Business Stand Out
Step 4: Develop a Strategic Growth Plan
With your financial goals set and market analysis complete, it’s time to develop a strategic growth plan that outlines how you’ll achieve your objectives in 2025. Consider various growth strategies, such as expanding product lines, entering new markets, or enhancing customer experience. Each strategy should align with your overall business goals and address the opportunities and threats identified in your SWOT analysis. Set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals for each strategy to ensure they are clear and actionable.
Next, create an actionable roadmap. Break down each growth strategy into actionable steps. Use project management tools to assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and track progress. An actionable roadmap not only provides a clear path to follow but also helps keep your team aligned and focused on achieving the set goals.
Setting SMART Business Goals for the Upcoming Year
Step 5: Plan for Flexibility and Risk Management
In today’s dynamic business environment, flexibility is key. While a solid plan is essential, it’s equally important to prepare for the unexpected. Plan for potential challenges like economic shifts, supply chain disruptions, or changes in client behavior. Identify critical aspects of your business that could be affected and create backup plans for each. For example, if your primary supplier faces a disruption, having an alternative supplier lined up can prevent delays.
Maintain flexibility in your business plan to quickly adapt to new opportunities or challenges. This might mean revisiting your strategy quarterly and making necessary adjustments based on the latest data and market conditions. Regular reviews will ensure your plan remains relevant and responsive to any changes throughout 2025.
How to Write a Business Plan for Small Business: 8 Steps
By following these five essential steps—assessing your current performance, defining clear financial goals, conducting market research, developing a strategic growth plan, and planning for flexibility—you can set your business up for success in 2025. Strategic planning is not just about setting goals; it’s about creating a roadmap that guides your business through the year’s opportunities and challenges.
Subscribe to the Insights blog to get weekly insights on the next way of working
Join our marketplace to search for consulting projects with top companies, related posts.

Learn more about MBO
Are you independent talent.
Learn how to start, run and grow your business with expert insights from MBO Partners
Are you an enterprise?
Learn how to find, manage and retain top-tier independent talent for your independent workforce.
Data driven reports
MBO Partners publishes influential reports, cited by government and other major media outlets.
Informed insights
Research and tools designed to uncover insights and develop groundbreaking solutions.
Search MBO Partners by typing keyword...
🪫 Your Subscription Ends Soon!
Time flies with great content! Renew in to keep enjoying all our premium content.
.cls-1{fill:#ffc742;}.cls-2,.cls-8{fill:#ffffff;}.cls-3{fill:#4a4a4a;}.cls-4{fill:#f7ead0;}.cls-4,.cls-9{opacity:0.5;}.cls-5{fill:#908152;}.cls-6{fill:#efa536;}.cls-7,.cls-8{opacity:0.7;}.cls-10,.cls-9{fill:#d9f0ff;} 70% Off the Quarterly Plan!
Take advantage of this incredible offer before it expires.
Why inheritance is more than silver and gold left in your name

Inheritance does not always have to be in material assets.

By Rufus Mwanyasi
Managing Director
Canaan Capital Limited
“A good man leaves an inheritance to his children’s children.” It’s always amazing how varied people react to this text. Some would much rather have their parents enjoy their retirement after their hard work.
Others who’d rather inherit their work ethic while some are convinced that a better inheritance is a good name, you know, a good name that opens doors.
Yet, they’re still others that believe education is the best form of inheritance (think common sense, good manners and a love for the downtrodden).

