Reported speech – Present Progressive – Sentences – Exercise
Task no. 2337.
Finish the sentences using Reported speech. Always change the tense, although it is sometimes not necessary.
Joe, "I'm drawing a picture." Joe said (that)
Joe said (that) he was drawing a picture .

Do you need help?
Reported speech
- Jenny, "I'm coming down." Jenny said (that) .
- Tim, "Jack is having breakfast." Tim said (that) .
- Jamy, "She's telling a joke." Jamy told me (that) .
- Mavis, "The dog is running after the cat." Mavis remarked (that) .
- Peter, "I'm playing the piano." Peter said (that) .
- Zack, "You're drinking tea." Zack mentioned (that) .
- Ella, "It's not raining." Ella remarked (that) .
- Jacob, "Riley is checking the computer." Jacob said (that) .
- Owen, "They aren't watching TV." Owen told me (that) .
- Nora, "He is learning Spanish words." Nora said (that) .
- You are here:
- Grammar Exercises
- Reported Speech
EnglishPost.org
Reported Speech: Structures and Examples
Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say.
Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words
The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
| Statement | She told me she was sick |
| Question | He asked me whether I was sick or not |
| Command | They ordered us to take a pill every day |
Table of Contents
Reported Speech Rules and Examples
Present tenses and reported speech, past tenses and reported speech, reported speech examples, reported speech and the simple present, reported speech and present continuous, reported speech and the simple past, reported speech and the past continuous, reported speech and the present perfect, reported speech and the past perfect, reported speech and ‘ can ’ and ‘can’t’, reported speech and ‘ will ’ and ‘ won’t ’, reported speech and could and couldn’t, reported speech and the future continuous, reported questions exercises online.
To turn sentences into Indirect Speech, you have to follow a set of rules and this is what makes reported speech difficult for some.
To make reported speech sentences, you need to manage English tenses well.
- Present Simple Tense changes into Past Simple Tense
- Present Progressive Tense changes into Past Progressive Tense
- Present Perfect Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Progressive Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense changes into Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense doesn’t change
- Past Perfect Progressive Tense doesn’t change
- Future Simple Tense changes into would
- Future Progressive Tense changes into “would be”
- Future Perfect Tense changes into “would have·
- Future Perfect Progressive Tense changes into “would have been”
These are some examples of sentences using indirect speech
The present simple tense usually changes to the past simple
| He said that he travelled a lot in his job | |
| I play video games a lot | She said that he played video games a lot |
| We run every morning | They said that they ran every morning |
| I do yoga every weekend | She said that he did yoga every weekend |
The present continuous tense usually changes to the past continuous.
| She said that her mom was cooking | |
| My brother is watching TV | He said that his brother was watching TV |
| My family is eating dinner | She said that her family was eating dinner |
| I am doing Yoga | She said that she was doing yoga |
The past simple tense usually changes to the past perfect
| My mom cooked dinner | She said that her mom had cooked dinner |
| My brother watched a movie | He said that his brother had watched a movie |
| My family just ate dinner | She said that her family just had eaten dinner |
| I really enjoyed the party | |
| Bill on Saturday | He said that Bill on Saturday |
The past continuous tense usually changes to the past perfect continuous.
| She said that her mom had been cooking dinner | |
| My brother was watching a movie | He said that his brother had been watching a movie |
| My family was talking in the room | She said that her family had been talking in the room |
| Derek was doing Yoga | She said that Derek was doing Yoga |
The present perfect tense usually changes to the past perfect tense
| My mom has been kind | She said that her mom had always been kind |
| My brother has worked hard | He said that his brother had worked hard |
| My girlfriend has contributed a lot | He said that his girlfriend has contributed a lot |
| My family has always helped | She said that her family had always helped |
The past perfect tense does not change
| My mom had been kind | She said that her mom had always been kind |
| My brother had worked hard | He said that his brother had worked hard |
| He has played very well | He said that he had played very well |
| My family had always helped | She said that her family had always helped |
‘ Can ’ and ‘can’t’ in direct speech change to ‘ could ’ and ‘ couldn’t ’
| She said that her mom couldn’t remember his name | |
| My brother can play soccer well | He said that his brother could play soccer well |
| My family can help you a lot | She said that her family could help me a lot |
| My mom can lend me money | She said that she could lend me money |
‘ Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
| to my wedding | She said that her mom to her wedding |
| My brother in my team | He said that his brother in her team |
| My family me with some money | She said that her family her with some money |
| She to Europe | She said that she to Europe |
Could and couldn’t doesn’t change
| go to the wedding | She said that her mom go to the wedding |
| My brother be in your team | He said that his brother be in your team |
| My family help me out | She said that her family help me out |
Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
| peech | |
| the car next Friday | She said that she the car next Friday |
| home | He said that he home |
| I g in Norway | He said that he in Norway |
| I exercises | He said that he exercises |
These are some online exercises to learn more about reported questions
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise
Manuel Campos
I am Jose Manuel, English professor and creator of EnglishPost.org, a blog whose mission is to share lessons for those who want to learn and improve their English
Related Articles

75 Sentences and Questions with Have and Has

50 Questions with Going to

Second Conditional Sentences and Questions

Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
| Simple present “I to go home.” | Simple past She said she to go home. |
| Present continuous “I a good book.” | Past continuous She said she a good book. |
| Simple past “I pasta for dinner last night.” | Past perfect She said she pasta for dinner the night before. |
| Present perfect “I just cleaning my room.” “My mother never to Japan.” | Past perfect She said she just cleaning her room. She said her mother never to Japan. |
| Can/can’t “I meet with you next Monday.” “Sorry, I talk now; I’m at work.” | Could/couldn’t She said she meet with me next Monday. She said she talk at the moment because she was at work. |
| Will/won’t “I pick him up from the airport.” “I tell anyone your secret.” | Would/wouldn’t She said she pick him up from the airport. She said she tell anyone my secret. |
| Should “You apologize.” | Should She said I apologize. |
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to Backshift in Reported Speech
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

British vs. American English Spelling

100 Superlatives: List & Examples

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.
Reported Speech in English
“Reported speech” might sound fancy, but it isn’t that complicated.
It’s just how you talk about what someone said.
Luckily, it’s pretty simple to learn the basics in English, beginning with the two types of reported speech: direct (reporting the exact words someone said) and indirect (reporting what someone said without using their exact words ).
Read this post to learn how to report speech, with tips and tricks for each, plenty of examples and a resources section that tells you about real world resources you can use to practice reporting speech.
How to Report Direct Speech
How to report indirect speech, reporting questions in indirect speech, verb tenses in indirect reported speech, simple present, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, simple past, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, simple future, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, authentic resources for practicing reported speech, novels and short stories, native english videos, celebrity profiles.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Direct speech refers to the exact words that a person says. You can “report” direct speech in a few different ways.
To see how this works, let’s pretend that I (Elisabeth) told some people that I liked green onions.
Here are some different ways that those people could explain what I said:
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” Elisabeth said.
- Thousands of learner friendly videos (especially beginners)
- Handpicked, organized, and annotated by FluentU's experts
- Integrated into courses for beginners

Direct speech: “I like green onions,” she told me. — In this sentence, we replace my name (Elisabeth) with the pronoun she.
In all of these examples, the part that was said is between quotation marks and is followed by a noun (“she” or “Elisabeth”) and a verb. Each of these verbs (“to say,” “to tell [someone],” “to explain”) are ways to describe someone talking. You can use any verb that refers to speech in this way.
You can also put the noun and verb before what was said.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like spaghetti.”
The example above would be much more likely to be said out loud than the first set of examples.
Here’s a conversation that might happen between two people:
- Interactive subtitles: click any word to see detailed examples and explanations
- Slow down or loop the tricky parts
- Show or hide subtitles
- Review words with our powerful learning engine
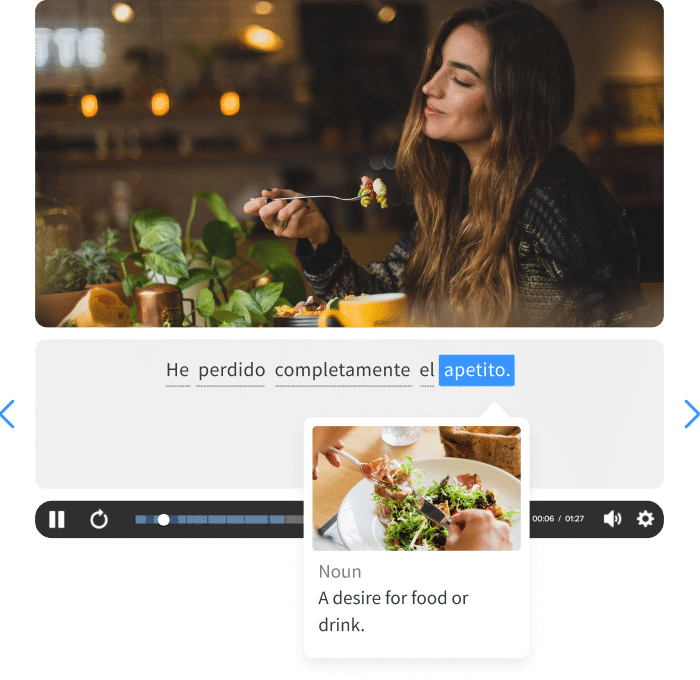
1: Did you ask her if she liked coffee?
2: Yeah, I asked her.
1: What did she say?
2. She said, “Yeah, I like coffee.” ( Direct speech )
Usually, reporting of direct speech is something you see in writing. It doesn’t happen as often when people are talking to each other.
Direct reported speech often happens in the past. However, there are all kinds of stories, including journalism pieces, profiles and fiction, where you might see speech reported in the present as well.
This is sometimes done when the author of the piece wants you to feel that you’re experiencing events in the present moment.
- Learn words in the context of sentences
- Swipe left or right to see more examples from other videos
- Go beyond just a superficial understanding

For example, a profile of Kristen Stewart in Vanity Fair has a funny moment that describes how the actress isn’t a very good swimmer:
Direct speech: “I don’t want to enter the water, ever,” she says. “If everyone’s going in the ocean, I’m like, no.”
Here, the speech is reported as though it’s in the present tense (“she says”) instead of in the past (“she said”).
In writing of all kinds, direct reported speech is often split into two or more parts, as it is above.
Here’s an example from Lewis Carroll’s “ Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland ,” where the speech is even more split up:
Direct speech: “I won’t indeed!” said Alice, in a great hurry to change the subject of conversation. “Are you—are you fond—of—of dogs?” The Mouse did not answer, so Alice went on eagerly: “There is such a nice little dog near our house I should like to show you!”
Reporting indirect speech is what happens when you explain what someone said without using their exact words.
- FluentU builds you up, so you can build sentences on your own
- Start with multiple-choice questions and advance through sentence building to producing your own output
- Go from understanding to speaking in a natural progression.
Let’s start with an example of direct reported speech like those used above.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like coffee.”
As indirect reported speech, it looks like this:
Indirect speech: Elisabeth said she liked coffee.
You can see that the subject (“I”) has been changed to “she,” to show who is being spoken about. If I’m reporting the direct speech of someone else, and this person says “I,” I’d repeat their sentence exactly as they said it. If I’m reporting this person’s speech indirectly to someone else, however, I’d speak about them in the third person—using “she,” “he” or “they.”
You may also notice that the tense changes here: If “I like coffee” is what she said, this can become “She liked coffee” in indirect speech.
- Images, examples, video examples, and tips
- Covering all the tricky edge cases, eg.: phrases, idioms, collocations, and separable verbs
- No reliance on volunteers or open source dictionaries
- 100,000+ hours spent by FluentU's team to create and maintain
However, you might just as often hear someone say something like, “She said she likes coffee.” Since people’s likes and preferences tend to change over time and not right away, it makes sense to keep them in the present tense.
Indirect speech often uses the word “that” before what was said:
Indirect speech: She said that she liked coffee.
There’s no real difference between “She said she liked coffee” and “She said that she liked coffee.” However, using “that” can help make the different parts of the sentence clearer.
Let’s look at a few other examples:
Indirect speech: I said I was going outside today.

Indirect speech: They told me that they wanted to order pizza.
Indirect speech: He mentioned it was raining.
Indirect speech: She said that her father was coming over for dinner.
You can see an example of reporting indirect speech in the funny video “ Cell Phone Crashing .” In this video, a traveler in an airport sits down next to another traveler talking on his cell phone. The first traveler pretends to be talking to someone on his phone, but he appears to be responding to the second traveler’s conversation, which leads to this exchange:
Woman: “Are you answering what I’m saying?”
Man “No, no… I’m on the phone with somebody, sorry. I don’t mean to be rude.” (Direct speech)
Woman: “What was that?”
Man: “I just said I was on the phone with somebody.” (Indirect speech)
When reporting questions in indirect speech, you can use words like “whether” or “if” with verbs that show questioning, such as “to ask” or “to wonder.”
Direct speech: She asked, “Is that a new restaurant?”
Indirect speech: She asked if that was a new restaurant.
In any case where you’re reporting a question, you can say that someone was “wondering” or “wanted to know” something. Notice that these verbs don’t directly show that someone asked a question. They don’t describe an action that happened at a single point in time. But you can usually assume that someone was wondering or wanted to know what they asked.
Indirect speech: She was wondering if that was a new restaurant.
Indirect speech: She wanted to know whether that was a new restaurant.
It can be tricky to know how to use tenses when reporting indirect speech. Let’s break it down, tense by tense.
Sometimes, indirect speech “ backshifts ,” or moves one tense further back into the past. We already saw this in the example from above:
Direct speech: She said, “I like coffee.”
Indirect speech: She said she liked coffee.
Also as mentioned above, backshifting doesn’t always happen. This might seem confusing, but it isn’t that difficult to understand once you start using reported speech regularly.
What tense you use in indirect reported speech often just depends on when what you’re reporting happened or was true.
Let’s look at some examples of how direct speech in certain tenses commonly changes (or doesn’t) when it’s reported as indirect speech.
To learn about all the English tenses (or for a quick review), check out this post .
Direct speech: I said, “I play video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I played video games (simple past) or I said that I play video games (simple present).
Backshifting into the past or staying in the present here can change the meaning slightly. If you use the first example, it’s unclear whether or not you still play video games; all we know is that you said you played them in the past.
If you use the second example, though, you probably still play video games (unless you were lying for some reason).
However, the difference in meaning is so small, you can use either one and you won’t have a problem.
Direct speech: I said, “I’m playing video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I was playing video games (past continuous) or I said that I’m playing video games (present continuous).
In this case, you’d likely use the first example if you were telling a story about something that happened in the past.
You could use the second example to repeat or stress what you just said. For example:
Hey, want to go for a walk?
Direct speech: No, I’m playing video games.
But it’s such a nice day!
Indirect speech: I said that I’m playing video games!
Direct speech: Marie said, “I have read that book.”
Indirect speech: Marie said that she had read that book (past perfect) or Marie said that she has read that book (present perfect).
The past perfect is used a lot in writing and other kinds of narration. This is because it helps point out an exact moment in time when something was true.
The past perfect isn’t quite as useful in conversation, where people are usually more interested in what’s true now. So, in a lot of cases, people would use the second example above when speaking.
Direct speech: She said, “I have been watching that show.”
Indirect speech: She said that she had been watching that show (past perfect continuous) or She said that she has been watching that show (present perfect continuous).
These examples are similar to the others above. You could use the first example whether or not this person was still watching the show, but if you used the second example, it’d probably seem like you either knew or guessed that she was still watching it.
Direct speech: You told me, “I charged my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had charged your phone (past perfect) or You told me that you charged your phone (simple past).
Here, most people would probably just use the second example, because it’s simpler, and gets across the same meaning.
Direct speech: You told me, “I was charging my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had been charging your phone (past perfect continuous) or You told me that you were charging your phone (past continuous).
Here, the difference is between whether you had been charging your phone before or were charging your phone at the time. However, a lot of people would still use the second example in either situation.
Direct speech: They explained, “We had bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Indirect speech: They explained that they had bathed the cat on Wednesday. (past perfect)
Once we start reporting the past perfect tenses, we don’t backshift because there are no tenses to backshift to.
So in this case, it’s simple. The tense stays exactly as is. However, many people might simplify even more and use the simple past, saying, “They explained that they bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Direct speech: They said, “The cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time!”
Indirect speech: They said that the cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time. (past perfect continuous)
Again, we don’t shift the tense back here; we leave it like it is. And again, a lot of people would report this speech as, “They said the cat was going outside and getting dirty for a long time.” It’s just a simpler way to say almost the same thing.
Direct speech: I told you, “I will be here no matter what.”
Indirect speech: I told you that I would be here no matter what. (present conditional)
At this point, we don’t just have to think about tenses, but grammatical mood, too. However, the idea is still pretty simple. We use the conditional (with “would”) to show that at the time the words were spoken, the future was uncertain.
In this case, you could also say, “I told you that I will be here no matter what,” but only if you “being here” is still something that you expect to happen in the future.
What matters here is what’s intended. Since this example shows a person reporting their own speech, it’s more likely that they’d want to stress the truth of their own intention, and so they might be more likely to use “will” than “would.”
But if you were reporting someone else’s words, you might be more likely to say something like, “She told me that she would be here no matter what.”
Direct speech: I said, “I’ll be waiting for your call.”
Indirect speech: I said that I would be waiting for your call. (conditional continuous)
These are similar to the above examples, but apply to a continuous or ongoing action.
Direct speech: She said, “I will have learned a lot about myself.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would have learned a lot about herself (conditional perfect) or She said that she will have learned a lot about herself (future perfect).
In this case, using the conditional (as in the first example) suggests that maybe a certain event didn’t happen, or something didn’t turn out as expected.
However, that might not always be the case, especially if this was a sentence that was written in an article or a work of fiction. The second example, however, suggests that the future that’s being talked about still hasn’t happened yet.
Direct speech: She said, “By next Tuesday, I will have been staying inside every day for the past month.”
Indirect speech: She said that by next Tuesday, she would have been staying inside every day for the past month (perfect continuous conditional) or She said that by next Tuesday, she will have been staying inside every day for the past month (past perfect continuous).
Again, in this case, the first example might suggest that the event didn’t happen. Maybe the person didn’t stay inside until next Tuesday! However, this could also just be a way of explaining that at the time she said this in the past, it was uncertain whether she really would stay inside for as long as she thought.
The second example, on the other hand, would only be used if next Tuesday hadn’t happened yet.
Let’s take a look at where you can find resources for practicing reporting speech in the real world.
One of the most common uses for reported speech is in fiction. You’ll find plenty of reported speech in novels and short stories . Look for books that have long sections of text with dialogue marked by quotation marks (“…”). Once you understand the different kinds of reported speech, you can look for it in your reading and use it in your own writing.
Writing your own stories is a great way to get even better at understanding reported speech.
One of the best ways to practice any aspect of English is to watch native English videos. By watching English speakers use the language, you can understand how reported speech is used in real world situations.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
Celebrity profiles, which you can find in print magazines and online, can help you find and practice reported speech, too. Celebrity profiles are stories that focus on a famous person. They often include some kind of interview. The writer will usually spend some time describing the person and then mention things that they say; this is when they use reported speech.
Because many of these profiles are written in the present tense, they can help you get used to the basics of reported speech without having to worry too much about different verb tenses.
While the above may seem really complicated, it isn’t that difficult to start using reported speech.
Mastering it may be a little difficult, but the truth is that many, many people who speak English as a first language struggle with it, too!
Reported speech is flexible, and even if you make mistakes, there’s a good chance that no one will notice.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