LUESBY: Adopt solid inheritance, succession plans

How should I prepare my child for inheritance?
These ones ask, “what good does great material possessions do if the heirs are uncultured and wasteful”?
Then, of course, there is the majority that regard inheritance as identical to money and are eagerly expecting a portion of it.
Unfortunately, out of this group, a huge category belongs to those unaware of what is left.
Here’s some context. To date, the unclaimed financial assets authority (UFAA) has received unclaimed financial assets in cash worth Sh31.8 billion. Out of this pool, only Sh2.1 billion has been paid out so far.
Non-cash assets include some 1.7 billion units of shares and 3,608 safe deposit boxes. Sometime last year, the authority issued a “no objection” notice for received claims complete with a list of the deceased. Interestingly, 71 percent of the deceased were male (64 percent in the previous year).
Limited data notwithstanding, we can still deduce that a lot of these assets seem to come from our male seniors who were not very open about where they invested and/or saved their money.
Why? There are as many reasons as stars in the sky. But a common and mostly unknown reason men do not tell their wives about money is to hide failed investments. This insecurity is often hidden behind a wall of silence. Another is to simply retain control.
In many marriages, power struggles are often centred on money. If the husband is the sole earner, he retains control over how the money is spent and saved, leaving the wife completely dependent on him. But we’ll not dwell here.
I can only speak of real consequences; hungry widows, children dropping out of school, creditors descending on family property, lifestyles upended, broken relationships, and so on.
Dealing with family dynamics after loss is enough of a burden on its own. Adding money shortages to this volatile situation makes the whole situation worse.
Two things we can take from this; to those alive; it’s our responsibility to update our addresses with banks and/or stockbrokers after any changes.
To those bereaved, it’s the responsibility of the next of kin to tell the administrator to go to the unclaimed asset authority to see what is there.
Note that claiming unclaimed property is a do-it-yourself job. More importantly, no one loses any unclaimed financial assets once remitted to the authority.
Indeed, it’s their job to hold assets in the public interest and guarantee everyone their right of reunification.
Finally, inheritance isn’t limited to money. Wisdom is more profitable than silver. Thankfully, one doesn’t have to file a claim to inherit it.
Mr Mwanyasi is MD, Canaan Capital Limited
Don't have an account? Register
PAYE Tax Calculator
Get it first.

Baku COP29 forum will navigate a contentious energy transition path

PRIME Centum to sell additional 19pc stake in Sidian Bank

PRIME M-Pesa Foundation loses bid to block Sh6.5m tax claim on workers’ pay
In the headlines.