Reported speech
Tense changes in reported speech
Indirect speech (reported speech) focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired.
| Phrase in Direct Speech | Equivalent in Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| "I always coffee", she said | She said that she always coffee. |
| "I a book", he explained. | He explained that he a book |
| "Bill on Saturday", he said. | He said that Bill on Saturday. |
| "I to Spain", he told me. | He told me that he to Spain. |
| "I the light," he explained. | He explained that he the light. |
| They complained, "We for hours". | They complained that they for hours. |
| "We in Paris", they told me. | They told me that they in Paris. |
| "I in Geneva on Monday", he said. | He said that he in Geneva on Monday. |
| She said, " the car next Friday". | She said that she the car next Friday. |
You do not need to change the tense if the reporting verb is in the present, or if the original statement was about something that is still true (but this is only for things which are general facts, and even then usually we like to change the tense) , e.g.
- He says he has missed the train but he'll catch the next one.
- We explained that it is very difficult to find our house.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
These modal verbs do not change in reported speech: might, could, would, should, ought to :
- We explained, "It could be difficult to find our house." = We explained that it could be difficult to find our house.
- She said, "I might bring a friend to the party." = She said that she might bring a friend to the party.
Course Curriculum
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins

- Messages ({{ ::newMessages }})
- Transcripts and statements
- Shop cart ({{ cart.items.length }})
- Sign Out Sign in

English Language Centre / Study Zone / Level 490 — Upper Intermediate / Grammar Topics / Reported Speech
Reported Speech
Introduction.
When reporting what someone said, we have to pay careful attention to our verb tenses. Generally, reported speech is introduced by the verb say (Other reporting verbs include tell, mention, inform). The verb is used in the past tense, said , which indicates that something was spoken in the past. For example:
“she said”, “he said”, “they said”
The main verb in the reported speech sentence is also in the past tense. In a sentence where the main verb is already in the past tense, then the verb changes to another past tense verb as it is moving further into the past.
Usually, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech. However, often if the speaker is reporting something soon after it has been said, there is no change in the verb tense. This is also true if the reported statement is a general truth. For example:
“The capital of Canada is Ottawa.” → Byron said that the capital of Canada is Ottawa.
Remember that in reported speech, there are no quotation marks.
| Quoted Speech (What the person actually said) | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Mark said, “I thirsty.” | Mark said (that) he thirsty. (Note: The use of is optional) |
Verbs usually change to the past in reported speech because we are talking about the past. For example:
| Quoted Speech (What the person actually said) | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Am/is | was |
| Are | were |
| Have/has | had |
| Can | could |
| Do/want/know | did/wanted/knew |
| Will | would |
In reported speech, the simple past ( I did ) often stays the same or it changes to the past perfect ( I had done ).
Examples of Verb Changes in Reported Speech
| Quoted Speech (What the person actually said) | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| “I tea”, she said. | She said (that) she tea. |
| “I French”, he said. | : He said (that) he French. |
| “Mike on Sunday”, Gayle said | Gayle said (that) Mike ( ) on Sunday. |
| to Russia”, she said. | She said (that) she to Russia. |
| “I my homework”, Kendall told me. | Kendall told me (that) she her homework. |
| “We for 3 hours.” | : They mentioned (that) they for 3 hours |
| “We in San Diego.” | : They told us (that) in San Diego. |
| She said, “We in Vancouver next year.” | She informed me (that) they in Vancouver next year. |
| He said, “I to marry her next spring.” | He said (that) he her next spring. |
- Join E-News
- Staff login
- Visit UVic.ca
- UVic My page
Visit Registration
Tel 250-472-4747 | Email [email protected]
2024 © Continuing Studies at UVic Legal Notices | Sitemap
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense
Learn how to convey a message what someone is saying, feeling or thinking in present continuous tense. Direct and indirect of present continuous tense rules and structures of affirmative, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative sentences along with examples.
For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules
Tense Change As a rule when you report something someone has said you go back a tense, therefore, when we report what someone is saying in present continuous we go one tense back. Instead we use past continuous tense in reported speech.
Affirmatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + be1 + V1ing + ROTS He said, “I am doing my homework.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS He told me that he was doing his homework.
Interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + be1 + S + V1ing + ROTS He asked, “Are you going to school?”
- Indirect speech: RP + if + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS He asked me if I was coming/going to school.
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + be1 not + V1ing + ROTS He said, “She is not listening to me.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + be2 not + V1ing + ROTS He said to me that she was not listening to him.
Negative interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + b2 not + S + V1ing + ROTS He asked, “Aren`t they staying with us for tonight?”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + if + S + be2 not + V1ing + ROTS He asked if they weren`t staying with them for that night.
WH/Information questions
- Direct speech: RP +, + WH + be1 + S + V1ing + ROTS She asked, “What are you buying tomorrow?”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + WH + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS She wanted to know what I was buying the next day.
More sentences:
Affirmative
- Direct speech: He said,” They are playing football.”
- Indirect speech: He said that they were playing football.
Interrogative
- Direct speech: He asked, “Are they playing football?”
- Indirect speech: He asked me if they were playing football.
- Direct speech: He said, “They are not playing football.”
- Indirect speech: He said that they were not playing football.
Negative interrogative
- Direct speech: He asked,” Aren’t they playing football?”
- Indirect speech: He asked me if they weren’t playing football.
Wh/ Information question
- Direct speech: He asked,” Where are they playing now?”
- Indirect speech: He wanted to know where they are playing now.
Check out Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers
If you would like to know more about direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech, check out more in the book below.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)

Related posts
Position of adverbs rules, what are compound modifiers in english, active and passive voice.
I really like this website please send me your topic in email
Hello Sudais Khattak, Please subscribe and then you will receive all updates through your email address.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Reported Speech Exercises
Perfect english grammar.

Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site:
( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech )
Reported Statements:
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Past Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Perfect Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Future Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Statement Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- 'Say' and 'Tell' (quite easy) (in PDF here)
Reported Questions:
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
Reported Orders and Requests:
- Reported Requests and Orders Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 1 (difficult) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 2 (difficult) (in PDF here)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
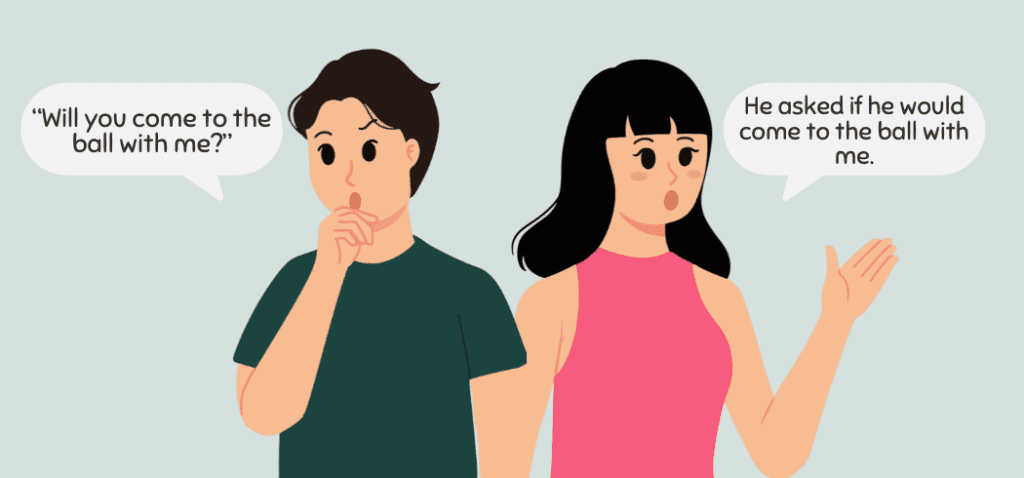

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
The Reported Speech

Table of Contents
What is reported speech, direct speech vs reported speech.
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| She says: “I like tuna fish.” | She says that she likes tuna fish. |
| She said: “I’m visiting Paris next weekend.” | She said that she was visiting Paris the following weekend. |
| He asked Betty: “Do you like cheese?” | He wanted to know if Betty liked cheese. |
Different types of reported speech
When you use reported speech, you either report:
A. Reporting statements
1- pronouns.
| Shifting back tense | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| (no backshift) | “I poems.” | He that he poems. |
| (backshift) | “I poems | He that he poems. |
Do not change the tense if the introductory clause (i.e., the reporting verb) is in the present tense (e. g. He says ). Note, however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person singular).
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| He said: “I happy” | He said that he happy |
| He said: “I for my keys” | He said that he for his keys |
| He said: “I New York last year” | He said that he New York the previous year. |
| He said: ” I here for a long time “ | He said that he there for a long time |
| He said: “They the work when I “ | He said that they the work when he “ |
| He said: “I football when the accident “ | He said that football when the accident |
| He said: “I football for two hours.” | He said that football for two hours |
| He said: “I a newspaper when the light “ | He said that he a newspaper when the light |
| He said: “I the door.” | He said that the door. |
| He said: “I a Mercedes if I rich” | He said that he a Mercedes if he rich |
3. Modal verbs
| Modal | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| can | “I do it.” | He said that he do it. |
| may | “ I go out?” | He wanted to know if he go out. |
| must | “She apply for the job.” | He said that she apply for the job. |
| will | “They call you.” | He told her that they call her. |
4- Place, demonstratives, and time expressions
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Time Expressions | |
| today | that day |
| now | then |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before/the previous week |
| next year | the following year/the next year/ the year after |
| tomorrow | the next day/the following day |
| Place | |
| here | there |
| Demonstratives | |
| this | that |
| these | those |
B. Reporting Questions
| Types of questions | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| With question words (what, why, where, how…) | “Why don’t you speak English?” | He asked me why I didn’t speak English. |
| Without question words (yes or no questions) | “Do you speak English?” | He asked me whether/if I spoke English. |
C. Reporting requests/commands
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| “Nancy, do the exercise.” | He told Nancy to do the exercise. |
| “Nancy, give me your pen, please.” | He asked Nancy to give him her pen. |
| Tenses are not relevant for requests, simply use / + verb (infinitive without “to”) |
| For affirmative use + infinitive (without to) For negative requests, use + infinitive (without to). |
D. Other transformations
Main clauses connected with and/but, punctuation rules of the reported speech, can we omit that in the reported speech, list of reporting verbs.
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| simple present | simple past |
| simple past | past perfect |
| present continuous | past continuous |
| past continuous | past perfect continuous |
| will | would |
| shall | should |
| may | might |
| can | could |
| must | had to |

Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense
English is a flexible language that helps us talk about things happening now or near now. We call one of the ways to do this the “present continuous tense.” It helps us explain actions as they are happening. In this article, we’ll learn how to use this tense when someone is talking directly or telling us what someone else said. We’ll make it simple with clear examples to understand better.
Understanding the Present Continuous Tense:
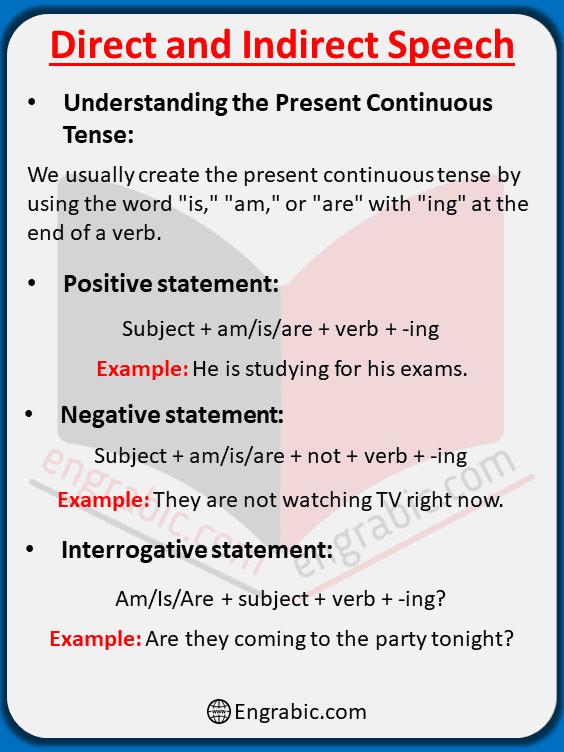
Present Continuous Tense Overview
Before we go to learn direct and indirect speech, let’s quickly go over how we make and use the present continuous tense. We usually create the present continuous tense by using the word “is,” “am,” or “are” with “ing” at the end of a verb.
Important Note : You can Download FREE PDF at the bottom
Positive statement: Subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing
Example: He is studying for his exams.
Negative statement: Subject + am/is/are + not + verb + -ing
Example: They are not watching TV right now.
Interrogative statement: Am/Is/Are + subject + verb + -ing?
Example: Are they coming to the party tonight?
Present Continuous Tense in Direct Speech:
Direct speech means we repeat exactly what someone said. When we tell others what someone is saying right now using the present continuous tense, we can put quotation marks around those words. Here are some examples:
Original Statement: Uzair said, “I am reading a great book.”
Direct Speech: Uzair said, “I am reading a great book.”
Original Statement: “We are going to the market,” they announced.
Direct Speech: “We are going to the market,” they announced.
Change the pronoun in the reporting verb: When changing the pronouns in sentences with the present continuous tense from direct speech to reported speech:
Direct Speech: “I am working on a project,” she said.
Reported Speech: She mentioned that she was working on a project.
To make a sentence from someone talking into a present continuous one, you change the words to fit what’s happening now or when you want to talk about. Here are some examples of how you can do that:
Change time expression:
Original Direct Speech: “I am studying for the exam.”
- Present Time: “He says, ‘I am studying for the exam right now.”
- Past Time: “He said, ‘I was studying for the exam yesterday.”
- Future Time: “He will say, ‘I am studying for the exam tomorrow.'”
Present Continuous Tense in Indirect Speech:
Indirect speech, which is also called reported speech, helps us share what someone said without repeating their words exactly.
Here are the rules for changing what someone said in the present continuous tense from direct speech to indirect speech:
Change the Verb Tense: In indirect speech, we usually talk about what someone said in a slightly different way. The words like “am,” “is,” or “are” change to “was” or “were,” but the action word with “ing” stays the same.
Direct Speech: He said, “I am studying for my exams.”
Indirect Speech: He said that she was studying for her exams.
Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense Examples

| “We are going to Changa Manga for a picnic.” they said | They said that they were going to Changa Manga for a picnic. |
| The boy said, “I am preparing well for the examination.” | The boy mentioned that he was preparing well for the examination. |
| “I am making the map of Pakistan,” he said. | He said that he was making the map of Pakistan. |
| The milkman said, “I am milking.” | The milkman mentioned that he was milking. |
| The fishermen said, “We are catching fish.” | The fishermen reported that they were catching fish. |
| Amjad said, “I am winding the watch.” | Amjad stated that he was winding the watch. |
| “We are printing a new book,” they said. | They mentioned that they were printing a new book. |
| “This cloth is selling cheap,” he said. | He mentioned that the cloth was selling cheap. |
| “He is turning the tap on,” she said. | She reported that he was turning the tap on. |
| “I am looking for my watch,” she said. | She said that she was looking for her watch. |
| “He said, ‘I am eating a meal.'” | He said that he was eating a meal. |
| He said, “I am driving the car.” | He said that he was driving the car. |
| “We are taking a shower,” they said. | They said that they were taking a shower. |
| “I am helping him,” | He said that he was helping him. |
| “The baby said, ‘I am crying because I am hungry.'” | The baby said that he was crying because he was hungry. |
| “I am traveling to Lahore,” he said. | He said that he was traveling to Lahore. |
| “They said, ‘We are talking on the phone.'” | They said that they were talking on the phone. |
| “I am winning,” | He said that he was winning. |
| “She is shouting,” he said. | He said that she was shouting. |
| “We are running,” they said. | They said that they were running. |
| “I am remembering the words,” | He/She said that they were remembering the words. |
| “I am sneezing due to fever,” he said. | He said that he was sneezing due to a fever. |
| “The boss said, ‘I am writing the letter,'” | The boss said that he was writing the letter. |
| “All the laborers said, ‘We are sleeping,’’ | All the laborers said that they were sleeping. |

Present Continuous Tense in Direct Speech Exercises with PDF

Present Continuous Tense in Direct Speech Exercise
Download FREE PDF Here
You may also like to read:
Direct and Indirect Narration with Rules and Examples
Direct and Indirect of Simple Present Tense
Active and Passive Voice with Rules and Examples
You may also like
Interjections – Definition, Rules and Examples
Interjection is one of the Parts of Speech, which is used to express sudden emotions, strong...
Future Indefinite Tense | Structures, Examples & Rules
The simple future tense is a fundamental aspect of English grammar that is used to talk about...

Parts of Speech | The 8 Parts of Speech with Examples and Rules
Parts of speech are fundamental categories that classify words based on their grammatical...
Participles | What Are Participles? | Definition and Examples
English Grammar has many branches and Important topics like Tenses, Direct Indirect Narration...
Leave a Comment X
Reported speech(present simple and continuos)
De:Zaray Corredor García
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers

Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10
Reported speech is an important part of learning English, especially in Class 10. It involves telling someone what another person has said, but without quoting their exact words . For example, instead of saying, "She said, 'I am going to the market,'" the reported speech would be, "She said that she was going to the market."