PRIME Taxpayers face bank account, PIN freezes for unpaid Sh10.58bn

PRIME Setback for Ruto as budget cuts hit dream industrial parks plan

China offers Africa $51bn, promises one million jobs
The University of Chicago The Law School
Innovation clinic—significant achievements for 2023-24.
The Innovation Clinic continued its track record of success during the 2023-2024 school year, facing unprecedented demand for our pro bono services as our reputation for providing high caliber transactional and regulatory representation spread. The overwhelming number of assistance requests we received from the University of Chicago, City of Chicago, and even national startup and venture capital communities enabled our students to cherry-pick the most interesting, pedagogically valuable assignments offered to them. Our focus on serving startups, rather than all small- to medium-sized businesses, and our specialization in the needs and considerations that these companies have, which differ substantially from the needs of more traditional small businesses, has proven to be a strong differentiator for the program both in terms of business development and prospective and current student interest, as has our further focus on tackling idiosyncratic, complex regulatory challenges for first-of-their kind startups. We are also beginning to enjoy more long-term relationships with clients who repeatedly engage us for multiple projects over the course of a year or more as their legal needs develop.
This year’s twelve students completed over twenty projects and represented clients in a very broad range of industries: mental health and wellbeing, content creation, medical education, biotech and drug discovery, chemistry, food and beverage, art, personal finance, renewable energy, fintech, consumer products and services, artificial intelligence (“AI”), and others. The matters that the students handled gave them an unparalleled view into the emerging companies and venture capital space, at a level of complexity and agency that most junior lawyers will not experience until several years into their careers.
Representative Engagements
While the Innovation Clinic’s engagements are highly confidential and cannot be described in detail, a high-level description of a representative sample of projects undertaken by the Innovation Clinic this year includes:
Transactional/Commercial Work
- A previous client developing a symptom-tracking wellness app for chronic disease sufferers engaged the Innovation Clinic again, this time to restructure its cap table by moving one founder’s interest in the company to a foreign holding company and subjecting the holding company to appropriate protections in favor of the startup.
- Another client with whom the Innovation Clinic had already worked several times engaged us for several new projects, including (1) restructuring their cap table and issuing equity to an additional, new founder, (2) drafting several different forms of license agreements that the company could use when generating content for the platform, covering situations in which the company would license existing content from other providers, jointly develop new content together with contractors or specialists that would then be jointly owned by all creators, or commission contractors to make content solely owned by the company, (3) drafting simple agreements for future equity (“Safes”) for the company to use in its seed stage fundraising round, and (4) drafting terms of service and a privacy policy for the platform.
- Yet another repeat client, an internet platform that supports independent artists by creating short films featuring the artists to promote their work and facilitates sales of the artists’ art through its platform, retained us this year to draft a form of independent contractor agreement that could be used when the company hires artists to be featured in content that the company’s Fortune 500 brand partners commission from the company, and to create capsule art collections that could be sold by these Fortune 500 brand partners in conjunction with the content promotion.
- We worked with a platform using AI to accelerate the Investigational New Drug (IND) approval and application process to draft a form of license agreement for use with its customers and an NDA for prospective investors.
- A novel personal finance platform for young, high-earning individuals engaged the Innovation Clinic to form an entity for the platform, including helping the founders to negotiate a deal among them with respect to roles and equity, terms that the equity would be subject to, and other post-incorporation matters, as well as to draft terms of service and a privacy policy for the platform.
- Students also formed an entity for a biotech therapeutics company founded by University of Chicago faculty members and an AI-powered legal billing management platform founded by University of Chicago students.
- A founder the Innovation Clinic had represented in connection with one venture engaged us on behalf of his other venture team to draft an equity incentive plan for the company as well as other required implementing documentation. His venture with which we previously worked also engaged us this year to draft Safes to be used with over twenty investors in a seed financing round.
More information regarding other types of transactional projects that we typically take on can be found here .
Regulatory Research and Advice
- A team of Innovation Clinic students invested a substantial portion of our regulatory time this year performing highly detailed and complicated research into public utilities laws of several states to advise a groundbreaking renewable energy technology company as to how its product might be regulated in these states and its clearest path to market. This project involved a review of not only the relevant state statutes but also an analysis of the interplay between state and federal statutes as it relates to public utilities law, the administrative codes of the relevant state executive branch agencies, and binding and non-binding administrative orders, decisions and guidance from such agencies in other contexts that could shed light on how such states would regulate this never-before-seen product that their laws clearly never contemplated could exist. The highly varied approach to utilities regulation in all states examined led to a nuanced set of analysis and recommendations for the client.
- In another significant research project, a separate team of Innovation Clinic students undertook a comprehensive review of all settlement orders and court decisions related to actions brought by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau for violations of the prohibition on unfair, deceptive, or abusive acts and practices under the Consumer Financial Protection Act, as well as selected relevant settlement orders, court decisions, and other formal and informal guidance documents related to actions brought by the Federal Trade Commission for violations of the prohibition on unfair or deceptive acts or practices under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, to assemble a playbook for a fintech company regarding compliance. This playbook, which distilled very complicated, voluminous legal decisions and concepts into a series of bullet points with clear, easy-to-follow rules and best practices, designed to be distributed to non-lawyers in many different facets of this business, covered all aspects of operations that could subject a company like this one to liability under the laws examined, including with respect to asset purchase transactions, marketing and consumer onboarding, usage of certain terms of art in advertising, disclosure requirements, fee structures, communications with customers, legal documentation requirements, customer service and support, debt collection practices, arrangements with third parties who act on the company’s behalf, and more.
Miscellaneous
- Last year’s students built upon the Innovation Clinic’s progress in shaping the rules promulgated by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (“FinCEN”) pursuant to the Corporate Transparency Act to create a client alert summarizing the final rule, its impact on startups, and what startups need to know in order to comply. When FinCEN issued additional guidance with respect to that final rule and changed portions of the final rule including timelines for compliance, this year’s students updated the alert, then distributed it to current and former clients to notify them of the need to comply. The final bulletin is available here .
- In furtherance of that work, additional Innovation Clinic students this year analyzed the impact of the final rule not just on the Innovation Clinic’s clients but also its impact on the Innovation Clinic, and how the Innovation Clinic should change its practices to ensure compliance and minimize risk to the Innovation Clinic. This also involved putting together a comprehensive filing guide for companies that are ready to file their certificates of incorporation to show them procedurally how to do so and explain the choices they must make during the filing process, so that the Innovation Clinic would not be involved in directing or controlling the filings and thus would not be considered a “company applicant” on any client’s Corporate Transparency Act filings with FinCEN.
- The Innovation Clinic also began producing thought leadership pieces regarding AI, leveraging our distinct and uniquely University of Chicago expertise in structuring early-stage companies and analyzing complex regulatory issues with a law and economics lens to add our voice to those speaking on this important topic. One student wrote about whether non-profits are really the most desirable form of entity for mitigating risks associated with AI development, and another team of students prepared an analysis of the EU’s AI Act, comparing it to the Executive Order on AI from President Biden, and recommended a path forward for an AI regulatory environment in the United States. Both pieces can be found here , with more to come!
Innovation Trek
Thanks to another generous gift from Douglas Clark, ’89, and managing partner of Wilson, Sonsini, Goodrich & Rosati, we were able to operationalize the second Innovation Trek over Spring Break 2024. The Innovation Trek provides University of Chicago Law School students with a rare opportunity to explore the innovation and venture capital ecosystem in its epicenter, Silicon Valley. The program enables participating students to learn from business and legal experts in a variety of different industries and roles within the ecosystem to see how the law and economics principles that students learn about in the classroom play out in the real world, and facilitates meaningful connections between alumni, students, and other speakers who are leaders in their fields. This year, we took twenty-three students (as opposed to twelve during the first Trek) and expanded the offering to include not just Innovation Clinic students but also interested students from our JD/MBA Program and Doctoroff Business Leadership Program. We also enjoyed four jam-packed days in Silicon Valley, expanding the trip from the two and a half days that we spent in the Bay Area during our 2022 Trek.
The substantive sessions of the Trek were varied and impactful, and enabled in no small part thanks to substantial contributions from numerous alumni of the Law School. Students were fortunate to visit Coinbase’s Mountain View headquarters to learn from legal leaders at the company on all things Coinbase, crypto, and in-house, Plug & Play Tech Center’s Sunnyvale location to learn more about its investment thesis and accelerator programming, and Google’s Moonshot Factory, X, where we heard from lawyers at a number of different Alphabet companies about their lives as in-house counsel and the varied roles that in-house lawyers can have. We were also hosted by Wilson, Sonsini, Goodrich & Rosati and Fenwick & West LLP where we held sessions featuring lawyers from those firms, alumni from within and outside of those firms, and non-lawyer industry experts on topics such as artificial intelligence, climate tech and renewables, intellectual property, biotech, investing in Silicon Valley, and growth stage companies, and general advice on career trajectories and strategies. We further held a young alumni roundtable, where our students got to speak with alumni who graduated in the past five years for intimate, candid discussions about life as junior associates. In total, our students heard from more than forty speakers, including over twenty University of Chicago alumni from various divisions.
The Trek didn’t stop with education, though. Throughout the week students also had the opportunity to network with speakers to learn more from them outside the confines of panel presentations and to grow their networks. We had a networking dinner with Kirkland & Ellis, a closing dinner with all Trek participants, and for the first time hosted an event for admitted students, Trek participants, and alumni to come together to share experiences and recruit the next generation of Law School students. Several speakers and students stayed in touch following the Trek, and this resulted not just in meaningful relationships but also in employment for some students who attended.
More information on the purposes of the Trek is available here , the full itinerary is available here , and one student participant’s story describing her reflections on and descriptions of her experience on the Trek is available here .
The Innovation Clinic is grateful to all of its clients for continuing to provide its students with challenging, high-quality legal work, and to the many alumni who engage with us for providing an irreplaceable client pipeline and for sharing their time and energy with our students. Our clients are breaking the mold and bringing innovations to market that will improve the lives of people around the world in numerous ways. We are glad to aid in their success in any way that we can. We look forward to another productive year in 2024-2025!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn what to include in the financial analysis section of your business plan, such as balance sheet, cash flow, profit and loss, break-even, and personnel expenses. Get tips on how to use visuals, check your math, and get help from a financial professional.