Practising Reported Speech Exercises For Class 10 helps students understand how to convey information accurately and clearly. In this article, there are different exercises prepared to test and improve your skills in reported speech. Each exercise comes with answers, students can check their work and learn from any mistakes. By working through these exercises, students will improve their ability to use reported speech correctly in different situations.
| . It’s integrated into the sentence. |
Reported Speech Exercises with Answers for Class 10
Try these Reported Speech exercises with answers for Class 10 to practise changing direct quotes into reported speech. Check your answers to see how well you understand the topic, and watch the Reported speech video for a clear explanation and more examples .
Reported Speech Dialogue Exercises for Class 10 CBSE with Answers
Exercise 1: Transform the following sentences into reported speech.
"I am going to the market," said Rahul.
"Are you coming to the party?" asked Riya.
"I will finish my homework later," said Tina.
"We have never been to Paris," they said.
"Did you see the new movie?" he asked.
"She can speak three languages," said Mr. Sharma.
"Please, close the door," she said.
"Why are you late?" asked the teacher.
"I don’t like spicy food," said Raj.
"You should take your medicine ," the doctor said.
"Where have you been?" she asked.
"I need a new pair of shoes," he said.
"Will you help me with this project?" she asked.
"I can’t find my keys," said John.
"I have completed my assignment," he said.
"Are they coming to the meeting?" she asked.
"We visited the museum yesterday," they said.
"Why didn’t you answer my call?" she asked.
"I am reading an interesting book," he said.
"Let’s go for a walk," she suggested.
"You must finish this work by tomorrow," he said.
"Did you enjoy the concert?" she asked.
"I don’t understand this chapter," said Ravi.
"Where is the nearest bus stop?" he asked.
"She will call you later," said Mr. Gupta.
"Can you lend me a pen?" he asked.
"I am not feeling well," she said.
"When does the train arrive?" he asked.
"Do you know where she went?" they asked.
"We are planning a surprise party," they said.
"I have a meeting at 5 PM," she said.
"Will it rain tomorrow?" he asked.
"I need to talk to you," she said.
"Did you hear the news?" he asked.
"I will be there on time ," she assured.
"Where can I find a taxi?" he asked.
"She is coming to the party," they said.
"Can you help me with this?" he asked.
"I have to leave now," she said.
"Are you sure about this?" he asked.
"I will call you later," he said.
"She told me that she was busy," he said.
"Did you see that movie?" she asked.
"I can’t come to the meeting," he said.
"Where did you put my book?" she asked.
"I am looking for my wallet," he said.
"Can you meet me tomorrow?" she asked.
"They are watching a movie," she said.
"Do you know his address?" he asked.
"I have been waiting for an hour," she said.
Rahul said that he was going to the market.
Riya asked if I was coming to the party.
Tina said that she would finish her homework later.
They said that they had never been to Paris.
He asked if I had seen the new movie.
Mr. Sharma said that she could speak three languages.
She requested to close the door.
The teacher asked why I was late.
Raj said that he didn’t like spicy food.
The doctor advised that I should take my medicine.
She asked where I had been.
He said that he needed a new pair of shoes.
She asked if I would help her with the project.
John said that he couldn’t find his keys.
He said that he had completed his assignment.
She asked if they were coming to the meeting.
They said that they had visited the museum the day before.
She asked why I hadn’t answered her call.
He said that he was reading an interesting book.
She suggested going for a walk.
He said that I had to finish the work by the next day.
She asked if I had enjoyed the concert.
Ravi said that he didn’t understand the chapter.
He asked where the nearest bus stop was.
Mr. Gupta said that she would call me later.
He asked if I could lend him a pen.
She said that she was not feeling well.
He asked when the train arrived.
They asked if I knew where she had gone.
They said that they were planning a surprise party.
She said that she had a meeting at 5 PM.
He asked if it would rain the next day.
She said that she needed to talk to me.
He asked if I had heard the news.
She assured me that she would be there on time.
He asked where he could find a taxi.
They said that she was coming to the party.
He asked if I could help him with that.
She said that she had to leave then.
He asked if I was sure about it.
He said that he would call me later.
He said that she had told him that she was busy.
She asked if I had seen that movie.
He said that he couldn’t come to the meeting.
She asked where I had put her book.
He said that he was looking for his wallet.
She asked if I could meet her the next day.
She said that they were watching a movie.
He asked if I knew his address.
She said that she had been waiting for an hour.
Exercise 2: Convert the following reported speech sentences back into direct speech .
She said that she was going to the store.
He asked if I had finished my homework.
The teacher mentioned that the exam was on Friday.
They said that they would be arriving late.
She warned me that the water was too hot.
He asked if she was coming to the party.
The manager said that the meeting was scheduled for 3 PM.
She told me that she had seen that movie before.
He said that he would help me with the project.
The doctor advised that I should get more rest.
She mentioned that she had lost her keys.
They asked if we could join them for dinner.
He said that he was not feeling well.
The professor explained that the assignment was due next week.
She said that they were planning a surprise party.
He informed me that he would be traveling abroad.
The guide said that the tour would start at noon.
She asked if I wanted to come with her.
He said that he had been working on the report all night.
They complained that the service was too slow.
The student said that he had forgotten his book.
She explained that she had a family emergency.
He mentioned that the flight was delayed.
They said that they had enjoyed the concert.
The chef suggested that we try the special dish.
She told me that she had won a prize.
He asked if I could help him with the assignment.
The coach said that practice would start at 5 PM.
She said that she was excited about the new job.
He stated that he had completed the project.
The police officer asked if I had seen anything suspicious.
She mentioned that she would be moving to a new city.
He informed me that the event was canceled.
The librarian said that the book was overdue.
She told him that she would call him later.
He said that he had missed the bus.
The employee mentioned that the system was down.
She asked if I could pick her up from the airport.
He said that they were going on vacation next month .
They complained that the hotel room was not clean.
The artist said that she had finished her painting.
She told me that they had already eaten dinner.
He asked if I had read the latest book in the series.
The teacher mentioned that the project was due soon.
She said that she would be arriving late.
He informed me that the deadline was extended.
The chef said that the food was almost ready.
She asked if we had seen her sunglasses.
He said that he would call me when he arrived.
The guide mentioned that the museum was closed on Mondays.
She said, "I am going to the store."
He asked, "Have you finished your homework?"
The teacher mentioned, "The exam is on Friday."
They said, "We will be arriving late."
She warned, "The water is too hot."
He asked, "Is she coming to the party?"
The manager said, "The meeting is scheduled for 3 PM."
She told me, "I have seen that movie before."
He said, "I will help you with the project."
The doctor advised, "You should get more rest."
She mentioned, "I have lost my keys."
They asked, "Can we join you for dinner?"
He said, "I am not feeling well."
The professor explained, "The assignment is due next week."
She said, "We are planning a surprise party."
He informed me, "I will be traveling abroad."
The guide said, "The tour will start at noon."
She asked, "Do you want to come with me?"
He said, "I have been working on the report all night."
They complained, "The service is too slow."
The student said, "I have forgotten my book."
She explained, "I have a family emergency."
He mentioned, "The flight is delayed."
They said, "We enjoyed the concert."
The chef suggested, "Try the special dish."
She told me, "I have won a prize."
He asked, "Can you help me with the assignment?"
The coach said, "Practice will start at 5 PM."
She said, "I am excited about the new job."
He stated, "I have completed the project."
The police officer asked, "Have you seen anything suspicious?"
She mentioned, "I will be moving to a new city."
He informed me, "The event is canceled."
The librarian said, "The book is overdue."
She told him, "I will call you later."
He said, "I missed the bus."
The employee mentioned, "The system is down."
She asked, "Can you pick me up from the airport?"
He said, "We are going on vacation next month."
They complained, "The hotel room is not clean."
The artist said, "I have finished my painting."
She told me, "We have already eaten dinner."
He asked, "Have you read the latest book in the series?"
The teacher mentioned, "The project is due soon."
She said, "I will be arriving late."
He informed me, "The deadline has been extended."
The chef said, "The food is almost ready."
She asked, "Have you seen my sunglasses?"
He said, "I will call you when I arrive."
The guide mentioned, "The museum is closed on Mondays."
Exercise 3: Reported Speech dialogue exercises for Class 10 CBSE with Answers
A: "I will meet you at the café at 3 PM," she said.
B: "I’ll be there," he replied.
A: "Please call me when you arrive," he said.
B: "I will definitely call," she promised.
A: "Can you help me with this project?" she asked.
B: "Of course, I’ll help you," he responded.
A: "I am planning to visit my parents next weekend," she said.
B: "That sounds nice," he replied.
A: "We need to finish this report by tomorrow," he said.
B: "I’ll get it done," she promised.
A: "Do you want to join us for lunch?" they asked.
B: "Yes, I’d love to join," she answered.
A: "The weather is going to be great this weekend," he said.
B: "I hope so," she replied.
A: "I have never been to Australia," she said.
B: "Neither have I," he replied.
A: "Please make sure to lock the door," he said.
B: "I will lock it," she assured.
A: "I am excited about the new movie," she said.
B: "Me too," he replied.
A: "We should start the meeting now," he suggested.
B: "I agree, let's begin," she said.
A: "Can you finish this by 5 PM?" he asked.
B: "I will try my best," she replied.
A: "I’m thinking of buying a new car," she said.
B: "That sounds like a good idea," he replied.
A: "Have you finished your assignment?" he asked.
B: "Not yet, but I’m working on it," she replied.
A: "I’ll be attending the conference next month," she said.
B: "I look forward to hearing about it," he replied.
A: "Please be on time for the meeting," he said.
B: "I will be punctual," she promised.
A: "I’m not sure if I can make it to the party," she said.
B: "I hope you can come," he replied.
A: "The train leaves at 8 AM," he said.
B: "I’ll make sure to be there early," she promised.
A: "Did you enjoy the book?" he asked.
B: "Yes, it was fantastic," she replied.
A: "I’ll send you the details later," she said.
B: "Thank you, I’ll wait for them," he replied.
A: "We have to submit the form by Friday," he said.
B: "I’ll get it done by then," she promised.
A: "Can you pass the salt, please?" she asked.
B: "Sure, here you go," he replied.
A: "I’m planning to take a vacation next month," she said.
B: "That sounds wonderful," he replied.
A: "Don’t forget to call me," he said.
B: "I won’t forget," she assured.
A: "I’ve never seen such a beautiful sunset," she said.
A: "Can you help me move this weekend?" he asked.
B: "I’m available to help," she replied.
A: "I have a dentist appointment tomorrow," she said.
B: "I hope it goes well," he replied.
A: "Please submit your reports by Monday," he said.
B: "I will submit them on Monday," she promised.
A: "We’re going to a concert tonight," she said.
B: "That sounds fun," he replied.
A: "I’m not feeling well today," he said.
B: "I hope you get better soon," she replied.
A: "I will finish my work before lunch," she said.
B: "Great, I’ll see you then," he replied.
A: "Can you give me a ride to the airport?" he asked.
B: "Yes, I can," she replied.
A: "I’ve completed the assignment," she said.
B: "That’s good to hear," he replied.
A: "Please let me know if you need any help," he said.
B: "Thank you, I will," she promised.
A: "I’m excited for the holiday season ," she said.
A: "I’ll be back by 10 PM," he said.
B: "Okay, I’ll see you then," she replied.
A: "Don’t forget to turn off the lights," she said.
B: "I’ll make sure to do that," he promised.
A: "The deadline for the project is next week," he said.
B: "I’ll work on it," she assured.
A: "Can you give me some feedback on my presentation?" she asked.
B: "Sure, I’ll review it," he replied.
A: "I’ll call you as soon as I arrive," he said.
B: "I’ll be waiting for your call," she replied.
A: "We need to discuss this further," she said.
B: "Let’s talk about it later," he replied.
A: "I’m planning a surprise party for her," she said.
B: "That’s exciting," he replied.
A: "Have you completed the budget report?" he asked.
B: "Yes, I finished it last night," she replied.
A: "I’ll get the tickets for the concert," he said.
B: "Thank you," she replied.
A: "I’ve booked a table for two," she said.
B: "Perfect, I’ll see you there," he replied.
A: "Can you meet me at the station?" he asked.
B: "I’ll be there on time," she assured.
A: "I’ve lost my wallet," he said.
B: "Let me help you find it," she offered.
A: "Please remember to bring your ID," she said.
B: "I won’t forget," he promised.
A: "I’m excited about the new project," he said.
B: "Me too," she replied.
A: "Can you check my email for me?" she asked.
B: "Sure, I’ll do that now," he replied.
Speaker A: She said that she would meet him at the café at 3 PM.
Speaker B: He replied that he would be there.
Speaker A: He said to call him when she arrived.
Speaker B: She promised that she would definitely call.
Speaker A: She asked if he could help her with the project.
Speaker B: He responded that he would help her.
Speaker A: She said that she was planning to visit her parents the following weekend.
Speaker B: He replied that it sounded nice.
Speaker A: He said that they needed to finish the report by the next day.
Speaker B: She promised that she would get it done.
Speaker A: They asked if she wanted to join them for lunch.
Speaker B: She answered that she would love to join.
Speaker A: He said that the weather was going to be great that weekend.
Speaker B: She replied that she hoped so.
Speaker A: She said that she had never been to Australia.
Speaker B: He replied that he had not been either.
Speaker A: He said to make sure to lock the door.
Speaker B: She assured him that she would lock it.
Speaker A: She said that she was excited about the new movie.
Speaker B: He replied that he was excited too.
Speaker A: He suggested that they should start the meeting then.
Speaker B: She agreed and said they should begin.
Speaker A: He asked if she could finish it by 5 PM.
Speaker B: She replied that she would try her best.
Speaker A: She said that she was thinking of buying a new car.
Speaker B: He replied that it sounded like a good idea.
Speaker A: He asked if she had finished her assignment.
Speaker B: She replied that she had not yet finished but was working on it.
Speaker A: She said that she would be attending the conference the following month.
Speaker B: He replied that he looked forward to hearing about it.
Speaker A: He said to be on time for the meeting.
Speaker B: She promised that she would be punctual.
Speaker A: She said that she was not sure if she could make it to the party.
Speaker B: He replied that he hoped she could come.
Speaker A: He said that the train left at 8 AM.
Speaker B: She promised that she would make sure to be there early.
Speaker A: He asked if she had enjoyed the book.
Speaker B: She replied that it was fantastic.
Speaker A: She said that she would send him the details later.
Speaker B: He replied that he would wait for them.
Speaker A: He said that they had to submit the form by Friday.
Speaker B: She promised that she would get it done by then.
Speaker A: She asked if he could pass the salt.
Speaker B: He replied that he would pass it.
Speaker A: She said that she was planning a vacation the following month.
Speaker B: He replied that it sounded wonderful.
Speaker A: He said not to forget to call him.
Speaker B: She assured him that she would not forget.
Speaker A: She said that she had never seen such a beautiful sunset.
Speaker B: He replied that he had not seen one either.
Speaker A: He asked if she could help him move that weekend.
Speaker B: She replied that she was available to help.
Speaker A: She said that she had a dentist appointment the next day.
Speaker B: He replied that he hoped it went well.
Speaker A: He said to submit the reports by Monday.
Speaker B: She promised that she would submit them on Monday.
Speaker A: She said that they were going to a concert that night.
Speaker B: He replied that it sounded fun.
Speaker A: He said that he was not feeling well that day.
Speaker B: She replied that she hoped he would get better soon.
Speaker A: She said that she would finish her work before lunch.
Speaker B: He replied that he would see her then.
Speaker A: He asked if she could give him a ride to the airport.
Speaker B: She replied that she could.
Speaker A: She said that she had completed the assignment.
Speaker B: He replied that it was good to hear.
Speaker A: He said to let him know if she needed any help.
Speaker B: She promised that she would.
Speaker A: She said that she was excited about the holiday season.
Speaker A: He said that he would be back by 10 PM.
Speaker B: She replied that she would see him then.
Speaker A: She said not to forget to turn off the lights.
Speaker B: He promised that he would make sure to do that.
Speaker A: He said that the deadline for the project was the following week.
Speaker B: She assured him that she would work on it.
Speaker A: She asked if he could give her some feedback on her presentation.
Speaker B: He replied that he would review it.
Speaker A: He said that he would call her as soon as he arrived.
Speaker B: She replied that she would be waiting for his call.
Speaker A: She said that they needed to discuss it further.
Speaker B: He replied that they should talk about it later.
Speaker A: She said that she was planning a surprise party for her.
Speaker B: He replied that it was exciting.
Speaker A: He asked if she had completed the budget report.
Speaker B: She replied that she had finished it the previous night.
Speaker A: He said that he would get the tickets for the concert.
Speaker B: She replied that she was thankful.
Speaker A: She said that she had booked a table for two.
Speaker B: He replied that he would see her there.
Speaker A: He asked if she could meet him at the station.
Speaker B: She assured him that she would be there on time.
Speaker A: He said that he had lost his wallet.
Speaker B: She offered to help him find it.
Speaker A: She said to remember to bring his ID.
Speaker B: He promised that he would not forget.
Speaker A: He said that he was excited about the new project.
Speaker B: She replied that she was excited too.
Speaker A: She asked if he could check her email for her.
Speaker B: He replied that he would do that then.
Still finding it difficult to answer these questions, Watch Common Mistakes in Reported Speech and improve your performance.
Test your Knowledge of Reported Speech
Task 1: Convert Direct Speech to Reported Speech
"I have been working here for five years," he said.
"Are you coming to the picnic tomorrow?" she asked.
"The package will arrive by Friday," the delivery man said.
"I forgot to bring my lunch," he admitted.
"We are moving to a new house next month," they said.
"Please finish your homework before dinner," the mother said.
"You should try the new restaurant," he suggested.
"I will help you with your maths problems," she promised.
"The movie starts at 8 PM," the ticket seller said.
"I have never been to Italy," she said.
Task 2: Convert Reported Speech to Direct Speech
He said that he was going to visit his parents the following week.
She asked if I could lend her my book.
The teacher mentioned that the test was postponed until next Friday.
They said that they had completed the project on time.
He explained that he had been studying for the exam all night.
The guide said that the museum would open at 10 AM.
She said that she had never seen such a beautiful garden.
He asked if we were interested in joining the new club.
The manager told us that the deadline had been extended.
They mentioned that they would be arriving late.
Task 3: Identify the Error
She said that she will meet us at the café.
He asked if I would help him with his project next week.
The teacher mentioned that the assignment was due yesterday.
They told me that they are going to the concert last night.
She said that she would have finished her work by now.
He asked if I have seen his keys.
The chef explained that the dish will be ready soon.
She said that she had forgot her phone at home.
They mentioned that the flight would have landed already.
He informed me that he would be arriving tomorrow.
Task 4: Complete the Reported Speech
"I am visiting my grandmother this weekend," she said. → She said that ______.
"Will you be at the meeting?" he asked. → He asked if ______.
"I have never tried sushi before," he said. → He said that ______.
"I will get the groceries later," she promised. → She promised that ______.
"Do not forget to lock the door," he said. → He said not to ______.
"I have already completed the task," she said. → She said that ______.
"We will go hiking if the weather is good," they said. → They said that ______.
"Please bring your notes to the class," the teacher said. → The teacher asked to ______.
"I cannot attend the event due to a prior commitment," she said. → She said that ______.
"The concert tickets are sold out," he said. → He said that ______.
Task 5: Transform the Dialogue
A: "I will meet you at the restaurant at 7 PM," she said.
B: "I will be there on time," he replied.
Reported Speech:
Speaker A: She said that ______.
Speaker B: He replied that ______.
A: "Please send me the details by email," he said.
B: "I will send them to you this evening," she promised.
Speaker A: He said that ______.
Speaker B: She promised that ______.
A: "We need to finish this project before the deadline," he said.
B: "I agree. Let's work on it together," she replied.
Speaker B: She replied that ______.
A: "Can you help me with this task?" he asked.
B: "Sure, I will assist you," she responded.
Speaker A: He asked if ______.
Speaker B: She responded that ______.
A: "I am excited about the vacation," she said.
B: "So am I," he replied.
Find out if you got them all right from the answers below.
She said that she had been working there for five years.
She asked if I was coming to the picnic the next day.
The delivery man said that the package would arrive by Friday.
He admitted that he had forgotten to bring his lunch.
They said that they were moving to a new house the following month.
The mother said to finish our homework before dinner.
He suggested trying the new restaurant.
She promised that she would help me with my math problems.
The ticket seller said that the movie started at 8 PM.
She said that she had never been to Italy.
He said, "I am going to visit my parents next week."
She asked, "Can you lend me your book?"
The teacher mentioned, "The test is postponed until next Friday."
They said, "We completed the project on time."
He explained, "I was studying for the exam all night."
The guide said, "The museum will open at 10 AM."
She said, "I have never seen such a beautiful garden."
He asked, "Are you interested in joining the new club?"
The manager told us, "The deadline has been extended."
They mentioned, "We will be arriving late."
Corrected: She said that she would meet us at the café.
Corrected: He asked if I would help him with his project the following week.
Corrected: The teacher mentioned that the assignment had been due yesterday.
Corrected: They told me that they were going to the concert the previous night.
Corrected: She said that she would have finished her work by now.
Corrected: He asked if I had seen his keys.
Corrected: The chef explained that the dish would be ready soon.
Corrected: She said that she had forgotten her phone at home.
Corrected: They mentioned that the flight would have already landed.
Corrected: He informed me that he would be arriving the next day.
She said that she was visiting her grandmother that weekend.
He asked if I would be at the meeting.
He said that he had never tried sushi before.
She promised that she would get the groceries later.
He said not to forget to lock the door.
She said that she had already completed the task.
They said that they would go hiking if the weather was good.
The teacher asked to bring our notes to the class.
She said that she could not attend the event due to a prior commitment.
He said that the concert tickets were sold out.
Speaker A: She said that she would meet me at the restaurant at 7 PM.
Speaker B: He replied that he would be there on time.
Speaker A: He said that he wanted the details sent by email.
Speaker B: She promised that she would send them that evening.
Speaker A: He said that they needed to finish the project before the deadline.
Speaker B: She replied that she agreed and suggested working on it together.
Speaker A: He asked if she could help him with the task.
Speaker B: She responded that she would assist him.
Speaker A: She said that she was excited about the vacation.
Takeaways from this Page
Practising reported speech helps you learn how to convey what others have said in a different way. Key points to remember are changing the verb tenses, adjusting pronouns, and keeping the meaning intact. For example, if someone says, "I am going," in reported speech it becomes, "She said she was going." It's also important to use reporting verbs like "said," "asked," and "promised" to show how the information is shared. Getting these elements right makes sure you communicate clearly and accurately, both in writing and speaking.