Learn the key components of a financial plan for your startup, such as income statement, cash flow, balance sheet, and break-even analysis. Get tips, examples, and a free template to create a financial section of your business plan.
Download and customize free Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF templates for your business plan financial statements, projections, and ratios. Learn how to use income, cash flow, balance sheet, and sales forecast templates to analyze and project your financial health.
Financial ratios and metrics. With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios. While including these metrics in your financial plan for a business plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall ...
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
Here are the five steps you'll want to take when conducting a strategic analysis of your financial statements. 1. Compare your forecast to your actuals monthly. So, if you're reviewing your business financials regularly, you're off to a good start. But to get even more value out of that financial review, you need to start comparing your ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders ...
A financial plan is an integral part of an overall business plan, ensuring financial objectives align with overall business goals. It typically contains a description of the business, financial statements, personnel plan, risk analysis and relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) and ratios.
Maintaining a Healthy Balance Sheet Over Time. Step 4: Forecasting Cash Flow. Why Cash Flow is Your Business's Weather Forecast. Step-by-Step Method for Creating a Cash Flow Forecast. My Great Cash Flow Mishap. Step 5: Bringing It All Together for Financial Analysis. How to Use Your Financials to Calculate Key Ratios.
Operating Budget: A detailed breakdown of income and expenses; provides a guide for how the company will operate from a "dollars" point of view. Break-Even Analysis: A projection of the revenue ...
Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis. Forecast expenses. Forecast sales. Build financial projections. The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company: 1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections.
How to do a financial analysis. 1. Collect your company's financial statements. Financial analysis helps you identify trends in your business's performance. To get the best insights, compare your business performance over time. Gather your recent financial statements, including your balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
The financials section of your business plan tells you and your potential investors, loan providers or partners whether your business idea makes economic sense. Without an impressive financials ...
A Federal Reserve study noted 78% and 92% of companies with above-average and excellent financial health, respectively, had annual income of at least $1 million. Forty percent of businesses with poor financial health, on the other hand, had revenue of less than $100,000. Additionally, the study found 90% of organizations with excellent ...
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth. Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ...
For small business owners, financial analysis can also help you weigh the impact that financial decisions might have on your company. For example, if you are considering borrowing money to launch a new product, your financial analysis can show how much you need, your historical success with similar products, and what you can expect from the launch.
Financial analysis is used to evaluate economic trends, set financial policy, build long-term plans for business activity, and identify projects or companies for investment. This is done through ...
Financial projections are forecasted analyses of your business' future that include income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements. We have found them to be an crucial part of your business plan for the following reasons: They can help prove or disprove the viability of your business idea. For example, if your initial projections ...
Financial statement analysis is used by internal and external stakeholders to evaluate business performance and value. Financial accounting calls for all companies to create a balance sheet ...
The financial section of your business plan should include a sales forecast, expenses budget, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and a profit and loss statement. Be sure to follow the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) set forth by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, a private-sector organization responsible for setting ...
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you'll need to plan for your business's future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any ...
For small businesses, financial models can answer some basic questions to ensure the revenue model is sound. The three-statement financial model helps a small business budget and track actual spend against that budget. This makes it easier to see potential slowdowns in cash flow and to know if and when to cut costs.
Analysis/Reporting of Financial Performance Full ownership of and responsibility for all aspects of the IMI BU P&L.Analysis of Sales and Market Share (including trending of data) to provide IMI management with insights into the business, early detection of risks/opportunities vs. plan, etc.Analysis and understanding of the commercial aspects of ...
Step 4: Develop a Strategic Growth Plan. With your financial goals set and market analysis complete, it's time to develop a strategic growth plan that outlines how you'll achieve your objectives in 2025. Consider various growth strategies, such as expanding product lines, entering new markets, or enhancing customer experience.
70% Off the Quarterly Plan! ... To date, the unclaimed financial assets authority (UFAA) has received unclaimed financial assets in cash worth Sh31.8 billion. ... PRIME Chinese firm's Sh1m deal ...
The 2024 Trump presidential campaign has endorsed several tax-related policy proposals. The Trump campaign supports extending the expiring provisions of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) and recommends additional reductions in the corporate tax rate to 15 percent.In addition, the Trump campaign favors eliminating income taxes on Social Security benefits.
General The Innovation Clinic continued its track record of success during the 2023-2024 school year, facing unprecedented demand for our pro bono services as our reputation for providing high caliber transactional and regulatory representation spread. The overwhelming number of assistance requests we received from the University of Chicago, City of Chicago, and even national startup and ...