FAQs on Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers
1. What is reported speech?
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of conveying what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. Instead of saying exactly what was spoken, you summarize or paraphrase it. For example, "He said, 'I am tired'" becomes "He said that he was tired."
2. How do you change tenses in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense usually shifts one step back from the original. For example:
Present simple becomes past simple (e.g., "She says, 'I work hard'" becomes "She said that she worked hard").
Present continuous becomes past continuous (e.g., "They are playing" becomes "They were playing").
3. Do you need to change pronouns in reported speech?
Yes, pronouns should be adjusted to match the perspective of the reporter. For example:
"I" changes to "he" or "she" (e.g., "I will come" becomes "He said that he would come").
4. What happens to the word order in reported speech?
The word order generally changes to fit the structure of the reporting sentence. For instance, "She said, 'I will go to the market'" changes to "She said that she would go to the market."
5. How do you report questions?
To report questions, you use reporting verbs like "asked" or "inquired" and change the question format into a statement. For example:
Direct: "Are you coming?"
Reported: "He asked if I was coming."
6. How can Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers help improve grammar skills?
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers help improve grammar by teaching students how to change tenses and pronouns when reporting what someone else said. These exercises show how to use verbs like "said" and "asked" correctly, and help students practice turning direct speech into reported speech. By working through these exercises and checking their answers, students can spot and fix common mistakes, which makes their grammar more accurate. Regular practice helps students become better at using correct grammar in writing and speaking, leading to clearer and more effective communication.
7. Do you need to use 'that' in reported speech?
Using "that" is optional but helps clarify the connection between the reporting verb and the reported speech. For example:
"She said, 'I am leaving'" can be reported as "She said that she was leaving" or simply "She said she was leaving."
8. How do you handle time expressions in reported speech?
Time expressions often need to be adjusted to fit the new context. For example:
"Today" changes to "that day," "tomorrow" becomes "the next day," and "yesterday" changes to "the day before."
9. Can you give an example of reporting a statement with a modal verb?
Yes. For instance, if someone says, "I can swim," it becomes "He said that he could swim" in reported speech.
10. Are there exceptions to changing tenses in reported speech?
Yes, if the reporting verb is in the present, or if the information remains true regardless of time, the tense might not change. For example:
"She says, 'I am tired'" remains, "She says that she is tired" in reported speech because the reporting verb is in the present.
Present continuous Reported speech
Examples from our community, 10,000+ results for 'present continuous reported speech'.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Ella, "It's not raining." Ella remarked (that) . Jacob, "Riley is checking the computer." Jacob said (that) . Owen, "They aren't watching TV." Owen told me (that) . Nora, "He is learning Spanish words." Nora said (that) . Sentences in Reported speech in the Present Progressive in English in an Online Exercise.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say. Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
"Reported speech" means talking about the things that other people have said. Read this post to learn about direct and indirect reported speech in English. Reported speech is an essential skill for gossiping, chatting with friends and keeping up with the news. ... Present Continuous. Direct speech: I said, ...
In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command. Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired. Phrase in Direct Speech. Equivalent in Reported Speech.
Generally, reported speech is introduced by the verb say (Other reporting verbs include tell, mention, inform). The verb is used in the past tense, said, which indicates that something was spoken in the past. For example: "she said", "he said", "they said". The main verb in the reported speech sentence is also in the past tense.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Session Grammar. Reported speech. One thing to remember: Move the tense back! 1) Present simple -> past simple "I know you." -> She said she knew him.. 2) Present continuous -> past continuous
English grammar exercise about reported speech with the present continuous tense. Login Contact Courses Membership Speaking Explanations Exercises Method. Reported Speech Exercise 10. Perfect English Grammar. This reported speech exercise looks at statements using the present continuous. Review reported statements here;
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Tense Change As a rule when you report something someone has said you go back a tense, therefore, when we report what someone is saying in present continuous we go one tense back. Instead we use past continuous tense in reported speech. Affirmatives. Direct speech: RP +, + S + be1 + V1ing + ROTS He said, "I am doing my homework."
Reported Speech. Greg: "I am cooking dinner Maya.". Maya: "Greg said he was cooking dinner.". So most often, the reported speech is going to be in the past tense, because the original statement, will now be in the past! *We will learn about reporting verbs in part 2 of this lesson, but for now we will just use said/told.
Perfect English Grammar. Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site: ( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech ) Reported Statements: Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here) Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy)
For example: Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken. Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting.
1. We use direct speech to quote a speaker's exact words. We put their words within quotation marks. We add a reporting verb such as "he said" or "she asked" before or after the quote. Example: He said, "I am happy.". 2. Reported speech is a way of reporting what someone said without using quotation marks.
Original Direct Speech: "I am studying for the exam.". Present Time: "He says, 'I am studying for the exam right now.". Past Time: "He said, 'I was studying for the exam yesterday.". Future Time: "He will say, 'I am studying for the exam tomorrow.'". Present Continuous Tense in Indirect Speech: Indirect speech, which is ...
Reported Speech or Indirect Speech (present continuous)
Country: Colombia. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Reported speech (2013113) From worksheet author: De:Zaray Corredor García. Other contents: present simple,present continuos, repoting verbs. Worksheet description: Objective Explanation: This worksheet aims to help students practice reported speech in ...
Reported speech is an important part of learning English, especially in Class 10. It involves telling someone what another person has said, but without quoting their exact words.For example, instead of saying, "She said, 'I am going to the market,'" the reported speech would be, "She said that she was going to the market."
REPORTED SPEECH Complete the sentence. by Tayenesantos. ELA. Reorder the words to make sentences in the present perfect simple and continuous Unjumble. by Nataliapisettas. any age English Inglês Present Perfect Present Perfect Continuous. 2.1 Pr. Simple Vs Pr. Continuous SpeakOut pre-intermediate Quiz. by Tatimrs.